00008911032021FYfalseP1MP5DP5DP3YP2Yhttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherAssetsNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherAssetsNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#AccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#AccruedLiabilitiesCurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrenthttp://fasb.org/us-gaap/2021-01-31#OtherLiabilitiesNoncurrent00008911032021-01-012021-12-3100008911032022-02-18xbrli:shares00008911032021-06-30iso4217:USD00008911032021-12-3100008911032020-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares00008911032020-01-012020-12-3100008911032019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CostOfSalesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SellingAndMarketingExpenseMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2019-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2018-12-3100008911032018-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:ParentMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:ParentMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2019-12-3100008911032019-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMemberus-gaap:ParentMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:FormerIACMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:ParentMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMemberus-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MatchGroupAndANGIHomeservicesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:FormerClassACommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TreasuryStockMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:RedeemableNoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ParentMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-31mtch:languangemtch:segment0000891103mtch:NewMatchCommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMember2021-01-012021-12-31mtch:app_store0000891103us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMembermtch:AppStoreAMember2021-01-012021-12-31xbrli:pure0000891103us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMembermtch:AppStoreBMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMembermtch:AppStoreAMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CustomerConcentrationRiskMembermtch:AppStoreBMemberus-gaap:AccountsReceivableMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembersrt:AmericasMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembersrt:AmericasMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembersrt:AmericasMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103srt:EuropeMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:EuropeMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103srt:EuropeMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:AsiaPacificAndOtherMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:AsiaPacificAndOtherMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:AsiaPacificAndOtherMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelThroughIntermediaryMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelThroughIntermediaryMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelThroughIntermediaryMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:TinderMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:TinderMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMembermtch:TinderMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:OtherBrandsMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:OtherBrandsMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:OtherBrandsMemberus-gaap:SalesChannelDirectlyToConsumerMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ComputerEquipmentAndCapitalizedSoftwareMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ComputerEquipmentAndCapitalizedSoftwareMembersrt:MaximumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:FurnitureAndOtherEquipmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2020-12-31mtch:unit0000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MinimumMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MaximumMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:IndefinitelivedIntangibleAssetsMembersrt:MaximumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:TradeNamesMembersrt:EuropeMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TradeNamesMembersrt:EuropeMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103srt:RevisionOfPriorPeriodAccountingStandardsUpdateAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Member2020-01-012020-12-310000891103srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103srt:RevisionOfPriorPeriodAccountingStandardsUpdateAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Member2019-01-012019-12-310000891103srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2020-12-3100008911032021-01-010000891103srt:RevisionOfPriorPeriodAccountingStandardsUpdateAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Member2021-01-010000891103us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMemberus-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Membersrt:CumulativeEffectPeriodOfAdoptionAdjustmentMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Membersrt:CumulativeEffectPeriodOfAdoptionAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:CarriedForwardIndefinitelyMemberus-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExpiresWithinTwentyYearsMemberus-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignCountryMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:CarriedForwardIndefinitelyMemberus-gaap:ForeignCountryMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignCountryMembermtch:ExpiresWithinTwentyYearsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ResearchMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExpiresWithinTwentyYearsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignCountryMemberus-gaap:GeneralBusinessMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExpiresWithinTenYearsMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:IACInterActiveCorpMemberus-gaap:DiscontinuedOperationsDisposedOfBySaleMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:IACInterActiveCorpMemberus-gaap:DiscontinuedOperationsDisposedOfBySaleMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:IACInterActiveCorpMemberus-gaap:DiscontinuedOperationsDisposedOfBySaleMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:HyperconnectIncMember2021-06-172021-06-170000891103mtch:HyperconnectIncMember2021-06-170000891103us-gaap:CustomerListsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CustomerListsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:TradeNamesMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:TradeNamesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CustomerListsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TechnologyBasedIntangibleAssetsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:TradeNamesMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:OtherIntangibleAssetsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:BankTimeDepositsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2020-12-310000891103mtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2020-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-09-220000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-09-222021-10-040000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Memberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2022-01-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-11-212021-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:TermLoanDueFebruary132027Memberus-gaap:LoansPayableMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:TermLoanDueFebruary132027Memberus-gaap:LoansPayableMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4625SeniorNotesDueJune12028Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4625SeniorNotesDueJune12028Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Member2020-12-310000891103mtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2020-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Member2020-02-130000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Memberus-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Memberus-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Member2020-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityDueFebruary132025Membersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:TermLoanDueFebruary132027Memberus-gaap:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBORMemberus-gaap:LoansPayableMember2020-02-132020-02-130000891103mtch:AmendedCreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LoansPayableMember2021-03-260000891103mtch:CreditFacilityAndTermLoanMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:CreditFacilityAndTermLoanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMembermtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMembermtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A3625SeniorNotesDueOctober12031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A6.375SeniorNotesdueJune012024Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4625SeniorNotesDueJune12028Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4625SeniorNotesDueJune12028Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMembermtch:A4625SeniorNotesDueJune12028Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A4125SeniorNotesDueAugust012030Memberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMembermtch:A5.625SeniorNotesdueFebruary152029Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodOneMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodTwoMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodThreeMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:DebtInstrumentRedemptionPeriodFourMembermtch:A5.00SeniorNotesdueDecember152027Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A6.375SeniorNotesdueJune012024Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2017-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2019-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-31mtch:trading_day0000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober120220875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:MatchGroupFinanceCo2IncMatchGroupFinanceCo3IncMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMembermtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Membermtch:ExchangeableNotesWarrantMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:ExchangeableNotesWarrantMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJune152026Member2021-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:ExchangeableNotesWarrantMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-040000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-042021-10-040000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-042021-10-040000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-040000891103mtch:A3625SeniorNotesDue2031Memberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2021-10-042021-10-04mtch:vote0000891103mtch:Series1MandatorilyExchangeablePreferredStockMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:Series2MandatorilyExchangeablePreferredStockMember2021-12-3100008911032020-07-012020-07-310000891103mtch:ExchangeableNotesHedgeMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-012021-10-310000891103us-gaap:SeniorNotesMembermtch:A0875ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueOctober12022Member2021-10-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AociGainLossDebtSecuritiesAvailableForSaleWithAllowanceForCreditLossParentMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AociGainLossDebtSecuritiesAvailableForSaleWithAllowanceForCreditLossParentMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AociGainLossDebtSecuritiesAvailableForSaleWithAllowanceForCreditLossParentMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AccumulatedTranslationAdjustmentMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AociGainLossDebtSecuritiesAvailableForSaleWithAllowanceForCreditLossParentMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AociGainLossDebtSecuritiesAvailableForSaleWithAllowanceForCreditLossParentMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2020-06-300000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Membermtch:ExchangeableNotesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:A200ExchangeableSeniorNotesDueJanuary152030Membermtch:ExchangeableNotesMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:StockOptionsWarrantsAndRestrictedStockUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:StockOptionsWarrantsAndRestrictedStockUnitsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:StockOptionsWarrantsAndRestrictedStockUnitsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsAndPerformanceBasedOptionsAndUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsAndPerformanceBasedOptionsAndUnitsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsAndPerformanceBasedOptionsAndUnitsMember2019-01-012019-12-31mtch:plan0000891103us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-31mtch:installment0000891103us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsMembersrt:MinimumMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:MaximumMembermtch:MarketBasedAwardsMember2021-01-012021-12-3100008911032020-07-012020-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeOneMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeOneMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeTwoMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeTwoMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeThreeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeThreeMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeFourMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeFourMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeFiveMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:ExercisePriceRangeFiveMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:RestrictedStockUnitsandPerformanceStockUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:RestrictedStockUnitsandPerformanceStockUnitsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:MarketBasedAwardsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-12-310000891103country:US2021-01-012021-12-310000891103country:US2020-01-012020-12-310000891103country:US2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:NonUsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:NonUsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:NonUsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103country:USus-gaap:SalesRevenueNetMemberus-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103country:US2021-12-310000891103country:US2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:NonUsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:NonUsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:PropertyPlantAndEquipmentMembercountry:USus-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:PurchaseCommitmentMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:LettersOfCreditAndSuretyBondsMember2021-12-31mtch:lawsuit0000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2018-08-142018-08-14mtch:plaintiff0000891103us-gaap:PendingLitigationMembermtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2018-08-142018-08-140000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2018-08-312018-08-310000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2019-06-132019-06-130000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2020-07-132020-07-130000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2020-09-032020-09-03mtch:arbitration0000891103mtch:TinderOptionholderLitigationMember2021-12-012021-12-010000891103srt:AffiliatedEntityMembermtch:LeasingArrangementsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103srt:AffiliatedEntityMembermtch:PassThroughTransactionsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:CommonStockMembermtch:SeparationAgreementMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMember2020-07-012020-07-310000891103mtch:TaxSharingAgreementMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:TaxSharingAgreementMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMemberus-gaap:OtherCurrentAssetsMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:TaxSharingAgreementMemberus-gaap:OtherNoncurrentAssetsMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMember2021-12-310000891103srt:AffiliatedEntityMembermtch:TransitionServicesAgreementMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:EquityAwardTransactionsMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103mtch:EquityAwardTransactionsMembersrt:AffiliatedEntityMember2021-12-3100008911032019-01-012019-06-300000891103country:US2021-01-012021-12-310000891103country:US2020-01-012020-12-310000891103country:US2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignPlanMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ForeignPlanMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:ComputerEquipmentAndCapitalizedSoftwareMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:ComputerEquipmentAndCapitalizedSoftwareMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:BuildingAndBuildingImprovementsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:LandMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:LandMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:FurnitureAndOtherEquipmentMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:FurnitureAndOtherEquipmentMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2020-12-3100008911032021-01-012021-03-3100008911032021-04-012021-06-3000008911032021-07-012021-09-3000008911032021-10-012021-12-3100008911032020-01-012020-03-3100008911032020-04-012020-06-3000008911032020-07-012020-09-3000008911032020-10-012020-12-310000891103srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2020-10-012020-12-310000891103srt:RevisionOfPriorPeriodAccountingStandardsUpdateAdjustmentMemberus-gaap:AccountingStandardsUpdate202006Member2020-10-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2021-12-310000891103mtch:OtherReservesMember2020-12-310000891103mtch:OtherReservesMember2021-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2020-01-012020-12-310000891103mtch:OtherReservesMember2019-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2018-12-310000891103us-gaap:ValuationAllowanceOfDeferredTaxAssetsMember2019-01-012019-12-310000891103mtch:OtherReservesMember2018-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| | | | | | | | |
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the Fiscal Year Ended | December 31, 2021 |
| Or |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from__________to__________ |
Commission File No. 001-34148
Match Group, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | | | | |
Delaware | | 59-2712887 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
8750 North Central Expressway, Suite 1400, Dallas, Texas 75231
(Address of Registrant’s principal executive offices and zip code)
(214) 576-9352
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Title of each class | | Trading Symbol | | Name of exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 | | MTCH | | The Nasdaq Global Market LLC |
| | | | (Nasdaq Global Select Market) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☑ | | Accelerated filer | ☐ | | Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | | Emerging growth company | ☐ | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal controls over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
As of February 18, 2022, there were 285,148,288 shares of common stock outstanding.
The aggregate market value of the voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2021 was $44,438,964,739. For the purpose of the foregoing calculation only, shares held by all directors and executive officers of the registrant are assumed to be held by affiliates of the registrant.
Documents Incorporated By Reference:
Portions of Part III of this Annual Report are incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s proxy statement for its 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cautionary Statement Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This annual report on Form 10-K contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. The use of words such as “anticipates,” “estimates,” “expects,” “plans” and “believes,” among others, generally identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements include, among others, statements relating to: Match Group’s future financial performance, Match Group’s business prospects and strategy, anticipated trends and prospects in the industries in which Match Group’s businesses operate and other similar matters. These forward-looking statements are based on Match Group management’s current expectations and assumptions about future events as of the date of this annual report, which are inherently subject to uncertainties, risks and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict.
Actual results could differ materially from those contained in these forward-looking statements for a variety of reasons, including, among others: the risk factors set forth in “Item 1A—Risk Factors.” Other unknown or unpredictable factors that could also adversely affect Match Group’s business, financial condition and results of operations may arise from time to time. In light of these risks and uncertainties, these forward-looking statements discussed in this annual report may not prove to be accurate. Accordingly, you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which only reflect the views of Match Group management as of the date of this annual report. Match Group does not undertake to update these forward-looking statements.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Who we are
Match Group, Inc., through its portfolio companies, is a leading provider of digital technologies designed to help people make meaningful connections. Our global portfolio of brands includes Tinder®, Match®, Hinge®, Meetic®, OkCupid®, Pairs™, PlentyOfFish®, OurTime®, Azar®, Hakuna™ Live, and more, each built to increase our users’ likelihood of connecting with others. Through our trusted brands, we provide tailored services to meet the varying preferences of our users. Our services are available in over 40 languages to our users all over the world.
As used herein, “Match Group,” the “Company,” “we,” “our,” “us,” and similar terms refer to Match Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries after the completion of the Separation (defined below), unless the context indicates otherwise.
Separation of Match Group and IAC
On June 30, 2020, the companies formerly known as Match Group, Inc. (referred to as “Former Match Group”) and IAC/InterActiveCorp (referred to as “Former IAC”) completed the separation of the Company from IAC through a series of transactions that resulted in two, separate public companies—(1) Match Group, which consists of the businesses of Former Match Group and certain financing subsidiaries previously owned by Former IAC, and (2) IAC/InterActiveCorp, formerly known as IAC Holdings, Inc. (“IAC”), consisting of Former IAC’s businesses other than Match Group (the “Separation”).
The following diagram illustrates the simplified organizational and ownership structure immediately prior to the Separation.

Under the terms of the Transaction Agreement (the “Transaction Agreement”) dated as of December 19, 2019 and amended as of April 28, 2020 and as further amended as of June 22, 2020, Former Match Group merged with and into Match Group Holdings II, LLC (“MG Holdings II”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group, with MG Holdings II surviving the merger as an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group. Former Match Group stockholders (other than Former IAC) received, through the merger, in exchange for each outstanding share of Former Match Group common stock that they held, one share of Match Group common stock and, at the holder’s election, either (i) $3.00 in cash or (ii) a fraction of a share of Match Group common stock with a value of $3.00 (calculated pursuant to the Transaction Agreement). As a result of the merger and other transactions contemplated by the Transaction Agreement, Former Match Group stockholders (other than Former IAC) became stockholders of the Company.
The following diagram illustrates the simplified organizational and ownership structure of IAC and Match Group immediately after the Separation.
The Company was incorporated in 1986 in Delaware and underwent many name changes before becoming IAC/InterActiveCorp prior to the Separation described above. Former Match Group completed an initial public offering in 2015 and had operated as a stand-alone public company since that time. Upon the Separation described above, the Company changed its name to Match Group, Inc.
The business of creating meaningful connections
Our goal is to spark meaningful connections for users around the world. Consumers’ preferences vary significantly, influenced in part by demographics, geography, cultural norms, religion, and intent (for example, seeking friendship, casual dating, or more serious relationships). As a result, the market for connecting with others through relationship technologies is fragmented, and no single service has been able to effectively serve the relationship technology category.
Prior to the proliferation of the internet and mobile devices, human connections traditionally were limited by social circles, geography, and time. People met through work colleagues, friends and family, in school, at church, at social gatherings, in bars and restaurants, or in other social settings. Today, the adoption of mobile technology and the internet has significantly expanded the ways in which people can create new interactions, and develop meaningful connections and relationships. Additionally, the ongoing adoption of technology into more aspects of daily life continues to further erode biases and stigmas across the world that previously served as barriers to individuals using technology to help find and develop those connections.
We believe that technologies that bring people together serve as a natural extension of the traditional means of meeting people and provide a number of benefits for users, including:
•Expanded options: Relationship technologies provide users access to a large pool of people they otherwise would not have a chance to meet.
•Efficiency: The search and recommending features, as well as the profile information available on relationship technologies, allow users to filter a large number of individuals in a short period of time, increasing the likelihood that users will make a connection with someone.
•More comfort and control: Compared to the traditional ways that people meet, relationship technologies provide an environment that reduces the awkwardness around identifying and reaching out to new people who are interested in connecting. This leads to many people who would otherwise be passive participants taking a more active role.
•Safely meet new people: Relationship technologies can offer a safer way to contact new people for the first-time by limiting the amount of personal information exchanged and providing an opportunity to vet a new connection before meeting in person, including via video communication.
•Convenience: The nature of the internet and the proliferation of mobile devices allow users to connect with new people at any time, regardless of where they are.
Depending on a person’s circumstances at any given time, relationship technologies can act as a supplement to, or substitute for, traditional means of meeting people. When selecting a relationship technology service, we believe that users consider the following attributes:
•Brand recognition and scale: Brand is very important. Users generally associate strong brands with a higher likelihood of success and more tools to help the user connect safely and securely. Generally, successful brands depend on large, active communities of users, strong algorithmic filtering technology, and awareness of successful usage among similar users.
•Successful experiences: Demonstrated success of other users attracts new users through word-of-mouth recommendations. Successful experiences also drive repeat usage.
•Community identification: Users typically look for relationship technologies that offer a community or communities to which the user can relate. By selecting a relationship technology service that is focused on a particular demographic, religion, geography, or intent, users can increase the likelihood that they will make a connection with someone with whom they identify.
•Service features and user experience: Users tend to gravitate towards relationship technologies that offer features and user experiences that resonate with them, such as question-based matching algorithms, location-based features, or search capabilities. User experience is also driven by the type of user interface (for example, using our patented Swipe® technology versus scrolling), a particular mix of free and paid features, ease of use, privacy, and security. Users expect every interaction with a relationship technology service to be seamless and intuitive.
Given varying consumer preferences, we have adopted a brand portfolio approach, through which we attempt to offer relationship technologies that collectively appeal to the broadest spectrum of consumers. We believe that this approach maximizes our ability to attract additional users.
Our portfolio
Making connections with other people online is a highly personal endeavor and consumers have a wide variety of preferences that determine what type of technologies they choose to make those connections. As a result, our strategy focuses on a portfolio approach of various brands in order to reach a broad range of users. Many of our brands have a long legacy, while others emerged during the time when mobile devices proliferated. The following is a list of our key brands:
Tinder. The Tinder® platform, incubated at the Company, was launched in 2012 and has since risen to scale and popularity faster than any other service in the online dating category, growing to over 10.6 million payers as of the fourth quarter of 2021. Tinder’s patented Swipe® technology has led to significant adoption, particularly among 18 to 30 year-old users, who were historically underserved by the online dating category. Tinder employs a freemium model, through which users are allowed to enjoy many of the core features of Tinder for free, including limited use of the Swipe Right® feature with unlimited communication with other users. However, to enjoy premium features, such as unlimited use of the Swipe Right feature, a Tinder user must subscribe to one of several subscription offerings: Tinder Plus®, launched in early 2015; Tinder Gold®, which was launched in late summer 2017; or Tinder Platinum®, launched in late 2020. Tinder users and subscribers may also pay for certain premium features, such as Super Likes™ and Boosts, on a pay-per-use basis. In 2021, Tinder launched Tinder Explore™, a hub within the app that hosts completely new, interactive ways to use Tinder, such as Hot Takes, Vibes, and the Swipe Night™ interactive series.
Match. The Match® platform was launched in 1995 and helped create the online dating category with the ability to search profiles and receive algorithmic recommendations. Match has since introduced a softer paywall to allow limited free access to messaging and other features before requiring a subscription, as well as a one-to-one real-time video feature. Additionally, Match offers its subscribers a higher level of service than most of our other brands, including access to date coaching services and profile reviews. Match is a brand that focuses on users with a higher level of intent to enter into a serious relationship and its services and marketing are designed to reinforce that purpose.
Hinge. Hinge® was launched in 2012 and has grown to be a popular app for relationship-minded individuals, particularly among the millennial and younger generations, in the United States, the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Australia. Hinge is a mobile-only experience and employs a freemium model. Hinge focuses on users with a higher level of intent to enter into a serious relationship and its services are designed to reinforce that purpose. In 2021, Hinge launched Video Prompts, Voice Prompts, and Voice Notes. With these new features, users can better showcase who they are through text, photos, video, and now, voice at different points in their dating journey.
Meetic. Meetic®, a leading European online dating brand based in France, was launched in 2001. Meetic is the most recognized dating app for singles over age 35 in Europe. Meetic is a brand that focuses on users with a higher level of intent to enter into a serious relationship and its service and marketing are designed to reinforce that purpose. In 2021, Meetic began offering a softer paywall revenue model. Meetic recently introduced online audio and video chat rooms into the Meetic experience.
OkCupid. OkCupid® was launched in 2004 and has attracted users through a Q&A approach to the dating category. OkCupid relies on a freemium model and has a loyal, culturally progressive user base predominately located in larger metropolitan areas in English-speaking markets, with an increasing presence in other global markets such as Israel, Germany, and Turkey.
Pairs. Pairs™ was launched in 2012 and is a leading provider of dating services in Japan, with a presence in Taiwan and South Korea. Pairs is a dating platform that was specifically designed to address social barriers generally associated with the use of dating services in Eastern Asian countries, particularly Japan.
PlentyOfFish. PlentyOfFish® was launched in 2003. Among its distinguishing features is the ability to both search profiles and receive algorithmic recommendations. PlentyOfFish has grown in popularity over the years and relies on a freemium model. PlentyOfFish has broad appeal in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, and a number of other international markets. In 2020, PlentyOfFish launched POF Live™, a one-to-many live streaming video feature that allows users to engage with other users at PlentyOfFish in a new and different format from traditional dating profiles.
OurTime. OurTime® is the largest community of singles over age 50 of any dating service. We offer this service in the United States, Canada, and a number of European markets.
Azar. Azar® was launched in 2014 and acquired in 2021 through our acquisition of Hyperconnect. Azar is a one-to-one video chat service powered by real-time language translations that allow users to meet and interact with a variety of people across the globe in their native language. Azar is primarily focused in the APAC and Other regions, with growth in Western Europe.
Hakuna Live. Hakuna™ Live was launched in 2019 and acquired in 2021 through our acquisition of Hyperconnect. Hakuna Live is an interactive, social app that allows for one-to-many live streaming experiences. Hakuna offers virtual gifting and its userbase is predominantly located in the APAC and Other regions.
In addition to the brands above, our portfolio includes brands such as Chispa™, BLK®, and Upward®, each of which brings the Swipe® feature made popular by Tinder to the Latino, Black, and Christian communities, respectively.
We strive to empower individual brand leaders with the authority and incentives to grow their respective brands. Our brands compete with each other and with third-party businesses on brand characteristics, service features, and business model.
We also work to apply a centralized discipline to our portfolio of brands and share best practices across our brands in order to quickly introduce new services and features, optimize marketing, increase growth, reduce costs, improve user safety, and maximize profitability. Additionally, we centralize certain other administrative
functions, such as legal, accounting, finance, and tax. We attempt to centrally facilitate excellence and efficiency across the entire portfolio by:
•centralizing operational functions across certain brands where we have strength in personnel and sufficient commonality of business interest (for example, ad sales, online marketing, and information technology are centralized across some, but not all, brands);
•developing talent across the portfolio to allow for development of specific proficiencies and promoting career advancement while maintaining the ability to deploy the best talent in the most critical positions across the company at any given time; and
•sharing analytics to leverage services and marketing successes across our businesses rapidly for competitive advantage.
Staying competitive
The industry for relationship technologies is competitive and has no single, dominant brand globally. We compete with a number of other companies that provide similar technologies for people to meet each other, including other online dating platforms; social media platforms; social-discovery apps; offline dating services, such as in-person matchmakers; and other traditional means of meeting people.
We believe that our ability to attract new users to our brands will depend primarily upon the following factors:
•our ability to continue to increase consumer acceptance and adoption of technologies to meet other people, particularly in emerging markets and other parts of the world where the associated stigma has not yet fully eroded;
•continued growth in internet access and smart phone adoption in certain regions of the world, particularly emerging markets;
•the continued strength of our established brands and the growth of our emerging brands;
•the breadth and depth of our active communities of users;
•our brands’ reputation for trust and safety;
•our ability to evolve our services to keep up with user requirements, social trends, and the ever-evolving technological landscape;
•our brands’ ability to keep up with the constantly changing regulatory landscape, in particular, as it relates to the regulation of consumer digital media platforms;
•our ability to efficiently acquire new users for our services;
•our ability to continue to optimize our monetization strategies; and
•the design and functionality of our services.
A large portion of customers use multiple services over a given period of time, either concurrently or sequentially, making our broad portfolio of brands a competitive advantage.
Where we earn our revenue
All our brands enable users to establish a profile and review other users’ profiles without charge. Each brand also offers additional features, some of which are free, and some of which require payment depending on the particular service. In general, access to premium features requires a subscription, which is typically offered in packages (generally ranging from one to six months), depending on the service and circumstance. Prices can differ meaningfully within a given brand depending on the duration of a subscription, the bundle of paid features that a user chooses to access, and whether or not a user is taking advantage of any special offers. In addition to subscriptions, many of our brands offer users certain features, such as the ability to promote themselves for a given period of time, or highlight themselves to a specific user, and these features are offered on a pay-per-use, or à la carte, basis. The precise mix of paid and premium features is established over time on a brand-by-brand basis and is subject to constant iteration and evolution.
Our direct revenue is primarily derived from users in the form of recurring subscriptions, which typically provide unlimited access to a bundle of features for a specified period of time, and to a lesser extent from à la carte features, where users pay a non-recurring fee for a specific consumable benefit or feature. Each of our brands offers a combination of free and paid features targeted to its unique community. In addition to direct revenue from our users, we generate indirect revenue from advertising, which comprises a much smaller percentage of our overall revenue as compared to direct revenue.
Dependencies on services provided by others
App Stores
We fully rely on the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store to distribute our mobile applications and related in-app services. While our mobile applications are free to download from these stores, we offer our users the opportunity to purchase subscriptions and certain à la carte features through these applications. We determine the prices at which these subscriptions and features are sold; however, currently, purchases of these subscriptions and features are required in most cases to be processed through the in-app payment systems provided by Apple and Google. Due to these requirements, we pay Apple and Google, as applicable, a meaningful share (generally 30%, although as of January 1, 2022 Google has reduced the percentage applicable to subscriptions to 15%) of the revenue we receive from these transactions.
Additionally, when our users and subscribers access and pay through the app stores, Apple and Google may receive personal data about our users and subscribers that we would otherwise receive if we transacted with our users and subscribers directly. Apple and Google have restricted our access to much of that data.
Both Apple and Google have broad discretion to change their respective terms and conditions applicable to the distribution of our applications, including the amount of, and requirement to pay, certain fees associated with purchases required to be facilitated by Apple and Google through their payment systems, and to interpret their respective terms and conditions in ways that may limit, eliminate or otherwise interfere with our ability to distribute our applications through their stores, the features we provide, the manner in which we market our in-app services, and our ability to access information about our users and subscribers that they collect. Apple or Google could also make changes to their operating systems or payment services that could negatively impact our business, including by unilaterally raising the prices for those services.
The manner in which Apple and Google operate these services is being reviewed by legislative and regulatory bodies globally. Notably, the Republic of Korea recently adopted legislation that prohibits Apple and Google from requiring that developers exclusively use Apple and Google to process payments. In the Netherlands, the Authority for Consumers and Markets found Apple’s requirement that online dating companies must exclusively use Apple’s in-app payment violates both Dutch and European Union law. Multiple other jurisdictions, including the European Union, United Kingdom, Russia, Japan, and India are investigating, considering regulatory action or considering legislation to restrict or prohibit these practices. The United States Congress, as well as a number of state legislatures, are also considering legislation that would regulate certain terms of the relationships between developers and Apple and Google and prohibit Apple and Google from requiring in-app payment processing.
Cloud and Other Services
We rely on third parties, primarily data-center service providers and cloud-based, hosted web service providers, such as Amazon Web Services, as well as third party computer systems, broadband and other communications systems and service providers, in connection with the provision of our applications generally, as well as to facilitate and process certain transactions with our users. We have no control over any of these third parties or their operations.
Problems experienced by third-party data center service providers and cloud-based, hosted web service providers, such as Amazon Web Services, upon which brands including Tinder, Pairs, and Hinge rely, the telecommunications network providers with which we or they contract, or with the systems through which telecommunications providers allocate capacity among their customers could also adversely affect us. Any changes in service levels at our data centers or hosted web service providers, such as Amazon Web Services, or any interruptions, outages or delays in our systems or those of our third party providers, or deterioration in the
performance of these systems, could impair our ability to provide our services or process transactions with our users, which would adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Sales and marketing
All of our brands rely on word-of-mouth, or free, user acquisition to varying degrees. Our brands also rely on paid user acquisition for a significant percentage of their users. Our online marketing activities generally consist of purchasing social media advertising, banner, and other display advertising, search engine marketing, email campaigns, video advertising, business development or partnership arrangements, creating content, and partnering with influencers, among other means to promote our services. Our offline marketing activities generally consist of television advertising, out-of-home advertising, and public relations efforts.
Intellectual property
We regard our intellectual property rights, including trademarks, domain names, and other intellectual property, as critical to our success.
For example, we rely heavily upon the use of trademarks (primarily Tinder®, Match®, PlentyOfFish®, OkCupid®, Meetic®, OurTime®, Pairs™, Hinge®, Swipe®, Azar®, and Hakuna™, and associated domain names, taglines and logos) to market our services and applications and build and maintain brand loyalty and recognition. We maintain an ongoing trademark and service mark registration program, pursuant to which we register our brand names, service names, taglines and logos and renew existing trademark and service mark registrations in the United States and other jurisdictions to the extent we determine it to be necessary or otherwise appropriate and cost-effective. In addition, we have a trademark and service mark monitoring policy pursuant to which we monitor applications filed by third parties to register trademarks and service marks that may be confusingly similar to ours, as well as potential unauthorized use of our material trademarks and service marks. Our enforcement of this policy affords us valuable protection under current laws, rules and regulations. We also reserve and register (to the extent available) and renew existing registrations for domain names that we believe are material to our business.
We also rely upon a combination of in-licensed third-party and proprietary trade secrets, including proprietary algorithms, and upon patented and patent-pending technologies, processes, and features relating to our recommendation process systems or features and services with expiration dates from 2023 to 2040. We have an ongoing invention recognition program pursuant to which we apply for patents to the extent we determine it to be core to our service or businesses or otherwise appropriate and cost-effective.
We rely on a combination of internal and external controls, including applicable laws, rules and regulations, and contractual restrictions with employees, contractors, customers, suppliers, affiliates, and others, to establish, protect, and otherwise control access to our various intellectual property rights.
Government regulation
We are subject to a variety of laws and regulations in the United States and abroad that involve matters that are important to or may otherwise impact our business, including, among others, broadband internet access, online commerce, advertising, user privacy, data protection, intermediary liability, protection of minors, consumer protection, general safety, sex-trafficking, taxation, money laundering, and securities law compliance. As a result, we could be subject to actions based on negligence, regulatory compliance, various torts, and trademark and copyright infringement, among other actions. See “Risk factors—Risks relating to our business—Our business is subject to complex and evolving U.S. and international laws and regulations, including with respect to data privacy and platform liability. These laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations, declines in user growth or engagement, claims, monetary penalties, or otherwise harm our business” and “—Risks relating to our business—We may fail to adequately protect our intellectual property rights or may be accused of infringing the intellectual property rights of third parties.”
Because we receive, store, and use a substantial amount of information received from or generated by our users, we are particularly impacted by laws and regulations governing privacy; the storage, sharing, use, processing, disclosure, and protection of personal data; and data breaches, in many of the countries in which we operate. For example, in 2016, the European Commission adopted the General Data Protection Act (which we
refer to as “GDPR”), a comprehensive EU privacy and data protection reform that became effective in May 2018. The act applies to companies established in the EU or otherwise providing services or monitoring the behavior of people located in the EU and provides for significant penalties in case of non-compliance as well as a private right of action for individual claimants. GDPR will continue to be interpreted by EU data protection regulators, which have and may in the future require that we make changes to our business practices, and could generate additional costs, risks, and liabilities. The EU is also considering an update to its Privacy and Electronic Communications (so-called “e-Privacy”) Directive, notably to amend rules on the use of cookies, direct marketing and processing of private communications and related metadata, which may also require that we make changes to our business practices and could generate additional costs, risks and liabilities. In July 2020, the Court of Justice of the EU declared transfers of personal data on the basis of the European Commission’s Privacy Shield Decision illegal and stipulated stricter requirements for the transfer of personal data based on standard contract clauses. This judgement and the resulting decisions and guidelines from EU supervisory authorities may require changes to our business practices and generate additional costs, risks and liabilities. Brexit could result in the application of new and conflicting data privacy and protection laws and standards to our operations in the United Kingdom and our handling of personal data of users located in the United Kingdom. At the same time, many countries in which we do business have already adopted or are also currently considering adopting privacy and data protection laws and regulations. Multiple legislative proposals concerning privacy and the protection of user information have been introduced in the U.S. Congress. Various U.S. state legislatures, including those in New York, Illinois, California, and many other states, are considering privacy legislation in 2022 and beyond. Other U.S. state legislatures have already passed and enacted privacy legislation, most prominently the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018, which was signed into law in June 2018 and came into effect on January 1, 2020, with full enforcement commencing on June 30, 2020. On November 3, 2020 the “California Privacy Rights Act of 2020” (CPRA) was enacted, which expands the state’s consumer privacy laws and creates a new government organization, the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA), to enforce the law. The majority of the CPRA’s provisions will enter into force on January 1, 2023, with a lookback to January 2022. In addition to California, comprehensive privacy laws were passed in Virginia and Colorado and are scheduled to enter into force in 2023. Additionally, the Federal Trade Commission has increased its focus on privacy and data security practices at digital companies, as evidenced by its levying, in July 2019, of a first-of-its kind, $5 billion fine against Facebook for privacy violations. Finally, talks of a U.S. federal privacy law are ongoing in Congress, with multiple proposals being considered, and may lead to the passing of a new law in 2022 or the coming years.
Concerns about harms and the use of dating products and social networking platforms for illegal conduct, such as romance scams, promotion of false or inaccurate information, financial fraud, and sex-trafficking, have produced and could continue to produce future legislation or other governmental action. For example, the EU and the United Kingdom are considering new legislation on this topic, with the United Kingdom having released its Online Harms White Paper and the EU introducing the Digital Services Act, which in each case, would expose platforms to similar or more expansive liability. In the United States, government authorities, elected officials, and political candidates have called for amendments to Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act that would purport to limit or remove protections afforded to interactive computer service providers. Proposed legislation includes the EARN IT Act, the PACT Act, the BAD ADS Act, the SAFE TECH Act, and others. If these proposed laws are passed, or if future legislation or governmental action is proposed or taken to address concerns regarding such harms, changes could be required to our products that could restrict or impose additional costs upon the conduct of our business generally or cause users to abandon our products. See “Risk factors—Risks relating to our business—Inappropriate actions by certain of our users could be attributed to us and damage our brands’ reputations, which in turn could adversely affect our business.”
Our global businesses are subject to a variety of complex and continuously evolving income and other tax frameworks. For example, the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (“OECD”) has reached political agreement for international tax reform, which includes expanding the jurisdiction of member countries to tax businesses based on some level of digital presence, as well as subjecting these companies to a global minimum tax rate of 15%. The OECD’s framework calls for countries to repeal digital services taxes once the OECD’s reforms around allocating new taxing rights to markets come into full force. The political agreement calls for reforms to be in force by 2023, and for the European Commission to put forward a draft directive to implement the OECD framework within the EU by the end of 2022. Given disagreements among the EU member countries on the implementation of the OECD framework, it is not clear that the deadline will be met.
As a provider of services with a subscription-based element, we are also subject to laws and regulations in certain U.S. states and other countries that apply to our automatically-renewing subscription payment models. For example, the EU’s Payment Services Directive (PSD2), which became effective in 2018, could impact our ability to process auto-renewal payments or offer promotional or differentiated pricing for users in the EU. Similar legislation or regulation, or changes to existing laws or regulations governing subscription payments, have been adopted or are being considered in many U.S. states.
Finally, certain U.S. states and certain countries in the Middle East and Asia have laws that specifically govern dating services.
Human talent
Our people are critical to Match Group’s continued success and we work hard to attract, retain and motivate qualified talent. As of December 31, 2021, we had approximately 2,500 full-time and approximately 40 part-time employees, which represents a 35% year-over-year increase in employee headcount, primarily due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect in the second quarter of 2021. We expect headcount growth to continue for the foreseeable future, particularly as we continue to focus on recruiting employees in technical functions such as software engineers. In addition, we plan to continue to hire a number of employees and contractors to continue to bolster various privacy, safety and data security initiatives as well as other functions to support our expected growth. As of December 31, 2021, approximately 59%, 15%, and 26% of our employees reside in the Americas, Europe, and APAC and Other regions, respectively, spanning 23 countries and reflecting various cultures, backgrounds, ages, sexes, gender identities, sexual orientations, and ethnicities. Our global workforce is highly educated, with the majority of our employees working in engineering or technical roles that are central to the technological and service innovations that drive our business. Competition for qualified talent has historically been intense, particularly for software engineers and other technical staff.
