Table of Contents
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 14, 2016
Registration Statement No. 333-203739
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C.
POST-EFFECTIVE AMENDMENT NO. 4
TO
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
SCHEDULE B
OF
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
THE KOREA DEVELOPMENT BANK
(Name of Registrant)
THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA
(Name of Co-Registrant and Guarantor)
Names and Addresses of Authorized Representatives:
| Nak Joo Seong or Jin Hwan Sah |
Suk-Kwon Na | |
| Duly Authorized Representatives in the United States of The Korea Development Bank 320 Park Avenue, 32nd Floor New York, New York 10022 |
Duly Authorized Representative in the United States of The Republic of Korea 335 East 45th Street New York, New York 10017 |
Copies to:
Jinduk Han, Esq.
Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP
c/o 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower
19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu
Seoul 04539, Korea
The securities registered hereby will be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to the procedures set forth in Securities Act Release Nos. 33-6240 and 33-6424.
Table of Contents
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This registration statement relates to US$1,810,000,000 aggregate amount of (i) debt securities (with or without warrants) of The Korea Development Bank to be offered from time to time as separate issues on terms and in the manner to be specified in a prospectus supplement to be delivered in connection with each such offering, (ii) guarantees that may be issued by The Korea Development Bank in respect of obligations of other parties on terms and in the manner to be specified in a prospectus supplement to be delivered in connection with each such issuance and (iii) guarantees that may be issued by The Republic of Korea in respect of debt securities of The Korea Development Bank on terms and in the manner to be specified in a prospectus supplement to be delivered in connection with each such issuance. The prospectus constituting a part of this registration statement relates to (i) the debt securities (with or without warrants) and guarantees to be issued by The Korea Development Bank, registered hereunder, (ii) guarantees to be issued by The Republic of Korea, registered hereunder and (iii) US$5,287,380,000 aggregate principal amount of debt securities (with or without warrants) and guarantees registered under Registration Statement No. 333-197061 (including an aggregate principal amount of US$200,000,000 of debt securities that may be sold by us from time to time in a continuous offering designated Medium-Term Notes, Series C, Due Not Less Than Nine Months From Date of Issue (the “Series C Notes”)). Among such securities, The Korea Development Bank has sold US$500,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 2.25% notes due 2020, US$750,000,000 3.375% notes due 2025, US$500,000,000 2.50% notes due 2021 and US$1,000,000,000 3.0% notes due 2026, and US$4,347,380,000 aggregate amount of securities remain unsold.
This registration statement contains a form of prospectus supplement filed as Exhibit K-1 to this registration statement, together with the supplement to that prospectus supplement filed as Exhibit K-2 to this registration statement, to be used in connection with the sale by us of the Series C Notes in a continuous offering.
Table of Contents
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED JUNE 14, 2016
PROSPECTUS

$4,347,380,000
The Korea Development Bank
Debt Securities
Warrants to Purchase Debt Securities
Guarantees
The Republic of Korea
Guarantees
We will provide the specific terms of these securities in supplements to this prospectus. You should read this prospectus and any prospectus supplement carefully before you invest.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
This prospectus is dated , 2016
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 7 | ||||
| 9 | ||||
| 15 | ||||
| 23 | ||||
| 24 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 26 | ||||
| 27 | ||||
| 32 | ||||
| 155 | ||||
| 155 | ||||
| 157 | ||||
| 160 | ||||
| 168 | ||||
| 175 | ||||
| 181 | ||||
| 184 | ||||
| 192 | ||||
| 195 | ||||
| 197 | ||||
| 200 | ||||
| 200 | ||||
| 207 | ||||
| 207 | ||||
| 208 | ||||
| Description of Guarantees to be Issued by The Republic of Korea |
209 | |||
| LIMITATIONS ON ISSUANCE OF BEARER DEBT SECURITIES AND BEARER WARRANTS |
210 | |||
| 211 | ||||
| 211 | ||||
| 213 | ||||
| 221 | ||||
| 222 | ||||
| 222 | ||||
| 222 | ||||
| 222 | ||||
| 223 | ||||
| 225 | ||||
i
Table of Contents
CERTAIN DEFINED TERMS AND CONVENTIONS
All references to the “Bank”, “we”, “our” or “us” mean The Korea Development Bank. All references to “Korea” or the “Republic” contained in this prospectus mean The Republic of Korea. All references to the “Government” mean the government of Korea.
Unless otherwise indicated,
all references to “won”, “Won” or “W” contained in this prospectus are to the currency of Korea, references to “U.S. dollars”, “Dollars”, “$”, “USD” or
“US$” are to the currency of the United States of America, references to “Euro”, “EUR” or “€” are to the currency of the European Union, references to “Japanese yen”, “JPY” or
“¥” are to the currency of Japan, references to “Singapore dollar” or “SGD” are to the currency of Singapore, references to “Swiss franc” or “CHF” are to the currency of Switzerland, references
to “pound sterling”, “GBP” or “£” are to the currency of the United Kingdom, references to “Chinese offshore renminbi” or “CNH” are to the currency of the People’s Republic of China traded
outside of mainland China, references to “Hong Kong dollar” or “HKD” are to the currency of Hong Kong, S.A.R., references to “Malaysian ringgit” or “MYR” are to the currency of Malaysia, references to
“Mexican Peso” or “MXN” are to the currency of the United Mexican States, references to “New Zealand Dollar” or “NZD” are to the currency of New Zealand, references to “Australian dollar” or
“AUD” are to the currency of Australia, references to “South African Rand” or “ZAR” are to the currency of South Africa, references to “Turkish Lira” or “TRY” are to the currency of Turkey,
references to “Norwegian krone” or “NOK” are to the currency of Norway and references to “Brazilian real” or “BRL” are to the currency of the Federative Republic of Brazil.
All discrepancies in any table between totals and the sums of the amounts listed are due to rounding.
Our separate financial information as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 included in this prospectus has been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards as adopted in Korea (“Korean IFRS” or “K-IFRS”). References in this prospectus to “separate” financial statements and information are to financial statements and information prepared on a non-consolidated basis. Unless specified otherwise, our financial and other information included in this prospectus is presented on a separate basis in accordance with Korean IFRS and does not include such information with respect to our subsidiaries. KDB Financial Group (or KDBFG), a financial holding company, and Korea Finance Corporation (or KoFC), a public policy financing vehicle and the parent company of KDBFG, both of which had originally been established by spinning off a portion of our assets, liabilities and equity in October 2009, merged with and into us on December 31, 2014. Note 48 of the notes to our separate financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 included in this prospectus provides information regarding the merger and the amounts of assets and liabilities acquired by us in connection with the merger.
1
Table of Contents
Unless otherwise specified in the applicable prospectus supplement, we will use the net proceeds from the sale of the securities for our general operations.
2
Table of Contents
We were established in 1954 as a government-owned financial institution pursuant to The Korea Development Bank Act, as amended (the “KDB Act”). Since our establishment, we have been the leading bank in the Republic with respect to the provision of long-term financing for projects designed to assist the nation’s economic growth and development. The Government directly owns all of our paid-in capital. Our registered office is located at 14, Eunhaeng-ro, Youngdeungpo-gu, Seoul, The Republic of Korea.
In June 2008, the Financial Services Commission announced the Government’s preliminary plan for our privatization and, in May 2009, the KDB Act was amended to facilitate our privatization. The preliminary plan reflected the Government’s intention to nurture a more competitive corporate and investment banking sector and trigger reorganization and further advancement of the Korean financial industry.
To implement our privatization, the Government established KDB Financial Group, or KDBFG, a financial holding company, and Korea Finance Corporation, or KoFC, a public policy financing vehicle, in October 2009, by spinning off a portion of our assets, liabilities and equity. In the spin-off, our interests in Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd., KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd. and KDB Capital Corp. were transferred to KDBFG, and our equity holdings in certain government-controlled companies, including Korea Electric Power Corporation, or KEPCO, and certain companies under restructuring programs, including Hyundai Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd., were transferred to KoFC. The Government transferred its ownership interest in us to KDBFG in exchange for all of KDBFG’s share capital on November 24, 2009.
The following diagram shows our ownership structure before and after the spin-off and the share transfer.
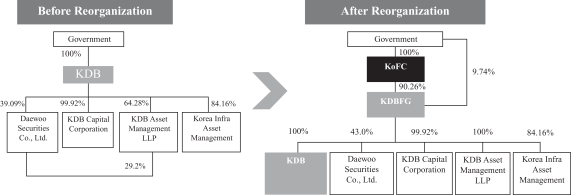
In April 2013, in light of continued uncertainties surrounding the global economy and the prolonged effects of the global financial crisis that commenced in the second half of 2008 on the Korean economy, as well as certain overlap of financial policy roles among different Government-owned banks and financial corporations, the Government launched a task force (the “Task Force”) to consider the reorganization of the financial policy roles of Government-owned banks and financial corporations, including the Government’s plan for our privatization. The Task Force, composed of representatives from various government branches responsible for overseeing such Government-owned entities as well as members of the academia, held a series of closed meetings, considered various reorganization options with respect to policy financing functions and reported their findings to the Financial Services Commission. In August 2013, pursuant to the findings of the Task Force, the Financial Services Commission announced the Government’s plan to reorganize Government-owned policy banks and financial corporations in order to streamline their overlapping functions and reinforce their policy financing roles for start-ups and small- and medium-sized enterprises, new growth industries and overseas projects. The plan called for, among other things, (i) the merger of KoFC and KDBFG into us and the transfer of
3
Table of Contents
KoFC’s overseas assets of approximately W2 trillion to The Export-Import Bank of Korea, or KEXIM, (ii) the sale of our subsidiaries that do not have policy
financing roles and (iii) the gradual reduction of our retail banking services.
In May 2014, the National Assembly amended the KDB Act to largely reflect the plan announced by the Financial Services Commission and halt our privatization and streamline the financial policy roles among
Government-owned banks and financial corporations in order to better respond systematically to rapidly changing domestic and international economic conditions. Under the amended KDB Act, which was amended in May 2014, the public policy financing
role was consolidated and strengthened, and KDBFG and KoFC (together with its subsidiaries) were merged into us on December 31, 2014 in order to utilize our rich experience and expertise in public policy financing, and we took over KoFC’s
role of providing public policy financial support to Korean companies, including managing and operating the Financial Market Stabilization Fund established pursuant to the Act on the Structural Improvement of the Financial Industry enacted in 2009,
while KoFC’s overseas assets of approximately W2 trillion were transferred to KEXIM. On December 31, 2014, the Government transferred all of its ownership interest in KoFC and KDBFG to us and in return received
3,036,079,768 new shares of us with an aggregate par value of W15,180.4 billion. As a newly merged entity, we have an authorized share capital of up to W30,000 billion and our paid-in capital was
W15,180.4 billion. As of the date of this prospectus, the Government owns 100% of our share capital.
The following diagram shows our ownership structure before and after the merger was effected under the amended KDB Act. Our ownership structure returned to our original ownership structure that existed prior to the spin-off and reorganization in October 2009.
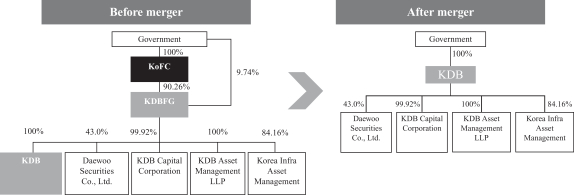
While the Government has halted its plan for our privatization, it has expressed its intention to privatize our subsidiaries that do not have policy financing roles, subject to market conditions.
Our primary purpose, as stated in the KDB Act, the KDB Decree and our Articles of Incorporation, is to “furnish funds in order to expedite the development of the national economy.” We make loans available to major industries for equipment, capital investment and the development of high technology, as well as for working capital.
As of
December 31, 2015, we had W140,968.3 billion of loans outstanding (including loans, call loans, domestic usance, bills of exchange bought, local letters of credit negotiation and loan-type suspense accounts pursuant to the
applicable guidelines without adjusting for allowance for possible loan losses, present value discounts and deferred loan fees), total assets of W224,460.7 billion and total equity of W25,255.6 billion, as
compared to W136,760.1 billion of loans outstanding, W217,833.2 billion of total assets and W25,412.6 billion of total equity as of December 31, 2014. In 2015, we recorded interest income
of W5,490.4 billion, interest expense of W3,912.2 billion and net loss of W1,895.1 billion, as compared to W4,750.4 billion of interest income, W2,761.9 billion of
interest expense and W183.5 billion of net income in 2014. See “—Selected Financial Statement Data.”
4
Table of Contents
Currently, the Government directly holds all of our paid-in capital. In addition to contributions to our capital, the Government provides direct financial support for our financing activities, in the form of loans or guarantees. The Government has the power to elect or dismiss our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, members of our Board of Directors and Auditor. Pursuant to the KDB Act, the Financial Services Commission has supervisory power and authority over matters relating to our general business including, but not limited to, capital adequacy and managerial soundness.
The Government supports our operations pursuant to Article 32 of the KDB Act. Article 32 provides that “the annual net losses of the Korea Development Bank shall be offset each year by the reserve, and if the reserve be insufficient, the deficit shall be replenished by the Government.” As a result of the KDB Act, the Government is generally responsible for our operations and is legally obligated to replenish any deficit that arises if our reserve, consisting of our surplus and capital surplus items, is insufficient to cover our annual net losses. In light of the above, if we had insufficient funds to make any payment under any of our obligations, including the debt securities and guarantees covered by this prospectus, the Government would take appropriate steps, such as by making a capital contribution, by allocating funds or by taking other action, to enable us to make such payment when due. The provisions of Article 32 do not, however, constitute a direct guarantee by the Government of our obligations under the debt securities or the guarantees, and the provisions of the KDB Act, including Article 32, may be amended at any time by action of the National Assembly.
In January 1998, the Government amended the KDB Act to:
| • | subordinate our borrowings from the Government to other indebtedness incurred in our operations; |
| • | allow the Government to offset any deficit that arises if our reserve fails to cover our annual net losses by transferring Government-owned property, including securities held by the Government, to us; and |
| • | allow direct injections of capital by the Government without prior National Assembly approval. |
The Government amended the KDB Act in May 1999 and the KDB Decree in March 2000, to allow the Financial Services Commission to supervise and regulate us in terms of capital adequacy and managerial soundness.
In March 2002, the Government amended the KDB Act to enable us, among other things, to:
| • | obtain low-cost funds from The Bank of Korea and from the issuance of debt securities (in addition to already permitted Industrial Finance Bonds), which funds may be used for increased levels of lending to small and medium size enterprises; |
| • | broaden the scope of borrowers to which we may extend working capital loans to include companies in the manufacturing industry, enterprises which are “closely related” to enhancing the corporate competitiveness of the manufacturing industry and leading-edge high-tech companies; and |
| • | extend credits to mergers and acquisitions projects intended to facilitate corporate restructuring efforts. |
In July 2005 and May 2009, the Government amended the KDB Act to provide that:
| (1) | our annual net profit, after adequate allowances are made for depreciation in assets, shall be distributed as follows: |
| (i) | forty percent or more of the net profit shall be credited to reserve, until the reserve amounts equal the total amount of paid-in capital; and |
| (ii) | any net profit remaining following the apportionment required under subparagraph (i) above shall be distributed in accordance with the resolution of our Board of Directors and the approval of our shareholders; |
5
Table of Contents
| (2) | accumulated amounts in reserve may be capitalized after offsetting any net losses; and |
| (3) | any distributions made in accordance with paragraph (1)(ii) above may be in the form of cash dividends or dividends in kind, provided that any distributions of dividends in kind must be made in accordance with applicable provisions of the KDB Decree. |
In February 2008, the Government further amended the KDB Act, primarily to transfer most of the Government’s supervisory authority over us from the Ministry of Strategy and Finance (formerly the Ministry of Finance and Economy) to the Financial Services Commission.
In May 2009, the Government amended the KDB Act to facilitate our privatization. The amendment provided for, among others:
| • | the preparation for the transformation of us from a special statutory entity into a corporation, including the application of the Banking Act as applicable; |
| • | the expansion of our operation scope that enables us to engage in commercial banking activities, including retail banking; |
| • | the provision of government guarantees for our mid-to-long term foreign currency debt outstanding at the time of initial sale of the Government’s stake in KDBFG (subject to the National Assembly’s authorization of the Government guarantee amount) and possible guarantees for our foreign currency debt incurred for the refinancing of such mid-to-long term foreign currency debt with the government guarantee during the period when the Government owns more than 50% of our shares; and |
| • | the establishment of KDBFG and KoFC and application of the Financial Holding Company Act to KDBFG. |
In May 2014, the Government and the National Assembly amended the KDB Act to streamline the financial policy roles among Government-owned banks and financial corporations in order to better respond systematically to rapidly changing domestic and international economic conditions by merging KDBFG and KoFC into us. The amended KDB Act provides, among others, that:
| • | the Government will halt its plan for our privatization; |
| • | public policy financing will be consolidated and strengthened through the newly merged entity; |
| • | we will comprehensively succeed to the properties, rights and obligations of KDBFG and KoFC upon the consummation of the merger; |
| • | the bonds issued by KDBFG and the policy bank bonds issued by the KoFC shall be deemed as the industrial financial bonds issued by us; |
| • | the business engaged in by KoFC in accordance with the Korea Finance Corporation Act or other laws and decrees will be continuously performed by us; and |
| • | the repayment of the principal of and interest on foreign currency debt (with an original maturity of one year or more at the time of issuance) incurred by KoFC and us before this amended KDB Act comes into force shall be guaranteed by the Government at the time of initial sale by the Government of its equity interest in us, subject to the approval by the National Assembly. |
The Minister of Strategy and Finance of the Republic has, on behalf of the Republic, signed the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part.
6
Table of Contents
As of December 31, 2015, our authorized capital was W30,000 billion and capitalization
was as follows:
| December
31, 2015(1) |
||||
| (billions of won) | ||||
| Long-term debt: |
||||
| Won currency borrowings |
||||
| Industrial finance bonds |
115,416.7 | |||
| Foreign currency borrowings |
6,512.4 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total long-term debt |
125,715.7 | (2)(3) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Capital: |
||||
| Paid-in capital |
17,235.4 | |||
| Capital surplus |
2,501.4 | |||
| Capital adjustments |
— | |||
| Retained earnings(4) |
4,949.6 | |||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
569.2 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total capital |
25,255.6 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total capitalization |
||||
|
|
|
|||
| (1) | Except as disclosed in this prospectus, there has been no material adverse change in our capitalization since December 31, 2015. |
| (2) | We have translated borrowings in foreign currencies into Won at the rate of |
| (3) | As of December 31, 2015, we had contingent liabilities totaling |
| (4) | Includes regulatory reserve for loan losses of |
Purpose and Authority
Since our establishment, we have been the leading bank in the Republic in providing long-term financing for projects designed to assist the nation’s economic growth and development.
Under the KDB Act, the KDB Decree and our Articles of Incorporation, our primary purpose is to “contribute to the sound development of the financial industry and the national economy by supplying and managing funds necessary for the development and promotion of industries, expansion of social infrastructure, development of regions, stabilization of the financial markets and facilitation of sustainable growth.” Since we serve the public policy objectives of the Government, we do not seek to maximize profits. We do, however, strive to maintain a level of profitability to strengthen our equity base and support growth in the volume of our business.
Under the KDB Act, we may:
| • | carry out activities necessary to accomplish the expansion of the national economy, subject to the approval of the Financial Services Commission; |
| • | provide loans or discount notes; |
7
Table of Contents
| • | subscribe to, underwrite or invest in securities; |
| • | guarantee or assume indebtedness; |
| • | raise funds by accepting demand deposits and time and savings deposits from the general public, issuing securities, borrowing from the Government, The Bank of Korea or other financial institutions, and borrowing from overseas; |
| • | execute foreign exchange transactions, including currency and interest swap transactions; |
| • | provide planning, management, research and other support services at the request of the Government, public bodies, financial institutions or enterprises; and |
| • | carry out other businesses incidental to the foregoing (subject to the approval of the Financial Services Commission). |
Government Support and Supervision
The Government owns directly all of our paid-in capital. On
February 20, 2000, the Government contributed W100 billion in cash to our capital. On December 29, 2000, we reduced our paid-in capital by W959.8 billion to offset our expected net loss for the year. To
compensate for the resulting deficit under the KDB Act, on June 20, 2001, the Government contributed W3 trillion in the form of shares of common stock of KEPCO to our capital. On December 29, 2001, the Government
contributed W50 billion in cash to our capital. On August 13, 2003, the Government contributed W80 billion in cash to our capital to support our existing fund for facilitating the Republic’s regional
economies. On April 30, 2004, the Government contributed W1 trillion in the form of shares of common stock of KEPCO and Korea Water Resources Corporation to our capital to support our lending to small-and medium-sized companies
and to compensate for our contribution to LG Card Ltd. in the form of loans, cash injections and debt-for-equity swaps. On December 19, 2008, the Government contributed W500 billion in the form of shares of common stock of
Korea Expressway Corporation to our capital and, in January 2009, the Government contributed W900 billion in cash to our capital, in each case to bolster our capital base in order to stabilize the Korean financial market by
supporting small and medium-sized enterprises and providing increased liquidity to corporations. In October 2009, our paid-in capital decreased by W400.0 billion in connection with the establishment by the Government of KDBFG and
KoFC by spinning off a portion of our assets, liabilities and equity (including paid-in capital). In March 2010, the Government, through KDBFG, made a further capital contribution of W10 billion in cash to our capital. In December
2013, the Government contributed W10 billion in cash to our capital. In December 2014, our paid-in capital increased by W5,918.5 billion in connection with the merger of KDBFG and KoFC into us as described
under the heading “Overview” and “Selected Financial Statement Data” in this prospectus. .” In April, July and September 2015, the Government contributed W2 trillion in the form of shares of common
stock of Korea Land & Housing Corporation and KEPCO, W40 billion in cash and W15 billion in cash, respectively, to our capital to support our fund for infrastructure projects, new growth engine,
high-tech and new renewable energy industries and business enterprises in general. Taking into account these capital contributions, reduction and merger, as of December 31, 2015, our total paid-in capital was W17,235.4 billion.
See “—Financial Statements and the Auditors—Notes to Separate Financial Statements of December 31, 2015 and 2014—Note 23.”
In addition to capital contributions, the Government directly supports our financing activities by:
| • | lending us funds to on-lend; |
| • | allowing us to administer Government loans made from a range of special Government funds; |
| • | allowing us to administer some of The Bank of Korea’s surplus foreign exchange holdings; and |
| • | allowing us to receive credit from The Bank of Korea. |
The Government also supports our operations pursuant to Articles 31 and 32 of the KDB Act. Article 31 provides that “40% or more of the annual net profit of the Korea Development Bank shall be transferred to reserve, until the reserve amounts equal the total amount of authorized capital” and that accumulated amounts in reserve
8
Table of Contents
may be capitalized. Article 32 provides that “the net losses of the Korea Development Bank shall be offset each fiscal year by the reserve, and if the reserve be insufficient, the deficit shall be replenished by the Government.”
As a result of the KDB Act, the Government is generally responsible for our operations and is legally obligated to replenish any deficit that arises if our reserve, consisting of our surplus and capital surplus items, is insufficient to cover our annual net losses. In light of the above, if we had insufficient funds to make any payment under any of our obligations, including the debt securities and the guarantees covered by this prospectus, the Government would take appropriate steps, such as by making a capital contribution, by allocating funds or by taking other action, to enable us to make such payment when due. The provisions of Article 32 do not, however, constitute a direct guarantee by the Government of our obligations under the debt securities or the guarantees, and the provisions of the KDB Act, including Article 32, may be amended at any time by action of the National Assembly.
The Government closely supervises our operations in the following ways:
| • | the Government has the power to elect or dismiss our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, members of our Board of Directors and Auditor; |
| • | within three months after the end of each fiscal year, we must submit our financial statements for the fiscal year to the Financial Services Commission; |
| • | the Financial Services Commission has broad authority to require reports from us on any matter and to examine our books, records and other documents. On the basis of the reports and examinations, the Financial Services Commission may issue any orders deemed necessary to enforce the KDB Act; |
| • | the Financial Services Commission must approve our operating manual, which sets out the guidelines for all principal operating matters; |
| • | the Financial Services Commission may supervise our operations to ensure managerial soundness based upon the KDB Decree and the Bank Supervisory Regulations of the Financial Services Commission and may issue orders deemed necessary for such supervision; and |
| • | we may amend our Articles of Incorporation only with the approval of the Financial Services Commission. |
In addition, the conditions of the IMF aid package stated that domestic banks in the Republic, including us, should undergo external audits from internationally recognized accounting firms. Accordingly, we have had our annual financial statements for years commencing 1998 audited by an external auditor. See “—Financial Statements and the Auditors” and “Experts.”
Pursuant to our most recently approved program of operations, we expect to support the reform and restructuring of the Republic’s economic and industrial structure, including financing of promising small and medium sized enterprises, providing export finance and encouraging investments in infrastructure necessary to promote consumer demand and industrial reorganization.
Selected Financial Statement Data
Unless specified otherwise, the information provided below is stated on a separate basis in accordance with Korean IFRS.
Merger of KDBFG and KoFC into KDB
In May 2014, the Government and the National Assembly amended the KDB Act, which came into effect on December 31, 2014, to streamline the financial policy roles among Government-owned banks and financial corporations in order to better respond systematically to rapidly changing domestic and international economic conditions by merging KDBFG and KoFC into us (the “Merger”). The Merger was effective on December 31, 2014. After the Merger, our ownership and organizational structure returned to our original ownership and
9
Table of Contents
organizational structure that existed prior to the establishment of KDBFG and KoFC through spin off and transfer of a portion of our assets, liabilities and equity in October 2009.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Position Data
The following table presents selected statements of financial position data regarding our assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity on a consolidated basis as of December 31, 2014 and 2015, which have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015.
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014(1) | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||
| Statements of Financial Position Data |
||||||||
| Total Loans(2) |
146,284.4 | 147,018.1 | ||||||
| Total Borrowings(3) |
211,757.3 | 198,247.4 | ||||||
| Total Assets |
276,704.8 | 309,491.8 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities |
247,004.2 | 275,549.4 | ||||||
| Equity |
29,700.6 | 33,942.3 | ||||||
| (1) | Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd., our associate, restated its consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014,
primarily due to errors in estimating construction costs, which affected our statements of financial position data as of December 31, 2014 (including a decrease in our assets by |
| (2) | Gross amount, which includes loans for facility development, loans for working capital, inter-bank loans, private loans, off-shore loan receivables, loans borrowed from overseas financial institutions, bills bought in foreign currencies, advance payments on acceptances and guarantees and other loans without adjusting for allowance for loan losses, present value discounts and deferred loan fees. |
| (3) | Total Borrowings include deposits, financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss, borrowings and debt issued. |
Consolidated Income Statement Data
Our selected income statement data included in the following table have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015.
| Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2014(1) | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||
| Income Statement Data |
||||||||
| Total Interest Income |
6,811.1 | 6,304.6 | ||||||
| Total Interest Expense |
4,670.5 | 4,053.6 | ||||||
| Net Interest Income |
2,140.6 | 2,251.0 | ||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
(131.9 | ) | (1,415.0 | ) | ||||
| Non-operating Income (Loss) |
497.4 | 4,101.4 | ||||||
| Income before Income Tax |
365.5 | 2,686.4 | ||||||
| Income Tax Benefit (expense) |
306.0 | (989.7 | ) | |||||
| Net Income |
878.7 | 1,753.4 | ||||||
| (1) | Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd., our associate, has restated its consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31,
2014, primarily due to errors in estimating construction costs, which affected our income statement data in 2014 (including a decrease in net income by |
10
Table of Contents
Separate Financial Statement Data
The following tables present selected separate financial information as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015, which has been derived from our audited separate financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 included in this prospectus. Note 48 of the notes to our separate financial statements as of and for the years December 31, 2014 and 2015 included in this prospectus provides information regarding the Merger and the amounts of assets and liabilities acquired by us in connection with the Merger. You should read the following financial statement data together with the financial statements and notes included in this prospectus.
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||
| Statements of Financial Position Data |
||||||||
| Total Loans(1) |
136,760.1 | 140,968.3 | ||||||
| Total Borrowings(2) |
178,851.7 | 182,852.1 | ||||||
| Total Assets |
217,833.2 | 224,460.7 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities |
192,420.6 | 199,205.1 | ||||||
| Equity |
25,412.6 | 25,255.6 | ||||||
| (1) | Gross amount, which includes loans for facility development, loans for working capital, inter-bank loans, private loans, off-shore loan receivables, loans borrowed from overseas financial institutions, bills bought in foreign currencies, advance payments on acceptances and guarantees and other loans without adjusting for allowance for loan losses, present value discounts and deferred loan fees. |
| (2) | Total Borrowings include deposits, financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss, borrowings and debt issued. |
As of December 31, 2015, our total assets increased by
3.0% to W224,460.7 billion from W217,833.2 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to an increase in loans to W140,968.3 billion from W136,760.1 billion and an
increase in available-for-sale financial assets to W41,291.6 billion from W38,160.0 billion.
As of December 31, 2015, our total liabilities increased by 3.5% to W199,205.1 billion from
W192,420.6 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to an increase in deposits to W39,934.9 billion from W37,605.7 billion, an increase in accounts payable to W4,730.1
billion from W2,622.2 billion and an increase in borrowings to W24,400.6 billion from W23,537.5 billion.
As of December 31, 2015, our total shareholders’ equity decreased by 0.6% to W25,255.6 billion from
W25,412.6 billion as of December 31, 2014, due to a decrease in retained earnings to W4,949.6 billion from W6,890.9 billion, a decrease in accumulated other comprehensive income to
W569.2 billion from W818.4 billion and a decrease in capital surplus to W2,501.4 billion from W2,522.9 billion, which more than offset an increase in paid-in capital to
W17,235.4 billion from W15,180.4 billion.
11
Table of Contents
Our selected income statement data included in the following table have been derived from our audited separate financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 included in this prospectus.
| Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||
| Income Statement Data |
||||||||
| Total Interest Income |
4,750.4 | 5,490.4 | ||||||
| Total Interest Expense |
2,761.9 | 3,912.2 | ||||||
| Net Interest Income |
1,988.5 | 1,578.2 | ||||||
| Operating Income (Loss) |
424.7 | (1,219.3 | ) | |||||
| Income before Income Tax |
216.8 | (2,360.8 | ) | |||||
| Income Tax Benefit (Expense) |
(33.3 | ) | 465.7 | |||||
| Net Income |
183.5 | (1,895.1 | ) | |||||
2015
We had net loss of
W1,895.1 billion in 2015 compared to net income of W183.5 billion in 2014, on a separate basis.
Principal factors for the net loss of W1,895.1 billion in 2015 compared to the net income of W183.5
billion in 2014 included:
| • | an increase in provision for loan losses to |
| • | an increase in impairment losses on investments in subsidiaries and associates to |
| • | a decrease in net interest income to |
| • | an increase in provision for other allowances to |
The above factors were partially offset by an increase in dividend income to W615.3 billion in 2015 from
W158.2 billion in 2014, primarily due to an increase in dividend income from KEPCO.
2014
We had net income of W183.5 billion in 2014 compared to net loss of W1,447.4 billion in 2013, on a
separate basis.
12
Table of Contents
Principal factors for the net income of W183.5 billion in 2014 compared to
the net loss of W1,447.4 billion in 2013 included:
| • | a decrease in impairment losses on investments in subsidiaries and associates to |
| • | net gain on foreign currency transactions of |
| • | a decrease in provision for other allowances to |
| • | an increase in reversals of provisions to |
| • | an increase in net interest income to |
The above
factors were partially offset by net loss on derivatives of W319.6 billion in 2014 compared to net gain of W251.3 billion in 2013, primarily due to valuation loss on derivative financial instruments.
Provisions for Possible Loan Losses and Loans in Arrears
We establish provisions for
possible losses from problem loans, including guarantees and other extensions of credit, based on the length of the delinquent periods and the nature of the loans, including guarantees and other extensions of credit. As of December 31, 2015, we
established provisions of W4,159.3 billion for possible loan losses, 73.4% higher than the provisions as of December 31, 2014 of W2,398.7 billion, primarily due to an increase in non-performing loans extended
to shipbuilding companies. The provisions for possible loan losses under Korean IFRS are recorded for those loans for which objective evidence of impairment exists as a result of one or more events that occurred after initial recognition and, if our
provision for possible loan losses is deemed insufficient for regulatory purposes, we compensate for the difference by recording a regulatory reserve for possible loan losses, which will be deducted from retained earnings. See “—Financial
Statements and the Auditors—Notes to Separate Financial Statements of December 31, 2015 and 2014—Notes 3(26), 23(4) and 23(5).”
Certain of our customers have restructured loans with their creditor banks. As of December 31, 2015, we have provided loans of
W3,074.7 billion for companies under workout, court receivership, court mediation and other restructuring procedures. In addition, as of such date, we held equity securities of such companies in the amount of W175.6
billion following debt-equity swaps. As of December 31, 2015, we had established provisions of W966.7 billion for such loans. We cannot assure you that actual results of the credit loss from the loans to these customers will
not exceed the provisions reserved.
13
Table of Contents
The following table provides information on our loan loss provisions.
| As of December 31, 2014(1) | As of December 31, 2015(1) | |||||||||||||||||
| Loan Amount |
Loan Loss Provisions |
Loan Amount |
Loan Loss Provisions |
|||||||||||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loan Classification |
Normal(2) | |||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary | 5,422.6 | 788.2 | 3,559.5 | 434.8 | ||||||||||||||
| Substandard | 1,731.1 | 499.9 | 4,768.1 | 2,536.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Doubtful | 369.5 | 304.0 | 827.1 | 566.8 | ||||||||||||||
| Expected Loss | 735.6 | 514.6 | 447.1 | 292.7 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | These figures include loans for facility development, loans for working capital, inter-bank loans, private loans, off-shore loan receivables, loans borrowed from overseas financial institutions, bills bought in foreign currencies, advance payments on acceptances and guarantees and other loans. |
| (2) | Includes loans guaranteed by the Government. Under Korean IFRS, we establish loan loss provisions for all loans including loans guaranteed by the Government. |
As of December 31, 2015, our
non-performing loans totaled W6,042.3 billion, representing 4.3% of our outstanding loans as of such date. Non-performing loans are defined as loans that are classified as substandard or below. On December 31, 2015, our legal
reserve was W5,473.9 billion, representing 3.9% of our outstanding loans as of such date.
Loans to Financially Troubled Companies
We have credit exposure (including loans, guarantees and
equity investments) to a number of financially troubled Korean companies including DSME, STX Offshore & Shipbuilding Co., Ltd., Daehan Shipbuildng Co., Ltd., Dongbu Steel Co., Ltd. and STX Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. As of
December 31, 2015, our credit extended to these companies totaled W14,761.2 billion, accounting for 6.6% of our total assets as of such date.
As of December 31, 2015, our exposure (including loans
classified as substandard or below and equity investment classified as estimated loss or below) to DSME increased to W6,485.3 billion from W4,417.4 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to the
extension of new loans. As of December 31, 2015, our exposure to STX Offshore & Shipbuilding was W4,876.5 billion, an increase from W3,898.8 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to the
extension of new loans. As of December 31, 2015, our exposure to Daehan Shipbuilding increased to W1,453.4 billion from W592.1 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to an increase in guarantees.
As of December 31, 2015, our exposure to Dongbu Steel decreased to W1.407.7 billion from W1,551.9 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to the redemption of certain existing loans. As of
December 31, 2015, our exposure to STX Heavy Industries decreased to W538.3 billion from W550.1 billion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to a decrease in guarantees.
As of December 31, 2015, we established provisions of
W40.9 billion for our exposure to Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering, W1,869.0 billion for STX Offshore & Shipbuilding, W88.1 billion for Daehan Shipbuidling, W243.3
billion for Dongbu Steel and W33.4 billion for STX Heavy Industries.
Companies in the STX Group, a large Korean conglomerate primarily engaged in shipbuilding and trading, have faced financial difficulties for the past several years due to prolonged slowdowns in the Korean construction, shipbuilding and shipping industries. STX Pan Ocean had been in court receivership since June 2013 and was sold to Harim Group in June 2015. STX Construction has been in court receivership since April 2013. STX Offshore & Shipbuilding had been in voluntary out-of-court debt restructuring program since 2013 before filing for court receivership in May 2016. The remaining troubled companies (including STX Corporation,
14
Table of Contents
STX Engine and STX Heavy Industries) are in voluntary out-of-court debt restructuring programs with their creditors. Companies in the Dongbu Group, a large Korean conglomerate providing industrial, chemical, shipping, insurance and financial products and services, have also been facing financial difficulties for the past several years due to the prolonged slowdown in the Korean construction industry and in the Korean economy in general. Certain troubled companies in the Dongbu Group are in voluntary out-of-court debt restructuring programs with their creditors, and Dongbu Steel entered into a voluntary workout agreement with its creditors in October 2015. We are the main creditor bank of STX Group and Dongbu Group.
During 2015, DSME, one of the largest shipbuilding and offshore construction companies in Korea, suffered from financial difficulties
primarily due to significant losses incurred in connection with the construction of offshore plants resulting from a prolonged slowdown in the global shipbuilding industry. In October 2015, we announced that we, along with The Export-Import Bank of
Korea, plan to extend additional financing of up to W4.2 trillion to DSME by the end of 2016, which includes debt-to-equity swaps, extension of additional loans and provision of other forms of liquidity support. In this connection,
in December 2015, we acquired W382.9 billion of new equity shares of DSME and our equity interest in DSME increased to 49.7% as of December 31, 2015 from 31.5% as of December 31, 2014. We are currently the largest shareholder of
DSME.
In the event that the financial condition of these companies or other large corporations to which we extended credits deteriorate in the future, we may be required to record additional provisions for credit losses, as well as charge-offs and valuation or impairment losses or losses on disposal, which may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In 2015, we sold non-performing loans worth W910.5 billion to Cyrus Capital Partners and UAMCO., Ltd.
Loan Operations
We mainly provide equipment capital loans, project loans and working capital loans to private Korean enterprises that undertake major industrial projects either directly or indirectly through on-lending. The loans generally cover over 50%, and in some cases as much as 100%, of the total project cost. Equipment capital loans include loans to major industries for development of high technology and for acquisition, improvement or repair of machinery and equipment. We disburse loan proceeds in installments to ensure that the borrower uses the loan for its intended purpose.
Before approving a loan, we consider:
| • | the economic benefits of the project to the Republic; |
| • | the extent to which the project serves priorities established by the Government’s industrial policy; |
| • | the project’s operational feasibility; |
| • | the loan’s and the project’s profitability; and |
| • | the quality of the borrower’s management. |
We charge, on average, interest of 1.8% over our prime rate, although we provide a discount between 0.2% and 0.7% to small- and medium-sized companies. We adjust the prime rate monthly. The spread depends on the purpose of the loan, maturity date and the borrower’s credit ratings. Certain loans bear interest at below market rates. Equipment capital loans generally have original maturities of three to five years, although we occasionally make equipment capital loans with longer maturities. Working capital loans usually mature within two years.
The Business Planning Department functions as our centralized policy-making and planning division with respect to our lending activities. The Business Planning Department formulates and revises our internal regulations on loan programs as well as setting basic lending guidelines.
15
Table of Contents
We have multiple levels of loan approval authority, depending on the loan amount and other factors such as the availability of collateral or guarantee, debt repayment ability and business prospects. The Credit Review Committee, Division Credit Review Committee, Division Credit Review Sub-Committee, General Manager each has authority to approve loans up to a specified amount. The amount differs depending on the type of loan and certain other factors, for example, whether a loan is collateralized or guaranteed.
Our overall risk management policy is set by the Risk Management Committee. For detailed information regarding our risk management policy and procedures, see “—Financial Statements and Auditors—Notes to Separate Financial Statements of December 31, 2015 and 2014—Note 49.”
The following table sets out, by currency and category of loan, our total outstanding loans:
Loans(1)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||
| Equipment Capital Loans: |
||||||||
| Domestic Currency |
||||||||
| Foreign Currency(2) |
9,134.4 | 8,689.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 60,708.8 | 60,309.8 | |||||||
| Working Capital Loans: |
||||||||
| Domestic Currency(3) |
45,268.0 | 48,760.1 | ||||||
| Foreign Currency(2) |
6,184.7 | 6,290.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 51,452.7 | 55,050.9 | |||||||
| Other Loans(4) |
24,598.6 | 25,607.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Loans |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Includes loans extended to affiliates. |
| (2) | Includes loans disbursed and repayable in Won, the amounts of which are based upon an equivalent amount of foreign currency. This type of loan totaled
|
| (3) | Includes loans on households. |
| (4) | Includes inter-bank loans, private loans, off-shore loan receivables, loans borrowed from overseas financial institutions, bills bought in foreign currencies, advance payments on acceptances and guarantees and other loans. |
As of December 31, 2015, we had W140,968.3 billion in outstanding loans, which represents a 3.1% increase from W136,760.1 billion of outstanding loans as of
December 31, 2014.
16
Table of Contents
Maturities of Outstanding Loans
The following table categorizes our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans by their remaining maturities:
Outstanding Equipment Capital and Working Capital Loans by Remaining Maturities(1)
| December 31, | As % of December 31, 2015 Total |
|||||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| (billions of won, except percentages) | ||||||||||||
| Loans with Remaining Maturities of One Year or Less |
37.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Loans with Remaining Maturities of More Than One Year |
72,236.1 | 71,875.9 | 62.3 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Includes loans extended to affiliates. |
Loans by Industrial Sector
The following table sets out the total amount of our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans, categorized by industry sector:
Outstanding Equipment Capital and Working Capital Loans by Industry Sector(1)
| December 31, | As % of December 31, 2015 Total |
|||||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| (billions of won, except percentages) | ||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
48.5 | % | ||||||||||
| Banking and Insurance |
24,307.6 | 25,132.3 | 21.8 | |||||||||
| Transportation |
7,266.4 | 6,805.6 | 5.9 | |||||||||
| Public Administration |
730.2 | 862.2 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| Electric, Gas and Water Supply Industry |
3,052.2 | 3,227.8 | 2.8 | |||||||||
| Others(2) |
23,175.0 | 23,333.2 | 20.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Percentage increase from previous period |
48.6 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||||||
| (1) | Includes loans extended to affiliates. |
| (2) | Includes wholesale and retail trade, real estate and leasing, and construction. |
The manufacturing sector accounted for 48.5% of our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans as of December 31, 2015. As of December 31, 2015, loans to the transportation equipment manufacturing businesses and metal product manufacturing businesses accounted for 19.7% and 13.0%, respectively, of our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans to the manufacturing sector.
Industrial Bank of Korea was our single largest borrower as of December 31, 2015, accounting for 4.2% of our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans. As of December 31, 2015, our five largest borrowers and 20 largest borrowers accounted for 11.3% and 24.9%, respectively, of our outstanding equipment capital and working capital loans.
17
Table of Contents
The following table breaks down the equipment capital and working capital loans to our 20 largest borrowers outstanding as of December 31, 2015 by industry sector:
20 Largest Borrowers by Industry Sector
| As % of
December 31, 2015 Total Outstanding Equipment Capital and Working Capital Loans to Our 20 Largest Borrowers |
||||
| Manufacturing |
35.7 | % | ||
| Banking and Insurance |
51.5 | |||
| Transportation |
3.4 | |||
| Public Administration |
2.2 | |||
| Others(1) |
7.2 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
100.0 | % | ||
|
|
|
|||
| (1) | Includes wholesale and retail trade, real estate and leasing, and construction. |
The following table categorizes the new loans made by us by industry sector:
New Loans by Industry Sector
| Year Ended December 31, | As % of Year Ended December 31, 2015 Total |
|||||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||
| (billions of won, except percentages) | ||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
57.3 | % | ||||||||||
| Banking and Insurance |
3,283.3 | 4,301.4 | 8.9 | |||||||||
| Transportation |
2,586.7 | 2,787.2 | 5.8 | |||||||||
| Electric, Gas and Water Supply Industry |
776.9 | 1,326.0 | 2.8 | |||||||||
| Others(1) |
10,926.0 | 12,098.6 | 25.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Percentage increase (decrease) from previous period |
21.5 | % | 6.7 | % | ||||||||
| (1) | Includes wholesale and retail trade, real estate and leasing, and construction. |
Loans by Categories
In addition to dividing our loans into equipment capital and working capital loans, we classify loans into several groupings, the most important being:
| • | industrial fund loans; |
| • | on-lending loans; |
| • | foreign currency loans; |
| • | local currency loans denominated in foreign currencies; |
| • | offshore loans in foreign countries; and |
| • | government fund loans. |
18
Table of Contents
The following table sets out equipment capital and working capital loans by categories as of December 31, 2015:
| Equipment Capital Loans(1) |
Working Capital Loans(1) |
|||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
% | December 31, 2015 |
% | |||||||||||||
| (billions of won, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Industrial fund loans |
72.5 | % | 64.1 | % | ||||||||||||
| On-lending loans |
5,372.5 | 8.9 | 9,101.8 | 16.5 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency loans |
6,125.6 | 10.2 | 1,272.4 | 2.3 | ||||||||||||
| Local currency loans denominated in foreign currencies |
147.3 | 0.2 | 89.5 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||
| Offshore loans in foreign currencies |
978.0 | 1.6 | 3,438.2 | 6.2 | ||||||||||||
| Government fund loans |
398.7 | 0.7 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Overdraft |
— | — | 451.0 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||
| Others(1) |
3,580.8 | 5.9 | 5,430.7 | 9.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (1) | Includes loans on households and loans extended to affiliates. |
Industrial Fund Loans. Industrial fund loans are equipment capital and working capital loans denominated in Won to borrowers in major industries to finance equipment and facilities.
We currently make equipment capital industrial fund loans at floating or fixed rates for terms of up to 10 years and for up to 100% of the equipment cost being financed. We make working capital industrial fund loans at floating or fixed rates and in amounts constituting up to 40% of the borrower’s estimated annual sales.
On-lending Loans. On-lending is a form of indirect financing that involves intermediary financial institutions which on-lend the funds provided by us to industrial borrowers and are responsible for repayment to us. Most of the funds provided by us through on-lending are ultimately lent to small- and medium-sized enterprises for their equipment purchases and working capital. We explicitly set detailed guidelines (including scope of borrowers, maturity and interest rates) for intermediary financial institutions to be followed when on-lending to the ultimate borrowers. We monitor our exposure to, and the credit standing of, each financial institution to which we lend. Borrowers do not apply directly to us and may only apply for our on-lending loans through their regular bank or another bank of their choice. The intermediary bank appraises the financial and business situation of the applicant and generally assumes liability for repayment to us. Although the processing of individual loans requires two formally separate loan approvals for each borrower, first by the intermediary bank and then by us, the ultimate borrower need only apply to the intermediary bank for approval.
Foreign Currency Loans. We extend loans denominated in U.S. dollars, Japanese yen or other foreign currencies principally to finance the purchase of industrial equipment from abroad or the implementation of overseas industrial development projects by Korean companies. We make these loans at floating interest rates with original maturities, in the case of equipment capital foreign currency loans, of up to 10 years and, in the case of working capital foreign currency loans, of up to three years.
Local Currency Loans Denominated in Foreign Currencies. We make local currency loans denominated in foreign currencies for the same purposes, and to the same borrowers, as foreign currency loans. Although we denominate the loans in foreign currency, the borrower receives and repays the loans in Won based on foreign exchange rates at the time of receipt and repayment. We currently make loans of this type at floating interest rates, with original maturities, in the case of equipment capital loans, of up to 10 years and, in the case of working capital loans, of up to three years.
19
Table of Contents
Offshore Loans in Foreign Currencies. We extend offshore loans in foreign currencies to finance:
| • | the purchase of industrial equipment and the implementation of overseas industrial projects by overseas subsidiaries and branches of Korean companies; and |
| • | the overseas industrial development projects of foreign government entities, international organizations and foreign companies. |
We make these loans at floating interest rates with original maturities, in the form of equipment capital foreign currency loans, of up to 10 years and, working capital foreign currency loans, of up to three years.
Government Fund Loans. We make government fund loans primarily to finance:
| • | water supply and drainage facilities; |
| • | the Seoul subway system; |
| • | freight terminal facilities; |
| • | hospitals; and |
| • | other facilities. |
Government fund loans that are equipment capital loans require approval by the appropriate Government ministry. We currently make government fund loans in Won at floating interest rates with original maturities of 10 to 20 years.
Other Loans. We also make special purpose fund loans for particular industries or projects using funds lent to us by the Government and foreign financial institutions. The Government funds that finance these loans include, among others:
| • | the Tourism Promotion Fund (hotel and resort projects); |
| • | the Rational Use of Energy Fund (energy conservation projects and collective energy supply projects); and |
| • | the Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises Promotion Fund (small- and medium-sized enterprises). |
For further information relating to such loans, see “—Sources of Funds.”
Guarantee Operations
We extend guarantees to our clients to facilitate their other borrowings and to finance major industrial projects. We guarantee Won-denominated corporate debentures, local currency loans, and other Won liabilities and foreign currency loans from domestic and overseas Korean financial institutions and from foreign institutions. The KDB Act and our Articles of Incorporation limit the aggregate amount of our industrial finance bond obligations and guarantee obligations. See “—Sources of Funds.”
We generally obtain collateral valued in excess of the original guarantee. We appraise the value of our collateral at least once a year. Depending on the borrower, the collateral may be industrial plants, real estate and/or marketable securities.
20
Table of Contents
The following table shows our outstanding guarantees:
Guarantees Outstanding
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2015 | |||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||
| Acceptances |
||||||||
| Guarantees on local borrowing |
1,573.9 | 1,057.0 | ||||||
| Guarantees on foreign borrowing |
5,902.9 | 8,099.8 | ||||||
| Letter of guarantee for importers |
48.3 | 32.7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
On November 13, 2002, we
entered into a guarantee agreement with KEPCO with respect to certain of KEPCO’s debt securities in connection with KEPCO’s restructuring and privatization. Pursuant to the guarantee agreement, we issued in February 2003 our guarantee to
holders of KEPCO’s Yankee and Global debt securities with final maturities ranging from 2003 to 2096 (although our guarantee obligations only run through 2016) in an aggregate principal amount of approximately W3.3 trillion,
based on exchange rates prevailing on the guarantee issuance date, February 25, 2003. As of December 31, 2015, the aggregate outstanding principal amount of KEPCO’s debt securities that are covered by our guarantees was
W209.8 billion. The guarantees described above constitute full, irrevocable and unconditional guarantees, on an unsecured and unsubordinated basis, in respect of the principal, interest and other payments due with respect to those
debt obligations. KEPCO paid and will continue to pay us an annual guarantee fee of 0.05% of (i) the aggregate outstanding principal amount of all issues of debt securities that will be covered by the benefit of our guarantee and (ii) the
sum of all interest payments due on such debt securities from the date of calculation until the earlier of their maturity or their stated redemption date.
We currently own approximately 32.9% of the outstanding shares of common stock of KEPCO, and the Government, which directly owns all of our paid-in capital, owns an additional 18.2% of such shares of KEPCO.
Investments
We invest in a range of Korean private and Government-owned enterprises but we will not take a controlling interest in a company unless the acquisition is necessary for the corporate restructuring of the
company. Although generally a long-term investor, we sell investments from time to time. In recent years, sales resulted principally from the Government’s privatization program, and we expect to continue such sales in the future. The Government
plans to sell its direct or indirect interest in certain private sector companies acquired during previous restructuring programs, including Daewoo Engineering & Construction Co., Ltd., depending on market conditions. In accordance with such
plan, we expect to sell our equity holdings in certain private sector companies if favorable opportunities for sale arise. Our equity investments increased to W35,696.8 billion as of December 31, 2015 from
W32,737.2 billion as of December 31, 2014.
The KDB Act and our Articles of Incorporation provide that the cost basis of our total equity investments may not exceed twice the sum of our paid-in capital and our reserve from profit. In addition,
pursuant to the KDB Decree, we may not acquire equity securities of a single company in excess of 15% of its entire voting shares. The 15% limit, however, does not apply to certain investments, including those in Government-controlled companies
financed by capital contributions from the Government. As of December 31, 2015, the cost basis of our equity investments subject to restriction under the KDB Act and our Articles of Incorporation totaled W35,696.8 billion,
equal to 78.6% of our equity investment ceiling. For a discussion of Korean accounting principles relating to our equity investments, see “—Financial Statements and the Auditors.”
21
Table of Contents
The following table sets out our equity investments by industry sector on a book value basis as of December 31, 2015:
Equity Investments
| Book Value as of December 31, 2015 |
||||
| (billions of won) | ||||
| Electric, Gas and Water Supply Industry |
||||
| Construction |
997.5 | |||
| Banking and Insurance |
10,892.1 | |||
| Real Estate Business |
2,659.4 | |||
| Manufacturing |
884.6 | |||
| Transportation |
1,593.3 | |||
| Others |
608.9 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
||||
|
|
|
|||
As of December 31, 2015,
we held total equity investments, on a book value basis, of W651.0 billion in one of our five largest borrowers and W1,417.6 billion in five of our 20 largest borrowers. We have not established a policy addressing
loans to enterprises in which we hold equity interests or equity interests in enterprises to which we have extended loans.
When possible, we use the prevailing market price of a security to determine the value of our interest. However, if no readily ascertainable market value exists for our holdings, we record these investments at the cost of acquisition. With respect to our equity interests in enterprises in which we hold more than 15% of interest, we value these investments annually, with certain exceptions, on a net asset value basis when the investee company releases its financial statements. As of December 31, 2015, the aggregate value of our equity investments accounted for approximately 107.9% of their aggregate cost basis.
As part of our investment activities, we underwrite straight and convertible bond issuances in Won for domestic corporations. We also invest in municipal bonds, extending funds to municipalities at subsidized interest rates, mostly to finance water supply and drainage infrastructure projects.
Other Activities
We engage in a range of industrial development activities in addition to providing loans and guarantees, including:
| • | conducting economic and industrial research; |
| • | performing engineering surveys; |
| • | providing business analyses and managerial assistance; and |
| • | offering trust services. |
As of December 31, 2015, we held in trust cash and other assets totaling W32,630.9 billion, and we generated in 2015
trust fee income equaling W184.0 billion. As of December 31, 2014, we held in trust cash and other assets totaling W30,827.3 billion, and we generated in 2014 trust fee income equaling W175.8
billion. Pursuant to Korean law, we segregate trust assets from our other assets; trust assets are not available to satisfy claims of our depositors or other creditors. Accordingly, we account for our trust accounts separately from our banking
accounts. However, if our trust operations fail to preserve the principal of our clients’ trust assets, we are responsible for covering the deficit either from previously established provisions in our trust accounts or by a
22
Table of Contents
transfer from our banking accounts. In 2014 and 2015, we did not transfer any funds from our banking accounts to cover deficits in our trust accounts. Surplus funds generated by the trust assets may be deposited into the clients’ accounts and earn interest. We reflect trust fees earned by us on our trust account management services as other operating revenues in the income statement of the banking accounts.
In addition to our capital and reserves, we obtain funds primarily from:
| • | borrowings from the Government; |
| • | issuances of bonds in the domestic and international capital markets; |
| • | borrowings from international financial institutions or foreign banks; and |
| • | deposits. |
All of our borrowings are unsecured.
Borrowings from the Government
We borrow from the Government’s general purpose funds and its special purpose funds. General purpose loans generally are in Won and have fixed interest rates and maturities ranging from five to 20 years. We incur special purpose loans, principally from the Tourism Promotion Fund, the Rational Use of Energy Fund and the Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises Promotion Fund, in connection with specific projects we finance. The Government links the interest rate and maturity of each special purpose borrowing to the terms of the financing we provide for the specific project.
The following table sets out our Government borrowings as of December 31, 2015:
| Type of Funds Borrowed |
As of December 31, 2015 |
|||
| (billions of won) | ||||
| General Purpose |
||||
| Special Purpose |
7,450.8 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
||||
|
|
|
|||
Domestic and International Capital Markets
We issue industrial finance bonds both in Korea and abroad, some of which the Government directly guarantees. We generally issue domestic bonds at fixed interest rates with original maturities of one to ten years.
The following table sets out the outstanding balance of our industrial finance bonds as of December 31, 2015:
| Outstanding Balance |
As of December 31, 2015 |
|||
| (billions of won) | ||||
| Denominated in Won |
||||
| Denominated in Other Currencies |
25,938.2 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
||||
|
|
|
|||
The KDB Act provides that the aggregate outstanding principal amount of our industrial finance bonds, other than those directly guaranteed or purchased by the Government, plus the aggregate outstanding amount of
23
Table of Contents
debt (including bonds and loans) guaranteed or purchased by us, other than those excepted by the KDB Act, may not exceed 30 times the sum of our paid-in capital and our reserve from profit. As of
December 31, 2015, the aggregate amount of our industrial finance bonds and guarantee obligations (including guarantee obligations relating to loans that had not been borrowed as of December 31, 2015) was W134,958.0
billion, equal to 19.8% of our authorized amount under the KDB Act, which was W681,279.2 billion.
In 2015, we issued W32.9 trillion in Won-denominated industrial finance bonds and W4.1 trillion in
industrial finance bonds denominated in other currencies. In 2016, we are targeting to issue approximately W30.0 trillion in Won-denominated industrial finance bonds and approximately W7.0 trillion in industrial
finance bonds denominated in other currencies, subject to change depending on our funding needs and market conditions.
Foreign Currency Borrowings
We borrow money from institutions, principally syndicates of commercial banks, outside the Republic in foreign currencies. We frequently enter into related interest rate and currency swap transactions. The loans generally have original maturities of one to five years. As of December 31, 2015, the outstanding amount of our foreign currency borrowings was US$10.2 billion.
Our long term and short term foreign currency
borrowings decreased to W11,904.9 billion as of December 31, 2015 from W12,139.6 billion as of December 31, 2014.
Deposits
We take demand deposits and time and savings deposits from
the general public. Time and savings deposits generally have maturities shorter than three years and bear interest at fixed rates. As of December 31, 2015, demand deposits held by us totaled W1,295.7 billion and time and
savings deposits held by us totaled W35,517.8 billion.
Debt Repayment Schedule
The following table sets out our principal repayment schedule as of December 31, 2015:
Debt Principal Repayment Schedule(1)
| Maturing on or before December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency(2)(3) |
2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | Thereafter | |||||||||||||||
| (billions of won) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Won |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign |
15,299.3 | 7,152.1 | 7,339.2 | 1,962.8 | 7,910.9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total Won Equivalent |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Excludes bonds sold under repurchase agreements and call money. |
| (2) | Borrowings in foreign currencies have been translated into Won at the market average exchange rates on December 31, 2015, as announced by the Seoul Money Brokerage Services Ltd. |
| (3) | We categorize debt with respect to which we have entered into currency swap agreements by our repayment currency under such agreements. |
24
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes, as of December 31 of the years indicated, our outstanding direct internal debt:
Direct Internal Debt
| (billions of Won) | ||||
| 2011 |
39,185.4 | |||
| 2012 |
37,515.4 | |||
| 2013 |
46,237.4 | |||
| 2014 |
99,441.9 | |||
| 2015 |
100,119.6 | |||
The following table summarizes, as of December 31 of the years indicated, our outstanding direct external debt:
Direct External Debt
| (billions of Won) | ||||
| 2011 |
31,107.9 | |||
| 2012 |
29,780.4 | |||
| 2013 |
31,080.3 | |||
| 2014 |
37,260.0 | |||
| 2015 |
37,341.4 | |||
The following table sets out, by currency and the equivalent amount in U.S. Dollars, our outstanding external bonds as of December 31, 2015:
External Bonds
| Amount in Original Currency |
Equivalent Amount in U.S. Dollars(1) |
|||||||
| (millions) | ||||||||
| US$ |
US$ | 14,969.0 | US$ | 14,969.0 | ||||
| Japanese yen (¥) |
¥ | 136,000.0 | 1,127.9 | |||||
| Euro (EUR) |
EUR | 1,046.0 | 1,142.9 | |||||
| Singapore dollar (SGD) |
SGD | 469.0 | 331.4 | |||||
| Hong Kong dollar (HKD) |
HKD | 4,895.0 | 631.5 | |||||
| Chinese offshore renminbi (CNH) |
CNH | 5,658.0 | 861.6 | |||||
| Swiss franc (CHF) |
CHF | 760.0 | 768.7 | |||||
| Brazilian real (BRL) |
BRL | 45.5 | 11.5 | |||||
| Australian dollar (AUD) |
AUD | 1,492.5 | 1,086.4 | |||||
| Great Britain Sterling (GBP) |
GBP | 250.0 | 370.3 | |||||
| Malaysian Ringgit (MYR) |
MYR | 500.0 | 116.5 | |||||
| Turkish Lira (TRY) |
TRY | — | — | |||||
| New Zealand dollar (NZD) |
NZD | 200.0 | 136.7 | |||||
| Mexican Peso (MXN) |
MXN | 144.0 | 8.3 | |||||
| Norwegian Krone (NOK) |
NOK | 700.0 | 79.6 | |||||
| South African Rand (ZAR) |
ZAR | 952.0 | 61.2 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
US$ | 21,703.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Amounts expressed in currencies other than US$ are converted to US$ at the exchange rate announced by the Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. in effect on December 31, 2015. |
25
Table of Contents
For further information on our outstanding indebtedness, see “—Tables and Supplementary Information.”
Debt Record
We have never defaulted in the payment of principal or interest on any of our obligations.
We operate overseas subsidiaries in Hong Kong, Dublin, Budapest, Sao Paulo and Tashkent. The subsidiaries engage in a variety of banking and merchant banking services, including:
| • | managing and underwriting new securities issues; |
| • | syndicating medium and long-term loans; |
| • | trading securities; |
| • | trading in the money market; and |
| • | providing investment management and advisory services. |
We currently maintain nine branches in Tokyo, Shanghai, Singapore, New York City, London, Beijing, Guangzhou, Qingdao and Shenyang and eight overseas representative offices in Frankfurt, Ho Chi Minh City, Abu Dhabi, Yangon, Moscow, Manila, Sydney and Bangkok.
Our head office is located at 14 Eunhaeng-ro Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul, Korea, a 35,996 square meter building completed in July 2001 and owned by us. In addition to the head office, we maintain 82 branches in major cities throughout the Republic, including 29 in Seoul. We generally lease our domestic and overseas offices under long-term leases.
