Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 0 - 10200
SEI INVESTMENTS COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Pennsylvania | 23-1707341 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 1 Freedom Valley Drive, Oaks, Pennsylvania | 19456-1100 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
610-676-1000
Registrant's telephone number, including area code
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $.01 per share | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC (The NASDAQ Global Select Market®) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Table of Contents
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | x | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $3.0 billion based on the closing price of $20.36 as reported by NASDAQ on June 30, 2010 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter). For purposes of making this calculation only, the registrant has defined affiliates as including all executive officers, directors and beneficial owners of more than ten percent of the common stock of the registrant.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common stock, as of the close of business on January 31, 2011:
| Common Stock, $.01 par value |
186,114,605 |
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the following documents are incorporated by reference herein:
| 1. | The definitive proxy statement relating to the registrant’s 2011 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this annual report, is incorporated by reference in Part III hereof. |
Table of Contents
Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2010
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 1 of 88
Table of Contents
PART I
Forward Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains certain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements involve certain known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, many of which are beyond our control, and are not limited to those discussed in Item 1A, “Risk Factors.” All statements that do not relate to historical or current facts are forward-looking statements. These statements may include words such as “anticipate,” “estimate,” “expect,” “project,” “intend,” “plan,” “believe,” and other words and terms of similar meaning in connection with any discussion of future operating or financial performance. In particular, these include statements relating to present or anticipated products and markets, future revenues, capital expenditures, expansion plans, future financing and liquidity, personnel, and other statements regarding matters that are not historical facts or statements of current condition.
Any or all forward-looking statements contained within this Annual Report on Form 10-K may turn out to be wrong. They can be affected by inaccurate assumptions we might make, or by known or unknown risks and uncertainties. Many factors mentioned in the discussion below will be important in determining future results. Consequently, we cannot guarantee any forward-looking statements. Actual future results may vary materially.
We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. You are advised, however, to consult any further disclosures we make on related subjects in our filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Overview
SEI (NASDAQ: SEIC) is a leading global provider of investment processing, fund processing, and investment management business outsourcing solutions that help corporations, financial institutions, financial advisors, and ultra-high-net-worth families create and manage wealth. As of December 31, 2010, through its subsidiaries and partnerships in which the company has a significant interest, SEI manages or administers $416.0 billion in mutual fund and pooled or separately managed assets, including $172.3 billion in assets under management and $243.7 billion in client assets under administration.
Our wealth management business solutions include:
| • | Investment processing and investment operations outsourcing solutions for banks, trust companies, independent wealth advisers, and investment managers; |
| • | Investment management programs to affluent individual investors and for institutional investors, including retirement plan sponsors, and not-for-profit organizations; and |
| • | Fund processing solutions for banks, investment management firms, and investment companies that sponsor and distribute mutual funds, hedge funds, and alternative investments. |
General Development of the Business
For over 40 years, SEI has been a leading provider of wealth management business solutions for the financial services industry.
We began doing business in 1968 by providing computer-based training simulations to instruct bank loan officers in credit lending practices.
1970s
We developed an investment accounting system for bank trust departments in 1972, and became a leading provider of investment processing outsourcing services to banks and trust institutions.
Page 2 of 88
Table of Contents
1980s
SEI became a public company in 1981. We entered the asset management business and launched a series of money market mutual funds for bank clients, and expanded our services to bank clients by offering mutual fund accounting services. We also began to provide investment operations outsourcing services.
1990s
We introduced our “Manager-of-Managers” investment process, and offered these programs to investment advisors who manage wealth for their high-net-worth clients. We entered the institutional investor market and began offering asset management programs to retirement plan sponsors and institutional investors in selected global markets, including the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, continental Europe, South Africa and East Asia.
2000s
We delivered broader, more strategic solutions for clients and markets, including a complete life and wealth platform for operating an investment advisory business, a total operational outsourcing solution for investment managers, a fully-integrated pension management system for retirement plan sponsors, and a complete life and wealth solution for ultra-high-net-worth families. We introduced Global Wealth Services, a next generation business solution integrating investment processing technology, operating processes, and investment management programs.
Strategy
We seek to achieve growth in earnings and shareholder value by strengthening our position as a provider of global wealth management solutions. To achieve this objective, we have implemented these strategies:
Create broader solutions for wealth service firms. Banks, investment managers and financial advisors seek to enter new markets, expand their service offerings, provide a differentiated experience to their clients, improve efficiencies, reduce risks, and better manage their businesses. We have developed and continue to develop next generation business solutions integrating technology, operating processes, and financial products designed to help these institutions better serve their clients and provide opportunities to improve their business success.
Help institutional investors manage retirement plans and operating capital. Retirement plan sponsors, not-for-profit organizations, and other institutional investors strive to meet their financial objectives while reducing business risk. We deliver customized investment management solutions, as part of a complete solution offering, that enable investors to make better decisions about their investments and to manage their assets more effectively.
Help affluent individual investors manage their life and wealth goals. These investors demand a holistic wealth management experience that focuses on their life goals and provides them with an integrated array of financial services that includes substantially more than traditional wealth management offerings. We help these investors identify their goals and offer comprehensive life and wealth advisory services including life planning, investments, and other financial services.
Expand globally. Global markets are large and present significant opportunities for growth. We have evolved U.S. business models for the global wealth management marketplace, focusing on the needs of institutional investors, private banks, independent wealth advisers, investment advisors, and affluent individual investors.
Fundamental Principles
We are guided by these fundamental principles in managing the business and adopting these growth strategies:
| • | Achieve organic growth in revenue and earnings. We seek to grow the business by providing additional services to clients, adding new clients, introducing new products, and adapting products for new markets. |
| • | Forge long-term client relationships. We strive to achieve high levels of customer satisfaction and to forge close and long lasting client relationships. We believe these relationships enable us to market additional services, and acquire knowledge and insights that fuel the product development process. |
| • | Invest in product development. We continually enhance products and services to keep pace with industry developments, regulatory requirements, and the emerging needs of markets and clients. We |
Page 3 of 88
Table of Contents
| believe ongoing investments in research and development give us a competitive advantage in our markets. |
| • | Maintain financial strength. We adopt business models that generate recurring revenues and positive cash flows. Predictable cash flows serve as a source of funds for continuing operations, investments in new products, common stock repurchases, and dividend payments. |
| • | Leverage investments across the business. We create scalable, enterprise-wide solutions designed to serve the needs of multiple markets, potentially offering operating efficiencies that can benefit corporate profitability. |
| • | Create value for shareholders. The objective of achieving long-term sustainable growth in revenues and earnings strongly influences the management of the business. This philosophy guides corporate management practices, strategic planning activities, and employee compensation practices. |
Products and Services
Investment Processing
Investment processing solutions consist of application and business process outsourcing services, and transaction-based services. We deliver these solutions to providers of institutional and private client wealth management services, including banks, trust companies, independent wealth advisers, and other financial services firms. We also deliver these solutions, combined with our investment management programs, to investment advisory firms that provide wealth management services to their advisory clients.
Our investment processing solutions are enabled through two platforms, TRUST 3000® and the Global Wealth Platform. TRUST 3000® is a comprehensive trust accounting and investment system that provides securities processing and investment accounting for all types of domestic and global securities, and support for multiple account types, including personal trust, corporate trust, institutional trust, and non-trust investment accounts. The Global Wealth Platform, currently offered to private banks and independent wealth advisers located in the United Kingdom, is an investment accounting and securities processing system with capabilities that include global securities processing, trade-date and multi-currency accounting and reporting. The platform is designed around the client and portfolio management processes. This enables financial firms to institutionalize their client processes around an investor’s investment objectives, facilitating a transition to model-based portfolio management, providing an improved client experience, while minimizing the expense and risk associated with investment operations. The Global Wealth Platform also offers enhanced client experience capabilities and improved operating efficiencies. We have focused significant development efforts on building the necessary functionality of the Global Wealth Platform with the objective of servicing financial institutions and investment advisors in the United States within the next 12 to 18 months.
Revenues from investment processing services are earned as monthly fees from contracted services including software licenses, information processing, and investment operations. These revenues are recognized in Information processing and software servicing fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations, and are primarily earned based upon the type and number of investor accounts serviced. Investment processing revenues may also be earned as a percentage of the clients’ assets processed on the platforms. Professional services revenues are earned from contracted, project-oriented services related to client implementations, and are recognized in Information processing and software servicing fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations. Transaction-based revenues are earned from trade execution services and are recognized as Transaction-based and trade execution fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Investment Management Programs
Investment management programs consist of money market, fixed-income and equity mutual funds and other collective investment products, alternative investment portfolios, and separately managed accounts. We serve as the administrator and investment advisor for many of these products. We distribute these programs primarily through investment advisory firms, including investment advisors and banks, and directly to institutional or individual investors.
We have expanded these investment management programs to include other consultative, operational, and technology components, and have created comprehensive solutions tailored to the needs of a specific market. These components may include investment strategies, consulting services, administrative and processing services, and technology tools.
Page 4 of 88
Table of Contents
Investors in our investment programs typically follow a customized investment strategy, and invest in a globally diversified portfolio that consists of multiple classes and investment styles, constructed according to our disciplined investment process. Our investment process is based on five principles: asset allocation and appropriate diversification, both of which are important to investment performance; a portfolio design process that identifies the drivers of investment returns for each asset class; manager selection, where we act as a manager-of-managers, selecting style-specific managers from a global network of money managers; a portfolio construction process implemented through selected managers, and properly diversified among asset classes and drivers of investment returns; and risk management processes that monitor portfolios to ensure risk objectives are met.
As of December 31, 2010, we managed $112.2 billion in assets including: $90.5 billion invested in fixed-income and equity funds, or through separately managed account programs; $10.5 billion invested in liquidity or money market funds; and $11.2 billion invested in collective trust fund programs. An additional $60.1 billion in assets is managed by our affiliate LSV Asset Management (LSV).
Revenues from investment management programs are primarily earned as a contractual percentage of net assets under management. These revenues are recognized in Asset management, administration and distribution fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Fund Processing
Fund processing solutions include a full range of administration and distribution support services for traditional investment products such as mutual funds, collective investment trusts, exchange-traded funds, and institutional and separate accounts. Administrative services include fund administration, portfolio and fund accounting; cash administration and treasury services; trustee and custodial services; legal, audit and tax support; and investor and distribution services. Distribution support services may include market and industry analyses to identify distribution opportunities.
We also provide comprehensive solutions to investment managers worldwide that sponsor and distribute alternative investments such as hedge funds, funds of hedge funds, and private equity funds, across both registered and partnership structures. We also offer operational outsourcing solutions for the administration and management of separately managed account programs, as well as total operational outsourcing solutions for investment management firms.
As of December 31, 2010, we administered $243.7 billion in assets for traditional and alternative investment products, including mutual funds, and pooled or separately managed account assets administered for our clients.
Revenues from fund processing are primarily earned based upon a contractual percentage of net assets under administration. These revenues are recognized in Asset management, administration and distribution fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Business Segments
Business segments are generally organized around our target markets. Financial information about each business segment is contained in Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. In January 2010, we deconsolidated the assets, liabilities and operations of LSV Asset Management in our financial statements. As a result, LSV is no longer considered a reportable business segment in 2010. Our business segments are:
Private Banks – provides investment processing and investment management programs to banks and trust institutions worldwide, independent wealth advisers located in the United Kingdom, and financial advisors in Canada;
Investment Advisors – provides investment management programs to affluent investors through a network of independent registered investment advisors, financial planners, and other investment professionals in the United States;
Institutional Investors – provides investment management programs and administrative outsourcing solutions to retirement plan sponsors, hospitals, and not-for-profit organizations worldwide;
Investment Managers – provides investment processing, fund processing, and operational outsourcing solutions to investment managers, fund companies and banking institutions located in the United States, and
Page 5 of 88
Table of Contents
to investment managers worldwide of alternative asset classes such as hedge funds, funds of hedge funds, and private equity funds across both registered and partnership structures; and
Investments in New Businesses – provides investment management programs to ultra-high-net-worth families residing in the United States through the SEI Wealth Network®.
The percentage of consolidated revenues generated by each business segment for the last three years was:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| Private Banks |
38 | % | 34 | % | 33 | % | ||||||
| Investment Advisors |
20 | % | 16 | % | 18 | % | ||||||
| Institutional Investors |
23 | % | 16 | % | 16 | % | ||||||
| Investment Managers |
18 | % | 13 | % | 11 | % | ||||||
| Investments in New Businesses |
1 | % | 1 | % | 1 | % | ||||||
| LSV |
N/A | 20 | % | 21 | % | |||||||
| 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||||||
Private Banks
The Private Banks segment delivers investment processing services and investment management programs to banks and trust institutions worldwide, independent wealth advisers located in the United Kingdom, and financial advisors in Canada.
Our investment processing services enable banks and trust institutions to reduce risk, improve quality, and gain operational efficiency thus enabling them to focus on growing their business and serving client needs. Investment processing solutions are delivered via two primary business models: the Global Wealth Technology Services (GWTS) model and the Global Wealth Services (GWS) model. In both models, we own, maintain and operate the software applications and information processing facilities.
Banks using our GWTS model outsource investment processing technology software and computer processing, but retain responsibility for investment operations, client administration, and investment management. Clients operate our GWTS solution remotely while fully supported by our data center using dedicated telecommunications networks. The GWTS model includes a dedicated relationship team that supports our client’s business. We assist our clients by strategically evaluating their systems and process needs as their businesses change.
The GWS model is an extension of our GWTS solution. It was designed for private banks and other trust organizations that prefer to outsource their entire investment operation. With the GWS solution, we assume the entire back-office processing function. The GWS model includes: investment processing; account access and reporting; audit, compliance and regulatory support data generation; custody and safekeeping of assets; income collections; securities settlement; and other related trust activities.
New clients undergo a business transformation process which can take a few months for smaller institutions and up to 15 months or more for larger institutions. During the transformation process, we collaborate with new clients to understand their strategic goals and objectives. During this transformation, systems, operations, and business processes are evaluated and optimized to meet client objectives. We typically earn a one-time implementation fee for these business transformation services.
Client contracts have initial terms that are generally three to seven years in length. At December 31, 2010, we had significant relationships with 114 banks and trust institutions in the United States, including trust departments of 11 of the 20 largest U.S. banks.
The Global Wealth Services solution will be further enhanced through the Global Wealth Platform. Target markets for this enhanced solution include private banks and independent wealth advisers in the United Kingdom, as well as community, regional, and national private banks in the United States. We believe the enhanced Global Wealth Services solution enabled by the new infrastructure will improve the client experience and place our clients in a superior position to serve the changing needs of their clients.
Our principal competitors in the investment processing business for this segment are: Temenos Group AG; Fidelity National Information Services, Inc. (formerly Metavante Corporation); SunGard Data Systems Inc.; State
Page 6 of 88
Table of Contents
Street Corporation; FiTECH LLC; Pershing LLC, a subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and smaller technology firms. Many large financial institutions develop, operate and maintain proprietary investment and trust accounting systems. We also consider these “in-house” solutions to be a form of competition.
Our investment management programs for banks and distribution partners are offered worldwide. At December 31, 2010, there were approximately 320 investment management clients worldwide. We also had single-product relationships with approximately 90 additional banks and trust institutions. The principal competitors for this business are: Dimensional Fund Advisors; Federated Investors, Inc.; LPL Financial Corporation; Russell Investment Group, a subsidiary of The Northwestern Mutual Life Insurance Company; discretionary portfolio managers and various multi-manager investment programs offered by other firms. We also consider ”in-house” internal asset management capabilities to be a form of competition.
Investment Advisors
The Investment Advisors segment offers wealth management solutions to registered investment advisors, many of whom are affiliated with or are registered as independent broker-dealers, financial planners, and life insurance agents located throughout the United States. These wealth management solutions include our investment management programs and back-office investment processing outsourcing services. We also help advisors manage and grow their businesses by giving them access to our marketing support programs, business assessment assistance and recommended management practices. Our solutions aim to help investment advisors reduce risk, improve quality, and gain operational efficiency to devote more of their resources to servicing their clients.
Advisors are responsible for the investor relationship which includes creating financial plans, implementing investment strategies and educating and servicing their customers. Advisors may customize portfolios to include separate account managers provided through our programs as well as SEI-sponsored mutual funds. Our wealth and investment programs are designed to be attractive to affluent or high-net-worth individual investors with over $250 thousand of investable assets and small to medium-sized institutional plans.
We continually enhance our offering to meet the emerging needs of our advisors and their end clients. For example, in 2010, we introduced the Advisor Portal which automates the interface between advisors and our back office operations.
Although we have agreements with over 5,800 financial advisors, our business is based primarily on approximately 1,100 clients who, at December 31, 2010, had at least $5.0 million each in customer assets invested in our mutual funds and separately managed accounts. Revenues are earned largely as a percentage of average assets under management.
The principal competition for our investment management products is from other money managers and mutual fund companies. In the advisor distributor channel, the principal competitors include AssetMark Investment Services Inc., Brinker Capital, EnvestNet Asset Management, Inc., Fidelity Investments, Lockwood Advisors, Inc., a subsidiary of The Bank of New York Mellon, Charles Schwab & Co., Inc., and other broker-dealers.
Institutional Investors
The Institutional Investors segment offers investment management programs and administrative outsourcing solutions for retirement plan sponsors, hospitals, and not-for-profit organizations globally. Clients can outsource their entire investment management needs and the administration for defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans, endowments, foundations and other balance sheet assets, as well as the administration of endowment and foundation asset pools.
The outsourcing program provides a strategic platform integrating the Manager-of-Managers investment process, plan administration services, and consulting services. Plan administration services include trustee, custodial, benefit payment services, record-keeping services, and donor administration. Consulting services include actuarial services, asset liability modeling, and the customization of an asset allocation plan that is designed to meet long-term objectives.
By outsourcing retirement plan services, we believe clients benefit from an investment approach built around an investment plan designed to meet the client’s long-term business and plan objectives and an investment process that removes the responsibility of manager selection. This approach is designed to reduce business risk, provide ongoing due diligence, and increase operational efficiency. Nonprofit organizations can manage volatility through more diversified portfolios and focus more resources on achieving their overall mission. Healthcare
Page 7 of 88
Table of Contents
organizations benefit from customized asset allocations that help provide improved balance sheet protection and overall financial risk management.
Fees are primarily earned as a percentage of average assets under management. At December 31, 2010, we had relationships with approximately 515 institutional investor clients. The principal competitors for this segment are Frank Russell Company, a subsidiary of The Northwestern Mutual Life Insurance Company, Northern Trust Corporation, and investment consultants.
Investment Managers
The Investment Manager Services segment provides comprehensive operations outsourcing solutions to investment managers globally. This array of back-, middle- and front-office investment processing services integrate best-in-class industry tools and technology to support a manager’s diverse business needs across multiple products and asset classes. Our clients are retail and institutional investment managers with global offerings that span the investment management industry. We offer managers support for traditional investment products such as mutual funds, collective investment trusts, exchange-traded funds, and institutional and separate accounts, by providing outsourcing services including accounting, administration, reconciliation, investor servicing and client reporting. We also provide comprehensive solutions to managers focused on alternative investments who manage hedge funds, funds of hedge funds, and private equity funds, across registered, partnership and separate account structures in the United States and overseas.
By applying operating services, technologies, and business and regulatory knowledge, our solutions help investment managers focus on their core competencies of portfolio management and investor relations. This allows them to better manage their business risk, improve accuracy and efficiency, and, through our proprietary and best of breed systems, receive tools and analytics through which to gain insight about, and better manage, their business.
Contracts for our outsourcing and investment processing services generally have terms ranging from one to five years. Fees are primarily earned as a percentage of average assets under management and administration. At December 31, 2010, we had relationships with approximately 190 investment management companies and alternative investment managers. Our competitors for this segment include GlobeOp Financial Services, Citco, and State Street Bank and Trust Company.
Investments in New Businesses
The Investments in New Businesses segment represents other business ventures intended to expand our investment solutions to include ultra-high-net-worth families who reside in the United States. This segment also includes the costs associated with business development in the Middle East, through our Dubai office. The family wealth management solution offers flexible family-office type services through a highly personalized solution while utilizing the Manager-of-Managers investment process.
The principal competitors for the family wealth solution are diversified financial services providers focused on the ultra-high-net-worth market.
Research and Development
We are devoting significant resources to research and development, including expenditures for new technology platforms, enhancements to existing technology platforms, and new investment products and services. We spent approximately $105.6 million in 2010, $103.9 million in 2009, and $117.5 million in 2008, of which we capitalized approximately $38.7 million in 2010, $43.9 million in 2009, and $56.2 million in 2008 relating to the development of new technology platforms. Total research and development expenditures as a percentage of revenues were 11.7 percent in 2010, 12.2 percent in 2009, and 11.9 percent in 2008. All percentages exclude the revenues of LSV.
The majority of our research and development spending is related to building our Global Wealth Platform (GWP). GWP combines business service processing with asset management and distribution services. The platform offers to our customers a client-centric, rather than an account-centric, process with model-based portfolio management services through a single platform. The platform utilizes our proprietary applications with those built by third-party providers, and integrates them into a single technology solution, providing a common user experience. This integration supports straight-through business processing and enables the transformation of our clients’ trust services from operational investment processing services to client value-added services.
Page 8 of 88
Table of Contents
The solution will serve U.K., European and U.S. markets. GWP provides the technology platform for the business solutions now being marketed to private banks and independent wealth adviser organizations in the United Kingdom. In U.S. markets, we believe the demand for the advanced capabilities of the new platform will enable us to market our services to global wealth managers and existing clients in the Private Banks segment and improve the services we offer in the Investment Advisors segment. It is our current expectation that GWP will be deployed in the United States within the next 12 to 18 months.
GWP will eventually be used at some level by all business segments. The front-end components will be used by us and by our clients to manage customer administration and portfolio management. The back-office components will streamline all investment-related activities and will eliminate manual processes and perform trade order execution and settlement activities.
Marketing and Sales
Our business solutions are directly marketed to potential clients in our target markets. We employ approximately 90 sales representatives who operate from offices located throughout the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, continental Europe, South Africa, Asia and other locations.
Customers
In 2010, no single customer accounted for more than ten percent of revenues in any business segment.
Personnel
At January 31, 2011, we had approximately 2,240 full-time and 50 part-time employees. None of our employees is unionized. Management considers employee relations to be generally good.
Regulatory Considerations
Our principal, regulated wholly-owned subsidiaries are SEI Investments Distribution Co., or SIDCO, SEI Investments Management Corporation, or SIMC, SEI Private Trust Company, or SPTC, SEI Trust Company, or STC, and SEI Investments (Europe) Limited, or SIEL. SIDCO is a broker-dealer registered with the SEC under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934 and is a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. SIMC is an investment advisor registered with the SEC under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. SPTC is a limited purpose federal thrift chartered and regulated by the United States Office of Thrift Supervision. STC is a Pennsylvania trust company, regulated by the Pennsylvania Department of Banking. SIEL is an investment manager and financial institution subject to regulation by the Financial Services Authority of the United Kingdom. In addition, various SEI subsidiaries are subject to the jurisdiction of regulatory authorities in Canada, the Republic of Ireland and other foreign countries. The Company has a minority ownership interest in LSV, which is also an investment advisor registered with the SEC.
SIDCO and SIMC are subject to various federal and state laws and regulations that grant supervisory agencies, including the SEC, broad administrative powers. In the event of a failure to comply with these laws and regulations, the possible sanctions that may be imposed include the suspension of individual employees, limitations on the permissibility of SIDCO, SIMC, SEI, and our other subsidiaries to engage in business for specified periods of time, the revocation of applicable registration as a broker-dealer or investment advisor, as the case may be, censures, and fines. SPTC and STC are subject to laws and regulations imposed by federal and state banking authorities. In the event of a failure to comply with these laws and regulations, restrictions, including revocation of applicable banking charter, may be placed on the business of these companies and fines or other sanctions may be imposed. Additionally, the securities and banking laws applicable to us and our subsidiaries provide for certain private rights of action that could give rise to civil litigation. Any litigation could have significant financial and non-financial consequences including monetary judgments and the requirement to take action or limit activities that could ultimately affect our business.
Compliance with existing and future regulations and responding to and complying with recent regulatory activity affecting broker-dealers, investment advisors, investment companies and their service providers and financial institutions could have a significant impact on us. We periodically undergo regulatory examinations and respond to regulatory inquiries and document requests. As a result of these examinations, inquiries and requests, we review our compliance procedures and business operations, and make changes as we deem necessary, some of which may result in increased expense or may reduce revenues.
Page 9 of 88
Table of Contents
We offer investment and banking products that also are subject to regulation by the federal and state securities and banking authorities, as well as foreign regulatory authorities, where applicable. Existing or future regulations that affect these products could lead to a reduction in sales of these products.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act signed into law in July 2010 makes extensive changes to the laws regulating financial services firms. Among other things, this Act abolishes the Office of Thrift Supervision and transfers its functions to the other federal banking agencies. The legislation requires significant rule-making and mandates multiple studies, which could result in additional legislative or regulatory action. We are currently evaluating the impact the legislation will have on us and our subsidiaries and the products and services we provide to our clients.
Our bank clients are subject to supervision by federal and state banking authorities concerning the manner in which such clients purchase and receive our products and services. Our plan sponsor clients and our subsidiaries providing services to those clients are subject to supervision by the Department of Labor and compliance with employee benefit regulations. Investment advisor and broker-dealer clients are regulated by the SEC and state securities authorities. Existing or future regulations applicable to our clients may affect our clients’ purchase of our products and services.
The fees and assessments imposed on our regulated subsidiaries by federal, state and foreign regulatory authorities could have a significant impact on us. In the current regulatory environment, the frequency and scope of regulatory reform may lead to an increase in fees and assessments resulting in increased expense, or an increase or change in regulatory requirements which could affect our operations and business.
In addition, see the discussion of governmental regulations in Item 1A “Risk Factors” for a description of the risks that proposed regulatory changes may present for our business.
Available Information
We maintain a website at www.seic.com and make available free of charge through the Investors section of this website our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. We include our website in this Annual Report on Form 10-K only as an inactive textual reference and do not intend it to be an active link to our website. The material on our website is not part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We believe that the risks and uncertainties described below are those that impose the greatest threat to the sustainability of our business. However, there are other risks and uncertainties that exist that may be unknown to us or, in the present opinion of our management, do not currently pose a material risk of harm to us. The risk and uncertainties facing our business, including those described below, could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
Our revenues and earnings are affected by changes in capital markets. A majority of our revenues are earned based on the value of assets invested in investment products that we manage or administer. Significant fluctuations in securities prices may materially affect the value of these assets and may also influence an investor’s decision to invest in and maintain an investment in a mutual fund or other investment product. As a result, our revenues and earnings derived from assets under management and administration could be adversely affected.
