
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
(Mark one)
For the fiscal year ended
or
|
For the transition period from |
|
|
|
to |
|
|
|
Commission File No.

|
||
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
|
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
|
|
|
||
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (
Securities registered under Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
Trading Symbol |
Name of each exchange on which registered |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large Accelerated Filer |
☐ |
|
☒ |
|
Non-Accelerated Filer |
☐ |
|
Smaller reporting company |
|
Emerging growth company |
|
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements.
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant's executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No
The aggregate market value of voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $
As of February 26, 2024, the registrant had
Documents Incorporated by Reference
Portions of the definitive Proxy Statement for the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which is to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report to the extent described herein.
CECO Environmental Corp. and Subsidiaries
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
For the year ended December 31, 2023
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Item |
|
Description |
|
Page |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1A. |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1B. |
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1C. |
|
Cybersecurity.................................................................................................................................................................................... |
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 2. |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 3. |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 4. |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 6. |
|
|
24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 7. |
|
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 7A. |
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 8. |
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9. |
|
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9A. |
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9B. |
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 9C |
|
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
|
|
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 11. |
|
|
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 12. |
|
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
|
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 13. |
|
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 14. |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
|
|
44 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 16. |
|
|
46 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|||
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) which are intended to be covered by the safe harbor for “forward-looking statements” provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Any statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, other than statements of historical fact, including statements about management’s beliefs and expectations, are forward-looking statements and should be evaluated as such. These statements are made on the basis of management’s views and assumptions regarding future events and business performance. We use words such as “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “intends,” “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “will,” “plan,” “should” and similar expressions to identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such statements. Potential risks and uncertainties, among others, that could cause actual results to differ materially are discussed under “Part I — Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and include, but are not limited to:
Many of these risks are beyond management’s ability to control or predict. Should one or more of these risks or uncertainties materialize, or should any related assumptions prove incorrect, actual results may vary in material aspects from those currently anticipated. Investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements as they speak only to our views as of the date the statement is made. Furthermore, the forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made. Except as required under the federal securities laws or the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), we undertake no obligation to update or review any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
1
PART I
Item 1. Business
General
CECO Environmental Corp. (“CECO”, “we”, “us”, "our" or the “Company”) is a leading environmentally focused, diversified industrial company, serving the broad landscape of industrial air, industrial water and energy transition markets globally by providing innovative technology and application expertise. We help companies grow their businesses with safe, clean, and more efficient solutions that help protect people, the environment and industrial equipment. Our solutions improve air and water quality, optimize emissions management, and increase the energy and process efficiency for highly engineered applications in power generation, midstream and downstream hydrocarbon processing and transport, chemical processing, electric vehicle production, polysilicon fabrication, semiconductor and electronics production, battery production and recycling, specialty metals, aluminum and steel production, beverage can manufacturing, and industrial and produced water and wastewater treatment, and a wide range of other industrial end markets.
Our customers include some of the largest natural gas processors, transmission and distribution companies, refineries, power generators, industrial manufacturing, engineering and construction companies, semiconductor manufacturers, compressor manufacturers, beverage can manufacturers, metals and minerals, and electric vehicle producers in the world.
We believe our value differentiators include, but are not limited to, our product and solutions performance quality, reliability, durability, on-time delivery and safety, all of which are underpinned by our core capabilities in advanced design and systems engineering, commercial excellence, and operational excellence. We believe these differentiators and core capabilities are critical to maintaining our competitive position. Additionally, we have built a spirit of continuous improvement to ensure we maintain our market leadership position.
With an installed base of operating systems and equipment in excess of $6 billion, we are targeting to grow a higher share of recurring revenue from aftermarket products and installed base value-added services, which we believe will provide a greater customer retention and loyalty, and increased business resiliency.
Industry Overview
We serve a growing multi-billion dollar global industrial market that is highly fragmented and comprised of many industrial sectors and niche applications. Our legacy sectors include industrial wastewater treatment, industrial ventilation systems and contamination controls and filtration, semiconductor fabrication, electronics manufacturing, baseload and backup power generation, hydrocarbon processing, chemical processing, natural gas processing and transport, automobile and aircraft production, polysilicon production, battery recycling, metals processing and production, and produced water treatment. Emerging sectors and applications include electric vehicle and battery production, desalination water transport, ultra-high purity water treatment for electrolysis and electronics production, naval/marine vessel oily water treatment, aluminum beverage can production, and lightweight, high-strength metals production.
We believe demand for our products and services will continue to be driven by the following factors:
2
These factors, individually or collectively, tend to drive increases in industrial capital spending that are not directly impacted by general economic conditions. In contrast, favorable conditions in the economy generally lead to plant expansions and the construction of new industrial sites. However, in a weak economy, customers tend to lengthen the time from initial inquiry to the purchase order or may elect to defer purchases.
3
Mission and Strategy
Our mission is to help companies grow their business with safe, clean and more efficient solutions that help protect their people, the environment and their industrial equipment and facilities.
We seek to fulfill this mission by providing leading solutions for niche, engineered applications in industrial air treatment and management, industrial water treatment, and the energy transition. We will continue to leverage our technologies and application expertise for customers around the world.
Our strategy to become a global leader in niche applications in industrial air treatment and management, industrial water treatment, and the energy transition is supported by an operating environment of performance excellence across the Company.
We constantly look for opportunities to apply our technology and expertise to new customers and in new geographies in our existing end markets, and to enter new end markets with our existing set of products and solutions. Acquisitions are a key part of our growth model and we constantly are seeking out value-added, accretive additions to the CECO portfolio aligned with our strategic focus in industrial air, industrial water and the energy transition.
We intend to continue to expand our customer base and end markets and have continued to pursue potential attractive growth opportunities both domestically and internationally.
Business Segments
Our reportable segments continue to be focused on attractive end markets and each segment is aligned to generate profitable growth for the Company with a compelling technology and solution set to benefit customers.
Competitive Strengths
Leading market position as a complete solution provider
We believe we are a leading provider of critical solutions in industrial air quality, industrial water treatment, and energy transition solutions. The multi-billion dollar global market is highly fragmented with numerous small and regional contracting firms separately supplying engineering services, fabrication, installation, testing and monitoring, products and spare parts. We offer our customers a complete end-to-end solution, including engineering and project management services, procurement and fabrication, construction and installation, aftermarket support, and sale of consumables, which allows our customers to avoid dealing with multiple vendors when managing projects.
Long-standing experience and customer relationships in growing industry
We have serviced the needs of our target markets for over 50 years. Our extensive experience and expertise in providing diversified solutions enhances our overall customer relationships, and provides us with a competitive advantage in our markets relative to other companies in the industry. We believe this is evidenced by strong relationships with many of our world-class customers. We believe no single competitor has the resources to offer a similar portfolio of product and service capabilities. We offer the depth of a large organization, while our lean organizational structure keeps us close to our customers and markets, allowing us to offer rapid and complete solutions in each unique situation.
