NORTHERN STATES POWER CO000007290912/312023FYFALSE0136125108P3YP1YP1YP2YP1Y00000729092023-01-012023-12-3100000729092024-02-21xbrli:shares00000729092023-06-30iso4217:USD00000729092022-01-012022-12-3100000729092021-01-012021-12-3100000729092022-12-3100000729092021-12-3100000729092020-12-3100000729092023-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares0000072909us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-31xbrli:pure0000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventorySuppliesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventorySuppliesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventoryFuelMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventoryFuelMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventoryNaturalGasMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PublicUtilitiesInventoryNaturalGasMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricGenerationEquipmentMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricGenerationEquipmentMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:GasTransmissionEquipmentMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:GasTransmissionEquipmentMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherCapitalizedPropertyPlantAndEquipmentMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ConstructionInProgressMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:LaCrosseWis.toMadisonWis.Memberus-gaap:JointlyOwnedElectricityGenerationPlantMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:JointlyOwnedElectricityGenerationPlantMembernspw:Capx2020TransmissionMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:PensionAndRetireeMedicalObligationsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:PensionAndRetireeMedicalObligationsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:EnvironmentalRestorationCostsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:EnvironmentalRestorationCostsMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:RecoverableDeferredTaxesOnAfudcRecordedInPlantMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:RecoverableDeferredTaxesOnAfudcRecordedInPlantMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:StateCommissionAdjustmentsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:StateCommissionAdjustmentsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AssetRetirementObligationCostsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AssetRetirementObligationCostsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:DeferredFuelCostsMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DeferredFuelCostsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DeferredFuelCostsMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:OtherRegulatoryAssetsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:OtherRegulatoryAssetsMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:PlantRemovalCostsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:PlantRemovalCostsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:DeferredIncomeTaxChargesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DeferredIncomeTaxChargesMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:DoeSettlementMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:DoeSettlementMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:DoeSettlementMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:DoeSettlementMember2022-12-310000072909srt:MinimumMembernspw:DeferredElectricEnergyCostsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:DeferredElectricEnergyCostsMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:DeferredElectricEnergyCostsMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:OtherRegulatoryLiabilitiesMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:OtherRegulatoryLiabilitiesMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2021-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2023-10-012023-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:MoneyPoolMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2023-10-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:CommercialPaperMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune152024Member2023-12-31utr:Rate0000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune152024Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune1520242Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune1520242Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSept.12038Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSept.12038Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueOct.12042Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueOct.12042Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueDecember12047Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueDecember12047Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSeptember12048Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSeptember12048Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueMay12051Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueMay12051Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueMay120512Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueMay120512Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSept152052Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueSept152052Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune152053Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:BondsMembernspw:SeriesDueJune152053Member2022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:InterchangeMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:InterchangeMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:OtherServicesMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMemberus-gaap:ProductMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:InterchangeMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:InterchangeMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:OtherServicesMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMemberus-gaap:ProductMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:ResidentialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:CommercialandIndustrialCustomersMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:OtherCustomersMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RetailDistributionMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:InterchangeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:InterchangeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:InterchangeMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMembernspw:OtherServicesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:OtherServicesMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMemberus-gaap:ProductMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:ProductMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMembernspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:AlternativeandOtherMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedElectricMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMemberus-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:IncomeTaxExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:IncomeTaxExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:IncomeTaxExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:NetDeferredTaxLiablilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:NetDeferredTaxLiablilityMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:NetDeferredTaxLiablilityMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:NetDeferredTaxLiablilityMember2022-12-310000072909stpr:WI2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashFlowHedgingMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPensionPlansPostretirementOrSupplementalPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:ParentCompanyMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPensionPlansPostretirementOrSupplementalPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:ParentCompanyMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPensionPlansPostretirementOrSupplementalPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:ParentCompanyMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPensionPlansPostretirementOrSupplementalPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:ParentCompanyMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909srt:ScenarioForecastMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:CommingledFundsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembersrt:ParentCompanyMember2023-12-31nspw:Plan0000072909us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMember2024-01-012024-01-310000072909us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2024-01-012024-01-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2024-01-012024-12-310000072909us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2024-01-012024-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OverfundedPlanMembernspw:NSPWisconsinMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:LongDurationFixedIncomeandInterestRateSwapSecuritiesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:LongDurationFixedIncomeandInterestRateSwapSecuritiesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:LongDurationFixedIncomeandInterestRateSwapSecuritiesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:LongDurationFixedIncomeandInterestRateSwapSecuritiesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:AlternativeInvestmentsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:AlternativeInvestmentsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:AlternativeInvestmentsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:AlternativeInvestmentsMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:ShorttointermediatefixedincomesecuritiesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:PensionPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:ShorttointermediatefixedincomesecuritiesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:ShorttointermediatefixedincomesecuritiesMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMembernspw:ShorttointermediatefixedincomesecuritiesMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherPostretirementBenefitPlansDefinedBenefitMemberus-gaap:CashAndCashEquivalentsMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:FERCProceedingMISOROEComplaintMembernspw:NSPMinnesotaandNSPWisconsinMemberMembernspw:FederalEnergyRegulatoryCommissionFERCMember2013-11-012013-11-300000072909nspw:FERCProceedingMISOROEComplaintMembernspw:NSPMinnesotaandNSPWisconsinMemberMembernspw:FederalEnergyRegulatoryCommissionFERCMember2015-02-012015-02-280000072909nspw:OtherMGPLandfillOrDisposalSitesMember2023-12-31nspw:Site0000072909us-gaap:CapitalAdditionsMembernspw:FederalCleanWaterActSection316bMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:ElectricPlantSteamProductionAsbestosMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:ElectricPlantSteamProductionAsbestosMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:ElectricPlantSteamProductionAsbestosMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricDistributionMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricDistributionMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPlantGasTransmissionAndDistributionMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPlantGasTransmissionAndDistributionMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPlantGasTransmissionAndDistributionMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:ElectricPlantSteamProductionAsbestosMember2021-12-310000072909nspw:ElectricPlantSteamProductionAsbestosMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricDistributionMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:ElectricDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPlantGasTransmissionAndDistributionMember2021-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPlantGasTransmissionAndDistributionMember2022-01-012022-12-31nspw:Counterparty0000072909us-gaap:InsuranceRelatedAssessmentsMembernspw:NspMinnesotaMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310000072909us-gaap:InsuranceRelatedAssessmentsMembernspw:NspMinnesotaMember2023-12-31nspw:Reactor0000072909us-gaap:InsuranceRelatedAssessmentsMembernspw:NspMinnesotaMember2023-01-012023-12-31nspw:Plant0000072909nspw:RDFwoodMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasSupplyMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasStorageAndTransportationMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedElectricSegmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OperatingSegmentsMembernspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMemberus-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMemberus-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMemberus-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:RegulatedNaturalGasSegmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllOtherSegmentsMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:IntersegmentEliminationMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMemberus-gaap:ElectricityUsRegulatedMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMemberus-gaap:ElectricityUsRegulatedMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMemberus-gaap:ElectricityUsRegulatedMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:PurchasedPowerMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:PurchasedPowerMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:PurchasedPowerMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:TransmissionExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:TransmissionExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:TransmissionExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPurchaseforResaleMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPurchaseforResaleMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909nspw:NaturalGasPurchaseforResaleMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:OtherExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:InterestExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:InterestExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:InterestExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909nspw:NspMinnesotaMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:NspMinnesotaMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:PscoMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:PscoMember2022-12-310000072909srt:SubsidiariesMember2023-12-310000072909srt:SubsidiariesMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMember2022-12-310000072909nspw:VoluntaryRetirementProgramMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-12-31nspw:Employees0000072909us-gaap:EmployeeSeveranceMembernspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-12-310000072909nspw:XcelEnergyMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909nspw:NSPWisconsinMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2020-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2023-01-012023-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2022-01-012022-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2021-01-012021-12-310000072909us-gaap:AllowanceForCreditLossMember2023-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023 or
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from _____ to _____
| | |
001-03140 |
| (Commission File Number) |
| | |
| Northern States Power Company |
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Wisconsin | | 39-0508315 |
| (State or Jurisdiction or Incorporation or Organization) | | (IRS Employer Identification No.) |
1414 West Hamilton Avenue | Eau Claire | Wisconsin | | 54701 |
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) | | (Zip Code) |
| | | | | |
| (715) | 737-2625 |
| (Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | | Trading Symbol(s) | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| N/A | | N/A | | N/A |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ☐ Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. ☐ Large accelerated filer ☐ Accelerated filer ☒ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐ Emerging growth company
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C.7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐ Yes ☒ No
As of Feb. 21, 2024, 933,000 shares of common stock, par value $100 per share, were outstanding, all of which were held by Xcel Energy Inc., a Minnesota corporation.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The information required by Item 14 of Form 10-K is set forth under the heading “Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – Audit and Non-Audit Fees” in Xcel Energy Inc.’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders which definitive Proxy Statement is expected to be filed with the SEC on or about April 9, 2024. Such information set forth under such heading is incorporated herein by this reference hereto.
Northern States Power Company meets the conditions set forth in General Instructions I(1)(a) and (b) of Form 10-K and is therefore filing this form with the reduced disclosure format permitted by General Instruction I(2).
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | | | | |
| PART I | | |
| Item 1 — | | |
| Item 1A — | | |
| Item 1B — | | |
| Item 1C — | | |
| Item 2 — | | |
| Item 3 — | | |
| Item 4 — | | |
| | |
| PART II | | |
| Item 5 — | | |
| Item 6 — | | |
| Item 7 — | | |
| Item 7A — | | |
| Item 8 — | | |
| Item 9 — | | |
| Item 9A — | | |
| Item 9B — | | |
| Item 9C — | | |
| | |
| PART III | | |
| Item 10 — | | |
| Item 11 — | | |
| Item 12 — | | |
| Item 13 — | | |
| Item 14 — | | |
| | |
| PART IV | | |
| Item 15 — | | |
| Item 16 — | | |
| | |
| |
This Form 10-K is filed by NSP-Wisconsin. NSP-Wisconsin is a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy Inc. Additional information on Xcel Energy is available in various filings with the SEC. This report should be read in its entirety.
PART I
Definitions of Abbreviations
| | | | | |
| Xcel Energy Inc.’s Subsidiaries and Affiliates (current and former) |
| e prime | e prime inc. |
| NSP-Minnesota | Northern States Power Company, a Minnesota corporation |
| NSP System | The electric production and transmission system of NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin operated on an integrated basis and managed by NSP-Minnesota |
| NSP-Wisconsin | Northern States Power Company, a Wisconsin corporation |
| PSCo | Public Service Company of Colorado |
| SPS | Southwestern Public Service Company |
| Utility subsidiaries | NSP-Minnesota, NSP-Wisconsin, PSCo and SPS |
| Xcel Energy | Xcel Energy Inc. and its subsidiaries |
| | | | | |
| Federal and State Regulatory Agencies |
| DOE | United States Department of Energy |
| DOT | Department of Transportation |
| EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
| FERC | Federal Energy Regulatory Commission |
| IRS | Internal Revenue Service |
| MPSC | Michigan Public Service Commission |
| NERC | North American Electric Reliability Corporation |
| NRC | Nuclear Regulatory Commission |
| PHMSA | Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration |
| PSCW | Public Service Commission of Wisconsin |
| SEC | Securities and Exchange Commission |
| | | | | |
| Other |
| AFUDC | Allowance for funds used during construction |
| ARO | Asset retirement obligation |
| ASC | Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification |
| C&I | Commercial and Industrial |
| CapX2020 | Alliance of electric cooperatives, municipals and investor-owned utilities in the upper Midwest involved in a joint transmission line planning and construction effort |
| CEO | Chief executive officer |
| CFO | Chief financial officer |
| |
| |
| | | | | |
| CWIP | Construction work in progress |
| D.C. Circuit | United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit |
| |
| EMANI | European Mutual Association for Nuclear Insurance |
| ETR | Effective tax rate |
| |
| GAAP | Generally accepted accounting principles |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| INPO | Institute of Nuclear Power Operations |
| ISO | Independent System Operator |
| ITC | Investment tax credit |
| MGP | Manufactured gas plant |
| MISO | Midcontinent Independent System Operator, Inc. |
| NAV | Net asset value |
| NEIL | Nuclear Electric Insurance Ltd. |
| NOL | Net operating loss |
| |
| O&M | Operating and maintenance |
| PFAS | Per- and PolyFluoroAlkyl Substances |
| PPA | Purchased power agreement |
| |
| RDF | Refuse-derived fuel |
| REC | Renewable energy credit |
| ROE | Return on equity |
| RTO | Regional Transmission Organization |
| SERP | Supplemental executive retirement plan |
| TCJA | 2017 federal tax reform enacted as Public Law No: 115-97, commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act |
| VIE | Variable interest entity |
| | | | | |
| Measurements |
| Bcf | Billion cubic feet |
| KV | Kilovolts |
| KWh | Kilowatt hours |
| MMBtu | Million British thermal units |
| MW | Megawatts |
| MWh | Megawatt hours |
| | |
| Where to Find More Information |
NSP-Wisconsin is a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy Inc. and Xcel Energy’s website address is www.xcelenergy.com. Xcel Energy makes available, free of charge through its website, its annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as soon as reasonably practicable after the reports are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The SEC maintains an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically at http://www.sec.gov. The information on Xcel Energy’s website is not a part of, or incorporated by reference in, this annual report on Form 10-K.
| | |
Forward-Looking Statements |
Except for the historical statements contained in this report, the matters discussed herein are forward-looking statements that are subject to certain risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Such forward-looking statements, including those relating to future sales, future expenses, future tax rates, future operating performance, estimated base capital expenditures and financing plans, projected capital additions and forecasted annual revenue requirements with respect to rider filings, expected rate increases to customers, expectations and intentions regarding regulatory proceedings, and expected impact on our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows of resettlement calculations and credit losses relating to certain energy transactions, as well as assumptions and other statements are intended to be identified in this document by the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “objective,” “outlook,” “plan,” “project,” “possible,” “potential,” “should,” “will,” “would” and similar expressions. Actual results may vary materially. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, and we expressly disclaim any obligation to update any forward-looking information. The following factors, in addition to those discussed elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended Dec. 31, 2023 (including risk factors listed from time to time by NSP-Wisconsin in reports filed with the SEC, including “Risk Factors” in Item 1A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K), could cause actual results to differ materially from management expectations as suggested by such forward-looking information: operational safety; successful long-term operational planning; commodity risks associated with energy markets and production; rising energy prices and fuel costs; qualified employee workforce and third-party contractor factors; violations of our Codes of Conduct; our ability to recover costs; changes in regulation; reductions in our credit ratings and the cost of maintaining certain contractual relationships; general economic conditions, including recessionary conditions, inflation rates, monetary fluctuations, supply chain constraints and their impact on capital expenditures and/or the ability of NSP-Wisconsin to obtain financing on favorable terms; availability or cost of capital; our customers’ and counterparties’ ability to pay their debts to us; assumptions and costs relating to funding our employee benefit plans and health care benefits; tax laws; uncertainty regarding epidemics, the duration and magnitude of business restrictions including shutdowns (domestically and globally), the potential impact on the workforce, including shortages of employees or third-party contractors due to quarantine policies, vaccination requirements or government restrictions, impacts on the transportation of goods and the generalized impact on the economy; effects of geopolitical events, including war and acts of terrorism; cybersecurity threats and data security breaches; seasonal weather patterns; changes in environmental laws and regulations; climate change and other weather events; natural disaster and resource depletion, including compliance with any accompanying legislative and regulatory changes; costs of potential regulatory penalties and wildfire damages in excess of liability insurance coverage; regulatory changes and/or limitations related to the use of natural gas as an energy source; challenging labor market conditions and our ability to attract and retain a qualified workforce; and our ability to execute on our strategies or achieve expectations related to environmental, social and governance matters including as a result of evolving legal, regulatory and other standards, processes, and assumptions, the pace of scientific and technological developments, increased costs, the availability of requisite financing, and changes in carbon markets.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Electric customers | 0.3 million | | | NSP-Wisconsin was incorporated in 1901 under the laws of Wisconsin. NSP-Wisconsin conducts business in Wisconsin and Michigan and generates, transmits, distributes and sells electricity. NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin electric operations are managed on the NSP System. NSP-Wisconsin also purchases, transports, distributes and sells natural gas to retail customers and transports customer-owned natural gas. |
| Natural gas customers | 0.1 million | | |
| Total assets | $3.7 billion | | |
| Rate Base (estimated) | $2.4 billion | | |
| GAAP ROE | 10.38% | | |
| Electric generating capacity | 551 MW | | |
| Gas storage capacity | 4.3 Bcf | | |
| Electric transmission lines (conductor miles) | 12,000 miles | | |
| Electric distribution lines (conductor miles) | 28,000 miles | | |
| Natural gas transmission lines | 3 miles | | |
| Natural gas distribution lines | 3,000 miles | | | |
Electric operations consist of energy supply, generation, transmission and distribution activities. NSP-Wisconsin had electric sales volume of 6,886 (millions of KWh), 0.3 million customers and electric revenues of $1,019 million for 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Electric Operations (percentage of total) | | Sales Volume | | Number of Customers | | Revenues |
| Residential | | 29 | % | | 85 | % | | 29 | % |
| C&I | | 71 | | | 15 | | | 48 | |
| Other | | <1 | | <1 | | 23 | |
Retail Sales/Revenue Statistics (a)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| KWh sales per retail customer | | 25,536 | | | 25,995 | |
| Revenue per retail customer | | $ | 2,967 | | | $ | 2,930 | |
| Residential revenue per KWh | | 15.35 | ¢ | | 14.64 | ¢ |
| C&I revenue per KWh | | 10.06 | ¢ | | 9.82 | ¢ |
| Total retail revenue per KWh | | 11.62 | ¢ | | 11.27 | ¢ |
(a)See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
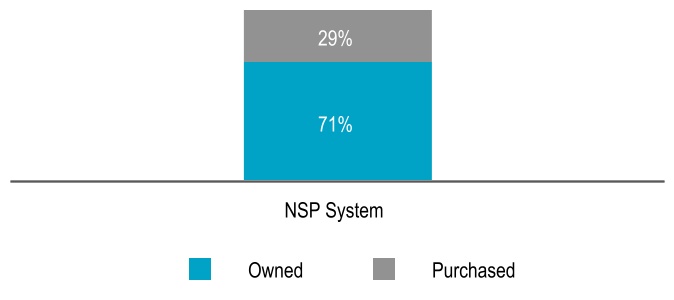
Owned and Purchased Energy Generation — 2023
Electric Energy Sources
Total electric energy generation by source for the year ended Dec. 31:
Carbon–Free — NSP System
The NSP System’s carbon–free energy portfolio includes nuclear, wind, hydroelectric, biomass and solar power from both owned generating facilities and PPAs. Carbon–free percentages will vary year over year based on system additions, commodity costs, weather, system demand and transmission constraints.
See Item 2 — Properties for further information.
Wind
Wind capacity is shown as net maximum capacity. Net maximum capacity is attainable only when wind conditions are sufficiently available
Owned — Owned and operated wind farms with corresponding capacity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Wind Farms | | Capacity (MW) | | Wind Farms | | Capacity (MW) |
| 17 | | 2,444 | | | 16 | | 2,352 |
PPAs — Number of PPAs with capacity range: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| PPAs | | Range (MW) | | PPAs | | Range (MW) |
| 120 | | 1 — 206 | | 129 | | 1 — 206 |
Current contracted wind capacity for PPAs was 2,066 MW and 2,163 MW in 2023 and 2022, respectively.
In 2023, the average cost of wind energy was $7 per MWh for owned generation and $33 per MWh under existing PPAs. In 2022, the average cost of wind energy was $18 per MWh for owned generation and $37 per MWh under existing PPAs.
Wind Development — The NSP System placed into service, repowered, or contracted for the following during 2023:
| | | | | | | | |
| Project | | Capacity (MW) |
| Northern Wind | | 92 |
| Grand Meadow Repower | | 99 |
The NSP System currently has 350 MW of approved owned wind repowering projects under development, estimated to be completed in 2025.
Solar
PPAs — Solar PPAs capacity by type:
| | | | | | | | |
| Type | | Capacity (MW) |
| Distributed Generation | | 1,117 | |
| Utility-Scale | | 269 | |
| Total | | 1,386 | |
The average cost of solar energy under existing PPAs was $90 per MWh and $79 per MWh in 2023 and 2022, respectively.
The NSP System currently has approximately 700 MW of owned solar under development approved at the Sherco site (expected to be placed in service in 2024 and 2025).
Nuclear
The NSP System has two nuclear plants (owned by NSP-Minnesota) with approximately 1,700 MW of total 2023 net summer dependable capacity. Our nuclear fleet safely and reliably generates carbon free electricity at consistently high levels of performance among the industry. NSP-Minnesota secures contracts for uranium concentrates, uranium conversion, uranium enrichment and fuel fabrication to operate its nuclear plants. NSP-Minnesota uses varying contract lengths as well as multiple producers for uranium concentrates, conversion services and enrichment services to minimize potential impacts caused by supply interruptions due to geographical and world political issues.
Nuclear Fuel Cost — Delivered cost per MMBtu of nuclear fuel consumed for owned electric generation and the percentage of total fuel requirements (nuclear, natural gas and coal):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Nuclear |
| | Cost | | Percent |
| 2023 | | $ | 0.76 | | | 50 | % |
| 2022 | | $ | 0.76 | | | 51 | % |
Other — NSP System
The NSP System’s other carbon-free energy portfolio includes hydro from owned generating facilities.
See Item 2 — Properties for further information.
Fossil Fuel — NSP System
The NSP System’s fossil fuel energy portfolio includes coal and natural gas power from both owned generating facilities and PPAs.
See Item 2 — Properties for further information.