We believe that an equitable and inclusive environment with diverse teams produces more creative solutions, results in better, more innovative services and is crucial to our efforts to attract and retain key talent. We work to support our goals of diversifying our workforce through recruiting, retention, and people development. Our goal is to create a culture where everybody, from everywhere and with every background, can contribute, grow, and thrive.
Our compensation and benefits programs are designed to attract and reward talented individuals who possess the skills necessary to support our business objectives, assist in the achievement of our strategic goals and create long-term value for our stockholders. In addition to salaries, these programs (which vary by country/region) include annual bonuses, stock-based awards, an employee stock purchase plan, retirement benefits, healthcare, and insurance benefits, paid time off, family leave, flexible work schedules, mental health and wellness programs, and employee assistance programs. We are committed to providing competitive and equitable pay. We base our compensation on market data and conduct evaluations of our compensation practices on a regular basis to determine the competitiveness and fairness of our packages.
We are committed to empowering our people with career advancement and learning opportunities. Our talent development programs provide employees with resources to help achieve their career goals, build management skills and contribute to and, where applicable, lead their organizations.
We regularly conduct anonymous surveys to seek feedback from our employees on a variety of topics, including but not limited to, confidence in company leadership, competitiveness of our compensation and benefits, career growth opportunities and ways to improve our company’s position as an employer of choice. The results are shared with our employees and reviewed by senior leadership, who analyze areas of progress or opportunity and prioritize actions and activities in response to this feedback to drive meaningful improvements in employee engagement.
We believe that our approach to talent has been instrumental in our growth, and has made Match Group a desirable destination for current and future employees.
Additional information
Company website and public filings. Investors and others should note that we announce material financial and operational information to our investors using our investor relations website at https://ir.mtch.com, Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filings, press releases, and public conference calls. We use these
channels as well as social media to communicate with our users and the public about our company, our services, and other issues. It is possible that the information we post on social media could be deemed to be material information. Accordingly, investors, the media, and others interested in our company should monitor the social media channels listed on our investor relations website in addition to following our SEC filings, press releases, and public conference calls. Neither the information on our website, nor the information on the website of any Match Group business, is incorporated by reference into this report, or into any other filings with, or into any other information furnished or submitted to, the SEC.
The Company makes available, free of charge through its website, its Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, and Current Reports on Form 8-K (including related amendments) as soon as reasonably practicable after they have been electronically filed with (or furnished to) the SEC.
Code of ethics. The Company’s code of ethics applies to all employees (including Match Group’s principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer) and directors and is posted on the Company’s website at https://ir.mtch.com under the heading of “Corporate Governance.” This code of ethics complies with Item 406 of SEC Regulation S-K and the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC. Any changes to the code of ethics that affect the provisions required by Item 406 of Regulation S-K, and any waivers of such provisions of the code of ethics for Match Group’s executive officers, senior financial officers or directors, will also be disclosed on Match Group’s website.
Relationship with IAC after the Separation
In connection with the Separation, the Company entered into certain agreements with IAC to govern the relationship between the Company and IAC following the Separation. These agreements, in certain cases, supersede the agreements entered into between Former Match Group and Former IAC in connection with Former Match Group’s IPO in November 2015 (the “IPO Agreements”) and include: a tax matters agreement; a transition services agreement; and an employee matters agreement. The IPO Agreements that were not superseded were terminated at closing of the Separation.
In addition to the agreements entered into at the time of the Separation, Match Group leases office space to IAC in a building owned by the Company in Los Angeles. Match Group also leased office space from IAC in New York City on a month-to-month basis through June 2021.
Tax Matters Agreement
Pursuant to the tax matters agreement, each of Match Group and IAC is responsible for certain tax liabilities and obligations following the transfer by Former IAC (i) to Match Group of certain assets and liabilities of, or related to, the businesses of Former IAC (other than Former Match Group) and (ii) to holders of Former IAC common stock and Former IAC Class B common stock, as a result of the reclassification and mandatory exchange of certain series of Former IAC exchangeable preferred stock (collectively, the “IAC Distribution”). Under the tax matters agreement, IAC generally is responsible for, and has agreed to indemnify Match Group against, any liabilities incurred as a result of the failure of the IAC Distribution to qualify for the intended tax-free treatment unless, subject to certain exceptions, the failure to so qualify is attributable to Match Group's or Former Match Group’s actions or failure to act, Match Group's or Former Match Group’s breach of certain representations or covenants or certain acquisitions of equity securities of Match Group, in each case, described in the tax matters agreement (a "Match Group fault-based action"). If the failure to so qualify is attributable to a Match Group fault-based action, Match Group is responsible for liabilities incurred as a result of such failure and will indemnify IAC against such liabilities so incurred by IAC or its affiliates.
Transition Services Agreement
Pursuant to the transition services agreement, as amended, IAC continues to provide minimal services to Match Group that Former IAC had historically provided to Former Match Group. Match Group continues to provide certain services to IAC that Former Match Group previously provided to Former IAC. The transition services agreement also provides that Match Group and IAC will make efforts to replace, amend, or divide certain joint contracts with third-parties relating to services or products used by both Match Group and IAC. Match Group and IAC also agreed to continue sharing certain services provided pursuant to certain third-party vendor contracts that were not replaced, amended, or divided prior to closing of the Separation.
Employee Matters Agreement
Pursuant to the amended and restated employee matters agreement, Match Group will reimburse IAC for the cost of any IAC equity awards held by the Company’s employees and former employees upon exercise or vesting. In addition, Match Group employees participated in IAC’s U.S. health and welfare plans, 401(k) plan and flexible benefits plan through December 31, 2020. Match Group reimbursed IAC for the costs of such participation in 2020 pursuant to the amended and restated employee matters agreement. Match Group established its own employee benefit plans effective January 1, 2021.
Other Agreements
The Transaction Agreement provides that each of Match Group and IAC has agreed to indemnify, defend and hold harmless the other party from and against any liabilities arising out of: (i) any asset or liability allocated to such party or the other members of such party's group under the Transaction Agreement or the businesses of such party's group after the closing of the Separation; (ii) any breach of, or failure to perform or comply with, any covenant, undertaking or obligation of a member of such party's group contained in the Transaction Agreement that survives the closing of the Separation or is contained in any ancillary agreement; and (iii) any untrue or misleading statement or alleged untrue or misleading statement of a material fact or omission, with respect to information contained in or incorporated into the Form S-4 Registration Statement (the “Form S-4”) filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) by IAC and Former IAC in connection with the Separation or the joint proxy statement/prospectus filed by Former IAC and Former Match Group with the SEC pursuant to the Form S-4.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Risks relating to our business
The industry for relationship technologies is competitive, with low switching costs and a consistent stream of new services and entrants, and innovation by our competitors may disrupt our business.
The industry for relationship technologies is competitive, with a consistent stream of new services and entrants. Some of our competitors may enjoy better competitive positions in certain geographical regions, user demographics or other key areas that we currently serve or may serve in the future. These advantages could enable these competitors to offer services that are more appealing to users and potential users than our services or to respond more quickly and/or cost-effectively than us to new or changing opportunities.
In addition, within the industry for relationship technologies generally, costs for consumers to switch between services are low, and consumers have a propensity to try new approaches to connecting with people and to use multiple services at the same time. As a result, new services, entrants, and business models are likely to continue to emerge. It is possible that a new service could gain rapid scale at the expense of existing brands through harnessing a new technology or a new or existing distribution channel, creating a new or different approach to connecting people or some other means.
Potential competitors include larger companies that could devote greater resources to the promotion or marketing of their services, take advantage of acquisition or other opportunities more readily or develop and expand their services more quickly than we do. Potential competitors also include established social media companies that may develop features or services that may compete with ours or operators of mobile operating systems and app stores. For example, Facebook has introduced a dating feature on its platform, which it has rolled out globally and has grown dramatically in size supported by Facebook’s massive worldwide user footprint. These social media and mobile platform competitors could use strong or dominant positions in one or more markets, and ready access to existing large pools of potential users and personal information regarding those users, to gain competitive advantages over us, including by offering different features or services that users may prefer or offering their services to users at no charge, which may enable them to acquire and engage users at the expense of our user growth or engagement.
If we are not able to compete effectively against our current or future competitors and services that may emerge, the size and level of engagement of our user base may decrease, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The limited operating history of our newer brands and services makes it difficult to evaluate our current business and future prospects.
We seek to tailor each of our brands and services to meet the preferences of specific communities of users. Building a given brand or service is generally an iterative process that occurs over a meaningful period of time and involves considerable resources and expenditures. Although certain of our newer brands and services have experienced significant growth over relatively short periods of time, the historical growth rates of these brands and services may not be an indication of future growth rates for such services or our newer brands and services generally. We have encountered, and may continue to encounter, risks and difficulties as we build our newer brands and services. The failure to successfully scale these brands and services and address these risks and difficulties could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our growth and profitability rely, in part, on our ability to attract and retain users through cost-effective marketing efforts. Any failure in these efforts could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Attracting and retaining users for our services involve considerable expenditures for online and offline marketing. Historically, we have had to increase our marketing expenditures over time in order to attract and retain users and sustain our growth.
Evolving consumer behavior can affect the availability of profitable marketing opportunities. For example, as traditional television viewership declines and as consumers spend more time on mobile devices rather than desktop computers, the reach of many of our traditional advertising channels continues to contract. Similarly, as consumers communicate less via email and more via text messaging, messaging apps and other virtual means,
the reach of email campaigns designed to attract new and repeat users (and retain current users) for our services is adversely impacted. Additionally, recent and future changes by large tech platforms, such as Apple and Google, to advertisers’ ability to access and use unique advertising identifiers, cookies and other information to acquire potential users, such as Apple’s new rules regarding the collection and use of identifiers for advertising (“IDFA”), have adversely impacted, and may continue to adversely impact, our advertising efforts. To continue to reach potential users and grow our businesses, we must identify and devote more of our overall marketing expenditures to newer advertising channels, such as mobile and online video platforms. Generally, the opportunities in and sophistication of newer advertising channels and methods continue to be less developed, proven and precise, making it more difficult to assess returns on investment associated with our advertising efforts and to cost-effectively identify potential users. There can be no assurance that we will be able to continue to appropriately manage our marketing efforts in response to these and other trends in the advertising industry. Any failure to do so could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our business and results of operations have been and may continue to be adversely affected by the recent COVID-19 outbreak or other similar outbreaks.
Our business could be materially and adversely affected by the outbreak of a widespread health epidemic or pandemic, including the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The COVID-19 pandemic has reached across the globe, resulting in the implementation of significant governmental measures intended to control the spread of the virus, including lockdowns, closures, quarantines, and travel bans, as well as changes in consumer behavior as individuals have become reluctant to engage in social activities with people outside their households. While some of these measures have been relaxed in certain parts of the world, ongoing and future prevention and mitigation measures, as well as the potential for some of these measures to be reinstituted in the event of repeat waves of the virus, have had and are likely to continue to have an adverse impact on global economic conditions and consumer confidence and spending, and could materially adversely affect demand, or users’ ability to pay, for our services.
A public health epidemic, including COVID-19, poses the risk that Match Group or its employees, contractors, vendors, and other business partners may be prevented or impaired from conducting ordinary course business activities for an indefinite period of time, including due to shutdowns necessitated for the health and wellbeing of our employees, the employees of business partners, or shutdowns that may be requested or mandated by governmental authorities. For example, early on in the pandemic, certain of our customer support vendors were impacted by government mandated shutdowns which adversely impacted the capability of the affected brands to respond timely and effectively to user inquiries and requests. In addition, in response to the COVID-19 outbreak, we have taken several precautions that may adversely impact employee productivity, such as continuing to allow employees to work remotely, imposing travel restrictions, and ongoing closures of office locations.
The ultimate extent of the impact of any epidemic, pandemic, or other health crisis on our business will depend on multiple factors that are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including its severity, location and duration, and actions taken to contain or prevent further its spread. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic could increase the magnitude of many of the other risks described in this annual report, and have other adverse effects on our operations that we are not currently able to predict. If our business and the markets in which we operate experience a prolonged occurrence of adverse public health conditions, such as COVID-19, it could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. See “Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Trends affecting our business—Impacts of the Coronavirus.”
Foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations could adversely affect our results of operations.
We operate in various international markets, including jurisdictions within the European Union (which we refer to as the “EU”) and Asia. During periods of a strengthening U.S. dollar, our international revenues will be reduced when translated into U.S. dollars. In addition, as foreign currency exchange rates fluctuate, the translation of our international revenues into U.S. dollar-denominated operating results affects the period-over-period comparability of such results and can result in foreign currency exchange gains and losses.
The departure of the United Kingdom from the European Union, commonly referred to as “Brexit,” has caused, and may continue to cause, volatility in currency exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and the British Pound and the full impact of Brexit remains uncertain. See ‘‘Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Principles of Financial Reporting—Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates on Revenue,“ and Item 7A—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk—Foreign Currency Exchange Risk.”
Distribution and marketing of, and access to, our services relies, in significant part, on a variety of third-party platforms, in particular, mobile app stores. If these third parties limit, prohibit, or otherwise interfere with features or services or change their policies in any material way, it could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We market and distribute our services (including related mobile applications) through a variety of third-party distribution channels, including Facebook, which has rolled out its own dating service. Our ability to market our brands on any given property or channel is subject to the policies of the relevant third party. Certain platforms and channels have, from time to time, limited or prohibited advertisements for our services for a variety of reasons, including poor behavior by other industry participants. There is no assurance that we will not be limited or prohibited from using certain marketing channels in the future. If this were to happen with a significant marketing channel and/or for a significant period of time, our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Additionally, our mobile applications are almost exclusively accessed through the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. Both Apple and Google have broad discretion to change their policies regarding their mobile operating systems and app stores in ways that may limit, eliminate or otherwise interfere with our ability to distribute or market our applications through their stores, our ability to update our applications, including to make bug fixes or other feature updates or upgrades, the features we provide, our ability to access native functionality or other aspects of mobile devices, and our ability to access information about our users that they collect. To the extent either or both of them do so, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected. For example, Apple made changes to its policy on the processing of Apple’s IDFA, requiring app users to opt in before their IDFA can be accessed by an app. As a consequence, the ability of advertisers to accurately target and measure the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns at the user level has been limited and we and other app developers have experienced increased cost per registration. Additionally, Apple and Google are known to retaliate against app developers who publicly or privately challenge their app store rules and policies, and such retaliation has and could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The success of our services will depend, in part, on our ability to access, collect, and use personal data about our users and subscribers.
We rely on the Apple App Store and Google Play Store to distribute and monetize our mobile applications. Our users and subscribers engage with these platforms directly and may be subject to requirements regarding the use of their payment systems for various transactions. As a result of this disintermediation, these platforms receive and do not share with us key user data that we would otherwise receive if we transacted with our users and subscribers directly. If these platforms continue to or increasingly limit, eliminate, or otherwise interfere with our ability to access, collect, and use key user data, our ability to identify and communicate with a meaningful portion of our user and subscriber bases and provide services to help keep our users safe may be adversely impacted. If so, our customer relationship management efforts, our ability to reach new segments of our user and subscriber bases and the population generally, the efficiency of our paid marketing efforts, the rates we are able to charge advertisers seeking to reach users and subscribers on our various properties, our ability to comply with applicable law, and our ability to identify and exclude users and subscribers whose access would violate applicable terms and conditions, including underage individuals and bad actors, may be negatively impacted, and our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
As the distribution of our services through app stores increases, in order to maintain our profit margins, we may need to offset increasing app store fees by decreasing traditional marketing expenditures, increasing user volume, or monetization per user or by engaging in other efforts to increase revenue or decrease costs generally, or our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We rely on the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store to distribute and monetize our mobile applications and related in-app services. While our mobile applications are generally free to download from these stores, we offer our users the opportunity to purchase subscriptions and certain à la carte features within these applications. We determine the prices at which these subscriptions and features are sold; however,
purchases of these subscriptions and features via our mobile applications are required to be processed through the in-app payment systems provided by Apple and Google. Due to these requirements, we pay Apple and Google, as applicable, a meaningful share (generally 30%) of the revenue we receive from these transactions (Google reduced its in-app purchase fees for subscription payments to 15% as of January 1, 2022). While we are constantly innovating on and creating our own payment systems and methods, given the ever increasing distribution of our services through app stores and the strict mandates to use the in-app payments systems tied into Apple’s and Google’s app stores, we may need to offset these increased app store fees by decreasing traditional marketing expenditures as a percentage of revenue, increasing user volume or monetization per user, or by engaging in other efforts to increase revenue or decrease costs generally, or our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected. Google announced that it will require all developers to process all in-app purchases of subscriptions and features entirely through their in-app payment system beginning on March 31, 2022, instead of the original date announced by Google of September 30, 2021. To date, Google has not enforced such a requirement, but if Google does so, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected. See “Item 1—Business—Dependencies on services provided by others—App Stores.”
We depend on our key personnel.
Our future success will depend upon our continued ability to identify, hire, develop, motivate, and retain highly skilled individuals across the globe, with the continued contributions of our senior management being especially critical to our success. Competition for well-qualified employees across Match Group and its various businesses is intense and our continued ability to compete effectively depends, in part, upon our ability to attract new employees. Effective succession planning is also important to our future success. If we fail to ensure the effective transfer of senior management knowledge and smooth transitions involving senior management across our various businesses, our ability to execute short and long term strategic, financial, and operating goals, as well as our business, financial condition, and results of operations generally, could be adversely affected.
Our success depends, in part, on the integrity of our systems and infrastructures and on our ability to enhance, expand, and adapt these systems and infrastructures in a timely and cost-effective manner.
To succeed, our systems and infrastructures must perform well on a consistent basis. We have experienced and may from time to time, experience system interruptions that make some or all of our systems or data unavailable and prevent our services from functioning properly for our users. Any such interruption could arise for any number of reasons. Further, our systems and infrastructures are vulnerable to damage from fire, power loss, telecommunications failures, acts of God, and similar events. While we have backup systems in place for certain aspects of our operations, not all of our systems and infrastructures are fully redundant, disaster recovery planning is not sufficient for all eventualities and our property and business interruption insurance coverage may not be adequate to fully compensate us for any losses that we may suffer. Any interruptions or outages, regardless of the cause, could negatively impact our users’ experiences with our platforms, tarnish our brands’ reputations, and decrease demand for our services, any or all of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We also continually work to expand and enhance the efficiency and scalability of our technology and network systems to improve the experience of our users, accommodate substantial increases in the volume of traffic to our various platforms, ensure acceptable load times for our services, and keep up with changes in technology and user preferences. Any failure to do so in a timely and cost-effective manner could adversely affect our users’ experience with our various services and thereby negatively impact the demand for our services, and could increase our costs, either of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may not be able to protect our systems and infrastructure from cyberattacks and may be adversely affected by cyberattacks experienced by third parties.
We are regularly under attack by perpetrators of random or targeted malicious technology-related events, such as cyberattacks, computer viruses, worms, bot attacks or other destructive or disruptive software, distributed denial of service attacks, and attempts to misappropriate customer information, including personal user data, credit card information, and account login credentials. While we have invested (and continue to invest) in the protection of our systems and infrastructure, in related personnel and training and in employing a data minimization strategy, where appropriate, there can be no assurance that our efforts will prevent
significant breaches in our systems or other such events from occurring. Some of our systems have experienced past security incidents, and, although they did not have a material adverse effect on our operating results, there can be no assurance of a similar result in the future. Any cyber or similar attack we are unable to protect ourselves against could damage our systems and infrastructure, prevent us from providing our services, tarnish our brand reputation, result in the disclosure of confidential or sensitive information of our users, and/or be costly to remedy, as well as subject us to investigations by regulatory authorities and/or litigation that could result in liability to third parties.
The impact of cyber or similar attacks experienced by third parties who provide services to us or otherwise process data on our behalf could have a similar effect on us. Moreover, even cyber or similar attacks that do not directly affect us or our third party service providers or data processors may result in widespread access to user account login credentials that such users have used across multiple internet sites, including our sites, or a loss of consumer confidence generally, which could make users less likely to use or continue to use online services generally, including our services. The occurrence of any of these events could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our success depends, in part, on the integrity of third-party systems and infrastructure.
We rely on third parties, primarily data center and cloud-based, hosted web service providers, such as Amazon Web Services, as well as third party computer systems, broadband and other communications systems, and service providers, in connection with the provision of our services generally, as well as to facilitate and process certain transactions with our users. We have no control over any of these third parties or their operations. Any changes in service levels at our data centers or hosted web service providers or any interruptions, outages, or delays in our systems or those of our third party providers, deterioration in the performance of these systems, or cyber or similar attacks on these systems could impair our ability to provide our services or process transactions with our users, which would adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations. See “Item 1—Business—Dependencies on services provided by others—Cloud and Other Services.”
If the security of personal and confidential or sensitive user information that we maintain and store is breached or otherwise accessed by unauthorized persons, it may be costly to mitigate the impact of such an event and our reputation could be harmed.
We receive, process, store, and transmit a significant amount of personal user and other confidential or sensitive information, including credit card information and user-to-user communications, and enable our users to share their personal information with each other. In some cases, we engage third party service providers to store this information. We continuously develop and maintain systems to protect the security, integrity, and confidentiality of this information, but we have experienced past incidents and cannot guarantee that inadvertent or unauthorized use or disclosure will not occur in the future or that third parties will not gain unauthorized access to this information despite our efforts. When such events occur, we may not be able to remedy them, be required by law to notify regulators and individuals whose personal information was used or disclosed without authorization, be subject to claims against us, including government enforcement actions, fines and litigation, and have to expend significant capital and other resources to mitigate the impact of such events, including developing and implementing protections to prevent future events of this nature from occurring. When breaches of security (or the security of our service providers) occur, the perception of the effectiveness of our security measures, the security measures of our service providers, and our reputation may be harmed, we may lose current and potential users and our various brands’ reputation and competitive positions may be tarnished, any or all of which might adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our business is subject to complex and evolving U.S. and international laws and regulations, including with respect to data privacy and platform liability. These laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in changes to our business practices, increased cost of operations, declines in user growth or engagement, claims, monetary penalties, or otherwise harm our business.
We are subject to a variety of laws and regulations in the United States and abroad that involve matters that are important to or may otherwise impact our business. See “Item 1—Business—Government regulation.” These U.S. federal, state, and municipal and foreign laws and regulations, which in some cases can be enforced by private parties in addition to government entities, are constantly evolving and subject to change. As a result,
the application, interpretation, and enforcement of these laws and regulations are often uncertain, particularly in the rapidly evolving industry in which we operate, and may be interpreted and applied inconsistently from state to state and country to country and inconsistently with our current policies and practices. These laws and regulations, as well as any associated inquiries, investigations or other government actions, may be costly to comply with and may delay or impede the development of new services, require changes to or cessation of certain business practices, result in negative publicity, increase our operating costs, require significant management time and attention, and subject us to remedies that may harm our business, including fines or modifications to existing business practices.
In the case of tax laws, positions that we have taken or will take are subject to interpretation by the relevant taxing authorities. While we believe that the positions we have taken to date comply with applicable law, there can be no assurances that the relevant taxing authorities will not take a contrary position, and if so, that such positions will not adversely affect us. Any events of this nature could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Proposed or new legislation and regulations could also adversely affect our business. See “Item 1—Business—Government regulation.” To the extent such new or more stringent measures are required to be implemented, impose new liability or limit or remove existing protections, our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
The adoption of any laws or regulations that adversely affect the popularity or growth in use of the internet or our services, including laws or regulations that undermine open and neutrally administered internet access, could decrease user demand for our service offerings and increase our cost of doing business. For example, in December 2017, the Federal Communications Commission adopted an order reversing net neutrality protections in the United States, including the repeal of specific rules against blocking, throttling or “paid prioritization” of content or services by internet service providers. To the extent internet service providers engage in such blocking, throttling, “paid prioritization” of content, or similar actions as a result of this order and the adoption of similar laws or regulations, our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We are subject to a number of risks related to credit card payments, including data security breaches and fraud that we or third parties experience, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We accept payment from our users primarily through credit card transactions and certain online payment service providers. When we or a third party experiences a data security breach involving credit card information, affected cardholders will often cancel their credit cards. In the case of a breach experienced by a third party, the more sizable the third party’s customer base and the greater the number of credit card accounts impacted, the more likely it is that our users would be impacted by such a breach. To the extent our users are affected by such a breach experienced by us or a third party, such users would need to be contacted to obtain new credit card information and process any pending transactions. It is likely that we would not be able to reach all affected users, and even if we could, some users’ new credit card information may not be obtained and some pending transactions may not be processed, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Even if our users are not directly impacted by a given data security breach, they may lose confidence in the ability of service providers to protect their personal information generally, which could cause them to stop using their credit cards online or choose alternative payment methods that are less convenient or more costly for us or otherwise restrict our ability to process payments without significant user effort.
Additionally, if we fail to adequately prevent fraudulent credit card transactions, we may face litigation, fines, governmental enforcement action, civil liability, diminished public perception of our security measures, significantly higher credit card-related and remediation costs, or refusal by credit card processors to continue to process payments on our behalf, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Inappropriate actions by certain of our users could be attributed to us and damage our brands’ reputations, which in turn could adversely affect our business.
Users of our services have been, and may in the future be, physically, financially, emotionally, or otherwise harmed by other individuals that such users met or may meet through the use of one of our services. When one or more of our users suffers or alleges to have suffered any such harm, we have in the past, and could in the future, experience negative publicity or legal action that could damage our reputation and our brands. Similar events affecting users of our competitors’ services have in the past, and could in the future, result in negative publicity for the dating industry generally, which could in turn negatively affect our business.
In addition, the reputations of our brands may be adversely affected by the actions of our users that are deemed to be hostile, offensive, defamatory, inappropriate, untrue, or unlawful. While we have systems and processes in place that aim to monitor and review the appropriateness of the content accessible through our services, and have adopted policies regarding illegal, offensive, or inappropriate use of our services, our users have in the past, and could in the future, nonetheless engage in activities that violate our policies. These safeguards may not be sufficient to avoid harm to our reputation and brands, especially if such hostile, offensive, or inappropriate use is well-publicized.
We may fail to adequately protect our intellectual property rights or may be accused of infringing the intellectual property rights of third parties.
We rely heavily upon our trademarks and related domain names and logos to market our brands and to build and maintain brand loyalty and recognition. We also rely upon patented and patent-pending proprietary technologies and trade secrets relating to our services.
We rely on a combination of laws, and contractual restrictions with employees, customers, suppliers, and others, to establish and protect our intellectual property rights. For example, we have generally registered and continue to apply to register and renew, or secure by contract where appropriate, trademarks and service marks as they are developed and used, and reserve, register, and renew domain names as we deem appropriate. Effective trademark protection may not be available or sought in every country in which our services are made available, and contractual disputes may affect the use of marks governed by private contract. Similarly, not every variation of a domain name may be available or registered, even if available.
We generally seek to apply for patents or other similar statutory protections as and when we deem appropriate, based on then-current facts and circumstances, and will continue to do so in the future. No assurances can be given that any patent application we have filed or will file will result in a patent being issued, or that any existing or future patents will afford adequate protection against competitors and similar technologies. In addition, no assurances can be given that third parties will not create new products or methods that achieve similar results without infringing upon patents we own.
Despite these measures, our intellectual property rights may still not be protected in a meaningful manner, challenges to contractual rights could arise, third parties could copy or otherwise obtain and use our intellectual property without authorization, our existing trademarks, patents, or trade secrets may be determined to be invalid or unenforceable, or laws and interpretations of laws regarding the enforceability of existing intellectual property rights may change over time in a manner that provides less protection. The occurrence of any of these events could tarnish of our brands’ reputation, limit our ability to market them, or impede our ability to effectively compete against competitors with similar technologies, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
From time to time, we have been subject to legal proceedings and claims, including claims of alleged infringement of trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual property rights held by third parties. In addition, litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce our intellectual property rights, protect our trade secrets, and patents or to determine the validity and scope of proprietary rights claimed by others. For example, in 2021, we settled patent and trademark infringement litigation against Muzmatch, and settled with several other infringers outside of litigation. Any litigation of this nature, regardless of outcome or merit, could result in substantial costs and diversion of management and technical resources, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We operate in various international markets, including certain markets in which we have limited experience. As a result, we face additional risks in connection with certain of our international operations.
Operating internationally, particularly in countries in which we have limited experience, exposes us to a number of risks in addition to those otherwise described in this annual report, such as:
•operational and compliance challenges caused by distance, language, and cultural differences;
•difficulties in staffing and managing international operations;
•differing levels of social and technological acceptance of our services or lack of acceptance of them generally;
•differing and potentially adverse tax laws;
•compliance challenges due to different laws and regulatory environments, particularly in the case of privacy, data security, intermediary or platform liability, and consumer protection;
•competitive environments that favor local businesses or local knowledge of such environments;
•limitations on the level of intellectual property protection; and
•trade sanctions, political unrest, terrorism, war, and epidemics or the threat of any of these events (such as COVID-19).
The occurrence of any or all of the events described above could adversely affect our international operations, which could in turn adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may experience operational and financial risks in connection with acquisitions.
We have made acquisitions in the past, including our acquisition of Hyperconnect in June 2021, and continue to seek potential acquisition candidates. We may experience operational and financial risks in connection with historical and future acquisitions if we are unable to:
•properly value prospective acquisitions, especially those with limited operating histories;
•fully identify potential risks and liabilities associated with acquired businesses;
•successfully integrate the operations and accounting, financial controls, management information, technology, human resources, and other administrative systems, of the acquired businesses with our existing operations and systems;
•retain or hire senior management and other key personnel at acquired businesses; and
•successfully support the acquired businesses in executing on strategic plans, including expansion into geographies where we have presence and experience.
Furthermore, we may not be successful in addressing other challenges encountered in connection with our acquisitions and the anticipated benefits of one or more of our acquisitions may not be realized. In addition, such acquisitions can result in material diversion of management’s attention or other resources from our existing businesses. The occurrence of any these events could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We are subject to litigation, and adverse outcomes in such litigation could have an adverse effect on our financial condition.
We are, and from time to time may become, subject to litigation and various legal proceedings, including litigation and proceedings related to employment matters, intellectual property matters, privacy and consumer protection laws, as well as stockholder derivative suits, class action lawsuits, mass arbitrations, and other matters, that involve claims for substantial amounts of money or for other relief, results in significant costs for legal representation, arbitration fees, or other legal or related services, or that might necessitate changes to our business or operations. The defense of these actions is time consuming and expensive. We evaluate these litigation claims and legal proceedings to assess the likelihood of unfavorable outcomes and to estimate, if possible, the amount of potential losses. Based on these assessments and estimates, we may establish reserves and/or disclose the relevant litigation claims or legal proceedings, as and when required or appropriate. These
assessments and estimates are based on information available to management at the time of such assessment or estimation and involve a significant amount of judgment. As a result, actual outcomes or losses could differ materially from those envisioned by our current assessments and estimates. Our failure to successfully defend or settle any of these litigations or legal proceedings could result in liability that, to the extent not covered by our insurance, could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. See “Item 3—Legal Proceedings.”
Risks relating to our indebtedness
Our indebtedness may affect our ability to operate our business, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. We and our subsidiaries may incur additional indebtedness, including secured indebtedness.
As of December 31, 2021, we had total debt outstanding of approximately $4.0 billion and borrowing availability of $749.6 million under our revolving credit facility.
Our indebtedness could have important consequences, such as:
•limiting our ability to obtain additional financing to fund working capital needs, acquisitions, capital expenditures, or other debt service requirements or for other purposes;
•limiting our ability to use operating cash flow to pursue acquisitions or invest in other areas, such as developing new brands, services, or exploiting business opportunities;
•restricting our business operations due to financial and operating covenants in the agreements governing our and certain of our subsidiaries’ existing and future indebtedness, including certain covenants that restrict the ability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends or make other distributions to us; and
•exposing us to potential events of default (if not cured or waived) under financial and operating covenants contained in our or our subsidiaries’ debt instruments that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and operating results.
Although the terms of our credit agreement and the indentures related to our senior notes contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions, and additional indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be significant. If new debt is added to our and our subsidiaries’ current debt levels, the risks described above could increase.
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness and may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness that may not be successful.
Our ability to satisfy our debt obligations will depend upon, among other things:
•our future financial and operating performance, which will be affected by prevailing economic conditions and financial, business, regulatory, and other factors, many of which are beyond our control; and
•our future ability to borrow under our revolving credit facility, the availability of which will depend on, among other things, our complying with the covenants in the then-existing agreements governing our indebtedness.
There can be no assurance that our business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations, or that we will be able to draw under our revolving credit facility or otherwise, in an amount sufficient to fund our liquidity needs.
If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to service our indebtedness, we may be forced to reduce or delay capital expenditures, sell assets, seek additional capital, or restructure or refinance our indebtedness. These alternative measures may not be successful and may not permit us to meet our scheduled debt service obligations. Our ability to restructure or refinance our debt will depend on the condition of the capital markets and our financial condition at such time. Any refinancing of our debt could be at higher interest rates and may require us to comply with more onerous covenants, which could further restrict our business
operations. In addition, the terms of existing or future debt agreements may restrict us from adopting some of these alternatives.
Variable rate indebtedness that we have incurred or may incur under our credit agreement will subject us to interest rate risk, which could cause our debt service obligations to increase significantly.
We currently have $425 million of indebtedness outstanding under our term loan and no outstanding borrowings under our revolving credit agreement. Borrowings under term loan are, and any borrowings under the revolving credit facility will be, at variable rates of interest. Indebtedness that bears interest at variable rates exposes us to interest rate risk. See “Item 7A—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk—Interest Rate Risk.”
Exchange of the exchangeable notes may dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders or may otherwise depress the price of our common stock.
We are obligated as a guarantor under the indentures relating to the exchangeable notes. The exchange of some or all of the exchangeable notes may dilute the ownership interests of our stockholders to the extent we deliver shares of our common stock upon exchange. While the exchangeable note hedges are expected to reduce the potential dilutive effect on our common stock upon any exchange and/or offset any cash payment the issuers of the exchangeable notes would be required to make in excess of the principal amount of the exchanged notes, the warrants have a dilutive effect to the extent that the market price per share of our common stock exceeds the strike price of the warrants. Any sales in the public market of our common stock issuable upon such exchange could adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock. In addition, the existence of the exchangeable notes may encourage short selling of our common stock by market participants because the exchange of the exchangeable notes could be used to satisfy short positions. In addition, the anticipated exchange of the exchangeable notes could depress the price of our common stock.
Risks relating to the Separation
We may be unable to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expect to achieve through the Separation.
We believe that the intended strategic and financial benefits of the Separation should be achieved. However, there can be no assurance of this or that we will be able to attract transaction partners using our capital stock as acquisition currency and that analysts and investors will regard our new corporate structure as more clear and simple than our former corporate structure.
If the transactions effected in connection with the Separation were to fail to qualify as generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we and our stockholders could suffer material adverse consequences.
Following the completion of the Separation and the merger of Former Match Group into a wholly-owned subsidiary (“Merger Sub”) of Former IAC (the “Merger”), Former Match Group’s successor became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group and most of Former IAC’s existing other subsidiaries came to be held under a separate public company. Former IAC and IAC received opinions from outside counsel that the Separation and related transactions taken together, and the Merger, were tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes. These opinions were based upon and rely on various facts and assumptions, as well as certain representations and undertakings of Former IAC, Former Match Group, IAC, and Match Group, including relating to the past and future conduct of Former IAC, Former Match Group, IAC, and Match Group. If any of these representations or undertakings is, or becomes, inaccurate or incomplete, or if any of the representations or covenants contained in any of the transaction-related agreements or in any document relating to the opinions of counsel is, or becomes, inaccurate or is not complied with by Former IAC, Former Match Group, IAC, Match Group, or any of their respective subsidiaries, the opinions of counsel may be invalid and the conclusions reached therein could be jeopardized.
