
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended
or
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from ___________ to __________
Commission file number:

(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
| ||
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
| (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
|
|
| ||
(Address of principal executive offices) |
| (Zip Code) |
(
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
☒ | Smaller reporting company | ||
Emerging growth company |
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date (May 12, 2023):
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Table of Contents
i |
| Table of Contents |
Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
In this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (this “Quarterly Report”) references to “we,” “our,” “us,” the “Company” or “Palatin” mean Palatin Technologies, Inc. and its subsidiary.
Statements in this Quarterly Report, as well as oral statements that may be made by us or by our officers, directors, or employees acting on our behalf, that are not historical facts constitute “forward-looking statements,” which are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). The forward-looking statements in this Quarterly Report do not constitute guarantees of future performance. Investors are cautioned that statements that are not strictly historical facts contained in this Quarterly Report, including, without limitation, the following are forward looking statements:
| · | our significant operating losses since our inception and our need to obtain additional financing has caused management to determine there is substantial doubt regarding our ability to continue as a going concern; |
|
|
|
| · | our expectation that we will incur losses for the foreseeable future and may never achieve or maintain profitability; |
|
|
|
| · | our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be adversely affected by global health epidemics, including the COVID-19 pandemic, such as, for example, increase in costs of and delays in conducting human clinical trials and the performance of our contractors and suppliers, reduction in our productivity or the productivity of our contractors and suppliers, supply chain constraints, and labor shortages; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to successfully commercialize Vyleesi® (the trade name for bremelanotide) for the treatment of premenopausal women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder (“HSDD”) in the United States, which may be adversely affected by delays or disruptions related to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical conflicts, and other economic and market conditions, including a decrease in discretionary spending; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to manage the infrastructure to successfully manufacture, through contract manufacturers, Vyleesi, and to successfully market and distribute Vyleesi in the United States, including successfully managing potential delays or impediments in the contract manufacturer chain; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to meet postmarketing commitments of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration; |
|
|
|
| · | our expectations regarding the potential market size and market acceptance for Vyleesi for HSDD in the United States and elsewhere in the world; |
|
|
|
| · | our expectations regarding performance of our exclusive licensees of Vyleesifor the treatment of premenopausal women with HSDD, which is a type of female sexual dysfunction, including: |
| o | Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical Industrial Development Co. Ltd. (“Fosun”), a subsidiary of Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical (Group) Co., Ltd., for the territories of the People’s Republic of China, Taiwan, Hong Kong S.A.R. and Macau S.A.R. (collectively, “China”), and |
|
|
|
| o | Kwangdong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (“Kwangdong”) for the Republic of Korea (“Korea”); |
| · | our expectations and the ability of our licensees to timely obtain approvals and successfully commercialize Vyleesi in countries other than the United States; |
|
|
|
| · | the results of clinical trials with our late stage products, including PL9643, an ophthalmic peptide solution for dry eye disease (“DED”), which entered Phase 3 clinical trials in the fourth quarter of calendar year 2021, and PL8177, an oral peptide formulation for treatment of ulcerative colitis, which entered Phase 2 clinical trials in the third quarter of calendar year 2022; |
|
|
|
| · | estimates of our expenses, future revenue and capital requirements; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to achieve profitability; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to obtain additional financing on terms acceptable to us, or at all, including unavailability of funds or delays in receiving funds as a result of the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical conflicts and other economic conditions such as inflation and changes in the interest rate environment; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to advance product candidates into, and successfully complete, clinical trials; |
|
|
|
| · | the initiation, timing, progress and results of future preclinical studies and clinical trials, and our research and development programs; |
ii |
| Table of Contents |
| · | the timing or likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals; |
|
|
|
| · | our expectations regarding the clinical efficacy and utility of our melanocortin agonist product candidates for treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune related diseases and disorders, including ocular indications; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to compete with other products and technologies treating the same or similar indications as our product candidates; |
|
|
|
| · | the ability of our third-party collaborators to timely carry out their duties under their agreements with us; |
|
|
|
| · | the ability of our contract manufacturers to perform their manufacturing activities for us in compliance with applicable regulations; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to recognize the potential value of our licensing arrangements with third parties; |
|
|
|
| · | the potential to achieve revenues from the sale of our product candidates; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to obtain adequate reimbursement from private insurers and other healthcare payers; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to maintain product liability insurance at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts, if at all; |
|
|
|
| · | the performance and retention of our management team, senior staff professionals, other employees, and third-party contractors and consultants; |
|
|
|
| · | the scope of protection we are able to establish and maintain for intellectual property rights covering our product candidates and technology in the United States and throughout the world; |
|
|
|
| · | our compliance with federal and state laws and regulations; |
|
|
|
| · | the timing and costs associated with obtaining regulatory approval for our product candidates, including delays and additional costs related to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic; |
|
|
|
| · | the impact of fluctuations in foreign exchange rates; |
|
|
|
| · | the impact of any geopolitical instability, economic uncertainty, financial markets volatility, or capital markets disruption resulting from the ongoing military conflict between Russia and Ukraine, and any resulting effects on our revenue, financial condition, or results of operations; |
|
|
|
| · | the impact of legislative or regulatory healthcare reforms in the United States; |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to adapt to changes in global economic conditions as well as competing products and technologies; and |
|
|
|
| · | our ability to remain listed on the NYSE American stock exchange. |
Such forward-looking statements involve risks, uncertainties and other factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from historical results or from any results expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Our future operating results are subject to risks and uncertainties and are dependent upon many factors, including, without limitation, the risks identified under the caption “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Quarterly Report, and any of those made in our other reports filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Except as required by law, we do not intend, and undertake no obligation, to publicly update forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this document or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
Palatin Technologies® and Vyleesi® are registered trademarks of Palatin Technologies, Inc., and Palatin™ and the Palatin logo are trademarks of Palatin Technologies, Inc. Other trademarks referred to in this report are the property of their respective owners.
iii |
| Table of Contents |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Item 1. Financial Statements.