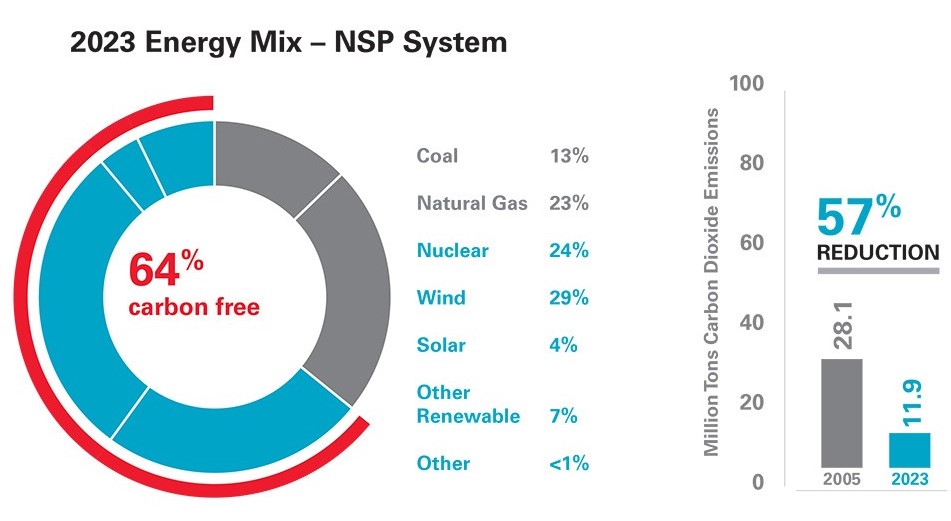
Coal
The NSP System owns and operates coal units with approximately 2,400 MW of total capacity, which provided 13% of NSP System’s energy mix in 2023. All of these units are approved for retirement by 2030. Amount includes Sherco Unit 2, which was retired on Dec. 31, 2023, net summer dependable capacity of 682 MW and approximately 100 MW derived from RDF and wood fuel sources.
Approved early coal plant retirements: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year | | Plant Unit | | Capacity (MW) | |
| 2026 | | Sherco 1 | | 680 | |
| 2028 | | A.S. King | | 511 | |
| 2030 | | Sherco 3 | | 517 | (a) |
(a)Based on the NSP System’s ownership percentage.
Coal Fuel Cost — Delivered cost per MMBtu of coal consumed for owned electric generation and the percentage of total fuel requirements (nuclear, natural gas and coal):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Coal (a) |
| | Cost | | Percent |
| 2023 | | $ | 2.43 | | | 29 | % |
| 2022 | | $ | 2.27 | | | 37 | % |
(a)Includes RDF and wood for the NSP System.
Natural Gas
The NSP System has seven natural gas plants with approximately 2,800 MW of total capacity, which provided 23% of NSP System’s energy mix in 2023.
Natural gas supplies, transportation and storage services for power plants are procured to provide an adequate supply of fuel. Remaining requirements are procured through a liquid spot market. Generally, natural gas supply contracts have variable pricing that is tied to natural gas indices. Natural gas supply and transportation agreements include obligations for the purchase and/or delivery of specified volumes or payments in lieu of delivery.
Natural Gas Cost — Delivered cost per MMBtu of natural gas consumed for owned electric generation and the percentage of total fuel requirements (nuclear, natural gas and coal):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Natural Gas |
| | Cost | | Percent |
| 2023 | | $ | 3.91 | | | 21 | % |
| 2022 | | 7.58 | | | 12 | |
Capacity and Demand
Uninterrupted system peak demand and occurrence date:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| System Peak Demand (MW) |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| 9,231 | | | Aug. 23 | | 9,245 | | | June 20 |
Transmission
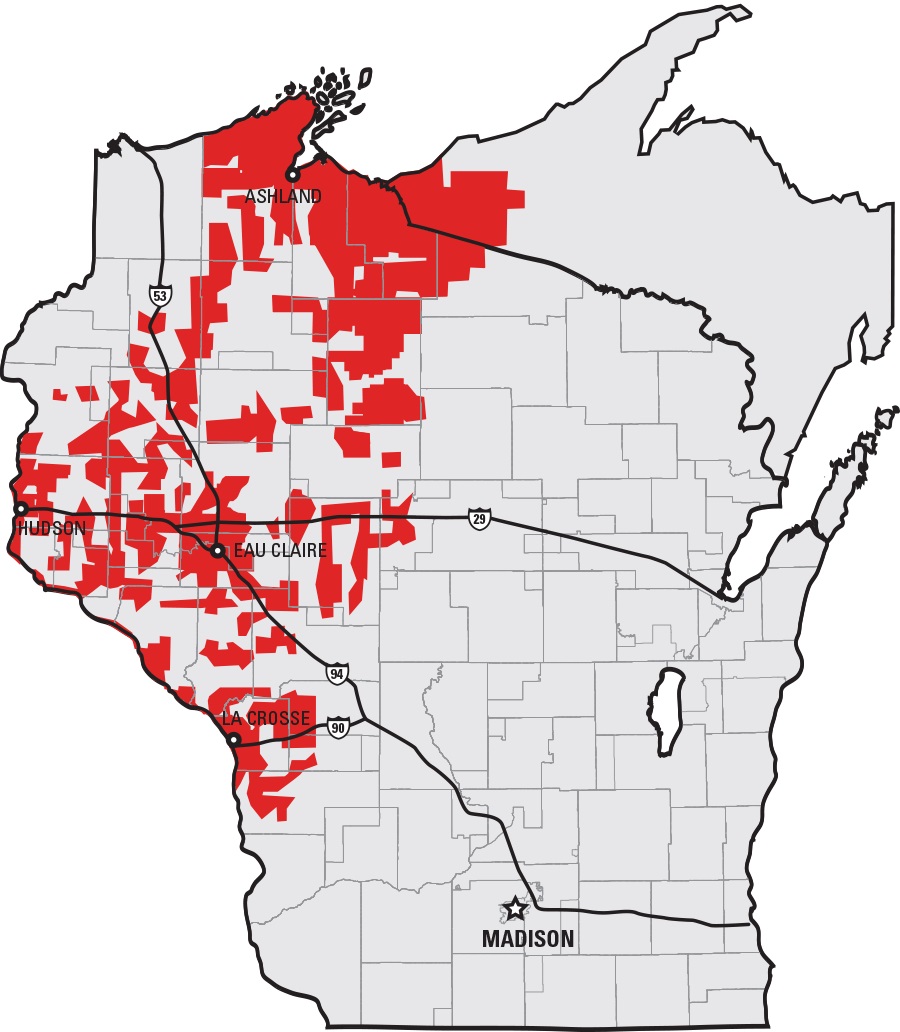
Transmission lines deliver electricity over long distances from power sources to substations closer to customers. A strong transmission system ensures continued reliable and affordable service, ability to meet state and regional energy policy goals, and support for a diverse generation mix, including renewable energy. NSP-Wisconsin owns approximately 12,000 conductor miles of transmission lines across the NSP System service territory.
NSP System plans to build approximately 1,200 additional conductor miles of transmission lines, primarily as part of the MISO Tranche 1 project estimated to be complete in 2028 and the MN Energy Connection.
See Item 2 — Properties for further information.
Distribution
Distribution lines allow electricity to travel at lower voltages from substations directly to customers. NSP-Wisconsin has a vast distribution network, owning and operating approximately 28,000 conductor miles of distribution lines across our service territory.
See Item 2 — Properties for further information.
Natural gas operations consist of purchase, transportation, and distribution of natural gas to end-use residential, C&I and transport customers. NSP-Wisconsin had natural gas deliveries of 20,671 (thousands of MMBtu), 0.1 million customers and natural gas revenues of $157 million for 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Natural Gas (percentage of total) | | Deliveries | | Number of Customers | | Revenues |
| Residential | | 34 | % | | 89 | % | | 54 | % |
| C&I | | 40 | | | 11 | | | 41 | |
| Transportation and other | | 26 | | | <1 | | 5 | |
Sales/Revenue Statistics (a) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| MMBtu sales per retail customer | | 125 | | | 143 | |
| Revenue per retail customer | | $ | 1,212 | | | $ | 1,570 | |
| Residential revenue per MMBtu | | 12.04 | | | 12.68 | |
| C&I revenue per MMBtu | | 7.70 | | | 9.41 | |
| Transportation and other revenue per MMBtu | | 0.65 | | | 0.71 | |
(a)See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
Capability and Demand
Natural gas supply requirements are categorized as firm or interruptible (customers with an alternate energy supply).
Maximum daily output (firm and interruptible) and occurrence date:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| MMBtu | | Date | | MMBtu | | Date |
| 158,029 | | | Jan. 30 | | 187,961 | | | Jan. 6 |
Natural Gas Supply and Cost
NSP-Wisconsin seeks natural gas supply, transportation and storage alternatives to yield a diversified portfolio, which increases flexibility and decrease interruption and financial risks and economical rates. In addition, NSP-Wisconsin conducts natural gas price hedging activities approved by its states’ commissions.
Average delivered cost per MMBtu of natural gas for regulated retail distribution:
NSP-Wisconsin has natural gas supply transportation and storage agreements that include obligations for purchase and/or delivery of specified volumes or to make payments in lieu of delivery.
Seasonality
Demand for electric power and natural gas is affected by seasonal differences in the weather. In general, peak sales of electricity occur in the summer months and peak sales of natural gas occur in the winter months. As a result, the overall operating results may fluctuate substantially on a seasonal basis. Additionally, NSP-Wisconsin’s operations have historically generated less revenues and income when weather conditions are warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer.
Competition
NSP-Wisconsin is subject to public policies that promote competition and development of energy markets. NSP-Wisconsin’s industrial and large commercial customers have the ability to generate their own electricity. In addition, customers may have the option of substituting other fuels or relocating their facilities to a lower cost region.
Customers have the opportunity to supply their own power with distributed generation including solar generation and can currently avoid paying for most of the fixed production, transmission and distribution costs incurred to serve them.
Wisconsin has incentives for the development of rooftop solar, community solar gardens and other distributed energy resources. Distributed generating resources are potential competitors to NSP-Wisconsin’s electric service business with these incentives and federal tax subsidies.
FERC Order No. 1000 established competition for ownership of certain new electric transmission facilities under Federal regulations. Some states have state laws that allow the incumbent a Right of First Refusal to own these transmission facilities.
FERC Order 2222 requires that RTO and ISO markets allow participation of aggregations of distributed energy resources. This order is expected to incentivize distributed energy resource adoption, however implementation is expected to vary by RTO/ISO and the near, medium, and long-term impacts of Order 2222 remain unclear.
NSP-Wisconsin has franchise agreements with cities subject to periodic renewal; however, a city could seek alternative means to access electric power or gas, such as municipalization. No municipalization activities are occurring presently.
While facing these challenges, NSP-Wisconsin believes its rates and services are competitive with alternatives currently available.
Public Utility Regulation
See Item 7 for discussion of public utility regulation.
Environmental Regulation
Our facilities are regulated by federal and state agencies that have jurisdiction over air emissions, water quality, wastewater discharges, solid and hazardous wastes or substances. Certain NSP-Wisconsin activities require registrations, permits, licenses, inspections and approvals from these agencies.
NSP-Wisconsin has received necessary authorizations for the construction and continued operation of its generation, transmission and distribution systems. Our facilities strive to operate in compliance with applicable environmental standards and related monitoring and reporting requirements.
However, it is not possible to determine what additional facilities or modifications to existing or planned facilities will be required as a result of changes to regulations, interpretations or enforcement policies or what effect future laws or regulations may have. We may be required to incur expenditures in the future for remediation of historic and current operating sites and other waste treatment, storage and disposal sites.
There are significant environmental regulations to encourage use of clean energy technologies and regulate emissions of GHGs. NSP-Wisconsin has undertaken numerous initiatives to meet current requirements and prepare for potential future regulations, reduce GHG emissions and respond to state renewable and energy efficiency goals. Future environmental regulations may result in substantial costs.
Emerging Environmental Regulation
Clean Air Act
Power Plant Greenhouse Gas Regulations — In May 2023, the EPA published proposed rules addressing control of CO2 emissions from the power sector. The rule proposed regulations for new natural gas generating units and emission guidelines for existing coal and certain natural gas generation. The proposed rules create subcategories of coal units based on planned retirement date and subcategories of natural gas combustion turbines and combined cycle units based on utilization. The CO2 control requirements vary by subcategory. Until final rules are issued, it is not certain what the impact will be on NSP-Wisconsin. NSP-Wisconsin believes that the cost of these initiatives or replacement generation would be recoverable through rates based on prior state commission practices.
Emerging Contaminants of Concern
PFAS are man-made chemicals that are widely used in consumer products and can persist and bio-accumulate in the environment. NSP-Wisconsin does not manufacture PFAS but because PFAS are so ubiquitous in products and the environment, it may impact our operations.
In September 2022, the EPA proposed to designate two types of PFAS as “hazardous substances” under the CERCLA. In March 2023, the EPA published a proposed rule that would establish enforceable drinking water standards for certain PFAS chemicals. Final rules are expected in 2024. Costs are uncertain until a final rule is published.
The proposed rules could result in new obligations for investigation and cleanup. NSP-Wisconsin is monitoring changes to state laws addressing PFAS. The impact of these proposed regulations is uncertain.
Other
Our operations are subject to workplace safety standards under the Federal Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970 (“OSHA”) and comparable state laws that regulate the protection of worker health and safety. In addition, the Company is subject to other government regulations impacting such matters as labor, competition, data privacy, etc. Based on information to date and because our policies and business practices are designed to comply with all applicable laws, we do not believe the effects of compliance on our operations, financial condition or cash flows are material.
As of Dec. 31, 2023, NSP-Wisconsin had 538 full-time employees and fifteen part-time employees, of which 406 were covered under collective-bargaining agreements.
Xcel Energy, which includes NSP-Wisconsin, is subject to a variety of risks, many of which are beyond our control. Risks that may adversely affect the business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows are described below. Although the risks are organized by heading, and each risk is described separately, many of the risks are interrelated. These risks should be carefully considered together with the other information set forth in this report and future reports that we file with the SEC.
While we believe we have identified and discussed below the key risk factors affecting our business, there may be additional risks and uncertainties that are not presently known or that are not currently believed to be significant that may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows in the future.
Oversight of Risk and Related Processes
NSP-Wisconsin’s Board of Directors is responsible for the oversight of material risk and maintaining an effective risk monitoring process. Management and the Board of Directors have responsibility for overseeing the identification and mitigation of key risks.
NSP-Wisconsin maintains a robust compliance program and promotes a culture of compliance beginning with the tone at the top. The risk mitigation process includes adherence to our Code of Conduct and compliance policies, operation of formal risk management structures and overall business management. NSP-Wisconsin further mitigates inherent risks through formal risk committees and corporate functions such as internal audit, and internal controls over financial reporting and legal.
Management identifies and analyzes risks to determine materiality and other attributes such as timing, probability and controllability. Identification and risk analysis occurs formally through risk assessment conducted by senior management, the financial disclosure process, hazard risk procedures, internal audit and compliance with financial and operational controls. Management also identifies and analyzes risk through the business planning process, development of goals and establishment of key performance indicators, including identification of barriers to implementing our strategy. The business planning process also identifies likelihood and mitigating factors to prevent the assumption of inappropriate risk to meet goals.
Management communicates regularly with the Board of Directors and its sole stockholder regarding risk. Senior management presents and communicates a periodic risk assessment to the Board of Directors providing information on the risks that management believes are material, including financial impact, timing, likelihood and mitigating factors. The Board of Directors regularly reviews management’s key risk assessments, which includes areas of existing and future macroeconomic, financial, operational, policy, environmental, safety and security risks.
The oversight, management and mitigation of risk is an integral and continuous part of the Board of Directors’ governance of NSP-Wisconsin. Processes are in place to confirm appropriate risk oversight, as well as identification and consideration of new risks.
Risks Associated with Our Business
Operational Risks
Our natural gas and electric generation/transmission and distribution operations involve numerous risks that may result in accidents and other operating risks and costs.
Our natural gas transmission and distribution activities include inherent hazards and operating risks, such as leaks, explosions, outages and mechanical problems. Our electric generation, transmission and distribution activities include inherent hazards and operating risks such as contact, fire and outages.
These risks could result in loss of life, significant property damage, environmental pollution, impairment of our operations and substantial financial losses to employees, third-party contractors, customers or the public. We maintain insurance against most, but not all, of these risks and losses. The occurrence of these events, if not fully covered by insurance, could have a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows as well as potential loss of reputation.
Other uncertainties and risks inherent in operating and maintaining NSP-Wisconsin's facilities include, but are not limited to:
•Risks associated with facility start-up operations, such as whether the facility will achieve projected operating performance on schedule and otherwise as planned.
•Failures in the availability, acquisition or transportation of fuel or other supplies.
•Impact of adverse weather conditions and natural disasters, including, tornadoes, icing events, floods, high winds and droughts.
•Performance below expected or contracted levels of output or efficiency.
•Availability of replacement equipment.
•Availability of adequate water resources and ability to satisfy water intake and discharge requirements.
•Availability or changes to wind patterns.
•Inability to identify, manage properly or mitigate equipment defects.
•Use of new or unproven technology.
•Risks associated with dependence on a specific type of fuel or fuel source, such as commodity price risk, availability of adequate fuel supply and transportation and lack of available alternative fuel sources.
•Increased competition due to, among other factors, new facilities, excess supply, shifting demand and regulatory changes.
Additionally, compliance with existing and potential new regulations related to the operation and maintenance of our natural gas infrastructure could result in significant costs. The PHMSA is responsible for administering the DOT’s national regulatory program to assure the safe transportation of natural gas, petroleum and other hazardous materials by pipelines. The PHMSA continues to develop regulations and other approaches to risk management to assure safety in design, construction, testing, operation, maintenance and emergency response of natural gas pipeline infrastructure. We have programs in place to comply with these regulations and systematically monitor and renew infrastructure over time, however, a significant incident or material finding of non-compliance could result in penalties and higher costs of operations.
Our natural gas and electric transmission and distribution operations are dependent upon complex information technology systems and network infrastructure, the failure of which could disrupt our normal business operations, which could have a material adverse effect on our ability to process transactions and provide services.
Our utility operations are subject to long-term planning and project risks.
Most utility investments are planned to be used for decades. Transmission and generation investments typically have long lead times and are planned well in advance of in-service dates and typically subject to long-term resource plans. These plans are based on numerous assumptions such as: sales growth, customer usage, commodity prices, economic activity, costs, regulatory mechanisms, customer behavior, available technology and public policy. Our long-term resource plan is dependent on our ability to obtain required approvals (including regulatory approval in jurisdictions where NSP-Wisconsin operates), develop necessary technical expertise, allocate and coordinate sufficient resources and adhere to budgets and timelines.
In addition, the long-term nature of both our planning processes and our asset lives are subject to risk. The utility sector is undergoing significant change (e.g., increases in energy efficiency, wider adoption of distributed generation and shifts away from fossil fuel generation to renewable generation). Customer adoption of these technologies and increased energy efficiency could result in excess transmission and generation resources, downward pressure on sales growth, and potentially stranded costs if we are not able to fully recover costs and investments.
The magnitude and timing of resource additions and changes in customer demand may not coincide with evolving customer preference for generation resources and end-uses, which introduces further uncertainty into long-term planning. Efforts to electrify the transportation and building sectors to reduce GHG emissions may result in higher electric demand and lower natural gas demand over time. New data centers and crypto mining facilities could generate significant increase in demand. Higher electric demand may require us to adopt new technologies and make significant transmission and distribution investments including advanced grid infrastructure, which increases exposure to overall grid instability and technology obsolescence. Evolving stakeholder preference for lower emissions from generation sources and end-uses, like heating, may impact our resource mix and put pressure on our ability to recover capital investments in natural gas generation and delivery. Multiple states may not agree as to the appropriate resource mix, which may lead to costs to comply with one jurisdiction that are not recoverable across all jurisdictions served by the same assets.
We require inputs such as coal, natural gas, uranium and water. Lack of availability of these resources could jeopardize long-term operations of our facilities or make them uneconomic to operate.
Our utility operations are highly dependent on suppliers to deliver components in accordance with short and long-term project schedules.
Our products contain components that are globally sourced from suppliers. A shortage of key components in which an alternative supplier is not identified could significantly impact operations and project plans for NSP-Wisconsin and our customers. Such impacts could include timing of projects and the potential for project cancellation. Failure to adhere to project budgets and timelines could adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
We are subject to commodity risks and other risks associated with energy markets and energy production.
A significant increase in fuel costs could cause a decline in customer demand, adverse regulatory outcomes and an increase in bad debt expense which may have a material impact on our results of operations. Despite existing fuel cost recovery mechanisms, higher fuel costs could significantly impact our results of operations if costs are not recovered. Delays in the timing of the collection of fuel cost recoveries could impact our cash flows and liquidity.
A significant disruption in supply could cause us to seek alternatives at potentially higher costs. Additionally, supply shortages may not be fully resolved, which negatively impacts our ability to provide services to our customers. Failure to provide service due to disruptions may also result in fines, penalties or cost disallowances through the regulatory process. Also, significantly higher energy or fuel costs relative to sales commitments negatively impacts our cash flows and results of operations.
We also engage in wholesale sales and purchases of electric capacity, energy and energy-related products as well as natural gas. In many markets, emission allowances and/or RECs are also needed to comply with various statutes and commission rulings. As a result, we are subject to market supply and commodity price risk.
Commodity price changes can affect the value of our commodity trading derivatives. We mark certain derivatives to estimated fair market value on a daily basis. Settlements can vary significantly from estimated fair values recorded and significant changes from the assumptions underlying our fair value estimates could cause earnings variability. The management of risks associated with hedging and trading is based, in part, on programs and procedures which utilize historical prices and trends.
Public perception often does not distinguish between pass through commodity costs and base rates. High commodity prices that are passed through to customer bills could impact our ability to recover costs for other improvements and operations.
Due to the uncertainty involved in price movements and potential deviation from historical pricing, NSP-Wisconsin is unable to fully assure that its risk management programs and procedures would be effective to protect against all significant adverse market deviations. In addition, NSP-Wisconsin cannot fully assure that its controls will be effective against all potential risks. If such programs and procedures are not effective, NSP-Wisconsin’s results of operations, financial condition or cash flows could be materially impacted.
Failure to attract and retain a qualified workforce could have an adverse effect on operations.
The competition for talent has become increasingly prevalent, and we have experienced increased employee turnover due to the condition of the labor market and decisions related to strategic workforce planning. In addition, specialized knowledge and skills are required for many of our positions, which may pose additional difficulty for us as we work to recruit, retain and motivate employees in this climate.