Notwithstanding receipt of the opinions of counsel regarding the transactions, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) could determine that some or all of the transactions effected in connection with the Separation should be treated as taxable for U.S. federal income tax purposes if it determines that any of the representations, assumptions, or undertakings upon which the opinions of counsel were based are inaccurate or have not been complied with. Moreover, even if the foregoing representations, assumptions, or undertakings are accurate and have been complied with, the opinions of counsel merely represent the judgment of such counsel and are not binding on the IRS or any court, and the IRS or a court may disagree with the conclusions in
the opinions of counsel. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not assert that the transactions effected in connection with the Separation do not qualify for tax-free treatment for U.S. federal income tax purposes or that a court would not sustain such a challenge. In the event the IRS were to prevail with such a challenge, parties to the Separation, including Match Group could be subject to tax with respect to the Separation.
For example, if the transactions effected in connection with the Separation were to fail to qualify as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (as amended, the “Code”), in general, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we would recognize a taxable gain as if the distribution of New IAC stock in connection with the Separation had been sold in a taxable sale for its fair market value. Even if the transactions effected in connection with the Separation were to otherwise qualify as a tax-free transaction under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code, taxable gain may be triggered under Section 355(e) of the Code if the transactions effected in connection with the Separation were, or later transactions are, deemed to be part of a plan (or series of related transactions) pursuant to which one or more persons acquire, directly or indirectly, shares representing a 50 percent or greater interest (by vote or value) in us or IAC. For this purpose, any acquisitions of (i) Former IAC stock or Former Match Group stock before the Separation or (ii) IAC stock or Match Group stock within the period beginning two years before the Separation and ending two years after the Separation are presumed to be part of such a plan, although we or IAC may be able to rebut that presumption.
In addition to potential tax liabilities relating to Former Match Group, we and our subsidiaries could be liable to satisfy any tax liabilities relating to Former IAC or IAC with respect to the Separation if their tax-free treatment for U.S. federal income tax purposes were successfully challenged by the IRS. While, in some cases, IAC may be obligated under the Tax Matters Agreement to indemnify us for some or all of such taxes, even in those cases, there is no assurance that they will in fact indemnify us.
In addition, if the Merger were determined to be taxable for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we would be subject to tax on the transfer of the assets of Former Match to Merger Sub. If we or our subsidiaries were required to pay taxes imposed on us with respect to the Separation, our cash flows would be adversely affected.
We may not be able to engage in desirable capital-raising or strategic transactions following the Separation.
We believe we will generally be able to engage in desirable capital-raising or strategic transactions. However, under current U.S. federal income tax law, a distribution that otherwise qualifies for tax-free treatment can be rendered taxable to the distributing corporation and its stockholders as a result of certain post-distribution transactions, including certain acquisitions of shares or assets of both the distributing corporation and the corporation the stock of which is distributed. To preserve the tax-free treatment of the transactions effected in connection with the Separation, the Tax Matters Agreement imposes certain restrictions on us and our subsidiaries during the two-year period following the Separation. Except in specific circumstances, we are generally restricted from (1) ceasing to actively conduct certain of our businesses; (2) entering into certain transactions or series of transactions pursuant to which all or a portion of our shares of common stock would be acquired, whether by merger or otherwise; (3) liquidating or merging or consolidating with any other person; (4) issuing equity securities beyond certain thresholds; (5) repurchasing shares of our common stock, other than in certain open-market transactions; or (6) taking or failing to take any other action that would cause the transactions effected in connection with the Separation to fail to qualify as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code. These restrictions may limit our ability to pursue certain equity issuances, strategic transactions, repurchases or other transactions that we may otherwise believe to be in the best interests of our stockholders or that might increase the value of our business.
Actual or potential conflicts of interest may develop between our management and directors, on the one hand, and the management and directors of IAC, on the other hand.
Certain of our directors and executive officers and directors of IAC own both Match Group common stock and IAC common stock. This ownership overlap could create, or appear to create, potential conflicts of interest when Match Group’s directors and IAC’s executive officers and directors face decisions that could have different implications for Match Group and IAC. For example, potential conflicts of interest could arise in connection with the resolution of any dispute between Match Group and IAC regarding the terms of the agreements governing
the Separation and the relationship between Match Group and IAC thereafter. Potential conflicts of interest could also arise if Match Group and IAC enter into any commercial arrangements in the future.
In addition, Joseph Levin serves as a director of Match Group while also serving as an executive officer of IAC, and Alan G. Spoon serves as a director of each of Match Group and IAC. We believe that having a limited number of senior IAC management members serve on our Board for a transitional period will be beneficial to us. However, the fact that Messrs. Levin and Spoon hold positions with both Match Group and IAC could create, or appear to create, potential conflicts of interest for each of them when facing decisions that may affect both Match Group and IAC, and each of them also faces conflicts of interest with regard to the allocation of his time between Match Group and IAC.
Our certificate of incorporation could prevent us from benefiting from corporate opportunities that might otherwise have been available to us.
Our certificate of incorporation includes a “corporate opportunity” provision in which Match Group and its affiliates renounce any interests or expectancy in corporate opportunities which become known to any of Match Group’s directors or officers who are also officers or directors of IAC.
Generally, Match Group’s officers or directors who are also IAC’s officers or directors will not be liable to Match Group or its stockholders for breach of any fiduciary duty because such person fails to communicate or offer to Match Group a corporate opportunity that has been communicated or offered to IAC, that may also be a corporate opportunity of Match Group or because such person communicates or offers to IAC any corporate opportunity that may also be a corporate opportunity of Match Group. In order for any Match Group director or officer who is also an IAC director or officer not to be liable to Match Group or its stockholders, such opportunity cannot become known to the officer or director in his or her capacity as a Match Group director or officer and cannot be presented to any party other than IAC. In addition, such officer or director cannot pursue such opportunity in his or her individual capacity. The corporate opportunity provision may exacerbate conflicts of interest between Match Group and IAC because the provision effectively permits any of Match Group’s directors or officers who also serve as an officer or director of IAC to choose to direct a corporate opportunity to IAC instead of to Match Group.
Risks relating to ownership of our common stock
You may experience dilution due to the issuance of additional securities in the future.
Our dilutive securities consist of vested and unvested options to purchase shares of our common stock, restricted stock unit awards, equity awards denominated in the equity of our non-public subsidiaries but settleable in shares of our common stock, the exchangeable notes, and the exchangeable note warrants.
These dilutive securities are reflected in our dilutive earnings per share calculation contained in our financial statements for fiscal years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019. For more information, see “Note 10—Earnings per Share” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Part II, Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” Intra-quarter movements in our stock price, could lead to more or less dilution than reflected in these calculations.
We do not expect to declare any regular cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
We have no current plans to pay cash dividends on our common stock. Instead, we anticipate that all of our future earnings will be retained to support our operations and to finance the growth and development of our business. We are not obligated to pay dividends on our common stock. Consequently, investors may need to rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on their investment. Investors seeking regular cash dividends should not purchase our common stock.
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws or Delaware law may discourage, delay, or prevent a change of control of our company or changes in our management and, therefore, depress the trading price of our common stock.
Delaware corporate law and our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that could discourage, delay or prevent a change in control of our company or changes in our management that the stockholders of our company may deem advantageous, including provisions which:
•authorize the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock that our board of directors could issue to increase the number of outstanding shares and to discourage a takeover attempt;
•establish a classified board of directors, as a result of which our board is divided into three classes, with each class serving for staggered three-year terms, which prevents stockholders from electing an entirely new board of directors at an annual meeting;
•prohibit stockholder action by written consent, thereby requiring all actions to be taken at a meeting of the stockholders;
•eliminate the ability of our stockholders to call special meetings of stockholders;
•provide that certain litigation against us can be brought only in Delaware (subject to certain exceptions); and
•provide that the board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter, or repeal our bylaws.
Any provision of our certificate of incorporation, our bylaws or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
Match Group believes that the facilities for its management and operations are generally adequate for its current and near-term future needs. Match Group’s facilities, whether owned or leased, are in various cities in the United States and abroad, generally consist of executive and administrative offices and data centers. We also believe that, if we require additional space, we will be able to lease additional facilities on commercially reasonable terms.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
Overview
We are, and from time to time may become, involved in various legal proceedings arising in the normal course of our business activities, such as trademark and patent infringement claims, trademark oppositions, and consumer or advertising complaints, as well as stockholder derivative actions, class action lawsuits, mass arbitrations, and other matters. The amounts that may be recovered in such matters may be subject to insurance coverage. The litigation matters described below involve issues or claims that may be of particular interest to our stockholders, regardless of whether any of these matters may be material to our financial position or operations based upon the standard set forth in the SEC’s rules.
Pursuant to the Transaction Agreement, we have agreed to indemnify IAC for matters relating to any business of Former Match Group, including indemnifying IAC for costs related to the matters described below other than the matter described under the heading “Newman Derivative and Stockholder Class Action Regarding Separation Transaction”.
The official names of legal proceedings in the descriptions below (shown in italics) reflect the original names of the parties when the proceedings were filed as opposed to the current names of the parties following the separation of Match Group and IAC.
Consumer Class Action Litigation Challenging Tinder’s Age-Tiered Pricing
On May 28, 2015, a putative state-wide class action was filed against Tinder in state court in California. See Allan Candelore v. Tinder, Inc., No. BC583162 (Superior Court of California, County of Los Angeles). The complaint principally alleged that Tinder violated California’s Unruh Civil Rights Act by offering and charging users age 30 and over a higher price than younger users for subscriptions to its premium Tinder Plus service. The complaint sought certification of a class of California Tinder Plus subscribers age 30 and over and damages in an unspecified amount. On December 29, 2015, in accordance with a prior ruling sustaining Tinder’s demurrer, the
court entered judgment dismissing the action. On January 29, 2018, the California Court of Appeal (Second Appellate District, Division Three) issued an opinion reversing the judgment of dismissal. On May 9, 2018, the California Supreme Court denied Tinder’s petition seeking interlocutory review of the Court of Appeal’s decision and the case was returned to the trial court for further proceedings.
In a related development, on June 21, 2019, in a substantially similar putative class action asserting the same substantive claims and pending in federal district court in California, the court entered judgment granting final approval of a class-wide settlement, the terms of which are not material to the Company. See Lisa Kim v. Tinder, Inc., No. 18-cv-3093 (Central District of California). Because the approved settlement class in Kim subsumes the proposed settlement class in Candelore, the judgment in Kim would effectively render Candelore a single-plaintiff lawsuit. Accordingly, on July 11, 2019, two objectors to the Kim settlement, represented by the plaintiff’s counsel in Candelore, filed a notice of appeal from the Kim judgment with the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. Oral argument on the appeal occurred on January 15, 2021. On August 17, 2021, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit reversed and remanded the district court’s decision. On November 3, 2021, the trial court granted preliminary approval of the settlement. On December 13, 2021, plaintiff filed an amended motion for final approval of the proposed settlement agreement, the terms of which are not material to the Company.
On November 13, 2019, the trial court in Candelore issued an order staying the class claims in the case pending the Ninth Circuit’s decision on the Kim appeal. On October 5, 2021, the trial court lifted the stay. We believe that the allegations in the Candelore lawsuit are without merit and will continue to defend vigorously against it.
Tinder Optionholder Litigation Against Former Match Group and Match Group
On August 14, 2018, ten then-current and former employees of Match Group, LLC or Tinder, Inc. (“Tinder”), a former subsidiary of Former Match Group, filed a lawsuit in New York state court against Former Match Group and Match Group. See Sean Rad et al. v. IAC/InterActiveCorp and Match Group, Inc., No. 654038/2018 (Supreme Court, New York County). The complaint alleged that in 2017, the defendants: (i) wrongfully interfered with a contractually established process for the independent valuation of Tinder by certain investment banks, resulting in a substantial undervaluation of Tinder and a consequent underpayment to the plaintiffs upon exercise of their Tinder stock options, and (ii) then wrongfully merged Tinder into Former Match Group, thereby depriving certain of the plaintiffs of their contractual right to later valuations of Tinder on a stand-alone basis. The complaint asserted claims for breach of contract, breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing, unjust enrichment, interference with contractual relations (as against Former Match Group only), and interference with prospective economic advantage, and sought compensatory damages in the amount of at least $2 billion, as well as punitive damages. On August 31, 2018, four plaintiffs who were still employed by Former Match Group filed a notice of discontinuance of their claims without prejudice, leaving the six former employees as the remaining plaintiffs. On June 13, 2019, the court issued a decision and order granting defendants’ motion to dismiss the claims for breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing and for unjust enrichments, as well as the merger-related claim for breach of contract as to two of the remaining six plaintiffs, and otherwise denying defendants’ motion to dismiss. On July 13, 2020, the four former plaintiffs filed arbitration demands with the American Arbitration Association asserting the same valuation claims and on September 3, 2020, the four arbitrations were consolidated. On August 24, 2021, the arbitrator granted our summary judgment with respect to the merger claims. On June 9, 2021, the plaintiffs in Rad filed a Note of Issue and Certificate of Readiness for Trial in which they amended the amount of damages they were claiming to “[m]ore than $5.6 billion”. On October 1, 2021, the court granted defendants’ motion for summary judgment on plaintiffs’ tort claims and breach of contract claims regarding the merger. Trial commenced on November 8, 2021. On December 1, 2021, the parties entered into a Binding Global Settlement Agreement Term Sheet, pursuant to which we will pay $441 million in 2022 to settle all claims in trial and in arbitration.
FTC Lawsuit Against Former Match Group
On September 25, 2019, the United States Federal Trade Commission (the “FTC”) filed a lawsuit in federal district court in Texas against Former Match Group. See FTC v. Match Group, Inc., No. 3:19:cv-02281-K (Northern District of Texas). The complaint alleges that, prior to mid-2018, for marketing purposes Match.com notified non-paying users that other users were attempting to communicate with them, even though Match.com had identified those subscriber accounts as potentially fraudulent, thereby inducing non-paying users to subscribe
and exposing them to the risk of fraud should they subscribe. The complaint also challenges the adequacy of Match.com’s disclosure of the terms of its six-month guarantee, the efficacy of its cancellation process, and its handling of chargeback disputes. The complaint seeks among other things permanent injunctive relief, civil penalties, restitution, disgorgement, and costs of suit. On October 9, 2020, the court granted the Company’s motion to stay the case until the United States Supreme Court issues a decision in the consolidated appeal of Federal Trade Commission v. Credit Bureau Center, LLC and AMG Capital Management, LLC v. FTC. On April 22, 2021, the Supreme Court issued its decision, rejecting that the FTC has the ability to seek equitable monetary relief using Section 13(b) of the FTC Act. We believe that the FTC’s claims regarding Match.com’s practices, policies, and procedures are without merit and will defend vigorously against them.
Securities Class Action Lawsuit Against Former Match Group
On October 3, 2019, a Former Match Group shareholder filed a securities class action lawsuit in federal district court in Texas against Former Match Group, its then Chief Executive Officer, and its Chief Financial Officer, on behalf of a class of acquirers of Former Match Group securities between August 6, 2019 and September 25, 2019. See Phillip R. Crutchfield v. Match Group, Inc., Amanda W. Ginsberg, and Gary Swidler, No. 3:19-cv-02356-C (Northern District of Texas). Invoking the allegations in the FTC lawsuit described above, the complaint alleges (i) that defendants failed to disclose to investors that Former Match Group induced customers to buy and upgrade subscriptions using misleading advertisements, that Former Match Group made it difficult for customers to cancel their subscriptions, and that, as a result, Former Match Group was likely to be subject to regulatory scrutiny; (ii) that Former Match Group lacked adequate disclosure controls and procedures; and (iii) that, as a result of the foregoing, defendants’ positive statements about Former Match Group’s business, operations, and prospects, were materially misleading and/or lacked a reasonable basis. On March 30, 2021, the court granted defendants’ motion to dismiss with leave to amend. Plaintiff filed an amended complaint on April 23, 2021. On November 19, 2021, the court denied defendants’ motion to dismiss. We believe that the allegations in this lawsuit are without merit and will defend vigorously against them.
Derivative Complaint against Former Match Group
On February 28, 2020, a Former Match Group shareholder filed a shareholder derivative complaint in federal district court in Delaware against Former Match Group and its board of directors seeking to recover unspecified monetary damages on behalf of the Company and require the Company to implement and maintain unspecified internal controls and corporate governance practices and procedures. See Michael Rubin et al. v. Match Group, Inc. et al., Case No. 1:20-cv-00299 (District of Delaware). Invoking the allegations of the FTC lawsuit and Crutchfield securities class action lawsuit described above, the complaint alleges that the defendants caused or failed to prevent the alleged issues giving rise to the FTC complaint, received or approved compensation tied to the alleged wrongful conduct and sold Former Match Group stock with inside knowledge of the purported conduct. The parties filed a proposed stipulation and order staying the case until the motion to dismiss is decided in the Crutchfield litigation. The court granted the stay on April 9, 2020. In light of the Crutchfield decision, the stay will be lifted. On February 25, 2021, another Match Group shareholder filed a shareholder derivative complaint in the Delaware Court of Chancery on behalf of nominal defendant Match Group, Inc. against its board of directors seeking to recover unspecified monetary damages. See Daniel Ochoa v. Match Group, Inc. et al, C.A. No. 2021-0158-MTZ (Delaware Court of Chancery). The complaint alleges federal securities laws violations and that Match Group’s directors breached their fiduciary duties by purportedly exercising inadequate oversight to prevent the alleged issues giving rise to the FTC complaint and by purportedly transacting in Match Group stock while possessing knowledge of these issues. On January 10, 2022, Ochoa filed an amended complaint. We believe that the allegations in these lawsuits are without merit and will defend vigorously against them.
Irish Data Protection Commission Inquiry Regarding Tinder’s Practices
On February 3, 2020, we received a letter from the Irish Data Protection Commission (the “DPC”) notifying us that the DPC has commenced an inquiry examining Tinder’s compliance with the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation, focusing on Tinder’s processes for handling access and deletion requests and Tinder’s user data retention policies. We are fully cooperating with the DPC in connection with this inquiry.
Newman Derivative and Stockholder Class Action Regarding Separation Transaction
On June 24, 2020, a Former Match Group shareholder filed a complaint in the Delaware Court of Chancery against Former Match Group and its board of directors, as well as Match Group, IAC Holdings, Inc., and Barry Diller seeking to recover unspecified monetary damages on behalf of the Company and directly as a result of his ownership of Former Match Group stock in relation to the separation of Former Match Group from its former majority shareholder, Match Group. See David Newman et al. v. IAC/Interactive Corp. et al., C.A. No. 2020-0505-MTZ (Delaware Court of Chancery). The complaint alleges that that the special committee established by Former Match Group’s board of directors to negotiate with Match Group regarding the separation transaction was not sufficiently independent of control from Match Group and Mr. Diller and that Former Match Group board members failed to adequately protect Former Match Group’s interest in negotiating the separation transaction, which resulted in a transaction that was unfair to Former Match Group and its shareholders. On January 21, 2021, the case was consolidated with other shareholder actions, and an amended complaint was filed on April 14, 2021. See In Re Match Group, Inc. Derivative Litigation, Consolidated C.A. No. 2020-0505-MTZ (Delaware Court of Chancery). Plaintiffs filed another amended complaint on November 2, 2021. Defendants filed a motion to dismiss on December 10, 2021. We believe that the allegations in this lawsuit are without merit and will defend vigorously against it.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosure
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters
Our common stock is quoted on the Nasdaq Global Select Market (“NASDAQ”) under the ticker symbol “MTCH.”
As of January 31, 2022, there were 982 holders of record of the Company’s common stock. Because the substantial majority of the outstanding shares of our common stock are held by brokers and other institutions on behalf of shareholders, we are not able to estimate the total number of beneficial shareholders represented by these record holders.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total return (assuming dividend reinvestment, as applicable) of Match Group common stock (including such cumulative total return of Former Match Group common stock for the period prior to, and adjusted for, the separation of Match Group and IAC), the NASDAQ Composite index, the Russell 1000 Technology Index, and the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index, in each case, based on $100 invested at the close of trading on December 31, 2016 through December 31, 2021. In accordance with applicable SEC rules, Match Group presents the cumulative return of peer issuers. Match Group has selected the NASDAQ Composite Index and the Russell 1000 Technology Index as its peer issuers because they both include companies engaged in many of the same businesses as Match Group. The returns shown are based on historical results and are not intended to suggest future performance.
COMPARISON OF CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN
Match Group, Inc. Common Stock
Among Match Group, Inc., the NASDAQ Composite Index,
the Russell 1000 Technology Index, and the S&P 500 Index
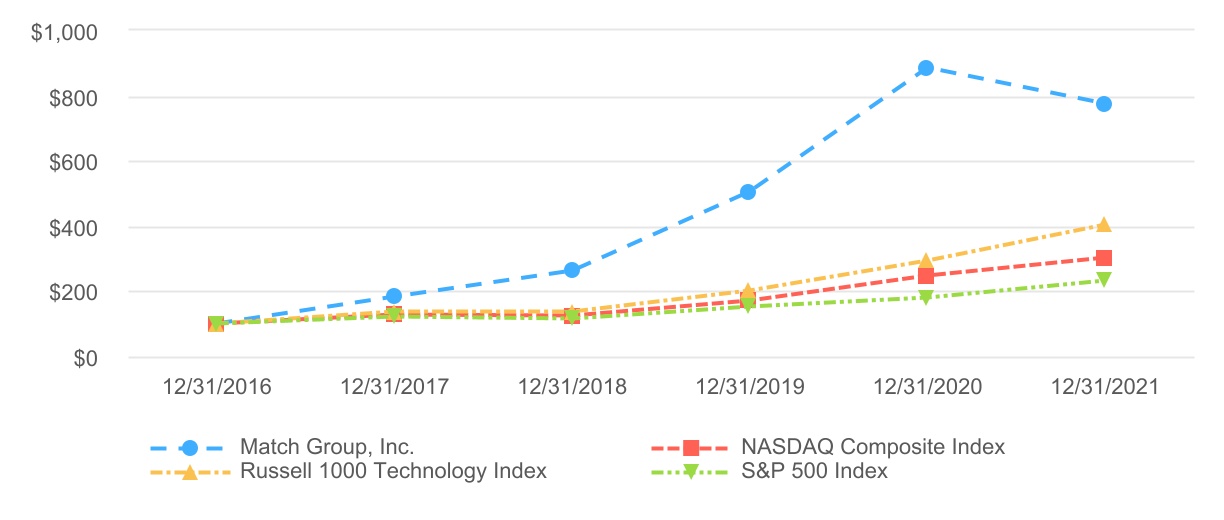
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 12/31/2016 | | 12/31/2017 | | 12/31/2018 | | 12/31/2019 | | 12/31/2020 | | 12/31/2021 |
| Match Group, Inc. | $100.00 | | $183.10 | | $263.14 | | $505.17 | | $884.15 | | $773.39 |
| NASDAQ Composite Index | $100.00 | | $128.63 | | $125.02 | | $170.95 | | $247.96 | | $303.04 |
| Russell 1000 Technology Index | $100.00 | | $137.32 | | $135.67 | | $199.72 | | $292.99 | | $401.90 |
| S&P 500 Index | $100.00 | | $120.79 | | $115.49 | | $151.84 | | $179.76 | | $231.31 |
Item 6. Reserved
Not applicable.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
2021 Developments
On March 26, 2021, Match Group Holdings II, LLC (“MG Holdings II”), amended its credit agreement to provide for a $400 million incremental “delayed draw” term loan facility (“Delayed Draw Term Loan”), the proceeds of which could be used only to finance a portion of the consideration for the acquisition of Hyperconnect, Inc. (“Hyperconnect”). The Delayed Draw Term Loan was terminated effective June 18, 2021 according to its terms.
On June 17, 2021, Match Group completed the acquisition of Hyperconnect. The purchase price was $1.75 billion, net of cash acquired. The acquisition was funded with cash on hand and the issuance of 5.9 million shares of Match Group common stock.
On October 4, 2021, MG Holdings II completed a private offering of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 3.625% Senior Notes. The proceeds from these notes were used to redeem a portion of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, for general corporate purposes, and to pay expenses associated with the offering.
On October 4, 2021, we repurchased approximately $414 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes for approximately $1.5 billion, including accrued and unpaid interest on the repurchased notes, funded with:
i.net proceeds of $879.0 million from a registered direct offering to the holders of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes being repurchased of 5,534,098 shares of our common stock at a price of $158.83 per share;
ii.approximately $420 million of net proceeds from the 3.625% Senior Notes offering; and
iii.net proceeds of approximately $201 million from the unwind of a proportionate amount of outstanding hedges and warrants corresponding to the 2022 Exchangeable Notes being repurchased.
In connection with these transactions, the statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021 reflects a loss of $14.5 million, included in other expense, net, primarily related to the change in fair value of the embedded derivative we recognized during the period between our entering into the various agreements on September 22, 2021 and settlement on October 4, 2021.
On December 1, 2021, we agreed to settle the pending, threatened, and potential claims at issue in Rad, et al. v IAC/InterActiveCorp, et al. and related arbitrations. Under the terms of the agreement, Match Group agreed to pay the plaintiffs and claimants $441 million and plaintiffs and claimants agreed to dismiss all claims in trial and in arbitration. We expect to pay the settlement amount in 2022 utilizing cash on hand. The $441 million settlement is included in other expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Updated Operating and Financial Metrics
In 2021, we adjusted our key operating and financial data to provide better insight into the performance of our business. We are disclosing this data in three geographic areas—Americas, Europe, and APAC and Other.
Additionally, rather than presenting Average Subscribers and Average Revenue per Subscriber (“ARPU”), we now present Payers and Revenue Per Payer (“RPP”) (as defined below). Unlike Average Subscribers, which included only users who purchase a subscription and were counted on a daily basis, Payers include all users from whom we earn revenue (including those who make only à la carte purchases) and are counted as unique users in a given month. Similarly, ARPU was a daily metric and included Direct Revenue sourced from subscribers only, whereas RPP is a monthly metric and includes all Direct Revenue. We believe that Payers and RPP, which account for non-subscriber users and the associated revenue, is more useful in evaluating the performance of our business.
We believe presenting Direct Revenue, Payers, and RPP in three geographic regions enables investors to better understand our operating performance and is appropriate given our expanding global footprint. The new metrics also better account for the increasing à la carte revenue as a percentage of total revenue that the company earns and enhance comparability with our peers.
Additionally, we have updated the title of our primary non-GAAP measure to “Adjusted Operating Income” from our previous title “Adjusted EBITDA.” We believe this updated title better reflects how management views the non-GAAP measure in relation to the closest GAAP measure, operating income. The calculation of the non-GAAP measure has not changed, and therefore the reconciliation of Net Income to Operating Income and to Adjusted Operating Income have not changed. See “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” below for the full definition of Adjusted Operating Income and a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders to Operating Income and Adjusted Operating Income.
Separation from IAC
On June 30, 2020, the companies formerly known as Match Group, Inc. (referred to as “Former Match Group”) and IAC/InterActiveCorp (referred to as “Former IAC”) completed the separation of the Company from IAC through a series of transactions that resulted in two, separate public companies—(1) Match Group, which consists of the businesses of Former Match Group and certain financing subsidiaries previously owned by Former IAC, and (2) IAC, consisting of Former IAC’s businesses other than Match Group (the “Separation”). As part of the Separation, Former Match Group merged with and into MG Holdings II, an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group, with MG Holdings II surviving the merger as an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group. As a result of the Separation, the operations of Former IAC businesses other than Match Group are presented as discontinued operations.
For additional information relating to the Separation and the related transactions and agreements, see “Part I—Item 1—Business—Separation of Match Group and IAC” and “Part I—Item 1—Business—Relationship with IAC after the Separation.”
Key Terms:
Operating and financial metrics:
•Americas includes North America, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean islands.
•Europe includes continental Europe, the British Isles, Iceland, Greenland, and Russia, but excludes Turkey (which is included in APAC and Other).
•APAC and Other includes Asia, Australia, the Pacific islands, the Middle East, and Africa.
•Direct Revenue is revenue that is received directly from end users of our products and includes both subscription and à la carte revenue.
•Indirect Revenue is revenue that is not received directly from an end user of our services, substantially all of which is advertising revenue.
•Payers are unique users at a brand level in a given month from whom we earned Direct Revenue. When presented as a quarter-to-date or year-to-date value, Payers represents the average of the monthly values for the respective period presented. At a consolidated level, duplicate Payers may exist when we earn revenue from the same individual at multiple brands in a given month, as we are unable to identify unique individuals across brands in the Match Group portfolio.
•Revenue Per Payer (“RPP”) is the average monthly revenue earned from a Payer and is Direct Revenue for a period divided by the Payers in the period, further divided by the number of months in the period.
Operating costs and expenses:
•Cost of revenue - consists primarily of the amortization of in-app purchase fees, compensation expense (including stock-based compensation expense) and other employee-related costs for personnel engaged in data center and customer care functions, credit card processing fees, hosting fees, live video costs, and data center rent, energy, and bandwidth costs. In-app purchase fees are monies paid to Apple and Google in connection with the processing of in-app purchases of subscriptions and service features through the in-app payment systems provided by Apple and Google.
•Selling and marketing expense - consists primarily of advertising expenditures and compensation expense (including stock-based compensation expense) and other employee-related costs for
personnel engaged in selling and marketing, and sales support functions. Advertising expenditures includes online marketing, including fees paid to search engines and social media sites, offline marketing (which is primarily television advertising), and payments to partners that direct traffic to our brands.
•General and administrative expense - consists primarily of compensation expense (including stock-based compensation expense) and other employee-related costs for personnel engaged in executive management, finance, legal, tax and human resources, acquisition-related contingent consideration fair value adjustments (described below), fees for professional services (including transaction-related costs for acquisitions), and facilities costs.
•Product development expense - consists primarily of compensation expense (including stock-based compensation expense) and other employee-related costs that are not capitalized for personnel engaged in the design, development, testing, and enhancement of service offerings and related technology.
Long-term debt:
•Credit Facility - The revolving credit facility under the credit agreement of MG Holdings II. At December 31, 2021, there was $0.4 million in outstanding letters of credit and $749.6 million of availability under the Credit Facility. As of December 31, 2020, there was $0.2 million in outstanding letters of credit and $749.8 million of availability under the Credit Facility.
•Term Loan - The term loan facility under the credit agreement of MG Holdings II. At December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, the Term Loan bore interest at LIBOR plus 1.75% and the then applicable rates were 1.91% and 1.96%, respectively. At December 31, 2021, $425 million was outstanding.
•6.375% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s 6.375% Senior Notes, which were redeemed on June 11, 2020 with the proceeds from the 4.625% Senior Notes.
•5.00% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s 5.00% Senior Notes due December 15, 2027, with interest payable each June 15 and December 15, which were issued on December 4, 2017. At December 31, 2021, $450 million aggregate principal amount was outstanding.
•4.625% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s 4.625% Senior Notes due June 1, 2028, with interest payable each June 1 and December 1, which were issued on May 19, 2020. At December 31, 2021, $500 million aggregate principal amount was outstanding.
•5.625% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s 5.625% Senior Notes due February 15, 2029, with interest payable each February 15 and August 15, which were issued on February 15, 2019. At December 31, 2021, $350 million aggregate principal amount was outstanding.
•4.125% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s 4.125% Senior Notes due August 1, 2030, with interest payable each February 1 and August 1, which were issued on February 11, 2020. At December 31, 2021, $500 million aggregate principal amount was outstanding.
•3.625% Senior Notes - MG Holdings II’s $500 million aggregate principal amount of 3.625% Senior Notes due October 1, 2031, with interest payable each April 1 and October 1, commencing on April 1, 2022, which were issued on October 4, 2021. The proceeds were used to repurchase $414.0 million of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, for general corporate purposes, and to pay expenses associated with the offering. At December 31, 2021, $500 million aggregate principal amount was outstanding.
•2022 Exchangeable Notes - During the third quarter of 2017, Match Group FinanceCo, Inc., a subsidiary of the Company, issued $517.5 million aggregate principal amount of 0.875% Exchangeable Senior Notes due October 1, 2022, which are exchangeable into shares of the Company's common stock. Interest is payable each April 1 and October 1. On October 4, 2021 we purchased $414.0 million aggregate principal amount of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes (as described above). During 2021, an additional $18.6 million aggregate principal amount of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes were presented for redemption, $3.0 million of which settled in the year ended December 31, 2021. The
outstanding balance of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes at December 31, 2021 was $100.5 million and is presented as a current liability.
•2026 Exchangeable Notes - During the second quarter of 2019, Match Group FinanceCo 2, Inc., a subsidiary of the Company, issued $575.0 million aggregate principal amount of 0.875% Exchangeable Senior Notes due June 15, 2026, which are exchangeable into shares of the Company's common stock. Interest is payable each June 15 and December 15. The outstanding balance of the 2026 Exchangeable Notes at December 31, 2021 was $575 million.
•2030 Exchangeable Notes - During the second quarter of 2019, Match Group FinanceCo 3, Inc., a subsidiary of the Company, issued $575.0 million aggregate principal amount of 2.00% Exchangeable Senior Notes due January 15, 2030, which are exchangeable into shares of the Company's common stock. Interest is payable each January 15 and July 15. The outstanding balance of the 2030 Exchangeable Notes at December 31, 2021 was $575 million.
Non-GAAP financial measure:
•Adjusted Operating Income - is a Non-GAAP financial measure. See “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” for the definition of Adjusted Operating Income and a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders to operating income and Adjusted Operating Income.
MANAGEMENT OVERVIEW
Match Group, Inc., through its portfolio companies, is a leading provider of digital technologies designed to help people make meaningful connections. Our global portfolio of brands includes Tinder®, Match®, Hinge®, Meetic®, OkCupid®, Pairs™, PlentyOfFish®, OurTime®, Azar®, Hakuna™ Live, and more, each built to increase our users’ likelihood of connecting with others. Through our trusted brands, we provide tailored services to meet the varying preferences of our users. Our services are available in over 40 languages to our users all over the world.
As used herein, “Match Group,” the “Company,” “we,” “our,” “us,” and similar terms refer to Match Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries, unless the context indicates otherwise.
Sources of Revenue
All our services provide the use of certain features for free and then offer a variety of additional features through a subscription or, for certain features, on a pay-per-use, or à la carte, basis. Our revenue is primarily derived directly from users in the form of recurring subscription fees and à la carte purchases.
Subscription revenue is presented net of credits and credit card chargebacks. Payers who purchase subscriptions or à la carte features pay in advance, primarily by using a credit card or through mobile app stores, and, subject to certain conditions identified in our terms and conditions, all purchases are final and nonrefundable. Fees collected, or contractually due, in advance for subscriptions are deferred and recognized as revenue using the straight-line method over the term of the applicable subscription period, which primarily ranges from one to six months, and corresponding in-app purchase fees incurred on such transactions, if any, are deferred and expensed over the same period. Revenue from the purchase of à la carte features is recognized based on usage. We also earn revenue from online advertising, which is recognized every time an ad is displayed.
Trends affecting our business
Over the last several years, we have seen significant changes in our business. Tinder has grown from incubation to the largest contributing brand in our portfolio with our more established brands returning to growth as well. This has allowed us to invest in or acquire brands such as Hyperconnect and Hinge and incubate new brands such as Chispa™, BLK®, and Upward®, where we have seen initial growth and we expect to see additional growth opportunities into the future. With our evolving portfolio of brands, we have seen a number of significant trends in our business in recent years, including the following:
Lower cost users. All of our brands rely on word-of-mouth, or free, user acquisition to varying degrees. Word-of-mouth acquisition is typically a function of scale (with larger communities driving greater numbers of referrals), youthfulness (with the viral effect being more pronounced in younger populations due, in part, to a significantly higher concentration of people seeking connections in any given social circle and the increased adoption of social media and similar platforms among such populations), and monetization rate (with people
generally more likely to talk openly about using technologies to meet people that are less heavily monetized). Additionally, some, but not all, of our brands spend meaningfully on paid marketing. Accordingly, the average amount we spend to acquire a user differs significantly across brands based in large part on each brand’s mix of paid and free acquisition channels. As our mix has shifted toward younger users, our mix of acquisition channels has shifted toward lower cost channels, driving a decline over the past several years in the average amount we spend to acquire a new user across our portfolio. As a percentage of revenue, our costs of acquiring users have declined.
Changing paid acquisition dynamics. Even as our acquisition of lower cost users increases, paid acquisition of users remains an important driver of our business. The channels through which we market our brands are always evolving, but we are currently in a period of rapid change as TV and video consumption patterns evolve and internet consumption occurs regularly on mobile devices. As we adapt our paid marketing activities to maximize user engagement with our brands, we may increase our use of paid advertising at brands where we traditionally relied on word-of-mouth engagement to leverage these shifts in media consumption patterns and fuel international growth. Other brands in our portfolio may reduce paid marketing activities to reflect the change in audience engagement.