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(unaudited)
|
| March 31, 2023 |
|
| June 30, 2022 |
| ||
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Cash and cash equivalents |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Right-of-use assets - operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Total assets |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK, AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
Accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Short-term operating lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Short-term finance lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long-term operating lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Long-term finance lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series B and Series C Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Escrowed proceeds |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series A Convertible: authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Common stock of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
issued and outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Accumulated deficit |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock, and stockholders’ equity |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 1 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(unaudited)
|
| Three Months Ended March 31, |
|
| Nine Months Ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
REVENUES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Product revenue, net |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||||
License and contract |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Total revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cost of products sold |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Research and development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Selling, general and administrative |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Gain on purchase commitment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
| |||
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss from operations |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investment income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Foreign currency (loss) gain |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
| ||
Interest expense |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Total other income (expense), net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss before income taxes |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Income tax benefit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
NET LOSS |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic and diluted net loss per common share |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding used in computing basic and diluted net loss per common share (Note 1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 2 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity
(unaudited)
Three Months Ended March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock |
|
| Stockholders' Equity |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Series B |
|
| Series C |
|
| Escrowed |
|
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
|
| Common Stock |
|
| Additional Paid-in |
|
| Accumulated |
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Proceeds |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Capital |
|
| Deficit |
|
| Total |
| ||||||||||||
Balance December 31, 2022 |
|
| - |
|
| $ |
|
|
| - |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| |||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Redemption of convertible series B & series C preferred stock |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Warrant exercises |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Net loss |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) | ||||||
Balance March 31, 2023 |
|
| - |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | - |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| |||||||||
Nine Months Ended March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock |
|
| Stockholders' Equity |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Series B |
|
| Series C |
|
| Escrowed |
|
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
|
| Common Stock |
|
| Additional Paid-in |
|
| Accumulated |
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Proceeds |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Capital |
|
| Deficit |
|
| Total |
| ||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2022 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| ||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Withholding taxes related to restricted stock units |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) | |||||
Redemption of convertible series B & series C preferred stock |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Sale of common stock and warrants, net of costs |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Warrant exercises |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Reverse stock split fractional shares |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||
Net loss |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) | ||||||
Balance, March 31, 2023 |
|
| - |
|
| $ |
|
|
| - |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 3 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(unaudited)
Three Months Ended March 31, 2022 |
|
| Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
| Preferred Stock |
|
| Common Stock |
|
| Paid-in |
|
| Accumulated |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Capital |
|
| Deficit |
|
| Total |
| |||||||
Balance, December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| ||||||
Stock-based compensation |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Withholding taxes related to restricted stock units |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) | ||
Net loss |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) | |||
Balance, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nine Months Ended March 31, 2022 |
|
| Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
| Preferred Stock |
|
| Common Stock |
|
| Paid-in |
|
| Accumulated |
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Shares |
|
| Amount |
|
| Capital |
|
| Deficit |
|
| Total |
| |||||||
Balance, June 30, 2021 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| ||||||
Stock-based compensation |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Withholding taxes related to restricted stock units |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) | ||
Warrant exercises |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Option exercises |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
Net loss |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) | |||
Balance, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ |
| ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 4 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(unaudited)
|
| Nine Months Ended March 31, |
| |||||
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
| ||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Net loss |
| $ | ( | ) |
| $ | ( | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Decrease in right-of-use asset |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Unrealized foreign currency transaction loss |
|
|
|
|
| ( | ) | |
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Gain on purchase commitment |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
| |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
| |
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Accounts payable |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
| |
Accrued expenses |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Operating lease liabilities |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Other liabilities |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payment of withholding taxes related to restricted stock units |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Proceeds from the sale of common stock and warrants, net of costs |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Payment of finance lease obligations |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Proceeds from exercise of warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NET DECREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, beginning of period |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS, end of period |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| 5 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(1) ORGANIZATION
Nature of Business – Palatin Technologies, Inc. (“Palatin” or the “Company”) is a biopharmaceutical company developing first-in-class medicines based on molecules that modulate the activity of the melanocortin and natriuretic peptide receptor systems. The Company’s product candidates are targeted, receptor-specific therapeutics for the treatment of diseases with significant unmet medical need and commercial potential.
Melanocortin Receptor System. The melanocortin receptor (“MCr”) system is involved in the regulation of food intake, satiety, metabolism, sexual function, inflammation, and immune system responses. There are five melanocortin receptors, MC1r through MC5r. Modulation of these receptors, through use of receptor-specific agonists, which activate receptor function, or receptor-specific antagonists, which block receptor function, can have significant pharmacological effects.
The Company’s commercial product, Vyleesi®, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) in June 2019 and was being marketed in the United States by AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“AMAG”) for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (“HSDD”) in premenopausal women pursuant to a license agreement between them for Vyleesi for North America, which was entered into on January 8, 2017 (the “AMAG License Agreement”). As disclosed in Note 5, the AMAG License Agreement was terminated effective July 24, 2020, and the Company is now marketing Vyleesi in the United States.
The Company’s product development activities focus primarily on MC1r agonists, with potential to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as dry eye disease, which is also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, uveitis, diabetic retinopathy, and inflammatory bowel disease. The Company believes that the MC1r agonist peptides in development have broad anti-inflammatory effects and appear to utilize mechanisms engaged by the endogenous melanocortin system in regulation of the immune system and resolution of inflammatory responses. The Company is also developing peptides that are active at more than one melanocortin receptor, and MC4r peptide and small molecule agonists with potential utility in obesity and metabolic-related disorders, including rare disease and orphan indications.
Reverse Stock Split - On August 30, 2022, a reverse stock split of 1-for-25 of issued and outstanding common stock was made effective by the Company. Retroactive effect for the reverse stock split was made to the Company’s outstanding common stock, stock options, common stock warrants, and preferred stock conversion features, including all share and per-share data, for all periods presented in the consolidated financial statements.
Business Risks and Liquidity – Since its inception, the Company has generally incurred negative cash flows from operations, and has expended, and expects to continue to expend, substantial funds to develop the capability to market and distribute Vyleesi in the United States and complete its planned product development efforts. As shown in the accompanying consolidated financial statements, the Company had an accumulated deficit as of March 31, 2023 of $
As of March 31, 2023, the Company’s cash and cash equivalents were $
The Company follows the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 205-40, Presentation of Financial Statements — Going Concern, which requires management to assess the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for one year after the date the consolidated financial statements are issued. While the Company has raised funding in the past, the ability to raise funding in future periods is not considered probable, as defined under the accounting standards. As such, under the requirements of ASC 205-40, management may not consider the potential for future funding in their assessment of the Company’s ability to meet its obligations for the next year.
| 6 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Based on the Company’s March 31, 2023 cash and cash equivalents, management has concluded that substantial doubt exists about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern for one year from the date these consolidated financial statements are issued. The Company is evaluating strategies to obtain additional funding for future operations which include but are not limited to obtaining equity financing, issuing debt, or reducing planned expenses. A failure to raise additional funding or to effectively implement cost reductions could harm the Company’s business, results of operations, and future prospects. If the Company is not able to secure adequate additional funding in future periods, the Company would be forced to make additional reductions in certain expenditures. This may include liquidating assets and suspending or curtailing planned programs. The Company may also have to delay, reduce the scope of, suspend, or eliminate one or more research and development programs or its commercialization efforts or pursue a strategic transaction. If the Company is unable to raise capital when needed or enter into a strategic transaction, then the Company may be required to cease operations, which could cause its stockholders to lose all or part of their investment. The consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming the Company will continue as a going concern, which contemplates the continuity of operations, the realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business. Assuming no additional funding and based on its current operating and development plans, the Company expects that existing cash and cash equivalents as of the date of this filing will be sufficient to fund currently anticipated operating expenses through calendar year 2023.
In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19, a disease caused by a novel strain of coronavirus, a pandemic. The Company has taken steps to ensure the safety and well-being of its employees and clinical trial patients to comply with guidance from federal, state, and local authorities, while working to ensure the sustainability of its business operations as this unprecedented situation continues to evolve. In mid-March 2020, the Company transitioned to a company-wide work from home policy. Business-critical activities continue to be subject to heightened precautions to ensure safety of employees. The Company continues to assess its policies, business continuity plans, and employee support.