Failure to hire, adequately train replacement employees, transfer knowledge/expertise or future availability and cost of contract labor may adversely affect the ability to manage and operate our business. Inability to attract and retain these employees could adversely impact our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Our businesses have collective bargaining agreements with labor unions. Failure to renew or renegotiate these contracts could lead to labor disruptions, including strikes or boycotts. Such disruptions or any negotiated wage or benefit increases could have a material adverse impact to our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
National unionization efforts could affect our business, as an increase in unionized workers could challenge our operational efficiency and increase costs.
Our operations use third-party contractors in addition to employees to perform periodic and ongoing work.
We rely on third-party contractors to perform operations, maintenance and construction work. Our contractual arrangements with these contractors typically include performance and safety standards, progress payments, insurance requirements and security for performance. Poor vendor performance or contractor unavailability could impact ongoing operations, restoration operations, regulatory recovery, our reputation and could introduce financial risk or risks of fines.
Our employees, directors, third-party contractors, or suppliers may violate or be perceived to violate our Codes of Conduct, which could have an adverse effect on our reputation.
We are exposed to risk of employee or third-party contractor fraud or misconduct. All employees and members of the Board of Directors are subject to compliance with our Code of Conduct and are required to participate in annual training. Additionally, suppliers are subject to compliance with our Supplier Code of Conduct. NSP-Wisconsin does not tolerate discrimination, violations of our Code of Conduct or other unacceptable behaviors. However, it is not always possible to identify and deter misconduct by employees and other third-parties, which may result in governmental investigations, other actions or lawsuits. If such actions are taken against us we may suffer loss of reputation and such actions could have a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Although we do not own any nuclear generating facilities, because our production and transmission system is operated on an integrated basis with NSP-Minnesota’s (an affiliate of NSP-Wisconsin) production and transmission system, we may be subject to risks associated with NSP-Minnesota’s nuclear generation.
NSP-Minnesota has two nuclear generation plants, Prairie Island and Monticello. Risks of nuclear generation include:
•Hazards associated with the use of radioactive material in energy production, including management, handling, storage and disposal.
•Limitations on insurance available to cover losses that may arise in connection with nuclear operations, as well as obligations to contribute to an insurance pool in the event of damages at a covered U.S. reactor.
•Technological and financial uncertainties related to the costs of decommissioning nuclear plants may cause our funding obligations to change.
The NRC has authority to impose licensing and safety-related requirements for the operation of nuclear generation facilities, including the ability to impose fines and/or shut down a unit until compliance is achieved. NRC safety requirements could necessitate substantial capital expenditures or an increase in operating expenses. In addition, the INPO reviews NSP-Minnesota’s nuclear operations. Compliance with the INPO’s recommendations could result in substantial capital expenditures or a substantial increase in operating expenses.
If a nuclear incident did occur, it could have a material impact on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows. Furthermore, non-compliance or the occurrence of a serious incident at other nuclear facilities could result in increased industry regulation, which may increase NSP-Minnesota’s compliance costs.
We share in the electric production and transmission costs of the NSP-Minnesota system, which is integrated with our system. Accordingly, our costs may be increased due to increased costs associated with NSP-Minnesota’s system.
Our electric production and transmission system is managed on an integrated basis with the electric production and transmission system of NSP-Minnesota. Pursuant to the Interchange Agreement between NSP-Minnesota and us, we share, on a proportional basis, all costs related to the generation and transmission facilities of the entire integrated NSP System, including capital costs. Accordingly, if the costs to operate the NSP System increase, or revenue decreases, whether as a result of state or federally mandated improvements or otherwise, our costs could also increase and our revenues could decrease and we cannot guarantee a full recovery of such costs through our rates at the time the costs are incurred.
We are a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy Inc. Xcel Energy Inc. can exercise substantial control over our dividend policy and business and operations and may exercise that control in a manner that may be perceived to be adverse to our interests.
All of the members of our Board of Directors, as well as many of our executive officers, are officers of Xcel Energy Inc. Our Board of Directors makes determinations with respect to a number of significant corporate events, including the payment of our dividends.
We have historically paid quarterly dividends to Xcel Energy Inc. If Xcel Energy Inc.’s cash requirements increase, our Board of Directors could decide to increase the dividends we pay to Xcel Energy Inc. to help support Xcel Energy Inc.’s cash needs. This could adversely affect our liquidity. The most restrictive dividend limitation for NSP-Wisconsin is imposed by our state regulatory commission. NSP-Wisconsin cannot pay annual dividends in excess of certain amounts if its calendar year average equity-to-total capitalization ratio is or falls below the state commission authorized level.
See Note 5 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
Financial Risks
Our profitability depends on our ability to recover costs and changes in regulation may impair our ability to recover costs from our customers.
We are subject to comprehensive regulation by federal and state utility regulatory agencies, including siting and construction of facilities, customer service and the rates that we can charge customers.
The profitability of our operations is dependent on our ability to recover the costs of providing energy and utility services and earn a return on capital investment. Our rates are generally regulated and are based on an analysis of our costs incurred in a test year. We are subject to future test years. Thus, the rates we are allowed to charge may or may not match our costs at any given time. Rate regulation is premised on providing an opportunity to earn a reasonable rate of return on invested capital.
There can also be no assurance that our regulatory commissions will judge all our costs to be prudent, which could result in disallowances, or that the regulatory process will always result in rates that will produce full recovery.
Overall, management believes prudently incurred costs are recoverable given the existing regulatory framework. However, there may be changes in the regulatory environment that could impair our ability to recover costs historically collected from customers, or we could exceed caps on capital costs required by commissions and result in less than full recovery.
Changes in the long-term cost-effectiveness or to the operating conditions of our assets may result in early retirements of utility facilities. While regulation typically provides cost recovery for these types of changes, there is no assurance that regulators would allow full recovery of all remaining costs.
Higher than expected inflation or tariffs may increase costs of construction and operations. Also, rising fuel costs could increase the risk that we will not be able to fully recover our fuel costs from our customers.
Adverse regulatory rulings (including changes in recovery mechanisms) or the imposition of additional regulations could have an adverse impact on our results of operations and materially affect our ability to meet our financial obligations, including debt payments and the payment of dividends on common stock.
Any reductions in our credit ratings could increase our financing costs and the cost of maintaining certain contractual relationships.
Our credit ratings are subject to change and our credit ratings may be lowered or withdrawn by a rating agency. Significant events including disallowance of costs, use of historic test years, elimination of riders or interim rates, increasing depreciation lives, lower returns on equity, changes to equity ratios and impacts of tax policy may impact our cash flows and credit metrics, potentially resulting in a change in our credit ratings. In addition, our credit ratings may change as a result of the differing methodologies or change in the methodologies used by the various rating agencies.
Any credit ratings downgrade could lead to higher borrowing costs or lower proceeds from equity issuances. It could also impact our ability to access capital markets. Also, we may enter into contracts that require posting of collateral or settlement if credit ratings fall below investment grade.
We are subject to capital market and interest rate risks.
Utility operations require significant capital investment. As a result, we frequently need to access capital markets. Any disruption in capital markets could have a material impact on our ability to fund our operations. Capital market disruption and financial market distress could prevent us from issuing commercial paper, issuing new securities or cause us to issue securities with unfavorable terms and conditions, such as higher interest rates or lower proceeds from equity issuances. Higher interest rates on short-term borrowings with variable interest rates could also have an adverse effect on our operating results.
We are subject to credit risks.
Credit risk includes the risk that our customers will not pay their bills, which may lead to a reduction in our cash flow and liquidity and an increase in bad debt expense. Credit risk is comprised of numerous factors including the price of products and services provided, the economy and unemployment rates.
Credit risk also includes the risk that counterparties that owe us money or product will become insolvent and may breach their obligations. Should the counterparties fail to perform, we may be forced to enter into alternative arrangements. In that event, our financial results could be adversely affected and incur losses.
We may have direct credit exposure as part of our local gas distribution company supply activity to financial institutions trading for their own accounts or issuing collateral support on behalf of other counterparties. We may also have some indirect credit exposure due to participation in organized markets, (e.g., MISO), in which any credit losses are socialized to all market participants.
We have additional indirect credit exposure to financial institutions from letters of credit provided as security by power suppliers under various purchased power contracts. If any of the credit ratings of the letter of credit issuers were to drop below investment grade, the supplier would need to replace that security with an acceptable substitute. If the security were not replaced, the party could be in default under the contract.
As we are a subsidiary of Xcel Energy Inc., we may be negatively affected by events impacting the credit or liquidity of Xcel Energy Inc. and its affiliates.
If either Standard & Poor’s Global Ratings or Moody’s Investor Services were to downgrade Xcel Energy Inc.’s debt securities below investment grade, it would increase Xcel Energy Inc.’s cost of capital and restrict its access to the capital markets. This could limit Xcel Energy Inc.’s ability to contribute equity or make loans to us, or may cause Xcel Energy Inc. to seek additional or accelerated funding from us in the form of dividends. If such event were to occur, we may need to seek alternative sources of funds to meet our cash needs.
As of Dec. 31, 2023, Xcel Energy Inc. and its utility subsidiaries had approximately $24.9 billion of long-term debt and $1.3 billion of short-term debt and current maturities. Xcel Energy Inc. provides various guarantees and bond indemnities supporting some of its subsidiaries by guaranteeing the payment or performance by these subsidiaries for specified agreements or transactions.
Xcel Energy also has other contingent liabilities resulting from various tax disputes and other matters. Xcel Energy Inc.’s exposure under the guarantees is based upon the net liability of the relevant subsidiary under the specified agreements or transactions. The majority of Xcel Energy Inc.’s guarantees limit its exposure to a maximum amount that is stated in the guarantees.
As of Dec. 31, 2023, Xcel Energy had the following guarantees outstanding:
•$951 million for performance and payment of Capital Services, LLC contracts for wind and solar generating equipment, with immaterial exposure.
•$100 million for performance on tax credit sale agreements of its subsidiaries, with immaterial exposure.
•$75 million for performance and payment of surety bonds for the benefit of itself and its subsidiaries, with total exposure that cannot be estimated at this time.
If Xcel Energy Inc. were to become obligated to make payments under these guarantees and bond indemnities or become obligated to fund other contingent liabilities, it could limit Xcel Energy Inc.’s ability to contribute equity or make loans to us, or may cause Xcel Energy Inc. to seek additional or accelerated funding from us in the form of dividends. If such event were to occur, we may need to seek alternative sources of funds to meet our cash needs.
Increasing costs of our defined benefit retirement plans and employee benefits may adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
We have defined benefit pension and postretirement plans that cover most of our employees. Assumptions related to future costs, return on investments, interest rates and other actuarial assumptions have a significant impact on our funding requirements of these plans. Estimates and assumptions may change. In addition, the Pension Protection Act sets the minimum funding requirements for defined benefit pension plans. Therefore, our funding requirements and contributions may change in the future. Also, the payout of a significant percentage of pension plan liabilities in a single year due to high numbers of retirements or employees leaving NSP-Wisconsin would trigger settlement accounting and could require NSP-Wisconsin to recognize incremental pension expense related to unrecognized plan losses in the year liabilities are paid. Changes in industry standards utilized in key assumptions (e.g., mortality tables) could have a significant impact on future obligations and benefit costs.
Increasing costs associated with health care plans may adversely affect our results of operations.
Increasing levels of large individual health care claims and overall health care claims could have an adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows. Health care legislation could also significantly impact our benefit programs and costs.
Federal tax law may significantly impact our business.
NSP-Wisconsin collects estimated federal, state and local tax payments through their regulated rates. Changes to federal tax law may benefit or adversely affect our earnings and customer costs. Tax depreciable lives and the value/availability of various tax credits or the timeliness of their utilization may impact the economics or selection of resources. If tax rates are increased, there could be timing delays before regulated rates provide for recovery of such tax increases in revenues. In addition, certain IRS tax policies such as tax normalization may impact our ability to economically deliver certain types of resources relative to market prices.
Macroeconomic Risks
Economic conditions impact our business.
Our operations are affected by economic conditions, which correlates to customers/sales growth (decline). Economic conditions may be impacted by recessionary factors, rising interest rates and insufficient financial sector liquidity leading to potential increased unemployment, which may impact customers’ ability to pay their bills which could lead to additional bad debt expense.
Additionally, NSP-Wisconsin faces competitive factors, which could have an adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Further, worldwide economic activity impacts the demand for basic commodities necessary for utility infrastructure, which may inhibit our ability to acquire sufficient supplies. We operate in a capital intensive industry and federal trade policy could significantly impact the cost of materials we use. There may be delays before these additional material costs can be recovered in rates.
The oil and gas industry represents our largest commercial and industrial customer base. Oil and natural gas prices are sensitive to market risk factors which may impact demand.
We face risks related to health epidemics and other outbreaks, which may have a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Health epidemics impact countries, communities, supply chains and markets. Uncertainty continues to exist regarding epidemics; the duration and magnitude of business restrictions including shutdowns (domestically and globally); the potential impact on the workforce including shortages of employees and third-party contractors due to quarantine policies, vaccination requirements or government restrictions; impacts on the transportation of goods, and the generalized impact on the economy.
We cannot ultimately predict whether an epidemic will have a material impact on our future liquidity, financial condition or results of operations. Nor can we predict the impact on the health of our employees, our supply chain or our ability to recover higher costs associated with managing an outbreak.
Operations could be impacted by war, terrorism or other events.
Our generation plants, fuel storage facilities, transmission and distribution facilities and information and control systems may be targets of terrorist activities. Any disruption could impact operations or result in a decrease in revenues and additional costs to repair and insure our assets. These disruptions could have a material impact on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. The potential for terrorism has subjected our operations to increased risks and could have a material effect on our business. We have incurred increased costs for security and capital expenditures in response to these risks. The insurance industry has also been affected by these events and the availability of insurance may decrease. In addition, insurance may have higher deductibles, higher premiums and more restrictive policy terms.
A disruption of the regional electric transmission grid, interstate natural gas pipeline infrastructure or other fuel sources, could negatively impact our business, brand and reputation. Because our facilities are part of an interconnected system, we face the risk of possible loss of business due to a disruption caused by the actions of a neighboring utility.
We also face the risks of possible loss of business due to significant events such as severe storms, temperature extremes, wildfires, widespread pandemic, generator or transmission facility outage, pipeline rupture, railroad disruption, operator error, sudden and significant increase or decrease in wind generation or a workforce disruption.
In addition, major catastrophic events throughout the world may disrupt our business. While we have business continuity plans in place, our ability to recover may be prolonged due to the type and extent of the event. NSP-Wisconsin participates in a global supply chain, which includes materials and components that are globally sourced. A prolonged disruption could result in the delay of equipment and materials that may impact our ability to connect, restore and reliably serve our customers.
A major disruption could result in a significant decrease in revenues, additional costs to repair assets, and an adverse impact on the cost and availability of insurance, which could have a material impact on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
A cybersecurity incident or security breach could have a material effect on our business.
We operate in an industry that requires the continued operation of sophisticated information technology, control systems and network infrastructure. In addition, we use our systems and infrastructure to create, collect, use, disclose, store, dispose of and otherwise process sensitive information, including Company data, customer energy usage data, and personal information regarding customers, employees and their dependents, contractors and other individuals.
Our generation, transmission, distribution and fuel storage facilities, information technology systems and other infrastructure or physical assets, as well as information processed in our systems (e.g., information regarding our customers, employees, operations, infrastructure and assets) could be affected by cybersecurity incidents, including those caused by human error.
The utility industry has been the target of several attacks on operational systems and has seen an increased volume and sophistication of cybersecurity incidents from international activist organizations, other countries and individuals. We expect to continue to experience attempts to compromise our information technology and control systems, network infrastructure and other assets. To date, no cybersecurity incident or attack has had a material impact on our business or results of operations.
Cybersecurity incidents could harm our businesses by limiting our generation, transmission and distribution capabilities, delaying our development and construction of new facilities or capital improvement projects to existing facilities, disrupting our customer operations or causing the release of customer information, all of which would likely receive state and federal regulatory scrutiny and could expose us to liability.
Our generation, transmission systems and natural gas pipelines are part of an interconnected system. Therefore, a disruption caused by the impact of a cybersecurity incident on the regional electric transmission grid, natural gas pipeline infrastructure or other fuel sources of our third-party service providers’ operations, could also negatively impact our business.
Generative Artificial Intelligence, such as large language models like ChatGPT, present a range of challenges and potential risks as we consider impacts to the business. These challenges involve navigating the complexities of creating and deploying AI models that generate content autonomously. Data privacy, legal concerns, and security issues are all risks as this technology continues to be adopted.
Our supply chain for procurement of digital equipment and services may expose software or hardware to these risks and could result in a breach or significant costs of remediation. We are unable to quantify the potential impact of cybersecurity threats or subsequent related actions. Cybersecurity incidents and regulatory action could result in a material decrease in revenues and may cause significant additional costs (e.g., penalties, third-party claims, repairs, insurance or compliance) and potentially disrupt our supply and markets for natural gas, oil and other fuels.
We maintain security measures to protect our information technology and control systems, network infrastructure and other assets. However, these assets and the information they process may be vulnerable to cybersecurity incidents, including asset failure or unauthorized access to assets or information.
A failure or breach of our technology systems or those of our third-party service providers could disrupt critical business functions and may negatively impact our business, our brand, and our reputation. The cybersecurity threat is dynamic and evolves continually, and our efforts to prioritize network protection may not be effective given the constant changes to threat vulnerability.
While the Company maintains insurance relating to cybersecurity events, such insurance is subject to a number of exclusions and may be insufficient to offset any losses, costs or damages experienced. Also, the market for cybersecurity insurance is relatively new and coverage available for cybersecurity events is evolving as the industry matures.
Our operating results may fluctuate on a seasonal and quarterly basis and can be adversely affected by milder weather.
Our electric and natural gas utility businesses are seasonal and weather patterns can have a material impact on our operating performance. Demand for electricity is often greater in the summer and winter months associated with cooling and heating. Because natural gas is heavily used for residential and commercial heating, the demand depends heavily upon weather patterns. A significant amount of natural gas revenues are recognized in the first and fourth quarters related to the heating season. Accordingly, our operations have historically generated less revenues and income when weather conditions are milder in the winter and cooler in the summer. Unusually mild winters and summers could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Public Policy Risks
Increased risks of regulatory penalties could negatively impact our business.
The Energy Act increased civil penalty authority for violation of FERC statutes, rules and orders. FERC can impose penalties of up to $1.5 million per violation per day, particularly as it relates to energy trading activities for both electricity and natural gas. In addition, NERC electric reliability standards and critical infrastructure protection requirements are mandatory and subject to potential financial penalties. Also, the PHMSA, Occupational Safety and Health Administration and other federal agencies have the authority to assess penalties.
In the event of serious incidents, these agencies may pursue penalties. In addition, certain states have the authority to impose substantial penalties. If a serious reliability, cybersecurity or safety incident did occur, it could have a material effect on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
The continued use of natural gas for both power generation and gas distribution have increasingly become a public policy advocacy target. These efforts may result in a limitation of natural gas as an energy source for both power generation and heating, which could impact our ability to reliably and affordably serve our customers.
In recent years, there have been various local and state agency proposals within and outside our service territories that would attempt to restrict the use and availability of natural gas. If such policies were to prevail, we may be forced to make new resource investment decisions which could potentially result in stranded costs if we are not able to fully recover costs and investments and impact the overall reliability of our service.
Environmental Policy Risks
We may be subject to legislative and regulatory responses to climate change, with which compliance could be difficult and costly.
Legislative and regulatory responses related to climate change may create financial risk as our facilities may be subject to additional regulation at either the state or federal level in the future. International agreements could additionally lead to future federal or state regulations.
In 2015, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change reached consensus among 190 nations on an agreement (the Paris Agreement) that establishes a framework for GHG mitigation actions by all countries, with a goal of holding the increase in global average temperature to below 2º Celsius above pre-industrial levels and an aspiration to limit the increase to 1.5º Celsius.
International commitments and agreements could result in future additional GHG reductions in the United States. In addition, in 2023 the EPA intends to publish draft regulations for GHG emissions from the power sector consistent with the agency’s Clean Air Act authorities.
Many states and localities continue to pursue their own climate policies. The steps Xcel Energy has taken to date to reduce GHG emissions, including energy efficiency measures, adding renewable generation and retiring or converting coal plants to natural gas, occurred under state-endorsed resource plans, renewable energy standards and other state policies.
We may be subject to climate change lawsuits. An adverse outcome could require substantial capital expenditures and possibly require payment of substantial penalties or damages. Defense costs associated with such litigation can also be significant and could affect results of operations, financial condition or cash flows if such costs are not recovered through regulated rates.
If our regulators do not allow us to recover all or a part of the cost of capital investment or the O&M costs incurred to comply with the mandates, it could have a material effect on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
We are subject to environmental laws and regulations, with which compliance could be difficult and costly.
We are subject to environmental laws and regulations that affect many aspects of our operations, including air emissions, water quality, wastewater discharges and the generation, transport and disposal of solid wastes and hazardous substances. Laws and regulations require us to obtain permits, licenses, and approvals and to comply with a variety of environmental requirements.
Environmental laws and regulations can also require us to restrict or limit the output of facilities or the use of certain fuels, shift generation to lower-emitting facilities, install pollution control equipment, clean up spills and other contamination and correct environmental hazards. Failure to meet requirements of environmental mandates may result in fines or penalties. We may be required to pay all or a portion of the cost to remediate sites where our past activities, or the activities of other parties, caused environmental contamination.
Changes in environmental policies and regulations or regulatory decisions may result in early retirements of our generation facilities. While regulation typically provides relief for these types of changes, there is no assurance that regulators would allow full recovery of all remaining costs.
We are subject to mandates to provide customers with clean energy, renewable energy and energy conservation offerings. It could have a material effect on our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows if our regulators do not allow us to recover the cost of capital investment or O&M costs incurred to comply with the requirements.
In addition, existing environmental laws or regulations may be revised and new laws or regulations may be adopted. We may also incur additional unanticipated obligations or liabilities under existing environmental laws and regulations.
We are subject to physical and financial risks associated with climate change and other weather, natural disaster and resource depletion impacts.
Climate change can create physical and financial risk. Physical risks include changes in weather conditions and extreme weather events.