4
Diversified equipment and solution portfolio and broad customer base
The global diversity of our offering and footprint and customer base provides us with multiple growth opportunities. We have a diversified customer base across a range of industries. We believe that the diversity of our customers, solutions, and end markets mitigates our risk of a potential fluctuation or downturn in demand from any individual industry or particular customer. We believe we have the resources and capabilities to meet the needs of our customers as they upgrade and expand domestically as well as into new international markets. Once systems have been installed and a relationship has been established with the customer, we are often awarded repetitive service and maintenance business as the customers’ processes change and modifications or additions to their systems become necessary.
Experienced management and engineering team
Our business management team has substantial experience in delivering highly-engineered solutions for industrial air quality, industrial water treatment, and energy transition applications. The collective experience of our teams enables us to pursue our strategy, and to successfully execute on our strategic and growth priorities. Our team includes approximately 400 engineers, designers, solution experts, and project managers whose industry experience and technical expertise enables them to have a deep understanding of the solutions that will best suit the needs of our customers. The experience and stability of our senior management, operating and engineering teams have been crucial to our recent growth and to developing and maintaining customer relationships, and increasing our market position.
Innovative solutions
We leverage our engineering and manufacturing expertise, fabrication partner network, and strong customer relationships to develop and deliver new products and solutions to address the identified needs of our customers or a particular end market. We thoroughly analyze each new opportunity by considering projected demand, pricing, and cost to deliver, and only pursue those opportunities that we believe will contribute to sustainable earnings growth. In addition, we seek to continually improve our legacy technologies, solutions, and applications with the aim to maintain competitiveness in our existing customer segments, and to adapt them to new industries and customers.
Disciplined acquisition program with successful integration
We believe that we have demonstrated an ability to successfully acquire and integrate companies with complementary product or service offerings. We will continue to seek and execute additional strategic acquisitions and focus on expanding our solution and product breadth and reach, as well as entering into adjacent customer segments and applications. We believe that the breadth and diversity of our products and services and our ability to deliver full solutions to various end markets provides us with multiple sources of stable growth, relative scale benefits, and a competitive advantage relative to other players in the industry, and we will continue to reinforce this advantage.
Products and Services
We provide a wide range of engineered and configured products and solutions including dampers and diverters, expansion joints, selective catalytic reduction systems, severe-service and industrial cyclones, dust collectors, thermal oxidizers, filtration systems, wet and dry scrubbers, separators and coalescers, water treatment packages, metallic and non-metallic pumps, industrial silencers and fluid handling equipment, and plant engineering services and engineered design build fabrication. Our products and solutions primarily compete on the basis of performance, track record, speed of delivery, quality, price and customer service.
Project Design and Research and Development
Our strategy is to produce and supply differentiated, specialized or configured products and solutions that are often tailored to the specifications of a customer or application. We start by understanding our customers’ needs, then by focusing our new product development efforts on those criteria that help protect our shared environment while improving a variety of operational outcomes including, but not limited to, facility uptime, production quality, employee safety, equipment protection and process performance.
5
We continually collaborate with our customers on projects to ensure the proper solution and customer satisfaction. The project development cycle may follow many different paths depending on the specifics of the job and end market. The cycle can take from one to more than twelve months from concept and design to production but may vary significantly depending on developments that occur during the process, including among others, the emergence of new environmental demands, changes in design specifications and ability to obtain necessary approvals.
Sales, Marketing and Support
Our global commercial strategy is to provide a solutions-based approach for our customers, which may take on the role of single source provider of technology, products and equipment for a particular project. When called upon, this strategy involves expanding our scope of supply by utilizing our portfolio of in-house technologies and those of third-party equipment suppliers, many of which have been long-standing partners evolved from pure supplier roles to value-added business partners. Where we identify a technology that is a critical element or commonly required for a solution, we will consider acquiring such technology to ensure we have the appropriate degree of strategic control. This enables us to leverage existing business with selective alliances of suppliers and application specific engineering expertise. Our value proposition to our customers is to provide competitively priced, customized solutions that leverage our vast project experience base and design library. Our industry-specific knowledge, accompanied by our product and service offerings, provides valuable benefits for our customers and synergies across our network of partners.
We sell and market our products and services with our own direct sales force in key regions including the United States, the Netherlands, United Kingdom, Canada, United Arab Emirates, India, China, Korea, and Singapore. Our direct sales and business development teams will work in conjunction with outside sales representatives in the North America, South America, Europe, Middle East, Southeast and East Asia, and India regions, when appropriate. We expect to continue expanding our sales and support capabilities and our network of outside sales representatives in key regions domestically and internationally.
We market our offerings to our customers through a variety of channels including, but not limited to, digital, web, social media, email campaigns, individual customer visits, product announcements, brochures, magazine articles, advertisements and cover or article features in trade journals and other publications. We also participate in public relations and promotional events, including industry tradeshows and technical conferences.
Our customer service organization and sales force provides our customers with technical assistance, use and maintenance information as well as other key information regarding their purchase. We also actively provide our customers with access to key information regarding changes and pending changes in environmental regulations as well as new product or service developments. We believe that maintaining a close relationship with our customers and providing them with the support they request improves their level of satisfaction and enables us to foresee their potential future product needs or service demands. Moreover, this approach can lead to sales of annual service and support contracts as well as consumables. Our website also provides our customers with online tools and technical resources.
Quality Assurance
In engineered systems, quality is defined as system performance. We review with our customers, before the contract is signed, the technical specification and the efficiency of the equipment that will be customized to meet their specific needs. We then review these same parameters internally to assure that warranties will be met. Standard project management and production management tools are used to help ensure that all work is done to specification and that project schedules are met. Equipment is tested at the site to ensure it is functioning properly.
Customers
We are not dependent upon any single customer, and no customer contributed 10% or more of our consolidated revenues for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, or 2021.
Suppliers and Subcontractors
We purchase our raw materials and supplies from a variety of global sources. When possible, we directly secure iron and steel sheet and plate products from steel mills, whereas other materials are purchased from a variety of steel service centers. Steel prices have traditionally been volatile, but we typically mitigate the risk of higher prices by including a “surcharge” on our standard products and tracking major materials industry indices and projections. On contract work, we try to mitigate the risk of higher prices by including the current price in our estimate and generally include price inflation clauses for protection.