In-App Purchase Fees. Purchases made by our customers through mobile applications, as opposed to desktop or mobile web, continue to increase. Purchases processed through the in-app payments systems provided by the Apple App Store and Google Play Store are subject to in-app purchase fees, which are generally 30% of the purchase price (Google reduced its in-app purchase fees for subscriptions to 15% as of January 1, 2022). As a result, the percentage of our revenues paid to Apple and Google continues to be a significant expense. In 2019, Tinder began offering subscribers an alternative payment method to Google’s in-app payment system similar to the payment alternatives other brands in our portfolio have historically offered to subscribers through mobile apps on Android. Google has announced that beginning in March 2022, all purchases will be required to be processed through the Google Play Store and subject to in-app purchase fees. To the extent that app stores fee change, or the mix of our revenue generated through app stores shifts, our results, in particular our profit measures, could be impacted.
The manner in which Apple and Google operate these services is being reviewed by legislative and regulatory bodies globally. Notably, the Republic of Korea recently adopted legislation that prohibits Apple and Google from requiring that developers exclusively use Apple and Google to process payments. In the Netherlands, the Authority for Consumers and Markets found Apple’s requirement that online dating companies must exclusively use Apple’s in-app payment violates both Dutch and European Union law. Multiple other jurisdictions, including the European Union, United Kingdom, Russia, Japan, and India are investigating, considering regulatory action or considering legislation to restrict or prohibit these practices. The United States Congress, as well as a number of state legislatures, are also considering legislation that would regulate certain terms of the relationships between developers and Apple and Google and prohibit Apple and Google from requiring in-app payment processing.
Increase in acceptance and growth of technologies to meet people globally. Over the past decade, there has been meaningful growth in the usage of technologies to meet people in North America and Western Europe, and we see the potential for similar growth in the rest of the world in the years ahead. As more internet-connected people seeking connections utilize technologies to meet people and the stigma around using such technologies continues to erode, we believe that there is potential for accelerating growth in the use of these technologies globally.
Increased consumption of video and live experiences. With more recent advances in technology, most notably live video, and with an increasing amount of time spent online, there are new ways that people want to meet and get to know one another that are more reflective of how people engage in-person. Our brands are evolving to incorporate a variety of new technologies that enable users to interact in a variety of ways including video capabilities and live experiences. These technologies were already being incorporated at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and we are continuing to further incorporate them into our portfolio of brands. We expect new technologies to continue to drive user engagement and expect other technologies beyond video and live experiences to be tested in our services and incorporated into our apps in the future.
Impacts of the Coronavirus. When the novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) first hit Western Europe and then certain major metropolitan centers in the U.S. in the Spring of 2020, particularly New York City, engagement
(messages sent, daily active users, Swipe® activity on the Tinder platform) increased significantly, but subscribers who purchase a subscription for the first time (“first-time subscribers”) declined at most of our brands as meeting in person was restricted. As we entered the summer months of 2020, propensity to pay rebounded across our portfolio, and first-time subscribers climbed amid reduced COVID-19 cases, but then faced new headwinds at the end of 2020, as the second wave of COVID-19 cases and related lockdowns took hold. In 2021, we saw a new normalization level as vaccines continued to roll out globally, even as several countries experienced a third wave of cases. We saw strong recovery in the U.S. and improvement in Europe as well, but important markets for us such as India, South Korea, Brazil, and Japan were further behind on the COVID-19 curve. The recent Omicron variant surge has caused a modest impact on our business, with rolling global effects as the wave passes through the U.S., Europe, and then, we expect, Asia. While we have continued to feel the effects of COVID-19 on our business as new waves and variants have emerged, the business has proven to be quite resilient over the last two years.
Other factors affecting the comparability of our results
Advertising spend. Our advertising spend, which is included in our selling and marketing expense, has consistently been one of our larger operating expenses. How we deploy our advertising spend varies among brands, with the majority of our advertising spend taking place online, including search engines, social media sites, streaming services and influencers. Additionally, some brands utilize television and out-of-home marketing campaigns, such as on outdoor billboards. For established brands, we seek to optimize for total return on advertising spend by frequently analyzing and adjusting spend to focus on marketing channels and markets that generate returns above our thresholds. Our data-driven approach provides us the flexibility to scale and optimize our advertising spend. We spend advertising dollars against an expected lifetime value of a Payer that is realized over a multi-year period; and while this advertising spend is intended to be profitable on that basis, it is nearly always negative during the period in which the expense is incurred. For newer brands that are gaining scale, or existing brands that are expanding into new geographies, we may make incremental advertising investments to establish the brand before optimizing monetization of the brand. In general, our more established brands spend a higher proportion of their revenue on advertising while our newer brands spend a lower proportion and tend to rely more on word of mouth and other viral marketing. Additionally, advertising spend is typically higher during the first quarter of our fiscal year, and lower during the fourth quarter. See “Seasonality” below.
Seasonality. Historically, our business has experienced seasonal fluctuations in quarterly operating results, particularly with respect to our profit measurements. This is driven primarily by a higher concentration of advertising spend in the first quarter, when advertising prices tend to be the lowest and demand for our services tends to be highest, and a lower concentration of advertising spend in the fourth quarter, when advertising costs tend to be highest and demand for our services tends to be lowest. Seasonality is not consistent across our brands, with brands targeted at older users generally showing more seasonality than brands targeted at younger users.
International markets. Our services are available across the world. Our international revenue represented 54% and 53% of our total revenue for years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. We vary our pricing to align with local market conditions and our international businesses typically earn revenue in local currencies. As foreign currency exchange rates change, translation of the statement of operations of our international businesses into U.S. dollars affects year-over-year comparability of operating results.
2021 Consolidated Results
In 2021, revenue, operating income and Adjusted Operating Income grew 25%, 14% and 19%, respectively, year-over-year. Revenue growth was primarily due to strong growth at Tinder, Hinge, and PlentyOfFish and the acquisition of Hyperconnect in June 2021. Operating income and Adjusted Operating Income grew at a slower rate than revenue primarily due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect, higher cost of revenue primarily due to in-app purchase fees, higher general and administrative expense primarily related to higher legal and other professional fees and increased compensation expense as a result of increased headcount, higher product development expenses from increased headcount at Tinder and Hinge, partially offset by lower selling and marketing expense as a percentage of revenue. Operating income was further impacted by higher amortization of intangibles due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect and higher stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to new grants made during the year and new grants associated with the Hyperconnect acquisition, partially offset by lower expense for award modifications.
Results of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Revenue | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Amounts in thousands, except ARPU) |
| Direct Revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas | $ | 1,512,057 | | | $ | 264,096 | | | 21% | | $ | 1,247,961 | | | $ | 157,803 | | | 14% | | $ | 1,090,158 | |
| Europe | 821,827 | | | 141,699 | | | 21% | | 680,128 | | | 95,716 | | | 16% | | 584,412 | |
| APAC and Other | 588,987 | | | 172,352 | | | 41% | | 416,635 | | | 84,031 | | | 25% | | 332,604 | |
| Total Direct Revenue | 2,922,871 | | | 578,147 | | | 25% | | 2,344,724 | | | 337,550 | | | 17% | | 2,007,174 | |
| Indirect Revenue | 60,406 | | | 13,861 | | | 30% | | 46,545 | | | 2,461 | | | 6% | | 44,084 | |
Total Revenue | $ | 2,983,277 | | | $ | 592,008 | | | 25% | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 340,011 | | | 17% | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct Revenue | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Tinder | $ | 1,649,757 | | | $ | 294,357 | | | 22% | | $ | 1,355,400 | | | $ | 203,355 | | | 18% | | $ | 1,152,045 | |
| Other brands | 1,273,114 | | | 283,790 | | | 29% | | 989,324 | | | 134,195 | | | 16% | | 855,129 | |
| Total Direct Revenue | $ | 2,922,871 | | | $ | 578,147 | | | 25% | | $ | 2,344,724 | | | $ | 337,550 | | | 17% | | $ | 2,007,174 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentage of Total Revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct Revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas | 51% | | | | | | 52% | | | | | | 53% |
| Europe | 27% | | | | | | 29% | | | | | | 28% |
| APAC and Other | 20% | | | | | | 17% | | | | | | 16% |
| Total Direct Revenue | 98% | | | | | | 98% | | | | | | 98% |
| Indirect Revenue | 2% | | | | | | 2% | | | | | | 2% |
| Total Revenue | 100% | | | | | | 100% | | | | | | 100% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Payers(a): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas | 8,009 | | | 896 | | | 13% | | 7,113 | | | 742 | | | 12% | | 6,371 | |
| Europe | 4,489 | | | 461 | | | 11% | | 4,028 | | | 430 | | | 12% | | 3,598 | |
| APAC and Other | 2,987 | | | 578 | | | 24% | | 2,409 | | | 418 | | | 21% | | 1,991 | |
| Total | 15,485 | | | 1,935 | | | 14% | | 13,550 | | | 1,590 | | | 13% | | 11,960 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Change calculated using non-rounded numbers) |
RPP(a): | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas | $ | 15.73 | | | $ | 1.11 | | | 8% | | $ | 14.62 | | | $ | 0.36 | | | 3% | | $ | 14.26 | |
| Europe | $ | 15.25 | | | $ | 1.18 | | | 8% | | $ | 14.07 | | | $ | 0.53 | | | 4% | | $ | 13.54 | |
| APAC and Other | $ | 16.43 | | | $ | 2.02 | | | 14% | | $ | 14.41 | | | $ | 0.49 | | | 4% | | $ | 13.92 | |
| Total | $ | 15.73 | | | $ | 1.31 | | | 9% | | $ | 14.42 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | 3% | | $ | 13.99 | |
(a) Our ability to eliminate duplicate Payers at a brand level for periods prior to Q2 2020 is impacted by data privacy requirements which require that we anonymize data after 12 months, therefore Payer data for those periods is likely overstated. Additionally, as Payers is a component of the RPP calculation, RPP is likely commensurately understated for these same periods due to these data privacy limitations.
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Americas Direct Revenue grew $264.1 million, or 21%, in 2021 versus 2020, driven by 13% growth in Payers and 8% growth in RPP. Growth in Payers was primarily driven by Tinder with contributions from Hinge and the Swipe® Apps (BLK, Chispa, and Upward). RPP growth was driven by both monetization growth at Hinge and á la carte purchases at Hinge, Tinder and PlentyOfFish.
Europe Direct Revenue grew $141.7 million, or 21%, in 2021 versus 2020, driven by 11% growth in Payers and 8% growth in RPP. Growth in Payers and RPP was primarily due to Tinder and, to a lesser extent, the acquisition of Hyperconnect. RPP growth was favorably impacted by the increased strength of the British pound and the Euro against the U.S. dollar compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.
APAC and Other Direct Revenue grew $172.4 million, or 41%, in 2021 versus 2020, driven by 24% growth in Payers and 14% growth in RPP. Payer growth was primarily driven by Tinder and the acquisition of Hyperconnect. RPP growth was primarily due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect.
Indirect Revenue increased $13.9 million primarily due to higher rates per impression and robust direct ad sales at Tinder.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Americas Direct Revenue grew $157.8 million, or 14%, in 2020 versus 2019, driven by 12% growth in Payers. Growth in Payers was primarily driven by Tinder with contributions from Hinge and the Swipe Apps (BLK, Chispa, and Upward).
Europe Direct Revenue grew $95.7 million, or 16%, in 2020 versus 2019, driven by 12% growth in Payers and 4% growth in RPP. Growth in Payers was primarily due to Tinder, and to a lesser extent, contributions from Meetic and Hinge. RPP growth was primarily due to Tinder and was favorably impacted by the increased strength of the Euro compared to the U.S. dollar between the two periods.
APAC and Other Direct Revenue grew $84.0 million, or 25%, in 2020 versus 2019, driven by 21% growth in Payers and 4% growth in RPP. Payer growth was primarily driven by Tinder and Pairs with additional contributions from OkCupid. RPP growth was driven by Pairs.
Indirect Revenue increased $2.5 million primarily due to higher rates per impression.
Cost of revenue (exclusive of depreciation) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
| Cost of revenue | $839,308 | | $203,475 | | 32% | | $635,833 | | $108,649 | | 21% | | $527,184 |
| Percentage of revenue | 28% | | | | | | 27% | | | | | | 26% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Cost of revenue increased in part due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect in the second quarter of 2021. Excluding the increase from the Hyperconnect acquisition, cost of revenue increased 23% primarily due to an increase in in-app purchase fees of $109.4 million, as revenue continues to be increasingly sourced through mobile app stores; an increase of $15.8 million in partner related costs associated with live video streaming; an increase in hosting fees of $12.6 million; and an increase in compensation expense of $11.9 million related to increased costs in customer care. Total in-app purchase fees for 2021, including Hyperconnect, were $552.6 million.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Cost of revenue increased due to an increase in in-app purchase fees of $50.0 million, as revenue continued to be increasingly sourced through mobile app stores; an increase in hosting fees of $24.0 million; an increase of $17.9 million in partner related costs associated with live video streaming; and an increase in compensation expense of $11.5 million related to increased headcount and other operating costs in customer care.
Selling and marketing expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
Selling and marketing expense | $566,459 | | $86,552 | | 18% | | $479,907 | | $52,467 | | 12% | | $427,440 |
| Percentage of revenue | 19% | | | | | | 20% | | | | | | 21% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Selling and marketing expense increased due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect in the second quarter of 2021, higher marketing spend at multiple brands, and an increase in compensation expense of $9.6 million related to increased headcount. Selling and marketing expense continued to decline as a percentage of revenue excluding Hyperconnect as we continue to generate revenue growth from brands with relatively lower marketing expense.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Selling and marketing expense increased primarily due to higher marketing spend at multiple brands, and an increase in compensation expense of $5.7 million. Selling and marketing expense continued to decline as a percentage of revenue as we continued to generate revenue growth from brands with relatively lower marketing expense.
General and administrative expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
General and administrative expense | $414,821 | | $103,614 | | 33% | | $311,207 | | $55,069 | | 21% | | $256,138 |
| Percentage of revenue | 14% | | | | | | 13% | | | | | | 12% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
General and administrative expense increased in part due to the post-acquisition expenses of Hyperconnect. Excluding Hyperconnect, general and administrative expense increased 26% primarily due to an increase of $29.0 million in legal and other professional fees; an increase in compensation expense of $20.5 million primarily related to an increase in headcount and an increase in stock-based compensation expense associated with new awards granted in the current year, partially offset by lower modification expense in 2021; $7.5 million of professional fees incurred to acquire Hyperconnect; an increase of $8.3 million for non-income taxes, primarily digital services taxes; and an increase in software license fees of $8.6 million.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
General and administrative expense increased primarily due to an increase in compensation of $39.3 million primarily related to an increase in headcount and an increase in stock-based compensation expense resulting from a modification charge in 2020; an increase of $6.7 million for non-income taxes, primarily digital services taxes; and an increase of $6.4 million in legal expenses.
Product development expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
Product development expense | $241,049 | | $71,238 | | 42% | | $169,811 | | $17,851 | | 12% | | $151,960 |
| Percentage of revenue | 8% | | | | | | 7% | | | | | | 7% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Product development expense increased in part due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect. Excluding Hyperconnect, product development expense increased 29% primarily due to an increase in compensation expense of $45.4 million primarily related to increased headcount at Tinder and Hinge, and an increase in stock-based compensation associated with new awards granted in the current year.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Product development expense increased primarily as a result of an increase of $18.7 million in compensation primarily due to increased headcount at Tinder.
Depreciation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
| Depreciation | $41,402 | | $131 | | —% | | $41,271 | | $6,916 | | 20% | | $34,355 |
| Percentage of revenue | 1% | | | | | | 2% | | | | | | 2% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Depreciation was flat compared to the prior year period.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Depreciation increased primarily due to an increase in internally developed software being placed in service.
Amortization of intangibles | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
| Amortization of intangibles | $28,559 | | $21,034 | | 280% | | $7,525 | | $(1,202) | | (14)% | | $8,727 |
| Percentage of revenue | 1% | | | | | | —% | | | | | | —% |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Amortization of intangibles increased primarily due to an increase in definite-lived intangibles related to the acquisition of Hyperconnect in the second quarter of 2021, partially offset by an impairment charge recorded in 2020.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Amortization of intangibles decreased primarily due to the decrease in impairment charges in 2020 as compared to impairment charges recorded in 2019.
Operating Income and Adjusted Operating Income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income | $851,679 | | $105,964 | | 14% | | $745,715 | | $100,261 | | 16% | | $645,454 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentage of revenue | 29% | | | | | | 31% | | | | | | 32% |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjusted Operating Income | $1,068,456 | | $171,677 | | 19% | | $896,779 | | $118,519 | | 15% | | $778,260 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percentage of revenue | 36% | | | | | | 38% | | | | | | 38% |
For a reconciliation of net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders to operating income and Adjusted Operating Income, see “Non-GAAP Financial Measures.”
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Operating income and Adjusted Operating Income increased 14% or $106.0 million and 19% or $171.7 million, respectively, primarily driven by the increase in revenue of $592.0 million which was driven by growth at Tinder, Hinge, and the acquisition of Hyperconnect and lower selling and marketing expense as a percentage of revenue, partially offset by an increase in cost of revenue due to higher in-app fees, as revenue continues to shift to mobile app stores, and an increase in general and administrative expense primarily due to professional fees and compensation expense. Operating income was further impacted by higher amortization of intangibles due to the acquisition of Hyperconnect and higher stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to new grants made during the year and new grants associated with the Hyperconnect acquisition, partially offset by lower expense for award modifications in 2021.
At December 31, 2021, there was $273.9 million of unrecognized compensation cost, net of estimated forfeitures, related to all equity-based awards, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 2.4 years.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Operating income and Adjusted Operating Income increased 16% or $100.3 million and 15% or $118.5 million, respectively, primarily as a result of the increase in revenue of $340.0 million driven by growth at multiple brands and lower selling and marketing expense as a percentage of revenue, partially offset by an increase in cost of revenue due to higher in-app purchase fees, as revenue was increasingly sourced through mobile app stores, increased web hosting fees, and live video costs.
Interest expense | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
Interest expense | $130,493 | | $(131) | | —% | | $130,624 | | $19,616 | | 18% | | $111,008 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020
Interest expense was flat compared to the prior year despite an increase in the total average principal amount of long-term debt outstanding due to lower interest rates on newer issuances of senior notes and a lower LIBOR rate on the Term Loan.
For the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019
Interest expense increased primarily due to the issuance of the 4.125% Senior Notes on February 11, 2020 and the issuance of the 4.625% Senior Notes on May 19, 2020. Additionally, the 2026 and 2030 Senior Exchangeable Notes were outstanding for the entire year. Partially offsetting these increases were decreases due to the redemption of the 6.375% Senior Notes during 2020 and a lower LIBOR rate on the Term Loan.
Other (expense) income, net | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
| Other (expense) income, net | $(465,038) | | $(480,899) | | NM | | $15,861 | | $17,887 | | NM | | $(2,026) |
________________________
NM = not meaningful
Other expense, net, in 2021 includes a $441.0 million loss related to the settlement of the former Tinder employee litigation, a $14.6 million loss related to the changes in fair value of derivatives created as we repurchased a portion of our outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, a $5.2 million inducement expense arising from the repurchased 2022 Exchangeable Notes, and $1.8 million in net foreign currency losses, partially offset by $2.4 million of fair market value gains on the net settlement of certain note hedges and warrants relating to the repurchased 2022 Exchangeable Notes.
Other income, net, in 2020 includes a legal settlement of $35.0 million and interest income of $2.7 million, partially offset by a loss on redemption of bonds of $16.5 million, expense of $3.4 million related to mark-to-market adjustments pertaining to liability classified equity instruments, and $0.6 million in net foreign currency losses in the period.
Other expense, net, in 2019 includes a $4.0 million impairment of an equity investment, expense of $1.7 million related to a mark-to-market adjustment pertaining to a liability classified equity instrument, and $0.9 million in net foreign currency losses in the period, partially offset by interest income of $4.4 million.
Income tax (benefit) provision | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in thousands) |
Income tax (benefit) provision | $(19,897) | | $(63,170) | | NM | | $43,273 | | $28,193 | | 187% | | $15,080 |
Effective income tax rate | NM | | | | | | 7% | | | | | | 3% |
For discussion of income taxes, see “Note 3—Income Taxes” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company recorded an income tax benefit of $19.9 million, despite pre-tax income, primarily due to excess tax benefits generated by the (i) exercise and vesting of stock-based awards and (ii) research credits. This benefit was partially offset by an increase in the valuation allowance for foreign losses and U.S. foreign tax credits.
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company recorded an income tax provision of $43.3 million, and $15.1 million, respectively, representing an effective tax rate of 7%, and 3%, respectively, which is lower than the U.S. statutory rate of 21% due primarily to excess tax benefits generated by (i) the exercise and vesting of stock-based awards and (ii) research credits. In 2020, these benefits were partially offset by an increase in the valuation allowance for U.S. foreign tax credits.
Related party transactions
For discussion of related party transactions, see “Note 15—Related Party Transactions” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
Match Group reports Adjusted Operating Income and Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects, both of which are supplemental measures to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). Adjusted Operating Income is among the primary metrics by which we evaluate the performance of our business, on which our internal budget is based, and by which management is compensated. Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects provides a comparable framework for assessing how our business performed without the effect of exchange rate differences when compared to prior periods. We believe that investors should have access to the same set of tools that we use in analyzing our results. These non-GAAP measures should be considered in addition to results prepared in accordance with GAAP, but should not be considered a substitute for or superior to GAAP results. Match Group endeavors to compensate for the limitations of the non-GAAP measures presented by providing the comparable GAAP measure with equal or greater prominence and descriptions of the reconciling items, including quantifying such items, to derive the non-GAAP measure. We encourage investors to examine the reconciling adjustments between the GAAP and non-GAAP measures, which we discuss below.
Adjusted Operating Income
Adjusted Operating Income is defined as operating income excluding: (1) stock-based compensation expense; (2) depreciation; and (3) acquisition-related items consisting of (i) amortization of intangible assets and impairments of goodwill and intangible assets, if applicable, and (ii) gains and losses recognized on changes in the fair value of contingent consideration arrangements. We believe this measure is useful for analysts and investors as this measure allows a more meaningful comparison between our performance and that of our competitors. The above items are excluded from our Adjusted Operating Income measure because they are non-cash in nature. Adjusted Operating Income has certain limitations because it excludes the impact of these expenses.
Non-Cash Expenses That Are Excluded From Adjusted Operating Income
Stock-based compensation expense consists principally of expense associated with the grants of stock options, restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance-based RSUs, and market-based awards. These expenses are not paid in cash, and we include the related shares in our fully diluted shares outstanding using the treasury stock method; however, performance-based RSUs and market-based awards are included only to the extent the applicable performance or market condition(s) have been met (assuming the end of the reporting period is the end of the contingency period). To the extent that stock-based awards are settled on a net basis, we remit the required tax-withholding amounts from our current funds.
Depreciation is a non-cash expense relating to our property and equipment and is computed using the straight-line method to allocate the cost of depreciable assets to operations over their estimated useful lives, or, in the case of leasehold improvements, the lease term, if shorter.
Amortization of intangible assets and impairments of goodwill and intangible assets are non-cash expenses related primarily to acquisitions. At the time of acquisition, the identifiable definite-lived intangible assets of the acquired company, such as customer lists, trade names, and technology, are valued and amortized over their estimated lives. Value is also assigned to (i) acquired indefinite-lived intangible assets, which consist of trade names and trademarks, and (ii) goodwill, which are not subject to amortization. An impairment is recorded when the carrying value of an intangible asset or goodwill exceeds its fair value. We believe that intangible assets represent costs incurred by the acquired company to build value prior to acquisition and the related amortization and impairment charges of intangible assets or goodwill, if applicable, are not ongoing costs of doing business.
The following table reconciles net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders to operating income and Adjusted Operating Income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 277,723 | | | $ | 162,329 | | | $ | 453,838 | |
Add back: | | | | | |
| Net (loss) earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests | (1,169) | | | 59,280 | | | 112,689 | |
| (Earnings) loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | (509) | | | 366,070 | | | (49,187) | |
| Income tax (benefit) provision | (19,897) | | | 43,273 | | | 15,080 | |
| Other expense (income), net | 465,038 | | | (15,861) | | | 2,026 | |
Interest expense | 130,493 | | | 130,624 | | | 111,008 | |
Operating Income | 851,679 | | | 745,715 | | | 645,454 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 146,816 | | | 102,268 | | | 89,724 | |
| Depreciation | 41,402 | | | 41,271 | | | 34,355 | |
Amortization of intangibles | 28,559 | | | 7,525 | | | 8,727 | |
| | | | | |
| Adjusted Operating Income | $ | 1,068,456 | | | $ | 896,779 | | | $ | 778,260 | |
Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates on Revenue
Due to our global reach, the impact of foreign exchange rates on the Company may be an important factor in understanding period over period comparisons if movement in exchange rates is significant. Since our results are reported in U.S. dollars, international revenue is favorably impacted as the U.S. dollar weakens relative to other currencies, and unfavorably impacted as the U.S. dollar strengthens relative to other currencies. We believe the presentation of revenue excluding the effects from foreign exchange, in addition to reported revenue, helps improve the ability to understand the Company’s performance because it excludes the impact of foreign currency volatility that is not indicative of Match Group’s core operating results.
Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects compares results between periods as if exchange rates had remained constant period over period. Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects is calculated by translating current period revenue using prior period exchange rates. The percentage change in revenue excluding foreign exchange effects is calculated by determining the change in current period revenue over prior period revenue where current period revenue is translated using prior period exchange rates.
The following tables present the impact of foreign exchange effects on total revenue and Direct Revenue by geographic region, and RPP on a total basis and by geographic region, for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 and the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to the year ended December 31, 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, | | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (Dollars in thousands) |
| Revenue, as reported | $ | 2,983,277 | | | $ | 592,008 | | | 25% | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 340,011 | | | 17% | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (35,191) | | | | | | | | | 6,412 | | | | | | | |
| Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 2,948,086 | | | $ | 556,817 | | | 23% | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 2,397,681 | | | $ | 346,423 | | | 17% | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas Direct Revenue, as reported | $ | 1,512,057 | | | $ | 264,096 | | | 21% | | $ | 1,247,961 | | | $ | 1,247,961 | | | $ | 157,803 | | | 14% | | $ | 1,090,158 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (1,471) | | | | | | | | | 14,619 | | | | | | | |
Americas Direct Revenue, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 1,510,586 | | | $ | 262,625 | | | 21% | | $ | 1,247,961 | | | $ | 1,262,580 | | | $ | 172,422 | | | 16% | | $ | 1,090,158 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Europe Direct Revenue, as reported | $ | 821,827 | | | $ | 141,699 | | | 21% | | $ | 680,128 | | | $ | 680,128 | | | $ | 95,716 | | | 16% | | $ | 584,412 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (33,894) | | | | | | | | | (7,551) | | | | | | | |
| Europe Direct Revenue, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 787,933 | | | $ | 107,805 | | | 16% | | $ | 680,128 | | | $ | 672,577 | | | $ | 88,165 | | | 15% | | $ | 584,412 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| APAC and Other Direct Revenue, as reported | $ | 588,987 | | | $ | 172,352 | | | 41% | | $ | 416,635 | | | $ | 416,635 | | | $ | 84,031 | | | 25% | | $ | 332,604 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | 917 | | | | | | | | | (828) | | | | | | | |
| APAC and Other Direct Revenue, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 589,904 | | | $ | 173,269 | | | 42% | | $ | 416,635 | | | $ | 415,807 | | | $ | 83,203 | | | 25% | | $ | 332,604 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, | | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2020 | | 2020 | | $ Change | | % Change | | 2019 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| RPP, as reported | $ | 15.73 | | | $ | 1.31 | | | 9% | | $ | 14.42 | | | $ | 14.42 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | 3% | | $ | 13.99 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (0.19) | | | | | | | | | 0.04 | | | | | | | |
| RPP, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 15.54 | | | $ | 1.12 | | | 8% | | $ | 14.42 | | | $ | 14.46 | | | $ | 0.47 | | | 3% | | $ | 13.99 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Americas RPP, as reported | $ | 15.73 | | | $ | 1.11 | | | 8% | | $ | 14.62 | | | $ | 14.62 | | | $ | 0.36 | | | 3% | | $ | 14.26 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (0.01) | | | | | | | | | 0.17 | | | | | | | |
| Americas RPP, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 15.72 | | | $ | 1.10 | | | 8% | | $ | 14.62 | | | $ | 14.79 | | | $ | 0.53 | | | 3% | | $ | 14.26 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Europe RPP, as reported | $ | 15.25 | | | 1.18 | | 8% | | $ | 14.07 | | | $ | 14.07 | | | 0.53 | | 4% | | $ | 13.54 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | (0.35) | | | | | | | | | (0.09) | | | | | | | |
| Europe RPP, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 14.90 | | | $ | 0.83 | | | 6% | | $ | 14.07 | | | $ | 13.98 | | | $ | 0.44 | | | 4% | | $ | 13.54 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| APAC and Other RPP, as reported | $ | 16.43 | | | $ | 2.02 | | | 14% | | $ | 14.41 | | | $ | 14.41 | | | $ | 0.49 | | | 4% | | $ | 13.92 | |
| Foreign exchange effects | 0.03 | | | | | | | | | (0.03) | | | | | | | |
| APAC and Other RPP, excluding foreign exchange effects | $ | 16.46 | | | $ | 2.05 | | | 14% | | $ | 14.41 | | | $ | 14.38 | | | $ | 0.46 | | | 4% | | $ | 13.92 | |
FINANCIAL POSITION, LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Financial Position | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Cash and cash equivalents: | | | |
United States | $ | 642,686 | | | $ | 581,038 | |
All other countries | 172,698 | | | 158,126 | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | $ | 815,384 | | | $ | 739,164 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Long-term debt, net: | | | |
| Credit Facility due February 13, 2025 | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Term Loan due February 13, 2027 | 425,000 | | | 425,000 | |
| | | |
5.00% Senior Notes due December 15, 2027 | 450,000 | | | 450,000 | |
| 4.625% Senior Notes due June 1, 2028 | 500,000 | | | 500,000 | |
| 5.625% Senior Notes due February 15, 2029 | 350,000 | | | 350,000 | |
| 4.125% Senior Notes due August 1, 2030 | 500,000 | | | 500,000 | |
| 3.625% Senior Notes due October 1, 2031 | 500,000 | | | — | |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | 100,500 | | | 517,500 | |
| 2026 Exchangeable Notes | 575,000 | | | 575,000 | |
| 2030 Exchangeable Notes | 575,000 | | | 575,000 | |
| Total long-term debt | 3,975,500 | | | 3,892,500 | |
| Less: Current maturities of long-term debt | 100,500 | | | — | |
Less: unamortized original issue discount and original issue premium, net | 5,215 | | | 6,029 | |
| Less: unamortized debt issuance costs | 40,364 | | | 45,541 | |
| Total long-term debt, net | $ | 3,829,421 | | | $ | 3,840,930 | |
Long-term Debt
For a detailed description of long-term debt, see “Note 7—Long-term Debt, net” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Cash Flow Information
In summary, the Company’s cash flows from continuing operations are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations | $ | 912,499 | | | $ | 788,552 | | | $ | 647,989 | |
Net cash used in investing activities attributable to continuing operations | (939,825) | | | (3,922,131) | | | (41,730) | |
Net cash provided by financing activities attributable to continuing operations | 111,106 | | | 1,787,846 | | | 654,024 | |
2021
Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations in 2021 includes adjustments to earnings consisting primarily of $146.8 million of stock-based compensation expense; $41.4 million of depreciation; $28.6 million of amortization of intangibles; and other adjustments of $27.7 million,
which includes amortization of deferred financing costs of $9.0 million. Partially offsetting these adjustments was deferred income tax benefit of $58.0 million. The increase in cash from changes in working capital primarily consists of an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses and other current liabilities of $458.8 million due mainly to the timing of payments, with the former Tinder employee litigation settlement, which is expected to be paid in 2022, being the primary component; and an increase in deferred revenue of $26.3 million, due mainly to growth in subscription sales. These increases in cash were partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable of $34.0 million primarily related to an increase in revenue.
Net cash used in investing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2021 consists primarily of cash used to acquire Hyperconnect, net of cash acquired, of $859.9 million, and capital expenditures of $80.0 million that are primarily related to internal development of software and computer hardware to support our services.
Net cash provided by financing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2021 is primarily due to proceeds from the settlement of certain note hedges of $1.1 billion, partially offset by an $882.2 million outflow related to the settlement of certain outstanding warrants, in each case associated with the settlement of a portion of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes; proceeds of $500.0 million from the issuance of the 3.625% Senior Notes; and $58.4 million of proceeds from the issuance of common stock pursuant to stock-based awards. These increases in cash were partially offset by payment of $630.7 million to repurchase a portion of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes and payment of $15.7 million for withholding taxes paid on behalf of employees for net settled equity awards.
2020
Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations in 2020 includes adjustments to earnings consisting primarily of $102.3 million of stock-based compensation expense, $41.3 million of depreciation, $7.5 million of amortization of intangibles; other adjustments of $27.3 million, which includes a loss on bond redemption of $16.5 million; and deferred income tax of $15.4 million. The increase in cash from changes in working capital primarily consists of an increase from income taxes payable and receivable of $16.9 million due primarily to the timing of tax payments and refunds; an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses and other current liabilities of $24.2 million due mainly to the timing of payments, including interest payments; and an increase in deferred revenue of $23.5 million, due mainly to growth in subscription sales. These increases in cash were partially offset by a decrease related to an increase in other assets of $33.2 million primarily related to an increase in prepaid hosting services and an increase in accounts receivable of $24.2 million primarily related to an increase in revenue.
Net cash used in investing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2020 consists primarily of $3.9 billion of net cash distributed to IAC related to the Separation, which was partially funded by $1.4 billion of net proceeds from the stock issuance in connection with the Separation as noted below, and capital expenditures of $42.4 million that are primarily related to internal development of software and computer hardware to support our services.
Net cash provided by financing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2020 is primarily due to proceeds of $1.4 billion from the stock offering in connection with the Separation, which were subsequently transferred to IAC as noted above, proceeds of $1.0 billion from the issuance of the 4.125% and 4.625% Senior Notes, partially offset by the redemption of the $400.0 million 6.375% Senior Notes, payments of $212.0 million for withholding taxes paid on behalf of employees for net settled equity awards of both Former Match Group and Match Group, and purchases of treasury stock of Former Match Group of $132.9 million.
2019
Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations in 2019 includes adjustments to earnings consisting primarily of $89.7 million of stock-based compensation expense, $34.4 million of depreciation, and $8.7 million of amortization of intangibles. Partially offsetting these adjustments was deferred income tax of $12.8 million primarily related to net operating loss created by settlement of stock-based awards. The decrease in cash from changes in working capital primarily consists of an increase in other assets of $24.2 million primarily related to an increase in prepaid hosting services, an increase in accounts receivable of $17.9 million primarily related to an increase in revenue, and a decrease from income taxes payable and receivable of $4.2 million due primarily to the timing of tax payments. These decreases in cash were partially offset by an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses and other current liabilities of $33.7 million due
mainly to the timing of payments, including interest payments, and an increase in deferred revenue of $9.5 million, due mainly to growth in subscription sales.
Net cash used in investing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2019 consists primarily of capital expenditures of $39.0 million that are primarily related to internal development of software and computer hardware to support our services.
Net cash provided by financing activities attributable to continuing operations in 2019 is primarily due to $1.2 billion from the issuance of the 2026 and 2030 Exchangeable Notes, proceeds of $350.0 million from the issuance of the 5.625% Senior Notes, and proceeds of $40.0 million from borrowings under the Credit Facility. Partially offsetting these proceeds were cash payments of $300.0 million for the repayment of borrowings under the Credit Facility, purchases of treasury stock of $216.4 million, $203.2 million for withholding taxes paid on behalf of employees for net settled equity awards, and $136.9 million used to pay the net premium on the 2026 and 2030 Exchangeable Notes hedge and warrant transactions.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company’s principal sources of liquidity are its cash flows generated from operations as well as cash and cash equivalents. At December 31, 2021, $749.6 million was available under the Credit Facility that expires on February 13, 2025.
The Company has various obligations related to long-term debt instruments and operating leases. For additional information on long-term debt, including a maturity schedule and interest rates, see “Note 7—Long-term Debt, net” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” For additional information on the operating leases, including a schedule of obligations by year, see “Note 13—Leases” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” The Company believes it has sufficient cash flows from operations to satisfy these future obligations.