The Company continues to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on the healthcare system and work with contract research organizations supporting its clinical, research, and development programs to mitigate risk to patients and its business and community partners, taking into account regulatory, institutional, and government guidance and policies.
The Company will receive a royalty on sales of Vyleesi by its licensees. It has licensed third parties to sell Vyleesi in China and Korea. The COVID-19 coronavirus could adversely impact the time required to obtain regulatory approvals to sell Vyleesi in China and Korea, which would delay when the Company receives royalty income from sales in those countries.
Concentrations – Concentrations in the Company’s assets and operations subject it to certain related risks. Financial instruments that subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk primarily consist of cash, cash equivalents, and accounts receivable. The Company’s cash and cash equivalents are primarily invested in one money market account sponsored by a large financial institution.
(2) BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The accompanying unaudited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”) for interim financial information and with the instructions to Form 10-Q. Accordingly, they do not include all of the information and footnote disclosures required to be presented for complete financial statements. In the opinion of management, these consolidated financial statements contain all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring adjustments) considered necessary for fair presentation. The results of operations for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023 may not necessarily be indicative of the results of operations expected for the full fiscal year.
The accompanying unaudited consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022, filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), which includes consolidated financial statements as of June 30, 2022 and 2021 and for the fiscal years then ended.
| 7 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(3) SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation – The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Palatin and its wholly-owned inactive subsidiary. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates – The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents – Cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand, cash in banks, and all highly liquid investments with a purchased maturity of less than three months. Cash equivalents consisted of $
Fair Value of Financial Instruments – The Company’s financial instruments consist primarily of cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable. Management believes that the carrying values of cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable are representative of their respective fair values based on the short-term nature of these instruments.
Credit Risk – Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash, cash equivalents, and accounts receivable. Total cash and cash equivalent balances have exceeded balances insured by the Federal Depository Insurance Company. Currently, product revenues and related accounts receivable are generated primarily from one specialty pharmacy.
Trade Accounts Receivable – Trade accounts receivable are amounts owed to the Company by its customers for product that has been delivered. The trade accounts receivable is recorded at the invoice amount, less prompt pay and other discounts, chargebacks, and an allowance for credit losses, if any. Credit losses have not been significant to date.
Inventories – Inventory is stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value, with cost being determined on a first-in, first-out basis.
On a quarterly basis, the Company reviews inventory levels to determine whether any obsolete, expired, or excess inventory exists. If any inventory is expected to expire prior to being sold, has a cost basis in excess of its net realizable value, is in excess of expected sales requirements as determined by internal sales forecasts, or fails to meet commercial sale specifications, the inventory is written down through a charge to operating expenses. Inventory consisting of Vyleesi has a shelf-life of three years from the date of manufacture.
Property and Equipment – Property and equipment consists of office and laboratory equipment, office furniture and leasehold improvements and includes assets acquired under finance leases. Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Depreciation is recognized using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets, generally five years for laboratory and computer equipment, seven years for office furniture and equipment, and the lesser of the term of the lease or the useful life for leasehold improvements. Amortization of assets acquired under finance leases is included in depreciation expense. Maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred while expenditures that extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized. Accumulated depreciation and amortization was $
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets – The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. To determine recoverability of a long-lived asset, management evaluates whether the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows from the asset are less than its carrying amount. If impairment is indicated, the long-lived asset would be written down to fair value. Fair value is determined by an evaluation of available price information at which assets could be bought or sold, including quoted market prices, if available, or the present value of the estimated future cash flows based on reasonable and supportable assumptions.
| 8 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Leases – At lease inception, the Company determines whether an arrangement is or contains a lease. Operating leases are included in operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets, short-term operating lease liabilities, and long-term operating lease liabilities in the consolidated financial statements. Finance leases are included in property and equipment for ROU assets, short-term finance lease liabilities, and long-term finance lease liabilities in the consolidated financial statements. ROU assets represent the Company’s right to use leased assets over the term of the lease. Lease liabilities represent the Company’s contractual obligation to make lease payments over the lease term. ROU assets and lease liabilities are recognized at the commencement date. The lease liability is measured as the present value of the lease payments over the lease term. The Company uses the rate implicit in the lease if it is determinable. When the rate implicit in the lease is not determinable, the Company uses an estimate based on a hypothetical rate provided by a third party as the Company currently does not have issued debt. Lease terms may include renewal or extension options to the extent they are reasonably certain to be exercised. The assessment of whether renewal or extension options are reasonably certain to be exercised is made at lease commencement. Factors considered in determining whether an option is reasonably certain of exercise include, but are not limited to, the value of any leasehold improvements, the value of renewal rates compared to market rates, and the presence of factors that would cause incremental costs to the Company if the option were not exercised.
The ROU asset is initially measured at cost, which comprises the initial amount of the lease liability adjusted for lease payments made at or before the lease commencement date, plus any initial direct costs incurred less any lease incentives received. For operating leases, the ROU asset is subsequently measured throughout the lease term at the carrying amount of the lease liability, plus initial direct costs, plus (minus) any prepaid (accrued) lease payments, less the unamortized balance of lease incentives received. Lease expense for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. For finance leases, the ROU asset is subsequently amortized using the straight-line method from the lease commencement date to the earlier of the end of its useful life or the end of the lease term unless the lease transfers ownership of the underlying asset to the Company or the Company is reasonably certain to exercise an option to purchase the underlying asset. In those cases, the ROU asset is amortized over the useful life of the underlying asset. Amortization of the ROU asset is recognized and presented as an operating expense separately from interest expense on the lease liability.
The Company has elected not to recognize an ROU asset and obligation for leases with an initial term of 12 months or less. The expense associated with short-term leases is included in selling, general and administrative expense in the statements of operations. To the extent a lease arrangement includes both lease and non-lease components, the Company has elected to account for the components as a single lease component.
Revenue Recognition – The Company recognizes product revenues in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The provisions of ASC Topic 606 require the following steps to determine revenue recognition: (1) Identify the contract(s) with a customer; (2) Identify the performance obligations in the contract; (3) Determine the transaction price; (4) Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and (5) Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
In accordance with ASC Topic 606, the Company recognizes product revenue when its performance obligation is satisfied by transferring control of the product to a customer. Per the Company’s contracts with customers, control of the product is transferred upon the conveyance of title, which occurs when the product is sold to and received by a customer. Trade accounts receivable due to the Company from contracts with its customers are stated separately in the consolidated balance sheet, net of various allowances as described in the Trade Accounts Receivable policy above.
Product revenues consist of sales of Vyleesi in the United States. The Company sells Vyleesi to specialty pharmacies at the wholesale acquisition cost and payment is currently made within approximately 30 days. In addition to distribution agreements with customers, the Company enters into arrangements with healthcare payers that provide for privately negotiated rebates, chargebacks, and discounts with respect to the purchase of the Company’s products.
