UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| x |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2017 OR |
|
| ¨ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ________ to ________ |
|
Commission File Number: 1-10883
|
WABASH NATIONAL CORPORATION (Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
||||
|
Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization)
1000 Sagamore Parkway South Lafayette, Indiana (Address of Principal Executive Offices) |
 |
52-1375208 (IRS Employer Identification Number)
47905 (Zip Code)
| ||
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (765) 771-5300
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $.01 Par Value | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer ¨ |
| Non-accelerated filer ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
| Emerging growth company ¨ | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2017 was $1,267,688,443 based upon the closing price of the Company's common stock as quoted on the New York Stock Exchange composite tape on such date.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant's common stock as of February 16, 2018 was 57,650,183.
Part III of this Form 10-K incorporates by reference certain portions of the registrant’s Proxy Statement for its Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed within 120 days after December 31, 2017.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
WABASH NATIONAL CORPORATION
FORM 10-K FOR THE FISCAL
YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017
| 2 |
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report of Wabash National Corporation (together with its subsidiaries, “Wabash,” “Company,” “us,” “we,” or “our”) contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”). Forward-looking statements may include the words “may,” “will,” “estimate,” “intend,” “continue,” “believe,” “expect,” “plan” or “anticipate” and other similar words. Our “forward-looking statements” include, but are not limited to, statements regarding:
| · | our business plan; |
| · | our ability to effectively integrate Supreme and realize expected synergies and benefits from the Supreme acquisition; |
| · | our expected revenues, income or loss; |
| · | our ability to manage our indebtedness; |
| · | our strategic plan and plans for future operations; |
| · | financing needs, plans and liquidity, including for working capital and capital expenditures; |
| · | our ability to achieve sustained profitability; |
| · | reliance on certain customers and corporate relationships; |
| · | availability and pricing of raw materials; |
| · | availability of capital and financing; |
| · | dependence on industry trends; |
| · | the outcome of any pending litigation or notice of environmental dispute; |
| · | export sales and new markets; |
| · | engineering and manufacturing capabilities and capacity; |
| · | our ability to develop and commercialize new products; |
| · | acceptance of new technologies and products; |
| · | government regulations; and |
| · | assumptions relating to the foregoing. |
Although we believe that the expectations expressed in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, actual results could differ materially from those projected or assumed in our forward-looking statements. Our future financial condition and results of operations, as well as any forward-looking statements, are subject to change and are subject to inherent risks and uncertainties, such as those disclosed in this Annual Report. Each forward-looking statement contained in this Annual Report reflects our management’s view only as of the date on which that forward-looking statement was made. We are not obligated to update forward-looking statements or publicly release the result of any revisions to them to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this Annual Report or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law.
Currently known risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations are described throughout this Annual Report, including in “Item 1A. Risk Factors.” We urge you to carefully review that section for a more complete discussion of the risks of an investment in our securities.
| 3 |
Overview
Wabash National Corporation (together with its subsidiaries, “Wabash,” “Wabash National,” “the Company,” “us,” “we,” or “our”) was founded in 1985 as a start-up company in Lafayette, Indiana. We are now a diversified industrial manufacturer and a leading producer of semi-trailers, truck bodies, specialized commercial vehicles, and liquid transportation systems. We design, manufacture and market a diverse range of products, including dry freight and refrigerated trailers, platform trailers, bulk tank trailers, dry and refrigerated truck bodies, truck-mounted tanks, intermodal equipment, aircraft refueling equipment, structural composite panels and products, trailer aerodynamic solutions, and specialty food grade and pharmaceutical equipment. We have achieved this diversification through acquisitions and product innovation. We continue to search for acquisitions that will increase margins, enhance business stability, create new products, reduce cyclicality, and provide operational synergies.
We believe our position as a leader in our key industries is the result of longstanding relationships with our core customers, our demonstrated ability to attract new customers, our broad and innovative product lines, our technological leadership, and our extensive distribution and service network. Our management team is focused on growing the company in a profitable and sustainable manner, while continuing to optimize operations to match the current demand environment, implementing cost savings initiatives and lean manufacturing techniques, strengthening our capital structure, developing innovative products that enable our customers to succeed, improving earnings and continuing diversification of the business into higher margin opportunities that leverage our intellectual and process capabilities.
Wabash was incorporated in Delaware in 1991 and is the successor by merger to a Maryland corporation organized in 1985. Our internet website is www.wabashnational.com. We make our electronic filings with the Securities Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), including our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports available on our website free of charge as soon as practicable after we file them with or furnish them to the SEC. Information on the website is not part of this Annual Report. We are listed on the NYSE under the ticker symbol “WNC”.
Operating Segments
Previously, we managed our business in two segments: Commercial Trailer Products and Diversified Products. In the third quarter of 2017, we completed the acquisition of Supreme Industries, Inc. (“Supreme”). As a result, we created a new reporting segment in the fourth quarter referred to as the Final Mile Products segment, which includes the Supreme operations and certain other truck body operations which were previously included in our Commercial Trailer Products segment. Certain corporate-related administrative costs, interest and income taxes are not allocated to these segments, but are reported in our Corporate and Eliminations segment. Financial results by operating segment, including information about revenue, measures of profit and loss, and financial information regarding geographic areas and export sales are discussed in Note 13, Segments, of the accompanying consolidated financial statements. By operating segment, net sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, were as follows (dollars in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Sales by Segment | ||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | $ | 1,348,382 | $ | 1,506,110 | $ | 1,582,240 | ||||||
| Diversified Products Group | 361,358 | 352,404 | 456,927 | |||||||||
| Final Mile Products | 70,461 | - | - | |||||||||
| Corporate and Eliminations | (13,040 | ) | (13,070 | ) | (11,679 | ) | ||||||
| Total | $ | 1,767,161 | $ | 1,845,444 | $ | 2,027,488 | ||||||
| 4 |
Commercial Trailer Products
Commercial Trailer Products segment sales as a percentage of our consolidated net sales and gross margin measured prior to intersegment eliminations were:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Percentage of net sales | 75.7 | % | 81.0 | % | 77.6 | % | ||||||
| Percentage of gross profit | 70.1 | % | 77.0 | % | 64.9 | % | ||||||
The Commercial Trailer Products segment manufactures standard and customized dry van, refrigerated van, and platform trailers and other transportation related equipment to customers who purchase directly from us or through independent dealers. We have been one of largest producers of van trailers in North America since 1994, with one of the most widely recognized brands in the industry. We seek to identify and produce proprietary custom products that offer exceptional value to customers with the potential to generate higher profit margin than standardized products. We believe that we have the engineering and manufacturing capability to produce these products efficiently. We introduced our proprietary composite product, DuraPlateâ, in 1996 and have experienced widespread truck trailer industry acceptance. Since 2002, sales of our DuraPlateâ trailers have represented approximately 95% of our total new dry van trailer sales. We are a significant producer of refrigerated trailer products as well as other specialty products, including converter dollies. Through our Transcraft subsidiary we are of the one the leading producers of steel and aluminum flatbed and dropdeck trailers. Our Commercial Trailer Products segment also operates a wood flooring production facility that manufactures laminated hard wood oak products for our van trailer products.
Commercial Trailer Products’ transportation equipment is marketed under the Wabashâ, DuraPlateâ, DuraPlateHDâ, DuraPlateâ XD-35®, ArcticLite®, RoadRailer®, Transcraft® and Benson® trademarks directly to customers and through independent dealers. Historically, we have focused on our longstanding core customers representing many of the largest companies in the trucking industry, but have expanded this focus over the past several years to include numerous additional key accounts. Our relationships with our core customers have been central to our growth since inception. We have also actively pursued the diversification of our customer base through our network of independent dealers. For our van business we utilize a total of 27 independent dealers with approximately 73 locations throughout North America to market and distribute our trailers. We distribute our flatbed and dropdeck trailers through a network of 75 independent dealers with approximately 124 locations throughout North America. In addition, we maintain a used fleet sales center to focus on selling both large and small fleet trade packages to the wholesale market.
Diversified Products
Diversified Products segment sales as a percentage of our consolidated net sales and gross margin measured prior to intersegment eliminations were:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Percentage of net sales | 20.3 | % | 19.0 | % | 22.4 | % | ||||||
| Percentage of gross profit | 26.8 | % | 23.0 | % | 35.1 | % | ||||||
| 5 |
The Diversified Products segment is comprised of four strategic business units: Tank Trailer, Process Systems, Composites, and Aviation & Truck Equipment, The Tank Trailer business sells products through several brands including Walker Transport, Brenner® Tank, Bulk International and Beall® Trailers. These brands represent leading positions in liquid transportation systems and include a full line of stainless steel and aluminum tank trailers for the North American chemical, dairy, food and beverage, and petroleum and energy services markets. Our Process Systems business includes brands such as Walker® Engineered Products and Extract Technology® and represent what we estimate to be leading positions in isolators, stationary silos and downflow booths around the world for the chemical, dairy, food and beverage, pharmaceutical and nuclear markets. The Aviation & Truck Equipment business is a leading manufacturer of truck-mounted tanks used in the aviation, refined fuel, heating oil, propane and liquid waste industries with products offered under the Garsite and Progress Tank brands. Our Composites business includes offerings under our DuraPlate® composite panel technology, which contains unique properties of strength and durability that can be utilized in numerous applications in addition to truck trailers and truck bodies. The Diversified Products segment has leveraged our DuraPlate® panel technology to develop numerous proprietary products, including a full line of aerodynamic solutions designed to improve overall trailer aerodynamics and fuel economy, most notably the DuraPlate® AeroSkirt®, AeroSkirt CX™, Ventix DRSTM and AeroFinTM. In addition, we utilize our DuraPlate® technology in the production of truck bodies, overhead doors, foldable portable storage containers, truck boxes, decking systems, and other industrial applications. These DuraPlate® composite products are sold to original equipment manufacturers and aftermarket customers.
The Diversified Products segment focuses on our commitment to expand our customer base, diversify our product offerings, end markets and revenues, and extend our market leadership by leveraging our intellectual property and technology, including our proprietary DuraPlate® panel technology, drawing on our core manufacturing expertise and making available products that are complementary to the truck and tank trailers and transportation equipment we offer. This segment includes a wide array of products and customer-specific solutions. Leveraging our intellectual property and technology and core manufacturing expertise into new applications and market sectors enables us to deliver greater value to our customers and shareholders.
Through these brands and product offerings, our Diversified Products segment now serves a variety of end markets. We expect to continue to focus on diversifying our Diversified Products segment to enhance our business model, strengthen our revenues and become a more diverse company that can deliver greater value to our shareholders.
Final Mile Products
Final Mile Products segment was established after completing the Supreme acquisition on September 27, 2017. Since this date, Final Mile Products segment sales as a percentage of our consolidated net sales and gross margin measured prior to intersegment eliminations were:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||
| 2017 | ||||
| Percentage of net sales | 4.0 | % | ||
| Percentage of gross profit | 3.1 | % | ||
Supreme is one of the nation’s leading manufacturers of specialized commercial vehicles, including cutaway and dry-freight van bodies, refrigerated units, and stake bodies. This acquisition allows us to accelerate our growth and expand our presence in the final mile space, with increased distribution paths and greater customer reach, and supports our objective to transform our business into a more diversified industrial manufacturer. Final Mile Product truck bodies are offered in aluminum, FiberPanel PW, FiberPanel HC, or DuraPlate®, and are marketed under Kold King®, Iner-City®, Spartan, as well as other Wabash brands that leverage our fleet-proven DuraPlate® technology utilized in dry van trailers. Our Final Mile Products also include our molded structural composite panels. With the acquisition of Supreme, our truck body line was expanded to include Classes 2 through 5, allowing us to serve a large variety of end customers in the final mile space. The dealer and distributor network for truck bodies consists of more than 1,000 commercial dealers and a limited number of truck equipment distributors.
Strategy
In addition to our commitment to long-term profitable growth within each of our reporting segments, our strategic initiatives include a focus on diversification efforts, both organic and strategic, to further transform Wabash into a diversified industrial manufacturer with a higher growth and margin profile and successfully deliver greater value to our shareholders. Organically, our focus is on profitably growing and diversifying our operations by leveraging our existing assets, capabilities, and technology into higher margin products and markets and thereby providing value-added customer solutions. Strategically, we continue to focus on our transition into a more diversified industrial manufacturer, profitably growing and further broadening the product portfolio we offer, the customers and end markets we serve and strengthening our geographic presence. In addition to our acquisition of Supreme, future acquisitions may further provide us the opportunity to move forward on this strategic initiative and our long-term plan to become a more diversified industrial manufacturer. Our most recent acquisitions have enabled us to recognize top-line growth, improved profitability, and margin expansion; provided us access to additional markets while expanding our manufacturing footprint; and allowed us to offer one of the broadest product portfolios in the transportation equipment industry.
| 6 |
Industry and Competition
Trucking in the U.S., according to the American Trucking Association (ATA), was estimated to be a $676 billion industry in 2016, representing approximately 80% of the total U.S. transportation industry revenue. Furthermore, ATA estimates that approximately 71% of all freight tonnage in 2016 was carried by trucks. Trailer demand is directly impacted by the amount of freight to be transported. ATA estimates that total freight tonnage carried by trucks will grow 34% by 2028. To meet this continued high demand for freight, truck carriers will need to replace and expand their fleets, which typically results in increased trailer orders.
Transportation in the U.S., including trucking, is a cyclical industry that has experienced three cycles over the last 20 years. In each of the last three cycles the decline in freight tonnage preceded the general U.S. economic downturn by approximately two and one-half years and the recovery has generally preceded that of the economy as a whole. The trailer industry generally follows the transportation industry, experiencing cycles in the early and late 90’s lasting approximately 58 and 67 months, respectively. Truck freight tonnage, according to ATA statistics, started declining year-over-year in 2006 and remained at depressed levels through 2009. The most recent cycle concluded in 2009, lasting a total of 89 months. After three consecutive years with total trailer demand well below normal replacement demand levels estimated to be approximately 220,000 trailers, the period ending December 2017 demonstrated five consecutive years of healthy demand in which it is estimated there were total trailer shipments of approximately 234,000, 269,000, 308,000, 286,000, and 287,000 for the years ended 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively. We expect to see continued strong demand for new trailer equipment as the economic and industry specific indicators we track, including ATA’s truck tonnage index, employment growth, housing and auto sectors, as well as the overall gross domestic product, appear to be trending in a positive direction.
Wabash, Great Dane, Utility and Hyundai Translead, are generally viewed as the top manufacturers in U.S. trailer shipments by volume. Our share of U.S. total trailer shipments in 2017 was approximately 19%. Trailer manufacturers compete primarily through the quality of their products, customer relationships, innovative technology, and price. We have seen others in the industry also pursue the development and use of composite sidewalls that compete directly with our DuraPlateâ products. Our product development is focused on maintaining a leading position with respect to these products and on development of new products and markets, leveraging our proprietary DuraPlate® product, as well as our expertise in the engineering and design of customized products.
The table below sets forth new trailers shipped for Wabash and, as provided by Trailer Body Builders Magazine, the principal producers within North America. The data represents all segments of the industry, except containers and chassis. For the years included below, we have participated primarily in the van, platform, and tank trailer segments. Van trailer demand, the largest segment within the trailer industry, has recovered from a low of approximately 52,000 trailers in 2009 to an estimated 223,000 van trailers in 2017.
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Wabash | 54,000 | 60,000 | 63,000 | 56,000 | 46,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Hyundai Translead | 58,000 | 49,000 | 43,000 | 34,000 | 27,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Great Dane | 46,000 | 48,000 | 52,000 | 48,000 | 44,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Utility | 43,000 | 46,000 | 49,000 | 41,000 | 39,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Stoughton | 15,000 | 16,000 | 15,000 | 13,000 | 12,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Other principal producers | 32,000 | 33,000 | 40,000 | 37,000 | 31,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Total Industry | 282,000 | 283,000 | 302,000 | 265,000 | 232,000 | (1) | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Data revised by publisher in a subsequent year. |
Our Diversified Products segment, in most cases, participates in markets different than our traditional van and platform trailer product offerings. The end markets that our Diversified Products segment serve are broader and more diverse than the trailer industry, including environmental, pharmaceutical, biotech, oil and gas, moving and storage, and specialty vehicle markets. In addition, our diversification efforts pertain to new and emerging markets and many of the products are driven by regulatory requirements or, in most cases, customer-specific needs. However, some of our diversification efforts are considered to be in the early growth stages and future success is largely dependent on continued customer adoption of our product solutions and general expansion of our customer base and distribution channels.
| 7 |
Our Final Mile Products segment competes in the specialized vehicle industry, which is highly competitive with only a few national competitors and many smaller, regional companies. As a result of this broad competition, we are often faced with competitive pricing pressures. Other competitive factors include quality of product, lead times, geographic proximity to customers, and the ability to manufacture a product customized to customer specifications. With our national presence and diverse product offerings, we believe that we are well positioned to meet the competitive challenges presented.
Competitive Strengths
We believe our core competitive strengths include:
| · | Long-Term Core Customer Relationships – We are the leading provider of trailers to a significant number of top tier trucking companies, generating a revenue base that has helped to sustain us as one of the market leaders. Our van products are preferred by many of the industry’s leading carriers. We are also a leading provider of liquid-transportation systems and engineered products and we have a strong customer base, consisting of mostly private fleets, and have earned a leading market position across many of the markets we serve. In addition, we are a leading manufacturer of truck bodies, and we have a strong customer base of large national fleet leasing companies. |
| · | Technology and Innovation – We continue to be recognized by the trucking industry as a leader in developing technology to provide value-added solutions for our customers that reduce trailer operating costs, improve revenue opportunities, and solve unique transportation problems. Throughout our history, we have been and we expect we will continue to be a leading innovator in the design and production of trailers and related products. Recent new trailer introductions and value-added options include the introduction of the Molded Structural Composite (MSCt) Refrigerated Van, the commercial launch of the Cold Chain Series Refrigerated Truck Body with molded structural composite technology, both offering advanced thermal and operational performance; Lean Duplex tank trailer, a stainless steel option that reduces weight while providing enhanced performance characteristics over typical chemical tank trailers; Trustlock Plus®, a proprietary single-lock rear door mechanism; and the DuraPlate® AeroSkirt®, Ventix DRSTM, AeroFinTM and AeroSkirt CXTM, durable aerodynamic solutions that, based on verified laboratory and track testing, provides improved fuel efficiencies of 9% or greater when used in specific combinations. |
Our DuraPlateâ proprietary technology offers what we believe to be a superior trailer, which customers value. A DuraPlateâ trailer is a composite plate trailer using material that contains a high-density polyethylene core bonded between high-strength steel skins. We believe that the competitive advantages of our DuraPlateâ trailers compared to standard trailers include providing a lower total cost of ownership through the following:
- Extended Service Life – operate three to five years longer;
- Lower Operating and Maintenance Costs – greater durability and performance;
- Less Downtime – higher utilization for fleets;
- Extended Warranty – warranty period for DuraPlateâ panels is ten years; and
- Improved Resale Value – higher trade-in and resale values.
We have been manufacturing DuraPlateâ trailers for over 22 years and through December 2017 have sold approximately 700,000 DuraPlate® trailers. We believe that this proven experience, combined with ownership and knowledge of the DuraPlateâ panel technology, will help ensure continued industry leadership in the future.
| 8 |
We have also focused on a customer-centered approach in developing product enhancements for other industries we serve. Some of the more recent innovations include: the development of mobile clean rooms, or self-contained laboratories, which are configured to provide isolation and containment solutions into a rapidly deployable and flexible manufacturing facility for pharmaceutical and other technology applications; the development of a Refined Fuel truck with integrated Auxiliary Power Unit designed to improve fuel efficiency and prolong the useful operating life of fuel delivery vehicles; introduction of a prototype Side Impact Guard (SIG) designed to prevent passenger car under ride in side collisions, introduction of advanced materials to remove over 300 pounds from the standard Dry Van; introduction of RIG-16 offset rear under ride guard, and the introduction of the Truck Body line leveraging our fleet-proven DuraPlate® technology for dry truck bodies as well as the introduction of a revolutionary proprietary composite designed to improve weight and thermal efficiency in refrigerated truck body applications. We will also be introducing a new modified core DuraPlate to remove 300 pounds from a dry van trailer in 2018. This will allow us to continue providing unrivaled value to our customers and differentiate Wabash from our competitors.
| · | Significant Market Share and Brand Recognition – We have been one of the three largest manufacturers of trailers in North America since 1994, with one of the most widely recognized brands in the industry. We are currently one of the largest producers of van trailers in North America and, according to data published by Trailer Body Builders Magazine, our Transcraft subsidiary is one of the leading producers of platform trailers. We are also the largest manufacturer of liquid stainless steel and aluminum tank trailers in North America through our Walker Transport, Brenner® Tank, Bulk International and Beall® brands. In addition, we are the second largest manufacturer of truck bodies in North America through our Supreme, Iner-City®, Spartan, and Kold King® brands. We participate broadly in the transportation industry through all of our business segments. As a percentage of our consolidated net sales, new trailer sales for our dry and refrigerated vans, platforms and tanks represented approximately 80% in 2017. |
| · | Committed Focus on Operational Excellence – Safety, quality, on-time delivery, productivity and cost reduction are the core elements of our program of continuous improvement. We currently maintain an ISO 14001 registration of the Environmental Management System at our Lafayette, Indiana; Cadiz, Kentucky; San Jose Iturbide, Mexico; Frankfort, Indiana; and Harrison, Arkansas facilities. In addition, we have achieved ISO 9001 registration of the Quality Management Systems at our Lafayette, Indiana and Cadiz, Kentucky facilities. |
| · | Corporate Culture – We benefit from an experienced, value-driven management team and dedicated workforce focused on operational excellence. Safety of our associates is our number one value and highest priority. |
| · | Extensive Distribution Network – We utilize a network of 27 independent dealers with approximately 73 locations throughout North America to distribute our van trailers, and our Transcraft distribution network consists of 75 independent dealers with approximately 124 locations throughout North America. Our tank trailers are distributed through a network of 58 independent dealers with 59 locations throughout North America. Additionally, our truck body dealer network consists of more than 1,000 commercial dealers. Our dealers primarily serve mid-market and smaller sized carriers and private fleets in the geographic region where the dealer is located and occasionally may sell to large fleets. |
Regulation
Truck trailer length, height, width, maximum weight capacity and other specifications are regulated by individual states. The federal government also regulates certain safety and environmental sustainability features incorporated in the design and use of truck and tank trailers, as well as truck bodies. These regulations include, requirements to install Electronic Logging Devices, the use of aerodynamic devices and fuel saving technologies, as well as operator restrictions as to hours of service and minimum driver safety standards (see the section on “Industry Trends” in Item 7 for more details on these regulations). In addition, most tank trailers we manufacture have specific federal regulations and restrictions that dictate tank design, material type and thickness. Manufacturing operations are subject to environmental laws enforced by federal, state and local agencies (see "Environmental Matters").
| 9 |
Products
Since our inception, we have expanded our product offerings from a single truck trailer dry van product to a broad range of transportation equipment and diversified industrial products. Wabash National manages a diverse product portfolio, maintains long-standing customer relationships, and focuses on innovative and breakthrough technologies within three operating segments.
Commercial Trailer Products segment sales represented approximately 76%, 81% and 78% of our consolidated net sales in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Our current Commercial Trailer Products segment primarily includes the following products:
| · | Dry Van Trailers. The dry van market represents our largest product line and includes trailers sold under DuraPlateâ, DuraPlateHDâ, and DuraPlate® XD-35® trademarks. Our DuraPlate® trailers utilize a proprietary technology that consists of a composite plate wall for increased durability and greater strength. |
| · | Platform Trailers. Platform trailers are sold under the Transcraft® and Benson® trademarks. Platform trailers consist of a trailer chassis with a flat or “drop” loading deck without permanent sides or a roof. These trailers are primarily utilized to haul steel coils, construction materials and large equipment. In addition to our all steel and combination steel and aluminum platform trailers, we also offer a premium all-aluminum platform trailer. |
| · | Refrigerated Trailers. Refrigerated trailers provide thermal efficiency, maximum payload capacity, and superior damage resistance. Our refrigerated trailers are sold under the ArcticLite® trademark and use our proprietary SolarGuard® technology, coupled with our foaming process, which we believe enables customers to achieve lower costs through reduced operating hours of refrigeration equipment and therefore reduced fuel consumption. In 2016, Wabash introduced a proprietary molded structural composite with thermal technology, which based on our testing provides improved thermal performance for refrigerated trailers by up to 25% and is up to 20% lighter than standard refrigerated trailers while still maintaining strength and durability. |
| · | Specialty Trailers. These products include a wide array of specialty equipment and services generally focused on products that require a higher degree of customer specifications and requirements. These specialty products include converter dollies, Big Tire Hauler, Steel Coil Hauler and RoadRailer® trailers. |
| · | Aftermarket Parts and Service. Aftermarket component products are manufactured to provide continued support to our customers throughout the life cycle of the trailer. Aurora Parts & Accessories, LLC is the exclusive supplier of the aftermarket component products for the company’s dry van, refrigerated and platform trailers. Utilizing our onsite service centers, we provide a wide array of quality aftermarket parts and services to our customers. Additionally, rail components are sold to provide continued support of the Road Railer® product line as well as to expand our offerings in the rail markets. |
| · | Used Trailers. These products includes the sale of used trailers through our used fleet sales center to facilitate new trailer sales with a focus on selling both large and small fleet trade packages to the wholesale market as well as through our branch network to enable us to remarket and promote new trailer sales. |
| · | Wood Products. We manufacture laminated hardwood oak flooring used primarily in our dry van trailer segment at our manufacturing operations located in Harrison, Arkansas. |
Diversified Products segment sales represented approximately 20%, 19% and 22% of our consolidated net sales in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Our current Diversified Products segment primarily includes the following products:
| · | Tank Trailers. Tank Trailers currently has several principal brands dedicated to transportation products including Walker Transport, Brenner® Tank, Bulk Tank International, and Beall® Trailers. Equipment sold under these brands include stainless steel and aluminum liquid and dry bulk tank trailers and other transport solutions for the dairy, food and beverage, chemical, environmental, petroleum and refined fuel industries. We also provide parts and maintenance and repair services for tank trailers and other related equipment through our six Brenner Tank Service centers. |
| 10 |
| - | Walker Transport – Founded as the original Walker business in 1943, the Walker Transport brand includes stainless steel tank trailers for the dairy, food and beverage end markets. |
| - | Brenner® Tank – Founded in 1900, Brenner® Tank manufactures stainless steel and aluminum tank trailers, dry bulk trailers, and fiberglass reinforced poly tank trailers, as well as vacuum tank trailers for the oil and gas, chemical, energy and environmental services end markets. |
| - | Bulk Tank International – Manufactures stainless steel tank trailers for the oil and gas and chemical end markets. |
| - | Beall® Trailers – With tank trailer production dating to 1928, the Beall® brand includes aluminum tank trailers and related tank trailer equipment for the dry bulk and petroleum end markets. |
| · | Process Systems. Process Systems currently sells products under the Walker Engineered Products and Extract Technology® brands and specializes in the design and production of a broad range of products including: a portfolio of products for storage, mixing and blending, including process vessels, as well as round horizontal and vertical storage silo tanks; containment and isolation systems for the pharmaceutical, chemical, and nuclear industries, including custom designed turnkey systems and spare components for full service and maintenance contracts; containment systems for the pharmaceutical, chemical and biotech markets; and mobile water storage tanks used in the oil and gas industry to pump high-pressure water into underground wells. |
| - | Walker Engineered Products – Since the 1960s, Walker has marketed stainless steel storage tanks and silos, mixers, and processors for the dairy, food and beverage, pharmaceutical, chemical, craft brewing, and biotech end markets under the Walker Engineered Products brand. |
| - | Extract Technology® – Since 1981, the Extract Technology® brand has included stainless steel isolators and downflow booths, as well as custom-fabricated equipment, including workstations and drum booths for the pharmaceutical, fine chemical, biotech and nuclear end markets. |
| · | Aviation & Truck Equipment. Aviation & Truck Equipment currently sells products under the Garsite and Progress Tank brands, which are dedicated to serving aircraft refuelers and hydrant dispensers for in-to-plane fueling companies, airlines, freight distribution companies and fuel marketers around the globe; military grade refueling and water tankers for applications and environments required by the military; truck mounted tanks for fuel delivery; and vacuum tankers. |
| - | Progress Tank – Since 1920, the Progress Tank brand has included aluminum and stainless steel truck-mounted tanks for the oil and gas and environmental end markets. |
| - | Garsite – Founded in 1952, Garsite is a value-added assembler of aircraft refuelers, hydrant dispensers, and above-ground fuel storage tanks for the aviation end market. |
| · | Composites. Our composite products expand the use of DuraPlate® composite panels, already a proven product in the semi-trailer market for over 20 years. Other composite product offerings include truck bodies, overhead doors, foldable portable storage containers, and other industrial applications. We continue to develop new products and actively explore markets that can benefit from the proven performance of our proprietary technology. In 2016, we entered into a collaboration with EconCore N.V. to manufacture and sell their patented honeycomb core production technology in the containment and transportation industries. We offer three solutions designed to significantly improve trailer aerodynamics and fuel economy featuring a trailer drag reduction system to manage airflow across the entire length of trailer, or Ventix DRSTM, an aerodynamic tail devised to direct airflow across the rear of the trailer, or AeroFinTM, and a new lighter version of our AeroSkirt design called AeroSkirt CXTM. We also offer our EPA Smartway®approved DuraPlate® AeroSkirt®. |
| 11 |
The Final Mile Products segment, established after the acquisition of Supreme, had 2017 sales representing approximately 4% of our consolidated net sales in 2017. The Final Mile Products segment primarily includes the following products:
| · | Signature Van Bodies. Signature van bodies range from 10 to 28 feet in length with exterior walls assembled from one of several material options including pre-painted aluminum, FiberPanel PW, FiberPanel HC, or DuraPlate®. Additional features include molded composite front and side corners, LED marker lights, sealed wiring harnesses, hardwood or pine flooring, and various door configurations to accommodate end-user loading and unloading requirements. This product is adaptable for a diverse range of uses in dry-freight transportation. |
| · | Iner-City® Cutaway Van Bodies. An ideal route truck for a variety of commercial applications, the Iner-City bodies are manufactured on cutaway chassis which allow access from the cab to the cargo area. Borrowing many design elements from Supreme’s larger van body, the Iner-City is shorter in length (10 to 18 feet) than a typical van body. |
| · | Spartan Service Bodies. Built on a cutaway chassis and constructed of FiberPanel PW, the Spartan cargo van provides the smooth maneuverability of a commercial van with the full-height and spacious cargo area of a truck body. In lengths of 10 to 14 feet and available with a variety of pre-designed options, the Spartan cargo van is a bridge product for those moving up from a traditional cargo van into the truck body category. |
| · | Kold King® Insulated Van Bodies. Kold King insulated bodies, in lengths up to 28 feet, provide versatility and dependability for temperature controlled applications. Flexible for either hand-load or pallet-load requirements, they are ideal for multi-stop distribution of both fresh and frozen products. |
| · | Stake Bodies. Stake bodies are flatbeds with various configurations of removable sides. The stake body is utilized for a broad range of agricultural and construction industries transportation needs. |
| · | Final Mile Series and Cold Chain Series. Introduced in 2015, we have combined fleet-proven equipment designs and advanced materials to create a line of high performance refrigerated and dry freight truck bodies for Class 6, 7, and 8 chassis. The truck body product leverages our fleet-proven DuraPlate® technology utilized in dry van trailers and also introduces a revolutionary proprietary molded structural composite designed to improve weight and thermal efficiency in refrigerated truck body applications. |
Customers
Our customer base has historically included many of the nation’s largest truckload (TL) common carriers, leasing companies, private fleet carriers, less-than-truckload (LTL) common carriers and package carriers. We continue to expand our customer base and diversify into the broader trailer market through our independent dealer and company-owned retail networks, as well as through strategic acquisitions. Furthermore, we continue to diversify our products organically by expanding the use of DuraPlate® composite panel technology through products such as DuraPlate® AeroSkirts®, truck bodies, overhead doors and portable storage containers as well as strategically through our acquisitions. All of these efforts have been accomplished while maintaining our relationships with our core customers. Our five largest customers together accounted for approximately 24%, 24% and 25% of our aggregate net sales in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. No individual customer accounted for more than 10% or more of our aggregate net sales during the past three years. International sales accounted for less than 10% of net sales for each of the last three years.