A majority of the securities held by our investment products are valued using quoted prices from active markets gathered by external pricing services. Securities for which market prices are not readily available are valued in accordance with procedures applicable to that investment product. These procedures may utilize unobservable inputs that are not gathered from any active markets and involve considerable judgment. If these valuations prove to be inaccurate, our revenues and earnings from assets under management could be adversely affected.
We are exposed to product development risk. We continually strive to increase revenues and meet our customers’ needs by introducing new products and services. As a result, we are subject to product development risk, which may result in loss if we are unable to develop and deliver fully functional products to our target markets that address our clients’ needs and that are developed on a timely basis and reflect an attractive value proposition. New product development is primarily for the purpose of enhancing our competitive position in the industry. In the event that we fail to develop products or services at an acceptable cost or on a timely basis or if we fail to deliver functional products and services which are of sound, economic value to our clients and our
Page 10 of 88
Table of Contents
target markets, or an inability to support the product in a cost-effective manner, we could suffer significant financial loss.
Consolidation within our target markets may affect our business. Merger and acquisition activity between banks and other financial institutions could reduce the number of existing and prospective clients or reduce the amount of revenue we receive from retained clients. Consolidation activities may also cause larger institutions to internalize some or all of our services. These factors may negatively impact our ability to generate future growth in revenues and earnings.
We are dependent upon third-party service providers in our operations. We utilize numerous third-party service providers in our operations, in the development of new products, and in the maintenance of our proprietary systems. A failure by a third-party service provider could expose us to an inability to provide contractual services to our clients in a timely basis. Additionally, if a third-party service provider is unable to provide these services, we may incur significant costs to either internalize some of these services or find a suitable alternative.
We serve as the investment advisor for many of the products offered through our investment management programs and utilize the services of investment sub-advisers to manage the majority of these assets. A failure in the performance of our due diligence processes and controls related to the supervision and oversight of these firms in detecting and addressing conflicts of interest, fraudulent activity, noncompliance with relevant securities and other laws could cause us to suffer financial loss, regulatory sanctions or damage to our reputation.
Poor fund performance may affect our revenues and earnings. Our ability to maintain our existing clients and attract new clients may be negatively affected if the performance of our mutual funds and other investment products, relative to market conditions and other comparable competitive investment products, is lower. Investors may decide to place their investable funds elsewhere which would reduce the amount of assets we manage resulting in a decrease in our revenues.
Our Company and our clients are subject to extensive governmental regulation. Our various business activities are conducted through entities which may be registered with or regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as an investment advisor, a broker-dealer, a transfer agent, or an investment company, with federal or state banking authorities as a trust company, or with federal banking authorities as a savings association holding company. Our broker-dealer is also a member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority and is subject to its rules and oversight. In addition, some of our foreign subsidiaries are registered with, and subject to the oversight of, regulatory authorities primarily in the United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland and Canada. Many of our clients are subject to substantial regulation by federal and state banking, securities or insurance authorities or the Department of Labor. Compliance with existing and future regulations, responding to and complying with recent regulatory activity affecting broker-dealers, investment advisors, investment companies and their service providers and financial institutions, and examination or other supervisory activities of our regulators or of the regulators of our clients, could have a significant impact on our operations or business.
We offer investment and banking products that also are subject to regulation by the federal and state securities and banking authorities, as well as foreign regulatory authorities, where applicable. Existing or future regulations that affect these products could lead to a reduction in sales of these products or an increase in the cost of providing these products.
The fees and assessments imposed on our regulated subsidiaries by federal, state and foreign regulatory authorities could have a significant impact on us. In the current regulatory environment, the frequency and scope of regulatory reform may lead to an increase in fees and assessments resulting in increased expense, or an increase or change in regulatory requirements which could affect our operations and business.
We are exposed to systems and technology risks. Through our proprietary systems, we maintain and process data for our clients that is critical to their business operations. An unanticipated interruption of service may have significant ramifications, such as lost data, damaged software codes, or inaccurate processing of transactions. As a result, the costs necessary to rectify these problems may be substantial.
We are exposed to data security risks. A failure to safeguard the integrity and confidentiality of client data and our proprietary data from the infiltration by an unauthorized user that is either stored on or transmitted between our proprietary systems or to other third party service provider systems may lead to modifications or theft of critical and sensitive data pertaining to us or our clients. The costs incurred to correct client data and prevent further unauthorized access to our data or client data could be extensive.
We are dependent upon third party approvals. Many of the investment advisors through which we distribute our investment offerings are affiliated with independent broker-dealers or other networks, which have regulatory responsibility for the advisor’s practice. As part of the regulatory oversight, these broker-dealers or networks must approve the use of our investment products by affiliated advisors within their networks. Failure to receive such approval, or the withdrawal of such approval, could adversely affect the marketing of our investment products.
We are exposed to operational risks. Operational risk generally refers to the risk of loss resulting from our operations, including, but not limited to, improper or unauthorized execution and processing of transactions, deficiencies in our operating systems, inefficiencies in our operational business units, business disruptions and inadequacies or breaches in our internal control
Page 11 of 88
Table of Contents
processes. We operate different businesses in diverse markets and are reliant on the ability of our employees and systems to process large volumes of transactions often within short time frames. In the event of a breakdown or improper operation of systems, human error or improper action by employees, we could suffer financial loss, regulatory sanctions or damage to our reputation. In order to mitigate and control operational risk, we continue to enhance policies and procedures that are designed to identify and manage operational risk.
Changes in, or interpretation of, accounting principles could affect our revenues and earnings. We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A change in these principles can have a significant effect on our reported results and may even retrospectively affect previously reported results.
Changes in, or interpretations of, tax rules and regulations may adversely affect our effective tax rates. Unanticipated changes in our tax rates could affect our future results of operations. Our future effective tax rates could be adversely affected by changes in tax laws or the interpretation of tax laws. We are subject to possible examinations of our income tax returns by the Internal Revenue Service and state and foreign tax authorities. We regularly assess the likelihood of outcomes resulting from these examinations to determine the adequacy of our provision for income taxes, however, there can be no assurance that the final determination of any examination will not have an adverse effect on our operating results or financial position.
Currency fluctuations could negatively affect our future revenues and earnings as our business grows globally. We operate and invest globally to expand our business into foreign markets. Our foreign subsidiaries use the local currency as the functional currency. As these businesses evolve, our exposure to changes in currency exchange rates may increase. Adverse movements in currency exchange rates may negatively affect our operating results, liquidity and financial condition.
We rely on our executive officers and senior management. Most of our executive officers and senior management personnel do not have employment agreements with us. The loss of these individuals may have a material adverse affect on our future operations.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Our corporate headquarters is located in Oaks, Pennsylvania and consists of nine buildings situated on approximately 90 acres. We own and operate the land and buildings, which encompass approximately 486,000 square feet of office space and 34,000 square feet of data center space. We lease other offices which aggregate 58,000 square feet. We also own a 3,400 square foot condominium that is used for business purposes in New York, New York.
One of the Company’s subsidiaries, SEI Investments Distribution Co. (SIDCO), has been named as a defendant in certain putative class action complaints (the Complaints) related to leveraged exchange traded funds (ETFs) advised by ProShares Advisors, LLC, which is a client of the Company. To date, the Complaints have been filed in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and in the United States District Court for the District of Maryland, although the three complaints filed in the District of Maryland have been voluntarily dismissed by the plaintiffs. Two of them were subsequently re-filed in the Southern District of New York. Two of the complaints filed in the Southern District of New York have been voluntarily dismissed by plaintiffs. The first complaint was filed on August 5, 2009. The Complaints are purportedly made on behalf of all persons that purchased or otherwise acquired shares in various ProShares ETFs pursuant or traceable to allegedly false and misleading registration statements, prospectuses and statements of additional information. The Complaints name as defendants ProShares Advisors, LLC; ProShares Trust, ProShares Trust II; SIDCO, and various officers and trustees to ProShares Advisors, LLC; ProShares Trust and ProShares Trust II. The Complaints allege that SIDCO was the distributor and principal underwriter for the various ProShares ETFs that were distributed to authorized participants and ultimately shareholders. The Complaints allege that the registration statements for the ProShares ETFs were materially false and misleading because they supposedly failed adequately to describe the nature and risks of the investments. The Complaints allege that SIDCO is liable for these purportedly material misstatements and omissions under Section 11 of the Securities Act of 1933. The Complaints seek unspecified compensatory and other damages, reasonable costs and other relief. The Complaints were consolidated, and an Amended Consolidated Class Action Complaint (Amended Complaint) was filed on September 24, 2010, which asserted the same claims and added a few individuals who alleged
Page 12 of 88
Table of Contents
served as “Attorney-in-fact” as defendants. Defendants filed a Motion to Dismiss the Amended Complaint on November 15, 2010. On December 15, 2010, lead plaintiff informed the Court and defendants that he intends to file a second amended consolidated complaint. While the outcome of this litigation is uncertain given its early phase, the Company believes that it has valid defenses to plaintiffs’ claims and intends to defend the lawsuits vigorously.
The Company has been named in five lawsuits that were filed in the 19th Judicial District Court for the Parish of East Baton Rouge, State of Louisiana. One of the five actions purports to set forth claims on behalf of a class and also names SEI Private Trust Company (SPTC) as a defendant. Two of the other actions also name SPTC as a defendant. All five actions name various defendants in addition to the Company, and, in all five actions, the plaintiffs purport to bring a cause of action against the Company under the Louisiana Securities Act. The putative class action originally included a claim against the Company for an alleged violation of the Louisiana Unfair Trade Practices Act. Two of the other five actions include claims for violations of the Louisiana Racketeering Act and possibly conspiracy. In addition, another group of plaintiffs have filed a lawsuit in the 23rd Judicial District Court for the Parish of Ascension, State of Louisiana, against the Company and other defendants asserting claims of negligence, breach of contract, breach of fiduciary duty, violations of the uniform fiduciaries law, negligent misrepresentation, detrimental reliance, violations of the Louisiana Securities Act and Louisiana Racketeering Act and conspiracy. The underlying allegations in all the actions are purportedly related to the role of SPTC in providing back-office services to Stanford Trust Company. The petitions in the lawsuits allege that the Company and SPTC aided and abetted or otherwise participated in the sale of “certificates of deposit” issued by Stanford International Bank. Two of the five actions filed in East Baton Rouge have been removed to federal court, and plaintiffs’ motions to remand are pending. These two cases have been transferred by the Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation to United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas. The case filed in Ascension was also removed to federal court and transferred by the Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation to the Northern District of Texas. The schedule for responding to that complaint has not yet been established. The Company and SPTC filed exceptions in the putative class action pending in East Baton Rouge, which the Court granted in part and dismissed the claims under the Louisiana Unfair Trade Practices Act and denied in part as to the other exceptions. The Company and SPTC filed an answer to the East Baton Rouge putative class action, and plaintiffs filed a motion for class certification. Class discovery has commenced, and a hearing on the motion for class certification is scheduled for March 2011. The response of the Company and SPTC to the petitions filed in the two non-class action cases remaining in East Baton Rouge is due in February 2011. While the outcome of this litigation is uncertain given its early phase, the Company and SPTC believe that they have valid defenses to plaintiffs’ claims and intend to defend the lawsuits vigorously.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Information about our executive officers is contained in Item 10 of this report and is incorporated by reference into this Part I.
Page 13 of 88
Table of Contents
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Price Range of Common Stock and Dividends:
Our common stock is traded on The Nasdaq Global Select Market® (NASDAQ) under the symbol “SEIC.” The following table shows the high and low sales prices for our common stock as reported by NASDAQ and the dividends declared on our common stock for the last two years. Our Board of Directors intends to declare future dividends on a semiannual basis.
| 2010 |
High | Low | Dividends | |||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 22.12 | $ | 16.77 | $ | — | ||||||
| Second Quarter |
24.41 | 19.93 | .10 | |||||||||
| Third Quarter |
22.14 | 17.35 | — | |||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
24.28 | 20.07 | .10 | |||||||||
| 2009 |
High | Low | Dividends | |||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 16.25 | $ | 9.19 | $ | — | ||||||
| Second Quarter |
18.52 | 11.74 | .08 | |||||||||
| Third Quarter |
20.00 | 16.66 | — | |||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
20.36 | 17.18 | .09 | |||||||||
As of January 31, 2011, we estimate that we had approximately 430 shareholders of record.
For information on our equity compensation plans, refer to Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements and Item 12 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Comparison of Cumulative Total Return of Common Stock, Industry Index and Nasdaq Market Index:
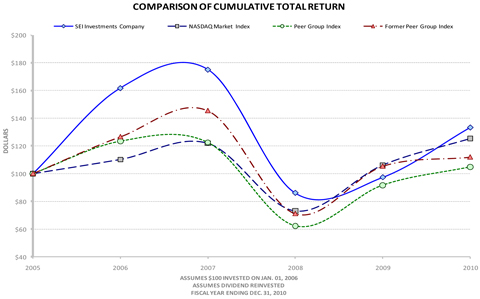
Page 14 of 88
Table of Contents
Our Peer Group Index is comprised of two industry indexes related to asset management and software application firms generally weighted to correspond proportionately to our revenues earned from asset management and information processing services. Our provider, Morningstar, is discontinuing the industry indexes of their subsidiary, Hemscott Group Limited, that we previously used and our Peer Group Index going forward will be based on the appropriate proportions of the Morningstar Asset Management Index and the Morningstar Software – Application Index. In 2010, our revenues from Asset management, administration and distribution fees and Information processing and software servicing fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations represented approximately 70 percent and 26 percent, respectively, of our total revenues.
The foregoing chart includes the new Peer Group Index (which is based on 70 percent of the Morningstar Asset Management Index and 30 percent of the Morningstar Software – Application Index, as well as, for comparison purposes, the Former Peer Group Index (which is based on 70 percent of the Hemscott Asset Management Index and 30 percent of the Hemscott Software - Application Index). The Morningstar indices used in calculating our Peer Group Index are published by Morningstar, Inc.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities:
Our Board of Directors has authorized the repurchase of up to $1.73 billion of our common stock. Currently, there is no expiration date for our common stock repurchase program.
Information regarding the repurchase of common stock during the three months ended December 31, 2010 is:
| Period |
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Program |
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Program |
||||||||||||
| October 1 – 31, 2010 |
50,000 | $ | 22.24 | 50,000 | $ | 138,980,000 | ||||||||||
| November 1 – 30, 2010 |
830,000 | 22.86 | 830,000 | 120,015,000 | ||||||||||||
| December 1 – 31, 2010 |
525,000 | 23.95 | 525,000 | 107,441,000 | ||||||||||||
| Total |
1,405,000 | $ | 23.24 | 1,405,000 | ||||||||||||
Page 15 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
(In thousands, except per-share data)
This table presents selected consolidated financial information for the five-year period ended December 31, 2010. This data should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 (A) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 900,835 | $ | 1,060,548 | $ | 1,247,919 | $ | 1,369,028 | $ | 1,175,749 | ||||||||||
| Total expenses |
683,302 | 696,841 | 751,570 | 775,053 | 677,298 | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
217,533 | 363,707 | 496,349 | 593,975 | 498,451 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense) |
152,248 | (1,389 | ) | (142,119 | ) | (8,556 | ) | 7,267 | ||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
369,781 | 362,318 | 354,230 | 585,419 | 505,718 | |||||||||||||||
| Income taxes |
136,461 | 89,886 | 86,703 | 151,182 | 123,218 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income |
233,320 | 272,432 | 267,527 | 434,237 | 382,500 | |||||||||||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest |
(1,633 | ) | (98,097 | ) | (128,273 | ) | (174,428 | ) | (145,510 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments |
231,687 | 174,335 | 139,254 | 259,809 | 236,990 | |||||||||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
$ | 1.23 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.20 | ||||||||||
| Shares used to calculate basic earnings per common share |
188,468 | 190,821 | 192,057 | 196,120 | 197,364 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 1.22 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.28 | $ | 1.17 | ||||||||||
| Shares used to calculate diluted earnings per common share |
190,321 | 191,783 | 195,233 | 202,231 | 203,266 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share |
$ | .20 | $ | .17 | $ | .16 | $ | .14 | $ | .12 | ||||||||||
| Financial Position as of December 31, |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 496,292 | $ | 590,877 | $ | 416,643 | $ | 360,921 | $ | 286,948 | ||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 1,377,223 | $ | 1,533,808 | $ | 1,341,715 | $ | 1,252,365 | $ | 1,079,705 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt (including current portion) |
$ | 95,000 | $ | 253,552 | $ | 31,532 | $ | 51,971 | $ | 80,638 | ||||||||||
| SEI Investments Shareholders’ equity |
$ | 1,041,570 | $ | 909,723 | $ | 769,152 | $ | 756,383 | $ | 630,512 | ||||||||||
| (A) | Beginning in 2010, we discontinued consolidating the accounts and operations of LSV and LSV Employee Group in our financial statements (See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding LSV and LSV Employee Group). |
Page 16 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
(In thousands, except per-share data)
This discussion reviews and analyzes the consolidated financial condition at December 31, 2010 and 2009, the consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008, and other factors that may affect future financial performance. This discussion should be read in conjunction with the Selected Financial Data included in Item 6 of this Annual Report and the Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report.
Overview
Consolidated Summary
We are a leading global provider of investment processing, fund processing, and investment management business outsourcing solutions that help corporations, financial institutions, financial advisors, and ultra-high-net-worth families create and manage wealth. Investment processing fees are earned as monthly fees for contracted services, including computer processing services, software licenses, and investment operations services, as well as transaction-based fees for providing securities valuation and trade-execution. Fund processing and investment management fees are earned as a percentage of average assets under management or administration. As of December 31, 2010, through our subsidiaries and partnerships in which we have a significant interest, we manage or administer $416.0 billion in mutual fund and pooled or separately managed assets, including $172.3 billion in assets under management and $243.7 billion in client assets under administration. In January 2010, we deconsolidated the assets, liabilities and operations of LSV Asset Management in our financial statements. As a result, LSV is no longer considered a reportable business segment in 2010 (See “Deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group” later in this discussion).
Our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended 2010, 2009 and 2008 were:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | Percent Change |
2008 | Percent Change |
|||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 900,835 | $ | 1,060,548 | (15 | %) | $ | 1,247,919 | (15 | %) | ||||||||||
| Expenses |
683,302 | 696,841 | (2 | %) | 751,570 | (7 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
217,533 | 363,707 | (40 | %) | 496,349 | (27 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Net gain (loss) from investments |
48,533 | (4,926 | ) | N/A | (158,018 | ) | (97 | %) | ||||||||||||
| Interest income, net of interest expense |
4,848 | 3,537 | 37 | % | 10,322 | (66 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Other (expense) income |
(590 | ) | 0 | N/A | 5,577 | N/A | ||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
99,457 | 0 | N/A | 0 | N/A | |||||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
369,781 | 362,318 | 2 | % | 354,230 | 2 | % | |||||||||||||
| Income taxes |
136,461 | 89,886 | 52 | % | 86,703 | 4 | % | |||||||||||||
| Net income |
233,320 | 272,432 | (14 | %) | 267,527 | 2 | % | |||||||||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest |
(1,633 | ) | (98,097 | ) | (98 | %) | (128,273 | ) | (24 | %) | ||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | 231,687 | $ | 174,335 | 33 | % | $ | 139,254 | 25 | % | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 1.22 | $ | .91 | 34 | % | $ | .71 | 28 | % | ||||||||||
Page 17 of 88
Table of Contents
Significant Items Impacting Our Financial Results in 2010
Revenues decreased $159.7 million, or 15 percent, to $900.8 million in 2010 compared to 2009. Net income attributable to SEI increased $57.4 million, or 33 percent, to $231.7 million and diluted earnings per share increased to $1.22 per share in 2010 compared to $0.91 per share in 2009. We believe the following items were significant to our business during 2010:
| • | Revenues in 2010 reflect the impact of deconsolidating LSV. Excluding the revenues from LSV in 2009, our revenues increased $52.2 million, or six percent, in 2010. This increase was primarily due to higher average asset balances under management and administration from improved capital markets. Our assets under management and administration, excluding LSV, increased $16.7 billion, or five percent, to $356.0 billion at December 31, 2010 from $339.2 billion at December 31, 2009. |
| • | New business activity in our Institutional Investors and Investment Managers segments also contributed to increased revenues. New client asset funding, as well as asset funding from existing clients, for our retirement and not-for-profit solutions in our Institutional Investors segment and for our hedge fund solution in our Investment Managers segment positively impacted revenues during 2010. |
| • | Our revenues from Transaction-based and trade execution fees fell $14.8 million, or 27 percent. This decline was a result of lower trading volumes in the capital markets. Our direct costs related to trade execution fees also declined, resulting in minimal impact to our earnings. |
| • | Revenues from investment processing fees in our Private Banks segment were negatively affected by the loss of two large U.S. bank clients involved in mergers and acquisitions as well as lost clients and fee concessions for contract renewals with U.S. regional and community banks. An increase in recurring revenues from new U.K. clients partially offset the decline in revenues; however, profitability improvement from this new business was limited due to developmental and operational costs related to the support of the Global Wealth Platform, as well as increased personnel expenses such as stock-based compensation and sales compensation costs. |
| • | Our percentage ownership of LSV remained at approximately 42 percent. Our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV in 2010 was $99.5 million, as compared to $75.4 million in 2009, an increase of 32 percent. LSV’s revenues significantly increased because of market appreciation in the value of assets under management from existing clients. LSV’s assets under management were $60.1 billion at December 31, 2010, as compared to $52.5 billion at December 31, 2009, an increase of 14 percent. |
| • | We recognized $44.2 million in gains from structured investment vehicles (SIV) securities in 2010 as compared to $5.8 million in losses in 2009. Approximately $27.5 million of the gain in 2010 resulted from cash payments received from the SIV securities that had been previously written down. During 2010, we sold three of the SIV securities originally purchased from our money market funds in 2009. Realized gains from these sales were not significant. In January 2011, we sold the Stanfield Victoria notes for a minimal realized gain leaving the Gryphon notes as our last remaining SIV security held (See Notes 5 and 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements). |
| • | Stock-based compensation costs in 2010 increased $12.3 million to $26.8 million as compared to $14.5 million in 2009. This increase was primarily due to the accelerated recognition of stock-based compensation expense from a change in our estimate of the attainment of performance vesting targets made during the year. |
| • | Compensation, benefits and other personnel costs increased $14.7 million in 2010 as compared to our costs in 2009 excluding LSV. This increase was due to increased salary and incentive compensation costs primarily from additions to our workforce. |
| • | We continued to invest in the development of the Global Wealth Platform and its operational infrastructure. During 2010, we capitalized $38.7 million for significant enhancements and new functionality for the platform, as compared to $43.9 million in 2009. Amortization expense related to the Global Wealth Platform was $22.5 million in 2010. |
| • | In 2010, we made principal payments of $138.0 million to reduce the outstanding balance of our credit facility. As of December 31, 2010, the outstanding balance of the credit facility was $95.0 million. |
Page 18 of 88
Table of Contents
| • | We continued our stock repurchase program during 2010 and purchased approximately 5,814,000 shares at an average price of approximately $20.81 per share for a total cost of $121.0 million. |
| • | Our effective tax rate in 2010 rose to 37.0 percent as compared 33.9 percent in 2009. Our tax rate in 2009 was favorably impacted by the recognition of certain tax benefits related to the conclusion of federal and state income tax audits. |
Significant Items Impacting Our Financial Results in 2009
Revenues decreased $187.4 million, or 15 percent, to $1.06 billion in 2009 compared to 2008. Net income attributable to SEI increased $35.1 million, or 25 percent, to $174.3 million and diluted earnings per share increased to $0.91 per share in 2009 compared to $0.71 per share in 2008. We believe the following items were significant to our business during 2009:
| • | Market depreciation from the historic downturn in the U.S. and global capital markets in the latter stages of 2008 and during the first quarter of 2009 severely impacted our assets under management, leading to a decline of $182.2 million, or 19 percent, in our Asset management, administration and distribution fees. The pace of the more moderate recovery during the second half of 2009 limited our ability to regain the level of asset-based revenues earned prior to 2008. |
| • | Although our asset-based revenues continued to be negatively affected by the depressed capital markets, the improvement in the capital markets which took hold during the third quarter 2009 served to increase our assets under management on a sequential, quarter-to-quarter basis. |
| • | The prevailing market uncertainty has extended our sales cycles; however, measured new business activity in our Institutional Investors and Investment Managers segments, primarily in the latter half of 2009, served to offset a portion of the year over year decline in our asset-based revenues from market depreciation. |
| • | Our revenues from Transaction-based and trade execution fees fell $7.2 million, or 11 percent. This decline was a result of unusually high trading volume from the extreme market volatility during the fourth quarter 2008. Our direct costs related to trade execution fees also declined, resulting in minimal impact to our earnings. |
| • | The sharp decline of the capital markets had a significant negative impact on the revenue and profits of LSV. Revenues earned by LSV were $212.0 million in 2009 compared to $263.3 million in the prior year comparable period, a decrease of $51.3 million or 19 percent. Our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV in 2009 was $75.4 million compared to $98.5 million in 2008, a decrease of $23.1 million or 23 percent. |
| • | Our earnings during 2009 and 2008 included losses of $5.8 million and $148.9 million, respectively, associated with SIV securities. In 2009, we purchased the remaining SIV securities from our money market funds and, as a result, all of our obligations to provide support to our funds were canceled. |
| • | We continued to invest in the Global Wealth Platform and its operational infrastructure. During 2009, we capitalized $43.9 million for significant enhancements and new functionality for the platform, as compared to $55.9 million in 2008. |
| • | We recognized an additional $15.4 million of amortization expense primarily in the Private Banks and Investment Advisors segments during the third and fourth quarters of 2009 due to a shortening in the useful life of previously capitalized software development costs for some components of the Global Wealth Platform. This change was due to the abandonment of these components upon a release of the platform which occurred in December 2009. |
| • | Our operating expenses during 2009 decreased across all of our business segments. A portion of these declines were due to lower direct costs related to reduced revenues. In addition, a significant portion of these declines resulted from initiatives to reduce discretionary expenses. Included in these actions were the elimination of non-strategic activities, process improvements and a reduction in our global workforce, which was undertaken during the first quarter of 2009. We incurred one-time termination costs associated with the workforce reduction of approximately $6.3 million during the first quarter of 2009. |
Page 19 of 88
Table of Contents
| • | We continued our stock repurchase program during 2009 and purchased approximately 3,198,000 shares at an average price of approximately $17 per share for a total cost of $54.1 million. |
| • | Our 2009 effective tax rate was 33.9 percent as compared to 38.1 percent in 2008. Our tax rate in 2009 was favorably impacted by the recognition of certain tax benefits related to the conclusion of federal and state income tax audits. Our 2008 tax rate was due to a higher than usual state tax rate. |
Forward Looking Information and Risk Factors
Certain information contained in this discussion is or may be considered forward-looking. Forward-looking statements relate to future operations, strategies, financial results or other developments. Forward-looking statements are based upon estimates and assumptions that involve certain risks and uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control or are subject to change. Although we believe our assumptions are reasonable, they could be inaccurate. Our actual future revenues and income could differ materially from our expected results. We have no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements.