The Company records product revenues net of allowances for direct and indirect fees, discounts, co-pay assistance programs, estimated chargebacks and rebates. Product sales are also subject to return rights, which have not been significant to date.
| 9 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Gross product sales offset by product sales allowances for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
|
| Three Months Ended March 31, |
|
| Nine Months Ended March 31, |
| ||||||||||
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Gross product sales |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||||
Provision for product sales allowances and accruals |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
|
| ( | ) |
Net sales |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||||
For licenses of intellectual property, the Company assesses at contract inception whether the intellectual property is distinct from other performance obligations identified in the arrangement. If the licensing of intellectual property is determined to be distinct, revenue is recognized for nonrefundable, upfront license fees when the license is transferred to the customer and the customer can use and benefit from the license. If the licensing of intellectual property is determined not to be distinct, then the license is bundled with other promises in the arrangement into one performance obligation. The Company determines if the bundled performance obligation is satisfied over time or at a point in time. If the Company concludes that the nonrefundable, upfront license fees will be recognized over time, the Company will assess the appropriate method of measuring proportional performance.
Regulatory milestone payments are excluded from the transaction price due to the inability to estimate the probability of reversal. Revenue relating to achievement of these milestones is recognized in the period in which the milestone is achieved.
Sales-based royalty and milestone payments resulting from customer contracts solely or predominately for the license of intellectual property will only be recognized upon occurrence of the underlying sale or achievement of the sales milestone in the future and such sales-based royalties and milestone payments will be recognized in the same period earned.
The Company recognizes revenue for reimbursements of research and development costs under collaboration agreements as the services are performed. The Company records these reimbursements as revenue and not as a reduction of research and development expenses as the Company is the principal in the research and development activities based upon its control of such activities, which is considered part of its ordinary activities.
Development milestone payments are generally due 30 business days after the milestone is achieved. Sales milestone payments are generally due 45 business days after the calendar year in which the sales milestone is achieved. Royalty payments are generally due on a quarterly basis 20 business days after being invoiced.
Research and Development Costs – The costs of research and development activities are charged to expense as incurred, including the cost of equipment for which there is no alternative future use.
Accrued Expenses – Third parties perform a significant portion of the Company’s development activities. The Company reviews the activities performed under all contracts each quarter and accrues expenses and the amount of any reimbursement to be received from its collaborators based upon the estimated amount of work completed considering milestones achieved. Estimating the value or stage of completion of certain services requires judgment based on available information. If the Company does not identify services performed for it but not billed by the service-provider, or if it underestimates or overestimates the value of services performed as of a given date, reported expenses will be understated or overstated.
Stock-Based Compensation – The Company charges to expense the fair value of stock options and other equity awards granted to employees and nonemployees for services. Compensation costs for stock-based awards with time-based vesting are determined using the quoted market price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date or for stock options, the value determined utilizing the Black-Scholes option pricing model, and are recognized on a straight-line basis, while awards containing a market condition are valued using multifactor Monte Carlo simulations and are recognized over the derived service period. Compensation costs for awards containing a performance condition are determined using the quoted price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date or for stock options, the value determined utilizing the Black Scholes option pricing model and are recognized based on the probability of achievement of the performance condition over the service period. Forfeitures are recognized as they occur.
| 10 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Income Taxes – The Company and its subsidiary file consolidated federal and separate-company state income tax returns. Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences or operating loss and tax credit carryforwards are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company has recorded and continues to maintain a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets based on the history of losses incurred and lack of experience projecting future product revenue and sales-based royalty and milestone payments.
Net Loss per Common Share – Basic and diluted loss per common share (“EPS”) are calculated in accordance with the provisions of FASB ASC Topic 260, Earnings per Share.
The Company’s Series B and Series C Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and warrants issued during the year ended June 30, 2022 met the definition of a participating security given their rights to participate in dividends if declared on common stock, which requires the Company to apply the two-class method to compute both basic and diluted net income or loss per share. The two-class method is an earnings allocation formula that treats participating securities as having rights to earnings that would otherwise have been available to common stockholders. In addition, as these securities are participating securities, the Company is required to calculate diluted net income or loss per share under the if-converted and treasury stock method in addition to the two-class method and utilize the most dilutive result. In periods where there is a net loss, no allocation of undistributed net loss to the Redeemable Convertible Preferred stockholders or warrant holders is performed as the holders of these securities are not contractually obligated to participate in the Company’s losses.
For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, no additional common shares were added to the computation of diluted EPS because to do so would have been anti-dilutive. The potential number of common shares excluded from diluted EPS during the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 was
Included in the weighted average common shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per common share are
Translation of foreign currencies – Transactions denominated in currencies other than the Company’s functional currency (US Dollar) are recorded based on exchange rates at the time such transactions arise. Subsequent changes in exchange rates result in transaction gains and losses, which are reflected in the consolidated statements of operations as unrealized (based on the applicable period-end exchange rate) or realized upon settlement of the transactions.
(4) New and recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2021, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2021-04, Earnings Per Share (Topic 260), Debt – Modifications and Extinguishments (Subtopic 470-50), Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718), and Derivatives and Hedging – Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Issuer’s Accounting for Certain Modifications or Exchanges of Freestanding Equity-Classified Written Call Options. The FASB issued this update to clarify and reduce diversity in an issuer’s accounting for modifications or exchanges of freestanding equity-classified written call options (for example, warrants) that remain equity classified after modification or exchange. The amendments in ASU No. 2021-04 are effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The guidance was applicable to the Company beginning July 1, 2022. The adoption of this standard did not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-06, Debt (Topic 470) and Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Accounting for Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity. The amendments in ASU No. 2020-06 address issues identified as a result of the complexity associated with applying U.S. GAAP for certain financial instruments with characteristics of liabilities and equity. The guidance is effective for public entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, and for interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. The Company early adopted this standard during the year ended June 30, 2022. The adoption of this standard did not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
| 11 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes. The amendments in this update simplify the accounting for income taxes by removing certain exceptions to the general principles in Topic 740. The amendments also improve consistent application and simplify U.S. GAAP for other areas of Topic 740 by clarifying and amending existing guidance. The guidance is effective for public entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2020, and for interim periods within those fiscal years. The guidance was applicable to the Company beginning July 1, 2021. The adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses: Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, which requires measurement and recognition of expected credit losses for financial assets held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. This is different from the current guidance as this will require immediate recognition of estimated credit losses expected to occur over the remaining life of many financial assets. The new guidance will be effective for the Company on July 1, 2023, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
(5) AGREEMENTS WITH AMAG
On January 8, 2017, the Company entered into the AMAG License Agreement pursuant to which the Company granted AMAG (i) an exclusive license in all countries of North America (the “Territory”), with the right to grant sub-licenses, to research, develop, and commercialize products containing Vyleesi (each a “Product”, and collectively, “Products”), (ii) a non-exclusive license in the Territory, with the right to grant sub-licenses, to manufacture the Products, and (iii) a non-exclusive license in all countries outside the Territory, with the right to grant sub-licenses, to research, develop, and manufacture (but not commercialize) the Products.
Following the satisfaction of certain conditions to closing, the AMAG License Agreement became effective on February 2, 2017. Under the AMAG License Agreement, in addition to certain initial and milestone payments, AMAG reimbursed the Company for certain reasonable, documented, direct out-of-pocket expenses incurred by the Company following February 2, 2017, in connection with development and regulatory activities necessary to file a New Drug Application (“NDA”) for Vyleesi for HSDD in the United States.
On June 4, 2018, the FDA accepted the Vyleesi NDA for filing and on June 21, 2019, the FDA granted approval of Vyleesi for use in the United States.