On December 1, 2021, we entered into an agreement to settle the pending, threatened, and potential claims at issue in Rad, et al. v. IAC/InterActiveCorp, et al. and related arbitrations for $441 million, which is expected to be paid in 2022 utilizing cash on hand.
The Company anticipates that it will need to make capital and other expenditures in connection with the development and expansion of its operations. The Company expects that 2022 cash capital expenditures will be between $65 million and $75 million, a decrease from 2021 cash capital expenditures as several leasehold and building improvements were completed in 2021.
We have entered into various purchase commitments, primarily consisting of web hosting services. Our obligations under these various purchase commitments are $56.0 million in 2022 and between $7.0 million and $12.5 million per year from 2023 through 2026.
The Company does not have any off-balance sheet arrangements, other than those described above, at December 31, 2021.
At December 31, 2021, all of the Company’s international cash can be repatriated without significant tax consequences.
Our indebtedness could limit our ability to: (i) obtain additional financing to fund working capital needs, acquisitions, capital expenditures, debt service, or other requirements; and (ii) use operating cash flow to pursue acquisitions or invest in other areas, such as developing properties and exploiting business opportunities. The Company may need to raise additional capital through future debt or equity financing to make additional acquisitions and investments or to provide for greater financial flexibility. Additional financing may not be available on terms favorable to the Company or at all.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
The following disclosure is provided to supplement the descriptions of Match Group’s accounting policies contained in “Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in regard to significant areas of judgment. Management of the Company is required to make certain estimates, judgments and assumptions during the preparation of its consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). These estimates, judgments and assumptions impact the reported amount of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses and the related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from these estimates. Because of the size of the financial statement elements to which they relate, some of our accounting policies and estimates have a more significant impact on our consolidated financial statements than others. What follows is a discussion of some of our more significant accounting policies and estimates.
Business Combinations
Acquisitions are an important part of our growth strategy. The purchase price of each acquisition is attributed to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their fair values at the date of acquisition, including identifiable intangible assets that either arise from a contractual or legal right or are separable from goodwill. The fair value of these intangible assets is based on valuations that use information and assumptions provided by management. The excess purchase price over the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets is recorded as goodwill and is assigned to the reporting unit that is expected to benefit from the combination as of the acquisition date.
Recoverability of Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
Goodwill is the Company’s largest asset with a carrying value of $2.4 billion and $1.3 billion at December 31, 2021 and 2020, representing 48% and 42%, respectively, of the Company’s total assets. Indefinite-lived intangible assets, which consist of the Company’s acquired trade names and trademarks, have a carrying value of $576.7 million and $226.6 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are assessed annually for impairment as of October 1, or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit or the fair value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset below its carrying value.
In performing its annual goodwill impairment assessment, the Company has the option under GAAP to qualitatively assess whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value; if the conclusion of the qualitative assessment is that there are no indicators of impairment, the Company does not perform a quantitative test, which would require a valuation of the reporting unit, as of October 1. If needed, the annual or interim quantitative test of the recovery of goodwill involves a comparison of the estimated fair value of each reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. If the estimated fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, goodwill of the reporting unit is not impaired. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its estimated fair value, an impairment loss equal to the excess is recorded. The 2021 and 2020 annual assessments did not identify any impairments.
As a result of the Separation in 2020, the Company had a negative carrying value for the Company’s annual goodwill test at both October 1, 2021 and 2020. Additionally, an impairment test of goodwill was not necessary because there were no factors identified that would indicate an impairment loss. The Company continued to have a negative carrying value at December 31, 2021.
While the Company has the option to qualitatively assess whether it is more likely than not that the fair values of its indefinite-lived intangible assets are less than their carrying values, the Company’s policy is to determine the fair value of each of its indefinite-lived intangible assets annually as of October 1, in part, because the level of effort required to perform the quantitative and qualitative assessments is essentially equivalent. Due to the recent acquisition of Hyperconnect and the process to allocate the purchase price as of the purchase date, the intangible assets of Hyperconnect were considered qualitatively as of October 1, 2021. For assets in which a quantitative assessment was performed, the Company determines the fair value of its indefinite-lived intangible assets using an avoided royalty DCF valuation analysis. Significant judgments inherent in this analysis include the selection of appropriate royalty and discount rates and estimating the amount and timing of expected future
cash flows. The discount rates used in the DCF analyses are intended to reflect the risks inherent in the expected future cash flows generated by the respective intangible assets. The royalty rates used in the DCF analyses are based upon an estimate of the royalty rates that a market participant would pay to license the Company’s trade names and trademarks. The future cash flows are based on the Company’s most recent forecast and budget and, for years beyond the budget, the Company’s estimates, which are based, in part, on forecasted growth rates. Assumptions used in the avoided royalty DCF analyses, including the discount rate and royalty rate, are assessed annually based on the actual and projected cash flows related to the asset, as well as macroeconomic and industry specific factors. The discount rates used in the Company’s annual indefinite-lived impairment assessment ranged from 10% to 16% in 2021 and 10% to 23% in 2020, and the royalty rates used ranged from 5% to 8% in both 2021 and 2020.
If the carrying value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds its estimated fair value, an impairment equal to the excess is recorded. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recognized an impairment charge related to the Match® brand in the UK and the Meetic brand in Europe of $4.6 million. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recognized an impairment charge on the Match brand in the UK of $6.6 million. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, no indefinite-lived intangible asset balance had an estimated fair value less than 110% of carrying value.
Recoverability and Estimated Useful Lives of Long-Lived Assets
We review the carrying value of all long-lived assets, consisting of property and equipment and definite-lived intangible assets, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. The carrying value of a long-lived asset is not recoverable if it exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the carrying value is deemed not to be recoverable, an impairment loss is recorded equal to the amount by which the carrying value of the long-lived asset exceeds its fair value. In addition, the Company reviews the useful lives of its long-lived assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that these lives may be changed. The carrying value of property and equipment and definite-lived intangible assets was $358.3 million and $112.1 million, at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Income Taxes
Match Group is subject to income taxes in the United States and numerous foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgment is required in determining our provision for income taxes and income tax assets and liabilities, including evaluating uncertainties in the application of accounting principles and complex tax laws.
We record a provision for income taxes for the anticipated tax consequences of our reported results of operations using the asset and liability method. Under this method, we recognize deferred income tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of asset and liabilities, as well as for net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be realized or settled. We recognize the deferred income tax effects of a change in tax rates in the period of enactment.
A valuation allowance is provided on deferred tax assets if it is determined that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be realized. We consider all available evidence, both positive and negative, including historical levels of income, expectations and risks associated with estimates of future taxable income, and tax planning strategies in assessing the need for a valuation allowance.
We recognize tax benefits from uncertain tax positions only if we believe that it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained based on the technical merits of the position. Such tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon settlement. This measurement step is inherently difficult and requires subjective estimations of such amounts to determine the probability of various possible outcomes. We consider many factors when evaluating and estimating our tax positions and tax benefits, which may require periodic adjustment. We make adjustments to our unrecognized tax benefits when facts and circumstances change, such as the closing of a tax audit or the refinement of an estimate. Although we believe that we have adequately reserved for our uncertain tax positions, the final outcome of these matters may vary significantly from our estimates. To the extent that the final outcome of these matters is different from the amounts recorded, such differences will affect the income tax provision in
the period in which such determination is made, and could have a material impact on our financial condition and operating results.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense of $146.8 million and $102.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Stock-based compensation at the Company is complex due to our desire to attract, retain, and reward employees at many of our brands by allowing them to benefit from the value they help to create. We also utilize equity awards as part of our acquisition strategy. We accomplish these objectives, in part, by issuing equity awards denominated in the equity of our non-public subsidiaries as well as in Match Group, Inc. We further refine this approach by tailoring the terms of equity awards as appropriate. For example, we issue certain equity awards with vesting conditioned on the achievement of specified performance targets such as revenue or profits; these awards are referred to as performance awards. In other cases, we condition the vesting of equity awards to the achievement of value targets for a specific subsidiary or the Company’s stock price; these awards are referred to as market-based awards.
The Company issues restricted stock units (“RSUs”) and performance-based stock units (“PSUs”). The value of RSUs with vesting subject only to continued service is based on the fair value of Match Group common stock on the grant date. The value of RSUs that include a market condition is based on fair value estimated using a lattice model. The value of RSUs is expensed as stock-based compensation expense over the applicable vesting term. For PSU grants, the expense is measured at the grant date as the fair value of Match Group common stock and expensed as stock-based compensation over the vesting term if the performance targets are considered probable of being achieved.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements, see “Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” to the consolidated financial statements included in “Item 8—Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
The Company’s exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to the Company’s long-term debt.
At December 31, 2021, the Company’s outstanding long-term debt was $4.0 billion, of which $3.5 billion consists of Senior Notes and Exchangeable Senior Notes that bear interest at fixed rates. If market rates decline, the Company runs the risk that the required payments on the fixed-rate debt will exceed those on debt based on market rates. A 100 basis point increase or decrease in the level of interest rates would, respectively, decrease or increase the fair value of the fixed-rate debt by $157.6 million. Such potential increase or decrease in fair value is based on certain simplifying assumptions, including a constant level and rate of fixed-rate debt for all maturities and an immediate across-the-board increase or decrease in the level of interest rates with no other subsequent changes for the remainder of the period. At December 31, 2021, the $425 million Term Loan bore interest at a variable rate, LIBOR plus 1.75%. At December 31, 2021, the rate in effect was 1.91%. If LIBOR were to increase or decrease by 100 basis points, then the annual interest expense and payments on the Term Loan would increase or decrease, respectively, by $4.3 million based upon the outstanding balance and rate in effect at December 31, 2021.
The Credit Facility and the Term Loan provide for a benchmark replacement should the LIBOR rate not be available. The rate used would be agreed to between the administrative agent and Match Group and may be based upon a secured overnight financing rate at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Additional information about the benchmark replacement can be found Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
The Company conducts business in certain foreign markets, primarily in various jurisdictions within the European Union (“EU”) and Asia. We are exposed to foreign exchange risk for primarily the Euro and British Pound (“GBP”).
For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, international revenue accounted for 54%, 53% and 53%, respectively, of our consolidated revenue. We have exposure to foreign currency exchange risk related to transactions carried out in a currency other than the U.S. dollar, and investments in foreign subsidiaries with a functional currency other than the U.S. dollar. As foreign currency exchange rates change, translation of the statement of operations of our international businesses into U.S. dollars affects year-over-year comparability of operating results. The average GBP and Euro exchange rates strengthened against the U.S. Dollar by 7% and 4%, respectively, in 2021 compared to 2020. Foreign currency exchange rate changes during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 positively impacted revenue by $35.2 million and negatively impacted revenue by $6.4 million, respectively, or 1% and less than 1% of total revenue, respectively. See “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” in “Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for the definition of Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects and a reconciliation of Revenue to Revenue excluding foreign exchange effects.
Foreign currency exchange losses included in the Company’s earnings for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 are $1.8 million, $0.6 million and $0.9 million, respectively.
Foreign currency exchange gains or losses historically have not been material to the Company. As a result, we have not historically hedged any foreign currency exposures, although we may hedge foreign currencies in the future to limit the impact of foreign currency exchange gains and losses. The continued growth and expansion of our international operations into new countries increases our exposure to foreign exchange rate fluctuations. Significant foreign exchange rate fluctuations, in the case of one currency or collectively with other currencies, could adversely affect our future results of operations.
Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Match Group, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Match Group, Inc. and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive operations, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a) (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated February 24, 2022 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
| | | | | |
| Acquisition of Hyperconnect, Inc. - Valuation of Acquired Intangible Assets |
| Description of the Matter | On June 17, 2021, the Company completed its acquisition of Hyperconnect, Inc. for net consideration of $1.75 billion, as disclosed in Note 5 to the consolidated financial statements. The transaction was accounted for as a business combination. Auditing the Company's accounting for its acquisition of Hyperconnect, Inc. was complex due to the significant estimation uncertainty in the Company’s determination of the fair value of identified intangible assets of $612 million, which principally consisted of trade names and associated trademarks and user bases. The significant estimation uncertainty was primarily due to the sensitivity of the respective fair values to underlying assumptions about the future performance of the acquired business. The Company used a discounted cash flow model to measure the intangible assets. The significant assumptions used to estimate the value of the intangible assets included discount rates, revenue growth rates, royalty rates and the projected cash flow terminal growth rates. These significant assumptions are forward looking and could be affected by future economic and market conditions. |
| |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company’s controls over its accounting for the business combination. For example, we tested controls over management's review of the valuation models and the significant assumptions described above used to develop such estimates. To test the estimated fair value of the trade names and associated trademarks and user bases, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, evaluating the Company’s selection of the valuation methodologies, evaluating the methods and significant assumptions used by the Company’s valuation specialist, and evaluating the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data supporting the significant assumptions and estimates. For example, we compared the significant assumptions to the historical results of the acquired business as well as to current industry, market, and economic trends and to the Company’s budgets and forecasts. We performed sensitivity analyses of significant assumptions to evaluate the change in the fair value of the identifiable intangible assets resulting from changes in the assumptions. We involved our valuation specialists to assist with our evaluation of the methodologies used by the Company and significant assumptions used in the fair value estimates. |
| |
| | | | | |
| Recoverability of Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets |
| Description of the Matter | As of December 31, 2021, the Company’s indefinite-lived intangible asset balance, excluding goodwill, was $576.7 million and consisted of trade names and trademarks. As disclosed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, indefinite-lived intangible assets are assessed annually for impairment as of October 1, or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset below its carrying value. Auditing management’s annual impairment tests for certain indefinite-lived intangible assets was complex and highly judgmental due to the significant estimation uncertainty required to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible assets. In particular, the Company’s fair value estimates for indefinite-lived intangible assets were sensitive to significant assumptions, such as discount rates, revenue growth rates, royalty rates and projected cash flow terminal growth rates, which are affected by expectations about future market or economic conditions. |
| |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company’s controls over its indefinite-lived intangible assets impairment review process. For example, we tested controls over the Company’s forecasting and budgeting process as well as controls over management’s review of the significant assumptions used to estimate the fair values of the indefinite-lived intangible assets. To test the estimated fair value of certain indefinite-lived intangible assets, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, assessing the methodologies and testing the significant assumptions discussed above and the underlying data used by the Company in its analysis. We compared the significant assumptions used by management to current industry and economic trends and to other guideline public companies and evaluated whether changes to the company’s business model would affect the significant assumptions. We assessed the historical accuracy of management’s estimates and performed sensitivity analyses of significant assumptions to evaluate the changes in the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible assets that would result from changes in the assumptions. For example, we evaluated management’s forecasted revenue to identify, understand and evaluate changes as compared to historical results. In addition, we involved an internal valuation specialist to assist in evaluating management’s methodologies and significant assumptions applied in developing the fair value estimates. |
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1996.
New York, New York
February 24, 2022
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| (In thousands, except share data) |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 815,384 | | | $ | 739,164 | |
| Short-term investments | 11,818 | | | — | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowance of $281 and $286, respectively | 188,482 | | | 137,023 | |
| | | |
| Other current assets | 202,568 | | | 144,025 | |
| | | |
| Total current assets | 1,218,252 | | | 1,020,212 | |
| | | |
| Property and equipment, net | 163,256 | | | 107,799 | |
| Goodwill | 2,411,996 | | | 1,270,532 | |
| Intangible assets, net | 771,697 | | | 230,900 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 334,937 | | | 293,487 | |
| | | |
| Other non-current assets | 163,150 | | | 123,524 | |
| | | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 5,063,288 | | | $ | 3,046,454 | |
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | |
| LIABILITIES | | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt, net | $ | 99,927 | | | $ | — | |
| | | |
| Accounts payable | 37,871 | | | 29,200 | |
| Deferred revenue | 262,131 | | | 239,088 | |
| | | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 768,366 | | | 231,748 | |
| | | |
| Total current liabilities | 1,168,295 | | | 500,036 | |
| Long-term debt, net | 3,829,421 | | | 3,840,930 | |
| Income taxes payable | 13,842 | | | 14,582 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 130,261 | | | 17,213 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 116,051 | | | 86,428 | |
| | | |
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 1,260 | | | 640 | |
| | | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | |
| | | |
| SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | |
Common stock; $0.001 par value; authorized 1,600,000,000 shares; 283,470,334 and 267,329,284 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively | 283 | | | 267 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 8,164,216 | | | 7,089,007 | |
| Retained deficit | (8,144,514) | | | (8,422,237) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (223,754) | | | (81,454) | |
| | | |
| Total Match Group, Inc. shareholders’ equity | (203,769) | | | (1,414,417) | |
| Noncontrolling interests | 7,927 | | | 1,042 | |
Total shareholders’ equity | (195,842) | | | (1,413,375) | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 5,063,288 | | | $ | 3,046,454 | |
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Revenue | $ | 2,983,277 | | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
| Operating costs and expenses: | | | | | |
Cost of revenue (exclusive of depreciation shown separately below) | 839,308 | | | 635,833 | | | 527,184 | |
| Selling and marketing expense | 566,459 | | | 479,907 | | | 427,440 | |
| General and administrative expense | 414,821 | | | 311,207 | | | 256,138 | |
| Product development expense | 241,049 | | | 169,811 | | | 151,960 | |
| Depreciation | 41,402 | | | 41,271 | | | 34,355 | |
| Amortization of intangibles | 28,559 | | | 7,525 | | | 8,727 | |
| Total operating costs and expenses | 2,131,598 | | | 1,645,554 | | | 1,405,804 | |
Operating income | 851,679 | | | 745,715 | | | 645,454 | |
| Interest expense | (130,493) | | | (130,624) | | | (111,008) | |
| | | | | |
Other (expense) income, net | (465,038) | | | 15,861 | | | (2,026) | |
Earnings from continuing operations, before tax | 256,148 | | | 630,952 | | | 532,420 | |
Income tax benefit (provision) | 19,897 | | | (43,273) | | | (15,080) | |
Net earnings from continuing operations | 276,045 | | | 587,679 | | | 517,340 | |
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | 509 | | | (366,070) | | | 49,187 | |
Net earnings | 276,554 | | | 221,609 | | | 566,527 | |
Net loss (earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,169 | | | (59,280) | | | (112,689) | |
Net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 277,723 | | | $ | 162,329 | | | $ | 453,838 | |
| | | | | |
| Net earnings per share from continuing operations: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 1.01 | | | $ | 2.36 | | | $ | 2.28 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.93 | | | $ | 2.09 | | | $ | 1.95 | |
| | | | | |
Net earnings per share attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 1.01 | | | $ | 0.73 | | | $ | 2.50 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.93 | | | $ | 0.66 | | | $ | 2.15 | |
| | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense by function: | | | | | |
| Cost of revenue | $ | 5,554 | | | $ | 4,201 | | | $ | 3,693 | |
| Selling and marketing expense | 7,941 | | | 5,141 | | | 5,112 | |
| General and administrative expense | 81,420 | | | 59,174 | | | 42,863 | |
| Product development expense | 51,901 | | | 33,752 | | | 38,056 | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 146,816 | | | $ | 102,268 | | | $ | 89,724 | |
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE OPERATIONS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Net earnings | $ | 276,554 | | | $ | 221,609 | | | $ | 566,527 | |
| Other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax | | | | | |
Change in foreign currency translation adjustment | (142,608) | | | 39,415 | | | (9,961) | |
Change in unrealized losses on available-for-sale securities | — | | | (1) | | | (5) | |
| Total other comprehensive (loss) income | (142,608) | | | 39,414 | | | (9,966) | |
| Comprehensive income | 133,946 | | | 261,023 | | | 556,561 | |
| Comprehensive loss (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests: | | | | | |
| Net loss (earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,169 | | | (59,280) | | | (112,689) | |
| Change in foreign currency translation adjustment attributable to noncontrolling interests | 308 | | | 1,072 | | | 2,023 | |
| Change in unrealized losses of available-for-sale debt securities attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Comprehensive loss (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,477 | | | (58,208) | | | (110,665) | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 135,423 | | | $ | 202,815 | | | $ | 445,896 | |
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Match Group, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity | | | | |
| | | | | Common Stock $0.001 Par Value | | Former IAC Common Stock $0.001 Par Value | | Former IAC Class B Convertible Common Stock $0.001 Par Value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Redeemable
Noncontrolling
Interests | | | $ | | Shares | | $ | | Shares | | $ | | Shares | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | Retained Earnings (Deficit) | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
(Loss) Income | | Treasury Stock | | Total
Match Group, Inc.
Shareholders’
Equity | | Noncontrolling
Interests | | Total
Shareholders’
Equity |
| | | | | (In thousands) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 | $ | 65,687 | | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | 262 | | | 262,303 | | | $ | 16 | | | 16,157 | | | $ | 11,968,881 | | | $ | 1,271,208 | | | $ | (128,722) | | | $ | (10,309,612) | | | $ | 2,802,033 | | | $ | 708,676 | | | $ | 3,510,709 | |
| Net earnings for the year ended December 31, 2019 | 2,835 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 453,838 | | | — | | | — | | | 453,838 | | | 109,854 | | | 563,692 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | 39 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (7,942) | | | — | | | (7,942) | | | (2,063) | | | (10,005) | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 148 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 82,619 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 82,619 | | | 155,457 | | | 238,076 | |
Issuance of Former IAC common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 927 | | | — | | | — | | | (82,463) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (82,462) | | | — | | | (82,462) | |
Issuance of Former Match Group and ANGI Homeservices common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (236,897) | | | — | | | 315 | | | — | | | (236,582) | | | (1,794) | | | (238,376) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of redeemable noncontrolling interests | (40,432) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Adjustment of redeemable noncontrolling interests to fair value | 11,554 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (11,554) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (11,554) | | | — | | | (11,554) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests created in acquisitions | 4,781 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of exchangeable note hedges, net of deferred tax assets | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (234,563) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (234,563) | | | — | | | (234,563) | |
| Issuance of warrants | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 166,520 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 166,520 | | | — | | | 166,520 | |
| Purchase of Match Group and ANGI treasury stock | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (274,302) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (274,302) | | | — | | | (274,302) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other | (85) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (81) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (81) | | | 146 | | | 65 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 | 44,527 | | | | — | | | — | | | 263 | | | 263,230 | | | 16 | | | 16,157 | | | 11,378,160 | | | 1,725,046 | | | (136,349) | | | (10,309,612) | | | 2,657,524 | | | 970,276 | | | 3,627,800 | |
| Net (loss) earnings for the year ended December 31, 2020 | (3,136) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 162,329 | | | — | | | — | | | 162,329 | | | 62,416 | | | 224,745 | |
| Other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax | (686) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40,486 | | | — | | | 40,486 | | | (386) | | | 40,100 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 15 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 134,528 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 134,528 | | | 86,363 | | | 220,891 | |
Issuance of Match Group common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | 8 | | | 8,373 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 155,285 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 155,293 | | | — | | | 155,293 | |
| Issuance of Former IAC common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 453 | | | — | | | — | | | (34,518) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (34,517) | | | — | | | (34,517) | |
| Issuance of Former Match Group and ANGI Homeservices common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (212,270) | | | — | | | 628 | | | — | | | (211,642) | | | (11,405) | | | (223,047) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of redeemable noncontrolling interests | (3,165) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Adjustment of redeemable noncontrolling interests to fair value | 6,669 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (6,669) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (6,669) | | | — | | | (6,669) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of Match Group and ANGI treasury stock | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (187,735) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (187,735) | | | — | | | (187,735) | |
| Retirement of treasury stock | — | | | | — | | | — | | | (184) | | | (184,340) | | | (10) | | | (10,368) | | | 194 | | | (10,309,612) | | | — | | | 10,309,612 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Exchange Common stock and Class B for Class M common stock and spin off IAC | (43,583) | | | | 184 | | | 183,749 | | | (80) | | | (79,343) | | | (6) | | | (5,789) | | | (4,745,323) | | | — | | | 13,781 | | | — | | | (4,731,444) | | | (498,792) | | | (5,230,236) | |
| Acquire Former Match Group noncontrolling interest | — | | | | 58 | | | 57,868 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 608,110 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 608,168 | | | (608,168) | | | — | |
| Issuance of common stock | — | | | | 17 | | | 17,339 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (17) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Other | (1) | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (738) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (738) | | | 738 | | | — | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | $ | 640 | | | | $ | 267 | | | 267,329 | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | 7,089,007 | | | $ | (8,422,237) | | | $ | (81,454) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (1,414,417) | | | $ | 1,042 | | | $ | (1,413,375) | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019 (continued) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Match Group, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity | | | | |
| | | | | Common Stock $0.001 Par Value | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Redeemable
Noncontrolling
Interests | | | $ | | Shares | | | | | | | | | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | Retained (Deficit) Earnings | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Loss | | | | Total
Match Group, Inc.
Shareholders’
Equity | | Noncontrolling
Interests | | Total
Shareholders’
Equity |
| | | | | (In thousands) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2020 | $ | 640 | | | | $ | 267 | | | 267,329 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 7,089,007 | | | $ | (8,422,237) | | | $ | (81,454) | | | | | $ | (1,414,417) | | | $ | 1,042 | | | $ | (1,413,375) | |
Net (loss) earnings for the year ended December 31, 2021 | (2,047) | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | 277,723 | | | — | | | | | 277,723 | | | 878 | | | 278,601 | |
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | — | | | (142,300) | | | | | (142,300) | | | (308) | | | (142,608) | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | — | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | 153,692 | | | — | | | — | | | | | 153,692 | | | — | | | 153,692 | |
| Issuance of Match Group common stock pursuant to stock-based awards, net of withholding taxes | — | | | | 5 | | | 4,678 | | | | | | | | | | | 42,709 | | | — | | | — | | | | | 42,714 | | | — | | | 42,714 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock for the acquisition of Hyperconnect | — | | | | 6 | | | 5,929 | | | | | | | | | | | 890,845 | | | — | | | — | | | | | 890,851 | | | — | | | 890,851 | |
| Adjustment of redeemable noncontrolling interests to fair value | 2,667 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (2,667) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (2,667) | | | — | | | (2,667) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustment of noncontrolling interests to fair value | — | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,835) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (1,835) | | | 1,835 | | | — | |
| Purchase of noncontrolling interest | — | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 943 | | | — | | | — | | | | | 943 | | | (2,571) | | | (1,628) | |
| Noncontrolling interest created by the exercise of subsidiary denominated equity award | — | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | (7,102) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (7,102) | | | 7,361 | | | 259 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Settlement and exercises of note hedges and warrants | — | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | 246,842 | | | — | | | — | | | | | 246,842 | | | — | | | 246,842 | |
| Settlement and exchanges of 2022 Exchangeable Notes | — | | | | 5 | | | 5,534 | | | | | | | | | | | (238,777) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (238,772) | | | — | | | (238,772) | |
| Other | — | | | | — | | | — | | | | | | | | | | | (9,441) | | | — | | | — | | | | | (9,441) | | | (310) | | | (9,751) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | $ | 1,260 | | | | $ | 283 | | | 283,470 | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 8,164,216 | | | $ | (8,144,514) | | | $ | (223,754) | | | | | $ | (203,769) | | | $ | 7,927 | | | $ | (195,842) | |
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Cash flows from operating activities attributable to continuing operations: | | | | | |
| Net earnings | $ | 276,554 | | | $ | 221,609 | | | $ | 566,527 | |
| Add back: (earnings) loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | (509) | | | 366,070 | | | (49,187) | |
| Net earnings from continuing operations | 276,045 | | | 587,679 | | | 517,340 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings from continuing operations to net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations: | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 146,816 | | | 102,268 | | | 89,724 | |
| Depreciation | 41,402 | | | 41,271 | | | 34,355 | |
| Amortization of intangibles | 28,559 | | | 7,525 | | | 8,727 | |
| | | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | (57,969) | | | 15,384 | | | (12,753) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other adjustments, net | 27,690 | | | 27,281 | | | 13,561 | |
| Changes in assets and liabilities | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (34,021) | | | (24,213) | | | (17,861) | |
| Other assets | 1,743 | | | (33,224) | | | (24,162) | |
| Accounts payable and other liabilities | 458,757 | | | 24,155 | | | 33,741 | |
| Income taxes payable and receivable | (2,854) | | | 16,913 | | | (4,161) | |
| Deferred revenue | 26,331 | | | 23,513 | | | 9,478 | |
Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to continuing operations | 912,499 | | | 788,552 | | | 647,989 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities attributable to continuing operations: | | | | | |
| Acquisitions, net of cash | (859,905) | | | — | | | (3,759) | |
| Capital expenditures | (79,971) | | | (42,376) | | | (39,035) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Purchases of investments | — | | | (9,115) | | | — | |
| Net cash distribution related to Separation of IAC | — | | | (3,870,550) | | | — | |
| Other, net | 51 | | | (90) | | | 1,064 | |
Net cash used in investing activities attributable to continuing operations | (939,825) | | | (3,922,131) | | | (41,730) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities attributable to continuing operations: | | | | | |
| Borrowings under the Credit Facility | — | | | 20,000 | | | 40,000 | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from Senior Notes offerings | 500,000 | | | 1,000,000 | | | 350,000 | |
| Proceeds from Exchangeable Senior Notes offerings | — | | | — | | | 1,150,000 | |
| Principal payment on Senior Notes | — | | | (400,000) | | | — | |
| Principal payments on Credit Facility | — | | | (20,000) | | | (300,000) | |
Payments to settle exchangeable notes | (630,658) | | | — | | | — | |
| Purchase of exchangeable note hedges | — | | | — | | | (303,428) | |
| Proceeds from issuance of warrants | — | | | — | | | 166,520 | |
Proceeds from the settlement of exchangeable note hedges | 1,089,592 | | | — | | | — | |
Payments to settle warrants related to exchangeable notes | (882,187) | | | — | | | — | |
| Debt issuance costs | (7,124) | | | (13,517) | | | (27,815) | |
| Purchase of Former Match Group treasury stock | — | | | (132,868) | | | (216,353) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from stock offering | — | | | 1,421,801 | | | — | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock pursuant to stock-based awards | 58,424 | | | 155,402 | | | — | |
| Withholding taxes paid on behalf of employees on net settled stock-based awards | (15,726) | | | (211,958) | | | (203,177) | |
| | | | | |
| Purchase of noncontrolling interests | (1,473) | | | (15,827) | | | (1,650) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other, net | 258 | | | (15,187) | | | (73) | |
Net cash provided by financing activities attributable to continuing operations | 111,106 | | | 1,787,846 | | | 654,024 | |
| Total cash provided by (used in) continuing operations | 83,780 | | | (1,345,733) | | | 1,260,283 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS (continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities attributable to discontinued operations | — | | | 13,630 | | | 289,949 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities attributable to discontinued operations | — | | | (963,420) | | | (287,798) | |
Net cash used in financing activities attributable to discontinued operations | — | | | (110,959) | | | (254,193) | |
| Total cash used in discontinued operations | — | | | (1,060,749) | | | (252,042) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | (7,570) | | | 5,426 | | | (1,568) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash | 76,210 | | | (2,401,056) | | | 1,006,673 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at beginning of period | 739,302 | | | 3,140,358 | | | 2,133,685 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash at end of period | $ | 815,512 | | | $ | 739,302 | | | $ | 3,140,358 | |
The accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements are an integral part of these statements.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1—ORGANIZATION
Match Group, Inc., through its portfolio companies, is a leading provider of digital technologies designed to help people make meaningful connections. Our global portfolio of brands includes Tinder®, Match®, Hinge®, Meetic®, OkCupid®, Pairs™, PlentyOfFish®, OurTime®, Azar®, Hakuna Live™, and more, each built to increase our users’ likelihood of connecting with others. Through our trusted brands, we provide tailored services to meet the varying preferences of our users. Our services are available in over 40 languages to our users all over the world. Match Group has one operating segment, Connections, which is managed as a portfolio of brands.
As used herein, “Match Group,” the “Company,” “we,” “our,” “us,” and similar terms refer to Match Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries after the completion of the Separation, unless the context indicates otherwise.
NOTE 2—SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation and Consolidation
The Company prepares its consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, all entities that are wholly-owned by the Company and all entities in which the Company has a controlling financial interest. Intercompany transactions and accounts have been eliminated.
Separation of Match Group and IAC and Discontinued Operations
On June 30, 2020, the companies formerly known as Match Group, Inc. (referred to as “Former Match Group”) and IAC/InterActiveCorp (referred to as “Former IAC”) completed the separation of the Company from IAC through a series of transactions that resulted in two, separate public companies—(1) Match Group, which consists of the businesses of Former Match Group and certain financing subsidiaries previously owned by Former IAC, and (2) IAC/InterActiveCorp, formerly known as IAC Holdings, Inc. (“IAC”), consisting of Former IAC’s businesses other than Match Group (the “Separation”). See “Note 8—Shareholders’ Equity” for additional information about the series of transactions.
Under the terms of the Transaction Agreement (the “Transaction Agreement”) dated as of December 19, 2019 and amended as of April 28, 2020 and as further amended as of June 22, 2020, Former Match Group merged with and into Match Group Holdings II, LLC (“MG Holdings II”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group, with MG Holdings II surviving the merger as an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Match Group. Former Match Group stockholders (other than Former IAC) received, through the merger, in exchange for each outstanding share of Former Match Group common stock that they held, one share of Match Group common stock and, at the holder’s election, either (i) $3.00 in cash or (ii) a fraction of a share of Match Group common stock with a value of $3.00 (calculated pursuant to the Transaction Agreement). As a result of the merger and other transactions contemplated by the Transaction Agreement, Former Match Group stockholders (other than Former IAC) became stockholders of the Company.
As a result of the Separation, the operations of Former IAC businesses other than Match Group are presented as discontinued operations. See “Note 4—Discontinued Operations” for additional details.
Accounting for Investments in Equity Securities
Investments in equity securities, other than those of our consolidated subsidiaries, are accounted for at fair value or under the measurement alternative of the Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-01, Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities, with any changes to fair value recognized within other income (expense), net each reporting period. Under the measurement alternative, equity investments without readily determinable fair values are carried at cost minus impairment, if any, plus or minus changes resulting from observable price changes in orderly transactions for identical or similar securities of the same issuer; value is generally determined based on a market approach as of the transaction date. A security will be considered identical or similar if it has identical or similar rights to the equity securities held by the Company. The Company reviews its investments in equity securities without readily determinable fair values for impairment each reporting period when there are
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
qualitative factors or events that indicate possible impairment. Factors we consider in making this determination include negative changes in industry and market conditions, financial performance, business prospects, and other relevant events and factors. When indicators of impairment exist, the Company prepares quantitative assessments of the fair value of our investments in equity securities, which require judgment and the use of estimates. When our assessment indicates that the fair value of the investment is below its carrying value, the Company writes down the investment to its fair value and records the corresponding charge within Other (expense) income, net.
Accounting Estimates
Management of the Company is required to make certain estimates, judgments, and assumptions during the preparation of its consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP. These estimates, judgments, and assumptions impact the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, and expenses and the related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
On an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates and judgments including those related to: the fair values of cash equivalents; the carrying value of accounts receivable, including the determination of the allowance for credit losses; the determination of revenue reserves; the carrying value of right-of-use assets (“ROU assets”); the useful lives and recoverability of definite-lived intangible assets and property and equipment; the recoverability of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets; the fair value of equity securities without readily determinable fair values; contingencies; unrecognized tax benefits; the valuation allowance for deferred income tax assets; the fair value of derivatives; and the fair value of and forfeiture rates for stock-based awards, among others. The Company bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience, its forecasts and budgets, and other factors that the Company considers relevant.
Revenue Recognition
The Company accounts for a contract with a customer when it has approval and commitment from all parties, the rights of the parties and payment terms are identified, the contract has commercial substance, and collectability of consideration is probable. Revenue is recognized when control of the promised services is transferred to our customers and in an amount that reflects the consideration the Company expects to be entitled to in exchange for those services.
The Company’s revenue is primarily derived directly from users in the form of recurring subscriptions. Subscription revenue is presented net of credits and credit card chargebacks. Subscribers pay in advance, primarily by credit card or through mobile app stores, and, subject to certain conditions identified in our terms and conditions, generally all purchases are final and nonrefundable. Revenue is initially deferred and is recognized using the straight-line method over the term of the applicable subscription period, which generally ranges from one to six months. Revenue is also earned from online advertising, the purchase of à la carte features and offline events. Online advertising revenue is recognized when an advertisement is displayed. Revenue from the purchase of à la carte features is recognized based on usage. Revenue associated with offline events is recognized when each event occurs.
As permitted under the practical expedient available under ASU No. 2014-09, the Company does not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations for (i) contracts with an original expected length of one year or less, (ii) contracts with variable consideration that is allocated entirely to unsatisfied performance obligations or to a wholly unsatisfied promise accounted for under the series guidance, and (iii) contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue at the amount which we have the right to invoice for services performed.