We have established relationships as a supplier to many large customers in the transportation industry, including the following:
| · | Truckload Carriers: Averitt Express, Inc.; Celadon Group, Inc.; Covenant Transportation Group, Inc.; Cowan Systems, LLC; Crete Carrier Corporation; Heartland Express, Inc.; J.B Hunt Transport, Inc.; Knight Transportation, Inc.; Schneider National, Inc.; Swift Transportation Corporation; U.S. Xpress Enterprises, Inc.; and Werner Enterprises, Inc. |
| 12 |
| · | Less-Than-Truckload Carriers: FedEx Corporation; Old Dominion Freight Lines, Inc.; R&L Carriers Inc.; Saia, Inc.: and YRC Worldwide, Inc. |
| · | Refrigerated Carriers: CR England, Inc.; K&B Transportation, Inc.; Prime, Inc.; and Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc. |
| · | Leasing Companies: Matlack Leasing; Penske Truck Leasing Company; Wells Fargo Equipment Finance, Inc.; and Xtra Lease, Inc. |
| · | Private Fleets: C&S Wholesale Grocers, Inc.; Dollar General Corporation; and Safeway, Inc. |
| · | Liquid Carriers: Dana Liquid Transport Corporation; Evergreen Tank Solutions LLC; Kenan Advantage Group, Inc.; Oakley Transport, Inc.; Quality Carriers, Inc.; Superior Tank, Inc.; and Trimac Transportation. |
Through our Diversified Products segment we also sell our products to several other customers including, but not limited to: Atlantic Aviation; GlaxoSmithKline Services Unlimited; W.M. Sprinkman; Dairy Farmers of America; Southwest Airlines Company; Nestlé; Matlack Leasing LLC; and Wabash Manufacturing, Inc. (an unaffiliated company)
Through our Final Mile Products segment we sell to fleet leasing customers and direct customers including, but not limited to: Budget Truck Rental, LLC; Enterprise Holdings, Inc.; Flowers Foods, Inc.; Penske Truck Leasing Company; Rent-A-Center; Ryder System, Inc.; and Southern Glazer’s Leasing, LLC.
Marketing and Distribution
We market and distribute our products through the following channels:
| · | Factory direct accounts; and |
| · | Independent dealerships. |
Factory direct accounts are generally large fleets that are high volume purchasers. Historically, we have focused on the factory direct market in which customers are highly knowledgeable of the life-cycle costs of equipment and, therefore, are best equipped to appreciate the innovative design and value-added features of our products, as well as the value proposition for lower total cost of ownership over the lifecycle of our products.
We also sell our van trailers through a network of 27 independent dealers with approximately 73 locations throughout North America. Our platform trailers are sold through 75 independent dealers with approximately 124 locations throughout North America. Our tank trailers are distributed through a network of 58 independent dealers with 59 locations throughout North America. Additionally, our truck body dealer network consists of more than 1,000 commercial dealers. Our dealers primarily serve mid-market and smaller sized carriers and private fleets in the geographic region where the dealer is located and occasionally may sell to large fleets. The dealers may also perform service and warranty work for our customers.
Raw Materials
We utilize a variety of raw materials and components including, specialty steel coil, stainless steel, plastic, aluminum, lumber, tires, landing gear, axles and suspensions, which we purchase from a limited number of suppliers. Costs of raw materials and component parts represented approximately 61%, 59%, and 63% of our consolidated net sales in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Raw material costs as a percentage of our consolidated net sales realized throughout 2017 are up compared to prior year as we have seen some increasing raw material costs. Significant price fluctuations or shortages in raw materials or finished components have had, and could have further, adverse effects on our results of operations. In 2018 and for the foreseeable future, we expect that the raw materials used in the greatest quantity will be steel, aluminum, plastic and wood. We will endeavor to pass along any raw material and component cost increases and, to minimize the effect of price fluctuations, we hedge certain commodities that have the potential to significantly impact our operations.
| 13 |
Backlog
Orders that have been confirmed by customers in writing, have defined delivery timeframes and can be produced during the next 18 months are included in our backlog. Orders that comprise our backlog may be subject to changes in quantities, delivery, specifications, terms or cancellation. Our backlog of orders at December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $1,213 million and $802 million, respectively, and we expect to complete the majority of our backlog orders as of December 31, 2017 within 12 months of this date.
Patents and Intellectual Property
We hold or have applied for 141 patents in the U.S. on various components and techniques utilized in our manufacture of transportation equipment and engineered products. In addition, we hold or have applied for 169 patents in foreign countries.
Our patents include intellectual property related to the manufacture of trailers, containers, and aerodynamic-related products using our proprietary DuraPlate® product as well as other lightweight panel products, truck body, trailer, and aerodynamic-related products utilizing other composite materials, our containment and isolation systems, and other engineered products – all of which we believe offer us a significant competitive advantage in the markets in which we compete.
Our DuraPlate® patent portfolio includes several patents and pending patent applications, which cover not only utilization of our DuraPlate® product in the manufacture of trailers, but also cover a number of aerodynamic-related products aimed at increasing the fuel efficiency of trailers. U.S. and foreign patents and patent applications in our DuraPlate® patent portfolio have expiration dates extending until 2036. Certain U.S. patents relating to the combined use of DuraPlate® panels and logistics systems within the sidewalls of our dry van trailers will not expire until 2027 or after; several other issued U.S. patents and pending patent applications relating to the use of DuraPlate® panels, or other composite materials, within aerodynamic-related products as well as modular storage and shipping containers will not begin to expire until after 2030. Additionally, we also believe that our proprietary DuraPlate® production process, which has been developed and refined since 1995, offers us a significant competitive advantage in the industry – above and beyond the benefits provided by any patent protection concerning the use and/or design of our DuraPlate® products. We believe the proprietary knowledge of this process and the significant intellectual and capital hurdles in creating a similar production process provide us with an advantage over others in the industry who utilize composite sandwich panel technology.
Our intellectual property portfolio further includes a number of patent applications related to the manufacture of truck bodies and trailers using polymer composite component parts. These patent applications cover the polymer composite component structure and method of manufacturing the same. We believe the intellectual property related to this emerging use of polymer composite technology in our industry will offer us a significant market advantage to create proprietary products exploiting this technology. These patent applications will not begin to expire until 2036. Additionally, our intellectual property portfolio includes patent applications related to the rear impact guard (RIG) and to a side impact guard (SIG) of a trailer. The RIG patent applications include new RIG designs which surpass the current and proposed federal regulatory RIG standards for the U.S. and Canada while the SIG patent applications include new and innovative designs for effectively protecting against side underride.
In addition, our intellectual property portfolio includes patents and patent applications covering many of our engineered products, including our containment and isolation systems, as well as many trailer industry components. These products have become highly desirable and are recognized for their innovation in the markets we serve. The engineered products patents and patent applications relate to our industry leading isolation systems, sold under the Extract Technologies® brand name. These patents will not begin to expire until 2021. The patents and patent applications relating to our proprietary trailer-industry componentry include, for example, those covering the Trust Lock Plus® door locking mechanism, the Max Clearance® Overhead Door System, which provides additional overhead clearance when an overhead-style rear door is in the opened position that would be comparable to that of swing-door models, the use of bonded intermediate logistics strips, the bonded D-ring hold-down device, bonded skylights, and the DuraPlate® arched roof. The patents covering these products will not expire before 2029. Further, another patented product sold by the Diversified Products segment includes the ShakerTank® trailer, a vibrating bulk tank trailer used in transporting viscous materials, whose patents will not expire before 2026. We believe all of these proprietary products offer us a competitive market advantage in the industries in which we compete.
| 14 |
We also hold or have applied for 49 trademarks in the U.S. as well as 64 trademarks in foreign countries. These trademarks include the Wabash®, Wabash National®, Transcraft®, Benson®, Extract Technology®, Beall®, Brenner®, and Supreme® brand names as well as trademarks associated with our proprietary products such as DuraPlate®, RoadRailer®, Transcraft Eagle®, Arctic Lite®, Kold King®, and Iner-City®. Additionally, we utilize several tradenames that are each well-recognized in their industries, including Walker Transport, Walker Stainless Equipment, Walker Engineered Products, Garsite, Bulk Tank International and Progress Tank. Our trademarks associated with additional proprietary products include MaxClearance® Overhead Door System, Trust Lock Plus®, EZ-7®, DuraPlate Aeroskirt®, Aeroskirt CX®, DuraPlate XD-35®, DuraPlate HD®, SolarGuard®, VentixDRS®, AeroFin®, AeroFin XL® and EZ-Adjust®. We believe these trademarks are important for the identification of our products and the associated customer goodwill; however, our business is not materially dependent on such trademarks.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses are charged to earnings as incurred and were $3.9 million, $6.4 million and $4.8 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Environmental Matters
Our facilities are subject to various environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to air emissions, wastewater discharges, the handling and disposal of solid and hazardous wastes and occupational safety and health. Our operations and facilities have been, and in the future may become, the subject of enforcement actions or proceedings for non-compliance with such laws or for remediation of company-related releases of substances into the environment. Resolution of such matters with regulators can result in commitments to compliance abatement or remediation programs and, in some cases, the payment of penalties (see “Legal Proceedings” in Item 3 for more details).
We believe that our facilities are in substantial compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations. Our facilities have incurred, and will continue to incur, capital and operating expenditures and other costs in complying with these laws and regulations. However, we currently do not anticipate that the future costs of environmental compliance will have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Employees
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had approximately 6,500 and 5,100 full-time employees, respectively. Throughout 2017, essentially all of our active employees were non-union. Our temporary employees represented approximately 10% of our overall production workforce as of December 31, 2017 as compared to approximately 14% at the end of the prior year period. We place a strong emphasis on maintaining good employee relations and development through competitive compensation and related benefits, a safe work environment and promoting educational programs and quality improvement teams.
Executive Officers of Wabash National Corporation
The following are the executive officers of the Company:
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Richard J. Giromini | 64 | Chief Executive Officer, Director | ||
| Brent L. Yeagy | 47 | President and Chief Operating Officer, Director | ||
| Kevin J. Page | 56 | Senior Vice President – Group President, Diversified Products Group | ||
| Michael N. Pettit | 43 | Senior Vice President – Group President, Final Mile Products | ||
| William D. Pitchford | 63 | Senior Vice President – Human Resources and Assistant Secretary | ||
| Dustin T. Smith | 40 | Senior Vice President – Group President, Commercial Trailer Products | ||
| Jeffery L. Taylor | 52 | Senior Vice President – Chief Financial Officer |
| 15 |
Richard J. Giromini. Mr. Giromini has served as our Chief Executive Officer since January 2007, and served as our President from that date until October 2016. On December 14, 2017, Mr. Giromini notified the Company that he will step down from his position as Chief Executive Officer on June 1, 2018. Mr. Giromini is expected to then continue his employment with the Company through June 1, 2019 to assist in the leadership transition. On June 1, 2019 Mr. Giromini will retire from the Company, and he will not stand for reelection to the Board of Directors at the 2019 Annual Meeting. Mr. Giromini joined the Company in July 2002, as Senior Vice President - Chief Operating Officer and served as our Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer from February 2005 until December 2005 when he was appointed President and a Director of the Company. Earlier experience includes 26 years in the transportation industry, having begun his career with General Motors Corporation (1976 – 1985), then serving in a variety of positions of increasing responsibility within the Tier 1 automotive and transportation sectors, most recently with Accuride Corporation (Senior Vice President and General Manager), AKW LP (President and CEO), and ITT Automotive (Director of Manufacturing). Mr. Giromini holds a Master of Science degree in Industrial Management and a Bachelor of Science degree in Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, both from Clarkson University. He is also a graduate of the Advanced Management Program at the Duke University Fuqua School of Management.
Brent L. Yeagy. Mr. Yeagy has served as our President and Chief Operating Officer, and a Director of the Company since October 2016. On December 15, 2017 the Board of Directors announced the appointment of Mr. Yeagy to serve as the Company’s President and Chief Executive Officer effective June 2, 2018. Mr. Yeagy had been Senior Vice President – Group President of Commercial Trailer Products Group from June 2013 to October 2016. Previously, he served as Vice President and General Manager for the Commercial Trailer Products Group from 2010 to 2013. Mr. Yeagy has held numerous operations related roles since joining Wabash National in February 2003. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Yeagy held various roles within Human Resources, Environmental Engineering and Safety Management for Delco Remy International from July 1999 through February 2003. Mr. Yeagy served in various Plant Engineering roles at Rexnord Corporation from December 1995 through June 1999. Mr. Yeagy is a veteran of the United States Navy, serving from 1991 to 1994. He received his Masters of Business Administration from Anderson University and his Master and Bachelor degrees in Science from Purdue University. He is also a graduate of the University of Michigan, Ross School of Business Program in Executive Management and the Stanford Executive Program.
Kevin J. Page. Mr. Page was appointed to Senior Vice President - Group President of Diversified Products Group on October 1, 2017. Mr. Page joined the Company in February 2017 as Vice President and General Manager, Final Mile and Distributed Services within Commercial Trailer Products. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Page was Interim President of Truck Accessories Group, LLC, manufacturer of fiberglass and aluminum truck caps and tonneaus, from June 2015 to September 2016, and Vice President of Sales, Marketing and Business Development from April 2012 to June 2015. Additionally, he served as President of Universal Trailer Cargo Group from June 2008 to December 2011. Mr. Page also had a 23-year tenure at Utilimaster Corporation serving in various sales roles, including Vice President of Sales and Marketing. Mr. Page has a Bachelor of Arts in Economics from Wabash College and an MBA (Executive) from Notre Dame. Throughout his career he has also completed programs at the University of Chicago, Harvard Business School, University of Michigan and American Management Association.
Michael N. Pettit. Mr. Pettit was appointed Senior Vice President – Group President of Final Mile Products effective January 1, 2018. Mr. Pettit previously served as Vice President – Finance/Investor Relations since 2014, and has recently served as the Company’s Final Mile Products segment integration leader, following the Company’s acquisition of Supreme in September 2017. He joined Wabash National in 2012 and has held a number of positions with increasing responsibility, including Director of Finance for Commercial Trailer Products. Prior to Wabash National, from 1998 to 2012, Mr. Pettit held various finance positions with increasing responsibility at Ford Motor Company. Mr. Pettit earned his Masters of Business Administration from Indiana University and his Bachelor of Science in Industrial Management from Purdue University.
William D. Pitchford. Mr. Pitchford was promoted to Senior Vice President – Human Resources and Assistant Secretary in June 2013. He joined the Company in December 2011 as Vice President – Human Resources with an extensive Human Resource background including executive leadership, talent management, training and development, labor relations, employee engagement, compensation design and organizational development. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Pitchford served as Vice President - Human Resources for Rio Tinto Alcan Corporation in Chicago, Illinois, from January 2009 to December 2010 and was with Ford Motor Company for more than 30 years where he held a variety of key leadership positions including Human Resources Director, Labor Relations Director and Senior Human Resources Manager. Mr. Pitchford holds a Master of Arts degree in Human Resources from Central Michigan University and a Bachelor of Science degree from Indiana State University.
| 16 |
Dustin T. Smith. Mr. Smith was appointed Senior Vice President and Group President, Commercial Trailer Products on October 1, 2017. Most recently he served as Senior Vice President and General Manager, Commercial Trailer Products. Mr. Smith joined Wabash National in 2007 and has held a number of positions with increasing responsibility, including Director of Finance, Director of Manufacturing, and Vice President of Manufacturing. Prior to Wabash National, from 2000 to 2007, Mr. Smith held various positions at Ford Motor Company in Dearborn Michigan, across both product development and manufacturing divisions, including Plant Controller. His more than 17 years of experience in finance and operations gives Mr. Smith a unique understanding of how manufacturing systems directly affect financial results. Mr. Smith holds a Bachelor of Science in Accounting and an MBA in Corporate Finance from Purdue University. He has also attended several executive programs at the Booth School of Management from University of Chicago, as well as Northwestern’s Kellogg School of Management.
Jeffery L. Taylor. Mr. Taylor was appointed Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer in January 2014. Mr. Taylor joined the company in July 2012 as Vice President of Finance and Investor Relations and was promoted to Vice President – Acting Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer in June 2013. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Taylor was with King Pharmaceuticals, Inc. from May 2006 to July 2011 as Vice President, Finance – Technical Operations, and with Eastman Chemical Company from June 1997 to May 2006 where he served in various positions of increasing responsibility within finance, accounting, investor relations and business management, including its Global Business Controller – Coatings, Adhesives, Specialty Polymers & Inks. Mr. Taylor earned his Masters of Business Administration from the University of Texas at Austin and his Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering from Arizona State University.
You should carefully consider the risks described below in addition to other information contained or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report before investing in our securities. Realization of any of the following risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
Risks Related to Our Business, Strategy and Operations
Our business is highly cyclical, which has had, and could have further, adverse effects on our sales and results of operations.
The truck trailer manufacturing industry historically has been and is expected to continue to be cyclical, as well as affected by overall economic conditions. Customers historically have replaced trailers in cycles that run from five to 12 years, depending on service and trailer type. Poor economic conditions can adversely affect demand for new trailers and has led to an overall aging of trailer fleets beyond a typical replacement cycle. Customers’ buying patterns can also be influenced by regulatory changes, such as federal hours-of-service rules as well as overall truck safety and federal emissions standards.
The steps we have taken to diversify our product offerings through the implementation of our strategic plan do not insulate us from this cyclicality. During downturns, we operate with a lower level of backlog and have had to temporarily slow down or halt production at some or all of our facilities, including extending normal shut down periods and reducing salaried headcount levels. An economic downturn may reduce, and in the past has reduced, demand for trailers and our other products, resulting in lower sales volumes, lower prices and decreased profits or losses.
Demand for our products is sensitive to economic conditions over which we have no control and that may adversely affect our revenues and profitability.
Demand for our products is sensitive to changes in economic conditions, including changes related to unemployment, consumer confidence, consumer income, new housing starts, industrial production, government regulations, and the availability of financing and interest rates. The status of these economic conditions periodically have an adverse effect on truck freight and the demand for and the pricing of our products, and have also resulted in, and could in the future result in, the inability of customers to meet their contractual terms or payment obligations, which could cause our operating revenues and profits to decline.
| 17 |
Global economic weakness could negatively impact our operations and financial performance.
While the trailer industry has recently experienced a period of strong demand levels, we cannot provide any assurances that we will be profitable in future periods or that we will be able to sustain or increase profitability in the future. Increasing our profitability will depend on several factors, including, our ability to increase our overall trailer volumes, improve our gross margins, gain continued momentum on our product diversification efforts and manage our expenses. If we are unable to sustain profitability in the future, we may not be able to meet our payment and other obligations under our outstanding debt agreements.
We continue to be reliant on the credit, housing and construction-related markets in the U.S. The same general economic concerns faced by us are also faced by our customers. We believe that some of our customers are highly leveraged and have limited access to capital, and their continued existence may be reliant on liquidity from global credit markets and other sources of external financing. Lack of liquidity by our customers could impact our ability to collect amounts owed to us. While we have taken steps to address these concerns through the implementation of our strategic plan, we are not immune to the pressures being faced by our industry or the global economy, and our results of operations may decline.
We may not be able to execute on our long-term strategic plan and growth initiatives, or meet our long-term financial goals.
Our long-term strategic plan is intended to generate long-term value for our shareholders while delivering profitable growth through all our business segments. The long-term financial goals that we expect to achieve as a result of our long-term strategic plan and organic growth initiatives are based on certain assumptions, which may prove to be incorrect. We cannot provide any assurance that we will be able to fully execute on our strategic plan or growth initiatives, which are subject to a variety of risks, including, our ability to: diversify the product offerings of our non-trailer businesses; leverage acquired businesses and assets to grow sales with our existing products; design and develop new products to meet the needs of our customers; increase the pricing of our products and services to offset cost increases and expand gross margins; and execute potential future acquisitions, mergers, and other business development opportunities. If we are unable to successfully execute on our strategic plan, we may experience increased competition, adverse financial consequences and a decrease in the value of our stock. Additionally, our management’s attention to the implementation of the strategic plan, which includes our efforts at diversification, may distract them from implementing our core business which may also have adverse financial consequences.
Our diversification strategy may not be successfully executed, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition to our commitment to long-term profitable growth within each of our existing reporting segments, our strategic initiatives include a focus on diversification, both organic and strategic, to continue to transform Wabash into a more diversified industrial manufacturer with a higher growth and margin profile and successfully deliver a greater value to our shareholders. Organically, our focus is on profitably growing and diversifying our operations by leveraging our existing assets, capabilities, and technology into higher margin products and markets and thereby providing value-added customer solutions. Strategically, we continue to focus on becoming a more diversified industrial manufacturer, broadening the product portfolio we offer, the customers and end markets we serve and our geographic reach.
Some of our existing diversification efforts are in the early growth stages and future success is largely dependent on continued customer adoption of our new product solutions and general expansion of our customer base and distribution channels. We also expect future acquisitions to form a key component of strategic diversification. Diversification through acquisitions involve identifying and executing on transactions and managing successfully the integration and growth of acquired companies and products, all of which involve significant resources and risk of failure. Diversification efforts put a strain on our administrative, operational and financial resources and make the determination of optimal resource allocation difficult. If our efforts to diversify the business organically and/or strategically do not meet the expectations we have, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
| 18 |
We have a limited number of suppliers of raw materials and components; increases in the price of raw materials or the inability to obtain raw materials could adversely affect our results of operations.
We currently rely on a limited number of suppliers for certain key components and raw materials in the manufacturing of our products, such as tires, landing gear, axles, suspensions, specialty steel coil, stainless steel, plastic, aluminum and lumber. From time to time, there have been and may in the future be shortages of supplies of raw materials or components, or our suppliers may place us on allocation, which would have an adverse impact on our ability to meet demand for our products. Shortages and allocations may result in inefficient operations and a build-up of inventory, which can negatively affect our working capital position. In addition, price volatility in commodities we purchase that impacts the pricing of raw materials could have negative impacts on our operating margins. The loss of any of our suppliers or their inability to meet our price, quality, quantity and delivery requirements could have a significant adverse impact on our results of operations.
Volatility in the supply of vehicle chassis and other vehicle components could adversely affect our Final Mile Products business.
With the exception of some specialty vehicle products, we generally do not purchase vehicle chassis for our inventory and accept shipments of vehicle chassis owned by dealers or end-users for the purpose of installing and/or manufacturing our specialized truck bodies on such chassis. Historically, General Motors Corporation (“GM”) and Ford Motor Company (“Ford”) have been the primary suppliers of chassis. In the event of a disruption in supply from one major supplier, we would attempt to use another major supplier, but there can be no assurance that this attempt would be successful. Nevertheless, in the event of chassis supply disruptions, there could be unforeseen consequences that may have a significant adverse effect on our truck body operations.
We also face risks relative to finance and storage charges for maintaining an excess supply of chassis from GM and Ford. Under the converter chassis pool agreements, if a chassis is not delivered to a customer within a specified time frame, we are required to pay finance or storage charges on such chassis.
A change in our customer relationships or in the financial condition of our customers has had, and could have further, adverse effects on our business.
We have longstanding relationships with a number of large customers to whom we supply our products. We do not have long-term agreements with these customers. Our success is dependent, to a significant extent, upon the continued strength of these relationships and the growth of our core customers. We often are unable to predict the level of demand for our products from these customers, or the timing of their orders. In addition, the same economic conditions that adversely affect us also often adversely affect our customers. Furthermore, we are subject to a concentration of risk as the five largest customers together accounted for approximately 24% of our aggregate net sales in 2017. While no customers over the previous three years have individually accounted for greater than 10% of our aggregate net sales, we have historically had individual customers who have accounted for greater than 10% of our aggregate net sales. The loss of a significant customer or unexpected delays in product purchases could further adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Significant competition in the industries in which we operate may result in our competitors offering new or better products and services or lower prices, which could result in a loss of customers and a decrease in our revenues.
The industries in which we participate are highly competitive. We compete with other manufacturers of varying sizes, some of which have substantial financial resources. Manufacturers compete primarily on the quality of their products, customer relationships, service availability and price. Barriers to entry in the standard trailer and truck body manufacturing industry are low. As a result, it is possible that additional competitors could enter the market at any time. In the recent past, manufacturing over-capacity and high leverage of some of our competitors, along with bankruptcies and financial stresses that affected the industry, contributed to significant pricing pressures.
If we are unable to successfully compete with other manufacturers, we could lose customers and our revenues may decline. In addition, competitive pressures in the industry may affect the market prices of our new and used equipment, which, in turn, may adversely affect our sales margins and results of operations.
| 19 |
Our Final Mile Products segment competes in the highly competitive specialized vehicle industry which may impact its financial results.
The competitive nature of the specialized vehicle industry creates a number of challenges for our Final Mile Products segment. Important factors include product pricing, quality of product, lead times, geographic proximity to customers, and the ability to manufacture a product customized to customer specifications. Specialized vehicles are produced by a number of smaller, regional companies which create product pricing pressures that could adversely impact our profits. Chassis manufacturers have not generally shown an interest in manufacturing specialized vehicles, including truck bodies, because such manufacturers’ highly-automated assembly line operations do not lend themselves to the efficient production of a wide variety of highly-specialized vehicles with various options and equipment.
Our technology and products may not achieve market acceptance or competing products could gain market share, which could adversely affect our competitive position.
We continue to optimize and expand our product offerings to meet our customer needs through our established brands, such as DuraPlate®, DuraPlateHD®, DuraPlate® XD-35®, DuraPlate AeroSkirt®, ArcticLite®, Transcraft®, Benson®, Walker Transport, Brenner® Tank, Garsite, Progress Tank, Bulk Tank International, and Extract Technology®, Supreme, Iner-City®, Spartan, and Kold King®. While we target product development to meet customer needs, there is no assurance that our product development efforts will be embraced and that we will meet our strategic goals, including sales projections. Companies in the truck transportation industry, a very fluid industry in which our customers primarily operate, make frequent changes to maximize their operations and profits.
We have seen a number of our competitors follow our leadership in the development and use of composite sidewalls that bring them into direct competition with our DuraPlateâ products. Our product development is focused on maintaining our leadership for these products but competitive pressures may erode our market share or margins. We hold patents on various components and techniques utilized in our manufacturing of transportation equipment and engineered products with expiration dates ranging from 2018 to 2036. We continue to take steps to protect our proprietary rights in our products and the processes used to produce them. However, the steps we have taken may not be sufficient or may not be enforced by a court of law. If we are unable to protect our intellectual properties, other parties may attempt to copy or otherwise obtain or use our products or technology. If competitors are able to use our technology, our ability to effectively compete could be harmed. In addition, litigation related to intellectual property could result in substantial costs and efforts which may not result in a successful outcome.
Our backlog may not be indicative of the level of our future revenues.
Our backlog represents future production for which we have written orders from our customers that can be produced in the next 18 months. Orders that comprise our backlog may be subject to changes in quantities, delivery, specifications and terms, or cancellation. Our reported backlog may not be converted to revenue in any particular period and actual revenue from such orders may not equal our backlog. Therefore, our backlog may not be indicative of the level of our future revenues.
International operations are subject to increased risks, which could harm our business, operating results and financial condition.
Our ability to manage our business and conduct operations internationally requires considerable management attention and resources and is subject to a number of risks, including the following:
| • | challenges caused by distance, language and cultural differences and by doing business with foreign agencies and governments; |
| • | longer payment cycles in some countries; |
| • | uncertainty regarding liability for services and content; |
| • | credit risk and higher levels of payment fraud; |
| • | currency exchange rate fluctuations and our ability to manage these fluctuations; |
| • | foreign exchange controls that might prevent us from repatriating cash earned outside the U.S.; |
| • | import and export requirements that may prevent us from shipping products or providing services to a particular market and may increase our operating costs; |
| 20 |
| • | potentially adverse tax consequences; |
| • | higher costs associated with doing business internationally; |
| • | different expectations regarding working hours, work culture and work-related benefits; and |
| • | different employee/employer relationships and the existence of workers’ councils and labor unions. |
Compliance with complex foreign and U.S. laws and regulations that apply to international operations may increase our cost of doing business and could expose us or our employees to fines, penalties and other liabilities. These numerous and sometimes conflicting laws and regulations include import and export requirements, content requirements, trade restrictions, tax laws, environmental laws and regulations, sanctions, internal and disclosure control rules, data privacy requirements, labor relations laws, and U.S. laws such as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and substantially equivalent local laws prohibiting corrupt payments to governmental officials and/or other foreign persons. Although we have policies and procedures designed to ensure compliance with these laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that our officers, employees, contractors or agents will not violate our policies. Any violation of the laws and regulations that apply to our operations and properties could result in, among other consequences, fines, environmental and other liabilities, criminal sanctions against us, our officers or our employees, and prohibitions on our ability to offer our products and services to one or more countries and could also materially damage our reputation, our brand, our efforts to diversify our business, our ability to attract and retain employees, our business and our operating results.
Disruption of our manufacturing operations would have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We manufacture our van trailer products at two facilities in Lafayette, Indiana, a flatbed trailer facility in Cadiz, Kentucky, a hardwood floor facility in Harrison, Arkansas, six liquid-transportation systems facilities in New Lisbon, Wisconsin; Fond du Lac, Wisconsin; Kansas City, Kansas; Portland, Oregon; and Queretaro, Mexico, three engineered products facilities in New Lisbon, Wisconsin; Elroy, Wisconsin; Huddersfield, United Kingdom, seven truck body facilities in Goshen, IN; Ligonier, IN; Cleburne, TX; Griffin, GA; Jonestown, PA; Moreno Valley, CA; and Lafayette, IN, and produce Composite products at facilities in Lafayette, Indiana and Frankfort, Indiana. An unexpected disruption in our production at any of these facilities for any length of time would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The inability to attract and retain key personnel could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our ability to operate our business and implement our strategies depends, in part, on the efforts of our executive officers and other key associates. Our future success depends, in large part, on our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel, including manufacturing personnel, sales professionals and engineers. The unexpected loss of services of any of our key personnel or the failure to attract or retain other qualified personnel could have an adverse effect on the operation of our business.
We rely significantly on information technology to support our operations and if we are unable to protect against service interruptions or security breaches, our business could be adversely impacted.