6
Typically, on turnkey projects, we subcontract manufacturing, electrical work, concrete work, controls, conveyors and insulation. We use subcontractors with whom we have good working relationships and review each project at the beginning and on an ongoing basis to help ensure that all work is being done according to our specifications. Subcontractors are generally paid when we are paid by our customers according to the terms of our contract with the customer. Our business model focuses on effective management of subcontractors and flow of raw and finished materials, which allows us to optimize working capital levels through reduction in certain assets and reduce capital expenditures.
While we believe we have a good relationship with our suppliers and subcontractors, we are currently experiencing shortages of raw materials and inflationary pressures for certain materials and labor. We expect these supply chain challenges and cost impacts to continue for the foreseeable future as markets continue to recover and supply chains further normalize. Although we have secured raw materials from existing and alternate suppliers and have taken other mitigating actions to mitigate supply disruptions, we cannot guarantee that we can continue to do so in the future. In this event, our business, results and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Backlog
Backlog (i.e., unfulfilled or remaining performance obligations) represents the sales we expect to recognize for our products and services for which control has not yet transferred to the customer. Backlog was $370.9 million as of December 31, 2023 as compared to $311.7 million as of December 31, 2022, an increase of $59.2 million or 19.0%. Backlog is adjusted on a quarterly basis for fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Substantially all backlog is expected to be delivered within 18 months, with a majority within 12 months. Backlog is not defined by United States generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") and our methodology for calculating backlog may not be consistent with methodologies used by other companies.
Competition
The markets we serve are highly fragmented with numerous small and regional participants. We believe no single company competes with us across the full range of our solutions and products. Competition in the markets we serve is based on a number of considerations, including past performance, track record, customer approvals, lead times, technology, applications experience, know-how, reputation, product warranties, service and price. Demand for our product can vary period over period depending on conditions in the markets we serve. We believe our product performance and quality, reliability, durability, on-time delivery, and safety supported by advanced engineering and operational excellence differentiate us from many of our competitors, including those competitors who often offer products at a lower price.
Due to the size and shipping weight of many of our projects, localized manufacturing/fabrication capabilities are very important to our customers. As a result, competition varies widely by region and industry. The market for our engineered products is reasonably competitive and is characterized by technological stability, continuously evolving environmental regulations, and increasing customer requirements. We believe that the additional competitive factors in our markets include:
We believe we compete favorably with respect to these factors.
Government Regulations
We believe our operations are in compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations. We believe that changes in environmental laws and regulations create opportunity given the nature of our business.
Our business is subject to numerous evolving laws and regulations. While there are not currently regulations proposed or pending that we believe will result in material capital, operating or other costs to the business at this time, such regulations could be proposed and/or passed into law in 2024 or beyond. Other regulations currently in place could be withdrawn and replaced with more stringent
7
requirements in 2024 or beyond. New laws and regulations and the costs of compliance with such new laws and regulations can only be broadly appraised until their implementation becomes more defined through regulatory guidance and enforcement.
Intellectual Property
We rely on a combination of patent, trademark, copyright and trade secret laws, employee and third-party nondisclosure/confidentiality agreements and license agreements to protect our intellectual property. We sell most of our products under a number of registered trade names, brand names and registered trademarks, which we believe are widely recognized in the industry. While we hold patents within a number of our businesses, we do not view our patents to be material to our business.
Human Capital Management
We have employees located throughout the globe. As of December 31, 2023, CECO had approximately 1,200 employees, across nine countries. Of our US employees, 131 are unionized in our Pennsylvania, Tennessee and North Carolina facilities. Outside the United States, we enter into employment contracts and agreements in those countries in which such relationships are mandatory or customary. The provisions of these agreements correspond in each case with the required or customary terms in the subject jurisdiction. We have historically maintained good employee relations and have successfully concluded all of our recent negotiations without a work stoppage. However, we cannot predict the outcome of future contract negotiations.
Our strong employee base, along with our uncompromising commitment to our values of customer first, accountability, relentless execution, respect, integrity and teamwork, provide the foundation of our company’s success. Employee safety and managing the risks associated with our workplace, is of paramount importance to CECO. We believe that all injuries, occupational illnesses and incidents are preventable, and we are committed to operating with a zero-incident culture. Through our environmental, health and safety program we implement policies and training programs, as well as perform self-audits, to ensure our colleagues leave the workplace safely every day. To better understand employee safety at the site level, we have safety committees and safety scorecards to share best practices between sites. CECO’s foundational commitment to safety is demonstrated by our world-class recordable and loss time rates. We currently share scorecard information monthly with our team members to foster visibility, accountability and commitment across our workplace, communicating and celebrating successful results across the enterprise. In addition to lagging indicators, such as injury performance, the scorecards highlight leading indicators such as safety observations and near-misses, as well as other proactive actions taken at each site to ensure worker safety. For the year ended December 31, 2023, CECO’s domestic Total Recordable Incident Rate (“TRIR”) was 1.5% as compared to our benchmark industry average TRIR of 4.3%.
We believe a diverse and inclusive workforce is critical to inspiring innovative thinking, creative problem-solving, performance, and results, so we cultivate an environment where team members feel valued, engaged, and inspired to give their best. The unique characteristics that shape each individual help inform our decisions as a company, and this mindset allows CECO to realize new opportunities and add value to our customers, partners, and stockholders.
As part of our efforts to expand CECO’s diverse workforce, we:
CECO’s commitment to expanding our diverse workforce and enhancing our inclusive culture is driven by our recognition that a workplace that is reflective of our global customer base establishes a firm foundation to drive creativity and innovation, which leads to problem solving, development, performance, and profitable business success.
We invest in programs and processes that develop our employees’ capabilities to ensure that we have the talent we need to execute our strategic business plans. Our Performance Management Program ensures that all leaders have clear priorities, and that their performance relative to these priorities is linked to their total rewards package. We conduct an annual code of conduct training that includes subject matter areas of: anti-corruption, discrimination, harassment, data privacy, appropriate use of company assets, protecting confidential information and how to report code violations. Each employee takes this annual training and follow up communications are conducted to ensure completion of the course by all employees. We also timely completed our mandated sexual harassment training courses with the specified employees.
We believe our management team has the experience necessary to effectively execute our strategy. Our platform leaders have significant industry experience and are supported by an experienced and talented management team who is dedicated to maintaining
8
and expanding our position as a global leader in our markets. For discussion of the risks related to attracting and retention of management and executive employees, refer to “Part I, Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Executive Officers of CECO
The following are the executive officers of the Company as of February 26, 2024. All officers serve for a one year term and until their successors are elected and qualified.