Effective July 24, 2020, the Company entered into a termination agreement (the “Termination Agreement”) with AMAG terminating the AMAG License Agreement. Under the terms of the Termination Agreement, the Company regained all development and commercialization rights for Vyleesi in the Territory. AMAG made a $
Under the Termination Agreement, AMAG provided certain transitional services to the Company for a period to ensure continued patient access to Vyleesi during the transition back to the Company. The Company reimbursed AMAG for the agreed upon costs of the transition services.
| 12 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(6) MANUFACTURING SUPPLY AGREEMENTS FOR VYLEESI
Pursuant to the Termination Agreement, the Company assumed Vyleesi manufacturing contracts with Catalent Belgium S.A. (“Catalent”), a subsidiary of Catalent Pharma Solutions, Inc., to manufacture drug product and prefilled syringes and assemble prefilled syringes into an auto-injector device (the “Catalent Agreement”); Ypsomed AG (“Ypsomed”), to manufacture the auto-injector device (the “Ypsomed Agreement”); and Lonza Ltd. (“Lonza”), to manufacture the active pharmaceutical ingredient peptide (the “Lonza Agreement”).
On September 29, 2020, the Company and Catalent entered into an agreement to terminate the Catalent Agreement (the “Catalent Termination Agreement”) in consideration for a one-time payment of six million euros (€6,000,000) which was paid in October 2020 and accrued as part of the estimated losses on inventory purchase commitments assumed as part of the Termination Agreement as discussed in Note 5.
The Company and Catalent then entered into a new Vyleesi manufacturing agreement (the “New Catalent Agreement”) which includes reduced minimum annual purchase requirements (see Note 12) as compared to the original Catalent Agreement and modification of other financial terms. The New Catalent Agreement provides that Catalent will provide manufacturing and supply services to Palatin related to production of Vyleesi, including that Catalent will supply specified minimums of Palatin’s requirements for Vyleesi during the term of the New Catalent Agreement through August 21, 2025, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the terms of the New Catalent Agreement. The initial term of the New Catalent Agreement will be automatically extended for one 24-month period unless either party notifies the other of its desire to terminate as of the end of the initial term. The New Catalent Agreement also includes customary terms and conditions relating to forecasting and minimum commitments, ordering, delivery, inspection and acceptance, and termination, among other matters.
The initial term of the Ypsomed Agreement is through December 31, 2025, with automatic renewal for successive one-year periods unless either party terminates the Ypsomed Agreement by ten months’ written notice prior to the expiration of the Ypsomed Agreement or any automatic renewal period. There are specified minimum purchase requirements under the Ypsomed Agreement, and under specified circumstances, termination fees may be payable upon termination of the Ypsomed Agreement by the Company (see Note 12).
The term of the Lonza Agreement was set to expire on December 31, 2022. In November 2022, Lonza and the Company amended the Lonza Agreement to extend contract peptide manufacturing services until June 30, 2024. The Company intends to seek to extend contract peptide manufacturing services with Lonza past June 30, 2024, and is also actively evaluating potential new contract manufacturers. Establishing a new contractual relationship and establishing and validating manufacturing in a manner that complies with FDA regulations is a time-consuming and costly process. The amendment reduced certain minimum purchase commitments that were previously accrued for in connection with the Termination Agreement. As a result, the Company recorded a gain on the purchase commitment of $
(7) AGREEMENT WITH FOSUN
On September 6, 2017, the Company entered into a license agreement with Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical Industrial Development Co. Ltd. (“Fosun”) for exclusive rights to commercialize Vyleesi in China (the “Fosun License Agreement”). Under the terms of the agreement, the Company received $
(8) AGREEMENT WITH KWANGDONG
On November 21, 2017, the Company entered into a license agreement with Kwangdong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (“Kwangdong”) for exclusive rights to commercialize Vyleesi in Korea (the “Kwangdong License Agreement”). Under the terms of the agreement, the Company received $
| 13 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(9) PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT ASSETS
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consist of the following:
|
| March 31, |
|
| June 30, |
| ||
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
| ||
Clinical / regulatory costs |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
Insurance premiums |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Vyleesi contractual advances |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
(10) FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The fair value of cash equivalents is classified using a hierarchy prioritized based on inputs. Level 1 inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 2 inputs are quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets or inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly through market corroboration, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs based on management’s own assumptions used to measure assets and liabilities at fair value. A financial asset’s or liability’s classification within the hierarchy is determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The following table provides the assets carried at fair value:
|
| Carrying Value |
|
| Quoted prices in active markets (Level 1) |
|
| Other quoted/observable inputs (Level 2) |
|
| Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) |
| ||||
March 31, 2023: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Money market account |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||||
June 30, 2022: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Money market account |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||||
(11) ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
|
| March 31, |
|
| June 30, |
| ||
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
| ||
Clinical / regulatory costs |
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
Other research related expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Professional services |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Personnel costs |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Selling expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| ||
(12) COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Inventory Purchases - As a result of the Termination Agreement and subsequent activity, the Company has certain supply agreements with manufacturers and suppliers, including the New Catalent Agreement, Lonza Agreement, and Ypsomed Agreement. The Company is required to make certain payments for the manufacture and supply of Vyleesi. The following table summarizes the contractual obligations under the New Catalent Agreement, Lonza Agreement, and Ypsomed Agreement as of March 31, 2023:
|
| Total |
|
| Current |
|
| 1 - 3 Years |
| |||
Inventory purchase commitments |
| $ |
|
| $ |
|
| $ |
| |||
| 14 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
As of March 31, 2023, the Company has $
The commitment contractual obligation amounts above are denominated in Swiss Francs and Euros and have been translated using period end exchange rates. The Company may experience a negative impact on future earnings and equity solely as a result of future foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations.
Contingencies - The Company accounts for litigation losses in accordance with ASC 450-20, Loss Contingencies. In addition, the Company is subject to other contingencies, such as product liability, arising in the ordinary course of business. Loss contingency provisions are recorded for probable losses when management is able to reasonably estimate the loss. Any outcome upon settlement that deviates from the Company’s best estimate may result in additional expense or in a reduction in expense in a future accounting period. The Company records legal expenses associated with such contingencies as incurred.
The Company is involved, from time to time, in various claims and legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of its business. The Company is not currently a party to any such claims or proceedings that, if decided adversely to it, would either individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, or results of operations.