We depend on a number of information technologies to integrate departments and functions, to enhance the ability to service customers, to improve our control environment and to manage our cost reduction initiatives. We have put in place a number of systems, processes, and practices designed to protect against the failure of our systems, as well as the misappropriation, exposure or corruption of the information stored thereon. Unintentional service disruptions or intentional actions such as intellectual property theft, cyber-attacks, unauthorized access or malicious software, may lead to such misappropriation, exposure or corruption if our protective measures prove to be inadequate. Any issues involving these critical business applications and infrastructure may adversely impact our ability to manage operations and the customers we serve. We could also encounter violations of applicable law or reputational damage from the disclosure of confidential business, customer, or employee information or the failure to protect the privacy rights of our employees in their personal identifying information. In addition, the disclosure of non-public information could lead to the loss of our intellectual property and diminished competitive advantages. Should any of the foregoing events occur, we may be required to incur significant costs to protect against damage caused by these disruptions or security breaches in the future.
| 21 |
We are subject to extensive governmental laws and regulations, and our costs related to compliance with, or our failure to comply with, existing or future laws and regulations could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The length, height, width, maximum weight capacity and other specifications of truck and tank trailers are regulated by individual states. The federal government also regulates certain trailer safety features, such as lamps, reflective devices, tires, air-brake systems and rear-impact guards. In addition, most tank trailers we manufacture have specific federal regulations and restrictions that dictate tank design, material type and thickness. Changes or anticipation of changes in these regulations can have a material impact on our financial results, as our customers may defer purchasing decisions and we may have to re-engineer products. We are subject to various environmental laws and regulations dealing with the transportation, storage, presence, use, disposal and handling of hazardous materials, discharge of storm water and underground fuel storage tanks, and we may be subject to liability associated with operations of prior owners of acquired property. In addition, we are subject to laws and regulations relating to the employment of our employees and labor-related practices.
If we are found to be in violation of applicable laws or regulations in the future, it could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Our costs of complying with these or any other current or future regulations may be material. In addition, if we fail to comply with existing or future laws and regulations, we may be subject to governmental or judicial fines or sanctions.
Regulations related to conflict-free minerals may force us to incur additional expenses and otherwise adversely affect our business and results of operations.
As mandated by the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Securities and Exchange Commission adopted rules regarding disclosure of the use of certain minerals, known as conflict minerals, originating from the Democratic Republic of Congo or adjoining countries. These requirements require ongoing due diligence efforts and disclosure requirements. We may incur significant costs to determine the source of any such minerals used in our products. We may also incur costs with respect to potential changes to products, processes or sources of supply as a consequence of our diligence activities. Further, the implementation of these rules and their effect on customer and/or supplier behavior could adversely affect the sourcing, supply and pricing of materials used in our products, as the number of suppliers offering conflict-free minerals could be limited. We may incur additional costs or face regulatory scrutiny if we determine that some of our products contain materials not determined to be conflict-free or if we are unable to sufficiently verify the origins of all conflict minerals used in our products. Accordingly, compliance with these rules could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and/or financial condition.
Product liability and other legal claims could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
As a manufacturer of products widely used in commerce, we are subject to product liability claims and litigation, as well as warranty claims. From time to time claims may involve material amounts and novel legal theories, and any insurance we carry may not provide adequate coverage to insulate us from material liabilities for these claims.
In addition to product liability claims, we are subject to legal proceedings and claims that arise in the ordinary course of business, such as workers' compensation claims, OSHA investigations, employment disputes and customer and supplier disputes arising out of the conduct of our business. Litigation may result in substantial costs and may divert management's attention and resources from the operation of our business, which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
| 22 |
An impairment in the carrying value of goodwill and other long-lived intangible assets could negatively affect our operating results.
We have a substantial amount of goodwill and purchased intangible assets on our balance sheet as a result of acquisitions. At December 31, 2017, approximately 59% of these long-lived intangible assets were concentrated in our Final Mile Products segment, 39% were concentrated in our Diversified Products segment, and 2% were concentrated in our Commercial Trailer Products segment. The carrying value of goodwill represents the fair value of an acquired business in excess of identifiable assets and liabilities as of the acquisition date. The carrying value of other long-lived intangible assets represents the fair value of trademarks and trade names, customer relationships and technology as of the acquisition date, net of accumulated amortization. Under generally accepted accounting principles, goodwill is required to be reviewed for impairment at least annually, or more frequently if potential interim indicators exist that could result in impairment, and other long-lived intangible assets require review for impairment only when indicators exist. If any business conditions or other factors cause profitability or cash flows to significantly decline, we may be required to record a non-cash impairment charge, which could adversely affect our operating results. Events and conditions that could result in impairment include a prolonged period of global economic weakness, a decline in economic conditions or a slow, weak economic recovery, sustained declines in the price of our common stock, adverse changes in the regulatory environment, adverse changes in the market share of our products, adverse changes in interest rates, or other factors leading to reductions in the long-term sales or profitability that we expect.
Our ability to fund operations and pay dividends is limited by our operational results, cash on hand, and available borrowing capacity under our revolving credit facility.
Our ability to fund our working capital needs and capital expenditures, and our ability to pay dividends on our common stock, is limited by the net cash provided by operations, cash on hand and available borrowings under our revolving credit facility. Declines in net cash provided by operations, increases in working capital requirements necessitated by an increased demand for our products and services, decreases in the availability under the revolving credit facility or changes in the credit our suppliers provide to us, could rapidly exhaust our liquidity.
We recently reinstituted a policy of paying regular quarterly dividends on our common stock, but there is no assurance that we will have the ability to continue a regular quarterly dividend.
In December 2016, our Board of Directors approved the reinstatement of a dividend program under which we will pay regular quarterly cash dividends to holders of our common stock. Prior to 2017, no dividends had been paid since the third quarter of 2008. Our ability to pay dividends, and our Board of Directors’ determination to maintain our current dividend policy, will depend on numerous factors, including:
| · | the state of our business, competition, and changes in our industry; |
| · | changes in the factors, assumptions, and other considerations made by our Board of Directors in reviewing and revising our dividend policy; |
| · | our future results of operations, financial condition, liquidity needs, and capital resources; and |
| · | our various expected cash needs, including cash interest and principal payments on our indebtedness, capital expenditures, the purchase price of acquisitions, and taxes. |
Each of the factors listed above could negatively affect our ability to pay dividends in accordance with our dividend policy or at all. In addition, the Board may elect to suspend or alter the current dividend policy at any time.
| 23 |
Changes to U.S. or foreign tax laws could affect our effective tax rate and our future profitability.
Changes in tax legislation could significantly impact our overall profitability, the provisions for income taxes, the amount of taxes payable and our deferred tax asset and liability balances. On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) was signed into law. The Act contains numerous new and changed provisions related to the U.S. federal taxation of domestic and foreign corporate operations. Although most of these provisions went into effect starting January 1, 2018 for calendar year corporate taxpayers, companies are still required to record the income tax accounting effects within the financial statements in the period of enactment. As such, management has included the estimated effects of remeasuring deferred taxes for the new U.S. federal income tax rate of 21% going into effect in 2018, as well as assessed our ability to realize deferred income tax assets in the future under the new rules. At December 31, 2017, we have not completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act, including with respect to the effects on our existing deferred tax balances. We will continue to monitor further regulatory guidance issued by the Department of Treasury and Internal Revenue Service with regard to new provisions under the Act, and make adjustments accordingly to these estimates over the one year measurement period as outlined under Staff Accounting Bulletin 118. However, the final impact of the Act may differ, possibly materially, from our current estimates.
Our substantial indebtedness could adversely affect our financial condition and prevent us from fulfilling our obligations thereunder.
As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately $558.5 million of total indebtedness, and approximately $169.6 million of additional borrowings were available and undrawn under the Credit Agreement (as defined below). We also have other contractual obligations and currently pay a regular quarterly dividend of approximately $0.075 per share, or approximately $4.7 million in the aggregate per quarter.
Our debt level could have significant consequences on future operations. For example, it could:
| · | negatively affect our ability to pay principal and interest on our debt; |
| · | increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions; |
| · | limit our ability to fund future capital expenditures and working capital, to engage in future acquisitions or development activities, or to otherwise realize the value of our assets and opportunities fully because of the need to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to payments of interest and principal or to comply with any restrictive terms of our debt; |
| · | limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry in which we operate; |
| · | impair our ability to obtain additional financing or to refinance our indebtedness in the future; |
| · | place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that may have proportionately less debt; and |
| · | impact our ability to continue to fund a regular quarterly dividend. |
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness and may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness, which may not be successful.
Our ability to make scheduled payments on or to refinance our debt obligations depends on our financial condition and operating performance, which are subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business, legislative, regulatory and other factors beyond our control. We may be unable to maintain a level of cash flows from operating activities sufficient to permit us to fund our day-to-day operations or to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on our indebtedness.
If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to fund our debt service obligations, and other cash requirements, we could face substantial liquidity problems and could be forced to reduce or delay capital expenditures or to sell assets or operations, seek additional capital or restructure or refinance our indebtedness. We may not be able to effect any such alternative measures, if necessary, on commercially reasonable terms or at all and, even if successful, such alternative actions may not allow us to meet our scheduled debt service obligations. The indenture governing the Senior Notes, the Credit Agreement, and Term Loan Credit Agreement (as defined below) restrict (a) our ability to dispose of assets and use the proceeds from any such dispositions and (b) the Company’s and our subsidiaries’ ability to raise debt or certain equity capital to be used to repay the our indebtedness when it becomes due. We may not be able to consummate those dispositions or to obtain proceeds in an amount sufficient to meet any debt service obligations then due.
| 24 |
Our inability to generate sufficient cash flows to satisfy our debt obligations, or to refinance our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms or at all, would materially and adversely affect our financial position and results of operations and our ability to satisfy our indebtedness.
If we cannot make scheduled payments on our debt, it will be in default and, as a result, holders of Senior Notes could declare all outstanding principal and interest to be due and payable, the lenders under the Credit Agreement and Term Loan Credit Agreement could terminate their commitments to loan money, our secured lenders could foreclose against the assets securing such borrowings and we could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation.
Despite current indebtedness levels, we may still be able to incur substantially more debt. This could further exacerbate the risks described above.
We and our subsidiaries have incurred substantial indebtedness in connection with the Supreme acquisition and may be able to incur substantial additional indebtedness in the future. Although the indenture governing the Senior Notes, the Credit Agreement, and Term Loan Credit Agreement contain, restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are and will be subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions and the additional indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. If new debt is added to our current debt levels, the related risks that we and our subsidiaries now face could intensify.
Provisions of the Convertible Notes and the Senior Notes could discourage a potential future acquisition of us by a third party.
Certain provisions of the Convertible Notes and the Senior Notes (each as defined below) could make it more difficult or more expensive for a third party to acquire us. Upon the occurrence of certain transactions constituting a fundamental change, holders of the Convertible Notes or the Senior Notes will have the right, at their option, to require us to repurchase all of their Convertible Notes or Senior Notes, as applicable, or any portion of the principal amount of such Convertible Notes or the Senior Notes, as applicable. We also may be required to issue additional shares upon conversion in the event of certain corporate transactions. In addition, the indentures governing the Convertible Notes and the Senior Notes prohibit us from engaging in certain mergers or acquisitions unless, among other things, the surviving entity assumes our obligations under the Convertible Notes and the Senior Notes. These and other provisions of the Convertible Notes and the Senior Notes could prevent or deter a third party from acquiring us even where the acquisition could be beneficial to our stockholders.
Our Term Loan Credit Agreement, Senior Notes indenture, and Revolving Credit Facility contain restrictive covenants that, if breached, could limit our financial and operating flexibility and subject us to other risks.
Our Term Loan Credit Agreement, Senior Notes indenture, and revolving credit facility include customary covenants limiting our ability to, among other things, pay cash dividends, incur debt or liens, redeem or repurchase stock, enter into transactions with affiliates, merge, dissolve, repay subordinated indebtedness, make investments and dispose of assets. As required under our Credit Agreement, we are required to maintain a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1.1 to 1.0 as of the end of any period of 12 fiscal months when excess availability under the facility is less than 10% of the total revolving commitment.
If availability under the Credit Agreement is less than 12.5% of the total revolving commitment or if there exists an event of default, amounts in any of the Borrowers’ and the Revolver Guarantors’ deposit accounts (other than certain excluded accounts) will be transferred daily into a blocked account held by the Revolver Agent and applied to reduce the outstanding amounts under the facility.
As of December 31, 2017, we believe we are in compliance with the provisions of our Term Loan Credit Agreement, Senior Notes indenture, and our revolving credit facility. Our ability to comply with the various terms and conditions in the future may be affected by events beyond our control, including prevailing economic, financial and industry conditions.
| 25 |
Risks Related to an Investment in Our Common Stock
Future sales of our common stock in the public market could lower the market price for our common stock.
In the future, we may sell additional shares of our common stock to raise capital. In addition, a substantial number of shares of our common stock are reserved for issuance upon the exercise of stock options and upon conversion of the Convertible Notes. We cannot predict the size of future issuances or the effect, if any, that they may have on the market price for our common stock. The issuance and sale of substantial amounts of common stock, or the perception that such issuances and sales may occur, could adversely affect the market price of our common stock and impair our ability to raise capital through the sale of additional equity securities.
Our common stock has experienced, and may continue to experience, price and trading volume volatility.
The trading price and volume of our common stock has been and may continue to be subject to large fluctuations. The market price and volume of our common stock may increase or decrease in response to a number of events and factors, including:
| · | trends in our industry and the markets in which we operate; |
| · | changes in the market price of the products we sell; |
| · | the introduction of new technologies or products by us or by our competitors; |
| · | changes in expectations as to our future financial performance, including financial estimates by securities analysts and investors; |
| · | operating results that vary from the expectations of securities analysts and investors; |
| · | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, financings or capital commitments; |
| · | changes in laws and regulations; |
| · | general economic and competitive conditions; and |
| · | changes in key management personnel. |
This volatility may adversely affect the prices of our common stock regardless of our operating performance. To the extent that the price of our common stock declines, our ability to raise funds through the issuance of equity or otherwise use our common stock as consideration will be reduced. These factors may limit our ability to implement our operating and growth plans.
Also, shareholders may from time to time engage in proxy solicitations, advance shareholder proposals or otherwise attempt to effect changes or acquire control over the Company. Such shareholder campaigns could disrupt the Company’s operations and divert the attention of the Company’s Board of Directors and senior management and employees from the pursuit of business strategies and adversely affect the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
Risks Related to the Supreme Acquisition
It may be difficult to integrate the business of Supreme into our current business.
If we experience greater than anticipated costs to integrate Supreme into our existing operations or are not able to achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisition, including cost savings and other synergies, our business and results of operations could be negatively affected. In addition, it is possible that the ongoing integration process could result in the loss of key employees, errors or delays in systems implementation, the disruption of our ongoing business or inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures and policies that adversely affect our ability to maintain relationships with customers and employees or to achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisition. Integration efforts also may divert management attention and resources. These integration matters may have an adverse effect on us, particularly during any transition period. In addition, although Supreme is subject to many of the same risks and uncertainties that we face in our business, the acquisition also involves our entering into or significantly expanding our existing presence in new product areas, markets and industries, which presents risks resulting from our relative inexperience in these new areas. We face the risk that we will not be successful with these products or in these new markets.
| 26 |
In addition, uncertainty about the effect of the acquisition on Supreme’s customers, employees or suppliers may have an adverse effect on Supreme. These uncertainties may impair our ability to attract, retain and motivate key personnel through the transition and into the future, and could cause disruptions in its relationships with customers, suppliers and other parties with which it deals.
We also expect that integration-related issues will place a significant burden on our and Supreme’s management, employees and internal resources, which could otherwise have been devoted to other business opportunities and improvements.
We have made certain assumptions relating to the Supreme acquisition that may prove to be materially inaccurate.
We have made certain assumptions relating to the Supreme acquisition which may prove to be inaccurate, including as a result of the failure to realize the expected benefits of the acquisition, higher than expected transaction and integration costs and unknown liabilities, as well as general economic and business conditions that adversely affect the combined company following the acquisition. These assumptions relate to numerous matters, including:
| · | our assessments of the asset quality and value of Supreme and its assets; |
| · | our projections of Supreme’s business and its future financial performance; |
| · | our ability to realize synergies related to supply chain optimization, commercialization and distribution of new and existing products, back office and administrative consolidation, and further implementation of manufacturing best practices; |
| · | costs to comply with, and liabilities related to, laws and regulations applicable to Supreme, including environmental laws and regulations; |
| · | our ability to maintain, develop and deepen relationships with Supreme’s customers; |
| · | our belief that the Final Mile Products segment served by Supreme will grow substantially in the future and tends to be less cyclical than the van and platform trailer markets historically served by Wabash; and |
| · | other financial and strategic risks of operating the acquired business. |
If one or more of these assumptions are incorrect, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, and operating results, and the perceived benefits from the acquisition may not be realized.
ITEM 1B—UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
We have manufacturing and retail operations located throughout the United States as well as facilities in Mexico and the United Kingdom. Properties owned by Wabash are subject to security interests held by our lenders. We believe the facilities we are now using are adequate and suitable for our current business operations and the currently foreseeable level of operations. The following table provides information regarding the locations of our major facilities which are in the following areas in the United States, Mexico and United Kingdom:
| 27 |
| Location | Owned or Leased | Description of Activities at Location | Segment | |||
| Ashland, Kentucky | Leased | Parts distribution | Diversified Products | |||
| Baton Rouge, Louisiana | Leased | Service and parts distribution | Diversified Products | |||
| Cadiz, Kentucky | Leased | Manufacturing | Commercial Trailer Products | |||
| Chicago, Illinois | Leased | Service and parts distribution | Diversified Products | |||
| Cleburne, Texas | Owned | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| Elroy, Wisconsin | Owned | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Fond du Lac, Wisconsin | Owned | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Frankfort, Indiana | Leased | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Goshen, Indiana | Owned | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| Griffin, Georgia | Owned | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| Harrison, Arkansas | Owned | Manufacturing | Commercial Trailer Products | |||
| Houston, Texas | Leased | Service and parts distribution | Diversified Products | |||
| Huddersfield, United Kingdom | Leased property/Owned building | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Jonestown, Pennsylvania | Owned | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| Kansas City, Kansas | Leased | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Lafayette, Indiana | Owned | Corporate Headquarters, Manufacturing and used trailers | Commercial Trailer Products, Diversifed Products and Final Mile Products | |||
| Ligonier, Indiana | Owned | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| Little Falls, Minnesota | Owned | Manufacturing | Commercial Trailer Products | |||
| Mauston, Wisconsin | Leased | Service and parts distribution | Diversified Products | |||
| Moreno Valley, California | Owned/Leased | Manufacturing | Final Mile Products | |||
| New Lisbon, Wisconsin | Owned/Leased | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Portland, Oregon | Owned | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Queretaro, Mexico | Owned | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| Tavares, Florida | Leased | Manufacturing | Diversified Products | |||
| West Memphis, Arkansas | Leased | Service and parts distribution | Diversified Products |
We are involved in a number of legal proceedings concerning matters arising in connection with the conduct of our business activities, and are periodically subject to governmental examinations (including by regulatory and tax authorities), and information gathering requests (collectively, "governmental examinations"). As of December 31, 2017, we were named as a defendant or were otherwise involved in numerous legal proceedings and governmental examinations in various jurisdictions, both in the United States and internationally.
We have recorded liabilities for certain of our outstanding legal proceedings and governmental examinations. A liability is accrued when it is both (a) probable that a loss with respect to the legal proceeding has occurred and (b) the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. We evaluate, on a quarterly basis, developments in legal proceedings and governmental examinations that could cause an increase or decrease in the amount of the liability that has been previously accrued. These legal proceedings, as well as governmental examinations, involve various lines of business and a variety of claims (including, but not limited to, common law tort, contract, antitrust and consumer protection claims), some of which present novel factual allegations and/or unique legal theories. While some matters pending against us specify the damages claimed by the plaintiff, many seek a not-yet-quantified amount of damages or are at very early stages of the legal process. Even when the amount of damages claimed against Wabash is stated, the claimed amount may be exaggerated and/or unsupported. As a result, it is not currently possible to estimate a range of possible loss beyond previously accrued liabilities relating to some matters including those described below. Such previously accrued liabilities may not represent our maximum loss exposure. The legal proceedings and governmental examinations underlying the estimated range will change from time to time and actual results may vary significantly from the currently accrued liabilities.
| 28 |
Based on our current knowledge, and taking into consideration litigation-related liabilities, we believe we are not a party to, nor are any of our properties the subject of, any pending legal proceeding or governmental examination other than the matters below, which are addressed individually, that could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition or liquidity if determined in a manner adverse to us. However, in light of the uncertainties involved in such matters, the ultimate outcome of a particular matter could be material to our operating results for a particular period depending on, among other factors, the size of the loss or liability imposed and the level of our income for that period. Costs associated with the litigation and settlements of legal matters are reported within General and Administrative Expenses in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Brazil Joint Venture
In March 2001, Bernard Krone Indústria e Comércio de Máquinas Agrícolas Ltda. (“BK”) filed suit against Wabash in the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba in the State of Paraná, Brazil. Because of the bankruptcy of BK, this proceeding is now pending before the Second Civil Court of Bankruptcies and Creditors Reorganization of Curitiba, State of Paraná (No. 232/99).
The case grows out of a joint venture agreement between BK and Wabash related to marketing of RoadRailer trailers in Brazil and other areas of South America. When BK was placed into the Brazilian equivalent of bankruptcy late in 2000, the joint venture was dissolved. BK subsequently filed its lawsuit against Wabash alleging that it was forced to terminate business with other companies because of the exclusivity and non-compete clauses purportedly found in the joint venture agreement. BK asserted damages, exclusive of any potentially court-imposed interest or inflation adjustments, of approximately R$20.8 million (Brazilian Reais). BK did not change the amount of damages it asserted following its filing of the case in 2001.
A bench (non-jury) trial was held on March 30, 2010 in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. On November 22, 2011, the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba partially granted BK’s claims, and ordered Wabash to pay BK lost profits, compensatory, economic and moral damages in excess of the amount of compensatory damages asserted by BK. The total ordered damages amount was approximately R$26.7 million (Brazilian Reais), which was approximately $8.1 million U.S. dollars using current exchange rates and exclusive of any potentially court-imposed interest, fees or inflation adjustments. On October 5, 2016, the Court of Appeals re-heard all facts and legal questions presented in the case, and ruled in favor of Wabash on all claims at issue. In doing so, the Court of Appeals dismissed all claims against Wabash and vacated the judgment and damages amounts previously ordered by the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba. On September 30, 2017, BK filed its notice for a special appeal of the Court of Appeals ruling to the Superior Court of Justice and the Supreme Federal Court. However, unless these higher courts find in favor of BK on any of its claims, the judgment of the Court of Appeals is final. As a result of the Court of Appeals ruling, Wabash does not expect that this proceeding will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition or results of operations; however, it will continue to monitor these legal proceedings.
Intellectual Property
In October 2006, we filed a patent infringement suit against Vanguard National Corporation (“Vanguard”) regarding our U.S. Patent Nos. 6,986,546 and 6,220,651 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Indiana (Civil Action No. 4:06-cv-135). We amended the Complaint in April 2007. In May 2007, Vanguard filed its Answer to the Amended Complaint, along with Counterclaims seeking findings of non-infringement, invalidity, and unenforceability of the subject patents. We filed a reply to Vanguard’s counterclaims in May 2007, denying any wrongdoing or merit to the allegations as set forth in the counterclaims. The case was stayed by agreement of the parties while the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“Patent Office”) undertook a reexamination of U.S. Patent No. 6,986,546. In June 2010, the Patent Office notified Wabash that the reexamination was completed and the Patent Office reissued U.S. Patent No. 6,986,546 without cancelling any claims of the patent. The parties have not yet petitioned the Court to lift the stay, and it is unknown at this time when the parties may do so.
We believe that our claims against Vanguard have merit and that the claims asserted by Vanguard are without merit. We intend to vigorously defend our position and intellectual property. We believe that the resolution of this lawsuit will not have a material adverse effect on our financial position, liquidity or future results of operations. However, at this stage of the proceeding, no assurance can be given as to the ultimate outcome of the case.
| 29 |
Walker Acquisition
In connection with our acquisition of Walker in May 2012, there is an outstanding claim of approximately $2.9 million for unpaid benefits owed by Walker that is currently in dispute and that, if required to be paid by us, is not expected to have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Environmental Disputes
In August 2014, we were noticed as a potentially responsible party (“PRP”) by the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control (“DHEC”) pertaining to the Philip Services Site located in Rock Hill, South Carolina pursuant to the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (“CERCLA”) and corresponding South Carolina statutes. PRPs include parties identified through manifest records as having contributed to deliveries of hazardous substances to the Philip Services Site between 1979 and 1999. The DHEC’s allegation that we are a PRP arises out of four manifest entries in 1989 under the name of a company unaffiliated with Wabash National (or any of its former or current subsidiaries) that purport to be delivering a de minimis amount of hazardous waste to the Philip Services Site “c/o Wabash National Corporation.” As such, the Philip Services Site PRP Group (“PRP Group”) notified Wabash in August 2014 that is was offering us the opportunity to resolve any liabilities associated with the Philip Services Site by entering into a Cash Out and Reopener Settlement Agreement (the “Settlement Agreement”) with the PRP Group, as well as a Consent Decree with the DHEC. We accepted an offer from the PRP Group to enter into the Settlement Agreement and Consent Decree, while reserving our rights to contest our liability for any deliveries of hazardous materials to the Philips Services Site. The requested settlement payment is immaterial to Wabash’s financial conditions or operations, and as a result, if the Settlement Agreement and Consent Decree are finalized, the payment to be made by us thereunder is not expected to have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
In January 2006, we received a letter from the North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources indicating that a site that we formerly owned near Charlotte, North Carolina has been included on the state's October 2005 Inactive Hazardous Waste Sites Priority List. The letter states that we were being notified in fulfillment of the state's “statutory duty” to notify those who own and those who at present are known to be responsible for each Site on the Priority List. Following receipt of this notice, no action has ever been requested from Wabash, and since 2006 we have not received any further communications regarding this matter from the state of North Carolina. We do not expect that this designation will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Supreme Litigation
Prior to our acquisition of Supreme, a complaint was filed against Supreme Corporation, a subsidiary of Supreme, in a suit (SVI, Inc. v. Supreme Corporation, Hometown Trolley (a/k/a Double K, Inc.) and Dustin Pence) in the United States District Court, District of Nevada on May 16, 2016. The plaintiff is Supreme’s former trolley distributor. The plaintiff filed an amended complaint on January 3, 2017, which alleges that Supreme’s sale of its trolley assets to another trolley manufacturer was improper. Supreme filed a motion to dismiss, which was granted in part on May 30, 2017. The remaining claims alleged against Supreme include: (i) misappropriation of trade secrets; (ii) civil conspiracy/collusion; (iii) tortious interference with contractual relationships; (iv) breach of contract; and (v) breach of the covenant of good faith and fair dealing. The plaintiff alleges damages amounting to approximately $40 million. However, due to the inherent risk of litigation, the outcome of this case is uncertain and unpredictable; and, further, management believes that the allegations are without merit and is vigorously defending the matter. As a result, management does not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
| 30 |
Prior to our acquisition of Supreme on November 4, 2016, a putative class action lawsuit was filed against our subsidiary, Supreme, Mark D. Weber (Supreme’s former Chief Executive Officer) and Matthew W. Long (Supreme’s former Chief Financial Officer) in the United States District Court for the Central District of California alleging the defendants violated Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and Rule 10b-5 by making material, misleading statements in July 2016 regarding projected backlog. The plaintiff seeks to recover unspecified damages. On February 14, 2017, the court transferred the venue of the case to the Northern District of Indiana upon the joint stipulation of the plaintiff and the defendants. An amended complaint was filed on April 24, 2017 challenging statements made during a putative class period of October 22, 2015 through October 21, 2016. Due to the inherent risk of litigation, the outcome of this case is uncertain and unpredictable; however, at this time, management believes that the allegations are without merit and is vigorously defending the matter. As a result, management does not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
ITEM 4—MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not Applicable.
ITEM 5—MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON STOCK, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Information Regarding our Common Stock
Our common stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange (ticker symbol: WNC). The number of record holders of our common stock at February 16, 2018 was 619.
In December 2016, our Board of Directors approved the reinstatement of a dividend program under which we pay regular quarterly cash dividends to holders of our common stock. We paid quarterly dividends of $0.06 per share on our common stock throughout 2017. On December 18, 2017 our Board of Directors approved an increase in the quarterly dividend to $0.075 per share payable beginning January 25, 2018 to holders of record on January 4, 2018. Prior to 2017, no dividends had been paid since the third quarter of 2008. Payments of cash dividends depends on our future earnings, capital availability, financial condition and the discretion of our Board of Directors.
Our Certificate of Incorporation, as amended and approved by our stockholders, authorizes 225 million shares of capital stock, consisting of 200 million shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and 25 million shares of preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share.
High and low stock prices as reported on the New York Stock Exchange for the last two years were:
| High | Low | |||||||
| 2017 | ||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 22.21 | $ | 15.79 | ||||
| Second Quarter | $ | 24.16 | $ | 19.01 | ||||
| Third Quarter | $ | 23.81 | $ | 18.25 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | $ | 23.12 | $ | 18.38 | ||||
| 2016 | ||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 13.57 | $ | 9.68 | ||||
| Second Quarter | $ | 14.97 | $ | 11.81 | ||||
| Third Quarter | $ | 14.72 | $ | 12.23 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | $ | 16.30 | $ | 10.74 | ||||
Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison of cumulative total returns for an investment in our common stock, the S&P 500 Composite Index and the Dow Jones Transportation Index. It covers the period commencing December 31, 2012 and ending December 31, 2017. The graph assumes that the value for the investment in our common stock and in each index was $100 on December 31, 2012.
| 31 |
Comparative of Cumulative Total Return
December 31, 2012 through December 31, 2017
among Wabash National Corporation, the S&P 500 Index
and the Dow Jones Transportation Index
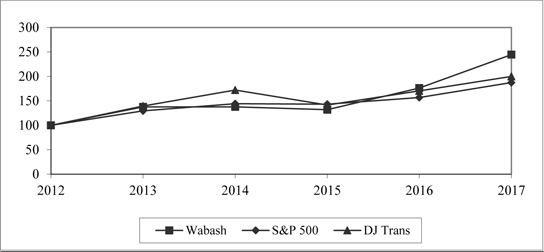
Purchases of Our Equity Securities
The Company’s share repurchase program (“Repurchase Program”) was approved by our Board of Directors and announced in February 2016. On February 24, 2017, the Board of Directors approved the repurchase of an additional $100 million in shares of common stock over a two year period. Stock repurchases under the Repurchase Program may be made in the open market or in private transactions at times and in amounts that management deems appropriate. Management may limit or terminate the Repurchase Program at any time based on market conditions, liquidity needs, or other factors. During the fourth quarter of 2017, there were 1,414,348 shares repurchased pursuant to our Repurchase Program. Additionally, for the quarter ended December 31, 2017, there were 6,822 shares surrendered or withheld to cover minimum employee tax withholding obligations upon the vesting of restricted stock awards. As of December 31, 2017, we had outstanding authorization from the Board of Directors to purchase up to $52.9 million of common stock based on settled trades as of that date.