Todd Gleason (53) has served as a director and Chief Executive Officer since July 2020, and is responsible for driving the company’s strategic vision and aligning the organization for optimal value creation. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Gleason most recently served, from April 2015 to July 2020, as President and Chief Executive Officer of Scientific Analytics Inc., a predictive analytic technologies and services company. Prior to that position, Mr. Gleason served from June 2007 to March 2015 in a number of senior officer and executive positions for Pentair plc, a water treatment company. During his tenure with Pentair, Mr. Gleason served as Senior Vice President and Corporate Officer from January 2013 to March 2015, President, Integration and Standardization from January 2010 to January 2013, and Vice President, Global Growth and Investor Relations from June 2007 to January 2010. Before joining Pentair, Mr. Gleason served as Vice President, Strategy and Investor Relations for American Standard Companies Inc. (later renamed to Trane Inc. prior to its acquisition by Ingersoll-Rand Company Limited), a global, diversified manufacturing company, and in a number of different roles (including as Chief Financial Officer, Honeywell Process Solutions) at Honeywell International Inc., a diversified technology and manufacturing company. Mr. Gleason holds a Masters of Science degrees in Management and Public Policy from Carnegie Mellon University and a Bachelors of Arts in International Studies and History from Wesleyan University. Mr. Gleason currently serves on the board of directors of NSF, whose stated mission is to protect human and planet health through their leading test and measurement, consulting, training and certification and development of industry leading standards. Previously, Mr. Gleason served on the board of Faradyne, a strategic joint venture between Pentair and Xylem.
Peter Johansson (59) has served as SVP, Chief Financial and Strategy Officer since August 2022. From April 2020 to August 2022, Mr. Johansson had been an independent strategy and business development consultant and joined CECO as a consultant in October 2021. From June 2014 through March 2020, he was EVP, Strategy, Corporate Development & Marketing for Accudyne Industries, LLC (“Accudyne”), where he was responsible for the formulation and execution of growth, value creation, business development, product line, and M&A strategies, and deployment of a product-line based operating model for an industry-leading portfolio of industrial air and gas compressors, broad pump solutions, rotary mixers, and valves. Prior to joining Accudyne, Mr. Johansson led the corporate, product-line, and M&A growth strategy and implementation of a differentiated business line operating model for IDEX Corporation. He has also held senior business, strategic business development, commercial and engineering leadership roles with ITT Inc., Trane Technologies PLC, WABCO Holdings, Inc., and Honeywell International, Inc. and its predecessor AlliedSignal Inc. Mr. Johansson earned a Bachelor of Science degree in Mechanical Engineering from Southern Methodist University of Dallas, Texas. He received his Master of Science degree in Mechanical Engineering from California State University at Fullerton, and his MBA from UCLA’s Anderson Graduate School of Management.
Lynn Watkins-Asiyanbi (49) has served as SVP, Chief Administrative and Legal Officer, and Corporate Secretary since August 2022. Prior to that, from June 2022 to August 2022, Ms. Watkins-Asiyanbi served as Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary. From June 2016 to June 2022, Ms. Watkins-Asiyanbi served in various roles of increasing responsibility within John Bean Technologies Corporation (“JBTC”), a publicly traded global food processing machinery and airport equipment company, most recently as its Deputy General Counsel (2018-2022), Chief Ethics/Compliance Officer (2020-2022), Global DEI Council Chair (2021-2022) and prior to that as Associate General Counsel at JBTC (from 2016 to 2018). Ms. Watkins-Asiyanbi has also served as a part of the W.W. Grainger, U.S. Foods, Mars, Inc. and General Mills, Inc. legal teams during her career, in addition to her significant legal experience at DLA Piper and Baker and McKenzie, both global law firms. Ms. Watkins-Asiyanbi holds a joint Juris Doctor and Master of Business Administration from Northwestern University’s Pritzker School of Law and the Kellogg School of Management and a Bachelor’s degree in Chemical Engineering and Economics from the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Available Information
We use the Investor Relations section of our website, www.cecoenviro.com, as a channel for routine distribution of important information, including news releases, investor presentations and financial information. We post filings as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC, including our annual, quarterly, and current reports on Forms 10-K, 10-Q, and 8-K; proxy statements; and any amendments to those reports or statements. All such postings and filings are available on our website free of charge. The SEC also maintains a website, www.sec.gov, that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. The content on any website referred to in this Annual Report on Form 10-K is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K unless expressly noted.
9
Item 1A. Risk Factors
An investment in our securities involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risk factors described below, together with the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, before you decide to invest in our securities. The risks described below are the material risks of which we are currently aware; however, they may not be the only risks that we may face. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently view as immaterial may also impair our business. Although the risks are organized by headings, and each risk is discussed separately, many are interrelated. If any of these risks develop into actual events, it could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows, and the trading price of your shares could decline and you may lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
Our business may be adversely affected by global economic conditions.
A national or global economic downturn or credit crisis may have a significant negative impact on our financial condition, future results of operations and cash flows. Specific risk factors related to these overall economic and credit conditions include the following:
These risk factors could reduce our product sales, increase our operating costs, impact our ability to collect customer receivables, lengthen our cash conversion cycle and increase our need for cash, which would ultimately decrease our profitability and negatively impact our financial condition. They could also limit our ability to expand through acquisitions due to the tightening of the credit markets.
Our dependence upon fixed-price contracts could adversely affect our operating results.
The majority of our projects are currently performed on a fixed-price basis, while a limited number of projects are currently performed on a time and materials basis. Under a fixed-price contract, we agree on the price that we will receive for the entire project, based upon a defined scope, which includes specific assumptions and project criteria. If our estimates of the costs to complete the project are below the actual costs that we incur, our margins will decrease, or we may incur a loss. The revenue, cost and gross profit realized on a fixed-price contract will often vary from the estimated amounts because of unforeseen conditions or changes in job conditions and variations in labor and equipment productivity over the term of the contract. While our fixed-price contracts are typically not individually material to our operating results, if we are unsuccessful in mitigating these risks, we may realize gross profits that are different from those originally estimated and incur reduced profitability or losses on projects. Depending on the size of a project, these variations from estimated contract performance could have a significant effect on our operating results. In general, turnkey contracts to be performed on a fixed-price basis involve an increased risk of significant variations. Generally, our contracts and projects vary in length, depending on the size and complexity of the project, project owner demands and other factors. The foregoing risks are exacerbated for projects with longer-term durations and the inherent difficulties in estimating costs and of the interrelationship of the integrated services to be provided under these contracts whereby unanticipated costs or delays in performing part of the contract can have compounding effects by increasing costs of performing other parts of the contract.
Accounting for contract revenue may result in material adjustments that would adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We derive a significant portion of our revenues from fixed price contracts. We recognize revenue as performance obligations are satisfied and the customer obtains control of the products and services. A significant amount of our revenue is recognized over a period of time as we perform under the contract because control of the work in process transfers continuously to the customer. For performance obligations to deliver products with continuous transfer of control to the customer, revenue is recognized based on the extent of progress towards completion of the performance obligation. Progress is measured based on the ratio of costs incurred to date to the total estimated costs to complete the performance obligation. For these contracts, the cost-to-cost measure best depicts the continuous transfer of goods or services to the customer.