Our customers’ energy needs vary with weather. To the extent weather conditions are affected by climate change, customers’ energy use could increase or decrease. Increased energy use due to weather changes may require us to invest in generating assets, transmission and infrastructure. Decreased energy use due to weather changes may result in decreased revenues.
Climate change may impact the economy, which could impact our sales and revenues. The price of energy has an impact on the economic health of our communities. The cost of additional regulatory requirements, such as regulation of GHG, could impact the availability of goods and prices charged by our suppliers, which would normally be borne by consumers through higher prices for energy and purchased goods. To the extent financial markets view climate change and emissions of GHGs as a financial risk, this could negatively affect our ability to access capital markets or cause us to receive less than ideal terms and conditions.
We establish strategies and expectations related to climate change and other environmental matters. Our ability to achieve any such strategies or expectations is subject to numerous factors and conditions, many of which are outside of our control. Examples of such factors include, but are not limited to, evolving legal, regulatory, and other standards, processes, and assumptions, the pace of scientific and technological developments, increased costs, the availability of requisite financing, and changes in carbon markets. Failures or delays (whether actual or perceived) in achieving our strategies or expectations related to climate change and other environmental matters could adversely affect our business, operations, and reputation, and increase risk of litigation.
Severe weather impacts our service territories, primarily when thunderstorms, flooding, tornadoes, wildfires and snow or ice storms or extreme temperatures (high heating/cooling days) occur. Extreme weather conditions in general require system backup and can contribute to increased system stress, including service interruptions. Extreme weather conditions creating high energy demand may raise electricity prices, increasing the cost of energy we provide to our customers.
To the extent the frequency of extreme weather events increases, this could increase our cost of providing service and result in more frequent service interruptions. Periods of extreme temperatures could also impact our ability to meet demand.
More frequent and severe drought conditions, extreme swings in amount and timing of precipitation, changes in vegetation, unseasonably warm temperatures, very low humidity, stronger winds and other factors have increased the duration of the wildfire season and the potential impact of an event. Also, the expansion of the wildland urban interface increases the wildfire risk to surrounding communities and NSP-Wisconsin's electric and natural gas infrastructure.
Other potential risks associated with wildfires and other climate events include the inability to secure sufficient insurance coverage, or increased costs of insurance, regulatory recovery risk, and the potential for a credit downgrade and subsequent additional costs to access capital markets.
While we carry liability insurance, given an extreme event, if NSP-Wisconsin was found to be liable for wildfire damages, amounts that potentially exceed our coverage could negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Drought or water depletion could adversely impact our ability to provide electricity to customers, cause early retirement of power plants and increase the cost for energy. Adverse events may result in increased insurance costs and/or decreased insurance availability. We may not recover all costs related to mitigating these physical and financial risks.
| | |
ITEM 1B — UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
NSP-Wisconsin is a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy. As such, its cybersecurity processes are maintained by Xcel Energy management and governed by its Board of Directors.
As described in Item 1A – Risk Factors, Xcel Energy operates in an industry that requires the continued operation of sophisticated information technology, control systems and network infrastructure, as such, our business is subject to the risk of interruption by cybersecurity incidents that range from attacks common to most industries, such as phishing and denial-of-service, to attacks from more sophisticated adversaries, including nation state actors, that target the critical infrastructure used in the operation of our business.
Xcel Energy has a security risk program in place to identify, assess, manage and report material risks from cybersecurity incidents. As a utility provider, Xcel Energy complies with reliability standards imposed by NERC, including critical infrastructure protection standards related to both cybersecurity and physical security. These standards imposed by NERC, in alignment with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, are the basis for which Xcel Energy has designed the cybersecurity control framework within its security risk program.
Annually, as part of Xcel Energy’s enterprise risk program, an integrated cybersecurity risk identification and assessment is completed across Xcel Energy’s business, including generation, transmission, distribution and fuel storage facilities, information technology systems and other infrastructure or physical assets as well as information processed in our systems (including systems hosted by third parties) that could be affected by cybersecurity incidents. This analysis includes the impact, likelihood, timeframe and controllability of cybersecurity risks and is presented to the Board of Directors. Management monitors and reviews the results of this analysis, integrating them into the enterprise risk assessment processes and implements appropriate mitigating actions as needed.
Xcel Energy’s cybersecurity policies, standards, practices and readiness are regularly assessed by third-party consultants. These partners are engaged to perform independent penetration testing and other security related services to assist in the prevention, detection, monitoring, mitigation and remediation of cybersecurity incidents and risks. The results of these assessments are communicated to management and the Board of Directors by the Chief Security Officer.
Xcel Energy employs a comprehensive risk based approach to assess the magnitude and significance of a vendor’s risk to Xcel Energy. Certain third-party service providers are subject to vendor security risk assessments at the time of integration, contract execution/renewal, and upon detection of any increase in risk profile. Xcel Energy uses a variety of inputs in such risk assessments, including information supplied by providers and third parties (including information analysis centers that share daily threat intelligence and improve organizational agility associated with management of cybersecurity risks). In addition, Xcel Energy requires certain third-party service providers to meet appropriate security requirements, controls and responsibilities. Xcel Energy deploys periodic monitoring activities to assess compliance with our cybersecurity control framework and investigates security incidents that have impacted our third-party service providers as appropriate.
Management has assigned responsibility for the security risk program to the Chief Security Officer who has extensive experience in critical infrastructure protection, including multiple years of experience with the Department of Defense. The Chief Security Officer is informed about and monitors prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation efforts through a team of security professionals, many of whom are Certified Information Systems Security Professionals, Certified Information Security Managers or have received other cybersecurity certifications. The team has extensive experience selecting, deploying and operating cybersecurity technologies, initiatives and processes that aid in preventing, remediating and mitigating known and unknown cybersecurity threats.
The Chief Security Officer or members of management brief the Board on routine and regular cybersecurity risk and threat updates, typically on a quarterly basis. In the event of a significant threat or incident, management and the Chief Security Officer leverage Xcel Energy’s incident response processes to assess impacts and resolve incidents. When a significant cybersecurity incident occurs, management communicates with the Board of Directors and relevant committees.
The Board of Directors oversees the risks associated with cybersecurity and the physical security of our assets, with information security matters being discussed at each regular board meeting as well as at the ONES and Audit Committee meetings throughout the year.
While the ONES Committee has primary committee responsibility for cybersecurity due to the operational issues involved, the Board of Directors has determined that the topic is of sufficient importance to warrant this comprehensive oversight approach. Augmenting such oversight efforts, the Board conducts drills to practice its response in a possible emergency situation to ensure it is well prepared and positioned to perform in a possible crisis.
Cybersecurity risks are a part of Xcel Energy’s normal course of business. To date, no cybersecurity incident or attack has had a material impact on our business or results of operations. As of Feb. 21, 2024 there have been no material cybersecurity incidents to report.
Virtually all of the utility plant property of NSP-Wisconsin is subject to the lien of its first mortgage bond indenture.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Station, Location and Unit at Dec. 31, 2023 | | Fuel | | Installed | | MW (a) | |
| Steam: | | | | | | | |
| Bay Front-Ashland, WI, 2 Units | | Wood/Natural Gas | | 1948 - 1956 | | 41 | | |
| French Island-La Crosse, WI, 2 Units | | Wood/RDF | | 1940 - 1948 | | 16 | | (b) |
| Combustion Turbine: | | | | | | | |
| French Island-La Crosse, WI, 2 Units | | Oil | | 1974 | | 119 | | |
| Wheaton-Eau Claire, WI, 5 Units | | Natural Gas/Oil | | 1973 | | 240 | | |
| Hydro: | | | | | | | |
| Various locations, 62 Units | | Hydro | | Various | | 135 | | |
| | | | Total | | 551 | | |
(a)Summer 2023 net dependable capacity.
(b)RDF is made from municipal solid waste.
Electric utility overhead and underground transmission and distribution lines (measured in conductor miles) at Dec. 31, 2023:
| | | | | |
| Conductor Miles | |
| Transmission | |
| |
| 345 KV | 3,019 | |
| |
| 161 KV | 1,818 | |
| |
| 115 KV | 1,862 | |
| Less than 115 KV | 5,467 | |
| Total Transmission | 12,166 | |
| Distribution | |
| Less than 115 KV | 27,971 | |
| Total | 40,137 | |
NSP-Wisconsin had 203 electric utility transmission and distribution substations at Dec. 31, 2023.
Natural gas utility mains at Dec. 31, 2023:
| | | | | |
| Miles | |
| Transmission | 3 | |
| Distribution | 2,564 | |
| | |
ITEM 3 — LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
NSP-Wisconsin is involved in various litigation matters in the ordinary course of business. The assessment of whether a loss is probable or is a reasonable possibility, and whether the loss or a range of loss is estimable, often involves a series of complex judgments about future events. Management maintains accruals for losses probable of being incurred and subject to reasonable estimation.
Management is sometimes unable to estimate an amount or range of a reasonably possible loss in certain situations, including but not limited to, when (1) the damages sought are indeterminate, (2) the proceedings are in the early stages, or (3) the matters involve novel or unsettled legal theories. In such cases, there is considerable uncertainty regarding the timing or ultimate resolution of such matters, including a possible eventual loss.
For current proceedings not specifically reported herein, management does not anticipate that the ultimate liabilities, if any, would have a material effect on NSP-Wisconsin’s consolidated financial statements. Legal fees are generally expensed as incurred.
See Note 10 to the consolidated financial statements, Item 1 and Item 7 for further information.
| | |
ITEM 4 — MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
None.
PART II
| | |
ITEM 5 — MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
NSP-Wisconsin is a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy Inc. and there is no market for its common equity securities.
The dividends declared during 2023 and 2022 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| First quarter | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 22 | |
| Second quarter | | 25 | | | 19 | |
| Third quarter | | 24 | | | 23 | |
| Fourth quarter | | 38 | | | 24 | |
| | |
ITEM 7 — MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
Discussion of financial condition and liquidity for NSP-Wisconsin is omitted per conditions set forth in General Instructions I(1)(a) and (b) of Form 10-K for wholly owned subsidiaries. It is replaced with management’s narrative analysis and the results of operations for the current year as set forth in General Instructions I(2)(a) of Form 10-K for wholly owned subsidiaries (reduced disclosure format).
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
The following discussion includes financial information prepared in accordance with GAAP, as well as certain non-GAAP financial measures such as ongoing earnings. Generally, a non-GAAP financial measure is a measure of a company’s financial performance, financial position or cash flows that is adjusted from measures calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP.
NSP-Wisconsin’s management uses non-GAAP measures for financial planning and analysis, for reporting of results to the Board of Directors, in determining performance-based compensation and communicating its earnings outlook to analysts and investors. Non-GAAP financial measures are intended to supplement investors’ understanding of our performance and should not be considered alternatives for financial measures presented in accordance with GAAP. These measures are discussed in more detail below and may not be comparable to other companies’ similarly titled non-GAAP financial measures.
Earnings Adjusted for Certain Items (Ongoing Earnings)
Ongoing earnings reflect adjustments to GAAP earnings (net income) for certain items.
We use these non-GAAP financial measures to evaluate and provide details of NSP-Wisconsin’s core earnings and underlying performance. For instance, to present ongoing earnings, we may adjust the related GAAP amounts for certain items that are non-recurring in nature. We believe these measurements are useful to investors to evaluate the actual and projected financial performance and contribution of NSP-Wisconsin. This non-GAAP financial measure should not be considered as an alternative to measures calculated and reported in accordance with GAAP.
The following table provides a reconciliation of GAAP earnings (net income) to ongoing earnings:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| GAAP net income | | $ | 136 | | | $ | 125 | |
| Workforce reduction expenses | | 5 | | | — | |
| Less: tax effect of adjustment | | (1) | | | — | |
| Ongoing earnings | | $ | 140 | | | $ | 125 | |
Workforce Reduction — In 2023, Xcel Energy implemented workforce actions to align resources and investments with our evolving business and customer needs, and streamline the organization for long-term success. Xcel Energy initiated a voluntary retirement program, under which approximately 400 eligible non-bargaining employees retired. Xcel Energy also eliminated approximately 150 non-bargaining employees through an involuntary severance program.
Total Xcel Energy workforce reduction expenses of $72 million were recorded in the fourth quarter of 2023, of which $5 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin. Given the non-recurring nature of this item, it has been excluded from ongoing earnings.
2023 Comparison with 2022
NSP-Wisconsin’s GAAP net income was $136 million for 2023 compared with $125 million for 2022. Ongoing net income was $140 million for 2023 compared with $125 million for 2022. The increase in ongoing earnings was primarily a result of higher recovery of electric infrastructure investment, partially offset by unfavorable weather and higher depreciation, O&M expenses, and interest charges.
Electric Margin
Electric margin is presented as electric revenues less electric fuel and purchased power expenses. Expenses incurred for electric fuel and purchased power are generally recovered through various regulatory recovery mechanisms. As a result, changes in these expenses are generally offset in operating revenues.
Electric revenues and fuel and purchased power expenses are impacted by fluctuations in the price of natural gas, coal and uranium. However, these price fluctuations generally have minimal impact on earnings impact due to fuel recovery mechanisms. In addition, electric customers receive a credit for production tax credits generated, which reduce electric revenue and income taxes.
Electric Revenues, Fuel and Purchased Power and Electric Margin
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Electric revenues | | $ | 1,019 | | | $ | 1,002 | |
| Electric fuel and purchased power | | (422) | | | (463) | |
| Electric margin | | $ | 597 | | | $ | 539 | |
Changes in Electric Margin
| | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 vs. 2022 |
| Regulatory rate outcomes | | $ | 37 | |
| Interchange agreement billings with NSP-Minnesota | | 20 | |
| Sales and demand | | 2 | |
| Estimated impact of weather | | (6) | |
| | |
| | |
| Other (net) | | 5 | |
| Total increase | | $ | 58 | |
Natural Gas Margin
Natural gas margin is presented as natural gas revenues less the cost of natural gas sold and transported. Expenses incurred for the cost of natural gas sold are generally recovered through various regulatory recovery mechanisms. As a result, changes in these expenses are generally offset in operating revenues.
Natural gas expense varies with changing sales and the cost of natural gas. However, fluctuations in the cost of natural gas generally have minimal earnings impact due to cost recovery mechanisms.
Natural Gas Revenues, Cost of Natural Gas Sold and Transported and Natural Gas Margin
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Natural gas revenues | | $ | 157 | | | $ | 198 | |
| Cost of natural gas sold and transported | | (80) | | | (116) | |
| Natural gas margin | | $ | 77 | | | $ | 82 | |
Changes in Natural Gas Margin
| | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 vs. 2022 |
| Estimated impact of weather | | $ | (7) | |
| Regulatory rate outcomes (Wisconsin and Michigan) | | 4 | |
| Other (net) | | (2) | |
| Total decrease | | $ | (5) | |
Non-Fuel Operating Expenses and Other Items
O&M Expenses — O&M expenses increased $16 million in 2023. The increase was primarily due to vegetation management and inflationary pressures including labor.
Depreciation and Amortization — Depreciation and amortization increased $12 million for 2023 compared with 2022, primarily due to system expansion.
Interest Charges — Interest charges increased $9 million for 2023, largely due to increased long-term debt levels and interest rates.
| | |
| Public Utility Regulation |
The FERC and various state and local regulatory commissions regulate NSP-Wisconsin. The electric and natural gas rates charged to customers of NSP-Wisconsin are approved by the FERC or the regulatory commissions in the states in which it operates.
Rates are designed to recover plant investment, operating costs and an allowed return on investment. NSP-Wisconsin requests changes in utility rates through commission filings.
Changes in operating costs can affect NSP-Wisconsin’s financial results, depending on the timing of rate case filings and implementation of final rates. Other factors affecting rate filings are new investments, sales, conservation and Demand Side Management efforts, and the cost of capital.
In addition, the regulatory commissions authorize the ROE, capital structure and depreciation rates in rate proceedings. Decisions by these regulators can significantly impact NSP-Wisconsin’s results of operations and credit quality.
See Rate Matters within Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
Summary of Regulatory Agencies / RTO and Areas of Jurisdiction
| | | | | | | | |
| Regulatory Body / RTO | | Additional Information |
| PSCW | | Retail rates, services and other aspects of electric and natural gas operations. Certifies the need for new generating plants and electric transmission lines before the facilities may be sited and built. The PSCW has a biennial base rate filing requirement. By June of each odd numbered year, NSP-Wisconsin must submit a rate filing for the test year beginning the following January. Pipeline safety compliance. |
| MPSC | | Retail rates, services and other aspects of electric and natural gas operations. Certifies the need for new generating plants and electric transmission lines before the facilities may be sited and built. Pipeline safety compliance. |
| FERC | | Wholesale electric operations, hydroelectric generation licensing, accounting practices, wholesale sales for resale, transmission of electricity in interstate commerce, compliance with NERC electric reliability standards, asset transactions and mergers and natural gas transactions in interstate commerce. |
| MISO | | NSP-Wisconsin is a transmission owning member of the MISO RTO that operates within the MISO RTO and wholesale energy market. NSP-Wisconsin and NSP-Minnesota are jointly authorized by the FERC to make wholesale electric sales at market-based prices. |
| DOT | | Pipeline safety compliance. |
Recovery Mechanisms | | | | | | | | |
| Mechanism | | Additional Information |
| Annual Fuel Cost Plan | | NSP-Wisconsin does not have an automatic electric fuel adjustment clause. Under Wisconsin rules, utilities submit a forward-looking annual fuel cost plan to the PSCW. Once the PSCW approves the plan, utilities defer the amount of any fuel cost under-recovery or over-recovery in excess of a 2% annual tolerance band, for future rate recovery or refund. Approval of a fuel cost plan and any rate adjustment for refund or recovery of deferred costs is determined by the PSCW. Rate recovery of deferred fuel cost is subject to an earnings test based on the most recently authorized ROE. Under-collections that exceed the 2% annual tolerance band may not be recovered if the utility earnings for that year exceed the authorized ROE. |
| Natural Gas Cost-Recovery Factor (MI) | | NSP-Wisconsin’s natural gas rates for Michigan customers include a natural gas cost-recovery factor, based on 12-month projections and trued-up to actual amounts on an annual basis. |
| Power Supply Cost Recovery Factors | | NSP-Wisconsin’s retail electric rate schedules for Michigan customers include power supply cost recovery factors, based on 12-month projections. After each 12-month period, a reconciliation is submitted whereby over-recoveries are refunded and any under-recoveries are collected from customers. |
| Purchased Gas Adjustment | | A retail cost-recovery mechanism to recover the actual cost of natural gas, transportation, and storage services. |
| Wisconsin Energy Efficiency Program | | The primary energy efficiency program is funded by the utilities, but operated by independent contractors subject to oversight by the PSCW and utilities. NSP-Wisconsin recovers these costs from customers. |
Recently Concluded Regulatory Proceedings
Wisconsin Rate Case — In 2023, NSP-Wisconsin filed a Wisconsin rate case seeking a revised electric increase of $25 million and a natural gas increase of $7 million. The filing was based on a 2024 forecast test year, a ROE of 10.25%, an equity ratio of 52.5% and a forecasted average net rate base of approximately $2.1 billion for the electric utility and $284 million for the natural gas utility.
In December 2023, the PSCW approved a ROE of 9.8% and an equity ratio of 52.5% as well as a rate increase of approximately $1 million for the electric utility. Adjustments to NSP-Wisconsin’s rate request included removal of a proposed residential affordability program and other earnings neutral adjustments and fuel and purchased power costs. The PSCW also approved a $5 million rate increase for the natural gas utility in 2024. The new rates were implemented on Jan. 1, 2024.
NSP System
Pending and Recently Concluded Regulatory Proceedings
2022 Upper Midwest IRP Resource Acquisition — Following the MPUC’s approval of NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin’s latest IRP in April 2022, NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin have been engaged in multiple resource acquisition processes and proceedings to meet the need identified in the IRP for the NSP System.
•In August 2022, NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin jointly filed an RFP seeking at least 900 MW of solar or solar plus storage capacity. In May 2023, NSP-Minnesota filed a recommended portfolio, which proposed an additional 250 MW of self-build solar generation at the site of our retiring Sherco coal units and a 100 MW solar PPA located in Wisconsin as part of the resource plan RFP. In September 2023, the MPUC approved the request for 350 MW, subject to a cost cap based on projected costs for the Sherco solar project.
•In the second quarter of 2023, NSP-Minnesota initiated the process with the MPUC for acquisition of 800 MW of firm dispatchable resources. In January 2024, NSP-Minnesota and other companies submitted proposed resources. NSP-Minnesota expects a decision by the fourth quarter of 2024.
•In July 2023, NSP-Wisconsin issued an RFP seeking approximately 650 MW of solar and/or solar plus storage development assets that will be developed in the 2027-2029 timeframe to replace the capacity from the retiring King Generating Station. The RFP closed in September 2023 and bids are being evaluated.
•In October 2023, NSP-Minnesota issued an RFP seeking approximately 1,200 MW of wind development assets to replace capacity and reutilize interconnection rights associated with the retiring Sherco coal facilities. The RFP closed in December 2023 and the NSP-Minnesota expects to file for approval of recommended projects by mid-2024.
2024 Upper Midwest Energy Plan — In February 2024, NSP-Minnesota filed its resource plan with the MPUC. Key components of the plan include the following:
•Reduced carbon emissions by more than 80%, potentially up to 88%, by 2030.
•Extends the operation of Prairie Island and Monticello nuclear plants through the early 2050s.
•Adds 3,600 MW of new wind and solar resources by 2030.
•Adds 600 MW of battery energy storage by 2030.
•Adds more than 2,200 MW of dispatchable resources by 2030.
NSP-Minnesota anticipates a MPUC decision in 2025.
Purchased Power and Transmission Services
The NSP System expects to use power plants, power purchases, conservation and DSM options, new generation facilities and expansion of power plants to meet its system capacity requirements.
Purchased Power — Through the Interchange Agreement, NSP-Wisconsin receives power purchased by NSP-Minnesota from other utilities and independent power producers. Long-term purchased power contracts for dispatchable resources typically require a capacity charge and an energy charge. NSP-Minnesota makes short-term purchases to meet system requirements, replace company owned generation, meet operating reserve obligations or obtain energy at a lower cost.