Directors and Management; Employees
Our Board of Directors has ultimate responsibility for management of our affairs. Under the KDB Act and our Articles of Incorporation, our Board of Directors is to consist of one Chief Executive Officer (who also serves as the Chairman of the Board of Directors), one Chief Operating Officer and not more than eight directors. Under the KDB Act, the President of the Republic appoints our Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors upon the recommendation of the Chairman of the Financial Services Commission. The Financial Services Commission appoints all of our directors upon the recommendation of our Chief Executive Officer. Under our Articles of Incorporation, our executive directors serve for three-year terms and they may be re-appointed, and our independent non-executive directors serve for two-year terms and they may be re-appointed; provided, however, that our independent non-executive directors shall not serve more than one year for each reappointment and shall not serve more than five years consecutively. Currently, the members of our Board of Directors are:
| Position |
Name |
Expiration of Term | ||
| Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors: |
Dong Geol Lee | February 4, 2019 | ||
| Chief Operating Officer and Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors |
Heui Kyoung Ryu | February 2, 2017 | ||
26
Table of Contents
| Position |
Name |
Expiration of Term | ||
| Executive Directors |
Hyung Chul Shin | April 10, 2017 | ||
| Dai Hyun Lee | December 30, 2017 | |||
| Independent Non-executive Directors |
Sang Heon Kim | August 1, 2016 | ||
| Jong Sub Sung | March 1, 2018 | |||
| Hi-Taek Shin | April 26, 2017 | |||
| Hay-Young Chung | April 26, 2017 | |||
| Jae Woon Koo | October 30, 2016 | |||
As of December 31, 2015, we employed 3,379 persons with 1,935 located in our Seoul head office.
Tables and Supplementary Information
A. External Debt of KDB
(1) External Bonds of KDB
| Currency |
Original Principal Amount |
Interest Rate (%) |
Issue Date | Maturity Date | Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 4.3 | May 13, 2009 | May 13, 2016 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
450,000,000 | 3.250 | September 9, 2010 | March 9, 2016 | 450,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
250,000,000 | 3.250 | September 9, 2010 | March 9, 2016 | 250,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 3.250 | September 9, 2010 | March 9, 2016 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
750,000,000 | 4.000 | March 9, 2011 | September 9, 2016 | 750,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
700,000,000 | 3.875 | November 4, 2011 | May 4, 2017 | 700,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 3.875 | November 4, 2011 | May 4, 2017 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
150,000,000 | 3.50 | February 22, 2012 | August 22, 2017 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
100,000,000 | 3.50 | February 22, 2012 | August 22, 2017 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
500,000,000 | 3.50 | February 22, 2012 | August 22, 2017 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
500,000,000 | 3.50 | July 5, 2012 | August 22, 2017 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 3.00 | September 14, 2012 | September 14, 2022 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
350,000,000 | 3.00 | September 14, 2012 | September 14, 2022 | 350,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
100,000,000 | 3.00 | September 14, 2012 | September 14, 2022 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 1.00 | January 22, 2013 | January 22, 2016 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 1.00 | January 22, 2013 | January 22, 2016 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
500,000,000 | 1.50 | January 22, 2013 | January 22, 2018 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.60 | March 21, 2013 | March 21, 2016 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 1.00 | June 10, 2013 | June 10, 2018 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
250,000,000 | 4.00 | August 27, 2013 | September 9, 2016 | 250,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 3.00 | September 17, 2013 | March 17, 2019 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
450,000,000 | 3.00 | September 17, 2013 | March 17, 2019 | 450,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
40,000,000 | 3.81 | October 30, 2013 | October 30, 2023 | 40,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 4.00 | November 1, 2013 | November 1, 2023 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.74 | November 5, 2013 | November 5, 2023 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.70 | November 6, 2013 | November 6, 2023 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
100,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.85 | November 8, 2013 | November 8, 2016 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3.79 | November 13, 2013 | November 13, 2023 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.8 | November 13, 2013 | November 13, 2023 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.75 | November 15, 2013 | November 15, 2023 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3.66 | November 26, 2013 | November 26, 2023 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
60,000,000 | 3.68 | November 26, 2013 | November 26, 2023 | 60,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.8 | December 12, 2013 | December 12, 2023 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3.8 | December 18, 2013 | December 18, 2023 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3.81 | December 18, 2013 | December 18, 2023 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
150,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.625 | January 22, 2014 | January 22, 2017 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
600,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.625 | January 22, 2014 | January 22, 2017 | 600,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
750,000,000 | 3.75 | January 22, 2014 | January 22, 2024 | 750,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 1.39 | March 17, 2014 | March 17, 2017 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3.605 | April 29, 2014 | April 29, 2024 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
27
Table of Contents
| Currency |
Original Principal Amount |
Interest Rate (%) |
Issue Date | Maturity Date | Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.62 | April 29, 2014 | April 29, 2024 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3.615 | April 30, 2014 | April 30, 2024 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
15,000,000 | 1.22 | May 9, 2014 | November 9, 2016 | 15,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 1.22 | May 9, 2014 | November 9, 2016 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
350,000,000 | 2.5 | September 11, 2014 | March 11, 2020 | 350,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
400,000,000 | 2.5 | September 11, 2014 | March 11, 2020 | 400,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.25 | November 14, 2014 | November 14, 2024 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 0.0325 | September 20, 2010 | September 20, 2016 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
550,000,000 | 0.0325 | September 20, 2010 | September 20, 2016 | 550,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
750,000,000 | 0.04625 | November 16, 2011 | November 16, 2021 | 750,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 0.0225 | August 7, 2012 | August 7, 2017 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 0.0225 | August 7, 2012 | August 7, 2017 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 0.0225 | September 24, 2012 | August 7, 2017 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 0.02875 | August 22, 2013 | August 22, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
300,000,000 | 0.02875 | August 22, 2013 | August 22, 2018 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
200,000,000 | 0.0385 | February 20, 2014 | February 20, 2024 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3.72 | April 9, 2014 | April 9, 2024 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3.72 | April 10, 2014 | April 10, 2024 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3.7 | April 11, 2014 | April 11, 2024 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.7 | April 11, 2014 | April 11, 2024 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 1.46 | April 22, 2014 | April 22, 2017 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
24,000,000 | 0.88 | May 16, 2014 | May 16, 2016 | 24,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.92 | August 8, 2013 | August 8, 2016 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 2.73 | February 6, 2015 | February 6, 2027 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
500,000,000 | 2.25 | May 18, 2015 | May 18, 2020 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3.01 | June 24, 2015 | June 24, 2025 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.376 | July 9, 2015 | July 9, 2025 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.33 | July 22, 2015 | July 22, 2025 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
10,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.37 | July 23, 2015 | July 23, 2017 | 10,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3.2 | August 6, 2015 | August 6, 2025 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
350,000,000 | 3.375 | September 16, 2015 | September 16, 2025 | 350,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
400,000,000 | 3.375 | September 16, 2015 | September 16, 2025 | 400,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
20,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.55 | October 15, 2015 | October 15, 2018 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.65 | November 4, 2015 | November 5, 2018 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
100,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.35 | November 4, 2015 | November 4, 2016 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.35 | November 5, 2015 | November 7, 2016 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
10,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.70 | November 6, 2015 | November 6, 2020 | 10,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
50,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.35 | November 19, 2015 | November 19, 2016 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
100,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.67 | November 27, 2015 | November 27, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| USD |
30,000,000 | 3M USD Libor + 0.35 | November 27, 2015 | November 27, 2016 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | USD | 14,969,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(1) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| SGD |
36,000,000 | 0.88 | March 21, 2013 | March 21, 2016 | 36,000,000 | |||||||||||
| SGD |
|
200,000,000 18,000,000 15,000,000 200,000,000 |
|
|
2.05 1.86 1.86 2.65 |
|
July 23, 2015 November 23, 2015 November 23, 2015 December 3, 2015 |
July 23, 2018 November 22, 2016 November 22, 2016 December 3, 2018 |
|
200,000,000 18,000,000 15,000,000 200,000,000 |
| |||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | SGD | 469,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(2) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| JPY |
15,000,000,000 | 3.22 | May 30, 2008 | May 30, 2018 | 15,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
2,400,000,000 | 1.91 | October 21, 2011 | October 21, 2016 | 2,400,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
3,700,000,000 | 1.31 | June 20, 2012 | June 20, 2017 | 3,700,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
3,500,000,000 | 0.66 | June 7, 2013 | June 7, 2016 | 3,500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
6,500,000,000 | 0.89 | June 7, 2013 | June 7, 2018 | 6,500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
35,000,000,000 | 0.43 | January 29, 2014 | January 29, 2016 | 35,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
15,000,000,000 | 0.69 | January 29, 2014 | January 29, 2019 | 15,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
10,100,000,000 | 0.28 | October 24, 2014 | October 24, 2016 | 10,100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
24,800,000,000 | 0.35 | October 24, 2014 | October 24, 2017 | 24,800,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
3,000,000,000 | 0.01 | May 11, 2011 | May 11, 2016 | 3,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
28
Table of Contents
| Currency |
Original Principal Amount |
Interest Rate (%) |
Issue Date | Maturity Date | Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| JPY |
7,000,000,000 | 0.0136 | September 22, 2011 | September 23, 2016 | 7,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
3,000,000,000 | 0.00685 | November 7,2012 | November 7, 2017 | 3,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| JPY |
7,000,000,000 | 0.0045 | May 2, 2014 | May 2, 2017 | 7,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | JPY | 136,000,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(3) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| HKD |
150,000,000 | 5.00 | November 20, 2007 | November 20, 2017 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
80,000,000 | 4.71 | December 18, 2007 | December 18, 2017 | 80,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
144,000,000 | 3.30 | October 20, 2011 | October 20, 2016 | 144,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
303,000,000 | 4.30 | October 21, 2011 | October 21, 2021 | 303,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
219,000,000 | 2.40 | September 6, 2011 | September 6, 2016 | 219,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
89,000,000 | 3.60 | September 16, 2011 | September 16, 2021 | 89,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
500,000,000 | 2.80 | April 3, 2012 | April 3, 2017 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
300,000,000 | 1.82 | April 26, 2013 | April 26, 2018 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
160,000,000 | 2.28 | October 31, 2013 | October 31, 2018 | 160,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
1,042,000,000 | 3.2 | April 3, 2014 | October 3, 2021 | 1,042,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
460,000,000 | 0.0342 | March 15, 2011 | March 15, 2016 | 460,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
388,000,000 | 0.0442 | April 12, 2011 | April 12, 2021 | 388,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
130,000,000 | 0.0228 | November 4, 2013 | November 4, 2018 | 130,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
160,000,000 | 1.73 | November 6, 2015 | May 6, 2019 | 160,000,000 | |||||||||||
| HKD |
|
300,000,000 316,000,000 |
|
|
1.85 1.88 |
|
November 19, 2015 November 23, 2015 |
November 19, 2018 November 23, 2018 |
|
300,000,000 316,000,000 |
| |||||
| HKD |
154,000,000 | 1.79 | December 3, 2015 | December 3, 2018 | 154,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | HKD | 4,895,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(4) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| CNH |
150,000,000 | 4.45 | November 8, 2013 | November 8, 2023 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
210,000,000 | 4.1 | December 18, 2013 | December 18, 2023 | 210,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
200,000,000 | 4.38 | February 13, 2015 | February 13, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
1,000,000,000 | 3.55 | June 19, 2015 | June 19, 2018 | 1,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
300,000,000 | 3.78 | July 9, 2015 | July 9, 2019 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
140,000,000 | 3.84 | July 17, 2015 | July 17, 2018 | 140,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
100,000,000 | 3.91 | July 20, 2015 | July 20, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
138,000,000 | 4.05 | July 24, 2015 | July 24, 2018 | 138,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
100,000,000 | 4.15 | July 27, 2015 | July 27, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
120,000,000 | 4.05 | August 17, 2015 | August 17, 2018 | 120,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
1,000,000,000 | 4.10 | August 24, 2015 | August 24, 2018 | 1,000,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
200,000,000 | 4.10 | August 24, 2015 | August 24, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
200,000,000 | 3.90 | November 19, 2015 | November 19, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
500,000,000 | 4.04 | December 8, 2015 | December 8, 2018 | 500,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
700,000,000 | 4.20 | December 15, 2015 | December 15, 2018 | 700,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CNH |
600,000,000 | 4.20 | December 15, 2015 | December 15, 2018 | 600,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | CNH | 5,658,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(5) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| EUR |
20,000,000 | 1.17 | December 24, 2012 | December 15, 2017 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
200,000,000 | 1.50 | May 30, 2013 | May 30, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
300,000,000 | 1.50 | May 30, 2013 | May 30, 2018 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
200,000,000 | 1.50 | July 23, 2013 | May 30, 2018 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
30,000,000 | 0.49 | May 23, 2014 | January 15, 2016 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
105,000,000 | 0.21 | September 22, 2014 | September 21, 2016 | 105,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
50,000,000 | 3M Euribor + 0.235 | September 24, 2014 | September 24, 2017 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
100,000,000 | 3M Euribor + 0.45 | October 28, 2014 | October 28, 2019 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
16,000,000 | 3M Euribor + 0.45 | October 30, 2014 | October 30, 2019 | 16,000,000 | |||||||||||
| EUR |
25,000,000 | 12M Euribor +0.02 | February 12, 2015 | August 12, 2019 | 25,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | EUR | 1,046,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(6) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| CHF |
180,000,000 | 1.438 | May 23, 2012 | May 23, 2016 | 180,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CHF |
180,000,000 | 1.000 | December 21, 2012 | December 21, 2018 | 180,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CHF |
100,000,000 | 0.01375 | October 2, 2013 | July 2, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
29
Table of Contents
| Currency |
Original Principal Amount |
Interest Rate (%) |
Issue Date | Maturity Date | Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| CHF |
150,000,000 | 0.01375 | October 2, 2013 | July 2, 2018 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| CHF |
150,000,000 | 0.02 | October 29, 2012 | October 29, 2018 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | CHF | 760,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(7) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| BRL |
45,500,000 | 7.02 | June 19, 2012 | June 21, 2017 | 45,500,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | BRL | 45,500,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(8) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| AUD |
100,000,000 | 4.50 | April 30, 2013 | April 30, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
20,000,000 | 4.14 | May 16, 2013 | May 16, 2016 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
25,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 1.45 | July 30, 2013 | July 30, 2018 | 25,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
30,000,000 | 5.15 | July 31, 2013 | July 31, 2018 | 30,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
47,500,000 | 4.23 | September 27, 2013 | September 26, 2017 | 47,500,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
250,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 3.05 | February 17, 2012 | February 17, 2016 | 250,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
50,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 1.10 | May 22, 2014 | November 22, 2019 | 50,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
150,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 1.10 | May 22, 2014 | November 22, 2019 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
200,000,000 | 4.50 | May 22, 2014 | November 22, 2019 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
300,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 1.27 | June 5, 2013 | June 5, 2017 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
20,000,000 | 3.37 | February 11, 2015 | February 11, 2022 | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||
| AUD |
300,000,000 | 3M BBSW + 1.03 | November 27, 2015 | November 27, 2018 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | AUD | 1,492,500,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(9) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| MYR |
300,000,000 | 4.05 | February 24, 2012 | February 24, 2016 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| MYR |
200,000,000 | 4.10 | February 24, 2012 | February 24, 2017 | 200,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | MYR | 500,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(10) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| MXN |
144,000,000 | 4.78 | September 27, 2013 | September 26, 2017 | 144,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | MXN | 144,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(11) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| NOK |
300,000,000 | 4.00 | October 23, 2013 | April 23, 2020 | 300,000,000 | |||||||||||
| NOK |
400,000,000 | 2.905 | July 21, 2015 | July 21, 2025 | 400,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | NOK | 700,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(12) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| ZAR |
822,000,000 | 7.76 | September 27, 2013 | September 26, 2017 | 822,000,000 | |||||||||||
| ZAR |
130,000,000 | 8.20 | June 30, 2015 | July 2, 2018 | 130,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | ZAR | 952,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(13) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| NZD |
100,000,000 | 5.25 | April 3, 2014 | April 3, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| NZD |
100,000,000 | 5.125 | November 13, 2014 | November 13, 2020 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | NZD | 200,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(14) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| GBP |
100,000,000 | 2.00 | November 20, 2014 | December 20, 2018 | 100,000,000 | |||||||||||
| GBP |
150,000,000 | 2.00 | November 20, 2014 | December 20, 2018 | 150,000,000 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency | GBP | 250,000,000 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(15) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total External Bonds of KDB in Equivalent Amount of Won |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (1) | U.S. dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of US$1.00 to Won 1,172.00, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (2) | Singapore dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of SGD 1.00 to Won 828.09, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
30
Table of Contents
| (3) | Japanese yen amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of JPY 100.00 to Won 972.01, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (4) | Hong Kong dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of HKD 1.00 to Won 151.21, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (5) | Chinese offshore renminbi amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of CNH 1.00 to Won 178.48, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (6) | Euro amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of EUR 1.00 to Won 1,280.53, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (7) | Swiss franc amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of CHF 1.00 to Won 1,185.39, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (8) | Brazilian real amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of BRL 1.00 to Won 295.90, the prevailing market rate on December 31, 2015. |
| (9) | Australian dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of AUD 1.00 to Won 853.10, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (10) | Malaysian ringgit amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of MYR 1.00 to Won 273.07, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (11) | Mexican Peso amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of MXN 1.00 to Won 67.40, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (12) | Norwegian Krone amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of NOK 1.00 to Won 133.30, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (13) | South African Rand amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of ZAR 1.00 to Won 75.32, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (14) | New Zealand dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of NZD 1.00 to Won 801.36, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
| (15) | Great Britain Sterling amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of GBP 1.00 to Won 1,735.91, the market average exchange rate in effect on December 31, 2015, as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
(2) External Borrowings of KDB
| Lender |
Classifications |
Range of Interest Rates | Range of Years of Issue |
Range of Years of Maturity |
Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015(1) |
|||||||||||||
| (%) | (millions of Won) | |||||||||||||||||
| JBIC |
Borrowings from JBIC | 1.73~2.16 | 2010~2013 | 2016~2025 | 206,279 | |||||||||||||
| Mizuho and others |
Borrowings from foreign banks | |
3M Libor + 0.40~3M Libor + 0.75 |
|
2013~2015 | 2016~2019 | 1,511,880 | |||||||||||
| Ministry of Strategy and Finance |
Exchange equalization fund borrowings in foreign currencies | 0.00~0.27 | 2014~2015 | 2016~2024 | 2,550,122 | |||||||||||||
| Toronto Dominion Bank Singapore and others |
Off-shore short-term borrowings | 0.19~0.39 | 2015 | 2016 | 721,641 | |||||||||||||
| HSBC and others |
Off-shore long-term borrowings | 3MLibor+0.30~+0.75 | 2013~2015 | 2016~2017 | 341,601 | |||||||||||||
| JBIC |
Off-shore borrowings from JBIC | |
1.79~6m Libor+1.20~4.27 |
|
2010~2013 | 2016~2022 | 96,019 | |||||||||||
| Others |
Short-term borrowings in foreign currency | 0.00~5.05 | 2015 | 2016 | 4,426,210 | |||||||||||||
| Long-term borrowings in foreign currency | 0.20~2.83 | 2013~2015 | 2016~2018 | 2,051,098 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total External Borrowings of KDB |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Converted to Won amounts at the relevant market average exchange rates in effect on December 31, 2015 as announced by Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. |
31
Table of Contents
B. Internal Debt of KDB
| Title |
Range of Interest Rates |
Range of Years of Issue |
Range of Years of Original Maturity |
Principal Amounts Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||||
| (%) | (millions of Won) | |||||||||||||||
| 1. Bonds |
||||||||||||||||
| Short-term Industrial Finance Bonds |
3.72 | 2011~2015 | 2012~2016 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Long-term Industrial Finance Bonds |
1.52~12.00 | 2005~2015 | 2011~2035 | 89,438,541 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Bonds |
1.52~12.00 | 2005~2015 | 2011~2035 | 89,438,546 | ||||||||||||
| 2. Borrowings |
||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Ministry of Strategy and Finance |
0.67~5.00 | 1996~2012 | 2016~2032 | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings from Industrial Bank of Korea |
0.60~1.59 | 2008~2015 | 2016~2020 | 3,819 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from Small Business Corp. |
1.32~3.62 | 2006~2015 | 2016~2023 | 177,231 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Ministry of Culture and Tourism |
0.05~2.50 | 2007~2015 | 2016~2027 | 1,855,349 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from Korea Energy Management Corporation |
0.25~3.65 | 2000~2015 | 2016~2030 | 986,247 | ||||||||||||
| Others |
0.00~4.30 | 2001~2015 | 2015~2044 | 4,428,170 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Borrowings(1) |
7,856,046 | |||||||||||||||
| 3. Other Debt(2) |
2,824,982 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Internal Floating Debt(3) |
1,500,005 | |||||||||||||||
| Total Internal Funded Debt(4) |
98,619,569 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Internal Debt |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (1) | Consist of short term borrowings in the amount of |
| (2) | Other debt includes bonds sold under repurchase agreements and call money. |
| (3) | Floating debt is debt that has a maturity at issuance of less than one year. |
| (4) | Funded debt is debt that has a maturity at issuance of one year or more. |
Financial Statements and the Auditors
The Government elects our Auditor who is responsible for examining our financial operations and auditing our financial statements and records. The present Auditor is Hyung-Chul Shin, who was appointed by the Financial Services Commission for a three-year term on April 11, 2014.
We prepare our financial statements annually for submission to the Financial Services Commission, accompanied by an opinion of the Auditor. Although we are not legally required to have financial statements audited by external independent auditors, an independent public accounting firm has audited our separate and consolidated financial statements commencing with such financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 1998. As of the date of this prospectus, our external independent auditor is KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp., located at 152, Teheran-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06236 (Yeoksam-dong, Gangnam Finance Center 27th Floor), Korea, which has audited our separate financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 included in this prospectus.
Our separate financial statements appearing in this prospectus were prepared in conformity with Korean IFRS, as summarized in “—Financial Statements and the Auditors—Notes to Separate Financial Statements of December 31, 2015 and 2014—Note 2.” These principles and procedures differ in certain material respects from generally accepted accounting principles in the United States.
32
Table of Contents
We generally record our debt securities investments, except for our trading portfolio of marketable debt securities, at the cost of acquisition (including incidental expenses related to purchase), computed on the specific identification method. We record our trading portfolio of marketable debt securities at market value. Starting in April 1999, we record all our debt securities investments at market value except for debt securities invested with the intention of holding until maturity, which we record at the cost of acquisition or amortized cost.
We record the value of our premises and equipment on our statements of financial position on the basis of a revaluation conducted as of July 1, 1998. The Minister of Strategy and Finance approved the revaluation in accordance with applicable Korean law. We value additions to premises and equipment since such date at cost.
33
Table of Contents

Independent Auditors’ Report
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
Korea Development Bank
We have audited the accompanying separate financial statements of Korea Development Bank (the “Bank”), which comprise the separate statements of financial position as at December 31, 2015 and 2014, the separate statements of comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity and cash flows for the years then ended, and notes, comprising a summary of significant accounting policies and other explanatory information.
Management’s Responsibilities for the Separate Financial Statements
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of these separate financial statements in accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards, and for such internal control as management determines is necessary to enable the preparation of separate financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error.
Auditors’ Responsibility
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these separate financial statements based on our audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with Korean Standards on Auditing. Those standards require that we comply with ethical requirements and plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the separate financial statements are free from material misstatement.
An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the separate financial statements. The procedures selected depend on our judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the separate financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, We consider internal control relevant to the entity’s preparation and fair presentation of the separate financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the entity’s internal control. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the separate financial statements.
We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion.
Opinion
In our opinion, the separate financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the separate financial position of the Bank as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 and its separate financial performance and its separate cash flows for the years then ended in accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards.
Emphasis of Matter
Without qualifying our opinion, we draw attention to Note 48 to the separate financial statements which states that KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation merged into the Bank, effective as of December 31, 2014. After the merger, the Bank is the merged entity, which is the surviving entity, while both KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation ceased to exist.
34
Table of Contents

Other Matter
Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd., which was the Bank’s associate, has restated the financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 due to the error of the total cost of construction estimation and other errors, which does not have an effect on the Bank’s separate financial statements.
The procedures and practices utilized in the Republic of Korea to audit the Bank’s separate financial statements may differ from those generally accepted and applied in other countries.
/s/ KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp.
Seoul, Korea
April 5, 2016
This report is effective as of April 5, 2016, the audit report date. Certain subsequent events or circumstances, which may occur between the audit report date and the time of reading this report, could have a material impact on the accompanying separate financial statements and notes thereto. Accordingly, the readers of the audit report should understand that the above audit report has not been updated to reflect the impact of such subsequent events or circumstances, if any.
35
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Separate Statements of Financial Position
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014
| (In millions of won) |
Notes | December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
4,44,45,48,49 | 5,974,543 | ||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
5,44,45,49 | 1,780,734 | 1,418,398 | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
6,44,45,48,49 | 41,291,619 | 38,160,025 | |||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
7,44,45,49 | 28,560 | 17,238 | |||||||||
| Loans |
8,44,45,48,49 | 136,789,649 | 134,314,466 | |||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
9,44,45,46,48,49 | 5,757,756 | 4,912,792 | |||||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
10,47,48 | 25,167,835 | 26,858,662 | |||||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
11,47,48 | 587,911 | 535,814 | |||||||||
| Investment property, net |
12,47,48 | 75,921 | 74,639 | |||||||||
| Intangible assets, net |
13,47,48 | 74,196 | 90,844 | |||||||||
| Deferred tax assets |
35,48 | 33,798 | 19,390 | |||||||||
| Current tax assets |
151,744 | — | ||||||||||
| Non-current assets held for sale |
15 | 1,839,114 | — | |||||||||
| Other assets |
14,44,48,49 | 6,003,096 | 5,456,358 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total assets |
217,833,169 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Liabilities |
||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss |
16,44,45,49 | 1,138,628 | ||||||||||
| Deposits |
17,44,45,49 | 39,934,892 | 37,605,714 | |||||||||
| Borrowings |
18,44,45,48,49 | 24,400,590 | 23,537,531 | |||||||||
| Bonds |
19,44,45,48,49 | 116,894,020 | 116,569,796 | |||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
9,44,45,46,48,49 | 5,642,363 | 4,789,154 | |||||||||
| Defined benefit liabilities |
20,48 | 53,360 | 32,130 | |||||||||
| Provisions |
21,48 | 744,883 | 333,894 | |||||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
35,48 | 1,549,234 | 1,998,496 | |||||||||
| Income taxes payable |
7,426 | 215,511 | ||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
22,44,48,49 | 8,355,699 | 6,199,712 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities |
199,205,085 | 192,420,566 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Equity |
||||||||||||
| Issued capital |
23 | 17,235,399 | 15,180,399 | |||||||||
| Capital surplus |
23 | 2,501,439 | 2,522,869 | |||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
23 | 569,190 | 818,422 | |||||||||
| Retained earnings |
23 | 4,949,598 | 6,890,913 | |||||||||
| (Regulatory reserve for loan losses of |
||||||||||||
| (Non-accumulated reserve for credit losses were amounted to |
||||||||||||
| (Obligated amount of provision for regulatory reserve for loan losses of |
||||||||||||
| (Planned regulatory reserve for loan losses of |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total equity |
25,255,626 | 25,412,603 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total liabilities and equity |
217,833,169 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
See accompanying notes to the separate financial statements.
36
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Separate Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
| (In millions of won, except earnings per share information) |
Notes | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Interest income |
24 | 4,750,441 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense |
24 | (3,912,214 | ) | (2,761,947 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net interest income |
1,578,219 | 1,988,494 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net fees and commission income |
25 | 519,794 | 442,244 | |||||||||
| Dividend income |
26 | 615,342 | 158,164 | |||||||||
| Net loss on financial instruments held-for-trading |
27 | (16,995 | ) | (6,324 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss on financial instruments designated at fair value through profit and loss |
28 | (26,459 | ) | (72,665 | ) | |||||||
| Net gain on available-for-sale financial assets |
29 | 230,620 | 49,056 | |||||||||
| Net loss on derivatives |
30 | (149,408 | ) | (319,618 | ) | |||||||
| Net foreign currency transaction gain |
31 | 271,963 | 384,669 | |||||||||
| Other operating income (loss), net |
32 | (788,235 | ) | 14,228 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Non-interest income, net |
656,622 | 649,754 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
8 | 2,810,098 | 1,656,759 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
33,47 | 643,997 | 556,800 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
47 | (1,219,254 | ) | 424,689 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Impairment loss on investments in subsidiaries and associates |
10 | (1,134,930 | ) | (211,086 | ) | |||||||
| Other non-operating income |
34 | 5,630 | 13,816 | |||||||||
| Other non-operating expense |
34 | (12,240 | ) | (10,608 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Non-operating expense, net |
(1,141,540 | ) | (207,878 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Profit (loss) before income taxes |
(2,360,794 | ) | 216,811 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
35 | (465,658 | ) | 33,342 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Profit (loss) for the year |
(1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (Profit (loss) for the year adjusted for regulatory reserve for loan losses :
(-) |
||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) for the year, net of tax Items that are or may be reclassified subsequently to profit or loss: |
||||||||||||
| Valuation gain (loss) on available-for-sale financial assets, net |
(239,578 | ) | 48,777 | |||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
28,035 | 21,302 | ||||||||||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
(4,036 | ) | (1,023 | ) | ||||||||
| Items that will not be reclassified to profit or loss: |
||||||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
(33,653 | ) | 25,442 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 23 | (249,232 | ) | 94,498 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total comprehensive income (loss) for the year |
277,967 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share |
||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted earnings (loss) per share (in won) |
36 | 99 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
See accompanying notes to the separate financial statements.
37
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Separate Statements of Changes in Equity
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
| (In millions of won) |
Issued capital |
Capital surplus |
Capital adjustment |
Accumulated other comprehensive income |
Retained earnings |
Total equity |
||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2014 |
44,373 | (51 | ) | 332,473 | 6,707,444 | 16,346,100 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Profit for the year |
— | — | — | — | 183,469 | 183,469 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets |
— | — | — | 48,777 | — | 48,777 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
— | — | — | 21,302 | — | 21,302 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
— | — | — | (1,023 | ) | — | (1,023 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Changes in remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
— | — | — | 25,442 | — | 25,442 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income for the year |
— | — | — | 94,498 | 183,469 | 277,967 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Paid in capital increase |
20,000 | — | (100 | ) | — | — | 19,900 | |||||||||||||||||
| Merger with controlling entities (Note 48) |
5,898,538 | 2,478,496 | 151 | 391,451 | — | 8,768,636 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Transaction with owners |
5,918,538 | 2,478,496 | 51 | 391,451 | — | 8,788,536 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
2,522,869 | — | 818,422 | 6,890,913 | 25,412,603 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2015 |
2,522,869 | — | 818,422 | 6,890,913 | 25,412,603 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Loss for the year |
— | — | — | — | (1,895,136 | ) | (1,895,136 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Changes in valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets |
— | — | — | (239,578 | ) | — | (239,578 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Changes in exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
— | — | — | 28,035 | — | 28,035 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Changes in valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
— | — | — | (4,036 | ) | — | (4,036 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Changes in remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
— | — | — | (33,653 | ) | — | (33,653 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss for the year |
— | — | — | (249,232 | ) | (1,895,136 | ) | (2,144,368 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Paid in capital increase |
2,055,000 | 66,571 | — | — | — | 2,121,571 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends |
— | — | — | — | (46,179 | ) | (46,179 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Others |
(88,001 | ) | — | — | — | (88,001 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Transaction with owners |
2,055,000 | (21,430 | ) | — | — | (46,179 | ) | 1,987,391 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 |
2,501,439 | — | 569,190 | 4,949,598 | 25,255,626 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to the separate financial statements.
38
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Separate Statements of Cash Flows
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
| (In millions of won) |
Notes | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Profit (loss) for the year |
183,469 | |||||||||||
| Adjustments for: |
||||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
35 | (465,658 | ) | 33,342 | ||||||||
| Interest income |
24 | (5,490,433 | ) | (4,750,441 | ) | |||||||
| Interest expense |
24 | 3,912,214 | 2,761,947 | |||||||||
| Dividend income |
26 | (615,342 | ) | (158,164 | ) | |||||||
| Loss (gain) on valuation of financial assets held for trading |
27 | 4,618 | (96 | ) | ||||||||
| Loss on valuation of financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss |
28 | 29,425 | 73,092 | |||||||||
| Gain on disposal of available-for-sale financial assets |
29 | (451,433 | ) | (383,221 | ) | |||||||
| Impairment loss on available-for-sale financial assets |
29 | 220,813 | 334,165 | |||||||||
| Loss on valuation of derivatives |
30 | 350,124 | 349,289 | |||||||||
| Net gain on fair value hedged items |
30 | (132,006 | ) | (110,621 | ) | |||||||
| Gain on foreign exchange translations |
31 | (328,739 | ) | (272,816 | ) | |||||||
| Loss (gain) on disposal of investments in subsidiaries and associates |
32 | 18,434 | (4,839 | ) | ||||||||
| Impairment loss on investments in subsidiaries and associates |
10 | 1,134,930 | 211,086 | |||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
8 | 2,810,098 | 1,656,759 | |||||||||
| Increase (reversal) of provision for payment guarantees |
21,32 | 243,678 | (269,485 | ) | ||||||||
| Increase (reversal) of provision for unused commitments |
21,32 | 48,273 | (6,961 | ) | ||||||||
| Increase of provision for possible losses from lawsuits |
21,32 | 9,770 | 7,162 | |||||||||
| Increase of financial guarantee liabilities |
21,32 | 96,265 | 1,053 | |||||||||
| Defined benefit costs |
20,33 | 37,363 | 34,705 | |||||||||
| Depreciation of property and equipment |
11,33 | 33,694 | 26,547 | |||||||||
| Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment |
34 | 14 | (8,407 | ) | ||||||||
| Depreciation of investment property |
12,34 | 1,507 | 1,559 | |||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
13,33 | 29,885 | 24,671 | |||||||||
| Impairment loss on intangible assets |
13,34 | 11 | 738 | |||||||||
| Other operating loss, net |
3,526 | 2,417 | ||||||||||
| Loss on redemption of debentures |
509 | 21 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 1,501,540 | (446,498 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Due from banks |
(659,561 | ) | 612,464 | |||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
(306,665 | ) | (32,786 | ) | ||||||||
| Loans |
(6,030,992 | ) | (12,720,448 | ) | ||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
2,354,029 | 3,131,856 | ||||||||||
| Other assets |
(457,193 | ) | 64,893 | |||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss |
454,565 | 387,620 | ||||||||||
| Deposits |
2,396,732 | 2,967,543 | ||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
(2,701,231 | ) | (3,206,500 | ) | ||||||||
| Defined benefit liabilities |
(60,530 | ) | (5,400 | ) | ||||||||
| Other liabilities |
2,622,313 | 435,376 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (2,388,533 | ) | (8,365,382 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Income taxes paid |
(431,885 | ) | (32,664 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest received |
5,318,795 | 4,721,132 | ||||||||||
| Interest paid |
(3,876,471 | ) | (2,622,194 | ) | ||||||||
| Dividends received |
615,342 | 158,164 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
(6,403,973 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
39
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Separate Statements of Cash Flows, Continued
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
| (In millions of won) |
Notes | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||
| Disposal of available-for-sale financial assets |
6 | 26,104,387 | ||||||||||
| Acquisition of available-for-sale financial assets |
6 | (36,013,583 | ) | (23,942,377 | ) | |||||||
| Redemption of held-to-maturity financial assets |
7 | 1,353 | 21,146 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of held-to-maturity financial assets |
7 | (11,203 | ) | (11,465 | ) | |||||||
| Disposal of property and equipment |
11 | 91 | 11,229 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of property and equipment |
11 | (88,330 | ) | (38,411 | ) | |||||||
| Disposal of intangible assets |
13 | 4 | 211 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of intangible assets |
13 | (13,191 | ) | (16,740 | ) | |||||||
| Disposal of investments in subsidiaries and associates |
1,043,089 | 180,326 | ||||||||||
| Acquisition of investments in subsidiaries and associates |
(1,403,867 | ) | (371,403 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
(2,087,742 | ) | 1,936,903 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings |
46,904,577 | 38,025,988 | ||||||||||
| Repayment of borrowings |
(46,121,872 | ) | (40,206,113 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of bonds |
37,029,845 | 28,764,309 | ||||||||||
| Repayment of bonds |
(37,880,107 | ) | (20,526,376 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issue of share capital |
55,000 | 19,900 | ||||||||||
| Dividends paid |
23 | (46,179 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Stock issuance costs |
(9,940 | ) | — | |||||||||
| Consideration transferred in the acquisition |
48 | — | (7,309 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
(68,676 | ) | 6,070,399 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Effects from changes in foreign currency exchange rate for cash and cash equivalents held |
313,731 | 256,621 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
(2,999,035 | ) | 1,859,950 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
9,019,914 | 7,159,964 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
42 | 9,019,914 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
See accompanying notes to the separate financial statements.
40
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
1. Reporting Entity
Korea Development Bank (the “Bank”) was established on April 1, 1954, in accordance with The Korea Development Bank Act to finance and manage major industrial projects.
The Bank is engaged in the banking industry under The Korea Development Bank Act and other applicable statutes, and in the fiduciary business in accordance with the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act.
Korea Finance Corporation (KoFC), the former ultimate parent company, and KDB Financial Group Inc. (KDBFG), the former immediate parent
company, were established by spin-offs of divisions of the Bank as of October 28, 2009. KoFC and KDBFG were merged into the Bank, effective as of December 31, 2014. Issued capital is W17,235,399 million with 3,447,079,768
shares of issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2015 and 100% of the Bank’s shares are owned by the government of the Republic of Korea.
The Bank’s head office is located in 14, Eunhaeng-ro (Yeouido-dong), Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul and its service network as of December 31, 2015 is as follows:
| Domestic | Overseas | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Head Office | Branches | Branches | Subsidiaries | Representative offices |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| KDB |
1 | 82 | 9 | 5 | 8 | 105 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
2. Basis of Preparation
(1) Statement of compliance
The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with the Korean International Financial Reporting Standards (“K-IFRS”), as prescribed in the Act on External Audits of Corporations in the Republic of Korea.
These financial statements are separate financial statements prepared in accordance with K-IFRS No.1027 ‘Separate Financial Statements’ presented by a parent, an investor with joint control of, or significant influence over, an investee, in which the investments are accounted for at cost.
(2) Basis of measurement
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for the following material items in the statement of financial position:
| • | Derivative financial instruments measured at fair value |
| • | Financial instruments measured at fair value through profit or loss |
| • | Available-for-sale financial instruments measured at fair value |
| • | Fair value hedged financial instruments with changes in fair value, due to hedged risks, recognized in profit or loss |
| • | Liabilities for defined benefit plans, which are recognized as net of the total present value of defined benefit obligations less the fair value of plan assets and unrecognized past service costs |
41
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
2. Basis of Preparation, Continued
(3) Functional and presentation currency
These financial statements are presented in Korean won
(“W”), which is the Bank’s functional currency and the currency of the primary economic environment in which the Bank operates.
(4) Use of estimates and judgments
The preparation of the financial statements in conformity with K-IFRS requires management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions are evaluated on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.
Information about critical judgments made by management in applying the Bank’s accounting policies that have the most significant effect on the amounts recognized in the separate financial statements is included in the following notes:
| • | Note 3.(7)—Impairment of financial assets |
| • | Note 3.(17)—Employee benefits |
Information about assumptions and estimation uncertainties that have a significant risk of resulting in a material adjustment within the next financial year is included in the following notes:
| • | Note 8—Loans and allowance for loan losses |
| • | Note 20—Defined benefit liabilities |
| • | Note 21—Provisions |
(5) Approval date for the separate financial statements
The separate financial statements were authorized for issue by the Board of Directors on March 29, 2016, which will be submitted for approval to the shareholders’ meeting to be held on March 30, 2016.
3. Significant Accounting Policies
The significant accounting policies applied by the Bank in preparation of its separate financial statements are included below. The accounting policies set out below have been applied consistently to all periods presented in these separate financial statements.
(1) Investments in subsidiaries and associates
The accompanying financial statements are separate financial statements in accordance with K-IFRS No.1027 ‘Separate Financial Statements’ and investments in subsidiaries and associates are accounted for at cost, not by performance and net asset reported by the investee. Dividends received from subsidiaries and associates are recognized as income as of the time the right to receive the dividends is established.
42
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(2) Business combination of entities under common control
The assets and liabilities acquired under business combinations under common control are recognized at the carrying amounts recognized previously in the separate financial statements of the ultimate parent. The difference between consideration transferred and carrying amounts of net assets acquired is recognized as part of share premium.
(3) Operating segments
The Bank makes decisions regarding allocation of resources to segments and categorizes segments, based on internal reports reviewed periodically by the chief operating decision maker, to assess performance. Information on segments reported to the chief operating decision maker includes items directly attributable to segments as well as those that can be allocated on a reasonable basis. Unallocated items mainly comprise corporate assets (such as the Bank Headquarters), head office expenses, and income tax assets and liabilities. The Bank recognizes the CEO as the chief operating decision maker.
(4) Foreign currency
(i) Foreign currency transactions
Transactions in foreign currencies are translated to the functional currency of the Bank, at exchange rates of the dates of transactions. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the reporting date are translated to the functional currency at the exchange rate at that date. The foreign currency gain or loss on monetary items is the difference between amortized cost in the functional currency at the beginning of the period, adjusted for effective interest and payments during the period, and the amortized cost in foreign currency translated at the exchange rate at the end of the reporting period. Non-monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies that are measured at fair value are translated to the functional currency at the exchange rate at the date that the fair value was determined.
Foreign currency differences arising on translation are recognized in profit or loss, except for differences arising on the translation of available for sale equity instruments, a financial liability designated as a hedge of the net investment in a foreign operation, or in a qualifying cash flow hedge, which are recognized in other comprehensive income. Non-monetary items that are measured in terms of historical cost in a foreign currency are translated using the exchange rate at the date of the transaction.
(ii) Foreign operations
If the presentation currency of the Bank is different from a foreign operation’s functional currency, the financial statements of the foreign operation are translated into the presentation currency using the following methods:
Unless the functional currency of foreign operations is in a state of hyper inflation, assets and liabilities of foreign operations are translated at the closing exchange rate at the end of the reporting period. Revenues and expenses on the statement of comprehensive income are translated at the exchange rates of the date of transaction. Foreign currency differences that arise from translation are recognized as other comprehensive income, and the disposal of a foreign operation is re-categorized as profit or loss as of the moment the disposal profit or loss is recognized.
43
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
Any goodwill arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation, and any adjustments in fair value to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities due to such acquisition, are treated as assets and liabilities of the foreign operation. Therefore, such are expressed in the functional currency of the foreign operations and, alongside other assets and liabilities of the foreign operation, translated at the closing exchange rate.
In the case of the disposal of a foreign operation, cumulative amounts of exchange difference regarding the foreign operation, recognized separately from other comprehensive income, are re-categorized from assets to profit or loss as of the moment the disposal profit or loss is recognized.
(iii) Foreign exchange of net investment in foreign operations
Monetary items receivable from or payable to a foreign operation, with none or little possibility of being settled in the foreseeable future, are considered a part of the net investment in the foreign operation. Therefore, the exchange difference is recognized as comprehensive profit or loss in the financial statement, and re-categorized to profit or loss as of the disposal of the related net investment.
(5) Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents comprise balances with original maturities of three months or less from the date of acquisition that are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in their fair value, including cash on hand, deposits held at call with banks and other highly liquid short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less.
(6) Non-derivative financial assets
The Bank recognizes and measures non-derivative financial assets by the following four categories: financial assets at fair value through profit or loss, held-to-maturity financial assets, loans and receivables, and available-for-sale financial assets. Moreover, the Bank recognizes financial assets in the statement of financial position as of the time the Bank becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instruments.
Non-derivative financial assets are measured at fair value upon initial recognition and, unless designated at fair value through profit or loss, transaction costs directly regarding acquisition and issuance of such assets are summed to the initial fair value.
(i) Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss
Any financial asset classified as held-for-trading or designated at fair value through profit or loss at initial recognition is categorized under financial assets at fair value through profit or loss. Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss (“FVTPL”) are measured at fair value upon initial recognition, and changes therein are recognized as profit or loss. Furthermore, transaction costs regarding acquisition upon initial recognition are recognized as profit or loss as incurred.
(ii) Held-to-maturity financial assets
If a non-derivative financial asset has a fixed maturity with a fixed or determinable payment, and the Bank has positive intent and ability to hold such an asset, it is classified as held-to-maturity financial assets. Subsequent to initial recognition, held-to-maturity financial assets are measured at amortized costs using the effective interest rate (“EIR”) method.
44
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(iii) Loans and receivables
Loans and receivables are non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an active market. Subsequent to initial recognition, loans and receivables are measured at amortized cost using the effective interest rate method. Furthermore, the effective interest rate method is applied to recognize interest incomes on financial investments.
(iv) Available-for-sale financial assets
Any non-derivative financial asset, not classified as financial assets at fair value through profit or loss, held-to-maturity financial assets, or loans and receivables, is classified as available-for-sale financial assets. Subsequent to initial recognition, such assets are measured at fair value. However, equity instruments that do not have a quoted market price in an active market and cannot be reliably measured, and any derivatives that are linked to these instruments and need to be settled upon the delivery of such equity instruments are measured at cost. Accumulated other comprehensive income, reflected in equity as fair value changes, is recognized as profit or loss as of the time the related available-for-sale asset is disposed of or the impairment loss is recognized. Furthermore, dividends earned whilst holding available-for-sale financial assets are recognized in the statement of comprehensive income upon the establishment of the right to receive the payment.
(v) De-recognition of financial assets
The Bank de-recognizes a financial asset when the rights to receive cash flow from an asset expire, or when it transfers the rights to receive cash flow and substantially all the risks and rewards from the ownership of a financial asset. In the case that the Bank has neither transferred nor retained substantially all the risks and rewards of an asset, the Bank de-recognizes any assets if it does not have control, and recognizes any assets to the extent of the Bank’s continuing involvement if it does have control. In the latter case, any associated liabilities are recognized by the Bank. In the case the Bank retains substantially all the risks and rewards from the ownership of an asset it does not have control of, the Bank continues to recognize the financial asset, and recognizes consideration received as financial liabilities.
(vi) Offsetting between financial assets and financial liabilities
Financial assets and liabilities are set-off only under the conditions that the Bank has legal rights to set-off the recognized amounts, and the intention to settle on a net basis or to realize assets and settle liabilities at the same time.
(7) Impairment of financial assets
The Bank assesses the possibility of objective evidence that may indicate any impairment of financial assets, except those designated at fair value through profit or loss, at each reporting date. A financial asset is defined as impaired if, as a result of one or more events after initial recognition, the estimated future cash flow of the asset has been affected. However, expected impairments from future events are not recognized, regardless of their likelihood.
45
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
Upon the finding of objective evidence to believe an asset is impaired, the impairment is measured and recognized in profit or loss as follows, according to the asset category:
(i) Impairment of loans and receivables
The Bank assesses, at each reporting date, whether objective evidence that indicate impairment of loans and receivables exist. If objective evidence shows that believe impairment has occurred, the amount of the loss is measured as the difference between the carrying amount of the asset and the present value of estimated future cash flows, discounted using the initial effective interest rate (“EIR”). Furthermore, the carrying amount of the asset is reduced through the use of an allowance account and the amount of the loss is recognized in the statement of comprehensive income.
All individually significant loans and advances are assessed for specific impairment. Those found not to be specifically impaired are then collectively assessed for any impairment that has been incurred but not yet identified. Loans and advances that are not individually significant are collectively assessed for impairment by grouping together loans and advances with similar risk characteristics.
In individual assessment, allowances on losses are computed using the discounted expected recoverable value, estimated by operating cash flows or collateral cash flow; in collective assessment, allowances on losses are computed using statistical methods based on obtainable historical loss experience.
The present value of estimated future cash flows is measured using the asset’s initial EIR. If the loan has a floating interest rate, the Bank uses the current EIR for the measurement. Future cash flows from collateral are estimated at net cash flow from disposal of collateral (deducting transaction cost).
For the purpose of a collective assessment of impairment, assets are analyzed on the basis of the Bank’s internal credit rating system that considers credit risk characteristics such as asset type, industry, geographical location, collateral type, past-due status and other relevant factors.
Future cash flows of the assets collectively assessed are estimated on the basis of historical loss experience for loans with similar credit risk characteristics. Historical loss experience is adjusted on the basis of current observable data to reflect the effects of current conditions on which the historical loss experience is based, and to remove the effects of conditions in the historical period that no longer exist. Estimates of changes in future cash flows reflect, and are directionally consistent with, changes in related observable data from year to year (such as changes in unemployment rates, property prices, commodity prices, payment status, or other factors that are indicative of incurred loss in the Bank and their magnitude). The methodology and assumptions used for estimating future cash flows are reviewed regularly to reduce any differences between loss estimates and actual loss experience.
If the terms of a financial asset are renegotiated or modified or an existing financial asset is replaced with a new one due to financial difficulties of the borrower, then an assessment is made of whether the financial asset should be de recognised. If the cash flows of the renegotiated asset are substantially different, then the contractual rights to cash flows from the original financial asset are deemed to have expired. In this case, the original financial asset is derecognised and the new financial asset is recognised at fair value. The impairment loss before an expected restructuring is measured as follows:
| • | If the expected restructuring will not result in derecognition of the existing asset, then the estimated cash flows arising from the modified financial asset are included in the measurement of the existing asset based on their expected timing and amounts discounted at the original effective interest rate of the existing financial asset. |
46
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
| • | If the expected restructuring will result in derecognition of the existing asset, then the expected fair value of the new asset is treated as the final cash flow from the existing financial asset at the time of its derecognition. This amount is discounted from the expected date of derecognition to the reporting date using the original effective interest rate of the existing financial asset. |
(ii) Impairment of available-for-sale financial assets
The Bank assesses, at each reporting date, whether objective evidence that indicate impairment of available-for-sale assets exist. If such objective evidence exists, the amount of the loss is measured as the difference between the acquisition cost and the current fair value.
An available-for-sale financial asset is considered to be impaired if there is a significant or prolonged decline in fair value of the asset below the acquisition cost. The Bank considers a 30% to be significant and a period of six months to be prolonged.
If, in a subsequent period, the fair value of a debt instrument increases and the increase can be objectively related to an event occurring after the impairment loss was recognized in, the impairment loss is reversed through the statement of comprehensive income. Moreover, the impairment loss is directly reduced from the carrying amount of the available-for-sale financial asset.
(iii) Impairment of held-to-maturity financial assets
The Bank assesses individually, at each reporting date, whether there is objective evidence that a held-to-maturity financial asset is impaired. If any such evidence exists, the amount of loss is measured as the difference between the carrying amount and the present value of estimated future cash flows, which is discounted using the initial EIR, and recognized in the statement of comprehensive income. If, in a subsequent period, the fair value of a financial asset held to maturity increases and the increase can be objectively related to an event occurring after the impairment was recognized, the impairment loss is reversed through the statement of comprehensive income. Moreover, the impairment loss is directly reduced from the carrying amount of the held-to-maturity financial asset.
(iv) Loss events of financial assets
Objective evidence that a financial asset is impaired include the following loss events:
| • | Significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor |
| • | A breach of contract, such as a default or delinquency in interest or principal payments |
| • | The granting of a concession to the borrower, for economic or legal reasons, that the lender would not otherwise consider |
| • | A state of high probability that the borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganization |
| • | The disappearance of an active market for that financial asset due to financial difficulties |
| • | The presence of observable data indicating a measurable decrease in the estimated future cash flows of a group of financial assets since the initial recognition of the group, although the decrease cannot yet be identified with the individual financial asset within the group |
47
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(8) Derivative financial instruments including hedge accounting
Derivative financial instruments are initially recognized at fair value upon agreement of the contract, and re-estimated at fair value subsequently. The recognition of profit or loss due to changes in fair value of derivative instruments is as stated below.
(i) Hedge accounting
Derivative financial instruments are accounted differently depending on whether or not hedge accounting is applied, and therefore, are classified into trading purpose derivatives and hedging purpose derivatives.
Upon the transaction of hedging purpose derivatives, two different types of hedge accounting are applied; a fair value hedge, and a cash flow hedge. A fair value hedge is a hedge of the exposure to changes in fair value of a recognized asset or liability or an unrecognized firm commitment, or an identified portion of such an asset, liability or firm commitment, that is attributable to a particular risk and could affect profit or loss. A cash flow hedge is a hedge of the exposure to variability in cash flows that (i) is attributable to a particular risk associated with a recognized asset or liability (such as all or some future interest payments on variable rate debt) or a highly probable forecast transaction and (ii) could affect profit or loss.
At inception of the hedge relationship, the Bank formally documents the relationship between the hedged item and the hedging instrument, including the nature of the risk, the objective and strategy for undertaking the hedge, and the method that will be used to assess the effectiveness of the hedging relationship. Also, at the inception of the hedge relationship, a formal assessment is undertaken to ensure the hedging instrument is expected to be highly effective in offsetting the designated risk in the hedged item and actual result was so.
Fair value hedge
For designated and qualifying fair value hedges, the change in the fair value of a hedging derivative is recognized in profit or loss in the statement of comprehensive income. Meanwhile, the change in the fair value of the hedged item, attributable to the risk hedged, is recorded as part of the carrying value of the hedged item and is also recognized in profit or loss in the statement of comprehensive income. When the hedge no longer meets the criteria for hedge accounting, the hedge relationship is terminated. For hedged item recorded at amortized cost, the difference between the carrying value of the hedged item on termination and the face value is amortized over the remaining term of the original hedge using the EIR.
Cash flow hedge
For designated and qualifying cash flow hedges, the effective portion of gain or loss on the hedging instruments is initially recognized directly in equity. The ineffective portion of the gain or loss on the hedging instrument is recognized immediately as gain or loss. When the hedged cash flow affects the profit or loss in statement of comprehensive income, the gain or loss on the hedging instrument is recorded in the corresponding income or expense line in profit or loss in the statement of comprehensive income. When a hedge no longer meets the criteria for hedge accounting, any cumulative gain or loss existing in equity at that time remains in equity and is recognized when the hedged forecasted transaction is ultimately recognized in the statement of comprehensive income. When a forecasted transaction is no longer expected to occur, the cumulative gain and loss that was reported in equity is immediately transferred to profit or loss in the statement of comprehensive income.
48
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(ii) Embedded derivative instruments
Derivatives embedded in other financial instruments or other host contracts are treated as separate derivatives. The Bank records embedded derivative instruments at fair value if their economic characteristics and risks are not clearly and closely related to those of the host contract. If the embedded derivative cannot be measured separately from the host contract, the Bank aggregately designates the host contract and embedded derivative as a financial instrument at fair value through profit or loss. Changes due to the fair value assessment of embedded derivative instruments are recognized in profit or loss.
(iii) Other derivative financial instruments
Changes in the fair value of other derivative financial instrument, not designated as a hedging instrument, are recognized immediately in profit or loss.
(9) Fair value of financial instruments
For financial instruments traded in active markets, the fair value is determined by referencing quoted market prices at each reporting date. For financial instruments not traded in an active market, the fair value is determined using appropriate valuation techniques. Such techniques may include discounted cash flow analysis or other valuation methods.
The Bank’s policies for measuring fair value of financial instruments at amortized costs are as follows:
| • | Cash and due from banks: Fair value of cash is considered equivalent to the carrying amount. In the case of due from banks on demand, which do not have a set maturity and can be realized instantly, the carrying amount is considered to be a close estimate of the fair value and is assumed so. In the case of other ordinary due from banks, the cash flow discount method is used to estimate the fair value. |
| • | Loans: The fair value of loans is the expected future cash flows, reflecting premature redemption ratio, discounted by the market interest rate, adjusted by spread considering the probability of default. Exceptions to this method include loans with credit line facilities, loans with a maturity of three months or less left and impaired loans, which the Bank assumes the carrying amount as the fair value. |
| • | Held-to-maturity financial assets: The fair value of held-to-maturity financial assets is computed by widely-accepted appraisal agencies upon request. |
| • | Deposits: The fair value of deposits is computed using the discounted cash flow method. However for deposits, whose cash flows cannot be estimated reasonably, the Bank assumes the carrying amount as the fair value. |
| • | Borrowings: For borrowings in Korean won, the fair value is computed using the discounted cash flow method. For borrowings in foreign currency, the fair value is computed by widely-accepted appraisal agencies upon request. |
| • | Bonds issued: The fair value of bonds in Korean won, except structured bonds in Korean won, is computed using the discounted cash flow method. For structured bonds in Korean won and bonds in foreign currency, the fair value is computed by widely-accepted appraisal agencies upon request. |
| • | Other financial assets and liabilities: The fair value of other financial assets and liabilities is computed using the discounted cash flow method. However, in cases cash flow cannot be estimated reasonably, the Bank assumes the carrying amount as the fair value. |
49
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(10) Day one profit or loss recognition
For financial instruments classified as level 3 on the fair value level hierarchy measured using input variables not observable in the market, the difference between the fair value at initial recognition and the transaction price, which is equivalent to Day one profit or loss, is amortized by using the straight line method over time.
(11) Property and equipment
The Bank’s property and equipment are recognized at the carrying amount at historical costs less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment in value. Historical costs include the expenditures directly related to the acquisition of assets.
Subsequent costs are recognized in the carrying amount of assets or, if appropriate, as separate assets if the probabilities future economic benefits associated with the assets will flow into the Bank and the costs can be measured reliably; the carrying amount of the replaced part is derecognized. Furthermore, any other repairs or maintenances are charged to profit or loss as incurred.
Land is not depreciated. Depreciation on other assets is calculated using the straight line method to the amount of residual value less acquisition cost over the following estimated useful lives:
| Type |
Useful lives (years) | |||
| Buildings |
20 ~ 50 | |||
| Structure |
10 ~ 40 | |||
| Leasehold improvements |
4 | |||
| Movable property |
4 | |||
Property and equipment are impaired when the carrying amount exceeds the recoverable amount. The Bank assesses residual value and economic life of its assets at each reporting date and makes adjustments to useful lives when necessary. Any gain or loss arising from the disposal of the asset (calculated as the difference between the net disposal proceeds and the carrying amount of the asset) is recognized in non-operating income (expense) in the statement of comprehensive income.
(12) Investment property
The Bank classifies property held for the purpose of rental income or benefits from capital appreciation as investment property. Investment property is measured initially at cost, including transaction costs. Subsequent to initial recognition, the cost model is applied. Subsequent to initial recognition, an item of investment property is carried at its cost less any accumulated depreciation and any accumulated impairment loss.
Investment properties are derecognized either when they have been disposed of or when the investment property is permanently withdrawn from use and no future economic benefit is expected from its disposal. The difference between the net disposal proceeds and the carrying amount of the asset is recognized in the statement of comprehensive income in the period of de-recognition. Reclassification to other account is made if there is a change in use of corresponding investment property.
50
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
Depreciation of investment property is calculated using the straight line method over its estimated useful lives as follows:
| Type |
Useful lives (years) | |||
| Buildings |
20 ~ 50 | |||
| Structure |
10 ~ 40 | |||
(13) Intangible assets
An intangible asset is recognized only when its cost can be measured reliably, and the probabilities future economic benefits from the asset will flow into the Bank are high. Separately acquired intangible assets are recognized at the acquisition cost, and subsequently, the cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment is recognized as the carrying amount.
Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized over a four-year to 30-year period of useful economic lives using the straight line method. At the end of each reporting period, the Bank reviews intangible assets for any evidence that indicate impairment, and upon the presence of such evidence, the Bank estimates the amount recoverable and recognizes the loss accordingly.
Intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not amortized, but are tested for impairment annually. Furthermore, the Bank reviews such intangible assets to determine whether or not it is appropriate to consider these assets to have indefinite useful lives. If in the case the Bank concludes an asset is not qualified to be classified as indefinite, prospective measures are taken to consider such an asset as finite.
(14) Impairment of non-financial assets
The Bank tests for any evidence of impairment in assets and reviews whether or not the impairment has taken place by estimating the recoverable amount, at the end of each reporting period. The recoverable amount is the higher of the fair value less cost and value in use of an asset.
Except for impairment losses in respect of goodwill which are never reversed, an impairment loss is reversed if there has been a change in the estimates used to determine the recoverable amount. The reversal is limited so that the carrying amount of the asset does not exceed its recoverable amount, nor exceeds the carrying amount that would have been determined, net of depreciation, had no impairment loss been recognized for the asset in prior years.
(15) Non-current assets held for sale
Non-current assets, or disposal groups comprising assets and liabilities, that are expected to be recovered primarily through sale rather than through continuing use, are classified as held for sale. In order to be classified as held for sale, the asset (or disposal group) must be available for immediate sale in its present condition and its sale must be highly probable. The assets or disposal group that are classified as non-current assets held for sale are measured at the lower of their carrying amount and fair value less cost to sell.
The Bank recognizes an impairment loss for any initial or subsequent write-down of an asset (or disposal group) to fair value less costs to sell, and a gain for any subsequent increase in fair value less costs to sell, up to the cumulative impairment loss previously recognized in accordance with K-IFRS No. 1036, ‘Impairment of Assets’.
A non-current asset that is classified as held for sale or part of a disposal group classified as held for sale is not depreciated (or amortized).
51
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(16) Non-derivative financial liabilities
The Bank classifies non-derivative financial liabilities into financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss or other financial liabilities, in accordance with the substance of the contractual arrangement and the definitions of financial liability. The Bank recognizes these financial liabilities in the statement of financial position when the Bank becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the financial liability.
(i) Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss in the current year include financial liabilities held for trading and financial liabilities designated at FVTPL upon initial recognition. Financial liabilities and derivatives are classified as financial instruments held for trading if they are acquired for the purpose of repurchasing in the near future. Financial liabilities are classified as financial liabilities at FVTPL upon initial recognition, when initial recognition designated as at fair value through profit or loss results in more relevant information. Financial liabilities at FVTPL are designated at fair value in subsequent measurements, and any related un-realized profit or loss is recognized as profit or loss.
(ii) Financial liabilities measured at amortized cost
Financial liabilities measured at amortized cost are recognized at fair value less cost less transaction cost upon initial recognition, and subsequently at amortized costs. The difference between the proceeds (net of transaction cost) and the redemption value is recognized in the statement of comprehensive income over the periods of the liabilities using the EIR.
Fees paid on the establishment of a loan facility are recognized as transaction costs of the loan, if the probability that some or all of the facility will be drawn down is high. If, however, there is not enough evidence to conclude a draw-down of some or all of the facility will occur, the fee is capitalized as a prepayment for liquidity services and amortized over the period of the facility to which it relates.
(iii) De-recognition of financial liabilities
A financial liability is de-recognized when the obligation under the liability is discharged, cancelled or expired. When an existing financial liability is replaced by another from the same lender on substantially different terms, or the terms of an existing liability are substantially modified, such an exchange or modification is treated as a de-recognition of the original liability and the recognition of a new liability. The difference between the carrying value of the original financial liability and the consideration paid is recognized in profit or loss.