Contract revenue and total direct cost estimates are reviewed and revised periodically as the work progresses and as change orders are approved, and adjustments are reflected in contract revenue in the period when these estimates are revised. These estimates are based
10
on management’s reasonable assumptions and our historical experience, and are only estimates. Variation of actual results from these assumptions, which are outside the control of management and can differ from our historical experience, could be material. To the extent that these adjustments result in an increase, a reduction or the elimination of previously reported contract revenue, we would recognize a credit or a charge against current earnings, which could be material.
Our inability to deliver our backlog on time could affect our future sales and profitability, and our relationships with our customers.
Our backlog was $370.9 million at December 31, 2023 and $311.7 million at December 31, 2022. Our ability to meet customer delivery schedules for our backlog is dependent on a number of factors including, but not limited to, access to the raw materials required for production, an adequately trained and capable workforce, project engineering expertise for certain large projects, sufficient internal manufacturing plant capacity, available subcontractors and appropriate planning and scheduling of manufacturing resources. Our failure to deliver in accordance with customer expectations may result in damage to existing customer relationships and result in the loss of future business. Failure to deliver backlog in accordance with expectations could negatively impact our financial performance and cause adverse changes in the market price of our common stock.
Volatility of oil and natural gas prices can adversely affect demand for our products and services.
Volatility in oil and natural gas prices can impact our customers’ activity levels and spending for our products and services. Current energy prices are important contributors to cash flow for our customers and their ability to fund capital expenditures. Lower oil and natural gas prices generally lead to decreased spending by our customers. While higher oil and natural gas prices generally lead to increased spending by our customers, sustained high energy prices can be an impediment to economic growth, and can therefore negatively impact spending by our customers. Our customers also take into account the volatility of energy prices and other risk factors by requiring higher returns for individual projects if there is a higher perceived risk. Any of these factors could affect the demand for oil and natural gas and could have a material effect on our results of operations.
Increasing costs for manufactured components, raw materials, transportation, health care and energy prices may adversely affect our profitability.
We use a broad range of manufactured components and raw materials in our products, including raw steel, steel-related components, resin, filtration media and equipment such as fans and motors. Materials, wages and subcontracting costs comprise the largest components of our total costs, and increases in the price of these items could materially increase our operating costs and materially adversely affect our profit margins. Similarly, transportation, steel and health care costs have risen steadily over the past few years and could represent an increasing burden for us. Although we try to contain these costs whenever possible, and although we try to pass along increased costs in the form of price increases to our customers, we may be unsuccessful in doing so, and even when successful, the timing of such price increases may lag significantly behind our incurrence of higher costs.
Our financial performance may vary significantly from period to period.
Our annual revenues and earnings have varied in the past and are likely to vary in the future. Our contracts generally stipulate customer-specific delivery terms and may have contract cycles of a year or more, which subjects these contracts to many factors beyond our control. In addition, contracts that are significantly larger in size than our typical contracts tend to intensify their impact on our annual operating results. Furthermore, as a significant portion of our operating costs are fixed, an unanticipated decrease in our revenues, a delay or cancellation of orders in backlog, or a decrease in the demand for our products, may have a significant impact on our annual operating results. Therefore, our annual operating results may be subject to significant variations and our operating performance in one period may not be indicative of our future performance.
Customers may cancel or delay projects. As a result, our backlog may not be indicative of our future revenue.
Customers may cancel or delay projects for reasons beyond our control. Our orders normally contain cancellation provisions that permit us to recover our costs, and, for most contracts, a portion of our anticipated profit in the event a customer cancels an order. If a customer elects to cancel an order, we may not realize the full amount of revenues included in our backlog. If projects are delayed, the timing of our revenues could be affected and projects may remain in our backlog for extended periods of time. Revenue recognition occurs over long periods of time and is subject to unanticipated delays. If we receive relatively large orders in any given quarter, fluctuations in the levels of our quarterly backlog can result because the backlog in that quarter may reach levels that may not be sustained in subsequent quarters. As a result, our backlog may not be indicative of our future revenues. With rare exceptions, we are not issued contracts until a customer is ready to start work on a project. Thus, it is our experience that the only relationship between the length of a project and the possibility that a project may be cancelled is simply the fact that there is more time involved. For example, in a year-long project as opposed to a three-month project, more time is available for the customer to experience a softening in its business, which may cause the customer to cancel a project.
11
We face significant competition in the markets we serve.
All of the product and solution categories in which we compete are highly fragmented and competitive. We compete in industrial markets against a number of local, regional and national manufacturers and suppliers in each of our product or service lines. Our products primarily compete on the basis of performance, quality, reliability, lead time, on-time delivery, and safety supported by advanced engineering and operational excellence. We must also be responsive to any technological developments, including expanded use of data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, and related changing customer requirements. Any failure by us to compete effectively in the markets we serve could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We may incur material costs as a result of existing or future product liability claims, or other claims and litigation that could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows; and our insurance coverage may not cover all claims or may be insufficient to cover the claims.
Despite our quality assurance measures, we may be exposed to product liability claims, other claims and litigation in the event that the use of our products results, or is alleged to result, in bodily injury and/or property damage or our products actually or allegedly fail to perform as expected. Such claims may also be accompanied by fraud and deceptive trade practices claims. While we maintain insurance coverage with respect to certain product liability and other claims, we may not be able to obtain such insurance on acceptable terms in the future, if at all, and any such insurance may not provide adequate coverage against product liability and other claims. Furthermore, our insurance may not cover damages from breach of contract by us or based on alleged fraud or deceptive trade practices. Any future damages that are not covered by insurance or are in excess of policy limits could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, product liability and other claims can be expensive to defend and can divert the attention of management and other personnel for significant periods of time, regardless of the ultimate outcome.
An unsuccessful defense of a product liability or other claim could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Even if we are successful in defending against a claim relating to our products, claims of this nature could cause our customers to lose confidence in our products and us.
Liability to customers under warranties may adversely affect our reputation, our ability to obtain future business and our results of operations.
We provide certain warranties as to the proper operation and conformance to specifications of the products we manufacture or produce. Failure of our products to operate properly or to meet specifications may increase our costs by requiring additional engineering resources and services, replacement of parts and equipment or monetary reimbursement to customers. We have in the past received warranty claims, are currently subject to warranty claims, and we expect to continue to receive warranty claims in the future. To the extent that we incur substantial warranty claims in any period, our reputation, our ability to obtain future business and our results of operations could be adversely affected.
Risks Related to our Business Model and Capital Structure
Our gross profit may be affected by shifts in our product mix.