Purchased Transmission Services — NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin have contracts with MISO and other regional transmission service providers to deliver power and energy to their customers.
Supply Chain
NSP-Wisconsin’s ability to meet customer energy requirements, respond to storm-related disruptions, and execute our capital expenditure program are dependent on maintaining an efficient supply chain. Manufacturing processes have experienced disruptions related to the scarcity of certain raw materials and interruptions in production and shipping. Inflationary pressures, labor shortages, and the impact of geopolitical events have further exacerbated these disruptions. NSP-Wisconsin continues to monitor the situation as it remains fluid and seeks to mitigate the impacts by securing alternative suppliers, modifying design standards, and adjusting the timing of work.
Additionally, certain products, components, and equipment, particularly in renewables categories, originate in countries that could face tariffs, fines, or restrictions from government or other regulatory bodies and present a cost and supply risk until there is sufficient capacity and supply base with adequate capacity to meet US needs.
Electric Meters and Transformers
Supply chain issues associated with semiconductors delayed the availability of AMI meters, which led to a reduced number of meters deployed in 2022. NSP-Wisconsin saw significant improvement in meter availability in 2023 and we expect normal conditions in 2024 and going forward. NSP-Wisconsin expects to complete AMI meter deployment in 2025.
Additionally, the availability of certain transformers is an industry-wide issue that has significantly impacted and in some cases resulted in delays to projects and new customer connections. Proposed governmental actions related to transformer efficiency standards may compound these delays in the future. NSP-Wisconsin continues to seek alternative suppliers and prioritize work plans to mitigate the impacts of supply constraints.
| | |
ITEM 7A — QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Derivatives, Risk Management and Market Risk
NSP-Wisconsin is exposed to a variety of market risks in the normal course of business. Market risk is the potential loss that may occur as a result of adverse changes in the market or fair value for a particular instrument or commodity. All financial and commodity-related instruments, including derivatives, are subject to market risk.
NSP-Wisconsin is exposed to the impact of adverse changes in price for energy and energy-related products, which is partially mitigated by the use of commodity derivatives. In addition to ongoing monitoring and maintaining credit policies intended to minimize overall credit risk, management takes steps to mitigate changes in credit and concentration risks associated with its derivatives and other contracts, including parental guarantees and requests of collateral. While NSP-Wisconsin expects that the counterparties will perform on the contracts underlying its derivatives, the contracts expose NSP-Wisconsin to credit and non-performance risk.
Distress in the financial markets may impact counterparty risk and the fair value of the securities in the pension fund.
Commodity Price Risk — We are exposed to commodity price risk in our electric and natural gas operations. Commodity price risk is managed by entering into long and short-term physical purchase and sales contracts for natural gas used in distribution activities.
Commodity price risk is also managed through the use of financial derivative instruments. Our risk management policy allows us to manage commodity price risk within each rate-regulated operation per commission approved hedge plans.
Interest Rate Risk — NSP-Wisconsin is subject to interest rate risk. NSP-Wisconsin’s risk management policy allows interest rate risk to be managed through the use of fixed rate debt, floating rate debt and interest rate derivatives.
A 100 basis point change in the benchmark rate on NSP-Wisconsin’s variable rate debt would impact pretax interest expense annually by an immaterial amount in Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022.
The value of pension and postretirement plan assets and benefit costs are impacted by changes in discount rates and expected return on plan assets. NSP-Wisconsin’s ongoing pension and postretirement investment strategy is based on plan-specific investment recommendations that seek to optimize potential investment risk and minimize interest rate risk associated with changes in the obligations as a plan’s funded status increases over time. The impacts of fluctuations in interest rates on pension and postretirement costs are mitigated by pension cost calculation methodologies and regulatory mechanisms that minimize the earnings impacts of such changes.
Credit Risk — NSP-Wisconsin is also exposed to credit risk. Credit risk relates to the risk of loss resulting from counterparties’ nonperformance on their contractual obligations. NSP-Wisconsin maintains credit policies intended to minimize overall credit risk and actively monitors these policies to reflect changes and scope of operations.
At Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, a 10% increase or decrease in commodity prices would have an immaterial impact on credit exposure.
NSP-Wisconsin conducts credit reviews for all wholesale, trading and non-trading commodity counterparties and employs credit risk controls, such as letters of credit, parental guarantees, master netting agreements and termination provisions. Credit exposure is monitored and, when necessary, the activity with a specific counterparty is limited until credit enhancement is provided. Distress in the financial markets could increase NSP-Wisconsin credit risk.
Fair Value Measurements
Derivative contracts, with the exception of those designated as normal purchases and normal sales, are reported at fair value. NSP-Wisconsin’s pension and other postretirement funds are also subject to fair value accounting. See Notes 8 and 9 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
| | |
ITEM 8 — FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
See Item 15-1 for an index of financial statements included herein.
See Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
Management Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of NSP-Wisconsin is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. NSP-Wisconsin’s internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to Xcel Energy Inc.’s and NSP-Wisconsin’s management and board of directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
NSP-Wisconsin management assessed the effectiveness of NSP-Wisconsin’s internal control over financial reporting as of Dec. 31, 2023. In making this assessment, it used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013). Based on our assessment, we believe that, as of Dec. 31, 2023, NSP-Wisconsin’s internal control over financial reporting is effective at the reasonable assurance level based on those criteria.
| | | | | | | | |
| /s/ ROBERT C. FRENZEL | | /s/ BRIAN J. VAN ABEL |
| Robert C. Frenzel | | Brian J. Van Abel |
| Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and Director | | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Director |
| Feb. 21, 2024 | | Feb. 21, 2024 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholder and the Board of Directors of Northern States Power Company, a Wisconsin corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Northern States Power Company and subsidiaries, a Wisconsin corporation (the "Company"), as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of income, common stockholder’s equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes and the schedule listed in the Index at Item 15 (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Regulatory Assets and Liabilities - Impact of Rate Regulation on the Financial Statements — Refer to Notes 4 and 10 to the consolidated financial statements.
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company is subject to rate regulation by state utility regulatory agencies, which have jurisdiction with respect to the rates of electric and natural gas distribution companies in Wisconsin and Michigan. The Company is also subject to the jurisdiction of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission for its wholesale electric operations, hydroelectric generation licensing, accounting practices, wholesale sales for resale, transmission of electricity in interstate commerce, compliance with North American Electric Reliability Corporation standards, asset transactions and mergers and natural gas transactions in interstate commerce, (collectively with state utility regulatory agencies, the “Commissions”). Management has determined it meets the requirements under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America to prepare its financial statements applying the specialized rules to account for the effects of cost-based rate regulation. Accounting for the economics of rate regulation affects multiple financial statement line items and disclosures, including property, plant and equipment, regulatory assets and liabilities, operating revenues and expenses, and income taxes.
The Company is subject to regulatory rate setting processes. Rates are determined and approved in regulatory proceedings based on an analysis of the Company’s costs to provide utility service and a return on, and recovery of, the Company’s investment in assets required to deliver services to customers. Accounting for the Company’s regulated operations provides that rate-regulated entities report assets and liabilities consistent with the recovery of those incurred costs in rates, if it is probable that such rates will be charged and collected. The Commissions’ regulation of rates is premised on the full recovery of incurred costs and a reasonable rate of return on invested capital. Decisions by the Commissions in the future will impact the accounting for regulated operations, including decisions about the amount of allowable costs and return on invested capital included in rates and any refunds that may be required. In the rate setting process, the Company’s rates result in the recording of regulatory assets and liabilities based on the probability of future cash flows. Regulatory assets generally represent incurred or accrued costs that have been deferred because future recovery from customers is probable. Regulatory liabilities generally represent amounts that are expected to be refunded to customers in future rates or amounts collected in current rates for future costs.
We identified the impact of rate regulation as a critical audit matter due to the significant judgments made by management to support its assertions about impacted account balances and disclosures and the high degree of subjectivity involved in assessing the impact of future regulatory orders on the financial statements. Management judgments include assessing the likelihood of recovery in future rates of incurred costs and refunds due to customers. Given that
management’s accounting judgments are based on assumptions about the outcome of future decisions by the Commissions, auditing these judgments required specialized knowledge of accounting for rate regulation and the rate setting process due to its inherent complexities.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the uncertainty of future decisions by the Commissions included the following, among others:
•We tested the effectiveness of management’s controls over the evaluation of the likelihood of (1) the recovery in future rates of costs deferred as regulatory assets, and (2) a refund or a future reduction in rates that should be reported as regulatory liabilities. We also tested the effectiveness of management’s controls over the recognition of regulatory assets or liabilities and the monitoring and evaluation of regulatory developments that may affect the likelihood of recovering costs in future rates or of a future reduction in rates.
•We evaluated the Company’s disclosures related to the impacts of rate regulation, including the balances recorded and regulatory developments.
•We read relevant regulatory orders issued by the Commissions for the Company, other regulatory filings, legal decisions and recommendations being evaluated by the Commissions, and other publicly available information to assess the likelihood of recovery in future rates or of a future reduction in rates. We evaluated historic orders for precedents of the Commissions’ treatment of similar costs under similar circumstances. We compared the regulatory orders, filings and other publicly available information to the Company’s recorded regulatory assets and liabilities for completeness.
•We obtained management’s analysis and correspondence from counsel, as appropriate, regarding regulatory assets or liabilities not yet addressed in a regulatory order to assess management’s assertion that amounts are probable of recovery or a future reduction in rates.
| | |
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP |
| Minneapolis, Minnesota |
| February 21, 2024 |
|
| We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2002. |
NSP-WISCONSIN AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(amounts in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended Dec. 31 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Operating revenues | | | | | |
| Electric, non-affiliates | $ | 815 | | | $ | 800 | | | $ | 733 | |
| Electric, affiliates | 204 | | | 202 | | | 189 | |
| Natural gas | 157 | | | 198 | | | 182 | |
| Other | 1 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Total operating revenues | 1,177 | | | 1,201 | | | 1,105 | |
| | | | | |
| Operating expenses | | | | | |
| Electric fuel and purchased power, non-affiliates | 14 | | | 17 | | | 20 | |
| Purchased power, affiliates | 408 | | | 446 | | | 408 | |
| Cost of natural gas sold and transported | 80 | | | 116 | | | 117 | |
| Operating and maintenance expenses | 239 | | | 223 | | | 198 | |
| Conservation program expenses | 13 | | | 13 | | | 13 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 170 | | | 158 | | | 147 | |
| Taxes (other than income taxes) | 34 | | | 31 | | | 28 | |
| Workforce reduction expenses | 5 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total operating expenses | 963 | | | 1,004 | | | 931 | |
| | | | | |
| Operating income | 214 | | | 197 | | | 174 | |
| | | | | |
| Other income (expense), net | 2 | | | (2) | | | (1) | |
| Allowance for funds used during construction — equity | 10 | | | 7 | | | 5 | |
| | | | | |
| Interest charges and financing costs | | | | | |
Interest charges — includes other financing costs of $2, $1 and $1, respectively | 54 | | | 45 | | | 42 | |
| Allowance for funds used during construction — debt | (4) | | | (3) | | | (2) | |
| Total interest charges and financing costs | 50 | | | 42 | | | 40 | |
| | | | | |
| Income before income taxes | 176 | | | 160 | | | 138 | |
| Income tax expense | 40 | | | 35 | | | 30 | |
| Net income | $ | 136 | | | $ | 125 | | | $ | 108 | |
| | | | | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NSP-WISCONSIN AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(amounts in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended Dec. 31 |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Operating activities | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 136 | | | $ | 125 | | | $ | 108 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 173 | | | 159 | | | 148 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | (12) | | | (2) | | | 9 | |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | | (10) | | | (7) | | | (5) | |
| Provision for bad debts | | 4 | | | 4 | | | 4 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | (4) | | | (13) | | | (5) | |
| Accrued unbilled revenues | | 11 | | | (5) | | | (16) | |
| Inventories | | (6) | | | (14) | | | (12) | |
| Other current assets | | 21 | | | (20) | | | (4) | |
| Accounts payable | | (6) | | | 5 | | | 8 | |
| Net regulatory assets and liabilities | | 44 | | | 18 | | | (41) | |
| Other current liabilities | | 2 | | | 16 | | | 2 | |
| Pension and other employee benefit obligations | | — | | | (4) | | | (9) | |
| Other, net | | 4 | | | (5) | | | (1) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | 357 | | | 257 | | | 186 | |
| | | | | | |
| Investing activities | | | | | | |
| Capital/construction expenditures | | (456) | | | (353) | | | (264) | |
| | | | | | |
| Investments in utility money pool arrangement | | (153) | | | (100) | | | (71) | |
| Repayments from money pool arrangement | | 153 | | | 100 | | | 71 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | (456) | | | (353) | | | (264) | |
| | | | | | |
| Financing activities | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from (repayments of) short-term borrowings, net | | 13 | | | (35) | | | 64 | |
| Borrowings under money pool arrangement | | 163 | | | 591 | | | 358 | |
| Repayments under money pool arrangement | | (163) | | | (591) | | | (358) | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | | 124 | | | 99 | | | 99 | |
| Repayments of long-term debt | | — | | | — | | | (19) | |
| Capital contributions from parent | | 75 | | | 114 | | | 46 | |
| Dividends paid to parent | | (109) | | | (91) | | | (103) | |
| | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | 103 | | | 87 | | | 87 | |
| | | | | | |
| Net change in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | 4 | | | (9) | | | 9 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of period | | 2 | | | 11 | | | 2 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of period | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 11 | |
| | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest (net of amounts capitalized) | | $ | (47) | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (38) | |
| Cash paid for income taxes, net | | (40) | | | (32) | | | (22) | |
| | | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing transactions: | | | | | | |
| Accrued property, plant and equipment additions | | $ | 31 | | | $ | 54 | | | $ | 43 | |
| Inventory transfers to property, plant and equipment | | 17 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | | 10 | | | 7 | | | 5 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NSP-WISCONSIN AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(amounts in millions, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Dec. 31 |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Current assets | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 2 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | | 89 | | | 84 | |
| Accrued unbilled revenues | | 63 | | | 74 | |
| Other receivables | | — | | | 19 | |
| Inventories | | 29 | | | 39 | |
| Regulatory assets | | 24 | | | 44 | |
| Prepaid taxes | | 28 | | | 27 | |
| Prepayments and other | | 6 | | | 11 | |
| Total current assets | | 245 | | | 300 | |
| | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | 3,237 | | | 2,914 | |
| | | | |
| Other assets | | | | |
| Regulatory assets | | 185 | | | 193 | |
| Other | | 3 | | | 3 | |
| Total other assets | | 188 | | | 196 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 3,670 | | | $ | 3,410 | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities and Equity | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | | | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | | 200 | | | — | |
| Short-term debt | | 60 | | | 47 | |
| Accounts payable | | 64 | | | 92 | |
| Accounts payable to affiliates | | 21 | | | 19 | |
| Dividends payable to parent | | 25 | | | 23 | |
| Regulatory liabilities | | 42 | | | 21 | |
| Taxes accrued | | 16 | | | 13 | |
| Accrued interest | | 13 | | | 12 | |
| Other | | 23 | | | 28 | |
| Total current liabilities | | 464 | | | 255 | |
| | | | |
| Deferred credits and other liabilities | | | | |
| Deferred income taxes | | 330 | | | 333 | |
| Deferred investment tax credits | | 5 | | | 5 | |
| Regulatory liabilities | | 407 | | | 383 | |
| Customer advances | | 25 | | | 23 | |
| Pension and employee benefit obligations | | 27 | | | 23 | |
| Other | | 35 | | | 43 | |
| Total deferred credits and other liabilities | | 829 | | | 810 | |
| | | | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | | |
| Capitalization | | | | |
| Long-term debt | | 1,011 | | | 1,086 | |
Common stock — 1,000,000 shares authorized of $100 par value; 933,000 shares outstanding at Dec. 31, 2023 and Dec. 31, 2022, respectively | | 93 | | | 93 | |
| Additional paid in capital | | 843 | | | 761 | |
| Retained earnings | | 430 | | | 405 | |
| Total common stockholder's equity | | 1,366 | | | 1,259 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | | $ | 3,670 | | | $ | 3,410 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NSP-WISCONSIN AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMMON STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY
(amounts in millions, except share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common Stock | | | | | | Total
Common
Stockholder’s
Equity |
| Shares | | Par Value | | Additional
Paid In
Capital | | Retained
Earnings | | |
| Balance at Dec. 31, 2020 | 933,000 | | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 605 | | | $ | 370 | | | | | $ | 1,068 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 108 | | | | | 108 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common dividends declared to parent | | | | | | | (110) | | | | | (110) | |
| Contribution of capital by parent | | | | | 37 | | | | | | | 37 | |
| Balance at Dec. 31, 2021 | 933,000 | | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 642 | | | $ | 368 | | | | | $ | 1,103 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 125 | | | | | 125 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common dividends declared to parent | | | | | | | (88) | | | | | (88) | |
| Contribution of capital by parent | | | | | 119 | | | | | | | 119 | |
| Balance at Dec. 31, 2022 | 933,000 | | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 761 | | | $ | 405 | | | | | $ | 1,259 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 136 | | | | | 136 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common dividends declared to parent | | | | | | | (111) | | | | | (111) | |
| Contribution of capital by parent | | | | | 82 | | | | | | | 82 | |
| Balance at Dec. 31, 2023 | 933,000 | | | $ | 93 | | | $ | 843 | | | $ | 430 | | | | | $ | 1,366 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NORTHERN STATES POWER COMPANY - WISCONSIN
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | |
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
General — NSP-Wisconsin is engaged in the regulated generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electricity and the regulated purchase, transportation, distribution and sale of natural gas.
NSP-Wisconsin’s consolidated financial statements include its wholly-owned subsidiaries and VIEs for which it is the primary beneficiary. In the consolidation process, all intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated. NSP-Wisconsin has investments in certain transmission facilities jointly owned with nonaffiliated utilities.
NSP-Wisconsin’s proportionate share of jointly owned facilities is recorded as property, plant and equipment on the consolidated balance sheets and NSP-Wisconsin’s proportionate share of operating costs associated with these facilities is included in its consolidated statements of income.
NSP-Wisconsin’s consolidated financial statements are presented in accordance with GAAP. All of NSP-Wisconsin’s underlying accounting records also conform to the FERC uniform system of accounts or to systems required by various state regulatory commissions. Certain amounts in the consolidated financial statements or notes have been reclassified for comparative purposes; however, such reclassifications did not affect net income, total assets, liabilities, equity or cash flows.
NSP-Wisconsin has evaluated events occurring after Dec. 31, 2023 up to the date of issuance of these consolidated financial statements. These statements contain all necessary adjustments and disclosures resulting from that evaluation.
Use of Estimates — NSP-Wisconsin uses estimates based on the best information available to record transactions and balances resulting from business operations.
Estimates are used for items such as plant depreciable lives or potential disallowances, AROs, certain regulatory assets and liabilities, tax provisions, uncollectible amounts, environmental costs, unbilled revenues, jurisdictional fuel and energy cost allocations and actuarially determined benefit costs. Recorded estimates are revised when better information becomes available or actual amounts can be determined. Revisions can affect operating results.
Regulatory Accounting — NSP-Wisconsin accounts for income and expense items in accordance with accounting guidance for regulated operations. Under this guidance:
•Certain costs, which would otherwise be charged to expense or other comprehensive income, are deferred as regulatory assets based on the expected ability to recover the costs in future rates.
•Certain credits, which would otherwise be reflected as income or other comprehensive income, are deferred as regulatory liabilities based on the expectation the amounts will be returned to customers in future rates or because the amounts were collected in rates prior to the costs being incurred.
Estimates and assumptions for recovery of deferred costs and refund of deferred credits are based on specific ratemaking decisions, precedent or other available information. Regulatory assets and liabilities are amortized consistent with the treatment in the rate setting process.
If changes in the regulatory environment occur, NSP-Wisconsin may no longer be eligible to apply this accounting treatment and may be required to eliminate regulatory assets and liabilities. Such changes could have a material effect on NSP-Wisconsin’s results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
See Note 4 for further information.
Income Taxes — NSP-Wisconsin accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method, which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the consolidated financial statements. Income taxes are deferred for all temporary differences between pretax financial and taxable income and between the book and tax bases of assets and liabilities utilizing rates that are scheduled to be in effect when the temporary differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in the period that includes the enactment date.
Utility rate regulation has resulted in the recognition of regulatory assets and liabilities related to income taxes. The effects of NSP-Wisconsin’s tax rate changes are generally subject to a normalization method of accounting. Therefore, the revaluation of most of its net deferred taxes upon a tax rate reduction results in the establishment of a net regulatory liability, refundable to utility customers over the remaining life of the related assets. NSP-Wisconsin anticipates that a tax rate increase would predominantly result in the establishment of a regulatory asset, subject to an evaluation of whether future recovery is expected.
Reversal of certain temporary differences are accounted for as current income tax expense due to the effects of past regulatory practices when deferred taxes were not required to be recorded due to the use of flow through accounting for ratemaking purposes.
Tax credits are recorded when earned unless there is a requirement to defer the benefit and amortize over the book depreciable lives of related property. The requirement to defer and amortize these credits specifically applies to certain federal ITCs, as determined by tax regulations and NSP-Wisconsin tax elections. For tax credits otherwise eligible to be recognized when earned, NSP-Wisconsin considers the impact of rate regulation to determine if these credits and related adjustments should be deferred as regulatory assets or liabilities.
Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax asset will not be realized.
NSP-Wisconsin measures and discloses uncertain tax positions that it has taken or expects to take in its income tax returns. A tax position is recognized in the consolidated financial statements when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination based on the technical merits of the position. Recognition of changes in uncertain tax positions are reflected as a component of income tax expense.
Interest and penalties related to income taxes are reported within Other income (expense), net or interest charges in the consolidated statements of income.
Xcel Energy Inc. and its subsidiaries, including NSP-Wisconsin file consolidated federal income tax returns as well as consolidated or separate state income tax returns. Federal income taxes paid by Xcel Energy Inc. are allocated to its subsidiaries based on separate company computations. A similar allocation is made for state income taxes paid by Xcel Energy Inc. in connection with consolidated state filings. Xcel Energy Inc. also allocates its own income tax benefits to its direct subsidiaries.