(17) Employee benefits
(i) Short-term employee benefits
Short-term employee benefits are employee benefits that are due to be settled wholly before 12 months after the end of the period in which the employees render the related service. When an employee has rendered service to the Bank during an accounting period, the Bank recognizes the undiscounted amount of short-term employee benefits expected to be paid in exchange for that service.
52
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(ii) Retirement benefits: defined contribution plans
A defined contribution plan is a pension plan under which the Bank pays fixed contributions into a separate fund. A defined benefit plan defines the amount of pension benefit that an employee will receive on retirement and is usually dependent on one or more factors such as years of service and compensation.
The Bank is no longer responsible for any foreseeable future liability after a certain amount or percentage of money is set aside for defined contribution plans. If the pension plan allows for early retirement, payments are recognized as employee benefits. If the contribution already paid exceeds the contribution due for service before the end of the reporting period, the Bank recognizes that excess as an asset to the extent that the prepayment will lead to a reduction in future payments or a cash refund.
(iii) Retirement benefits: defined benefit plans
The Bank’s net obligation in respect of defined benefit plans is calculated by estimating the amount of future benefit that employees have earned in the current and prior periods, discounting that amount and deducting the fair value of any plan assets. The calculation of defined benefit obligations is performed annually by a qualified actuary using the projected unit credit method. The present value of the defined benefit obligation is determined by discounting the estimated future cash outflows using interest rates of high-quality corporate bonds that are denominated in the currency in which the benefits will be paid, and have terms to maturity similar to the terms of the related pension liability.
Remeasurements of the net defined benefit liabilities (assets), which comprise actuarial gains and losses, the return on plan assets (excluding interest) and the effect of the asset ceiling (if any, excluding interest), are recognised immediately in other comprehensive income.
(18) Provisions
Provisions are recognized when the Bank has a present legal or constructive obligation as a result of a past event, it is probable that an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation and a reliable estimate can be made of the amount of the obligation.
(19) Financial guarantees
Financial guarantee contracts are contracts that require the issuer (the Bank) to make specified payments to reimburse the holder for a loss it incurs because a specified debtor fails to make payments when due, in accordance with the original or changed terms of a debt instrument. Financial guarantees are initially recognized in the financial statements at fair value on the date the guarantee was given, and amortized over the period of the guarantee. Subsequent to initial recognition, the Bank’s liabilities under such guarantees are measured at the higher of:
| • | The amount determined in accordance with K-IFRS No. 1037 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets and |
| • | The initial amount less amortization of fees recognized in accordance with K-IFRS No. 1018 Revenue |
(20) Securities under resale or repurchase agreements
Securities purchased under agreements to resell are recorded as other loans and receivables and the related interest from these securities is recorded as interest income; securities sold under agreements to repurchase are recorded as other borrowings, and the related interest from these securities is recorded as interest expense.
53
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(21) Interest income and expense
Interest income and expense are recognized in profit or loss using the effective interest method. The effective interest method measures the amortized costs of financial instruments and allocates the interest income or expense during the related period.
Upon the calculation of the effective interest rate, the Bank estimates future cash flows by taking into consideration all contractual terms of the financial instrument, but not future credit loss. The calculation also reflects any fees or points paid or received, transaction costs and any related premiums or discounts. In the case that the cash flow and expected duration of a financial instrument cannot be estimated reliably, the effective interest rate is calculated by the contractual cash flow during the contract period.
Once an impairment loss has been recognized on a financial asset or a group of similar assets, subsequent interest income is recognized on the interest rate that was used to discount future cash flow for the purpose of measuring the impairment loss.
(22) Fees and commission income
Fees and commission income and expense are classified as follows according to related regulations:
(i) Fees and commission from financial instruments
Fees and commission income and expense that are integral to the effective interest rate on a financial asset or liability are included in the measurement of the effective interest rate. It includes those related to evaluation of the borrowers’ financial status, guarantee, collateral, other agreements and related evaluation as well as business transaction, rewards for activities, such as document preparation and recording and setup fees incurred during issuance of financial liabilities. However, when financial instruments are classified as financial instruments at fair value through profit or loss, fees and commission are recognized as revenue upon initial recognition.
(ii) Fees and commission from services
Fees and commission income charged in exchange for services to be performed during a certain period of time such as asset management fees, consignment fees and assurance service fees are recognized as the related services are performed.
(iii) Fees and commission from significant transaction
Fees and commission from significant transactions, such as trading stocks and other securities, negotiation and mediation activities for third parties, for instance business transfer and takeover, are recognized when transactions are completed.
(23) Dividend income
Dividend income is recognized upon the establishment of the Bank’s right to receive the payment.
54
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
(24) Income tax expense
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred income tax. Current income tax and deferred income tax are recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that the tax arises from a transaction or event, which is recognized in other comprehensive income or directly in equity, or a business combination.
The Bank recognizes deferred income tax liabilities for all taxable temporary differences associated with investments in subsidiaries, associates, except to the extent that the Bank is able to control the timing of the reversal of the temporary difference and it is probable that the temporary difference will not reverse in the foreseeable future. The Bank recognizes deferred income tax assets for all deductible temporary differences arising from investments in associates, to the extent that it is probable that the temporary difference will reverse in the foreseeable future and taxable profit will be available against which the temporary difference can be utilized.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are measured at the tax rates that are expected to apply to the reporting period when the assets are realized or the liabilities settled, based on tax rates (and tax laws) that have been enacted or substantively enacted by the end of the reporting period.
The measurement of deferred income tax assets and liabilities reflects the income tax effects that would follow from the manner in which the Bank expects, at the end of the reporting period, to recover or settle the carrying amount of its assets and liabilities.
The carrying amount of a deferred income tax asset is reviewed at the end of each reporting period and reduced to the extent that it is no longer probable that sufficient taxable profit will be available to allow the benefit of part or all of that deferred income tax asset to be utilized.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are off-set only if the Bank has a legally enforceable right to off-set the related current income tax assets and liabilities, and the assets and liabilities relate to income tax levied by the same tax authority and are intended to be settled on a net basis.
Additional income taxes arising from dividend payments are recognized when expenses related to dividend payments are recognized.
(25) Accounting for trust accounts
The Bank, for the purpose of financial reporting, differentiates trust assets from identifiable assets according to the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act. Furthermore, the Bank receives trust fees from the application, management and disposal of trust assets, and appropriates such amounts as fees from trust accounts.
Meanwhile, in the case the fee from an unspecified principal and interests guaranteed money in trust does not meet the principal or interest amount, even after appropriating deficit with trust fees and special reserve, the Bank fills in the remaining deficit in the trust account and appropriates such amounts as losses on trust accounts.
(26) Regulatory reserve for loan loss
In the case that the total sum of allowance for possible loan loss does not meet the amount prescribed in Article 29(1) of the Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business, the Bank, according to K-IFRS, records the difference at the end of each reporting period, and records the equal amount as a reserve for loan loss.
55
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
3. Significant Accounting Policies, Continued
In the case that the existing total sum of reserve for possible loan loss exceeds the amount needed to be set aside as of the closing date, the surplus is to be reversed. Furthermore, in the case that undisposed deficit exists, reserves for loan loss is saved from the time the undisposed deficit is disposed.
(27) Earnings per share
The Bank represents its diluted and basic earnings per common share in the separate comprehensive statement of income. Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) is calculated by dividing net profit attributable to shareholders of the Bank by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the reporting period. Diluted earnings per share is calculated by adjusting net profit attributable to common shareholders of the Bank, considering dilution effects from all potential common shares, and the weighted average number of common shares outstanding.
(28) New standards and interpretations not yet adopted
The following new standards, interpretations and amendments to existing standards have been published and are mandatory for the Bank for annual periods beginning after January 1, 2015, and the Bank has not early adopted them.
The Bank is in the process of evaluating the impact of the following amendments on its separate financial statements:
K-IFRS No. 1109, ‘Financial Instruments’
K-IFRS 1109, published in December 2015, replaces the existing guidance in K-IFRS No. 1039, Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement. K-IFRS 1109 includes revised guidance on the classification and measurement of financial instruments, a new expected credit loss model for calculating impairment on financial assets, and new general hedge accounting requirements. It also carries forward the guidance on recognition and derecognition of financial instruments from K-IFRS No. 1039. K-IFRS 1109 is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2018, with early adoption permitted.
K-IFRS No. 1115, ‘Revenue from Contracts with Customers’
K-IFRS 1115, published in January 2016, establishes a comprehensive framework for determining whether, how much and when revenue is recognized. It replaces existing revenue recognition guidance, including K-IFRS No. 1018, Revenue, K-IFRS No. 1011, Construction Contracts and K-IFRS No. 2113, Customer Loyalty Programmes. K-IFRS 1115 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2018, with early adoption permitted.
K-IFRS No. 1027 ‘Separate Financial Statements’
Amendments to K-IFRS 1027 introduced equity accounting as a third option in the entity’s separate financial statements, in addition to the existing cost and fair value options. This amendment is effective for annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2016, with early adoption permitted.
56
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
4. Cash and Due from Banks
| (1) | Cash and due from banks as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Cash |
93,801 | |||||||
| Due from banks in Korean won: |
||||||||
| Due from Bank of Korea |
1,367,960 | 1,127,162 | ||||||
| Other due from banks in Korean won |
896 | 104,687 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,368,856 | 1,231,849 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Due from banks in foreign currencies/off-shores |
3,437,522 | 4,648,998 | ||||||
| Provisions |
(112 | ) | (105 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,974,543 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (2) | Restricted due from banks as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Reserve deposit |
813,498 | |||||||
| Others |
142,058 | 97,086 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 910,584 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
5. Financial Assets Held for Trading
| (1) | Financial assets held for trading as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Financial assets held for trading denominated in Korean won: |
||||||||
| Equity securities: |
||||||||
| Stocks and equity investments |
15,122 | |||||||
| Debt securities: |
||||||||
| Government and public bonds |
1,120,203 | 986,037 | ||||||
| Financial bonds |
588,003 | 347,293 | ||||||
| Corporate bonds |
— | 20,017 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,708,206 | 1,353,347 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,715,494 | 1,368,469 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Financial assets held for trading denominated in foreign currencies/off-shores: |
||||||||
| Debt securities |
65,240 | 39,724 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 65,240 | 39,724 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loaned financial assets held for trading: |
||||||||
| Debt securities |
— | 10,205 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,418,398 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
57
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
5. Financial Assets Held for Trading, Continued
| (2) | Details of debt securities in financial assets held for trading as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Face value | Acquisition cost |
Fair value (Carrying amounts) |
||||||||||
| Government and public bonds in Korean won |
1,122,670 | 1,120,203 | ||||||||||
| Financial bonds in Korean won |
590,000 | 588,684 | 588,003 | |||||||||
| Debt securities in foreign currencies /off-shores |
64,706 | 63,673 | 65,240 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 1,775,027 | 1,773,446 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Face value | Acquisition cost |
Fair value (Carrying amounts) |
||||||||||
| Government and public bonds in Korean won |
983,679 | 986,037 | ||||||||||
| Financial bonds in Korean won |
350,000 | 347,345 | 347,293 | |||||||||
| Corporate bonds in Korean won |
20,000 | 20,018 | 20,017 | |||||||||
| Debt securities in foreign currencies /off-shores |
39,681 | 38,752 | 39,724 | |||||||||
| Loaned debt securities |
10,000 | 10,110 | 10,205 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 1,399,904 | 1,403,276 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
6. Available-for-Sale Financial Assets
| (1) | Available-for-sale financial assets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets denominated in Korean won: |
||||||||
| Equity securities: |
||||||||
| Stocks and equity investments |
8,945,741 | |||||||
| Beneficiary certificates |
6,435,675 | 4,246,301 | ||||||
| Others |
172,400 | 33,356 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 16,057,540 | 13,225,398 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Debt securities: |
||||||||
| Government and public bonds |
1,749,734 | 451,039 | ||||||
| Financial bonds |
6,218,681 | 6,964,023 | ||||||
| Corporate bonds |
13,146,033 | 13,653,028 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 21,114,448 | 21,068,090 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 37,171,988 | 34,293,488 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets denominated in foreign currencies/off-shores: |
||||||||
| Equity securities |
421,137 | 455,793 | ||||||
| Debt securities |
3,698,494 | 3,410,744 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 4,119,631 | 3,866,537 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 38,160,025 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
58
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
6. Available-for-Sale Financial Assets, Continued
Equity securities with no quoted market prices in active markets and for which the fair
value cannot be measured reliably are recorded at cost in the amount of W7,340,684million as of December 31, 2015 (W5,046,707 million as of December 31, 2014).
| (2) | Changes in available-for-sale financial assets for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
25,534,233 | |||||||
| Acquisition |
36,013,583 | 23,942,377 | ||||||
| Disposal |
(33,927,700 | ) | (25,724,134 | ) | ||||
| Change due to amortization |
(27,299 | ) | (1,054 | ) | ||||
| Unrealized change in fair value recorded in equity |
(318,813 | ) | 64,363 | |||||
| Impairment loss |
(264,711 | ) | (355,532 | ) | ||||
| Reversal of impairment loss |
43,898 | 21,367 | ||||||
| Reclassification |
(55,093 | ) | (14,994 | ) | ||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
225,141 | 86,180 | ||||||
| Others(*1) |
1,442,588 | 108,652 | ||||||
| Acquisition of parent company |
— | 14,498,567 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
38,160,025 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (*1) | Others represents KOREA LAND & HOUSING CORPORATION’s equity amounts |
59
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
6. Available-for-Sale Financial Assets, Continued
| (3) | Equity securities with disposal restrictions in available-for-sale financial assets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Company |
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||
| Number of shares |
Carrying amount |
Restricted period | ||||||||||
| KUKJE, Machinery Co., Ltd. |
3,492,000 | Until December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
| KUMHO Tire Co., Inc. |
21,339,320 | 143,614 | Undecided | |||||||||
| TAIHAN ELECTRIC WIRE CO., LTD. |
19,658,200 | 45,017 | Until October 20, 2016 | |||||||||
| Jaeyoung Solutec Co., Ltd. |
1,962,000 | 5,386 | Until December 31, 2017 | |||||||||
| Hyundai Cement Co., Ltd. |
1,433,800 | 15,752 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Dongbu Corporation |
869,141 | 8,013 | Until March 4, 2016 | |||||||||
| CHINHUNG INTERNATIONAL INC. |
13,113,200 | 30,160 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Samho International Co., Ltd. |
183,000 | 2,846 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Ajin P and P Co., Ltd. |
516,270 | 5,412 | Undecided | |||||||||
| Young Gwang Stainless Co., Ltd. |
413,000 | 510 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Oriental Precison & Engineering Co., Ltd.(*1) |
8,498,343 | 18,186 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| KPM Tech Co., Ltd. |
57,714 | 338 | Until December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
| Cosmetech Co., Ltd. |
11,768,000 | 2,483 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| Force Tec Co., Ltd. |
1,428,571 | 1 | Until December 31, 2017 | |||||||||
| Hanchang Paper Co., Ltd. |
3,204,600 | 4,246 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||||
| GMP CO., LTD. |
10,392,000 | 3,377 | Until December 31, 2017 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 98,329,159 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (*1) | The number of shares has decreased after the decision of capital reduction during the year ended December 31, 2015. |
| Company |
December 31, 2014 | |||||||||
| Number of shares |
Carrying amount |
Restricted period | ||||||||
| Keangnam Enterprises LTD. |
2,916,400 | Until December 31, 2016 | ||||||||
| KUKJE, Machinery Co., Ltd. |
3,492,000 | 10,357 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| KUMHO Industrial Co., Ltd. |
1,517,608 | 34,450 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| KUMHO Tire Co., Inc.(*1) |
21,339,320 | 206,351 | Undecided | |||||||
| TAIHAN ELECTRIC WIRE CO., LTD. |
9,982,200 | 10,231 | Until December 31, 2015 | |||||||
| Osung LST Co., Ltd. |
17,290,267 | 21,008 | Until December 31, 2017 | |||||||
| Jaeyoung Solutec Co., Ltd. |
1,962,000 | 2,786 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Hyundai Cement Co., Ltd. |
1,433,800 | 15,127 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Samho International Co., Ltd. |
183,000 | 2,406 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Ajin P and P Co., Ltd. |
516,270 | 5,721 | Undecided | |||||||
| Young Gwang Stainless Co., Ltd. |
413,000 | — | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Oriental Precison & Engineering Co., Ltd. |
62,700,511 | 41,257 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| KPM Tech Co., Ltd. |
57,714 | 111 | Until December 31, 2015 | |||||||
| Cosmetech Co., Ltd. |
11,768,000 | 2,648 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Force Tec Co., Ltd. |
1,428,571 | 1 | Until December 31, 2017 | |||||||
| Hanchang Paper Co., Ltd.(*1) |
3,204,600 | 2,134 | Until December 31, 2016 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 140,205,261 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (*1) | Disposal of some shares of equity securities acquired through debt-for-equity swap for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
60
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
6. Available-for-Sale Financial Assets, Continued
| (4) | Details of debt securities in available-for-sale financial assets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Face value | Acquisition cost |
Fair value (carrying amounts) |
||||||||||
| Government and public bonds in Korean won |
1,752,594 | 1,749,734 | ||||||||||
| Financial bonds in Korean won |
6,278,719 | 6,223,001 | 6,218,681 | |||||||||
| Corporate bonds in Korean won |
13,409,285 | 13,409,970 | 13,146,033 | |||||||||
| Debt securities denominated in foreign currencies /off shores |
3,691,162 | 4,285,667 | 3,698,494 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 25,671,232 | 24,812,942 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Face value | Acquisition cost |
Fair value (carrying amounts) |
||||||||||
| Government and public bonds in Korean won |
448,753 | 451,039 | ||||||||||
| Financial bonds in Korean won |
6,976,274 | 6,870,795 | 6,964,023 | |||||||||
| Corporate bonds in Korean won |
13,817,691 | 13,815,262 | 13,653,028 | |||||||||
| Debt securities denominated in foreign currencies /off shores |
3,370,336 | 4,122,625 | 3,410,744 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 25,257,435 | 24,478,834 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
7. Held-to-Maturity Financial Assets
| (1) | Held-to-maturity financial assets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Fair value | Amortized cost |
Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets in Korean won: |
||||||||||||||||
| Government and public bonds |
5,473 | 5,899 | 6,850 | |||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds |
23,647 | 23,647 | 11,339 | 11,339 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 29,120 | 17,238 | 18,189 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (2) | Changes in held-to-maturity financial assets for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
27,109 | |||||||
| Acquisition |
11,203 | 11,465 | ||||||
| Redemption |
(1,353 | ) | (21,146 | ) | ||||
| Change due to amortization |
98 | (166 | ) | |||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
1,374 | (24 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
17,238 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
61
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
8. Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses
| (1) | Loans and allowance for loan losses as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Fair value | Amortized cost |
Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
3,130,913 | 42,086,815 | 41,135,493 | |||||||||||||
| Loans for facility development |
45,497,491 | 44,341,539 | 51,574,448 | 51,779,986 | ||||||||||||
| Loans for households |
51,803,021 | 52,030,618 | 3,181,148 | 3,232,064 | ||||||||||||
| Inter-bank loans |
1,529,774 | 1,404,547 | 1,149,146 | 1,064,195 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 101,910,155 | 100,907,617 | 97,991,557 | 97,211,738 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Loans in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
14,984,481 | 15,715,987 | 15,319,099 | 15,820,744 | ||||||||||||
| Inter-bank loans |
2,617,923 | 2,617,426 | 588,028 | 588,069 | ||||||||||||
| Loans borrowed from overseas financial institutions |
206,279 | 212,231 | 218,227 | 224,242 | ||||||||||||
| Off-shore loans receivables |
9,154,474 | 9,541,787 | 8,622,662 | 8,997,653 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 26,963,157 | 28,087,431 | 24,748,016 | 25,630,708 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Other loans receivables: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bills bought in foreign currency |
1,710,518 | 1,669,570 | 1,599,989 | 1,582,147 | ||||||||||||
| Advance payments on acceptances and guarantees |
195,383 | 110,998 | 258,087 | 120,817 | ||||||||||||
| Privately-placed corporate bonds |
3,164,801 | 3,001,907 | 3,053,225 | 2,870,586 | ||||||||||||
| Others |
7,024,315 | 6,955,957 | 9,109,227 | 9,110,370 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 12,095,017 | 11,738,432 | 14,020,528 | 13,683,920 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 140,968,329 | 140,733,480 | 136,760,101 | 136,526,366 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Less: |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
(4,159,300 | ) | (2,398,658 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Present value discount |
(23,361 | ) | (55,418 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Deferred loan origination costs and fees |
3,981 | 8,441 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 134,314,466 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
62
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
8. Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses, Continued
| (2) | Changes in allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans
for working capital |
Loans for facility development |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opening balance |
549,483 | 11,052 | 164,621 | 260,705 | 242,484 | 2,398,658 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
1,369,519 | 340,831 | 2,314 | 273,833 | 436,432 | 387,169 | 2,810,098 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Write-offs |
(224,347 | ) | (191,968 | ) | (3,576 | ) | (104,339 | ) | — | (120,606 | ) | (644,836 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Recovery |
78 | 17,705 | — | 18,908 | 4,475 | 1,552 | 42,718 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sale |
(106,443 | ) | (63,664 | ) | — | (5,195 | ) | (10,823 | ) | (9,602 | ) | (195,727 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Debt-for-equity swap |
(94,139 | ) | (22,715 | ) | — | — | (27,740 | ) | (195 | ) | (144,789 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
— | — | — | 9,941 | 355 | 14,893 | 25,189 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
(64,056 | ) | (71,510 | ) | — | (5,012 | ) | (24,832 | ) | 33,399 | (132,011 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Closing balance |
558,163 | 9,790 | 352,757 | 638,572 | 549,094 | 4,159,300 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans
for working capital |
Loans for facility development |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Opening balance |
229,177 | 8,126 | 121,876 | 323,362 | 149,393 | 1,773,150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
1,067,839 | 328,070 | 2,926 | (75,232 | ) | 222,972 | 110,184 | 1,656,759 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Write-offs |
(167,618 | ) | (76,061 | ) | — | — | (101,410 | ) | (12,409 | ) | (357,498 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Recovery |
— | 4,715 | — | 83,179 | — | — | 87,894 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Sale |
(48,742 | ) | (16,819 | ) | — | (1,576 | ) | (32,121 | ) | (203 | ) | (99,461 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Debt-for-equity swap |
(700,661 | ) | 7,271 | — | — | (192,452 | ) | — | (885,842 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
— | — | — | 8,460 | — | — | 8,460 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of parent company |
89,129 | 102,787 | — | 32,302 | 11,831 | 1,268 | 237,317 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
(10,850 | ) | (29,657 | ) | — | (4,388 | ) | 28,523 | (5,749 | ) | (22,121 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Closing balance |
549,483 | 11,052 | 164,621 | 260,705 | 242,484 | 2,398,658 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (3) | Losses related to loans for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
(1,656,759 | ) | ||||||
| Losses on disposal of loan |
(198,525 | ) | (10,295 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1,667,054 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
63
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
8. Loans and Allowance for Loan Losses, Continued
| (4) | Changes in net deferred loan origination cost and fees for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
5,328 | |||||||
| New deferrals |
14,846 | 38,984 | ||||||
| Amortization |
(19,306 | ) | (15,674 | ) | ||||
| Acquisition of parent company |
— | (20,197 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
8,441 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
9. Derivative Financial Instruments
The Bank’s derivative financial instruments consist of trading derivatives and hedging derivatives, depending on the nature of each transaction. The Bank enters into hedging derivative transactions mainly for the purpose of hedging risk related to changes in fair values of the underlying assets and liabilities and future cash flows.
The Bank enters into trading derivative transactions such as futures, forwards, swaps and options for arbitrage transactions by speculating on the future value of the underlying asset. Derivatives held-for trading transactions include contracts with the Bank’s clients and its liquidation position.
For the purpose of hedging the exposure to the variability of fair values and cash flows of funds in Korean won by changes in interest rate or the purpose of hedging the exposure to the variability of fair values of funds in foreign currencies by changes in currency exchange rate or interest rate, the Bank mainly uses interest swaps or currency swaps. The main counterparties are foreign financial institutions and local banks. In addition, to hedge the exposure to the variability of fair values of bonds in foreign currencies by changes in interest rate or foreign exchange rate, the Bank mainly uses interest swaps or currency swaps.
The notional amounts outstanding for derivative contracts and the carrying amounts of the derivative financial instruments as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Notional amounts | Carrying amounts | |||||||||||||||
| Buy | Sell | Asset | Liability | |||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivative financial instruments: |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
311,769,470 | 2,221,817 | 2,030,304 | |||||||||||||
| Currency |
71,810,294 | 68,482,619 | 2,741,654 | 2,634,783 | ||||||||||||
| Stock |
79,991 | 258,762 | 324 | 1,315 | ||||||||||||
| Commodities |
97,541 | 97,540 | 26,884 | 26,884 | ||||||||||||
| Embedded derivatives |
252,592 | — | 34,461 | — | ||||||||||||
| Allowance and other adjustments |
— | — | (43,634 | ) | (4,789 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 379,975,824 | 380,608,391 | 4,981,506 | 4,688,497 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivative financial instruments: |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate(*1) |
24,349,973 | 24,349,973 | 752,954 | 49,674 | ||||||||||||
| Currency |
6,463,014 | 7,410,478 | 24,748 | 904,287 | ||||||||||||
| Allowance and other adjustments |
— | — | (1,452 | ) | (95 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 30,812,987 | 31,760,451 | 776,250 | 953,866 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 412,368,842 | 5,757,756 | 5,642,363 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (*1) | The expected maximum period for which derivative contracts, applied the cash flow hedge accounting, are exposed to risk of cash flow fluctuation is until September 11, 2020. |
64
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
9. Derivative Financial Instruments, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Notional amounts | Carrying amounts | |||||||||||||||
| Buy | Sell | Asset | Liability | |||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivative financial instruments: |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
300,231,635 | 2,294,826 | 2,140,241 | |||||||||||||
| Currency |
49,230,373 | 46,584,072 | 1,687,671 | 1,705,896 | ||||||||||||
| Stock |
42,037 | 118,193 | 2,008 | 322 | ||||||||||||
| Commodities |
282,950 | 282,950 | 39,185 | 39,372 | ||||||||||||
| Embedded derivatives |
405,633 | — | 37,966 | — | ||||||||||||
| Allowance and other adjustments |
— | — | (11,471 | ) | (1,747 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 348,084,876 | 347,216,850 | 4,050,185 | 3,884,084 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivative financial instruments: |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
22,069,120 | 22,069,120 | 840,842 | 57,089 | ||||||||||||
| Currency |
7,198,098 | 8,071,890 | 24,007 | 848,050 | ||||||||||||
| Allowance and other adjustments |
— | — | (2,242 | ) | (69 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 29,267,218 | 30,141,010 | 862,607 | 905,070 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 377,357,860 | 4,912,792 | 4,789,154 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
65
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates
| (1) | Investments in subsidiaries and associates as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||
| Subsidiaries: |
||||||||
| KDB Asia Ltd. |
214,807 | |||||||
| KDB Ireland Ltd. |
62,389 | 62,389 | ||||||
| KDB Bank Uzbekistan |
47,937 | 47,937 | ||||||
| KDB Bank Europe Ltd. |
151,952 | 151,952 | ||||||
| Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A(*1) |
35,848 | 35,848 | ||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*2) |
— | 1,775,758 | ||||||
| KDB Capital Corporation |
597,290 | 597,290 | ||||||
| KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd.(*2) |
— | 63,356 | ||||||
| KDB Infrastructure Investment Asset Management Co., Ltd. |
16,843 | 16,843 | ||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*3) |
689,452 | — | ||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund |
13,399 | 14,917 | ||||||
| KDB Electronic Power PEF |
48,263 | 68,144 | ||||||
| Korea Education Fund |
71,712 | 75,249 | ||||||
| Korea BTL Fund I |
217,052 | 227,693 | ||||||
| Korea Railroad Fund I |
175,573 | 211,628 | ||||||
| KDB Turn Around PEF(*4) |
2,651 | 2,651 | ||||||
| KDB Consus Value PEF(*5) |
406,295 | 163,766 | ||||||
| Components and Materials M&A PEF(*6) |
7,994 | 63,352 | ||||||
| KDB Value PEF VI |
1,706,220 | 1,636,000 | ||||||
| KDB Value PEF VII |
62,417 | 31,630 | ||||||
| KDB Sigma PEF |
— | 68,174 | ||||||
| KDB Sigma PEF II |
86,250 | — | ||||||
| KOFC-KBIC Frontier Champ 2010-5 PEF |
21,425 | 26,175 | ||||||
| KTB Korea-Australia Global Cooperation Fund |
18,143 | 17,136 | ||||||
| KDBC IP Investment Fund 2 |
5,057 | 8,057 | ||||||
| KOFC-KIS Pioneer Champ 2010-4 venture investment fund |
7,185 | 18,498 | ||||||
| KoFC-KDB Materials and Components Investment Fund No. 1 |
— | 46,090 | ||||||
| Busan Hi - technology Industrial Complex Co., Ltd. |
150 | 150 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,645,490 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Associates: |
||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd. |
16,044,556 | |||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*3) |
— | 1,052,166 | ||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. |
273,830 | 273,830 | ||||||
| Korea Tourism Organization |
337,286 | 337,286 | ||||||
| Korea Appraisal Board |
58,492 | 58,492 | ||||||
| Korea Maritime Guarantee Co., Ltd. |
49,856 | 29,856 | ||||||
| GM Korea Company(*7) |
68,115 | 287,774 | ||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund II |
203,602 | 181,289 | ||||||
| Troika Resources Investment PEF(*8) |
23,337 | 101,775 | ||||||
| Shinbundang Railroad Co., Ltd.(*9) |
27,963 | 29,072 | ||||||
| STX Engine Co,. Ltd.(*10) |
47,889 | 4 | ||||||
| Others(*11) |
2,490,094 | 2,817,072 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 20,501,531 | 21,213,172 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 26,858,662 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
66
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| (*1) | The Bank recognized |
| (*2) | Investments in Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd. and KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd. are classified into non-current assets held for sale as of December 31, 2015 as the sale procedure which includes the selection of a priority negotiation partner was in progress as of December 31, 2015. |
| (*3) | The Bank obtained control of Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. due to the acquisition of 75,769,311 shares (par value of |
| (*4) | The Bank recognized |
| (*5) | The Bank recognized |
| (*6) | The investment securities of Components and Materials M&A PEF is decreased by |
| (*7) | The Bank recognized |
| (*8) | The Bank recognized |
| (*9) | The Bank recognized |
| (*10) | The Bank acquired an additional 9,111,500 shares of the associate’s with voting rights after debt-for-equity swap decision of The Creditor Financial Institutions Committee on March 31, 2015. |
| (*11) | The Bank recognized |
67
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| (2) | The market value of marketable investments in subsidiaries and associates as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Market value | Carrying amounts | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. |
1,123,050 | 689,452 | 1,052,166 | |||||||||||||
| STX corporation(*1) |
40,637 | 39,928 | 10,507 | 10,507 | ||||||||||||
| STX Heavy Industries Co., Ltd.(*1)(*2) |
34,544 | 32,012 | 11,943 | 2,769 | ||||||||||||
| STX Engine Co,. Ltd.(*1)(*2) |
65,485 | 14,565 | 47,889 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*3) |
1,330,359 | 1,380,932 | — | 1,775,758 | ||||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd. |
10,561,763 | 8,205,229 | 16,921,067 | 16,044,556 | ||||||||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. |
2,010,760 | 1,024,689 | 273,830 | 273,830 | ||||||||||||
| Dongbu Steel Co., Ltd. |
28,100 | — | 5 | — | ||||||||||||
| Osung LST Co., Ltd. |
13,746 | — | 8,472 | — | ||||||||||||
| (*1) | The Bank has obtained significant influence due to The Creditor Financial Institutions Committee’s debt-for-equity swap decision based upon the Corporate Restructuring Promotion Act. |
| (*2) | The associate’s market value as of December 31, 2014 was the closing price previous to the trading suspension. The value as of December 31, 2015 represents the current market as the active market for the equity has resumed during the period ended December 31, 2015. |
| (*3) | The investee was classified from investments in subsidiaries into non-current assets held for sale. |
68
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| (3) | The key financial information of subsidiaries and associates invested and ownership ratios as of and for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | Fiscal year end |
Industry | Assets | Liabilities | Equity | Operating revenue |
Net income (loss) |
Total Comprehe -nsive income (loss) |
Ratio (%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subsidiaries : |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Asia Ltd. |
Hongkong | December | Finance | 1,119,809 | 274,570 | 58,831 | (2,687 | ) | 6,146 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Ireland Ltd. |
Ireland | December | Finance | 391,559 | 325,708 | 65,851 | 19,865 | (15,760 | ) | (11,983 | ) | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Bank Uzbekistan |
Uzbekisatan | December | Finance | 1,135,025 | 1,031,989 | 103,036 | 47,135 | 22,824 | 18,367 | 86.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Bank Europe Ltd. |
Hungary | December | Finance | 867,214 | 800,106 | 67,108 | 104,018 | (21,977 | ) | (25,745 | ) | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A |
Brazil | December | Finance | 271,279 | 247,874 | 23,405 | 250,146 | 416 | (14,859 | ) | 100.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*1)(*2) |
Korea | December | Finance | 34,841,940 | 30,456,640 | 4,385,300 | 5,076,963 | 298,847 | 292,826 | 43.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Capital Corporation |
Korea | December | Finance | 5,018,425 | 4,321,907 | 696,518 | 130,633 | 99,255 | 123,870 | 99.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd.(*2) |
Korea | December | Finance | 75,316 | 9,848 | 65,468 | 19,252 | 2,501 | 2,502 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Infrastructure Investment Asset Management Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Finance | 27,941 | 4,990 | 22,951 | 17,714 | 7,870 | 7,937 | 84.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 19,055,817 | 18,619,340 | 436,477 | 15,007,090 | (3,194,945 | ) | (2,807,695 | ) | 49.74 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
13,460 | 6 | 13,454 | 1,211 | 1,061 | 1,061 | 85.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Electronic Power PEF(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
94,806 | 17 | 94,789 | 6,577 | 6,321 | 6,321 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Education Fund(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
144,410 | 8 | 144,402 | 6,318 | 5,931 | 5,931 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea BTL Fund I(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
527,254 | 361 | 526,893 | 24,124 | 22,496 | 22,496 | 41.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Railroad Fund I(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
355,887 | 14 | 355,873 | 17,660 | 16,657 | 16,657 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Venture M&A PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
119 | 7,910 | (7,791 | ) | — | — | — | 57.56 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Turn Around PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
3,652 | — | 3,652 | 27 | 26 | 26 | 95.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Consus Value PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
15,474,147 | 14,746,735 | 727,412 | 3,850,904 | (139,023 | ) | (166,000 | ) | 58.59 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components and Materials M&A PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
17,485 | 5,259 | 12,226 | 13,750 | (1,693 | ) | (14,806 | ) | 83.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Value PEF VI |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
11,980,513 | 8,645,869 | 3,334,644 | 10,270,593 | (77,713 | ) | (78,076 | ) | 99.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Value PEF VII(*4) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
194,806 | 71,867 | 122,939 | 546 | (1,181 | ) | 1,130 | 50.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Sigma PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
170 | — | 170 | 63,687 | 50,815 | 50,815 | 60.87 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Sigma PEF II |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
144,228 | 286 | 143,942 | 5 | 241 | 192 | 60.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KOFC-KBIC Frontier Champ 2010-5 PEF(*1) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
51,934 | 145 | 51,789 | 9,469 | 9,270 | 8,939 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KTB Korea-Australia Global Cooperation Fund |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
18,761 | 992 | 17,769 | — | (1,329 | ) | (1,329 | ) | 95.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
69
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | Fiscal year end |
Industry | Assets | Liabilities | Equity | Operating revenue |
Net income (loss) |
Total Comprehe -nsive income (loss) |
Ratio (%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associates : |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Electricity Generation |
107,314,884 | 67,942,475 | 58,957,722 | 13,289,127 | 13,308,132 | 32.90 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 2,712,295 | 1,540,443 | 1,171,852 | 2,901,032 | 180,566 | 159,491 | 26.41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Tourism Organization |
Korea | December | Culture and Tourism administration |
1,345,127 | 364,848 | 980,279 | 728,583 | (12,637 | ) | (17,143 | ) | 43.58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Appraisal Board |
Korea | December | Appraisal | 233,369 | 36,506 | 196,863 | 137,330 | 12,435 | 9,036 | 30.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Marine Guarantee Insurance |
Korea | December | Finance | 122,331 | 427 | 121,904 | 967 | (2,263 | ) | (2,262 | ) | 40.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| GM Korea Company(*5)(*6) |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 7,683,488 | 6,790,687 | 892,801 | 12,565,528 | (748,301 | ) | (710,502 | ) | 17.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund II |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
780,028 | 6,158 | 773,870 | 50,521 | 42,551 | 42,551 | 26.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Troika Resources Investment PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
42,275 | 1,331 | 40,944 | (138,597 | ) | (144,297 | ) | (144,297 | ) | 54.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shinbundang Railroad Co., Ltd.(*7) |
Korea | December | Other | 782,160 | 909,878 | (127,718 | ) | 59,663 | (61,006 | ) | (61,006 | ) | 10.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||
70
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | Fiscal year end |
Industry | Assets | Liabilities | Equity | Operating revenue |
Net income (loss) |
Total Comprehe -nsive income (loss) |
Ratio (%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subsidiaries : |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Asia Ltd. |
Hongkong | December | Finance | 847,410 | 277,080 | 45,750 | 16,485 | 30,866 | 100.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Ireland Ltd. |
Ireland | December | Finance | 355,636 | 274,930 | 80,706 | 18,002 | 4,867 | 8,324 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Bank Uzbekistan |
Uzbekisatan | December | Finance | 950,334 | 862,194 | 88,140 | 39,772 | 17,759 | 11,011 | 86.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Bank Europe Ltd. |
Hungary | December | Finance | 767,681 | 674,827 | 92,854 | 69,839 | (31,021 | ) | (51,187 | ) | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A |
Brazil | December | Finance | 217,013 | 178,749 | 38,264 | 167,978 | (41,478 | ) | (53,198 | ) | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Korea | December | Finance | 30,613,292 | 26,439,033 | 4,174,259 | 4,021,794 | 205,195 | 310,940 | 43.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Capital Corporation |
Korea | December | Finance | 4,300,919 | 3,698,273 | 602,646 | 431,770 | 105,251 | 132,007 | 99.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Finance | 83,646 | 20,291 | 63,355 | 15,784 | 1,298 | 1,295 | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Investment Asset Management Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Finance | 24,538 | 4,525 | 20,013 | 14,454 | 6,303 | 6,249 | 84.16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
15,349 | 6 | 15,343 | 4,635 | 4,445 | 4,445 | 85.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Electronic Power PEF(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
134,197 | 24 | 134,173 | 10,826 | 10,420 | 10,420 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Education Fund(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
151,977 | 9 | 151,968 | 7,113 | 6,708 | 6,708 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea BTL Fund I(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
554,660 | 379 | 554,281 | 27,119 | 25,412 | 25,412 | 41.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Railroad Fund I(*3) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
430,037 | 17 | 430,020 | 18,973 | 17,943 | 17,943 | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Turn Around PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
3,625 | — | 3,625 | 40 | (1,613 | ) | (1,613 | ) | 95.17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Consus Value PEF(*4) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
13,884,320 | 13,308,596 | 575,724 | 3,350,635 | (76,306 | ) | 53,377 | 40.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components & Materials M&A PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
87,495 | 5,545 | 81,950 | 3,050 | (4,098 | ) | 22,224 | 83.33 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Value PEF VI |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
11,892,982 | 8,505,662 | 3,387,320 | 10,371,775 | (100,766 | ) | (137,814 | ) | 99.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Value PEF VII(*4) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
123,758 | 63,522 | 60,236 | 2,150 | (5,582 | ) | (3,024 | ) | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KDB Sigma PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
471,703 | 393,787 | 77,916 | 104,410 | (34,082 | ) | (34,082 | ) | 60.87 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KoFC-KBIC Frontier Champ 2010-5 PEF(*1) |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
52,499 | 148 | 52,351 | 15,842 | 957 | (2,292 | ) | 50.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| KTB Korea-Australia Global Cooperation Fund |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
18,735 | 697 | 18,038 | 3 | (1,687 | ) | (1,687 | ) | 95.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| KoFC-KDB Materials and Components Investment Fund No.1 |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
43,180 | — | 43,180 | 2,008 | (3,517 | ) | (3,517 | ) | 100.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
71
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
10. Investments in Subsidiaries and Associates, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Country | Fiscal year end |
Industry | Assets | Liabilities | Equity | Operating revenue |
Net income (loss) |
Total Comprehe -nsive income (loss) |
Ratio (%) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Associates : |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Electricity Generation |
108,883,279 | 54,825,010 | 57,474,883 | 2,686,873 | 2,335,827 | 29.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 18,519,114 | 15,577,260 | 2,941,854 | 15,455,330 | (783,933 | ) | (795,693 | ) | 31.46 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 2,096,813 | 1,060,083 | 1,036,730 | 2,314,884 | 111,109 | 94,736 | 26.41 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Tourism Organization |
Korea | December | Culture and Tourism administration |
1,395,195 | 409,939 | 985,256 | 887,595 | 18,633 | 13,826 | 43.58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Appraisal Board |
Korea | December | Appraisal | 221,905 | 30,734 | 191,171 | 113,836 | 9,585 | 9,585 | 30.60 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Marine Guarantee Insurance. |
Korea | December | Finance | 59,712 | — | 59,712 | — | — | — | 50.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GM Korea Company(*5)(*6) |
Korea | December | Manufacturing | 8,296,545 | 6,713,083 | 1,583,462 | 15,485,362 | (74,753 | ) | (135,102 | ) | 17.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea Infrastructure Fund II |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
689,143 | 1,326 | 687,817 | 46,448 | 39,239 | 39,239 | 26.67 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Troika Resources Investment PEF |
Korea | December | Financial investment |
186,853 | 1,613 | 185,240 | (89,978 | ) | (120,812 | ) | (120,812 | ) | 45.79 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shinbundang Railroad Co., Ltd.(*7) |
Korea | December | Other | 809,742 | 876,455 | (66,713 | ) | 56,004 | (66,074 | ) | (66,074 | ) | 10.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (*1) | Although the controlling entity holds less than half of the other entity’s voting rights, the controlling entity exercised its power as an executive member, influenced the other entity’s profit, and is exposed to variable profit, and therefore, the other entity is classified as a subsidiary. |
| (*2) | Investments in Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd. and KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd. are classified from investments in subsidiaries into non-current assets held for sale as of December 31, 2015. |
| (*3) | The investees are financed by KDB and managed by KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd. and KDB Infrastructure Investments Asset Management Co., Ltd.. They were classified as a subsidiary even though the Bank holds less than half of the voting rights because the Bank has the exposure to variable returns, and the ability to use power over the investee to affect the amount of the investors returns through its power over the investee. |
| (*4) | The entity is classified as a subsidiary as the Bank has power over the relevant activities as a single GP, is significantly exposed to variable returns, and has the ability to use power over the investee to affect the amount of the investor’s returns. |
| (*5) | Although the Bank’s ownership of GM Korea Company is less than 20%, the Bank has classified it as the associate as the Bank is considered to have significant influence over GM Korea Company by exercising rights to elect board of directors, etc. |
| (*6) | The ownership ratio of Shinbundang Railroad Co. Ltd. is above 20% upon the consideration of shares owned by the Bank’s subsidiaries. Therefore, the Bank exercises significant influence over the associate, Shinbundang Railroad. |
72
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
11. Property and Equipment
Changes in property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 |
Acquisition/ depreciation |
Disposal | Reclassification | Foreign exchange differences |
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition cost: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
20 | — | (1,669 | ) | 12 | 255,152 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
374,126 | 4,719 | (17 | ) | (1,706 | ) | 32 | 377,154 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
30,286 | 10,171 | (828 | ) | 124 | 137 | 39,890 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicles |
1,294 | 320 | (254 | ) | — | 36 | 1,396 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment |
46,368 | 4,537 | (265 | ) | — | 157 | 50,797 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Construction in progress |
124 | 51,371 | — | (124 | ) | — | 51,371 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
112,102 | 17,192 | (66 | ) | — | 85 | 129,313 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 821,089 | 88,330 | (1,430 | ) | (3,375 | ) | 459 | 905,073 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
133,912 | 11,292 | (15 | ) | (586 | ) | 27 | 144,630 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
22,510 | 5,377 | (798 | ) | — | (138 | ) | 26,951 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicles |
889 | 447 | (219 | ) | — | 29 | 1,146 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment |
35,977 | 3,903 | (245 | ) | — | 129 | 39,764 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
86,603 | 12,675 | (48 | ) | — | 57 | 99,287 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 279,891 | 33,694 | (1,325 | ) | (586 | ) | 104 | 311,778 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Impairment loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
3,023 | — | — | — | — | 3,023 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
2,361 | — | — | — | — | 2,361 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 5,384 | — | — | — | — | 5,384 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 54,636 | (105 | ) | (2,789 | ) | 355 | 587,911 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
73
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
11. Property and Equipment, Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014 |
Acquisition/ depreciation |
Disposal | Reclassification | Foreign exchange differences |
Acquisition of parent company |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition cost: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
9,448 | (1,996 | ) | 12,332 | (20 | ) | 30,731 | 256,789 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
293,514 | 10,777 | (1,364 | ) | 22,056 | (53 | ) | 49,196 | 374,126 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
27,521 | 602 | (657 | ) | 2,386 | (68 | ) | 502 | 30,286 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicles |
1,173 | 267 | (154 | ) | — | 8 | — | 1,294 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment |
40,385 | 2,580 | (901 | ) | — | (60 | ) | 4,364 | 46,368 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Construction in progress |
— | 5,987 | — | (5,863 | ) | — | — | 124 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
92,068 | 8,750 | (766 | ) | — | 22 | 12,028 | 112,102 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 660,955 | 38,411 | (5,838 | ) | 30,911 | (171 | ) | 96,821 | 821,089 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
98,398 | 8,796 | (602 | ) | 8,350 | (46 | ) | 19,016 | 133,912 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
18,295 | 4,451 | (637 | ) | — | (98 | ) | 499 | 22,510 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Vehicles |
880 | 160 | (154 | ) | — | 3 | — | 889 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment |
30,086 | 3,217 | (871 | ) | — | (65 | ) | 3,610 | 35,977 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
68,152 | 9,923 | (752 | ) | — | 12 | 9,268 | 86,603 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 215,811 | 26,547 | (3,016 | ) | 8,350 | (194 | ) | 32,393 | 279,891 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Impairment loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
3,023 | — | — | — | — | — | 3,023 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
2,361 | — | — | — | — | — | 2,361 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 5,384 | — | — | — | — | — | 5,384 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 11,864 | (2,822 | ) | 22,561 | 23 | 64,428 | 535,814 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
74
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
12. Investment Property
Changes in investment property for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 |
Acquisition/ depreciation |
Reclassification | December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||||
| Acquisition cost: |
||||||||||||||||
| Land |
— | 1,669 | 54,259 | |||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
38,813 | — | 1,706 | 40,519 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 91,403 | — | 3,375 | 94,778 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: |
||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
13,789 | 1,507 | 586 | 15,882 | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated impairment loss: |
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Land |
1,197 | — | — | 1,197 | ||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
1,778 | — | — | 1,778 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 2,975 | — | — | 2,975 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (1,507 | ) | 2,789 | 75,921 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The fair value of the
Bank’s investment property, as determined on the basis of valuation by an independent appraiser, amounts to W81,630 million as of December 31, 2015 (W78,524 million as of December 31, 2014). Additionally, fair
value of investment in property is classified as level 3 according to the fair value hierarchy in Note 44.
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014 |
Acquisition/ depreciation |
Reclassification | Acquisition of parent company |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition cost: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
— | (12,332 | ) | 9,467 | 52,590 | |||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
43,151 | — | (18,579 | ) | 14,241 | 38,813 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 98,606 | — | (30,911 | ) | 23,708 | 91,403 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Accumulated depreciation: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
14,936 | 1,559 | (8,350 | ) | 5,644 | 13,789 | ||||||||||||||
| Accumulated impairment loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Land |
1,197 | — | — | — | 1,197 | |||||||||||||||
| Buildings and structures |
1,778 | — | — | — | 1,778 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 2,975 | — | — | — | 2,975 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1,559 | ) | (22,561 | ) | 18,064 | 74,639 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
75
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
13. Intangible Assets
Changes in intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 |
Acquisition | Disposal | Amortization | Impairment loss |
Foreign exchange differences |
December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Development expense |
8,870 | — | (21,474 | ) | — | 1 | 48,516 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment usage right |
847 | — | — | (58 | ) | — | 42 | 831 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other deposits provided |
11,655 | — | (4 | ) | — | (11 | ) | 1 | 11,641 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
17,223 | 4,321 | — | (8,353 | ) | — | 17 | 13,208 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 13,191 | (4 | ) | (29,885 | ) | (11 | ) | 61 | 74,196 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014 |
Acquisition | Disposal | Amortization | Impairment loss |
Foreign exchange differences |
Acquisition of parent company |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Development expense |
12,088 | — | (17,313 | ) | — | 2 | 9,931 | 61,119 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equipment usage right |
877 | — | — | (57 | ) | — | 27 | — | 847 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other deposits provided |
10,906 | 363 | (211 | ) | — | (738 | ) | (1 | ) | 1,336 | 11,655 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
17,457 | 4,289 | — | (7,301 | ) | — | (49 | ) | 2,827 | 17,223 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 16,740 | (211 | ) | (24,671 | ) | (738 | ) | (21 | ) | 14,094 | 90,844 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
14. Other Assets
Other assets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Accounts receivable |
4,185,497 | |||||||
| Unsettled domestic exchange receivables |
566,624 | 604,080 | ||||||
| Accrued income |
473,385 | 496,646 | ||||||
| Guarantee deposits |
166,128 | 161,942 | ||||||
| Financial guarantee asset |
34,870 | 40,524 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses |
5,396 | 7,007 | ||||||
| Advance payments |
535 | 874 | ||||||
| Others |
46,541 | 35,319 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6,079,198 | 5,531,889 | |||||||
| Allowance for possible losses |
(72,221 | ) | (70,281 | ) | ||||
| Present value discount |
(3,881 | ) | (5,250 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,456,358 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The carrying amount of
financial assets included in other assets above amounted to W5,956,547 million as of December 31, 2015, (W5,421,457 million as of December 31, 2014) and their fair value amounted to W5,964,635
million as of December 31, 2015 (W5,422,962 million as of December 31, 2014).
76
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
15. Non-current Assets Held for Sale and Non-current Liabilities Held for Sale
| (1) | The Bank issued the public notice for the block trade of Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd and KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd, on October 8, 2015. The Bank selected MIRAE ASSET SECURITIES CO.,LTD as the priority negotiation partner on December 24, 2015 and concluded the stock purchase agreement contract on March 18, 2016. The Bank classified Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd and KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd, from investments in subsidiaries into non-current assets held for sale. |
| (2) | Non-current assets held for sale as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Non-current assets held for sale |
||||||||
| Investment in subsidiaries |
— | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Bank measured and classified the assets into non-current assets held for sale, at the lower of carrying amount and fair value less costs to sell. There is no impairment loss as the fair value less costs to sell, measured under the contract price with the priority negotiation partner, is higher than the carrying amount.
16. Financial Liabilities Designated at Fair Value Through Profit or Loss
| (1) | Financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Borrowings |
4,958 | |||||||
| Bonds |
1,619,438 | 1,133,670 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 1,138,628 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The borrowings designated at “Fair Value Through Profit or Loss” (FVTPL) consist of equity-index-linked securities. Through designating embedded derivatives and host contracts as FVTPL items, changes in fair value of complex financial products are recognized in profit or loss. Changes in fair value of structured bonds which hedge accounting are applied, are recognized in profit or loss, but structured bonds with no hedge accounting applied to, are measured at amortized costs. Therefore structured bonds which are economically hedged but for which hedge accounting is not applied have been designated at FVTPL in order to eliminate mismatch in measurements of accounting profit and loss.
| (2) | The difference between the carrying amount and contractual cash flow amount of financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Carrying amount |
1,138,628 | |||||||
| Contractual cash flow amounts |
1,408,665 | 950,994 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Difference |
187,634 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
77
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
17. Deposits
Deposits as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost | Fair value | Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Deposits in Korean won: |
||||||||||||||||
| Demand deposits |
221,596 | 160,806 | 160,806 | |||||||||||||
| Time and savings deposits |
34,227,299 | 34,264,950 | 31,663,351 | 31,712,090 | ||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposit |
515,351 | 515,514 | 108,786 | 109,096 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 34,964,246 | 35,002,060 | 31,932,943 | 31,981,992 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Deposits in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Demand deposits |
955,224 | 955,224 | 744,665 | 744,665 | ||||||||||||
| Time and savings deposits |
1,290,474 | 1,290,284 | 1,813,628 | 1,813,962 | ||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposit |
2,606,035 | 2,610,366 | 2,978,027 | 2,980,481 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 4,851,733 | 4,855,874 | 5,536,320 | 5,539,108 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Off-shore deposits in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Demand deposits |
118,913 | 118,913 | 136,451 | 136,451 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 39,976,847 | 37,605,714 | 37,657,551 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
18. Borrowings
| (1) | Borrowings as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Minimum interest rate (%) |
Maximum interest rate (%) |
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings in Korean won |
0.00 | 5.00 | 7,856,046 | 7,814,201 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings in foreign currencies |
0.00 | 5.05 | 10,745,590 | 10,858,933 | ||||||||||||
| Off-shore borrowings in foreign currencies |
0.19 | 4.27 | 1,159,260 | 1,162,494 | ||||||||||||
| Others |
0.07 | 6.55 | 4,682,743 | 4,683,345 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 24,443,639 | 24,518,973 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Deferred borrowing costs |
(3,489 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Discount on borrowings |
(39,560 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 24,400,590 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Minimum interest rate (%) |
Maximum interest rate (%) |
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings in Korean won |
0.00 | 5.05 | 7,459,870 | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings in foreign currencies |
0.02 | 6.65 | 10,215,872 | 10,281,576 | ||||||||||||
| Off-shore borrowings in foreign currencies |
0.19 | 4.28 | 1,923,739 | 1,926,752 | ||||||||||||
| Others |
0.05 | 5.15 | 3,947,181 | 3,949,164 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 23,541,615 | 23,617,362 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Deferred borrowing costs |
(4,084 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
78
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
18. Borrowings, Continued
| (2) | Borrowings in Korean won before adjusting for gains and losses on deferred borrowing costs as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Lender |
Classification |
Annual interest rate (%) |
December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||
| Ministry of Strategy and Finance |
Borrowings from government fund (*1) | 0.67 ~ 5.00 | 495,587 | |||||||||||
| Industrial Bank of Korea |
Borrowings from industrial technology fund | 0.60 ~ 1.59 | 3,819 | 3,092 | ||||||||||
| Small & Medium Business Corp. |
Borrowings from small and medium enterprise promotion fund | 1.32 ~ 3.62 | 177,231 | 248,825 | ||||||||||
| Ministry of Culture and Tourism |
Borrowings from tourism promotion fund | 0.05 ~ 2.50 | 1,855,349 | 1,490,344 | ||||||||||
| Korea Energy Management Corporation |
Borrowings from fund for rational use of energy | 0.25 ~ 3.65 | 986,247 | 1,151,113 | ||||||||||
| Local governments |
Borrowings from local small and medium enterprise promotion fund | 0.20 ~ 4.30 | 78,605 | 88,033 | ||||||||||
| The Bank of Korea |
Borrowings from Bank of Korea | 0.50 ~ 1.00 | 4,069,430 | 3,702,438 | ||||||||||
| Others |
Borrowings from environment improvement support fund and others | 0.00 ~ 3.35 | 280,135 | 275,391 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 7,454,823 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (*1) | Borrowings from government fund are subordinated borrowings. |
79
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
18. Borrowings, Continued
| (3) | Borrowings and off-shore borrowings in foreign currencies before adjusting for gains and losses on deferred borrowing costs as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Lender |
Classification |
Annual interest rate (%) |
December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||
| Japan Bank for International Cooperation (“JBIC”) |
Borrowings from JBIC | 1.73 ~ 2.16 | 218,227 | |||||||||
| Mizuho and others |
Bank loans from foreign funds | 3M Libor+0.40 ~ 3M Libor+0.75 |
1,511,880 | 1,209,120 | ||||||||
| Ministry of Strategy and Finance |
Exchange equalization fund borrowings in foreign currencies | 0.00 ~ 0.27 | 2,550,122 | 1,015,786 | ||||||||
| TORONTO DOMINION BANK SINGAPORE and others |
Off-shore short term borrowings | 0.19 ~ 0.39 | 686,481 | 1,101,689 | ||||||||
| 3M Telerate+0.40 ~ 3M Telerate+0.42 |
35,160 | 32,976 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 721,641 | 1,134,665 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| National Bank Of ABU DHABI and others |
Off-shore long term borrowings | 3M Libor+0.30 ~ 3M Libor+0.75 |
341,601 | 353,783 | ||||||||
| 3M Libor+0.75 ~ 3M Telerate+0.75 |
— | 329,760 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 341,601 | 683,543 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Japan Bank for International Cooperation (“JBIC”) |
Off-shore borrowings from JBIC | 1.79 | 62,538 | 67,850 | ||||||||
| 6M Libor+1.20 ~ 4.27 | 33,481 | 37,681 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 96,019 | 105,531 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Others |
Short term borrowings in foreign currencies | 0.00 ~ 5.05 | 4,426,210 | 5,767,387 | ||||||||
| Long term borrowings in foreign currencies | 0.20 ~ 2.83 | 2,051,098 | 2,005,352 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 12,139,611 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
80
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
19. Bonds
| (1) | Bonds as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Minimum interest rate (%) |
Maximum interest rate (%) |
Amortized cost |
Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Bonds in Korean won: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
1.54 | 7.29 | 91,096,981 | |||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(15,236 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
91,306 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 91,014,616 | 91,096,981 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Bonds in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
3M Libor+0.27 | 3M Libor+2.58 | 16,311,947 | 16,087,863 | ||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(33,587 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Premium on bonds |
4,859 | |||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
(180,832 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 16,102,387 | 16,087,863 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Off-shore bonds: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
3M Libor+0.35 | 3M Libor+4.30 | 9,947,109 | 9,850,360 | ||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(23,891 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Premium on bonds |
4,145 | |||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
(150,346 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 9,777,017 | 9,850,360 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 117,035,204 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
81
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
19. Bonds, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Minimum interest rate (%) |
Maximum interest rate (%) |
Amortized cost |
Fair value | |||||||||||||
| Bonds in Korean won: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
2.03 | 8.43 | 92,616,911 | |||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(34,211 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Premium on bonds |
4 | |||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
184,771 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 91,201,735 | 92,616,911 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Bonds in foreign currencies: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
3M Libor+0.20 | 3M Libor+2.58 | 17,062,488 | 17,160,814 | ||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(43,900 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Premium on bonds |
9,086 | |||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
(412,758 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 16,614,916 | 17,160,814 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Off-shore bonds: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
3M Libor+0.24 | 3M Libor+4.30 | 9,049,836 | 8,925,601 | ||||||||||||
| Discount on bonds |
(23,180 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Premium on bonds |
8,324 | |||||||||||||||
| Valuation adjustment for fair value hedges |
(281,835 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 8,753,145 | 8,925,601 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 118,703,326 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
20. Defined Benefit Liabilities
The Bank implements a defined benefit retirement pension plan based on employee compensation benefits and service periods. The plan assets are in trusts with Kookmin Bank, Samsung Life Insurance co., Ltd., etc.
| (1) | Details of defined benefit liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Present value of defined benefit liabilities |
211,148 | |||||||
| Fair value of plan assets |
(229,505 | ) | (179,018 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 32,130 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
82
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
20. Defined Benefit Liabilities, Continued
| (2) | Changes in defined benefit liabilities for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Present value of defined benefit liabilities |
Fair value of plan assets |
Defined benefit liabilities (assets) |
||||||||||
| Opening balance |
(179,018 | ) | 32,130 | |||||||||
| Current service costs |
32,529 | — | 32,529 | |||||||||
| Past service costs |
3,882 | — | 3,882 | |||||||||
| Interest expense (income) |
6,759 | (5,807 | ) | 952 | ||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Demographic assumption |
32 | — | 32 | |||||||||
| Financial assumption |
34,518 | 2,250 | 36,768 | |||||||||
| Experience adjustment |
7,597 | — | 7,597 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 42,147 | 2,250 | 44,397 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Benefits paid by the plan |
(13,600 | ) | 13,070 | (530 | ) | |||||||
| Contribution from the Bank |
— | (60,000 | ) | (60,000 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Closing balance |
(229,505 | ) | 53,360 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Present value of defined benefit liabilities |
Fair value of plan assets |
Defined benefit liabilities (assets) |
||||||||||
| Opening balance |
(178,119 | ) | 25,166 | |||||||||
| Current service costs |
36,288 | — | 36,288 | |||||||||
| Past service costs |
(2,237 | ) | — | (2,237 | ) | |||||||
| Interest expense (income) |
8,199 | (7,545 | ) | 654 | ||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Demographic assumption |
(63,526 | ) | — | (63,526 | ) | |||||||
| Financial assumption |
23,894 | 2,966 | 26,860 | |||||||||
| Experience adjustment |
3,101 | — | 3,101 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (36,531 | ) | 2,966 | (33,565 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Benefits paid by the plan |
(9,080 | ) | 8,680 | (400 | ) | |||||||
| Contribution |
— | (5,000 | ) | (5,000 | ) | |||||||
| Acquisition of parent company |
11,224 | — | 11,224 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Closing balance |
(179,018 | ) | 32,130 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (3) | Fair value of plan assets for each type as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Quoted market prices |
Unquoted market prices |
Quoted market prices |
Unquoted market prices |
|||||||||||||
| Due from banks |
229,505 | — | 179,018 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
83
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
20. Defined Benefit Liabilities, Continued
| (4) | Defined benefit costs recognized in profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Current service costs |
36,288 | |||||||
| Past service costs |
3,882 | (2,237 | ) | |||||
| Interest expense (income), net |
952 | 654 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 34,705 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (5) | The principal actuarial assumptions used as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Discount rate (%) |
2.83 | 3.28 | ||||||
| Future salary increasing rate (%) |
6.77 | 5.96 | ||||||
| (6) | The present value sensitivity of defined benefit liabilities as principal actuarial assumptions change as of December 31, 2015 is as follows: |
| Sensitivity | ||||||||
| 1% increase in assumption |
1% decrease
in assumption |
|||||||
| Discount rate |
10.04% decrease | 11.91% increase | ||||||
| Future salary increasing rate |
11.32% increase | 9.78% decrease | ||||||
| (7) | The weighted-average expected time to maturity of defined benefit liabilities is 11.07 years as of December 31, 2015 (10.33 years as of December 31, 2014), and the
expected contributions to the plan until the upcoming annual reporting period amount to |
21. Provisions
| (1) | Changes in provisions for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for payment guarantees |
Provision for unused commitments |
Financial guarantee provision |
Lawsuit provision |
Other provision |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Opening balance |
20,341 | 22,069 | 9,043 | 6,076 | 333,894 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Increase of provision |
243,678 | 48,273 | 96,265 | 9,770 | — | 397,986 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
12,427 | 1,344 | (21 | ) | — | — | 13,750 | |||||||||||||||||
| Others |
— | — | — | (747 | ) | — | (747 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Closing balance |
69,958 | 118,313 | 18,066 | 6,076 | 744,883 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
84
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
21. Provisions, Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for payment guarantees |
Provision for unused commitments |
Financial guarantee provision |
Lawsuit provision |
Other provision |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Opening balance |
25,847 | 9,939 | 1,881 | 1,032 | 550,024 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Increase (reversal) of provision |
(269,485 | ) | (6,961 | ) | 1,053 | 7,162 | — | (268,231 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange differences |
(599 | ) | 389 | 25 | — | — | (185 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of parent company |
35,124 | 1,066 | 11,052 | — | 5,044 | 52,286 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Closing balance |
20,341 | 22,069 | 9,043 | 6,076 | 333,894 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (2) | Provision for payment guarantees |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees, unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees and bills endorsed are not recognized on the statement of financial position, but are disclosed as off-statement of financial position items in the notes to the financial statements. The Bank provides a provision for such off-statement of financial position items, applying a Credit Conversion Factor (“CCF”) and provision rates, and records the provision as a reserve for possible losses on acceptances and guarantees.
| (3) | Provision for unused commitments |
The Bank records a provision for a certain portion of unused credit lines which is calculated using a CCF as provision for unused commitments applying provision rates.
| (4) | Provision for possible losses from lawsuits |
As of December 31, 2015, the Bank is involved in 21 lawsuits as a plaintiff and 33 lawsuits as a defendant. The aggregate amount of claims
as a plaintiff and a defendant amounted to W232,817 million and W479,659 million, respectively. The Bank provided a provision against contingent loss from pending lawsuits as of December 31, 2015 and additional
losses may be incurred depending on the final result of pending lawsuits.