Certain of our products have higher gross profit margins than others. Consequently, changes in the product mix of our sales from quarter-to-quarter or from year-to-year can have a significant impact on our reported gross profit margins. Certain of our products also have a much higher internally manufactured cost component. Therefore, changes from quarter-to-quarter or from year-to-year can have a significant impact on our reported gross profit margins. In addition, contracts with a higher percentage of subcontracted work or equipment purchases may result in lower gross profit margins.
Our manufacturing operations are dependent on third-party suppliers.
Although we are not dependent on any one supplier, we are dependent on the ability of our third-party suppliers to supply our raw materials, as well as certain specific component parts and sub-assemblies. The third-party suppliers upon which we depend may default on their obligations to us due to bankruptcy, insolvency, lack of liquidity, adverse economic conditions, operational failure, fraud, loss of key personnel, health-related shutdowns, or other reasons. We cannot ensure that our third-party suppliers will dedicate sufficient resources to meet our scheduled delivery requirements or that our suppliers will have sufficient resources to satisfy our requirements during any period of sustained demand. Failure of suppliers to supply, or delays in supplying, our raw materials or certain components, or allocations in the supply of certain high demand raw components, for any reason, including, without limitation, disruptions in our suppliers’ due to cybersecurity incidents, terrorist activity, public health crises, fires or other natural disasters could
12
materially adversely affect our operations and ability to meet our own delivery schedules on a timely and competitive basis. Additionally, our third-party suppliers may provide us with raw materials or component parts that fail to meet our expectations or the expectations of our customers, which could subject us to product liability claims, other claims and litigation.
Our use of subcontractors could potentially harm our profitability and business reputation.
Occasionally we act as a prime contractor in some of the projects we undertake. In our capacity as lead provider, and when acting as a prime contractor, we perform a portion of the work on our projects with our own resources and typically subcontract activities such as manufacturing, electrical work, concrete work, insulation, conveyors and controls. In our industry, the lead contractor is normally responsible for the performance of the entire contract, including subcontract work. Thus, when acting as a prime contractor, we are subject to risk associated with the failure of one or more subcontractors to perform as anticipated.
We employ subcontractors at various locations around the world to meet our customers’ needs in a timely manner, meet local content requirements and reduce costs. Subcontractors generally perform the majority of our manufacturing for international customers. We also utilize subcontractors in North America. The use of subcontractors decreases our control over the performance of these functions and could result in project delays, escalated costs and substandard quality. These risks could adversely affect our profitability and business reputation. In addition, many of our competitors use the same subcontractors that we use and could potentially influence our ability to hire these subcontractors. If we were to lose relationships with key subcontractors, our business could be adversely impacted.
A significant portion of our accounts receivable are related to larger contracts, which increases our exposure to credit risk.
Significant portions of our sales are to customers who place large orders for custom products and whose activities are related to the power generation and oil and gas industries. As a result, our exposure to credit risk is affected to some degree by conditions within these industries and governmental and or political conditions. We frequently attempt to reduce our exposure to credit risk by requiring progress or milestone payments and letters of credit as well as closely monitoring the credit worthiness of our customers. However, the continuing economic climate and other unanticipated events that affect our customers could have a materially adverse impact on our operating results.
Changes in billing terms can increase our exposure to working capital and credit risk.
Our products are generally sold under contracts that allow us to bill upon the completion of certain agreed upon milestones or upon actual shipment of the product, and certain contracts include a retention provision. We attempt to negotiate progress-billing milestones on all large contracts to help us manage the working capital and credit risk associated with these large contracts. Consequently, shifts in the billing terms of the contracts in our backlog from period to period can increase our requirement for working capital and can increase our exposure to credit risk.
Currency fluctuations may reduce profits on our foreign sales or increase our costs, either of which could adversely affect our financial results.
Given that approximately 33% of our 2023 revenues are outside the United States, we are subject to the impact of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Although our financial results are reported in U.S. dollars, a portion of our sales and operating costs are realized in foreign currencies. Our sales and profitability are impacted by the movement of the U.S. dollar against foreign currencies in the countries in which we generate sales and conduct operations. Long-term fluctuations in relative currency values could have an adverse effect on our operations and financial conditions.
If our goodwill or indefinite lived intangibles become impaired, we may be required to recognize charges that would adversely impact our results of operations.
As of December 31, 2023, goodwill and indefinite lived intangibles were $220.9 million, or 36.8%, of our total assets. Goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets are not amortized, but instead are subject to annual impairment evaluations (or more frequently if circumstances require). Major factors that influence our evaluations are estimates for future revenue and expenses associated with the specific intangible asset or the reporting unit in which the goodwill resides. This is the most sensitive of our estimates related to our evaluations. Other factors considered in our evaluations include assumptions as to the business climate, industry and economic conditions. These assumptions are subjective and different estimates could have a significant impact on the results of our analyses. While management, based on current forecasts and outlooks, believes that the assumptions and estimates are reasonable, we can make no assurances that future actual operating results will be realized as planned and that there will not be material impairment charges as a result. In particular, an economic downturn could have a material adverse impact on our customers thereby forcing them to reduce or curtail doing business with us and such a result may materially affect the amount of cash flow generated by our future operations. Any
13
write-down of goodwill or intangible assets resulting from future periodic evaluations could adversely materially impact our results of operations.
We may incur costs as a result of certain restructuring activities, which may negatively impact our financial results, and we may not achieve some or all of the expected benefits of our restructuring plans.
We are continuously seeking the most cost-effective means and structure to serve our customers, protect our stockholders and respond to changes in our markets. From time to time, we may engage in restructuring activities in an effort to improve cost competitiveness and profitability. We may not achieve the desired or anticipated benefits from these restructuring activities. As a result, restructuring costs may vary significantly from year to year depending on the scope of such activities. Such restructuring costs and expenses could adversely impact our financial results.
We are party to asbestos-containing product litigation that could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our subsidiary, Met-Pro, along with numerous other third parties, has been named as a defendant in asbestos-related lawsuits filed against a large number of industrial companies including, in particular, those in the pump and fluid handling industries. In management’s opinion, the complaints typically have been vague, general and speculative, alleging that Met-Pro, along with the numerous other defendants, sold unidentified asbestos-containing products and engaged in other related actions that caused injuries (including death) and loss to the plaintiffs. The Company’s insurers have hired attorneys who, together with the Company, are vigorously defending these cases. The Company believes that its insurance coverage is adequate for the cases currently pending against the Company and for the foreseeable future, assuming a continuation of the current volume, nature of cases and settlement amounts. However, the Company has no control over the number and nature of cases that are filed against it, nor as to the financial health of its insurers or their position as to coverage. The Company also presently believes that none of the pending cases will have a material adverse impact upon the Company’s results of operations, liquidity or financial condition.
See Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements contained in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information regarding the asbestos-related litigation in which we are involved.
We have $138.6 million of indebtedness as of December 31, 2023, and incurrence of additional indebtedness could adversely affect our ability to operate our business, remain in compliance with debt covenants, make payments on our debt and limit our growth.
Our outstanding indebtedness could have important consequences for investors, including the following:
Our ability to meet our expenses and debt obligations will depend on our future performance, which will be affected by financial, business, economic, regulatory and other factors. We will not be able to control many of these factors. We cannot be certain that our earnings will be sufficient to allow us to pay the principal and interest on our existing or future debt and meet our other obligations. If we do not have enough money to service our existing or future debt, we may be required to refinance all or part of our existing or future debt, sell assets, borrow more money or raise equity. We may not be able to refinance our existing or future debt, sell assets, borrow more money or raise equity on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
14
Our ability to execute our growth strategies may be limited by our ability to secure and retain additional financing on terms reasonably acceptable to us or at all. Certain of our competitors are larger companies that may have greater access to capital, and therefore may have a competitive advantage over us should our access to capital be limited.
We might be unable to protect our intellectual property rights and our products could infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which could expose us to costly disputes.
Although we believe that our products do not infringe patents or violate the proprietary rights of others, it is possible that our existing patent rights may not be valid or that infringement of existing or future patents or proprietary rights may occur. In the event our products infringe patents or proprietary rights of others, we may be required to modify the design of our products or obtain a license for certain technology. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to do so in a timely manner, upon acceptable terms and conditions, or at all. Failure to do any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect upon our business. Moreover, if our products infringe patents or proprietary rights of others, we could, under certain circumstances, become liable for damages, which also could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Risks related to our pension plan may adversely impact our results of operations and cash flow.
Significant changes in actual investment return on pension assets, discount rates and other factors may adversely affect our results of operations and pension plan contributions in future periods. GAAP requires that we calculate the income or expense of our plan using actuarial valuations. These valuations reflect assumptions about financial markets and interest rates. We establish the discount rate used to determine the present value of the projected and accumulated benefit obligation at the end of each year based upon the available market rates for high quality, fixed-income investments. An increase in the discount rate would increase future pension expense and, conversely, a decrease in the discount rate would decrease future pension expense. Funding requirements for our pension plan may become more significant. The ultimate amounts to be contributed are dependent upon, among other things, interest rates, underlying asset returns and the impact of legislative or regulatory changes related to pension funding obligations.
We may be subject to substantial withdrawal liability assessments in the future related to multiemployer pension plans to which certain of our subsidiaries make contributions pursuant to collective bargaining agreements.
Under applicable federal law, any employer contributing to a multiemployer pension plan that completely ceases participating in the plan while the plan is underfunded is subject to payment of such employer’s assessed share of the aggregate unfunded vested benefits of the plan. In certain circumstances, an employer can be assessed a withdrawal liability for a partial withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan. If any of these adverse events were to occur in the future, it could result in a substantial withdrawal liability assessment that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We have made and may make future acquisitions or divestitures, which involve numerous risks that could impact our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our operating strategy has involved expanding or contracting our scope of products and services through selective acquisitions or divestitures and the formation or elimination of new business units that are then integrated or separated into or out of our family of turnkey system providers. We have acquired other businesses, product or service lines, assets or technologies that are complementary to our business. We may be unable to find or consummate future acquisitions at acceptable prices and terms. We continually evaluate potential acquisition opportunities in the ordinary course of business.
Although we conduct what we believe to be a prudent level of investigation regarding the operating and financial condition of the businesses, product or service lines, assets or technologies we purchase, an unavoidable level of risk remains regarding their actual operating and financial condition. Until we actually assume operating control of these businesses, product or service lines, assets or technologies, we may not be able to ascertain their actual value or understand potential liabilities. This is particularly true with respect to acquisitions outside the United States.
In addition, acquisitions of businesses may require additional debt or equity financing, resulting in additional leverage or dilution of ownership. Our Credit Facility contains certain covenants that limit, or which may have the effect of limiting, among other things, acquisitions, capital expenditures, the sale of assets and the incurrence of additional indebtedness.
Societal responses to climate change could adversely affect our business and performance, including indirectly through impacts on our customers.
Concerns over the long-term impacts of climate change have led and will continue to lead to governmental efforts around the world to mitigate those impacts. Consumers and businesses also may change their behavior as a result of these concerns. We and our customers
15
will need to respond to new laws and regulations as well as consumer and business preferences resulting from climate change concerns. We and our customers may face cost increases, asset value reductions and operating process changes. The impact on our customers will likely vary depending on their specific attributes, including reliance on or role in carbon intensive activities. Among the impacts to us could be a drop in demand for our products and services, particularly in oil and gas industries. In addition, we could face reductions in our creditworthiness or in the value of our assets securing loans. Our efforts to take these risks into account in making business decisions, including by increasing our business with climate-friendly companies, may not be effective in protecting us from the negative impact of new laws and regulations or changes in consumer or business behavior.
Global climate change and related emphasis on environmental, social and governance ("ESG") matters by various stakeholders could negatively affect our business.
Customer, investor and employee expectations relating to ESG have been rapidly evolving and increasing. In addition, government organizations are enhancing or advancing legal and regulatory requirements specific to ESG matters. The heightened stakeholder focus on ESG issues related to our business requires the continuous monitoring of various and evolving laws, regulations, standards and expectations and the associated reporting requirements. A failure to adequately meet stakeholder expectations may result in noncompliance, the loss of business, reputational impacts, diluted market valuation, an inability to attract customers and an inability to attract and retain top talent. In addition, our adoption of certain standards or mandated compliance to certain requirements could necessitate additional investments that could impact our profitability.
Climate changes, such as extreme weather conditions, create financial risk to our business. Global physical climate changes, including unseasonable weather conditions, could result in reduced demand or product obsolescence for certain of our customers’ products and/or price modifications for our customers’ products and the resources needed to produce them. This could in turn put pressure on our manufacturing costs and result in reduced profit margin associated with certain of our customer programs, or loss of customer programs that we may not be able to replace.
Risks Related to Human Capital Management
The loss of key personnel or inability to attract and retain additional personnel could affect our ability to successfully grow our business.
Our future success depends upon the continued service of our executive officers and other key management and technical personnel, and on our ability to continue to identify, attract, retain and motivate them. Implementing our business strategy requires specialized engineering and other talent, as our revenues are highly dependent on technological and product innovations. The market for employees in our industry is extremely competitive, and competitors for talent, particularly engineering talent, increasingly attempt to hire, and to varying degrees have been successful in hiring, our employees. If we are unable to attract and retain qualified employees, our business may be harmed.