Among the risks and uncertainties which may affect our future operations, strategies, financial results or other developments are those risks described in Item 1A “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report. The following items are, in our opinion, anticipated to occur in the next 12 to 18 months:
| • | We will continue to invest in the Global Wealth Platform and its operational infrastructure because it is vital to our future growth strategy. We anticipate that capitalized development expenditures in 2011 will remain relatively consistent with those in 2010. We will continue to implement enhancements and upgrades to the platform through a series of releases. Our current developmental and operational efforts are primarily focused on expanding the functionality of the current version of the platform for existing private bank and wealth managers in the United Kingdom as well as building the necessary functionality in order to service financial institutions and investment advisors in the United States. We are also investing in automation aimed at enhancing our operational efficiency and scale. A significant portion of the costs for these efforts will not be capitalized and; therefore, our operational costs related to the platform are expected to increase, primarily impacting the operating margins of the Private Banks and Investment Advisors segments. |
| • | We expect our operating margin for the Private Banks segment in 2011 to also be pressured by the extended lead time required to fully realize recurring revenues from new Global Wealth Services clients serviced on the Global Wealth Platform. The revenue recognition time frame for new clients serviced on the platform will be longer than our prior implementations of investment processing clients supported by TRUST 3000® as the conversion process generally occurs over a longer period of time. Profitability gains for the Private Banks segment will also be pressured by the limited number of fully implemented clients serviced on the platform as we continue our efforts to improve the operational efficiency and scale of the Global Wealth Services solution. |
| • | During 2010, our stock-based compensation costs increased $12.3 million to $26.8 million because some option grants achieved their performance vesting targets sooner than was originally expected. This was due largely to increased asset-based revenues from improved capital market conditions and significant gains realized from our SIV securities. Based on our current estimates and assumptions, we expect our stock-based compensation costs in 2011 to be approximately $3.6 million per quarter. |
Deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group
In January 2010, new accounting guidance pertaining to the consolidation of variable interest entities (VIE or VIEs) became effective. Under the new guidance, we are not considered to be the primary beneficiary of LSV Employee Group and discontinued consolidating the accounts of LSV and LSV Employee Group. Our interest in LSV is accounted for using the equity method because of our less than 50 percent ownership. Our interest in the net assets of LSV is reflected in Investment in unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet and our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV is reflected in Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations. The deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group had no effect on Net income attributable to SEI. Prior period financial statements are not reclassified for the new accounting guidance. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information pertaining to the deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group.
Page 20 of 88
Table of Contents
The following proforma Consolidated Statements of Operations presents the years ended 2010, 2009 and 2008 as if LSV and LSV Employee Group was deconsolidated on January 1, 2008. This proforma statement is being provided for informational and comparative purposes only and is not a restatement or reclassification of previously reported statements.
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 Actual |
2009 Proforma (Unaudited) |
Percent Change |
2008 Proforma (Unaudited) |
Percent Change |
|||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 900,835 | $ | 848,587 | 6 | % | $ | 984,651 | (14 | %) | ||||||||||
| Expenses |
683,302 | 658,434 | 4 | % | 714,758 | (8 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
217,533 | 190,153 | 14 | % | 269,893 | (30 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Net gain (loss) from investments |
48,533 | (4,926 | ) | N/A | (158,018 | ) | (97 | %) | ||||||||||||
| Interest income, net of interest expense |
4,848 | 5,013 | (3 | %) | 12,121 | (59 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Other (expense) income |
(590 | ) | 0 | N/A | 5,577 | N/A | ||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
99,457 | 75,415 | 32 | % | 98,971 | (24 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
369,781 | 265,655 | 39 | % | 228,544 | 16 | % | |||||||||||||
| Income taxes |
136,461 | 89,886 | 52 | % | 86,703 | 4 | % | |||||||||||||
| Net income |
233,320 | 175,769 | 33 | % | 141,841 | 24 | % | |||||||||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest |
(1,633 | ) | (1,434 | ) | 14 | % | (2,587 | ) | (45 | %) | ||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | 231,687 | $ | 174,335 | 33 | % | $ | 139,254 | 25 | % | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 1.22 | $ | .91 | 34 | % | $ | .71 | 28 | % | ||||||||||
Page 21 of 88
Table of Contents
Asset Balances
This table presents assets of our clients, or of our clients’ customers, for which we provide management or administrative services through our subsidiaries and partnerships in which we have a significant interest. These assets are not included in our balance sheets because we do not own them.
| Asset Balances | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | Percent Change |
2008 | Percent Change |
||||||||||||||||
| Private Banks: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 13,512 | $ | 12,690 | 6 | % | $ | 10,573 | 20 | % | ||||||||||
| Collective trust fund programs |
626 | 1,067 | (41 | %) | 1,145 | (7 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
5,120 | 6,035 | (15 | %) | 9,194 | (34 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 19,258 | $ | 19,792 | (3 | %) | $ | 20,912 | (5 | %) | ||||||||||
| Client proprietary assets under administration |
10,672 | 11,213 | (5 | %) | 10,622 | 6 | % | |||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 29,930 | $ | 31,005 | (3 | %) | $ | 31,534 | (2 | %) | ||||||||||
| Investment Advisors: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 27,680 | $ | 25,392 | 9 | % | $ | 21,631 | 17 | % | ||||||||||
| Collective trust fund programs |
1,820 | 2,423 | (25 | %) | 2,606 | (7 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
1,641 | 1,929 | (15 | %) | 3,436 | (44 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 31,141 | $ | 29,744 | 5 | % | $ | 27,673 | 7 | % | ||||||||||
| Institutional Investors: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 48,699 | $ | 44,322 | 10 | % | $ | 34,966 | 27 | % | ||||||||||
| Collective trust fund programs |
623 | 684 | (9 | %) | 942 | (27 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
3,382 | 3,370 | 0 | % | 4,582 | (26 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 52,704 | $ | 48,376 | 9 | % | $ | 40,490 | 19 | % | ||||||||||
| Investment Managers: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 1 | $ | 4 | (75 | %) | $ | 8 | (50 | %) | ||||||||||
| Collective trust fund programs |
8,177 | 7,428 | 10 | % | 5,974 | 24 | % | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
313 | 412 | (24 | %) | 869 | (53 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 8,491 | $ | 7,844 | 8 | % | $ | 6,851 | 14 | % | ||||||||||
| Client proprietary assets under administration |
233,079 | 221,680 | 5 | % | 234,628 | (6 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 241,570 | $ | 229,524 | 5 | % | $ | 241,479 | (5 | %) | ||||||||||
| Investments in New Businesses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 569 | $ | 520 | 9 | % | $ | 519 | 0 | % | ||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
65 | 75 | (13 | %) | 153 | (51 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 634 | $ | 595 | 7 | % | $ | 672 | (11 | %) | ||||||||||
| LSV: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 60,058 | $ | 52,488 | 14 | % | $ | 37,714 | 39 | % | ||||||||||
| Consolidated: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Equity and fixed-income programs |
$ | 150,519 | $ | 135,416 | 11 | % | $ | 105,411 | 28 | % | ||||||||||
| Collective trust fund programs |
11,246 | 11,602 | (3 | %) | 10,667 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||
| Liquidity funds |
10,521 | 11,821 | (11 | %) | 18,234 | (35 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management |
$ | 172,286 | $ | 158,839 | 8 | % | $ | 134,312 | 18 | % | ||||||||||
| Client proprietary assets under administration |
243,751 | 232,893 | 5 | % | 245,250 | (5 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total assets under management and administration |
$ | 416,037 | $ | 391,732 | 6 | % | $ | 379,562 | 3 | % | ||||||||||
Page 22 of 88
Table of Contents
Assets under management are total assets of our clients or their customers invested in our equity and fixed-income investment programs, collective trust fund programs, and liquidity funds for which we provide asset management services. Assets under management and administration are total assets of our clients or their customers for whom we provide administrative services, including client proprietary fund balances for which we provide administration and/or distribution services.
Business Segments
Revenues, Expenses, and Operating Profit (Loss) for our business segments, excluding LSV, for the year ended 2010 compared to the year ended 2009, and for the year ended 2009 compared to the year ended 2008 are:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | Percent Change |
2008 | Percent Change |
|||||||||||||||
| Private Banks: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 346,668 | $ | 361,273 | (4 | %) | $ | 408,500 | (12 | %) | ||||||||||
| Expenses |
310,633 | 309,300 | 0 | % | 326,661 | (5 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Profit |
36,035 | 51,973 | (31 | %) | 81,839 | (36 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Margin |
10 | % | 14 | % | 20 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Investment Advisors: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
183,378 | 166,097 | 10 | % | 223,164 | (26 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Expenses |
110,388 | 109,418 | 1 | % | 122,231 | (10 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Profit |
72,990 | 56,679 | 29 | % | 100,933 | (44 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Margin |
40 | % | 34 | % | 45 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Institutional Investors: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
206,531 | 177,721 | 16 | % | 198,154 | (10 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Expenses |
106,934 | 99,924 | 7 | % | 112,866 | (11 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Profit |
99,597 | 77,797 | 28 | % | 85,288 | (9 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Margin |
48 | % | 44 | % | 43 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Investment Managers: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
160,159 | 139,004 | 15 | % | 147,968 | (6 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Expenses |
103,421 | 93,074 | 11 | % | 101,078 | (8 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Profit |
56,738 | 45,930 | 24 | % | 46,890 | (2 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Margin |
35 | % | 33 | % | 32 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Investments in New Businesses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
4,099 | 4,492 | (9 | %) | 6,865 | (35 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Expenses |
12,676 | 11,625 | 9 | % | 15,795 | (26 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Operating Loss |
(8,577 | ) | (7,133 | ) | 20 | % | (8,930 | ) | (20 | %) | ||||||||||
| Operating Margin |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||
For additional information pertaining to our business segments, see Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Page 23 of 88
Table of Contents
Private Banks
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | Percent Change |
2008 | Percent Change |
|||||||||||||||
| Revenues: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment processing and software servicing fees |
$ | 229,247 | $ | 230,214 | 0 | % | $ | 225,994 | 2 | % | ||||||||||
| Asset management, administration & distribution fees |
87,288 | 84,529 | 3 | % | 129,466 | (35 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Transaction-based and trade execution fees |
30,133 | 46,530 | (35 | %) | 53,040 | (12 | %) | |||||||||||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 346,668 | $ | 361,273 | (4 | %) | $ | 408,500 | (12 | %) | ||||||||||
Revenues decreased $14.6 million, or four percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2010 were primarily affected by:
| • | Decreased trade execution fees due to lower trading volumes in the capital markets; |
| • | Decreased investment processing fees for our Global Wealth Technology Services solution; including non-recurring deconversion and contract buyout fees, due to the loss of two large U.S. bank clients involved in mergers and acquisitions; |
| • | Lower investment processing fees from both lost clients and fee concessions for contract renewals with U.S. regional and community banks for our Global Wealth Services solution; and |
| • | Lower fees from our liquidity products due to voluntary fee waivers; partially offset by |
| • | Increased investment processing fees for our Global Wealth Services solution, including non-recurring project fees, because of new United Kingdom wealth advisory firms implemented onto the Global Wealth Platform; and |
| • | Increased investment management fees from existing international clients due to higher assets under management from improved capital markets. |
Revenues decreased $47.2 million, or 12 percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2009 were primarily affected by:
| • | Decreased investment management fees from existing international clients due to lower average levels of assets under management from sharply declining capital markets in the fourth quarter 2008 and first quarter 2009; |
| • | Decreased investment management fees from negative cash flows, particularly from non-U.S. clients; |
| • | Decreased trade execution fees due to the absence during 2009 of the significant volatility in the capital markets that occurred primarily in the fourth quarter 2008; and |
| • | Decreased investment processing fees in our Global Wealth Services solution from existing U.S. clients; partially offset by |
| • | Increased non-recurring fees relating to mergers and acquisition activity among investment processing clients. |
Operating margins were 10 percent in 2010 and 14 percent in 2009. Operating income decreased $15.9 million, or 31 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Operating income in 2010 was primarily affected by:
| • | The decrease in revenues; |
| • | Increased non-capitalized development costs as well as operating costs relating to the Global Wealth Platform; |
| • | Increased direct expenses associated with increased investment management fees from existing international clients; |
| • | An increase in stock-based compensation costs primarily due to the acceleration in recognition of stock-based compensation, net of the reversal of stock-based compensation costs, due to a change in management’s estimate of the attainment of certain performance vesting targets; and |
| • | Increased sales compensation expenses due to sales of new business; partially offset by |
| • | Decreased direct expenses associated with the decreased trade execution fees; |
| • | Additional amortization expense of $10.1 million in 2009 related to the shortening in useful life of certain components related to the Global Wealth Platform; and |
| • | Decreased one-time termination costs associated with the workforce reduction in first quarter 2009, net of one-time termination costs in first quarter 2010. |
Page 24 of 88
Table of Contents
Operating margins were 14 percent in 2009 and 20 percent in 2008. Operating income decreased $29.9 million, or 36 percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Operating income in 2009 was primarily affected by:
| • | The aforementioned decline in revenues; and |
| • | Additional amortization expense of $10.1 million related to the shortening in useful life of certain components related to the Global Wealth Platform; partially offset by |
| • | Decreased direct expenses associated with the lower investment management fees and trade execution fees; |
| • | Decreased salary, travel and other personnel expenses; and |
| • | Decreased discretionary marketing and promotion expenses associated with cost containment measures. |
Investment Advisors
Revenues increased $17.3 million, or ten percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2010 were primarily affected by:
| • | Increased investment management fees from existing clients due to higher assets under management caused by improved capital markets; and |
| • | An increase in the average basis points earned on assets due to client-directed shifts from liquidity products to our equity and fixed income programs. |
Revenues decreased $57.1 million, or 26 percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2009 were primarily affected by:
| • | Decreased investment management fees from existing clients due to lower average levels of assets under management from sharply declining capital markets in the fourth quarter 2008 and first quarter 2009; and |
| • | Decreased investment management fees from continued negative net cash flows. |
Operating margins were 40 percent in 2010 and 34 percent in 2009. Operating income increased $16.3 million, or 29 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Operating income in 2010 was primarily affected by:
| • | An increase in revenues; |
| • | Additional amortization expense of $3.7 million in 2009 related to the shortening in useful life of certain components related to the Global Wealth Platform; and |
| • | Decreased one-time termination costs associated with the workforce reduction in first quarter 2009; partially offset by |
| • | An increase in stock-based compensation costs primarily due to the acceleration in recognition of stock-based compensation, net of the reversal of stock-based compensation costs, due to a change in management’s estimate of the attainment of certain performance vesting targets; and |
| • | A charge of approximately $1.0 million related to a processing error in the third quarter 2010. |
Operating margins were 34 percent in 2009 and 45 percent in 2008. Operating income decreased $44.3 million, or 44 percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Operating income in 2009 was primarily affected by:
| • | The aforementioned decline in revenues; and |
| • | Additional amortization expense of $3.7 million related to the shortening in useful life of certain components related to the Global Wealth Platform; partially offset by |
| • | Decreased direct expenses associated with the lower investment management fees; |
| • | Decreased salary, travel and other personnel expenses; and |
| • | Decreased discretionary marketing and promotion expenses associated with cost containment measures. |
Institutional Investors
Revenues increased $28.8 million, or 16 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2010 were primarily affected by:
| • | Increased investment management fees from existing clients due to higher assets under management caused by improved capital markets as well as additional asset funding from existing clients; and |
| • | Asset funding from new sales of our retirement and not-for-profit solutions; partially offset by |
| • | Client losses. |
Page 25 of 88
Table of Contents
Revenues decreased $20.4 million, or ten percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2009 were primarily affected by:
| • | Decreased investment management fees from existing clients due to lower assets under management from sharply declining capital markets in the fourth quarter 2008 and first quarter 2009 and client losses; and |
| • | Decreased investment management fees from unfavorable foreign currency fluctuations in revenues from our international clients; partially offset by |
| • | Asset funding from new sales of our retirement and not-for-profit solutions; and |
| • | Asset funding from existing clients. |
Operating margins were 48 percent in 2010 and 44 percent in 2009. Operating income increased $21.8 million, or 28 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Operating income during 2010 was primarily affected by:
| • | An increase in revenues; and |
| • | A charge of approximately $2.2 million related to an operational error in the third quarter of 2009; partially offset by |
| • | An increase in stock-based compensation costs primarily due to the acceleration in recognition of stock-based compensation, net of the reversal of stock-based compensation costs, due to a change in management’s estimate of the attainment of certain performance vesting targets; |
| • | An increase in personnel expenses; and |
| • | Increased direct expenses associated with higher investment management fees. |
Operating margins were 44 percent in 2009 and 43 percent in 2008. Operating income decreased $7.5 million, or nine percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Operating income during 2009 was primarily affected by:
| • | The aforementioned decline in revenues; and |
| • | A one-time charge of approximately $2.2 million related to an operational error in the third quarter 2009; partially offset by |
| • | Decreased direct expenses associated with the lower investment management fees; |
| • | Decreased salary, travel and other personnel expenses; |
| • | Decreased sales compensation expenses due to the reduced amount of sales of new business; and |
| • | Decreased discretionary marketing and promotion expenses associated with cost containment measures. |
Investment Managers
Revenues increased $21.2 million, or 15 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2010 were primarily affected by:
| • | Cash flows from new clients, primarily hedge fund clients; and |
| • | Net positive cash flows from existing hedge fund clients mainly due to higher valuations from capital market increases; partially offset by |
| • | Client losses. |
Revenues decreased $9.0 million, or six percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Revenues during 2009 were primarily affected by:
| • | Negative cash flows from existing hedge fund clients due to lower valuations from capital market declines in the fourth quarter 2008 and first quarter 2009 as well as client redemptions; and |
| • | Negative cash flows from traditional fund administration clients due to the aforementioned capital market declines; partially offset by |
| • | Cash flows from new clients, primarily hedge fund clients. |
Operating margins were 35 percent in 2010 and 33 percent in 2009. Operating income increased $10.8 million, or 24 percent, in 2010 compared to the prior year. Operating income during 2010 was primarily affected by:
| • | An increase in revenues; partially offset by |
| • | An increase in stock-based compensation costs primarily due to the acceleration in recognition of stock-based compensation, net of the reversal of stock-based compensation costs, due to a change in management’s estimate of the attainment of certain performance vesting targets; |
| • | An increase in personnel expenses; and |
| • | Increased technology and other investment spending for the development of new products and services. |
Page 26 of 88
Table of Contents
Operating margins were 33 percent in 2009 and 32 percent in 2008. Operating income decreased $1.0 million, or two percent, in 2009 compared to the prior year. Operating income during 2009 was primarily affected by:
| • | The aforementioned decline in revenues; partially offset by |
| • | Decreased salary, travel and other personnel expenses; and |
| • | Decreased discretionary consulting and outsourcing expenses associated with cost containment measures. |
Other
Other Income and Expense Items
Other income and expense items on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations consist of:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Net gain (loss) from investments |
$ | 48,533 | $ | (4,926 | ) | $ | (158,018 | ) | ||||
| Interest and dividend income |
6,326 | 7,281 | 13,740 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(1,478 | ) | (3,744 | ) | (3,418 | ) | ||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(590 | ) | 0 | 5,577 | ||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
99,457 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Total other income and expense items, net |
$ | 152,258 | $ | (1,389 | ) | $ | (142,119 | ) | ||||
Net gain (loss) from investments
Net gain (loss) from investments consists of:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Gains (losses) from SIV securities and Capital Support Agreements |
$ | 44,247 | $ | (5,778 | ) | $ | (158,182 | ) | ||||
| Net realized and unrealized gains from marketable securities |
1,214 | 1,753 | 2,144 | |||||||||
| Other-than-temporary declines in market value |
0 | (901 | ) | (1,961 | ) | |||||||
| Other gains (losses) |
3,072 | 0 | (19 | ) | ||||||||
| Net gain (loss) from investments |
$ | 48,533 | $ | (4,926 | ) | $ | (158,018 | ) | ||||
We entered into Capital Support Agreements in late 2007 with several of our money market funds in order to protect our clients and shareholders of the funds from the liquidity issues stemming from the subprime mortgage crisis. These funds held senior notes issued by structured investment vehicles (SIV or SIVs) which failed to make payments on their outstanding notes on the scheduled maturity dates. In 2008 and 2009, we purchased all of the SIV securities from our funds covered under the Capital Support Agreements for a total cash purchase price of $328.4 million. As a result of these purchases, the Capital Support Agreements with the funds were canceled. We record the SIV securities at fair value and recognize unrealized gains and losses of the securities in current earnings. These gains and losses from the purchases of the SIV securities, as well as the changes in our former obligations related to the Capital Support Agreements, are included in Gains (losses) from SIV securities and Capital Support Agreements in the preceding table.
We recognized a $3.1 million gain in 2010 due to the sale of our ownership interest in a small company that was involved in a merger. This gain is reflected in Other gains (losses) in the preceding table.
Interest and dividend income
Interest and dividend income is primarily based upon the amount of our cash balances and cash equivalents that are invested daily. The decreases in interest income in 2010 and 2009 compared to the prior years were due to declines in interest rates earned on our cash balances and lower yields earned from our cash equivalents.
Page 27 of 88
Table of Contents
Interest expense
Interest expense in 2010 and 2009 includes the interest charges and fees related to the borrowings under our credit facility. The decline in interest expense in 2010 was due to the deconsolidation of LSV Employee Group since our interest expense in 2009 also included the interest charges related to their borrowings. The increase in interest expense in 2009 as compared to 2008 was attributable to the aggregate borrowings of $254.0 million commencing in March 2009 through our credit facility to finance the purchases of SIV securities from our money market funds. We incurred interest expense of approximately $1.4 million and $1.9 million in 2010 and 2009, respectively, related to our borrowings under the credit facility. Interest expense for the debt associated with LSV Employee Group included in our interest expense was approximately $1.5 million and $2.3 million in 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Other (expense) income, net
Other (expense) income in 2008 relates to an adjustment for interest costs associated with borrowings in prior years at a time when various capital projects were underway. We incorrectly expensed all interest costs rather than capitalizing these costs as part of the cost basis of these capital projects (See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements).
Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate
Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate includes our less than 50 percent ownership in LSV. We deconsolidated the accounts and operations of LSV in January 2010. In 2009, LSV was a business segment and, therefore, our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV was included in the results of our business segments. Our total partnership interest in LSV remained at approximately 42 percent during 2010 and 2009. Our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV was $99.5 million in 2010 as compared to $75.4 million in 2009, an increase of 32 percent. The increase in 2010 was due to increased assets under management from existing clients because of improved capital markets. LSV’s assets under management increased $7.6 billion to $60.1 billion at December 31, 2010 as compared to $52.5 billion at December 31, 2009, an increase of 14 percent. In 2009, our proportionate share in the earnings of LSV decreased to $75.4 million from $98.5 million in 2008, a decrease of $23.1 million, or 23 percent. The decline in 2009 was due to decreased assets under management because of unfavorable capital market conditions. See Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information pertaining to the deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group.
Noncontrolling interest
Noncontrolling interest in 2009 primarily includes the amount owned by other partners of LSV and LSV Employee Group.
Income Taxes
Our effective tax rate was 37.0 percent in 2010, 33.9 percent in 2009, and 38.1 percent in 2008. The 2009 effective tax rate is lower than 2010 and 2008 due to the recognition of certain tax benefits related to the conclusion of federal and state income tax audits. Our effective tax rate for 2009 excluding the net reduction relating to tax uncertainties was 37.0 percent. The 2008 effective tax rate was higher due to state tax impact relating to the expense associated with the Capital Support Agreements.
Page 28 of 88
Table of Contents
Stock-Based Compensation
During 2010 and 2009, we recognized approximately $26.8 million and $14.5 million, respectively, in stock-based compensation expense, an increase of $12.3 million. This increase consisted of the following components:
| Change in Stock-Based Compensation Expense |
||||
| Stock-based compensation cost recognized in 2010 for grants made in December 2009 (1) |
$ | 14,647 | ||
| Reversal of previously recognized stock-based compensation expense |
(6,375 | ) | ||
| Change in management’s estimate of expected vesting of stock options for grants that were outstanding at December 31, 2009 (2) |
5,534 | |||
| Stock-based compensation cost associated with options that vested in 2009 |
(1,097 | ) | ||
| Other items |
(429 | ) | ||
| $ | 12,280 | |||
| (1) | Includes a change in management estimate of expected vesting of stock option grants of $6,129 during 2010. |
| (2) | Excludes options granted in December 2009. |
For more information pertaining to stock-based compensation, see Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Fair Value Measurements
The fair value of our financial assets is determined in accordance with the fair value hierarchy. The fair value of most of our financial assets is determined using Level 1 or Level 2 inputs and consist mainly of investments in equity and fixed-income mutual funds that are quoted daily and Government National Mortgage Association securities that are single issuer pools that are valued based on current market data of similar assets. Level 3 financial assets consist of SIV securities. We did not have any financial liabilities at December 31, 2010 or 2009. See Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information pertaining to the valuation of SIV securities.
Page 29 of 88
Table of Contents
The table below presents a reconciliation for all of our financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the period from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010:
| Trading Securities Issued by SIVs |
Other
Trading Securities |
Capital Support Agreements |
||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2009 |
$ | 5,713 | $ | 1,697 | $ | (173,983 | ) | |||||
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net |
294,762 | (1,536 | ) | 0 | ||||||||
| Transfer of Capital Support Agreement at purchase |
(179,654 | ) | 0 | 179,654 | ||||||||
| Total gains (losses) (realized/unrealized): |
||||||||||||
| Included in earnings |
(107 | ) | (161 | ) | (5,671 | ) | ||||||
| Included in other comprehensive income |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Transfers in and out of Level 3 |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2009 |
$ | 120,714 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net |
(64,316 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Total gains (losses) (realized/unrealized): |
||||||||||||
| Included in earnings |
44,247 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Included in other comprehensive income |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Transfers in and out of Level 3 |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2010 |
$ | 100,645 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 229,326 | $ | 345,471 | $ | 284,728 | ||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(41,475 | ) | (338,912 | ) | (86,299 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(282,436 | ) | 167,675 | (142,707 | ) | |||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
(94,585 | ) | 174,234 | 55,722 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
590,877 | 416,643 | 360,921 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year |
$ | 496,292 | $ | 590,877 | $ | 416,643 | ||||||
Cash requirements and liquidity needs are primarily funded through our cash flow from operations and our capacity for additional borrowing. At December 31, 2010, our unused sources of liquidity consisted of cash and cash equivalents and the amount available under our five-year, $300.0 million credit facility. Our credit facility is an unsecured senior revolving line of credit with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., individually and as agent, and a syndicate of other lenders. The credit facility is scheduled to expire in July 2012, at which time any aggregate principal amount of loans outstanding must be paid in full. During 2009, we borrowed $254.0 million through the credit facility to purchase SIV securities from SEI-sponsored money market funds. Through December 2010, we made principal payments of $159.0 million to reduce the outstanding balance of our credit facility. As of December 31, 2010, the outstanding balance of the credit facility was $95.0 million (See Note 7 to the Consolidated Financial Statements).