See Note 7 for further information.
Property, Plant and Equipment and Depreciation in Regulated Operations — Property, plant and equipment is stated at original cost. The cost of plant includes direct labor and materials, contracted work, overhead costs and AFUDC. The cost of plant retired is charged to accumulated depreciation and amortization. Amounts recovered in rates for future removal costs are recorded as regulatory liabilities. Significant additions or improvements extending asset lives are capitalized, while repairs and maintenance costs and replacement of items determined to be less than a unit of property are charged to expense as incurred.
Property, plant and equipment is tested for impairment when it is determined that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. A loss is recognized in the current period if it becomes probable that part of a cost of a plant under construction or recently completed plant will be disallowed for recovery from customers and a reasonable estimate of the disallowance can be made. For investments in property, plant and equipment that are abandoned and not expected to go into service, incurred costs and related deferred tax amounts are compared to the discounted estimated future rate recovery, and a loss is recognized, if necessary.
Depreciation expense is recorded using the straight-line method over the plant’s commission approved useful life. Actuarial life studies are performed and submitted to the state and federal commissions for review. Upon acceptance by the various commissions, the resulting lives and net salvage rates are used to calculate depreciation. Plant removal costs are typically recognized at the amounts recovered in rates as authorized by the applicable regulator. Accumulated removal costs are reflected in the consolidated balance sheet as a regulatory liability. Depreciation expense, expressed as a percentage of average depreciable property, was approximately 3.6% in 2023, 2022 and 2021.
See Note 3 for further information.
AROs — NSP-Wisconsin records AROs as a liability in the period incurred (if fair value can be reasonably estimated), with the offsetting/associated costs capitalized as a long-lived asset. The liability is generally increased over time by applying the effective interest method of accretion and the capitalized costs are typically depreciated over the useful life of the long-lived asset. Changes resulting from revisions to timing or amounts of expected asset retirement cash flows are recognized as an increase or a decrease in the ARO.
See Note 10 for further information.
Benefit Plans and Other Postretirement Benefits — NSP-Wisconsin maintains pension and postretirement benefit plans for eligible employees. Recognizing the cost of providing benefits and measuring the projected benefit obligation of these plans requires management to make various assumptions and estimates.
Certain unrecognized actuarial gains and losses and unrecognized prior service costs or credits are deferred as regulatory assets and liabilities, rather than recorded as other comprehensive income, based on regulatory recovery mechanisms.
See Note 9 for further information.
Environmental Costs — Environmental costs are recorded when it is probable NSP-Wisconsin is liable for remediation costs and the amount can be reasonably estimated. Costs are deferred as a regulatory asset if it is probable the costs will be recovered from customers in future rates. Otherwise, the costs are expensed. For certain environmental costs related to facilities currently in use, such as for emission-control equipment, the cost is capitalized and depreciated over the life of the plant.
Estimated remediation costs are regularly adjusted as estimates are revised and remediation is performed. If other participating potentially responsible parties exist and acknowledge their potential involvement with a site, costs are estimated and recorded only for NSP-Wisconsin’s expected share of the cost.
Estimated future expenditures to restore sites are treated as a capitalized cost of plant retirement. The depreciation expense levels recoverable in rates include a provision for removal expenses. Removal costs recovered in rates before the related costs are incurred are classified as a regulatory liability.
See Note 10 for further information.
Revenue from Contracts with Customers — Performance obligations related to the sale of energy are satisfied as energy is delivered to customers. NSP-Wisconsin recognizes revenue that corresponds to the price of the energy delivered to the customer. The measurement of energy sales to customers is generally based on the reading of their meters, which occurs systematically throughout the month. At the end of each month, amounts of energy delivered to customers since the date of the last meter reading are estimated, and the corresponding unbilled revenue is recognized.
A separate financing component of collections from customers is not recognized as contract terms are short-term in nature. Revenues are net of any excise or sales taxes or fees.
NSP-Wisconsin has various rate-adjustment mechanisms that provide for the recovery of natural gas, electric fuel and purchased energy costs. Cost-adjustment tariffs may increase or decrease the level of revenue collected from customers and are revised periodically for differences between the total amount collected under the clauses and the costs incurred. When applicable, fuel cost over-recoveries (the excess of fuel revenue billed to customers over fuel costs incurred) are deferred as regulatory liabilities and under-recoveries (the excess of fuel costs incurred over fuel revenues billed to customers) are deferred as regulatory assets. NSP-Wisconsin must submit a forward looking fuel cost plan annually for approval by the PSCW. The rules also allow for deferral of any under-recovery or over-recovery of fuel costs in excess of a 2% annual tolerance band, for future rate recovery or refund, subject to PSCW approval.
Cash and Cash Equivalents — NSP-Wisconsin considers investments in instruments with a remaining maturity of three months or less at the time of purchase to be cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Bad Debts — Accounts receivable are stated at the actual billed amount net of an allowance for bad debts. NSP-Wisconsin establishes an allowance for uncollectible receivables based on a policy that reflects its expected exposure to the credit risk of customers.
As of Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, the allowance for bad debts was $9 million.
Inventory — Inventory is recorded at the lower of average cost or net realizable value and consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Inventories | | | | |
| Materials and supplies | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 8 | |
| Fuel | | 10 | | | 11 | |
| Natural gas | | 8 | | | 20 | |
| Total inventories | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 39 | |
Fair Value Measurements — NSP-Wisconsin presents cash equivalents, interest rate derivatives, rabbi trust assets, commodity derivatives, pension and postretirement plan assets at estimated fair values in its consolidated financial statements.
For interest rate derivatives, quoted prices based primarily on observable market interest rate curves are used to estimate fair value. For commodity derivatives, the most observable inputs available are generally used to determine the fair value of each contract. In the absence of a quoted price, quoted prices for similar contracts or internally prepared valuation models may be used to determine fair value.
For the pension and postretirement plan assets, published trading data and pricing models, generally using the most observable inputs available, are utilized to determine fair value for each security.
See Notes 8 and 9 for further information.
Derivative Instruments — NSP-Wisconsin uses derivative instruments in connection with its commodity trading activities, and to manage risk associated with changes in interest rates and utility commodity prices, including forward contracts, futures, swaps and options. Derivatives not qualifying for the normal purchases and normal sales exception are recorded on the consolidated balance sheets at fair value as derivative instruments. Classification of changes in fair value for those derivative instruments is dependent on the designation of a qualifying hedging relationship.
Changes in fair value of derivative instruments not designated in a qualifying hedging relationship are reflected in current earnings or as a regulatory asset or liability. Classification as a regulatory asset or liability is based on commission approved regulatory recovery mechanisms.
Gains or losses on commodity trading transactions are recorded as a component of electric operating revenues.
Normal Purchases and Normal Sales — NSP-Wisconsin enters into contracts for purchases and sales of commodities for use in its operations. At inception, contracts are evaluated to determine whether they contain a derivative, and if so, whether they may be exempted from derivative accounting if designated as normal purchases or normal sales.
See Note 8 for further information.
Other Utility Items
AFUDC — AFUDC represents the cost of capital used to finance utility construction activity and is computed by applying a composite financing rate to qualified CWIP. The amount of AFUDC capitalized as a utility construction cost is credited to other nonoperating income (for equity capital) and interest charges (for debt capital). AFUDC amounts capitalized are included in NSP-Wisconsin’s rate base.
Alternative Revenue — Certain rate rider mechanisms qualify as alternative revenue programs. These mechanisms arise from instances in which the regulator authorizes a future surcharge in response to past activities or completed events. When certain criteria are met, including expected collection within 24 months, revenue is recognized, which may include incentives and return on rate base items.
The mechanisms are revised periodically for differences between total amount collected and the revenue earned, which may increase or decrease the level of revenue collected from customers. Alternative revenues arising from these programs are presented on a gross basis and disclosed separately from revenue from contracts with customers.
See Note 6 for further information.
Conservation Programs — NSP-Wisconsin participates in and funds conservation programs in its retail jurisdictions to assist customers in conserving energy and reducing peak demand on the electric and natural gas systems. NSP-Wisconsin recovers approved conservation program costs in base rate revenue.
For operations in the state of Wisconsin, NSP-Wisconsin is required to contribute 1.2% of its three-year average annual operating revenues to the statewide energy efficiency and renewable resource program Focus on Energy. Funding is collected through base rates, and there is no financial incentive provided to the utility. The PSCW has oversight of Focus on Energy including auditing and verification of programs. The program portfolio is outsourced to a third-party administrator who subcontracts as necessary to implement programs.
Emissions Allowances — Emissions allowances are recorded at cost, including broker commission fees. The inventory accounting model is utilized for all emissions allowances and any sales of these allowances are included in electric revenues.
RECs — Cost of RECs that are utilized for compliance is recorded as electric fuel and purchased power expense. An inventory accounting model is used to account for RECs.
| | |
2. Accounting Pronouncements |
Recently IssuedSegment Reporting — In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07 – Segment Reporting (Topic 280) – Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which extends the existing requirements for annual disclosures to quarterly periods, and requires that both annual and quarterly disclosures present segment expenses using line items consistent with information regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker. The ASU is effective for annual periods beginning after Dec. 15, 2023 and quarterly periods beginning after Dec. 15, 2024, and NSP-Wisconsin does not expect implementation of the new disclosure guidance to have a material impact to its consolidated financial statements.
Income Taxes — In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09 – Income Taxes (Topic 740) – Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, with new disclosure requirements including presentation of prescribed line items in the effective tax rate reconciliation and disclosures regarding state and local tax payments. The ASU is effective for annual periods beginning after Dec. 15, 2024, and NSP-Wisconsin does not expect implementation of the new disclosure guidance to have a material impact to its consolidated financial statements.
| | |
3. Property, Plant, and Equipment |
Major classes of property, plant and equipment
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | | | |
| Electric plant | | $ | 3,845 | | | $ | 3,579 | |
| Natural gas plant | | 502 | | | 465 | |
| Common and other property | | 278 | | | 260 | |
| CWIP | | 252 | | | 174 | |
| Total property, plant and equipment | | 4,877 | | | 4,478 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation | | (1,640) | | | (1,564) | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | $ | 3,237 | | | $ | 2,914 | |
Joint Ownership of Transmission Facilities
Jointly owned assets as of Dec. 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars, Except Percent Owned) | | Plant in Service | | Accumulated Depreciation | | | | Percent Owned |
| Electric transmission: | | | | | | | | |
| La Crosse, WI to Madison, WI | | $ | 178 | | | $ | 25 | | | | | 37 | % |
| CapX2020 | | 169 | | | 39 | | | | | 80 | |
Total (a) | | $ | 347 | | | $ | 64 | | | | | |
(a)Projects additionally include $1 million in CWIP.
NSP-Wisconsin’s share of operating expenses and construction expenditures is included in the applicable utility accounts. Respective owners are responsible for providing their own financing.
| | |
4. Regulatory Assets and Liabilities |
Regulatory assets and liabilities are created for amounts that regulators may allow to be collected or may require to be paid back to customers in future electric and natural gas rates. NSP-Wisconsin would be required to recognize the write-off of regulatory assets and liabilities in net income or other comprehensive income if changes in the utility industry no longer allow for the application of regulatory accounting guidance under GAAP.
Components of regulatory assets:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | See Note(s) | | Remaining Amortization Period | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Regulatory Assets | | | | | | Current | | Noncurrent | | Current | | Noncurrent |
| Pension and retiree medical obligations | | 9 | | Various | | 2 | | | 62 | | | 2 | | | 61 | |
| Environmental remediation costs | | 1, 10 | | Various | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 63 | |
| Recoverable deferred taxes on AFUDC | | | | Plant lives | | — | | | 26 | | | — | | | 20 | |
| State commission adjustments | | | | Plant lives | | 1 | | | 22 | | | 1 | | | 22 | |
Net AROs (a) | | 1, 10 | | Various | | — | | | 21 | | | — | | | 18 | |
| Deferred natural gas and electric energy/fuel costs | | 7 | | Less than one year | | 1 | | | — | | | 23 | | | — | |
| Other | | | | Various | | 7 | | | 6 | | | 5 | | | 9 | |
| Total regulatory assets | | | | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 185 | | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 193 | |
(a)Includes amounts recorded for future recovery of AROs, less amounts recovered through NSP-Wisconsin’s share of nuclear decommissioning accruals and gains from decommissioning investments.
Components of regulatory liabilities:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | See Note(s) | | Remaining Amortization Period | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Regulatory Liabilities | | | | | | Current | | Noncurrent | | Current | | Noncurrent |
| Plant removal costs | | 1, 10 | | Various | | $ | — | | | $ | 251 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 223 | |
Deferred income tax adjustments and TCJA refunds (a) | | 7 | | Various | | — | | | 140 | | | — | | | 144 | |
| DOE Settlement | | | | One to two years | | 4 | | | 6 | | | 12 | | | 3 | |
| Deferred natural gas and electric energy/fuel costs | | | | Less than one year | | 28 | | | — | | | 5 | | | — | |
| Other | | | | Various | | 10 | | | 10 | | | 4 | | | 13 | |
| Total regulatory liabilities | | | | | | $ | 42 | | | $ | 407 | | | $ | 21 | | | $ | 383 | |
(a)Includes the revaluation of recoverable/regulated plant accumulated deferred income taxes and revaluation impact of non-plant accumulated deferred income taxes due to the TCJA.
NSP-Wisconsin’s regulatory assets not earning a return include the unfunded portion of pension and retiree medical obligations and net AROs (i.e. deferrals for where cash has not been disbursed). At Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no regulatory assets of past expenditures that were not eligible to earn a return.
| | |
5. Borrowings and Other Financing Instruments |
Short Term Borrowings
NSP-Wisconsin meets its short-term liquidity requirements primarily through the issuance of commercial paper and borrowings under its credit facility and the money pool.
Money Pool — Xcel Energy Inc. and its utility subsidiaries have established a money pool arrangement that allows for short-term investments in and borrowings between the utility subsidiaries. Xcel Energy Inc. may make investments in the utility subsidiaries at market-based interest rates; however, the money pool arrangement does not allow the utility subsidiaries to make investments in Xcel Energy Inc.
Money pool borrowings:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars, Except Interest Rates) | | Three Months Ended Dec. 31, 2023 | | Year Ended |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Borrowing limit | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | |
| Amount outstanding at period end | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Average amount outstanding | | 7 | | | 6 | | | 25 | | | 16 | |
| Maximum amount outstanding | | 43 | | | 43 | | | 81 | | | 78 | |
| Weighted average interest rate, computed on a daily basis | | 5.34 | % | | 4.98 | % | | 1.10 | % | | 0.05 | % |
| Weighted average interest rate at period end | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A |
Commercial Paper — Commercial paper outstanding:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars, Except Interest Rates) | | Three Months Ended Dec. 31, 2023 | | Year Ended Dec. 31 |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Borrowing limit | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 150 | |
| Amount outstanding at period end | | 60 | | | 60 | | | 47 | | | 83 | |
| Average amount outstanding | | 10 | | | 15 | | | 18 | | | 3 | |
| Maximum amount outstanding | | 74 | | | 93 | | | 123 | | | 83 | |
| Weighted average interest rate, computed on a daily basis | | 5.48 | % | | 4.85 | % | | 1.03 | % | | 0.18 | % |
| Weighted average interest rate at end of period | | 5.50 | | | 5.50 | | | 4.55 | | | 0.21 | |
Letters of Credit — NSP-Wisconsin may use letters of credit, typically with terms of one year, to provide financial guarantees for certain operating obligations. At Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, there were immaterial letters of credit outstanding.
Credit Facility — In order to use commercial paper programs to fulfill short-term funding needs, NSP-Wisconsin must have revolving credit facilities in place at least equal to the amount of their respective commercial paper borrowing limits and cannot issue commercial paper exceeding available capacity under these credit facilities.
The lines of credit provide short-term financing in the form of notes payable to banks, letters of credit and back-up support for commercial paper borrowings.
Features of the credit facility:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt-to-Total Capitalization Ratio (a) | | Amount Facility May Be Increased (millions of dollars) | | Additional Periods for Which a One-Year Extension May Be Requested (b) |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | | | |
| 48.2 | % | | 47.4 | % | | N/A | | 1 | |
(a)The credit facility has a financial covenant requiring that the debt-to-total capitalization ratio be less than or equal to 65%.
(b)All extension requests are subject to majority bank group approval.
The credit facility has a cross-default provision that NSP-Wisconsin would be in default on borrowings under the facility if NSP-Wisconsin or any of its subsidiaries, whose total assets exceed 15% of NSP-Wisconsin’s consolidated total assets, default on certain indebtedness in an aggregate principal amount exceeding $75 million.
If NSP-Wisconsin does not comply with the covenant, an event of default may be declared, and if not remedied, any outstanding amounts due under the facility can be declared due by the lender. As of Dec. 31, 2023, NSP-Wisconsin was in compliance with all financial covenants.
NSP-Wisconsin had the following committed credit facility available as of Dec. 31, 2023 (in millions of dollars):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Credit Facility (a) | | Drawn (b) | | Available |
| $ | 150 | | | $ | 60 | | | $ | 90 | |
(a)This credit facility matures in September 2027.
(b)Includes outstanding commercial paper.
All credit facility bank borrowings, outstanding letters of credit and outstanding commercial paper reduce the available capacity under the credit facility. NSP-Wisconsin had no direct advances on the facility outstanding at Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Other Short-Term Borrowings — Clearwater Investments, Inc., a NSP-Wisconsin subsidiary, had an immaterial note payable to Xcel Energy Inc. at Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Long-Term Borrowings and Other Financing Instruments
Generally, the property of NSP-Wisconsin is subject to the lien of its first mortgage indenture for the benefit of bondholders. Debt premiums, discounts and expenses are amortized over the life of the related debt. The premiums, discounts and expenses for refinanced debt are deferred and amortized over the life of new issuance.
Long-term debt obligations for NSP-Wisconsin as of Dec. 31 (in millions of dollars): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing Instrument | | Interest Rate | | Maturity Date | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| First mortgage bonds | | 3.30 | % | | June 15, 2024 | | $ | 100 | | | $ | 100 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 3.30 | | | June 15, 2024 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 6.375 | | | Sept. 1, 2038 | | 200 | | | 200 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 3.70 | | | Oct. 1, 2042 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 3.75 | | | Dec. 1, 2047 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 4.20 | | | Sept. 1, 2048 | | 200 | | | 200 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 3.05 | | | May 1, 2051 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
| First mortgage bonds | | 2.82 | | | May 1, 2051 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
First mortgage bonds (a) | | 4.86 | | | Sept. 15, 2052 | | 100 | | | 100 | |
First mortgage bonds (b) | | 5.30 | | | June 15, 2053 | | 125 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Unamortized discount | | | | | | (3) | | | (3) | |
| Unamortized debt issuance cost | | | | | | (11) | | | (11) | |
| Current maturities | | | | | | (200) | | | — | |
| Total long-term debt | | | | | | $ | 1,011 | | | $ | 1,086 | |
(a)2022 financing.
(b)2023 financing.
Maturities of long-term debt:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | |
| 2024 | | $ | 200 | |
| 2025 | | — | |
| 2026 | | — | |
| 2027 | | — | |
| 2028 | | — | |
Deferred Financing Costs — Deferred financing costs of approximately $11 million, net of amortization, are presented as a deduction from the carrying amount of long-term debt at both Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022.
Dividend Restrictions — NSP-Wisconsin’s dividends are subject to the FERC’s jurisdiction, which prohibits the payment of dividends out of capital accounts. Dividends are solely to be paid from retained earnings.
NSP-Wisconsin’s state regulatory commission additionally imposes dividend limitations, which are more restrictive than those imposed by the FERC.
Requirements and actuals as of Dec. 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity to Total Capitalization Ratio Required Range (a) | | Equity to Total Capitalization Ratio Actual |
| Low | | High | | 2023 |
| 52.5 | % | | N/A | | 52.7 | % |
(a)NSP-Wisconsin cannot pay annual dividends in excess of forecasted levels if its average equity-to-total capitalization ratio falls below the commission authorized level.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Unrestricted Retained Earnings | | Total Capitalization | | Limit on Total Capitalization |
| $ | 9 | million | | $ | 2,520 | million | | N/A |
.
Revenue is classified by the type of goods/services rendered and market/customer type. NSP-Wisconsin’s operating revenues consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended Dec. 31, 2023 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Electric | | Natural Gas | | All Other | | Total |
| Major revenue types | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers: |
| Residential | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 84 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 383 | |
| C&I | | 494 | | | 65 | | | — | | | 559 | |
| Other | | 7 | | | — | | | 1 | | | 8 | |
| Total retail | | 800 | | | 149 | | | 1 | | | 950 | |
| Interchange | | 204 | | | — | | | — | | | 204 | |
| Other | | 3 | | | 5 | | | — | | | 8 | |
| Total revenue from contracts with customers | | 1,007 | | | 154 | | | 1 | | | 1,162 | |
| Alternative revenue and other | | 12 | | | 3 | | | — | | | 15 | |
| Total revenues | | $ | 1,019 | | | $ | 157 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1,177 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended Dec. 31, 2022 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Electric | | Natural Gas | | All Other | | Total |
| Major revenue types | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers: |
| Residential | | $ | 293 | | | $ | 103 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 396 | |
| C&I | | 485 | | | 87 | | | — | | | 572 | |
| Other | | 7 | | | — | | | — | | | 7 | |
| Total retail | | 785 | | | 190 | | | — | | | 975 | |
| Interchange | | 202 | | | — | | | — | | | 202 | |
| Other | | 4 | | | 4 | | | — | | | 8 | |
| Total revenue from contracts with customers | | 991 | | | 194 | | | — | | | 1,185 | |
| Alternative revenue and other | | 11 | | | 4 | | | 1 | | | 16 | |
| Total revenues | | $ | 1,002 | | | $ | 198 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended Dec. 31, 2021 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Electric | | Natural Gas | | All Other | | Total |
| Major revenue types | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue from contracts with customers: |
| Residential | | $ | 272 | | | $ | 91 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 363 | |
| C&I | | 441 | | | 85 | | | — | | | 526 | |
| Other | | 8 | | | — | | | 1 | | | 9 | |
| Total retail | | 721 | | | 176 | | | 1 | | | 898 | |
| Interchange | | 189 | | | — | | | — | | | 189 | |
| Other | | — | | | 4 | | | — | | | 4 | |
| Total revenue from contracts with customers | | 910 | | | 180 | | | 1 | | | 1,091 | |
| Alternative revenue and other | | 12 | | | 2 | | | — | | | 14 | |
| Total revenues | | $ | 922 | | | $ | 182 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1,105 | |
Total income tax expense from operations differs from the amount computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate to income before income tax expense.