85
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
21. Provisions, Continued
Major lawsuits in progress as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||
| Contents | Amounts | Status of lawsuit | ||||||
| Plaintiff:(*4) |
||||||||
| GYENGGI URBAN INNOVATION CORPORATION |
Claim for refund of investments |
1st trial ruled partially in favor of the bank; 2st trial in progress | ||||||
| SH Corporation |
Claim for damages | 9,720 | 1st trial ruled against the Bank; 2st trial in progress | |||||
| KB CAPITAL CO.,LTD |
Claim for damages | 17,795 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| Korea Trade Insurance Corporation |
Short-term export credit insurance |
46,394 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| Defendant: |
||||||||
| Hanhwa Chemical Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Performance bonds | 1st, 2nd trials
ruled in favor of the Bank; Pending appeals | ||||||
| Shinhan Bank and 1 other(*2) |
Claim for damages | 58,474 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| KAMCO 8th Joint Investment SPC LLC(*2) |
Claim for refund of impairment sale payment |
36,333 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| GYENGGI URBAN INNOVATION CORPORATION(*3) |
Delivery of stocks and stock transfer, etc |
24,348 | 1st trial ruled against the Bank; 2st trial in progress | |||||
| (*1) | As the 1st and 2nd trials ruled in favor of the Bank, the Bank did not record provisions. |
| (*2) | As the 1st trials are in progress, the Bank did not record provisions. |
| (*3) | As the 1st trial ruled in favor of the plaintiff, the Bank has recorded provisions related to this claim. |
| (*4) | The Bank considers the likelihood of favorable rulings in these cases to be possible. |
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Contents | Amounts | Status of lawsuit | ||||||
| Plaintiff: |
||||||||
| 28 Samsung affiliates (including Samsung Electronics) (*1) |
Deposit contracts, etc. | Final ruling (2015.01.29) | ||||||
| GYENGGI URBAN INNOVATION CORPORATION |
Claim for refund of investments |
19,100 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| SH Corporation |
Claim for damages | 9,720 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
86
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
21. Provisions, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Contents | Amounts | Status of lawsuit | ||||||
| Defendant: |
||||||||
| Hanhwa Chemical Co., Ltd. |
Performance bonds | 1st,
2nd trials ruled in favor of the Bank; Pending appeals | ||||||
| KAMCO 8th JV Securitization Specialty Co., Ltd |
Claim for refund of impairment sale payment |
36,333 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| GYENGGI URBAN INNOVATION CORPORATION |
Delivery of stocks and Stock transfer, etc |
24,348 | 1st trial in progress | |||||
| (*1) | The financial institution creditors of Renault Samsung Motors (including KDB) filed a lawsuit against Kun-hee Lee and 28 Samsung affiliates (including Samsung
Electronics), claiming compensation for delays in payment of liquidated damages and contract bills based on the agreement signed on August 24, 1999. On January 29, 2015, the court decided partially in favour of the plaintiff in the last instance. On
March 27, 2015, the Bank recognized |
| (5) | Other provision |
The Bank recognised other provision as a reserve for other miscellaneous purpose.
22. Other Liabilities
Other liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Accounts payable |
2,662,181 | |||||||
| Accrued expense |
1,668,308 | 1,784,532 | ||||||
| Advance receipts |
2,544 | 1,144 | ||||||
| Unearned income |
47,996 | 48,279 | ||||||
| Deposits withholding tax |
26,125 | 40,873 | ||||||
| Guarantee money received |
35,820 | 89,155 | ||||||
| Foreign exchanges payable |
31,005 | 225,199 | ||||||
| Domestic exchanges payable |
418,345 | 461,950 | ||||||
| Borrowing from trust accounts |
1,278,311 | 589,081 | ||||||
| Financial guarantee liability |
41,884 | 49,254 | ||||||
| Suspense payable |
32,926 | 115,356 | ||||||
| Others |
42,692 | 133,123 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 8,356,043 | 6,200,127 | |||||||
| Present value discount |
(344 | ) | (415 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6,199,712 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
87
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
22. Other Liabilities, Continued
The carrying amount of financial liabilities included in other liabilities above
amounted to W8,194,931 million as of December 31, 2015 (W5,920,686 million as of December 31, 2014) and their fair value amounted to W8,194,982 million as of December 31, 2015
(W5,920,769 million as of December 31, 2014).
23. Equity
(1) Issued capital
The Bank is authorized to issue up to 6,000 million shares
of common stock and has 3,447,079,768 shares issued as of December 31, 2015 (3,036,079,768 shares issued as of December 31, 2014), and outstanding with a total par value of W17,235,399 million as of December 31, 2015
(W15,180,399 million as of December 31, 2014).
(2) Capital surplus
Capital surplus as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Paid-in capital in excess of par value |
— | |||||||
| Surplus from capital reduction(*1) |
44,373 | 44,373 | ||||||
| Other capital surplus(*2) |
2,390,495 | 2,478,496 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 2,501,439 | 2,522,869 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (*1) | The Bank reduced |
| (*2) | The difference in the amount of shares issued and the carrying value of net asset acquired occurring from the merger of the Bank with KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation was recognized as other capital surplus. |
88
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
23. Equity, Continued
(3) Accumulated other comprehensive income
| (i) | Accumulated other comprehensive income as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||
| Valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets (before tax) |
1,075,984 | |||||||
| Income tax effect |
(183,898 | ) | (260,384 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 576,022 | 815,600 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations: |
||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations (before tax) |
(437 | ) | (37,421 | ) | ||||
| Income tax effect |
107 | 9,056 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (330 | ) | (28,365 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
||||||||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge (before tax) |
(23,616 | ) | (18,293 | ) | ||||
| Income tax effect |
5,714 | 4,427 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (17,902 | ) | (13,866 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities: |
||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities (before tax) |
15,040 | 59,437 | ||||||
| Income tax effect |
(3,640 | ) | (14,384 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 11,400 | 45,053 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 818,422 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (ii) | Changes in accumulated other comprehensive income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 |
Increase (Decrease) |
Tax Effect |
December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||||
| Valuation loss on available-for-sale financial assets |
(316,064 | ) | 76,486 | 576,022 | ||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
(28,365 | ) | 36,984 | (8,949 | ) | (330 | ) | |||||||||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
(13,866 | ) | (5,323 | ) | 1,287 | (17,902 | ) | |||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
45,053 | (44,397 | ) | 10,744 | 11,400 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (328,800 | ) | 79,568 | 569,190 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
89
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
23. Equity, Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014 |
Increase (decrease) |
Tax effect |
Acquisition of parent company |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
| Valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets |
64,363 | (15,586 | ) | 404,892 | 815,600 | |||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
(49,667 | ) | 28,102 | (6,800 | ) | — | (28,365 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
— | (1,350 | ) | 327 | (12,843 | ) | (13,866 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
20,209 | 33,565 | (8,123 | ) | (598 | ) | 45,053 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 124,680 | (30,182 | ) | 391,451 | 818,422 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
(4) Retained earnings
The Korea Development Bank Act requires the Bank to appropriate at least 40% of net income as a legal reserve. This reserve can be transferred to paid-in capital or offset an accumulated deficit. In accordance with the Korea Development Bank Act, the Bank offsets an accumulated deficit with reserves. If the reserve is insufficient to offset the accumulated deficit, the Korean government is responsible for the deficit.
| (i) | Retained earnings as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Legal reserve |
5,400,519 | |||||||
| Voluntary reserve |
||||||||
| Regulatory reserve for loan losses |
1,370,828 | 1,306,925 | ||||||
| Unappropriated retained earnings (accumulated deficits) |
(1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6,890,913 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (ii) | Changes in legal reserve for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
6,022,263 | |||||||
| Transfer from (contribution to) unappropriated retained earnings |
73,387 | (621,744 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
5,400,519 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
90
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
23. Equity, Continued
| (iii) | Changes in unappropriated retained earnings (accumulated deficits) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
(621,744 | ) | ||||||
| Profit (loss) for the year |
(1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | |||||
| Transfer from (contribution to) legal reserve |
(73,387 | ) | 621,744 | |||||
| Contribution to regulatory reserve for loan losses |
(63,903 | ) | — | |||||
| Dividends |
(46,179 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
183,469 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (iv) | Statements of appropriation of retained earnings (disposal of deficits) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| I. Unappropriated retained earnings (accumulated deficits): |
||||||||
| Unappropriated retained earning carried forward from the prior year |
— | |||||||
| Profit (loss) for the year |
(1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| II. Appropriation of retained earnings (disposal of deficits): |
||||||||
| Legal reserve (transfer from legal reserve) |
(1,895,136 | ) | 73,387 | |||||
| Regulatory reserve for loan losses |
— | 63,903 | ||||||
| Dividends |
||||||||
| (dividends per share |
— | 46,179 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1,895,136 | ) | 183,469 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| III. Unappropriated retained earnings (accumulated deficits) to be carried over to subsequent year |
— | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
(5) Regulatory reserve for loan losses
The Bank is required to provide a regulatory reserve for loan losses in accordance with Regulations on Supervision of Banking Business 29(1) and (2). The details of regulatory reserve for loan losses are as follows:
| (i) | Regulatory reserve for loan losses as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
1,306,925 | |||||||
| Planned reserve for loan losses |
— | 63,903 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
1,370,828 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
91
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
23. Equity, Continued
| (ii) | Obligated amount of provision for regulatory reserve for loan losses and profit (loss) after adjusting regulatory reserve for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Profit (loss) for the year |
183,469 | |||||||
| Obligated amount of provision for regulatory reserve for loan losses |
— | (46,751 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Profit (loss) after adjusting regulatory reserve for loan losses |
136,718 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Profit (loss) per share after adjusting regulatory reserve for loan losses (in won) |
73 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
24. Net Interest Income
Net interest income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Interest income: |
||||||||
| Due from banks |
46,647 | |||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
53,300 | 59,293 | ||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
656,971 | 614,257 | ||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
1,125 | 629 | ||||||
| Loans |
4,740,953 | 4,029,615 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,490,433 | 4,750,441 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Interest expense: |
||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss |
(66,957 | ) | (44,837 | ) | ||||
| Deposits |
(728,964 | ) | (894,555 | ) | ||||
| Borrowings |
(225,573 | ) | (273,205 | ) | ||||
| Bonds |
(2,890,720 | ) | (1,549,350 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (3,912,214 | ) | (2,761,947 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net interest income |
1,988,494 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Interest received from
impaired assets relating to loan receivables for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were W131,494 million and W22,947 million, respectively, and there was no interest received from impaired assets related to
financial assets other than loans.
92
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
25. Net Fees and Commission Income
Net fees and commission income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Fees and commission income: |
||||||||
| Loan commissions |
190,133 | |||||||
| Underwriting and investment consulting commissions |
184,338 | 168,597 | ||||||
| Brokerage and agency commissions |
14,923 | 13,146 | ||||||
| Trust and retirement pension plan commissions |
39,832 | 28,510 | ||||||
| Fees on asset management commissions |
1,047 | 2,612 | ||||||
| Other fees |
96,466 | 64,993 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 553,230 | 467,991 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Fees and commission expenses: |
||||||||
| Brokerage and agency fees |
(10,880 | ) | (8,702 | ) | ||||
| Other fees |
(22,556 | ) | (17,045 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (33,436 | ) | (25,747 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 442,244 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
26. Dividend Income
Dividend income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
377 | |||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
203,594 | 76,622 | ||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
411,426 | 81,165 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 158,164 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
27. Net Loss on Financial Assets Held for Trading
Net loss related to financial assets held for trading for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Gains on financial assets held for trading: |
||||||||
| Gains on sale |
20,319 | |||||||
| Gains on valuation |
711 | 3,837 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 22,705 | 24,156 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on financial assets held for trading: |
||||||||
| Losses on sale |
(34,123 | ) | (26,442 | ) | ||||
| Losses on valuation |
(5,329 | ) | (3,741 | ) | ||||
| Purchase related expense |
(248 | ) | (297 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (39,700 | ) | (30,480 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (6,324 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
93
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
28. Net Loss on Financial Liabilities Designated at Fair Value Through Profit or Loss
Net loss related to financial liabilities designated at fair value through profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Gains on financial liabilities designated at FVTPL: |
||||||||
| Gains on redemption |
469 | |||||||
| Gains on valuation |
3,315 | 2,789 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6,869 | 3,258 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on financial liabilities designated at FVTPL: |
||||||||
| Losses on redemption |
(588 | ) | (42 | ) | ||||
| Losses on valuation |
(32,740 | ) | (75,881 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (33,328 | ) | (75,923 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (72,665 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
29. Net Gain on Available-for-sale Financial Assets
Net gain on available-for-sale financial assets for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Gains on available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||
| Gains on sale |
416,182 | |||||||
| Reversal of impairment losses |
43,898 | 21,367 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 533,756 | 437,549 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||
| Losses on sale |
(38,425 | ) | (32,961 | ) | ||||
| Impairment losses |
(264,711 | ) | (355,532 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (303,136 | ) | (388,493 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 49,056 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
94
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
30. Net Gain (Loss) on Derivatives
Net Gain (Loss) on derivatives for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Net gain (loss) on trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Gains on trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Interest |
2,701,958 | |||||||
| Currency |
5,772,460 | 4,680,371 | ||||||
| Stock |
3,147 | 2,136 | ||||||
| Commodity |
103,172 | 99,411 | ||||||
| Embedded derivatives |
96,411 | 21,261 | ||||||
| Gains on adjustment of derivatives |
5,045 | 6,222 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 8,312,057 | 7,511,359 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Interest |
(2,321,747 | ) | (2,652,239 | ) | ||||
| Currency |
(5,501,632 | ) | (4,852,495 | ) | ||||
| Stock |
(2,923 | ) | (1,013 | ) | ||||
| Commodity |
(102,714 | ) | (99,225 | ) | ||||
| Embedded derivatives |
(12,760 | ) | (49,780 | ) | ||||
| Losses on adjustment of derivatives |
(42,044 | ) | (11,014 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (7,983,820 | ) | (7,665,766 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (154,407 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
95
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
30. Net Gain (Loss) on Derivatives, Continued
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Net loss on hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Gains on hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Interest |
248,913 | |||||||
| Currency |
391,317 | 65,389 | ||||||
| Gains on adjustment of derivatives |
1,859 | 2,034 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 468,411 | 316,336 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||
| Interest |
(148,267 | ) | (50,015 | ) | ||||
| Currency |
(929,301 | ) | (539,804 | ) | ||||
| Losses on adjustment of derivatives |
(494 | ) | (2,349 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1,078,062 | ) | (592,168 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (609,651 | ) | (275,832 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net gain on fair value hedged items: |
||||||||
| Gains on fair value hedged items: |
||||||||
| Gains on valuation |
299,905 | 332,194 | ||||||
| Gains on redemption |
176,318 | 88,528 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 476,223 | 420,722 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Losses on fair value hedged items: |
||||||||
| Losses on valuation |
(305,920 | ) | (260,306 | ) | ||||
| Losses on redemption |
(38,297 | ) | (49,795 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (344,217 | ) | (310,101 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 132,006 | 110,621 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (319,618 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Related with cash flow hedge,
the Bank recognized W123 million of gain in the statement of comprehensive income as the uneffective portion for the year ended December 31, 2015. No gain or loss were recognized as the uneffective portion for the year ended
December 31, 2014.
31. Net Foreign Currency Transaction Gain
Net foreign currency transaction gain for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Net gain (loss) on foreign exchange transactions: |
||||||||
| Gains on sales |
716,348 | |||||||
| Losses on sales |
(841,727 | ) | (604,495 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (56,776 | ) | 111,853 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net gain on foreign exchange translations: |
||||||||
| Gains on foreign exchange translations |
2,558,672 | 1,264,570 | ||||||
| Losses on foreign exchange translations |
(2,229,933 | ) | (991,754 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 328,739 | 272,816 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 384,669 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
96
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
32. Other Operating Income (Loss), net
Other operating income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Other operating income: |
||||||||
| Gains on sale of loans |
65,963 | |||||||
| Reversal of other provisions |
— | 117 | ||||||
| Gains on disposal of investments in subsidiaries and associates |
1,148 | 5,671 | ||||||
| Reversal of provisions |
6,963 | 314,620 | ||||||
| Others |
101,053 | 6,431 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 212,673 | 392,802 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Other operating expenses: |
||||||||
| Losses on sale of loans |
(302,034 | ) | (76,258 | ) | ||||
| Contribution to provision for other assets |
(3,526 | ) | (2,533 | ) | ||||
| Losses on disposal of investments in subsidiaries and associates |
(19,582 | ) | (832 | ) | ||||
| Provision for other allowances |
(404,949 | ) | (46,389 | ) | ||||
| Insurance expenses |
(58,808 | ) | (59,540 | ) | ||||
| Credit guarantee fund salary |
(131,137 | ) | (119,790 | ) | ||||
| Educational taxes |
(43,183 | ) | (36,384 | ) | ||||
| Foreign security contributions |
(17,509 | ) | (18,049 | ) | ||||
| Others |
(20,180 | ) | (18,799 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1,000,908 | ) | (378,574 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 14,228 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
97
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
33. General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Payroll costs: |
||||||||
| Short-term employee benefits |
271,293 | |||||||
| Defined benefit costs |
37,363 | 34,705 | ||||||
| Defined contribution costs |
1,462 | 472 | ||||||
| Termination benefits |
— | 4,258 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 356,413 | 310,728 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Depreciation and amortization: |
||||||||
| Depreciation of property and equipment |
33,694 | 26,547 | ||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
29,885 | 24,671 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 63,579 | 51,218 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Other: |
||||||||
| Employee welfare benefits |
26,258 | 23,725 | ||||||
| Rent expenses |
27,115 | 24,165 | ||||||
| Taxes and dues |
22,310 | 18,696 | ||||||
| Advertising expenses |
18,996 | 17,859 | ||||||
| Electronic data processing expenses |
57,119 | 49,416 | ||||||
| Fees and charges |
28,063 | 24,285 | ||||||
| Others |
44,144 | 36,708 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 224,005 | 194,854 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 556,800 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
98
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
34. Non-Operating Income and Expense
Non-operating income and expense for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Non-operating income: |
||||||||
| Gain on disposal of property and equipment |
8,494 | |||||||
| Rental income on investment property |
1,248 | 1,235 | ||||||
| Others |
4,304 | 4,087 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,630 | 13,816 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Non-operatingexpenses: |
||||||||
| Losses on disposal of property and equipment |
(92 | ) | (87 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation of investment property |
(1,507 | ) | (1,559 | ) | ||||
| Impairment losses on intangible assets |
(11 | ) | (738 | ) | ||||
| Donations |
(8,947 | ) | (7,868 | ) | ||||
| Others |
(1,683 | ) | (356 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (12,240 | ) | (10,608 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 3,208 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
35. Income Tax Expense (Benefit)
| (1) | Income tax expenses (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Current income tax (*1) |
332,489 | |||||||
| Changes in deferred income taxes on temporary differences |
(463,670 | ) | (268,965 | ) | ||||
| Deferred income tax recognized directly to equity |
79,568 | (30,182 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
33,342 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (*1) | Includes changes such as those that arise from final tax returns |
| (2) | Profit (loss) before income taxes and income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Profit (loss) before income taxes |
216,811 | |||||||
| Income taxes calculated using enacted tax rates (24.2%) |
(571,312 | ) | 52,468 | |||||
| Adjustments: |
||||||||
| Non-deductible losses and tax free gains |
(7,240 | ) | 10,023 | |||||
| Non-recognition effect of deferred income taxes |
150,290 | (2,428 | ) | |||||
| Tax credit |
— | (14,965 | ) | |||||
| Net adjustments for prior year |
(39,107 | ) | (24,767 | ) | ||||
| Others |
1,711 | 13,011 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 105,654 | (19,126 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
33,342 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Effective tax rate |
19.72 | % | 15.38 | % | ||||
99
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
35. Income Tax Expense (Benefit), Continued
| (3) | Changes in temporary differences and deferred tax assets (liabilities) for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015(*1) |
Decrease | Increase | December 31, 2015 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative |
(149,023 | ) | (222,474 | ) | (222,474 | ) | (53,839 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
(12,131,939 | ) | 2,346 | 664,361 | (11,469,924 | ) | (2,756,990 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Gains on fair value hedged items valuation |
(483,771 | ) | (483,771 | ) | (284,952 | ) | (284,952 | ) | (68,958 | ) | ||||||||||
| Losses on foreign exchange translation for hedged liabilities |
845,527 | 845,527 | 618,458 | 618,458 | 149,667 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses on investment bonds |
283,129 | 28,035 | 123,300 | 378,394 | 91,571 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses on investment securities |
1,546,799 | 616,119 | 108,815 | 1,039,495 | 251,558 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for employee retirement benefits |
179,992 | 13,542 | 85,317 | 251,767 | 60,927 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits for severance insurance |
(167,145 | ) | (13,542 | ) | (75,901 | ) | (229,504 | ) | (55,540 | ) | ||||||||||
| Held-for-trading securities |
(70,457 | ) | (9,307 | ) | (1,592 | ) | (62,742 | ) | (15,184 | ) | ||||||||||
| Available-for-sale bonds |
(149,965 | ) | — | — | (149,965 | ) | (36,291 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Bad debt charge |
1,823,176 | 65,470 | 131,943 | 1,889,649 | 457,295 | |||||||||||||||
| Other provisions |
(183,001 | ) | 323,700 | 669,280 | 162,579 | 39,344 | ||||||||||||||
| Property impairment losses |
7,494 | 172 | — | 7,322 | 1,772 | |||||||||||||||
| Accrued dividends |
1,710 | — | — | 1,710 | 414 | |||||||||||||||
| Loan origination fees |
(12,426 | ) | (12,426 | ) | (7,470 | ) | (7,470 | ) | (1,808 | ) | ||||||||||
| Gains on sales of loans |
(471,646 | ) | (422,284 | ) | 14,273 | (35,089 | ) | (8,491 | ) | |||||||||||
| Others |
220,477 | 272,863 | 1,825,597 | 1,773,211 | 429,117 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (8,911,069 | ) | 1,077,421 | 3,648,955 | (6,339,535 | ) | (1,515,436 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Temporary differences from unrecognized deferred tax assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
90,016 | 5,630 | 480,004 | 564,390 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,083,051 | 4,128,959 | (5,775,145 | ) | (1,515,436 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (*1) | Deferred income taxes as of January 1, 2015 reflected previous year’s additional tax adjustment after the financial statements were issued. |
100
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
35. Income Tax Expense (Benefit), Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014(*1) |
Decrease | Increase | December 31, 2014 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivative |
(455,982 | ) | (140,271 | ) | (140,271 | ) | (33,946 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
71,691 | — | (12,170,522 | ) | (12,098,831 | ) | (2,777,795 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Gains on fair value hedged items valuation |
(233,536 | ) | (233,536 | ) | (483,771 | ) | (483,771 | ) | (117,073 | ) | ||||||||||
| Losses on foreign exchange translation for hedged liabilities |
244,343 | 244,343 | 845,527 | 845,527 | 204,617 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses on investment bonds |
413,928 | 105,239 | 45,000 | 353,689 | 85,593 | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment losses on investment securities |
1,326,779 | 92,727 | 407,052 | 1,641,104 | 397,147 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for employee retirement benefits |
173,188 | 9,150 | 15,953 | 179,991 | 43,548 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits for severance insurance |
(178,119 | ) | (9,015 | ) | (733 | ) | (169,837 | ) | (41,101 | ) | ||||||||||
| Held-for-trading securities |
1,786 | 2,125 | (70,118 | ) | (70,457 | ) | (17,051 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale bonds |
(151,197 | ) | (380 | ) | — | (150,817 | ) | (36,498 | ) | |||||||||||
| Bad debt charge |
711,947 | 117,193 | 1,321,636 | 1,916,390 | 463,766 | |||||||||||||||
| Other provisions |
447,494 | 549,692 | 322,983 | 220,785 | 53,430 | |||||||||||||||
| Property impairment losses |
7,667 | 173 | — | 7,494 | 1,814 | |||||||||||||||
| Accrued dividends |
226,174 | 213,771 | — | 12,403 | 3,002 | |||||||||||||||
| Loan origination cost (fees) |
(13,703 | ) | (13,703 | ) | 52,551 | 52,551 | 12,717 | |||||||||||||
| Gains on sales of loans |
(494,490 | ) | (18,551 | ) | 3,135 | (472,804 | ) | (114,418 | ) | |||||||||||
| Others |
(173,256 | ) | 132,277 | (136,035 | ) | (441,568 | ) | (106,858 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,924,714 | 735,523 | (9,987,613 | ) | (8,798,422 | ) | (1,979,106 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Temporary differences from unrecognized deferred tax assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
318,779 | 114,838 | 105,695 | 309,636 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 850,361 | (9,881,918 | ) | (8,488,786 | ) | (1,979,106 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (*1) | Deferred income taxes as of January 1, 2014 reflected previous year’s additional tax adjustment after the financial statements were issued. |
101
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
35. Income Tax Expense (Benefit), Continued
| (4) | Changes in deferred income taxes recognized directly to equity for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
December 31, 2014 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
Changes in deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
||||||||||||||||
| Gains on valuation of available-for-sale financial assets |
(183,898 | ) | 815,600 | (260,384 | ) | 76,486 | ||||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
(330 | ) | 107 | (28,365 | ) | 9,056 | (8,949 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Losses on valuation of cash flow hedge |
(17,902 | ) | 5,714 | (13,866 | ) | 4,427 | 1,287 | |||||||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
11,400 | (3,640 | ) | 45,053 | (14,384 | ) | 10,744 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (181,717 | ) | 818,422 | (261,285 | ) | 79,568 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
December 31, 2013 |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
Changes in deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
||||||||||||||||
| Gains on valuation of available-for-sale financial assets |
(260,384 | ) | 361,931 | (115,532 | ) | (144,852 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Exchange differences on translation of foreign operations |
(28,365 | ) | 9,056 | (49,667 | ) | 15,856 | (6,800 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Losses on valuation of cash flow hedge |
(13,866 | ) | 4,427 | — | — | 4,427 | ||||||||||||||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
45,053 | (14,384 | ) | 20,209 | (6,452 | ) | (7,932 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (261,285 | ) | 332,473 | (106,128 | ) | (155,157 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
102
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
36. Earnings (Loss) per Share
(1) Basic earnings (loss) per share
The Bank’s basic earnings (loss) per share for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are computed as follows:
(i) Basic earnings (loss) per share
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Profit (loss) attributable to ordinary shareholders of the Bank (A) |
183,468,922,858 | |||||||
| Weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding (B) |
3,342,071,549 | 1,859,056,365 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per share (A/B) |
99 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
(ii) Weighted-average number of shares of ordinary shares outstanding
| 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Number of ordinary shares |
Days | Cumulative shares |
||||||||||
| Number of ordinary shares outstanding (A) |
3,036,079,768 | 365 | 1,108,169,115,320 | |||||||||
| Increased paid-in capital (B) |
400,000,000 | 275 | 110,000,000,000 | |||||||||
| Increased paid-in capital (C) |
8,000,000 | 176 | 1,408,000,000 | |||||||||
| Increased paid-in capital (D) |
3,000,000 | 93 | 279,000,000 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Cumulative shares (E=A+B+C+D) |
1,219,856,115,320 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding (E/365) |
3,342,071,549 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Number of ordinary shares |
Days | Cumulative shares |
||||||||||
| Number of ordinary shares outstanding (A) |
1,852,372,235 | 364 | 674,263,493,540 | |||||||||
| Increased paid-in capital (B) |
4,000,000 | 314 | 1,256,000,000 | |||||||||
| Retirement and issuance of shares (C) |
3,036,079,768 | 1 | 3,036,079,768 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Cumulative shares (D=A+B+C) |
678,555,573,308 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding (D/365) |
1,859,056,365 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
(2) Diluted earnings (loss) per share
Diluted and basic earnings (loss) per share for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are equal because there is no potential dilutive instrument.
103
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
37. Pledged Assets
Assets pledged by the Bank as collateral as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Pledged assets | Related liabilities | Pledged assets | Related liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets(*1) |
6,119,412 | 8,703,923 | 5,586,234 | |||||||||||||
| (*1) | Pledged as collateral related to bonds sold under repurchase agreements, borrowings, derivatives, and etc. |
38. Guarantees and Commitments
Guarantees and commitments as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||
| Confirmed acceptances and guarantees: |
||||||||
| Acceptances in foreign currency |
760,550 | |||||||
| Guarantees for bond issuance |
1,707,829 | 1,047,027 | ||||||
| Guarantees for loans |
1,234,382 | 1,075,100 | ||||||
| Acceptances for foreign loans |
607 | 1,056 | ||||||
| Guarantee of on-lending debt |
32,661 | 48,285 | ||||||
| Acceptances for letter of guarantee |
83,906 | 131,624 | ||||||
| Others |
6,130,706 | 5,223,067 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 9,964,029 | 8,286,709 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees: |
||||||||
| Letter of guarantee |
2,048,160 | 2,036,364 | ||||||
| Others |
4,329,573 | 1,811,300 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6,377,733 | 3,847,664 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments: |
||||||||
| Commitments on loans |
5,164,417 | 4,970,077 | ||||||
| Securities purchase agreement |
2,020,595 | 2,020,595 | ||||||
| Others |
189,800 | 151,601 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 7,374,812 | 7,142,273 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 19,276,646 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
104
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
39. Day One Profit or Loss
Changes in deferred day one profit or loss for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Opening balance |
(4,262 | ) | ||||||
| New deferrals |
2,330 | 1,370 | ||||||
| Recognized in current profit or loss |
478 | 2,397 | ||||||
| Others (end of transaction, etc.) |
(278 | ) | 472 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Closing balance |
(23 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Deferred day one profit or loss arose from derivative financial instruments at level 3 on the fair value hierarchy.
40. Trust Accounts
| (1) | Amounts recognized relating to trust accounts as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Accrued trust management fee |
18,447 | |||||||
| Deposits |
421,762 | 1,720,217 | ||||||
| Trust accounts payable |
1,160,613 | 542,857 | ||||||
| Accrued interest on deposits |
10,989 | 14,757 | ||||||
| (2) | Transactions with trust accounts for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Fees on trust accounts |
27,190 | |||||||
| Gains from trading of derivative instruments |
1,409 | 2,060 | ||||||
| Interest expenses on deposits |
(39,256 | ) | (45,343 | ) | ||||
| Interest expenses of trust accounts payable |
(14,060 | ) | (10,520 | ) | ||||
| (3) | Principals guaranteed money trust and principals and interest guaranteed money trust |
The carrying amounts of principals guaranteed money trust and principals and interest guaranteed money trust as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Principals guaranteed money trust |
279,246 | |||||||
| Principals and interest guaranteed money trust and non-guaranteed trust |
222,734 | 216,052 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 495,298 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Principal of money trust |
462,619 | |||||||
| Income from trust deposits payable |
33,884 | 32,679 | ||||||
105
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
41. Related Party Transactions
| (1) | The Bank’s related parties as of December 31, 2015 are as follows: |
| Classification |
Corporate name | |
| Subsidiaries |
KDB Asia Ltd., KDB Ireland Ltd., KDB Bank Uzbekistan, KDB Bank Europe Ltd., Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A, Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd., KDB Capital Corporation, KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd., KDB Infrastructure Investment Asset Management Co., Ltd., Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd., Korea Infrastructure Fund and 4 others, Principals guaranteed trust accounts of KDB, Principals and interests guaranteed interest trust accounts of KDB, KDB Venture M&A PEF, KDB Turn Around PEF, KDB Consus Value PEF, Components and Materials M&A PEF, KDB Value PEF VI, KDB Value PEF VII, KDB Sigma PEF, KDB Sigma PEF II and 2 others, KDBC IP Investment Fund 2, KoFC-KIS Pioneer Champ 2010-4 venture investment fund, Busan Hi - technology Industrial Complex Co., Ltd., K-Five 4th Securitization Specialty Co., Ltd. and 5 others, KIAMCO Road Investment Private Fund Special Asset Trust 2 and 42 others | |
| Associates |
Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd., Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd., Korea Tourism Organization, Korea Appraisal Board, Korea Maritime Guarantee Co., Ltd., GM Korea Company and 126 others, Korea Infrastructure Fund II, Troika Resources Investment PEF and 59 others, NPS 06-2 Neoplux Corporate Restructuring Fund and 76 others | |
| Others |
Key management personnel |
106
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| (2) | Significant balances with related parties as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Account |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Subsidiaries: |
||||||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Derivative financial assets | 118,964 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 2,273 | 5,089 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 5,571 | 35,711 | ||||||||
| Bonds | 1,331,886 | 790,584 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 89,902 | 96,481 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 5,396 | 4,434 | ||||||||
| KDB Capital Corporation(*1) |
Loans | 159,016 | — | |||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (47 | ) | — | |||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 6,939 | 5,030 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 19 | — | ||||||||
| Deposits | 4,709 | 25,295 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | — | 1,276 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 538 | 484 | ||||||||
| KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Deposits | 182 | 282 | |||||||
| KDB Infrastructure Investments Asset Management Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Deposits | 3,100 | 2,660 | |||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*2) |
Securities | 43,624 | — | |||||||
| Loans | 2,523,830 | 1,934,985 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (12,101 | ) | (1,465 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 235,699 | — | ||||||||
| Other assets | 2,650 | 476 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 472,400 | 14,194 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 1,961 | 36,876 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 575 | 40,340 | ||||||||
| Other provisions | 28,856 | — | ||||||||
| KDB Ireland Ltd. |
Loans | 320,797 | 268,111 | |||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (116 | ) | (87 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 3,774 | 5,122 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 329 | 393 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 116 | 222 | ||||||||
| KDB Bank Europe Ltd. |
Cash and due from banks | 474,007 | 321,476 | |||||||
| Loans | 11,720 | 10,992 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (13 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 907 | 5,196 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 1,093 | 1,009 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 5,649 | 256 | ||||||||
107
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| Account |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A. |
Cash and due from banks | — | ||||||||
| Loans | 117,200 | 54,960 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (42 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||
| Other assets | 290 | — | ||||||||
| KDB Asia Ltd. |
Cash and due from banks | 192,625 | 181,873 | |||||||
| Loans | 70,320 | 65,952 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (8 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 1,001 | 1,443 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 366 | 210 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 12 | 2 | ||||||||
| Borrowings | — | 19,786 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 25 | 35 | ||||||||
| KDB Value PEF VI |
Securities | 50,162 | 50,428 | |||||||
| Loans | 1,367,598 | 1,357,986 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (3,572 | ) | (3,208 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 38,740 | 17,994 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 26,918 | 28,248 | ||||||||
| Allowance of other assets | (67 | ) | (58 | ) | ||||||
| Deposits | 39,363 | 86,851 | ||||||||
| Borrowings | 5,762 | 7,057 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 41,555 | 27,889 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 144 | 1,680 | ||||||||
| Other provisions | 290 | 1 | ||||||||
| Others |
Securities | 229,680 | 354,946 | |||||||
| Loans | 208,405 | 122,205 | ||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | (1,782 | ) | (1,794 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 28,842 | 10,644 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 6,090 | 5,904 | ||||||||
| Allowance of other assets | (3 | ) | — | |||||||
| Deposits | 31,361 | 19,943 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 1,617 | 253 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 2,978 | 2,625 | ||||||||
| Other provisions | 1,550 | — | ||||||||
| Associates: |
||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd.(*3) |
Securities | 289,432 | 1,513,541 | |||||||
| Loans | 79,865 | 59,778 | ||||||||
| Allowances for loan losses | (34 | ) | — | |||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 2,233 | 4,723 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 309 | 4,837 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 68,406 | — | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 8,856 | 2,737 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 233 | 1 | ||||||||
108
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| Account |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd.(*3) |
Securities | — | 50,749 | |||||||
| Loans | 99,392 | 104,484 | ||||||||
| Allowances for loan losses | (53 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other assets | 415 | 201 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 390 | 1,924 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 256 | 159 | ||||||||
| Others |
Securities | 4,813 | 52,770 | |||||||
| Loans | 5,325,926 | 3,650,228 | ||||||||
| Allowances for loan losses | (2,152,018 | ) | (433,835 | ) | ||||||
| Derivative financial assets | 112,135 | 34,906 | ||||||||
| Other assets | 286 | 38 | ||||||||
| Deposits | 817,722 | 542,548 | ||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities | 3,906 | 50,028 | ||||||||
| Other liabilities | 269,196 | 329,520 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 12,107,542 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (*1) | The Bank’s merge with KoFC and KDBFG for the year ended December 31, 2014 has changed the entities from the companies under common control into the Bank’s subsidiaries. |
| (*2) | Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. was the Bank’s associate as of December 31, 2014 and has been included in the Bank’s subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2015. |
| (*3) | The entities were included into the Bank’s associates due to the Bank’s merge with KoFC and KDBFG for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
| (3) | Significant profit or loss with related parties for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Account | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| Subsidiaries: |
||||||||||
| Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Interest income | 261 | ||||||||
| Dividend income | 35,120 | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
111,917 | 174,254 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (16,287 | ) | (20,576 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (101,344 | ) | (157,796 | ) | ||||||
| KDB Capital Corporation(*1) |
Interest income | 895 | — | |||||||
| Dividend income | 30,317 | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
14,085 | 11,747 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | — | (37 | ) | |||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (19 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (3,385 | ) | (8,826 | ) | ||||||
109
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| Account | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| KDB Asset Management Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Dividend income | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
36 | — | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | — | (29 | ) | |||||||
| KDB Infrastructure Investments Asset Management Co., Ltd(*1) |
Dividend income | 4,208 | — | |||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
336 | — | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (25 | ) | (36 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (2 | ) | — | |||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*2) |
Interest income | 49,434 | 45,516 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 9,033 | 18,065 | ||||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
4,513 | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission | ||||||||||
| income, other income | 239,845 | 117,274 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (2,571 | ) | (1,079 | ) | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (17,907 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (36,350 | ) | (28,316 | ) | ||||||
| KDB Ireland Ltd. |
Interest income | 2,033 | 2,163 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 2,873 | 5,520 | ||||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
76 | 40 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission | ||||||||||
| income, other income | 190 | 149 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (134 | ) | (19 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (2,231 | ) | (2,241 | ) | ||||||
| KDB Bank Europe Ltd. |
Interest income | 4,284 | 4,536 | |||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
45 | 158 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission | ||||||||||
| income, other income | 4,751 | 5,733 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (44 | ) | (51 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (10,843 | ) | (2,263 | ) | ||||||
| Banco KDB Do Brazil S.A. |
Interest income | 794 | 2,470 | |||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
18 | 45 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission | ||||||||||
| income, other income | — | 2 | ||||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (24 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (5 | ) | 4 | |||||||
110
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| Account | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| KDB Asia Ltd. |
Interest income | 1,927 | ||||||||
| Dividend income | 8,655 | 11,040 | ||||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
97 | 100 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
1,562 | 1,376 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (91 | ) | (87 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (1,202 | ) | (1,793 | ) | ||||||
| KDB Value PEF VI |
Interest income | 56,817 | 58,313 | |||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
58,937 | 26,423 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (82 | ) | (791 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (28,845 | ) | (34,856 | ) | ||||||
| Others |
Interest income | 17,390 | 10,686 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 120,785 | 81,325 | ||||||||
| Reversal of allowance for loan losses |
11,558 | 15,970 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
49,598 | 25,395 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (525 | ) | (895 | ) | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (14,510 | ) | (7,604 | ) | ||||||
| Other operating expenses | (5,473 | ) | (2,410 | ) | ||||||
| Associates: |
||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd.(*3) |
Interest income | 21,218 | 60,607 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 96,087 | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
4,394 | 4,683 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (2,732 | ) | — | |||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (6 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (9,440 | ) | (2,746 | ) | ||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd.(*3) |
Interest income | 5,024 | 4,391 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 6,436 | — | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
2,614 | 462 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (33 | ) | (274 | ) | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (37 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (319 | ) | (164 | ) | ||||||
| Others |
Interest income | 274,845 | 103,687 | |||||||
| Dividend income | 176,090 | 10,271 | ||||||||
| Fees and commission income, other income |
268,298 | 255,506 | ||||||||
111
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| Account | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
| Interest expenses | (6,837 | ) | (3,152 | ) | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses | (1,629,340 | ) | — | |||||||
| Other operating expenses | (245,814 | ) | (810,608 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (26,554 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (*1) | The Bank’s merge with KoFC and KDBFG for the year ended December 31, 2014 has changed the entities from the companies under common control into the Bank’s subsidiaries. |
| (*2) | Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. was the Bank’s associate as of December 31, 2014 and has been included in the Bank’s subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2015. |
| (*3) | The entities were included into the Bank’s associates due to the Bank’s merge with KoFC and KDBFG for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
| (4) | Details of guarantees and commitments to the related parties as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Account |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||||
| Subsidiaries: |
||||||||||
| KDB Value VI PEF |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees |
181,119 | ||||||||
| Unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees |
67,156 | — | ||||||||
| Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd.(*1) |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees |
1,066,762 | 266,470 | |||||||
| Unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees |
2,473,623 | 409,321 | ||||||||
| Others |
Loan commitments |
520,000 | 523,900 | |||||||
| Associates: |
||||||||||
| Korea Electric Power Co., Ltd. |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees |
209,773 | 198,684 | |||||||
| Korea Aerospace Industries Co., Ltd. |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees |
540,169 | 297,474 | |||||||
| Unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees |
102,843 | — | ||||||||
| Others |
Confirmed acceptances and guarantees |
1,134,625 | 1,177,610 | |||||||
| Unconfirmed acceptances and guarantees |
867,998 | 715,541 | ||||||||
| Loan commitments |
250,111 | 19,200 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 3,789,319 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (*1) | Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co., Ltd. was the Bank’s associate as of December 31, 2014 and has been included in the Bank’s subsidiary for the year ended December 31, 2015. |
112
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
41. Related Party Transactions, Continued
| (5) | Details of compensation to key management personnel for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Short-term employee benefits |
4,853 | |||||||
| Post-employment benefits |
506 | 802 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 5,655 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (6) | Details of assets pledged as collaterals to the related parties as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
| Carrying amounts | Amounts collateralized |
Secured party | ||||||||
| Available-for-sale debt securities |
18,700 | Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd. | ||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||
| Carrying amounts | Amounts collateralized |
Secured party | ||||||||
| Available-for-sale debt securities |
16,000 | Daewoo Securities Co., Ltd. | ||||||||
| (7) | Details of assets pledged as collaterals from the related parties as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
| Carrying amounts | Amounts collateralized |
Secured party | ||||||||
| Securities denominated in foreign currencies |
78,055 | KDB Ireland Ltd. | ||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||
| Carrying amounts | Amounts collateralized |
Secured party | ||||||||
| Securities denominated in foreign currencies |
57,783 | KDB Ireland Ltd. | ||||||||
113
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
42. Statements of Cash Flows
| (1) | Cash and cash equivalents in the statements of cash flows as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Cash and due from banks: |
||||||||
| Cash and foreign currencies |
93,801 | |||||||
| Due from banks denominated in Korean won |
1,368,856 | 1,231,849 | ||||||
| Due from banks denominated in foreign currencies |
3,437,522 | 4,648,998 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 4,878,890 | 5,974,648 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Less: Restricted due from banks, others |
(2,897,554 | ) | (2,237,985 | ) | ||||
| Add: Financial instruments reaching maturity within three months from date of acquisition |
||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading: |
||||||||
| Government and public bonds |
110,513 | 50,224 | ||||||
| Loans: |
||||||||
| Call-loans |
2,676,162 | 4,933,613 | ||||||
| Inter-bank loans |
1,252,868 | 299,414 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 3,929,030 | 5,233,027 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 4,039,543 | 5,283,251 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
9,019,914 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (2) | Significant transactions not involving cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| Decrease in loans due to write-offs |
357,498 | |||||||
| Increase in available-for-sale financial assets due to debt-for-equity swap |
242,588 | 108,652 | ||||||
| Increase of available-for-sale financial assets due to the contribution from the government |
1,200,000 | — | ||||||
| Increase of investments in associates due to the contribution from the government |
876,511 | — | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accumulated other comprehensive income due to securities valuation |
(316,064 | ) | 64,363 | |||||
| Deferred income tax effect due to securities valuation |
76,486 | (15,586 | ) | |||||
| Reclassification of available-for-sale financial assets to investments in subsidiaries and associates |
42,653 | 26,823 | ||||||
| Reclassification of loans to the investments in subsidiaries and associates |
23,708 | — | ||||||
| Reclassification of investments in subsidiaries and associates to available-for-sale financial assets |
2,000 | 8,860 | ||||||
| Reclassification of investments in subsidiaries and associates to non-current assets held for sale |
1,839,114 | — | ||||||
| Transfer from investment property to property and equipment |
314 | 22,561 | ||||||
| Transfer from property and equipment to investment property |
3,103 | — | ||||||
| Consideration for merger with controlling entities |
— | 5,898,538 | ||||||
114
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
43. Transfers of Financial Instruments
Details of financial assets and liabilities related to repurchase agreements sold and loaned debt securities that do not qualify for derecognition as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
| Characteristics of transactions |
Carrying amounts for transferred assets |
Carrying amounts for related liabilities |
Carrying amounts for transferred assets |
Carrying amounts for related liabilities |
||||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements sold |
2,124,836 | 2,857,455 | 1,860,444 | |||||||||||||
| Loaned debt securities |
— | — | 10,205 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 2,124,836 | 2,867,660 | 1,860,444 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities
The Bank classifies and discloses fair value of the financial instruments into the following three-level hierarchy:
| • | Level 1: Financial instruments measured at quoted prices from active markets are classified as fair value level 1. |
| • | Level 2: Financial instruments measured using valuation techniques where all significant inputs are observable market data are classified as level 2. |
| • | Level 3: Financial instruments measured using valuation techniques where one or more significant inputs are not based on observable market data are classified as level 3. |
(1) Fair value hierarchy of financial instruments measured at fair value
| (i) | The fair value hierarchy of financial instruments measured at fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
703,261 | — | 1,780,734 | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
2,576,602 | 27,627,457 | 11,087,560 | 41,291,619 | ||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
37 | 5,683,843 | 73,876 | 5,757,756 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 34,014,561 | 11,161,436 | 48,830,109 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
1,619,439 | 3,179 | 1,622,618 | |||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
59 | 5,553,941 | 88,363 | 5,642,363 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 7,173,380 | 91,542 | 7,264,981 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
115
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
488,065 | — | 1,418,398 | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
1,926,084 | 26,978,409 | 9,255,532 | 38,160,025 | ||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
3 | 4,842,756 | 70,033 | 4,912,792 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 32,309,230 | 9,325,565 | 44,491,215 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
1,133,670 | 4,958 | 1,138,628 | |||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
5 | 4,744,243 | 44,906 | 4,789,154 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 5,877,913 | 49,864 | 5,927,782 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (ii) | Changes in the fair value of level 3 financial instruments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2015 |
Profit or loss |
Other comprehensive income |
Acquisition/ Issue |
Sale/ Settlement |
December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
(16,704 | ) | (73,520 | ) | 2,378,755 | (456,503 | ) | 11,087,560 | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
70,033 | (174,306 | ) | — | 244,718 | (66,569 | ) | 73,876 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (191,010 | ) | (73,520 | ) | 2,623,473 | (523,072 | ) | 11,161,436 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
691 | — | — | (2,470 | ) | 3,179 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
44,906 | (159,147 | ) | — | 208,704 | (6,100 | ) | 88,363 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (158,456 | ) | — | 208,704 | (8,570 | ) | 91,542 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
116
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 1, 2014 |
Profit or loss |
Other comprehensive income |
Acquisition/ Issue |
Sale/ Settlement |
Acquisition of parent company |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
(46,844 | ) | (143,983 | ) | 709,556 | (137,867 | ) | 7,025,817 | 9,255,532 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
83,989 | (50,893 | ) | — | 78,806 | (41,869 | ) | — | 70,033 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (97,737 | ) | (143,983 | ) | 788,362 | (179,736 | ) | 7,025,817 | 9,325,565 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
(2,379 | ) | — | 1,293 | (3,245 | ) | — | 4,958 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
23,723 | (73,592 | ) | — | 105,180 | (10,405 | ) | — | 44,906 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (75,971 | ) | — | 106,473 | (13,650 | ) | — | 49,864 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
117
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| (iii) | Details of valuation technique and inputs used in the fair value measurement categorized within level 2 of the fair value hierarchy of financial instruments measured at fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Valuation technique |
Input | |||
| Financial assets held for trading: |
||||
| Equity securities |
Net asset value approach | Underlying asset price | ||
| Debt securities |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||
| Equity securities |
Net asset value approach | Underlying asset price | ||
| Debt securities |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Derivatives financial assets: |
||||
| Interest rate swaps |
Discounted cash flow method, | Discount rate, | ||
| Currency forwards, swaps |
Black-Scholes model, | Exchange rate, | ||
| Currency options |
Modified Black model, | Volatility, | ||
| Commodities options |
Formula model | Commodity index | ||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL: |
||||
| Bonds |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| (iv) | Details of valuation technique and quantitative information about unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement categorized within level 3 of the fair value hierarchy of financial instruments measured at fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||
| Valuation technique |
Unobservable input |
Range (%) | ||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||
| Equity securities |
Discounted cash flow | Discount rate | 2.93 ~ 28.00 | |||
| method, | Growth rate | 0.00 | ||||
| Rate of increase in | ||||||
| liquidation value | 0.00 | |||||
| Rate of increase in | ||||||
| property disposal price | 1.80 | |||||
| Discount rate of | ||||||
| rent cash flow | 8.01 | |||||
| Volatility | 8.20 ~ 22.19 | |||||
| Derivatives financial assets: |
||||||
| Interest rate swaps |
Discounted cash flow | Volatility | 19.69 ~ 26.33 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | 0.02 ~ 0.97 | ||||
| Interest rate options |
Modified Black model | Volatility | 19.69 ~ 26.33 | |||
| Stock index options |
Black-Scholes model | Volatility | 15.36 ~ 87.44 | |||
| Equity options |
Finite difference | Volatility | 15.36 ~ 87.44 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | (-)0.02 ~ 0.70 | ||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL: |
||||||
| Borrowings |
Finite difference | Volatility | 15.36 ~ 87.44 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | (-)0.02 ~ 0.70 | ||||
118
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||
| Valuation technique |
Unobservable input |
Range (%) | ||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||
| Equity securities |
Discounted cash flow | Discount rate | 4.48 ~ 19.40 | |||
| method, | Growth rate | 0.00 | ||||
| risk- adjusted discount | Rate of increase in | |||||
| rate method, | liquidation value | 0.00 | ||||
| relative value approach. | Rate of increase in | |||||
| property disposal price | 2.00 | |||||
| Discount rate of | ||||||
| rent cash flow | 8.01 | |||||
| Derivatives financial assets: |
||||||
| Interest rate swaps |
Discounted cash flow | Volatility | 12.50 ~ 21.20 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | (-)0.63 ~ 0.94 | ||||
| Interest rate options |
Modified Black model | Volatility | 12.50 ~ 21.20 | |||
| Stock index options |
Black-Scholes model | Volatility | 19.00 ~ 57.00 | |||
| Equity options |
Finite difference | Volatility | 19.00 ~ 57.00 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | 0.10 ~ 0.48 | ||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL: |
||||||
| Borrowings |
Finite difference | Volatility | 19.00 ~ 57.00 | |||
| method | Correlation coefficient | 0.10 ~ 0.48 | ||||
| (v) | The sensitivity analysis on changes in unobservable inputs for financial instruments categorized within level 3 of the fair value hierarchy of financial instruments measured at fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 is as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Profit(loss) for the year | Comprehensive income(loss) | |||||||||||||||
| Favorable change |
Unfavorable change |
Favorable change |
Unfavorable change |
|||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets(*1) |
— | 1,178,299 | (331,081 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Derivatives financial instruments(*2) |
4,479 | (7,775 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL(*2) |
57 | (71 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (7,846 | ) | 1,178,299 | (331,081 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Profit(loss) for the year | Comprehensive income(loss) | |||||||||||||||
| Favorable change |
Unfavorable change |
Favorable change |
Unfavorable change |
|||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets(*1) |
— | 1,640,978 | (389,774 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Derivatives financial instruments(*2) |
10,786 | (10,968 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL(*2) |
71 | (76 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (11,044 | ) | 1,640,978 | (389,774 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (*1) | Sensitivity amounts of equity securities are calculated by increasing and decreasing the correlations between the discount rates(-1~1%) and the growth rates(0~1%) or the rate of increase in liquidation value(-1~1%) which are significant unobservable inputs. Sensitivity amounts for beneficiary certificates are calculated by |
119
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| increasing and decreasing the correlations between the discount rate of rent cash flow(-1~1%) and the rate of increase in property disposal price(-1~1%), only when they consist of real properties. Other than that, it is difficult to measure the sensitivity amounts of beneficiary certificates for practical reasons. |
| (*2) | Sensitivity amounts of derivatives financial instruments and financial liabilities designated at FVTPL are calculated by increasing and decreasing the correlation coefficient and volatility(-10~10%) which are significant unobservable inputs. |
| (2) | Fair value hierarchy of financial instruments disclosed by fair value |
| (i) | The fair value hierarchy of financial instruments disclosed by fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks(*1) |
2,897,442 | — | 4,878,778 | |||||||||||||
| Loans(*1) |
— | 2,676,162 | 138,057,318 | 140,733,480 | ||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
5,473 | 23,647 | — | 29,120 | ||||||||||||
| Other financial assets(*1) |
— | 5,213,745 | 750,890 | 5,964,635 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 10,810,996 | 138,808,208 | 151,606,013 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Deposits(*1) |
1,295,733 | 38,681,114 | 39,976,847 | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings(*1) |
— | 2,557,451 | 21,961,522 | 24,518,973 | ||||||||||||
| Bonds |
— | 117,035,204 | — | 117,035,204 | ||||||||||||
| Other financial liabilities(*1) |
— | 5,066,290 | 3,128,692 | 8,194,982 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 125,954,678 | 63,771,328 | 189,726,006 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks(*1) |
2,237,880 | — | 5,974,543 | |||||||||||||
| Loans(*1) |
— | 4,933,613 | 131,592,753 | 136,526,366 | ||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
6,850 | 11,339 | — | 18,189 | ||||||||||||
| Other financial assets(*1) |
— | 3,215,399 | 2,207,563 | 5,422,962 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 10,398,231 | 133,800,316 | 147,942,060 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Deposits(*1) |
1,041,922 | 36,615,629 | 37,657,551 | |||||||||||||
| Borrowings(*1) |
— | 2,085,951 | 21,531,411 | 23,617,362 | ||||||||||||
| Bonds |
— | 118,703,326 | — | 118,703,326 | ||||||||||||
| Other financial liabilities(*1) |
— | 3,072,936 | 2,847,833 | 5,920,769 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 124,904,135 | 60,994,873 | 185,899,008 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (*1) | For financial instruments categorized as level 2, the carrying amount is considered a reasonable approximation of the fair value and is thus, disclosed as the fair value. |
120
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
44. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| (ii) | Details of valuation technique and inputs used in the fair value measurement categorized within level 2 and 3 of the fair value hierarchy of financial instruments disclosed by fair value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Valuation technique |
Input | |||
| Level 2 |
||||
| Financial assets: |
||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||
| Bonds |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Level 3 |
||||
| Financial assets: |
||||
| Loans |
Discounted cash flow method | Credit spread, Other spread, Prepayment rate | ||
| Other financial assets |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||
| Deposits |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread, | ||
| Prepayment rate | ||||
| Borrowings |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
| Other financial liabilities |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||
| Valuation technique |
Input | |||
| Level 2 |
||||
| Financial assets: |
||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||
| Bonds |
Discounted cash flow method | Discount rate | ||
| Level 3 |
||||
| Financial assets: |
||||
| Loans |
Discounted cash flow method | Credit spread, Other spread, Prepayment rate | ||
| Other financial assets |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||
| Deposits |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread, | ||
| Prepayment rate | ||||
| Borrowings |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
| Other financial liabilities |
Discounted cash flow method | Other spread | ||
121
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
45. Categories of Financial Assets and Liabilities
Categories of financial assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
Financial instruments held for trading |
Financial instruments designated at FVTPL |
Available- for-sale financial instruments |
Held-to- maturity financial instruments |
Loan and receivables |
Financial liabilities measured at amortized cost |
Hedging purpose derivative instruments |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
— | — | — | — | 2,897,442 | — | — | 4,878,778 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
110,513 | 1,670,221 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,780,734 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
— | — | — | 41,291,619 | — | — | — | — | 41,291,619 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
— | — | — | — | 28,560 | — | — | — | 28,560 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
3,929,030 | — | — | — | — | 132,860,619 | — | — | 136,789,649 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
— | 4,981,506 | — | — | — | — | — | 776,250 | 5,757,756 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other financial assets |
— | — | — | — | — | 5,956,547 | — | — | 5,956,547 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 6,651,727 | — | 41,291,619 | 28,560 | 141,714,608 | — | 776,250 | 196,483,643 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
— | 1,622,618 | — | — | — | — | — | 1,622,618 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 39,934,892 | — | 39,934,892 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 24,400,590 | — | 24,400,590 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 116,894,020 | — | 116,894,020 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
— | 4,688,497 | — | — | — | — | — | 953,866 | 5,642,363 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other financial liabilities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 8,194,931 | — | 8,194,931 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 4,688,497 | 1,622,618 | — | — | — | 189,424,433 | 953,866 | 196,689,414 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
122
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
45. Categories of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
Financial instruments held for trading |
Financial instruments designated at FVTPL |
Available- for-sale financial instruments |
Held-to- maturity financial instruments |
Loan and receivables |
Financial liabilities measured at amortized cost |
Hedging purpose derivative instruments |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
— | — | — | — | 2,237,880 | — | — | 5,974,543 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
50,224 | 1,368,174 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,418,398 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
— | — | — | 38,160,025 | — | — | — | — | 38,160,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
— | — | — | — | 17,238 | — | — | — | 17,238 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
5,233,027 | — | — | — | — | 129,081,439 | — | — | 134,314,466 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
— | 4,050,185 | — | — | — | — | — | 862,607 | 4,912,792 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other financial assets |
— | — | — | — | — | 5,421,457 | — | — | 5,421,457 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 5,418,359 | — | 38,160,025 | 17,238 | 136,740,776 | — | 862,607 | 190,218,919 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
— | 1,138,628 | — | — | — | — | — | 1,138,628 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 37,605,714 | — | 37,605,714 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 23,537,531 | — | 23,537,531 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 116,569,796 | — | 116,569,796 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
— | 3,884,084 | — | — | — | — | — | 905,070 | 4,789,154 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other financial liabilities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,920,686 | — | 5,920,686 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 3,884,084 | 1,138,628 | — | — | — | 183,633,727 | 905,070 | 189,561,509 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
123
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
46. Offsetting of Financial Assets and Liabilities
Details of financial instruments subject to offsetting, enforceable master netting agreements or similar agreements as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts of recognized financial asset |
Gross amounts of recognized financial liabilities set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts of financial assets presented in the statement of financial position |
Related amounts not set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial instruments |
Cash collateral received |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets(*1) |
— | 5,757,756 | 3,469,468 | — | 2,288,288 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Receivable spot exchange(*1) |
4,647,121 | — | 4,647,121 | 4,480,782 | — | 166,339 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unsettled domestic exchange receivables |
1,975,610 | 1,408,986 | 566,624 | — | — | 566,624 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Security deposits for repurchase agreements sold |
2,948,186 | — | 2,948,186 | 2,124,836 | — | 823,350 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements bought |
434,854 | — | 434,854 | 434,854 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Receivables from securities transaction |
34,008 | — | 34,008 | 34,008 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,408,986 | 14,388,549 | 10,543,948 | — | 3,844,601 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts of recognized financial liabilities |
Gross amounts of recognized financial assets set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts of financial liabilities presented in the statement of financial position |
Related amounts not set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial instruments |
Cash collateral received |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities(*1) |
— | 5,642,363 | 4,038,156 | — | 1,604,207 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding spot exchange(*1) |
4,647,945 | — | 4,647,945 | 4,480,782 | — | 167,163 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unsettled domestic exchange payables |
1,827,331 | 1,408,986 | 418,345 | — | — | 418,345 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements sold |
2,124,836 | — | 2,124,836 | 2,124,836 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Payables from securities transaction |
30,356 | — | 30,356 | 30,356 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,408,986 | 12,863,845 | 10,674,130 | — | 2,189,715 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
124
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
46. Offsetting of Financial Assets and Liabilities, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts of recognized financial asset |
Gross amounts of recognized financial liabilities set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts of financial assets presented in the statement of financial position |
Related amounts not set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial instruments |
Cash collateral received |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets(*1) |
— | 4,912,792 | 3,411,752 | 41,758 | 1,459,282 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Receivable spot exchange(*1) |
2,611,319 | — | 2,611,319 | 2,575,345 | — | 35,974 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Domestic exchange receivables |
1,723,326 | 1,119,246 | 604,080 | — | — | 604,080 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Security deposits for repurchase agreements sold |
2,857,455 | — | 2,857,455 | 1,860,444 | — | 997,011 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements bought |
299,451 | — | 299,451 | 299,451 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loaned debt securities |
10,205 | — | 10,205 | 10,205 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Receivables from securities transaction |
13,046 | — | 13,046 | 13,046 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,119,246 | 11,308,348 | 8,170,243 | 41,758 | 3,096,347 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross amounts of recognized financial liabilities |
Gross amounts of recognized financial assets set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts of financial liabilities presented in the statement of financial position |
Related amounts not set off in the statement of financial position |
Net amounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial instruments |
Cash collateral received |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities(*1) |
— | 4,789,154 | 3,628,140 | — | 1,161,014 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding spot exchange(*1) |
2,610,986 | — | 2,610,986 | 2,575,345 | — | 35,641 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unsettled domestic exchange payables |
1,581,196 | 1,119,246 | 461,950 | — | — | 461,950 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements sold |
1,860,444 | — | 1,860,444 | 1,860,444 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Payables from securities transaction |
566 | — | 566 | 566 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,119,246 | 9,723,100 | 8,064,495 | — | 1,658,605 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (*1) | For the derivatives covered by the ISDA derivative contracts, all contracts are settled and the net amount of derivative contracts is measured and paid based on the liquidation value if the counterparty files for bankruptcy or has any credit issues. |
125
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
47. Operating Segments
| (1) | The Bank has four reportable segments, as described below, which are the Bank’s strategic business units. The following summary describes the operations in each of the Bank’s reportable segments: |
| Industry |
General information | |
| Corporate finance |
Provides trading services, and loans to corporate customers | |
| Investment finance |
Provides consulting services to corporate such as capital finance, restructuring, etc. | |
| Asset management |
Provides asset management services to individual and corporate customers | |
| Others |
Any other segment not mentioned above |
| (2) | Operating income (loss) from external customers and among operating segments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate finance |
Investment finance |
Asset management |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) from external customers |
(1,691,659 | ) | 41,028 | 720,485 | (1,219,254 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) from intersegment sales |
(7,434 | ) | 484,402 | — | (476,968 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1,207,257 | ) | 41,028 | 243,517 | (1,219,254 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate finance |
Investment finance |
Asset management |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) from external customers |
(566,121 | ) | 21,047 | 584,028 | 424,689 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) from intersegment sales |
34,823 | 204,807 | — | (239,630 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (361,314 | ) | 21,047 | 344,398 | 424,689 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (*1) | Others contains treasury department, other miscellaneous segments, and reconciling items. |
| (3) | Details of segment results for the Bank’s reportable segments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate finance |
Investment finance |
Asset management |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
150,285 | 9,426 | 235,675 | 1,578,219 | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest income (loss), net |
593,920 | 526,572 | 41,435 | (83,258 | ) | 1,078,669 | ||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) related to securities(*1) |
(75,572 | ) | 182,139 | — | 107,058 | 213,625 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,701,181 | 858,996 | 50,861 | 259,475 | 2,870,513 | ||||||||||||||||
| General administrative expenses |
(531,863 | ) | (87,771 | ) | (9,833 | ) | (14,530 | ) | (643,997 | ) | ||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses and others(*2) |
(1,465,860 | ) | (1,978,482 | ) | — | (1,428 | ) | (3,445,770 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
(1,207,257 | ) | 41,028 | 243,517 | (1,219,254 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
126
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
47. Operating Segments, Continued
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate finance |
Investment finance |
Asset management |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income (expense) |
(5,200 | ) | 5,029 | 522,875 | 1,988,494 | |||||||||||||||
| Non-interest income (loss), net |
305,883 | 166,629 | 26,768 | (143,740 | ) | 355,540 | ||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) related to securities(*1) |
125,889 | (157,909 | ) | — | 79,589 | 47,569 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,897,562 | 3,520 | 31,797 | 458,724 | 2,391,603 | ||||||||||||||||
| General administrative expenses |
(354,526 | ) | (88,256 | ) | (10,750 | ) | (103,268 | ) | (556,800 | ) | ||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses and others(*2) |
(1,122,478 | ) | (276,578 | ) | — | (11,058 | ) | (1,410,114 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
(361,314 | ) | 21,047 | 344,398 | 424,689 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (*1) | Income related to securities is composed of losses (gains) related to financial assets held for trading and available-for-sale financial assets. |
| (*2) | Provision for loan losses and others comprises of provision for loan losses, provision for derivative credit risks, losses (gains) on sales of loans, and provision for other losses. |
| (4) | Geographical revenue information about the Bank’s operating segments for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the geographical non-current asset information as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows: |
| Revenues(*1) | Non-current assets(*2) | |||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | December 31, 2015 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||||||
| Domestic |
13,923,968 | 25,901,145 | 27,556,072 | |||||||||||||
| Overseas |
676,710 | 882,970 | 4,718 | 3,887 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 14,806,938 | 25,905,863 | 27,559,959 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (*1) | Revenues consist of interest income, fees and commission income, income related to securities, foreign currency transaction gain, gain on derivative, other operating income and provision for loan losses. |
| (*2) | Non-current assets consist of investments in subsidiaries and associates, property and equipments, investment properties, intangible assets, and non-current assets held for sale. |
127
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
48. Merger with Controlling Entities
(1) General Information
The Bank merged with its controlling entities, KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation, in accordance with the Korean Development Bank Act as of December 31, 2014. Through the merger, KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation become predecessor entities, and the Bank, the sole existing entity after the merger. Progress of the merger is as follows:
| • | October 7, 2014, Merger agreement approved and agreed by board of directors (*1) |
| • | October 17, 2014, Merger agreement signed |
| • | October 29, 2014, Merger plans approved by the Financial Service Commission |
| • | December 31, 2014, Announcement of merger during the general meeting of shareholders, merger registration |
| (*1) | The merger agreement approval during the general shareholders meeting is replaced with the agreement approved by the board of directors according to the Korean Development Bank Act. |
All of
the 1,856,372,235 shares(par value of W9,281,861 million, W5,000 per share) that were originally issued and 100% retained by KDB Financial Group Inc., were retired following the merger. The government of the
Republic of Korea, a shareholder of KDB Financial Group Inc. and Korea Finance Corporation, was issued new shares of 3,036,079,768 shares (par value of W15,180,399 million, W5,000 per share).