Due to the adoption of new accounting guidance, we discontinued consolidating the accounts of LSV and LSV Employee Group in January 2010 (See “Deconsolidation of LSV and LSV Employee Group” earlier in this discussion). Because of the deconsolidation, we no longer include the amount of cash and cash equivalents of LSV and LSV Employee Group on our balance sheet. The deconsolidation resulted in a net reduction of $37.1 million in our cash and cash equivalents in 2010 classified as net cash used in investing activities.
Page 30 of 88
Table of Contents
Our cash and cash equivalents include accounts managed by our subsidiaries and minority-owned subsidiaries that are used in their operations or to cover specific business and regulatory requirements. The availability of this cash for other purposes beyond the operations of these subsidiaries may be limited. As of January 31, 2011, the amount of cash and cash equivalents considered free and immediately accessible for other general corporate purposes was $335.0 million.
The availability of our credit facility is subject to the compliance with certain covenants set forth in the agreement. The credit facility contains covenants which restrict our ability to engage in mergers, consolidations, asset sales, investments, transactions with affiliates, or to incur liens, as defined in the agreement. In the event of a default under the credit facility, we would also be restricted from paying dividends on, or repurchasing, our common stock. Currently, our ability to borrow from the credit facility is not limited by any covenant of the agreement. Of all of the covenants, we believe the leverage ratio is the most restrictive. The leverage ratio is calculated as consolidated indebtedness divided by earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and other items as defined by the covenant during the last four quarters (EBITDA). The amount of consolidated indebtedness according to the terms of the covenant include the outstanding debt of LSV Employee Group. We must maintain a ratio of consolidated indebtedness of not more than 1.75 times the amount of EBITDA at December 31, 2010 and at all times thereafter until the expiration of the agreement. As of December 31, 2010, our leverage ratio was 0.24 times EBITDA. We do not anticipate that this covenant or any covenant of the credit facility will restrict our ability to utilize the credit facility.
The decline in cash flows from operations of $116.1 million in 2010 compared to 2009 was primarily due to tax benefits received for net realized losses from SIV securities in 2009 which significantly reduced our tax payments in the prior year period.
We have long-term contractual agreements with banks, investment advisors, money managers and other financial institutions. These firms continue to meet the scheduled payment terms under these contracts. We have no reason to believe that any of our clients will be unable to satisfy current and future obligations. We believe our clients represent stable and well-respected firms that will continue to remain viable entities over the long-term. We do not have any significant collectibility issues regarding our receivables as of December 31, 2010 and we have not received any indications that we should anticipate significant collectibility issues regarding our receivables in the near term.
Net cash used in investing activities includes:
| • | Purchases, sales and maturities of marketable securities. We had cash outflows of $39.1 million for the purchase of marketable securities in 2010 as compared to $322.5 million in 2009. Marketable securities purchased in 2010 primarily consisted of investments for the start-up of new investment products and additional GNMA securities to satisfy applicable regulatory requirements of SPTC. Marketable securities purchased in 2009 consist primarily of SIV securities acquired from SEI-sponsored money market funds. Sales and maturities of marketable securities, including principal prepayments received from our GNMA and SIV securities were $87.0 million in 2010 as compared to $52.8 million in 2009. |
| • | The capitalization of costs incurred in developing computer software. We will continue the development of the Global Wealth Platform through a series of releases to expand the functionality of the platform. We capitalized $38.7 million of software development costs in 2010 as compared to $43.9 million in 2009. Amounts capitalized in 2010 and 2009 include costs for significant enhancements and upgrades to the platform. |
| • | Capital expenditures. Our capital expenditures in 2010 primarily include equipment for our data center operations. Capital expenditures in 2009 primarily include new computer-related equipment associated with our investment processing platforms. |
Net cash used in financing activities includes:
| • | Borrowings on long-term debt. We borrowed $254.0 million in 2009 through our credit facility to finance our purchases of SIV securities from SEI-sponsored money market funds. There were no borrowings related to our credit facility in 2010. |
| • | Principal payments of our debt. We made principal payments of $138.0 million in 2010 and $21.0 million in 2009 to reduce the outstanding debt associated with our credit facility. Principal payments in 2009 include payments of $11.0 million made by LSV Employee Group for amounts previously included in our debt. Due to the deconsolidation of LSV Employee Group in January 2010, we no longer include the principal payments of LSV Employee Group in cash flows from financing activities. |
Page 31 of 88
Table of Contents
| • | Dividend payments. Cash dividends paid were $54.6 million or $.29 per share in 2010, $30.6 million or $.16 per share in 2009 and $28.9 million or $.15 per share in 2008. Our Board of Directors declared a cash dividend of $.10 per share on December 14, 2010. The dividend was paid on December 30, 2010 for $18.6 million. The increase in dividends paid in 2010 was due to the payment date of the December 2010 dividend occurring in the calendar year as compared to the payment date of the dividends declared in December 2009 and 2008 which occurred in January of the following year. |
| • | The repurchase of our common stock. Our Board of Directors has authorized the repurchase of up to $1.73 billion worth of our common stock. Through January 31, 2011, we repurchased approximately 264.1 million shares of our common stock at a cost of $1.6 billion and had $101.7 million of authorization remaining for the purchase of our common stock under this program. Currently, there is no expiration date for our common stock repurchase program. The following table lists information regarding repurchases of our common stock during 2010, 2009, and 2008: |
| Year |
Total Number of Shares Repurchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Cost (in thousands) |
|||||||||
| 2010 |
5,814,000 | $ | 20.81 | $ | 120,982 | |||||||
| 2009 |
3,198,000 | 16.92 | 54,114 | |||||||||
| 2008 |
5,778,000 | 22.44 | 129,633 | |||||||||
We believe our operating cash flow, available borrowing capacity, and existing cash and cash equivalents should provide adequate funds for ongoing operations; continued investment in new products and equipment; our common stock repurchase program; principal payments on our debt; and future dividend payments.
Significant Arrangement
On January 24, 2006, we entered into a Guaranty and Collateral Agreement with LSV Employee Group, LaSalle Bank National Association and certain other lenders. We entered into the agreement in order to facilitate the acquisition of certain partnership interests of LSV by LSV Employee Group. Additional information pertaining to the agreement is presented in Note 2 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Contractual Obligations and Contingent Obligations
As of December 31, 2010, the Company is obligated to make payments in connection with its lines of credit, debt obligations, operating leases, maintenance contracts and other commitments in the amounts listed below. The Company has no unrecorded obligations other than the items noted in the following table:
| Total | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 to 2014 |
2015 and Thereafter |
||||||||||||||||
| Line of credit (a) |
$ | 96,363 | $ | 871 | $ | 95,492 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||||||
| Operating leases and maintenance agreements (b) |
55,004 | 15,254 | 14,719 | 13,939 | 11,092 | |||||||||||||||
| Other commitments (c) |
767 | 767 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 152,134 | $ | 16,892 | $ | 110,211 | $ | 13,939 | $ | 11,092 | ||||||||||
| (a) | Amounts include estimated interest expense and commitment fees for our credit facility. See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| (b) | See Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| (c) | Amount includes the portion of uncertain tax liabilities classified as a current liability. The actual cash payment associated with these commitments may differ. See Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
Page 32 of 88
Table of Contents
Critical Accounting Policies
The accompanying consolidated financial statements and supplementary information were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. Our significant accounting policies are discussed in Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. Inherent in the application of many of these accounting policies is the need for management to make estimates and judgments in the determination of certain revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities. Materially different financial results can occur as circumstances change and additional information becomes known. We believe that the following accounting policies require extensive judgment by our management to determine the recognition and timing of amounts recorded in our financial statements.
Revenue Recognition:
Revenues are recognized in the periods in which the related services are performed provided that persuasive evidence of an agreement exists, the fee is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is reasonably assured. Cash received by us in advance of the performance of services is deferred and recognized as revenue when earned. Our principal sources of revenues are: (1) asset management, administration and distribution fees calculated as a percentage of the total average daily net assets under management or administration; (2) information processing and software servicing fees that are recurring in nature and earned based upon the number of trust accounts being serviced and non-recurring project fees that are earned based upon contractual agreements related to client implementations; and (3) transaction-based fees for providing trade-execution services. The majority of our revenues are based on contractual arrangements. Certain portions of our revenues require management’s consideration of the nature of the client relationship in determining whether to recognize as revenue the gross amount billed or net amount retained after payments are made to vendors for certain services related to the product or service offering.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts:
We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of some of our clients to make their scheduled payments. The allowance for doubtful accounts is based on the total amount of outstanding receivables and an aging analysis at each balance sheet date. Other factors are considered in determining the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts, such as historical trends, the financial condition of our clients and other factors that may be deemed appropriate. Based upon this analysis, the allowance for doubtful accounts is adjusted to an amount that is sufficient to cover expected losses from doubtful accounts.
Fair Value of Financial Assets and Liabilities:
We determine the fair value of our financial assets and liabilities in accordance with the fair value hierarchy. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The accounting standard also establishes a fair value hierarchy which requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The fair value hierarchy describes three levels of inputs that may be used to measure fair value:
Level 1 – Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities without adjustment;
Level 2 – Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices, such as quoted prices for similar assets, quoted prices in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data; and
Level 3 – Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and are significant to the fair value of those assets or liabilities.
The use of Level 3 inputs to determine the fair value of our financial assets requires considerable judgment by management. Our Level 3 financial assets consist of SIV securities we own. We did not have any financial liabilities at December 31, 2010 or 2009 (See Fair Value Measurements section earlier in this discussion).
We review our investments in marketable securities on a quarterly basis with regard to impairment. Some of the factors considered in determining other-than-temporary impairment for our equity securities include, but are not limited to, significant or prolonged declines in the fair value of our investments, our ability and intent to retain the investment for a period sufficient to allow the value to recover, and the financial condition of the
Page 33 of 88
Table of Contents
investment. Some of the factors considered in determining other-than-temporary impairment for our debt securities include, but are not limited to, our intent to sell the security, the likelihood that we will be required to sell the security before recovering its cost, and our expectation to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security even if we do not intend to sell the security. After considering these factors, if we believe that a decline is other-than-temporary, the carrying value of the investment is written down to its fair value through current period earnings.
Computer Software Development Costs:
We utilize internally developed computer software as part of our product offering. In the development of a new software product, substantial consideration must be given by management to determine whether costs incurred are research and development costs, or internal software development costs eligible for capitalization. Management must consider a number of different factors during their evaluation of each computer software development project that includes estimates and assumptions. Costs considered to be research and development are expensed as incurred. After meeting specific requirements, internal software development costs are capitalized as incurred. The capitalization and ongoing assessment of recoverability of software development costs requires considerable judgment by management with respect to certain external factors, including, but not limited to, technological and economic feasibility, and estimated economic life. Amortization of capitalized software development costs begins when the product is ready for its intended use. Capitalized software development costs are amortized on a product-by-product basis using the straight-line method over the estimated economic life of the product or enhancement.
We evaluate the carrying value of our capitalized software when circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. The review of capitalized software for impairment requires significant assumptions about operating strategies, underlying technologies utilized, and external market factors. Our capitalized software was developed using mainstream technologies that are industry standards and are based on technology developed by multiple vendors that are significant industry leaders. External market factors include, but are not limited to, expected levels of competition, barriers to entry by potential competitors, stability in the target market and governmental regulations. In 2010, we determined that no events or change in circumstances had occurred that would indicate that our capitalized software development costs were impaired (See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements).
Income Tax Accounting:
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, income tax expense is recognized for the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year. In addition, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities, and for operating losses and tax credit carryforwards. Management must make assumptions, judgments and estimates to determine our current provision for income taxes and also our deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance to be recorded against a deferred tax asset.
Our assumptions, judgments and estimates relative to the current provision for income taxes take into account current tax laws, our interpretation of current tax laws and possible outcomes of current and future audits conducted by foreign and domestic tax authorities. We have established reserves for income taxes to address potential exposures involving tax positions that could be challenged by tax authorities. Although we believe our assumptions, judgments and estimates are reasonable, changes in tax laws or our interpretation of tax laws and the resolution of any future tax audits could significantly impact the amounts provided for income taxes in our consolidated financial statements.
Our assumptions, judgments and estimates relative to the value of a deferred tax asset take into account predictions of the amount and category of future taxable income, such as income from operations or capital gains income. Actual operating results and the underlying amount and category of income in future years could render our current assumptions, judgments and estimates of recoverable net deferred taxes inaccurate. Any of the assumptions, judgments and estimates mentioned above could cause our actual income tax obligations to differ from our estimates, thus materially impacting our financial position and results of operations.
Stock-Based Compensation:
Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period, which is the vesting period. We currently use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options. The determination of the fair value of stock-based payment awards on the date of grant using an option-pricing model is affected by our stock price as well as various other assumptions. These assumptions include our expected stock price volatility over
Page 34 of 88
Table of Contents
the term of the awards, actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors, risk-free interest rate and expected dividends. We are required to estimate forfeitures at the time of grant and revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The amount of stock-based compensation expense that is recognized in a given period is dependent upon management’s estimate of when the earnings per share targets are expected to be achieved. If this estimate proves to be inaccurate, the remaining amount of stock-based compensation expense could be accelerated, spread out over a longer period, or reversed. We currently base our expectations for these assumptions from historical data and other applicable factors. These expectations are subject to change in future periods.
The assessment of critical accounting policies is not meant to be an all-inclusive discussion of the uncertainties to financial results that can occur from the application of the full range of our accounting policies. Materially different financial results could occur in the application of other accounting policies as well. Also, materially different results can occur upon the adoption of new accounting standards.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2010, the FASB issued a final Accounting Standards Update that sets forth additional requirements and guidance regarding disclosures of fair value measurements. The new standard requires the gross presentation of activity within the Level 3 fair value measurement rollforward and details of transfers in and out of Level 1 and 2 fair value measurements. It also clarifies two existing disclosure requirements on the level of disaggregation of fair value measurements and disclosures on inputs and valuation techniques. The new requirements and guidance are effective for interim and annual periods beginning in the first quarter 2010 except that the Level 3 rollforward is effective in the first quarter 2011. The adoption of the new requirements and guidance effective in the first quarter 2010 did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements. We do not expect the adoption of the guidance pertaining to the Level 3 rollforward to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
See the discussion of New Accounting Pronouncements in Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Page 35 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Interest Rate Risk - Our exposure to changes in interest rates primarily relates to our investment portfolio and our costs of borrowing related to the outstanding debt associated with our credit facility. Our excess cash is principally invested in short-term, highly liquid financial instruments, mainly money market mutual funds, with a substantial portion of such investments having initial maturities of three months or less. The holdings in our investment portfolio most sensitive to interest rate risk include Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA) securities. With the exception of measures taken to support our SEI-sponsored money market mutual funds, we place our investments in financial instruments that meet high credit quality standards. While changes in interest rates could decrease our interest income or increase our interest expense, we do not believe that we have a material exposure to changes in interest rates. We do not undertake any specific actions to cover our exposure to interest rate risk and are not a party to any interest rate risk management transactions.
Page 36 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
All other schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, or not required, or because the required information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto.
Page 37 of 88
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders
of SEI Investments Company:
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the accompanying index present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of SEI Investments Company and its subsidiaries (“the Company”) at December 31, 2010 and 2009, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2010 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the accompanying index presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2010, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
February 24, 2011
Page 38 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands) | and Subsidiaries |
| December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | ||||||||
| Assets |
Current Assets: | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 496,292 | $ | 590,877 | ||||||
| Restricted cash | 4,000 | 20,000 | ||||||||
| Receivables from regulated investment companies | 29,282 | 28,134 | ||||||||
| Receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $1,195 and $3,348 (Note 4) | 136,490 | 184,317 | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes, net | 1,387 | 2,283 | ||||||||
| Other current assets | 16,268 | 15,792 | ||||||||
| Total Current Assets |
683,719 | 841,403 | ||||||||
| Property and Equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $166,816 and $158,113 (Note 4) |
140,568 | 146,053 | ||||||||
| Capitalized Software, net of accumulated amortization of $90,947 and $67,894 | 294,332 | 278,656 | ||||||||
| Investments Available for Sale (Note 6) | 74,770 | 55,701 | ||||||||
| Trading Securities (Note 6) | 104,594 | 126,196 | ||||||||
| Investment in Unconsolidated Affiliate (Note 2) | 64,409 | 0 | ||||||||
| Goodwill (Note 2) | 0 | 22,842 | ||||||||
| Intangible Assets, net of accumulated amortization of $31,182 (Note 2) | 0 | 44,859 | ||||||||
| Other Assets, net | 14,831 | 18,098 | ||||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 1,377,223 | $ | 1,533,808 | ||||||
Page 39 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands, except par value) | and Subsidiaries |
| December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | ||||||||
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity |
Current Liabilities: | |||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 0 | $ | 6,400 | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
4,582 | 2,851 | ||||||||
| Accrued liabilities (Note 4) | 121,410 | 152,944 | ||||||||
| Deferred revenue | 1,608 | 860 | ||||||||
| Total Current Liabilities |
127,600 | 163,055 | ||||||||
| Long-term Debt (Note 7) | 95,000 | 247,152 | ||||||||
| Deferred Income Taxes | 92,253 | 86,257 | ||||||||
| Other Long-term Liabilities (Note 12) | 5,645 | 5,726 | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities |
320,498 | 502,190 | ||||||||
| Commitments and Contingencies (Note 11) | ||||||||||
| Equity: | ||||||||||
| SEI Investments shareholders’ equity: |
||||||||||
| Series Preferred stock, $.05 par value, 50 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding |
0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Common stock, $.01 par value, 750,000 shares authorized; 186,141 and 190,208 shares issued and outstanding |
1,861 | 1,902 | ||||||||
| Capital in excess of par value |
565,393 | 522,080 | ||||||||
| Retained earnings |
471,159 | 384,483 | ||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income, net |
3,157 | 1,258 | ||||||||
| Total SEI Investments Shareholders’ Equity |
1,041,570 | 909,723 | ||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
15,155 | 121,895 | ||||||||
| Total Equity |
1,056,725 | 1,031,618 | ||||||||
| Total Liabilities and Equity |
$ | 1,377,223 | $ | 1,533,808 | ||||||
Page 40 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Statements of Operations | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands, except per-share data) | and Subsidiaries |
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Revenues: |
||||||||||||
| Asset management, administration and distribution fees |
$ | 628,535 | $ | 773,186 | $ | 955,399 | ||||||
| Information processing and software servicing fees |
231,529 | 231,807 | 229,807 | |||||||||
| Transaction-based and trade execution fees |
40,771 | 55,555 | 62,713 | |||||||||
| Total revenues |
900,835 | 1,060,548 | 1,247,919 | |||||||||
| Expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Subadvisory, distribution and other asset management costs |
89,746 | 85,810 | 104,434 | |||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and royalties |
52,609 | 61,735 | 67,538 | |||||||||
| Compensation, benefits and other personnel |
269,165 | 274,675 | 293,860 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
26,783 | 14,503 | 16,010 | |||||||||
| Consulting, outsourcing and professional fees |
89,033 | 81,694 | 103,789 | |||||||||
| Data processing and computer related |
41,064 | 45,403 | 44,602 | |||||||||
| Facilities, supplies and other costs |
68,952 | 66,882 | 74,378 | |||||||||
| Amortization |
24,048 | 44,608 | 24,927 | |||||||||
| Depreciation |
21,902 | 21,531 | 22,032 | |||||||||
| Total expenses |
683,302 | 696,841 | 751,570 | |||||||||
| Income from operations |
217,533 | 363,707 | 496,349 | |||||||||
| Net gain (loss) from investments |
48,533 | (4,926 | ) | (158,018 | ) | |||||||
| Interest and dividend income |
6,326 | 7,281 | 13,740 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(1,478 | ) | (3,744 | ) | (3,418 | ) | ||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(590 | ) | 0 | 5,577 | ||||||||
| Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
99,457 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Net income before income taxes |
369,781 | 362,318 | 354,230 | |||||||||
| Income taxes |
136,461 | 89,886 | 86,703 | |||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 233,320 | $ | 272,432 | $ | 267,527 | ||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest |
(1,633 | ) | (98,097 | ) | (128,273 | ) | ||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | 231,687 | $ | 174,335 | $ | 139,254 | ||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
$ | 1.23 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.73 | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 1.22 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.71 | ||||||
Page 41 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands) | and Subsidiaries |
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 233,320 | $ | 272,432 | $ | 267,527 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive gain (loss), net of tax: |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
2,205 | 8,734 | (18,961 | ) | ||||||||
| Unrealized holding gain (loss) on investments: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding gains (losses) during the period, net of income taxes of $(486), $(1,065) and $1,522 |
484 | 2,124 | (2,484 | ) | ||||||||
| Less: reclassification adjustment for gains (losses) realized in net income, net of income taxes of $56, $(222) and $(107) |
(105 | ) | 360 | 144 | ||||||||
| Total other comprehensive gain (loss), net of taxes |
2,584 | 11,218 | (21,301 | ) | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income |
235,904 | 283,650 | 246,226 | |||||||||
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(2,318 | ) | (99,894 | ) | (123,123 | ) | ||||||
| Comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments |
$ | 233,586 | $ | 183,756 | $ | 123,103 | ||||||
Page 42 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands) | and Subsidiaries |
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Shares of Common Stock |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
190,208 | 191,195 | 194,375 | |||||||||
| Purchase and retirement of common stock |
(5,814 | ) | (3,198 | ) | (5,778 | ) | ||||||
| Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan |
114 | 156 | 144 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
1,633 | 2,055 | 2,454 | |||||||||
| Ending balance |
186,141 | 190,208 | 191,195 | |||||||||
| Common Stock |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 1,902 | $ | 1,912 | $ | 1,944 | ||||||
| Purchase and retirement of common stock |
(58 | ) | (32 | ) | (58 | ) | ||||||
| Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan |
1 | 2 | 1 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
16 | 20 | 25 | |||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 1,861 | $ | 1,902 | $ | 1,912 | ||||||
| Capital In Excess of Par Value |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 522,080 | $ | 485,721 | $ | 445,474 | ||||||
| Purchase and retirement of common stock |
(13,426 | ) | (6,970 | ) | (11,666 | ) | ||||||
| Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan |
1,902 | 2,035 | 2,830 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
26,177 | 21,607 | 25,601 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
26,783 | 13,962 | 16,010 | |||||||||
| Tax benefit on stock options exercised |
1,877 | 5,725 | 7,472 | |||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 565,393 | $ | 522,080 | $ | 485,721 | ||||||
| Retained Earnings |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 384,483 | $ | 289,682 | $ | 298,975 | ||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
231,687 | 174,335 | 139,254 | |||||||||
| Purchase and retirement of common stock |
(107,498 | ) | (47,112 | ) | (117,911 | ) | ||||||
| Dividends declared |
(37,513 | ) | (32,422 | ) | (30,636 | ) | ||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 471,159 | $ | 384,483 | $ | 289,682 | ||||||
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 1,258 | $ | (8,163 | ) | $ | 7,988 | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) |
1,899 | 9,421 | (16,151 | ) | ||||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 3,157 | $ | 1,258 | $ | (8,163 | ) | |||||
| Total SEI Investments Shareholders’ Equity |
$ | 1,041,570 | $ | 909,723 | $ | 769,152 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
$ | 15,155 | $ | 121,895 | $ | 109,722 | ||||||
| Total Equity |
$ | 1,056,725 | $ | 1,031,618 | $ | 878,874 | ||||||
Page 43 of 88
Table of Contents
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | SEI Investments Company | |
| (In thousands) | and Subsidiaries |
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 233,320 | $ | 272,432 | $ | 267,527 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Amortization |
24,048 | 44,608 | 24,927 | |||||||||
| Depreciation |
21,902 | 21,531 | 22,032 | |||||||||
| Equity in the earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
(99,457 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Distributions received from unconsolidated affiliate |
72,060 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Payments to partners of LSV |
0 | (87,337 | ) | (144,399 | ) | |||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
26,783 | 14,503 | 16,010 | |||||||||
| Provision for losses on receivables |
(1,004 | ) | 692 | (376 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred income tax expense (benefit) |
6,461 | 67,265 | (34,727 | ) | ||||||||
| Net realized (gains) losses from investments |
(48,533 | ) | 178,007 | 7,196 | ||||||||
| Capitalized interest |
0 | 0 | (5,577 | ) | ||||||||
| Other-than-temporary declines in market value |
0 | 901 | 1,961 | |||||||||
| Change in other long-term liabilities |
(81 | ) | 1,659 | (7,828 | ) | |||||||
| Other |
2,473 | 3,508 | (25,210 | ) | ||||||||
| Change in current assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in: |
||||||||||||
| Restricted cash for broker-dealer operations |
16,000 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Receivables from regulated investment companies |
(1,148 | ) | 230 | 9,834 | ||||||||
| Receivables |
(11,032 | ) | (3,885 | ) | 56,527 | |||||||
| Other current assets |
(1,101 | ) | 197 | (1,422 | ) | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) in: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
1,734 | (9,457 | ) | 3,618 | ||||||||
| Capital Support Agreements |
0 | (173,983 | ) | 148,861 | ||||||||
| Payable to regulated investment companies |
0 | (97 | ) | (504 | ) | |||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
(13,847 | ) | 15,367 | (54,200 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred revenue |
748 | (670 | ) | 478 | ||||||||
| Total adjustments |
(3,994 | ) | 73,039 | 17,201 | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 229,326 | $ | 345,471 | $ | 284,728 | ||||||
Page 44 of 88
Table of Contents
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Reductions (additions) to restricted cash |
$ | 0 | (6,000 | ) | (3,750 | ) | ||||||
| Additions to property and equipment |
(13,611 | ) | (19,272 | ) | (26,326 | ) | ||||||
| Additions to capitalized software |
(38,729 | ) | (43,944 | ) | (51,976 | ) | ||||||
| Purchases of marketable securities |
(39,085 | ) | (322,528 | ) | (61,648 | ) | ||||||
| Prepayments and maturities of marketable securities |
58,174 | 32,002 | 33,779 | |||||||||
| Sales of marketable securities |
28,859 | 20,830 | 26,924 | |||||||||
| Cash paid for purchase of joint venture |
0 | 0 | (3,302 | ) | ||||||||
| LSV and LSV Employee Group cash balances, net (A) |
(37,083 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(41,475 | ) | (338,912 | ) | (86,299 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from borrowings on long-term debt |
0 | 254,000 | 0 | |||||||||
| Payments on long-term debt |
(138,000 | ) | (31,980 | ) | (20,439 | ) | ||||||
| Purchase and retirement of common stock |
(119,775 | ) | (53,136 | ) | (129,251 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
28,096 | 23,664 | 28,457 | |||||||||
| Tax benefit on stock options exercised |
1,877 | 5,725 | 7,472 | |||||||||
| Payment of dividends |
(54,634 | ) | (30,598 | ) | (28,946 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(282,436 | ) | 167,675 | (142,707 | ) | |||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
(94,585 | ) | 174,234 | 55,722 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
590,877 | 416,643 | 360,921 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year |
$ | 496,292 | $ | 590,877 | $ | 416,643 | ||||||
| Interest paid |
$ | 1,488 | $ | 4,676 | $ | 3,629 | ||||||
| Income taxes paid |
$ | 145,553 | $ | 9,052 | $ | 126,269 | ||||||
| Non-cash financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Dividends declared but not paid |
$ | 0 | $ | 17,121 | $ | 15,297 | ||||||
| (A) | Cash balances, net of the partnership distribution payment received in January 2010, of LSV and LSV Employee Group at December 31, 2009 removed due to the deconsolidation of the accounts and operations of LSV and LSV Employee Group in January 2010 (See Note 2). |
Page 45 of 88
Table of Contents
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | SEI Investments Company | |
| (all figures are in thousands except per-share data) | and Subsidiaries |
Note 1 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies:
Nature of Operations
SEI Investments Company (the Company), a Pennsylvania corporation, provides investment processing, fund processing, and investment management business outsourcing solutions to corporations, financial institutions, financial advisors, and ultra-high-net-worth families in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, continental Europe, and other various locations throughout the world. Investment processing solutions utilize the Company’s proprietary software system to track investment activities in multiple types of investment accounts, including personal trust, corporate trust, institutional trust, and non-trust investment accounts, thereby allowing banks and trust companies to outsource trust and investment related activities. Revenues from investment processing solutions are recognized in Information processing and software servicing fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations, except for fees earned associated with trade execution services.