Effective income tax rate for years ended Dec. 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Federal statutory rate | | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % |
| State income tax on pretax income, net of federal tax effect | | 6.2 | | | 6.2 | | | 6.2 | |
| Decreases in tax from: | | | | | | |
Plant regulatory differences (a) | | (3.4) | | | (3.8) | | | (4.1) | |
| Other tax credits, net NOL & tax credit allowances | | (0.6) | | | (0.8) | | | (1.0) | |
| Other, net | | (0.5) | | | (0.7) | | | (0.4) | |
| Effective income tax rate | | 22.7 | % | | 21.9 | % | | 21.7 | % |
(a)Plant regulatory differences primarily relate to the credit of excess deferred taxes to customers through the average rate assumption method. Income tax benefits associated with the credit are offset by corresponding revenue reductions.
Components of income tax expense for years ended Dec. 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Current federal tax expense | | $ | 37 | | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 17 | |
| Current state tax expense | | 15 | | | 9 | | | 4 | |
| Deferred federal tax (benefit) expense | | (10) | | | (5) | | | 3 | |
| Deferred state tax (benefit) expense | | (3) | | | 3 | | | 6 | |
| Deferred change in unrecognized tax expense | | 1 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total income tax expense | | $ | 40 | | | $ | 35 | | | $ | 30 | |
Components of deferred income tax expense as of Dec. 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Deferred tax (benefit) expense excluding items below | | $ | (3) | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 18 | |
| Amortization and adjustments to deferred income taxes on income tax regulatory assets and liabilities | | (10) | | | (10) | | | (10) | |
| Other | | 1 | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Deferred tax (benefit) expense | | $ | (12) | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | 9 | |
Components of the net deferred tax liability as of Dec. 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 (a) |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
| Difference between book and tax bases of property | | $ | 350 | | | $ | 343 | |
| Regulatory assets | | 22 | | | 24 | |
| Pension expense | | 10 | | | 10 | |
| Deferred fuel costs | | — | | | 6 | |
| Other | | 7 | | | 8 | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | | $ | 389 | | | $ | 391 | |
| | | | |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | |
| Regulatory liabilities | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 35 | |
| Rate refund | | 10 | | | 3 | |
| Environmental remediation | | 4 | | | 4 | |
| Other employee benefits | | 4 | | | 3 | |
| Tax credit carryforward | | 3 | | | 7 | |
| Deferred ITCs | | 2 | | | 2 | |
| Other | | 4 | | | 4 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | | $ | 59 | | | $ | 58 | |
| Net deferred tax liability | | $ | 330 | | | $ | 333 | |
(a)Prior periods have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
Other Income Tax Matters — NOL amounts represent the tax loss that is carried forward and tax credits represent the deferred tax asset. NOL and tax credit carryforwards as of Dec. 31 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Federal tax credit carryforwards | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 7 | |
| State NOL carryforward | | 2 | | | 2 | |
Federal carryforward periods expire between 2037 and 2043 and state carryforward periods expire in 2031.
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
Federal Audit — NSP-Wisconsin is a member of the Xcel Energy affiliated group that files a consolidated federal income tax return. Statute of limitations applicable to Xcel Energy’s consolidated federal income tax returns expire as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Tax Year(s) | | Expiration |
| 2014 - 2016 | | March 2025 |
| 2020 | | September 2024 |
Additionally, the statute of limitations related to certain federal tax credit carryforwards will remain open until those credits are utilized in subsequent returns. Further, the statute of limitations related to the additional federal tax loss carryback claim filed in 2020 has been extended. As of Dec. 31, 2023 the IRS issued its Revenue Agent’s Report related to the federal tax loss carryback claim. The Company materially agrees with the report and re-recognized the related benefit in Dec. 2023.
State Audits — NSP-Wisconsin is a member of the Xcel Energy affiliated group that files consolidated state income tax returns. As of Dec. 31, 2023, NSP-Wisconsin’s earliest open tax years that are subject to examination by state taxing authorities under applicable statutes of limitations are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| State | | Tax Year(s) | | Expiration |
| Wisconsin | | 2016-2018 | | May 2024 |
| Wisconsin | | 2019 | | October 2024 |
In 2021, Wisconsin began an audit of tax years 2016-2019. As of Dec. 31, 2023 no material adjustments have been proposed.
Unrecognized tax benefit balance includes permanent tax positions, which if recognized would affect the ETR. In addition, the unrecognized tax benefit balance includes temporary tax positions for which deductibility is highly certain, but for which there is uncertainty about the timing. A change in the timing of deductibility would not affect the ETR but would accelerate the payment to the taxing authority.
Unrecognized tax benefits — permanent vs. temporary:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Unrecognized tax benefit — Permanent tax positions | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 2 | |
| Unrecognized tax benefit — Temporary tax positions | | — | | | 1 | |
| Total unrecognized tax benefit | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 3 | |
Changes in unrecognized tax benefits:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance at Jan. 1 | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 2 | |
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | | — | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Balance at Dec. 31 | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 3 | |
Unrecognized tax benefits were reduced by tax benefits associated with NOL and tax credit carryforwards:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| NOL and tax credit carryforwards | | $ | (2) | | | $ | (2) | |
As IRS audits resume and state audits progress, it is reasonably possible that the amount of unrecognized tax benefit could decrease up to approximately $1 million in the next 12 months.
Payable for interest related to unrecognized tax benefits is partially offset by the interest benefit associated with NOL and tax credit carryforwards. Payables for interest related to unrecognized tax benefits at Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were not material. No amounts were accrued for penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as of Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 or 2021.
| | |
8. Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities |
Fair Value Measurements
Accounting guidance for fair value measurements and disclosures provides a hierarchical framework for disclosing the observability of the inputs utilized in measuring assets and liabilities at fair value.
•Level 1 — Quoted prices are available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reporting date. The types of assets and liabilities included in Level 1 are actively traded instruments with observable actual trading prices.
•Level 2 — Pricing inputs are other than actual trading prices in active markets, but are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date. The types of assets and liabilities included in Level 2 are typically either comparable to actively traded securities or contracts or priced with models using highly observable inputs.
•Level 3 — Significant inputs to pricing have little or no observability as of the reporting date. The types of assets and liabilities included in Level 3 include those valued with models requiring significant judgment or estimation.
Specific valuation methods include:
Commodity derivatives — Methods used to measure the fair value of commodity derivative forwards and options utilize forward prices and volatilities, as well as pricing adjustments for specific delivery locations, and are generally assigned a Level 2 classification. When contracts relate to inactive delivery locations or extend to periods beyond those readily observable on active exchanges, the significance of the use of less observable inputs on a valuation is evaluated, and may result in Level 3 classification.
Derivative Activities and Fair Value Measurements
NSP-Wisconsin enters into derivative instruments, including forward contracts, futures, swaps and options, to manage risk in connection with changes in utility commodity prices.
Commodity Derivatives — NSP-Wisconsin enters into derivative instruments to manage variability of future cash flows from changes in commodity prices in its electric and natural gas operations. This could include the purchase or sale of natural gas to generate electric energy and natural gas for resale.
As of Dec. 31, 2023, NSP-Wisconsin had no commodity contracts designated as cash flow hedges.
Consideration of Credit Risk and Concentrations — NSP-Wisconsin continuously monitors the creditworthiness of counterparties to its interest rate derivatives and commodity derivative contracts prior to settlement, and assesses each counterparty’s ability to perform on the transactions set forth in the contracts. Impact of credit risk was immaterial to the fair value of unsettled commodity derivatives presented on the consolidated balance sheets.
Recurring Derivative Fair Value Measurements
Changes in the fair value of natural gas commodity derivatives resulted in immaterial net losses and gains for the year ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, which were recognized as regulatory assets and liabilities. The classification as a regulatory asset or liability is based on a commission approved regulatory recovery mechanism.
During the years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, immaterial pre-tax losses were recognized during the period in income related to option premium amortization.
NSP-Wisconsin had immaterial outstanding derivative assets or liabilities measured at fair value as of Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022.
NSP-Wisconsin had no derivative instruments designated as fair value hedges during the years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Fair Value of Long-Term Debt
As of Dec. 31, other financial instruments for which the carrying amount did not equal fair value:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Carrying Amount | | Fair Value | | Carrying Amount | | Fair Value |
| Long-term debt, including current portion | | $ | 1,211 | | | $ | 1,117 | | | $ | 1,086 | | | $ | 980 | |
Fair value of NSP-Wisconsin’s long-term debt is estimated based on recent trades and observable spreads from benchmark interest rates for similar securities. Fair value estimates are based on information available to management as of Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, and given the observability of the inputs, fair values presented for long-term debt were assigned as Level 2.
| | |
9. Benefit Plans and Other Postretirement Benefits |
Pension and Postretirement Health Care Benefits
Xcel Energy, which includes NSP-Wisconsin, has several noncontributory, qualified, defined benefit pension plans that cover almost all employees. All newly hired or rehired employees participate under the Cash Balance formula, which is based on pay credits using a percentage of annual eligible pay and annual interest credits.
The average annual interest crediting rates for these plans was 4.67, 4.86 and 1.96 percent in 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
Some employees may participate under legacy formulas such as the traditional final average pay or pension equity. Xcel Energy’s policy is to fully fund into an external trust the actuarially determined pension costs subject to the limitations of applicable employee benefit and tax laws.
In addition to the qualified pension plans, Xcel Energy maintains a SERP and a nonqualified pension plan. The SERP is maintained for certain executives who participated in the plan in 2008, when the SERP was closed to new participants.
The nonqualified pension plan provides benefits for compensation that is in excess of the limits applicable to the qualified pension plans, with distributions funded by Xcel Energy’s consolidated operating cash flows.
Obligations of the SERP and nonqualified plan as of Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022 were $12 million and $11 million, respectively, of which the amounts attributable to NSP-Wisconsin were immaterial in both years. Xcel Energy recognized net benefit cost for the SERP and nonqualified plans of $2 million and $17 million in 2023 and 2022, respectively, of which amounts attributable to NSP-Wisconsin were immaterial.
Xcel Energy’s postretirement health care benefit plan is a continuation of certain welfare benefit programs for current employees. A full time employee’s date of hire or a retiree’s date of retirement determine eligibility for each of the programs.
Xcel Energy’s investment-return assumption considers the expected long-term performance for each of the asset classes in its pension and postretirement health care portfolio. Xcel Energy considers the historical returns achieved by its asset portfolios over long time periods, as well as the long-term projected return levels from investment experts. Xcel Energy and NSP-Wisconsin continually review their pension assumptions.
Pension cost determination assumes a forecasted mix of investment types over the long-term.
•Investment returns in 2023 were above the assumed level of 7.25%.
•Investment returns in 2022 were below the assumed level of 6.60%.
•Investment returns in 2021 were above the assumed level of 6.60%.
•In 2024, NSP-Wisconsin’s expected investment-return assumption is 7.25%.
Pension plan and postretirement benefit assets are invested in a portfolio according to Xcel Energy’s return, liquidity and diversification objectives to provide a source of funding for plan obligations and minimize contributions to the plan, within appropriate levels of risk.
The principal mechanism for achieving these objectives is the asset allocation given the long-term risk, return, correlation and liquidity characteristics of each particular asset class.
There were no significant concentrations of risk in any industry, index, or entity. Market volatility can impact even well-diversified portfolios and significantly affect the return levels achieved by the assets in any year.
Xcel Energy’s ongoing investment strategy is based on plan-specific investment recommendations that seek to minimize potential investment and interest rate risk as a plan’s funded status increases over time.
The investment recommendations consider many factors and generally result in a greater percentage of long-duration fixed income securities being allocated to specific plans having relatively higher funded status ratios and a greater percentage of growth assets being allocated to plans having relatively lower funded status ratios.
Plan Assets
For each of the fair value hierarchy levels, NSP-Wisconsin’s pension plan assets measured at fair value:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Dec. 31, 2023 (a) | | Dec. 31, 2022 (a) |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Measured at NAV | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Measured at NAV | | Total |
| Cash equivalents | | $ | 8 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 4 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4 | |
| Commingled funds | | 19 | | | — | | | — | | | 45 | | | 64 | | | 35 | | | — | | | — | | | 34 | | | 69 | |
| Debt securities | | — | | | 22 | | | — | | | — | | | 22 | | | — | | | 22 | | | — | | | — | | | 22 | |
| Equity securities | | 1 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 2 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 95 | | | $ | 41 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 34 | | | $ | 97 | |
(a)See Note 8 for further information on fair value measurement inputs and methods.
NSP-Wisconsin has immaterial postretirement benefit plan assets that were measured at fair value at Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022.
Immaterial assets were transferred in or out of Level 3 for 2023. No assets were transferred in or out of Level 3 for 2022.
Funded Status — Comparisons of the actuarially computed benefit obligation, changes in plan assets and funded status of the pension and postretirement health care plans for NSP-Wisconsin are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Change in Benefit Obligation: | | | | | | | | |
| Obligation at Jan. 1 | | $ | 112 | | | $ | 141 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 11 | |
| Service cost | | 4 | | | 5 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest cost | | 6 | | | 4 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Actuarial (gain) loss | | 1 | | | (21) | | | — | | | (3) | |
| Benefit payments | | (11) | | | (17) | | | (1) | | | (1) | |
| Obligation at Dec. 31 | | $ | 112 | | | $ | 112 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 8 | |
| Change in Fair Value of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at Jan. 1 | | $ | 97 | | | $ | 137 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Actual return on plan assets | | 5 | | | (24) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Employer contributions | | 4 | | | 1 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Benefit payments | | (11) | | | (17) | | | (1) | | | (1) | |
| Fair value of plan assets at Dec. 31 | | $ | 95 | | | $ | 97 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Funded status of plans at Dec. 31 | | $ | (17) | | | $ | (15) | | | $ | (8) | | | $ | (8) | |
| Amounts recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheet at Dec. 31: | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (1) | | | $ | — | |
| Noncurrent liabilities | | (17) | | | (15) | | | (7) | | | (8) | |
| Net amounts recognized | | $ | (17) | | | $ | (15) | | | $ | (8) | | | $ | (8) | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits |
| Significant Assumptions Used to Measure Benefit Obligations: | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate for year-end valuation | | 5.49 | % | | 5.80 | % | | 5.54 | % | | 5.80 | % |
| Expected average long-term increase in compensation level | | 4.25 | % | | 4.25 | % | | N/A | | N/A |
| Mortality table | | Pri-2012 | | Pri-2012 | | Pri-2012 | | Pri-2012 |
| Health care costs trend rate — initial: Pre-65 | | N/A | | N/A | | 6.50 | % | | 6.50 | % |
| Health care costs trend rate — initial: Post-65 | | N/A | | N/A | | 5.50 | % | | 5.50 | % |
| Ultimate trend assumption — initial: Pre-65 | | N/A | | N/A | | 4.50 | % | | 4.50 | % |
| Ultimate trend assumption — initial: Post-65 | | N/A | | N/A | | 4.50 | % | | 4.50 | % |
| Years until ultimate trend is reached | | N/A | | N/A | | 6 | | 7 |
Accumulated benefit obligation for the pension plan was $100 million and $101 million as of Dec. 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Net Periodic Benefit Cost (Credit) — Net periodic benefit cost (credit), other than the service cost component, is included in other expense in the consolidated statements of income.
Components of net periodic benefit cost (credit) and amounts recognized in other comprehensive income and regulatory assets and liabilities:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Service cost | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 5 | | | $ | 5 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Interest cost | | 6 | | | 4 | | | 4 | | | 1 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Expected return on plan assets | | (8) | | | (8) | | | (8) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of net loss | | 2 | | | 3 | | | 5 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Settlement charge (a) | | — | | | 6 | | | 5 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net periodic pension cost | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 11 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | |
| Effects of regulation | | — | | | (2) | | | (3) | | | — | | | | | — | |
| Net benefit cost recognized for financial reporting | | $ | 4 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | |
| Significant Assumptions Used to Measure Costs: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | | 5.80 | % | | 3.08 | % | | 2.71 | % | | 5.80 | % | | 3.09 | % | | 2.65 | % |
| Expected average long-term increase in compensation level | | 4.25 | | | 3.75 | | | 3.75 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Expected average long-term rate of return on assets | | 7.25 | | | 6.60 | | | 6.60 | | | 5.00 | | | 4.10 | | | 4.10 | |
(a)A settlement charge is required when the amount of all lump-sum distributions during the year is greater than the sum of the service and interest cost components of the annual net periodic pension cost. There were no settlement charges recorded to the qualified pension plans in 2023. In 2022, as a result of lump-sum distributions during the plan years, NSP-Wisconsin recorded a total pension settlement charge of $5 million, of which $1 million was recorded in the income statement.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Amounts Not Yet Recognized as Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost: | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 4 | |
| Prior service credit | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 4 | |
| Amounts Not Yet Recognized as Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost Have Been Recorded as Follows Based Upon Expected Recovery in Rates: | | | | | | | | |
| Current regulatory assets | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 1 | | | | | $ | — | |
| Noncurrent regulatory assets | | 46 | | | 44 | | | 3 | | | 4 | |
| Total | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 4 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Measurement date | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 | | Dec. 31, 2023 | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
Cash Flows — Funding requirements can be impacted by changes to actuarial assumptions, actual asset levels and other calculations prescribed by the requirements of income tax and other pension-related regulations. Required contributions were made in 2020-2023 to meet minimum funding requirements.
Total voluntary and required pension funding contributions across all four of Xcel Energy’s pension plans were as follows:
•$100 million in January 2024, of which $7 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$50 million in 2023, of which $4 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$50 million in 2022, of which $1 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$131 million in 2021, of which $5 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
The postretirement health care plans have no funding requirements other than fulfilling benefit payment obligations when claims are presented and approved. Additional cash funding requirements are prescribed by certain state and federal rate regulatory authorities.
Xcel Energy’s voluntary postretirement funding contributions were as follows:
•$11 million expected in 2024, of which $1 million is attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$11 million during 2023, of which an immaterial amount was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$13 million during 2022, of which $1 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
•$15 million during 2021, of which $2 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin.
Target asset allocations:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Long-duration fixed income and interest rate swap securities | | 38 | % | | 38 | % | | — | % | | — | % |
| Domestic and international equity securities | | 31 | | | 33 | | | 9 | | | 16 | |
| Alternative investments | | 20 | | | 18 | | | 13 | | | 12 | |
| Short-to-intermediate fixed income securities | | 9 | | | 9 | | | 77 | | | 71 | |
| Cash | | 2 | | | 2 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
| Total | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
The asset allocations above reflect target allocations approved in the calendar year to take effect in the subsequent year.
Plan Amendments — In 2023, Xcel Energy amended the Xcel Energy Pension Plan and Xcel Energy Inc. Nonbargaining Pension Plan (South) to reduce supplemental social security benefits for all active participants on and after Jan. 1, 2024.
In 2022, there were no significant plan amendments made which affected the postretirement benefit obligation.
In 2021, Xcel Energy amended the Xcel Energy Pension Plan and Xcel Energy Inc. Nonbargaining Pension Plan (South) to reduce supplemental benefits for non-bargaining participants as well as to allow the transfer of a portion of non-qualified pension obligations into the qualified plans.
Projected Benefit Payments
NSP-Wisconsin’s projected benefit payments:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Projected
Pension Benefit
Payments | | Net Projected Postretirement Health Care Benefit Payments (a) | | | | |
| 2024 | | $ | 17 | | | $ | 1 | | | | | |
| 2025 | | 8 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| 2026 | | 8 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| 2027 | | 9 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| 2028 | | 10 | | | 1 | | | | | |
| 2029-2033 | | 51 | | | 3 | | | | | |
(a)Amount is reported net of expected Medicare Part D subsidies, which are immaterial.
Voluntary Retirement Program
Incremental to amounts presented above for postretirement benefits, Xcel Energy, which includes NSP-Wisconsin, recognized new post employment costs and obligations in the fourth quarter of 2023 for employees accepted to a voluntary retirement program.
Utilizing employee information and the following inputs, the estimated NSP-Wisconsin obligations for the program of $2 million for health plan subsidies and an immaterial amount for other medical benefits, each commencing in 2024, were recognized in the fourth quarter of 2023. These unfunded obligations are presented in other current liabilities and noncurrent pension and employee benefit obligations in the consolidated balance sheet as of Dec. 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| Significant Assumptions to Measure Benefit Obligations: | | 2023 |
| Discount rate for year-end valuation | | 5.50 | % |
| Mortality table | | PRI-2012 |
| Health care costs trend rate and ultimate trend assumption | | 7.00 | % |
Defined Contribution Plans
Xcel Energy, which includes NSP-Wisconsin, maintains 401(k) and other defined contribution plans that cover most employees. The expense to these plans for NSP-Wisconsin was approximately $2 million in 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Multiemployer Plans
NSP-Wisconsin contributes to several union multiemployer pension plans, none of which are individually significant. These plans provide pension benefits to certain union employees who may perform services for multiple employers and do not participate in the NSP-Wisconsin sponsored pension plans. Contributing to these types of plans creates risk that differs from providing benefits under NSP-Wisconsin sponsored plans, in that if another participating employer ceases to contribute to a multiemployer pension plan, additional unfunded obligations may need to be funded over time by remaining participating employers.
| | |
10. Commitments and Contingencies |
Legal
NSP-Wisconsin is involved in various litigation matters in the ordinary course of business. The assessment of whether a loss is probable or is a reasonable possibility, and whether the loss or a range of loss is estimable, often involves a series of complex judgments about future events. Management maintains accruals for losses probable of being incurred and subject to reasonable estimation.
Management is sometimes unable to estimate an amount or range of a reasonably possible loss in certain situations, including but not limited to when (1) the damages sought are indeterminate, (2) the proceedings are in the early stages, or (3) the matters involve novel or unsettled legal theories.