(13) STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY AND REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK
Series B and C Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock – On May 11, 2022, Palatin entered into a securities purchase agreement with institutional investors, and on May 12, 2022, Palatin issued and sold
Given that the fee and other costs were not refundable to the Company as of June 30, 2022, regardless of the election selected by the investors, the $750,000 fee, the fair value of the warrants ($
The Company called a meeting of stockholders on June 24, 2022 to seek approval of, among other things, an amendment to its certificate of incorporation authorizing a reverse stock split. Except as otherwise required by law, holders of the Series B Preferred Stock and Series C Preferred Stock were entitled to vote only on the reverse stock split and any adjournment of the meeting relating to the reverse stock split. The Company’s common stock, outstanding Series A Preferred Stock, the Series B Preferred Stock and the Series C Preferred Stock voted as a single class on an as-if converted basis. The holders of Series B Preferred Stock had votes equal to the number of shares of common stock into which the Series B Preferred Stock is convertible.
| 15 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Series A Convertible Preferred Stock – As of March 31, 2023,
Financing Transactions – On October 31, 2022, the Company entered into a securities purchase agreement with a certain institutional investor to sell, in a registered direct offering (the “Offering”), an aggregate of (i)
The Common Warrants have an exercise price of $
The proceeds from the Offering, after deducting the placement agent fees and expenses and other estimated offering expenses, were $
On June 21, 2019, the Company entered into an equity distribution agreement (the “2019 Equity Distribution Agreement”) with Canaccord Genuity LLC (“Canaccord”), pursuant to which the Company may, from time to time, sell shares of the Company’s common stock at market prices by methods deemed to be an “at-the-market offering” as defined in Rule 415 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. The 2019 Equity Distribution Agreement and related prospectus is limited to sales of up to an aggregate maximum $40.0 million of shares of the Company’s common stock. The Company pays Canaccord 3.0% of the gross proceeds as a commission.
No proceeds were raised under the 2019 Equity Distribution Agreement during the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. On April 12, 2023, the Company entered into a new equity distribution agreement with Canaccord Genuity LLC. (See note 15).
Stock Purchase Warrants- As of March 31, 2023, the Company had outstanding warrants for shares of common stock as follows:
|
| Shares of Common |
|
| Exercise Price per |
|
| Latest Expiration | |||
Description |
| Stock |
|
| Share |
|
| Date | |||
May 2022 Warrants |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| ||||
November 2022 Common Warrants |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| ||||
November 2022 Placement Agent Warrants |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
| ||||
| 16 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Stock Options – For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, the Company recorded stock-based compensation related to stock options of $
A summary of stock option activity is as follows:
|
| Number of Shares |
|
| Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|
| Weighted Average Remaining Term in Years |
|
| Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Outstanding - June 30, 2022 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ | - |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Forfeited |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Exercised |
|
| - |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Expired |
|
| ( | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Outstanding - March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| $ |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercisable at March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expected to vest at March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
| $ |
|
|
|
|
| $ |
| ||||
On December 16, 2022, Carl Spana, President and CEO of the Company, and Stephen T. Wills, CFO, COO and Executive Vice President of the Company, voluntarily contributed stock options previously issued to them to purchase
Stock options granted to the Company’s executive officers and employees generally vest over a 48-month period, while stock options granted to its non-employee directors vest over a 12-month period.
Included in the outstanding options in the table above are
Restricted Stock Units – For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, the Company recorded stock-based compensation related to restricted stock units of $
A summary of restricted stock unit activity is as follows:
Outstanding at June 30, 2022 |
|
|
| |
Granted |
|
| - |
|
Forfeited |
|
| ( | ) |
Vested |
|
| ( | ) |
Fractional shares |
|
| ( | ) |
Outstanding at March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
Included in outstanding restricted stock units in the table above are
| 17 |
| Table of Contents |
PALATIN TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
and Subsidiary
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Time-based restricted stock units granted to the Company’s executive officers, employees and non-employee directors generally vest over 48 months, 48 months, and 12 months, respectively.
Included in the outstanding restricted stock units in the table above are
In June 2021, the Company granted
(14) INCOME TAXES
The Company has participated in the State of New Jersey’s Technology Business Tax Certificate Transfer Program (the “Program”) sponsored by The New Jersey Economic Development Authority. The Program enables approved biotechnology companies with unused Net Operating Losses (“NOLs”) and unused research and development credits (“R&D credits”) to sell these tax benefits for at least 80% of the value of the tax benefits to unaffiliated, profitable corporate taxpayers in the State of New Jersey. The Company received final approval in December 2022 for the sale of NOLs and R&D credits that resulted in the receipt of $
(15) SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On April 12, 2023, the Company entered into a new equity distribution agreement with Canaccord Genuity LLC (“Canaccord”) (the “2023 Equity Distribution Agreement”), pursuant to which the Company may, from time to time, sell shares of the Company’s common stock at market prices by methods deemed to be an “at-the-market offering” as defined in Rule 415 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. The 2023 Equity Distribution Agreement and related prospectus is limited to sales of up to an aggregate maximum $
| 18 |
| Table of Contents |
Item 2. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes to the consolidated financial statements filed as part of this report and the audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022.
The following discussion and analysis contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws. You are urged to carefully review our description and examples of forward-looking statements included earlier in this Quarterly Report immediately prior to Part I, under the heading “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.” Forward-looking statements are subject to risk that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in the forward-looking statements. You are urged to carefully review the disclosures we make concerning risks and other factors that may affect our business and operating results, including those made in this Quarterly Report and our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022, as well as any of those made in our other reports filed with the SEC. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements included herein, which speak only as of the date of this document. We do not intend, and undertake no obligation, to publish revised forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this document or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our significant accounting policies, which are described in the notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this report and in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022, have not changed since and during the three months ended March 31, 2023. We believe that our accounting policies and estimates relating to the carrying value of inventory, revenue recognition, accrued expenses, purchase commitment liabilities, and stock-based compensation are the most critical.
Our Business
We are a biopharmaceutical company developing first-in-class medicines based on molecules that modulate the activity of the melanocortin and natriuretic peptide receptor systems. Our product candidates are targeted, receptor-specific therapeutics for the treatment of diseases with significant unmet medical need and commercial potential.
Melanocortin Receptor System. The melanocortin receptor (“MCr”) system has effects on food intake, metabolism, sexual function, inflammation, and immune system responses. There are five melanocortin receptors, MC1r through MC5r. Modulation of these receptors, through use of receptor-specific agonists, which activate receptor function, or receptor-specific antagonists, which block receptor function, can have significant pharmacological effects.
Our commercial product, Vyleesi®, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) in June 2019 and was being marketed in the United States by AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“AMAG”) for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire disorder (“HSDD”) in premenopausal women pursuant to a license agreement between them for Vyleesi for North America, which was entered into on January 8, 2017 (the “AMAG License Agreement”). As disclosed in Note 5 to the Financial Statements, the AMAG License Agreement was terminated effective July 24, 2020, and we are now marketing Vyleesi in North America.
Our new product development activities focus primarily on MC1r agonists, with potential to treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases such as dry eye disease, which is also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, uveitis, diabetic retinopathy, and inflammatory bowel disease. We believe that the MC1r agonist peptides in development have broad anti-inflammatory effects and appear to utilize mechanisms engaged by the endogenous melanocortin system in regulation of the immune system and resolution of inflammatory responses. We are also developing peptides that are active at more than one melanocortin receptor, and MC4r peptide and small molecule agonists with potential utility in obesity and metabolic-related disorders, including rare disease and orphan indications.
| 19 |
| Table of Contents |
Pipeline Overview
The following chart illustrates the status of our drug development programs and Vyleesi, which has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of premenopausal women with acquired, generalized HSDD.