The fund processing solution offers a full range of administration and distribution support services to mutual funds, collective trust funds, single-manager hedge funds, funds of hedge funds, private equity funds and other types of investment funds. Administrative services include fund accounting, trustee and custodial support, legal support, transfer agency and shareholder servicing. Distribution support services range from market and industry insight and analysis to identifying distribution opportunities. Revenues from fund processing solutions are recognized in Asset management, administration and distribution fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Investment management programs consist of mutual funds, alternative investments and separate accounts. These include a series of money market, equity, fixed-income and alternative investment portfolios, primarily in the form of registered investment companies. The Company serves as the administrator and investment advisor for many of these products. Revenues from investment management programs are recognized in Asset management, administration and distribution fees on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Principles of Consolidation
The Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries and entities in which it holds a controlling financial interest. The Company determines whether it has a controlling financial interest either by its decision-making ability through voting interests or by the extent of the Company’s participation in the economic risks and rewards of the entity through variable interests. The Company accounts for noncontrolling interests in consolidated entities for which the Company’s controlling financial interest is less than 100 percent. The Company’s principal subsidiaries are SEI Investments Distribution Co. (SIDCO), SEI Investments Management Corporation (SIMC), SEI Private Trust Company (SPTC), SEI Trust Company (STC), SEI Global Services, Inc. (SGSI) and SEI Investments (Europe) Limited (SIEL). All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
In January 2010, new accounting guidance pertaining to the consolidation of VIEs became effective. Under the new guidance, the Company was not considered the primary beneficiary of LSV Employee Group. The Company, therefore, discontinued consolidating the accounts and operations of LSV Asset Management (LSV) and LSV Employee Group in its financial statements. The Company accounts for its interest in LSV using the equity method because of its less than 50 percent ownership. The Company’s interest in the net assets of LSV is reflected in Investment in unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet and its interest in the earnings of LSV is reflected in Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations. The deconsolidation of LSV had no effect on Net income attributable to SEI. Prior period financial statements are not reclassified for the new accounting guidance.
Noncontrolling interest on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets includes the interest of other shareholders in a joint venture of the Company in an asset management firm located in South Korea. At December 31, 2009, Noncontrolling interest also included the amount owned by other partners of LSV and LSV Employee Group.
Variable Interest Entities
The Company has involvement with various variable interest entities (VIE or VIEs). These VIEs consist of LSV Employee Group and investment products established for clients created in the form of various types of legal entity structures. In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board
Page 46 of 88
Table of Contents
(FASB) issued new guidance related to the consolidation of VIEs. This guidance changed how a company determines when an entity that is insufficiently capitalized or is not controlled through voting common stock should be consolidated. The determination of whether a company is required to consolidate an entity is based on, among other things, an entity’s purpose and design, a company’s ability to direct the activities of the entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance, and whether a company is obligated to absorb losses or receive benefits that could be potentially significant to the entity. The new guidance requires ongoing reassessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a VIE and requires additional disclosures about an enterprises involvement in VIEs. The new guidance became effective January 1, 2010.
Under the new guidance, LSV Employee Group remains a VIE. However, the Company is not considered the primary beneficiary because it does not have the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of LSV Employee Group either directly or through any financial responsibility from the Guaranty Agreement. As of January 1, 2010, the Company discontinued consolidating the accounts of LSV Employee Group. The Company does not have any direct equity interest in LSV Employee Group (See Note 2).
In January 2010, the FASB deferred the new guidance for certain types of investment entities. The deferral allows asset managers that have no obligation to fund potentially significant losses of an investment entity to continue to apply the previous guidance to investment entities that have attributes of entities defined in the “Investment Company Guide.” The deferral applies to many mutual funds, hedge funds, private equity funds, venture capital and certain other types of entities. Also, money market funds subject to rule 2a-7 of the Investment Company Act of 1940 qualify for deferral. However, the deferral does not apply to the new disclosure requirements. All of the Company’s investment products where the Company is the sponsor and/or investment manager that are VIEs qualify for the deferral; therefore, the Company will continue to apply the previous guidance for the consolidation of VIEs (See Note 3).
Management’s Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s principal sources of revenues are: (1) asset management, administration and distribution fees earned based upon a contractual percentage of net assets under management or administration; (2) information processing and software servicing fees that are either recurring and primarily earned based upon the number of trust accounts being serviced or non-recurring and based upon project-oriented contractual agreements related to client implementations; and (3) transaction-based fees for providing trade-execution services. The majority of the Company’s revenues are based on contractual arrangements. Revenues are recognized in the periods in which the related services are performed provided that persuasive evidence of an agreement exists, the fee is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is reasonably assured. Cash received by the Company in advance of the performance of services is deferred and recognized as revenue when earned. Reimbursements received for out-of-pocket expenses incurred are recorded as revenue. Certain portions of the Company’s revenues require management’s consideration of the nature of the client relationship in determining whether to recognize as revenue the gross amount billed or net amount retained after payments are made to suppliers for certain services related to the product or service offering.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers investment instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include $383,946 and $438,690 at December 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively, primarily invested in SEI-sponsored open-ended money market mutual funds. Cash and cash equivalents at December 31, 2009 includes $57,061 from LSV (See Note 2).
Page 47 of 88
Table of Contents
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash at December 31, 2010 and 2009 includes $3,000 segregated for regulatory purposes related to trade-execution services conducted by SIEL. Restricted cash also includes $1,000 and $17,000 at December 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively, segregated in special reserve accounts for the benefit of SIDCO customers in accordance with certain rules established by the Securities and Exchange Commission for broker-dealers.
Allowances for Doubtful Accounts
The Company provides an allowance for doubtful accounts equal to the estimated uncollectible amounts. The Company’s estimate is based on historical collection experience and a review of the current status of trade accounts receivable.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments which potentially expose the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents and trade receivables. Cash equivalents are principally invested in short-term money market funds or placed with major banks and high-credit qualified financial institutions. Cash deposits maintained with institutions are in excess of federally insured limits. Concentrations of credit risk with respect to our receivables are limited due to the large number of clients and their dispersion across geographic areas. No single group or customer represents greater than ten percent of total accounts receivable.
Property and Equipment
Property and Equipment are recorded at cost. Expenditures for major additions and improvements are capitalized and minor replacements, maintenance, and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Construction in progress includes the cost of construction and other direct costs attributable to the construction. When property and equipment are retired or disposed of, the related cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is included in the results of operations for the respective period. Depreciation is provided over the estimated useful lives using the straight line method for financial statement purposes. No provision for depreciation is made for construction in progress until such time as the relevant assets are completed and put into service. The Company uses other depreciation methods, generally accelerated, for tax purposes where appropriate. Buildings and building improvements are depreciated over 25 to 39 years. Equipment, purchased software and furniture and fixtures have useful lives ranging from three to five years. Amortization of leasehold improvements is computed using the straight line method over the shorter of the remaining lease term or the estimated useful lives of the improvements.
Marketable Securities
The classification of investments in marketable securities is determined at the time of purchase and reevaluated at each balance sheet date. Debt and equity securities classified as available-for-sale are reported at fair value as determined by the most recently traded price of each security at the balance sheet date. Unrealized gains and losses, net of income taxes, are reported as a separate component of comprehensive income. The Company records all of its trading securities on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets at fair value. Unrealized gains and losses from the change in fair value of these securities are recognized in current period earnings. The specific identification method is used to compute the realized gains and losses on all of the Company’s marketable securities (See Note 6).
The Company evaluates the realizable value of its marketable securities on a quarterly basis. In the event that the carrying value of an investment exceeds its fair value and the decline in value is determined to be other-than-temporary, an impairment charge is recorded and a new cost basis for the investment is established. Some of the factors considered in determining other-than-temporary impairment for equity securities include, but are not limited to, significant or prolonged declines in the fair value of the investments, the Company’s ability and intent to retain the investment for a period sufficient to allow the value to recover, and the financial condition of the investment. Some of the factors considered in determining other-than-temporary impairment for debt securities include, but are not limited to, the intent of management to sell the security, the likelihood that the Company will be required to sell the security before recovering its cost, and management’s expectation to recover the entire amortized cost basis of the security even if there is no intent to sell the security.
Page 48 of 88
Table of Contents
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The fair value hierarchy requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The fair value hierarchy describes three levels of inputs that may be used by the Company to measure fair value:
Level 1 – Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities without adjustment. The Company’s Level 1 assets primarily include investments in mutual funds sponsored by SEI and LSV that are quoted daily.
Level 2 – Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices, such as quoted prices for similar assets, quoted prices in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. The Company’s Level 2 assets primarily include securities issued by GNMA with quoted prices that are traded less frequently than exchange-traded instruments. The Company uses a pricing vendor to value its GNMA securities. The pricing vendor uses a pricing model with inputs that are observable in the market or can be derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data for similar pools of GNMA securities.
Level 3 – Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. Level 3 assets and liabilities include financial instruments whose value is determined using pricing models, or similar techniques, as well as instruments for which the determination of fair value requires significant judgment by management. The Company’s Level 3 financial assets include SIV securities and any change in fair value for these securities is recognized in the current period.
The fair value of an asset or liability may include inputs from more than one level in the fair value hierarchy. The lowest level of significant inputs used to value the asset or liability determines which level the asset or liability is classified in its entirety.
See Note 5 for information on related disclosures regarding fair value measurements.
Capitalized Software
Costs incurred for the development of internal use software to be offered in a hosting arrangement is capitalized during the development stage of the software application. These costs include direct external and internal costs to design the software configuration and interfaces, coding, installation, and testing. Costs incurred during the preliminary and post-implementation stages of the software application are expensed as incurred. Costs associated with significant enhancements to a software application are capitalized while costs incurred to maintain existing software applications are expensed as incurred. The capitalization of software development costs requires considerable judgment by management with respect to certain external factors, including, but not limited to, technological and economic feasibility, and estimated economic life. Capitalized software development costs during these past several years relates to the further development of the Global Wealth Platform (GWP). GWP provides the technology platform underpinning many of our business solutions. The initial version of GWP was placed into service in July 2007. Further enhancements and upgrades will continue to occur through a series of releases that will eventually provide the full functionality of GWP servicing clients across multiple jurisdictions. As of December 31, 2010, the net book value of GWP was $268,647 (net of accumulated amortization of $62,152), including $24,248 of capitalized software development costs in-progress associated with future releases to GWP. The Company capitalized $38,729, $43,944, and $56,162 of software development costs during 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively. The amount capitalized in 2008 includes $4,186, net of $382 in accumulated amortization, consisting of an out-of-period adjustment for interest costs on outstanding borrowings of the Company for the years 2002 through 2007.
Amortization of capitalized software development costs begins when the product is ready for its intended use. Capitalized software development costs are amortized on a product-by-product basis using the straight-line method over the estimated economic life of the product or enhancement, which is primarily 3 to 15 years, with a weighted average remaining life of approximately 11.5 years. Amortization expense was $23,053, $35,894, and $16,980 in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively, and
Page 49 of 88
Table of Contents
is included in Amortization expense on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations. GWP has an estimated useful life of 15 years and a weighted average remaining life of 11.5 years. The Company abandoned certain components within GWP that were replaced in late 2009. The useful life of these components was shortened so that the remaining net book value of $15,502 was fully amortized commensurate with the new release. Amortization expense in 2009 on the Consolidated Statements of Operations includes $15,502 of accelerated amortization for these components.
The Company evaluates the carrying value of capitalized software development costs when circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. The review of capitalized software development costs for impairment requires significant assumptions about operating strategies, underlying technologies utilized, and external market factors. External market factors include, but are not limited to, expected levels of competition, barriers to entry by potential competitors, stability in the target market and governmental regulations. In 2010 and 2009, the Company determined that no events or change in circumstances had occurred that would indicate that capitalized software development costs were impaired. Therefore, the Company did not recognize any impairment charges for any of its capitalized software development costs in 2010 or 2009.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Asset
Goodwill is not amortized but is reviewed for impairment annually or more frequently if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. The provisions of accounting guidance require that a two-step, fair value based test be performed to assess goodwill for impairment. In the first step, the fair value of each reporting unit is compared with its carrying value, including goodwill. If the fair value exceeds the carrying value, goodwill is not impaired and no further testing is performed. The second step is performed if the carrying value exceeds the fair value. The second step requires an allocation of fair value to the individual assets and liabilities using a purchase price allocation in order to determine the implied fair value of goodwill. If the implied fair value of goodwill is less than the carrying amount, an impairment loss is recognized. The Company estimates the fair value of the LSV reporting unit primarily based upon an earnings multiple approach. This approach requires an estimate of future expected cash flows from the LSV reporting unit which involves significant assumptions by management.
The Company reviews long-lived assets and identifiable definite-lived intangible assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of these assets may not be recoverable. For purposes of recognizing and measuring an impairment loss, a long-lived asset is grouped with other assets and liabilities at the lowest level for which identifiable cash flows are largely independent. It is impossible to distinguish between the cash flows generated by goodwill and intangible assets and, therefore, the LSV other intangible asset is grouped with all of the other assets of LSV, including Goodwill, for purposes of recognizing and measuring an impairment loss. To date, the Company has not recognized any impairment loss for any of its Goodwill or Other Intangible Assets.
Income Taxes
The Company applies the asset and liability approach to account for income taxes whereby deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities are individually classified as current and non-current based on their characteristics.
Foreign Currency Translation
The assets and liabilities and results of operations of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are measured using the foreign subsidiary’s local currency as the functional currency. Assets and liabilities have been translated into U.S. dollars using the rates of exchange at the balance sheet dates. The results of operations have been translated into U.S. dollars at average exchange rates prevailing during the period. The resulting translation gain and loss adjustments are recorded as a separate component of comprehensive income.
Page 50 of 88
Table of Contents
Transaction gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations are included in the results of operations in the periods in which they occur, and are immaterial for each of the years in the three year period ended December 31, 2010.
Earnings Per Common Share
Basic earnings per common share is computed by dividing net income attributable to SEI Investments common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per common share is computed by dividing net income attributable to SEI Investments common shareholders by the combination of the weighted average number of common shares outstanding and the dilutive potential common shares, such as stock options, outstanding during the period. The calculations of basic and diluted earnings per share for 2010, 2009, and 2008 are:
| For the Year ended December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI (Numerator) |
Shares (Denominator) |
Per-Share Amount |
||||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
$ | 231,687 | 188,468 | $ | 1.23 | |||||||
| Dilutive effect of stock options |
0 | 1,853 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 231,687 | 190,321 | $ | 1.22 | |||||||
| For the Year ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI (Numerator) |
Shares (Denominator) |
Per-Share Amount |
||||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
$ | 174,335 | 190,821 | $ | 0.91 | |||||||
| Dilutive effect of stock options |
0 | 962 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 174,335 | 191,783 | $ | 0.91 | |||||||
| For the Year ended December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI (Numerator) |
Shares (Denominator) |
Per-Share Amount |
||||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
$ | 139,254 | 192,057 | $ | 0.73 | |||||||
| Dilutive effect of stock options |
0 | 3,176 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 139,254 | 195,233 | $ | 0.71 | |||||||
Employee stock options to purchase approximately 13,181,000, 22,997,000, and 13,654,000 shares of common stock, with an average exercise price per share of $23.79, $21.47, and $23.26, were outstanding during 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively, but not included in the computation of diluted earnings per common share because the option’s exercise price was greater than the average market price of the Company’s common stock and the effect on diluted earnings per common share would have been anti-dilutive (See Note 8).
Stock-Based Compensation
Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period, which is the vesting period. The Company uses historical data to estimate pre-vesting forfeitures and record stock-based compensation expense only for those awards that are expected to vest. The amount of stock-based compensation expense that is recognized in a given period is dependent upon management’s estimate of when the vesting targets are expected to be achieved. If this estimate proves to be inaccurate, the remaining amount of
Page 51 of 88
Table of Contents
stock-based compensation expense could be accelerated, spread out over a longer period, or reversed (See Note 8).
Out of Period Adjustments
During the three month period ended December 31, 2008, the Company recorded an adjustment related to interest costs associated with borrowings in prior years when the Company was involved with various capital projects. Prior to that quarter, the Company incorrectly expensed all interest costs rather than capitalizing a portion of these costs as part of the cost basis of these capital projects. The Company did not have any interest costs in 2008 eligible for capitalization. The Company does not believe these prior period adjustments were quantitatively or qualitatively material to the financial results for any of its previously issued annual or interim financial statements through September 30, 2008. Had these errors been recorded in the proper periods, Net income would increase by $3,740 in 2007 and years prior. Retained earnings on January 1, 2006 would increase by $3,265. As a result, the Company did not restate any previously issued annual or interim financial statements. The net impact of the adjustments was an increase in Net income before taxes of $5,577 and an increase in Net income of $3,453 ($.02 diluted earnings per share) in the fourth quarter 2008. These non-cash adjustments were recognized in Other (expense) income on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations and did not have any effect on any of the Company’s business segments.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2010, the FASB issued a final Accounting Standards Update that sets forth additional requirements and guidance regarding disclosures of fair value measurements. The new standard requires the gross presentation of activity within the Level 3 fair value measurement roll forward and details of transfers in and out of Level 1 and 2 fair value measurements. It also clarifies two existing disclosure requirements on the level of disaggregation of fair value measurements and disclosures on inputs and valuation techniques. The new requirements and guidance are effective for interim and annual periods beginning in the first quarter 2010 except that the Level 3 rollforward is effective in the first quarter 2011. The adoption of the new requirements and guidance effective in the first quarter 2010 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. The Company does not expect the adoption of the guidance pertaining to the Level 3 rollforward to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
Reclassifications
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
Note 2 – LSV and LSV Employee Group
The Company has an investment in LSV, a general partnership and registered investment advisor that provides investment advisory services to institutions, including pension plans and investment companies. LSV is currently an investment sub-advisor for a number of SEI-sponsored mutual funds. The Company’s total partnership interest in LSV was approximately 42 percent during 2010 and 2009.
LSV Employee Group is owned by several current employees of LSV and was formed for the sole purpose of owning a partnership interest in LSV. The Company does not own any interest in LSV Employee Group. In 2006, LSV Employee Group purchased an eight percent interest in LSV from two existing partners. LSV Employee Group obtained financing in the form of a term loan pursuant to the terms of a Credit Agreement to purchase the eight percent interest in LSV. The Company agreed to provide a Guaranty Agreement to the lenders of all obligations of LSV Employee Group under the Credit Agreement. The lenders have the right to seek payment from the Company of all obligations of LSV Employee Group under the Credit Agreement in the event of default. The Company’s direct interest in LSV was unchanged as a result of this transaction.
As a result of providing the Guaranty Agreement, LSV Employee Group became a VIE and the Company was considered the primary beneficiary. Also, given the Company’s direct ownership of 43 percent in LSV at the time of this transaction in 2006 and its controlling interest in LSV Employee Group through the Guaranty Agreement, the Company was required to consolidate the assets, liabilities and operations of LSV and LSV Employee Group. The partnership interest of the other existing partners of LSV was included in Noncontrolling interest.
Page 52 of 88
Table of Contents
In January 2010, new accounting guidance pertaining to the consolidation of VIEs became effective. Under the new guidance, the Company was not considered the primary beneficiary of LSV Employee Group. The Company, therefore, discontinued consolidating the accounts and operations of LSV and LSV Employee Group in its financial statements. The Company accounts for its interest in LSV using the equity method because of its less than 50 percent ownership. The Company’s interest in the net assets of LSV is reflected in Investment in unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet and its interest in the earnings of LSV is reflected in Equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliate on the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations. The deconsolidation of LSV had no effect on Net income attributable to SEI. Prior period financial statements are not reclassified for the new accounting guidance.
LSV Asset Management
At December 31, 2010, the Company’s total investment in LSV was $64,409. The investment in LSV exceeded the underlying equity in the net assets of LSV by $4,154, of which $3,062 is considered goodwill embedded in the investment. The Company receives partnership distributions from LSV on a quarterly basis. The Company received partnership distribution payments from LSV for $93,302, $73,518 and $123,086 in 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The partnership distribution payment of $21,242 received in January 2010 is reflected in LSV and LSV Employee Group cash balances, net on the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
These tables contain condensed financial information of LSV:
| Condensed Statement of Operations Year ended December 31, |
2010 | |||
| Revenues |
$ | 273,381 | ||
| Net income |
$ | 239,981 | ||
| Condensed Balance Sheet December 31, |
2010 | |||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 64,464 | ||
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $369 |
75,056 | |||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
848 | |||
| Non-current assets |
4,159 | |||
| Total assets |
$ | 144,527 | ||
| Current liabilities |
$ | 11,199 | ||
| Partners’ capital |
133,328 | |||
| Total liabilities and partners’ capital |
$ | 144,527 | ||
LSV Employee Group
At the time of LSV Employee Group’s purchase of an eight percent interest in LSV, it was determined that $72,220 of the purchase price related to identifiable intangible assets and $19,780 was goodwill. The identifiable intangible assets have an estimated useful life of ten years and were amortized on a straight-line basis. Goodwill of $19,780 and intangible assets of $43,332 (net of accumulated amortization of $28,888) are included in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet at December 31, 2009 but were the assets of LSV Employee Group. These amounts were eliminated through
Page 53 of 88
Table of Contents
Noncontrolling interest. Amortization expense in 2009 and 2008 on the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations includes $7,222 pertaining to the amortization of the intangible assets, but was eliminated through Noncontrolling interest and had no impact on net income.
In order to finance a portion of the purchase price, LSV Employee Group obtained financing from Bank of America, N.A. (Bank of America) and certain other lenders in the form of a term loan pursuant to the terms of a Credit Agreement. The principal amount of the term loan was $82,800. In January 2011, LSV Employee Group and Bank of America agreed to amend the Credit Agreement and extend the maturity date of the loan from January 2011 to July 2012. The Company’s obligations under the Guaranty Agreement remain in full force and effect with respect to the amended Credit Agreement. The principal amount and interest of the term loan are paid in quarterly installments. As of December 31, 2010, the remaining unpaid principal balance of the term loan was $10,091. This amount is not reflected, nor is it required to be reflected, in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet at December 31, 2010. LSV Employee Group made principal payments of $10,461 during 2010. The deconsolidation of LSV Employee Group did not relinquish the Company’s obligation under the Guaranty Agreement. In the event of default by LSV Employee Group, the Company would still be obligated under the Guaranty Agreement to make any required payments to the lenders according to the term loan.
At December 31, 2009, prior to the deconsolidation of LSV Employee Group, the unpaid principal balance of the term loan was $20,552, of which $6,400 was classified as current and included in Current portion of long-term debt and the remaining $14,152 was included in Long-term debt on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Interest expense in 2009 and 2008 on the Consolidated Statement of Operations includes $1,510 and $2,285, respectively, in interest costs associated with the borrowings of LSV Employee Group which was eliminated through Noncontrolling interest and had no impact on net income.
In January 2011, LSV Employee Group made a principal payment of $2,511. As of January 31, 2011, the remaining unpaid principal balance of the term loan was $7,580. Due to the fact that LSV Employee Group has satisfied all payment requirements relating to the term loan, the Company, in its capacity as guarantor, currently has no obligation to make any payments under the Guaranty Agreement. Furthermore, the Company fully expects that LSV Employee Group will meet all of its future obligations regarding the term loan.