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Amount That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| October 2017 | 1,999 | $ | 11.81 | 0 | $ | 80.7 | ||||||||||
| November 2017 | 920,697 | $ | 19.36 | 920,697 | $ | 62.8 | ||||||||||
| December 2017 | 498,474 | $ | 20.09 | 493,651 | $ | 52.9 | ||||||||||
| Total | 1,421,170 | $ | 19.60 | 1,414,348 | $ | 52.9 | ||||||||||
ITEM 6—SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following selected consolidated financial data with respect to Wabash National for each of the five years in the period ending December 31, 2017, have been derived from our consolidated financial statements. The following information should be read in conjunction with Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report.
| 32 |
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 1,767,161 | $ | 1,845,444 | $ | 2,027,489 | $ | 1,863,315 | $ | 1,635,686 | ||||||||||
| Cost of sales | 1,506,286 | 1,519,910 | 1,724,046 | 1,630,681 | 1,420,563 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 260,875 | $ | 325,534 | $ | 303,443 | $ | 232,634 | $ | 215,123 | ||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 103,413 | 101,399 | 100,728 | 88,370 | 89,263 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 17,041 | 19,940 | 21,259 | 21,878 | 21,786 | |||||||||||||||
| Acquisition expenses | 9,605 | - | - | - | 883 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill and other intangibles | - | 1,663 | 1,087 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations | $ | 130,816 | $ | 202,532 | $ | 180,369 | $ | 122,386 | $ | 103,191 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | (16,400 | ) | (15,663 | ) | (19,548 | ) | (22,165 | ) | (26,308 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other, net | 8,122 | (1,452 | ) | 2,490 | (1,759 | ) | 740 | |||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes | $ | 122,538 | $ | 185,417 | $ | 163,311 | $ | 98,462 | $ | 77,623 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 11,116 | 65,984 | 59,022 | 37,532 | 31,094 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | $ | 60,930 | $ | 46,529 | ||||||||||
| Dividends declared per share | $ | 0.255 | $ | 0.060 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||||
| Basic net income per common share | $ | 1.88 | $ | 1.87 | $ | 1.55 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 0.67 | ||||||||||
| Diluted net income per common share | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.50 | $ | 0.85 | $ | 0.67 | ||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Working capital | $ | 292,723 | $ | 314,791 | $ | 318,430 | $ | 298,802 | $ | 232,638 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 1,351,513 | $ | 898,733 | $ | 950,126 | $ | 928,651 | $ | 912,245 | ||||||||||
| Total debt and capital leases | $ | 551,413 | $ | 237,836 | $ | 315,633 | $ | 332,527 | $ | 370,595 | ||||||||||
| Stockholders' equity | $ | 506,063 | $ | 472,391 | $ | 439,811 | $ | 390,832 | $ | 322,379 | ||||||||||
ITEM 7—MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A) describes the matters that we consider to be important to understanding the results of our operations for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and our capital resources and liquidity as of December 31, 2017. Our discussion begins with our assessment of the condition of the North American trailer industry along with a summary of the actions we have taken to strengthen the Company. We then analyze the results of our operations for the last three years, including the trends in the overall business and our operating segments, followed by a discussion of our cash flows and liquidity, capital markets events and transactions, our credit facility and contractual commitments. We also provide a review of the critical accounting judgments and estimates that we have made that we believe are most important to an understanding of our MD&A and our consolidated financial statements. These are the critical accounting policies that affect the recognition and measurement of our transactions and the balances in our consolidated financial statements. We conclude our MD&A with information on recent accounting pronouncements that we adopted during the year, if any, as well as those not yet adopted that may have an impact on our financial accounting practices.
| 33 |
As a result of the acquisition of Supreme in the third quarter of 2017, we now manage our business in three segments: Commercial Trailer Products, Diversified Products, and Final Mile Products. The Commercial Trailer Products segment manufactures standard and customized van and platform trailers and other transportation related equipment for customers who purchase directly from us or through independent dealers. The Diversified Products segment, comprised of four strategic business units including, Tank Trailer, Aviation & Truck Equipment, Process Systems, and Composites, focuses on our commitment to expand our customer base and diversify our product offerings and revenues. The Diversified Products segment also seeks to extend our market leadership by leveraging the proprietary DuraPlate® panel technology, drawing on our core manufacturing expertise and making available products that are complementary to truck and tank trailers and transportation equipment. The Final Mile Products segment manufactures specialized commercial vehicles that are attached to a truck chassis, including cutaway and dry-freight van bodies, refrigerated units, and stake bodies, for customers who purchase directly from us or through independent dealers. The acquisition of Supreme, a leading manufacturer of specialized commercial vehicles, is the continuation of our growth and diversification strategy into the rapidly growing final mile space. The Final Mile Products segment was created in the fourth quarter of 2017.
Executive Summary
2017 provided another year of strong overall demand for trailers. According to ACT estimates, total new trailer industry shipments were 287,000 units in 2017, consistent with shipment volumes in 2016. It also represents the second best year in the past fifteen and is the seventh consecutive year that total trailer demand exceeded normal replacement demand levels, currently estimated to be approximately 220,000 trailers per year.
The overall strength in the Company’s operating performance highlights the success of our growth and diversification initiatives driven by our long-term strategic plan to continue to transform the Company into a diversified industrial manufacturer with a higher growth and margin profile, while maintaining our focus and expertise in lean and six sigma optimization initiatives. After five consecutive years of record profitability, a small reset was seemingly inevitable at some point. Operating income in 2017 totaled $130.8 million and operating income margin was 7.4%, both are the third best performance in our history only surpassed by 2015 and 2016 performance. The addition of the Supreme truck body business in September 2017 was a key accomplishment as it not only adds immediate revenue and profit opportunity, but also provides significant diversification into a high-growth segment driven by the ever-increasing adoption of e-commerce.
In addition to our commitment to sustain profitable growth within each of our existing reporting segments, our long-term strategic initiatives included a focus on diversification efforts, both organic and strategic, to continue to transform Wabash into a diversified industrial manufacturer with a higher growth and margin profile and successfully deliver a greater value to our shareholders. Our ability to generate solid margins and cash flows and a healthy balance sheet positions the Company with ample resources to (1) fund our internal capital needs to support both organic growth and productivity improvements, (2) assure continued reduction of our debt obligations, (3) return capital to shareholders and (4) selectively pursue strategic acquisitions. As evidenced by our purchase of Supreme in September 2017, we continue our internal effort to strategically identify potential acquisition targets that we believe can create shareholder value and accelerate our growth and diversification efforts, while leveraging our strong competencies in manufacturing execution, sourcing and innovative engineering leadership to assure strong value creation. Organically, our focus is on profitably growing and diversifying our operations through leveraging our existing assets, capabilities and technology into higher margin products and markets and thereby providing value-added customer solutions.
Throughout 2017 we demonstrated our commitment to be responsible stewards of the business by maintaining a balanced approach to capital allocation. Our continuing strong operational performance, healthy backlog and industry outlook, and financial position provided us the opportunity to take specific actions as part of the ongoing commitment to prudently manage the overall financial risks of the Company, returning capital to our shareholders and deleveraging our balance sheet. These actions included completing $70 million in share repurchases as authorized by our Board of Directors in both February 2016 and February 2017, executing agreements with existing holders of our outstanding Convertible Notes to purchase approximately $4 million in principal, and paying dividends in excess of $15 million. In December 2017, we announced an increase of the regular quarterly dividend paid to the holders of our common stock. Collectively, these actions demonstrate our confidence in the financial outlook of the company and our ability to generate cash flow, both near and long term, and reinforces our overall commitment to deliver shareholder value while maintaining the flexibility to continue to execute our strategic plan for profitable growth and diversification.
| 34 |
The outlook for the overall trailer market for 2018 continues to indicate a strong demand environment. In fact, the most recent estimates from industry forecasters, ACT and FTR, indicate demand levels expected to be in excess of the estimated replacement demand in every year through 2022. More specifically, ACT is currently estimating 2018 demand will be approximately 299,000 trailers, an increase of 4.3% as compared to the previous year period, with 2019 through 2022 industry demand levels ranging between 256,000 and 285,000 trailers. In addition, FTR anticipates trailer production for 2018 to remain strong at approximately 290,000 trailers, an increase of 1.8% as compared to 2017 levels. This continued strong demand environment for new trailer equipment as well as the positive economic and industry specific indicators we monitor reinforce our belief that the current trailer demand cycle will be an extended cycle with a strong likelihood for several more years of demand above replacement levels.
In spite of a strong forecasted demand environment, there remain downside risks relating to issues with both the domestic and global economies, including the housing, energy and construction-related markets in the U.S. Other potential risks as we proceed into 2018 will primarily relate to our ability to effectively manage our manufacturing operations as well as the cost and supply of raw materials, commodities and components. Significant increases in the cost of certain commodities, raw materials or components have had and may continue to have an adverse effect on our results of operations. As has been our practice, we will endeavor to pass raw material and component price increases to our customers in addition to continuing our cost management and hedging activities in an effort to minimize the risk that changes in material costs could have on our operating results. In addition, we rely on a limited number of suppliers for certain key components and raw materials in the manufacturing of our products, including tires, landing gear, axles, suspensions, aluminum extrusions, and specialty steel coil. At the current and expected demand levels, there may be shortages of supplies of raw materials or components which would have an adverse impact on our ability to meet demand for our products. Despite these risks, we believe we are well positioned to capitalize on the expected strong overall demand levels while maintaining or growing margins through improvements in product pricing as well as productivity and other operational excellence initiatives.
We remain committed to enhancing and diversifying our business model through the organic and strategic initiatives discussed above in the Annual Report. We believe we remain well-positioned for long-term success in the transportation industry because: (1) our core customers are among the dominant participants in the trucking industry; (2) our DuraPlate® and other industry leading brands continue to have a strong market acceptance; (3) our focus is on developing solutions that reduce our customers’ trailer maintenance and operating costs providing the best overall value; and (4) our presence throughout North America utilizing our extensive dealer network to market and sell our products. Continuing to identify attractive opportunities to leverage our core competencies, proprietary technology and core manufacturing expertise into new applications and end markets enables us to deliver greater value to our customers and shareholders.
Operating Performance
We measure our operating performance in five key areas – Safety/Morale, Quality, Delivery, Cost Reduction and Environment. We maintain a continuous improvement mindset in each of these key performance areas. Our mantra of being better today than yesterday and better tomorrow than we are today is simple, straightforward and easily understood by all our employees.
| · | Safety/Morale. The safety of our employees is our number one value and highest priority. We continually focus on reducing the severity and frequency of workplace injuries to create a safe environment for our employees and minimize workers compensation costs. We believe that our improved environmental, health and safety management translates into higher labor productivity and lower costs as a result of less time away from work and improved system management. In ten of the last eleven years at least one of our manufacturing sites has been recognized for safety including recent awards from the Truck Trailer Manufacturer Association’s Plant Safety Awards granted to our New Lisbon, Wisconsin and San Jose, Mexico facilities. In 2017, our Cadiz, Kentucky facility received the Governor’s Award for Safety and Health. Our focus on safety also extends beyond our facilities. We are a founding member of the Cargo Tank Risk Management Committee, a group dedicated to reducing the hazards faced by workers on and around cargo tanks. |
| 35 |
| · | Quality. We monitor product quality on a continual basis through a number of means for both internal and external performance as follows: |
| - | Internal performance. Our primary internal quality measurement is Process Yield. Process Yield is a performance metric that measures the impact of all aspects of the business on our ability to ship our products at the end of the production process. As with previous years, the expectations of the highest quality product continue to increase while maintaining Process Yield performance and reducing rework. In addition, we currently maintain an ISO 9001 registration of our Quality Management System at our Lafayette operations. |
| - | External performance. We actively track our warranty claims and costs to identify and drive improvement opportunities in quality and reliability. Early life cycle warranty claims for our van trailers are trended for performance monitoring. Using a unit based warranty reporting process to track performance and document failure rates, early life cycle warranty units per 100 trailers shipped averaged approximately 3.3, 2.6, and 2.0 units in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. Continued low claim rates have been driven by our successful execution of continuous improvement programs centered on process variation reduction, and responding to the input from our customers. We expect that these activities will continue to drive down our total warranty cost profile. |
| · | Delivery/Productivity. We measure productivity on many fronts. Some key indicators include production line cycle-time, labor-hours per trailer and inventory levels. Improvements over the last several years in these areas have translated into significant improvements in our ability to better manage inventory flow and control costs. |
| - | During the past several years Commercial Trailer Products has focused on productivity enhancements within manufacturing assembly and sub-assembly areas through developing the capability for mixed model production. These efforts have resulted in throughput improvements in our Lafayette, Indiana, and Cadiz, Kentucky facilities. |
| - | Through deployment of the Wabash Management System, all of our business reporting segments have focused on increasing velocity at all our manufacturing locations. We have engaged in extensive lean training and deployed purposeful capital to accelerate our productivity initiatives. |
| · | Cost Reduction and our Operating System. The Wabash Manufacturing System allows us to develop and scale high standards of excellence across the organization. We believe in a “One Wabash” approach and standardized processes to drive and monitor performance inside our manufacturing facilities. Continuous improvement is a fundamental component of our operational excellence focus. Our balanced scorecard process, one example, has allowed us to improve all areas of manufacturing including safety, quality, on-time delivery, cost reduction, employee morale and environment. By focusing on continuous improvement and utilizing our balanced scorecard process we have realized total cost per unit reductions as a result of increased capacity utilization of all facilities while maintaining a lower level of fixed overhead. We are investing capital in our processes to reduce variable cost, lower inherent safety risk in our processes, and improve overall consistency in our manufacturing processes. This approach continues to drive value in both the products we offer our customers and the processes our associates work within. |
| · | Environment. We strive to manufacture products that are both socially responsible and environmentally sustainable. We demonstrate our commitment to sustainability by maintaining ISO 14001 registration of our Environmental Management System at our Lafayette, Indiana; Cadiz, Kentucky; San Jose Iturbide, Mexico; Frankfort, Indiana; Portland, Oregon; and Harrison, Arkansas locations. In 2005, our Lafayette, Indiana facility was one of the first trailer manufacturing operations in the world to be ISO 14001 registered. Being ISO 14001 registered requires us to demonstrate quantifiable and third-party verified environmental improvements. In 2017, our Frankfort, Indiana facility also achieved ISO 14001 registration. At our facilities, we have initiated employee-based recycling programs that reduce waste being sent to the landfill, installed a fifty-five foot wind turbine to produce electricity and reduce our carbon emissions, and restored a natural wildlife habitat to enhance the environment and protect native animals. Our Portland, Oregon facility also received the City of Portland’s Sustainability at Work certification in 2017. |
| 36 |
Industry Trends
Truck transportation in the U.S., according to the ATA, was estimated to be a $676 billion industry in 2016. ATA estimates that approximately 71% of all freight tonnage is carried by trucks. Trailer demand is a direct function of the amount of freight to be transported. To monitor the state of the industry, we evaluate a number of indicators related to trailer manufacturing and the transportation industry. Recent trends we have observed include the following:
| · | Transportation / Trailer Cycle. The trailer industry generally follows the transportation industry cycles. After three consecutive years with total trailer demand well below normal replacement demand levels estimated to be between 200,000 trailers and 220,000 trailers, the five year period ending December 2015 demonstrated consecutive years of significant improvement in which the total trailer market increased year-over-year approximately 64%, 14%, 1%, 15% and 15% for 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014 and 2015, respectively, with total shipments of approximately 204,000, 232,000, 234,000, 269,000 and 308,000, respectively. The 2015 trailer shipments represent an all-time industry record. In 2016, trailer shipments decreased to approximately 286,000 units, but increased in 2017 by approximately 0.3% year-over-year to approximately 287,000 units. As we enter the ninth year of an economic recovery, ACT is estimating demand within the trailer industry in 2018 at approximately 299,000 and forecasting continued strong demand levels into the foreseeable future with estimated annual average demand for the four year period ending 2022 to be approximately 265,000 new trailers. Our view is generally consistent with ACT that trailer demand will remain significantly above replacement levels for 2018 and has the potential to remain above replacement levels for several years beyond 2018. |
| · | New Trailer Orders. According to ACT, total orders in 2017 were approximately 314,000 trailers, a 38% increase from 227,000 trailers ordered in 2016. Total orders for the dry van segment, the largest within the trailer industry, were approximately 204,000, an increase of 54% from 2016. |
| · | Transportation Regulations and Legislation. There are several different areas within both federal and state government regulations and legislation that are expected to have an impact on trailer demand, including: |
| - | The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (the “FMCSA”) has taken steps in recent years to improve truck safety standards, particularly by implementing the Compliance, Safety, and Accountability (“CSA”) program as well as requiring Electronic Logging Devices (“ELDs”). CSA is considered a comprehensive driver and fleet rating system that measures both the freight carriers and drivers on several safety related criteria, including driver safety, equipment maintenance and overall condition of trailers. This system drives increased awareness and action by carriers since enforcement actions were targeted and implemented beginning in June 2011. CSA is generally believed to have contributed to the tightening of the supply of drivers and capacity after 2011 as carriers took measures to improve their rating. The FMCSA issued a mandate that all carriers must install ELDs by December 2017. Industry estimates on carrier productivity losses as a result of ELDs range from 3% to 10%. We believe this ruling is likely to have a more significant impact on capacity than anticipated and may ultimately drive increased demand for new equipment as carriers attempt to recover lost productivity. While industry estimates vary, it is likely that only roughly half the industry utilizes ELDs right now, meaning that a good portion of owner-operators and carriers will either adopt the new technology, shut down, or be acquired starting in 2018. |
| 37 |
| - | In July 2013, a new FMCSA hours-of-service rule went into effect, reducing total driver hours from 82 hours per week to 70 hours. Congress included language in the 2016 spending package that requires the agency to meet an appropriate safety, driver health and driver longevity standard before re-imposing those restrictions. Specifically, the language prohibits FMCSA from reinstating certain sections of the rule’s 34-hour restart provisions unless an FMCSA study finds that they result in statistically significant improvements in safety and driver health, among other things. In 2017, the DOT released the findings of the study that failed to “explicitly identify a net benefit” from two suspended provisions of the hours of service rules regarding the 34-hour restart. We believe, the simple 34-hour restart rule, with no additional restrictions, will likely remain in place for the foreseeable future. Nevertheless, we believe the rule will keep trucking equipment utilization at record-high levels and, therefore, increase the general need for equipment. |
| - | The US Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) and National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (“NHTSA”) proposed new greenhouse gas regulations in July 2015, in an effort to reduce fuel consumption and production of carbon dioxide of heavy duty commercial vehicles. Following a comment period, the final rule was released in August 2016. The regulations are presently under review processes in Congress, within the EPA, and NHTSA that will ultimately determine whether this rule actually goes into effect. The Phase 2 greenhouse gas trailer (“GHG2”) rules were initially set to require compliance starting in January 2018. The Truck Trailer Manufacturers Association (“TTMA”) filed a petition in the U.S. Court of Appeals seeking review of the rule as it relates to the authority of the agencies to regulate trailers under the Clean Air Act. In addition, TTMA also filed for a Stay to suspend enforcement of the rule, to allow time for the EPA and NHTSA to reconsider the trailer provisions in the rule. In October 2017, the Court of Appeals granted the motion for Stay of the GHG2 rule as it applies to trailers. Ultimately, while compliance is on hold, the final impact on the trailer industry will not be known until there is a final ruling on the TTMA lawsuit. The rule itself focuses mainly on van trailers, and is divided into four increasingly stringent greenhouse gas reduction standards. The rule requires fuel saving technologies on van trailers, such as trailer side skirts, low rolling resistance tires, and automatic tire inflation systems. For tank trailers and flatbed trailers, the rule will require low rolling resistant tires and automotive tire inflation systems. More stringent van trailer standards would come into play in model years 2021, 2024 and 2027 – requiring more advanced fuel efficiency technologies, such are rear boat tails and higher percentage improvement side skirts and tires. In addition to increasing the cost of a trailer, these regulations may also lead to a higher demand for various aerodynamic device products. |
| - | In December 2017, the California Air Resource Board (“CARB”) has unveiled its own proposal for new greenhouse gas standards for medium- and heavy-duty trucks and trailers that operating in California. The CARB rules are similar to the EPA’s current GHG2 standards for the vehicles but CARB made additions to counter pending EPA challenges to repeal rules pertaining to trailers. It is likely that CARB’s adoption of the regulations - currently scheduled to take place at a Feb. 2018 meeting – that will require trailers be equipped with the fuel savings technologies outlined in the EPA GHG2 rules. We believe the likely start date will be in 2020. We will continue to monitor the CARB rulemaking. |
| · | Other Developments. Other developments and potential impacts on the industry include: |
| - | While we believe the need for trailer equipment will be positively impacted by the legislative and regulatory changes addressed above, these demand drivers could be offset by factors that contribute to the increased concentration and density of loads, including the miniaturization of electronic products and packaging optimization of bulk goods. Increases in load concentration or density could contribute to decreased need or demand for dry van trailers. |
| - | Trucking company profitability, which can be influenced by factors such as fuel prices, freight tonnage volumes, and government regulations, is highly correlated with the overall economy of the U.S. Carrier profitability significantly impacts demand for, and the financial ability to purchase new trailers. |
| - | Fleet equipment utilization has been rising due to increasing freight volumes, new government regulations and shortages of qualified truck drivers. As a result, trucking companies are under increased pressure to look for alternative ways to move freight, leading to more intermodal freight movement. We believe that railroads are at or near capacity, which will limit their ability to respond to freight demand pressures. Therefore, we expect that the majority of freight will continue to be moved by truck and, according to ATA, freight tonnage carried by trucks is expected to increase approximately 34% by 2028. |
| 38 |
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth certain operating data as a percentage of net sales for the periods indicated:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Cost of sales | 85.2 | 82.0 | 85.0 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 14.8 | 18.0 | 15.0 | |||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 4.4 | 4.0 | 3.6 | |||||||||
| Selling expenses | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.3 | |||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | |||||||||
| Other Operating Expenses | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||||
| Income from operations | 7.4 | 11.3 | 8.9 | |||||||||
| Interest expense | (1.0 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (0.9 | ) | ||||||
| Other, net | 0.5 | (0.1 | ) | 0.1 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 6.9 | 10.4 | 8.1 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 0.6 | 3.6 | 3.1 | |||||||||
| Net income | 6.3 | % | 6.8 | % | 5.0 | % | ||||||
2017 Compared to 2016
Net Sales
Net sales in 2017 decreased $78.3 million, or 4.2%, compared to the 2016 period. By business segment, net sales prior to intersegment eliminations and related units sold were as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 39 |
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (prior to elimination of intersegment sales) | Change | |||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | $ | % | |||||||||||||
| Sales by Segment | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | $ | 1,348,382 | $ | 1,506,110 | $ | (157,728 | ) | (10.5 | ) | |||||||
| Diversified Products | 361,358 | 352,404 | 8,954 | 2.5 | ||||||||||||
| Final Mile Products | 70,461 | - | 70,461 | |||||||||||||
| Eliminations | (13,040 | ) | (13,070 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,767,161 | $ | 1,845,444 | $ | (78,283 | ) | (4.2 | ) | |||||||
| New Trailers | (units) | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | 52,800 | 58,850 | (6,050 | ) | (10.3 | ) | ||||||||||
| Diversified Products | 2,250 | 2,100 | 150 | 7.1 | ||||||||||||
| Final Mile Products | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Eliminations | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 55,050 | 60,950 | (5,900 | ) | (9.7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Used Trailers | (units) | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | 1,050 | 950 | 100 | 10.5 | ||||||||||||
| Diversified Products | 100 | 100 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Final Mile Products | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Eliminations | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 1,150 | 1,050 | 100 | 9.5 | ||||||||||||
Commercial Trailer Products segment sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, were $1.3 billion in 2017, a decrease of $157.7 million, or 10.5%, compared to 2016. The decrease in sales was primarily due to a 10.3% decrease in new trailer shipments as 52,800 trailers were shipped in 2017 compared to 58,850 trailer shipments in the prior year. Used trailer sales decreased $1.3 million, or 10.6%, compared to the prior year due to the product mix available through fleet trade packages. Parts and service sales in 2017 decreased $8.0 million, or 14.3%, compared to 2016 primarily due to fewer retail branch locations throughout 2017 as compared to the prior year.
Diversified Products segment sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, were $361.4 million in 2017, an increase of $9.0 million, or 2.5%, compared to 2016. New trailer sales increased $10.5 million, or 8.1%, due to a 7.1% increase in new trailer shipments, as approximately 2,250 trailers were shipped in 2017 compared to 2,100 trailers shipped in the prior year on higher demand for tank trailers. Sales of our components, parts and service product offerings in 2017 increased $6.3 million, or 5.9%, compared to the prior year due to strong demand for our composite product offerings. Equipment and other sales decreased $7.5 million, or 7.4%, due to lower demand for our non-trailer truck mounted equipment and other engineered products.
Final Mile Product segment sales, prior to the eliminations of intersegment sales, were $70.5 million in 2017 for this newly created segment.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales was $1.5 billion in both 2017 and 2016. Cost of sales is comprised of material costs, a variable expense, and other manufacturing costs, comprised of both fixed and variable expenses, including direct and indirect labor, outbound freight, and overhead expenses.
Commercial Trailer Products segment cost of sales was $1.2 billion in 2017, a decrease of $88.4 million, or 7.0%, compared to the prior year period. The decrease was primarily driven by a $70.3 million reduction in materials costs as lower production volumes more than offset the increase in commodity costs as compared to the prior year period. Other manufacturing costs decreased $18.1 million as compared to the prior year period due to lower new trailer production volumes.
| 40 |
Diversified Products segment cost of sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was $291.2 million in 2017, an increase of $14.4 million, or 5.2%, compared to the prior period. The increase was primarily driven by a $10.5 million increase in materials costs due to increased commodity costs and a $3.9 million increase in other manufacturing costs related to increased volume and product mix.
Final Mile Product segment cost of sales was $62.3 million in 2017 for this newly created segment.
Gross Profit
Gross profit was $260.9 million in 2017, a decrease of $64.7 million, or 19.9% from 2016. Gross profit as a percentage of sales was 14.8% in 2017 as compared to 18.0% in 2016. Gross profit by segment was as follows (in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | $ | % | |||||||||||||
| Gross Profit by Segment: | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | $ | 183,912 | $ | 253,274 | $ | (69,362 | ) | (27.4 | ) | |||||||
| Diversified Products | 70,159 | 75,630 | (5,471 | ) | (7.2 | ) | ||||||||||
| Final Mile Products | 8,150 | - | 8,150 | |||||||||||||
| Corporate and Eliminations | (1,346 | ) | (3,371 | ) | 2,025 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 260,875 | $ | 325,533 | $ | (64,658 | ) | (19.9 | ) | |||||||
Commercial Trailer Products segment gross profit was $183.9 million in 2017 compared to $253.3 million in the prior year, a decrease of $69.4 million. Gross profit, as a percentage of net sales prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was 13.6% in 2017 as compared to 16.8% in 2016, a decrease of 320 basis points. The decreases in gross profit and gross profit margin as compared to the prior year was primarily driven by lower shipments of new trailers, increases in commodity costs, and labor constraints resulting in higher overtime requirements to meet current demand.
Diversified Products segment gross profit was $70.2 million in 2017 compared to $75.6 million in 2016. Gross profit, as a percentage of net sales prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was 19.4% in 2017 compared to 21.5% in 2016. The decrease in gross profit as a percentage of net sales, as compared to the prior year, was due primarily to product mix and higher commodity costs.
Final Mile Product segment gross profit was $8.2 million in 2017 for this newly created segment. Gross profit, as a percentage of sales, was 11.6% in 2017.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses in 2017 increased $3.7 million, or 5.0%, from the prior year. The increase was largely due to the inclusion of Supreme, which added expenses of $6.8 million in the current year period. The Supreme expenses were offset by a $3.0 million decrease in employee related costs, including costs associated with employee incentive programs. General and administrative expenses, as a percentage of net sales, were 4.4% in 2017 compared to 4.0% in 2016.
Selling Expenses
Selling expenses were $25.6 million in 2017, a decrease of $1.7 million, or 6.2%, compared to the prior year. The decrease was largely due to lower employee related costs, including costs associated with employee incentive programs, which were partially offset by the inclusion of Supreme, which added $3.0 million in expense during the current year. As a percentage of net sales, selling expenses were 1.5% in both 2017 and 2016.
| 41 |
Amortization of Intangibles
Amortization of intangibles was $17.0 million in 2017 compared to $19.9 million in 2016. Amortization of intangibles for both periods primarily includes amortization expense recognized for intangible assets recorded from the acquisition of Walker in May 2012 and certain assets acquired from Beall in February 2013.
Acquisition Expenses
Acquisition expenses totaling $9.6 million for 2017 represent costs incurred in connection with the acquisition of Supreme including fees paid to an investment banker for acquisition services and the related bridge financing commitment, as well as professional fees for diligence, legal, and accounting.
Other Income (Expense)
Interest expense in 2017 totaled $16.4 million compared to $15.7 million in the prior year. Interest expense for both periods primarily related to interest and non-cash accretion charges on our Convertible Notes and Term Loan Credit Agreement. The increase from the prior year is primarily due to the issuance of our Senior Notes in September 2017 related to the financing of a portion of the Supreme acquisition, partially offset by the repurchase of the Convertible Notes completed over the previous year.
Other, net for 2017 represented income of $8.1 million as compared to expense of $1.5 million for the prior year period. The current year period primarily consists of a gain on the sale of certain retail branch assets.
Income Taxes
We recognized income tax expense of $11.1 million in 2017 compared to $66.0 million in the prior year. The effective tax rate for 2017 was 9.1%, which differs from the U.S. Federal statutory rate of 35% primarily due to the impact of the revaluation of deferred income taxes associated with the change in the US federal income tax rate with the enactment of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act on December 22, 2017. In addition, the rate for 2017 includes a tax benefit related to the release of income tax reserves resulting from the closing of open tax years to which those reserves related. Cash taxes paid in 2017 were $41.2 million.
2016 Compared to 2015
Net Sales
Net sales in 2016 decreased $182.0 million, or 9.0%, compared to the 2015 period. By business segment, net sales prior to intersegment eliminations and related units sold were as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 42 |
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (prior to elimination of intersegment sales) | Change | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | $ | % | |||||||||||||
| Sales by Segment | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | $ | 1,506,110 | $ | 1,582,241 | $ | (76,131 | ) | (4.8 | ) | |||||||
| Diversified Products | 352,404 | 456,927 | (104,523 | ) | (22.9 | ) | ||||||||||
| Eliminations | (13,070 | ) | (11,679 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 1,845,444 | $ | 2,027,489 | $ | (182,045 | ) | (9.0 | ) | |||||||
| New Trailers | (units) | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | 58,850 | 61,300 | (2,450 | ) | (4.0 | ) | ||||||||||
| Diversified Products | 2,100 | 3,400 | (1,300 | ) | (38.2 | ) | ||||||||||
| Eliminations | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 60,950 | 64,700 | (3,750 | ) | (5.8 | ) | ||||||||||
| Used Trailers | (units) | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | 950 | 1,900 | (950 | ) | (50.0 | ) | ||||||||||
| Diversified Products | 100 | 150 | (50 | ) | (33.3 | ) | ||||||||||
| Eliminations | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 1,050 | 2,050 | (1,000 | ) | (48.8 | ) | ||||||||||
Commercial Trailer Products segment sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, were $1.5 billion in 2016, a decrease of $76.1 million, or 4.8%, compared to 2015. The decrease in sales was primarily due to a 4.0% decrease in new trailer shipments as 58,850 trailers were shipped in 2016 compared to 61,300 trailer shipments in 2015. Used trailer sales decreased $19.0 million, or 61.3%, compared to 2015 due to decreased availability and selective management of product through fleet trade packages as approximately 950 fewer used trailers shipped in 2016 as compared to the prior year. Parts and service sales in 2016 decreased $4.3 million, or 7.1%, compared to 2015 primarily due to fewer retail branch locations throughout 2016 as compared to the prior year.