(2) Measurement of assets and liabilities
The business combination is a transaction under common control. Therefore the Bank recognizes the acquired assets and liabilities as carrying amounts in the consolidated financial statements of the ultimate parent company, KoFC, as of December 30, 2014. And the Bank reflects the difference between the consideration paid and the capital of the acquiree in the capital surplus.
128
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
48. Merger with Controlling Entities, Continued
(3) Amount of acquired assets and liabilities
The acquired assets and liabilities recognized as of December 31, 2014 are as follows:
| Classification |
Amounts | |||
| Assets |
||||
| Cash and due from banks |
||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
14,496,982 | |||
| Loans |
26,739,472 | |||
| Derivative financial assets |
254,739 | |||
| Investments in subsidiaries and associates |
21,884,099 | |||
| Property and equipment |
64,428 | |||
| Investment property |
18,064 | |||
| Intangible assets |
14,094 | |||
| Deferred tax assets |
650 | |||
| Other assets |
1,533,263 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| 68,141,533 | ||||
|
|
|
|||
| Liabilities |
||||
| Borrowings |
3,677,446 | |||
| Bonds |
52,077,882 | |||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
299,430 | |||
| Defined benefit liabilities |
11,224 | |||
| Provisions |
52,286 | |||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
2,838,223 | |||
| Other liabilities |
409,097 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| 59,365,588 | ||||
|
|
|
|||
| Equity |
||||
| Valuation gain on available-for-sale financial assets |
404,892 | |||
| Valuation loss on cash flow hedge |
(12,843 | ) | ||
| Remeasurements of defined benefit liabilities |
(598 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| 391,451 | ||||
|
|
|
|||
| The acquired assets, liabilities and equity |
||||
|
|
|
|||
| Consideration transferred in the acquisition |
5,898,538 | |||
| Registration tax |
7,309 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Other capital surplus |
||||
|
|
|
|||
129
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management
(1) Introduction
(i) Objectives and principles
The Bank’s risk management aims to maintain financial soundness and effectively manage various risks pertinent to the nature of the Bank’s business. The Bank has set up and fulfilled policies to manage risks timely and effectively. Pursuant to the policies, the Bank’s risks shall be
| • | managed comprehensively and independently, |
| • | recognized timely, evaluated exactly and managed effectively, |
| • | maintained to the extent that the risks balance with profit, |
| • | diversified appropriately to avoid concentration on specific segments, |
| • | managed to prevent excessive exposure by the setting up and managing of tolerance limits and guidelines. |
(ii) Risk management strategy and process
The Bank’s risk management business is separated into two different stages; the ‘metrification stage,’ in which risks are estimated and monitored, and the ‘integration stage,’ in which information gained during the risk management process is integrated and used in management strategies. Risk management is recognized as a key component of the Bank’s management, and seeks to change from its previously adaptive and limited role to more leading and comprehensive role.
Furthermore, the Bank focuses on consistent communication among different departments in order to establish a progressive consensus on risk management.
(iii) Risk management governance
Risk Management Committee
The Bank’s Risk Management Committee (the “Committee”) is composed of the President of the committee (an outside director), and seven other commissioners including the CEO of the Bank. The Committee functions to establish policies of risk management, evaluate the capital adequacy of the Bank, discuss material issues relating to risk management, and present preliminary decisions on such matters.
The CEO of the Bank and the head of Risk Management Department
The CEO of the Bank, according to the policies of risk management, performs his or her role to manage and direct risk management in order to sustain efficiency and internal control. The head of the Risk Management Department is responsible for supervising the overall administration of the Bank’s risk management business and providing risk-related information to members of the board of directors and the Bank’s management.
Risk Management Practice Committee
The Bank’s Risk Management Practice Committee is composed of the main leaders of business segments, and exercises its role to review matters for decision on allocation by segment of internal capital limits, within the scope that risk management committee regulated, and other material risk-related matters.
130
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management, Continued
(iv) Performance of risk management committee
The Risk Management Committee performs comprehensive reviews of all the affairs related to risk management and deliberates the decisions of the board of directors. For the year ended December 31, 2015 the key activities of the Risk Management Committee are as follows:
| • | Major decision |
| • | Changes in probability of default for BIS capital ratio |
| • | The management of the interest of the retirement pension product with guarantee of principal and interest |
| • | The management of BIS ratio management, and limit of internal capital for the year 2015 |
| • | The emergency financing plan for the year 2015 |
| • | Major reporting |
| • | Resolutions from the Credit Committee on the quarterly basis |
| • | Integrated crisis analysis on the semi-annually basis |
| • | Recent global financial trends and regulatory countermeasures |
| • | Allocation and management standards of internal capital limits for 2015 |
| • | The management plan for the risk from the financial subsidiaries |
| • | The plan for the improvement of the credit rating system |
| • | The plan of proceeding of the enterprise credit rating system |
| • | The result of the simulation of the Business continuity plan |
| • | Corporate credit ratings for 2015 |
| • | The plan for the improvement of exposure limit management system |
| • | The result of the credit rating system and post suitability verification for 2015 |
(v) Improvement of risk management system
For the continuous improvement of risk management, financial soundness and capital adequacy, the Bank performs the following:
| • | Continuous improvement of Basel |
| • | Improvements in the internal capital adequacy assessment system, in line with the guidelines set by the Financial Supervisory Service (“FSS”) in 2008, to manage capital adequacy more effectively |
| • | Improvements in the credit assessment system on Low Default Portfolio (“LDP”) |
| • | Elaboration of risk measuring criteria including credit risk parameters and measurement logics |
| • | Pre-operation of the Advanced Measurement Approach (“AMA”) since 2009, in arrangement with the FSS, to apply the risk management AMA |
131
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management, Continued
| • | Expansion of risk management infrastructure to the global IB level |
| • | Establishment of the RAPM system in order to reflect risks to the Bank’s business and support decision-making upon management, and application of performance assessment at the branch level since 2010 |
| • | Enforcement of risk management related to irregular compound derivatives and validation of the derivative pricing model developed by the Bank’s Front Office |
| • | Risk management of retail banking |
| • | On-going planning of asset expansion in the retail banking risk management operations sector of the department of risk management since the introduction of retail loan business in 2010 |
| • | Establishment and application of assessment and approval standards by retail loan instruments, and expansion of retail banking risk management infrastructure such as accumulating databases in order to support analytic decision-making and develop a personal credit assessment model through the establishment of a “retail banking Data Mart” |
(vi) Risk management reporting and measuring system
The Bank endeavours consistently to objectively and rationally measure and manage all significant risks considering the characteristics of operational areas, assets and risks. In relation to reporting and measurement, the Bank has developed application systems as follows:
| Application system | Approach | Completion date |
Major function | |||
| Corporate Credit Rating System |
Logit Model | Jun. 2004 Mar. 2008 Mar. 2010 Mar. 2012 | Calculate corporate credit rating Corporate credit rating system based on K-IFRS buildup | |||
| Credit Risk Measurement System |
Credit Risk+ Credit Metrics | Jul. 2003 Nov. 2007 | Summarize exposures, manage exposure limits and calculate Credit VaR | |||
| Market Risk Management System |
Risk Watch | Jun. 2002 | Summarize position, manage exposure limits and calculate Market VaR | |||
| Interest/Liquidity Risk Management System |
OFSA Fermat |
Feb. 2006 Mar. 2014 | Calculate repricing gap, duration gap, VaR and EaR | |||
| Operational Risk Management System |
Standardized Approach AMA | May. 2006 May. 2009 | Manage process and calculate CSA, KRI, OP and VaR Pre-operate the AMA | |||
| BIS capital ratio calculation system |
Fermat RaY |
Sep. 2006 Dec. 2013 | Calculation of equity and credit risk-weighted assets |
132
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management, Continued
(vii) Response to Basel
The Korean authority implemented Basel II as of January 2008, and adopted the Standardized Approach and the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach. The Advanced Approaches were adopted later in 2009.
In conformity with the implementation roadmap of Basel II, the Bank obtained the approval to use the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach on credit risk from the FSS in July 2008 and has applied the approach since late June 2008. The Bank applies the Standardized Approach on market risks and operational risks.
To establish credibility and maintain financial soundness, the Bank plans to adopt the Advanced Approaches (Credit risk: Advanced Internal Ratings-Based Approach, Operational risk: Advanced Measurement Approach etc) by continuously improving related systems and policies. Furthermore, the Bank completed the “Basel III standard risk management system” in preparation of the adoption of the Basel III regulations announced on December 1, 2013. Starting from 2013 year-end, the BIS capital adequacy ratio was measured in accordance to the Basel III regulations.
(viii) Internal capital adequacy assessment process
Internal capital adequacy assessment process is defined as the process that the Bank aggregates significant risks, calculates its internal capital, compares the internal capital with the available capital and assesses its internal capital adequacy.
| • | Internal capital adequacy assessment |
For the purpose of the internal capital adequacy assessment, the Bank calculates its aggregated internal capital and available capital by evaluating all significant risks and taking into account the quality and components of capital, and then assesses the internal capital adequacy by comparing the aggregated internal capital with the available capital.
| • | Goal setting of internal capital management |
The Bank sets up and manages an internal capital limit on an annual basis, through the approval of the Risk Management Committee, in order to maintain internal capital adequacy by managing internal capital (integrated risks) within the extent of available capital.
The prior year’s internal capital, analysis of domestic and foreign environment changes in the current year, and the direction and size of operations are all reflected in the goal setting of internal capital management to calculate the integrated internal capital scale. Moreover, Bank for International Settlements(“BIS”) capital adequacy ratio and risk appetite are taken into consideration in the goal setting of internal capital management.
| • | Allocation of internal capital |
The Bank’s entire internal capital is allocated to each headquarter and department, according to the extent of possible risk faced and size of operations, after the Risk Management Committee’s deliberation and the board of directors’ approval. The allocated internal capital is monitored regularly and managed using various management methods. The results of monitoring and managing the allocated internal capital are reported to the Risk Management Committee. In case of any material changes in the Bank’s business plan or risk operation strategy, the Bank adjusts the allocations elastically.
133
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management, Continued
| • | Composition of internal capital |
Internal capital comprises all the significant risks of the Bank and is composed of quantifiable and non-quantifiable risks. Quantifiable risks are composed of credit risk, market risk, interest rate risk, operational risk and credit concentration risk, foreign currency settlement risk, and are risks measured quantitatively by applying reasonable methodology using objective data. Non-quantifiable risks are composed of strategy risk, reputation risk, residual risk on asset securitization and furthermore. Non-quantifiable risks are those risks that cannot be measured quantitatively because of lack of data or the absence of appropriate measuring methodologies.
(2) Credit Risk
(i) Concept
Credit risk can be defined as potential loss resulting from the refusal to perform obligations or default of counterparties. More generally, it is used to refer to the possibility of economic loss from loans that are not fully paid off or are restructured on less beneficial terms.
(ii) Approach to credit risk management
Summary of credit risk management
The Bank regards credit risk as the most significant risk area in its business operations, and accordingly, closely monitors its credit risk exposure. The Bank manages both credit risks at portfolio level and at individual credit level. At portfolio level, the Bank reduces credit concentration and restructures the portfolio in such a way to maximize profitability considering the risk level. To avoid credit concentration on a particular sector, the Bank manages credit limits by client, group, and industry. The Bank also resets exposure management directives for each industry by conducting an industry credit evaluation twice a year.
At the individual credit level, the relationship manager (“RM”), the credit officer (“CO”) and the Credit Review Committee manage each borrower’s credit risk.
Post management and insolvent borrower management
The Bank monitors the borrower’s credit rating from the date of the loan to the date of the final collection of debt consistently, and inspects the borrower’s status regularly and frequently in order to prevent the generation of new bad debts and to stabilize the number of debt recoveries.
In addition, an early warning system is operated to spot borrowers that are highly likely to be insolvent. The early warning system provides financial information, financial transaction information, public information and market information of the borrower, and such information is used by the RM and the CO to monitor and manage changes in the borrower’s credit rating.
Under the early warning system, a borrower that is highly likely to be insolvent is classified as an early warning borrower or a precautionary borrower The Bank sets up a specific and applicable stabilization plan for such a borrower considering the borrower’s characteristics. Furthermore, sub-standard borrowers are classified as insolvent borrowers, and are managed intensively by the Bank, which takes legal proceedings, disposals or corporate turnaround measures if necessary.
134
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Classification of asset soundness and provision of allowance for loss
Classification of asset soundness is fulfilled by the analysis and assessment of credit risk. The classification is used in order to provision an appropriate allowance, prevent further occurrences of insolvent assets and promote the normalization of existing insolvent assets to enhance the stabilization of asset operations.
Based on the Financial Supervisory Regulations of the Republic of Korea, the Bank has established standards and guidelines on the classification of asset soundness, according to the Forward Looking Criteria (“FLC”), which reflects not only the borrower’s past records of repayment but also their future debt repayment capability.
In conformity with these standards, the Bank classifies the soundness of its assets as “normal”, “precautionary”, “substandard”, “doubtful”, or “estimated loss” and differentiates the coverage ratio by the level of classification.
Loans
Details of loans as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Neither past due nor impaired |
129,807,569 | |||||||
| Past due but not impaired |
402,789 | 128,759 | ||||||
| Impaired |
6,550,658 | 6,823,773 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 140,968,329 | 136,760,101 | |||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
(4,159,300 | ) | (2,398,658 | ) | ||||
| Present value discount |
(23,361 | ) | (55,418 | ) | ||||
| Deferred loan origination costs and fees |
3,981 | 8,441 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net value |
134,314,466 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Ratio of allowance for loan losses to total loans |
2.95 | % | 1.75 | % | ||||
Loans that are neither past due nor impaired
Loans that are neither past due nor impaired as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| AAA ~ B- (Normal) |
50,093,508 | 4,593,050 | 25,825,636 | 2,005,386 | 7,815,902 | 131,014,589 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCC (Precautionary) |
891,341 | 363,949 | — | 199,182 | 266,716 | 123,429 | 1,844,617 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| CC (Substandard) |
60,575 | 57,394 | — | 629,625 | 306,220 | 101,862 | 1,155,676 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| C (Doubtful) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| D (Estimated loss) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 50,514,851 | 4,593,050 | 26,654,443 | 2,578,322 | 8,041,193 | 134,014,882 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
135
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| AAA ~ B- (Normal) |
49,669,053 | 4,322,696 | 24,353,063 | 2,417,248 | 9,960,031 | 128,205,021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCC (Precautionary) |
673,429 | 300,685 | — | 177,311 | 34,668 | 294,278 | 1,480,371 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| CC (Substandard) |
31,866 | 9,362 | — | 218 | 56,932 | 23,799 | 122,177 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| C (Doubtful) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| D (Estimated loss) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 49,979,100 | 4,322,696 | 24,530,592 | 2,508,848 | 10,278,108 | 129,807,569 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Loans that are past due but not impaired
Loans that are past due but not impaired as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 30 days |
80,252 | 10,805 | 172,469 | 2,000 | 9,273 | 376,875 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 30 ~ 60 days |
6,478 | 11,920 | 1,019 | — | — | 212 | 19,629 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 60 ~ 90 days |
65 | 6,220 | — | — | — | — | 6,285 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 98,392 | 11,824 | 172,469 | 2,000 | 9,485 | 402,789 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 30 days |
59,255 | 2,876 | 39,598 | 1,450 | 574 | 125,302 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 30 ~ 60 days |
368 | 450 | 274 | — | — | — | 1,092 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 60 ~ 90 days |
— | 317 | 178 | — | 1,870 | — | 2,365 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 60,022 | 3,328 | 39,598 | 3,320 | 574 | 128,759 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
136
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Impaired loans
Impaired loans as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans
for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Impaired Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Individual |
1,164,279 | — | 50,476 | 578,674 | 854,150 | 6,306,521 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Collective |
96,906 | 25,499 | 4,770 | 85,769 | 5,804 | 25,389 | 244,137 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 1,189,778 | 4,770 | 136,245 | 584,478 | 879,539 | 6,550,658 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans in Korean won | Other loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans for working capital |
Loans for facility developments |
Others | Loans in foreign currencies |
Private placed corporate bonds |
Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Impaired Loans: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Individual |
1,498,110 | — | 114,604 | 533,207 | 668,579 | 6,609,015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Collective |
82,158 | 37,215 | 4,271 | 63,222 | 7,850 | 20,042 | 214,758 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 1,535,325 | 4,271 | 177,826 | 541,057 | 688,621 | 6,823,773 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
(iii) Measurement methodology of credit risk
Pursuant to Basel III, the Bank selects the measurement methodology of credit risk considering the complexity of measurement, measurement factors, estimating methods and others. Measurement approaches are divided into Standardized Approach and Internal Ratings-Based Approach.
Standardized Approach (“SA”)
In the case of the Standardized Approach, the risk weights are applied according to the credit rating assessed by External Credit Assessment Institution (“ECAI”). Risk weights in each credit rating are as follows:
| Credit rating (*1) |
Corporate | Country | Bank |
Asset securitization | ||||
| AAA ~ AA- |
20.00% | 0.00% | 20.00% | 20.00% | ||||
| A+ ~ A- |
50.00% | 20.00% | 50.00% | 50.00% | ||||
| BBB+ ~ BBB- |
100.00% | 50.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | ||||
| BB+ ~ BB- |
100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 350.00% | ||||
| B+ ~ B- |
150.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | Deducted from Equity (1,250%) | ||||
| Below B- |
150.00% | 150.00% | 150.00% | ” | ||||
| Unrated |
100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | ” |
| (*1) | Credit rating refer to those evaluated by global credit rating agencies such as S&P or Moody’s |
137
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
The OECD, S&P, Moody’s and Fitch are designated as foreign ECAI and Korea Investors Service Co., Ltd., NICE Investors Services Co., Ltd. and the Korea Ratings Co., Ltd. are designated as domestic ECAI.
The Bank applies the credit rating based on the corresponding loan and same borrower’s unsecured senior loans. In the case the borrower’s risk weight is higher than the unrated exposure’s risk weight (100%), the higher weight is applied. In the case the borrower has more than one rating, the higher weight of the two lowest weights (second best criteria) is applied.
Internal Ratings-Based Approach (“IRB”)
To use the Internal Ratings-Based Approach, a bank must be approved by the FSS and should also meet the requirement pre-set by the FSS.
In relation to Basel II that has been adopted domestically as of January 2008, the Bank gained approval from the FSS to use the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach in July 2008. The Bank has calculated credit risk-weighted assets using the approach since late June 2008.
Measurement method of credit risk-weighted asset
The Bank calculates credit risk-weighted assets of corporate exposures and asset securitization exposures using the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach as of December 31, 2015.
The Standardized Approach is applied to country exposures, public institution exposures and bank exposures according to the interpretation of the FSS permanently, and applied to overseas subsidiary and the Bank’s branch pursuant to prior consultation with the FSS.
The Standard Approach is applied to special finance, non-residents, non-banking financial institutions currently, and will be replaced by the Internal Ratings-Based Approach in the future.
| <Approved measurement method> | ||||
| Measurement method |
Exposure | |||
|
Standardized Approach |
Permanent | |||
| SA (*1) | —Countries, public institutions and banks | |||
| SA (*2) | —Overseas subsidiaries and branches, and other assets | |||
| Foundation Internal |
—Corporate and small and medium enterprises and asset securitization (at each credit level) | |||
| Application of IRB by phase |
—Special lending, non-residence, non-bank financial institutions | |||
| (*1) | Pursuant to the interpretation of the FSS, the Standardized Approach is applied to the exposures of governments, banks and other public institutions. |
| (*2) | The Standardized Approach is applied, pursuant to prior consultation with the FSS, in the case the credit risk-weighted assets of a specific business segment is less than 15% of the entire credit risk-weighted assets. |
The mitigated effect of credit risks reflects the related policies which consider eligible collateral and guarantees. The Bank calculates the credit risk-weighted assets using the capital adequacy ratio.
138
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Upon the calculation of credit risk-weighted assets for derivatives, the Bank takes into consideration the set-off effects of transactions under legally enforceable rights to set-off to calculate exposures.
Exposure less credit risk mitigation by asset type as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Exposure | Credit risk mitigation |
Exposure less credit risk mitigation |
||||||||||
| Government |
— | 17,272,360 | ||||||||||
| Bank |
17,462,101 | — | 17,462,101 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
139,519,518 | (434,529 | ) | 139,084,989 | ||||||||
| Stock |
29,508,512 | — | 29,508,512 | |||||||||
| Indirect investments |
4,499,295 | — | 4,499,295 | |||||||||
| Asset securitization |
4,848,090 | — | 4,848,090 | |||||||||
| Over-the-counter derivatives |
9,983,539 | (5,453,988 | ) | 4,529,551 | ||||||||
| Retail assets |
3,112,058 | (12,911 | ) | 3,099,147 | ||||||||
| Others |
64,012,739 | (1,432,694 | ) | 62,580,045 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (7,334,122 | ) | 282,884,090 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||
| Exposure | Credit risk mitigation |
Exposure less credit risk mitigation |
||||||||||
| Government |
— | 17,598,368 | ||||||||||
| Bank |
19,771,779 | — | 19,771,779 | |||||||||
| Corporate |
133,890,444 | (314,084 | ) | 133,576,360 | ||||||||
| Stock |
28,961,181 | — | 28,961,181 | |||||||||
| Indirect investments |
3,080,647 | — | 3,080,647 | |||||||||
| Asset securitization |
4,026,945 | — | 4,026,945 | |||||||||
| Over-the-counter derivatives |
8,331,185 | (4,932,238 | ) | 3,398,947 | ||||||||
| Retail assets |
3,289,945 | (54,860 | ) | 3,235,085 | ||||||||
| Others |
53,893,317 | (1,972,114 | ) | 51,921,203 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (7,273,296 | ) | 265,570,515 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The credit exposure is on a consolidated basis as required by the regulator and used internally for risk management purposes.
139
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Credit rating model
The results of credit rating are presented as grades through an assessment of the debt repayment capacity that the principal and interest of debt securities or loans are redeemed while complying with contractual redemption schedule.
Using the Bank’s internal credit rating model, the Bank classifies debtors’ credit rating into 10 grades (AAA~D). Plus sign (+) and minus sign (-) are attached to the grades (AA~B) to distinguish the difference between credits in the same grade. As a result, the Bank’s credit rating model uses 20 grades.
The Bank’s regular credit rating process is carried out once a year and in the case of the change of debtor’s credit condition, the credit rating is frequently adjusted as necessary to retain the adequacy of credit rating.
The results of credit rating is applied to various areas such as discrimination of loan processes, loan limit, loan interest rate, post loan management standard process, credit risk measurement, and allowance for loan losses assessment.
Credit process control structure
According to the Principle of Checks and Balances the Bank has established the credit process control structure by which the credit rating system operates appropriately.
| • | Independent assessment of credit rating: The Bank’s business segment (RM) and credit rating assessment segment (CO) are independently operated |
| • | Independent control of credit rating system: The control of credit rating system including the development of credit rating model is independently implemented by the Bank’s Risk Management Department. |
| • | Independent verification of credit rating system: Credit rating system is independently verified by the validation team of the Consulting Service Department. |
| • | Internal audit of credit rating process: Credit rating process is audited by the Bank’s internal audit department. |
| • | Role of the Board of Directors and the Bank’s management: Major issues relating to credit process are approved by the Board of Directors and are regularly monitored by the Bank’s top management. |
The Bank reviews debt serviceability based on a credit analysis when handling loans. Depending on the results, credit loan preservation is adjusted as necessary using such methods as interest rate preservation due to credit risk.
The Bank evaluates the value of the collateral, performing ability and legal validity of the guarantee at the initial acquisition. The Bank re-evaluates the provided collateral and guarantees regularly for them to be reasonably preserved.
For guarantees, the Bank demands a corresponding written guarantee according to loan handling standards and the guarantor’s credit rating is independently calculated when in conformance with the credit rating endowment method.
140
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
(iv) Credit exposure
Geographical information of credit exposure
Geographical information of credit exposure as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea | UK | USA | Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Due from banks (excluding due from BOK) |
86,846 | 142,298 | 1,063,360 | 3,438,418 | ||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
14,541,790 | 763,321 | 637,429 | 421,890 | 16,364,430 | |||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
— | — | — | 23,648 | 23,648 | |||||||||||||||
| Loans |
131,001,756 | 427,836 | 535,783 | 4,395,855 | 136,361,230 | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
774,500 | 1,579 | — | 1,617 | 777,696 | |||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
5,818,154 | 40,249 | 7,046 | 167,223 | 6,032,672 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 154,282,114 | 1,319,831 | 1,322,556 | 6,073,593 | 162,998,094 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Financial guarantees |
15,889,842 | — | 215,784 | 236,137 | 16,341,763 | |||||||||||||||
| Credit related commitment (Commitments on loans and others) |
6,773,318 | 24,584 | 225,105 | 351,804 | 7,374,811 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 22,663,160 | 24,584 | 440,889 | 587,941 | 23,716,574 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,344,415 | 1,763,445 | 6,661,534 | 186,714,668 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Korea | UK | USA | Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Due from banks (excluding due from BOK) |
121,938 | 261,916 | 1,002,566 | 4,753,686 | ||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
13,662,439 | 677,198 | 510,356 | 442,494 | 15,292,487 | |||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
— | — | — | 11,340 | 11,340 | |||||||||||||||
| Loans |
128,650,703 | 276,292 | 650,727 | 4,652,097 | 134,229,819 | |||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
863,183 | 1,474 | — | 191 | 864,848 | |||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
5,351,109 | 45,985 | 6,432 | 28,762 | 5,432,288 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 151,894,700 | 1,122,887 | 1,429,431 | 6,137,450 | 160,584,468 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Financial guarantees |
11,863,362 | — | 143,317 | 127,695 | 12,134,374 | |||||||||||||||
| Credit related commitment (Commitments on loans and others) |
6,485,046 | 111,516 | 199,731 | 345,980 | 7,142,273 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 18,348,408 | 111,516 | 343,048 | 473,675 | 19,276,647 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 1,234,403 | 1,772,479 | 6,611,125 | 179,861,115 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
141
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Industry information of credit exposure
Industry information of credit exposure as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing | Service | Others | Total | |||||||||||||
| Due from banks (excluding due from BOK) |
3,026,198 | 412,220 | 3,438,418 | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
4,704,758 | 9,772,231 | 1,887,441 | 16,364,430 | ||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
— | — | 23,648 | 23,648 | ||||||||||||
| Loans |
63,963,030 | 61,074,745 | 11,323,455 | 136,361,230 | ||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
— | 777,696 | — | 777,696 | ||||||||||||
| Other assets |
130,011 | 213,606 | 5,689,055 | 6,032,672 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 68,797,799 | 74,864,476 | 19,335,819 | 162,998,094 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial guarantees |
12,862,362 | 2,443,549 | 1,035,852 | 16,341,763 | ||||||||||||
| Credit related commitment (Commitments on loans and others) |
614,740 | 4,685,958 | 2,074,113 | 7,374,811 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 13,477,102 | 7,129,507 | 3,109,965 | 23,716,574 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 81,993,983 | 22,445,784 | 186,714,668 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing | Service | Others | Total | |||||||||||||
| Due from banks (excluding due from BOK) |
4,182,831 | 570,855 | 4,753,686 | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
4,532,118 | 8,919,309 | 1,841,060 | 15,292,487 | ||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Bonds (excluding government bonds) |
— | — | 11,340 | 11,340 | ||||||||||||
| Loans |
62,661,910 | 60,470,685 | 11,097,224 | 134,229,819 | ||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
— | 864,848 | — | 864,848 | ||||||||||||
| Other assets |
96,384 | 217,810 | 5,118,094 | 5,432,288 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 67,290,412 | 74,655,483 | 18,638,573 | 160,584,468 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Financial guarantees |
8,682,351 | 2,245,665 | 1,206,358 | 12,134,374 | ||||||||||||
| Credit related commitment (Commitments on loans and others) |
615,758 | 4,210,578 | 2,315,937 | 7,142,273 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 9,298,109 | 6,456,243 | 3,522,295 | 19,276,647 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 81,111,726 | 22,160,868 | 179,861,115 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
142
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Credit rating information of credit exposure
Credit rating information of credit exposure as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Due from banks |
Available-for-sale financial assets |
Held-to-maturity financial assets |
Total | |||||||||||||
| AAA ~ AA- |
2,396,325 | — | 2,609,703 | |||||||||||||
| A+ ~ A- |
1,631,190 | 4,207,833 | — | 5,839,023 | ||||||||||||
| BBB+ ~ BB- |
1,269,731 | 8,334,859 | 11,844 | 9,616,434 | ||||||||||||
| Less than BB- |
— | 181,844 | — | 181,844 | ||||||||||||
| Unrated |
324,119 | 1,243,569 | 11,804 | 1,579,492 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 16,364,430 | 23,648 | 19,826,496 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Due from banks |
Available-for-sale financial assets |
Held-to-maturity financial assets |
Total | |||||||||||||
| AAA ~ AA- |
2,107,957 | — | 2,817,039 | |||||||||||||
| A+ ~ A- |
3,255,871 | 3,494,789 | — | 6,750,660 | ||||||||||||
| BBB+ ~ BB- |
601,381 | 7,772,633 | 11,340 | 8,385,354 | ||||||||||||
| Less than BB- |
— | 443,804 | — | 443,804 | ||||||||||||
| Unrated |
187,352 | 1,473,304 | — | 1,660,656 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 15,292,487 | 11,340 | 20,057,513 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
(3) Capital management activities
(i) Capital adequacy
The FSS approved the Bank’s use of the Foundation Internal Ratings-Based Approach in July 2008. The Bank has been using the same approach when calculating credit risk-weighted assets since the end of June, 2008. The equity capital ratio and equity capital according to the standards of the Bank for International Settlements are calculated for the purpose of such disclosure. The equity capital ratio and equity capital are calculated on a consolidated basis. In conformity with the Banking Act, which is based on the implementation of Basel III on December 1, 2013, the regulatory capital is divided into the following two categories.
Tier 1 capital
- Common Equity Tier 1
Regulatory capital that represents the most subordinated claim in liquidation of the Bank, takes the first and proportionately greatest share of any losses as they occur, and which principal is never repaid outside of liquidation meets the criteria for classification as common equity, including capital stock, capital surplus, retained earnings, qualifying noncontrolling interest in subsidiaries, and accumulated other comprehensive income as common equity Tier 1.
143
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
- Additional Tier 1 capital
Capital stock and capital surplus related to issuance of capital securities that are subordinated, have non-cumulative and conditional dividends or interests, and have no maturity or step-up conditions.
Tier 2 capital (Supplementary Tier 2 capital)
Regulatory capital that fulfills supplementary capital adequacy requirements, and includes subordinated debt with maturities over 5 years and allowance for loan losses in conformity with external regulatory standards and internal standards.
The BIS capital adequacy ratio and capital in accordance to Basel III standards as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
BIS capital adequacy ratio
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Equity capital based on BIS (A): |
||||||||
| Tier 1 capital |
||||||||
| Common Equity Tier 1 |
23,452,961 | |||||||
| Additional Tier 1 capital |
1,553,158 | 1,882,284 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 29,126,707 | 25,335,245 | |||||||
| Tier 2 capital |
4,611,071 | 3,897,953 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 33,737,778 | 29,233,198 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Risk-weighted assets (B): |
||||||||
| Credit risk-weighted assets |
225,215,979 | 203,500,725 | ||||||
| Market risk-weighted assets |
6,934,967 | 7,371,563 | ||||||
| Operational risk-weighted assets |
6,059,533 | 6,033,418 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 216,905,706 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| BIS capital adequacy ratio (A/B): |
14.16 | % | 13.48 | % | ||||
| Tier 1 capital ratio |
12.23 | % | 11.68 | % | ||||
| Common Equity Tier 1 ratio |
11.58 | % | 10.81 | % | ||||
| Additional Tier 1 capital ratio |
0.65 | % | 0.87 | % | ||||
| Tier 2 capital ratio |
1.93 | % | 1.80 | % | ||||
144
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Equity capital based on BIS
| December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
| Equity capital (A+B) |
29,233,198 | |||||||
| Tier 1 capital (A=C+D): |
||||||||
| Common Equity Tier 1 (C) |
||||||||
| Capital stock |
17,235,399 | 15,180,399 | ||||||
| Capital surplus |
1,565,666 | 1,608,052 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
7,832,331 | 6,153,971 | ||||||
| Non-controlling interest |
1,751 | 1,831 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income |
908,954 | 718,399 | ||||||
| Other capital adjustments |
222,436 | 220,562 | ||||||
| Common stock deductibles |
(192,988 | ) | (430,253 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 27,573,549 | 23,452,961 | |||||||
| Additional Tier 1 capital (D) |
||||||||
| Non-controlling interest |
1,553,158 | 1,882,284 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 29,126,707 | 25,335,245 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Tier 2 capital (B): |
||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts, etc. |
1,303,241 | 1,050,980 | ||||||
| Non-qualified capital securities |
1,806,418 | 2,064,477 | ||||||
| Qualified capital securities |
1,400,000 | 700,000 | ||||||
| Non-controlling interest |
101,412 | 82,496 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 3,897,953 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
(4) Market risk
(i) Concept
Market risk is defined as the possibility of potential loss on a trading position resulting from fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates and the price of stocks 1and derivatives. Trading position is exposed to risks, such as interest rate, stock price, and foreign exchange rate, etc. Non-trading position is mostly exposed to interest rates. Accordingly, the Bank classifies market risks into those exposed from trading position or those exposed from non-trading position.
(ii) Market risks of trading positions
Management method on market risks arising from trading positions
Trading position includes securities, foreign exchange position, and derivatives which are traded for short-term profits.
Market risk is managed using VaR limit and loss limit. VaR limit is calculated in the view of entire bank and the calculated VaR limit is distributed into each department and each type (stock price, interest rate, foreign exchange rate and option). The trading department regulates and operates terms of stop loss and investment limits.
145
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Using the Standardized Approach and internal model of VaR, the Bank’s VaR is measured daily and the measured VaR is used for risk monitoring and limit management. In the estimation of VaR, the historical simulation and two other supplemental procedures are used: variance-covariance matrix and Monte Carlo simulation. Through the stress test and back test, the estimation of VaR is validated daily.
In estimating market risk, the Standardized Approach and the internal model are used. The Standardized Approach is used in order to calculate the required capital from market risk and the internal model is used in order to manage risks internally.
Since July 2007 the Bank has measured one-day VaR through the historical simulation method using the time series data of past 250 days under a 99% confidence level. The calculated VaR is monitored on a daily basis. However, this approach does have some shortcomings. VaR estimates possible losses over a certain period at a particular confidence level using past market movement data. Past market movement, however, is not necessarily a good indicator of future events, as there may be conditions and circumstances in the future that the model does not anticipate. As a result, the timing and magnitude of the actual losses can be different depending on the assumptions made at the time of calculation.
In the implementation of the stress test, the Bank applies three scenarios based on the fluctuation of market index that occurred at the time of the historical events that resulted in the significant shock such as the IMF crisis and the 9/11 attacks. The stress test is implemented by the system daily in order to provide for crisis occurrences. Furthermore, the Bank is conducting a contingency plan for market risk management. The plan distinguishes the crisis condition into three stages—precautious stage, precrisis stage and crisis stage—through the measurement of the market volatility.
For the validation of the market risk measurement methodology, the Bank daily implements the back testing that compares the simulated loss, the actual loss and the previous day’s VaR. In addition, the Bank enforces the market risk management relating to irregular compound derivatives through the validation of the derivative pricing model developed by the Bank’s Front Office.
VaR of trading position
The Bank’s VaR of trading position as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average | Max | Min | December 31, 2015 |
|||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
5,000 | 1,799 | 4,533 | |||||||||||||
| Stock price |
250 | 734 | 23 | 72 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange rate |
1,436 | 9,526 | 504 | 9,526 | ||||||||||||
| Commodity |
5 | 1,349 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Option |
267 | 701 | 96 | 658 | ||||||||||||
| Diversification effect |
(1,262 | ) | (6,266 | ) | (322 | ) | (5,094 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 9,695 | 2,100 | 9,695 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
146
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average | Max | Min | December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
5,214 | 1,005 | 1,280 | |||||||||||||
| Stock price |
747 | 1,358 | 110 | 546 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange rate |
808 | 3,777 | 243 | 1,040 | ||||||||||||
| Option |
272 | 1,192 | 80 | 252 | ||||||||||||
| Diversification effect |
(1,310 | ) | (5,468 | ) | (65 | ) | (1,040 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| 6,073 | 1,373 | 2,078 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
(iii) Market risks of non-trading positions
Management method on market risks arising from non-trading positions
The most critical market risk that arises in non-trading position is the interest rate risk. Interest rate risk is defined as the likely loss resulting from the unfavorable fluctuation of interest rate in the Bank’s financial condition and is measured by interest rate VaR and interest rate EaR.
Interest rate VaR is the maximum amount of decrease in net asset value resulting from the unfavorable fluctuation of interest rate. Interest rate EaR is the maximum amount of decrease in net interest income resulting from the unfavorable fluctuation of interest rate for a year.
The Bank’s interest rate VaR and interest rate EaR are measured through the simulation of conclusive interest rate scenario with the FERMAT and are reported on a monthly basis to the Risk Management Committee. The Management’s target of interest rate VaR and interest rate EaR are approved at the beginning of the year. Additionally, the interest rate VaR and interest rate EaR on consolidated basis are calculated using the Standardized Approach in order to retain the consistency in the methods used by the Bank and its subsidiaries
EaR/VaR of non-trading positions
The Bank’s EaR and VaR of non-trading positions as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||
| Interest rate shock |
Interest rate VaR | Interest rate EaR | ||
| 2.00% | 98,171 | |||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||
| Interest rate shock |
Interest rate VaR | Interest rate EaR | ||
| 2.00% | 164,035 | |||
147
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
(iv) Foreign currency risk
Outstanding balances by currency with significant exposure as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KRW | USD | EUR | JPY | GBP | Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
3,342,169 | 6,063 | 39,247 | 4,584 | 55,231 | 4,878,778 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
1,715,494 | 65,240 | — | — | — | — | 1,780,734 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
37,171,988 | 3,834,664 | 50,879 | 141,244 | — | 92,844 | 41,291,619 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
4,913 | 23,647 | — | — | — | — | 28,560 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
102,350,948 | 32,229,459 | 723,483 | 1,394,994 | 49,917 | 40,848 | 136,789,649 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
4,770,240 | 952,730 | 20,308 | 7,984 | — | 6,494 | 5,757,756 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
3,374,651 | 2,045,778 | 42,334 | 150,232 | 498 | 343,054 | 5,956,547 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total financial assets |
150,819,718 | 42,493,687 | 843,067 | 1,733,701 | 54,999 | 538,471 | 196,483,643 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
1,622,618 | — | — | — | — | — | 1,622,618 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
34,964,246 | 4,687,905 | 17,988 | 262,546 | 165 | 2,042 | 39,934,892 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
10,642,305 | 12,455,795 | 125,977 | 1,174,504 | — | 2,009 | 24,400,590 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
90,504,862 | 17,964,007 | 1,484,674 | 1,418,624 | 434,497 | 5,087,356 | 116,894,020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
4,880,612 | 728,307 | 24,184 | 6,807 | — | 2,453 | 5,642,363 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
5,350,444 | 2,241,974 | 48,237 | 170,718 | 981 | 382,577 | 8,194,931 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities |
147,965,087 | 38,077,988 | 1,701,060 | 3,033,199 | 435,643 | 5,476,437 | 196,689,414 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Net financial position |
4,415,699 | (857,993 | ) | (1,299,498 | ) | (380,644 | ) | (4,937,966 | ) | (205,771 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
148
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KRW | USD | EUR | JPY | GBP | Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
4,549,959 | 4,891 | 57,706 | 1,294 | 44,350 | 5,974,543 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
1,378,674 | 39,724 | — | — | — | — | 1,418,398 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
34,293,488 | 3,567,314 | 62,315 | 150,914 | — | 85,994 | 38,160,025 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
5,898 | 11,340 | — | — | — | — | 17,238 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
100,839,819 | 30,665,306 | 760,736 | 1,802,938 | 79,205 | 166,462 | 134,314,466 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial assets |
3,860,104 | 995,400 | 39,640 | 8,864 | — | 8,784 | 4,912,792 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
2,434,937 | 2,568,998 | 256,556 | 79,303 | 10,269 | 71,394 | 5,421,457 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total financial assets |
144,129,263 | 42,398,041 | 1,124,138 | 2,099,725 | 90,768 | 376,984 | 190,218,919 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
1,138,628 | — | — | — | — | — | 1,138,628 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
31,932,943 | 5,230,164 | 35,575 | 406,094 | 73 | 865 | 37,605,714 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
9,851,886 | 11,507,929 | 705,425 | 1,466,261 | — | 6,030 | 23,537,531 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
90,357,163 | 16,875,121 | 1,847,216 | 1,910,870 | 433,870 | 5,145,556 | 116,569,796 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative financial liabilities |
3,818,699 | 897,559 | 38,599 | 30,417 | — | 3,880 | 4,789,154 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
3,539,019 | 1,974,354 | 229,820 | 64,519 | 11,244 | 101,730 | 5,920,686 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities |
140,638,338 | 36,485,127 | 2,856,635 | 3,878,161 | 445,187 | 5,258,061 | 189,561,509 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Net financial position |
5,912,914 | (1,732,497 | ) | (1,778,436 | ) | (354,419 | ) | (4,881,077 | ) | 657,410 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
149
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
49. Risk Management, Continued
(5) Liquidity risk management
(i) Concept
Liquidity risk is defined as the possibility of potential loss due to a temporary shortage in funds caused by a maturity mismatch or an unexpected capital outlay. Liquidity risk increases when funding rates rise, assets are sold below a normal price, or a good investment opportunity is missed.
(ii) Approach to liquidity risk management
The Bank manages its liquidity risks as follows:
Allowable limit for liquidity risk
| • | The allowable limit for liquidity risk sets LCR, foreign currency liquidity ratio, and remaining maturity gap |
| • | The management standards with regards to the allowable limit for liquidity risk should be set using separate and stringent set ratios in accordance with the FSS guidelines. |
<Measurement Methodology>
| • | LCR : (Maturing liquidity asset in the interval / Maturing liquidity liability in the interval) X 100 |
| • | Foreign currency liquidity ratio : (Maturing liquidity asset in the interval / Maturing liquidity liability in the interval) X 100 |
| • | Remaining maturity gap : (Maturing liquidity asset in the interval—Maturing liquidity liability in the interval) / total assets X 100 |
Early warning indicator
In order to identify prematurely and cope with worsening liquidity risk trends, the Bank has set up 13 indexes such as the “Foreign Exchange Stabilization Bond CDS Premium,” and measures the trend monthly, weekly and daily as a means for establishing the allowable liquidity risk limit complementary measures.
Stress-Test analysis and contingency plan
The Bank evaluates the effects on the liquidity risk and identifies the inherent flaws. In the case where an unpredictable and significant liquidity crisis occurs, the Bank executes risk situation analysis quarterly based on crisis specific to the Bank, market risk and complex emergency, and reports to the Risk Management Committee for the purpose of the Bank’s solvency securitization.
150
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
(iii) Analysis on remaining contractual maturity of financial instruments
Remaining contractual maturity risks of non-derivative financial instruments including interest payment as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month | 1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
230,206 | 732,647 | 507,467 | 2,277 | 4,932,540 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
1,780,734 | — | — | — | — | 1,780,734 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
239,697 | 712,299 | 13,703,782 | 15,179,957 | 13,354,563 | 43,190,298 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
16 | 1 | 14,034 | 15,965 | — | 30,016 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
10,437,948 | 13,100,914 | 44,932,063 | 62,009,960 | 17,527,508 | 148,008,393 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
5,215,290 | — | — | — | 744,110 | 5,959,400 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total financial asset |
14,043,420 | 59,382,526 | 77,713,349 | 31,628,458 | 203,901,381 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
113,780 | 569,296 | 262,144 | 1,176,878 | 2,298,809 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
15,026,497 | 6,154,963 | 16,720,835 | 2,455,149 | 297,536 | 40,654,980 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
5,502,490 | 2,516,252 | 8,946,213 | 6,493,828 | 1,498,915 | 24,957,698 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
4,024,749 | 8,129,568 | 33,281,834 | 62,094,598 | 18,320,297 | 125,851,046 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
6,377,327 | 1,766,910 | — | — | 53,880 | 8,198,117 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities |
18,681,473 | 59,518,178 | 71,305,719 | 21,347,506 | 201,960,650 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
151
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month | 1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
317,448 | 436,954 | 250,801 | 105,064 | 5,995,653 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Financial assets held for trading |
1,418,398 | — | — | — | — | 1,418,398 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale financial assets |
370,345 | 4,201,999 | 7,980,954 | 15,502,215 | 11,838,387 | 39,893,900 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity financial assets |
35 | — | 2,038 | 16,819 | — | 18,892 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loans |
11,099,336 | 11,724,522 | 41,696,127 | 65,649,662 | 14,993,470 | 145,163,117 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets |
3,220,682 | — | — | — | 7,174,423 | 10,395,105 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total financial asset |
16,243,969 | 50,116,073 | 81,419,497 | 34,111,344 | 202,885,065 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financial liabilities designated at FVTPL |
— | 318,061 | 335,726 | 1,122,980 | 1,776,767 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
5,810,417 | 6,836,178 | 18,463,724 | 7,272,797 | 376,997 | 38,760,113 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings |
5,289,378 | 5,743,308 | 6,799,281 | 4,619,720 | 1,444,371 | 23,896,058 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bonds |
3,833,701 | 7,764,941 | 29,405,642 | 68,274,544 | 17,332,918 | 126,611,746 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
3,777,958 | 2,130,024 | 10,950 | 48,306 | 7,943,813 | 13,911,051 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total financial liabilities |
22,474,451 | 54,997,658 | 80,551,093 | 28,221,079 | 204,955,735 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Remaining contractual maturity risks of derivative financial instruments as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
Net settlement of derivative financial instruments
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
33 | (265 | ) | — | — | (208 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
7,164 | 9,020 | (44,239 | ) | 38,523 | (178,784 | ) | (168,316 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Stock |
(43 | ) | — | — | — | — | (43 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
40,376 | 79,401 | 136,261 | 729,405 | 3,125,962 | 4,111,405 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 88,454 | 91,757 | 767,928 | 2,947,178 | 3,942,838 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
152
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
1,260 | 1,926 | — | — | 4,079 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
(3,795 | ) | (3,113 | ) | (48,398 | ) | (24,433 | ) | 150,673 | 70,934 | ||||||||||||||
| Stock |
217 | 34 | 3 | — | — | 254 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate |
9,658 | 132,619 | 100,586 | 746,674 | 3,816,007 | 4,805,544 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 130,800 | 54,117 | 722,241 | 3,966,680 | 4,880,811 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Gross settlement of derivative instruments
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow |
23,312,883 | 50,986,102 | 36,310,645 | 1,749,220 | 153,894,415 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow |
33,558,569 | 23,389,424 | 50,820,227 | 36,142,362 | 1,745,941 | 145,656,523 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow |
1,212,213 | 1,379,386 | 2,029,374 | 18,338,716 | 1,300,822 | 24,260,511 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow |
1,278,455 | 1,520,341 | 2,039,557 | 18,873,947 | 1,290,673 | 25,002,973 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total inflow |
24,692,269 | 53,015,476 | 54,649,361 | 3,050,042 | 178,154,926 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total outflow |
24,909,765 | 52,859,784 | 55,016,309 | 3,036,614 | 170,659,496 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Trading purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow |
12,999,424 | 37,026,139 | 33,702,490 | 1,348,906 | 98,012,339 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow |
12,865,373 | 12,959,933 | 36,932,889 | 33,548,466 | 1,357,014 | 97,663,675 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Hedging purpose derivatives: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inflow |
175,735 | 529,898 | 6,366,830 | 16,797,720 | 1,448,433 | 25,318,616 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Outflow |
181,838 | 564,432 | 6,593,476 | 17,191,962 | 1,432,264 | 25,963,972 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total inflow |
13,529,322 | 43,392,969 | 50,500,210 | 2,797,339 | 123,330,955 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total outflow |
13,524,365 | 43,526,365 | 50,740,428 | 2,789,278 | 123,627,647 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
153
Table of Contents
Korea Development Bank
Notes to the Separate Financial Statements
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
(In millions of won)
49. Risk Management, Continued
Remaining contractual maturity risks of guarantees and commitments as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
| December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Balance: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Guarantees |
1,785,982 | 4,627,002 | 7,998,388 | 53,910 | 16,341,762 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Commitments |
395,574 | 197,210 | 818,646 | 3,612,148 | 2,351,234 | 7,374,812 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,983,192 | 5,445,648 | 11,610,536 | 2,405,144 | 23,716,574 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Within 1 month |
1 ~ 3 months | 3 ~ 12 months | 1 ~ 5 years | Over 5 years | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Off-Balance: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Guarantees |
1,743,053 | 3,991,669 | 4,797,363 | 67,164 | 12,134,373 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Commitments |
525,607 | 27,480 | 1,083,979 | 3,013,767 | 2,491,440 | 7,142,273 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| 1,770,533 | 5,075,648 | 7,811,130 | 2,558,604 | 19,276,646 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
154
Table of Contents
Territory and Population
Located generally south of the 38th parallel on the Korean peninsula, The Republic of Korea covers about 38,000 square miles, approximately one-fourth of which is arable. The Republic has a population of approximately 51 million people. The country’s largest city and capital, Seoul, has a population of about 10 million people.
Map of the Republic of Korea
Political History
Dr. Rhee Seungman, who was elected President in each of 1948, 1952, 1956 and 1960, dominated the years after the Republic’s founding in 1948. Shortly after President Rhee’s resignation in 1960 in response to student-led demonstrations, a group of military leaders headed by Park Chung Hee assumed power by coup. The military leaders established a civilian government, and the country elected Mr. Park as President in October 1963. President Park served as President until his assassination in 1979 following a period of increasing strife between the Government and its critics. The Government declared martial law and formed an interim
155
Table of Contents
government under Prime Minister Choi Kyu Hah, who became the next President. After clashes between the Government and its critics, President Choi resigned, and General Chun Doo Hwan, who took control of the Korean army, became President in 1980.
In late 1980, the country approved, by national referendum, a new Constitution, providing for indirect election of the President by an electoral college and for certain democratic reforms, and shortly thereafter, in early 1981, re-elected President Chun.
Responding to public demonstrations in 1987, the legislature revised the Constitution to provide for direct election of the President. In December 1987, Roh Tae Woo won the Presidency by a narrow plurality, after opposition parties led by Kim Young Sam and Kim Dae Jung failed to unite behind a single candidate. In February 1990, two opposition political parties, including the one led by Kim Young Sam, merged into President Roh’s ruling Democratic Liberal Party.
In December 1992, the country elected Kim Young Sam as President. The election of a civilian and former opposition party leader considerably lessened the controversy concerning the legitimacy of the political regime. President Kim’s administration reformed the political sector and deregulated and internationalized the Korean economy.
In December 1997, the country elected Kim Dae Jung as President. President Kim’s party, the Millennium Democratic Party (formerly known as the National Congress for New Politics), formed a coalition with the United Liberal Democrats led by Kim Jong Pil, with Kim Jong Pil becoming the first prime minister in President Kim’s administration. The coalition, which temporarily ended before the election held in April 2000, continued with the appointment of Lee Han Dong of the United Liberal Democrats as the Prime Minister in June 2000. The coalition again ended in September 2001.
In December 2002, the country elected Roh Moo Hyun as President. President Roh and his supporters left the Millennium Democratic Party in 2003 and formed a new party, the Uri Party, in November 2003. On August 15, 2007, 85 members of the National Assembly, previously belonging to the Uri Party, or the Democratic Party, formed the United New Democratic Party (the “UNDP”). The Uri Party merged into the UNDP on August 20, 2007. In February 2008, the UNDP merged back into the Democratic Party. In December 2011, the Democratic Party merged with the Citizens Unity Party to form the Democratic United Party, which changed its name to the Democratic Party in May 2013.
In December 2007, the country elected Lee Myung-Bak as President. He commenced his term on February 25, 2008. The Lee administration pursued a lively market economy through deregulation, free trade and the attraction of foreign investment.
In December 2012, the country elected Park Geun-hye as President. She commenced her term on February 25, 2013. The Park administration’s key policy priorities include:
| • | facilitating the growth of small and medium-enterprises and job creation; |
| • | seeking a productive welfare system based on customized welfare benefits and job training; |
| • | promoting clean and renewable energy technologies; |
| • | facilitating new growth engine industries; |
| • | taking initiatives on the denuclearization of North Korea; and |
| • | establishing an efficient government by reorganizing government functions. |
156
Table of Contents
Government and Administrative Structure
Governmental authority in the Republic is centralized and concentrated in a strong Presidency. The President is elected by popular vote and can only serve one term of five years. The President chairs the State Council, which consists of the prime minister, the deputy prime ministers, the respective heads of Government ministries and the ministers of state. The President can select the members of the State Council and appoint or remove all other Government officials, except for elected local officials.
The President can veto new legislation and take emergency measures in cases of natural disaster, serious fiscal or economic crisis, state of war or other similar circumstances. The President must promptly seek the concurrence of the National Assembly for any emergency measures taken and failing to do so automatically invalidates the emergency measures. In the case of martial law, the President may declare martial law without the consent of the National Assembly; provided, however, that the National Assembly may request the President to rescind such martial law.
The National Assembly exercises the country’s legislative power. The Election for Public Offices Act provide for the direct election of about 82% of the members of the National Assembly and the distribution of the remaining seats proportionately among parties winning more than 5 seats in the direct election or receiving over 3% of the popular vote. National Assembly members serve four-year terms. The National Assembly enacts laws, ratifies treaties and approves the national budget. The executive branch drafts most legislation and submits it to the National Assembly for approval.
The country’s judicial branch comprises the Supreme Court, the Constitutional Court and lower courts of various levels. The President appoints the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court and appoints the other Justices of the Supreme Court upon the recommendation of the Chief Justice. All appointments to the Supreme Court require the consent of the National Assembly. The Chief Justice, with the consent of the conference of Supreme Court Justices, appoints all the other judges in Korea. Supreme Court Justices serve for six years and all other judges serve for ten years. Other than the Chief Justice, justices and judges may be reappointed to successive terms.
The President formally appoints all nine judges of the Constitutional Court, but three judges must be designated by the National Assembly and three by the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court. Constitutional Court judges serve for six years and may be reappointed to successive terms.
Administratively, the Republic comprises eight provinces, one special autonomous province (Jeju), one special city (Seoul), six metropolitan cities (Busan, Daegu, Incheon, Gwangju, Daejon and Ulsan) and one special autonomous city (Sejong). From 1961 to 1995, the national government controlled the provinces and the President appointed provincial officials. Local autonomy, including the election of provincial officials, was reintroduced in June 1995.
Political Parties
The 20th legislative general election was held on April 13, 2016 and the term of the National Assembly members elected in the 20th legislative general election commenced on May 30, 2016. Currently, there are three major political parties: the Saenuri Party, or SP, to which President Park Geun-hye belongs, The Minjoo Party of Korea, or MPK (formerly known as the New Politics Alliance for Democracy, or NPAD, before certain of its members left in December 2015 to form a new party), and People’s Party, or PP, which was established in February 2016 by certain former members of the NPAD.