Proforma Financial Information (Unaudited)
The unaudited proforma financial information as of December 31, 2009 and for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 presents the financial position and historical results of the Company as if the accounts and operations of LSV and LSV Employee Group had not been consolidated and LSV had been accounted for under the equity method. Net income attributable to SEI and diluted earnings per share were unchanged due to this transaction but are presented for the purpose of clarification.
| Proforma Unaudited Condensed Balance Sheets December 31, |
2009 | |||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 532,552 | ||
| Restricted cash |
20,000 | |||
| Receivables from regulated investment companies |
28,134 | |||
| Receivables, net |
117,925 | |||
| Other current assets |
17,450 | |||
| Total Current Assets |
716,061 | |||
| Property and Equipment, net |
144,252 | |||
| Capitalized software, net |
278,656 | |||
| Investments available for sale |
55,671 | |||
| Trading securities |
126,196 | |||
| Equity in unconsolidated affiliate |
56,698 | |||
| Other assets, net |
18,023 | |||
| Total Assets |
$ | 1,395,557 | ||
Page 54 of 88
Table of Contents
| Current liabilities |
148,014 | |||
| Long-term debt |
233,000 | |||
| Deferred income taxes |
86,257 | |||
| Other long-term liabilities |
5,726 | |||
| Total SEI Investments Shareholders’ Equity |
909,723 | |||
| Noncontrolling interest |
12,837 | |||
| Total Equity |
922,560 | |||
| Total Liabilities and Equity |
$ | 1,395,557 | ||
| Proforma Unaudited Condensed Statement of Operations Year ended December 31, |
2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 848,587 | $ | 984,651 | ||||
| Expenses |
(658,434 | ) | (714,758 | ) | ||||
| Income from operations |
190,153 | 269,893 | ||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
87 | (140,320 | ) | |||||
| Equity in the earnings of unconsolidated affiliate |
75,415 | 98,971 | ||||||
| Net income before income taxes |
265,655 | 228,544 | ||||||
| Income taxes |
89,886 | 86,703 | ||||||
| Net income |
175,769 | 141,841 | ||||||
| Less: Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest |
(1,434 | ) | (2,587 | ) | ||||
| Net income attributable to SEI Investments |
$ | 174,335 | $ | 139,254 | ||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 0.91 | $ | 0.71 | ||||
Note 3 – Variable Interest Entities – Investment Products
The Company has created numerous investment products for its clients in various types of legal entity structures. The Company serves as the Manager, Administrator and Distributor for these investment products and may also serve as the Trustee for some of the investment products. Clients are the equity investors and participate in proportion to their ownership percentage in the net income and net capital gains of the products, and, on liquidation, will participate in proportion to their ownership percentage in the remaining net assets of the products after satisfaction of outstanding liabilities.
An entity that lacks decision-making rights is a VIE. In some circumstances, the Manager or Trustee of the Company’s investment products controls the governing decisions about the investment activities with respect to the ongoing operations of the investment products without the equity investors possessing the right to remove the Manager or Trustee. Therefore, the equity investors, as a group, do not have the ability to make decisions that have an impact on the ongoing activities of such investment products. Consequently, some of the Company’s investment products have been determined to be VIEs at inception.
The VIEs are marketed with investment objectives to generate positive returns; however, the nature of such investments exposes the investors to the risk that the value of the VIEs may increase or decrease. The purpose and design of the VIEs are to achieve the investment objective by implementing strategies which are designed to minimize potential losses; however, there is no assurance given that these strategies will be successful.
Page 55 of 88
Table of Contents
The Company does not have a significant equity investment in any of the VIEs and does not have an obligation to enter into any guarantee agreements with the VIEs. The fees paid to the decision maker of a VIE are considered to be variable interests if the decision maker is not subject to substantive kick-out rights. The fees paid to the Company represent a variable interest when the decision maker is not subject to substantive kick-out rights.
The Company is not the primary beneficiary of the VIEs because the expected fees and the expected return on any investment into the VIE by the Company relative to the expected returns of the VIE to the equity investor holders does not approach 50 percent of the expected losses or gains of the VIEs. Therefore, the Company is not required to consolidate any investment products that are VIEs into its financial statements. The Company’s variable interest in the VIEs, which consists of management fees and in some situations, seed capital, would not be considered a significant variable interest.
The risks to the Company associated with its involvement with any of the investment products that are VIEs are limited to the cash flows received from the revenue generated for asset management, administration and distribution services and any equity investments in the VIEs. Both of these items are immaterial. The Company has no other financial obligation to the VIEs.
Amounts relating to fees received from the VIEs included in Receivables and amounts relating to equity investments in the VIEs included in Investments Available for Sale on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets are immaterial to the total current assets of the Company.
Note 4 – Composition of Certain Financial Statement Captions
Receivables
Receivables on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets consist of:
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| Trade receivables |
$ | 34,528 | $ | 40,499 | ||||
| Fees earned, not billed |
93,506 | 144,325 | ||||||
| Other receivables |
9,651 | 2,841 | ||||||
| 137,685 | 187,665 | |||||||
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts |
(1,195 | ) | (3,348 | ) | ||||
| Receivables, net |
$ | 136,490 | $ | 184,317 | ||||
Fees earned, not billed represents receivables earned but unbilled and results from timing differences between services provided and contractual billing schedules. These billing schedules generally provide for fees to be billed on a quarterly basis.
Receivables from regulated investment companies on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets primarily represent fees receivable for distribution, investment advisory, and administration services to various regulated investment companies sponsored by SEI (See Note 14).
Receivables at December 31, 2009 include $66,392, net of $1,149 of allowance for doubtful accounts, of receivables of LSV, of which $59,241 was included in Fees earned, not billed.
Page 56 of 88
Table of Contents
Property and Equipment
Property and Equipment on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets consists of:
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| Buildings |
$ | 135,935 | $ | 131,376 | ||||
| Equipment |
63,902 | 62,634 | ||||||
| Land |
9,890 | 9,719 | ||||||
| Purchased software |
74,720 | 70,035 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
18,566 | 19,817 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
4,250 | 5,739 | ||||||
| Construction in progress |
121 | 4,846 | ||||||
| 307,384 | 304,166 | |||||||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation |
(166,816 | ) | (158,113 | ) | ||||
| Property and Equipment, net |
$ | 140,568 | $ | 146,053 | ||||
Depreciation expense related to property and equipment for 2010, 2009, and 2008 was $21,902, $21,531, and $22,032, respectively.
Other Assets
Other assets consist of long-term prepaid expenses, deposits and various other assets. Amortization expense for certain other assets for 2010, 2009, and 2008 was $995, $1,055 and $340, respectively.
The Company recognized gains of $3,072 in 2010 due to the sale of its entire ownership interest in a small, private company that was involved in a merger. The Company’s investment in the firm had been accounted for under the cost basis. The gain is reflected in Net gain (loss) on investments on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Accrued Liabilities
Accrued Liabilities on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets consist of:
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| Accrued employee compensation |
$ | 43,747 | $ | 41,897 | ||||
| Accrued employee benefits and other personnel |
6,988 | 6,241 | ||||||
| Accrued consulting, outsourcing and professional fees |
16,390 | 16,123 | ||||||
| Accrued brokerage fees |
11,756 | 15,840 | ||||||
| Accrued other brokerage and royalties |
2,718 | 2,214 | ||||||
| Accrued subadvisory and investment officer fees |
8,935 | 8,458 | ||||||
| Accrued other asset management fees |
6,185 | 6,923 | ||||||
| Accrued income taxes |
2,077 | 20,561 | ||||||
| Accrued dividend payable |
0 | 17,121 | ||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
22,614 | 17,566 | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
$ | 121,410 | $ | 152,944 | ||||
Note 5 – Fair Value Measurements
The fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities is determined in accordance with the fair value hierarchy. The fair value of the Company’s financial assets, except for the fair value of senior notes issued by structured investment vehicles (SIVs), is determined using Level 1 or Level 2 inputs and consist mainly of investments in equity and fixed-income mutual funds that are quoted daily and Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA) securities that are single issuer pools that are valued based on current market data for the specific issue owned or pools of similar GNMA
Page 57 of 88
Table of Contents
securities. Level 3 financial assets consist of senior note obligations issued by SIVs. The Company did not have any Level 3 financial liabilities at December 31, 2010 or 2009. The Company provided support to two of its money market mutual funds that held SIV securities during 2009 and 2008 in the form of Capital Support Agreements; however, these agreements were terminated upon the Company’s purchase of the remaining SIV securities from the funds in 2009. The Capital Support Agreements were considered derivative securities, for which the fair value was determined using the same model to value the SIV securities. There were no transfers of financial assets between levels within the fair value hierarchy during 2010.
Valuation of SIV Securities
The underlying collateral of the SIV securities is mainly comprised of asset-backed securities and collateralized debt obligations. The Company received prices for all of its SIV securities from two independent third party firms. Given the lack of any reliable market data on the SIV securities, the firms utilized a valuation model that employs a net asset approach which considers the value of the underlying collateral of the SIV securities to determine the fair value of the SIV securities. Management evaluates the prices received from these firms and considers other information, such as the existence of any current market activity, to determine the fair value of the SIV securities. The underlying collateral is specifically identified by its CUSIP or ISIN number.
The valuation model maintained by the third party firm to value the SIV securities (except the Stanfield Victoria note) attempts to obtain price quotes for each security that comprises the underlying collateral of the SIV securities. Price quotes are primarily obtained from two pricing vendors that are independent entities of the firm that maintains the valuation model. Other pricing vendors may be used in limited situations when a security quote cannot be obtained from either of the two primary pricing vendors. The average of the two quotes received is used to value each security. A portion of the securities that comprise the underlying collateral of the SIV securities are not priced by the pricing vendors. For these securities that lack price quotes, the last price quote received will be adjusted by the weighted average percentage movement of securities held as collateral within the same sector classification or based upon the weighted average movement of all priced securities. For example, a residential mortgage-backed security that has not received a quote for an extended period of time will be adjusted by the weighted average percentage movement of all quoted residential mortgage-backed securities held as collateral by the SIV security. Additionally, the securities are aggregated by type or sector (i.e. home equity line of credit, sub-prime 1st liens, residential mortgage-backed securities, etc.) and the weighted average quote of all securities within a sector held by the SIV is compared with the range of quotes received for similar securities within the same sector from the trading desk of an affiliate of the third party firm that maintains the SIV valuation model. The weighted average quote of all securities within a sector held by the SIV must be within the range of quotes received from the trading desk within that same sector. If the weighted average quote for all securities within a sector held by the SIV is outside that range, the average quote received from the pricing vendors may be adjusted. In any event, the value assigned to each security held by the SIV will be the lower of (i) the average of the quotes received from the pricing vendors or (ii) the lowest quote received from the trading desk for a similar security.
The pricing vendors used by the firm that maintains the valuation model utilize widely-accepted pricing models, which are evaluated by the pricing vendor, that vary by asset class and incorporate available trade, bid, and other market information. The market inputs that these pricing vendors seek for their evaluation of securities include: benchmark yields, reported trades, broker/dealer quotes, issuer spreads, two-sided markets, benchmark securities, bids, offers and other available market data. Broker quotes may be binding or non-binding. For certain security types, additional inputs may be used. The pricing vendors may prioritize inputs differently from time to time for any security based on current market conditions. For each asset class, the pricing vendor has a team of evaluators that gather information from market sources and integrate relevant credit information, perceived market movements and sector news into the evaluated pricing models. For a structured security evaluation, including mortgage-backed securities, these evaluators would consider various characteristics including issuer, vintage, purpose of loan, collateral attributes, prepayment speeds and credit ratings in order to properly identify trades and quotes for similar securities which are gathered for use in the evaluation process. Evaluators follow multiple review processes throughout each month that assess the available market, credit and deal level information in support of the evaluation process. If it is determined that sufficient objectively verifiable information does not exist to support a security’s valuation, the pricing vendor will discontinue providing a quote on that security. As previously stated, securities that lack a quote from a pricing vendor are valued using the most recent quoted price and adjusting that price by
Page 58 of 88
Table of Contents
the weighted average percentage change in the respective sector of all other similar securities that are held by the SIV.
The model used by the second independent valuation firm to determine the fair value of the Stanfield Victoria note also utilized a net asset approach that attempts to value the underlying collateral of the SIV securities through the use of industry accepted and proprietary valuation techniques and models. This approach combines advanced analytics with real-time market information that incorporate structural and fundamental analysis, collateral characteristics and recent market developments. Each security that makes up the underlying collateral is analyzed by using observable collateral characteristics and credit statistics in order to project future performance and expected cash flows for each individual security. The projected cash flows incorporate assumptions and expectations based upon the foregoing analysis of the collateral characteristics such as, but not limited to, default probabilities, recovery rates, prepayment speeds and loss severities. Expected future cash flows are discounted at an appropriate yield derived from the individual security, structural and collateral characteristics, trading levels and other available market data. Different modeling techniques and associated inputs and assumptions may be used to project future cash flows for each security depending upon the asset classification of that individual security (i.e. residential mortgage-backed security, commercial mortgage-backed security, collateralized debt obligations, etc.). The aggregate value of the discounted cash flows of the underlying collateral is compared to the total remaining par value of the collateral to determine the expected recovery price, or fair value, of the remaining note obligations.
Management may also consider, when available, price quotes from brokers and dealers. If a price quote is available, management will compare this number to the fair value derived from the valuation models of the two independent firms giving consideration to other market factors and risk premiums. Given the lack of any significant trading activity for any of the SIV securities owned by the Company, management believes that market prices for any SIV securities may not represent the implied fair value of the SIV securities owned by the Company.
Management evaluates current market transactions, if any, for each of the SIV securities. In the event a market transaction does exist for a SIV security, management evaluates the publicly available information surrounding the transaction in order to assess if the price used represents the fair value for the SIV security. In management’s opinion, the current market for SIV securities does not represent any orderly and efficient market.
The fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities of the Company was determined using the following inputs:
| At December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||||
| Equity available-for-sale securities |
$ | 5,853 | $ | 5,853 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| Fixed-income available-for-sale securities |
68,917 | 0 | 68,917 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Trading securities issued by SIVs |
100,645 | 0 | 0 | 100,645 | ||||||||||||
| Other trading securities |
3,949 | 3,949 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 179,364 | $ | 9,802 | $ | 68,917 | $ | 100,645 | |||||||||
Page 59 of 88
Table of Contents
| At December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||||
| Equity available-for-sale securities |
$ | 3,511 | $ | 3,511 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||||
| Fixed-income available-for-sale securities |
52,190 | 0 | 52,190 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| Trading securities issued by SIVs |
120,714 | 0 | 0 | 120,714 | ||||||||||||
| Other trading securities |
5,482 | 5,482 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 181,897 | $ | 8,993 | $ | 52,190 | $ | 120,714 | |||||||||
The table below presents a reconciliation for all assets and liabilities of the Company measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the period from January 1, 2009 to December 31, 2010:
| Trading Securities Issued by SIVs |
Other
Trading Securities |
Capital Support Agreements |
||||||||||
| Balance, January 1, 2009 |
$ | 5,713 | $ | 1,697 | $ | (173,983 | ) | |||||
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net |
294,762 | (1,536 | ) | 0 | ||||||||
| Transfer of Capital Support Agreement at purchase |
(179,654 | ) | 0 | 179,654 | ||||||||
| Total gains or (losses) (realized/unrealized): |
||||||||||||
| Included in earnings |
(107 | ) | (161 | ) | (5,671 | ) | ||||||
| Included in other comprehensive income |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Transfers in and out of Level 3 |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2009 |
$ | 120,714 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net |
(64,316 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Total gains or (losses) (realized/unrealized): |
||||||||||||
| Included in earnings |
44,247 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Included in other comprehensive income |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Transfers in and out of Level 3 |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2010 |
$ | 100,645 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | ||||||
Page 60 of 88
Table of Contents
Note 6 – Marketable Securities
Investments Available For Sale
Investments available for sale classified as non-current assets consist of:
| For the Year ended December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized (Losses) |
Fair Value |
|||||||||||||
| SEI-sponsored mutual funds |
$ | 5,086 | $ | 279 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 5,351 | |||||||
| Other mutual funds |
443 | 59 | 0 | 502 | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities |
67,118 | 1,799 | 0 | 68,917 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 72,647 | $ | 2,137 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | 74,770 | ||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized (Losses) |
Fair Value |
|||||||||||||
| SEI-sponsored mutual funds |
$ | 580 | $ | 0 | $ | (40 | ) | $ | 540 | |||||||
| Other mutual funds |
3,111 | 0 | (140 | ) | 2,971 | |||||||||||
| Debt securities |
50,696 | 1,494 | 0 | 52,190 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 54,387 | $ | 1,494 | $ | (180 | ) | $ | 55,701 | ||||||||
Net unrealized holding gains were $1,339 (net of income tax expense of $784) at December 31, 2010. Net unrealized holding gains were $960 (net of income tax expense of $354) at December 31, 2009. These unrealized gains and losses are reported as separate components of Accumulated other comprehensive income on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company recognized gross realized gains from available-for-sale securities of $184, $440 and $1,806 in 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Gross realized losses in 2009 were $123. Gross realized losses in 2010 were minimal. There were no realized losses from available-for-sale securities in 2008.
The Company had investments in two SEI-sponsored mutual funds which primarily invest in fixed-income securities, including debt securities issued by municipalities and mortgage-backed securities. In 2008, management determined the decline in market value for these mutual funds was other-than-temporary and recorded an impairment charge of $1,961. In 2009, management determined that the further decline in market value for one of these mutual funds was other-than-temporary and, therefore, recorded another impairment charge for $901. The other-than-temporary impairment charges in 2009 and 2008 are included in Net gain (loss) on investments on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Derivatives held by the Company were in the form of equity contracts for the purpose of hedging market risk of certain available for sale securities and held only for the purpose of hedging such risk and not for speculation. The Company did not own any derivative financial instruments to hedge market risk of available for sale securities in 2010 or 2009. Net gain (loss) from investments on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations includes net gains of $676 in 2008 from changes in the fair value of derivative instruments.
The Company’s debt securities are issued by the Government National Mortgage Association and are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. These securities were purchased to satisfy applicable regulatory requirements of SPTC and have maturity dates which range from 2020 to 2040.
Page 61 of 88
Table of Contents
Trading Securities
Trading securities of the Company consist of:
| For the Year ended December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized (Losses) |
Fair Value |
|||||||||||||
| SIV securities |
$ | 231,026 | $ | 0 | $ | (130,381 | ) | $ | 100,645 | |||||||
| LSV-sponsored mutual funds |
2,049 | 1,900 | 0 | 3,949 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 233,075 | $ | 1,900 | $ | (130,381 | ) | $ | 104,594 | ||||||||
| For the Year ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized (Losses) |
Fair Value |
|||||||||||||
| SIV securities |
$ | 309,796 | $ | 0 | $ | (189,082 | ) | $ | 120,714 | |||||||
| LSV-sponsored mutual funds |
4,000 | 1,482 | 0 | 5,482 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 313,796 | $ | 1,482 | $ | (189,082 | ) | $ | 126,196 | ||||||||
The Company records all of its trading securities on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets at fair value. Unrealized gains and losses from the change in fair value of these securities are recognized in Net gain (loss) from investments on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Through December 31, 2010, the Company recognized $144,835 in cumulative losses from SIV securities. During 2010, the Company recognized gains from SIV securities of $44,247, of which $27,510 resulted from cash payments received from the SIV securities and $16,460 was from a net increase in fair value at December 31, 2010. In addition, the Company recognized a net gain of $277 from sales of three SIV securities during 2010. The cumulative loss recognized by the Company pertaining to these SIV securities sold in 2010 was $17,944. During 2009, the Company recognized losses of $5,778 from SIV securities and SIV-related issues. The net gains (losses) from the SIV securities and SIV-related issues are reflected in Net gain (loss) from investments on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
In January 2011, the Company sold the senior note obligation originally issued by Stanfield Victoria. There was no gain or loss recognized by the Company from the sale of the note as the fair value of the Stanfield Victoria note at December 31, 2010 was not different than the sale price received. Currently, the Company’s remaining SIV security consists of the senior note obligation issued by Gryphon.
The Company has an investment related to the startup of mutual funds sponsored by LSV. These are U.S. dollar denominated funds that invests primarily in securities of Canadian and Australian companies as well as various other global securities. The underlying securities held by the funds are translated into U.S. dollars within the funds. During the three months ended June 30, 2010, the Company sold a portion of its investment in the LSV-sponsored funds. Additionally, the Company sold all of the equity and currency futures contracts originally purchased as part of an economic strategy to minimize exposure to price and currency risk related to the investment. The net gains recognized from the partial sale of the LSV-sponsored funds and the equity and futures contracts were minimal. As of December 31, 2010, the Company’s remaining investment in the LSV-sponsored funds had a cost value of $2,049 and a fair value of $3,949.
Page 62 of 88
Table of Contents
Note 7 – Lines of Credit:
The Company has a five-year $300,000 Credit Agreement (the Credit Facility) which expires in July 2012, at which time any aggregate principal amount of loans outstanding becomes payable in full. Any borrowings made under the Credit Facility will accrue interest at 0.450 percent above the London Interbank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”). There is also a commitment fee equal to 0.09 percent per annum on the daily unused portion of the facility. The aggregate amount of the Credit Facility may be increased by an additional $100,000 under certain conditions set forth in the agreement. The Credit Facility, as amended, contains covenants that restrict the ability of the Company to engage in mergers, consolidations, asset sales, investments, transactions with affiliates, or to incur liens, as defined in the agreement. In the event of a default under the Credit Facility, the Company would also be restricted from paying dividends on, or repurchasing, its common stock without the approval of the lenders. None of the covenants of the Credit Facility negatively affect the Company’s liquidity or capital resources. Both the interest rate and commitment fee prices may increase if the Company’s leverage ratio reaches certain levels. Upon the occurrence of certain financial or economic events, significant corporate events, or certain other events of default constituting an event of default under the Credit Facility, all loans outstanding may be declared immediately due and payable and all commitments under the Credit Facility may be terminated.
In 2009, the Company borrowed $254,000 from the Credit Facility to finance the purchase of SIV securities from SEI-sponsored money market mutual funds (See Note 6). The Company made principal payments of $138,000 and $21,000 during 2010 and 2009, respectively. As of December 31, 2010, the outstanding balance of the Credit Facility was $95,000 and is included in Long-term debt on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet. The Company was in compliance with all covenants of the Credit Facility during 2010.
As of December 31, 2010, the Company’s ability to borrow from the Credit Facility is not limited by any covenant of the agreement. In management’s opinion, the leverage ratio is the most restrictive of all of the covenants contained in the Credit Facility. The leverage ratio is calculated as consolidated indebtedness divided by earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and other items as defined by the covenant during the last four quarters (EBITDA). According to the terms of the agreement, the Company must continue to include the outstanding debt of LSV Employee Group in the calculation of consolidated indebtedness. The Company must maintain at all times a ratio of consolidated indebtedness of not more than 1.75 times the amount of EBITDA. As of December 31, 2010, the Company’s leverage ratio was 0.24 times EBITDA.
The average rates applied to the Credit Facility during 2010 and 2009 were 0.77 percent and 1.05 percent, respectively. The Company incurred $1,478, $2,491, and $1,019 in interest charges and commitment fees relating to all lines of credit during 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively, and is reflected in Interest expense on the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company considers the book value of long-term debt related to the borrowings through the Credit Facility to be representative of its fair value.
The Company’s Canadian subsidiary has a credit facility agreement (the Canadian Credit Facility) for the purpose of facilitating the settlement of mutual fund transactions. The Canadian Credit Facility has no stated expiration date. The amount of the facility is generally limited to $2,000 Canadian dollars or the equivalent amount in U.S. dollars. The Canadian Credit Facility does not contain any covenants which restrict the liquidity or capital resources of the Company. The Company had no borrowings under the Canadian Credit Facility and was in compliance with all covenants during 2010.
Note 8 - Shareholders’ Equity:
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company currently has one active equity compensation plan, the 2007 Equity Compensation Plan (the 2007 Plan), which provides for the grant of incentive stock options, non-qualified stock options and stock appreciation rights with respect to up to 20 million shares of common stock of the Company, subject to adjustment for stock splits, reclassifications, mergers and other events. Permitted grantees under the 2007 Plan include employees, non-employee directors and consultants who perform services for the Company. The plan is administered by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company. There were no grants of incentive stock options or stock appreciation rights made under the plan in 2010 or 2009.
Page 63 of 88
Table of Contents
The Company discontinued any further grants under the Company’s 1998 Equity Compensation Plan (the 1998 Plan) as a result of the approval of the 2007 Plan. No options are available for grant from this plan. Grants made from the 1998 Plan continue in effect under the terms of the grant.
All outstanding stock options have performance-based vesting provisions that tie the vesting of stock options to the Company’s financial performance. The Company’s stock options vest at a rate of 50 percent when a specified diluted earning per share target is achieved, and the remaining 50 percent when a second, higher specified diluted earnings per share target is achieved. Stock options granted prior to 2006 fully vest after seven years from the date of grant. Beginning in 2006, the seven year vesting trigger was eliminated and, as a result, options do not vest due to the passage of time but solely as a result of achievement of the financial vesting targets. Earnings per share targets are calculated exclusive of stock-based compensation expense, net of tax. The diluted earnings per share targets are established at time of grant and are measured annually on December 31. The amount of stock-based compensation expense is based upon management’s estimate of when the earnings per share targets may be achieved. If management’s estimate of the attainment of the earnings per share targets proves to be inaccurate, the remaining amount of stock-based compensation expense could be accelerated, spread out over a longer period, or reversed. This may cause volatility in the recognition of stock-based compensation expense in future periods and could materially affect the Company’s net income and net income per share.
The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options. The determination of the fair value of stock options on the date of grant using an option-pricing model is affected by the price of the Company’s common stock as well as other variables. These variables include expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, actual and projected employee stock exercise behaviors, risk-free interest rate and expected dividends. The Company primarily uses historical data to estimate the variables used in the option-pricing model except expected volatility. The Company uses a combination of historical and implied volatility. The Company estimates forfeitures at the time of grant and may revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The Company uses historical data to estimate pre-vesting forfeitures and record stock-based compensation expense only for those awards that are expected to vest. Stock-based compensation is amortized over the requisite service periods of the awards, which are generally the vesting periods.
The weighted average fair value of the Company’s stock options granted during 2010, 2009 and 2008 were $9.65, $7.24 and $7.35, respectively, using the following assumptions:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
7.45 | 7.49 | 7.28 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility |
36.35 | % | 37.44 | % | 52.66 | % | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
0.84 | % | 1.02 | % | 1.02 | % | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
3.01 | % | 3.31 | % | 2.27 | % | ||||||
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense in its Consolidated Financial Statements in 2010, 2009 and 2008 as follows:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
$ | 26,783 | $ | 14,503 | $ | 16,010 | ||||||
| Less: Deferred tax benefit |
(10,068 | ) | (4,636 | ) | (4,972 | ) | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense, net of tax |
$ | 16,715 | $ | 9,867 | $ | 11,038 | ||||||
During 2010, the Company revised its estimates of when some vesting targets are expected to be achieved. These changes in management’s estimates resulted in an increase of $11,663 in stock-based compensation expense in 2010. Additionally, during the three months ended September 30, 2010, the Company reversed $6,375 of previously-recognized stock-based compensation costs pertaining to option grants which management does not expect to vest. Management does not expect to recognize any compensation cost associated with these option grants. As of December 31, 2010, these option grants have an unrecognized compensation cost of $27,460.
Page 64 of 88
Table of Contents
The Company reduced the amount of stock-based compensation expense recognized in 2009 and 2008 by $8,223 and $6,023 due to a change in management’s estimate of when certain vesting targets are expected to be achieved.