Diversified Products segment sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, were $352.4 million in 2016, down $104.5 million, or 22.9%, compared to 2015. New trailer sales decreased $88.4 million, or 40.1%, due to a 38.2% decrease in new trailer shipments, as approximately 2,100 trailers were shipped in 2016 compared to 3,400 trailers shipped in 2015. Sales of our components, parts and service product offerings in 2016 were comparable to 2015. Equipment and other sales decreased $13.5 million, or 11.1%, due to lower demand for our non-trailer truck mounted equipment and other engineered products.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales was $1.5 billion, a decrease of $204.1 million, or 11.8%, as compared to 2015. Cost of sales is comprised of material costs, a variable expense, and other manufacturing costs, comprised of both fixed and variable expenses, including direct and indirect labor, outbound freight, and overhead expenses.
Commercial Trailer Products segment cost of sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was $1.3 billion in 2016, a decrease of $131.6 million, or 9.5%, compared to 2015. The decrease was primarily driven by a $131.2 million reduction in materials costs attributable to lower new trailer production volumes, as well as lower commodity costs and continued optimization through product design and sourcing.
Diversified Products segment cost of sales, prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was $276.8 million in 2016, an decrease of $73.1 million, or 20.9%, compared to 2015. The decrease was primarily driven by a $58.7 million reduction in materials costs and a $14.4 million decrease in other manufacturing due primarily to decreased sales volumes resulting from weaker tank trailer demand, lower material costs and continued operational efficiencies as compared to 2015.
| 43 |
Gross Profit
Gross profit was $325.5 million in 2016, an improvement of $22.1 million, or 7.3% from 2015. Gross profit as a percentage of sales was 18.0% in 2016 as compared to 15.0% in 2015. Gross profit by segment was as follows (in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | $ | % | |||||||||||||
| Gross Profit by Segment: | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Trailer Products | $ | 253,274 | $ | 197,777 | $ | 55,497 | 28.1 | |||||||||
| Diversified Products | 75,630 | 107,023 | (31,393 | ) | (29.3 | ) | ||||||||||
| Corporate and Eliminations | (3,370 | ) | (1,357 | ) | (2,013 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total | $ | 325,534 | $ | 303,443 | $ | 22,091 | 7.3 | |||||||||
Commercial Trailer Products segment gross profit was $253.3 million in 2016 compared to $197.8 million in 2015, an increase of $55 million. Gross profit, as a percentage of net sales prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was 16.8% in 2016 as compared to 12.5% in 2015, an increase of 430 basis points. The increases in gross profit and profit margin as compared to 2015 was primarily driven by improved pricing, favorable material costs, including cost optimization through product design and sourcing, and continued operational efficiencies.
Diversified Products segment gross profit was $75.6 million in 2016 compared to $107.0 million in 2015. Gross profit, as a percentage of net sales prior to the elimination of intersegment sales, was 21.5% in 2016 compared to 23.4% in 2015. The decrease in gross profit as a percentage of net sales, as compared to 2015, was due primarily to lower sales volume and the reduced leverage of fixed costs from lower production levels which more than offset the favorable material costs and continued operational efficiencies.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses in 2016 increased $0.6 million, or 0.9%, from 2015 as a result of a $2.7 million increase in outside service and professional fee expenditures, as well as a $0.9 million increase in various other operating expenses, primarily information technology related costs. These increases were offset by a $3.0 million decrease in employee related costs, including costs associated with employee incentive programs. General and administrative expenses, as a percentage of net sales, were 4.0% in 2016 compared to 3.6% in 2015.
Selling Expenses
Selling expenses were $27.3 million in 2016, an increase of $0.1 million, or 0.1%, compared to 2015 as a $0.3 million increase in advertising and promotional efforts were partially offset by lower employee related costs, including costs associated with employee incentive programs. As a percentage of net sales, selling expenses were 1.5% in 2016 compared to 1.3% in 2015.
Amortization of Intangibles
Amortization of intangibles was $19.9 million in 2016 compared to $21.3 million in 2015. Amortization of intangibles for both periods primarily includes amortization expense recognized for intangible assets recorded from the acquisition of Walker in May 2012 and certain assets acquired from Beall in February 2013.
Other Operating Expenses
Other operating expenses of $1.7 million in 2016 is the impairment of goodwill recognized during the second quarter of 2016. Based on an analysis we performed to determine the allocations of goodwill with the realignment of our reporting segments, we determined a portion of goodwill allocated to our retail branch operations was impaired as the fair value of reporting did not exceed its carrying value resulting in an impairment charge for the Commercial Trailer Products reporting segment.
| 44 |
Other Income (Expense)
Interest expense in 2016 totaled $15.7 million compared to $19.5 million in 2015. Interest expense for both periods primarily related to interest and non-cash accretion charges on our Convertible Notes and Term Loan Credit Agreement. The decrease from the prior year is primarily due to Convertible Notes repurchases completed in late 2015 and during the first and fourth quarters of 2016.
Other, net for 2016 represented expense of $1.5 million as compared to income of $2.5 million for 2015. The current year expense includes $1.9 million loss on debt extinguishment for voluntary purchases of our outstanding Convertible Notes partially offset by a $0.3 million gain on the transition of our retail branches to independent dealer facilities. The 2015 period primarily consists of an $8.3 million gain on the sale of our former retail branch real estate in Fontana, California and Portland, Oregon partially offset by $5.3 million of accelerated amortization and related fees in connection with the refinancing of our Term Loan Credit Agreement in March 2015 and $0.3 million of charges incurred in connection with the amendment to our Credit Agreement in June 2015.
Income Taxes
We recognized income tax expense of $66.0 million in 2016 compared to $59.0 million in 2015. The effective tax rate for 2016 was 35.6%, which differs from the U.S. Federal statutory rate of 35% primarily due to the impact of state and local taxes offset by the benefit of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code domestic manufacturing deduction. In addition, the rate for 2016 includes a tax benefit related to employee share-based payment awards, which are now recorded as an income tax expense (or benefit) in earnings effective with the adoption of a new accounting standard. Cash taxes paid in 2016 were $68.9 million.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Capital Structure
Our capital structure is comprised of a mix of debt and equity. As of December 31, 2017, our debt to equity ratio was approximately 1.1:1.0. Our long-term objective is to generate operating cash flows sufficient to support the growth within our businesses and increase shareholder value. We intend to achieve this objective through a balanced capital allocation strategy of maintaining strong liquidity, deleveraging our balance sheet, investing in the business, both organically and strategically, and returning capital to our shareholders. Throughout 2017, and in keeping to this balanced approach, several actions were taken to demonstrate our commitment to prudently manage the overall financial risk and increase shareholder value through a return of capital. These actions include the repurchase of $70.1 million of our common stock under the share repurchase program approved by our Board of Directors, reinstating our quarterly dividend in 2017 totaling $0.24 per share and $15.3 million, as well as completing the purchase of $4.4 million in principal of our outstanding Convertible Notes (see “Debt Agreements and Related Amendments” section below for details). For 2018, we expect to continue our commitment to fund our working capital requirements and capital expenditures while also returning capital to our shareholders and deleveraging our balance sheet through cash flows from operations as well as available borrowings under our existing Credit Agreement.
Debt Agreements and Related Amendments
Convertible Senior Notes
In April 2012, we issued Convertible Senior Notes due 2018 (the “Convertible Notes”) in a public offering with an aggregate principal amount of $150 million. The Convertible Notes bear interest at the rate of 3.375% per annum from the date of issuance, payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1, and mature on May 1, 2018. The Convertible Notes are senior unsecured obligations and rank equally with our existing and future senior unsecured debt. We used the net proceeds of $145.1 million from the sale of the Convertible Notes to fund a portion of the purchase price of the acquisition of Walker in May 2012.
| 45 |
As of December 31, 2017, and at any time until the close of business on the second business day immediately preceding the maturity date, the Convertible Notes are convertible by their holders into cash, shares of our common stock or any combination thereof at our election, at an initial conversion rate of 85.4372 shares of our common stock per $1,000 in principal amount of Notes, which is equal to an initial conversion price of approximately $11.70 per share.
If the Convertible Notes outstanding at December 31, 2017 had been converted as of December 31, 2017, the if-converted value would exceed the principal amount by approximately $38 million. It is our intent to settle conversions in cash for both the principal portion and the excess of the conversion value over the principal portion. The Convertible Notes mature on May 1, 2018 and are classified as current within the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet.
We account separately for the liability and equity components of the Convertible Notes in accordance with authoritative guidance for convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash upon conversion. The guidance requires the carrying amount of the liability component to be estimated by measuring the fair value of a similar liability that does not have an associated conversion feature. We determined that senior, unsecured corporate bonds traded on the market represent a similar liability to the Convertible Notes without the conversion option. Based on market data available for publicly traded, senior, unsecured corporate bonds issued by companies in the same industry and with similar maturity, we estimated the implied interest rate of the Convertible Notes to be 7.0%, assuming no conversion option. Assumptions used in the estimate represent what market participants would use in pricing the liability component, including market interest rates, credit standing, and yield curves, all of which are defined as Level 2 observable inputs. The estimated implied interest rate was applied to the Convertible Notes, which resulted in a fair value of the liability component of $123.8 million upon issuance, calculated as the present value of implied future payments based on the $150.0 million aggregate principal amount. The $21.7 million difference between the cash proceeds before offering expenses of $145.5 million and the estimated fair value of the liability component was recorded in additional paid-in capital. The discount on the liability portion of the Convertible Notes is being amortized over the life of the Convertible Notes using the effective interest rate method.
During 2017, we acquired $4.4 million in principal of such Convertible Notes for $8.0 million, excluding accrued interest. Additionally, in 2016 we acquired $82.0 million in principal for $98.9 million, excluding accrued interest. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 we recognized a loss on debt extinguishment of $0.1 million and $1.9 million, respectively, for repurchase activity, which is included in Other, net on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Senior Notes
On September 26, 2017, we issued Senior Notes due 2025 (the “Senior Notes”) in an offering pursuant to Rule 144A or Regulation S under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, with an aggregate principal amount of $325 million. The Senior Notes bear interest at the rate of 5.50% per annum from the date of issuance, and will pay interest semi-annually in cash on April 1 and October 1 of each year, beginning on April 1, 2018. We used the net proceeds of $318.9 million from the sale of the Senior Notes to finance a portion of the acquisition of Supreme and to pay related fees and expenses.
The Senior Notes will mature on October 1, 2025. At any time prior to October 1, 2020, we may redeem some or all of the Senior Notes for cash at a redemption price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes being redeemed plus an applicable make-whole premium set forth in the indenture for the Senior Notes and accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date. Prior to October 1, 2020, we may redeem up to 40% of the Senior Notes at a redemption price of 105.50% of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date, with the proceeds of certain equity offerings so long as if, after any such redemption occurs, at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes remains outstanding. On and after October 1, 2020, we may redeem some or all of the Senior Notes at redemption prices (expressed as percentages of principal amount) equal to 102.750% for the twelve-month period beginning on October 1, 2020, 101.375% for the twelve-month period beginning October 1, 2021 and 100.000% beginning on October 1, 2022, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date. Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control (as defined in the indenture for the Senior Notes), unless we have exercised our optional redemption right in respect of the Senior Notes, the holders of the Senior Notes have the right to require us to repurchase all or a portion of the Senior Notes at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes, plus any accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the date of repurchase.
| 46 |
The Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by all of our direct and indirect existing and future domestic restricted subsidiaries, subject to certain restrictions. The Senior Notes and related guarantees are our and the guarantors’ general unsecured senior obligations and are subordinate to all of our and the guarantors’ existing and future secured debt to the extent of the assets securing that secured obligation. In addition, the Senior Notes are structurally subordinate to any existing and future debt of any of our subsidiaries that are not guarantors, to the extent of the assets of those subsidiaries.
The indenture for the Senior Notes restricts our ability and the ability of certain of its subsidiaries to: (i) incur additional indebtedness; (ii) pay dividends or make other distributions in respect of, or repurchase or redeem, its capital stock or with respect to any other interest or participation in, or measured by, its profits; (iii) make loans and certain investments; (iv) sell assets; (v) create or incur liens; (vi) enter into transactions with affiliates; and (vii) consolidate, merge or sell all or substantially all of its assets. These covenants are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications. During any time when the Senior Notes are rated investment grade by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. and Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services and no event of default has occurred or is continuing, many of such covenants will be suspended and the Company and its subsidiaries will not be subject to such covenants during such period.
The indenture for the Senior Notes contains customary events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of covenants, failure to pay certain judgments and certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency and reorganization. If an event of default occurs and is continuing, the principal amount of the Senior Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, may be declared immediately due and payable. These amounts automatically become due and payable if an event of default relating to certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization occurs.
Contractual coupon interest expense and accretion of discount and fees for the Senior Notes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $4.8 million and is included in Interest Expense on our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Revolving Credit Agreement
In May 2012, we entered into the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (as subsequently amended, the “Credit Agreement”), dated as of May 8, 2012, among us, certain of our subsidiaries from time to time party thereto (together with us, the “Borrowers”), the several lenders from time to time party thereto, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as arranger and administrative agent (the “Agent”). The Credit Agreement provides for, among other things, (x) a $175 million senior secured revolving credit facility that matures on June 4, 2020, subject to certain springing maturity events and (y) an uncommitted accordion feature allowing for an increase to the availability under the revolving credit facility of up to $50 million, subject to certain conditions (the “Revolving Credit Facility”).
The Revolving Credit Facility (i) bears interest, at the Borrowers’ election, at (x) LIBOR (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin ranging from 150 basis points to 200 basis points, or (y) a base rate plus a margin ranging from 50 basis points to 100 basis points, in each case, based upon the monthly average excess availability under the Revolving Credit Facility, (ii) requires us to pay a monthly unused line fee equal to 25 basis points times the average unused availability under the Revolving Credit Facility, (iii) provides that if availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than 12.5% of the total commitment under the Revolving Credit Facility or if there exists an event of default, amounts in any of the Borrowers’ and the subsidiary guarantors’ deposit accounts (other than certain excluded accounts) will be transferred daily into a blocked account held by the Agent and applied to reduce the outstanding amounts under the Revolving Credit Facility, and (iv) requires us to maintain a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1.1 to 1.0 as of the end of any period of 12 fiscal months when excess availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than 10% of the total commitment under the Revolving Credit Facility.
In connection with, and in order to permit under the Credit Agreement, the Senior Notes offering and the acquisition of Supreme, on August 16, 2017, we entered into the Third Amendment to the Credit Agreement (the “Third Amendment”). The Third Amendment also permitted us to incur certain other indebtedness in connection with the acquisition of Supreme and to acquire certain liens and obligations of Supreme upon the consummation of the acquisition.
| 47 |
The Credit Agreement is guaranteed by certain of our subsidiaries (the “Revolver Guarantors”) and is secured by (i) first priority security interests (subject only to customary permitted liens and certain other permitted liens) in substantially all personal property of the Borrowers and the Revolver Guarantors, consisting of accounts receivable, inventory, cash, deposit and securities accounts and any cash or other assets in such accounts and, to the extent evidencing or otherwise related to such property, all general intangibles, licenses, intercompany debt, letter of credit rights, commercial tort claims, chattel paper, instruments, supporting obligations, documents and payment intangibles (collectively, the “Revolver Priority Collateral”), and (ii) second-priority liens on and security interests in (subject only to the liens securing the Term Loan Credit Agreement (as defined below), customary permitted liens and certain other permitted liens) (A) equity interests of each direct subsidiary held by the Borrower and each Revolver Guarantor (subject to customary limitations in the case of the equity of foreign subsidiaries), and (B) substantially all other tangible and intangible assets of the Borrowers and the Revolver Guarantors including equipment, general intangibles, intercompany notes, insurance policies, investment property, intellectual property and material owned real property (in each case, except to the extent constituting Revolver Priority Collateral) (collectively, the “Term Priority Collateral”). The respective priorities of the security interests securing the Credit Agreement and the Term Loan Credit Agreement are governed by an Intercreditor Agreement between the Revolver Agent and the Term Agent (as defined below) (the “Intercreditor Agreement”).
The Credit Agreement contains customary covenants limiting our ability to, among other things, pay cash dividends, incur debt or liens, redeem or repurchase stock, enter into transactions with affiliates, merge, dissolve, pay off subordinated indebtedness, make investments and dispose of assets. Subject to the terms of the Intercreditor Agreement, if the covenants under the Credit Agreement are breached, the lenders may, subject to various customary cure rights, require the immediate payment of all amounts outstanding and foreclose on collateral. Other customary events of default in the Credit Agreement include, without limitation, failure to pay obligations when due, initiation of insolvency proceedings, defaults on certain other indebtedness, and the incurrence of certain judgments that are not stayed, satisfied, bonded or discharged within 30 days.
As of December 31, 2017, we were in compliance with all covenants of the Credit Agreement.
Term Loan Credit Agreement
In May 2012, we entered into a Term Loan Credit Agreement (as amended, the “Term Loan Credit Agreement”), dated as of May 8, 2012, among us, the several lenders from time to time party thereto, Morgan Stanley Senior Funding, Inc., as administrative agent (the “Term Agent”), joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, and Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, which provides for, among other things, (x) a senior secured term loan of $188.0 million that matures on March 19, 2022, subject to certain springing maturity events (the “Term Loans”), and (y) an uncommitted accordion feature to provide for additional senior secured term loans of up to $75 million plus an unlimited amount provided that the senior secured leverage ratio would not exceed 3.00 to 1.00, subject to certain conditions (the “Term Loan Facility”).
On February 24, 2017, we entered into Amendment No. 3 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 3”). As of February 24, 2017, $189.5 million of the Tranche B-2 Loans were outstanding. Under Amendment No. 3, the lenders agreed to provide us term loans in the same aggregate principal amount of the outstanding Tranche B-2 Loans (the “Tranche B-3 Loans”), which were used to refinance the outstanding Tranche B-2 Loans.
In connection with, and in order to permit under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, the Senior Notes offering and the acquisition of Supreme, on August 18, 2017, we entered into Amendment No. 4 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 4”). Amendment No. 4 also permitted us to incur certain other indebtedness in connection with the Supreme acquisition and to acquire certain liens and obligations of Supreme upon the consummation of the Supreme acquisition.
Furthermore, on November 17, 2017, we entered into Amendment No. 5 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 5”). As of the Amendment No. 5 date, $188.0 million of the Term Loans were outstanding. Under Amendment No. 5, the lenders agreed to provide us term loans in the same aggregate principal amount of the outstanding Term Loans (“Tranche B-4 Loans”), which were used to refinance the outstanding Term Loans.
The Tranche B-4 Loans amortize in equal quarterly installments in aggregate amounts equal to 0.25% of the initial principal amount of the Tranche B-4 Loans, with the balance payable at maturity, and bear interest at a rate, at the Company’s election, equal to (i) LIBOR (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin of 225 basis points or (ii) a base rate (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin of 125 basis points. We are not subject to any financial covenants under the Term Loan Facility.
| 48 |
The Term Loan Credit Agreement is guaranteed by certain of our subsidiaries, and is secured by (i) first-priority liens on and security interests in the Term Priority Collateral, and (ii) second-priority security interests in the Revolver Priority Collateral.
The Term Loan Credit Agreement contains customary covenants limiting our ability to, among other things, pay cash dividends, incur debt or liens, redeem or repurchase stock, enter into transactions with affiliates, merge, dissolve, pay off subordinated indebtedness, make investments and dispose of assets. Subject to the terms of the Intercreditor Agreement, if the covenants under the Term Loan Credit Agreement are breached, the lenders may, subject to various customary cure rights, require the immediate payment of all amounts outstanding and foreclose on collateral. Other customary events of default in the Term Loan Credit Agreement include, without limitation, failure to pay obligations when due, initiation of insolvency proceedings, defaults on certain other indebtedness, and the incurrence of certain judgments that are not stayed, satisfied, bonded or discharged within 60 days.
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, we paid interest of $7.4 million, $8.3 million, and $8.5 million, respectively, and principal of $1.9 million, $1.9 million and $1.4 million, respectively. We recognized a loss on debt extinguishment of $0.7 million during 2017 in connection with Amendment No. 3 and Amendment No. 5, which was included in Other, net on our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. As of December 31, 2017, we had $187.6 million outstanding under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, of which $1.9 million was classified as current on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet.
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 we incurred charges of $0.2 million, $0.2 million, and $0.3 million, respectively, for amortization of fees and original issuance discount, which is included in Interest Expense in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Cash Flow
2017 compared to 2016
Cash provided by operating activities for 2017 totaled $144.4 million, compared to $178.8 million in 2016. The cash provided by operations during the current year period was the result of net income adjusted for various non-cash activities, including depreciation, amortization, gain (loss) on the sale of assets, deferred taxes, loss on debt extinguishment, stock-based compensation, accretion of debt discount and impairment of goodwill and intangibles, of $137.1 million, and a $7.3 million decrease in our working capital. Changes in key working capital accounts for 2017 and 2016 are summarized below (in thousands):
| Source (Use) of cash: | 2017 | 2016 | Change | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | 31,943 | $ | (809 | ) | $ | 32,752 | |||||
| Inventories | $ | (13,158 | ) | $ | 24,969 | $ | (38,127 | ) | ||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | (963 | ) | $ | (13,002 | ) | $ | 12,039 | ||||
| Net (use) source of cash | $ | 17,822 | $ | 11,158 | $ | 6,664 | ||||||
Accounts receivable decreased by $31.9 million in 2017 as compared to an increase of $0.8 million in the prior year period. Days sales outstanding, a measure of working capital efficiency that measures the amount of time a receivable is outstanding, decreased to approximately 25 days as of December 31, 2017, compared to 30 days in 2016. The decrease in accounts receivable for 2017 was primarily the result of strong customer collections. Inventory increased by $13.2 million during 2017 as compared to a decrease of $25.0 million in 2016. The increase in inventory for the 2017 period was primarily due to higher raw materials inventories for the expected strong demand environment for January 2018 as compared to January 2017. Our inventory turns, a commonly used measure of working capital efficiency that measures how quickly inventory turns per year was approximately 7 times in 2017 compared to 8 times in 2016. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities decreased by $1.0 million in 2017 compared to a decrease of $13.0 million for 2016. The decrease in 2017 was primarily due to decreases in accruals pertaining to employee salaries and related incentive compensation offset by increased accounts payable due to timing of production. Days payable outstanding, a measure of working capital efficiency that measures the amount of time a payable is outstanding, was 21 days in 2017 and 16 days in 2016.
| 49 |
Investing activities used $332.2 million during 2017 compared to $17.3 million used in 2016. Investing activities for 2017 was primarily related to the acquisition of Supreme completed in the third quarter for $323.5 million, net of cash acquired. It also includes capital expenditures to support growth and improvement initiatives at our facilities totaling $26.1 million. These uses of cash were partially offset by proceeds from sale of assets totaling $17.3 million, primarily related to the sale of our former branch locations. Cash used in investing activities in 2016 included capital expenditures to support growth and improvement initiatives at our facilities totaling $20.3 million, partially offset by proceeds from the sale of certain branch location assets totaling $3.0 million.
Financing activities provided $215.9 million during 2017, as the issuance of our new $325 million Senior Notes was partially offset by repurchases of common stock through our share repurchase program totaling $70.1 million, cash dividends paid to our shareholders and holders of our Convertible Notes of $15.3 million, and the payment of principal under various debt and lease obligations totaling $18.3 million. Financing activities used $176.8 million during 2016 primarily due to the repurchases of common stock through our share repurchase program totaling $77.0 million and repurchase of Convertible Notes totaling $98.9 million, excluding accrued interest.
As of December 31, 2017, our liquidity position, defined as cash on hand and available borrowing capacity, amounted to $361.1 million, representing an increase of $28.1 million from December 31, 2016. Total debt and capital lease obligations amounted to $551.4 million as of December 31, 2017. As we continue to see a strong demand environment within the trailer industry and excellence in operational performance across all business segments, we believe our liquidity is adequate to fund our currently planned operations, working capital needs and capital expenditures for 2018.
2016 compared to 2015
Cash provided by operating activities for 2016 totaled $178.8 million, compared to $131.8 million in 2015. The cash provided by operations during the 2016 period was the result of net income adjusted for various non-cash activities, including depreciation, amortization, gain (loss) on the sale of assets, deferred taxes, loss on debt extinguishment, stock-based compensation, accretion of debt discount and impairment of goodwill and intangibles, of $179.4 million, and a $0.7 million increase in our working capital. Changes in key working capital accounts for 2016 and 2015 are summarized below (in thousands):
| Source (Use) of cash: | 2016 | 2015 | Change | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | (809 | ) | $ | (17,618 | ) | $ | 16,809 | ||||
| Inventories | $ | 24,969 | $ | 10,162 | $ | 14,807 | ||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | (13,002 | ) | $ | (12,243 | ) | $ | (759 | ) | |||
| Net (use) source of cash | $ | 11,158 | $ | (19,699 | ) | $ | 30,857 | |||||
Accounts receivable increased by $0.8 million in 2016 as compared to an increase of $17.6 million in the prior year period. Days sales outstanding, a measure of working capital efficiency that measures the amount of time a receivable is outstanding, increased to approximately 30 days as of December 31, 2016, compared to 25 days in 2015. The increase in accounts receivable for 2016 was primarily the result of the timing of shipments. Inventory decreased by $25.0 million during 2016 as compared to a decrease of $10.2 million in 2015. The decrease in inventory for the 2016 period was primarily due to lower finished goods inventories as customer shipments exceeded production, and lower raw materials inventories due to improved inventory management and expected lower demand volume for January 2017 as compared to January 2016. Our inventory turns, a commonly used measure of working capital efficiency that measures how quickly inventory turns per year was approximately 8 times in 2016 and 2015. Accounts payable and accrued liabilities decreased by $13.0 million in 2016 compared to a decrease of $12.2 million for 2015. The decrease in 2016 was primarily due to timing of production and a decrease in accruals pertaining to employee salaries and related incentive compensation. Days payable outstanding, a measure of working capital efficiency that measures the amount of time a payable is outstanding, was 16 days in 2016 and 2015.
Investing activities used $17.3 million during 2016 compared to $7.6 million used in 2015. Investing activities for 2016 include capital expenditures to support growth and improvement initiatives at our facilities totaling $20.3 million, partially offset by proceeds from the sale of certain branch location assets totaling $3.0 million. Cash used in investing activities in 2015 was primarily related to capital expenditures totaling $20.8 million, partially offset by proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment totaling $13.2 million, which was comprised primarily of the sale of our former retail branch real estate.
| 50 |
Financing activities used $176.8 million during 2016, primarily due to the repurchases of common stock through our share repurchase program totaling $77.0 million and repurchase of Notes totaling $98.9 million, excluding accrued interest. Financing activities used $91.4 million during 2015 primarily due to the repurchases of common stock through our share repurchase program totaling $60.1 million, repurchase of Notes totaling $22.9 million, excluding accrued interest, principal payments under existing debt and capital lease obligations of $6.1 million, and debt issuance costs of $2.6 million in relation to amendments to our Term Loan Credit Agreement and Credit Agreement.
Capital Expenditures
Capital spending amounted to $26.1 million for 2017 and is anticipated to be in the range of $40 million to $50 million for 2018. Capital spending for 2017 was primarily utilized to support maintenance, growth, and productivity improvement initiatives within our facilities. For 2018, the increase in expected capital spending is attributable to the acquisition of Supreme, which we expect to spend in the range of $10 to $12 million and our continued investment in growth and productivity improvement initiatives across all our facilities.
Off-Balance Sheet Transactions
As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately $5.2 million in operating lease commitments, inclusive of Supreme. We did not enter into any material off-balance sheet debt or operating lease transactions during the year.
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
A summary of payments of our contractual obligations and commercial commitments, both on and off balance sheet, as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| DEBT: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revolving Facility (due 2020) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||||
| Convertible Senior Notes (due 2018) | 44,561 | - | - | - | - | - | 44,561 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Term Loan Credit Facility (due 2022) | 1,880 | 1,880 | 1,880 | 1,880 | 180,057 | - | 187,577 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Senior Notes (due 2025) | - | - | - | - | - | 325,000 | 325,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Debt | 92 | - | - | - | - | - | 92 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Leases (including principal and interest) | 361 | 361 | 361 | 361 | 30 | - | 1,474 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL DEBT | $ | 46,894 | $ | 2,241 | $ | 2,241 | $ | 2,241 | $ | 180,087 | $ | 325,000 | $ | 558,704 | ||||||||||||||
| OTHER: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating Leases | $ | 2,466 | $ | 1,364 | $ | 688 | $ | 439 | $ | 254 | $ | - | $ | 5,211 | ||||||||||||||
| TOTAL OTHER | $ | 2,466 | $ | 1,364 | $ | 688 | $ | 439 | $ | 254 | $ | - | $ | 5,211 | ||||||||||||||
| OTHER COMMERCIAL COMMITMENTS: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters of Credit | $ | 5,303 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,303 | ||||||||||||||
| Raw Material Purchase Commitments | 58,658 | - | - | - | - | - | 58,658 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Chassis Converter Pool Agreements | 21,523 | - | - | - | - | - | 21,523 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL OTHER COMMERCIAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COMMITMENTS | $ | 85,484 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 85,484 | ||||||||||||||
| TOTAL OBLIGATIONS | $ | 134,844 | $ | 3,605 | $ | 2,929 | $ | 2,680 | $ | 180,341 | $ | 325,000 | $ | 649,399 | ||||||||||||||
Scheduled payments for our Revolving Credit Facility exclude interest payments as rates are variable. Borrowings under the Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at a variable rate based on the London Interbank Offer Rate (LIBOR) or a base rate determined by the lender’s prime rate plus an applicable margin, as defined in the agreement. Outstanding borrowings under the Revolving Credit Facility bear interest at a rate, at our election, equal to (i) LIBOR plus a margin ranging from 1.50% to 2.00% or (ii) a base rate plus a margin ranging from 0.50% to 1.00%, in each case depending upon the monthly average excess availability under the Revolving Credit Facility. We are required to pay a monthly unused line fee equal to 0.25% times the average daily unused availability along with other customary fees and expenses of our agent and lenders.
| 51 |
Scheduled payments for our Convertible Notes exclude interest payments. The Notes bear interest at the rate of 3.375% per annum from the date of issuance, payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1.
Scheduled payments for our Term Loan Credit Agreement, as amended, exclude interest payments as rates are variable. Borrowings under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, as amended, bear interest at a variable rate, at our election, equal to (i) LIBOR (subject to a floor of 0.00%) plus a margin of 2.25% or (ii) a base rate (subject to a floor of 0.00%) plus a margin of 1.25%. The Term Loan Credit Agreement matures in March 2022 subject to certain springing maturity events.