157
Table of Contents
As of June 13, 2016, the parties control the following number of seats in the National Assembly:
| SP | MPK | PP | Others | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Number of seats |
122 | 123 | 38 | 17 | 300 | |||||||||||||||
Relations with North Korea
Relations between the Republic and North Korea have been tense over most of the Republic’s history. The Korean War, which took place between 1950 and 1953 began with the invasion of the Republic by communist forces from North Korea and, following a military stalemate, an armistice was reached establishing a demilitarized zone monitored by the United Nations in the vicinity of the 38th parallel.
North Korea maintains a regular military force estimated at more than 1,000,000 troops, mostly concentrated near the northern border of the demilitarized zone. The Republic’s military forces, composed of approximately 650,000 regular troops and almost 3.0 million reserves, maintain a state of military preparedness along the southern border of the demilitarized zone. In addition, the United States has historically maintained its military presence in the Republic. In October 2004, the United States and the Republic agreed to a three-phase withdrawal of approximately one-third of the 37,500 troops stationed in the Republic by the end of 2008. By the end of 2004, 5,000 U.S. troops departed the Republic in the first phase of such withdrawal and in the plan’s second phase, the United States removed 5,000 troops by the end of 2006. In the final phase, another 2,500 U.S. troops were scheduled to depart by the end of 2008. In April 2008, however, the United States and the Republic decided not to proceed with the final phase of withdrawal and agreed to maintain 28,500 U.S. troops in the Republic. In February 2007, the United States and the Republic agreed to dissolve their joint command structure by 2012, which would allow the Republic to assume the command of its own armed forces in the event of war on the Korean peninsula. In June 2010, however, the United States and the Republic agreed to delay the dissolution of their joint command structure to 2015. In October 2014, the United States and the Republic further agreed to implement a conditions-based approach to the dissolution of their joint command structure at an appropriate future date.
Relations between Korea and North Korea have been tense throughout Korea’s modern history. The level of tension between the two Koreas has fluctuated and may increase abruptly as a result of current and future events. In particular, since the death of Kim Jong-il in December 2011, there has been increased uncertainty with respect to the future of North Korea’s political leadership and concern regarding its implications for political and economic stability in the region. Although Kim Jong-il’s third son, Kim Jong-eun has assumed power as his father’s designated successor, the long-term outcome of such leadership transition remains uncertain.
In addition, there have been heightened security concerns in recent years stemming from North Korea’s nuclear weapons and long-range missile programs as well as its hostile military and other actions against Korea. Some of the significant incidents in recent years include the following:
| • | North Korea renounced its obligations under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in January 2003 and conducted three rounds of nuclear tests between October 2006 to February 2013, which increased tensions in the region and elicited strong objections worldwide. In January 2016, North Korea announced that it had successfully tested a hydrogen bomb, its fourth nuclear test and allegedly first test using hydrogen, which is more explosive than plutonium. In February 2016, North Korea tested its intercontinental ballistic missile technology and launched a long-range missile, which it claimed to have launched a satellite into orbit. In response, the Government condemned the provocations and flagrant violations of relevant United Nations Security Council resolutions and withdrew Korean personnel from the inter-Korea Gaesong Industrial Complex and announced its closing. In March 2016, the United Nations Security Council unanimously passed a resolution condemning North Korea’s actions and significantly expanding the scope of sanctions applicable to North Korea. |
158
Table of Contents
| • | In August 2015, two Korean soldiers were seriously wounded in landmine explosions while on routine patrol of the southern side of the demilitarized zone. The Government and the United Nations Command announced that the landmines were emplaced by North Korea, and in response, the Korean army restarted its loudspeaker propaganda broadcasts directed at the northern side of the demilitarized zone. The North Korean army retaliated by firing artillery rounds at the loudspeakers resulting in both sides being placed on the highest level of military readiness. High-ranking officials from the Government and North Korea subsequently met for discussions intending to diffuse military tensions and released a joint statement whereby, among other things, North Korea expressed regret over the landmine explosions that wounded the Korean soldiers. |
| • | In March 2010, a Korean naval vessel was destroyed by an underwater explosion, killing many of the crewmen on board. The Government formally accused North Korea of causing the sinking, while North Korea denied responsibility. Moreover, in November 2010, North Korea fired more than one hundred artillery shells that hit Korea’s Yeonpyeong Island near the Northern Limit Line, which acts as the de facto maritime boundary between Korea and North Korea on the west coast of the Korean peninsula, causing casualties and significant property damage. The Government condemned North Korea for the attack and vowed stern retaliation should there be further provocation. |
North Korea’s economy also faces severe challenges, which may aggravate social and political pressures within North Korea. There can be no assurance that the level of tension on the Korean peninsula will not escalate in the future or that such escalation will not have a material adverse impact on the Republic’s economy. Any further increase in tension, which may occur, for example, if North Korea experiences a leadership crisis, high-level contacts between the Republic and North Korea break down or military hostilities occur, could have a material adverse effect on the Republic’s economy. Over the longer term, reunification of the two Koreas could occur. Reunification may entail a significant economic commitment by the Republic.
Foreign Relations and International Organizations
The Republic maintains diplomatic relations with most nations of the world, most importantly with the United States with which it entered into a mutual defense treaty and several economic agreements. The Republic also has important relationships with Japan and China, its largest trading partners together with the United States.
The Republic belongs to a number of supranational organizations, including:
| • | United Nations; |
| • | the International Monetary Fund, or the IMF; |
| • | the World Bank; |
| • | the Asian Development Bank, or ADB; |
| • | the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency; |
| • | the International Finance Corporation; |
| • | the International Development Association; |
| • | the African Development Bank; |
| • | the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development; |
| • | the Bank for International Settlements; |
| • | the World Trade Organization, or WTO; |
| • | the Inter-American Development Bank, or IDB; and |
| • | the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, or OECD. |
159
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth information regarding certain of the Republic’s key economic indicators for the periods indicated.
| As of or for the year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars and trillions of Won, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GDP Growth (at current prices) |
5.3 | % | 3.4 | % | 3.8 | % | 4.0 | % | 4.9 | % | ||||||||||
| GDP Growth (at chained 2010 year prices) |
3.7 | % | 2.3 | % | 2.9 | % | 3.3 | % | 2.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Inflation |
4.0 | % | 2.2 | % | 1.3 | % | 1.3 | % | 0.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Unemployment(1) |
3.4 | % | 3.2 | % | 3.1 | % | 3.5 | % | 3.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Trade Surplus(2) |
$ | 30.8 | $ | 28.3 | $ | 44.0 | $ | 47.2 | $ | 90.3 | ||||||||||
| Foreign Currency Reserves |
$ | 306.4 | $ | 327.0 | $ | 346.5 | $ | 363.6 | $ | 368.0 | ||||||||||
| External Liabilities(3) |
$ | 400.0 | $ | 408.9 | $ | 423.5 | $ | 424.4 | $ | 396.6 | (6) | |||||||||
| Fiscal Balance |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Internal Debt of the Government(4) (as % of GDP(5)) |
29.7 | % | 30.9 | % | 32.8 | % | 34.6 | (6) | 37.4 | (6) | ||||||||||
| Direct External Debt of the Government(4) (as % of GDP(5)) |
0.7 | % | 0.6 | % | 0.6 | % | 0.5 | (6) | 0.5 | (6) | ||||||||||
| (1) | Average for year. |
| (2) | Derived from customs clearance statistics on a C.I.F. basis, meaning that the price of goods include insurance and freight cost. |
| (3) | Calculated under the criteria based on the sixth edition of Balance of Payment Manual, or BPM6, published by the International Monetary Fund in December 2010. |
| (4) | Does not include guarantees by the Government. See “—Debt—External and Internal Debt of the Government—Guarantees by the Government” for information on outstanding guarantees by the Government. |
| (5) | At chained 2010 year prices. |
| (6) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea
Worldwide Economic and Financial Difficulties
In recent years, the global financial markets have experienced significant volatility as a result of, among other things:
| • | the financial difficulties affecting many governments worldwide, in particular in southern Europe and Latin America; |
| • | the slowdown of economic growth in China and other major emerging market economies; |
| • | interest rate fluctuations as well as the possibility of increases in policy rates by the U.S. Federal Reserve and other central banks; |
| • | political and social instability in various countries in the Middle East and Northern Africa, including Iraq, Syria and Yemen, as well as in the Ukraine and Russia; and |
| • | fluctuations in oil and commodity prices. |
In light of the high level of interdependence of the global economy, any of the foregoing developments could have a material adverse effect on the Korean economy and financial markets.
160
Table of Contents
As a result of adverse global and Korean economic conditions, there has been significant volatility in the Korea Composite Stock Index in recent years, due to adverse global financial and economic conditions. See “—The Financial System—Securities Markets”. There is no guarantee that the stock prices of Korean companies will not decline again in the future. Future declines in the index and large amounts of sales of Korean securities by foreign investors and subsequent repatriation of the proceeds of such sales may continue to adversely affect the value of the Won, the foreign currency reserves held by financial institutions in Korea, and the ability of Korean companies and banks to raise capital. In addition, the value of the Won relative to major foreign currencies in general and the U.S. dollar in particular has fluctuated widely in recent years. A depreciation of the Won will increase the cost of imported goods and services and the Won revenue needed by Korean companies to service foreign currency-denominated debt.
In the event that such difficult conditions in the global credit markets continue or the global economy deteriorates in the future, the Korean economy could be adversely affected and Korean banks may be forced to fund their operations at a higher cost or may be unable to raise as much funding as they need to support their lending and other activities.
Furthermore, while many governments worldwide are considering or are in the process of implementing “exit strategies”, in the form of reduced government spending, higher interest rates or otherwise, with respect to the economic stimulus measures adopted in response to the global financial crisis, such strategies may, for reasons related to timing, magnitude or other factors, have the unintended consequence of prolonging or worsening global economic and financial difficulties.
In addition to the global developments, domestic developments that could lead or contribute to a material adverse effect on the Korean economy include, among other things, the following:
| • | steadily rising household debt consisting of housing loans and merchandise credit, which increased to approximately |
| • | a slowdown in consumer spending and depressed consumer sentiment, due in part to national tragedies including the sinking of the Sewol passenger ferry in April 2014, which led to the death of hundreds of passengers, and the outbreak of infectious diseases, such as the outbreak of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (“MERS”) in May 2015, which resulted in the death of over 30 people and the quarantine of thousands; |
| • | a decrease in tax revenue and a substantial increase in the Korean government’s expenditures for pension and social welfare programs, due in part to an aging population (defined as the population of people aged 65 years or older) that accounts for 13.1% of the Republic’s total population as of December 31, 2015, an increase from 7.2% as of December 31, 2000, and is expected to surpass 15% in 2020 and 20% in 2026, which could lead to the Korean government’s budget deficit; |
| • | increasing delinquencies and credit defaults by consumer and small- and medium-sized enterprise borrowers; |
| • | decreases in the market prices of Korean real estate; and |
| • | the occurrence of severe health epidemics, including epidemics that affect the livestock industry. |
Gross Domestic Product
GDP measures the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country for a given period and reveals whether a country’s productive output rises or falls over time. Economists present GDP in both current market prices and “real” or “inflation-adjusted” terms. In March 2009, the Republic adopted a method known as the “chain-linked” measure of GDP, replacing the previous fixed-base, or “constant” measure of GDP, to show the real growth of the aggregate economic activity, as recommended by the System of National Accounts
161
Table of Contents
1993. GDP at current market prices values a country’s output using the actual prices of each year, whereas the “chain-linked” measure of GDP is compiled by using “chained indices” linking volume growth between consecutive time periods. In March 2014, the Republic published a revised GDP calculation method by implementing the System of National Accounts 2008 and updating the reference year from 2005 to 2010 to align Korean national accounts statistics with the recommendations of the new international standards for compiling national economic accounts and to maintain comparability with other nations’ accounts. The main components of these revisions include, among other things, (i) recognizing expenditures for research and development and creative activity for the products of entertainment, literary and artistic originals as fixed investment, (ii) incorporating a wide array of new and revised source data such as the economic census, the population and housing census and 2010 benchmark input-output tables, which provide thorough and detailed information on the structure of the Korean economy, (iii) developing supply-use tables, which provide a statistical tool for ensuring consistency among the production, expenditure and income approaches to measuring GDP and (iv) recording merchandise trade transactions based on ownership changes rather than movements of goods across the national frontier.
162
Table of Contents
The following table sets out the composition of the Republic’s GDP at current market and chained 2010 year prices and the annual average increase in the Republic’s GDP.
Gross Domestic Product
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | As % of GDP 2015(1) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Domestic Product at Current Market Prices: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Private |
679,141.5 | 707,614.0 | 727,799.9 | 748,200.8 | 771,211.9 | 49.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government |
194,381.2 | 204,324.2 | 214,467.3 | 224,724.2 | 237,135.1 | 15.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Capital Formation |
439,236.1 | 427,028.5 | 416,000.3 | 435,078.1 | 444,014.9 | 28.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exports of Goods and Services |
742,936.0 | 776,062.4 | 770,114.8 | 747,134.3 | 715,411.3 | 45.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Less Imports of Goods and Services |
(723,013.8 | ) | (737,572.4 | ) | (698,936.9 | ) | (669,058.0 | ) | (606,942.0 | ) | (38.9 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Statistical Discrepancy |
— | — | — | — | (2,239.7 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Expenditures on Gross Domestic Product |
1,332,681.0 | 1,377,456.7 | 1,429,445.4 | 1,486,079.3 | 1,558,591.6 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net Factor Income from the Rest of the World |
7,848.8 | 14,138.8 | 10,199.0 | 4,684.5 | 7,223.9 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross National Income(2) |
1,340,529.8 | 1,391,595.5 | 1,439,644.4 | 1,490,763.9 | 1,565,815.5 | 100.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Domestic Product at Chained 2010 Year Prices: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Private |
655,181.1 | 667,781.2 | 680,349.5 | 692,236.0 | 707,151.7 | 48.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government |
187,158.2 | 193,473.5 | 199,783.4 | 205,869.2 | 212,797.8 | 14.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Capital Formation |
419,282.7 | 409,639.9 | 409,153.8 | 430,685.5 | 459,783.1 | 31.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exports of Goods and Services |
719,943.2 | 756,558.4 | 788,788.0 | 804,797.1 | 811,040.9 | 55.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Less Imports of Goods and Services |
(668,931.5 | ) | (685,009.4 | ) | (696,724.6 | ) | (706,938.4 | ) | (729,744.7 | ) | (49.8 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Statistical Discrepancy |
(740.9 | ) | (142.1 | ) | (172.8 | ) | 1,019.1 | 2,508.1 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Expenditures on Gross Domestic Product(3) |
1,311,892.7 | 1,341,966.5 | 1,380,832.6 | 1,426,972.4 | 1,464,244.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net Factor Income from the Rest of the World in the Terms of Trade |
7,573.1 | 13,577.8 | 10,037.5 | 4,706.4 | 7,126.7 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Trading Gains and Losses from Changes in the Terms of Trade |
(32,183.6 | ) | (33,075.1 | ) | (19,138.8 | ) | (14,000.4 | ) | 39,146.7 | 2.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Gross National Income(4) |
1,287,282.2 | 1,322,449.9 | 1,371,733.1 | 1,417,814.2 | 1,510,626.5 | 103.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Percentage Increase (Decrease) of GDP over Previous Year At Current Prices |
5.3 | 3.4 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 4.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
| At Chained 2010 Year Prices |
3.7 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 2.6 | |||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
| (2) | GDP plus net factor income from the rest of the world is equal to the Republic’s gross national product. |
| (3) | Under the “chain-linked” measure of GDP, the components of GDP will not necessarily add to the total GDP. |
| (4) | Under the “chain-linked” measure of Gross National Income, the components of Gross National Income will not necessarily add to the total Gross National Income. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
163
Table of Contents
The following table sets out the Republic’s GDP by economic sector at current market prices:
Gross Domestic Product by Economic Sector
(at current market prices)
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | As % of GDP 2015 (1) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Sectors: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries |
30,454.0 | 30,775.1 | 30,437.2 | 31,560.3 | 32,741.0 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining and Manufacturing |
381,808.0 | 390,288.6 | 406,127.7 | 411,030.4 | 420,585.3 | 27.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining and Quarrying |
2,287.0 | 2,278.5 | 2,471.0 | 2,520.2 | 2,543.3 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
379,521.0 | 388,010.1 | 403,656.7 | 408,510.2 | 418,042.0 | 26.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Electricity, Gas and Water Supply |
23,994.1 | 26,178.2 | 30,238.7 | 37,373.8 | 45,120.7 | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Construction |
58,587.3 | 59,959.4 | 64,250.5 | 67,266.7 | 72,751.3 | 4.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Services: |
715,112.9 | 744,253.9 | 772,184.1 | 807,624.1 | 846,410.3 | 54.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale and Retail Trade, Restaurants and Hotels |
140,705.3 | 146,807.7 | 150,251.9 | 152,205.2 | 156,097.0 | 10.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Transportation and Storage |
42,458.7 | 43,570.7 | 46,772.0 | 50,306.8 | 57,371.9 | 3.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Finance and Insurance |
77,872.6 | 75,808.5 | 72,478.1 | 75,859.8 | 77,990.7 | 5.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate and Leasing |
94,716.1 | 98,923.6 | 103,527.1 | 109,549.0 | 115,169.7 | 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Information and Communication |
46,827.0 | 48,774.2 | 50,589.2 | 52,510.8 | 54,125.7 | 3.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Activities |
83,277.4 | 88,828.1 | 94,758.4 | 100,936.7 | 105,893.4 | 6.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Public Administration and Defense |
83,290.8 | 88,654.6 | 93,776.3 | 98,333.5 | 104,678.4 | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Education |
66,559.6 | 68,546.3 | 71,599.3 | 74,007.8 | 76,582.5 | 4.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Health and Social Work |
46,656.1 | 50,031.3 | 52,851.5 | 57,129.7 | 61,150.7 | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cultural and Other Services |
32,749.4 | 34,309.0 | 35,580.3 | 36,784.7 | 37,350.4 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes Less Subsidies on Products |
122,724.8 | 126,001.4 | 126,207.2 | 131,224.0 | 140,983.0 | 9.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Domestic Product at Current Market Prices |
1,332,681.0 | 1,377,456.7 | 1,429,445.4 | 1,486,079.3 | 1,558,591.6 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net Factor Income from the Rest of the World |
7,848.8 | 14,138.8 | 10,199.0 | 4,684.5 | 7,223.9 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross National Income at Current Market Price |
1,340,529.8 | 1,391,595.5 | 1,439,644.4 | 1,490,763.9 | 1,565,815.5 | 100.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
164
Table of Contents
The following table sets out the Republic’s GDP per capita:
Gross Domestic Product per capita
(at current market prices)
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | ||||||||||||||||
| GDP per capita (thousands of Won) |
26,772 | 27,547 | 28,464 | 29,472 | 30,792 | |||||||||||||||
| GDP per capita (U.S. dollar) |
24,160 | 24,445 | 25,993 | 27,983 | 27,214 | |||||||||||||||
| Average Exchange Rate (in Won per U.S. dollar) |
1,108.1 | 1,126.9 | 1,095.0 | 1,053.2 | 1,131.5 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
The following table sets out the Republic’s Gross National Income, or GNI, per capita:
Gross National Income per capita
(at current market prices)
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | ||||||||||||||||
| GNI per capita (thousands of Won) |
26,929 | 27,829 | 28,667 | 29,565 | 30,935 | |||||||||||||||
| GNI per capita (U.S. dollar) |
24,302 | 24,696 | 26,179 | 28,071 | 27,340 | |||||||||||||||
| Average Exchange Rate (in Won per U.S. dollar) |
1,108.1 | 1,126.9 | 1,095.0 | 1,053.2 | 1,131.5 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
165
Table of Contents
The following table sets out the Republic’s GDP by economic sector at chained 2010 year prices:
Gross Domestic Product by Economic Sector
(at chained 2010 year prices)
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | As % of GDP 2015(1) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Sectors: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries |
27,744.6 | 27,506.9 | 28,357.7 | 29,378.2 | 28,951.1 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining and Manufacturing |
376,958.3 | 385,853.1 | 399,73.1 | 413,839.1 | 418,970.9 | 28.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining and Quarrying |
2,176.3 | 2,170.5 | 2,347.1 | 2,344.40 | 2,327.7 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
374,782.0 | 383,682.6 | 397,426.0 | 411,494.7 | 416,643.2 | 28.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Electricity, Gas and Water Supply |
25,687.4 | 26,710.3 | 26,629.2 | 27,327.9 | 29,027.3 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Construction |
55,432.2 | 54,430.5 | 56,044.1 | 56,470.9 | 58,174.8 | 4.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Services: |
699,580.8 | 718,906.2 | 739,463.1 | 763,853.5 | 785,490.9 | 53.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale and Retail Trade, Restaurants and Hotels |
137,058.1 | 141,698.2 | 145,620.3 | 149,150.5 | 152,318.6 | 10.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Transportation and Storage |
46,157.9 | 46,877.6 | 47,556.1 | 48,646.9 | 49,974.0 | 3.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Finance and Insurance |
72,741.3 | 75,547.3 | 78,583.9 | 83,020.5 | 88,215.6 | 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate and Leasing |
93,383.7 | 93,182.9 | 93,999.5 | 97,112.9 | 98,937.0 | 6.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Information and Communication |
47,931.6 | 50,199.3 | 52,773.2 | 55,164.8 | 56,455.4 | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Business Activities |
80,913.7 | 83,352.8 | 87,244.6 | 91,424.0 | 95,055.1 | 6.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Public Administration and Defense |
80,639.1 | 82,940.5 | 85,024.5 | 87,052.8 | 89,401.5 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Education |
63,806.6 | 64,386.6 | 64,773.0 | 64,865.2 | 65,235.5 | 4.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Health and Social Work |
45,483.3 | 48,693.4 | 51,247.1 | 54,740.1 | 57,804.5 | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cultural and Other Services |
31,465.5 | 31,972.6 | 32,683.2 | 33,106.0 | 33,066.5 | 2.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes Less Subsidies on Products |
126,489.5 | 128,708.4 | 130,627.4 | 136,454.6 | 143,681.6 | 9.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Domestic Product at Chained 2010 Year Prices(2) |
1,311,892.7 | 1,341,966.5 | 1,380,832.6 | 1,426,972.4 | 1,464,244.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
| (2) | Under the “chain-linked” measure of GDP, the components of GDP will not necessarily add to the total GDP. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
GDP growth in 2011 was 3.7% at chained 2010 year prices, as aggregate private and general government consumption expenditures increased by 2.7%, exports of goods and services increased by 15.1% and gross domestic fixed capital formation increased by 0.8%, each compared with 2010.
GDP growth in 2012 was 2.3% at chained 2010 year prices, as aggregate private and general government consumption expenditures increased by 2.2% and exports of goods and services increased by 5.1%, which more than offset a decrease in gross domestic fixed capital formation by 0.5%, each compared with 2011.
GDP growth in 2013 was 2.9% at chained 2010 year prices, as aggregate private and general government consumption expenditures increased by 2.2%, exports of goods and services increased by 4.3% and gross domestic fixed capital formation increased by 3.3%, each compared with 2012.
166
Table of Contents
GDP growth in 2014 was 3.3% at chained 2010 year prices, as aggregate private and general government consumption expenditures increased by 2.0%, exports of goods and services increased by 2.8% and gross domestic fixed capital formation increased by 3.1%, each compared with 2013.
Based on preliminary data, GDP growth in 2015 was 2.6% at chained 2010 year prices, as aggregate private and general government consumption expenditures increased by 2.4%, gross domestic fixed capital formation increased by 3.8% and exports of goods and services increased by 0.4%, each compared with 2014.
167
Table of Contents
Principal Sectors of the Economy
Industrial Sectors
The following table sets out production indices for the principal industrial products of the Republic and their relative contribution to total industrial production:
Industrial Production
(2010 = 100)
| Index Weight(1) |
2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(2) | |||||||||||||||||||
| All Industries |
10,000.0 | 106.0 | 107.4 | 108.2 | 108.2 | 107.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining and Manufacturing |
9,611.6 | 106.0 | 107.5 | 108.2 | 108.3 | 107.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mining |
33.9 | 104.5 | 99.8 | 103.8 | 95.7 | 96.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Petroleum, Crude Petroleum and Natural Gas |
8.7 | 91.6 | 90.2 | 86.2 | 71.1 | 59.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Metal Ores |
0.9 | 124.9 | 108.5 | 98.4 | 99.9 | 78.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-metallic Minerals |
24.3 | 108.4 | 102.9 | 110.3 | 104.3 | 111.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing |
9,577.7 | 106.0 | 107.5 | 108.2 | 108.3 | 107.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Food Products |
434.4 | 101.9 | 103.4 | 103.7 | 104.7 | 106.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Beverage Products |
82.4 | 103.5 | 108.2 | 108.8 | 110.0 | 111.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tobacco Products |
43.2 | 101.6 | 105.6 | 96.5 | 103.9 | 96.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Textiles |
160.6 | 101.5 | 99.1 | 97.6 | 95.8 | 92.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wearing Apparel, Clothing Accessories and Fur Articles |
145.2 | 100.6 | 97.9 | 93.6 | 88.1 | 85.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tanning and Dressing of Leather, Luggage and Footwear |
42.1 | 101.1 | 98.2 | 111.5 | 109.8 | 100.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Wood and Products of Wood and Cork (Except Furniture) |
31.7 | 97.5 | 87.9 | 92.9 | 89.1 | 91.7 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pulp, Paper and Paper Products |
126.8 | 102.3 | 102.7 | 105.1 | 105.2 | 104.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Printing and Reproduction of Recorded Media |
50.2 | 91.8 | 90.5 | 86.8 | 86.5 | 84.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Coke, hard-coal and lignite fuel briquettes and Refined Petroleum Products |
471.0 | 106.9 | 109.1 | 104.6 | 108.9 | 115.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chemicals and Chemical Products |
847.5 | 102.7 | 106.6 | 110.9 | 111.8 | 113.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pharmaceuticals, Medicinal Chemicals and Botanical Products |
144.1 | 100.3 | 101.2 | 103.2 | 104.6 | 107.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Rubber and Plastic Products |
421.1 | 105.1 | 106.4 | 109.9 | 110.4 | 109.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-metallic Minerals |
271.7 | 100.3 | 95.2 | 100.6 | 96.7 | 99.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Basic Metals |
827.6 | 106.2 | 106.8 | 106.0 | 109.9 | 107.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Fabricated Metal Products |
557.8 | 108.9 | 117.9 | 117.3 | 121.2 | 115.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Electronic Components, Computer, Radio, Television and Communication Equipment and Apparatuses |
1,794.3 | 107.1 | 109.7 | 113.6 | 111.5 | 113.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Medical, Precision and Optical Instruments, Watches and Clocks |
148.1 | 105.6 | 111.6 | 124.2 | 110.6 | 104.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical Equipment |
479.5 | 100.8 | 98.8 | 97.0 | 97.7 | 94.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Machinery and Equipment |
803.6 | 109.3 | 107.0 | 102.7 | 104.8 | 100.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Motor Vehicles, Trailers and Semitrailers |
1,076.4 | 114.7 | 114.5 | 116.1 | 118.9 | 120.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Transport Equipment |
506.5 | 101.7 | 107.1 | 101.7 | 89.5 | 79.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Furniture |
69.5 | 105.4 | 98.2 | 97.2 | 104.2 | 112.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Products |
42.4 | 102.2 | 103.8 | 104.9 | 104.8 | 101.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Electricity, Gas |
388.4 | 104.5 | 106.4 | 106.8 | 107.6 | 106.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total Index |
10,000.0 | 106.0 | 107.4 | 108.2 | 108.2 | 107.5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Index weights were established on the basis of an industrial census in 2010 and reflect the average annual value added by production in each of the classifications shown, expressed as a percentage of total value added in the mining, manufacturing and electricity and gas industries in that year. |
| (2) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea National Statistical Office.
168
Table of Contents
Industrial production increased by 6.0% in 2011, primarily due to increased exports and domestic consumption. Industrial production increased by 1.3% in 2012, primarily due to increased domestic consumption. Industrial production increased by 0.7% in 2013, primarily due to increased exports. Industrial production remained unchanged in 2014. Based on preliminary data, industrial production decreased by 0.6% in 2015, primarily due to decreased exports.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector increased production by 6.0% in 2011, primarily due to increased domestic consumption and exports, by 1.4% in 2012, primarily due to increased demand for consumer electronics products, electronic equipment and chemical products, by 0.7% in 2013, primarily due to increased demand for consumer electronics products, electronic equipment, chemical products, medical equipment and transport equipment, and by 0.1% in 2014, primarily due to increased demand for basic metals, machinery and equipment and motor vehicles, trailers and semitrailers. Based on preliminary data, the manufacturing sector decreased production by 0.6% in 2015, primarily due to decreased demand for basic metals, fabricated metal products, other machinery and equipment, and other transport equipment.
Automobiles. In 2011, automobile production increased by 9.0%, domestic sales volume recorded an increase of 0.6% and export sales volume recorded an increase of 13.7%, compared with 2010, primarily due to increased demand for automobiles in the United States, Brazil, Russia and China. In 2012, automobile production decreased by 2.1%, domestic sales volume recorded a decrease of 4.3% and export sales volume recorded an increase of 0.6%, compared with 2011, primarily due to decreased domestic demand for automobiles. In 2013, automobile production decreased by 0.9%, domestic sales volume recorded a decrease of 2.0% and export sales volume recorded a decrease of 2.6%, compared with 2012, primarily due to decreased supply of automobiles resulting mainly from partial strikes by unionized workers of automobile manufacturers in August 2013 and the appreciation of the Won against the US dollar and the Japanese Yen. In 2014, automobile production increased by 0.1% and domestic sales volume recorded an increase of 4.6%, compared with 2013, primarily due to increased domestic demand for recreational vehicles, and export sales volume recorded a decrease of 0.8%, compared with 2013, primarily due to decreased demand for automobiles in Eastern Europe and South America. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, automobile production increased by 0.7% and domestic sales volume recorded an increase of 7.7%, compared with 2014, primarily due to continued increase in domestic demand for recreational vehicles, and export sales volume recorded a decrease of 2.8%, compared with 2014, primarily due to decreased demand for automobiles in China, Russia, Eastern Europe and South America.
Electronics. In 2011, electronics production amounted
to W314,314 billion, an increase of 1.5% from the previous year, and exports amounted to US$156.6 billion, an increase of 1.8% from the previous year, primarily due to continued increase in global demand for mobile phones and tablet
computers. In 2011, export sales of semiconductor memory chips constituted approximately 9.0% of the Republic’s total exports. In 2012, electronics production amounted to W314,558 billion, an increase of 0.1% from the previous
year, primarily due to increased domestic demand for mobile phones and non-memory semiconductors, and exports amounted to US$155.2 billion, a decrease of 0.9% from the previous year, primarily due to adverse economic conditions in European
countries. In 2012, export sales of semiconductor memory chips constituted approximately 9.2% of the Republic’s total exports. In 2013, electronics production amounted to W334,402 billion, an increase of 6.3% from the previous
year, and exports amounted to US$169.4 billion, an increase of 9.1% from the previous year, primarily due to increases in demand for mobile phones in emerging markets and global demand for non-memory semiconductors. In 2013, export sales of
semiconductor memory chips constituted approximately 10.2% of the Republic’s total exports. In 2014, electronics production amounted to W330,716 billion, an increase of 1.5% from the previous year, and exports amounted to
US$173.9 billion, an increase of 2.7% from the previous year, primarily due to increases in demand for mobile phones and semiconductors. In 2014, export sales of semiconductor memory chips constituted approximately 10.9% of the Republic’s total
exports. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, electronics production amounted to W325,906 billion, a dcrease of 1.5% from the previous year, and exports amounted to US$172.9 billion, a decrease of 0.6% from the previous year,
primarily
169
Table of Contents
due to adverse global economic conditions and the expansion of overseas production. In 2015, export sales of semiconductor memory chips constituted approximately 11.9% of the Republic’s total exports.
Iron and Steel. In 2010, crude steel production totaled 58.9 million tons, an increase of 20.2% from 2009, and domestic sales volume and export sales volume increased by 21.6% and 21.1%, respectively, primarily due to the recovery of global demand for crude steel products. In 2011, crude steel production totaled 68.5 million tons, an increase of 16.3% from 2010, and domestic sales volume and export sales volume increased by 5.8% and 16.9%, respectively, primarily due to continued increase in global demand for crude steel products. In 2012, crude steel production totaled 69.1 million tons, an increase of 0.9% from 2011, and domestic sales volume decreased by 5.1% but export sales volume increased by 4.8%, primarily due to adverse conditions in the domestic shipbuilding and construction industries. In 2013, crude steel production totaled 66.1 million tons, a decrease of 4.4% from 2012, and domestic sales volume and export sales volume decreased by 4.3% and 4.2%, respectively, primarily due to the appreciation of the Won against the US dollar and the Japanese Yen and excess supply from China. In 2014, crude steel production totaled 71.5 million tons, an increase of 8.3% from 2013, and domestic sales volume and export sales volume increased by 7.2% and 10.5%, respectively, primarily due to the recovery of domestic and global demand for crude steel products. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, crude steel production totaled 69.7 million tons, a decrease of 2.6% from 2014, and export sales volume decreased by 2.2%, primarily due to excess supply from China and adverse conditions in the domestic and global shipbuilding and construction industries.
Shipbuilding. In 2011, the Republic’s shipbuilding orders amounted to approximately 12 million compensated gross tons, an increase of 50.0% compared to 2010, primarily due to increased demand for large container carriers, LNG carriers and floating production storage and offloading vessels. In 2012, the Republic’s shipbuilding orders amounted to approximately 8 million compensated gross tons, a decrease of 33.3% compared to 2011, primarily due to a downturn in the shipping and shipbuilding industry. In 2013, the Republic’s shipbuilding orders amounted to approximately 19 million compensated gross tons, an increase of 137.5% compared to 2012, primarily due to increased demand for LNG carriers, bulk carriers and container carriers. In 2014, the Republic’s shipbuilding orders amounted to approximately 13 million compensated gross tons, a decrease of 31.6% compared to 2013, primarily due to a downturn in the domestic and global shipbuilding industry. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, the Republic’s shipbuilding orders amounted to approximately 10 million compensated gross tons, a decrease of 23.1% compared to 2014, primarily due to the continued downturn in the domestic and global shipbuilding industry.
Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
The Government’s agricultural policy has traditionally focused on:
| • | grain production; |
| • | development of irrigation systems; |
| • | land consolidation and reclamation; |
| • | seed improvement; |
| • | mechanization measures to combat drought and flood damage; and |
| • | increasing agricultural incomes. |
Recently, however, the Government has increased emphasis on cultivating profitable crops and strengthening international competitiveness in anticipation of opening the domestic agricultural market.
In 2011, rice production decreased 2.3% from 2010 to 4.2 million tons. In 2012, rice production decreased 4.7% from 2011 to 4.0 million tons. In 2013, rice production increased 5.0% from 2012 to 4.2 million tons. In 2014, rice production remained at 4.2 million tons. In 2015, rice production increased 2.4% from 2014 to 4.3 million tons. Due to limited crop yields resulting from geographical and physical constraints, the Republic depends on imports for certain basic foodstuffs.
170
Table of Contents
The Government is seeking to develop the fishing industry by encouraging the building of large fishing vessels and modernizing fishing equipment, marketing techniques and distribution outlets.
In 2011, the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industry decreased by 2.1% compared to 2010, primarily due to unfavorable weather conditions, including heavy rains, during the summer and a decrease in fishing catch. In 2012, the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industry decreased by 0.6% compared to 2011, primarily due to unfavorable weather conditions, including severe typhoons, which more than offset an increase in the livestock industry. In 2013, the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industry increased by 3.1% compared to 2012, primarily due to an increase in the cultivation and livestock industry. Based on preliminary data, in 2014, the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industry increased by 2.6% compared to 2013, primarily due to increases in the price of certain livestock items, which led to increases in production and the establishment of new agriculture and fishery companies. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, the agriculture, forestry and fisheries industry decreased by 1.6% compared to 2014, primarily due to unfavorable weather conditions.
Construction
In 2011, the construction industry decreased by 4.3% compared to 2010, primarily due to a decrease in the construction of residential and commercial buildings. In 2012, the construction industry decreased by 1.6% compared to 2011, primarily due to a decrease in the construction of residential buildings and port facilities. In 2013, the construction industry increased by 3.0% compared to 2012, primarily due to an increase in the construction of residential and commercial buildings. In 2014, the construction industry increased by 0.6% compared to 2013, primarily due to an increase in the construction of private residential buildings. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, the construction industry increased by 3.2% compared to 2014, primarily due to an increase in the construction of private residential and commercial buildings.
Electricity and Gas
The following table sets out the Republic’s dependence on imports for energy consumption:
Dependence on Imports for Energy Consumption
| Total Primary Energy Supply |
Imports | Imports Dependence Ratio |
||||||||||
| (millions of tons of oil equivalents, except ratios) | ||||||||||||
| 2011 |
276.6 | 267.0 | 96.5 | |||||||||
| 2012 |
278.7 | 267.6 | 96.0 | |||||||||
| 2013 |
280.3 | 268.2 | 95.7 | |||||||||
| 2014 |
282.9 | 269.4 | 95.2 | |||||||||
| 2015(1) |
285.0 | 271.4 | 95.2 | |||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary. |
Source: Korea Energy Economics Institute; Korea National Statistical Office.
Korea has almost no domestic oil or gas production and depends on imported oil and gas to meet its energy requirements. Accordingly, the international prices of oil and gas significantly affect the Korean economy. Any significant long-term increase in the prices of oil and gas will increase inflationary pressures in Korea and adversely affect the Republic’s balance of trade.
171
Table of Contents
To reduce its dependence on oil and gas imports, the Government has encouraged energy conservation and energy source diversification emphasizing nuclear energy. The following table sets out the principal primary sources of energy consumed in the Republic, expressed in oil equivalents and as a percentage of total energy consumption.
Consumption of Energy by Source
| Coal | Petroleum | Nuclear | Others(1) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quantity | % | Quantity | % | Quantity | % | Quantity | % | Quantity | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (millions of tons of oil equivalents, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 |
83.5 | 30.2 | 105.1 | 38.0 | 33.2 | 12.0 | 54.8 | 19.8 | 276.6 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 |
81.1 | 29.1 | 106.2 | 38.1 | 31.8 | 11.4 | 59.6 | 21.4 | 278.7 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
81.9 | 29.2 | 105.8 | 37.7 | 29.3 | 10.5 | 63.3 | 22.6 | 280.3 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 |
84.6 | 29.9 | 104.9 | 37.1 | 33.0 | 11.7 | 60.4 | 21.4 | 282.9 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 |
84.5 | 29.6 | 109.4 | 38.4 | 34.8 | 12.2 | 56.4 | 19.8 | 285.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes natural gas, hydroelectric power and renewable energy. |
Source: Korea Energy Economics Institute; The Bank of Korea.
The Republic’s first nuclear power plant went into full operation in 1978 with a rated generating capacity of 587 megawatts. As of December 31, 2015, the Republic had 24 nuclear plants with a total estimated nuclear power generating capacity of 21,716 megawatts and six nuclear plants under construction. In January 2014, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy released its Second Energy Master Plan and revised the target proportion of nuclear supply in the Korea’s energy supply mix from 41% by 2030 to a range from 22% to 29% by 2035. In addition, in July 2015, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy approved the construction of two additional nuclear power plants, which together with previously announced plans to build nuclear power plants would bring the number of nuclear power plants to 36 by 2029. The Government plans to expand infrastructure to supply natural gas to households, pursue a long-term strategy of overseas energy development projects to ensure supply stability, increase clean and renewable energy and provide support for research and development pertaining to green technologies.
Services Sector
In 2011, the service industry increased by 3.0% compared to 2010 as the transportation and storage sector increased by 3.8%, the wholesale and retail trade, restaurants and hotels sector increased by 5.1% and the real estate and leasing sector increased by 2.2%, each compared with 2010. In 2012, the service industry increased by 2.7% compared to 2011 as the health and social work sector increased by 7.1%, the finance and insurance sector increased by 3.6% and the wholesale and retail trade, restaurants and hotels sector increased by 3.4%, each compared with 2011. In 2013, the service industry increased by 2.8% compared to 2012 as the business activities sector increased by 4.7%, the finance and insurance sector increased by 3.6% and the health and social work sector increased by 5.2%, each compared with 2012. In 2014, the service industry increased by 3.1% compared to 2013 as the health and social work sector increased by 7.5%, the finance and insurance sector increased by 5.7% and the business activities sector increased by 4.1%, each compared with 2013. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, the service industry increased by 2.8% compared to 2014 as the finance and insurance sector increased by 6.7%, the business activities sector increased by 3.6% and the health and social work sector increased by 5.8%, each compared with 2014.
172
Table of Contents
Prices, Wages and Employment
The following table shows selected price and wage indices and unemployment rates:
| Producer Price Index(1) |
Increase (Decrease) Over Previous Year |
Consumer Price Index(1) |
Increase (Decrease) Over Previous Year |
Wage Index(1)(2) |
Increase (Decrease) Over Previous Year |
Unemployment Rate(1)(3) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| (2010=100) | (%) | (2010=100) | (%) | (2010=100) | (%) | (%) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 |
106.7 | 6.7 | 104.0 | 4.0 | 100.3 | 0.3 | 3.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 |
107.5 | 0.7 | 106.3 | 2.2 | 109.1 | 8.8 | 3.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
105.7 | (1.6 | ) | 107.7 | 1.3 | 116.4 | 6.7 | 3.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 |
105.2 | (0.5 | ) | 109.0 | 1.3 | 123.1 | 5.8 | 3.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 |
110.0 | (4.0 | ) | 109.8 | 0.7 | N/A | (4) | N/A | (4) | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Average for year. |
| (2) | Nominal wage index of average earnings in manufacturing industry. |
| (3) | Expressed as a percentage of the economically active population. |
| (4) | Not available. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea National Statistical Office.
In 2011, the inflation rate increased to 4.0%, primarily due to increased oil prices in the first quarter as well as decreased supply in agricultural goods caused by unusually low temperatures in the spring and heavy rainfall in the summer. In 2012, the inflation rate decreased to 2.2%, primarily due to weakened aggregate demand and the implementation of new policies, including free school lunches. In 2013, the inflation rate decreased to 1.3%, primarily due to increased supply of agricultural goods. In 2014, the inflation rate remained at 1.3%, primarily due to increases in the prices of electricity, gas, water supply, food products and education, which were offset by lower oil prices. In 2015, the inflation rate decreased to 0.7%, primarily due to lower oil prices.
In 2011, the unemployment rate decreased to 3.4%, primarily due to an increase in the number of workers employed in the service industry (including healthcare, social welfare and education). In 2012, the unemployment rate decreased to 3.2%, primarily due to the continued increase in the number of workers employed in the service industry. In 2013, the unemployment rate decreased to 3.1%, primarily due to the continued increase in the number of workers employed in the service industry. In 2014, the unemployment rate increased to 3.5%, primarily due to the sluggishness of the domestic economy. In 2015, the unemployment rate increased to 3.6%, primarily due to the continued sluggishness of the domestic economy.
From 1992 to 2009, the economically active population of the Republic increased by approximately 24.8% to 24.3 million, while the number of employees increased by approximately 23.7% to 23.5 million. The economically active population over 15 years old as a percentage of the total over-15 population has remained between 60% and 63% over the past decade. Literacy among workers under 50 is almost universal. As of December 31, 2015, the economically active population of the Republic was 26.9 million and the number of employees was 25.9 million.
173
Table of Contents
The following table shows selected employment information by industry and by gender:
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (all figures in percentages, except as indicated) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Labor force (in thousands of persons) |
24,244 | 24,681 | 25,066 | 25,599 | 25,936 | |||||||||||||||
| Employment by Industry: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing |
6.4 | 6.2 | 6.1 | 5.7 | 5.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Mining and Manufacturing |
16.9 | 16.7 | 16.8 | 17.0 | 17.4 | |||||||||||||||
| S.O.C & Services |
76.7 | 77.1 | 77.2 | 77.4 | 77.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Electricity, Transport, Communication and Finance |
12.2 | 12.1 | 12.2 | 11.9 | 11.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Business, Private & Public Service and Other Services |
34.6 | 35.1 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 35.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Construction |
7.2 | 7.2 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Wholesale & Retail Trade, Hotels and Restaurants |
22.7 | 22.7 | 22.5 | 23.0 | 23.0 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total Employed |
100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Employment by Gender: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Male |
58.4 | 58.3 | 58.1 | 58.0 | 57.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Female |
41.6 | 41.7 | 41.9 | 42.0 | 42.3 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total Employed |
100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Source: The Bank of Korea
As of July 1, 2004, the Republic adopted a five-day workweek for large corporations with over 1,000 employees, publicly-owned (state-run) companies, banks and insurance companies, reducing working hours from 44 to 40 hours a week. The adoption of the five-day workweek has been extended to companies with over 300 employees and to government employees as of July 1, 2005 and to companies with over 100 employees as of July 1, 2006. Companies with more than 50 employees adopted the five-day workweek as of July 1, 2007 and those with over 20 adopted the five-day workweek as of July 1, 2008. Companies with less than 20 employees also adopted the five-day workweek on July 1, 2011.
Approximately 10.3% of the Republic’s workers were unionized as of December 31, 2014. Labor unrest in connection with demands by unionized workers for better wages and working conditions and greater job security occur from time to time in the Republic. Some of the significant incidents in recent years include the following:
| • | In July 2011, unionized employees at Standard Chartered Korea (formerly, SC First Bank) engaged in a two-month strike, the longest in the Republic’s banking sector, demanding that the bank scrap performance-related pay reforms. |
| • | In June 2012, unionized taxi drivers went on their first nationwide strike demanding fare increases and protesting against increased fuel costs. |
| • | In August 2012, unionized workers of Hyundai Motor Company went on a series of partial strikes demanding a higher bonus increase and the end of overnight shifts. |
| • | In August 2013, unionized workers at Hyundai Motor Company and Kia Motors Corporation went on partial strikes demanding higher wages. |
| • | In December 2013, unionized workers at the state owned Korea Railroad Corporation (“Korail”) went on strike against Korail’s plan to establish a separate company to operate a new bullet train line fearing that such plan would eventually lead to privatization of Korail and layoffs of existing workers. |
| • | In November 2014, unionized workers at Hyundai Heavy Industries went on a series of partial strikes demanding higher wages. |
174
Table of Contents
| • | In April 2015, tens of thousands of members of the Korean Confederation of Trade Unions, which includes teacher and civil servant union groups, went on general strike demanding that the Government scrap its plans to reform the labor market and pension program for public workers. |
Actions such as these by labor unions may hinder implementation of the labor reform measures and disrupt the Government’s plans to create a more flexible labor market. Although much effort is being expended to resolve labor disputes in a peaceful manner, there can be no assurance that further labor unrest will not occur in the future. Continued labor unrest in key industries of the Republic may have an adverse effect on the economy.
In 1997, the Korean Confederation of Trade Unions organized a political alliance, which led to the formation of the Democratic Labor Party in January 2000. The Democratic Labor Party merged with The New People’s Participation Party and changed its name to The Unified Progressive Party (“UPP”) in December 2011. In October 2012, the UPP split and seven UPP members of the National Assembly and their supporters formed a new party, the Progressive Justice Party, which changed its name to the Justice Party in July 2013. In December 2014, the Constitutional Court ordered the dissolution of the UPP and the removal of the party’s five lawmakers from the National Assembly for violating the Republic’s Constitution after certain of its members were convicted of trying to instigate an armed rebellion and supporting North Korea. In the legislative general election held on April 13, 2016, the Justice Party won six seats in the National Assembly, and the members-elect will begin their four-year terms on May 30, 2016.
Structure of the Financial Sector
The Republic’s financial sector includes the following categories of financial institutions:
| • | The Bank of Korea; |
| • | banking institutions; |
| • | non-bank financial institutions; and |
| • | other financial entities, including: |
| • | financial investment companies; |
| • | credit guarantee institutions; |
| • | venture capital companies; and |
| • | miscellaneous others. |
To increase transparency in financial transactions and enhance the integrity and efficiency of the financial markets, Korean law requires that financial institutions confirm that their clients use their real names when transacting business. To ease the liquidity crisis, the Government altered the real-name financial transactions system during 1998, to allow the sale or deposit of foreign currencies through domestic financial institutions and the purchase of certain bonds, including Government bonds, without identification. The Government also strengthened confidentiality protection for private financial transactions.
In July 2007, the Korean National Assembly passed the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act or FSCMA, under which various industry-based capital markets regulatory systems currently were consolidated into a single regulatory system. The FSCMA, which became effective in February 2009, expands the scope of permitted investment-related financial products and activities through expansive definitions of financial instruments and function-based regulations that allow financial investment companies to offer a wider range of financial services, as well as strengthening investor protection and disclosure requirements..
175
Table of Contents
Prior to the effective date of the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act, separate laws regulated various types of financial institutions depending on the type of the financial institution (for example, securities companies, futures companies, trust business companies and asset management companies) and subjected financial institutions to different licensing and ongoing regulatory requirements (for example, under the Securities and Exchange Act, the Futures Business Act and the Indirect Investment Asset Management Business Act). By applying one uniform set of rules to financial businesses having the same economic function, the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act attempts to improve and address issues caused by the previous regulatory system under which the same economic function relating to capital markets-related business were governed by multiple regulations. To this end, the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act categorizes capital markets-related businesses into six different functions, as follows:
| • | investment dealing (trading and underwriting of financial investment products); |
| • | investment brokerage (brokerage of financial investment products); |
| • | collective investment (establishment of collective investment schemes and the management thereof); |
| • | investment advice; |
| • | discretionary investment management; and |
| • | trusts (together with the five businesses set forth above, “Financial Investment Businesses”). |
Accordingly, all financial businesses relating to financial investment products are reclassified as one or more of the Financial Investment Businesses described above, and financial institutions are subject to the regulations applicable to their relevant Financial Investment Businesses, irrespective of what type of financial institution it is. For example, under the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act, derivative businesses conducted by securities companies and future companies will be subject to the same regulations under the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act, at least in principle.
The banking business and the insurance business are not subject to the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act and will continue to be regulated under separate laws; provided, however, that they are subject to the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act if their activities involve any Financial Investment Businesses requiring a license based on the Financial Investment Services and Capital Markets Act.
Banking Industry
The banking industry comprises commercial banks and specialized banks. Commercial banks serve the general public and corporate sectors. They include nationwide banks, regional banks and branches of foreign banks. Regional banks provide services similar to nationwide banks, but operate in a geographically restricted region. Branches of foreign banks have operated in the Republic since 1967 but provide a relatively small proportion of the country’s banking services. As of December 31, 2015, there were six nationwide banks, six regional banks and 42 foreign banks with branches operating in the Republic.
Specialized banks meet the needs of specific sectors of the economy in accordance with Government policy; they are organized under, or chartered by, special laws. Specialized banks include:
| • | The Korea Development Bank; |
| • | The Export-Import Bank of Korea; |
| • | The Industrial Bank of Korea; |
| • | National Federation of Fisheries Cooperatives; and |
| • | NH Bank. |
176
Table of Contents
The economic difficulties in 1997 and 1998 caused an increase in Korean banks’ non-performing assets and a decline in capital adequacy ratios of Korean banks. From 1998 through 2002, the Financial Services Commission amended banking regulations several times to adopt more stringent criteria for non-performing assets that more closely followed international standards. Non-performing assets are assets classified as doubtful or estimated loss under Korean banking regulations.
The following table sets out the total loans (including loans in Won and loans in foreign currencies) and non-performing assets of Korean banks.
| Total Loans | Non-Performing Assets(1) |
Percentage of Total |
||||||||||
| (trillions of won) | (percentage) | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 |
1,387.6 | 18.8 | 1.4 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2012 |
1,390.9 | 18.5 | 1.3 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2013 |
1,441.6 | 25.7 | 1.8 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2014 |
1,557.9 | 24.2 | 1.6 | |||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
1,664.3 | 28.5 | 1.7 | |||||||||
| (1) | Assets classified as substandard or below. |
Source: Financial Supervisory Service.
As of December 31, 2014, loans denominated in Won held
by these banks increased by 8.0% to W1,255.8 trillion from W1,162.8 trillion as of December 31, 2013, primarily due to (i) an increase in household loans by 8.2% to
W518.2 trillion as of December 31, 2014 from W479.0 trillion as of December 31, 2013, (ii) an increase in loans to small and medium-enterprises by 6.8% to W522.4 trillion as of
December 31, 2014 from W489.0 trillion as of December 31, 2013 and (iii) an increase in loans to large corporations by 10.5% to W183.5 trillion as of December 31, 2014 from
W166.1 trillion as of December 31, 2013. Based on preliminary data, as of December 31, 2015, loans denominated in Won held by these banks increased by 16.3% to W1,352.9 trillion from
W1,162.8 trillion as of December 31, 2014, primarily due to (i) an increase in household loans by 8.6% to W562.8 trillion as of December 31, 2015 from W518.2 trillion as of
December 31, 2014 and (ii) an increase in loans to small and medium-enterprises by 10.4% to W576.6 trillion as of December 31, 2015 from W522.4 trillion as of December 31, 2014.
In 2011, these banks posted an aggregate net profit of
W11.8 trillion, compared to an aggregate net profit of W9.3 trillion in 2010, primarily due to decreased non-performing loans. In 2012, these banks posted an aggregate net profit of W8.7 trillion,
compared to an aggregate net profit of W11.8 trillion in 2011, primarily due to a decrease in gain on sale of equity securities and an increase in impairment loss on available-for-sale securities. In 2013, these banks posted an
aggregate net profit of W3.9 trillion, compared to an aggregate net profit of W8.7 trillion in 2012, primarily due to decreased net interest income and increased loan loss provisions. In 2014, these banks
posted an aggregate net profit of W6.0 trillion, compared to an aggregate net profit of W3.9 trillion in 2013, primarily due to decreased loan loss provisions. Based on preliminary data, in 2015, these banks posted
an aggregate net profit of W3.5 trillion, compared to an aggregate net profit of W6.0 trillion in 2014, primarily due to increased loan loss provisions.
Non-Bank Financial Institutions
Non-bank financial institutions include:
| • | savings institutions, including trust accounts of banks, mutual savings banks, credit unions, mutual credit facilities, community credit cooperatives and postal savings; |
| • | life insurance institutions; and |
| • | credit card companies. |
177
Table of Contents
As of December 31, 2015, 79 mutual savings banks, 23 life insurance institutions, which includes joint venture life insurance institutions and wholly-owned subsidiaries of foreign life insurance companies, and eight credit card companies operated in the Republic.
Money Markets
In the Republic, the money markets consist of the call market and markets for a wide range of other short-term financial instruments, including treasury bills, monetary stabilization bonds, negotiable certificates of deposits, repurchase agreements and commercial paper.
Securities Markets
On January 27, 2005, the Korea Exchange was established pursuant to the now repealed Korea Securities and Futures Exchange Act by consolidating the Korea Stock Exchange, the Korea Futures Exchange, the KOSDAQ Stock Market, Inc., or the KOSDAQ, and the KOSDAQ Committee of the Korea Securities Dealers Association, which had formerly managed the KOSDAQ. There are three major markets operated by the Korea Exchange: the KRX KOSPI Market, the KRX KOSDAQ Market, and the KRX Derivatives Market. The Korea Exchange has two trading floors located in Seoul, one for the KRX KOSPI Market and one for the KRX KOSDAQ Market, and one trading floor in Busan for the KRX Derivatives Market. The Korea Exchange is a joint stock company with limited liability, the shares of which are held by (i) financial investment companies that were formerly members of the Korea Futures Exchange or the Korea Stock Exchange and (ii) the stockholders of the KOSDAQ. Currently, the Korea Exchange is the only stock exchange in Korea and is operated by membership, having as its members Korean financial investment companies and some Korean branches of foreign financial investment companies.
The Korea Exchange publishes the Korea Composite Stock Price Index every ten seconds, which is an index of all equity securities listed on the Korea Exchange. The Korea Composite Stock Price Index is computed using the aggregate value method, whereby the market capitalizations of all listed companies are aggregated, subject to certain adjustments, and this aggregate is expressed as a percentage of the aggregate market capitalization of all listed companies as of the base date, January 4, 1980.
178
Table of Contents
The following table shows the value of the Korea Composite Stock Price Index as of the dates indicated:
| December 30, 2010 |
2,051.0 | |||
| January 31, 2011 |
2,069.7 | |||
| February 28, 2011 |
1,939.3 | |||
| March 31, 2011 |
2,106.7 | |||
| April 30, 2011 |
2,192.4 | |||
| May 31, 2011 |
2,142.5 | |||
| June 30, 2011 |
2,100.7 | |||
| July 29, 2011 |
2,133.2 | |||
| August 31, 2011 |
1,880.1 | |||
| September 30, 2011 |
1,769.7 | |||
| October 31, 2011 |
1,909.0 | |||
| November 30, 2011 |
1,847.5 | |||
| December 29, 2011 |
1,825.7 | |||
| January 31, 2012 |
1,955.8 | |||
| February 29, 2012 |
2,030.3 | |||
| March 31, 2012 |
2,014.0 | |||
| April 30, 2012 |
1,982.0 | |||
| May 31, 2012 |
1,843.5 | |||
| June 29, 2012 |
1,854.0 | |||
| July 31, 2012 |
1,882.0 | |||
| August 31, 2012 |
1,905.1 | |||
| September 28, 2012 |
1,996.2 | |||
| October 31, 2012 |
1,912.1 | |||
| November 30, 2012 |
1,932.9 | |||
| December 28, 2012 |
1,997.1 | |||
| January 31, 2013 |
1,961.9 | |||
| February 28, 2013 |
2,026.5 | |||
| March 29, 2013 |
2,004.9 | |||
| April 30, 2013 |
1,964.0 | |||
| May 30, 2013 |
2,001.1 | |||
| June 28, 2013 |
1,863.3 | |||
| July 31, 2013 |
1,914.0 | |||
| August 30, 2013 |
1,926.4 | |||
| September 30, 2013 |
1,997.0 | |||
| October 31, 2013 |
2,030.1 | |||
| November 29, 2013 |
2,044.9 | |||
| December 30, 2013 |
2,011.3 | |||
| January 29, 2014 |
1,941.2 | |||
| February 28, 2014 |
1,980.0 | |||
| March 31, 2014 |
1,985.6 | |||
| April 30, 2014 |
1,961.8 | |||
| May 30, 2014 |
1,995.0 | |||
| June 30, 2014 |
2,002.2 | |||
| July 31, 2014 |
2,076.1 | |||
| August 29, 2014 |
2,068.5 | |||
| September 30, 2014 |
2,020.1 | |||
| October 31, 2014 |
1,964.4 | |||
| November 28, 2014 |
1,980.8 |
179
Table of Contents
| December 31, 2014 |
1,915.6 | |||
| January 30, 2015 |
1,949.3 | |||
| February 27, 2015 |
1,985.8 | |||
| March 31, 2015 |
2,041.0 | |||
| April 30, 2015 |
2,127.2 | |||
| May 29, 2015 |
2,114.8 | |||
| June 30, 2015 |
2,074.2 | |||
| July 31, 2015 |
2,030.2 | |||
| August 29, 2015 |
1,941.5 | |||
| September 30, 2015 |
1,962.8 | |||
| October 30, 2015 |
2,029.5 | |||
| November 30, 2015 |
1,992.0 | |||
| December 30, 2015 |
1,960.3 | |||
| January 29, 2016 |
1,912.1 | |||
| February 29, 2016 |
1,916.7 | |||
| March 31, 2016 |
1,995.8 | |||
| April 29, 2016 |
1,994.2 | |||
| May 31, 2016 |
1,983.4 |
On December 27, 1997, the last day of trading in 1997, the index stood at 376.3, a sharp decline from 647.1 on September 30, 1997. The fall resulted from growing concerns about the Republic’s weakening financial and corporate sectors, the Republic’s falling foreign currency reserves, the sharp depreciation of the Won against the U.S. Dollar and other external factors, such as a sharp decline in stock prices in Hong Kong on October 24, 1997 and financial turmoil in Southeast Asian countries. The Korea Composite Stock Price Index recovered to reach 2,064.9 in late 2007 but since then the index declined. As liquidity and credit concerns and volatility in the global financial markets increased significantly since September 2008, there was a significant overall decline in the stock prices of Korean companies during the fourth quarter of 2008 and first half of 2009 and continuing volatility since then. The index was 1,979.1 on June 13, 2016.
Supervision System
The Office of Bank Supervision, the Securities Supervisory Board, the Insurance Supervisory Board and all other financial sector regulatory bodies merged in January 1999 to form the Financial Services Commission. The Financial Services Commission acts as the executive body over the Financial Supervisory Service. The Financial Services Commission reports to, but operates independently of, the Prime Minister’s office.
The Ministry of Strategy and Finance focuses on financial policy and foreign currency regulations. The Bank of Korea manages monetary policy focusing on price stabilization.
Deposit Insurance System
The Republic’s deposit insurance system insures amounts on deposit with banks, non-bank financial institutions, securities companies and life insurance companies.
Since January 2001,
deposits at any single financial institution are insured only up to W50 million per person regardless of the amount deposited.
The Government excluded certain deposits, such as repurchase agreements, from the insurance scheme, expanded the definition of unsound financial institutions to which the insurance scheme would apply and gradually increased the insurance premiums payable by insured financial institutions.
180
Table of Contents
The Bank of Korea
The Bank of Korea was established in 1950 as Korea’s central bank and the country’s sole currency issuing bank. A seven-member Monetary Policy Committee, chaired by the Governor of The Bank of Korea, formulates and controls monetary and credit policies.
Inflation targeting is the basic system of operation for Korean monetary policy. The consumer price index is used as The Bank of Korea’s target indicator. To achieve its established inflation target, the Monetary Policy Committee of The Bank of Korea determines and announces the “Bank of Korea Base Rate,” the reference rate applied in transactions such as repurchase agreements between The Bank of Korea and its financial institution counterparts. The Bank of Korea uses open market operations as its primary instrument to keep the call rate in line with the Monetary Policy Committee’s target rate. In addition, The Bank of Korea is able to establish policies regarding its lending to banks in Korea and their reserve requirements.