Transaction Price
The objective of determining the transaction price is to estimate the amount of consideration the Company is due in exchange for its services, including amounts that are variable. The Company determines the total transaction price, including an estimate of any variable consideration, at contract inception and reassesses this estimate each reporting period.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company excludes from the measurement of transaction price all taxes assessed by governmental authorities that are both (i) imposed on and concurrent with a specific revenue-producing transaction and (ii) collected from customers. Accordingly, such tax amounts are not included as a component of revenue or cost of revenue.
For contracts that have an original duration of one year or less, the Company uses the practical expedient available under ASU No. 2014-09 applicable to such contracts and does not consider the time value of money.
Assets Recognized from the Costs to Obtain a Contract with a Customer
The Company has determined that certain costs, primarily mobile app store fees, meet the requirements to be capitalized as a cost of obtaining a contract. The Company recognizes an asset for these costs if we expect to recover those costs. Mobile app store fees are amortized over the period of contract performance. Specifically, the Company capitalizes and amortizes mobile app store fees over the term of the applicable subscription.
During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recognized expense of $552.6 million and $414.7 million, respectively, related to the amortization of these costs. The contract asset balances at December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019 related to costs to obtain a contract are $41.7 million, $33.5 million, and $28.5 million, respectively, included in “Other current assets” in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
Accounts Receivables, Net of Allowance for Credit Losses and Revenue Reserves
The majority of our users purchase our services through mobile app stores. At December 31, 2021, two mobile app stores accounted for approximately 67% and 12%, respectively, of our gross accounts receivables. The comparable amounts at December 31, 2020 were 65% and 11%, respectively. We evaluate the credit worthiness of these two mobile app stores on an ongoing basis and do not require collateral from these entities. We generally collect these balances between 30 and 45 days following the purchase. Payments made directly through our applications are processed by third-party payment processors. We generally collect these balances within 3 to 5 days following the purchase. The Company also maintains allowances to reserve for potential credits issued to users or other revenue adjustments. The amounts of these reserves are based primarily upon historical experience.
Accounts receivable related to indirect revenue include amounts billed and currently due from customers. The Company maintains an allowance for credit losses to provide for the estimated amount of accounts receivable that will not be collected. The allowance for credit losses is based upon historical collection trends adjusted for economic conditions using reasonable and supportable forecasts. The time between the Company issuance of an invoice and payment due date is not significant; customer payments that are not collected in advance of the transfer of promised services are generally due no later than 30 days from invoice date.
Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue consists of advance payments that are received or are contractually due in advance of the Company’s performance. The Company’s deferred revenue is reported on a contract by contract basis at the end of each reporting period. The Company classifies deferred revenue as current when the term of the applicable subscription period or expected completion of our performance obligation is one year or less. The deferred revenue balances are $262.1 million, $239.1 million, and $218.8 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, and 2019, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, the Company recognized $239.1 million and $218.8 million of revenue that was included in the deferred revenue balance as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, there is no non-current portion of deferred revenue.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Disaggregation of Revenue
The following table presents disaggregated revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Direct Revenue: | | | | | |
| Americas | $ | 1,512,057 | | | $ | 1,247,961 | | | $ | 1,090,158 | |
| Europe | 821,827 | | | 680,128 | | | 584,412 | |
| APAC and Other | 588,987 | | | 416,635 | | | 332,604 | |
| Total Direct Revenue | 2,922,871 | | | 2,344,724 | | | 2,007,174 | |
Indirect Revenue (principally advertising revenue) | 60,406 | | | 46,545 | | | 44,084 | |
| Total Revenue | $ | 2,983,277 | | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
| | | | | |
| Direct Revenue | | | | | |
| Tinder | $ | 1,649,757 | | | $ | 1,355,400 | | | $ | 1,152,045 | |
| Other brands | 1,273,114 | | | 989,324 | | | 855,129 | |
| Total Direct Revenue | $ | 2,922,871 | | | $ | 2,344,724 | | | $ | 2,007,174 | |
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash and short-term investments, with maturities of less than 91 days from the date of purchase. Domestically, cash equivalents primarily consist of (i) AAA rated government money market funds and (ii) time deposits. Internationally, cash equivalents primarily consist of (i) time deposits and (ii) money market funds.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, including significant improvements, are recorded at cost. Repairs and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets or, in the case of leasehold improvements, the lease term, if shorter. | | | | | |
| Asset Category | Estimated
Useful Lives |
| Buildings and building improvements | 10 to 39 years |
| Computer equipment and capitalized software | 2 to 3 years |
| Furniture and other equipment | 5 years |
| Leasehold improvements | 6 to 10 years |
The Company capitalizes certain internal use software costs including external direct costs utilized in developing or obtaining the software and compensation for personnel directly associated with the development of the software. Capitalization of such costs begins when the preliminary project stage is complete and ceases when the project is substantially complete and ready for its intended purpose. The net book value of capitalized internal use software is $53.5 million and $39.7 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Business Combinations
The purchase price of each acquisition is attributed to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their fair values at the date of acquisition, including identifiable intangible assets that either arise from a contractual or legal right or are separable from goodwill. The Company typically engages outside valuation experts to assist in the allocation of purchase price to the identifiable intangible assets acquired, but management has ultimate responsibility for the valuation methods, models, and inputs used and the resulting purchase price allocation. The excess purchase price over the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets is
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
recorded as goodwill and assigned to the reporting unit that is expected to benefit from the combination as of the acquisition date.
Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The Company assesses goodwill on its one reporting unit and indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment annually as of October 1, or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit or the fair value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset below its carrying value.
When the Company elects to perform a qualitative assessment and concludes it is not more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, no further assessment of that reporting unit’s goodwill is necessary; otherwise, a quantitative assessment is performed and the fair value of the reporting unit is determined. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, an impairment loss equal to the excess is recorded.
As a result of the Separation in 2020, the Company had a negative carrying value for the Company’s annual goodwill test at both October 1, 2020 and 2021. Additionally, an impairment test of goodwill was not necessary because there were no factors identified that would indicate an impairment loss. The Company continued to have a negative carrying value at December 31, 2021.
The Company foregoes a qualitative assessment and tests goodwill for impairment when it concludes that it is more likely than not that there may be an impairment. If needed, the annual or interim quantitative test of the recovery of goodwill involves a comparison of the estimated fair value of the Company’s reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. If the estimated fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, goodwill of the reporting unit is not impaired. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its estimated fair value, an impairment loss equal to the excess is recorded.
While the Company has the option to qualitatively assess whether it is more likely than not that the fair values of its indefinite-lived intangible assets are less than their carrying values, the Company’s policy is to determine the fair value of each of its indefinite-lived intangible assets annually as of October 1, in part, because the level of effort required to perform the quantitative and qualitative assessments is essentially equivalent. Due to the recent acquisition of Hyperconnect and the process to allocate the purchase price as of the purchase date, the intangible assets of Hyperconnect were considered qualitatively as of October 1, 2021. For assets in which a quantitative assessment was performed, the Company determines the fair value of its indefinite-lived intangible assets using an avoided royalty discounted cash flow (“DCF”) valuation analysis. Significant judgments inherent in this analysis include the selection of appropriate royalty and discount rates and estimating the amount and timing of expected future cash flows. The discount rates used in the DCF analyses are intended to reflect the risks inherent in the expected future cash flows generated by the respective intangible assets. The royalty rates used in the DCF analyses are based upon an estimate of the royalty rates that a market participant would pay to license the Company’s trade names and trademarks. The future cash flows are based on the Company’s most recent forecast and budget and, for years beyond the budget, the Company’s estimates, which are based, in part, on forecasted growth rates. Assumptions used in the avoided royalty DCF analyses, including the discount rate and royalty rate, are assessed annually based on the actual and projected cash flows related to the asset, as well as macroeconomic and industry specific factors. The discount rates used in the Company’s annual indefinite-lived impairment assessment ranged from 10% to 16% in 2021 and 10% to 23% in 2020, and the royalty rates used ranged from 5% to 8% in both 2021 and 2020. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recognized an impairment charge related to the Match brand in the UK and the Meetic brand in Europe of $4.6 million, which is included within amortization. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recognized an impairment charge on the Match brand in the UK of $6.6 million, which is included within amortization. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, no indefinite-lived intangible asset balance had an estimated fair value less than 110% of carrying value.
Long-Lived Assets and Intangible Assets with Definite Lives
Long-lived assets, which consist of ROU assets, property and equipment, and intangible assets with definite lives, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. The carrying value of a long-lived asset is not recoverable if it exceeds the
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the carrying value is deemed not to be recoverable, an impairment loss is recorded equal to the amount by which the carrying value of the long-lived asset exceeds its fair value. Amortization of definite-lived intangible assets is computed either on a straight-line basis or based on the pattern in which the economic benefits of the asset will be realized.
Fair Value Measurements
The Company categorizes its financial instruments measured at fair value into a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used in pricing the asset or liability. The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are:
•Level 1: Observable inputs obtained from independent sources, such as quoted market prices for identical assets and liabilities in active markets.
•Level 2: Other inputs, which are observable directly or indirectly, such as quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets, quoted market prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data. The fair values of the Company’s Level 2 financial assets are primarily obtained from observable market prices for identical underlying securities that may not be actively traded. Certain of these securities may have different market prices from multiple market data sources, in which case an average market price is used.
•Level 3: Unobservable inputs for which there is little or no market data and require the Company to develop its own assumptions, based on the best information available in the circumstances, about the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the assets or liabilities.
The Company’s non-financial assets, such as goodwill, intangible assets, ROU assets, and property and equipment, are adjusted to fair value only when an impairment is recognized. The Company’s financial assets, comprising of equity securities without readily determinable fair values, are adjusted to fair value when observable price changes are identified or an impairment is recognized. Such fair value measurements are based predominantly on Level 3 inputs.
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are expensed in the period incurred (when the advertisement first runs for production costs that are initially capitalized) and represent online marketing, including fees paid to search engines and social media sites; offline marketing, which is primarily television advertising; and payments to partners who direct traffic to our websites. Advertising expense is $510.3 million, $438.7 million and $388.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Legal Costs
Legal costs are expensed as incurred.
Income Taxes
We are subject to income taxes in the United States and numerous foreign jurisdictions. Significant judgement is required in determining our provision for income taxes and income tax assets and liabilities, including evaluating uncertainties in the application of accounting principles and complex tax laws.
The Company accounts for income taxes under the liability method, and deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial reporting amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be realized or settled. A valuation allowance is provided if it is determined that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax asset will not be realized.
We recognize tax benefits from uncertain tax positions only if we believe that it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained based on the technical merits of the position. Such tax benefits are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon settlement. The
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Company records interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share is computed by dividing net earnings attributable to Match Group shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if stock options and other commitments to issue common stock using the treasury stock or the as if converted methods, as applicable. See “Note 10—Earnings per Share” for additional information on dilutive securities.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transaction Gains and Losses
The financial position and operating results of foreign entities whose primary economic environment is based on their local currency are consolidated using the local currency as the functional currency. These local currency assets and liabilities are translated at the rates of exchange as of the balance sheet date, and local currency revenue and expenses of these operations are translated at average rates of exchange during the period. Translation gains and losses are included in accumulated other comprehensive income as a component of shareholders’ equity. Transaction gains and losses resulting from assets and liabilities denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are included in the consolidated statement of operations as a component of “other (expense) income, net.” See “Note 17—Consolidated Financial Statement Details” for additional information regarding foreign currency exchange gains and losses.
Translation gains and losses relating to foreign entities that are liquidated or substantially liquidated are reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive loss into earnings. A loss of $0.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2020 is included in “other (expense) income, net” in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. There were no such gains or losses for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2019.
Stock-Based Compensation
Stock-based compensation is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is generally expensed over the requisite service period. See “Note 11—Stock-based Compensation” for a discussion of the Company’s stock-based compensation plans.
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests
Noncontrolling interests in the consolidated subsidiaries of the Company are ordinarily reported on the consolidated balance sheet within shareholders’ equity, separately from the Company’s equity. However, securities that are redeemable at the option of the holder and not solely within the control of the issuer must be classified outside of shareholders’ equity. Accordingly, all noncontrolling interests that are redeemable at the option of the holder are presented outside of shareholders’ equity in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
In connection with the acquisition of certain subsidiaries, management of these businesses has retained an ownership interest. The Company is party to fair value put and call arrangements with respect to these interests. These put and call arrangements allow management of these businesses to require the Company to purchase their interests, or allow the Company to acquire such interests, at fair value. These put and call arrangements do not meet the definition of a derivative instrument as the put agreements do not provide for net settlement. These put and call arrangements become exercisable by the Company and the counterparty at various future dates. One of these arrangements was exercised during each of the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. These put arrangements are exercisable by the counter-party outside the control of the Company. Accordingly, to the extent that the fair value of these interests exceeds the value determined by normal noncontrolling interest accounting, the value of such interests is adjusted to fair value with a corresponding adjustment to additional paid-in capital. During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019, the Company recorded adjustments of $2.7 million, $6.7 million, and $11.6 million, respectively, to increase these interests to fair value. Fair value determinations require high levels of judgment and are based on various valuation techniques, including market comparables and discounted cash flow projections.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Certain Risks and Concentrations
The Company’s business is subject to certain risks and concentrations, including dependence on third-party technology providers, exposure to risks associated with online commerce security and credit card fraud.
Financial instruments, which potentially subject the Company to concentration of credit risk, consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are principally maintained with financial institutions and are not covered by deposit insurance.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting pronouncements adopted by the Company
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-06, which simplifies the accounting for certain financial instruments with characteristics of liabilities and equity, including convertible instruments and contracts in an entity’s own equity. Among other changes, ASU 2020-06 removes from U.S. GAAP the liability and equity separation model for convertible instruments with a cash conversion feature, and as a result, after adoption, entities will no longer separately present in equity an embedded conversion feature for such debt. Similarly, the discount resulting from the embedded conversion feature will no longer be amortized into income as interest expense over the life of the instrument. Instead, entities will account for a convertible debt instrument wholly as debt unless (1) a convertible instrument contains features that require bifurcation as a derivative under ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging, or (2) a convertible debt instrument was issued at a substantial premium. ASU 2020-06 requires the application of the if-converted method to calculate the impact of convertible instruments on diluted earnings per share, which results in increased dilutive securities as the assumption of cash settlement of the notes is not available for the purpose of calculating earnings per share. The provisions of ASU 2020-06 are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2021, with early adoption permitted for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2020, and can be adopted on either a fully retrospective or modified retrospective basis.
The Company early adopted ASU No. 2020-06 as of January 1, 2021 on a fully retrospective basis. The impact of adopting ASU No. 2020-06 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 | | Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| Prior to the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | After adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | Effect of adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | Prior to the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | After adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | Effect of adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Statement of operations impacts | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | $ | 174,791 | | | $ | 130,624 | | | $ | (44,167) | | | $ | 140,570 | | | $ | 111,008 | | | $ | (29,562) | |
| Income tax provision | $ | 32,874 | | | $ | 43,273 | | | $ | 10,399 | | | $ | 8,225 | | | $ | 15,080 | | | $ | 6,855 | |
| Net earnings from continuing operations | $ | 553,911 | | | $ | 587,679 | | | $ | 33,768 | | | $ | 494,633 | | | $ | 517,340 | | | $ | 22,707 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net earnings per share from continuing operations: |
| Basic | $ | 2.21 | | | $ | 2.36 | | | $ | 0.15 | | | $ | 2.15 | | | $ | 2.28 | | | $ | 0.13 | |
| Diluted | $ | 2.00 | | | $ | 2.09 | | | $ | 0.09 | | | $ | 1.88 | | | $ | 1.95 | | | $ | 0.07 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average dilutive shares outstanding | 242,464 | | | 256,020 | | | 13,556 | | | 194,349 | | | 201,782 | | | 7,433 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Prior to the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | After adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | Effect of adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Balance sheet impacts at December 31, 2020: | | | | | |
| Non-current deferred tax asset | $ | 224,013 | | | $ | 293,487 | | | $ | 69,474 | |
| Long-term debt, net | $ | 3,534,706 | | | $ | 3,840,930 | | | $ | 306,224 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | $ | 7,394,646 | | | $ | 7,089,007 | | | $ | (305,639) | |
| Retained deficit | $ | (8,491,126) | | | $ | (8,422,237) | | | $ | 68,889 | |
The impact of the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 at December 31, 2018 resulted in an increase to retained earnings of $12.4 million and a decrease in additional paid-in capital of $53.5 million.
As the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 did not impact cash, the operating cash flows from continuing operations were not impacted. Certain reconciliation line items to net earnings from continuing operations were adjusted to reflect the impact of the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06.
Accounting pronouncements not yet adopted by the Company
In October 2021, the FASB issued ASU No. 2021-08, which requires entities to recognize and measure contract assets and contract liabilities acquired in a business combination in accordance with ASC Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The update will generally result in an entity recognizing contract assets and contract liabilities as if the acquirer had originated the contracts, which, for the most part, results in no change to the value of deferred revenue when measured in purchase accounting. The new standard is effective on a prospective basis for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of the new standard is not expected to have a material impact on our operating results, financial position, or cash flows.
Reclassifications
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
NOTE 3—INCOME TAXES
U.S. and foreign earnings before income taxes are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| U.S. | $ | 184,835 | | | $ | 547,969 | | | $ | 454,036 | |
| Foreign | 71,313 | | | 82,983 | | | 78,384 | |
| Total | $ | 256,148 | | | $ | 630,952 | | | $ | 532,420 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The components of the provision (benefit) for income taxes are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Current income tax provision (benefit): | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | 15 | | | $ | (2,044) | | | $ | 964 | |
| State | 3,192 | | | 1,640 | | | 342 | |
| Foreign | 34,865 | | | 28,293 | | | 26,527 | |
| Current income tax provision | 38,072 | | | 27,889 | | | 27,833 | |
| Deferred income tax provision (benefit): | | | | | |
| Federal | (32,723) | | | 31,025 | | | (2,159) | |
| State | (18,627) | | | (10,451) | | | (9,698) | |
| Foreign | (6,619) | | | (5,190) | | | (896) | |
| Deferred income tax (benefit) provision | (57,969) | | | 15,384 | | | (12,753) | |
| Income tax (benefit) provision | $ | (19,897) | | | $ | 43,273 | | | $ | 15,080 | |
The tax effects of cumulative temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are presented below. The valuation allowance is primarily related to deferred tax assets for foreign net operating losses and U.S. foreign tax credits. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 85,613 | | | $ | 152,346 | |
| Tax credit carryforwards | 128,731 | | | 102,012 | |
| Disallowed interest carryforwards | 52,104 | | | 56,630 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 15,491 | | | 16,073 | |
| Accrued expenses | 116,415 | | | 9,283 | |
| Exchangeable notes | 52,177 | | | 64,212 | |
| Other | 33,211 | | | 25,532 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 483,742 | | | 426,088 | |
| Less valuation allowance | (86,071) | | | (71,090) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | 397,671 | | | 354,998 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| Intangible assets | (165,551) | | | (44,200) | |
| Right-of-use assets | (21,784) | | | (17,306) | |
| Property and equipment | (4,923) | | | (17,218) | |
| Other | (737) | | | — | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (192,995) | | | (78,724) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 204,676 | | | $ | 276,274 | |
The Company’s tax group for federal and consolidated state income tax purposes includes Former IAC up to and including the Separation date. As a result of the Separation, the Company’s net deferred tax asset was adjusted via additional paid-in capital for tax attributes allocated to Match Group from our consolidated federal and state income tax returns. A preliminary allocation was recorded as of June 30, 2020. The final adjustment
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
recorded in 2021 as a result of filing the 2020 consolidated federal and state income tax returns was not significant.
At December 31, 2021, the Company has federal and state net operating losses (“NOLs”) of $174.1 million and $276.5 million, respectively. If not utilized, $17.3 million of the federal NOLs can be carried forward indefinitely, and $156.8 million will expire at various times between 2031 and 2037. Of the state NOLs, $3.8 million can be carried forward indefinitely and $272.7 million will expire at various times between 2024 and 2041. Federal and state NOLs of $142.6 million and $252.1 million, respectively, can be used against future taxable income without restriction and the remaining NOLs will be subject to limitations under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code, separate return limitations, federal taxable income limitations, and applicable state law. At December 31, 2021, the Company has foreign NOLs of $131.9 million available to offset future income. Of these foreign NOLs, $99.6 million can be carried forward indefinitely and $32.3 million will expire at various times between 2022 and 2038. During 2021, the Company recognized tax benefits related to NOLs of $2.2 million. At December 31, 2021, the Company has federal and foreign disallowed interest carryforwards of $154.6 million and $69.4 million, respectively, that can be carried forward indefinitely and can be used against future taxable income.
At December 31, 2021, the Company has tax credit carryforwards of $162.7 million. Of this amount, $125.1 million relates to federal and state tax credits for research activities, of which $80.8 million will expire at various times between 2033 and 2041. Our credit carryforwards also include $37.0 million of foreign tax credits, of which $35.1 million will expire primarily in 2027.
The Company regularly assesses the realizability of deferred tax assets considering all available evidence, including, to the extent applicable, the nature, frequency and severity of prior cumulative losses, forecasts of future taxable income, tax filing status, the duration of statutory carryforward periods, available tax planning and historical experience.
During the year ended December 31, 2021, we recorded an increase to the valuation allowance of $15.0 million primarily related to foreign losses for which we do not believe a tax benefit is more likely than not to be realized. At December 31, 2021, the Company had a valuation allowance of $86.1 million related to the portion of credits, NOLs, and other deferred tax assets for which it is more likely than not that the tax benefit will not be realized.
A reconciliation of the income tax provision to the amounts computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate to earnings before income taxes is shown as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
Income tax provision at the federal statutory rate of 21% | $ | 53,791 | | | $ | 132,500 | | | $ | 111,808 | |
| | | | | |
| State income taxes, net of effect of federal tax benefit | 4,530 | | | 8,803 | | | 10,274 | |
| Stock-based compensation | (63,751) | | | (112,203) | | | (90,374) | |
| Research credits | (25,830) | | | (21,306) | | | (27,248) | |
| Change in valuation allowance | 8,523 | | | 29,787 | | | — | |
| Foreign income taxed at a different statutory rate | 5,808 | | | 4,884 | | | 3,526 | |
| Withholding taxes | 1,057 | | | 2,933 | | | 5,023 | |
| Change in uncertain tax positions | (948) | | | (5,770) | | | (637) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Other, net | (3,077) | | | 3,645 | | | 2,708 | |
| Income tax (benefit) provision | $ | (19,897) | | | $ | 43,273 | | | $ | 15,080 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits, including penalties but excluding interest, is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 45,624 | | | $ | 53,324 | | | $ | 35,679 | |
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 8,107 | | | 7,818 | | | 11,221 | |
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | 1,353 | | | 1,772 | | | 7,599 | |
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (1,028) | | | — | | | (283) | |
| Settlements | (2,348) | | | (16,512) | | | — | |
| Expiration of applicable statute of limitations | (878) | | | (778) | | | (892) | |
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 50,830 | | | $ | 45,624 | | | $ | 53,324 | |
The Company recognizes interest and, if applicable, penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in the income tax provision. Our income tax provision, for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019, includes a (decrease) or increase of interest and penalties of $(0.3) million, $(1.7) million, and $0.1 million, respectively. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, noncurrent income taxes payable include accrued interest and penalties of $1.5 million and $1.9 million, respectively.
Match Group is routinely under audit by federal, state, local and foreign authorities in the area of income tax. These audits include questioning the timing and the amount of income and deductions and the allocation of income and deductions among various tax jurisdictions. The Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) has substantially completed its audit of the Company’s federal income tax returns for the years ended December 31, 2013 through 2017 and has begun its audit of the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019. The statute of limitations for years 2013 through 2019 has been extended to December 31, 2023. We are no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examinations for years prior to 2013. Returns filed in various other jurisdictions are open to examination for tax years beginning with 2009. Although we believe that we have adequately reserved for our uncertain tax positions, the final tax outcome of these matters may vary significantly from our estimates.
At December 31, 2021 and 2020, unrecognized tax benefits, including interest, were $51.8 million and $46.7 million, respectively. If unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2021 are subsequently recognized, $46.0 million, net of related deferred tax assets and interest, would reduce income tax expense. The comparable amount as of December 31, 2020 was $41.8 million. The Company believes that it is reasonably possible that its unrecognized tax benefits could decrease by approximately $0.9 million by December 31, 2022, primarily due to settlements and expirations of statutes of limitations.
Generally, our ability to distribute the $172.7 million cash and cash equivalents held by our foreign subsidiaries at December 31, 2021 is limited to that subsidiary’s distributable reserves and after considering other corporate legal restrictions. Our earnings in foreign jurisdictions are generally available for distribution to the U.S. without significant tax consequences.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 4—DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS
As part of the Separation described in “Note 1—Organization,” the operations of Former IAC businesses other than Match Group are presented as discontinued operations.
The key components of earnings (loss) from discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019 consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Revenue | $ | — | | | $ | 1,410,485 | | | $ | 2,705,797 | |
| Operating costs and expenses | — | | | (1,840,178) | | | (2,769,918) | |
| Operating loss | — | | | (429,693) | | | (64,121) | |
| Interest expense | — | | | (3,772) | | | (12,993) | |
| Other (expense) income | — | | | (2,503) | | | 68,767 | |
| Income tax benefit | 509 | | | 69,898 | | | 57,534 | |
| Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations | $ | 509 | | | $ | (366,070) | | | $ | 49,187 | |
NOTE 5—GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Goodwill and intangible assets, net, are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Goodwill | $ | 2,411,996 | | | $ | 1,270,532 | |
| Intangible assets with indefinite lives | 576,653 | | | 226,605 | |
| Intangible assets with definite lives, net | 195,044 | | | 4,295 | |
| Total goodwill and intangible assets, net | $ | 3,183,693 | | | $ | 1,501,432 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recognized an impairment charge on the Match® brand in the UK of $6.6 million. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recognized additional impairment charges totaling $4.6 million related to the Match brand in the UK and the Meetic brand in Europe as the outbreak of COVID-19 placed additional pressure on projected 2020 revenues at these brands. These charges are included within amortization expense in the consolidated statement of operations for the years then ended.
The following table presents the balance of goodwill, including the changes in the carrying value of goodwill, for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 1,270,532 | | | $ | 1,239,839 | |
| Additions | 1,243,063 | | | — | |
| | | |
| Foreign Exchange Translation | (101,599) | | | 30,948 | |
| Other | — | | | (255) | |
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 2,411,996 | | | $ | 1,270,532 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
On June 17, 2021, Match Group completed the acquisition of all capital stock of Hyperconnect, Inc. (“Hyperconnect”), a leading social discovery and video technology company based in Seoul, South Korea. The acquisition increases our presence in certain Asian markets and enhances the real-time video capabilities of Match Group. The accounting purchase price was $1.75 billion, which consisted of $859.9 million of cash, net of cash acquired, and 5.9 million shares of Match Group common stock at a basis of the closing market price on the acquisition date. The purchase price has been preliminarily allocated to goodwill of $1.2 billion that is not deductible for tax purposes; intangible assets of $612.0 million primarily consisting of tradenames and associated trademarks, both of which are indefinite life intangible assets, with a related deferred tax liability of $134.7 million; and $30.4 million of other net assets. The allocation of the accounting purchase price, which is based on Level 3 inputs, is substantially complete and will be finalized within the allowable measurement period.
Intangible assets with indefinite lives are trade names and trademarks acquired in various acquisitions. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, intangible assets with definite lives are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2021 |
| Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net | | Weighted-Average
Useful Life
(Years) |
| | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) | | |
| Customer lists | $ | 129,427 | | | $ | (15,487) | | | $ | 113,940 | | | 4.9 |
| Patent and technology | 99,512 | | | (18,657) | | | 80,855 | | | 4.2 |
| Trade names | 1,354 | | | (1,193) | | | 161 | | | 1.3 |
| | | | | | | |
| Other | 425 | | | (337) | | | 88 | | | 2.7 |
| Total | $ | 230,718 | | | $ | (35,674) | | | $ | 195,044 | | | 4.6 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 | | |
| Gross
Carrying
Amount | | Accumulated
Amortization | | Net | | Weighted-Average
Useful Life
(Years) | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) | | | | |
| Customer lists | $ | 288 | | | $ | (288) | | | $ | — | | | — | | |
| Patent and technology | 11,044 | | | (6,943) | | | 4,101 | | | 9.3 | | |
| Trade names | 5,114 | | | (5,114) | | | — | | | — | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Other | 3,400 | | | (3,206) | | | 194 | | | 3.0 | | |
| Total | $ | 19,846 | | | $ | (15,551) | | | $ | 4,295 | | | 9.0 | | |
At December 31, 2021, amortization of intangible assets with definite lives is estimated to be as follows: | | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| 2022 | $ | 51,336 | |
| 2023 | 49,081 | |
| 2024 | 47,164 | |
| 2025 | 35,035 | |
| 2026 and thereafter | 12,428 | |
| Total | $ | 195,044 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 6—FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Equity securities without readily determinable fair values
At both December 31, 2021 and 2020, the carrying value of the Company’s investments in equity securities without readily determinable fair values totaled $14.2 million, and is included in “Other non-current assets” in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. The cumulative downward adjustments (including impairments) to the carrying value of equity securities without readily determinable fair values held as of December 31, 2021, since the adoption of ASU 2016-01 on January 1, 2018 through December 31, 2021, were $2.1 million. For both the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, there were no adjustments to the carrying value of equity securities without readily determinable fair values. For the year ended December 31, 2019, we recognized an impairment charge of $4.0 million which is included in “Other (expense) income, net” in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
Fair Value Measurements
The following tables present the Company’s financial instruments that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2021 |
| | Quoted Market
Prices in Active
Markets for
Identical Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs
(Level 2) | | | | Total
Fair Value
Measurements |
| | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents: | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 260,582 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 260,582 | |
| Time deposits | — | | | 36,831 | | | | | 36,831 | |
| Short-term investments: | | | | | | | |
| Time deposits | — | | | 11,818 | | | | | 11,818 | |
| Total | $ | 260,582 | | | $ | 48,649 | | | | | $ | 309,231 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2020 |
| | Quoted Market
Prices in Active
Markets for
Identical Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs
(Level 2) | | | | Total
Fair Value
Measurements |
| | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents: | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 147,615 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 147,615 | |
| Time deposits | — | | | 50,000 | | | | | 50,000 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 147,615 | | | $ | 50,000 | | | | | $ | 197,615 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Financial instruments measured at fair value only for disclosure purposes
The following table presents the carrying value and the fair value of financial instruments measured at fair value only for disclosure purposes. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| Carrying Value | | Fair Value | | Carrying Value | | Fair Value |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
Current maturities of long-term debt, net (a)(b)(c) | $ | (84,333) | | | $ | (254,472) | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Long-term debt, net (b)(c) | $ | (3,829,421) | | | $ | (4,725,403) | | | $ | (3,840,930) | | | $ | (6,267,976) | |
______________________
(a)The carrying value excludes the $15.6 million aggregate principal amount of the exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes as that amount is carried at fair value as described below.
(b)At December 31, 2021, the carrying value of current maturities of long-term debt, net includes unamortized debt issuance costs of $0.6 million. At December 31, 2021 and 2020, the carrying value of long-term debt, net includes unamortized original issue discount and debt issuance costs of $45.6 million and $51.6 million, respectively.
(c)At December 31, 2021, the fair value of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, 2026 Exchangeable Notes, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes is $302.2 million, $932.6 million, and $1,017.7 million, respectively. At December 31, 2020, the fair value of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, 2026 Exchangeable Notes, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes is $1,780.3 million, $1,052.1 million, and $1,113.9 million, respectively.
At December 31, 2021 and 2020, the fair value of long-term debt, net is estimated using observable market prices or indices for similar liabilities, which are Level 2 inputs.
Derivatives associated with the repurchase and exchanges of 2022 Exchangeable Notes
On September 22, 2021, we entered into privately negotiated agreements with a limited number of holders of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes to repurchase a portion of the outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes. The Company determined that the terms of the repurchase agreements included an embedded derivative, indexed to the value of the Company’s stock, that required bifurcation and separate accounting as a derivative liability under ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging. The Company measures embedded derivatives at their estimated fair value and recognizes changes in their estimated fair value in net income during the current reporting period.
At the inception of these agreements on September 22, 2021, the fair value of the embedded derivative was zero and the number of shares to be issued to holders of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes was not yet determinable. At September 30, 2021, under the terms of the agreements, the number of shares to be issued became fixed at 5.5 million. The corresponding loss of $14.5 million, related to the change in the fair value of the embedded derivative, which was driven by an increase in our stock price from September 22, 2021 to October 4, 2021, the settlement date of the transaction, was recorded within “other (expense) income, net” in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
During the year ended December 31, 2021, $18.6 million aggregate principal amount of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes were presented for exchange prior to maturity at the option of the noteholder, $3.0 million of which was settled during the year ended December 31, 2021 and $15.6 million of which will be settled in January 2022. In accordance with the 2022 Exchangeable Notes Indenture, the Company elected to settle these exchanges entirely in cash with the settlement amount determined by the volume weighted average price of Match Group common stock over a 40-day measurement period. At the time that the Company elected cash settlement, the embedded derivative for the conversion option of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes no longer qualified for the derivative scope exception for contracts indexed to an entity’s own equity. We recognized an obligation of $48.5 million in “accrued expenses and other current liabilities” to settle the conversion option as of the date of the exchanges, with an offset to paid-in capital. Subsequently, we recognized $9.7 million in gains, which is included in “other (expense) income, net” within the accompanying consolidated statement of
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
operations for the year ended December 31, 2021 related to the change in the fair value of the embedded derivative between the date we elected to settle in cash and the end of the 40-day measurement period, or December 31, 2021, if the measurement period extended past year-end.
For the exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes that were still outstanding at December 31, 2021 and were settled in January 2022, the following items were outstanding on the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2021:
•The fair value of the outstanding embedded derivative of $7.4 million, which is included as an asset within “other current assets;”
•the aggregate principal amount of $15.6 million for 2022 Exchangeable Notes presented for exchange, which is presented within “current maturities of long-term debt, net;” and
•an incremental $39.5 million liability recorded on the date of exchange, which is presented within “accrued expenses and other current liabilities.“
Additionally, when the Company elected to settle the exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes entirely in cash, a proportionate amount of note hedges were also exercised and were settled in cash based on the same 40-day measurement period to determine the settlement value. Similar to the exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes, the derivative scope exception for contracts indexed to an entity’s own equity no longer applied to the exercised note hedges as a result of the requirement to settle the securities in cash. We recognized an asset of $48.5 million related to the settlement of these note hedges, with an offset to paid-in capital. Subsequently, we recognized a loss of $9.7 million, which is included in “other (expense) income, net” in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021 related to the change in the related derivative fair value between the date we elected to settle in cash and the end of the 40-day measurement period, or December 31, 2021, if the measurement period extended past year-end. For the exercised note hedges that were settled in January 2022, the fair value of the outstanding note hedges at December 31, 2021 is $32.1 million, which is included as an asset within “other current assets” on the consolidated balance sheet.
At December 31, 2021, the net position of the various assets and liabilities associated with the unsettled exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes and the note hedges, described above, is a $15.6 million liability, representing the principal amount of the exchanged 2022 Exchangeable Notes, which was settled in January 2022.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 7—LONG-TERM DEBT, NET
Long-term debt, net consists of: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Credit Facility due February 13, 2025 | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Term Loan due February 13, 2027 | 425,000 | | | 425,000 | |
| | | |
| | | |
5.00% Senior Notes due December 15, 2027 (the “5.00% Senior Notes”); interest payable each June 15 and December 15 | 450,000 | | | 450,000 | |
4.625% Senior Notes due June 1, 2028 (the “4.625% Senior Notes”); interest payable each June 1 and December 1 | 500,000 | | | 500,000 | |
5.625% Senior Notes due February 15, 2029 (the “5.625% Senior Notes”); interest payable each February 15 and August 15 | 350,000 | | | 350,000 | |
4.125% Senior Notes due August 1, 2030 (the “4.125% Senior Notes”); interest payable each February 1 and August 1 | 500,000 | | | 500,000 | |
3.625% Senior Notes due October 1, 2031 (the “3.625% Senior Notes”); interest payable each April 1 and October 1 commencing on April 1, 2022 | 500,000 | | | — | |
0.875% Exchangeable Senior Notes due October 1, 2022 (the “2022 Exchangeable Notes”); interest payable each April 1 and October 1 | 100,500 | | | 517,500 | |
0.875% Exchangeable Senior Notes due June 15, 2026 (the “2026 Exchangeable Notes”); interest payable each June 15 and December 15 | 575,000 | | | 575,000 | |
2.00% Exchangeable Senior Notes due January 15, 2030 (the “2030 Exchangeable Notes”); interest payable each January 15 and July 15 | 575,000 | | | 575,000 | |
| Total long-term debt | 3,975,500 | | | 3,892,500 | |
| Less: Current maturities of long-term debt | 100,500 | | | — | |
| Less: Unamortized original issue discount | 5,215 | | | 6,029 | |
| Less: Unamortized debt issuance costs | 40,364 | | | 45,541 | |
| Total long-term debt, net | $ | 3,829,421 | | | $ | 3,840,930 | |
Credit Facility and Term Loan
Our wholly-owned subsidiary, Match Group Holdings II, LLC (“MG Holdings II”) is the borrower under a credit agreement (as amended, the “Credit Agreement”) that provides for the Credit Facility and the Term Loan. The Credit Agreement provides for a benchmark replacement should the LIBOR rate not be available in the future. The rate used would be agreed to between the administrative agent and the Company and may be based upon a secured overnight financing rate at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. Additional information about the benchmark replacement can be found in Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement.