Scheduled payments for our Senior Notes exclude interest payments. The Senior Notes bear interest at the rate of 5.5% per annum from the date of issuance, payable semi-annually on April 1 and October 1.
Capital leases represent future minimum lease payments including interest. Operating leases represent the total future minimum lease payments.
We have standby letters of credit totaling $5.3 million issued in connection with workers compensation claims and surety bonds.
We have $58.7 million in purchase commitments through December 2018 for various raw material commodities, including aluminum, steel and nickel as well as other raw material components which are within normal production requirements.
We, through our subsidiary Supreme, obtain most vehicle chassis for our specialized vehicle products directly from the chassis manufacturers under converter pool agreements. Chassis are obtained from the manufacturers based on orders from customers, and in some cases, for unallocated orders. The agreements generally state that the manufacturer will provide a supply of chassis to be maintained at our facilities with the condition that we will store such chassis and will not move, sell, or otherwise dispose of such chassis except under the terms of the agreement. In addition, the manufacturer typically retains the sole authority to authorize commencement of work on the chassis and to make certain other decisions with respect to the chassis including the terms and pricing of sales of the chassis to the manufacturer’s dealers. The manufacturer also does not transfer the certificate of origin to us nor permit us to sell or transfer the chassis to anyone other than the manufacturer (for ultimate resale to a dealer). Although we are party to related financing agreements with manufacturers, we have not historically settled, nor do we expect to in the future settle, any related obligations in cash. Instead, the obligation is settled by the manufacturer upon reassignment of the chassis to an accepted dealer, and the dealer is invoiced for the chassis by the manufacturer. Under these agreements, if the chassis is not delivered to a customer within a specified time frame we are required to pay a finance or storage charge on the chassis. Additionally, we receives finance support funds from manufacturers when the chassis are assigned into our chassis pool. Typically, chassis are converted and delivered to customers within 90 days of the receipt of the chassis.
Significant Accounting Policies and Critical Accounting Estimates
Our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements. Certain of our accounting policies require the application of significant judgment by management in selecting the appropriate assumptions for calculating financial estimates. By their nature, these judgments are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty. These judgments are based on our historical experience, terms of existing contracts, evaluation of trends in the industry, information provided by our customers and information available from other outside sources, as appropriate.
We consider an accounting estimate to be critical if it requires us to make assumptions about matters that were uncertain at the time we were making the estimate or changes in the estimate or different estimates that we could have selected would have had a material impact on our financial condition or results of operations.
| 52 |
The table below presents information about the nature and rationale for our critical accounting estimates:
| Balance Sheet Caption |
Critical Estimate Item |
Nature of Estimates Required |
Assumptions/ Approaches Used |
Key Factors | ||||
| Other accrued liabilities and other non-current liabilities | Warranty | Estimating warranty requires us to forecast the resolution of existing claims and expected future claims on products sold. | We base our estimate on historical trends of products sold and payment amounts, combined with our current understanding of the status of existing claims, recall campaigns and discussions with our customers. | Failure rates and estimated repair costs | ||||
| Accounts receivable | Allowance for doubtful accounts | Estimating the allowance for doubtful accounts requires us to estimate the financial capability of customers to pay for products. | We base our estimates on historical experience, the length of time an account is outstanding, evaluation of customer’s financial condition and information from credit rating services. | Customer financial condition | ||||
| Inventories | Lower of cost or market write-downs | We evaluate future demand for products, market conditions and incentive programs. | Estimates are based on recent sales data, historical experience, external market analysis and third party appraisal services. |
Market conditions
Product type | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment, intangible assets, goodwill and other assets | Impairment of long- lived assets | We are required periodically to review the recoverability of certain of our assets based on projections of anticipated future cash flows, including future profitability assessments of various product lines. | We estimate cash flows using internal budgets based on recent sales data, and independent trailer production volume to assist with estimating future demand. |
Future production estimates
|
In addition, there are other items within our financial statements that require estimation, but are not as critical as those discussed above. Changes in estimates used in these and other items could have a significant effect on our consolidated financial statements. The determination of the fair market value of our finished goods, primarily consisting of new trailers, and used trailer inventories are subject to variation, particularly in times of rapidly changing market conditions. A 5% change in the valuation of our finished goods and used trailer inventories at December 31, 2017, would be approximately $3.1 million.
Other
Inflation
Inflation impacts prices paid for labor, materials and supplies. Significant increases in the costs of production or certain commodities, raw materials, and components could have an adverse impact on our results of operations. As has been our practice, we will endeavor to offset the impact of inflation through selective price increases, productivity improvements and hedging activities.
New Accounting Pronouncements
For information related to new accounting standards, see Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
ITEM 7A–QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
In addition to the risks inherent in our operations, we have exposure to financial and market risk resulting from volatility in commodity prices and interest rates. The following discussion provides additional detail regarding our exposure to these risks.
| 53 |
| a. | Commodity Price Risks |
We are exposed to fluctuation in commodity prices through the purchase of various raw materials that are processed from commodities such as aluminum, steel, lumber, nickel, copper and polyethylene. Given the historical volatility of certain commodity prices, this exposure can significantly impact product costs. We manage some of our commodity price changes by entering into fixed price contracts with our suppliers. As of December 31, 2017, we had $58.7 million in raw material purchase commitments through December 2018 for materials that will be used in the production process, as compared to $57.8 million as of December 31, 2016. We typically do not set prices for our products more than 45-90 days in advance of our commodity purchases and can, subject to competitive market conditions, take into account the cost of the commodity in setting our prices for each order. To the extent that we are unable to offset the increased commodity costs in our product prices, our results would be materially and adversely affected.
| b. | Interest Rates |
As of December 31, 2017, we had no floating rate debt outstanding under our Revolving Credit Facility and for 2017 we maintained no floating rate borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility. In addition, as of December 31, 2017, we had outstanding borrowings under our Term Loan Credit Agreement, as amended, totaling $187.6 million that bear interest at a floating rate, subject to a minimum interest rate. Based on the average borrowings under our revolving facility and the outstanding indebtedness under our Term Loan Credit Agreement a hypothetical 100 basis-point change in the floating interest rate would result in a corresponding change in interest expense over a one-year period of $1.9 million. This sensitivity analysis does not account for the change in the competitive environment indirectly related to the change in interest rates and the potential managerial action taken in response to these changes.
| c. | Foreign Exchange Rates |
We are subject to fluctuations in the British pound sterling and Mexican peso exchange rates that impact transactions with our foreign subsidiaries, as well as U.S. denominated transactions between these foreign subsidiaries and unrelated parties. A five percent change in the British pound sterling or Mexican peso exchange rates would have an immaterial impact on results of operations. We do not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for speculative purposes.
| 54 |
ITEM 8—FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
| 55 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of Wabash National Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Wabash National Corporation (the “Company“) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, stockholders‘ equity and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements“). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with US generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated February 28, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company‘s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company‘s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the US federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
| /s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP | |
| We have served as the Company‘s auditor since 2002. | |
| Indianapolis, Indiana | |
| February 28, 2018 |
| 56 |
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Dollars in thousands)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 191,521 | $ | 163,467 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 146,836 | 153,634 | ||||||
| Inventories | 180,735 | 139,953 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other | 57,299 | 24,351 | ||||||
| Total current assets | $ | 576,391 | $ | 481,405 | ||||
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT | 195,363 | 134,138 | ||||||
| DEFERRED INCOME TAXES | - | 20,343 | ||||||
| GOODWILL | 317,464 | 148,367 | ||||||
| INTANGIBLE ASSETS | 237,030 | 94,405 | ||||||
| OTHER ASSETS | 25,265 | 20,075 | ||||||
| $ | 1,351,513 | $ | 898,733 | |||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 46,020 | $ | 2,468 | ||||
| Current portion of capital lease obligations | 290 | 494 | ||||||
| Accounts payable | 108,448 | 71,338 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities | 128,910 | 92,314 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | $ | 283,668 | $ | 166,614 | ||||
| LONG-TERM DEBT | 504,091 | 233,465 | ||||||
| CAPITAL LEASE OBLIGATIONS | 1,012 | 1,409 | ||||||
| DEFERRED INCOME TAXES | 36,955 | 499 | ||||||
| OTHER NONCURRENT LIABILITIES | 19,724 | 24,355 | ||||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES | ||||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | ||||||||
| Common stock 200,000,000 shares authorized, $0.01 par value, 57,564,493 and 60,129,631 shares outstanding, respectively | 737 | 725 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 653,435 | 640,883 | ||||||
| Retained earnings | 98,728 | 3,591 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (2,385 | ) | (2,847 | ) | ||||
| Treasury stock at cost, 16,207,740 and 12,474,109 common shares, respectively | (244,452 | ) | (169,961 | ) | ||||
| Total stockholders' equity | $ | 506,063 | $ | 472,391 | ||||
| $ | 1,351,513 | $ | 898,733 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Statements.
| 57 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| NET SALES | $ | 1,767,161 | $ | 1,845,444 | $ | 2,027,489 | ||||||
| COST OF SALES | 1,506,286 | 1,519,910 | 1,724,046 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 260,875 | $ | 325,534 | $ | 303,443 | ||||||
| GENERAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE EXPENSES | 77,825 | 74,129 | 73,495 | |||||||||
| SELLING EXPENSES | 25,588 | 27,270 | 27,233 | |||||||||
| AMORTIZATION OF INTANGIBLES | 17,041 | 19,940 | 21,259 | |||||||||
| ACQUISITON EXPENSES | 9,605 | - | - | |||||||||
| OTHER OPERATING EXPENSES | - | 1,663 | 1,087 | |||||||||
| Income from operations | $ | 130,816 | $ | 202,532 | $ | 180,369 | ||||||
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | (16,400 | ) | (15,663 | ) | (19,548 | ) | ||||||
| Other, net | 8,122 | (1,452 | ) | 2,490 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes | $ | 122,538 | $ | 185,417 | $ | 163,311 | ||||||
| INCOME TAX EXPENSE | 11,116 | 65,984 | 59,022 | |||||||||
| Net income | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | ||||||
| DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER SHARE | $ | 0.255 | $ | 0.060 | $ | - | ||||||
| BASIC NET INCOME PER SHARE | $ | 1.88 | $ | 1.87 | $ | 1.55 | ||||||
| DILUTED NET INCOME PER SHARE | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.50 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Statements.
| 58 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(Dollars in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| NET INCOME | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income: | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | 487 | (1,347 | ) | (863 | ) | |||||||
| Unrealized holding loss on investments | (25 | ) | - | - | ||||||||
| Total other comprehensive (loss) income | 462 | (1,347 | ) | (863 | ) | |||||||
| COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | $ | 111,884 | $ | 118,086 | $ | 103,426 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Statements.
| 59 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
(Dollars in thousands)
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | Retained | Other | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid-In | Earnings | Comprehensive | Treasury | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | (Deficit) | Losses | Stock | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2014 | 68,998,069 | $ | 709 | $ | 635,606 | $ | (216,198 | ) | $ | (637 | ) | $ | (28,648 | ) | $ | 390,832 | ||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 104,289 | 104,289 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | (863 | ) | (863 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 396,389 | 4 | 10,006 | 10,010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchase | (4,651,570 | ) | (61,757 | ) | (61,757 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity component of convertible senior notes repurchase | (4,714 | ) | (4,714 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issued in connection with: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercises | 186,622 | 2 | 2,010 | 2,012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2015 | 64,929,510 | $ | 715 | $ | 642,908 | $ | (111,909 | ) | $ | (1,500 | ) | $ | (90,405 | ) | $ | 439,809 | ||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 119,433 | 119,433 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | (1,347 | ) | (1,347 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 615,066 | 6 | 12,031 | 12,037 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchase | (5,832,387 | ) | (79,556 | ) | (79,556 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity component of convertible senior notes repurchase | (18,883 | ) | (18,883 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock dividends | (3,933 | ) | (3,933 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issued in connection with: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercises | 417,442 | 4 | 4,827 | 4,831 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2016 | 60,129,631 | $ | 725 | $ | 640,883 | $ | 3,591 | $ | (2,847 | ) | $ | (169,961 | ) | $ | 472,391 | |||||||||||||
| Net income for the year | 111,422 | 111,422 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 487 | 487 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 650,218 | 7 | 10,422 | 10,429 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchase | (3,726,809 | ) | (74,491 | ) | (74,491 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity component of convertible senior notes repurchase | (3,655 | ) | (3,655 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock dividends | (16,285 | ) | (16,285 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding loss on investments, net of tax | (25 | ) | (25 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issued in connection with: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock option exercises | 511,453 | 5 | 5,785 | 5,790 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCES, December 31, 2017 | 57,564,493 | $ | 737 | $ | 653,435 | $ | 98,728 | $ | (2,385 | ) | $ | (244,452 | ) | $ | 506,063 | |||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Statements.
| 60 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by | ||||||||||||
| operating activities | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation | 18,012 | 16,830 | 16,739 | |||||||||
| Amortization of intangibles | 17,041 | 19,940 | 21,259 | |||||||||
| Net (gain) loss on sale of property, plant and equipment | (8,046 | ) | 101 | (8,299 | ) | |||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | 799 | 1,895 | 5,808 | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | (14,682 | ) | 4,044 | (7,749 | ) | |||||||
| Stock-based compensation | 10,429 | 12,038 | 10,010 | |||||||||
| Non-cash interest expense | 2,258 | 3,475 | 5,222 | |||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill and other intangibles | - | 1,663 | 1,087 | |||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 31,943 | (809 | ) | (17,618 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories | (13,158 | ) | 24,969 | 10,162 | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other | (2,014 | ) | (10,147 | ) | 1,786 | |||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | (963 | ) | (13,002 | ) | (12,243 | ) | ||||||
| Other, net | (8,662 | ) | (1,680 | ) | 1,342 | |||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 144,379 | $ | 178,750 | $ | 131,795 | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | (26,056 | ) | (20,342 | ) | (20,847 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment | 10,860 | 19 | 13,203 | |||||||||
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (323,487 | ) | - | - | ||||||||
| Other, net | 6,443 | 3,014 | - | |||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (332,240 | ) | $ | (17,309 | ) | $ | (7,644 | ) | |||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 5,790 | 4,831 | 2,012 | |||||||||
| Borrowings under senior notes | 325,000 | - | - | |||||||||
| Dividends paid | (15,315 | ) | - | - | ||||||||
| Borrowings under revolving credit facilities | 713 | 618 | 1,134 | |||||||||
| Payments under revolving credit facilities | (713 | ) | (618 | ) | (1,134 | ) | ||||||
| Principal payments under capital lease obligations | (600 | ) | (779 | ) | (4,201 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of term loan credit facility | 377,519 | - | 192,845 | |||||||||
| Principal payments under term loan credit facility | (386,577 | ) | (1,928 | ) | (194,291 | ) | ||||||
| Principal payments under industrial revenue bond | (583 | ) | (473 | ) | (496 | ) | ||||||
| Debt issuance costs paid | (6,783 | ) | - | (2,587 | ) | |||||||
| Convertible senior notes repurchase | (8,045 | ) | (98,922 | ) | (22,936 | ) | ||||||
| Stock repurchase | (74,491 | ) | (79,556 | ) | (61,757 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | $ | 215,915 | $ | (176,827 | ) | $ | (91,411 | ) | ||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 28,054 | $ | (15,386 | ) | $ | 32,740 | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 163,467 | 178,853 | 146,113 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 191,521 | $ | 163,467 | $ | 178,853 | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the period for | ||||||||||||
| Interest | $ | 8,394 | $ | 12,656 | $ | 14,578 | ||||||
| Income taxes | $ | 41,391 | $ | 68,870 | $ | 66,283 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these Consolidated Statements.
| 61 |
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 1. | DESCRIPTION OF THE BUSINESS |
Wabash National Corporation (the “Company,” “Wabash” or “Wabash National”) manufactures a diverse range of products including: dry freight and refrigerated trailers, platform trailers, bulk tank trailers, dry and refrigerated truck bodies, truck-mounted tanks, intermodal equipment, aircraft refueling equipment, structural composite panels and products, trailer aerodynamic solutions, and specialty food grade and pharmaceutical equipment. Its innovative products are sold under the following brand names: Wabash National®, Beall®, Benson®, Brenner® Tank, Bulk Tank International, DuraPlate®, Extract Technology®, Garsite, Progress Tank, Supreme, Transcraft®, Walker Engineered Products, and Walker Transport.
| 2. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
| a. | Basis of Consolidation |
The consolidated financial statements reflect the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned and majority-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany profits, transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
| b. | Use of Estimates |
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that directly affect the amounts reported in its consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
| c. | Revenue Recognition |
The Company recognizes revenue from the sale of its products when the customer has made a fixed commitment to purchase a product for a fixed or determinable price, collection is reasonably assured under the Company’s normal billing and credit terms and ownership and all risk of loss has been transferred to the buyer, which is normally upon shipment to or pick up by the customer. Revenues on certain contracts are recorded on a percentage of completion method, measured by actual total cost incurred to the total estimated costs for each project. The Company excludes from revenue vehicle chassis obtained through its converter pool agreements as the original equipment manufacturer (“OEM”) retains full rights and ownership of the chassis for ultimate sale to an authorized OEM dealer. Revenues exclude all taxes collected from the customer. Shipping and handling fees are included in Net Sales and the associated costs included in Cost of Sales in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| d. | Used Trailer Trade Commitments and Residual Value Guarantees |
In the normal course of business, the Company commits to accept used trailers on trade for new trailer purchases. These commitments arise related to future new trailer orders at the time a new trailer order is placed by the customer. The Company acquired used trailers on trade of $9.5 million, $4.6 million, and $12.8 million in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had $3.2 million in outstanding trade commitments which also represented the estimated net realizable value of the underlying used trailer. The Company had no outstanding trade commitments as of December 31, 2016. On occasion, the amount of the trade allowance provided for in the used trailer commitments, or cost, may exceed the net realizable value of the underlying used trailer. In these instances, the Company’s policy is to recognize the loss related to these commitments at the time the new trailer revenue is recognized. Net realizable value of used trailers is measured considering market sales data for comparable types of trailers.
| e. | Cash and Cash Equivalents |
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at the time of purchase.
| 62 |
| f. | Accounts Receivable |
Accounts receivable are shown net of allowance for doubtful accounts and primarily include trade receivables. The Company records and maintains a provision for doubtful accounts for customers based upon a variety of factors including the Company’s historical collection experience, the length of time the account has been outstanding and the financial condition of the customer. If the circumstances related to specific customers were to change, the Company’s estimates with respect to the collectability of the related accounts could be further adjusted. The Company’s policy is to write-off receivables when they are determined to be uncollectible. Provisions to the allowance for doubtful accounts are charged to Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The following table presents the changes in the allowance for doubtful accounts (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 951 | $ | 956 | $ | 1,047 | ||||||
| Provision | 119 | 117 | 145 | |||||||||
| Write-offs, net of recoveries | (201 | ) | (122 | ) | (236 | ) | ||||||
| Balance at end of year | $ | 869 | $ | 951 | $ | 956 | ||||||
| g. | Inventories |
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost, determined on either the first-in, first-out or average cost method, or market. The cost of manufactured inventory includes raw material, labor and overhead. Inventories, net of reserves, consist of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Raw materials and components | $ | 83,834 | $ | 53,388 | ||||
| Finished goods | 54,000 | 57,297 | ||||||
| Work in progress | 29,123 | 18,422 | ||||||
| Used trailers | 7,330 | 2,490 | ||||||
| Aftermarket parts | 6,448 | 8,356 | ||||||
| $ | 180,735 | $ | 139,953 | |||||
| h. | Prepaid Expenses and Other |
Prepaid expenses and other as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 consists of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Chassis converter pool agreements | $ | 18,326 | $ | - | ||||
| Income tax receivables | 10,821 | 6,926 | ||||||
| Assets held for sale | 10,777 | 5,788 | ||||||
| Insurance premiums & maintenance agreements | 6,860 | 3,555 | ||||||
| All other | 10,515 | 8,082 | ||||||
| $ | 57,299 | $ | 24,351 | |||||
Chassis converter pool agreements represent chassis transferred to the Company on a restricted basis by the manufacturer, who retains the sole authority to authorize commencement of work on the chassis and to make certain other decisions with respect to the chassis including the terms and pricing of sales to the manufacturer’s dealers. Assets held for sale are related to the Company’s former locations which are being actively marketed for sale. Insurance premiums and maintenance agreements are charged to expense over the contractual life, which is generally one year or less. Other prepaid items consist primarily of costs in excess of billings on contracts for which the Company recognizes revenue on a percentage of completion basis and investments held by the Company’s captive insurance subsidiary.
| 63 |
| i. | Property, Plant and Equipment |
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred, while expenditures that extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized. Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the depreciable assets. The estimated useful lives are up to 33 years for buildings and building improvements and range from three to ten years for machinery and equipment. Depreciation expense, which is recorded in Cost of Sales and General and Administrative Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, as appropriate, on property, plant and equipment was $16.7 million, $15.9 million, and $16.0 million in 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively, and includes amortization of assets recorded in connection with the Company’s capital lease agreements. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the assets related to the Company’s capital lease agreements are recorded within Property, Plant and Equipment in the Consolidated Balance Sheet for the amount of $3.2 million and $4.3 million, respectively, net of accumulated depreciation of $1.4 million and $1.9 million, respectively.
Property, plant and equipment consist of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Land | $ | 34,493 | $ | 20,958 | ||||
| Buildings and building improvements | 139,636 | 110,789 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 254,544 | 231,094 | ||||||
| Construction in progress | 17,672 | 12,116 | ||||||
| $ | 446,345 | $ | 374,957 | |||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (250,982 | ) | (240,819 | ) | ||||
| $ | 195,363 | $ | 134,138 | |||||
| j. | Intangible Assets |
As of December 31, 2017, the balances of intangible assets, other than goodwill, were as follows (in thousands):
| Weighted Average Amortization Period | Gross Intangible Assets | Accumulated Amortization | Net Intangible Assets | |||||||||||
| Tradenames and trademarks | 20 years | $ | 57,894 | $ | (14,034 | ) | $ | 43,860 | ||||||
| Customer relationships | 10 years | 290,415 | (105,567 | ) | 184,848 | |||||||||
| Technology | 12 years | 16,517 | (8,694 | ) | 7,823 | |||||||||
| Backlog | less than 1 year | 2,200 | (1,701 | ) | 499 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 367,026 | $ | (129,996 | ) | $ | 237,030 | |||||||
As of December 31, 2016, the balances of intangible assets, other than goodwill, were as follows (in thousands):
| Weighted Average Amortization Period | Gross Intangible Assets | Accumulated Amortization | Net Intangible Assets | |||||||||||
| Tradenames and trademarks | 20 years | $ | 37,894 | $ | (11,864 | ) | $ | 26,030 | ||||||
| Customer relationships | 10 years | 151,090 | (92,686 | ) | 58,404 | |||||||||
| Technology | 12 years | 16,517 | (6,546 | ) | 9,971 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 205,501 | $ | (111,096 | ) | $ | 94,405 | |||||||
| 64 |
Intangible asset amortization expense was $17.0 million, $19.9 million, and $21.3 million for 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively. Annual intangible asset amortization expense for the next 5 fiscal years is estimated to be $20.4 million in 2018; $21.6 million in 2019; $23.1 million in 2020; $24.4 million in 2021; and $19.5 million in 2022.
| k. | Goodwill |
Goodwill represents the excess purchase price over fair value of the net assets acquired. The Company reviews goodwill for impairment, at the reporting unit level, annually on October 1 and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate its carrying value may not be recoverable. In accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other, goodwill is reviewed for impairment utilizing either a qualitative assessment or a two-step quantitative process.
The Company has the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads to a determination that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. In assessing the qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, the Company assesses relevant events and circumstances that may impact the fair value and the carrying amount of the reporting unit. The identification of relevant events and circumstances and how these may impact a reporting unit's fair value or carrying amount involve significant judgments and assumptions. The judgments and assumptions include the identification of macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance and Company specific events and making the assessment on whether each relevant factor will impact the impairment test positively or negatively and the magnitude of any such impact. If, after assessing the totality of events or circumstances, the Company determines it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then performing the two-step impairment test is unnecessary.
For reporting units in which the Company performs the two-step quantitative analysis, the first step compares the carrying value, including goodwill, of each reporting unit with its estimated fair value. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, the goodwill is not considered impaired. If the carrying value is greater than the fair value, this suggests that an impairment may exist and a second step is required in which the implied fair value of goodwill is calculated as the excess of the fair value of the reporting unit over the fair values assigned to its assets and liabilities. If this implied fair value is less than the carrying value, the difference is recognized as an impairment loss charged to the reporting unit. In assessing goodwill using this quantitative approach, the Company establishes fair value for the purpose of impairment testing by averaging the fair value using an income and market approach. The income approach employs a discounted cash flow model incorporating similar pricing concepts used to calculate fair value in an acquisition due diligence process and a discount rate that takes into account the Company’s estimated average cost of capital. The market approach employs market multiples based on comparable publicly traded companies in similar industries as the reporting unit. Estimates of fair value are established using current and forward multiples adjusted for size and performance of the reporting unit relative to peer companies.
During the fourth quarters of 2017 and 2016, the Company completed its goodwill impairment test using the quantitative assessment. During the second quarter of 2016, in connection with the realignment of the Company’s reporting segments, the Company performed an analysis to determine the allocations of goodwill and test for impairment. Furthermore, for 2015, the Company completed its goodwill impairment testing during the fourth quarter using the qualitative approach. Based on these assessments and in connection with the realignment of the Company’s reporting segments in the second quarter of 2016, it determined that the portion of goodwill allocated to the retail branch operations was impaired as the fair value of the reporting unit did not exceed its carrying value resulting in an impairment charge for the Commercial Trailer Products reporting segment of $1.7 million. Based on all other assessments performed in each of the last three years, the Company believed it was more likely than not that the fair value of its reporting units were greater than their carrying amount and no additional impairment of goodwill was recognized.
As of December 31, 2017, the carrying amount of goodwill totaled $317.5 million which was allocated to its reporting segment in the following amounts: Final Mile Products - $169.2 million; Diversified Products - $145.6 million; and, Commercial Trailer Products - $2.7 million. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the changes in the carrying amounts of goodwill were as follows (in thousands):
| 65 |
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Balance as of January 1 | $ | 148,367 | $ | 149,718 | ||||
| Acquisition of Supreme | 169,235 | - | ||||||
| Effects of foreign currency | (138 | ) | 312 | |||||
| Impairment of goodwill | - | (1,663 | ) | |||||
| Balance as of December 31 | $ | 317,464 | $ | 148,367 | ||||
| l. | Other Assets |
The Company capitalizes the cost of computer software developed or obtained for internal use. Capitalized software is amortized using the straight-line method over three to seven years. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had software costs, net of amortization, of $7.3 million and $5.4 million, respectively. Amortization expense for 2017, 2016, and 2015 was $1.3 million, $1.0 million, and $0.7 million, respectively.
| m. | Long-Lived Assets |
Long-lived assets, consisting primarily of intangible assets and property, plant and equipment, are reviewed for impairment whenever facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. Specifically, this process involves comparing an asset’s carrying value to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows the asset is expected to generate over its remaining life. If this process were to result in the conclusion that the carrying value of a long-lived asset would not be recoverable, a write-down of the asset to fair value would be recorded through a charge to operations. Fair value is determined based upon discounted cash flows or appraisals as appropriate.
| n. | Other Accrued Liabilities |
The following table presents the major components of Other Accrued Liabilities (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Payroll and related taxes | $ | 27,840 | $ | 26,793 | ||||
| Customer deposits | 26,059 | 19,302 | ||||||
| Warranty | 20,132 | 20,520 | ||||||
| Chassis converter pool agreements | 18,326 | - | ||||||
| Self-insurance | 9,996 | 8,387 | ||||||
| Accrued taxes | 9,224 | 6,400 | ||||||
| All other | 17,333 | 10,912 | ||||||
| $ | 128,910 | $ | 92,314 | |||||
The following table presents the changes in the product warranty accrual included in Other Accrued Liabilities (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Balance as of January 1 | $ | 20,520 | $ | 19,709 | ||||
| Provision for warranties issued in current year | 5,873 | 6,601 | ||||||
| Supreme acquisition | 1,421 | - | ||||||
| (Recovery of) Provision for pre-existing warranties | (970 | ) | 560 | |||||
| Payments | (6,712 | ) | (6,350 | ) | ||||
| Balance as of December 31 | $ | 20,132 | $ | 20,520 | ||||
| 66 |
The Company offers a limited warranty for its products with a coverage period that ranges between one and five years, except that the coverage period for DuraPlate® trailer panels is ten years. The Company passes through component manufacturers’ warranties to our customers. The Company’s policy is to accrue the estimated cost of warranty coverage at the time of the sale.
The following table presents the changes in the self-insurance accrual included in Other Accrued Liabilities (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Balance as of January 1 | $ | 8,387 | $ | 7,677 | ||||
| Expense | 38,817 | 41,470 | ||||||
| Supreme Acquisition | 2,555 | - | ||||||
| Payments | (39,763 | ) | (40,760 | ) | ||||
| Balance as of December 31 | $ | 9,996 | $ | 8,387 | ||||
The Company is self-insured up to specified limits for medical and workers’ compensation coverage. The self-insurance reserves have been recorded to reflect the undiscounted estimated liabilities, including claims incurred but not reported, as well as catastrophic claims as appropriate.
| o. | Income Taxes |
The Company determines its provision or benefit for income taxes under the asset and liability method. The asset and liability method measures the expected tax impact at current enacted rates of future taxable income or deductions resulting from differences in the tax and financial reporting basis of assets and liabilities reflected in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Future tax benefits of tax losses and credit carryforwards are recognized as deferred tax assets. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to the extent management determines that it is more-likely-than-not the Company would not realize the value of these assets.
The Company accounts for income tax contingencies by prescribing a “more-likely-than-not” recognition threshold that a tax position is required to meet before being recognized in the financial statements.
| p. | Concentration of Credit Risk |
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to significant concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash, cash equivalents and customer receivables. We place our cash and cash equivalents with high quality financial institutions. Generally, we do not require collateral or other security to support customer receivables.
| q. | Research and Development |
Research and development expenses are charged to earnings as incurred and were $3.9 million, $6.4 million and $4.8 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
| r. | New Accounting Pronouncements |
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606), which supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 605, Revenue. Furthermore, the FASB issued additional amendments and technical corrections related to ASU 2014-09 during 2016 and 2017, which are considered in our evaluation of this standard. This ASU is based on the principle that revenue is recognized to depict the transfer of goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The ASU also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts, including significant judgments and changes in judgments and assets recognized from costs incurred to obtain or fulfill a contract. The Company has identified the revenue streams and the related performance obligations and pricing arrangements within each of its product lines. The Company has evaluated contractual terms, such as customer acceptance clauses, payment terms, transferring of control to the customer, shipping instructions, and timing of shipments, and the timing of revenue recognition against the new standards with no findings that impact the Company’s financial statements. The Company is using the modified retrospective method to transition to the new standard, which is effective January 1, 2018.
| 67 |
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). This update requires lessees to recognize, on the balance sheet, assets and liabilities for the rights and obligations created by leases of greater than twelve months. Leases will be classified as either finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition in the income statement. This guidance will be effective for the Company as of January 1, 2019. A modified retrospective transition method is required. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), Restricted Cash, which requires entities to show the changes in the total of cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows. When cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents are presented in more than one item on the balance sheet, a reconciliation of the totals in the statement of cash flows to the related captions in the balance sheet is required. This guidance will be effective for the Company as of January 1, 2018. Entities will be required to apply the guidance retrospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-04, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment (“ASU 2017-4”). ASU 2017-4 eliminates Step 2 of the current goodwill impairment test, which requires a hypothetical purchase price allocation to measure goodwill impairment. A goodwill impairment loss will instead be measured at the amount by which a reporting unit's carrying value exceeds its fair value, not to exceed the recorded amount of goodwill. The new standard is effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and should be applied on a prospective basis. Early adoption is permitted for annual or interim goodwill impairment testing performed after January 1, 2017. The Company believes that the adoption of the provisions of ASU 2017-04 will not have a material impact on its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
| 3. | ACQUISITION OF SUPREME INDUSTRIES, INC. |
On September 27, 2017, the Company completed the acquisition of Supreme Industries, Inc. (“Supreme”) following a cash tender offer by the Company for all outstanding shares of Supreme’s Class A and Class B common stock for $21 per share and an aggregate consideration paid of $360.4 million. The Company financed the Supreme acquisition and related fees and expenses using the proceeds of the Company’s $325 million offering in aggregate principal amount of 5.50% senior unsecured notes due 2025 (as described in further detail in Note 6) and available cash and cash equivalents.