Interest Rates
On July 12, 2007, The Bank of Korea raised the policy rate to 4.75% from 4.5%, and raised it further to 5.0% on August 9, 2007. The rationale for this change was the concern that the ample market liquidity might put upside pressure on inflation in the medium to long term as the economic upswing continued. On August 7, 2008, The Bank of Korea raised the policy rate to 5.25% from 5.0%, taking the view that inflation in consumer prices had picked up its pace, due to the direct and indirect effects of high oil prices, at a time when domestic economic activity had slackened. On October 9, 2008, The Bank of Korea cut its policy rate to 5.0% from 5.25%, and continued to lower it further to 4.25% on October 27, 2008, 4.0% on November 7, 2008, 3.0% on December 11, 2008, 2.5% on January 9, 2009 and 2.0% on February 12, 2009, in order to address financial market instability and to help combat the slowdown of the domestic economy. On July 9, 2010, The Bank of Korea raised the policy rate to 2.25% from 2.0%, which was further raised to 2.5% on November 16, 2010, in response to signs of inflationary pressures and the continued growth of domestic economy. On January 13, 2011, The Bank of Korea raised the policy rate to 2.75%, which was further increased to 3.0% on March 10, 2011 and to 3.25% on June 10, 2011, in response to inflationary pressures driven mainly by rises in the prices of petroleum products and farm products. The Bank of Korea lowered its policy rate to 3.0% from 3.25% on July 12, 2012, which was further lowered to 2.75% on October 11, 2012, 2.5% on May 9, 2013, 2.25% on August 14, 2014, 2.0% on October 15, 2014, 1.75% on March 12, 2015, 1.5% on June 11, 2015 and 1.25% on June 9, 2016, in order to address the sluggishness of the global and domestic economy.
With the deregulation of interest rates on banks’ demand deposits on February 2, 2004, The Bank of Korea completed the interest rate deregulation based upon the “Four-Stage Interest Rate Liberalization Plan” announced in 1991. The prohibition on the payment of interest on ordinary checking accounts was, however, maintained.
Money Supply
The following table shows the volume of the Republic’s money supply:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Money Supply (M1)(1) |
442,077.5 | 470,010.6 | 515,643.4 | 585,822.6 | 708,452.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Quasi-money(2) |
1,309,380.9 | 1,365,631.0 | 1,405,151.6 | 1,491,411.4 | 1,538,922.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Money Supply (M2)(3) |
1,751,458.4 | 1,835,641.6 | 1,920,795.0 | 2,077,234.0 | 2,247,375.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Percentage Increase Over Previous Year |
5.5 | % | 4.8 | % | 4.6 | % | 8.1 | % | 8.2 | % | ||||||||||
| (1) | Consists of currency in circulation and demand and instant access savings deposits at financial institutions. |
181
Table of Contents
| (2) | Includes time and installment savings deposits, marketable instruments, yield-based dividend instruments and financial debentures, excluding financial instruments with a maturity of more than two years. |
| (3) | Money Supply (M2) is the sum of Money Supply (M1) and quasi-money. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
Exchange Controls
Authorized foreign exchange banks, as registered with the Ministry of Strategy and Finance, handle foreign exchange transactions. The ministry has designated other types of financial institutions to handle foreign exchange transactions on a limited basis.
Korean laws and regulations generally require a report to either the Ministry of Strategy and Finance, The Bank of Korea or authorized foreign exchange banks, as applicable, for issuances of international bonds and other instruments, overseas investments and certain other transactions involving foreign exchange payments.
In 1994 and 1995, the Government relaxed regulations of foreign exchange position ceilings and foreign exchange transaction documentation and created free Won accounts which may be opened by non-residents at Korean foreign exchange banks. The Won funds deposited into the free Won accounts may be converted into foreign currencies and remitted outside Korea without any governmental approval. In December 1996, after joining the OECD, the Republic freed the repatriation of investment funds, dividends and profits, as well as loan repayments and interest payments. The Government continues to reduce exchange controls in response to changes in the world economy, including the new trade regime under the WTO, anticipating that such foreign exchange reform will improve the Republic’s competitiveness and encourage strategic alliances between domestic and foreign entities.
In September 1998, the National Assembly passed the Foreign Exchange Transactions Act, which became effective in April 1999 and has subsequently been amended numerous times. In principle, most currency and capital transactions, including, among others, the following transactions, have been liberalized:
| • | the investment in real property located overseas by Korean companies and financial institutions; |
| • | the establishment of overseas branches and subsidiaries by Korean companies and financial institutions; |
| • | the investment by non-residents in deposits and trust products having more than one year maturities; and |
| • | the issuance of debentures by non-residents in the Korean market. |
To minimize the adverse effects from further opening of the Korean capital markets, the Ministry of Strategy and Finance is authorized to introduce a variable deposit requirement system to restrict the influx of short-term speculative funds.
The Government has also embarked on a second set of liberalization initiatives starting in January 2001, under which ceilings on international payments for Korean residents have been eliminated, including overseas travel expenses, overseas inheritance remittances and emigration expenses. Overseas deposits, trusts, acquisitions of foreign securities and other foreign capital transactions made by residents and the making of deposits in Korean currency by non-residents have also been liberalized. In line with the foregoing liberalization, measures will also be adopted to curb illegal foreign exchange transactions and to stabilize the foreign exchange market.
Effective as of January 1, 2006, the Government liberalized the regulations governing “capital transactions.” The regulations provide that no regulatory approvals are required for any capital transactions. The capital transactions previously subject to approval requirements are now subject only to reporting requirements.
182
Table of Contents
In January 2010, the Financial Supervisory Services released FX Derivative Transactions Risk Management Guideline to prevent over-hedging of foreign exchange risk by corporate investors. According to the guideline as amended in July 2010, if a corporate investor, other than a financial institution or a public enterprise, wishes to enter into a foreign exchange forward, option or swap agreement with a bank, the bank is required to verify whether the corporate investor’s assets, liabilities or contracts face foreign exchange risks that could be mitigated by a foreign exchange forward, option or swap agreement. In addition, the bank is required to ensure that the corporate investor’s risk hedge ratio, which is the ratio of the aggregate notional amount to the aggregate amount of risk, does not exceed 100%.
Foreign Exchange
The following table shows the exchange rate between the Won and the U.S. Dollar (in Won per U.S. Dollar) as announced by the Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. as of the dates indicated:
| Won/U.S. Dollar Exchange Rate |
||||
| December 30, 2010 |
1,138.9 | |||
| January 31, 2011 |
1,114.3 | |||
| February 28, 2011 |
1,127.9 | |||
| March 31, 2011 |
1,107.2 | |||
| April 29, 2011 |
1,072.3 | |||
| May 31, 2011 |
1,080.6 | |||
| June 30, 2011 |
1,078.1 | |||
| July 29, 2011 |
1,052.6 | |||
| August 31, 2011 |
1,071.7 | |||
| September 30, 2011 |
1,179.5 | |||
| October 31, 2011 |
1,104.9 | |||
| November 30, 2011 |
1,150.3 | |||
| December 30, 2011 |
1,153.3 | |||
| January 31, 2012 |
1,125.0 | |||
| February 29, 2012 |
1,126.5 | |||
| March 30, 2012 |
1,137.8 | |||
| April 30, 2012 |
1,134.2 | |||
| May 31, 2012 |
1,177.8 | |||
| June 29, 2012 |
1,153.8 | |||
| July 31, 2012 |
1,136.2 | |||
| August 31, 2012 |
1,134.6 | |||
| September 28, 2012 |
1,118.6 | |||
| October 31, 2012 |
1,094.1 | |||
| November 30, 2012 |
1,084.7 | |||
| December 31, 2012 |
1,071.1 | |||
| January 31, 2013 |
1,082.7 | |||
| February 28, 2013 |
1,085.4 | |||
| March 29, 2013 |
1,112.1 | |||
| April 30, 2013 |
1,108.1 | |||
| May 31, 2013 |
1,128.3 | |||
| June 28, 2013 |
1,149.7 | |||
| July 31, 2013 |
1,113.6 | |||
| August 30, 2013 |
1,110.9 | |||
| September 30, 2013 |
1,075.6 | |||
| October 31, 2013 |
1,061.4 | |||
| November 29, 2013 |
1,062.1 | |||
183
Table of Contents
| Won/U.S. Dollar Exchange Rate |
||||
| December 31, 2013 |
1,055.3 | |||
| January 29, 2014 |
1,079.2 | |||
| February 28, 2014 |
1,067.7 | |||
| March 31, 2014 |
1,068.8 | |||
| April 30, 2014 |
1,031.7 | |||
| May 30, 2014 |
1,021.6 | |||
| June 30, 2014 |
1,014.4 | |||
| July 31, 2014 |
1,024.3 | |||
| August 29, 2014 |
1,013.6 | |||
| September 30, 2014 |
1,059.6 | |||
| October 31, 2014 |
1,054.0 | |||
| November 28, 2014 |
1,101.1 | |||
| February 28, 2014 |
1,067.7 | |||
| December 31, 2014 |
1,099.2 | |||
| January 30, 2015 |
1,090.8 | |||
| February 27, 2015 |
1,099.2 | |||
| March 31, 2015 |
1,105.0 | |||
| April 30, 2015 |
1,068.1 | |||
| May 29, 2015 |
1,108.0 | |||
| June 30, 2015 |
1,124.1 | |||
| July 31, 2015 |
1,166.3 | |||
| August 31, 2015 |
1,176.3 | |||
| September 30, 2015 |
1,194.5 | |||
| October 30, 2015 |
1,142.3 | |||
| November 30, 2015 |
1,150.4 | |||
| December 31, 2015 |
1,172.0 | |||
| January 29, 2016 |
1,208.4 | |||
| February 29, 2016 |
1,235.4 | |||
| March 31, 2016 |
1,153.5 | |||
| April 29, 2016 |
1,143.9 | |||
| May 31, 2016 |
1,190.6 | |||
Prior to November 1997, the
Government had permitted exchange rates to float within a daily range of 2.25%. In response to the substantial downward pressures on the Won caused by the Republic’s economic difficulties in late 1997, in November 1997, the Government expanded
the range of permitted daily exchange rate fluctuations to 10%. The Government eliminated the daily exchange rate band in December 1997, and the Won now floats according to market forces. The value of the Won relative to the U.S. dollar depreciated
from W888.1 to US$1.00 on June 30, 1997 to W1,964.8 to US$1.00 on December 24, 1997. Due to improved economic conditions and increases in trade surplus, the Won has generally appreciated against the
U.S. dollar, although the trend reversed in March 2008. During the period from January 2, 2008 through April 16, 2009, the value of the Won relative to the U.S. dollar declined by approximately 29.9%, due primarily to adverse economic
conditions resulting from liquidity and credit concerns and volatility in the global credit and financial markets and repatriations by foreign investors of their investments in the Korean stock market. The market average exchange rate was
W1,163.1 to US$1.00 on June 13, 2016.
Balance of Payments and Foreign Trade
Balance of Payments
Balance of payments figures measure the relative flow of goods, services and capital into and out of the country as represented in the current balance and the capital balance. The current balance tracks a country’s trade in goods and services and transfer payments and measures whether a country is living within its income from
184
Table of Contents
trading and investments. The capital balance covers all transactions involving the transfer of capital into and out of the country, including loans and investments. The overall balance represents the sum of the current and capital balances. An overall balance surplus indicates a net inflow of foreign currencies, thereby increasing demand for and strengthening the local currency. An overall balance deficit indicates a net outflow of foreign currencies, thereby decreasing demand for and weakening the local currency. The financial account mirrors the overall balance. If the overall balance is positive, the surplus, which represents the nation’s savings, finances the overall deficit of the country’s trading partners. Accordingly, the financial account will indicate cash outflows equal to the overall surplus. If, however, the overall balance is negative, the nation has an international deficit which must be financed. Accordingly, the financial account will indicate cash inflows equal to the overall deficit.
The following table sets out certain information with respect to the Republic’s balance of payments:
Balance of Payments(1)
| Classification |
2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(4) | |||||||||||||||
| (millions of dollars) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Account |
18,655.8 | 50,835.0 | 81,148.2 | 84,373.0 | 105,955.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Goods |
29,089.9 | 49,406.0 | 82,781.0 | 88,885.4 | 120,374.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Exports(2) |
587,099.7 | 603,509.2 | 618,156.9 | 613,020.6 | 548,933.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Imports(2) |
558,009.8 | 554,103.2 | 535,375.9 | 524,135.2 | 428,559.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Services |
(12,279.1 | ) | (5,213.6 | ) | (6,499.2 | ) | (3,678.5 | ) | (15,707.9 | ) | ||||||||||
| Income |
6,560.6 | 12,116.7 | 9,055.7 | 4,150.8 | 5,901.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Current Transfers |
(4,715.6 | ) | (5,474.1 | ) | (4,189.3 | ) | (4,984.7 | ) | (4,612.9 | ) | ||||||||||
| Capital and Financial Account |
(24,203.8 | ) | 51,540.7 | 80,077.6 | 89,325.1 | 109,562.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Capital Account |
(112.0 | ) | (41.7 | ) | (27.0 | ) | (8.9 | ) | (64.7 | ) | ||||||||||
| Financial Account(3) |
24,315.8 | 51,582.4 | 80,104.6 | 89,334.0 | 109,626.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Errors and Omissions |
5,772.0 | 789.1 | (1,016.6 | ) | 4,969.9 | 3,736.4 | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Figures are prepared based on the sixth edition of Balance of Payment Manual, or BPM6, published by International Monetary Fund in December 2010 and implemented by the Government in December 2013. |
| (2) | These entries are derived from trade statistics and are valued on a free on board basis, meaning that the insurance and freight costs are not included. |
| (3) | Includes borrowings from the IMF, syndicated bank loans and short-term borrowings. |
| (4) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea.
The Republic recorded a current account surplus of approximately US$84.4 billion in 2014. The current account surplus in 2014 increased from the current account surplus of US$81.1 billion in 2013, primarily due to an increase in surplus from the goods account.
Based on preliminary data, the Republic recorded a current account surplus of approximately US$106.0 billion in 2015. The current account surplus in 2015 increased from the current account surplus of US$84.4 billion in 2014, primarily due to an increase in surplus from the goods account which more than offset an increase in deficit from the services account.
Foreign Direct Investment
Since 1960, the Government has adopted a broad range of related laws, administrative rules and regulations, providing a framework for the conduct and regulation of foreign investment activities. In September 1998, the Government promulgated the Foreign Investment Promotion Act, or the FIPA, which replaced previous foreign direct investment related laws, rules and regulations, to promote inbound foreign investments by providing
185
Table of Contents
incentives to, and facilitating investment activities in the Republic by, foreign nationals. The FIPA prescribes, among others, procedural requirements for inbound foreign investments, incentives for foreign investments such as tax reductions, and requirements relating to designation and development of foreign investment target regions. The Government believes that providing a stable and receptive environment for foreign direct investment will accelerate the inflow of foreign capital, technology and management techniques.
The following table sets forth information regarding annual foreign direct investment in the Republic for the periods indicated.
Foreign Direct Investment
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Contracted and Reported Investment |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Greenfield Investment(1) |
11.7 | 12.5 | 9.6 | 11.0 | 14.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Merger & Acquisition |
2.0 | 3.8 | 5.0 | 8.0 | 6.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
13.7 | 16.3 | 14.5 | 19.0 | 20.9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Actual Investment |
6.6 | 10.7 | 9.8 | 12.1 | 16.3 | (2) | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | Includes building new factories and operational facilities. |
| (2) | Preliminary. |
Source: Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy
In 2015, the contracted and reported amount of foreign direct investment in the Republic increased to US$20.9 billion from US$19.0 billion in 2014, primarily due to an increase in foreign investment in the service sector to US$14.7 billion in 2015 from US$11.2 billion in 2014 which more than offset a decrease in foreign investment in the manufacturing sector to US$4.6 billion in 2015 from US$7.6 billion in 2014.
186
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth information regarding the source of foreign direct investment by region and country for the periods indicated:
Foreign Direct Investment by Region and Country
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| North America |
||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S.A |
2.4 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 5.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Others |
1.3 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 2.9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 3.7 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 8.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Asia |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Japan |
2.3 | 4.5 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 1.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Hong Kong |
0.6 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Singapore |
0.6 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||
| China |
0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Others |
0.2 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.7 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 4.4 | 8.8 | 5.0 | 6.8 | 8.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| European Union |
||||||||||||||||||||
| England |
0.9 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Netherlands |
1.0 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 2.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Germany |
1.5 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||
| France |
0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Luxembourg |
0.1 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Others |
1.7 | 1.2 | 2.6 | 1.6 | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 5.4 | 3.0 | 4.9 | 6.7 | 2.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Others regions and countries |
0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.4 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
13.7 | 16.3 | 14.5 | 19.0 | 20.9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Source: Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy
Trade Balance
Trade balance figures measure the difference between a country’s exports and imports. If exports exceed imports the country has a trade balance surplus while if imports exceed exports the country has a deficit. A deficit, indicating that a country’s receipts from abroad fall short of its payments to foreigners, must be financed, rendering the country a debtor nation. A surplus, indicating that a country’s receipts exceed its payments to foreigners, allows the country to finance its trading partners’ net deficit to the extent of the surplus, rendering the country a creditor nation.
187
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the Republic’s trade balance for the periods indicated:
Trade Balance
| Exports(1) | As % of GDP(2) |
Imports(3) | As % of GDP(2) |
Balance of Trade |
Exports as % of Imports |
|||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 |
555.2 | 46.9 | % | 524.4 | 44.3 | % | 30.8 | 105.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2012 |
547.9 | 46.0 | % | 519.6 | 43.6 | % | 28.3 | 105.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2013 |
559.6 | 44.4 | % | 515.6 | 40.9 | % | 44.0 | 108.5 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2014 |
572.7 | 44.1 | % | 525.5 | 40.5 | % | 47.2 | 109.0 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2015(4) |
526.9 | 42.2 | % | 436.6 | 35.0 | % | 90.3 | 120.7 | ||||||||||||||||
| (1) | These entries are derived from customs clearance statistics on a C.I.F. basis, meaning that the price of goods include insurance and freight cost. |
| (2) | At chained 2010 year prices. |
| (3) | These entries are derived from customs clearance statistics on a C.I.F. basis, meaning that the price of goods include insurance and freight cost. |
| (4) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea Customs Service.
The Republic, due to its lack of natural resources, relies on extensive trading activity for growth. The country meets virtually all domestic requirements for petroleum, wood and rubber with imports, as well as much of its coal and iron needs. Exports consistently represent a high percentage of GDP and, accordingly, the international economic environment is of crucial importance to the Republic’s economy.
The following tables give information regarding the Republic’s exports and imports by major commodity groups:
Exports by Major Commodity Groups (C.I.F.)(1)
| 2011 | As % of 2011 Total |
2012 | As % of 2012 Total |
2013 | As % of 2013 Total |
2014 | As % of 2014 Total |
2015(2) | As % of 2015 Total(2) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foods & Consumer Goods |
6.5 | 1.2 | 6.8 | 1.2 | 6.7 | 1.1 | 7.0 | 1.2 | 6.8 | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Raw Materials and Fuels |
61.7 | 11.1 | 65.4 | 11.9 | 61.2 | 10.9 | 59.2 | 10.3 | 39.5 | 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Petroleum & Derivatives |
52.0 | 9.4 | 56.6 | 10.3 | 53.2 | 9.5 | 51.2 | 8.9 | 32.4 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
9.7 | 1.7 | 8.8 | 1.6 | 8.0 | 1.4 | 8.0 | 1.4 | 7.1 | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Light Industrial Products |
38.9 | 7.0 | 40.5 | 7.4 | 39.0 | 6.9 | 38.6 | 6.7 | 35.4 | 6.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heavy & Chemical Industrial Products |
448.0 | 80.7 | 435.2 | 79.3 | 452.8 | 77.8 | 467.9 | 81.7 | 445.1 | 84.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronic & Electronic Products |
156.9 | 28.3 | 156.0 | 28.5 | 171.2 | 30.6 | 174.4 | 30.5 | 170.5 | 32.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemicals & Chemical Products |
59.1 | 10.6 | 59.6 | 10.9 | 64.4 | 11.5 | 65.6 | 11.5 | 55.9 | 10.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metal Goods |
48.6 | 8.8 | 47.2 | 8.6 | 43.6 | 7.8 | 47.5 | 8.3 | 41.4 | 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery & Precision Equipment |
54.5 | 9.8 | 55.7 | 10.2 | 55.3 | 9.9 | 57.9 | 10.1 | 57.4 | 10.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Equipment |
124.7 | 22.5 | 112.1 | 20.5 | 113.1 | 20.2 | 116.5 | 20.3 | 112.8 | 21.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Passenger Cars |
40.9 | 7.4 | 42.4 | 7.7 | 44.3 | 7.9 | 44.8 | 7.8 | 41.8 | 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ship & Boat |
54.6 | 9.8 | 38.2 | 7.0 | 36.2 | 6.5 | 38.7 | 6.8 | 38.8 | 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
29.2 | 5.3 | 31.5 | 5.7 | 32.6 | 5.8 | 33.0 | 5.8 | 32.2 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
4.2 | 0.8 | 4.6 | 0.8 | 5.2 | 0.9 | 6.0 | 1.0 | 7.1 | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
555.2 | 100.0 | 547.9 | 100.0 | 559.6 | 100.0 | 572.7 | 100.0 | 526.9 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | These entries are derived from customs clearance statistics. C.I.F. means that the price of goods includes insurance and freight costs. |
| (2) | Preliminary |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea Customs Service.
188
Table of Contents
Imports by Major Commodity Groups (C.I.F.)(1)
| 2011 | As % of 2011 Total |
2012 | As % of 2012 Total |
2013 | As % of 2013 Total |
2014 | As % of 2014 Total |
2015(2) | As % of 2015 Total(2) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Industrial Materials and Fuels |
324.8 | 61.9 | 325.1 | 62.6 | 313.8 | 60.9 | 311.2 | 59.2 | 219.1 | 50.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crude Petroleum |
100.8 | 19.2 | 108.3 | 20.8 | 99.4 | 19.3 | 94.9 | 18.1 | 55.1 | 12.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mineral |
31.1 | 5.9 | 28.3 | 5.4 | 24.7 | 4.8 | 24.6 | 4.7 | 17.6 | 4.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemicals |
44.2 | 8.4 | 43.8 | 8.4 | 43.2 | 8.4 | 43.9 | 8.4 | 39.6 | 9.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Iron & Steel Products |
30.4 | 5.8 | 26.4 | 5.1 | 24.6 | 4.8 | 27.0 | 5.1 | 21.2 | 4.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-ferrous Metal |
15.1 | 2.9 | 12.6 | 2.4 | 12.5 | 2.4 | 12.8 | 2.4 | 11.6 | 2.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
103.2 | 19.7 | 105.7 | 20.3 | 109.4 | 21.2 | 108.0 | 20.5 | 74.0 | 16.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Goods |
146.5 | 27.9 | 140.3 | 27.0 | 144.2 | 28.0 | 149.0 | 28.3 | 150.8 | 34.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery & Precision Equipment |
50.5 | 9.6 | 49.8 | 9.6 | 50.1 | 9.7 | 50.8 | 9.7 | 49.1 | 11.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electric & Electronic Machines |
80.1 | 15.3 | 76.3 | 14.7 | 80.9 | 15.7 | 84.5 | 16.1 | 87.5 | 20.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Equipment |
13.9 | 2.7 | 12.1 | 2.3 | 11.3 | 2.2 | 11.6 | 2.2 | 12.4 | 2.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
2.0 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 1.9 | 0.4 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 1.8 | 0.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Goods |
53.1 | 10.1 | 54.2 | 10.4 | 58.2 | 11.3 | 65.3 | 12.4 | 66.7 | 15.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cereals |
7.5 | 1.4 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 8.5 | 1.6 | 7.9 | 1.5 | 6.9 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Goods for Direct Consumption |
15.0 | 2.9 | 14.3 | 2.8 | 14.5 | 2.8 | 16.7 | 3.2 | 17.1 | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Durable Goods |
18.6 | 3.5 | 19.4 | 3.7 | 21.0 | 4.1 | 24.7 | 4.7 | 26.6 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consumer Nondurable Goods |
12.1 | 2.3 | 12.6 | 2.4 | 14.3 | 2.8 | 16.0 | 3.0 | 16.1 | 3.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
524.4 | 100.0 | 519.6 | 100.0 | 515.6 | 100.0 | 525.5 | 100.0 | 436.6 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | These entries are derived from customs clearance statistics. C.I.F. means that the price of goods includes insurance and freight costs. |
| (2) | Preliminary. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea Customs Service.
In 2011, the Republic recorded a trade surplus of US$30.8 billion. Exports increased by 19.0% to US$555.2 billion in 2011 from US$466.4 billion in 2010, primarily due to increased demand for mobile phones, consumer electronics products and automobiles from China and the emerging markets. Imports increased by 23.3% to US$524.4 billion in 2011 from US$425.2 billion in 2010, primarily due to an increase in oil and raw material prices.
In 2012, the Republic recorded a trade surplus of US$28.3 billion. Exports decreased by 1.3% to US$547.9 billion in 2012 from US$555.2 billion in 2011, primarily due to adverse economic conditions in European countries. Imports decreased by 0.9% to US$519.6 billion in 2012 from US$524.4 billion in 2011, primarily due to decreased investment spending.
In 2013, the Republic recorded a trade surplus of US$44.1 billion. Exports increased by 2.1% to US$559.7 billion in 2013 from US$547.9 billion in 2012, primarily due to increased demand for wireless communication devices, semiconductors and other information technology related products from the United States, China and the Southeast Asian nations. Imports decreased by 0.8% to US$515.6 billion in 2013 from US$519.6 billion in 2012, primarily due to decreased imports of oil, iron and steel.
Based on preliminary data, the Republic recorded a trade surplus of US$47.2 billion in 2014. Exports increased by 2.3% to US$572.7 billion in 2014 from US$559.6 billion in 2013, primarily due to increased demand for semiconductors, wireless communication devices, iron and steel from the United States, the EU and the Southeast Asian nations. Imports increased by 1.9% to US$525.5 billion in 2014 from US$515.6 billion in 2013, primarily due to increased imports of cars, components for wireless communication devices and beef.
Based on preliminary data, the Republic recorded a trade surplus of US$90.3 billion in 2015. Exports decreased by 8.7% to US$526.9 billion in 2015 from US$572.7 billion in 2014, primarily due to adverse global economic conditions. Imports decreased by 20.4% to US$436.6 billion in 2015 from US$525.5 billion of imports in 2014, primarily due to a decrease in oil prices, which also decreased unit prices of major raw materials.
189
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth the Republic’s exports trading partners:
Exports
| 2011 | As % of 2011 Total |
2012 | As % of 2012 Total |
2013 | As % of 2013 Total |
2014 | As % of 2014 Total |
2015(1) | As % of 2015 Total(1) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (millions of dollars, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China |
134,185.0 | 24.2 | 134,322.6 | 24.5 | 145,869.5 | 26.1 | 145,287.7 | 25.4 | 137,123.9 | 26.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States |
56,207.7 | 10.1 | 58,524.6 | 10.7 | 62,052.5 | 11.1 | 70,284.9 | 12.3 | 69,832.1 | 13.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japan |
39,679.7 | 7.1 | 38,796.1 | 7.1 | 34,662.3 | 6.2 | 32,183.8 | 5.6 | 25,576.5 | 4.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hong Kong |
30,968.4 | 5.6 | 32,606.2 | 6.0 | 27,756.3 | 5.0 | 27,256.4 | 4.8 | 30,418.2 | 5.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singapore |
20,839.0 | 3.8 | 22,887.9 | 4.2 | 22,289.0 | 4.0 | 23,749.9 | 4.1 | 15,011.2 | 2.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vietnam |
13,464.9 | 2.4 | 15,946.0 | 2.9 | 21,087.6 | 3.8 | 22,351.7 | 3.9 | 27,770.8 | 5.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan |
18,206.0 | 3.3 | 14,814.9 | 2.7 | 15,699.1 | 2.8 | 15,077.4 | 2.6 | 12,004.3 | 2.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| India |
12,654.1 | 2.3 | 11,922.0 | 2.2 | 11,375.8 | 2.0 | 12,782.5 | 2.2 | 12,029.6 | 2.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesia |
13,564.5 | 2.4 | 13,955.0 | 2.5 | 11,568.2 | 2.1 | 11,360.7 | 2.0 | 7,872.4 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mexico |
9,729.1 | 1.8 | 9,042.4 | 1.7 | 9,727.4 | 1.7 | 10,846.0 | 1.9 | 10,891.9 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia |
8,163.8 | 1.5 | 9,250.5 | 1.7 | 9,563.1 | 1.7 | 10,282.5 | 1.8 | 10,830.6 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Russia |
10,304.9 | 1.9 | 11,097.1 | 2.0 | 11,149.1 | 2.0 | 10,129.2 | 1.8 | 4,685.7 | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany |
9,500.9 | 1.7 | 7,509.7 | 1.4 | 7,907.9 | 1.4 | 7,570.9 | 1.3 | 6,220.2 | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others(2) |
177,745.7 | 32.0 | 167,194.8 | 30.5 | 168,924.6 | 30.2 | 173,501.0 | 30.3 | 156,489.1 | 29.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
555,213.7 | 100.0 | 547,869.8 | 100.0 | 559,632.4 | 100.0 | 572,664.6 | 100.0 | 526,756.5 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary |
| (2) | Includes more than 200 countries and regions. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea Customs Service.
The following table sets forth the Republic’s imports trading partners:
Imports
| 2011 | As % of 2011 Total |
2012 | As % of 2012 Total |
2013 | As % of 2013 Total |
2014 | As % of 2014 Total |
2015(1) | As % of 2015 Total(1) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (millions of dollars, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China |
86,432.2 | 16.5 | 80,784.6 | 15.5 | 83,052.9 | 16.1 | 90,082.2 | 17.1 | 90,250.3 | 20.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japan |
68,320.2 | 13.0 | 64,363.1 | 12.4 | 60,029.4 | 11.6 | 53,768.3 | 10.2 | 45,853.8 | 10.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States |
44,569.0 | 8.5 | 43,341.0 | 8.3 | 41,511.9 | 8.1 | 45,283.3 | 8.6 | 44,024.4 | 10.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Saudi Arabia |
36,972.6 | 7.1 | 39,707.1 | 7.6 | 37,665.2 | 7.3 | 36,694.5 | 7.0 | 19,561.5 | 4.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Qatar |
20,749.4 | 4.0 | 25,504.7 | 4.9 | 25,873.8 | 5.0 | 25,723.1 | 4.9 | 16,474.8 | 3.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Australia |
26,316.3 | 5.0 | 22,987.9 | 4.4 | 20,784.6 | 4.0 | 20,413.0 | 3.9 | 16,437.8 | 3.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany |
16,962.6 | 3.2 | 17,645.4 | 3.4 | 19,336.0 | 3.8 | 21,298.8 | 4.0 | 20,956.5 | 4.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kuwait |
16,959.6 | 3.2 | 18,297.1 | 3.5 | 18,725.1 | 3.6 | 16,892.0 | 3.2 | 8,973.4 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan |
14,693.6 | 2.8 | 14,012.0 | 2.7 | 14,632.6 | 2.8 | 15,689.8 | 3.0 | 16,653.9 | 3.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United Arab Emirates |
14,759.4 | 2.8 | 15,115.3 | 2.9 | 18,122.9 | 3.5 | 16,194.3 | 3.1 | 8,614.7 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indonesia |
17,216.4 | 3.3 | 15,676.3 | 3.0 | 13,190.0 | 2.6 | 12,266.3 | 2.3 | 8,850.4 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Malaysia |
10,467.8 | 2.0 | 9,796.4 | 1.9 | 11,095.8 | 2.2 | 11,097.9 | 2.1 | 8,609.4 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others(2) |
149,994.0 | 28.6 | 152,353.6 | 29.3 | 151,565.3 | 29.4 | 160,111.0 | 30.5 | 131,238.1 | 30.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
524,413.1 | 100.0 | 519,584.5 | 100.0 | 515,585.5 | 100.0 | 525,514.5 | 100.0 | 436,499.0 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary |
| (2) | Includes more than 200 countries and regions. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; Korea Customs Service.
190
Table of Contents
In the past, the outbreak of severe health epidemics in Korea and various parts of the world increased uncertainty about prospects for international trade and economic growth for affected countries, as well as world economic prospects in general. In response to these outbreaks, the Government issued advisories on disease prevention and conducted special monitoring. In May 2015, an outbreak of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, or MERS, resulted in the death of over 30 people and the quarantine of thousands. The Government continued to cooperate with regional and international efforts to develop and implement additional measures to contain and prevent MERS and other diseases. Another outbreak of MERS or similar incidents in the future may have an adverse effect on Korean and world economies and on international trade.
In recent years, the value of the Won relative to the U.S. dollar and Japanese Yen has fluctuated widely. An appreciation of the Won against the U.S. dollar and Japanese Yen increases the Won value of the Republic’s export sales and diminishes the price-competitiveness of export goods in foreign markets in U.S. dollar and Japanese Yen terms, respectively. However, it also decreases the cost of imported raw materials in Won terms and the cost in Won of servicing the Republic’s U.S. dollar and Japanese Yen denominated debt. In general, when the Won appreciates, export dependent sectors of the Korean economy, including automobiles, electronics and shipbuilding, suffer from the resulting pressure on the price-competitiveness of export goods, which may lead to reduced profit margins and loss in market share, more than offsetting a decrease in the cost of imported raw materials. If the Won continues to appreciate, the export dependent sectors of the Korean economy may suffer reduced profit margins or a net loss, which could result in a material adverse effect on the Korean economy.
Since the Government announced its plans to pursue free trade agreements, or FTAs, in 2003, the Republic has signed FTAs with key trading partners. The Republic has had bilateral FTAs in effect with Chile since 2004, Singapore since 2006, India since 2010, Peru since 2011, the United States since 2012, Turkey since 2013, Australia since 2014, Canada since January 2015 and China, New Zealand and Vietnam since December 2015. The Republic has also signed bilateral FTAs with Columbia and Turkey, which have yet to come into effect, and is currently in negotiations with a number of other key trading partners, including Indonesia and Japan. In addition, the Republic has had regional FTAs in effect with the European Free Trade Association since 2006, Association of Southeast Asian Nations since 2009 and the European Union since 2011.
Non-Commodities Trade Balance
The Republic had a non-commodities trade deficit of US$10.4 billion in 2011, a non-commodities trade surplus of US$1.4 billion in 2012, a non-commodities trade deficit of US$1.6 billion in 2013 and a non-commodities trade deficit of US$3.5 billion in 2014. Based on preliminary data, the Republic had a non-commodities trade deficit of US$14.4 billion in 2015.
191
Table of Contents
Foreign Currency Reserves
The foreign currency reserves are external assets that are readily available to and controlled by monetary authorities for meeting balance of payments financing needs and for other related purposes. The following table shows the Republic’s total official foreign currency reserves:
Total Official Reserves
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (millions of dollars) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gold(1) |
$ | 2,166.6 | $ | 3,761.4 | $ | 4,794.5 | $ | 4,794.7 | $ | 4,794.7 | ||||||||||
| Foreign Exchange(2) |
298,232.9 | 316,897.7 | 335,647.5 | 353,600.5 | 358,513.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total Gold and Foreign Exchange |
300,399.5 | 320,659.1 | 340,442.0 | 358,395.2 | 363,308.5 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Reserve Position at IMF |
2,556.2 | 2,783.6 | 2,527.7 | 1,917.1 | 1,411.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Special Drawing Rights |
3,446.7 | 3,525.6 | 3,489.9 | 3,280.5 | 3,241.4 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total Official Reserves |
$ | 306,402.5 | $ | 326,968.4 | $ | 346,459.6 | $ | 363,592.7 | $ | 367,961.9 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | For this purpose, domestically-owned gold is valued at US$42.22 per troy ounce (31.1035 grams) and gold deposited overseas is calculated at cost of purchase. |
| (2) | More than 95% of the Republic’s foreign currency reserves are comprised of convertible foreign currencies. |
Source: The Bank of Korea; International Monetary Fund
The Government’s foreign currency reserves increased to US$262.2 billion as of December 31, 2007 from US$8.9 billion as of December 31, 1997, primarily due to continued balance of trade surpluses and capital inflows. In 2008, the Government’s foreign currency reserves decreased, falling to US$201.2 billion as of December 31, 2008, partially as a result of the Government’s use of the foreign currency reserve to provide foreign currency liquidity to Korean financial institutions. The Government’s foreign currency reserves increased to US$306.4 billion as of December 31, 2011, US$327.0 billion as of December 31, 2012, US$346.5 billion as of December 31, 2013, US$363.6 billion as of December 31, 2014 and US$368.0 billion as of December 31, 2015, primarily due to continued trade surpluses and capital inflows. The amount of the Government’s foreign currency reserve was US$369.8 billion as of March 31, 2016.
The Ministry of Strategy and Finance prepares the Government budget and administers the Government’s finances.
The Government’s fiscal year commences on January 1. The Government must submit the budget, which is drafted by the Minister of Strategy and Finance and approved by the President of the Republic, to the National Assembly not later than 90 days prior to the start of the fiscal year and may submit supplementary budgets revising the original budget at any time during the fiscal year.
2014 budgeted revenues increased by 3.7% to
W338.9 trillion from W326.9 trillion in 2013, led by an increase in budgeted tax revenues (including revenues from income tax and value added tax). 2014 budgeted expenditures and net lending increased by 3.3%
to W325.4 trillion from W315.1 trillion in 2013, led by increases in budgeted expenditures on social security, public assistance, childcare and welfare services for senior citizens. The 2014 budget anticipated
a W13.5 billion budget surplus.
192
Table of Contents
2015 budgeted revenues increased by 3.6% to W351.1 trillion from
W338.9 trillion in 2014, led by an increase in budgeted tax revenues (including revenues from income tax, value added tax and social security contributions). 2015 budgeted expenditures and net lending increased by 5.8% to
W344.2 trillion from W325.4 trillion in 2014, led by increases in budgeted expenditures on economic growth, social security, public assistance, military services and welfare services for senior citizens,
unemployed people and temporary workers. The 2015 budget anticipated a W6.9 billion budget surplus.
2016 budgeted revenues increased by 2.6% to W360.1 trillion from W351.1 trillion in 2015, led by an
increase in budgeted tax revenues (including revenues from social security contributions and income tax). 2016 budgeted expenditures and net lending increased by 3.2% to W355.3 trillion from W344.2 trillion in
2015, led by increases in budgeted expenditures on economic growth (including research and development), welfare services for senior citizens, unemployed people and temporary workers, promotion of cultural industries, military services, public
assistance, child care and education. The 2016 budget anticipated a W4.8 billion budget surplus.
193
Table of Contents
The following table shows consolidated Government revenues and expenditures:
Consolidated Central Government Revenues and Expenditures
| Actual | Budget | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Revenues |
292,323 | 311,456 | 314,438 | 320,895 | 339,186 | 338,867 | 351,139 | 360,111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Revenues |
289,797 | 307,754 | 311,136 | 318,185 | 335,911 | 334,653 | 346,636 | 355,980 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Tax Revenues |
231,273 | 246,918 | 248,046 | 255,313 | 270,974 | 268,415 | 276,583 | 283,467 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes on income, profits and capital gains |
87,161 | 91,699 | 91,674 | 95,976 | 105,751 | 100,400 | 103,378 | 106,816 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Social security contributions |
38,892 | 43,904 | 46,140 | 49,793 | 53,089 | 51,962 | 55,441 | 60,530 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax on property |
8,713 | 8,832 | 8,591 | 9,054 | 11,113 | 9,754 | 10,134 | 10,303 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes on goods and services |
71,519 | 77,811 | 77,642 | 79,055 | 79,442 | 80,924 | 83,272 | 84,196 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes on international trade and transaction |
10,990 | 9,816 | 10,562 | 8,721 | 8,495 | 10,551 | 9,882 | 8,708 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other tax |
13,998 | 14,857 | 13,438 | 12,715 | 13,084 | 14,824 | 14,477 | 12,915 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-Tax Revenues |
58,524 | 60,836 | 63,089 | 62,872 | 64,936 | 66,238 | 70,053 | 72,513 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating surpluses of departmental enterprise sales and property income |
24,675 | 25,242 | 24,591 | 23,112 | 22,129 | 23,999 | 23,816 | 25,920 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Administration fees & charges and non-industrial sales |
6,973 | 7,364 | 8,537 | 7,997 | 8,664 | 8,437 | 10,403 | 8,578 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fines and forfeits |
17,180 | 17,488 | 18,164 | 19,556 | 20,777 | 20,769 | 21,962 | 23,484 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contributions to government employee pension fund |
7,303 | 8,134 | 8,776 | 9,915 | 10,929 | 10,034 | 10,458 | 11,372 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current revenue of non-financial public enterprises |
2,393 | 2,608 | 3,021 | 2,292 | 2,437 | 2,999 | 3,415 | 3,159 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Revenues |
2,527 | 3,702 | 3,302 | 2,710 | 3,276 | 4,214 | 4,502 | 4,131 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Expenditures and Net Lending |
273,694 | 292,977 | 300,238 | 312,394 | 339,351 | 325,378 | 344,174 | 355,277 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Expenditures |
269,768 | 286,921 | 302,036 | 311,507 | 330,537 | 320,075 | 335,397 | 345,858 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Expenditures |
235,458 | 252,620 | 268,019 | 280,466 | 296,216 | 287,226 | 300,963 | 313,820 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expenditure on goods and service |
52,989 | 55,384 | 57,769 | 59,616 | 63,160 | 64,470 | 68,865 | 69,715 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest payment |
14,566 | 14,239 | 13,386 | 14,057 | 14,056 | 14,439 | 14,293 | 14,434 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Subsidies and other current transfers |
165,233 | 179,433 | 193,451 | 203,649 | 216,189 | 204,638 | 214,125 | 226,011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current expenditure of non-financial public enterprises |
2,670 | 3,564 | 3,414 | 3,143 | 2,810 | 3,679 | 3,681 | 3,661 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital Expenditures |
34,310 | 34,301 | 34,017 | 31,041 | 34,322 | 32,850 | 34,433 | 32,038 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Lending |
3,926 | 6,056 | (1,798 | ) | 888 | 8,814 | 5,303 | 8,778 | 9,419 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Ministry of Strategy and Finance; The Bank of Korea; Korea National Statistical Office
The consolidated Government account consists of a General Account, Special Accounts (including a non-financial public enterprise special account) and Public Funds. The Government segregates the accounts of certain functions of the Government into Special Accounts and Public Funds for more effective administration and fiscal control. The Special Accounts and Public Funds relate to business type activities, such as economic development, road and railway construction and maintenance, monopolies, and communications developments and the administration of loans received from official international financial organizations and foreign governments.
194
Table of Contents
Revenues derive mainly from national taxes and non-tax revenues. Taxes in Korea can be roughly classified into the following types:
| • | income tax and capital gains tax, |
| • | property tax, |
| • | value-added tax, |
| • | customs duty tax, and |
| • | other taxes. |
Income tax and capital gains tax are imposed on income derived from labor, business operation and ownership of assets and profits derived from capital appreciation. Income tax and capital gains tax, depending on the type of taxpayer, can be further classified into corporate income tax and individual income tax. Property tax is imposed on exchange or ownership of property and includes inheritance tax and gift tax. Value-added tax is imposed on value added to goods and services. Customs duty tax is imposed on imported goods. Other taxes include tax on certain securities transactions and a stamp tax for certain documents.
Expenditures include general administration, national defense, community service, education, health, social security, certain annuities and pensions and local finance, which involves the transfer of tax revenues to local governments.
For 2011, the Republic recorded total revenues of W292.3 trillion and total expenditures and
net lending of W273.7 trillion. The Republic had a fiscal surplus of W18.6 trillion in 2011.
For 2012, the Republic recorded total revenues of W311.5 trillion and total expenditures and net lending of
W293.0 trillion. The Republic had a fiscal surplus of W18.5 trillion in 2012.
For 2013, the Republic recorded total revenues of W314.4 trillion and total expenditures and net lending of
W300.2 trillion. The Republic had a fiscal surplus of W14.2 trillion in 2013.
For 2014, the Republic recorded total revenues of W320.9 trillion and total expenditures and net lending of
W312.4 trillion. The Republic had a fiscal surplus of W8.5 trillion in 2014.
Based on preliminary data, the Republic recorded total revenues of W339.2 trillion and total expenditures and net lending
of W339.4 trillion in 2015. The Republic had a fiscal deficit of W0.2 trillion in 2015.
The Government estimates that the total outstanding debt of the Government (including guarantees by the Government) as of
December 31, 2014 amounted to approximately W532.2 trillion, an increase of 7.1% over the previous year. The Government estimates that the total outstanding debt of the Government (including guarantees by the Government) as of
December 31, 2015 amounted to approximately W582.9 trillion, an increase of 9.5% over the previous year. The Ministry of Strategy and Finance administers the national debt of the Republic.
195
Table of Contents
External and Internal Debt of the Government
The following table sets out, by currency and the equivalent amount in U.S. Dollars, the estimated outstanding direct external debt of the Government as of December 31, 2015:
Direct External Debt of the Government
| Amount in Original Currency |
Equivalent Amount in U.S. Dollars(1) |
|||||||
| (millions) | ||||||||
| US$ |
US$ | 4,428.7 | US$ | 4,428.7 | ||||
| Chinese Yuan (CNY) |
CNY | 3,000.0 | 462.2 | |||||
| Euro (EUR) |
EUR | 1,125.0 | 1,229.2 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
US$ | 6,120.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Amounts expressed in currencies other than US$ are converted to US$ at the arbitrage rate announced by the Seoul Money Brokerage Services, Ltd. in effect on December 31, 2015. |
The following table summarizes, as of December 31 of the years indicated, the outstanding direct internal debt of the Republic:
Direct Internal Debt of the Government
| (billions of Won) | ||||
| 2011 |
390,249.4 | |||
| 2012 |
414,213.5 | |||
| 2013 |
453,674.0 | |||
| 2014 |
493,584.9 | |||
| 2015 |
547,625.6 | |||
The following table sets out all guarantees by the Government of indebtedness of others:
Guarantees by the Government
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of Won) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Domestic |
33,799.1 | 32,783.6 | 32,978.5 | 29,158.4 | 26,393.8 | |||||||||||||||
| External(1) |
1,258.6 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
35,057.7 | 32,783.6 | 32,978.5 | 29,158.4 | 26,393.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Converted to Won at foreign exchange banks’ telegraphed transfer selling rates to customers or the market average exchange rates in effect on December 31 of each year. |
For further information on the outstanding indebtedness, including guarantees, of the Republic, see “—Tables and Supplementary Information”.
196
Table of Contents
External Liabilities
The following tables set out certain information regarding the Republic’s external liabilities calculated under the criteria based on the sixth edition of Balance of Payment Manual, or BPM6, published by the International Monetary Fund in December 2010 and implemented by the Government in December 2013. Under BPM6, in particular, prepayments received in connection with the construction of ships are excluded from the external debt.
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015(1) | ||||||||||||||||
| (billions of dollars) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term Debt |
260.3 | 281.0 | 311.7 | 308.0 | 287.8 | |||||||||||||||
| General Government |
59.8 | 60.8 | 63.0 | 65.2 | 62.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Monetary Authorities |
14.2 | 21.2 | 29.2 | 25.9 | 19.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Banks |
93.4 | 97.8 | 102.2 | 104.0 | 102.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Other Sectors |
92.9 | 101.2 | 117.4 | 112.9 | 103.3 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Short-term Debt |
139.8 | 128.0 | 111.8 | 116.4 | 108.7 | |||||||||||||||
| General Government |
0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 2.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Monetary Authorities |
8.9 | 14.9 | 10.8 | 12.2 | 14.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Banks |
102.9 | 85.4 | 77.9 | 79.9 | 73.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Other Sectors |
27.5 | 27.7 | 23.0 | 22.5 | 18.5 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total External Liabilities |
400.0 | 408.9 | 423.5 | 424.4 | 396.6 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Preliminary |
Debt Record
The Government has always paid when due the full amount of principal of, interest on, and amortization of sinking fund requirements of, all of its indebtedness.
Tables and Supplementary Information
A. External Debt of the Government
(1) External Bonds of the Government
| Series |
Issue Date | Maturity Date | Interest Rate (%) |
Currency | Original Principal Amount |
Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||||||||||
| 2005-001 |
November 2, 2005 | November 3, 2025 | 5.625 | USD | 400,000,000 | 400,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2006-001 |
December 7, 2006 | December 7, 2016 | 5.125 | USD | 500,000,000 | 500,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2006-002 |
December 7, 2006 | December 7, 2021 | 4.25 | EUR | 375,000,000 | 375,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009-002 |
April 16, 2009 | April 16, 2019 | 7.125 | USD | 1,500,000,000 | 1,500,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2013-001 |
September 11, 2013 | September 11, 2023 | 3.875 | USD | 1,000,000,000 | 1,000,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2014-001 |
June 10, 2014 | June 10, 2044 | 4.125 | USD | 1,000,000,000 | 1,000,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2014-002 |
June 10, 2014 | June 10, 2024 | 2.125 | EUR | 750,000,000 | 750,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2015-003 |
December 16, 2015 | December 16, 2018 | 3.000 | CNY | 3,000,000,000 | 3,000,000,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total External Bonds in Original Currencies |
|
USD | 4,400,000,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| EUR | 1,125,000,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| CNY | 3,000,000,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total External Bonds in Equivalent Amount of Won(1) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | U.S. dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of US$1.00 to |
197
Table of Contents
|
Euro amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of EUR1.00 to |
(2) External Borrowings of the Government
a. Borrowings in U.S. Dollars
| Date of Borrowing |
Original Maturity (Years) |
Interest Rate (%) |
Original Principal Amount (USD) |
Principal Amount Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 (USD) |
||||||||||||
| April 12, 1973 |
43 | 3 | 5,300,000 | 165,208 | ||||||||||||
| September 13, 1975 |
41 | 3 | 5,000,000 | 163,645 | ||||||||||||
| September 13, 1975 |
41 | 3 | 5,000,000 | 163,824 | ||||||||||||
| September 13, 1975 |
41 | 3 | 5,000,000 | 243,617 | ||||||||||||
| February 18, 1976 |
40 | 3 | 11,900,000 | 532,155 | ||||||||||||
| February 18, 1976 |
40 | 3 | 27,900,000 | 773,944 | ||||||||||||
| February 18, 1976 |
40 | 3 | 23,400,000 | 1,665,514 | ||||||||||||
| February 18, 1976 |
40 | 3 | 90,800,000 | 2,754,899 | ||||||||||||
| July 21, 1977 |
41 | 3 | 59,500,000 | 5,381,017 | ||||||||||||
| July 21, 1977 |
40 | 3 | 43,800,000 | 2,648,244 | ||||||||||||
| June 7, 1979 |
30 | 3 | 40,000,000 | 4,836,568 | ||||||||||||
| January 25, 1980 |
40 | 3 | 30,000,000 | 4,534,412 | ||||||||||||
| May 18, 1981 |
40 | 3 | 27,000,000 | 4,794,130 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Original Currency |
|
USD | 28,657,177 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Subtotal in Equivalent Amount of Won(1) |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (1) | U.S. dollar amounts are converted to Won amounts at the rate of US$1.00 to |
B. External Guaranteed Debt of the Government
None.
198
Table of Contents
C. Internal Debt of the Government
| Title |
Range of Interest Rates |
Range of Years of Issue |
Range of Years of Original Maturity |
Principal Amounts Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||||
| (%) | (billions of Won) | |||||||||||||||
| 1. Bonds |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest-Bearing Treasury Bond for Treasury Bond Management Fund |
1.125-5.75 | 2006-2015 | 2016-2044 | 485,103.8 | ||||||||||||
| Interest-Bearing Treasury Bond for National Housing I |
2.0-3.0 | 2006-2015 | 2011-2020 | 56,833.5 | ||||||||||||
| Interest-Bearing Treasury Bond for National Housing II |
0.0-3.0 | 1991-2012 | 2011-2030 | 2,429.3 | ||||||||||||
| Interest-Bearing Treasury Bond for National Housing III |
0 | 2005 | 2015 | 9.5 | ||||||||||||
| Non-interest-Bearing Treasury Bond for Contribution to International Organizations(1) |
— | 1967-1985 | — | 9.4 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Bonds |
544,385.5 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 2. Borrowings |
||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings from The Bank of Korea |
1.627-1.704 | 2015 | 2016 | 1,280.1 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Sports Promotion Fund |
2.845 | 2014 | 2017 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from The Korea Foundation Fund |
1.995-2.845 | 2014 | 2017 | 40.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Korea Credit Guarantee Fund |
2.305-2.755 | 2014 | 2018 | 455.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from Korea Technology Finance Corporation |
2.305-2.755 | 2014 | 2018 | 195.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Credit Guarantee Fund for Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Suppliers |
1.875-3.215 | 2014 | 2019 | 1,100.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Government Employees’ Pension Fund |
1.467 | 2015 | 2018 | 10.0 | ||||||||||||
| Borrowings from the Film Industry Development Fund |
1.735-2.87 | 2014 | 2018 | 60.0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Borrowings |
3,240.1 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Internal Funded Debt |
547,625.6 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| (1) | Interest Rates and Years of Maturity not applicable. |
D. Internal Guaranteed Debt of the Government
| Title |
Range of Interest Rates |
Range of Years of Issue |
Range of Years of Original Maturity |
Principal Amounts Outstanding as of December 31, 2015 |
||||||||||||
| (%) | (billions of Won) | |||||||||||||||
| 1. Bonds of Government-Affiliated Corporations |
||||||||||||||||
| Korea Deposit Insurance Corporation |
2.12-4.14 | 2011-2015 | 2016-2020 | 14,710.0 | ||||||||||||
| Korea Student Aid Foundation |
Floating-5.07 | 2010-2015 | 2016-2032 | 11,640.0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Bonds |
26,350.0 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| 2. Borrowings of Government-Affiliated Corporations |
||||||||||||||||
| Rural Development Corporation and Federation of Farmland |
5.5 | 1989 | 2023 | 43.8 | ||||||||||||
| Total Borrowings |
43.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total Internal Guaranteed Debt |
26,393.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
199
Table of Contents
Description of Debt Securities
We will issue debt securities under a fiscal agency agreement or agreements. The description below summarizes the material provisions of the debt securities and the fiscal agency agreement. Since it is only a summary, the description may not contain all of the information that may be important to you as a potential investor in the debt securities. Therefore, we urge you to read the form of fiscal agency agreement and the form of global debt security before deciding whether to invest in the debt securities. We have filed a copy of these documents with the Securities and Exchange Commission as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. You should refer to such exhibits for more complete information.
The financial terms and other specific terms of your debt securities will be described in the prospectus supplement relating to your debt securities. The description in the prospectus supplement will supplement this description or, to the extent inconsistent with this description, replace it.
We will appoint a fiscal agent or agents in connection with debt securities whose duties will be governed by the fiscal agency agreement. We may replace the fiscal agent or appoint different fiscal agents for different series of debt securities.
General Terms of the Debt Securities
We may issue debt securities in separate series at various times. The Republic may irrevocably guarantee the payment of principal of, and interest on, one or more series of debt securities. The prospectus supplement that relates to your debt securities will specify some or all of the following terms:
| • | the aggregate principal amount; |
| • | the currency of denomination and payment; |
| • | any limitation on principal amount and authorized denominations; |
| • | the percentage of their principal amount at which the debt securities will be issued; |
| • | the maturity date or dates; |
| • | the interest rate for the debt securities and, if variable, the method by which the interest rate will be calculated; |
| • | whether any amount payable in respect of the debt securities will be determined based on an index or formula, and how any such amount will be determined; |
| • | the dates from which interest, if any, will accrue for payment of interest and the record dates for any such interest payments; |
| • | where and how we will pay principal and interest; |
| • | whether and in what circumstances the debt securities may be redeemed before maturity; |
| • | any sinking fund or similar provision; |
| • | whether any part or all of the debt securities will be in the form of a global security and the circumstances in which a global security is exchangeable for certificated securities; |
| • | if issued in certificated form, whether the debt securities will be in bearer form with interest coupons, if any, or in registered form without interest coupons, or both forms, and any restrictions on exchanges from one form to the other; |
| • | whether any of the terms set out herein will differ for the debt securities; |
200
Table of Contents
| • | whether the Republic will irrevocably guarantee the payment of principal of, and interest on, the debt securities; and |
| • | other specific provisions. |
Depending on the terms of the debt securities we issue, the prospectus supplement relating to the debt securities may also describe applicable U.S. federal income tax and other considerations additional to the disclosure in this prospectus.
Unless otherwise specified in the applicable prospectus supplement, we will maintain at an office in the Borough of Manhattan, The City of New York, a register for the registration of transfers of debt securities issued in registered form.
Payments of Principal, Premium and Interest
On every payment date specified in the relevant prospectus supplement, we will pay the principal, premium and/or interest due on that date to the registered holder of the relevant debt security at the close of business on the related record date. We will make all payments at the place and in the currency set out in the prospectus supplement. Unless otherwise specified in the relevant prospectus supplement or the debt securities, we will make payments in U.S. dollars at the New York office of the fiscal agent or, outside the United States, at the office of any paying agent. Unless otherwise specified in the applicable prospectus supplement or debt securities, we will pay interest by check, payable to the registered holder.
We will make any payments on debt securities in bearer form at the offices and agencies of the fiscal agent or any other paying agent outside the United States as we may designate. At the option of the holder of the bearer debt securities, we will make such payments by check or by transfer to an account maintained by the holder with a bank located outside of the United States. We will not make payments on bearer debt securities at the corporate trust office of the fiscal agent in the United States or at any other paying agency in the United States. In addition, we will not make any payment by mail to an address in the United States or by transfer to an account maintained by a holder of bearer debt securities with a bank in the United States. Nevertheless, we will make payments on a bearer debt security denominated and payable in U.S. dollars at an office or agency in the United States if:
| • | payment outside the United States is illegal or effectively precluded by exchange controls or other similar restrictions; and |
| • | the payment is then permitted under United States law, without material adverse consequences to us. |
If we issue bearer debt securities, we will designate the offices of at least one paying agent outside the United States as the location for payment.
Repayment of Funds; Prescription
If no one claims money paid by us to the fiscal agent for the payment of principal or interest in respect of any series of debt securities for two years after the payment was due and payable, the fiscal agent or paying agent will repay the money to us. After such repayment, the fiscal agent or paying agent will not be liable with respect to the amounts so repaid, and you may look only to us for any payment under the debt securities.
Under Korean law, you will not be permitted to file a claim against us for payment of principal or interest on any series of debt securities unless you do so within five years, in the case of principal, and two years, in the case of interest, from the date on which payment was due.
201
Table of Contents
Global Securities
The prospectus supplement relating to a series of debt securities will indicate whether any of that series of debt securities will be represented by a global security. The prospectus supplement will also describe any unique specific terms of the depositary arrangement with respect to that series. Unless otherwise specified in the prospectus supplement, we anticipate that the following provisions will apply to depositary arrangements.
Registered Ownership of the Global Security
The global security will be registered in the name of a depositary identified in the prospectus supplement, or its nominee, and will be deposited with the depositary, its nominee or a custodian. The depositary, or its nominee, will therefore be considered the sole owner or holder of debt securities represented by the global security for all purposes under the fiscal agency agreement. Except as specified below or in the applicable prospectus supplement, beneficial owners:
| • | will not be entitled to have any of the debt securities represented by the global security registered in their names; |
| • | will not receive physical delivery of any debt securities in definitive form; |
| • | will not be considered the owners or holders of the debt securities; |
| • | must rely on the procedures of the depositary and, if applicable, any participants (institutions that have accounts with the depositary or a nominee of the depositary, such as securities brokers and dealers) to exercise any rights of a holder; and |
| • | will receive payments of principal and interest from the depositary or its participants rather than directly from us. |
We understand that, under existing industry practice, the depositary and participants will allow beneficial owners to take all actions required of, and exercise all rights granted to, the registered holders of the debt securities.
We will register debt securities in the name of a person other than the depositary or its nominee only if:
| • | the depositary for a series of debt securities is unwilling or unable to continue as depositary; or |
| • | we determine, in our sole discretion, not to have a series of debt securities represented by a global security. |
In either such instance, an owner of a beneficial interest in a global security will be entitled to registration of a principal amount of debt securities equal to its beneficial interest in its name and to physical delivery of the debt securities in definitive form.
Beneficial Interests in and Payments on a Global Security
Only participants, and persons that may hold beneficial interests through participants, can own a beneficial interest in the global security. The depositary keeps records of the ownership and transfer of beneficial interests in the global security by its participants. In turn, participants keep records of the ownership and transfer of beneficial interests in the global security by other persons (such as their customers). No other records of the ownership and transfer of beneficial interests in the global security will be kept.
All payments on a global security will be made to the depositary or its nominee. When the depositary receives payment of principal or interest on the global security, we expect the depositary to credit its participants’ accounts with amounts that correspond to their respective beneficial interests in the global security. We also expect that, after the participants’ accounts are credited, the participants will credit the accounts of the owners of beneficial interests in the global security with amounts that correspond to the owners’ respective beneficial interests in the global security.
202
Table of Contents
The depositary and its participants establish policies and procedures governing payments, transfers, exchanges and other important matters that affect owners of beneficial interests in a global security. The depositary and its participants may change these policies and procedures from time to time. We have no responsibility or liability for the records of ownership of beneficial interests in the global security, or for payments made or not made to owners of such beneficial interests. We also have no responsibility or liability for any aspect of the relationship between the depositary and its participants or for any aspect of the relationship between participants and owners of beneficial interests in the global security.
Bearer Securities
We may issue debt securities in a series in the form of one or more bearer global debt securities deposited with a common depositary for the Euroclear and Clearstream, or with a nominee identified in the applicable prospectus supplement. The specific terms and procedures, including the specific terms of the depositary arrangement, with respect to any portion of a series of debt securities to be represented by a global security will be described in the applicable prospectus supplement.
Additional Amounts
We will make all payments of principal of, and premium and interest, if any, on the debt securities without withholding or deducting any present or future taxes imposed by the Republic or any of its political subdivisions, unless required by law. If Korean law requires us to deduct or withhold taxes, we will pay additional amounts as necessary to ensure that you receive the same amount as you would have received without such withholding or deduction.
We will not pay, however, any additional amounts if you are liable for Korean tax because:
| • | you are connected with the Republic other than by merely owning the debt security or receiving income or payments on the debt security; |
| • | you failed to complete and submit a declaration of your status as a non-resident of the Republic after we or the relevant tax authority requested you to do so; or |
| • | you failed to present your debt security for payment within 30 days of when the payment is due or, if the fiscal agent did not receive the money prior to the due date, the date notice is given to holders that the fiscal agent has received the full amount due to holders. Nevertheless, we will pay additional amounts to the extent you would have been entitled to such amounts had you presented your debt security for payment on the last day of the 30-day period. |
We will not pay any additional amounts for taxes on the debt securities except for taxes payable through deduction or withholding from payments of principal, premium or interest. Examples of the types of taxes for which we will not pay additional amounts include the following: estate or inheritance taxes, gift taxes, sales or transfer taxes, personal property or related taxes, assessments or other governmental charges. We will also not pay any additional amounts for taxes imposed pursuant to Sections 1471 through 1474 of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, U.S. Treasury regulations or administrative guidance promulgated thereunder or any law implementing an intergovernmental approach thereto (“FATCA”). We will pay stamp or other similar taxes that may be imposed by the Republic, the United States or any political subdivision or taxing authority in one of those two countries on the fiscal agency agreement or be payable in connection with the issuance of the debt securities.