The Credit Facility has a borrowing capacity of $750 million and matures on February 13, 2025. At both December 31, 2021 and 2020, there were no outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility. At December 31, 2021, there was $0.4 million in outstanding letters of credit and $749.6 million of availability under the Credit Facility. At December 31, 2020, there was $0.2 million in outstanding letters of credit and $749.8 million of availability under the Credit Facility. The annual commitment fee on undrawn funds, which is based on MG Holdings II’s consolidated net leverage ratio, was 25 basis points as of December 31, 2021. Borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest, at MG Holdings II’s option, at a base rate or LIBOR, in each case plus an applicable margin, based on MG Holdings II’s consolidated net leverage ratio. If MG Holdings II borrows under the Credit Facility, it will be required to maintain a consolidated net leverage ratio of not more than 5.0 to 1.0.
At both December 31, 2021 and 2020, the outstanding balance on the Term Loan was $425 million. The Term Loan bears interest at LIBOR plus 1.75%, which was 1.91% and 1.96% at December 31, 2021 and 2020,
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
respectively. The Term Loan matures on February 13, 2027. Interest payments are due at least quarterly through the term of the loan. The Term Loan provides for annual principal payments as part of an excess cash flow sweep provision, the amount of which, if any, is governed by the secured net leverage ratio set forth in the Credit Agreement.
On March 26, 2021, MG Holdings II entered into an amendment of the Credit Agreement to provide for a $400 million Delayed Draw Term Loan, the proceeds of which could have been used only to finance a portion of the consideration for the acquisition of Hyperconnect. The Delayed Draw Term Loan was terminated effective June 18, 2021, in accordance with its terms.
The Credit Agreement includes covenants that would limit the ability of MG Holdings II to pay dividends, make distributions, or repurchase MG Holdings II’s stock in the event MG Holdings II’s secured net leverage ratio exceeds 2.0 to 1.0, while the Term Loan remains outstanding and, thereafter, if MG Holdings II’s consolidated net leverage ratio exceeds 4.0 to 1.0, or if an event of default has occurred. The Credit Agreement includes additional covenants that limit the ability of MG Holdings II and its subsidiaries to, among other things, incur indebtedness, pay dividends or make distributions. Obligations under the Credit Facility and Term Loan are unconditionally guaranteed by certain MG Holdings II wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries and are also secured by the stock of certain MG Holdings II domestic and foreign subsidiaries. The Term Loan and outstanding borrowings, if any, under the Credit Facility rank equally with each other, and have priority over the Senior Notes to the extent of the value of the assets securing the borrowings under the Credit Agreement.
Senior Notes
The 3.625% Senior Notes were issued on October 4, 2021. The proceeds from these notes were used to redeem a portion of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes and for general corporate purposes. At any time prior to October 1, 2026, these notes may be redeemed at a redemption price equal to the sum of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest and a make-whole premium set forth in the indenture governing the notes. Thereafter, these notes may be redeemed at the redemption prices set forth below, together with accrued and unpaid interest to the applicable redemption date: | | | | | |
| Beginning October 1, | Percentage |
| 2026 | 101.813% |
| 2027 | 101.208% |
| 2028 | 100.604% |
| 2029 and thereafter | 100.000% |
The 4.625% Senior Notes were issued on May 19, 2020. The proceeds from these notes were used to redeem the outstanding 6.375% Senior Notes, to pay expenses associated with the offering, and for general corporate purposes. At any time prior to June 1, 2023, these notes may be redeemed at a redemption price equal to the sum of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest and a make-whole premium set forth in the indenture governing the notes. Thereafter, these notes may be redeemed at the redemption prices set forth below, together with accrued and unpaid interest to the applicable redemption date: | | | | | | |
| Beginning June 1, | Percentage | |
| 2023 | 102.313% | |
| 2024 | 101.156% | |
| 2025 and thereafter | 100.000% | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The 4.125% Senior Notes were issued on February 11, 2020. The proceeds from these notes were used to fund a portion of the $3.00 per common share of Former Match Group that was payable in connection with the Separation. At any time prior to May 1, 2025, these notes may be redeemed at a redemption price equal to the sum of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest and a make-whole premium set forth in the indenture governing the notes. Thereafter, these notes may be redeemed at the redemption prices set forth below, together with accrued and unpaid interest to the applicable redemption date: | | | | | |
| Beginning May 1, | Percentage |
| 2025 | 102.063% |
| 2026 | 101.375% |
| 2027 | 100.688% |
| 2028 and thereafter | 100.000% |
The 5.625% Senior Notes were issued on February 15, 2019. The proceeds from these notes were used to repay outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility, to pay expenses associated with the offering, and for general corporate purposes. At any time prior to February 15, 2024, these notes may be redeemed at a redemption price equal to the sum of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest and a make-whole premium set forth in the indenture governing the notes. Thereafter, these notes may be redeemed at the redemption prices set forth below, together with accrued and unpaid interest to the applicable redemption date: | | | | | |
| Beginning February 15, | Percentage |
| 2024 | 102.813% |
| 2025 | 101.875% |
| 2026 | 100.938% |
| 2027 and thereafter | 100.000% |
The 5.00% Senior Notes were issued on December 4, 2017. The proceeds, along with cash on hand, were used to redeem then outstanding senior notes and pay the related call premium. At any time prior to December 15, 2022, these notes may be redeemed at a redemption price equal to the sum of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest and a make-whole premium set forth in the indenture governing the notes. Thereafter, these notes may be redeemed at the redemption prices set forth below, together with accrued and unpaid interest thereon to the applicable redemption date: | | | | | |
| Beginning December 15, | Percentage |
| 2022 | 102.500% |
| 2023 | 101.667% |
| 2024 | 100.833% |
| 2025 and thereafter | 100.000% |
The 6.375% Senior Notes were redeemed on June 11, 2020 with proceeds from the 4.625% Senior Notes. The related call premium of $12.8 million and $2.9 million of unamortized original issue discount and debt issuance costs related to the 6.375% Senior Notes are included in “Other (expense) income, net” in the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020.
The indenture governing the 5.00% Senior Notes contains covenants that would limit MG Holdings II’s ability to pay dividends or to make distributions and repurchase or redeem MG Holdings II’s stock in the event a default has occurred or MG Holdings II’s consolidated leverage ratio (as defined in the indenture) exceeds 5.0 to 1.0. At December 31, 2021, there were no limitations pursuant thereto. There are additional covenants in the 5.00% Senior Notes indenture that limit the ability of MG Holdings II and its subsidiaries to, among other things, (i) incur indebtedness, make investments, or sell assets in the event MG Holdings II is not in compliance with specified financial ratios, and (ii) incur liens, enter into agreements restricting their ability to pay dividends, enter into transactions with affiliates, or consolidate, merge or sell substantially all of their assets. The indentures
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
governing the 3.625%, 4.125%, 4.625%, and 5.625% Senior Notes are less restrictive than the indentures governing the 5.00% Senior Notes and generally only limit MG Holdings II’s and its subsidiaries’ ability to, among other things, create liens on assets, or consolidate, merge, sell or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of their assets.
The Senior Notes all rank equally in right of payment.
Exchangeable Notes
During 2017, Match Group FinanceCo, Inc., a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, issued $517.5 million aggregate principal amount of its 2022 Exchangeable Notes. During 2019, Match Group FinanceCo 2, Inc. and Match Group FinanceCo 3, Inc., direct, wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Company, issued $575.0 million aggregate principal amount of its 2026 Exchangeable Notes and $575.0 million aggregate principal amount of its 2030 Exchangeable Notes, respectively.
The 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes (collectively the “Exchangeable Notes”) are guaranteed by the Company but are not guaranteed by MG Holdings II or any of its subsidiaries.
The following table presents details of the exchangeable features: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of shares of the Company’s Common Stock into which each $1,000 of Principal of the Exchangeable Notes is Exchangeable(a) | | Approximate Equivalent Exchange Price per Share(a) | | Exchangeable Date |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | 22.7331 | | $ | 43.99 | | | July 1, 2022 |
| 2026 Exchangeable Notes | 11.4259 | | $ | 87.52 | | | March 15, 2026 |
| 2030 Exchangeable Notes | 11.8739 | | $ | 84.22 | | | October 15, 2029 |
______________________
(a)Subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified events.
As more specifically set forth in the applicable indentures, the Exchangeable Notes are exchangeable under the following circumstances:
(1) during any calendar quarter (and only during such calendar quarter), if the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during the period of 30 consecutive trading days ending on, and including, the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter is greater than or equal to 130% of the exchange price on each applicable trading day;
(2) during the five-business day period after any five-consecutive trading day period in which the trading price per $1,000 principal amount of notes for each trading day of the measurement period was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock and the exchange rate on each such trading day;
(3) if the issuer calls the notes for redemption, at any time prior to the close of business on the scheduled trading day immediately preceding the redemption date; or
(4) upon the occurrence of specified corporate events as further described in the indentures governing the respective Exchangeable Notes.
On or after the respective exchangeable dates noted in the table above, until the close of business on the second scheduled trading day immediately preceding the maturity date, holders may exchange all or any portion of their Exchangeable Notes regardless of the foregoing conditions. Upon exchange, the issuer, in its sole discretion, has the option to settle the Exchangeable Notes with any of the three following alternatives: (1) shares of the Company’s common stock, (2) cash or (3) a combination of cash and shares of the Company's common stock. It is the Company’s intention to settle the Exchangeable Notes with cash equal to the face amount of the notes upon exchange. Any dilution arising from the 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes would be mitigated by the 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes Hedges (defined below), respectively.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company’s 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes were all exchangeable as of December 31, 2021. During the year ended December 31, 2021, a portion of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes were presented for exchange, see “Redemption and exchange of 2022 Exchangeable Notes and related note hedges and warrants” below for details. No other Exchangeable Notes were presented for exchange during the year ended December 31, 2021. None of the Exchangeable Notes were exchanged, or presented for exchange, during the year ended December 31, 2020.
The following table presents the if-converted value that exceeded the principal of each Exchangeable Note outstanding as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 based on the Company’s stock price on December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| | | |
| (In millions) |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | $ | 170.4 | | | $ | 1,261.2 | |
| 2026 Exchangeable Notes | $ | 293.9 | | | $ | 418.3 | |
| 2030 Exchangeable Notes | $ | 327.9 | | | $ | 457.2 | |
Additionally, all or any portion of the 2026 Exchangeable Notes and 2030 Exchangeable Notes may be redeemed for cash, at the respective issuer’s option, on or after June 20, 2023 and July 20, 2026, respectively, if the last reported sale price of the Company’s common stock has been at least 130% of the exchange price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive), including at least one of the five trading days immediately preceding the date on which the notice of redemption is provided, during any 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the trading day immediately preceding the date on which the applicable issuer provides notice of redemption, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount to be redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the redemption date.
The following table sets forth the components of the outstanding Exchangeable Notes as of December 31, 2021 and 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | | 2026 Exchangeable Notes | | 2030 Exchangeable Notes | | 2022 Exchangeable Notes | | 2026 Exchangeable Notes | | 2030 Exchangeable Notes |
| |
| (In thousands) |
| Principal | $ | 100,500 | | | $ | 575,000 | | | $ | 575,000 | | | $ | 517,500 | | | $ | 575,000 | | | $ | 575,000 | |
| Less: unamortized debt issuance costs | 573 | | | 7,130 | | | 8,638 | | | 6,511 | | | 8,700 | | | 9,627 | |
| Net carrying value included in current maturities of long-term debt, net | $ | 99,927 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Net carrying value included in long-term debt, net | $ | — | | | $ | 567,870 | | | $ | 566,362 | | | $ | 510,989 | | | $ | 566,300 | | | $ | 565,373 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table sets forth interest expense recognized related to the Exchangeable Notes for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | | 2026 Exchangeable Notes | | 2030 Exchangeable Notes |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 3,525 | | | $ | 5,031 | | | $ | 11,500 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 2,939 | | | 1,570 | | | 989 | |
| Total interest expense recognized | $ | 6,464 | | | $ | 6,601 | | | $ | 12,489 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | | 2026 Exchangeable Notes | | 2030 Exchangeable Notes |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 4,528 | | | $ | 5,031 | | | $ | 11,500 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 3,646 | | | 1,533 | | | 950 | |
| Total interest expense recognized | $ | 8,174 | | | $ | 6,564 | | | $ | 12,450 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes | | 2026 Exchangeable Notes | | 2030 Exchangeable Notes |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Contractual interest expense | $ | 4,528 | | | $ | 2,963 | | | $ | 6,772 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 3,578 | | | 897 | | | 550 | |
| Total interest expense recognized | $ | 8,106 | | | $ | 3,860 | | | $ | 7,322 | |
The effective interest rates for the 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes are 1.6%, 1.2%, and 2.2%, respectively.
Exchangeable Notes Hedges and Warrants
In connection with the Exchangeable Notes offerings, the Company purchased call options allowing the Company to purchase initially (subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified events) the same number of shares that would be issuable upon the exchange of the applicable Exchangeable Notes at the price per share set forth below (the “Exchangeable Notes Hedge”), and sold warrants allowing the counterparty to purchase (subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified events) shares at the per share price set forth below (the “Exchangeable Notes Warrants”).
The Exchangeable Notes Hedges are expected to reduce the potential dilutive effect on the Company’s common stock upon any exchange of notes and/or offset any cash payment Match Group FinanceCo, Inc., Match Group FinanceCo 2, Inc. or Match Group FinanceCo 3, Inc. is required to make in excess of the principal amount of the exchanged notes. The Exchangeable Notes Warrants have a dilutive effect on the Company’s common stock to the extent that the market price per share of the Company common stock exceeds their respective strike prices.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following tables present details of the Exchangeable Notes Hedges and Warrants outstanding at December 31, 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares(a) | | Approximate Equivalent Exchange Price per Share(a) |
| | | |
| (Shares in millions) |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes Hedge | 1.9 | | $ | 43.99 | |
| 2026 Exchangeable Notes Hedge | 6.6 | | $ | 87.52 | |
| 2030 Exchangeable Notes Hedge | 6.8 | | $ | 84.22 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares(a) | | Weighted Average Strike Price per Share(a) |
| | | |
| (Shares in millions) |
| 2022 Exchangeable Notes Warrants | 2.4 | | $ | 68.22 | |
| 2026 Exchangeable Notes Warrants | 6.6 | | $ | 134.76 | |
| 2030 Exchangeable Notes Warrants | 6.8 | | $ | 134.82 | |
______________________
(a)Subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified events.
Redemption and exchanges of 2022 Exchangeable Notes and related note hedges and warrants
During the year ended December 31, 2021, $18.6 million aggregate principal amount of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes were presented for exchange, of which $15.6 million aggregate principal amount was not settled as of December 31, 2021. The principal amount of this remaining $15.6 million is classified as “current maturities of long-term debt, net” and the fair value in excess of the principal value on the date of exchange is recorded as a current liability within “accrued expenses and other current liabilities.” These obligations were settled in January 2022. See “Note 6—Financial Instruments” for additional information.
In connection with the 2022 Exchangeable Notes presented for exchange during the year ended December 31, 2021, we exercised 0.4 million underlying shares of the related 2022 Exchangeable Notes Hedges, which were valued based on the volume weighted average price of Match Group common stock over a 40-day measurement period. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company received $6.6 million in cash related to these hedge settlements and a $32.1 million derivative asset is included in other current assets at December 31, 2021 with respect to the hedges that were still subject to the 40-day measurement period as of year-end.
On October 4, 2021, we repurchased $414.0 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes, pursuant to privately negotiated agreements executed on September 22, 2021, for approximately $1.5 billion, including accrued and unpaid interest on the repurchased notes, funded with (i) net proceeds of $879.0 million from a registered direct offering to the holders of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes being repurchased of 5,534,098 shares of our common stock at a price of $158.83 per share, (ii) approximately $420 million of net proceeds from the 3.625% Senior Notes offering; and (iii) net proceeds of approximately $201 million from the unwind of a proportionate amount of outstanding hedges and warrants, each representing 9.4 million underlying shares, corresponding to the 2022 Exchangeable Notes repurchased. See “Note 6—Financial Instruments” for additional information.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Long-term debt maturities | | | | | |
| Years Ending December 31, | (In thousands) |
| 2022 | $ | 100,500 | |
| |
| |
| |
| 2026 | 575,000 | |
| 2027 | 875,000 | |
| 2028 | 500,000 | |
| 2029 | 350,000 | |
| 2030 | 1,075,000 | |
| 2031 | 500,000 | |
| |
| Total | 3,975,500 | |
| Less: Current maturities of long-term debt | 100,500 | |
| Less: Unamortized original issue discount | 5,215 | |
| Less: Unamortized debt issuance costs | 40,364 | |
| Total long-term debt, net | $ | 3,829,421 | |
NOTE 8—SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Description of Common Stock
Holders of Match Group common stock are entitled to one vote per share on all matters to be voted upon by the stockholders. Holders of Match Group common stock are entitled to receive, share for share, such dividends as may be declared by Match Group’s Board of Directors out of funds legally available therefor. In the event of a liquidation, dissolution, or winding up, holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to receive ratably the assets available for distribution to stockholders after payment of all liabilities.
Reserved Common Shares
In connection with equity compensation plans, the Exchangeable Notes, and warrants, 75.0 million shares of Match Group common stock are reserved at December 31, 2021.
Retirement of Treasury Stock
On June 30, 2020, prior to the Separation, Former IAC retired all Former IAC common stock and Class B common stock then held in treasury. There are no shares of common stock held in treasury at December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Preferred Stock
The Company has authorized 100,000,000 shares, $0.01 par value per share, of preferred stock. No shares have been issued under this authorization.
Series of equity transactions related to the Separation of Former IAC
Upon the consummation of the Separation, holders of Former IAC common stock exchanged each share of common stock for (i) one share of Series 1 Mandatorily Exchangeable Preferred Stock, which was immediately exchanged for one share of IAC common stock and then retired; and (ii) 2.1584 shares of Match Group common stock, par value $0.001 per share.
Upon the consummation of the Separation, holders of Former IAC Class B common stock exchanged each share of Class B common stock for (i) one share of Series 2 Mandatorily Exchangeable Preferred Stock, which was immediately exchanged for one share of IAC Class B common stock and then retired; and (ii) 2.1584 shares of Match Group common stock, par value $0.001 per share.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Issuance of Common Stock
In July 2020, in connection with the Separation, Former IAC completed the sale of an additional 17.3 million newly issued Match Group common shares. The proceeds of $1.4 billion, net of associated fees, were transferred directly to IAC.
In October 2021, we completed the sale of 5.5 million common shares. The net proceeds of $879.0 million were used to repurchase $414.0 million aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 2022 Exchangeable Notes. See “Note 7—Long-term Debt, net” for additional information on the redemption of a portion of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 9—ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
The following tables present the components of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income and items reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive loss into earnings. | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
| Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment | | | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (81,454) | | | | | $ | (81,454) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | (142,300) | | | | | (142,300) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (223,754) | | | | | $ | (223,754) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment | | Unrealized (Loss) Gain on Available-For-Sale Security | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (136,349) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (136,349) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 40,655 | | | (1) | | | 40,654 | |
| Amounts reclassified into earnings | (168) | | | — | | | (168) | |
| Net period other comprehensive income (loss) | 40,487 | | | (1) | | | 40,486 | |
| Allocation of accumulated other comprehensive loss related to the noncontrolling interests | 628 | | | — | | | 628 | |
| Separation of IAC | 13,780 | | | 1 | | | 13,781 | |
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (81,454) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (81,454) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| Foreign Currency Translation Adjustment | | Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-For-Sale Security | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | (128,726) | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | (128,722) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | (7,938) | | | (4) | | | (7,942) | |
| | | | | |
| Net period other comprehensive loss | (7,938) | | | (4) | | | (7,942) | |
| Allocation of accumulated other comprehensive loss related to the noncontrolling interests | 315 | | | — | | | 315 | |
| Balance at December 31 | $ | (136,349) | | | $ | — | | | $ | (136,349) | |
At December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, there was no tax benefit or provision on the accumulated other comprehensive loss.
NOTE 10—EARNINGS PER SHARE
As a result of the Separation, weighted average basic and dilutive shares outstanding for all periods prior to the Separation reflect the share position of Former IAC multiplied by the Separation exchange ratio of 2.1584. The following table sets forth the computation of the basic and diluted earnings per share attributable to Match Group shareholders: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Basic | | Diluted | | Basic | | Diluted | | Basic | | Diluted |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Numerator | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net earnings from continuing operations | $ | 276,045 | | | $ | 276,045 | | | $ | 587,679 | | | $ | 587,679 | | | $ | 517,340 | | | $ | 517,340 | |
Net loss (earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,169 | | | 1,169 | | | (59,599) | | | (59,599) | | | (103,401) | | | (103,401) | |
Impact from subsidiaries' dilutive securities of continuing operations(a) | — | | | (993) | | | — | | | (9,999) | | | — | | | (25,997) | |
Interest on dilutive Exchangeable Notes, net of income tax(b) | — | | | 6,616 | | | — | | | 16,300 | | | — | | | 5,791 | |
Net earnings from continuing operations attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 277,214 | | | $ | 282,837 | | | $ | 528,080 | | | $ | 534,381 | | | $ | 413,939 | | | $ | 393,733 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | $ | 509 | | | $ | 509 | | | $ | (366,070) | | | $ | (366,070) | | | $ | 49,187 | | | $ | 49,187 | |
Net earnings (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests of discontinued operations | — | | | — | | | 319 | | | 319 | | | (9,288) | | | (9,288) | |
Impact from subsidiaries’ dilutive securities of discontinued operations(a) | — | | | — | | | — | | | (240) | | | — | | | (67) | |
Net earnings (loss) from discontinued operations attributable to shareholders | 509 | | | 509 | | | (365,751) | | | (365,991) | | | 39,899 | | | 39,832 | |
Net earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 277,723 | | | $ | 283,346 | | | $ | 162,329 | | | $ | 168,390 | | | $ | 453,838 | | | $ | 433,565 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Denominator | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average basic shares outstanding | 275,004 | | | 275,004 | | | 223,433 | | | 223,433 | | | 181,869 | | | 181,869 | |
Dilutive securities(a)(c)(d) | — | | | 13,866 | | | — | | | 12,157 | | | — | | | 10,129 | |
Dilutive shares from Exchangeable Notes, if-converted(b) | — | | | 15,970 | | | — | | | 20,430 | | | — | | | 9,784 | |
Denominator for earnings per share—weighted average shares(a)(c)(d) | 275,004 | | | 304,840 | | | 223,433 | | | 256,020 | | | 181,869 | | | 201,782 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings per share from continuing operations | $ | 1.01 | | | $ | 0.93 | | | $ | 2.36 | | | $ | 2.09 | | | $ | 2.28 | | | $ | 1.95 | |
(Loss) earnings per share from discontinued operations, net of tax | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (1.64) | | | $ | (1.43) | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | 0.20 | |
Earnings per share attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders | $ | 1.01 | | | $ | 0.93 | | | $ | 0.73 | | | $ | 0.66 | | | $ | 2.50 | | | $ | 2.15 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
______________________
(a)Prior to the Separation, Former IAC had the option to settle certain Former Match Group and ANGI Homeservices (“ANGI”) stock-based awards with Former IAC shares. For the period prior to the Separation in the year ended December 31, 2020, for continuing operations it was more dilutive for Former Match Group to settle certain Former Match Group equity awards; and for discontinued operations it was more dilutive for ANGI to settle certain ANGI equity awards. For the year ended December 31, 2019, for continuing operations it was more dilutive for Former Match Group to settle certain Former Match Group equity awards; and for discontinued operations, it was more dilutive for Former IAC to settle certain ANGI equity awards.
(b)The Company uses the if-converted method for calculating the dilutive impact of the outstanding Exchangeable Notes. For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company adjusted net earnings from continuing operations attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders for the cash interest expense, net of income taxes, incurred on the 2022 and 2026 Exchangeable Notes and dilutive shares were included for the same set of notes at the Match Group exchange rates. For the year ended December 31, 2021 the 2030 Exchangeable Notes were not more dilutive under the if-converted method and therefore the weighted average 6.8 million shares related to the 2030 Exchangeable Notes are excluded from dilutive securities. For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company adjusted net earnings from continuing operations attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders for the cash interest expense, net of income taxes, incurred on the 2022, 2026, and 2030 Exchangeable Notes and dilutive shares were included for the same set of notes at the Match Group exchange rates. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company adjusted net earnings from continuing operations attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders for the cash interest expense, net of income taxes, incurred on the 2022 and 2026 Exchangeable Notes and dilutive shares were included for the same set of notes at the Former IAC exchange rates multiplied by the Separation exchange ratio. For the year ended December 31, 2019 the 2030 Exchangeable Notes were not more dilutive under the if-converted method and therefore the weighted average 2.5 million shares related to the 2030 Exchangeable Notes are excluded from dilutive securities.
(c)If the effect is dilutive, weighted average common shares outstanding include the incremental shares that would be issued upon the assumed exercise of stock options, warrants, and subsidiary denominated equity and vesting of restricted stock units. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019, 0.9 million, 13.4 million and 15.7 million potentially dilutive securities, respectively, are excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive.
(d)Market-based awards and performance-based stock units (“PSUs”) are considered contingently issuable shares. Shares issuable upon exercise or vesting of market-based awards and PSUs are included in the denominator for earnings per share if (i) the applicable market or performance condition(s) has been met and (ii) the inclusion of the market-based awards and PSUs is dilutive for the respective reporting periods. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019, 1.0 million, 0.4 million, and 0.4 million market-based awards and PSUs, respectively, were excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because the market or performance conditions had not been met.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 11—STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
The Company currently has three active stock and annual incentive plans; two Former Match Group plans were assumed as part of the Separation (the 2015 and 2017 plans) and another plan was approved by shareholders on June 25, 2020 (the 2020 plan). The 2015 and 2017 plans cover stock options to acquire shares of Match Group common stock, RSUs, and stock settled stock appreciation rights denominated in the equity of certain of our subsidiaries, in each case with respect to awards previously granted by Former Match Group prior to the Separation, as well as provide for the future grant of equity awards by the Company. The 2015 and 2017 plans authorize the Company to grant awards to its employees, officers, directors and consultants. At December 31, 2021, there were 32.6 million shares available for the future grant of equity awards under the 2015 and 2017 plans collectively. The 2020 plan covers options previously granted by Former IAC that converted into Match Group options as a result of the Separation; no additional grants can be made from this plan.
The 2015 and 2017 plans have a stated term of ten years and provide that the exercise price of stock options granted will not be less than the market price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. Neither plan specifies grant dates or vesting schedules of awards as those determinations have been delegated to the Compensation and Human Resources Committee of Match Group’s Board of Directors (the “Committee”). Each grant agreement reflects the vesting schedule for that particular grant as determined by the Committee. Stock options outstanding will generally vest in four equal annual installments over a four-year period. RSUs outstanding generally vest over a three- or four-year period. Market-based awards outstanding generally vest over a two- to four-year period.
Stock-based compensation expense recognized in the consolidated statement of operations includes expense related to the Company’s stock options and RSUs, market-based RSUs and PSUs for which vesting is considered probable, and equity instruments denominated in shares of subsidiaries. The amount of stock-based compensation expense recognized is net of estimated forfeitures, as the expense recorded is based on awards that are ultimately expected to vest. The forfeiture rate is estimated at the grant date based on historical experience and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from the estimated rate. At December 31, 2021, there is $270.9 million of unrecognized compensation cost, net of estimated forfeitures, related to all outstanding equity-based awards, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 2.4 years.
The total income tax benefit recognized in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 related to all stock-based compensation is $95.1 million, $136.6 million and $110.4 million, respectively.
The aggregate income tax benefit recognized related to the exercise of stock options for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019 is $53.8 million, $105.5 million, and $73.4 million, respectively. As the Company is currently in a NOL position there will be some delay in the timing of the realization of cash benefit of income tax deductions related to stock-based compensation because it will be dependent upon the amount and timing of future taxable income and the timing of estimated income tax payments.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Stock Options
Stock options outstanding at December 31, 2021 and changes during the year ended December 31, 2021 are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2021 |
| | Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (In Years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value |
| | | | | | | |
| | (Shares and intrinsic value in thousands) |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 7,425 | | | $ | 19.48 | | | | | |
| Converted sub-equity options | 3 | | | 37.49 | | | | | |
| Increase due to acquisition | 267 | | | 30.30 | | | | | |
| Exercised | (2,926) | | | 18.52 | | | | | |
| Forfeited | (280) | | | 23.06 | | | | | |
| Expired | (21) | | | 12.55 | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 4,468 | | | $ | 20.58 | | | 4.9 | | $ | 498,936 | |
| Options exercisable | 4,193 | | | $ | 19.85 | | | 4.7 | | $ | 471,347 | |
______________________
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the difference between Match Group’s closing stock price on the last trading day of 2021 and the exercise price, multiplied by the number of in-the-money options that would have been exercised had option holders exercised their options on December 31, 2021. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2021 is $406.1 million. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the period from the Separation on July 1, 2020 to December 31, 2020 is $737.9 million.
The following table summarizes the information about stock options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options Outstanding | | Options Exercisable |
| Range of Exercise Prices | Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life in Years | | Weighted-Average
Exercise
Price | | Exercisable at December 31, 2021 | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life in Years | | Weighted-Average
Exercise
Price |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Shares in thousands) |
$0.01 to $10.00 | 671 | | | 4.6 | | $ | 7.92 | | | 631 | | | 4.3 | | $ | 8.38 | |
$10.01 to $20.00 | 1,545 | | | 4.4 | | 14.78 | | | 1,544 | | | 4.4 | | 14.78 | |
$20.01 to $30.00 | 1,794 | | | 4.9 | | 24.62 | | | 1,698 | | | 4.9 | | 24.37 | |
$30.01 to $40.00 | 152 | | | 6.1 | | 35.58 | | | 147 | | | 6.1 | | 35.76 | |
$40.01 to $50.00 | 306 | | | 7.6 | | 46.49 | | | 173 | | | 6.2 | | 49.12 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 4,468 | | | 4.9 | | $ | 20.58 | | | 4,193 | | | 4.7 | | $ | 19.85 | |
Cash received from Match Group stock option exercises for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $58.4 million and $155.4 million, respectively. No cash was received from stock option exercises for the year ended December 31, 2019.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Restricted Stock Units, Performance-Based Stock Units, and Market-Based Awards
RSUs, PSUs, and market-based awards are awards in the form of phantom shares or units denominated in a hypothetical equivalent number of shares of Match Group common stock and with the value of each RSU and PSU equal to the fair value of Match Group common stock at the date of grant. For market-based awards, the grant date fair value was estimated using a lattice model that incorporates a Monte Carlo simulation of the valuation of a wholly-owned business. Each RSU, PSU, and market-based award grant is subject to service-based vesting, where a specific period of continued employment must pass before an award vests. PSUs also include performance-based vesting conditions, where certain performance targets set at the time of grant must be achieved before an award vests. The number of market-based awards that ultimately vest is based on a valuation of a wholly-owned business. For RSU grants, the expense is measured at the grant date as the fair value of Match Group common stock and expensed as stock-based compensation over the vesting term. For PSU grants, the expense is measured at the grant date as the fair value of Match Group common stock and expensed as stock-based compensation over the vesting term if the performance targets are considered probable of being achieved.
Unvested RSUs, PSUs, and market-based awards outstanding at December 31, 2021 and changes during the year ended December 31, 2021 are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | RSUs | | PSUs | | Market-based awards |
| | Number of shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of shares(a) | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of shares(a) | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (Shares in thousands) |
| Unvested at January 1, 2021 | 3,299 | | | $ | 63.02 | | | 550 | | | $ | 74.59 | | | 714 | | | $ | 19.34 | |
| Granted | 1,452 | | | 157.61 | | | 212 | | | 159.23 | | | 803 | | | 159.67 | |
| Vested | (1,195) | | | 56.46 | | | — | | | — | | | (559) | | | 19.81 | |
| Forfeited | (436) | | | 93.27 | | | (221) | | | 97.42 | | | (146) | | | 148.66 | |
| Expired | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (30) | | | 20.84 | |
| Unvested at December 31, 2021 | 3,120 | | | $ | 105.33 | | | 541 | | | $ | 98.41 | | | 782 | | | $ | 138.95 | |
______________________
(a)Represents the maximum shares issuable.
The weighted average fair value of RSUs and PSUs granted during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, based on market prices of Match Group’s common stock on the grant date, was $157.81 and $104.74, respectively. The total fair value of RSUs that vested during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $67.5 million and $14.8 million, respectively. No PSUs vested during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
There were 0.8 million market-based awards granted during the year ended December 31, 2021. The vesting of the awards granted in the current period are dependent upon the Company’s total shareholder return relative to the Nasdaq 100 Total Return Index over the performance period. There were no market-based awards granted during the year ended December 31, 2020. The total fair value of market-based awards that vested during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $11.1 million and $2.5 million, respectively.
Equity Instruments Denominated in Shares of Certain Subsidiaries
The Company has granted stock settled stock appreciation rights denominated in the equity of certain non-publicly traded subsidiaries to employees and management of those subsidiaries. These equity awards vest over a specified period of time or upon the occurrence of certain specified events. The value of the stock settled stock appreciation rights is based on the equity value of these subsidiaries. Accordingly, these awards only have value to the extent the relevant business appreciates in value above the initial value utilized to determine the exercise price. These awards can have significant value in the event of significant appreciation. The fair value of the common stock of these subsidiaries is generally determined through a third-party valuation pursuant to the terms of the respective subsidiary equity plan. These equity awards are settled on a net basis, with the award
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
holder entitled to receive a payment in shares of Match Group common stock with a total value equal to the intrinsic value of the award at exercise. The number of shares of Match Group common stock ultimately needed to settle these awards may vary significantly from the estimated number below as a result of movements in our stock price and/or a determination of fair value of the relevant subsidiary that differs from our estimate. The expense associated with these equity awards is initially measured at fair value at the grant date and is expensed as stock-based compensation over the vesting term. At December 31, 2021, the number of shares of Match Group common stock that would be required to settle these awards at estimated fair values, including vested and unvested awards, net of an assumed 50% withholding tax, is 1.0 million shares. The withholding taxes, which would be paid by the Company on behalf of the employees at exercise, required to settle the vested and unvested awards at estimated fair values on December 31, 2021 is $126.9 million assuming a 50% withholding tax rate. The corresponding number of shares and withholding tax amount as of December 31, 2020 were 0.3 million shares and $39.6 million.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Match Group, Inc. 2021 Global Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "ESPP") was approved by the Company’s shareholders on June 15, 2021. Under the ESPP, eligible employees may purchase the Company’s common stock at a 15% discount of the stock price at the lower of the market price of our common stock on the date of commencement of the applicable offering period or on the last day of each six-month purchase period, subject to certain purchase limits.
Under the ESPP, employees purchased less than 0.1 million shares at an average price per share of $126.16 during the year ended December 31, 2021. At December 31, 2021, there were 3.0 million shares available for future issuance under the ESPP. At December 31, 2021, there is $3.0 million of unrecognized compensation cost, net of estimated forfeitures, related to the ESPP, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 0.6 years.