Supreme is one of the nation’s leading manufacturers of specialized commercial vehicles, including cutaway and dry-freight van bodies, refrigerated units, and stake bodies. Supreme has manufacturing facilities in Goshen and Ligonier, Indiana; Jonestown, Pennsylvania; Cleburne, Texas; Griffin, Georgia; and Moreno Valley, California. Supreme will be part of a new Final Mile Products segment created by the Company in the fourth quarter of 2017. This acquisition allows the Company to accelerate our growth and greatly expand our presence in the final mile space, with increased distribution paths and greater customer reach, and supports the Company’s objective to transform it into a more diversified industrial manufacturer.
The Company incurred various costs related to the Supreme acquisition including fees paid to an investment banker for acquisition services and the related bridge financing commitment as well as professional fees for diligence, legal and accounting totaling $9.6 million. These costs have been recorded as Acquisition Expenses in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The aggregate purchase price of $360.4 million was allocated to the opening balance sheet of Supreme at September 27, 2017, the date of acquisition, which is still preliminary and subject to adjustment as follows (in thousands):
| 68 |
| Cash | $ | 36,878 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 25,146 | |||
| Inventories | 34,084 | |||
| Prepaid expense and other | 21,730 | |||
| Property, plant, and equipment | 59,891 | |||
| Intangibles | 161,200 | |||
| Goodwill | 169,235 | |||
| Other assets | 127 | |||
| Total assets acquired | $ | 508,291 | ||
| Current portion of long term debt | $ | 7,167 | ||
| Accounts payable | 10,546 | |||
| Other accrued liabilites | 55,350 | |||
| Deferred income taxes | 71,946 | |||
| Long term liabilities | 2,917 | |||
| Total liabilities assumed | $ | 147,926 | ||
| Net assets acquired | $ | 360,365 | ||
| Acquisition, net of cash acquired | $ | 323,487 |
Intangible assets of $161.2 million were preliminarily recorded as a result of the acquisition and consist of the following (in thousands):
| Amount | Useful Life | |||||
| Tradename | $ | 20,000 | 20 years | |||
| Customer relationships | 139,000 | 15 years | ||||
| Backlog | 2,200 | Less than 1 year | ||||
| $ | 161,200 | |||||
Goodwill of $169.2 million was preliminarily recorded as a result of the acquisition. The Company does not expect the amount recorded as goodwill for the Supreme acquisition to be deductible for tax purposes. The process of completing the valuations of the identified intangible assets, including tax assets and liabilities, is being completed. Goodwill, calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the net assets recognized and represents the estimated future economic benefits arising from other assets acquired that could not be individually identified and separately recognized, is comprised of operational synergies that are expected to be realized in both the short and long-term and the opportunity to enter new market sectors with higher margin potential, which will enable us to deliver greater value to our customers and shareholders. During the fourth quarter of 2017, the Company made certain adjustments to its purchase price allocation to adjust intangibles; property, plant, and equipment; and deferred tax liabilities, which resulted in a $3.8 million increase in goodwill. Additional adjustments to intangibles, taxes and liabilities as well as resulting adjustments to goodwill may be necessary as the Company completes the valuation of acquired assets and liabilities. The Company expects the process of completing the valuations to be completed during the first quarter of 2018.
Unaudited Pro forma Results
The results of Supreme are included in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations from the date of acquisition, including $67.1 million in revenue and net loss of $1.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The following unaudited pro forma information is shown below as if the acquisition of Supreme had been completed as of the beginning of the earliest period presented (in thousands):
| 69 |
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Sales | $ | 1,998,043 | $ | 2,139,404 | ||||
| Net income | $ | 117,786 | $ | 124,323 | ||||
The information presented above is for informational purposes only and is not necessarily indicative of the actual results that would have occurred had the acquisition been consummated at the beginning of the respective periods, nor is it necessarily indicative of future operating results of the combined companies under the ownership and management of the Company.
| 4. | PER SHARE OF COMMON STOCK |
Per share results have been calculated based on the average number of common shares outstanding. The calculation of basic and diluted net income per share is determined using net income applicable to common stockholders as the numerator and the number of shares included in the denominator as follows (in thousands, except per share amounts):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Basic net income per share: | ||||||||||||
| Net income applicable to common stockholders | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding | 59,358 | 63,729 | 67,201 | |||||||||
| Basic net income per share | $ | 1.88 | $ | 1.87 | $ | 1.55 | ||||||
| Diluted net income per share: | ||||||||||||
| Net income applicable to common stockholders | $ | 111,422 | $ | 119,433 | $ | 104,289 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding | 59,358 | 63,729 | 67,201 | |||||||||
| Dilutive shares from assumed conversion of convertible senior notes | 1,726 | 794 | 1,128 | |||||||||
| Dilutive stock options and restricted stock | 1,515 | 1,239 | 1,039 | |||||||||
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 62,599 | 65,762 | 69,368 | |||||||||
| Diluted net income per share | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.82 | $ | 1.50 | ||||||
For the period ending December 31, 2017, there were no options excluded from average diluted shares outstanding as the average market price of the common shares was greater than the exercise price. The periods ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 exclude options to purchase common shares totaling 503 and 666, respectively, because the exercise prices were greater than the average market price of the common shares. In addition, the calculation of diluted net income per share for each period includes the impact of the Company’s Notes as the average stock price of the Company’s common stock during these periods was above the initial conversion price of approximately $11.70 per share.
| 5. | LEASE ARRANGEMENTS |
The Company leases office space, manufacturing, warehouse and service facilities and equipment for varying periods under both operating and capital lease agreements. Future minimum lease payments required under these lease commitments as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
| 70 |
| Capital Leases | Operating Leases | |||||||
| 2018 | 361 | 2,466 | ||||||
| 2019 | 361 | 1,364 | ||||||
| 2020 | 361 | 688 | ||||||
| 2021 | 361 | 439 | ||||||
| 2022 | 30 | 254 | ||||||
| Thereafter | - | - | ||||||
| Total minimum lease payments | $ | 1,474 | $ | 5,211 | ||||
| Interest | (172 | ) | ||||||
| Present value of net minimum lease payments | $ | 1,302 | ||||||
Total rental expense was $6.5 million, $6.2 million, and $6.2 million for 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
| 6. | DEBT |
Long-term debt consists of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Convertible senior notes due 2018 | $ | 44,561 | $ | 48,951 | ||||
| Senior notes due 2025 | 325,000 | - | ||||||
| Term loan credit agreement | 187,579 | 189,470 | ||||||
| Other debt | 93 | 676 | ||||||
| $ | 557,233 | $ | 239,097 | |||||
| Less: unamortized discount and fees | (7,122 | ) | (3,164 | ) | ||||
| Less: current portion | (46,020 | ) | (2,468 | ) | ||||
| $ | 504,091 | $ | 233,465 | |||||
Convertible Senior Notes
In April 2012, the Company issued Convertible Senior Notes due 2018 (the “Convertible Notes”) with an aggregate principal amount of $150 million in a public offering. The Convertible Notes bear interest at a rate of 3.375% per annum from the date of issuance, payable semi-annually on May 1 and November 1, and mature on May 1, 2018. The Convertible Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company ranking equally with its existing and future senior unsecured debt. The Company used the net proceeds of $145.1 million from the sale of the Convertible Notes to fund a portion of the purchase price of the acquisition of Walker Group Holdings (“Walker”) in May 2012.
As of December 31, 2017, and at any time until the close of business on the second business day immediately preceding the maturity date, the Convertible Notes are convertible by their holders into cash, shares of the Company’s common stock or any combination thereof at the Company’s election, at an initial conversion rate of 85.4372 shares of the Company’s common stock per $1,000 in principal amount of Convertible Notes, which is equal to an initial conversion price of approximately $11.70 per share.
If the Convertible Notes outstanding at December 31, 2017 had been converted as of December 31, 2017, the if-converted value would exceed the principal amount by approximately $38 million. It is the Company’s intent to settle conversions in cash for both the principal portion and the excess of the conversion value over the principal portion. The Convertible Notes mature on May 1, 2018 and are classified as current within the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet.
| 71 |
The Company accounts separately for the liability and equity components of the Convertible Notes in accordance with authoritative guidance for convertible debt instruments that may be settled in cash upon conversion. The guidance requires the carrying amount of the liability component to be estimated by measuring the fair value of a similar liability that does not have an associated conversion feature. The Company determined that senior, unsecured corporate bonds traded on the market represent a similar liability to the Convertible Notes without the conversion option. Based on market data available for publicly traded, senior, unsecured corporate bonds issued by companies in the same industry and with similar maturity, the Company estimated the implied interest rate of the Convertible Notes to be 7.0%, assuming no conversion option. Assumptions used in the estimate represent what market participants would use in pricing the liability component, including market interest rates, credit standing, and yield curves, all of which are defined as Level 2 observable inputs (as defined below). The estimated implied interest rate was applied to the Convertible Notes, which resulted in a fair value of the liability component of $123.8 million upon issuance, calculated as the present value of implied future payments based on the $150.0 million aggregate principal amount. The $21.7 million difference between the cash proceeds before offering expenses of $145.5 million and the estimated fair value of the liability component was recorded in additional paid-in capital. The discount on the liability portion of the Convertible Notes is being amortized over the life of the Convertible Notes using the effective interest rate method.
During 2017, the Company acquired $4.4 million in principal of such Convertible Notes for $8.0 million, excluding accrued interest. Additionally, in 2016 the Company acquired $82.0 million in principal for $98.9 million, excluding accrued interest. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company recognized a loss on debt extinguishment of $0.1 million and $1.9 million, respectively, for repurchase activity, which is included in Other, net on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company applies the treasury stock method in calculating the dilutive impact of the Convertible Notes. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Convertible Notes had a dilutive impact.
The following table summarizes information about the equity and liability components of the Convertible Notes (dollars in thousands):
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Principal amount of the Notes outstanding | $ | 44,561 | $ | 48,951 | ||||
| Unamortized discount and fees of liability component | (514 | ) | (2,183 | ) | ||||
| Net carrying amount of liability component | 44,047 | 46,768 | ||||||
| Less: current portion | (44,047 | ) | - | |||||
| Long-term debt | $ | - | $ | 46,768 | ||||
| Carrying value of equity component, net of issuance costs | $ | (7,626 | ) | $ | (3,971 | ) | ||
| Remaining amortization period of discount on the liability component | 0.4 years | 1.3 years | ||||||
Contractual coupon interest expense and accretion of discount and fees on the liability component for the Convertible Notes for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 included in Interest Expense on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations were as follows (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Contractual coupon interest expense | $ | 1,570 | $ | 3,198 | $ | 5,063 | ||||||
| Accretion of discount and fees on the liability component | $ | 1,537 | $ | 2,902 | $ | 4,324 | ||||||
Senior Notes
On September 26, 2017 the Company issued Senior Notes due 2025 (the “Senior Notes”) in an offering pursuant to Rule 144A or Regulation S under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, with an aggregate principal amount of $325 million. The Senior Notes bear interest at the rate of 5.50% per annum from the date of issuance, and will pay interest semi-annually in cash on April 1 and October 1 of each year, beginning on April 1, 2018. The Company used the net proceeds of $318.9 million from the sale of the Senior Notes to finance a portion of the acquisition of Supreme and to pay related fees and expenses.
| 72 |
The Senior Notes will mature on October 1, 2025. At any time prior to October 1, 2020, the Company may redeem some or all of the Senior Notes for cash at a redemption price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes being redeemed plus an applicable make-whole premium set forth in the indenture for the Senior Notes and accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date. Prior to October 1, 2020, the Company may redeem up to 40% of the Senior Notes at a redemption price of 105.50% of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date, with the proceeds of certain equity offerings so long as if, after any such redemption occurs, at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes remains outstanding. On and after October 1, 2020, the Company may redeem some or all of the Senior Notes at redemption prices (expressed as percentages of principal amount) equal to 102.750% for the twelve-month period beginning on October 1, 2020, 101.375% for the twelve-month period beginning October 1, 2021 and 100.000% beginning on October 1, 2022, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the redemption date. Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control (as defined in the indenture for the Senior Notes), unless the Company has exercised its optional redemption right in respect of the Senior Notes, the holders of the Senior Notes have the right to require the Company to repurchase all or a portion of the Senior Notes at a price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of the Senior Notes, plus any accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the date of repurchase.
The Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by all direct and indirect existing and future domestic restricted subsidiaries, subject to certain restrictions. The Senior Notes and related guarantees are the Company and the guarantors’ general unsecured senior obligations and are subordinate to all of the Company and the guarantors’ existing and future secured debt to the extent of the assets securing that secured obligation. In addition, the Senior Notes are structurally subordinate to any existing and future debt of any of the Company’s subsidiaries that are not guarantors, to the extent of the assets of those subsidiaries.
The indenture for the Senior Notes restricts the Company’s ability and the ability of certain of its subsidiaries to: (i) incur additional indebtedness; (ii) pay dividends or make other distributions in respect of, or repurchase or redeem, its capital stock or with respect to any other interest or participation in, or measured by, its profits; (iii) make loans and certain investments; (iv) sell assets; (v) create or incur liens; (vi) enter into transactions with affiliates; and (vii) consolidate, merge or sell all or substantially all of its assets. These covenants are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications. During any time when the Senior Notes are rated investment grade by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. and Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services and no event of default has occurred or is continuing, many of such covenants will be suspended and the Company and its subsidiaries will not be subject to such covenants during such period.
The indenture for the Senior Notes contains customary events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of covenants, failure to pay certain judgments and certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency and reorganization. If an event of default occurs and is continuing, the principal amount of the Senior Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, may be declared immediately due and payable. These amounts automatically become due and payable if an event of default relating to certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization occurs.
Contractual coupon interest expense and accretion of discount and fees for the Senior Notes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $4.8 million and is included in Interest Expense on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Revolving Credit Agreement
In May 2012, the Company entered into the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (as subsequently amended, the “Credit Agreement”), dated as of May 8, 2012, among the Company, certain subsidiaries of the Company from time to time party thereto (together with the Company, the “Borrowers”), the several lenders from time to time party thereto, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as arranger and administrative agent (the “Agent”). The Credit Agreement provides for, among other things, (x) a $175 million senior secured revolving credit facility that matures on June 4, 2020, subject to certain springing maturity events and (y) an uncommitted accordion feature allowing for an increase to the availability under the revolving credit facility of up to $50 million, subject to certain conditions (the “Revolving Credit Facility”).
| 73 |
The Revolving Credit Facility (i) bears interest, at the Borrowers’ election, at (x) LIBOR (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin ranging from 150 basis points to 200 basis points, or (y) a base rate plus a margin ranging from 50 basis points to 100 basis points, in each case, based upon the monthly average excess availability under the Revolving Credit Facility, (ii) requires the Company to pay a monthly unused line fee equal to 25 basis points times the average unused availability under the Revolving Credit Facility, (iii) provides that if availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than 12.5% of the total commitment under the Revolving Credit Facility or if there exists an event of default, amounts in any of the Borrowers’ and the subsidiary guarantors’ deposit accounts (other than certain excluded accounts) will be transferred daily into a blocked account held by the Agent and applied to reduce the outstanding amounts under the Revolving Credit Facility, and (iv) requires the Company to maintain a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1.1 to 1.0 as of the end of any period of 12 fiscal months when excess availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than 10% of the total commitment under the Revolving Credit Facility.
In connection with, and in order to permit under the Credit Agreement, the Senior Notes offering and the acquisition of Supreme, on August 16, 2017, the Company entered into the Third Amendment to the Credit Agreement (the “Third Amendment”). The Third Amendment also permitted the Company to incur certain other indebtedness in connection with the acquisition of Supreme and to acquire certain liens and obligations of Supreme upon the consummation of the acquisition.
The Credit Agreement is guaranteed by certain of the Company’s subsidiaries (the “Revolver Guarantors”) and is secured by (i) first priority security interests (subject only to customary permitted liens and certain other permitted liens) in substantially all personal property of the Borrowers and the Revolver Guarantors, consisting of accounts receivable, inventory, cash, deposit and securities accounts and any cash or other assets in such accounts and, to the extent evidencing or otherwise related to such property, all general intangibles, licenses, intercompany debt, letter of credit rights, commercial tort claims, chattel paper, instruments, supporting obligations, documents and payment intangibles (collectively, the “Revolver Priority Collateral”), and (ii) second-priority liens on and security interests in (subject only to the liens securing the Term Loan Credit Agreement (as defined below), customary permitted liens and certain other permitted liens) (A) equity interests of each direct subsidiary held by the Borrower and each Revolver Guarantor (subject to customary limitations in the case of the equity of foreign subsidiaries), and (B) substantially all other tangible and intangible assets of the Borrowers and the Revolver Guarantors including equipment, general intangibles, intercompany notes, insurance policies, investment property, intellectual property and material owned real property (in each case, except to the extent constituting Revolver Priority Collateral) (collectively, the “Term Priority Collateral”). The respective priorities of the security interests securing the Credit Agreement and the Term Loan Credit Agreement are governed by an Intercreditor Agreement between the Revolver Agent and the Term Agent (as defined below) (the “Intercreditor Agreement”).
The Credit Agreement contains customary covenants limiting the Company’s ability to, among other things, pay cash dividends, incur debt or liens, redeem or repurchase stock, enter into transactions with affiliates, merge, dissolve, pay off subordinated indebtedness, make investments and dispose of assets. Subject to the terms of the Intercreditor Agreement, if the covenants under the Credit Agreement are breached, the lenders may, subject to various customary cure rights, require the immediate payment of all amounts outstanding and foreclose on collateral. Other customary events of default in the Credit Agreement include, without limitation, failure to pay obligations when due, initiation of insolvency proceedings, defaults on certain other indebtedness, and the incurrence of certain judgments that are not stayed, satisfied, bonded or discharged within 30 days.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had no outstanding borrowings under the Credit Agreement and was in compliance with all covenants. The Company’s liquidity position, defined as cash on hand and available borrowing capacity on the Revolving Credit Facility, amounted to $361.2 million as of December 31, 2017.
Term Loan Credit Agreement
In May 2012, the Company entered into the Term Lo an Credit Agreement (as amended, the “Term Loan Credit Agreement”), dated as of May 8, 2012, among the Company, the several lenders from time to time party thereto, Morgan Stanley Senior Funding, Inc., as administrative agent (the “Term Agent”), joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, and Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as joint lead arranger and joint bookrunner, which provides for, among other things, (x) a senior secured term loan of $188.0 million that matures on March 19, 2022, subject to certain springing maturity events (the “Term Loans”), and (y) an uncommitted accordion feature to provide for additional senior secured term loans of up to $75 million plus an unlimited amount provided that the senior secured leverage ratio would not exceed 3.00 to 1.00, subject to certain conditions (the “Term Loan Facility”).
| 74 |
On February 24, 2017, the Company entered into Amendment No. 3 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 3”). As of February 24, 2017, $189.5 million of the Tranche B-2 Loans were outstanding. Under Amendment No. 3, the lenders agreed to provide to the Company term loans in the same aggregate principal amount of the outstanding Tranche B-2 Loans (the “Tranche B-3 Loans”), which were used to refinance the outstanding Tranche B-2 Loans.
In connection with, and in order to permit under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, the Senior Notes offering and the acquisition of Supreme, on August 18, 2017, the Company entered into Amendment No. 4 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 4”). Amendment No. 4 also permitted the Company to incur certain other indebtedness in connection with the Supreme acquisition and to acquire certain liens and obligations of Supreme upon the consummation of the Supreme acquisition.
Furthermore, on November 17, 2017, the Company entered into Amendment No. 5 to the Term Loan Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 5”). As of the Amendment No. 5 date, $188.0 million of the Term Loans were outstanding. Under Amendment No. 5, the lenders agreed to provide to the Company term loans in the same aggregate principal amount of the outstanding Term Loans (“Tranche B-4 Loans”), which were used to refinance the outstanding Term Loans.
The Tranche B-4 Loans shall amortize in equal quarterly installments in aggregate amounts equal to 0.25% of the initial principal amount of the Tranche B-4 Loans, with the balance payable at maturity, and bear interest at a rate, at the Company’s election, equal to (i) LIBOR (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin of 225 basis points or (ii) a base rate (subject to a floor of 0%) plus a margin of 125 basis points. The Company is not subject to any financial covenants under the Term Loan Facility.
The Term Loan Credit Agreement is guaranteed by certain of the Company’s subsidiaries, and is secured by (i) first-priority liens on and security interests in the Term Priority Collateral, and (ii) second-priority security interests in the Revolver Priority Collateral.
The Term Loan Credit Agreement contains customary covenants limiting the Company’s ability to, among other things, pay cash dividends, incur debt or liens, redeem or repurchase stock, enter into transactions with affiliates, merge, dissolve, pay off subordinated indebtedness, make investments and dispose of assets. Subject to the terms of the Intercreditor Agreement, if the covenants under the Term Loan Credit Agreement are breached, the lenders may, subject to various customary cure rights, require the immediate payment of all amounts outstanding and foreclose on collateral. Other customary events of default in the Term Loan Credit Agreement include, without limitation, failure to pay obligations when due, initiation of insolvency proceedings, defaults on certain other indebtedness, and the incurrence of certain judgments that are not stayed, satisfied, bonded or discharged within 60 days.
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, under the Term Loan Credit Agreement the Company paid interest of $7.4 million, $8.3 million and $8.5 million, respectively, and principal of $1.9 million, $1.9 million and $1.4 million, respectively. In connection with Amendment No. 3 and Amendment No. 5, the Company recognized a loss on debt extinguishment of $0.7 million during 2017 which is included in Other, net on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had $187.6 million outstanding under the Term Loan Credit Agreement, of which $1.9 million was classified as current on the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet.
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, the Company incurred charges of $0.2 million, $0.2 million and $0.3 million, respectively, for amortization of fees and original issuance discount which is included in Interest Expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
| 7. | FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS |
The Company’s fair value measurements are based upon a three-level valuation hierarchy. These valuation techniques are based upon the transparency of inputs (observable and unobservable) to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. Observable inputs reflect market data obtained from independent sources, while unobservable inputs reflect the Company’s market assumptions. These two types of inputs create the following fair value hierarchy:
| 75 |
| · | Level 1 — Valuation is based on quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets; |
| · | Level 2 — Valuation is based on quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for the full term of the financial instrument; and |
| · | Level 3 — Valuation is based upon other unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement. |
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
The Company maintains a non-qualified deferred compensation plan which is offered to senior management and other key employees. The amount owed to participants is an unfunded and unsecured general obligation of the Company. Participants are offered various investment options with which to invest the amount owed to them, and the plan administrator maintains a record of the liability owed to participants by investment. To minimize the impact of the change in market value of this liability, the Company has elected to purchase a separate portfolio of investments through the plan administrator similar to those chosen by the participant.
The investments purchased by the Company include mutual funds, $1.4 million of which are classified as Level 1, and life-insurance contracts valued based on the performance of underlying mutual funds, $13.8 million of which are classified as Level 2.
Additionally, upon the Company’s acquisition of Supreme, the Company acquired a pool of investments made by a wholly owned captive insurance subsidiary. These investments are comprised of mutual funds, $2.9 million of which are classified as Level 1.
Estimated Fair Value of Debt
The estimated fair value of debt at December 31, 2017 consists primarily of the Convertible Senior Notes due 2018, Senior Notes due 2025 and borrowings under the Term Loan Credit Agreement (see Note 6). The fair value of the Convertible Senior Notes due 2018, Senior Notes due 2025, Term Loan Credit Agreement and the Revolving Credit Facility are based upon third party pricing sources, which generally do not represent daily market activity or represent data obtained from an exchange, and are classified as Level 2. The interest rates on the Company’s borrowings under the Revolving Credit Facility are adjusted regularly to reflect current market rates and thus carrying value approximates fair value for these borrowings. All other debt and capital lease obligations approximate their fair value as determined by discounted cash flows and are classified as Level 3.
The Company’s carrying and estimated fair value of debt at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016 were as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Fair Value | Carrying | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Value | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Instrument | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Convertible senior notes due 2018 | $ | 44,046 | $ | - | $ | 83,605 | $ | - | $ | 46,768 | $ | - | $ | 69,721 | $ | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Senior notes due 2025 | 319,377 | - | 328,250 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Term loan credit agreement | 186,620 | - | 188,048 | - | 188,540 | - | 189,470 | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other debt | 67 | - | - | 67 | 625 | - | - | 625 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital lease obligations | 1,302 | - | - | 1,302 | 1,903 | - | - | 1,903 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 551,412 | $ | - | $ | 599,903 | $ | 1,369 | $ | 237,836 | $ | - | $ | 259,191 | $ | 2,528 | |||||||||||||||||
| 8. | STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
On February 24, 2017, the Board of Directors approved the extension of the company’s existing stock repurchase program for an additional two-year period and authorizing up to an additional $100 million in repurchases. Stock repurchases under this program may be made in the open market or in private transactions at times and in amounts determined by the Company. As of December 31, 2017, $52.9 million remained available under the program.
| 76 |
The Board of Directors has the authority to issue common and unclassed preferred stock of up to 200 million shares and 25 million shares, respectively, with par value of $0.01 per share, as well as to fix dividends, voting and conversion rights, redemption provisions, liquidation preferences and other rights and restrictions.
| 9. | STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION |
On May 18, 2017, the shareholders of the Company approved the 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2017 Incentive Plan”) which authorizes 3,150,000 shares for issuance under the plan. Awards granted under the 2017 Incentive Plan may be in the form of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, other share-based awards and cash awards to directors, officers and other eligible employees of the Company.
The Company recognizes all share-based awards to eligible employees based upon their fair value. The Company’s policy is to recognize expense for awards that have service conditions only subject to graded vesting using the straight-line attribution method. Total stock-based compensation expense was $10.4 million, $12.0 million and $10.0 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The amount of compensation costs related to nonvested stock options and restricted stock not yet recognized was $11.6 million at December 31, 2017, for which the weighted average remaining life was 1.8 years.
Restricted Stock
Restricted stock awards vest over a period of one to three years and may be based on the achievement of specific financial performance metrics. These shares are valued at the market price on the date of grant and are forfeitable in the event of terminated employment prior to vesting.
A summary of all restricted stock activity during 2017 is as follows:
| Weighted | ||||||||
| Average | ||||||||
| Number of | Grant Date | |||||||
| Shares | Fair Value | |||||||
| Restricted Stock Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 1,963,725 | $ | 14.20 | |||||
| Granted | 794,700 | $ | 21.65 | |||||
| Vested | (657,040 | ) | $ | 14.33 | ||||
| Forfeited | (255,758 | ) | $ | 16.58 | ||||
| Restricted Stock Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 1,845,627 | $ | 17.11 | |||||
During 2017, 2016 and 2015, the Company granted 794,700, 1,105,010 and 667,126 shares of restricted stock, respectively, with aggregate fair values on the date of grant of $17.2 million, $14.7 million and $9.9 million, respectively. The total fair value of restricted stock that vested during 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $13.5 million, $7.4 million and $5.6 million, respectively.
Stock Options
Stock options are awarded with an exercise price equal to the market price of the underlying stock on the date of grant, become fully exercisable three years after the date of grant and expire ten years after the date of grant. No stock options have been granted by the Company since February 2015.
| 77 |
A summary of all stock option activity during 2017 is as follows:
| Number of Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life | Aggregate Intrinsic Value ($ in millions) | |||||||||||||
| Options Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 1,273,754 | $ | 11.13 | 5.1 | $ | 6.0 | ||||||||||
| Exercised | (511,453 | ) | $ | 11.32 | $ | 4.4 | ||||||||||
| Forfeited | (8,753 | ) | $ | 14.16 | ||||||||||||
| Expired | (510 | ) | $ | 13.32 | ||||||||||||
| Options Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 753,038 | $ | 10.96 | 4.4 | $ | 8.1 | ||||||||||
| Options Exercisable at December 31, 2017 | 704,858 | $ | 10.74 | 4.2 | $ | 7.7 | ||||||||||
The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $4.4 million, $1.3 million and $0.6 million, respectively.
| 10. | EMPLOYEE SAVINGS PLANS |
Substantially all of the Company’s employees are eligible to participate in a defined contribution plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. The Company also provides a non-qualified defined contribution plan for senior management and certain key employees. Both plans provide for the Company to match, in cash, a percentage of each employee’s contributions up to certain limits. The Company’s matching contribution and related expense for these plans was approximately $7.3 million, $7.0 million, and $7.3 million for 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
| 11. | INCOME TAXES |
| a. | Income Before Income Taxes |
The consolidated income (loss) before income taxes for 2017, 2016 and 2015 consists of the following (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Domestic | $ | 121,897 | $ | 185,042 | $ | 163,325 | ||||||
| Foreign | 641 | 375 | (14 | ) | ||||||||
| Total income before income taxes | $ | 122,538 | $ | 185,417 | $ | 163,311 | ||||||
| b. | Income Tax Expense |
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) was enacted on December 22, 2017. The Act contains numerous new and changed provisions related to the US federal taxation of domestic and foreign corporate operations. Although most of these provisions go into effect starting January 1, 2018 for calendar year corporate taxpayers, companies are still required to record the income tax accounting effects within the financial statements in the period of enactment. As such, the Company has included the estimated effects of remeasuring deferred taxes for the new US federal income tax rate of 21% going into effect in 2018, as well as assessed its ability to realize deferred income tax assets in the future under the new rules. At December 31, 2017, we have not completed our accounting for the tax effects of enactment of the Act; however, in certain cases, as described below, we have made a reasonable estimate of the effects on our existing deferred tax balances.