As of December 31, 2010, there was approximately $52,049 of unrecognized compensation cost remaining, adjusted for estimated forfeitures, related to unvested employee stock options that the Company expects will vest. The Company estimates that compensation cost will be recognized according to the following schedule:
| Period |
Stock-Based Compensation Expense |
|||
| 2011 |
$ | 14,560 | ||
| 2012 |
14,427 | |||
| 2013 |
12,533 | |||
| 2014 |
5,550 | |||
| 2015 |
3,286 | |||
| 2016 |
1,693 | |||
| $ | 52,049 | |||
This table presents certain information relating to the Company’s stock option plans for 2010, 2009, and 2008:
| Number of Shares |
Weighted Avg. Price |
|||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2007 |
27,767,000 | $ | 20.02 | |||||
| Granted |
4,539,000 | 14.65 | ||||||
| Exercised |
(2,454,000 | ) | 10.44 | |||||
| Expired or canceled |
(969,000 | ) | 22.92 | |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2008 |
28,883,000 | $ | 19.90 | |||||
| Granted |
4,222,000 | 17.66 | ||||||
| Exercised |
(2,055,000 | ) | 10.53 | |||||
| Expired or canceled |
(2,086,000 | ) | 21.87 | |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2009 |
28,964,000 | $ | 20.09 | |||||
| Granted |
2,883,000 | 23.84 | ||||||
| Exercised |
(1,633,000 | ) | 16.04 | |||||
| Expired or canceled |
(2,333,000 | ) | 23.68 | |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2010 |
27,881,000 | $ | 20.42 | |||||
| Exercisable as of December 31, 2010 |
14,247,000 | $ | 17.58 | |||||
| Available for future grant as of December 31, 2010 |
6,741,000 | |||||||
As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, there were 11,801,000 and 13,245,000 shares exercisable, respectively. The expiration dates for options outstanding at December 31, 2010 range from May 29, 2011 to December 14, 2020 with a weighted average remaining contractual life of 6.1 years.
Upon exercise of stock options, the Company will issue new shares of its common shares. The Company does not hold any shares in treasury. The total intrinsic value of options exercised during 2010 and 2009 was $9,961 and $14,015, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding and options exercisable as of December 31, 2010 was $94,032 and $88,538,
Page 65 of 88
Table of Contents
respectively. The total intrinsic value for options outstanding and options exercisable is calculated as the difference between the market value of the Company’s common stock as of December 31, 2010 and the exercise price of the shares. The market value of the Company’s common stock as of December 31, 2010 was $23.79 as reported by the Nasdaq Stock Market, LLC.
This table summarizes information relating to all options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2010:
| Options Outstanding at December 31, 2010 |
Options Exercisable at December 31, 2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices (Per Share) |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price (Per Share) |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price (Per Share) |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 14.05 – 14.62 | 4,156,000 | $ | 14.62 | 7.99 | 2,081,000 | $ | 14.62 | 7.98 | |||||||||||||||||
| 14.71 – 16.61 | 4,821,000 | 14.79 | 2.70 | 4,592,000 | 14.77 | 2.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 17.35 – 19.28 | 6,907,000 | 18.32 | 7.36 | 3,371,000 | 18.30 | 7.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 19.53 – 23.86 | 7,110,000 | 22.47 | 5.82 | 4,188,000 | 21.50 | 2.95 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 27.03 – 32.49 | 4,887,000 | 30.88 | 6.46 | 15,000 | 27.03 | 6.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 27,881,000 | 14,247,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, there was $141,438 and $139,561 available in the pool of windfall tax benefits.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Company has an employee stock purchase plan that provides for offerings of common stock to eligible employees at a price equal to 85 percent of the fair market value of the stock at the end of the stock purchase period, as defined. The Company has reserved 15,600,000 shares for issuance under this plan. At December 31, 2010, 11,364,000 cumulative shares have been issued. Costs incurred by the Company related to the employee stock purchase plan were immaterial in 2010, 2009 and 2008.
Common Stock Buyback
The Board of Directors has authorized the purchase of the Company’s common stock on the open market or through private transactions of up to an aggregate of $1.728 billion. Through December 31, 2010, a total of 263,813,439 shares at an aggregate cost of $1.621 billion have been purchased and retired. The Company purchased 5,814,083 shares at a cost of $120,982 during 2010.
The Company immediately retires its common stock when purchased. Upon retirement, the Company reduces Capital in excess of par value for the average capital per share outstanding and the remainder is charged against Retained earnings. If the Company reduces its Retained earnings to zero, any subsequent purchases of common stock will be charged entirely to Capital in excess of par value.
Rights Agreement
In December 2008, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a dividend distribution pursuant to a Rights Agreement (the Rights Agreement) which became effective on January 6, 2009. The purpose of the Rights Agreement is to deter coercive or unfair takeover tactics and to prevent a person or group (an Acquiring Person) from acquiring control of the Company without offering a fair price to all shareholders. Under the Rights Agreement, all common shareholders receive one Right for each common share outstanding. Each Right entitles the registered holder to purchase from the Company a unit consisting of one twenty-thousandths of a share of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Shares, $.05 par value per share, or a combination of securities and assets of equivalent value, at a purchase price of $150.00 per unit, subject to adjustment. The Rights will become exercisable and
Page 66 of 88
Table of Contents
trade separately from the common stock ten days following a public announcement that an Acquiring Person has beneficial ownership of more than 20 percent of the outstanding common stock of the Company or the commencement of a tender or exchange offer that would result in an Acquiring Person owning 20 percent or more of the outstanding common stock of the Company. Upon exercise, holders, other than an Acquiring Person, will have the right to purchase the common stock of the Company equal to twice the value of the exercise price of the Rights. In lieu of requiring payment of the purchase price upon exercise of the Rights following certain events, the Company may permit the holders simply to surrender the Rights, in which event they will be entitled to receive common shares and other property, as the case may be, with a value of 50 percent of what could be purchased by payment of the full purchase price. The Rights, which do not have voting rights, will expire on January 6, 2019, and may be redeemed by the Company any time until ten days following the announcement of an Acquiring Person at a price of $.01 per Right.
Cash Dividends
On May 25, 2010, the Board of Directors declared a cash dividend of $.10 per share on the Company’s common stock, which was paid on June 28, 2010, to shareholders of record on June 23, 2010. On December 14, 2010, the Board of Directors declared a cash dividend of $.10 per share on the Company’s common stock, which was paid on December 30, 2010, to shareholders of record on December 23, 2010.
The cash dividends declared in 2010, 2009, and 2008 were $37,513, $32,422, and $30,636, respectively. The Board of Directors has indicated its intention to declare future cash dividends on a semiannual basis.
Noncontrolling Interest
The following table provides a reconciliation of Noncontrolling interest on the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Noncontrolling interest |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 121,895 | $ | 109,722 | $ | 138,151 | ||||||
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
1,633 | 98,097 | 128,273 | |||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
685 | 1,797 | (5,150 | ) | ||||||||
| Deconsolidation of LSV |
(65,522 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Deconsolidation of LSV Employee Group |
(43,536 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests |
0 | (87,337 | ) | (144,399 | ) | |||||||
| Other |
0 | (384 | ) | (7,153 | ) | |||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 15,155 | $ | 121,895 | $ | 109,722 | ||||||
Page 67 of 88
Table of Contents
Note 9 – Accumulated Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income consists of net income and other gains and losses affecting shareholders’ equity that are excluded from net income. For the Company, comprehensive income includes unrealized gains and losses on available for sale securities and foreign currency translation adjustments. The Company presents comprehensive income in its Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income. Components of Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) consisted of:
| Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments |
Unrealized Holding Gains (Losses) On Investments |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
||||||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income at January 1, 2008 |
$ | 9,174 | $ | 816 | $ | 9,990 | ||||||
| Less: Total accumulated comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest at January 1, 2008 |
(2,002 | ) | 0 | (2,002 | ) | |||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments Company at January 1, 2008 |
$ | 7,172 | $ | 816 | $ | 7,988 | ||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(18,961 | ) | (2,340 | ) | (21,301 | ) | ||||||
| Less: Total comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
5,150 | 0 | 5,150 | |||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | (13,811 | ) | $ | (2,340 | ) | $ | (16,151 | ) | |||
| Total accumulated comprehensive loss at December 31, 2008 |
(9,787 | ) | (1,524 | ) | (11,311 | ) | ||||||
| Less: Total accumulated comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest at December 31, 2008 |
3,148 | 0 | 3,148 | |||||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive loss attributable to SEI Investments Company at December 31, 2008 |
$ | (6,639 | ) | $ | (1,524 | ) | $ | (8,163 | ) | |||
| Total comprehensive income |
8,734 | 2,484 | 11,218 | |||||||||
| Less: Total comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(1,797 | ) | 0 | (1,797 | ) | |||||||
| Total comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | 6,937 | $ | 2,484 | $ | 9,421 | ||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income (loss) at December 31, 2009 |
(1,053 | ) | 960 | (93 | ) | |||||||
| Less: Total accumulated comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest at December 31, 2009 |
1,351 | 0 | 1,351 | |||||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments Company at December 31, 2009 |
$ | 298 | $ | 960 | $ | 1,258 | ||||||
Page 68 of 88
Table of Contents
| Total comprehensive income |
2,205 | 379 | 2,584 | |||||||||
| Less: Total comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
(685 | ) | 0 | (685 | ) | |||||||
| Total comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments Company |
$ | 1,520 | $ | 379 | $ | 1,899 | ||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income at December 31, 2010 |
1,152 | 1,339 | 2,491 | |||||||||
| Less: Total accumulated comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest at December 31, 2010 |
666 | 0 | 666 | |||||||||
| Total accumulated comprehensive income attributable to SEI Investments Company at December 31, 2010 |
$ | 1,818 | $ | 1,339 | $ | 3,157 | ||||||
Note 10 - Employee Benefit Plan:
The Company has a tax-qualified defined contribution plan (the Plan). The Plan provides retirement benefits, including provisions for early retirement and disability benefits, as well as a tax-deferred savings feature. After satisfying certain requirements, participants are vested in employer contributions at the time the contributions are made. All Company contributions are discretionary and are made from available profits. The Company contributed $4,496, $4,327, and $4,844 to the Plan in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
Note 11 - Commitments and Contingencies:
The Company leases certain of its facilities, data processing equipment, and software under non-cancelable operating leases, some which contain escalation clauses for increased taxes and operating expenses. The Company has entered into maintenance agreements primarily for its data processing equipment. Rent expense was $17,210, $19,022, and $21,535 in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
The aggregate noncancellable minimum commitments at December 31, 2010, other than those related to the lines of credit, are:
| 2011 |
$ | 15,254 | ||
| 2012 |
14,719 | |||
| 2013 |
10,278 | |||
| 2014 |
3,661 | |||
| 2015 and thereafter |
11,092 | |||
| $ | 55,004 | |||
In the ordinary course of business, the Company from time to time enters into contracts containing indemnification obligations of the Company. These obligations may require the Company to make payments to another party upon the occurrence of certain events including the failure by the Company to meet its performance obligations under the contract. These contractual indemnification provisions are often standard contractual terms of the nature customarily found in the type of contracts entered into by the Company. In many cases, there are no stated or notional amounts included in the indemnification provisions. There are no amounts reflected on the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2010 and 2009 related to these indemnifications.
In the normal course of business, the Company is party to various claims and legal proceedings. One of the Company’s subsidiaries, SIDCO, has been named as a defendant in certain putative class action complaints (the Complaints) related to leveraged exchange traded funds (ETFs) advised by ProShares Advisors, LLC, which is a client of the Company. To date, the Complaints have been filed in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and in the United States District Court for the
Page 69 of 88
Table of Contents
District of Maryland, although the three complaints filed in the District of Maryland have been voluntarily dismissed by the plaintiffs. Two of them were subsequently re-filed in the Southern District of New York. Two of the complaints filed in the Southern District of New York have been voluntarily dismissed by plaintiffs. The first complaint was filed on August 5, 2009. The Complaints are purportedly made on behalf of all persons that purchased or otherwise acquired shares in various ProShares ETFs pursuant or traceable to allegedly false and misleading registration statements, prospectuses and statements of additional information. The Complaints name as defendants ProShares Advisors, LLC; ProShares Trust, ProShares Trust II; SIDCO, and various officers and trustees to ProShares Advisors, LLC; ProShares Trust and ProShares Trust II. The Complaints allege that SIDCO was the distributor and principal underwriter for the various ProShares ETFs that were distributed to authorized participants and ultimately shareholders. The Complaints allege that the registration statements for the ProShares ETFs were materially false and misleading because they supposedly failed adequately to describe the nature and risks of the investments. The Complaints allege that SIDCO is liable for these purportedly material misstatements and omissions under Section 11 of the Securities Act of 1933. The Complaints seek unspecified compensatory and other damages, reasonable costs and other relief. The Complaints were consolidated, and an Amended Consolidated Class Action Complaint (Amended Complaint) was filed on September 24, 2010, which asserted the same claims and added a few individuals who alleged served as “Attorney-in-fact” as defendants. Defendants filed a Motion to Dismiss the Amended Complaint on November 15, 2010. On December 15, 2010, lead plaintiff informed the Court and defendants that he intends to file a second amended consolidated complaint. While the outcome of this litigation is uncertain given its early phase, the Company believes that it has valid defenses to plaintiffs’ claims and intends to defend the lawsuits vigorously.
The Company has been named in five lawsuits that were filed in the 19th Judicial District Court for the Parish of East Baton Rouge, State of Louisiana. One of the five actions purports to set forth claims on behalf of a class and also names SPTC as a defendant. Two of the other actions also name SPTC as a defendant. All five actions name various defendants in addition to the Company, and, in all five actions, the plaintiffs purport to bring a cause of action against the Company under the Louisiana Securities Act. The putative class action originally included a claim against the Company for an alleged violation of the Louisiana Unfair Trade Practices Act. Two of the other five actions include claims for violations of the Louisiana Racketeering Act and possibly conspiracy. In addition, another group of plaintiffs have filed a lawsuit in the 23rd Judicial District Court for the Parish of Ascension, State of Louisiana, against the Company and other defendants asserting claims of negligence, breach of contract, breach of fiduciary duty, violations of the uniform fiduciaries law, negligent misrepresentation, detrimental reliance, violations of the Louisiana Securities Act and Louisiana Racketeering Act and conspiracy. The underlying allegations in all the actions are purportedly related to the role of SPTC in providing back-office services to Stanford Trust Company. The petitions in the lawsuits allege that the Company and SPTC aided and abetted or otherwise participated in the sale of “certificates of deposit” issued by Stanford International Bank. Two of the five actions filed in East Baton Rouge have been removed to federal court, and plaintiffs’ motions to remand are pending. These two cases have been transferred by the Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation to United States District Court for the Northern District of Texas. The case filed in Ascension was also removed to federal court and transferred by the Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation to the Northern District of Texas. The schedule for responding to that complaint has not yet been established. The Company and SPTC filed exceptions in the putative class action pending in East Baton Rouge, which the Court granted in part and dismissed the claims under the Louisiana Unfair Trade Practices Act and denied in part as to the other exceptions. The Company and SPTC filed an answer to the East Baton Rouge putative class action, and plaintiffs filed a motion for class certification. Class discovery has commenced, and a hearing on the motion for class certification is scheduled for March 2011. The response of the Company and SPTC to the petitions filed in the two non-class action cases remaining in East Baton Rouge is due in February 2011. While the outcome of this litigation is uncertain given its early phase, the Company and SPTC believe that they have valid defenses to plaintiffs’ claims and intend to defend the lawsuits vigorously.
Page 70 of 88
Table of Contents
Note 12 - Income Taxes:
The federal and state and foreign income tax provision is summarized as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Current |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 116,388 | $ | 16,012 | $ | 104,984 | ||||||
| State |
8,698 | 664 | 9,023 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
3,365 | 5,412 | 6,440 | |||||||||
| 128,451 | 22,088 | 120,447 | ||||||||||
| Deferred, including current deferred |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
6,085 | 61,443 | (37,180 | ) | ||||||||
| State |
1,509 | 5,822 | 2,453 | |||||||||
| 7,594 | 67,265 | (34,727 | ) | |||||||||
| Income taxes attributable to the Noncontrolling interest (1) |
416 | 533 | 983 | |||||||||
| Total income taxes |
$ | 136,461 | $ | 89,886 | $ | 86,703 | ||||||
| (1) | There is no income tax provision for LSV due to its partnership structure. |
Annual tax provisions include amounts considered sufficient to pay assessments that may result from examination of prior year tax returns; however, the amount ultimately paid upon resolution of issues raised may differ materially from the amount accrued. The examination and the resolution process may last longer than one year.
The components of Net income before income taxes are summarized as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | 360,937 | $ | 255,390 | $ | 340,991 | ||||||
| Foreign |
6,795 | 8,300 | 13,241 | |||||||||
| $ | 367,732 | $ | 263,690 | $ | 354,232 | |||||||
The effective income tax rate differs from the federal income tax statutory rate due to the following:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| State taxes, net of Federal tax benefit |
2.0 | 1.5 | 3.3 | |||||||||
| Foreign tax expense and tax rate differential |
0.4 | 1.1 | 0.7 | |||||||||
| Research and development tax credit |
(0.5 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (1.3 | ) | ||||||
| Valuation allowance on capital losses, PA loss carryforwards and other, net |
0 | 0 | (0.2 | ) | ||||||||
| Net reduction of uncertain tax positions(2) |
0.2 | (2.7 | ) | 0 | ||||||||
| Other, net |
(0.1 | ) | (0.2 | ) | 0.6 | |||||||
| 37.0 | % | 33.9 | % | 38.1 | % | |||||||
| (2) | For 2010, 0.14 percent relates to federal issues and the remaining balance 0.06 percent relates to state tax issues. For 2009, 2.0 percent relates to research and development tax |
Page 71 of 88
Table of Contents
| credit settled with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), 0.5 percent relates to federal issues settled with the IRS and the remaining 0.2 percent relates to state tax issues. |
Undistributed earnings of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries amounted to approximately $58,178 at December 31, 2010. Those earnings are considered to be indefinitely reinvested and, accordingly, no U.S. federal and state income taxes have been provided thereon. Upon distribution of those earnings, in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to both U.S. income taxes, subject to an adjustment for foreign tax credits, and withholding taxes payable to the various foreign countries. Determination of the amount of unrecognized deferred U.S. income tax liability is not practicable because of the complexities associated with its hypothetical calculation, including the availability, or lack thereof, of foreign tax credits to reduce a portion of the U.S. liability.
Deferred income taxes for 2010, 2009, and 2008 reflect the impact of temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and such amounts as measured by tax laws and regulations. Principal items comprising the deferred income tax provision are:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Difference in financial reporting and income tax depreciation methods |
$ | 1,381 | $ | (86 | ) | $ | 2,792 | |||||
| Reserves not currently deductible |
774 | 394 | 2,800 | |||||||||
| Reserves for Capital Support Agreements and basis difference in SIV securities |
4,822 | 60,491 | (49,792 | ) | ||||||||
| Capitalized software currently deductible for tax purposes, net of amortization |
5,734 | 2,876 | 12,220 | |||||||||
| State deferred income taxes |
1,519 | 2,394 | 1,595 | |||||||||
| Revenue and expense recognized in different periods for financial reporting and income tax purposes |
(562 | ) | (122 | ) | 1,599 | |||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
(7,457 | ) | (4,386 | ) | (4,567 | ) | ||||||
| Uncertain tax positions |
(106 | ) | 2,861 | (297 | ) | |||||||
| Other, net |
1,489 | 2,843 | (1,077 | ) | ||||||||
| $ | 7,594 | $ | 67,265 | $ | (34,727 | ) | ||||||
The net deferred income tax liability is comprised of:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | ||||||
| Current deferred income taxes: |
||||||||
| Gross assets |
$ | 1,388 | $ | 2,333 | ||||
| Gross liabilities |
(1 | ) | (50 | ) | ||||
| 1,387 | 2,283 | |||||||
| Valuation allowance |
0 | 0 | ||||||
| 1,387 | 2,283 | |||||||
| Long-term deferred income taxes: |
||||||||
| Gross assets |
59,892 | 50,810 | ||||||
| Gross liabilities |
(143,137 | ) | (130,850 | ) | ||||
| (83,245 | ) | (80,040 | ) | |||||
| Valuation allowance |
(9,008 | ) | (6,217 | ) | ||||
| (92,253 | ) | (86,257 | ) | |||||
| Net deferred income tax liability |
$ | (90,866 | ) | $ | (83,974 | ) | ||
Page 72 of 88
Table of Contents
The valuation allowances against deferred tax assets at December 31, 2010 and 2009 are related to state net operating losses from certain domestic subsidiaries. Certain state tax statutes significantly limit the utilization of net operating losses for domestic subsidiaries. Furthermore, these net operating losses cannot be used to offset the net income of other subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2010, the Company fully utilized its capital loss carryforward in the amount of $4,256.
The tax effect of significant temporary differences representing deferred tax liabilities is:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | ||||||
| Difference in financial reporting and income tax depreciation methods |
$ | (11,402 | ) | $ | (10,879 | ) | ||
| Reserves not currently deductible |
472 | 905 | ||||||
| Capitalized software currently deductible for tax purposes, net of amortization |
(132,030 | ) | (123,693 | ) | ||||
| State deferred income taxes |
5,337 | 4,565 | ||||||
| Revenue and expense recognized in different periods for financial reporting and income tax purposes |
3,015 | 2,300 | ||||||
| Unrealized holding loss (gain) on investments |
(5,292 | ) | (338 | ) | ||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
40,096 | 31,052 | ||||||
| State net operating loss carryforward |
16,634 | 15,518 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance on deferred tax assets |
(9,008 | ) | (6,217 | ) | ||||
| Federal benefit of state tax deduction for uncertain tax positions |
1,542 | 1,518 | ||||||
| Capital loss, net of valuation allowance |
0 | 1,527 | ||||||
| Other, net |
(230 | ) | (232 | ) | ||||
| Net deferred income tax liability |
$ | (90,866 | ) | $ | (83,974 | ) | ||
The Company recognizes tax liabilities in accordance with the applicable accounting guidance and adjusts these liabilities when management’s judgment changes as a result of the evaluation of new information not previously available. Due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different than from our current estimate of the tax liabilities. The Company’s total unrecognized tax benefit, not including interest and penalties, as of December 31, 2010 was $5,723, of which $4,870 would affect the effective tax rate if the Company were to recognize the tax benefit. The gross amount of uncertain tax liability of $767 which is expected to be paid within one year is included in Current liabilities while the remaining amount of $5,645 is included in Other long-term liabilities on the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. During the year ended December 31, 2010, the Company recognized $432 of previously unrecognized tax benefits relating to the lapse of the statute of limitation for certain state filings.
The Company files a consolidated federal income tax return and separate income tax returns with various states. Certain subsidiaries of the Company file tax returns in foreign jurisdictions. The Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examination for years before 2008 and is no longer subject to state, local or foreign income tax examinations by authorities for years before 2001.
Page 73 of 88
Table of Contents
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefit is as follows:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1 |
$ | 4,989 | $ | 13,453 | $ | 13,329 | ||||||
| Tax positions related to current year: |
||||||||||||
| Gross additions |
1,372 | 1,905 | 1,288 | |||||||||
| Gross reductions |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| 1,372 | 1,905 | 1,288 | ||||||||||
| Tax positions related to prior years: |
||||||||||||
| Gross additions |
0 | 0 | 468 | |||||||||
| Gross reductions |
(104 | ) | 0 | (273 | ) | |||||||
| (104 | ) | 0 | 195 | |||||||||
| Settlements |
(102 | ) | (9,888 | ) | 0 | |||||||
| Lapses on statute of limitations |
(432 | ) | (481 | ) | (1,359 | ) | ||||||
| Balance as of December 31 |
$ | 5,723 | $ | 4,989 | $ | 13,453 | ||||||
The above reconciliation of the gross unrecognized tax benefit will differ from the amount which would affect the effective tax rate because of the recognition of the federal and state tax benefits.
The Company classifies all interest and penalties as income tax expense. The Company has recorded $690, $864 and $2,337 in liabilities for tax related interest and penalties in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
The Company estimates it will recognize $499 of unrecognized tax benefits within the next twelve months due to lapses on the statute of limitation.
The Company includes its direct and indirect subsidiaries in its U.S. consolidated federal income tax return. The Company’s tax sharing allocation agreement provides that any subsidiary having taxable income will pay a tax liability equivalent to what that subsidiary would have paid if it filed a separate income tax return. If the separately calculated federal income tax provision for any subsidiary results in a tax loss, the current benefit resulting from such loss, to the extent utilizable on a separate return basis, is accrued and paid to that subsidiary.
Note 13 - Business Segment Information:
The Company’s reportable business segments are:
Private Banks – provides investment processing and investment management programs to banks and trust institutions worldwide, independent wealth advisers located in the United Kingdom, and financial advisors in Canada;
Investment Advisors – provides investment management programs to affluent investors through a network of independent registered investment advisors, financial planners, and other investment professionals in the United States;
Institutional Investors – provides investment management programs and administrative outsourcing solutions to retirement plan sponsors, hospitals, and not-for-profit organizations worldwide;
Investment Managers – provides investment processing, fund processing, and operational outsourcing solutions to investment managers, fund companies and banking institutions located in the United States, and to investment managers worldwide of alternative asset classes such as hedge funds, funds of hedge funds, and private equity funds across both registered and partnership structures; and
Page 74 of 88
Table of Contents
Investments in New Businesses – provides investment management programs to ultra-high-net-worth families residing in the United States through the SEI Wealth Network®.
In January 2010, the Company deconsolidated the assets, liabilities and operations of LSV Asset Management. As a result, LSV is no longer considered a reportable business segment in 2010.
In 2010 and 2009, no single customer accounted for more than ten percent of revenues in any business segment.