Capitalization of Stock-Based Compensation
For the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, $6.4 million and $5.1 million, respectively, of stock-based compensation was capitalized related to internal use software development. No amounts were capitalized for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Modifications of awards
During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, the Company modified certain equity awards and recognized modification charges in continuing operations of $10.2 million, $21.2 million and $7.1 million, respectively.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 12—GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
Revenue by geography is based on where the customer is located. Geographic information about revenue and long-lived assets is presented below: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Revenue | | | | | |
| United States | $ | 1,362,658 | | | $ | 1,121,957 | | | $ | 972,747 | |
| All other countries | 1,620,619 | | | 1,269,312 | | | 1,078,511 | |
| Total | $ | 2,983,277 | | | $ | 2,391,269 | | | $ | 2,051,258 | |
The United States is the only country from which revenue is greater than 10 percent of total revenue. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Long-lived assets (excluding goodwill and intangible assets) | | | |
| United States | $ | 133,513 | | | $ | 91,683 | |
| All other countries | 29,743 | | | 16,116 | |
| Total | $ | 163,256 | | | $ | 107,799 | |
The United States is the only country from which long-lived assets (excluding goodwill and intangible assets) is greater than 10 percent of total long-lived assets (excluding goodwill and intangible assets).
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 13—LEASES
The Company leases office space, data center facilities, and equipment used in connection with its operations under various operating leases, many of which contain escalation clauses. Through June 2021, one of these lease agreements related to a property owned by IAC. See “Note 15—Related Party Transactions” for additional information on the intercompany lease agreement.
ROU assets represent the Company’s right to use the underlying assets for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the present value of the Company’s obligation to make payments arising from leases. ROU assets and related lease liabilities are based on the present value of fixed lease payments over the lease term using the Company’s incremental borrowing rates on the lease commencement date or January 1, 2019 for leases that commenced prior to that date. The Company combines the lease and non-lease components of lease payments in determining ROU assets and related lease liabilities. If the lease includes one or more options to extend the term of the lease, the renewal option is considered in the lease term if it is reasonably certain the Company will exercise the options. Lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. As permitted by ASC 842, leases with an initial term of twelve months or less (“short-term leases”) are not recorded on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
Variable lease payments consist primarily of common area maintenance, utilities, and taxes, which are not included in the recognition of ROU assets and related lease liabilities. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leases | | Balance Sheet Classification | | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| | | | (In thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | |
| Right-of-use assets | | Other non-current assets | | $ | 113,582 | | | $ | 85,009 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Current lease liabilities | | Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | | $ | 10,618 | | | $ | 7,143 | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | Other long-term liabilities | | 113,533 | | | 83,489 | |
| Total lease liabilities | | | | $ | 124,151 | | | $ | 90,632 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease Cost | | Income Statement Classification | | Year Ended December 31, 2021 | | Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| | | | | | |
| | | | (In thousands) |
| Fixed lease cost | | Cost of revenue | | $ | 2,280 | | | $ | 3,215 | |
| | | | | | |
| Fixed lease cost | | General and administrative expense | | 22,772 | | | 15,548 | |
| | | | | | |
Total fixed lease cost(a) | | | | 25,052 | | | 18,763 | |
| | | | | | |
| Variable lease cost | | Cost of revenue | | 80 | | | 312 | |
| Variable lease cost | | General and administrative expense | | 2,768 | | | 2,882 | |
| Total variable lease cost | | | | 2,848 | | | 3,194 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Net lease cost | | | | $ | 27,900 | | | $ | 21,957 | |
______________________
(a)Includes approximately $3.5 million and $2.7 million of short-term lease cost, and $0.5 million and $1.2 million of sublease income, for the years ended December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Maturities of lease liabilities as of December 31, 2021: | | | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| 2022 | | $ | 19,882 | |
| 2023 | | 19,768 | |
| 2024 | | 16,201 | |
| 2025 | | 15,140 | |
| 2026 | | 13,286 | |
| After 2026 | | 66,535 | |
| Total | | 150,812 | |
| Less: Interest | | (20,680) | |
| Less: Tenant improvement receivables | | (5,981) | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | | $ | 124,151 | |
The following are the weighted average assumptions used for lease term and discount rate: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| Remaining lease term | | | 9.2 years | | 10.6 years |
| Discount rate | | | 3.03 | % | | 3.80 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, 2021 | | Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Other information: | | | | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease liabilities | | $ | 53,492 | | | $ | 69,886 | |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | $ | 18,345 | | | $ | 14,809 | |
NOTE 14—COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Commitments
The Company has funding commitments in the form of purchase obligations and surety bonds. The purchase obligations due in less than one year are $56.0 million, the purchase obligations due between one and three years are $15.5 million, and purchase obligations due between three and five years are $23.5 million, for a total of $95.0 million in purchase obligations. The purchase obligations primarily relate to web hosting services. Letters of credit and surety bonds totaling $0.5 million are currently outstanding as of December 31, 2021.
Contingencies
In the ordinary course of business, the Company is a party to various lawsuits. The Company establishes reserves for specific legal matters when it determines that the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome is probable and the loss is reasonably estimable. Management has also identified certain other legal matters where we believe an unfavorable outcome is not probable and, therefore, no reserve is established. Although management currently believes that resolving claims against us, including claims where an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible, will not have a material impact on the liquidity, results of operations, or financial condition of the Company, these matters are subject to inherent uncertainties and management’s view of these matters may change in the future. The Company also evaluates other contingent matters, including income and non-income tax contingencies, to assess the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome and estimated extent of potential loss. It is possible that an unfavorable outcome of one or more of these lawsuits or other contingencies could have a material impact on the liquidity, results of operations, or financial condition of the Company. See “Note 3—Income Taxes” for additional information related to income tax contingencies.
Pursuant to the Transaction Agreement, we have agreed to indemnify IAC for matters relating to any business of Former Match Group, including indemnifying IAC for costs related to the matters described below.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The official names of legal proceedings in the descriptions below (shown in italics) reflect the original names of the parties when the proceedings were filed as opposed to the current names of the parties following the separation of Match Group and IAC.
Tinder Optionholder Litigation Against Former Match Group and Match Group
On August 14, 2018, ten then-current and former employees of Match Group, LLC or Tinder, Inc. (“Tinder”), a former subsidiary of Former Match Group, filed a lawsuit in New York state court against Former Match Group and Match Group. See Sean Rad et al. v. IAC/InterActiveCorp and Match Group, Inc., No. 654038/2018 (Supreme Court, New York County). The complaint alleged that in 2017, the defendants: (i) wrongfully interfered with a contractually established process for the independent valuation of Tinder by certain investment banks, resulting in a substantial undervaluation of Tinder and a consequent underpayment to the plaintiffs upon exercise of their Tinder stock options, and (ii) then wrongfully merged Tinder into Former Match Group, thereby depriving certain of the plaintiffs of their contractual right to later valuations of Tinder on a stand-alone basis. The complaint asserted claims for breach of contract, breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing, unjust enrichment, interference with contractual relations (as against Former Match Group only), and interference with prospective economic advantage, and sought compensatory damages in the amount of at least $2 billion, as well as punitive damages. On August 31, 2018, four plaintiffs who were still employed by Former Match Group filed a notice of discontinuance of their claims without prejudice, leaving the six former employees as the remaining plaintiffs. On June 13, 2019, the court issued a decision and order granting defendants’ motion to dismiss the claims for breach of the implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing and for unjust enrichments, as well as the merger-related claim for breach of contract as to two of the remaining six plaintiffs, and otherwise denying defendants’ motion to dismiss. On July 13, 2020, the four former plaintiffs filed arbitration demands with the American Arbitration Association asserting the same valuation claims and on September 3, 2020, the four arbitrations were consolidated. Trial commenced on November 8, 2021. On December 1, 2021, the parties entered into a Binding Global Settlement Agreement Term Sheet, pursuant to which we will pay $441 million in 2022 to settle all claims in trial and in arbitration.
FTC Lawsuit Against Former Match Group
On September 25, 2019, the FTC filed a lawsuit in federal district court in Texas against Former Match Group. See FTC v. Match Group, Inc., No. 3:19:cv-02281-K (Northern District of Texas). The complaint alleges that, prior to mid-2018, for marketing purposes Match.com notified non-paying users that other users were attempting to communicate with them, even though Match.com had identified those subscriber accounts as potentially fraudulent, thereby inducing non-paying users to subscribe and exposing them to the risk of fraud should they subscribe. The complaint also challenges the adequacy of Match.com’s disclosure of the terms of its six-month guarantee, the efficacy of its cancellation process, and its handling of chargeback disputes. The complaint seeks among other things permanent injunctive relief, civil penalties, restitution, disgorgement, and costs of suit. On October 9, 2020, the court granted the Company’s motion to stay the case until the United States Supreme Court issues a decision in the consolidated appeal of Federal Trade Commission v. Credit Bureau Center, LLC and AMG Capital Management, LLC v. FTC. We believe that the FTC’s claims regarding Match.com’s practices, policies, and procedures are without merit and will defend vigorously against them.
NOTE 15—RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Relationship with IAC following the Separation
In connection with the Separation, the Company entered into certain agreements with IAC to govern the relationship between the Company and IAC following the Separation. These agreements, in certain cases, supersede the agreements entered into between Former Match Group and Former IAC in connection with Former Match Group’s IPO in November 2015 (the “IPO Agreements”) and include: a tax matters agreement; a transition services agreement; and an employee matters agreement. The IPO Agreements that were not superseded were terminated at closing of the Separation.
In addition to the agreements entered into at the time of the Separation, Match Group leases office space to IAC in a building owned by the Company in Los Angeles. Match Group also leased office space from IAC in New York City through June 2021. For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company received less than
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
$0.1 million from IAC pursuant to the Los Angeles lease and the Company paid $0.3 million to IAC pursuant to the New York City lease.
Match Group has a receivable balance of $0.2 million due from IAC at December 31, 2021, excluding items discussed in the “Tax Matters Agreement” section below.
In July 2020, in connection with the Separation, the sale of 17.3 million newly issued shares of Match Group common stock was completed by IAC. The proceeds of $1.4 billion, net of associated fees, were transferred directly to IAC pursuant to the terms of the Transaction Agreement.
Tax Matters Agreement
Pursuant to the tax matters agreement, each of Match Group and IAC is responsible for certain tax liabilities and obligations following the transfer by Former IAC (i) to Match Group of certain assets and liabilities of, or related to, the businesses of Former IAC (other than Former Match Group), and (ii) to holders of Former IAC common stock and Former IAC Class B common stock, as a result of the reclassification and mandatory exchange of certain series of Former IAC exchangeable preferred stock (collectively, the “IAC Distribution”). Under the tax matters agreement, IAC generally is responsible for, and has agreed to indemnify Match Group against, any liabilities incurred as a result of the failure of the IAC Distribution to qualify for the intended tax-free treatment unless, subject to certain exceptions, the failure to so qualify is attributable to Match Group's or Former Match Group’s actions or failure to act, Match Group's or Former Match Group’s breach of certain representations or covenants or certain acquisitions of equity securities of Match Group, in each case, described in the tax matters agreement (a "Match Group fault-based action"). If the failure to so qualify is attributable to a Match Group fault-based action, Match Group is responsible for liabilities incurred as a result of such failure and will indemnify IAC against such liabilities so incurred by IAC or its affiliates.
Under the tax matters agreement, as of December 31, 2021, Match Group is obligated to remit to IAC $1.3 million of expected state tax refunds relating to tax years prior to the Separation. This obligation is included in “Accrued expenses and other current liabilities” in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. Additionally, IAC is obligated to indemnify Match Group for IAC’s share of tax liabilities related to various periods prior to the Separation. At December 31, 2021, a receivable of $1.8 million is included in “Other current assets” in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet representing an estimate of the amount that Match Group is expected to be indemnified under this arrangement. At December 31, 2021, Match Group has an indemnification asset of $0.6 million included in “Other non-current assets” in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet for uncertain tax positions that related to Former IAC prior to the Separation.
Transition Services Agreement
Pursuant to the transition services agreement, IAC continues to provide minimal services to Match Group that Former IAC had historically provided to Former Match Group. Match Group also provides certain services to IAC that Former Match Group previously provided to Former IAC. The transition services agreement also provides that Match Group and IAC will make efforts to replace, amend, or divide certain joint contracts with third-parties relating to services or products used by both Match Group and IAC. Match Group and IAC also agreed to continue sharing certain services provided pursuant to certain third-party vendor contracts that were not replaced, amended, or divided prior to closing of the Separation.
For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company paid IAC less than $0.1 million related to services provided by IAC under the transition services agreement. Additionally, the Company received $7.6 million from IAC for services provided under the transition services agreement.
Employee Matters Agreement
Pursuant to the amended and restated employee matters agreement, Match Group will reimburse IAC for the cost of any IAC equity awards held by the Company’s employees and former employees upon exercise or vesting. In addition, Match Group employees continued to participate in IAC’s U.S. health and welfare plans, 401(k) plan and flexible benefits plan through December 31, 2020 and Match Group reimbursed IAC for the costs of such participation pursuant to the amended and restated employee matters agreement. Match Group established its own employee benefit plans effective January 1, 2021.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company paid IAC $0.1 million for the cost of IAC equity awards held by the Company’s employees upon vesting. At December 31, 2020, the Company has accrued $1.3 million as the estimated cost due to IAC for IAC equity awards held by Match Group employees.
Other Agreements
The Transaction Agreement provides that each of Match Group and IAC has agreed to indemnify, defend and hold harmless the other party from and against any liabilities arising out of: (i) any asset or liability allocated to such party or the other members of such party's group under the Transaction Agreement or the businesses of such party's group after the closing of the Separation; (ii) any breach of, or failure to perform or comply with, any covenant, undertaking or obligation of a member of such party's group contained in the Transaction Agreement that survives the closing of the Separation or is contained in any ancillary agreement; and (iii) any untrue or misleading statement or alleged untrue or misleading statement of a material fact or omission, with respect to information contained in or incorporated into the Form S-4 Registration Statement (the “Form S-4”) filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) by IAC and Former IAC in connection with the Separation or the joint proxy statement/prospectus filed by Former IAC and Former Match Group with the SEC pursuant to the Form S-4.
NOTE 16—BENEFIT PLANS
Pursuant to the Match Group Retirement Savings Plan (the “Match Group Plan”), employees are eligible to participate in a retirement savings plan sponsored by the Company in the United States, which is qualified under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. Participating employees may contribute up to 75% of their pre-tax earnings, but not more than statutory limits. The employer match under the Match Group Plan is 100% of the first 10% of a participant’s eligible earnings, subject to IRS limits on the Company’s matching contribution that a participant contributes to the Match Group Plan. The Company’s common stock is not an available investment option under the Match Group Plan.
Prior to January 1, 2021, Match Group employees were eligible to participate in a retirement savings plan sponsored by IAC in the United States pursuant to the Employee Matters Agreement with IAC (the “IAC Plan”). Beginning January 1, 2021, all investments in the IAC plan were transferred to the Match Group Plan. The employer match under the IAC plan was 100% of the first 10% of a participant’s eligible earnings. Prior to July 2019, the employer match under the IAC Plan was fifty cents for each dollar a participant contributed in the Plan, with a maximum contribution of 3% of a participant’s eligible earnings.
Matching contributions under the plans for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 were $10.9 million, $8.6 million and $5.8 million, respectively. The increase in matching contributions from 2019 to 2020 is primarily due to the aforementioned change of the Company’s matching contribution in the second half of 2019.
Matching contributions are invested in the same manner that each participant’s voluntary contributions are invested under the respective plans. Under the IAC Plan and prior to the Separation, an available investment option was IAC common stock, but neither participant nor matching contributions were required to be invested in IAC common stock.
Internationally, Match Group also has or participates in various benefit plans, primarily defined contribution plans. The Company’s contributions for these plans for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 were $5.4 million, $3.8 million and $3.1 million, respectively.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 17—CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENT DETAILS | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Other current assets: | | | |
| Prepaid expenses | $ | 78,952 | | | $ | 71,793 | |
| Capitalized mobile app fees | 41,744 | | | 33,539 | |
| Other | 81,872 | | | 38,693 | |
| Other current assets | $ | 202,568 | | | $ | 144,025 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Property and equipment, net: | | | |
| Computer equipment and capitalized software | $ | 171,335 | | | $ | 167,863 | |
| Buildings and building improvements | 61,841 | | | 45,476 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 40,895 | | | 28,711 | |
| Land | 11,565 | | | 11,565 | |
| Furniture and other equipment | 19,593 | | | 9,031 | |
| Projects in progress | 39,769 | | | 14,474 | |
| 344,998 | | | 277,120 | |
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (181,742) | | | (169,321) | |
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 163,256 | | | $ | 107,799 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities: | | | |
| Accrued legal settlement | $ | 441,000 | | | $ | — | |
| Accrued employee compensation and benefits | 88,670 | | | 65,239 | |
| Accrued advertising expense | 47,686 | | | 57,140 | |
| Accrued non-income taxes | 32,725 | | | 29,600 | |
| Accrued interest expense | 30,110 | | | 26,922 | |
| | | |
| Other | 128,175 | | | 52,847 | |
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | $ | 768,366 | | | $ | 231,748 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Other (expense) income, net | $ | (465,038) | | | $ | 15,861 | | | $ | (2,026) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Other expense, net, in 2021 includes a $441.0 million loss related to the former Tinder employee litigation settlement, a $14.6 million loss related to the changes in fair value of an embedded derivative arising from the repurchase of a portion of the 2022 Exchangeable Notes, a $5.2 million inducement expense arising from the repurchased 2022 Exchangeable Notes, and $1.8 million in net foreign currency losses, partially offset by $2.4 million of gains on the net settlement of the note hedges and warrants.
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Other income, net in 2020 includes a legal settlement of $35.0 million and interest income of $2.7 million, partially offset by a loss on redemption of bonds of $16.5 million, expense of $3.4 million related to a mark-to-market adjustment pertaining to a liability classified equity instrument, and $0.6 million in net foreign currency losses.
Other expense, net, in 2019 includes a $4.0 million impairment of an equity investment, expense of $1.7 million related to a mark-to-market adjustment pertaining to a liability classified equity instrument, and $0.9 million in net foreign currency losses, partially offset by interest income of $4.4 million.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash reported within the consolidated balance sheet to the total amounts shown in the consolidated statement of cash flows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| | | | | | | |
| (In thousands) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 815,384 | | | $ | 739,164 | | | $ | 465,676 | | | $ | 186,947 | |
Restricted cash included in other current assets | 128 | | | 138 | | | 127 | | | 193 | |
| | | | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash included in current assets of discontinued operations | — | | | — | | | 2,674,146 | | | 1,946,125 | |
Restricted cash included in non-current assets of discontinued operations | — | | | — | | | 409 | | | 420 | |
Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash as shown on the consolidated statement of cash flow | $ | 815,512 | | | $ | 739,302 | | | $ | 3,140,358 | | | $ | 2,133,685 | |
Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| Cash paid (received) during the year for: | | | | | |
| Interest | $ | 117,528 | | | $ | 115,957 | | | $ | 85,559 | |
Income tax payments | $ | 54,766 | | | $ | 41,024 | | | $ | 34,583 | |
| Income tax refunds | $ | (13,840) | | | $ | (30,048) | | | $ | (2,589) | |
| Noncash issuance of common stock for the acquisition of Hyperconnect | $ | 890,851 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
NOTE 18—QUARTERLY RESULTS (UNAUDITED) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Quarter Ended
March 31 | | Quarter Ended
June 30 | | Quarter Ended September 30 | | Quarter Ended December 31 |
| | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Year Ended December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | $ | 667,612 | | | $ | 707,760 | | | $ | 801,835 | | | $ | 806,070 | |
| Cost of revenue | 179,455 | | | 193,099 | | | 232,211 | | | 234,543 | |
| Operating income | 189,258 | | | 209,914 | | | 220,590 | | | 231,917 | |
Earnings (loss) from continuing operations (b) | 173,848 | | | 140,020 | | | 130,901 | | | (168,724) | |
| Earnings from discontinued operations | — | | | 509 | | | — | | | — | |
Net earnings (loss) attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders (d) | 174,250 | | | 140,895 | | | 131,210 | | | (168,632) | |
| Per share information from continuing operations attributable to the Match Group, Inc. shareholders: |
Basic (a) | $ | 0.65 | | | $ | 0.52 | | | $ | 0.47 | | | $ | (0.60) | |
Diluted (a) | $ | 0.57 | | | $ | 0.46 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | (0.60) | |
| Per share information attributable to the Match Group, Inc. shareholders: |
Basic (a) | $ | 0.65 | | | $ | 0.52 | | | $ | 0.47 | | | $ | (0.60) | |
Diluted (a) | $ | 0.57 | | | $ | 0.46 | | | $ | 0.43 | | | $ | (0.60) | |
| | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | $ | 544,642 | | | $ | 555,450 | | | $ | 639,770 | | | $ | 651,407 | |
| Cost of revenue | 143,894 | | | 148,853 | | | 169,823 | | | 173,263 | |
| Operating income | 137,372 | | | 195,594 | | | 200,167 | | | 212,582 | |
Earnings from continuing operations (d) | 157,534 | | | 141,397 | | | 140,113 | | | 148,635 | |
(Loss) earnings from discontinued operations (c) | (331,967) | | | (34,611) | | | 508 | | | — | |
Net (loss) earnings attributable to Match Group, Inc. shareholders (c)(d) | (202,830) | | | 74,917 | | | 141,207 | | | 149,035 | |
| Per share information from continuing operations attributable to the Match Group, Inc. shareholders: |
Basic (a)(d) | $ | 0.69 | | | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.54 | | | $ | 0.56 | |
Diluted (a)(d) | $ | 0.61 | | | $ | 0.54 | | | $ | 0.47 | | | $ | 0.50 | |
| Per share information attributable to the Match Group, Inc. shareholders: |
Basic (a)(c) | $ | (1.11) | | | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | 0.54 | | | $ | 0.56 | |
Diluted (a)(c) | $ | (1.00) | | | $ | 0.36 | | | $ | 0.47 | | | $ | 0.50 | |
______________________
(a)Quarterly per share amounts may not add to the related annual per share amount because of differences in the average common shares outstanding during each period.
(b)Loss from continuing operations for the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2021 includes $441 million related to the former Tinder employee litigation settlement.
(c)The operations of Former IAC business other than Match Group are presented as discontinued operations as part of the Separation described in “Note 1—Organization.”
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
(d)The Company early adopted ASU No. 2020-06 as of January 1, 2021 on a fully retrospective basis. The impact of adopting ASU No. 2020-06 on the quarter ended December 31, 2020 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Quarter Ended December 31, 2020 |
| Prior to the adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | After adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 | | Effect of adoption of ASU No. 2020-06 |
| | | | | |
| (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Statement of operations impacts | | | | | |
| Interest expense | $ | 43,306 | | | $ | 31,970 | | | $ | (11,336) | |
| Income tax provision | $ | (25,617) | | | $ | (28,497) | | | $ | (2,880) | |
| Net earnings from continuing operations | $ | 140,179 | | | $ | 148,635 | | | $ | 8,456 | |
| | | | | |
| Net earnings per share from continuing operations: |
| Basic | $ | 0.53 | | | $ | 0.56 | | | $ | 0.03 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.48 | | | $ | 0.50 | | | $ | 0.02 | |
| | | | | |
Weighted average dilutive shares outstanding | 294,975 | | | 307,582 | | | 12,607 | |
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of the Company’s Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company monitors and evaluates on an ongoing basis its disclosure controls and procedures in order to improve their overall effectiveness. In the course of these evaluations, the Company modifies and refines its internal processes as conditions warrant.
As required by Rule 13a-15(b) of the Exchange Act, Match Group management, including the Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and the Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), conducted an evaluation, as of the end of the period covered by this report, of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(e). Based on this evaluation, the CEO and the CFO concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of the period covered by this report.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act) for the Company. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021. In making this assessment, our management used the criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in “Internal Control—Integrated Framework” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. Based on this assessment, management has determined that, as of December 31, 2021, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective. The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their attestation report, included herein.
SEC staff guidance discusses the exclusion of an acquired business’s internal controls from management’s annual assessment of the internal controls over financial reporting when it is not possible to conduct assessments for the acquired business in the period between the acquisition date and the date of management’s assessment. We completed the acquisition of Hyperconnect, Inc. (“Hyperconnect”) on June 17, 2021. Management has excluded Hyperconnect from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021. Hyperconnect is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company with total assets (excluding goodwill and other intangible assets, which were included in this assessment) and total revenues representing 2% and 4%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The Company monitors and evaluates on an ongoing basis its internal control over financial reporting in order to improve its overall effectiveness. In the course of these evaluations, the Company modifies and refines its internal processes as conditions warrant. As required by Rule 13a-15(d), Match Group management, including the CEO and the CFO, also conducted an evaluation of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting to determine whether any changes occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2021 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Based on that evaluation, there has been no such change during the quarter ended December 31, 2021.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Match Group, Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Match Group, Inc. and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Match Group, Inc. and subsidiaries (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on the COSO criteria.
As indicated in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Hyperconnect, Inc., which is included in the 2021 consolidated financial statements of the Company and constituted 2% of total assets (excluding goodwill and other intangible assets, which were included in management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting) as of December 31, 2021 and 4% of revenues for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of the Company also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Hyperconnect, Inc.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheet of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive operations, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a), and our report dated February 24, 2022 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
February 24, 2022
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
The information required by Part III (Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14) has been incorporated by reference to Match Group’s definitive Proxy Statement to be used in connection with its 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “2022 Proxy Statement”), as set forth below in accordance with General Instruction G(3) of Form 10-K.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K relating to directors and executive officers of Match Group is set forth in the sections entitled “Information Concerning Director Nominees and Other Board Members” and “Information Concerning Match Group Executive Officers Who Are Not Directors,” respectively, in the 2022 Proxy Statement. The information required by Item 406 of Regulation S-K relating to Match Group’s Code of Ethics is set forth under the caption “Part I-Item 1-Business-Additional Information-Code of ethics” of this annual report and is incorporated herein by reference. The information required by subsections (c)(3), (d)(4) and (d)(5) of Item 407 of Regulation S-K is set forth in the sections entitled “Corporate Governance” and “The Board and Board Committees” in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by Item 402 of Regulation S-K relating to executive and director compensation is set forth in the sections entitled “Executive Compensation” and “Director Compensation” in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The information required by subsections (e)(4) and (e)(5) of Item 407 of Regulation S-K relating to certain compensation committee matters is set forth in the sections entitled “The Board and Board Committees,” “Compensation Committee Report” and “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference; provided, that the information set forth in the section entitled “Compensation Committee Report” shall be deemed furnished herein and shall not be deemed incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information regarding ownership of Match Group common stock required by Item 403 of Regulation S-K and securities authorized for issuance under Match Group’s various equity compensation plans required by Item 201(d) of Regulation S-K is set forth in the sections entitled “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information,” respectively, in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Information regarding certain relationships and related transactions involving Match Group required by Item 404 of Regulation S-K and director independence determinations required by Item 407(a) of Regulation S-K is set forth in the sections entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions” and “Corporate Governance,” respectively, in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
Information required by Item 9(e) of Schedule 14A regarding the fees and services of Match Group’s independent registered public accounting firm and the pre-approval policies and procedures applicable to services provided to Match Group by such firm is set forth in the sections entitled “Fees Paid to Our Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” and “Audit and Non-Audit Services Pre-Approval Policy,” respectively, in the 2022 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) List of documents filed as part of this Report:
(1) Consolidated Financial Statements of Match Group, Inc.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm: Ernst & Young LLP (PCAOB ID: 42).
Consolidated Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Consolidated Statement of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019.
Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019.
Consolidated Statement of Shareholders’ Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019.
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 2020, and 2019.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
(2) Consolidated Financial Statement Schedule of Match Group, Inc. | | | | | | | | |
| | |
Schedule
Number | | |
| II | | Valuation and Qualifying Accounts. |
All other financial statements and schedules not listed have been omitted since the required information is either included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or the notes thereto, is not applicable or is not required.
(3) Exhibits
See Exhibit Index below for a complete list of Exhibits to this report.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
EXHIBIT INDEX
The documents set forth below, numbered in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K, are filed herewith, incorporated by reference herein by reference to the location indicated, or furnished herewith. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | Filed (†) or
Furnished (‡)
Herewith
(as indicated) |
Exhibit
No. | | Exhibit Description | | Form | | SEC
File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing
Date | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 2.1 | | 12/20/2019 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 2.1 | | 4/28/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 2.1 | | 6/22/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 2.1 | | 2/10/2021 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-34148 | | 2.1 | | 8/6/2021 | | |
| | | | 8-A/A | | 000-20570 | | 3.1 | | 8/12/2005 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.1 | | 8/22/2008 | | |
| | | | 8-A/A | | 001-34148 | | 3.4 | | 7/1/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-A/A | | 001-34148 | | 3.5 | | 7/1/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-A/A | | 001-34148 | | 3.6 | | 7/1/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-A/A | | 001-34148 | | 3.7 | | 7/1/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.5 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.6 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.7 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.8 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.9 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.10 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 3.2 | | 4/30/2021 | | |
| | | | 10-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.1 | | 2/25/2021 | | |
| | | | S-4/A | | 333-236420 | | 4.3 | | 4/28/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 4.1 | | 5/20/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 4.1 | | 10/6/2017 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | Filed (†) or
Furnished (‡)
Herewith
(as indicated) |
Exhibit
No. | | Exhibit Description | | Form | | SEC
File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing
Date | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.3 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 4.1 | | 5/28/2019 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.5 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 000-20570 | | 4.2 | | 5/28/2019 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.7 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 4.1 | | 12/4/2017 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.9 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 4.1 | | 5/20/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.11 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 4.1 | | 2/15/2019 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.13 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 4.1 | | 2/11/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.15 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 4.1 | | 10/5/2021 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.1 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-34148 | | 10.1 | | 8/6/2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | Filed (†) or
Furnished (‡)
Herewith
(as indicated) |
Exhibit
No. | | Exhibit Description | | Form | | SEC
File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing
Date | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-34148 | | 10.1 | | 11/8/2021 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.2 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.3 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | S-4/A | | 333-236420 | | Annex F | | 4/28/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 6/21/2018 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.5 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 11/9/2017 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-37636 | | 10.2 | | 11/9/2017 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-34148 | | 10.2 | | 5/7/2021 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.5 | | 11/24/2015 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 8/4/2017 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.10 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 10-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.7 | | 2/28/2017 | | |
| | | | 10-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.8 | | 2/28/2017 | | |
| | | | 10-Q | | 001-34148 | | 10.2 | | 8/6/2021 | | |
| | | | 8-K/A | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 2/20/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.14 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 8/14/2018 | | |
| | | | 8-K/A | | 001-37636 | | 10.2 | | 2/20/2020 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.17 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | Filed (†) or
Furnished (‡)
Herewith
(as indicated) |
Exhibit
No. | | Exhibit Description | | Form | | SEC
File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing
Date | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.2 | | 8/14/2018 | | |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.19 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | † |
| | | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.1 | | 10/27/2020 | | |
| | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of November 16, 2015, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto | | 10-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.11 | | 3/28/2016 | | |
| | Amendment No. 3, dated as of December 8, 2016, to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended and restated as of November 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 16, 2015, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 12/8/2016 | | |
| | Amendment No. 4, dated as of August 14, 2017, to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended and restated as of November 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 8, 2016, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 8/17/2017 | | |
| | Amendment No. 5 dated as of December 7, 2018 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended and restated as of November 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 8, 2016, and as further amended as of August 14, 2017, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and the other parties thereto | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 12/13/2018 | | |
| | Amendment No. 6 dated as of February 13, 2020 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended and restated as of November 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 8, 2016, as further amended as of August 14, 2017 and as further amended as of December 7, 2018, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and the other parties thereto | | 8-K | | 001-37636 | | 10.1 | | 2/20/2020 | | |
| | Joinder and Reaffirmation Agreement, dated as June 30, 2020, by and among Match Group, Inc., Match Group Holdings II, LLC, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of November 16, 2015, among Match Group, Inc. (Former Match Group), as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the other parties thereto, as amended | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.25 | | 7/2/2020 | | |
| | Amendment No. 7 dated as of March 26, 2021 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 7, 2015, as amended and restated as of November 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 16, 2015, as further amended as of December 8, 2016, as further amended as of August 14, 2017, as further amended as of December 17, 2018 and as further amended as of February 13, 2020, among Match Group Holdings II, LLC, as borrower, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and the other parties thereto | | 8-K | | 001-34148 | | 10.1 | | 3/31/2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Incorporated by Reference | | Filed (†) or
Furnished (‡)
Herewith
(as indicated) |
Exhibit
No. | | Exhibit Description | | Form | | SEC
File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing
Date | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | † |
| | | | | | | | | | | | † |
| | | | | | | | | | | | † |
| | | | | | | | | | | | † |
| | | | | | | | | | | | ‡ |
| | | | | | | | | | | | ‡ |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | | | | | | | | | | † |
| 101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | † |
| 101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | † |
| 101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | † |
| 101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | † |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) | | | | | | | | | | |
______________________
(1)Reflects management contracts and management and director compensatory plans.
* Certain schedules and exhibits to the Transaction Agreement have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K. The Company hereby agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any omitted schedule and/or exhibit to the SEC upon request.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| February 24, 2022 | | MATCH GROUP, INC. |
| | | By: | | /s/ GARY SWIDLER |
| | | | Gary Swidler |
| | | | Chief Operating Officer and Chief Financial Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities indicated on February 24, 2022: | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title |
| | | |
| /s/ SHARMISTHA DUBEY | | Chief Executive Officer and Director
(Principal Executive Officer) |
| Sharmistha Dubey | | |
| | |
| /s/ GARY SWIDLER | | Chief Operating Officer and Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer) |
| Gary Swidler | | |
| | |
| /s/ PHILIP D. EIGENMANN | | Chief Accounting Officer
(Principal Accounting Officer) |
| Philip D. Eigenmann | | |
| | |
| /s/ THOMAS J. McINERNEY | | Chairman of the Board |
| Thomas J. McInerney | | |
| | |
| /s/ STEPHEN BAILEY | | Director |
| Stephen Bailey | | |
| | |
| /s/ MELISSA BRENNER | | Director |
| Melissa Brenner | | |
| | |
| /s/ JOSEPH LEVIN | | Director |
| Joseph Levin | | |
| | |
| /s/ ANN L. McDANIEL | | Director |
| Ann L. McDaniel | | |
| | |
| /s/ WENDI MURDOCH | | Director |
| Wendi Murdoch | | |
| | |
| /s/ RYAN REYNOLDS | | Director |
| Ryan Reynolds | | |
| | |
| /s/ GLENN H. SCHIFFMAN | | Director |
| Glenn H. Schiffman | | |
| | |
| /s/ PAMELA S. SEYMON | | Director |
| Pamela S. Seymon | | |
| | |
| /s/ ALAN G. SPOON | | Director |
| Alan G. Spoon | | |
Schedule II
MATCH GROUP, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Description | Balance at
Beginning of Period | | Charges to
Earnings | | Charges to
Other Accounts | | Deductions | | Balance at
End of Period |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | (In thousands) |
| 2021 | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | $ | 286 | | | $ | 43 | | (a) | $ | (2) | | | $ | (46) | | (d) | $ | 281 | |
| Deferred tax valuation allowance | 71,090 | | | 15,969 | | (b) | (988) | | (f) | — | | | 86,071 | |
| Other reserves | 3,380 | | | | | | | | | 8,499 | |
| 2020 | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 578 | | | $ | (22) | | (a) | $ | (234) | | | $ | (36) | | (d) | $ | 286 | |
| Deferred tax valuation allowance | 52,913 | | | 35,261 | | (b) | (17,084) | | (c) | — | | | 71,090 | |
| Other reserves | 2,901 | | | | | | | | | 3,380 | |
| 2019 | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 724 | | | $ | 79 | | (a) | $ | (8) | | | $ | (217) | | (d) | $ | 578 | |
| Deferred tax valuation allowance | 45,483 | | | 7,472 | | (e) | (42) | | (f) | — | | | 52,913 | |
| Other reserves | 3,008 | | | | | | | | | 2,901 | |
______________________
(a)Additions to the allowance for credit losses and doubtful accounts are charged to expense, net of the recovery of previous year expenses.
(b)Amount is primarily related to foreign tax credits, foreign net operating losses, and foreign interest deductions.
(c)Amount is primarily related to a reduction in the valuation allowance as a result of the preliminary allocation of tax attributes between Match Group and IAC in conjunction with the Separation.
(d)Write-off of fully reserved accounts receivable.
(e)Amount is primarily related to foreign and state net operating losses and foreign interest deduction carryforwards.
(f)Amount is related to currency translation adjustments on foreign net operating losses.