The Company remeasured certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates that are expected to be in effect at the time the tax deduction or taxable item will be reported in the Company’s tax return (i.e. when they are expected to reverse in the future), which is generally 21%. However, the Company is still analyzing certain aspects of the Act and refining calculations, which could potentially affect the measurement of these balances or potentially give rise to new deferred tax amounts. The provisional amount recorded related to the remeasurement resulted in a decrease to our deferred tax balance of $19.7 million, which reduced the Company’s income tax expense for year ended December 31, 2017.
| 78 |
The Company assessed the impacts of the new provisions associated with the deductibility of executive compensation under Internal Revenue Code Section 162(m), and the associated “grandfathering” rules within the Act to provide taxpayers transition relief when applying the change in law. Starting with the 2018 tax year, the Act will no longer permit the exclusion of performance-based compensation, as well as CFO compensation, from the deduction limits set forth in Section 162(m). Within the Act are transition relief provisions for which the Company believes it would qualify when assessing the future deductibility of executive compensation. As such, we are currently recognizing a deferred income tax asset associated with the future tax deductions of equity-based compensation for the executives whose compensation falls under the new limitation rules in the amount of $3.1 million. The Company will monitor future guidance set forth by the Department of Treasury with regard to Section 162(m) provisions under the Act, and true up this estimate as appropriate within the one year measurement period required under Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (SAB 118) issued by the SEC.
The consolidated income tax expense for 2017, 2016 and 2015 consists of the following components (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Current | ||||||||||||
| Federal | $ | 21,316 | $ | 51,489 | $ | 58,090 | ||||||
| State | 4,327 | 10,307 | 8,627 | |||||||||
| Foreign | 155 | 144 | 54 | |||||||||
| $ | 25,798 | $ | 61,940 | $ | 66,771 | |||||||
| Deferred | ||||||||||||
| Federal | $ | (16,065 | ) | $ | 3,448 | $ | (7,930 | ) | ||||
| State | 1,459 | 686 | 288 | |||||||||
| Foreign | (76 | ) | (90 | ) | (107 | ) | ||||||
| $ | (14,682 | ) | $ | 4,044 | $ | (7,749 | ) | |||||
| Total consolidated expense | $ | 11,116 | $ | 65,984 | $ | 59,022 | ||||||
The following table provides a reconciliation of differences from the U.S. Federal statutory rate of 35% as follows (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Pretax book income | $ | 122,538 | $ | 185,417 | $ | 163,311 | ||||||
| Federal tax expense at 35% statutory rate | 42,888 | 64,896 | 57,159 | |||||||||
| State and local income taxes (net of federal benefit) | 5,047 | 7,145 | 6,190 | |||||||||
| Benefit of domestic production deduction | (3,450 | ) | (5,065 | ) | (5,255 | ) | ||||||
| Change in income tax reserves | (11,925 | ) | 862 | 641 | ||||||||
| Remeasurement of deferred taxes | (19,796 | ) | - | - | ||||||||
| Other | (1,648 | ) | (1,854 | ) | 287 | |||||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 11,116 | $ | 65,984 | $ | 59,022 | ||||||
| 79 |
| c. | Deferred Taxes |
The Company’s deferred income taxes are primarily due to temporary differences between financial and income tax reporting for incentive compensation, depreciation of property, plant and equipment, amortization of intangibles, other accrued liabilities and net operating loss carryforwards (“NOLs”).
Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Companies are required to assess whether valuation allowances should be established against their deferred tax assets based on the consideration of all available evidence, both positive and negative, using a “more likely than not” standard. In making such judgments, significant weight is given to evidence that can be objectively verified.
The Company assesses, on a quarterly basis, the realizability of its deferred tax assets by evaluating all available evidence, both positive and negative, including: (1) the cumulative results of operations in recent years, (2) the nature of recent losses, if applicable, (3) estimates of future taxable income, (4) the length of NOLs and (5) the uncertainty associated with a possible change in ownership, which imposes an annual limitation on the use of these carryforwards.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company retained a valuation allowance of $1.2 million against deferred tax assets related to various state and local NOLs that are subject to restrictive rules for future utilization.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had no U.S. federal tax NOLs. The Company had various multistate income tax NOLs aggregating approximately $53 million which will expire beginning in 2018, if unused.
The components of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 were as follows (in thousands):
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets | ||||||||
| Tax credits and loss carryforwards | $ | 1,710 | $ | 260 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities | 6,629 | 9,852 | ||||||
| Incentive compensation | 13,867 | 21,206 | ||||||
| Other | 2,852 | 4,084 | ||||||
| $ | 25,058 | $ | 35,402 | |||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | $ | (12,813 | ) | $ | (5,823 | ) | ||
| Intangibles | (45,960 | ) | (5,299 | ) | ||||
| Other | (2,003 | ) | (3,264 | ) | ||||
| $ | (60,776 | ) | $ | (14,386 | ) | |||
| Net deferred tax asset before valuation allowances and reserves | $ | (35,718 | ) | $ | 21,016 | |||
| Valuation allowances | (1,237 | ) | (1,172 | ) | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset or liability | $ | (36,955 | ) | $ | 19,844 | |||
| 80 |
| d. | Tax Reserves |
The Company’s policy with respect to interest and penalties associated with reserves or allowances for uncertain tax positions is to classify such interest and penalties in Income Tax Expense on the Consolidated Statement of Operations. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the total amount of unrecognized income tax benefits was approximately $0.8 million and $12.7 million, respectively, all of which, if recognized, would impact the effective income tax rate of the Company. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had recorded a total of $0.3 and $2.1 million, respectively of accrued interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions. The year over year reduction in the accrual balances relates to the release of income tax reserves upon closing of the federal income tax audit for the 2014 tax year. The Company foresees no significant changes to the facts and circumstances underlying its reserves and allowances for uncertain income tax positions as reasonably possible during the next 12 months. As of December 31, 2017, the Company is subject to unexpired statutes of limitation for U.S. federal income taxes for the years 2015 and 2016. The Company is also subject to unexpired statutes of limitation for Indiana state income taxes for the years 2014 through 2016.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits was as follows (in thousands) and all balances as of December 31, 2017 were included in Deferred Income Taxes in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet:
| Balance at January 1, 2016 | $ | 10,625 | ||
| Decrease in prior year tax positions | - | |||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 10,625 | ||
| Decrease in prior year tax positions | (10,130 | ) | ||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 495 |
| 12. | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
| a. | Litigation |
The Company is involved in a number of legal proceedings concerning matters arising in connection with the conduct of its business activities, and is periodically subject to governmental examinations (including by regulatory and tax authorities), and information gathering requests (collectively, "governmental examinations"). As of December 31, 2017, the Company was named as a defendant or was otherwise involved in numerous legal proceedings and governmental examinations in various jurisdictions, both in the United States and internationally.
The Company has recorded liabilities for certain of its outstanding legal proceedings and governmental examinations. A liability is accrued when it is both (a) probable that a loss with respect to the legal proceeding has occurred and (b) the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company evaluates, on a quarterly basis, developments in legal proceedings and governmental examinations that could cause an increase or decrease in the amount of the liability that has been previously accrued. These legal proceedings, as well as governmental examinations, involve various lines of business of the Company and a variety of claims (including, but not limited to, common law tort, contract, antitrust and consumer protection claims), some of which present novel factual allegations and/or unique legal theories. While some matters pending against the Company specify the damages claimed by the plaintiff, many seek a not-yet-quantified amount of damages or are at very early stages of the legal process. Even when the amount of damages claimed against the Company are stated, the claimed amount may be exaggerated and/or unsupported. As a result, it is not currently possible to estimate a range of possible loss beyond previously accrued liabilities relating to some matters including those described below. Such previously accrued liabilities may not represent the Company's maximum loss exposure. The legal proceedings and governmental examinations underlying the estimated range will change from time to time and actual results may vary significantly from the currently accrued liabilities.
| 81 |
Based on its current knowledge, and taking into consideration its litigation-related liabilities, the Company believes it is not a party to, nor are any of its properties the subject of, any pending legal proceeding or governmental examination other than the matters below, which are addressed individually, that would have a material adverse effect on the Company's consolidated financial condition or liquidity if determined in a manner adverse to the Company. However, in light of the uncertainties involved in such matters, the ultimate outcome of a particular matter could be material to the Company's operating results for a particular period depending on, among other factors, the size of the loss or liability imposed and the level of the Company's income for that period. Costs associated with the litigation and settlements of legal matters are reported within General and Administrative Expenses in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Brazil Joint Venture
In March 2001, Bernard Krone Indústria e Comércio de Máquinas Agrícolas Ltda. (“BK”) filed suit against the Company in the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba in the State of Paraná, Brazil. Because of the bankruptcy of BK, this proceeding is now pending before the Second Civil Court of Bankruptcies and Creditors Reorganization of Curitiba, State of Paraná (No. 232/99).
The case grows out of a joint venture agreement between BK and the Company related to marketing of RoadRailer trailers in Brazil and other areas of South America. When BK was placed into the Brazilian equivalent of bankruptcy late in 2000, the joint venture was dissolved. BK subsequently filed its lawsuit against the Company alleging that it was forced to terminate business with other companies because of the exclusivity and non-compete clauses purportedly found in the joint venture agreement. BK asserted damages, exclusive of any potentially court-imposed interest or inflation adjustments, of approximately R$20.8 million (Brazilian Reais). BK did not change the amount of damages asserted following its filing of the case in 2001.
A bench (non-jury) trial was held on March 30, 2010 in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. On November 22, 2011, the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba partially granted BK’s claims, and ordered Wabash to pay BK lost profits, compensatory, economic and moral damages in excess of the amount of compensatory damages asserted by BK. The total ordered damages amount was approximately R$26.7 million (Brazilian Reais), which was approximately $8.1 million U.S. dollars using the exchange rate as of December 31, 2017 and exclusive of any potentially court-imposed interest, fees or inflation adjustments. On October 5, 2016, the Court of Appeals re-heard all facts and legal questions presented in the case, and ruled in favor of the Company on all claims at issue. In doing so, the Court of Appeals dismissed all claims against the Company and vacated the judgment and damages previously ordered by the Fourth Civil Court of Curitiba. On September 30, 2017, BK filed its notice for a special appeal of the Court of Appeals ruling to the Superior Court of Justice and the Supreme Federal Court. However, unless these higher courts find in favor of BK on any of its claims, the judgment of the Court of Appeals is final. As a result of the Court of Appeals ruling, the Company does not expect that this proceeding will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition or results of operations; however, it will continue to monitor these legal proceedings.
Intellectual Property
In October 2006, the Company filed a patent infringement suit against Vanguard National Corporation (“Vanguard”) regarding the Company’s U.S. Patent Nos. 6,986,546 and 6,220,651 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Indiana (Civil Action No. 4:06-cv-135). The Company amended the Complaint in April 2007. In May 2007, Vanguard filed its Answer to the Amended Complaint, along with Counterclaims seeking findings of non-infringement, invalidity, and unenforceability of the subject patents. The Company filed a reply to Vanguard’s counterclaims in May 2007, denying any wrongdoing or merit to the allegations as set forth in the counterclaims. The case was stayed by agreement of the parties while the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“Patent Office”) undertook a reexamination of U.S. Patent No. 6,986,546. In June 2010, the Patent Office notified the Company that the reexamination was completed and the Patent Office reissued U.S. Patent No. 6,986,546 without cancelling any claims of the patent. The parties have not yet petitioned the Court to lift the stay, and it is unknown at this time when the parties may do so.
The Company believes that its claims against Vanguard have merit and that the claims asserted by Vanguard are without merit. The Company intends to vigorously defend its position and intellectual property. The Company believes that the resolution of this lawsuit will not have a material adverse effect on its financial position, liquidity or future results of operations. However, at this stage of the proceeding, no assurance can be given as to the ultimate outcome of the case.
| 82 |
Walker Acquisition
In connection with the Company’s acquisition of Walker in May 2012, there is an outstanding claim of approximately $2.9 million for unpaid benefits that is currently in dispute and that, if required to be paid by the Company, is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Environmental Disputes
In August 2014, the Company was noticed as a potentially responsible party (“PRP”) by the South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control (“DHEC”) pertaining to the Philip Services Site located in Rock Hill, South Carolina pursuant to the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (“CERCLA”) and corresponding South Carolina statutes. PRPs include parties identified through manifest records as having contributed to deliveries of hazardous substances to the Philip Services Site between 1979 and 1999. The DHEC’s allegation that the Company was a PRP arises out of four manifest entries in 1989 under the name of a company unaffiliated with Wabash National (or any of its former or current subsidiaries) that purport to be delivering a de minimis amount of hazardous waste to the Philip Services Site “c/o Wabash National Corporation.” As such, the Philip Services Site PRP Group (“PRP Group”) notified Wabash in August 2014 that it was offering the Company the opportunity to resolve any liabilities associated with the Philip Services Site by entering into a Cash Out and Reopener Settlement Agreement (the “Settlement Agreement”) with the PRP Group, as well as a Consent Decree with the DHEC. The Company has accepted the offer from the PRP Group to enter into the Settlement Agreement and Consent Decree, while reserving its rights to contest its liability for any deliveries of hazardous materials to the Philips Services Site. The requested settlement payment is immaterial to the Company’s financial conditions or operations, and as a result, if the Settlement Agreement and Consent Decree are finalized, the payment to be made by the Company thereunder is not expected to have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
In January 2006, the Company received a letter from the North Carolina Department of Environment and Natural Resources indicating that a site that the Company formerly owned near Charlotte, North Carolina has been included on the state's October 2005 Inactive Hazardous Waste Sites Priority List. The letter states that the Company was being notified in fulfillment of the state's “statutory duty” to notify those who own and those who at present are known to be responsible for each Site on the Priority List. Following receipt of this notice, no action has ever been requested from the Company, and since 2006 the Company has not received any further communications regarding this matter from the state of North Carolina. The Company does not expect that this designation will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition or results of operations.
Supreme Litigation
Prior to the Company’s acquisition of Supreme, a complaint was filed against Supreme Corporation, a subsidiary of Supreme, in a suit (SVI, Inc. v. Supreme Corporation, Hometown Trolley (a/k/a Double K, Inc.) and Dustin Pence) in the United States District Court, District of Nevada on May 16, 2016. The plaintiff is Supreme Corporation’s (“SC”) former trolley distributor. The plaintiff filed an amended complaint on January 3, 2017, which alleges that SC’s sale of its trolley assets to another trolley manufacturer was improper. SC filed a motion to dismiss, which was granted in part on May 30, 2017. The remaining claims alleged against SC include: (i) misappropriation of trade secrets; (ii) civil conspiracy/collusion; (iii) tortious interference with contractual relationships; (iv) breach of contract; and (v) breach of the covenant of good faith and fair dealing. The plaintiff alleges damages amounting to approximately $40 million. However, due to the inherent risk of litigation, the outcome of this case is uncertain and unpredictable; and, further, management believes that the allegations are without merit and is vigorously defending the matter. As a result, management does not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Prior to the Company’s acquisition of Supreme, on November 4, 2016, a putative class action lawsuit was filed against the Company’s subsidiary, Supreme Industries, Inc., Mark D. Weber (Supreme’s Chief Executive Officer) and Matthew W. Long (Supreme’s former Chief Financial Officer) in the United States District Court for the Central District of California alleging the defendants violated Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and Rule 10b-5 by making material, misleading statements in July 2016 regarding projected backlog. The plaintiff seeks to recover unspecified damages. On February 14, 2017, the court transferred the venue of the case to the Northern District of Indiana upon the joint stipulation of the plaintiff and the defendants. An amended complaint was filed on April 24, 2017 challenging statements made during a putative class period of October 22, 2015 through October 21, 2016. Due to the inherent risk of litigation, the outcome of this case is uncertain and unpredictable; however, at this time, management believes that the allegations are without merit and is vigorously defending the matter. As a result, management does not believe this matter will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
| 83 |
| b. | Environmental Litigation Commitments and Contingencies |
The Company generates and handles certain material, wastes and emissions in the normal course of operations that are subject to various and evolving federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations.
The Company assesses its environmental liabilities on an on-going basis by evaluating currently available facts, existing technology, presently enacted laws and regulations as well as experience in past treatment and remediation efforts. Based on these evaluations, the Company estimates a lower and upper range for treatment and remediation efforts and recognizes a liability for such probable costs based on the information available at the time. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had reserved estimated remediation costs of $0.3 million for activities at existing and former properties which are recorded within Other Accrued Liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
| c. | Letters of Credit |
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had standby letters of credit totaling $5.3 million issued in connection with workers compensation claims and surety bonds.
| d. | Purchase Commitments |
The Company has $58.7 million in purchase commitments through December 2017 for various raw material commodities, including aluminum, steel and nickel as well as other raw material components which are within normal production requirements.
| e. | Chassis Converter Pool Agreements |
The Company, through its subsidiary Supreme, obtains most vehicle chassis for its specialized vehicle products directly from the chassis manufacturers under converter pool agreements. Chassis are obtained from the manufacturers based on orders from customers, and in some cases, for unallocated orders. The agreements generally state that the manufacturer will provide a supply of chassis to be maintained at the Company’s facilities with the condition that we will store such chassis and will not move, sell, or otherwise dispose of such chassis except under the terms of the agreement. In addition, the manufacturer typically retains the sole authority to authorize commencement of work on the chassis and to make certain other decisions with respect to the chassis including the terms and pricing of sales of the chassis to the manufacturer’s dealers. The manufacturer also does not transfer the certificate of origin to the Company nor permit the Company to sell or transfer the chassis to anyone other than the manufacturer (for ultimate resale to a dealer). Although the Company is party to related finance agreements with manufacturers, the Company has not historically settled, nor expects to in the future settle, any related obligations in cash. Instead, the obligation is settled by the manufacturer upon reassignment of the chassis to an accepted dealer, and the dealer is invoiced for the chassis by the manufacturer. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2017 the Company’s outstanding chassis converter pool with the manufacturer totaled $18.3 million and has included this financing agreement on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets within Prepaid expenses and other and Other accrued liabilities. All other chassis programs through its Supreme subsidiary are handled as consigned inventory belonging to the manufacturer and totaled approximately $3.2 million. Under these agreements, if the chassis is not delivered to a customer within a specified time frame the Company is required to pay a finance or storage charge on the chassis. Additionally, the Company receives finance support funds from manufacturers when the chassis are assigned into the Company’s chassis pool. Typically, chassis are converted and delivered to customers within 90 days of the receipt of the chassis by the Company.
| 84 |
| 13. | SEGMENTS |
| a. | Segment Reporting |
Previously, the Company managed its business in two segments: Commercial Trailer Products and Diversified Products. In the third quarter of 2017, the Company completed the acquisition of Supreme. As a result, the Company implemented a new reporting segment during the fourth quarter referred to as the Final Mile Products segment, which includes the operations of Supreme and other truck body activities previously reported in the Company’s Commercial Trailer Products segment. The Commercial Trailer Products segment manufactures standard and customized van and platform trailers and other transportation related equipment to customers who purchase directly from the Company or through independent dealers. The Diversified Products segment, comprised of four strategic business units including, Tank Trailer, Aviation & Truck Equipment, Process Systems and Composites, focuses on the Company’s commitment to expand its customer base, diversify its product offerings and revenues and extend its market leadership by leveraging its proprietary DuraPlate® panel technology, drawing on its core manufacturing expertise and making available products that are complementary to truck and tank trailers and transportation equipment.
The accounting policies of the segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies except that the Company evaluates segment performance based on income from operations. The Company has not allocated certain corporate related administrative costs, interest and income taxes included in the corporate and eliminations segment to the Company’s other reportable segments. The Company accounts for intersegment sales and transfers at cost plus a specified mark-up.
Reportable segment information is as follows (in thousands):
| 85 |
| Commercial | Diversified | Final Mile | Corporate and | |||||||||||||||||
| Trailer Products | Products | Products | Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | ||||||||||||||||||||
| External customers | $ | 1,348,251 | $ | 348,449 | $ | 70,461 | $ | - | $ | 1,767,161 | ||||||||||
| Intersegment sales | 131 | 12,909 | - | (13,040 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total net sales | $ | 1,348,382 | $ | 361,358 | $ | 70,461 | $ | (13,040 | ) | $ | 1,767,161 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 9,975 | 22,236 | 1,152 | 1,690 | 35,053 | |||||||||||||||
| Income (Loss) from operations | 151,999 | 20,376 | (2,098 | ) | (39,461 | ) | 130,816 | |||||||||||||
| Reconciling items to net income | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 16,400 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other, net | (8,122 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 11,116 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 111,422 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | $ | 311,705 | $ | 340,651 | $ | 404,246 | $ | 294,911 | $ | 1,351,513 | ||||||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | ||||||||||||||||||||
| External customers | $ | 1,506,070 | $ | 339,374 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 1,845,444 | ||||||||||
| Intersegment sales | 40 | 13,030 | - | (13,070 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total net sales | $ | 1,506,110 | $ | 352,404 | $ | - | $ | (13,070 | ) | $ | 1,845,444 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 12,345 | 22,970 | - | 1,454 | 36,769 | |||||||||||||||
| Income (Loss) from operations | 212,351 | 24,595 | - | (34,414 | ) | 202,532 | ||||||||||||||
| Reconciling items to net income | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 15,663 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other, net | 1,452 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 65,984 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 119,433 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | $ | 312,848 | $ | 370,338 | $ | - | $ | 215,547 | $ | 898,733 | ||||||||||
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | ||||||||||||||||||||
| External customers | $ | 1,582,019 | $ | 445,470 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2,027,489 | ||||||||||
| Intersegment sales | 222 | 11,457 | - | (11,679 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| Total net sales | $ | 1,582,241 | $ | 456,927 | $ | - | $ | (11,679 | ) | $ | 2,027,489 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 12,674 | 23,888 | - | 1,436 | 37,998 | |||||||||||||||
| Income (Loss) from operations | 159,385 | 51,078 | - | (30,094 | ) | 180,369 | ||||||||||||||
| Reconciling items to net income | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 19,548 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other, net | (2,490 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense | 59,022 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 104,289 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | $ | 336,235 | $ | 397,892 | $ | - | $ | 215,543 | $ | 949,670 | ||||||||||
| b. | Customer Concentration |
The Company is subject to a concentration of risk as the five largest customers together accounted for approximately 24%, 24% and 25% of the Company’s aggregate net sales in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. In addition, for each of the last three years there were no customers whose revenue individually represented 10% or more of our aggregate net sales. International sales accounted for less than 10% in each of the last three years.
| 86 |
| c. | Product Information |
The Company offers products primarily in four general categories: (1) new trailers, (2) used trailers, (3) components, parts and service and (4) equipment and other. The following table sets forth the major product categories and their percentage of consolidated net sales (dollars in thousands):
| Commercial | Diversified | Final Mile | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trailer Products | Products | Products | Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year
ended December 31, 2017 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| New trailers | 1,273,584 | 140,105 | - | - | 1,413,689 | 80.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Used trailers | 10,720 | 3,278 | - | - | 13,998 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Components, parts and service | 48,008 | 117,681 | 1,877 | (13,040 | ) | 154,526 | 8.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Equipment and other | 16,070 | 100,294 | 68,584 | - | 184,948 | 10.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total net external sales | 1,348,382 | 361,358 | 70,461 | (13,040 | ) | 1,767,161 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Commercial | Diversified | Final Mile | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trailer Products | Products | Products | Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| New trailers | 1,421,586 | 129,639 | - | (89 | ) | 1,551,136 | 84.1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Used trailers | 11,998 | 3,176 | - | - | 15,174 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Components, parts and service | 56,191 | 111,519 | - | (12,955 | ) | 154,755 | 8.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Equipment and other | 16,335 | 108,070 | - | (26 | ) | 124,379 | 6.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total net external sales | 1,506,110 | 352,404 | - | (13,070 | ) | 1,845,444 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Commercial | Diversified | Final Mile | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trailer Products | Products | Products | Eliminations | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| New trailers | 1,474,201 | 218,028 | - | - | 1,692,229 | 83.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Used trailers | 31,022 | 4,558 | - | - | 35,580 | 1.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Components, parts and service | 60,482 | 119,696 | - | (11,628 | ) | 168,550 | 8.3 | |||||||||||||||||
| Equipment and other | 16,536 | 114,645 | - | (51 | ) | 131,130 | 6.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total net external sales | 1,582,241 | 456,927 | - | (11,679 | ) | 2,027,489 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||||
| 14. | CONSOLIDATED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED) |
The following is a summary of the unaudited quarterly results of operations for fiscal years 2017, 2016 and 2015 (dollars in thousands, except per share amounts):
| 87 |
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | |||||||||||||
| Quarter | Quarter | Quarter | Quarter | |||||||||||||
| 2017 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 362,716 | $ | 435,903 | $ | 425,098 | $ | 543,444 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 59,357 | 67,679 | 60,963 | 72,876 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | 20,173 | 22,945 | 18,947 | 49,357 | ||||||||||||
| Basic net income per share(1) | 0.34 | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted net income per share(1) | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.80 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 447,676 | $ | 471,439 | $ | 464,272 | $ | 462,057 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 79,526 | 91,064 | 83,459 | 71,485 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | 27,523 | 35,532 | 33,378 | 23,000 | ||||||||||||
| Basic net income per share(1) | 0.42 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.37 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted net income per share(1) | 0.42 | 0.53 | 0.51 | 0.36 | ||||||||||||
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 437,597 | $ | 514,831 | $ | 531,350 | $ | 543,711 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 57,197 | 72,405 | 86,022 | 87,819 | ||||||||||||
| Net income | 10,474 | 28,649 | 31,880 | 33,286 | ||||||||||||
| Basic net income per share(1) | 0.15 | 0.42 | 0.48 | 0.50 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted net income per share(1) | 0.15 | 0.41 | 0.47 | 0.50 | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Basic and diluted net income per share is computed independently for each of the quarters presented. Therefore, the sum of the quarterly net income per share may differ from annual net income per share due to rounding. |
ITEM 9—CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None
ITEM 9A—CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and board of directors that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Based on an evaluation conducted under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017, including those procedures described below, we, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, determined that those controls and procedures were effective.
Changes in Internal Controls
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act, identified in connection with the evaluation required by Rules 13a-15(d) and 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act that occurred during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017 that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
| 88 |
Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The management of Wabash National Corporation (“the Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of the financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles; (3) provide reasonable assurance that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (4) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies and procedures may deteriorate.
Management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Supreme Industries, Inc., which is included in the Company’s 2017 consolidated financial statements and constituted $404.2 million of the Company’s total assets as of December 31, 2017 and $67.1 million of the Company’s sales for the year then ended.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (COSO). Based on this assessment, management has concluded that internal control over financial reporting is effective as of December 31, 2017.
Ernst & Young LLP, an Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, has audited the Company’s consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2017, and its report on internal controls over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 appears on the following page.
| Richard J. Giromini | Chief Executive Officer | |
| Jeffery L. Taylor | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |
| February 28, 2018 | ||
| 89 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of Wabash National Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited Wabash National Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Wabash National Corporation (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on the COSO criteria.
As indicated in the accompanying Report of Management on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management's assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Supreme Industries, Inc., which is included in the 2017 consolidated financial statements of Wabash National Corporation and constituted $404.2 million and $358.7 million of total and net assets, respectively, as of December 31, 2017, and $67.1 million and $1.6 million of sales and pretax loss, respectively, for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of Wabash National Corporation also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Supreme Industries, Inc.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of Wabash National Corporation as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017 and our report dated February 28, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Indianapolis, Indiana
February 28, 2018
| 90 |
None.
ITEM 10—EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The Company hereby incorporates by reference the information contained under the heading “Executive Officers of Wabash National Corporation” from Item 1 Part I of this Annual Report.
The Company hereby incorporates by reference the information contained under the headings “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” or “Election of Directors” from its definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to stockholders of the Company and filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report in connection with the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held May 17, 2018.
Code of Ethics
As part of our system of corporate governance, our Board of Directors has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics (“Code of Ethics”) that is specifically applicable to our Chief Executive Officer and Senior Financial Officers. This Code of Ethics is available within the Corporate Governance section of the Investor Relations page of our website at www.wabashnational.com. We will disclose any waivers for our Chief Executive Officer or Senior Financial Officers under, or any amendments to, our Code of Ethics by posting such information on our website at the address above.
ITEM 11—EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The Company hereby incorporates by reference the information contained under the headings “Executive Compensation" and “Director Compensation” from its definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to the stockholders of the Company and filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report in connection with the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held May 17, 2018.
ITEM 12—SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The Company hereby incorporates by reference the information contained under the headings "Beneficial Ownership of Common Stock” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” from its definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to the stockholders of the Company and filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report in connection with the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 17, 2018.
ITEM 13—CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The Company hereby incorporates by reference the information contained under the headings “Election of Directors” and “Related Persons Transactions Policy” from its definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to the stockholders of the Company and filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report in connection with the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 17, 2018.
ITEM 14—PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Information required by Item 14 of this form and the audit committee’s pre-approval policies and procedures regarding the engagement of the principal accountant are incorporated herein by reference to the information contained under the heading “Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement to be delivered to the stockholders of the Company and filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report in connection with the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 17, 2018.
| 91 |
ITEM 15—EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
| (a) | Financial Statements: The Company has included all required financial statements in Item 8 of this Annual Report. The financial statement schedules have been omitted as they are not applicable or the required information is included in the Notes to the consolidated financial statements. |
| (b) | Exhibits: Reference is made to the Exhibit Index of this Annual Report for a list of exhibits filed with this Annual Report or incorporated herein by reference to the document. |
ITEM 16 – FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
EXHIBIT INDEX
| 4.05 | Form of 5.50% Senior Notes due 2025 (24) |
| 10.01# | Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of June 28, 2002, by and between the Company and Richard J. Giromini (2) |
| 92 |
| # | Management contract or compensatory plan | |
| + | Confidential treatment has been granted with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the SEC. | |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-27317) filed on May 16, 1997 | |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2005 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on December 16, 2015 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on January 8, 2007 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on May 24, 2007 (File No. 1-10883) |
| 93 |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on June 10, 2015 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on August 4, 2009 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (11) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on May 25, 2011 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (12) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on September 14, 2011 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (13) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on March 27, 2012 (File No.001-10883) | |
| (14) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on April 23, 2012 (File No.001-10883) | |
| (15) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on May 14, 2012 (File No 001-10883) | |
| (16) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on April 29, 2013 (File No 001-10883) | |
| (17) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on March 23, 2015 (File No 001-10883) | |
| (18) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on February 27, 2017 (File No 001-10883) | |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on May 5, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (20) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form S-8 filed on May 18, 2017 (File No. 333-218085) | |
| (21) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on August 9, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (22) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on August 22, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (23) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on September 15, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (24) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (25) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on November 22, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (26) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on December 15, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (27) | Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Form 8-K filed on December 15, 2017 (File No. 1-10883) | |
| (28) | Filed herewith |
| 94 |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
WABASH NATIONAL CORPORATION
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Jeffery L. Taylor |
| Jeffery L. Taylor | ||
| Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| Date | Signature and Title | ||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Richard J. Giromini | |
| Richard J. Giromini | |||
| Chief Executive Officer, Director | |||
| (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Jeffery L. Taylor | |
| Jeffery L. Taylor | |||
| Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Brent L. Yeagy | |
| Richard J. Giromini | |||
| President and Chief Operating Officer, Director | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Martin C. Jischke | |
| Dr. Martin C. Jischke | |||
| Chairman of the Board of Directors | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ John G. Boss | |
| John G. Boss | |||
| Director | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: |
/s/ John E. Kunz | |
| John E. Kunz | |||
| Director | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Larry J. Magee | |
| Larry J. Magee | |||
| Director | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Ann D. Murtlow | |
| Ann D. Murtlow | |||
| Director | |||
| February 28, 2018 | By: | /s/ Scott K. Sorensen | |
| Scott K. Sorensen | |||
| Director | |||
| 95 |