The following tables highlight certain financial information about each of the Company’s business segments for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008:
| 2010 | Private Banks |
Investment Advisors |
Institutional Investors |
Investment Managers |
Investments In New Businesses |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 346,668 | $ | 183,378 | $ | 206,531 | $ | 160,159 | $ | 4,099 | $ | 900,835 | ||||||||||||
| Expenses |
310,633 | 110,388 | 106,934 | 103,421 | 12,676 | 644,052 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) |
$ | 36,035 | $ | 72,990 | $ | 99,597 | $ | 56,738 | $ | (8,577 | ) | $ | 256,783 | |||||||||||
| Profit margin |
10 | % | 40 | % | 48 | % | 35 | % | N/A | 29 | % | |||||||||||||
| 2009 | Private Banks |
Investment Advisors |
Institutional Investors |
Investment Managers |
Investments In New Businesses |
LSV | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 361,273 | $ | 166,097 | $ | 177,721 | $ | 139,004 | $ | 4,492 | $ | 211,961 | $ | 1,060,548 | ||||||||||||||
| Expenses (1) |
309,300 | 109,418 | 99,924 | 93,074 | 11,625 | 136,580 | 759,921 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) |
$ | 51,973 | $ | 56,679 | $ | 77,797 | $ | 45,930 | $ | (7,133 | ) | $ | 75,381 | $ | 300,627 | |||||||||||||
| Profit margin |
14 | % | 34 | % | 44 | % | 33 | % | N/A | 36 | % | 28 | % | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 | Private Banks |
Investment Advisors |
Institutional Investors |
Investment Managers |
Investments In New Businesses |
LSV | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 408,500 | $ | 223,164 | $ | 198,154 | $ | 147,968 | $ | 6,865 | $ | 263,268 | $ | 1,247,919 | ||||||||||||||
| Expenses (1) |
326,661 | 122,231 | 112,866 | 101,078 | 15,795 | 164,783 | 843,414 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) |
$ | 81,839 | $ | 100,933 | $ | 85,288 | $ | 46,890 | $ | (8,930 | ) | $ | 98,485 | $ | 404,505 | |||||||||||||
| Profit margin |
20 | % | 45 | % | 43 | % | 32 | % | N/A | 37 | % | 32 | % | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, LSV includes $105,471 and $135,251, respectively, of noncontrolling interest of the other partners of LSV. |
Page 75 of 88
Table of Contents
A reconciliation of the total reported for the business segments to income from operations in the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Total operating profit from segments above |
$ | 256,783 | $ | 300,627 | $ | 404,505 | ||||||
| Corporate overhead expenses |
(40,715 | ) | (36,529 | ) | (38,955 | ) | ||||||
| Noncontrolling interest reflected in segments |
1,465 | 106,905 | 138,079 | |||||||||
| LSV Employee Group expenses (2) |
0 | (7,296 | ) | (7,280 | ) | |||||||
| Income from operations |
$ | 217,533 | $ | 363,707 | $ | 496,349 | ||||||
| (2) | Includes $7,222 in 2009 and 2008 of amortization expense related to intangible assets. |
The following tables provide additional information for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 pertaining to our business segments:
| Year Ended December 31, |
Capital Expenditures | Depreciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Private Banks |
$ | 32,982 | $ | 39,364 | $ | 48,467 | $ | 15,704 | $ | 15,415 | $ | 15,088 | ||||||||||||
| Investment Advisors |
11,691 | 13,607 | 17,005 | 2,384 | 2,286 | 2,609 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Institutional Investors |
2,601 | 2,665 | 4,434 | 1,170 | 1,108 | 1,251 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment Managers |
3,659 | 4,306 | 5,467 | 1,891 | 1,580 | 1,805 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investments in New Businesses |
608 | 831 | 1,166 | 148 | 176 | 253 | ||||||||||||||||||
| LSV |
0 | 1,358 | 156 | 0 | 395 | 382 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total from business segments |
$ | 51,541 | $ | 62,131 | $ | 76,695 | $ | 21,297 | $ | 20,960 | $ | 21,388 | ||||||||||||
| LSV Employee Group |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate Overhead (A) |
799 | 1,085 | 7,184 | 605 | 571 | 644 | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 52,340 | $ | 63,216 | $ | 83,879 | $ | 21,902 | $ | 21,531 | $ | 22,032 | |||||||||||||
| (A) | Includes an Out of period adjustment related to capitalized interest for $5,777 in 2008 (See Note 1). |
| Amortization | ||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| Private Banks |
$ | 15,100 | $ | 24,058 | $ | 11,324 | ||||||
| Investment Advisors |
5,467 | 8,550 | 3,985 | |||||||||
| Institutional Investors |
1,213 | 927 | 406 | |||||||||
| Investment Managers |
820 | 688 | 359 | |||||||||
| Investments in New Businesses |
477 | 1,897 | 1,140 | |||||||||
| LSV |
0 | 436 | 437 | |||||||||
| Total from business segments |
$ | 23,077 | $ | 36,556 | $ | 17,651 | ||||||
| LSV Employee Group |
0 | 7,280 | 7,001 | |||||||||
| Corporate Overhead |
971 | 772 | 275 | |||||||||
| $ | 24,048 | $ | 44,608 | $ | 24,927 | |||||||
Page 76 of 88
Table of Contents
| Total Assets | ||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| Private Banks |
$ | 460,261 | $ | 428,367 | ||||
| Investment Advisors |
113,111 | 108,426 | ||||||
| Institutional Investors |
72,867 | 68,101 | ||||||
| Investment Managers |
96,378 | 102,682 | ||||||
| Investments in New Businesses |
6,801 | 9,669 | ||||||
| LSV |
0 | 127,152 | ||||||
| Total from business segments |
$ | 749,418 | $ | 844,397 | ||||
| LSV Employee Group |
0 | 63,117 | ||||||
| Corporate Overhead (3) |
627,805 | 626,294 | ||||||
| $ | 1,377,223 | $ | 1,533,808 | |||||
| (3) | Unallocated assets primarily consist of cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, and certain other shared services assets. |
The following table presents revenues based on the location of the use of the products or services:
| For the Year Ended December 31, |
2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||
| United States |
$ | 767,068 | $ | 950,891 | $ | 1,103,727 | ||||||
| International operations |
133,767 | 109,657 | 144,192 | |||||||||
| $ | 900,835 | $ | 1,060,548 | $ | 1,247,919 | |||||||
The following table presents assets based on their location:
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| United States |
$ | 1,193,775 | $ | 1,380,038 | ||||
| International operations |
183,448 | 153,770 | ||||||
| $ | 1,377,223 | $ | 1,533,808 | |||||
Note 14 - Related Party Transactions:
The Company, either by itself or through its wholly-owned subsidiaries, is a party to Investment Advisory and Administration Agreements with regulated investment companies (RICs) and other investment products which are administered by the Company. These investment products are offered to clients of the Company and its subsidiaries. Under the Investment Advisory and Administration Agreements, the Company receives a fee for providing investment advisory, administrative, and accounting services. The investment advisory and administration fee is a fixed percentage, referred to as basis points, of the average daily net assets, subject to certain limitations. Investment advisory and administration fees received by the Company totaled $354,341, $334,084, and $425,136, in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively. The Company is also a party to various agreements with several RICs which are advised and/or administered by the Company. The Company receives a fee for providing shareholder, administrative and distribution services pursuant to the provisions of various shareholder service, administrative service, and distribution plans adopted by the RICs. These fees totaled $36,007, $33,008, and $50,689 in 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively. A portion of the transaction costs incurred by the RICs for securities transactions are directed to the Company’s broker-dealer subsidiary in its capacity as an introducing broker-dealer.
Page 77 of 88
Table of Contents
The Company recognized $4,875, $4,300, and $2,891 in commissions during 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
Note 15 - Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited):
| For the Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| 2010 |
March 31 | June 30 | Sept. 30 | Dec. 31 | ||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 221,535 | $ | 228,388 | $ | 219,513 | $ | 231,399 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
$ | 96,127 | $ | 86,442 | $ | 91,032 | $ | 96,180 | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI |
$ | 59,420 | $ | 53,478 | $ | 56,389 | $ | 62,400 | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per share |
$ | .31 | $ | .28 | $ | .30 | $ | .33 | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share |
$ | .31 | $ | .28 | $ | .30 | $ | .33 | ||||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
37.9 | % | 37.8 | % | 37.8 | % | 37.0 | % | ||||||||
| Total SIV-related gains |
$ | 17,349 | $ | 3,913 | $ | 8,728 | $ | 14,257 | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share (1) |
$ | .06 | $ | .01 | $ | .03 | $ | .05 | ||||||||
| (1) | Attributable to SIV-related gains. |
| For the Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| 2009 |
March 31 | June 30 | Sept. 30 | Dec. 31 | ||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 248,611 | $ | 252,009 | $ | 275,933 | $ | 283,995 | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
$ | 59,992 | $ | 88,339 | $ | 111,782 | $ | 102,205 | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to SEI |
$ | 34,200 | $ | 41,571 | $ | 52,727 | $ | 45,837 | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per share |
$ | .18 | $ | .22 | $ | .28 | $ | .24 | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share |
$ | .18 | $ | .22 | $ | .27 | $ | .24 | ||||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
20.5 | % | 36.8 | % | 37.0 | % | 35.7 | % | ||||||||
| Total SIV-related gains (losses) |
$ | (14,442 | ) | $ | (2,260 | ) | $ | 14,912 | $ | (3,989 | ) | |||||
| Diluted earnings per share (2) |
$ | (.05 | ) | $ | (.01 | ) | $ | .05 | $ | (.01 | ) | |||||
| (2) | Attributable to SIV-related gains (losses). |
Our effective tax rate in the first quarter of 2009 was favorably impacted by the recognition of certain tax benefits related to the conclusion of federal and state income tax audits.
Page 78 of 88
Table of Contents
SEI INVESTMENTS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
SCHEDULE II - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
FOR THE THREE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2010, 2009, AND 2008
| Additions | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Balance at Beginning of Year |
Charged to Costs and Expenses |
Charged to Other Accounts |
(Deductions) | Balance at End of Year |
|||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 |
$ | 3,348 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | (2,153 | ) | $ | 1,195 | |||||||||
| 2009 |
2,656 | 692 | 0 | 0 | 3,348 | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 |
3,032 | 0 | 0 | (376 | ) | 2,656 | ||||||||||||||
| Deferred income tax valuation allowance: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 |
$ | 6,217 | $ | 1,443 | $ | 1,348 | $ | 0 | $ | 9,008 | ||||||||||
| 2009 |
13,897 | (32 | ) | 0 | (7,648 | ) | 6,217 | |||||||||||||
| 2008 |
13,315 | 0 | 6,821 | (6,239 | ) | 13,897 | ||||||||||||||
Page 79 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as such term is defined under Rule 13a-15(e) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective as of the end of the period covered by this annual report to provide reasonable assurance that the information required to be disclosed by us in reports filed under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by an issuer in the reports that it files or submits under the Act is accumulated and communicated to the issuer’s management including its principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on our evaluation under the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2010.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2010 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No change in our internal control over financial reporting occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2010 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
Page 80 of 88
Table of Contents
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Identification of Directors
Information with respect to the members of the Board of Directors of the Company is set forth under the caption “Election of Directors” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Identification of Executive Officers
The Board of Directors of the Company has determined that the Company’s executive officers within the meaning of Rule 3b-7 promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are as follows:
ALFRED P. WEST, JR., 68, has been the Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since its inception in 1968. Mr. West was President from June 1979 to August 1990.
KEVIN P. BARR, 45, has been an employee of the Company since May 2000. Mr. Barr has been an Executive Vice President since May 2008.
KATHY C. HEILIG, 52, has been an employee of the Company since November 1987. Ms. Heilig has been Chief Accounting Officer and Controller since May 1999. Ms. Heilig was Treasurer from May 1997 to May 2005.
N. JEFFREY KLAUDER, 58, has been Executive Vice President and General Counsel of the Company since August 2004. Prior to August 2004, Mr. Klauder was a partner of Morgan Lewis & Bockius, LLP, a law firm.
EDWARD D. LOUGHLIN, 60, has been an employee of the Company since September 1979. Mr. Loughlin has been an Executive Vice President since May 1993 and a Senior Vice President since January 1988.
DENNIS J. MCGONIGLE, 50, has been an employee of the Company since August 1985. Mr. McGonigle has been the Chief Financial Officer since December 2002 and an Executive Vice President since July 1996 and a Senior Vice President since May 1995.
STEPHEN G. MEYER, 46, has been an employee of the Company since November 1992. Mr. Meyer has been an Executive Vice President since December 2006 and a Senior Vice President since December 2005.
JOSEPH P. UJOBAI, 49, has been an employee of the Company since May 1998. Mr. Ujobai has been an Executive Vice President since May 2003 and a Senior Vice President since January 2001.
WAYNE M. WITHROW, 55, has been an employee of the Company since January 1990. Mr. Withrow has been an Executive Vice President since March 2000 and a Senior Vice President since January 1994. Mr. Withrow was Chief Information Officer from March 2000 to May 2002.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Information with respect to the Section 16(a) compliance of the directors and executive officers of the Company is set forth under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Code of Conduct
The Company has adopted a Code of Conduct applicable to all of its employees, including its executive officers, as well as a Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers. The Code of Conduct and the Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers is posted on our website, www.seic.com under the Corporate Governance section.
Page 81 of 88
Table of Contents
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Information required by this item is set forth under the caption “Executive Compensation” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
Information required by this item is set forth under the caption “Ownership of Shares” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
The following table provides information regarding the aggregate number of securities to be issued under all of our equity compensation plans upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants, and other rights and their weighted-average exercise price as of December 31, 2010. Material features of each of the plans reflected in the table are described below.
|
Number of (a) |
Weighted –average (b) |
Number of securities (c) |
||||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (1) |
27,880,590 | $ | 20.42 | 6,741,275 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||||
| Total |
27,880,590 | $ | 20.42 | 6,741,275 | ||||||||
| (1) | Consists of: (i) the 2007 Equity Compensation Plan, and (ii) the Amended and Restated 1998 Equity Compensation Plan. |
The 2007 Equity Compensation Plan:
On April 3, 2007, the Board of Directors adopted the 2007 Equity Compensation Plan (the 2007 Plan), and the Company’s shareholders approved the adoption of the 2007 Plan on May 23, 2007. The 2007 Plan provides for grants of stock options (incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options) and stock appreciation rights (SARs) to all employees (including employees who are also directors) of the Company or its subsidiaries, consultants and advisors who perform valuable services to the Company or its subsidiaries and members of the Board of Directors who are not employees of the Company. The Company has not granted any incentive stock options or stock appreciation rights under the 2007 Plan.
The 2007 Plan is administered and interpreted by the Compensation Committee; however, the Board of Directors or its delegate will make grants under the 2007 Plan to non-employee directors. The Compensation Committee has the authority to (i) determine the individuals to whom grants will be made under the 2007 Plan, (ii) determine the type, size and terms of the grants, (iii) determine the time when grants will be made and the duration of any applicable exercise or restriction period, including the exercisability and the acceleration of exercisability, (iv) amend the terms of any previously issued grant, (v) adopt guidelines separate for the 2007 Plan that set forth the specific terms and conditions for grants under the 2007 Plan, and (vi) deal with any other matters arising under the 2007 Plan.
Options granted under the 2007 Plan may be “incentive stock options,” which are intended to qualify within the meaning of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code, and “nonqualified stock options” which are not intended to so qualify. Options are granted under the 2007 Plan with an exercise price equal to or greater than the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant and the term of may not exceed ten years from the date of grant. The vesting period for options commences on the date of grant, or upon the achievement of such vesting requirements, and ends on such date as is determined in each case by the
Page 82 of 88
Table of Contents
Compensation Committee, in its sole discretion, which is specified in the grant letter. Options may be exercised only while the participant is actively employed by or actively providing service to the Company unless the Compensation Committee provides for a period after such employment or service in which the option may be exercised.
The Compensation Committee may grant SARs to anyone eligible to participate in the 2007 Plan. Upon exercise of a SAR, the participant will receive an amount equal to the excess of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of exercise over the base amount set forth in the grant letter. Such payment to the participant will be in cash, in shares of common stock, or in a combination of cash and shares of common stock. The Compensation Committee will determine the period when SARs vest and become exercisable, the base amount of the SARs, and whether SARs will be granted in connection with, or independently of, any options. SARs may be exercised only while the participant is actively employed by or actively providing service to the Company unless the Compensation Committee provides for a period after such employment or service in which the option may be exercised.
If there is any change in the number or kind of shares of common stock outstanding by reason of a stock dividend, spin-off, recapitalization, stock split, or combination or exchange of shares, by reason of a merger, reorganization or consolidation, by reason of a recapitalization or change in par value or by reason of any other extraordinary or unusual event affecting the outstanding common stock as a class without the Company’s receipt of consideration, or if the value of outstanding shares of common stock is substantially reduced as a result of a spin-off or the Company’s payment of an extraordinary dividend or distribution, the maximum number of shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2007 Plan, the maximum number of shares of common stock which any individual may receive pursuant to grants in any year, the kind and number of shares covered by outstanding grants, the kind and number of shares issued and to be issued under the 2007 Plan, and the price per share or the applicable market value of such grants shall be appropriately adjusted by the Compensation Committee, in such manner as the Compensation Committee deems appropriate, to reflect any increase or decrease in the number of, or change in the kind or value of, the issued shares of common stock to preclude, to the extent practicable, the enlargement or dilution of rights and benefits under the 2007 Plan and such outstanding grants.
In the event of a change in control, the Compensation Committee may take any of the following actions with respect to outstanding grants: (i) determine that outstanding options and SARs will be fully exercisable as of the date of the change in control or at such other time as the Compensation Committee determines, (ii) require that participants surrender their options and SARs in exchange for payment by the Company, in cash or shares of common stock as determined by the Compensation Committee, in an amount equal to the amount by which the then-fair market value subject to the participant’s unexercised options and SARs exceeds the exercise price of the option or the base amount of the SAR, as applicable, (iii) after giving participants the opportunity to exercise their options and SARs, the Compensation Committee may terminate any or all unexercised options and SARs at such time as the Compensation Committee determines appropriate, or (iv) determine that grants that remain outstanding after the change in control will be converted to similar grants of the surviving corporation.
The Board of Directors may amend or terminate the 2007 Plan at any time, subject to shareholder approval. No grants may be issued under the 2007 Plan after June 1, 2017.
As of December 31, 2010, options to acquire 13,258,725 shares were outstanding under the 2007 Plan, out of a total of 20,000,000 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under the 2007 Plan. A total of 6,741,275 shares of common stock remain available for issuance under the 2007 Plan for future grants.
The 1998 Equity Compensation Plan:
On May 21, 1998, the Board of Directors adopted the 1998 Equity Compensation Plan (the 1998 Plan), and the Company’s shareholders approved the adoption of the 1998 Plan. The Board of Directors had made certain amendments to the 1998 Plan after its adoption that did not require shareholder approval. The 1998 Plan was most recently amended and restated in May 2003. The 1998 Plan provided for grants of stock options (incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options), stock appreciation rights, restricted stock and performance units to all employees (including employees who were also directors) of the Company or its subsidiaries, consultants and advisors who performed valuable services to the Company or its subsidiaries and members of the Board of Directors who were not employees of the Company. The Company did not grant any incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock or performance units under the 1998 Plan. The 1998 Plan was terminated by the Board of Directors in April 2007, and no further options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock and performance units may be granted. However, options granted under the 1998 Plan prior to its termination continue in effect under the terms of the grant and the 1998 Plan.
Page 83 of 88
Table of Contents
All options that were granted under the 1998 Plan to employees and consultants were granted at the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant, become exercisable ratably upon the attainment of specific diluted earnings per share targets or in their entirety after seven years from the date of grant (for grants prior to 2006), and expire ten years from the date of grant.
The 1998 Plan provided that non-employee members of the Board of Directors would receive automatic grants of nonqualified stock options. Each non-employee director who first became a member of the Board of Directors after the effective date of the 1998 Plan, but before the termination of the 1998 Plan, received a non-qualified stock option to purchase 8,000 shares. In addition, each non-employee director received a non-qualified stock option to purchase 4,000 shares pursuant to the 1998 Plan. The exercise prices for these options were equal to the fair market value of the Company’s stock on the date of grant, the term is ten years from the date of grant, and the options became exercisable ratably over the first four anniversaries of the date of grant (unless otherwise determined by the Compensation Committee).
If the Company is consolidated or merged into another corporation, each optionee with an outstanding option under the 1998 Plan will receive, upon exercise of the option, the same consideration as other shareholders of the Company received in connection with the transaction. If all or substantially all of the assets of the Company are sold or exchanged (other than by merger or consolidation), each optionee will have the right to exercise the option in full within ten days after the Compensation Committee provides notice of the right to exercise the option, and any portion of the option not exercised will lapse.
As of December 31, 2010, options to acquire 14,621,865 shares were outstanding under the 1998 Plan, out of a total of 40,444,000 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under the 1998 Plan.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Information required by this item is set forth under the captions “Election of Directors,” “Executive Compensation,” and “Director Compensation” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
Information required by this item is set forth under the caption “Ratification or Appointment of Independent Public Accountants” in the Company’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Page 84 of 88
Table of Contents
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
| 1 and 2. | Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules. The following is a list of the Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company and its subsidiaries and supplementary data filed as part of Item 8 hereof: | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations — For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 |
||||
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity — For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 |
||||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008 |
||||
| All other schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, or not required, or because the required information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto. | ||||
| 3. | Exhibits, Including Those Incorporated by Reference. The exhibits to this Report are listed on the accompanying index to exhibits and are incorporated herein by reference or are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. | |||
Page 85 of 88
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| SEI INVESTMENTS COMPANY | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Dennis J. McGonigle | |||||
| Dennis J. McGonigle | ||||||||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on dates indicated.
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Alfred P. West, Jr. | |||||
| Alfred P. West, Jr. | ||||||||
| Chairman of the Board, | ||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer, | ||||||||
| and Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Carmen V. Romeo | |||||
| Carmen V. Romeo | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Richard B. Lieb | |||||
| Richard B. Lieb | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ William M. Doran | |||||
| William M. Doran | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Henry H. Porter, Jr. | |||||
| Henry H. Porter, Jr. | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Kathryn M. McCarthy | |||||
| Kathryn M. McCarthy | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
| Date | February 24, 2011 |
By | /s/ Sarah W. Blumenstein | |||||
| Sarah W. Blumenstein | ||||||||
| Director | ||||||||
Page 86 of 88
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
The following is a list of exhibits filed as part of this annual report on Form 10-K. For exhibits incorporated by reference, the location of the exhibit in the previous filing is indicated in parentheses.
| 3.1 | Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant as amended on January 21, 1983. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1982.) | |
| 3.1.2 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated May 21, 1992. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.1.2 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1992.) | |
| 3.1.3 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated May 26, 1994. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.1.3 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1994.) | |
| 3.1.4 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated November 21, 1996. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.1.4 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1996.) | |
| 3.1.5 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated February 14, 2001. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.1.4 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2000.) | |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated By-Laws. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 6, 2009.) | |
| 3.2.1* | Amendment of Section 3.02 of the Amended and Restated Bylaws. | |
| 4.1 | Rights Agreement dated January 6, 2009. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 6, 2009.) | |
| 4.2 | Statement with Respect to Shares of a Domestic Corporation amending the designations of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Shares as a series of the Series Preferred Stock of the Company, dated January 6, 2009. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 4.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 6, 2009.) | |
| Note: Exhibits 10.4 through 10.11 constitute the management contracts and executive compensatory plans or arrangements in which certain of the directors and executive officers of the Registrant participate. | ||
| 10.4 | 1998 Equity Compensation Plan, Amended and Restated as of April 8, 2003. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-111224) filed December 16, 2003.) | |
| 10.4.1 | Amendment 2006-1 to the 1998 Equity Compensation Plan, Amended and Restated as of April 8, 2003. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.4.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2006.) | |
| 10.5 | Employee Stock Purchase Plan as Amended and Restated on May 20, 2008. (Incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 20, 2008.) | |
| 10.6 | SEI Capital Accumulation Plan. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 99(e) to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-41343) filed December 2, 1997.) | |
| 10.9 | Employment Agreement, dated June 25, 2004, between N. Jeffrey Klauder and the Registrant. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.9 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2006.) | |
| 10.10 | 2007 Equity Compensation Plan. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.10 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 11, 2007.) | |
| 10.21 | Guaranty and Collateral Agreement, dated as of January 24, 2006 by and among SEI Investments Company, LSV Employee Group, LLC, the Grantors party thereto and LaSalle Bank National Association as Administrative Agent (including the underlying Credit Agreement dated as of January 24, 2006 by and among LSV Employee Group, LLC, LSV Asset Management, the Lenders party thereto and LaSalle Bank National Association as Administrative Agent to which the Guaranty and Collateral Agreement relates). (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 30, 2006.) | |
| 10.21.1 | Third Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of January 18, 2011 by and among LSV Employee Group, LLC, LSV Asset Management, and Bank of America, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.21.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 18, 2011.) | |
| 10.22 | Credit Facility, dated January 14, 2003 between Royal Bank of Canada and SEI Investments Canada Company, a subsidiary of SEI Investments Company. (Incorporated by reference to | |
Page 87 of 88
Table of Contents
| exhibit 10.22 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005.) | ||
| 10.22.1 | First Amendment, dated June 15, 2005 to Credit Facility, dated January 14, 2003 between Royal Bank of Canada and SEI Investments Canada Company, a subsidiary of SEI Investments Company. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.22.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005.) | |
| 10.22.2 | Second Amendment, dated February 20, 2006 to Credit Facility, dated January 14, 2003 between Royal Bank of Canada and SEI Investments Canada Company, a subsidiary of SEI Investments Company. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.22.2 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005.) | |
| 10.23 | $200,000 Credit Agreement, dated July 25, 2007, among SEI Investments Company, the Lenders Party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., Wachovia Bank, National Association, Bank of America, N.A., Manufacturers and Traders Trust Company and PNC Bank, National Association. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated July 24, 2007.) | |
| 10.23.1 | First Amendment, dated November 7, 2007, to $200,000 Credit Agreement, dated July 25, 2007. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended September 30, 2007.) | |
| 10.23.2 | Second Amendment, dated March 19, 2008, to $200,000 Credit Agreement, dated July 25, 2007. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.23.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated March 19, 2008.) | |
| 10.23.3 | Third Amendment, dated November 5, 2008, to $200,000 Credit Agreement, dated July 25, 2007. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.23.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended September 30, 2008.) | |
| 10.23.4 | Fourth Amendment, dated November 26, 2008, to $200,000 Credit Agreement, dated July 25, 2007. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.23.4 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated November 26, 2008.) | |
| 14 | Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 14 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2003.) | |
| 21* | Subsidiaries of the Registrant. | |
| 23.1* | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | |
| 23.2* | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm relating to the financial statements of LSV Asset Management. | |
| 31.1* | Rule 13a-15(e)/15d-15(e) Certification of Chief Executive Officer. | |
| 31.2* | Rule 13a-15(e)/15d-15(e) Certification of Chief Financial Officer. | |
| 32* | Section 1350 Certifications. | |
| 99 | Financial Statements of LSV Asset Management dated December 31, 2005 and 2004. (Incorporated by reference to exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005.) | |
| 99.1* | Financial Statements of LSV Asset Management dated December 31, 2010 and 2009. | |
| 101.INS* | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE* | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF* |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
| * | Filed herewith as an exhibit to this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
Page 88 of 88