In such cases, there is considerable uncertainty regarding the timing or ultimate resolution, including a possible eventual loss. For current proceedings not specifically reported herein, management does not anticipate that the ultimate liabilities, if any, would have a material effect on NSP-Wisconsin’s consolidated financial statements. Legal fees are generally expensed as incurred.
Gas Trading Litigation — e prime is a wholly owned subsidiary of Xcel Energy. e prime was in the business of natural gas trading and marketing but has not engaged in natural gas trading or marketing activities since 2003. Multiple lawsuits involving multiple plaintiffs seeking monetary damages were commenced against e prime and its affiliates, including Xcel Energy, between 2003 and 2009 alleging fraud and anticompetitive activities in conspiring to restrain the trade of natural gas and manipulate natural gas prices. Cases were all consolidated in the U.S. District Court in Nevada.
One case remains active which includes a multi-district litigation matter consisting of a Wisconsin purported class (Arandell Corp.). The Court issued a ruling in June 2022 granting plaintiffs’ class certification. In April 2023, the Seventh Circuit Court of Appeals heard the defendants’ appeal challenging whether the district court properly assessed class certification. A decision relating to class certification is expected imminently. Xcel Energy considers the reasonably possible loss associated with this litigation to be immaterial
Rate Matters
NSP-Wisconsin is involved in various regulatory proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business. Until resolution, typically in the form of a rate order, uncertainties may exist regarding the ultimate rate treatment for certain activities and transactions. Amounts have been recognized for probable and reasonably estimable losses that may result. Unless otherwise disclosed, any reasonably possible range of loss in excess of any recognized amount is not expected to have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
MISO ROE Complaints — In November 2013 and February 2015, customer groups filed two ROE complaints against MISO TOs, which includes NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin. The first complaint requested a reduction in base ROE transmission formula rates from 12.38% to 9.15% for the time period of Nov. 12, 2013 to Feb. 11, 2015, and removal of ROE adders (including those for RTO membership). The second complaint requested, for a subsequent time period, a base ROE reduction from 12.38% to 8.67%.
The FERC subsequently issued various related orders related to ROE methodology/calculations and timing. NSP-Minnesota has processed refunds to customers for applicable complaint periods based on the ROE in the most recent applicable opinions.
The MISO TOs and various other parties have filed petitions for review of the FERC’s most recent applicable opinions at the D.C. Circuit. In August 2022, the D.C. Circuit ruled that FERC had not adequately supported its conclusions, vacated FERC’s related orders and remanded the issue back to FERC for further proceedings, which remain pending. Additional exposure, if any related to this matter is expected to be immaterial.
Environmental
New and changing federal and state environmental mandates can create financial liabilities for NSP-Wisconsin, which are normally recovered through the regulated rate process.
Site Remediation
Various federal and state environmental laws impose liability where hazardous substances or other regulated materials have been released to the environment. NSP-Wisconsin may sometimes pay all or a portion of the cost to remediate sites where past activities of NSP-Wisconsin’s predecessors or other parties have caused environmental contamination. Environmental contingencies could arise from various situations, including sites of former MGPs; and third-party sites, such as landfills, for which NSP-Wisconsin is alleged to have sent wastes to that site.
MGP, Landfill and Disposal Sites
NSP-Wisconsin is investigating, remediating or performing post-closure actions at one MGP, landfill or other disposal sites across its service territories.
NSP-Wisconsin has recognized approximately $13 million of costs/liabilities from final resolution of these issues, however, the outcome and timing are unknown. In addition, there may be insurance recovery and/or recovery from other potentially responsible parties, offsetting a portion of costs incurred.
Environmental Requirements — Water and Waste
Federal Clean Water Act Section 316(b) — The Federal Clean Water Act requires the EPA to regulate cooling water intake structures to assure they reflect the best technology available for minimizing impingement and entrainment of aquatic species. NSP-Wisconsin estimates capital expenditures of approximately $5 million may be required to comply with the requirements. NSP-Wisconsin believes two plants could be required to make improvements to reduce impingement and entrainment. NSP-Wisconsin anticipates these costs will be recoverable through regulatory mechanisms.
Environmental Requirements — Air
Clean Air Act NOx Allowance Allocations — In June 2023, the EPA published final regulations under the "Good Neighbor" provisions of the Clean Air Act. The final rule applies to generation facilities in Wisconsin, as well as other states outside of our service territory. The rule establishes an allowance trading program for NOx that will impact NSP-Wisconsin’s fossil fuel-fired electric generating facilities. Applicable facilities will have to secure additional allowances, install NOx controls and/or develop a strategy of operations that utilizes the existing allowance allocations. Guidelines are also established for allowance banking and emission limit backstops.
While the financial impacts of the final rule are uncertain and dependent on market forces and anticipated generation, NSP-Wisconsin anticipates the costs would be recoverable through regulatory mechanisms.
AROs — AROs have been recorded for NSP-Wisconsin’s assets.
NSP-Wisconsin’s AROs were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Jan. 1, 2023 | | Accretion | | Cash Flow Revisions (a) | | Dec. 31, 2023 |
| Electric | | | | | | | | |
| Steam, hydro and other production | | $ | 10 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (1) | | | $ | 9 | |
| Distribution | | 5 | | | — | | | — | | | 5 | |
| Natural gas | | | | | | | | |
| Distribution | | 13 | | | 1 | | | (6) | | | 8 | |
Total liability (b) | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | (7) | | | $ | 22 | |
(a)In 2023, AROs were revised for changes in timing and estimates of cash flows. Changes in gas distribution AROs were a result of updated mileage of gas lines and number of services, as well as changes to inflation and discount rate assumptions.
(b)Included in other long-term liabilities balance in the consolidated balance sheet.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2022 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Jan. 1, 2022 | | Accretion | | Cash Flow Revisions (a) | | Dec. 31, 2022 |
| Electric | | | | | | | | |
| Steam, hydro and other production | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 10 | |
| Distribution | | 5 | | | — | | | — | | | 5 | |
| Natural gas | | | | | | | | |
| Distribution | | 12 | | | — | | | 1 | | | 13 | |
Total liability (b) | | $ | 26 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 28 | |
(a)In 2022, AROs were revised for changes in timing and estimates of cash flows.
(b)Included in other long-term liabilities balance in the consolidated balance sheet.
Indeterminate AROs — Outside of the recorded asbestos AROs, other plants or buildings may contain asbestos due to the age of many of NSP-Wisconsin’s facilities, but no confirmation or measurement of the cost of removal could be determined as of Dec. 31, 2023. Therefore, an ARO has not been recorded for these facilities.
Joint Operating System
The electric production and transmission system of NSP-Wisconsin is managed as the NSP System. The electric production and transmission costs of the entire NSP System are shared by NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin. A FERC approved agreement between the two companies, called the Interchange Agreement, provides for the sharing of all costs of generation and transmission facilities of the system, including capital costs. Such costs include current and potential obligations of NSP-Minnesota related to its nuclear generating facilities.
NSP-Minnesota’s public liability for claims from any nuclear incident is limited to $16.2 billion under the Price-Anderson amendment to the Atomic Energy Act. NSP-Minnesota has secured $450 million of coverage for its public liability exposure with a pool of insurance companies. The remaining $15.8 billion of exposure is funded by the Secondary Financial Protection Program available from assessments by the federal government.
NSP-Minnesota is subject to assessments of up to $166 million per reactor-incident for each of its three reactors, for public liability arising from a nuclear incident at any licensed nuclear facility in the United States. The maximum funding requirement is $24.7 million per reactor-incident during any one year. Maximum assessments are subject to inflation adjustments by the NRC.
NSP-Minnesota purchases insurance for property damage and site decontamination cleanup costs from NEIL and EMANI. The coverage limits are $2.8 billion for each of NSP-Minnesota’s two nuclear plant sites. NEIL also provides business interruption insurance coverage up to $490 million and $420 million at Monticello and Prairie Island, respectively, including the cost of replacement power during prolonged accidental outages of nuclear generating units. Premiums are expensed over the policy term.
All companies insured with NEIL are subject to retroactive premium adjustments if losses exceed accumulated reserve funds. Capital has been accumulated in the reserve funds of NEIL and EMANI to the extent that NSP-Minnesota would have no exposure for retroactive premium assessments in case of a single incident under the business interruption and the property damage insurance coverage. NSP-Minnesota could be subject to annual maximum assessments of $15 million for business interruption insurance and $32 million for property damage insurance if losses exceed accumulated reserve funds.
Fuel Contracts
NSP-Wisconsin has entered into various long-term commitments for the purchase and delivery of a significant portion of its refuse-derived fuel/wood and natural gas requirements. These contracts expire between 2024 and 2033. NSP-Wisconsin is required to pay additional amounts depending on actual quantities shipped under these agreements.
As NSP-Wisconsin does not have an automatic electric fuel adjustment clause for Wisconsin retail customers, NSP-Wisconsin utilizes deferred accounting treatment for future rate recovery or refund when fuel costs differ from the amount included in rates by more than 2% on an annual basis, as determined by the PSCW after an opportunity for a hearing and an earnings test based on NSP-Wisconsin’s authorized ROE.
Estimated minimum purchases under these contracts as of Dec. 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | RDF/wood | | Natural gas
supply | | Natural gas
storage and
transportation |
| 2024 | | $ | 6 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 21 | |
| 2025 | | 1 | | | — | | | 19 | |
| 2026 | | 1 | | | — | | | 19 | |
| 2027 | | — | | | — | | | 13 | |
| 2028 | | 1 | | | — | | | 3 | |
| Thereafter | | 1 | | | — | | | 8 | |
Total (a) | | $ | 10 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 83 | |
(a)Excludes additional amounts allocated to NSP-Minnesota through intercompany charges.
Additional expenditures for fuel and natural gas storage and transportation will be required to meet expected future electric generation and natural gas needs.
NSP-Wisconsin evaluates performance based on profit or loss generated from the product or service provided. These segments are managed separately because the revenue streams are dependent upon regulated rate recovery, which is separately determined for each segment.
NSP-Wisconsin has the following reportable segments:
•Regulated Electric — The regulated electric utility segment generates, purchases, transmits, distributes and sells electricity in Michigan and Wisconsin.
•Regulated Natural Gas — The regulated natural gas utility segment purchases, transports, stores, distributes and sells natural gas in portions of Michigan and Wisconsin.
NSP-Wisconsin also presents All Other, which includes operating segments with revenues below the necessary quantitative thresholds. Those operating segments primarily include investments in rental housing projects that qualify for low-income housing tax credits.
Asset and capital expenditure information is not provided for NSP-Wisconsin’s reportable segments. As an integrated electric and natural gas utility, NSP-Wisconsin operates significant assets that are not dedicated to a specific business segment. Reporting assets and capital expenditures by business segment would require arbitrary and potentially misleading allocations, which may not necessarily reflect the assets that would be required for the operation of the business segments on a stand-alone basis.
Certain costs, such as common depreciation, common O&M expenses and interest expense are allocated based on cost causation allocators across each segment. In addition, a general allocator is used for certain general and administrative expenses, including office supplies, rent, property insurance and general advertising.
NSP-Wisconsin’s segment information:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Regulated Electric | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Total revenues (a) | | $ | 1,019 | | | $ | 1,002 | | | $ | 922 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 142 | | | 131 | | | 120 | |
| Interest charges and financing costs | | 45 | | | 38 | | | 36 | |
| Income tax expense | | 38 | | | 29 | | | 27 | |
| Net income | | 126 | | | 105 | | | 98 | |
| Regulated Natural Gas | | | | | | |
| Operating revenues — external | | $ | 157 | | | $ | 198 | | | $ | 182 | |
| Intersegment revenue | | 1 | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Total revenues | | $ | 158 | | | $ | 198 | | | $ | 183 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 28 | | | 27 | | | 27 | |
| Interest charges and financing costs | | 5 | | | 4 | | | 4 | |
| Income tax expense | | 2 | | | 6 | | | 2 | |
| Net income | | 9 | | | 17 | | | 7 | |
| All Other | | | | | | |
| Total revenues | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | 1 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Income tax expense | | — | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Net income | | 1 | | | 3 | | | 3 | |
| | | | | | |
| Consolidated Total | | | | | | |
Total revenues (a) | | $ | 1,178 | | | $ | 1,201 | | | $ | 1,106 | |
| Reconciling eliminations | | (1) | | | — | | | (1) | |
| Total operating revenues | | $ | 1,177 | | | $ | 1,201 | | | $ | 1,105 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 170 | | | 158 | | | 147 | |
| Interest charges and financing costs | | 50 | | | 42 | | | 40 | |
| Income tax expense | | 40 | | | 35 | | | 30 | |
| Net income | | 136 | | | 125 | | | 108 | |
(a)Operating revenues include $204 million, $202 million and $189 million of affiliate electric revenue for the years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. See Note 12 for further information.
| | |
12. Related Party Transactions |
Xcel Energy Services Inc. provides management, administrative and other services for the subsidiaries of Xcel Energy Inc., including NSP-Wisconsin. The services are provided and billed to each subsidiary in accordance with service agreements executed by each subsidiary. NSP-Wisconsin uses services provided by Xcel Energy Services Inc. whenever possible. Costs are charged directly to the subsidiary and are allocated if they cannot be directly assigned.
Xcel Energy, Inc., NSP-Minnesota, NSP-Wisconsin, PSCo and SPS have established a utility money pool arrangement.
The electric production and transmission costs of the entire NSP System are shared by NSP-Minnesota and NSP-Wisconsin. The Interchange Agreement provides for the sharing of all costs of generation and transmission facilities of the system, including capital costs.
Significant affiliate transactions among the companies and related parties including billings under the Interchange Agreement for the years ended Dec. 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Operating revenues: | | | | | | |
| Electric | | $ | 204 | | | $ | 202 | | | $ | 189 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
Purchased power (a) | | 424 | | | 445 | | | 408 | |
| Transmission expense | | 69 | | | 68 | | | 64 | |
| Natural gas purchased for resale | | 1 | | | — | | | 1 | |
| Other operating expenses — paid to Xcel Energy Services Inc. | | 119 | | | 114 | | | 99 | |
| Interest income | | 1 | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest expense | | 1 | | | 1 | | | — | |
(a)Amount includes $16 million deferred fuel cost regulatory asset for the year ended Dec. 31 2023, and an immaterial amount of fuel costs amortized or deferred for the years ended Dec. 31, 2022 and 2021.
Accounts receivable and payable with affiliates at Dec. 31 were:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | Accounts Receivable | | Accounts Payable | | Accounts Receivable | | Accounts Payable |
| NSP-Minnesota | | $ | — | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4 | |
| PSCo | | 1 | | | — | | | 2 | | | — | |
| Other subsidiaries of Xcel Energy Inc. | | 12 | | | 13 | | | 6 | | | 15 | |
| | $ | 13 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 19 | |
In 2023, Xcel Energy implemented workforce actions to align resources and investments with evolving business and customer needs, and streamline the organization for long-term success.
In September 2023, Xcel Energy announced a voluntary retirement program to a group of eligible non-bargaining employees, with an enhanced retirement package including certain health care and cash benefits for accepted employees. Approximately 400 employees retired under this program in December 2023.
In November 2023, Xcel Energy, Inc. also reduced its non-bargaining workforce by approximately 150 employees through an involuntary severance program.
In the fourth quarter of 2023, Xcel Energy recorded total expense of $72 million related to these workforce actions, of which $5 million was attributable to NSP-Wisconsin. Expenses relate to the estimated cost of future health plan subsidies and other medical benefits for the voluntary retirement program, as well as severance and other employee payouts and legal and other professional fees.
For further information on the estimated obligations for future health plan subsidies and other medical benefits, see Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements.
| | |
ITEM 9 — CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| | |
ITEM 9A — CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
NSP-Wisconsin maintains a set of disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms. In addition, the disclosure controls and procedures ensure that information required to be disclosed is accumulated and communicated to management, including the CEO and CFO, allowing timely decisions regarding required disclosure. As of Dec. 31, 2023, based on an evaluation carried out under the supervision and with the participation of NSP-Wisconsin’s management, including the CEO and CFO, of the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures, the CEO and CFO have concluded that NSP-Wisconsin’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
No changes in NSP-Wisconsin’s internal control over financial reporting occurred during the most recent fiscal quarter ended Dec. 31, 2023 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, NSP-Wisconsin’s internal control over financial reporting. NSP-Wisconsin maintains internal control over financial reporting to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of the financial reporting. NSP-Wisconsin has evaluated and documented its controls in process activities, general computer activities, and on an entity-wide level.
During the year and in preparation for issuing its report for the year ended Dec. 31, 2023 on internal controls under section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, NSP-Wisconsin conducted testing and monitoring of its internal control over financial reporting. Based on the control evaluation, testing and remediation performed, NSP-Wisconsin did not identify any material control weaknesses, as defined under the standards and rules issued by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, as approved by the SEC and as indicated in NSP-Wisconsin’s Management Report on Internal Controls over Financial Reporting, which is contained in Item 8 herein.
This annual report does not include an attestation report of NSP-Wisconsin’s independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by NSP-Wisconsin’s independent registered public accounting firm pursuant to the rules of the SEC that permit NSP-Wisconsin to provide only management’s report in this annual report.
| | |
ITEM 9B — OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
| | |
| ITEM 9C — DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTION |
None.
PART III
Items 10, 11 and 12 of Part III of Form 10-K have been omitted from this report for NSP-Wisconsin in accordance with conditions set forth in general instructions I(1)(a) and (b) of Form 10-K for wholly-owned subsidiaries.
| | |
ITEM 10 — DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
| | |
ITEM 11 — EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
| | |
ITEM 12 — SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
| | |
ITEM 13 — CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Information required under this Item is contained in Xcel Energy Inc.’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which is incorporated by reference.
| | |
ITEM 14 — PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
Information required under this Item (aggregate fees billed to us by our principal accountant, Deloitte & Touche LLP (PCAOB ID No. 34)) is contained in Xcel Energy Inc.’s Proxy Statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which is incorporated by reference.
PART IV
| | |
| ITEM 15 — EXHIBIT AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 1 | Consolidated Financial Statements | | |
| Management Report on Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting — For the year ended Dec. 31, 2023. | | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm — Financial Statements | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Income — For each of the three years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income — For each of the three years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — For each of the three years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. | | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets — As of Dec. 31, 2023, 2022. | | |
| Consolidated Statements of Common Stockholder’s Equity — For each of the three years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. | | |
| | | |
| 2 | Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves for each of the years ended Dec. 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. | | |
| | | |
| 3 | Exhibits | | |
| * | Indicates incorporation by reference | | |
| + | Executive Compensation Arrangements and Benefit Plans Covering Executive Officers and Directors | | |
| | | |
| Exhibit Number | Description | Report or Registration Statement | Exhibit Reference |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form S-4 dated Jan. 21, 2004 | 3.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2018 | 3.02 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form S-3 dated April 18, 2018 | 4(c)(3) |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated Sept. 25, 2000 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated Sept. 3, 2008 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated Oct. 10, 2012 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated June 23, 2014 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated Dec. 4, 2017 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated Sept. 12, 2018 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated May 26, 2020 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated July 20, 2021 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated July 15, 2022 | 4.01 |
| | NSP-Wisconsin Form 8-K dated May 10, 2023 | 4.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2008 | 10.02 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2008 | 10.05 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2011 | 10.18 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2016 | 10.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2018 | 10.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2020 | 10.02 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2020 | 10.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2008 | 10.17 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2008 | 10.07 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2011 | 10.17 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2013 | 10.22 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended Sept. 30, 2016 | 10.01 |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended Sept. 30, 2017 | 10.1 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2018 | 10.34 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2019 | 10.32 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2023 | 10.16 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 8-K dated Dec. 10, 2021 | 10.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2023 | 10.18 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2023 | 10.01 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Definitive Proxy Statement dated April 5, 2011 | Appendix A |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2018 | 10.36 |
| | Xcel Energy Inc. Form U5B dated Nov. 16, 2000 | H-1 |
| Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of Sept. 19, 2022, among NSP-Wisconsin, as Borrower, the several lenders from time to time parties thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Bank of America, N.A. and Barclays Bank PLC, as Syndication Agents, and Citibank, N.A., MUFG Bank, Ltd. and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Documentation Agents | Xcel Energy Inc. Form 8-K dated Sept. 19, 2022 | 99.05 |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| 101.INS | Inline XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document |
| 101.SCH | Inline XBRL Schema |
| 101.CAL | Inline XBRL Calculation |
| 101.DEF | Inline XBRL Definition |
| 101.LAB | Inline XBRL Label |
| 101.PRE | Inline XBRL Presentation |
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
SCHEDULE II
NSP-Wisconsin and Subsidiaries Valuation and Qualifying Accounts Years Ended Dec. 31 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Allowance for bad debts |
| (Millions of Dollars) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance at Jan. 1 | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 8 | |
| Additions charged to costs and expenses | | 4 | | | 4 | | | 4 | |
Additions charged to other accounts (a) | | 1 | | | 1 | | | 1 | |
Deductions from reserves (b) | | (5) | | | (4) | | | (5) | |
| Balance at Dec. 31 | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | 8 | |
(a)Recovery of amounts previously written-off.
(b)Deductions related primarily to bad debt write-offs.
| | |
ITEM 16 — FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
None.
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this annual report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| | NORTHERN STATES POWER COMPANY
(A WISCONSIN CORPORATION) |
| | |
| Feb. 21, 2024 | | /s/ BRIAN J. VAN ABEL |
| | Brian J. Van Abel |
| | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Director |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities on the date indicated above.
| | | | | | | | |
| /s/ ROBERT C. FRENZEL | | /s/ KARL J. HOESLY |
| Robert C. Frenzel | | Karl J. Hoesly |
| Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and Director | | President and Director |
| (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | |
| /s/ BRIAN J. VAN ABEL | | |
| Brian J. Van Abel | | |
| Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Director | | |
| (Principal Accounting Officer and Principal Financial Officer) | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION TO BE FURNISHED WITH REPORTS FILED PURSUANT TO SECTION 15(D) OF THE ACT BY REGISTRANTS WHICH HAVE NOT REGISTERED SECURITIES PURSUANT TO SECTION 12 OF THE ACT
NSP-Wisconsin has not sent, and does not expect to send, an annual report or proxy statement to its security holder.