Status of Debt Securities
The debt securities will:
| • | constitute our direct, unconditional, unsecured and unsubordinated obligations; |
203
Table of Contents
| • | rank at least equally in right of payment among themselves, regardless of when issued or currency of payment; and |
| • | rank at least equally in right of payment with all of our other unsecured and unsubordinated obligations, subject to certain statutory exceptions under Korean law. |
Negative Pledge Covenant
If any debt securities are outstanding, we will not create or permit any security interests on our assets as security for any of our indebtedness or guarantees issued by us, unless the security interest also secures our obligations under the debt securities.
We may, however, create or permit a security interest:
| • | on any promissory debt securities or commercial paper discounted or otherwise provided as security to or issued or held by us created in favor of The Bank of Korea in the normal operation of The Bank of Korea’s discount facilities or facilities for the funding of loans by us to our customers; or |
| • | on any asset (or documents of title to such asset) incurred when the asset was purchased or improved to secure payment of the cost of the activity; or |
| • | of a statutory nature arising in the ordinary course of our business but unrelated to our activities of borrowing or raising money; or |
| • | on any real estate owned by us imposed by a tenant of such real estate as security for repayment of any key money paid by the tenant; or |
| • | arising by operation of Korean law or given preference by law following our failure to meet an obligation, although we will not permit such a security interest to exist for more than 30 days. |
Events of Default
Unless otherwise specified in the applicable prospectus supplement in connection with a particular offering of debt securities, each of the following constitutes an event of default with respect to any series of debt securities:
| 1. | Non-Payment: we do not pay principal or interest or premium or deposit any sinking fund payment on any debt securities of the series when due and such failure to pay continues for 30 days. |
| 2. | Breach of Other Obligations: we fail to observe or perform any of the covenants in the series of debt securities (other than non-payment) for 60 days after written notice of the default is delivered to us at the corporate trust office of the fiscal agent in New York City by holders representing at least 10% of the aggregate principal amount of the debt securities of the series. |
| 3. | Cross Default and Cross Acceleration: |
| • | we default on any External Indebtedness, and, as a result, becomes obligated to pay an amount equal to or greater than US$10,000,000 in aggregate principal amount prior to its due date; or |
| • | we fail to pay when due, including any grace period, any of our External Indebtedness in aggregate principal amount equal to or greater than US$10,000,000 or we fail to pay when requested and required by the terms thereof any guarantee for External Indebtedness of another person equal to or greater than US$10,000,000 in aggregate principal amount. |
| 4, | Moratorium/Default: |
| • | the Republic declares a general moratorium on the payment of its External Indebtedness, including obligations under guarantees; |
204
Table of Contents
| • | the Republic becomes liable to repay prior to maturity any amount of External Indebtedness, including obligations under guarantees, as a result of a default under such External Indebtedness or obligations; or |
| • | the international monetary reserves of the Republic become subject to a security interest or segregation or other preferential arrangement for the benefit of any creditors. |
| 5. | Bankruptcy: |
| • | we are declared bankrupt or insolvent by any court or administrative agency with jurisdiction over us; |
| • | we pass a resolution to apply for bankruptcy or to request the appointment of a receiver or trustee or similar official in insolvency; |
| • | a substantial part of our assets are liquidated; or |
| • | we cease to conduct the banking business. |
| 6. | Cessation of Government Control or Failure of Support: the Republic ceases to (directly or indirectly) control us or fails to provide financial support for us as required under Article 32 of the KDB Act as of the issue date of the debt securities of such series. |
For purposes of the foregoing, “External Indebtedness” means any obligation for the payment or repayment of money borrowed that is denominated in a currency other than the currency of the Republic.
As used in paragraph 6 above, “control” means the acquisition or control of a majority of our voting share capital or the right to appoint and/or remove all or the majority of the members of our board of directors or other governing body, whether obtained directly or indirectly, and whether obtained by ownership of share capital, the possession of voting rights, contract or otherwise.
If an event of default occurs, any holder may declare the principal amount of debt securities that it holds to be immediately due and payable by written notice to us and the fiscal agent.
You should note that:
| • | despite the procedure described above, no debt securities may be declared due and payable if we cure the applicable event of default before we receive the written notice from the debt security holder; |
| • | we are not required to provide periodic evidence of the absence of defaults; and |
| • | the fiscal agency agreement does not require us to notify holders of the debt securities of an event of default or grant any debt security holder a right to examine the security register. |
Modifications and Amendments; Debt Securityholders’ Meetings
Each holder of a series of debt securities must consent to any amendment or modification of the terms of that series of debt securities or the fiscal agency agreement that would, among other things:
| • | change the stated maturity of the principal of the debt securities or any installment of interest; |
| • | reduce the principal amount of such series of debt securities or the portion of the principal amount payable upon acceleration of such debt securities; |
| • | change the debt security’s interest rate or premium payable; |
| • | change the currency of payment of principal, interest or premium; |
205
Table of Contents
| • | amend either the procedures provided for a redemption event or the definition of a redemption event; |
| • | shorten the period during which we are not allowed to redeem the debt securities or grant us a right to redeem the debt securities which we previously did not have; or |
| • | reduce the percentage of the outstanding principal amount needed to modify or amend the fiscal agency agreement or the terms of such series of debt securities. |
We may, with the exception of the above changes, with the consent of the holders of at least 66 2/3% in principal amount of the debt securities of a series that are outstanding, modify and amend other terms of that series of debt securities.
We may at any time call a meeting of the holders of a series of debt securities to seek the holders of the debt securities’ approval of the modification, or amendment, or obtain a waiver, of any provision of that series of debt securities. The meeting will be held at the time and place in the Borough of Manhattan in New York City as determined by the fiscal agent. The notice calling the meeting must be given at least 30 days and not more than 60 days prior to the meeting.
While an event of default with respect to a series of debt securities is continuing, holders of at least 10% of the aggregate principal amount of that series of debt securities may compel the fiscal agent to call a meeting of all holders of debt securities of that series.
Holders of debt securities who hold, in the aggregate, a majority in principal amount of the debt securities of the series that are outstanding at the time will constitute a quorum at a meeting. At the reconvening of any meeting adjourned for a lack of a quorum, the persons entitled to vote 25% in principal amount of the debt securities of the series that are outstanding at the time will constitute a quorum for taking any action set out in the original notice. To vote at a meeting, a person must either hold outstanding debt securities of the relevant series or be duly appointed as a proxy for a debt securityholder. The fiscal agent will make all rules governing the conduct of any meeting.
The fiscal agency agreement and a series of debt securities may be modified or amended, without the consent of the holders of the debt securities, to:
| • | add covenants made by us that benefit holders of the debt securities; |
| • | surrender any right or power given to us; |
| • | secure the debt securities; |
| • | permit registered securities to be exchanged for bearer securities or relax or eliminate restrictions on the payment of principal, premium or interest on bearer securities to the extent permitted under United States Department of Treasury regulations, provided that holders of the debt securities do not suffer any adverse tax consequences as a result; and |
| • | cure any ambiguity or correct or supplement any defective provision in the fiscal agency agreement or the debt securities, without materially and adversely affecting the interests of the holders of the debt securities. |
Fiscal Agent
The fiscal agency agreement governs the duties of each fiscal agent. We may maintain bank accounts and a banking relationship with each fiscal agent. The fiscal agent is our agent and does not act as a trustee for the holders of the debt securities.
206
Table of Contents
Further Issues of Debt Securities
We may, without the consent of the holders of the debt securities, create and issue additional debt securities with the same terms and conditions as any series of debt securities (or that are the same except for the amount of the first interest payment and for the interest paid on the series of debt securities prior to the issuance of the additional debt securities). We may consolidate such additional debt securities with the outstanding debt securities to form a single series.
The description below summarizes some of the provisions of warrants for the purchase of debt securities that we may issue from time to time and of the warrant agreement. Copies of the forms of warrants and the warrant agreement are or will be filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. Since it is only a summary, the description may not contain all of the information that is important to you as a potential investor in the warrants.
The description of the warrants that will be contained in the prospectus supplement will supplement this description and, to the extent inconsistent with this description, replace it.
General Terms of the Warrants
Each series of warrants will be issued under a warrant agreement to be entered into between us and a bank or trust company, as warrant agent. The prospectus supplement relating to the series of warrants will describe:
| • | the terms of the debt securities purchasable upon exercise of the warrants, as described above under “—Description of Debt Securities—General Terms of the Debt Securities”; |
| • | the principal amount of debt securities purchasable upon exercise of one warrant and the exercise price; |
| • | the procedures and conditions for the exercise of the warrants; |
| • | the dates on which the right to exercise the warrants begins and expires; |
| • | whether and under what conditions the warrants may be terminated or canceled by us; |
| • | whether and under what conditions the warrants and any debt securities issued with the warrants will be separately transferable; |
| • | whether the warrants will be issued in bearer or registered form; |
| • | whether the warrants will be exchangeable between registered and bearer form, and, if issued in registered form, where they may be transferred and registered; and |
| • | other specific provisions. |
Terms Applicable to Debt Securities and Warrants
Governing Law
The fiscal agency agreement, any warrant agreement and the debt securities and any warrants will be governed by the laws of the State of New York without regard to any principles of New York law requiring the application of the laws of another jurisdiction. Nevertheless, all matters governing our authorization, execution and delivery of the debt securities and the fiscal agency agreement and any warrants and warrant agreement by us will be governed by the laws of the Republic.
207
Table of Contents
Jurisdiction and Consent to Service
We are owned by a foreign sovereign government and all of our directors and executive officers and some of the experts named in this prospectus are residents of Korea. In addition, all or most of our assets and the assets of the people named in the preceding sentence are located outside of the United States. For that reason, you may have difficultly serving process on us or the individuals described above in the United States or enforcing in a U.S. court a U.S.-court judgment based on the U.S. federal securities laws. Our Korean counsel has informed us that there would be certain conditions to be met under Korean law regarding the enforceability in Korea, either in original actions or in actions for the enforcement of U.S.-court judgments, of civil liabilities based on the U.S. federal securities laws.
We have appointed the General Manager of our New York Branch, Mr. Nak Joo Seong, and the Senior Deputy General Manager of our New York Branch, Mr. Jin Hwan Sah, and each of their successors in the future, as our authorized agents to receive service of process in any suit which a holder of any series of debt securities or warrants may bring in any state or federal court in New York City and we have accepted the jurisdiction of those courts for those actions. Our New York Branch is located at 320 Park Avenue, 32nd Floor, New York, New York 10022. These appointments are irrevocable as long as any amounts of principal, premium or interest remain payable by us to the Fiscal Agent under any series of debt securities or any warrants have not expired or otherwise terminated under their terms. If for any reason either of these two men ceases to act as our authorized agent or ceases to have an address in Manhattan, we shall appoint a replacement. The appointment of agents for receipt of service of process and the acceptance of jurisdiction of state or federal courts in New York City do not, however, apply to actions brought under the United States federal securities laws. We may also be sued in courts having jurisdiction over us located in the Republic.
We will irrevocably consent to any relief and process in connection with a suit against us in relation to the debt securities or warrants, including the enforcement or execution of any order or judgment of the court. To the extent permitted by law, we will waive irrevocably any immunity from jurisdiction to which we might otherwise be entitled in any suit based on any series of debt securities or warrants.
Foreign Exchange Controls
Before we may issue debt securities outside the Republic, the Minister of Strategy and Finance of Korea must receive a report with respect to the issuance by us of debt securities in accordance with the Foreign Exchange Transaction Act and the Foreign Exchange Transaction Regulation of Korea. After issuance of debt securities outside the Republic, we are required to notify the Minister of Strategy and Finance of such issuance. No further approval or authorization is required for us to pay principal of or interest on the debt securities.
Description of Guarantees to be Issued by Us
The description below summarizes some of the provisions of the guarantees that we may issue from time to time. Copies of the forms of guarantees are or will be filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. Since it is only a summary, the description may not contain all of the information that is important to you as a potential beneficiary of a guarantee.
The description of a guarantee that will be contained in the prospectus supplement will supplement this description and, to the extent inconsistent with this description, replace it.
General Terms of the Guarantees
Each guarantee will be issued by us as guarantor. The prospectus supplement relating to a guarantee will specify:
| • | the relevant obligor and the obligations guaranteed under the guarantee; |
208
Table of Contents
| • | the nature and scope of the guarantee, including whether or not it is irrevocable and unconditional; |
| • | the status of the guarantee in relation to our other obligations; |
| • | the governing law of the guarantee; and |
| • | other relevant provisions of the guarantee. |
Description of Guarantees to be Issued by The Republic of Korea
The description below summarizes some of the provisions of the guarantees that the Republic may issue from time to time to guarantee our debt securities. Since it is only a summary, the description may not contain all of the information that is important to you as a potential beneficiary of a guarantee.
The prospectus supplement relating to a guarantee to be issued by the Republic will specify other specific provisions. The description of a guarantee to be issued by the Republic that will be contained in the prospectus supplement will supplement this description and, to the extent inconsistent with this description, replace it.
General Terms of the Guarantees
Each guarantee will be issued by the Republic as guarantor. The prospectus supplement relating to a guarantee will specify:
| • | the relevant obligor and the obligations guaranteed under the guarantee; |
| • | the nature and scope of the guarantee, including whether or not it is irrevocable and unconditional; |
| • | the status of the guarantee in relation to the Republic’s other obligations; |
| • | the governing law of the guarantee; and |
| • | other relevant provisions of the guarantee. |
209
Table of Contents
LIMITATIONS ON ISSUANCE OF BEARER DEBT SECURITIES AND BEARER WARRANTS
Bearer securities will not be offered, sold or delivered in the United States or its possessions or to a United States person; except in certain circumstances permitted by United States tax regulations. Bearer securities will initially be represented by temporary global securities, without interest coupons, deposited with a common depositary in London for Euroclear and Clearstream for credit to designated accounts. Unless otherwise indicated in the prospectus supplement:
| • | each temporary global security will be exchangeable for definitive bearer securities on or after the date that is 40 days after issuance only upon receipt of certification of non-United States beneficial ownership of the temporary global security as provided for in United States tax regulations, provided that no bearer security will be mailed or otherwise delivered to any location in the United States in connection with the exchange; and |
| • | any interest payable on any portion of a temporary global security with respect to any interest payment date occurring prior to the issuance of definitive bearer securities will be paid only upon receipt of certification of non-United States beneficial ownership of the temporary global security as provided for in United States tax regulations. |
Bearer securities, other than temporary global debt securities, and any related coupons will bear the following legend: “Any United States person who holds this obligation will be subject to limitations under the United States federal income tax laws, including the limitations provided in Section 165(j) and 1287(a) of the Internal Revenue Code.” The sections referred to in the legend provide that, with certain exceptions, a United States person who holds a bearer security or coupon will not be allowed to deduct any loss realized on the disposition of the bearer security, and any gain, which might otherwise be characterized as capital gain, recognized on the disposition will be treated as ordinary income.
For purposes of this section, “United States person” means:
| • | a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| • | a corporation, partnership or other entity created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or any political subdivision thereof; or |
| • | an estate or trust the income of which is subject to United States federal income taxation regardless of its source. |
For purposes of this section, “United States” means the United States of America, including each state and the District of Columbia, its territories, possessions and other areas subject to its jurisdiction.
210
Table of Contents
The following discussion summarizes certain Korean tax and U.S. federal income tax considerations that may be relevant to you if you invest in debt securities. This summary is based on laws, regulations, rulings and decisions in effect as of the date of this Prospectus. These laws, regulations, rulings and/or decisions may change; any such change could apply retroactively and could affect the continued validity of this summary.
This summary does not describe all of the tax considerations that may be relevant to you or your situation, particularly if you are subject to special tax rules. You should consult your tax adviser about the tax consequences of holding the debt securities, including the relevance to your particular situation of the considerations discussed below, as well as of state, local or other tax laws.
The following summary of Korean tax considerations applies to you so long as you are not:
| • | a resident of Korea; |
| • | a corporation with registered head office or main office located in Korea; |
| • | a corporation of which the place of effective management is located in Korea; or |
| • | engaged in a trade or business in Korea through a permanent establishment or a fixed base to which the relevant income is attributable or with which the relevant income is effectively connected. |
Tax on Interest Payments
Under current Korean tax laws, when we make payments of interest to you (excluding payments to your permanent establishment in Korea) on the debt securities denominated in a foreign currency, no amount will be withheld from such payments for, or on account of, taxes of any kind imposed, levied, withheld or assessed by Korea or any political subdivision or taxing authority thereof or therein, provided that the offering of the debt securities is deemed to be an overseas issuance under Korean tax law.
Tax on Capital Gains
You will not be subject to any Korean income or withholding taxes in connection with the sale, exchange or other disposition of the debt securities, if (i) such sale, exchange or disposition is made to other non-residents or non-Korean corporations (other than their permanent establishments in Korea) or (ii) such sale, exchange or disposition takes place outside Korea, provided that the issuance of the debt securities is deemed to be an overseas issuance under Korean tax law. If you sell, exchange or otherwise dispose of the debt securities to a Korean resident or a Korean corporation (or the Korean permanent establishment of a non-resident or a non-Korean corporation) and such sale, exchange or disposition is made within Korea, any gain realized on the transaction will be taxable at ordinary Korean withholding tax rates (the lower of (subject to the production of satisfactory evidence of the acquisition costs and certain direct transaction costs) 22% of net gain or 11% of the gross sale proceeds with respect to such transaction), unless an exemption is available under an applicable income tax treaty. For example, if you are a resident of the United States for the purposes of the income tax treaty currently in force between Korea and the United States, you are generally entitled to an exemption from Korean taxation in respect of any gain realized on a disposition of the debt securities, regardless of whether the disposition is to a Korean resident. For more information regarding tax treaties, please refer to the heading “—Tax Treaties” below.
211
Table of Contents
Inheritance Tax and Gift Tax
If you die while you are the holder of the debt security, the subsequent transfer of the debt security by way of succession will be subject to Korean inheritance tax. Similarly, if you transfer the debt security as a gift, the donee will be subject to Korean gift tax and you may be required to pay the gift tax if the donee fails to do so or the donee is a non-resident.
Stamp Duty
You will not be subject to any Korean securities transaction tax, stamp duty, registration tax or similar documentary tax in respect of or in connection with a transfer of any debt securities or in connection with the exercise of exchange rights or conversion rights that may be acquired with the debt securities.
Guarantees
Although there are no Korean tax laws, regulations, rulings or decisions specific to the payment under the guarantee herein, we believe any payments of interest on and principal amount of the debt securities (or the issue price if the debt securities were originally issued at a discount) by the Republic under the Republic’s guarantee on the debt securities denominated in a foreign currency (provided that the offering of the debt securities is deemed to be an overseas issuance under Korean tax law) and issued by us or any payments of interest on and principal amount of the debt securities (or the issue price if the debt securities were originally issued at a discount) by us under our guarantee on the debt securities denominated in a foreign currency (provided that the offering of the debt securities is deemed to be an overseas issuance under Korean tax law) and issued by a third-party Korean issuer are not subject to withholding tax. Further details of the tax consequences of the holders of our debt securities guaranteed by the Republic or third-party debt securities guaranteed by us may be provided in the relevant prospectus supplement.
Tax Treaties
At the date of this prospectus, Korea has tax treaties with, among others, Australia, Austria, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Czech Republic, Denmark, Egypt, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Mexico, Mongolia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Pakistan, Philippines, Poland, Republic of Fiji, Romania, Singapore, Spain, Sri Lanka, Sweden, Switzerland, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States of America and Vietnam under which the rate of withholding tax on interest and dividends is reduced, generally to between 5% and 15%, and the tax on capital gains is often eliminated.
With respect to any gains subject to Korean withholding tax, as described under “—Tax on Capital Gains” above, you should inquire for yourself whether you are entitled to the benefit of a tax treaty with Korea. It will be your responsibility to claim the benefits of any tax treaty that may exist between your country and Korea in respect of capital gains, and to provide to the purchaser of the debt securities, or the relevant securities company handling the debt securities, as applicable, a certificate as to your country of tax residence. In the absence of sufficient proof, the purchaser, or the relevant securities company, as the case may be, must withhold tax at the normal rates.
Furthermore, in order to claim the benefit of a tax rate reduction or tax exemption available under the applicable tax treaties, you should submit to the payer of such Korean source income an application (for reduced withholding tax rate, “application for entitlement to reduced tax rate” and in the case of exemption from withholding tax, “application for exemption” under a tax treaty along with a certificate of the non-resident holder’s tax residence issued by a competent authority of the non-resident holder’s residence country) as the beneficial owner (“BO Application”). Such application should be submitted to the withholding agent prior to the payment date of the relevant income. Subject to certain exceptions, where the relevant income is paid to an overseas investment vehicle (which is not the beneficial owner of such income) (“OIV”), a beneficial owner claiming the benefit of an applicable tax treaty with respect to such income must submit its BO Application to
212
Table of Contents
such OIV, which must submit an OIV report and a schedule of beneficial owners to the withholding agent prior to the payment date of such income. In the case of a tax exemption application, the withholding agent is required to submit such application (together with the applicable OIV report in the case of income paid to an OIV) to the relevant district tax office by the ninth day of the month following the date of the payment of such income.
At present, Korea has not entered into tax treaties regarding inheritance or gift tax.
Warrants
A description of the tax consequences of an investment in warrants will be provided in the applicable prospectus supplement.
United States Tax Considerations
The following discussion summarizes certain U.S. federal income tax considerations that may be relevant to you if you invest in debt securities and are a U.S. holder, and, to a limited extent, if you are a non-U.S. holder. You will be a U.S. holder if you are an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States, a U.S. domestic corporation, or any other person that is subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis in respect of its investment in a debt security. This summary deals only with U.S. holders that hold debt securities as capital assets for tax purposes. This summary does not apply to you if you are an investor that is subject to special tax rules, such as:
| • | a bank or thrift; |
| • | a real estate investment trust; |
| • | a regulated investment company; |
| • | an insurance company; |
| • | a dealer in securities or currencies; |
| • | a trader in securities or commodities that elects mark-to-market treatment; |
| • | a person that will hold debt securities as a hedge against currency risk or as a position in a straddle or conversion transaction for tax purposes, or as part of a “synthetic security” or other integrated financial transaction; |
| • | an entity taxed as a partnership and partners therein; |
| • | a tax exempt organization; or |
| • | a person whose functional currency for tax purposes is not the U.S. dollar. |
A non-U.S. holder is a beneficial owner of a debt security that is not a U.S. holder.
This summary is based on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), its legislative history, existing and proposed regulations promulgated thereunder, and published rulings and court decisions, all as currently in effect. These laws are subject to change, possibly on a retroactive basis. This summary addresses only U.S. federal income tax consequences, and does not address state, local, or foreign tax laws, or the Medicare tax on net investment income. This summary does not discuss tax considerations relevant to the ownership and disposal of bearer securities.
This summary deals only with debt securities that are properly treated as indebtedness for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Any special U.S. federal income tax considerations relevant to a particular issuance of debt securities will be discussed in the applicable prospectus supplement. You should consult your tax adviser about the tax consequences of holding debt securities, including the relevance to your particular situation of the considerations discussed below, as well as of state, local or other tax laws.
213
Table of Contents
Payments or Accruals of Interest
Payments or accruals of “qualified stated interest” (as defined below) on a debt security will be taxable to you as ordinary interest income at the time that you receive or accrue such amounts, in accordance with your regular method of tax accounting. If you use the cash method of tax accounting and you receive payments of interest pursuant to the terms of a debt security in a currency other than U.S. dollars, a “foreign currency”, the amount of interest income you will realize will be the U.S. dollar value of the foreign currency payment based on the exchange rate in effect on the date you receive the payment regardless of whether you convert the payment into U.S. dollars. If you are an accrual-basis U.S. holder, the amount of interest income you will realize will be based on the average exchange rate in effect during the interest accrual period or, with respect to an interest accrual period that spans two taxable years, at the average exchange rate for the partial period within the taxable year. Alternatively, as an accrual-basis U.S. holder you may elect to translate all interest income on foreign currency-denominated debt securities at the spot rate on the last day of the accrual period (or the last day of the taxable year, in the case of an accrual period that spans more than one taxable year), or on the date that you receive the interest payment if that date is within five business days of the end of the accrual period. If you make this election you must apply it consistently to all debt instruments from year to year and you cannot change the election without the consent of the Internal Revenue Service. If you use the accrual method of accounting for tax purposes you will recognize foreign currency gain or loss on the receipt of a foreign currency interest payment if the exchange rate in effect on the date the payment is received differs from the rate applicable to a previous accrual of that interest income. This foreign currency gain or loss will be treated as ordinary income or loss, but generally will not be treated as an adjustment to interest income received on the debt security.
Purchase, Sale and Retirement of Notes
Initially, your tax basis in a debt security generally will equal the cost of the debt security to you. Your basis will increase by any amounts that you are required to include in income under the rules governing original issue discount and market discount, and will decrease by the amount of any amortized premium and any payments other than qualified stated interest made on the debt security. The rules for determining these amounts are discussed below. If you purchase a debt security that is denominated in a foreign currency, the cost to you, and therefore generally your initial tax basis, will be the U.S. dollar value of the foreign currency purchase price on the date of purchase calculated at the exchange rate in effect on that date. If the foreign currency-denominated debt security is traded on an established securities market and you are a cash-basis taxpayer, or if you are an accrual-basis taxpayer that makes a special election, then you will determine the U.S. dollar value of the cost of the debt security by translating the amount of the foreign currency that you paid for the debt security at the spot rate of exchange on the settlement date of your purchase. The amount of any subsequent adjustments to your tax basis in a foreign currency-denominated debt security in respect of original issue discount, market discount and premium will be determined in the manner described below. If you convert U.S. dollars into a foreign currency and then immediately use that foreign currency to purchase a debt security, you generally will not have any taxable gain or loss as a result of the purchase.
When you sell or exchange a debt security, or if a debt security is retired, you generally will recognize gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount you realize on the transaction, less any accrued qualified stated interest, which will be subject to tax in the manner described above, and your tax basis in the debt security. If you sell or exchange a debt security for a foreign currency, or receive foreign currency on the retirement of a debt security, the amount you will realize for U.S. tax purposes generally will be the dollar value of the foreign currency that you receive calculated at the exchange rate in effect on the date the foreign currency debt security is disposed of or retired. If you dispose of a foreign currency debt security that is traded on an established securities market and you are a cash-basis U.S. holder, or if you are an accrual-basis holder that makes a special election, then you will determine the U.S. dollar value of the amount realized by translating the amount at the spot rate of exchange on the settlement date of the sale, exchange or retirement.
The special election available to you if you are an accrual-basis taxpayer in respect of the purchase and sale of foreign currency debt securities traded on an established securities market, which is discussed in the
214
Table of Contents
two preceding paragraphs, must be applied consistently to all debt instruments from year to year and cannot be changed without the consent of the Internal Revenue Service.
Except as discussed below with respect to market discount, short-term debt securities and foreign currency gain or loss, the gain or loss that you recognize on the sale, exchange or retirement of a debt security generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if you have held the debt security for more than one year. The Code provides preferential treatment under certain circumstances for net long-term capital gains recognized by individual investors. The ability of U.S. holders to offset capital losses against ordinary income is limited.
The gain or loss that you recognize on the sale, exchange or retirement of a foreign currency debt security generally will be treated as ordinary income or loss to the extent that the gain or loss is attributable to changes in exchange rates during the period in which you held the debt security. This foreign currency gain or loss will not be treated as an adjustment to interest income that you receive on the debt security.
Original Issue Discount
If we issue debt securities at a discount from their stated redemption price at maturity, and the discount is equal to or more than the product of one-fourth of one percent (0.25%) of the stated redemption price at maturity of the debt securities multiplied by the number of whole years to their maturity, the debt securities will be “Original Issue Discount Debt Securities.” The difference between the issue price and their stated redemption price at maturity will be the “original issue discount.” The “issue price” of the debt securities will be the first price at which a substantial amount of the debt securities are sold to the public (i.e., excluding sales of debt securities to underwriters, placement agents, wholesalers, or similar persons). The “stated redemption price at maturity” will include all payments under the debt securities other than payments of qualified stated interest. The term “qualified stated interest” generally means stated interest that is unconditionally payable in cash or property, other than debt instruments issued by the Company, at least annually during the entire term of a debt security at a single fixed interest rate or, subject to certain conditions, based on one or more interest indices.
If you invest in Original Issue Discount Debt Securities you generally will be subject to the special tax accounting rules for original issue discount obligations provided by the Internal Revenue Code and certain Treasury regulations (the “OID regulations”). You should be aware that, as described in greater detail below, if you invest in an Original Issue Discount Debt Security you generally will be required to include original issue discount in ordinary gross income for U.S. federal income tax purposes as it accrues, before you receive the cash attributable to that income.
In general, and regardless of whether you use the cash or the accrual method of tax accounting, if you are the holder of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security with a maturity greater than one year, you will be required to include in ordinary gross income the sum of the “daily portions” of original issue discount on that debt security for all days during the taxable year that you own the debt security. The daily portions of original issue discount on an Original Issue Discount Debt Security are determined by allocating to each day in any accrual period a ratable portion of the original issue discount allocable to that period. Accrual periods may be any length and may vary in length over the term of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security, so long as no accrual period is longer than one year and each scheduled payment of principal or interest occurs on the first or last day of an accrual period. If you are the initial holder of the debt security, the amount of original issue discount on an Original Issue Discount Debt Security allocable to each accrual period is determined by:
| (i) | multiplying the “adjusted issue price” (as defined below) of the debt security at the beginning of the accrual period by a fraction, the numerator of which is the annual yield to maturity of the debt security and the denominator of which is the number of accrual periods in a year; and |
| (ii) | subtracting from that product the amount, if any, payable as qualified stated interest allocable to that accrual period. |
215
Table of Contents
In the case of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security that is a floating rate debt security, both the “annual yield to maturity” and the qualified stated interest will be determined for these purposes as though the debt security had borne interest in all periods at a fixed rate generally equal to the rate that would be applicable to interest payments on the debt security on its date of issue or, in the case of some floating rate debt securities, the rate that reflects the yield that is reasonably expected for the debt security. Additional rules may apply if interest on a floating rate debt security is based on more than one interest index. The “adjusted issue price” of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security at the beginning of any accrual period will generally be the sum of its issue price, including any accrued interest, and the amount of original issue discount allocable to all prior accrual periods, reduced by the amount of all payments other than any qualified stated interest payments on the debt security in all prior accrual periods. All payments on an Original Issue Discount Debt Security, other than qualified stated interest, will generally be viewed first as payments of previously accrued original issue discount, to the extent of the previously accrued discount, with payments considered made from the earliest accrual periods first, and then as a payment of principal. The “annual yield to maturity” of a debt security is the discount rate, appropriately adjusted to reflect the length of accrual periods, that causes the present value on the issue date of all payments on the debt security to equal the issue price. As a result of this “constant yield” method of including original issue discount income, the amounts you will be required to include in your gross income if you invest in an Original Issue Discount Debt Security denominated in U.S. dollars will generally be less in the early years and greater in the later years than amounts that would be includible on a straight-line basis.
You generally may make an irrevocable election to include in income your entire return on a debt security (i.e., the excess of all remaining payments to be received on the debt security, including payments of qualified stated interest, over the amount you paid for the debt security) under the constant yield method described above. For debt securities purchased at a premium or bearing market discount in your hands, if you make this election you will also be deemed to have made the election (discussed below under “Premium and Market Discount”) to amortize premium or to accrue market discount in income currently on a constant yield basis.
In the case of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security that is also a foreign currency-denominated debt security, you should determine the U.S. dollar amount includible as original issue discount for each accrual period by (i) calculating the amount of original issue discount allocable to each accrual period in the foreign currency using the constant yield method, and (ii) translating the foreign currency amount so determined at the average exchange rate in effect during that accrual period (or, with respect to an interest accrual period that spans two taxable years, at the average exchange rate for each partial period). Alternatively, you may translate the foreign currency amount so determined at the spot rate of exchange on the last day of the accrual period (or the last day of the taxable year, for an accrual period that spans two taxable years), or at the spot rate of exchange on the date of receipt, if that date is within five business days of the last day of the accrual period, provided that you have made the election described under “—Payments or Accruals of Interest” above. Because exchange rates may fluctuate, if you are the holder of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security that is also a foreign currency debt security you may recognize a different amount of original issue discount income in each accrual period than would be the case if you were the holder of an otherwise similar Original Issue Discount Debt Security denominated in U.S. dollars. Upon the receipt of an amount attributable to original issue discount, whether in connection with a payment of an amount that is not qualified stated interest or the sale or retirement of the Original Issue Discount Debt Security, you will recognize ordinary income or loss measured by the difference between the amount received, translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rate in effect on the date of receipt or on the date of disposition of the Original Issue Discount Debt Security, as the case may be, and the amount accrued, using the exchange rate applicable to such previous accrual.
If you purchase an Original Issue Discount Debt Security outside of the initial offering at a cost less than its “remaining redemption amount”, or if you purchase an Original Issue Discount Debt Security in the initial offering at a price other than the debt security’s issue price, you will also generally be required to include in gross income the daily portions of original issue discount, calculated as described above. However, if you acquire an Original Issue Discount Debt Security at a price greater than its adjusted issue price, you will be entitled to reduce your periodic inclusions of original issue discount to reflect the premium paid over the adjusted issue
216
Table of Contents
price. The remaining redemption amount for an Original Issue Discount Debt Security is the total of all future payments to be made on the debt security other than qualified stated interest.
Floating rate debt securities generally will be treated as “variable rate debt instruments” under the OID regulations. Accordingly, the stated interest on a floating rate debt security generally will be treated as qualified stated interest, and such a debt security will not have original issue discount solely as a result of the fact that it provides for interest at a variable rate. A floating rate debt security that does not qualify as a variable rate debt instrument will be subject to special rules (the “contingent payment regulations”) that govern the tax treatment of debt obligations that provide for contingent payments (“contingent debt obligations”). A detailed description of the tax considerations relevant to U.S. holders of any such debt securities will be provided in the applicable prospectus supplement.
Certain debt securities may be redeemed prior to maturity, either at our option or at the option of the holder, or may have special repayment or interest rate reset features as indicated in the prospectus supplement. Original Issue Discount Debt Securities containing these features may be subject to rules that differ from the general rules discussed above. If you purchase Original Issue Discount Debt Securities with these features, you should carefully examine the prospectus supplement and consult your tax adviser about their treatment since the tax consequences with respect to original issue discount will depend, in part, on the particular terms and features of the debt securities.
Short-Term Debt Securities
The rules described above will also generally apply to Original Issue Discount Debt Securities with maturities of one year or less (“short-term debt securities”), but with some modifications.
First, the original issue discount rules treat none of the interest on a short-term debt security as qualified stated interest, but treat a short-term debt security as having original issue discount. Thus, all short-term debt securities will be Original Issue Discount Debt Securities. Except as noted below, if you are a cash-basis holder of a short-term debt security and you do not identify the short-term debt security as part of a hedging transaction you will generally not be required to accrue original issue discount currently, but you will be required to treat any gain realized on a sale, exchange or retirement of the debt security as ordinary income to the extent such gain does not exceed the original issue discount accrued with respect to the debt security during the period you held the debt security. You may not be allowed to deduct all of the interest paid or accrued on any indebtedness incurred or maintained to purchase or carry a short-term debt security until the maturity of the debt security or its earlier disposition in a taxable transaction. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if you are a cash-basis U.S. holder of a short-term debt security you may elect to accrue original issue discount on a current basis, in which case the limitation on the deductibility of interest described above will not apply. A U.S. holder using the accrual method of tax accounting and some cash method holders, including banks, securities dealers, regulated investment companies and certain trust funds, generally will be required to include original issue discount on a short-term debt security in gross income on a current basis. Original issue discount will be treated as accruing for these purposes on a ratable basis or, at the election of the holder, on a constant yield basis based on daily compounding.
Second, regardless of whether you are a cash- or accrual-basis holder, if you are the holder of a short-term debt security you can elect to accrue any “acquisition discount” with respect to the debt security on a current basis. Acquisition discount is the excess of the debt security’s stated redemption price at maturity (i.e., all amounts payable on the short-term debt security) over the purchase price. Acquisition discount will be treated as accruing ratably or, at the election of the holder, under a constant yield method based on daily compounding. If you elect to accrue acquisition discount, the original issue discount rules will not apply.
Finally, the market discount rules described below will not apply to short-term debt securities.
217
Table of Contents
As described above, certain of the debt securities may be subject to special redemption features. These features may affect the determination of whether a debt security has a maturity of one year or less and thus is a short-term debt security. If you purchase debt securities with these features, you should carefully examine the prospectus supplement and consult your tax adviser about these features.
Premium and Market Discount
If you purchase a debt security at a cost greater than the debt security’s remaining redemption amount, you will be considered to have purchased the debt security at a premium, and you may elect to amortize the premium as an offset to interest income, using a constant yield method, over the remaining term of the debt security. If you make this election, it generally will apply to all debt instruments that you hold at the time of the election, as well as any debt instruments that you subsequently acquire. In addition, you may not revoke the election without the consent of the Internal Revenue Service. If you elect to amortize the premium you will be required to reduce your tax basis in the debt security by the amount of the premium amortized during your holding period. Original Issue Discount Debt Securities purchased at a premium will not be subject to the original issue discount rules described above. In the case of premium on a foreign currency debt security, you should calculate the amortization of the premium in the foreign currency. Amortization deductions attributable to a period reduce interest payments in respect of that period, and therefore are translated into U.S. dollars at the rate that you use for those interest payments. Exchange gain or loss will be realized with respect to amortized premium on a foreign currency debt security based on the difference between the exchange rate computed on the date or dates the premium is amortized against interest payments on the debt security and the exchange rate on the date when the holder acquired the debt security. For a U.S. holder that does not elect to amortize premium, the amount of premium will be included in your tax basis when the debt security matures or is disposed of. Therefore, if you do not elect to amortize premium and you hold the debt security to maturity, you generally will be required to treat the premium as capital loss when the debt security matures.
If you purchase a debt security at a price that is lower than the debt security’s remaining redemption amount, or in the case of an Original Issue Discount Debt Security, the debt security’s adjusted issue price, by 0.25% or more of the remaining redemption amount, or adjusted issue price, multiplied by the number of remaining whole years to maturity, the debt security will be considered to bear “market discount” in your hands. In this case, any gain that you realize on the disposition of the debt security generally will be treated as ordinary interest income to the extent of the market discount that accrued on the debt security during your holding period. In addition, you could be required to defer the deduction of a portion of the interest paid on any indebtedness that you incurred or continued to purchase or carry the debt security. In general, market discount will be treated as accruing ratably over the term of the debt security, or, at your election, under a constant yield method. You must accrue market discount on a foreign currency debt security in the specified currency. The amount that you will be required to include in income in respect of accrued market discount will be the U.S. dollar value of the accrued amount, generally calculated at the exchange rate in effect on the date that you dispose of the debt security.
You may elect to include market discount in gross income currently as it accrues (on either a ratable or constant yield basis), in lieu of treating a portion of any gain realized on a sale of the debt security as ordinary income. If you elect to include market discount on a current basis, the interest deduction deferral rule described above will not apply. If you do make such an election, it will apply to all market discount debt instruments that you acquire on or after the first day of the first taxable year to which the election applies. The election may not be revoked without the consent of the Internal Revenue Service. Any accrued market discount on a foreign currency debt security that is currently includible in income will be translated into U.S. dollars at the average exchange rate for the accrual period (or portion thereof within the holder’s taxable year).
Indexed Notes and Other Notes Providing for Contingent Payments
The contingent payment regulations generally require accrual of interest income on a constant yield basis in respect of contingent debt obligations at a yield determined at the time of issuance of the obligation, and may
218
Table of Contents
require adjustments to these accruals when any contingent payments are made. In addition, special rules may apply to floating rate debt securities if the interest payable on the debt securities is based on more than one interest index. We will provide a detailed description of the tax considerations relevant to U.S. holders of any debt securities that are subject to the special rules discussed in this paragraph in the relevant prospectus supplement.
Foreign Currency-Denominated Debt Security and Reportable Transactions
A U.S. holder that participates in a “reportable transaction” will be required to disclose its participation to the Internal Revenue Service. The scope and application of these rules is not entirely clear. A U.S. holder may be required to treat a foreign currency exchange loss relating to a foreign currency-denominated debt security as a reportable transaction if the loss exceeds $50,000 in a single taxable year if the U.S. holder is an individual or trust, or higher amounts for other U.S. holders. In the event the acquisition, ownership or disposition of a foreign currency-denominated debt security constitutes participation in a “reportable transaction” for purposes of these rules, a U.S. holder will be required to disclose its investment to the Internal Revenue Service, currently on Form 8886. Prospective purchasers should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of these rules to the acquisition, ownership or disposition of foreign currency-denominated debt securities.
Specified Foreign Financial Assets
Certain U.S. holders that own “specified foreign financial assets” with an aggregate value in excess of $50,000 are generally required to file an information statement along with their tax returns, currently on Form 8938, with respect to such assets. “Specified foreign financial assets” include any financial accounts held at a non-U.S. financial institution, as well as securities issued by a non-U.S. issuer (which may include debt securities issued in certificated form) that are not held in accounts maintained by financial institutions. Higher reporting thresholds apply to certain individuals living abroad and to certain married individuals. U.S. holders who fail to report the required information could be subject to substantial penalties. Prospective investors should consult their own tax advisors concerning the application of these rules to their investment in the debt securities, including the application of the rules to their particular circumstances.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
The paying agent must file information returns with the United States Internal Revenue Service in connection with debt security payments made to certain United States persons. If you are a United States person, you generally will not be subject to United States backup withholding tax on such payments if you provide your taxpayer identification number to the paying agent. You may also be subject to information reporting and backup withholding tax requirements with respect to the proceeds from a sale of the debt securities. If you are not a United States person, in order to avoid information reporting and backup withholding tax requirements you may have to comply with certification procedures to establish that you are not a United States person. The amount of any backup withholding from a payment to a U.S. or non-U.S. taxpayer will be allowed as a credit against the holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability and may entitle the holder to a refund, provided that the required information is timely furnished to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act
We or a non-U.S. financial institution through which payments are made may be required pursuant to FATCA to collect and provide to the U.S. Internal Revenue Service or another tax authority substantial information regarding investors in debt securities. As such, holders may be required to provide information and tax documentation regarding their tax identities as well as that of their direct and indirect owners. Additionally, starting at the earliest on January 1, 2019, “foreign passthru payments” (a term not yet defined) may be subject to withholding under FATCA. Withholding on such payments under FATCA will not apply to debt securities issued before the date that is six months after the publication of final regulations defining “foreign passthru payment,” unless the debt securities are materially modified on or after such date.
219
Table of Contents
By purchasing the Notes, U.S. holders agree to provide an IRS form W-9, and whatever other information may be necessary for us to comply with these reporting obligations. If an amount of, or in respect of, U.S. withholding tax were to be deducted or withheld from payments on the debt securities as a result of an investor’s failure to comply with these rules, neither we nor any paying agent nor any other person would be required to pay additional amounts with respect to any debt securities as a result of the deduction or withholding of such tax. You should consult your tax advisors on how FATCA may apply to payments you receive under the debt securities.
Warrants
A description of the tax consequences of an investment in warrants will be provided in the applicable prospectus supplement.
Guarantees
A description of the tax consequences of an investment in guarantees will be provided in the applicable prospectus supplement.
220
Table of Contents
We and the Republic, if a guarantee by the Republic is furnished, may sell or issue the debt securities, warrants or guarantees in any of three ways:
| • | through underwriters or dealers; |
| • | directly to one or more purchasers; or |
| • | through agents. |
The prospectus supplement relating to a particular series of debt securities, warrants or guarantees will state:
| • | the names of any underwriters; |
| • | the purchase price of the securities; |
| • | the proceeds to us from the sale; |
| • | any underwriting discounts and other compensation; |
| • | the initial public offering price; |
| • | any discounts or concessions allowed or paid to dealers; and |
| • | any securities exchanges on which the securities will be listed. |
Any underwriter involved in the sale of securities will acquire the securities for its own account. The underwriters may resell the securities from time to time in one or more transactions, including negotiated transactions, at a fixed public offering price or at varying prices to be determined at the time of sale. The securities may be offered to the public either by underwriting syndicates represented by managing underwriters or by underwriters without a syndicate. Unless the prospectus supplement states otherwise, certain conditions must be satisfied before the underwriters become obligated to purchase securities from us and the Republic, if applicable, and they will be obligated to purchase all of the securities if any are purchased. The underwriters may change any initial public offering price and any discounts or concessions allowed or reallowed or paid to dealers.
If we and the Republic, if a guarantee by the Republic is furnished, sell any securities through agents, the prospectus supplement will identify the agent and indicate any commissions payable by us and the Republic, if applicable. Unless the prospectus supplement states otherwise, all agents will act on a best efforts basis and will not acquire the securities for their own account.
We and the Republic, if a guarantee by the Republic is furnished, may authorize agents, underwriters or dealers to solicit offers by certain specified entities to purchase the securities from us and the Republic, if applicable, at the public offering price set forth in a prospectus supplement pursuant to delayed delivery contracts. The prospectus supplement will set out the conditions of the delayed delivery contracts and the commission receivable by the agents, underwriters or dealers for soliciting the contracts.
We and the Republic, if a guarantee by the Republic is furnished, may offer debt securities as consideration for the purchase of other of our debt securities, either in connection with a publicly announced tender offer or in privately negotiated transactions. The offer may be in addition to or in lieu of sales of debt securities directly or through underwriters or agents. We may offer guarantees as consideration for transactions involving securities of other issuers.
Agents and underwriters may be entitled to indemnification by us against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or to contribution from us with respect to certain payments which the agents or underwriters may be required to make. Agents and underwriters may be customers of, engage in transactions with, or perform services (including commercial and investment banking services) for us and the Republic in the ordinary course of business.
221
Table of Contents
The validity of any particular series of debt securities or warrants issued with debt securities or any guarantees will be passed upon for us and any underwriters or agents by United States and Korean counsel identified in the related prospectus supplement.
AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVES IN THE UNITED STATES
Our authorized agents in the United States are Mr. Nak Joo Seong, General Manager of our New York Branch, or Mr. Jin Hwan Sah, Senior Deputy General Manager of our New York Branch. The address of our New York Branch is 320 Park Avenue, 32nd Floor, New York, New York 10022. The authorized representative of the Republic in the United States is Mr. Suk-Kwon Na, Financial Attache, Korean Consulate General in New York, located at 335 East 45th Street, New York, New York 10017.
OFFICIAL STATEMENTS AND DOCUMENTS
Our President and Chairman of the Board of Directors, in his official capacity, has supplied the information set forth under “The Korea Development Bank” (except for the information set out under “The Korea Development Bank—Business—Government Support and Supervision”). Such information is stated on his authority.
The Minister of Strategy and Finance of The Republic of Korea, in his official capacity, has supplied the information set out under “The Korea Development Bank—Business—Government Support and Supervision” and “The Republic of Korea.” Such information is stated on his authority. The documents identified in the portion of this prospectus captioned “The Republic of Korea” as the sources of financial or statistical data are official public documents of the Republic or its agencies and instrumentalities.
Our separate financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2015 have been included in this prospectus in reliance upon the report of KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp., independent auditors, appearing elsewhere herein, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
222
Table of Contents
This prospectus includes future expectations, projections or “forward-looking statements”, as defined in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The words “believe”, “expect”, “anticipate”, “estimate”, “project” and similar words identify forward-looking statements. In addition, all statements other than statements of historical facts included in this prospectus are forward-looking statements. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we can give no assurance that such expectations will prove correct. This prospectus discloses important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations (“Cautionary Statements”). All subsequent written and oral forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the Cautionary Statements.
Factors that could adversely affect the future performance of the Korean economy include:
| • | increased sovereign default risks in selected countries and the resulting adverse effects on the global financial markets; |
| • | adverse conditions and volatility in the United States and worldwide credit and financial markets and the general weakness of the global economy; |
| • | adverse changes or volatility in foreign currency reserve levels, commodity prices (including oil prices), exchange rates (including fluctuation of the U.S. dollar or Japanese Yen exchange rates or revaluation of the Chinese Renminbi), interest rates and stock markets; |
| • | continuing adverse conditions in the economies of countries and regions that are important export markets for Korea, such as the United States, Europe, Japan and China, or in emerging market economies in Asia or elsewhere; |
| • | substantial decreases in the market prices of Korean real estate; |
| • | a continuing rise in the level of household debt and increasing delinquencies and credit defaults by consumer and small and medium sized enterprise borrowers; |
| • | declines in consumer confidence and a slowdown in consumer spending; |
| • | adverse developments in the economies of countries that are important export markets for the Republic, such as the United States, Europe, Japan and China, or in emerging market economies in Asia or elsewhere; |
| • | difficulties in the financial sector in Korea, including the savings bank sector; |
| • | the continued growth of the Chinese economy, to the extent its benefits (such as increased exports to China) are outweighed by its costs (such as competition in export markets or for foreign investment and the relocation of the manufacturing base from the Republic to China), as well as a slowdown in the growth of China’s economy, which is Korea’s most important export market; |
| • | social and labor unrest; |
| • | a decrease in tax revenues and a substantial increase in the Government’s expenditures for fiscal stimulus measures, unemployment compensation and other economic and social programs that, together, would lead to an increased government budget deficit; |
| • | financial problems or lack of progress in the restructuring of Korean conglomerates, other large troubled companies, their suppliers or the financial sector; |
| • | loss of investor confidence arising from corporate accounting irregularities and corporate governance issues at certain Korean conglomerates; |
| • | increases in social expenditures to support an aging population in Korea or decreases in economic productivity due to the declining population size in Korea; |
223
Table of Contents
| • | the economic impact of any pending or future free trade agreements; |
| • | geo-political uncertainty and risk of further attacks by terrorist groups around the world; |
| • | the occurrence of severe health epidemics in Korea and other parts of the world including an outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS, swine or avian flu, Ebola or Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, or MERS; |
| • | deterioration in economic or diplomatic relations between the Republic and its trading partners or allies, including deterioration resulting from trade disputes or disagreements in foreign policy; |
| • | political uncertainty or increasing strife among or within political parties in the Republic; |
| • | hostilities or unrest involving oil producing countries in the Middle East and Northern Africa and any material disruption in the supply of oil or increase in the price of oil; |
| • | the occurrence of severe earthquakes, tsunamis or other natural or man-made disasters in Korea and other parts of the world, particularly in trading partners; and |
| • | an increase in the level of tension or an outbreak of hostilities between North Korea and the Republic or the United States. |
224
Table of Contents
We filed a registration statement with respect to the securities with the Securities and Exchange Commission under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and its related rules and regulations. You can find additional information concerning ourselves and the securities in the registration statement and any pre- or post-effective amendment, including its various exhibits, which may be inspected at the public reference facilities maintained by the Securities and Exchange Commission at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. These filings are also available to the public from the Securities and Exchange Commission’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
225
Table of Contents
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN THE PROSPECTUS
Item 11. Estimated Expenses.*
It is estimated that our expenses in connection with the sale of the debt securities, warrants and guarantees hereunder, exclusive of compensation payable to underwriters and agents, will be as follows:
| SEC Registration Fee |
US$ | 573,000 | ||
| Printing Costs |
250,000 | |||
| Legal Fees and Expenses |
450,000 | |||
| Fiscal Agent Fees and Expenses |
50,000 | |||
| Blue Sky Fees and Expenses |
50,000 | |||
| Rating Agencies’ Fees |
350,000 | |||
| Miscellaneous (including amounts to be paid to underwriters in lieu of reimbursement of certain expenses) |
600,000 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
US$ | 2,323,000 | ||
|
|
|
| * | Based on three underwritten offerings of the debt securities. |
UNDERTAKINGS
The Registrants hereby undertake:
| (a) | To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this Registration Statement: |
| (i) | To include any prospectus required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933; |
| (ii) | To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of this Registration Statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereto) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in this Registration Statement; and |
| (iii) | To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in this Registration Statement or any material change to such information in this Registration Statement; |
| (b) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof; and |
| (c) | To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering. |
| (d) | That, for purposes of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser: |
each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration
II-1
Table of Contents
statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
| (e) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities: |
The undersigned registrants undertake that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrants pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrants will be sellers to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser;
| (i) | Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrants relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424; |
| (ii) | Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrants or used or referred to by the undersigned registrants; |
| (iii) | The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrants or their securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrants; and |
| (iv) | Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrants to the purchaser. |
II-2
Table of Contents
CONTENTS
This Registration Statement is comprised of:
| (1) | Facing Sheet. |
| (2) | Explanatory Note. |
| (3) | Part I, consisting of the Prospectus. |
| (4) | Part II, consisting of pages II-1 to II-9 |
| (5) | The following Exhibits: |
| A-1 | - | Form of Underwriting Agreement Standard Terms, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit A to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-38873). | ||||
| B-1 | - | Form of Fiscal Agency Agreement, including forms of Debt Securities, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-44818). | ||||
| B-2 | - | Form of global Debt Security that bears interest at a fixed rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-156305). | ||||
| B-3 | - | Form of Amendment No. 1 to Fiscal Agency Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-3 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-111608). | ||||
| C-1 | - | Form of Warrant Agreement, including form of Warrants.* | ||||
| C-2 | - | Form of Guarantee Agreement, including form of Guarantees, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit C-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-97299). | ||||
| C-3 | - | Form of Solicitation Indemnification Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit C-3 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-97299). | ||||
| D-1 | - | Consent of the Chief Executive Officer & Chairman of The Korea Development Bank (included on page II-5). | ||||
| D-2 | - | Power of Attorney of the Chief Executive Officer & Chairman of The Korea Development Bank. | ||||
| E-1 | - | Consent of the Minister of Strategy and Finance of The Republic of Korea (included on Page II-6). | ||||
| E-2 | - | Power of Attorney of the Minister of Strategy and Finance of The Republic of Korea, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit E-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-156305). | ||||
| F | - | Consent of KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. | ||||
| G-1 | - | Letter appointing certain persons as authorized agents of The Korea Development Bank in the United States. | ||||
| G-2 | - | Letter appointing Authorized Agents of The Republic of Korea in the United States (included in Exhibit E-2). | ||||
| H | - | The Korea Development Bank Act, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit H to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-197061). | ||||
| I | - | The Enforcement Decree of The Korea Development Bank Act.** | ||||
| J | - | The Articles of Incorporation of The Korea Development Bank.** | ||||
II-3
Table of Contents
| K-1 | - | Form of Prospectus Supplement relating to The Korea Development Bank’s Medium-Term Notes, Series C, Due Not Less Than Nine Months From Date of Issue (the “Series C Notes”), incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit K-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| K-2 | - | Form of Supplement to the Prospectus Supplement relating to the Korea Development Bank’s Series C Notes, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit K-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| L | - | Form of Distribution Agreement between The Korea Development Bank and the Agents named therein relating to the offer or sale from time to time of the Series C Notes, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit L to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| M-1 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, c/o 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of the Debt Securities (with or without Warrants).** | ||||
| M-2 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Kim & Chang, 39, Sajik-ro 8-gil, Jongno-gu, Seoul, Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of the Debt Securities (with or without Warrants) and the Guarantees to be issued by The Republic of Korea.** | ||||
| M-3 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.25% Notes due 2020.** | ||||
| M-4 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Hwang Mok Park P.C., 9th Floor, Shinhan Bank Building, 20, Sejong-daero 9-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul 100-724, The Republic of Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.25% Notes due 2020.** | ||||
| M-5 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.50% Notes due 2021 and US$1,000,000,000 3.00% Notes due 2026.** | ||||
| M-6 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Kim & Chang, 39, Sajik-ro 8-gil, Jongno-gu, Seoul, Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.50% Notes due 2021 and US$1,000,000,000 3.00% Notes due 2026.** | ||||
| N-1 | - | Form of the Series C Note that bears interest at a fixed rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit N-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| N-2 | - | Form of the Series C Note that bears interest at a floating rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit N-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| O | - | Form of Calculation Agency Agreement between The Korea Development Bank and the calculation agent named therein relating to the Series C Notes that bear interest at a floating rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit O to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||||
| * | May be filed by amendment. |
| ** | Previously filed. |
II-4
Table of Contents
SIGNATURE OF THE KOREA DEVELOPMENT BANK
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, The Korea Development Bank has duly caused this Registration Statement or amendment thereto to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in Seoul, The Republic of Korea, on the 14th day of June, 2016.
| THE KOREA DEVELOPMENT BANK | ||
| By: |
DONG GEOL LEE*† | |
| Chief Executive Officer & Chairman | ||
| †By: |
/S/ SANG PIL KO | |
| Sang Pil Ko | ||
| (Attorney-in-fact) | ||
| * | Consent is hereby given to use of his name in connection with the information specified in this Registration Statement or amendment thereto to have been supplied by him and stated on his authority. |
II-5
Table of Contents
SIGNATURE OF THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, The Republic of Korea has duly caused this Registration Statement or amendment thereto to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in The City of New York, New York, on the 14th day of June, 2016.
| THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA | ||
| By: |
IL HO YOO*† | |
| Minister of Strategy and Finance | ||
| †By: |
/S/ SUK-KWON NA | |
| Suk-Kwon Na | ||
| (Attorney-in-fact) | ||
| * | Consent is hereby given to use of his name in connection with the information specified in this Registration Statement or amendment thereto to have been supplied by him and stated on his authority. |
II-6
Table of Contents
SIGNATURE OF AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE
OF THE KOREA DEVELOPMENT BANK
Pursuant to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the undersigned, a duly authorized representative in the United States of The Korea Development Bank, has signed this Registration Statement or amendment thereto in The City of New York, New York, on the 14th day of June, 2016.
| †By: |
/s/ NAK JOO SEONG | |
| Nak Joo Seong | ||
| New York Branch | ||
| The Korea Development Bank | ||
II-7
Table of Contents
SIGNATURE OF AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE
OF THE KOREA DEVELOPMENT BANK
Pursuant to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the undersigned, a duly authorized representative in the United States of The Korea Development Bank, has signed this Registration Statement or amendment thereto in The City of New York, New York, on the 14th day of June, 2016.
| †By: |
/s/ JIN HWAN SAH | |
| Jin Hwan Sah | ||
| New York Branch | ||
| The Korea Development Bank | ||
II-8
Table of Contents
SIGNATURE OF AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE
OF THE REPUBLIC OF KOREA
Pursuant to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the undersigned, a duly authorized representative in the United States of The Republic of Korea, has signed this Registration Statement or amendment thereto in The City of New York, New York, on the 14th day of June, 2016.
| †By: |
/s/ SUK-KWON NA | |
| Suk-Kwon Na | ||
| Financial Attaché | ||
| Korean Consulate General in New York | ||
II-9
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| A-1 | - | Form of Underwriting Agreement Standard Terms, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit A to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-38873). | ||
| B-1 | - | Form of Fiscal Agency Agreement, including forms of Debt Securities, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-44818). | ||
| B-2 | - | Form of global Debt Security that bears interest at a fixed rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 33-156305). | ||
| B-3 | - | Form of Amendment No. 1 to Fiscal Agency Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit B-3 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-111608). | ||
| C-1 | - | Form of Warrant Agreement, including form of Warrants.* | ||
| C-2 | - | Form of Guarantee Agreement, including form of Guarantees, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit C-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-97299). | ||
| C-3 | - | Form of Solicitation Indemnification Agreement, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit C-3 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-97299). | ||
| D-1 | - | Consent of the Chief Executive Officer & Chairman of The Korea Development Bank (included on page II-5). | ||
| D-2 | - | Power of Attorney of the Chief Executive Officer & Chairman of The Korea Development Bank. | ||
| E-1 | - | Consent of the Minister of Strategy and Finance of The Republic of Korea (included on Page II-6). | ||
| E-2 | - | Power of Attorney of the Minister of Strategy and Finance of The Republic of Korea, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit E-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-156305). | ||
| F | - | Consent of KPMG Samjong Accounting Corp. | ||
| G-1 | - | Letter appointing certain persons as authorized agents of The Korea Development Bank in the United States. | ||
| G-2 | - | Letter appointing Authorized Agents of The Republic of Korea in the United States (included in Exhibit E-2). | ||
| H | - | The Korea Development Bank Act, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit H to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-197061). | ||
| I | - | The Enforcement Decree of The Korea Development Bank Act.** | ||
| J | - | The Articles of Incorporation of The Korea Development Bank.** | ||
| K-1 | - | Form of Prospectus Supplement relating to The Korea Development Bank’s Medium-Term Notes, Series C, Due Not Less Than Nine Months From Date of Issue (the “Series C Notes”), incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit K-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
| K-2 | - | Form of Supplement to the Prospectus Supplement relating to the Korea Development Bank’s Series C Notes, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit K-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
| L | - | Form of Distribution Agreement between The Korea Development Bank and the Agents named therein relating to the offer or sale from time to time of the Series C Notes, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit L to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
Table of Contents
| M-1 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, c/o 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of the Debt Securities (with or without Warrants).** | ||
| M-2 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Kim & Chang, 39, Sajik-ro 8-gil, Jongno-gu, Seoul, Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of the Debt Securities (with or without Warrants) and the Guarantees to be issued by The Republic of Korea.** | ||
| M-3 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.25% Notes due 2020.** | ||
| M-4 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Hwang Mok Park P.C., 9th Floor, Shinhan Bank Building, 20, Sejong-daero 9-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul 100-724, The Republic of Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.25% Notes due 2020.** | ||
| M-5 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton LLP, 19th Floor, Ferrum Tower, 19, Eulji-ro 5-gil, Jung-gu, Seoul, Korea, United States counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.50% Notes due 2021 and US$1,000,000,000 3.00% Notes due 2026.** | ||
| M-6 | - | Opinion (including consent) of Kim & Chang, 39, Sajik-ro 8-gil, Jongno-gu, Seoul, Korea, Korean counsel to The Korea Development Bank, in respect of the legality of The Korea Development Bank’s US$500,000,000 2.50% Notes due 2021 and US$1,000,000,000 3.00% Notes due 2026.** | ||
| N-1 | - | Form of the Series C Note that bears interest at a fixed rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit N-1 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
| N-2 | - | Form of the Series C Note that bears interest at a floating rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit N-2 to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
| O | - | Form of Calculation Agency Agreement between The Korea Development Bank and the calculation agent named therein relating to the Series C Notes that bear interest at a floating rate, incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit O to the Registration Statement of The Korea Development Bank (No. 333-6866). | ||
| * | May be filed by amendment. |
| ** | Previously filed. |