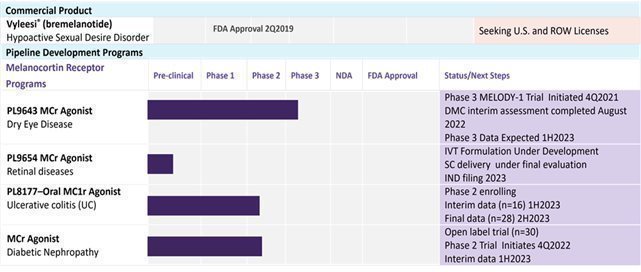
Our Strategy
Key elements of our business strategy include:
| · | Maximizing revenue from Vyleesi by marketing Vyleesi in the United States, supporting our existing licensees for China and Korea, and licensing Vyleesi for the United States and additional regions; |
|
|
|
| · | Maintaining a team to create, develop and commercialize MCr products addressing unmet medical needs; |
|
|
|
| · | Entering into strategic alliances and partnerships with pharmaceutical companies to facilitate the development, manufacture, marketing, sale, and distribution of product candidates that we are developing; |
|
|
|
| · | Partially funding our product development programs with the cash flow generated from Vyleesi and existing license agreements, as well as any future research, collaboration, or license agreements; and |
|
|
|
| · | Completing development and seeking regulatory approval of certain of our other product candidates. |
Corporate Information
We were incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware on November 21, 1986 and commenced operations in the biopharmaceutical area in 1996. Our corporate offices are located at 4B Cedar Brook Drive, Cedar Brook Corporate Center, Cranbury, New Jersey 08512, and our telephone number is (609) 495-2200. We maintain an Internet site, where among other things, we make available free of charge on and through this website our Forms 3, 4 and 5, annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) and Section 16 of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Our website and the information contained in it or connected to it are not incorporated into this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q. The reference to our website is an inactive textual reference only.
The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC (www.sec.gov).
Results of Operations
Three and Nine months ended March 31, 2023 compared to the Three and Nine months ended March 31, 2022:
Revenues – For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, we recognized $1,195,675 and 3,091,745 in product revenue, net of allowances, respectively. For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, we recognized $216,097 and $447,719 in product revenue, net of allowances, respectively. The increase in net revenue was a result of increased sales volume and reduced product sales allowances as a percentage of gross sales during the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, compared to the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022.
Cost of Products Sold – Cost of products sold was $129,235 and $314,438 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively, compared to $46,908 and $130,012 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively.
| 20 |
| Table of Contents |
Research and Development – Research and development expenses were $4,830,327 and $15,224,896 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively, compared to $4,980,074 and $13,891,235 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively. The decrease in research and development expenses for the three months ended March 31, 2023, compared to the three ended March 31, 2022, was a result of decreased spending on our MCr programs. The increase in research and development expenses for the nine months ended March 31, 2023, compared to the nine months ended March 31, 2022, was a result of increased spending on our MCr programs.
Research and development expenses related to our Vyleesi, MCr programs and other preclinical programs were $3,261,362 and $10,519,814 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively, compared to $3,560,507 and $9,957,780 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively.
The amounts of project spending above exclude general research and development spending, which was $1,568,965 and $4,705,082 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively compared to $1,419,567 and $3,933,455 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively. The increase in general research and development spending for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, compared to the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, was primarily attributable to an increase in compensation related expenses.
Cumulative spending from inception to March 31, 2023, was approximately $311,900,000 on our Vyleesi program and approximately $203,600,000 on all our other programs (which include PL3994, melanocortin receptor agonists, other discovery programs and terminated programs). Due to various risk factors described in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022, under “Risk Factors,” including the difficulty in currently estimating the costs and timing of future Phase 1 clinical trials and larger-scale Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials for any product under development, we cannot predict with reasonable certainty when, if ever, a program will advance to the next stage of development or be successfully completed, or when, if ever, related net cash inflows will be generated.
Selling, General and Administrative – Selling, general and administrative expenses, which consist mainly of compensation and related costs, were $3,537,376 and $10,220,518 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively, compared to $3,009,528 and $10,163,830 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively. The increase in selling, general and administrative expenses for the three months ended March 31, 2023 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2022 was primarily attributable to an increase in selling expenses relating to Vyleesi of $1,250,751 and $857,151, respectively. The increase in selling, general and administrative expenses for the nine months ended March 31, 2023, compared to the nine months ended March 31, 2022 was primarily attributable to an increase in consulting fees offset by a decrease in selling expenses relating to Vyleesi of $3,520,005 and $3,990,614, respectively.
Gain on Purchase Commitment - Gain on purchase commitments was $1,027,322 for the nine months ended March 31, 2023 as a result of the Company amending the minimum purchase commitment that was previously reserved under the Lonza Agreement.
Other Income (Expense) – Total other income, net was $153,344 and $138,362 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, respectively, compared to $188,827 and $56,677 for the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, respectively. For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2023, the Company recognized investment income of $234,044 and $509,006 respectively, offset by foreign currency exchange loss of $77,266 and $352,121, respectively, and interest expense of $3,434 and $18,523, respectively. For the three and nine months ended March 31, 2022, the Company recognized foreign currency exchange gain of $190,719 and $64,000, respectively, and investment income of $1,127 and $4,100, respectively offset by interest expense of $3,019 and $11,423, respectively.
Income Tax Benefit – Income tax benefit for the nine months ended March 31, 2023, was $4,674,999 as a result of the Company selling NOLs and R&D credits.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since inception, we have generally incurred net operating losses, primarily related to spending on our research and development programs. We have financed our net operating losses primarily through debt and equity financings and amounts received under collaborative and license agreements.
| 21 |
| Table of Contents |
Our product candidates are at various stages of development and will require significant further research, development, and testing and some may never be successfully developed or commercialized. We may experience uncertainties, delays, difficulties, and expenses commonly experienced by early-stage biopharmaceutical companies, which may include unanticipated problems and additional costs relating to:
| · | the development and testing of products in animals and humans; |
|
|
|
| · | product approval or clearance; |
|
|
|
| · | regulatory compliance; |
|
|
|
| · | good manufacturing practices (“GMP”) compliance; |
|
|
|
| · | intellectual property rights; |
|
|
|
| · | product introduction; |
|
|
|
| · | marketing, sales, and competition; and |
|
|
|
| · | obtaining sufficient capital. |
Failure to enter into or successfully perform under collaboration agreements and obtain timely regulatory approval for our product candidates and indications would impact our ability to generate revenues and could make it more difficult to attract investment capital for funding our operations. Any of these possibilities could materially and adversely affect our operations and require us to curtail or cease certain programs.
During the nine months ended March 31, 2023, net cash used in operating activities was $18,813,237 compared to $22,203,901 for the nine months ended March 31, 2022. The decrease in cash used in operations for the nine months ended March 31, 2023 compared to the nine months ended March 31, 2022 was primarily related to the Company’s sale of NOL’s and working capital changes.
During the nine months ended March 31, 2023, net cash used in investing activities was $381,531 compared to $224,258 for nine months ended March 31, 2022. The increase was related to purchases of equipment and leasehold improvements.
During the nine months ended March 31, 2023, net cash provided by financing activities was $8,887,944, which consisted of proceeds from the sale of common stock and warrants, net of costs of $9,109,117 and proceeds from exercise of warrants of $78, offset by $146,062 of payment of withholding taxes related to restricted stock units and $75,189 related to payment of finance lease obligations. During the nine months ended March 31, 2022, net cash provided by financing activities was $42,771, which consisted of proceeds from the exercise of warrants of $280,000 and proceeds from the exercise of stock options of $16,132, offset by payment of withholding taxes related to restricted stock units of $221,311 and payment of finance lease obligations of $32,050.
We have incurred cumulative negative cash flows from operations since our inception, and have expended, and expect to continue to expend in the future, substantial funds to develop the capability to market and distribute Vyleesi in the United States and to complete our planned product development efforts. Continued operations are dependent upon our ability to generate future income from sales of Vyleesi in the United States and from existing licenses, including royalties and milestones, to complete equity or debt financing activities and to enter into additional licensing or collaboration arrangements. As of March 31, 2023, our cash and cash equivalents were $19,632,330 and our current liabilities were $11,851,363.
Our obligations include aggregate lease obligations of $406,167 for the twelve-month period ending March 31, 2024 and $393,631 for the twelve-month periods ending March 31, 2025 and 2026, and aggregate inventory purchase commitments of $6,894,250 which include $3,122,850 in current liabilities as of March 31, 2023 and $3,771,400 included in other long term liabilities.
We intend to utilize existing capital resources for general corporate purposes and working capital, including establishing marketing and distribution capabilities for Vyleesi in the United States and preclinical and clinical development of our MC1r and MC4r programs, and development of other portfolio products.
Based on our March 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents, we have concluded that substantial doubt exists about our ability to continue as a going concern for one year from the date our consolidated financial statements are issued. We are evaluating strategies to obtain additional funding for future operations which include but are not limited to obtaining equity financing, issuing debt, or reducing planned expenses. A failure to raise additional funding or to effectively implement cost reductions could harm our business, results of operations, and future prospects. If we are not able to secure adequate additional funding in future periods, we would be forced to make additional reductions in certain expenditures. This may include liquidating assets and suspending or curtailing planned programs. We may also have to delay, reduce the scope of, suspend, or eliminate one or more research and development programs or its commercialization efforts or pursue a strategic transaction. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or enter into a strategic transaction, then we may be required to cease operations, which could cause our stockholders to lose all or part of their investment. Based on our current operating and development plans, we expect that our existing cash and cash equivalents as of the date of this filing will be sufficient to fund currently anticipated operating expenses through calendar year 2023.
| 22 |
| Table of Contents |
We will need additional funding to complete required clinical trials for our product candidates and development programs and, if those clinical trials are successful (which we cannot predict), to complete submission of required regulatory applications to the FDA. However, the COVID-19 pandemic and its resulting impact to economic conditions may negatively impact our operations, including possible effects on our financial condition, ability to access the capital markets on attractive terms or at all, liquidity, operations, suppliers, industry, and workforce. We will continue to evaluate the impact that these events could have on the operations, financial position, and the results of operations and cash flows during fiscal year 2023 and beyond.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
None.
Contractual Obligations
There have been no material changes outside the ordinary course of business to our contractual obligations and commitments, as disclosed in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Not required to be provided by smaller reporting companies.
Item 4. Controls and Procedures.
Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e), as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of March 31, 2023.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2023 that have materially affected, or that are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| 23 |
| Table of Contents |
PART II – OTHER INFORMATION
Item 1. Legal Proceedings.
We may be involved, from time to time, in various claims and legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of our business. We are not currently a party to any claim or legal proceeding.
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
This report and other documents we file with the SEC contain forward-looking statements that are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections about us, our future performance, our business, our beliefs, and our management’s assumptions. These statements are not guarantees of future performance, and they involve certain risks, uncertainties and assumptions that are difficult to predict. You should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties facing our business.
Other than set forth below, there have been no material changes to our risk factors disclosed in Part I, Item 1A, of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended June 30, 2022.
There are risks associated with the Reverse Stock Split.
A certificate of amendment of Palatin’s certificate of incorporation for a 1-for-25 reverse split of Palatin’s issued and outstanding common stock was effective as of 5:00 p.m. Eastern Time on August 30, 2022 (the “Reverse Stock Split”). There are risks associated with the Reverse Stock Split and there is no assurance that:
| · | the market price per share of our common stock after the Reverse Stock Split will rise in proportion to the reduction in the number of shares of our common stock outstanding before the Reverse Stock Split or if it does rise that it will sustain the increase in the share price; |
|
|
|
| · | the Reverse Stock Split will result in a per share price that will attract brokers and investors who do not trade in lower priced stocks; |
|
|
|
| · | the Reverse Stock Split will result in a per share price that will increase our ability to attract and retain employees and other service providers and maintain the minimum stock price required for continued listing on the NYSE American; or |
|
|
|
| · | the liquidity of our common stock will increase. |
Unstable market and economic conditions and adverse developments with respect to financial institutions and associated liquidity risk may have serious adverse consequences on our business, financial condition and stock price.
The global credit and financial markets have recently experienced extreme volatility and disruptions, including severely diminished liquidity and credit availability, declines in consumer confidence, declines in economic growth, rising interest and inflation rates, increases in unemployment rates and uncertainty about economic stability. Future adverse developments with respect to specific financial institutions or the broader financial services industry may lead to market-wide liquidity shortages, impair the ability of companies to access near-term working capital needs, and create additional market and economic uncertainty. Our general business strategy may be adversely affected by any such economic downturn, liquidity shortages, volatile business environment, or continued unpredictable and unstable market conditions. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, or if adverse developments are experienced by financial institutions, it may cause short-term liquidity risk and also make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, more onerous with respect to financial and operating covenants and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance, and stock price.
Item 2. Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds.
None.
Item 3. Defaults Upon Senior Securities.
None.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
Item 5. Other Information.
Not applicable
| 24 |
| Table of Contents |
Item 6. Exhibits.
Exhibits filed or furnished with this report:
Exhibit Number |
| Description |
| Filed Herewith | Form | Filing Date | SEC File No. |
|
| 8-K | September 17, 2021 | 001-15543 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Palatin Technologies, Inc., as amended. |
|
| 10-K | September 27, 2013 | 001-15543 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8-K | August 31, 2022 | 001-15543 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| X |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| * |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| * |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Instance Document (the instance document does not appear on the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document). |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE |
| Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
104 |
| Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
|
|
|
|
|
*In accordance with Item 601(b)(32)(ii) of Regulation S-K and SEC Release Nos. 33-8238 and 34-47986, Final Rule: Management’s Reports on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting and Certification of Disclosure in Exchange Act Periodic Reports, the certification furnished in Exhibits 32.1 and 32.2 hereto are deemed to accompany this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and will not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act. Such certification will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent that the registrant specifically incorporates it by reference.
| 25 |
| Table of Contents |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
|
| Palatin Technologies, Inc. |
|
|
| (Registrant) |
|
| |||
|
| /s/ Carl Spana |
|
Date: May 15, 2023 |
| Carl Spana, Ph.D. President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| /s/ Stephen T. Wills |
|
Date: May 15, 2023 |
| Stephen T. Wills, CPA, MST Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Operating Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
|
| 26 |