Work stoppages or similar difficulties could significantly disrupt our operations.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 200 of our approximately 1,200 employees are represented by international or independent labor unions under various union contracts, which, for our covered employees in the United States, expire between November 12, 2025 and May 1, 2026. It is possible that our workforce will become more unionized in the future. Although we consider our employee relations to generally be good, our existing labor agreements may not prevent a strike or work stoppage at one or more of our facilities, which may have a material adverse effect on our business. Unionization activities could also increase our costs, which could have an adverse effect on our profitability.
Additionally, a work stoppage at one of our suppliers could adversely affect our operations if an alternative source of supply were not readily available. Work stoppages by employees of our customers also could result in reduced demand for our products.
Information Technology and Cybersecurity Risks
Our dependence on information systems and the failure of such systems, could significantly disrupt our business and negatively affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We are highly dependent on information systems that are increasingly operated by third parties and as a result we have a limited ability to ensure their continued operation. We rely on information technology systems, networks and infrastructure in managing our day-to-day operations. In the event of systems failure or interruption, including those related to force majeure, telecommunications failures, criminal acts, including hardware or software break-ins or extortion attempts, or viruses, or other cybersecurity incidents, we
16
will have limited ability to affect the timing and success of systems restoration and any resulting interruption in our ability to manage and operate our business could have a material adverse effect on our operating results.
Increased information technology cybersecurity threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime could pose a risk to our systems, networks, and products.
Increased global information technology cybersecurity threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime pose a risk to the security of our systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of our data and communications. While we attempt to mitigate these risks by employing a number of measures, including employee training, comprehensive monitoring of our networks and systems, and maintenance of backup and protective systems, our systems, networks and products remain potentially vulnerable to advanced persistent threats. Depending on their nature and scope, such threats could potentially lead to the compromise of confidential information and communications, improper use of our systems and networks, manipulation and destruction of data, defective products, production downtimes and operational disruptions, which in turn could adversely affect our reputation, competitiveness and results of operations. We have cybersecurity insurance related to a breach event covering expenses for notification, credit monitoring, investigation, crisis management, public relations and legal advice. However, damage and claims arising from such incidents may not be covered or exceed the amount of any insurance available or may result in increased cybersecurity and other insurance premiums. In response to an increased reliance on our information technology systems, we have taken proactive measures to strengthen our information technology systems, including completion of a National Institute of Standards and Technology ("NIST") assessment, upgraded security patches across all servers, development of best-in-class hack protection service, implementation of recurring company-wide security training and enablement of advanced security for our major information systems. Management provides the Audit Committee with regular cybersecurity program updates including cybersecurity posture, risk management activities, and emerging risk.
Furthermore, the Company may have access to sensitive, confidential, or personal data or information that may be subject to privacy and security laws, regulations, or other contractually-imposed controls. Despite our use of reasonable and appropriate controls, material security breaches, theft, misplaced, lost or corrupted data, programming, or employee errors and/or malfeasance could lead to the compromise or improper use of such sensitive, confidential, or personal data or information, resulting in possible negative consequences, such as fines, ransom demands, penalties, loss of reputation, competitiveness or customers, or other negative consequences resulting in adverse impacts to our results of operations or financial condition.
Regulatory Compliance and International Operations Risks
Disruptions in the political, regulatory, economic and social conditions of the countries in which we conduct business could negatively impact our business, financial condition and profits.
We operate and do business in many countries in addition to the United States. For the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 33% of our total revenue was derived from products or services ultimately delivered or provided to end users outside the United States. As part of our operating strategy, we intend to expand our international operations through internal growth and selected acquisitions. Operations outside of the United States, particularly in emerging markets, are subject to a variety of risks that are different from or are in addition to the risks we face within the United States. Among others, these risks include: (i) local, economic, political and social conditions, including potential hyperinflationary conditions and political instability in certain countries; (ii) tax-related risks, including the imposition of taxes and the lack of beneficial treaties, that result in a higher effective tax rate for us; (iii) imposition of limitations on the remittance of dividends and payments by foreign subsidiaries; (iv) difficulties in enforcing agreements and collecting receivables through certain foreign local systems; (v) domestic and foreign customs, tariffs and quotas or other trade barriers; (vi) risk of nationalization of private enterprises by foreign governments; (vii) managing and obtaining support and distribution channels for overseas operations; (viii) hiring and retaining qualified management personnel for our overseas operations; and (ix) the results of new trade agreements and changes in membership to international coalitions or unions.
We are also exposed to risks relating to U.S. policy with respect to companies doing business in foreign jurisdictions. Changes in laws or policies governing the terms of foreign trade, in particular increased trade restrictions, tariffs or taxes on import from countries where we procure or manufacture products, such as China, could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations. For instance, the U.S. and Chinese governments have imposed a series of significant incremental retaliatory tariffs to certain imported goods. Given the uncertainty regarding the duration of the imposed tariffs, as well as the potential for additional tariffs by the U.S., China or other countries, as well as other changes in tax policy, trade regulations or trade agreements, and the Company’s ability to implement strategies to mitigate the impact of changes in tax policy, tariffs or other trade regulations, our exposure to the risks described above could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
In addition, compliance with foreign and domestic legal and regulatory requirements, including import, export, defense regulations and foreign exchange controls and anti-corruption laws, as discussed below, such as the FCPA (as defined below), the U.K. Bribery
17
Act (as defined below), the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulations and similar laws of other jurisdictions, could adversely impact our ability to compete against companies in such jurisdictions. Moreover, the violation of such laws or regulations, by us or our representatives, could result in severe penalties including monetary fines, criminal proceedings and suspension of export privileges.
The occurrence of one or more of the foregoing factors could have a material adverse effect on our international operations or upon our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We could be adversely affected by violations of the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar anti-bribery laws worldwide.
The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act ("FCPA"), the U.K. Bribery Act of 2010 ("U.K. Bribery Act"), and similar anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Our policies mandate compliance with these anti-bribery laws. We operate in many parts of the world that have experienced governmental corruption to some degree and, in certain circumstances, strict compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with local customs and practices. Despite our training and compliance programs, there is no assurance that our internal control policies and procedures will protect us from acts committed by our employees or agents. If we are found to be liable for FCPA, U.K. Bribery Act or other similar violations (either due to our own acts or due to the acts of others), we could be subject to civil and criminal penalties or other sanctions, which could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition, and profits.
Our business can be significantly affected by changes in regulatory standards.
The markets that the Company serves are characterized by competitively imposed process standards and regulatory requirements, each of which influences the demand for our products and services. Changes in legislative, regulatory or industrial requirements may render certain of our products and processes obsolete. Conversely, these changes may present new business opportunities for us. Acceptance of new products and services may also be affected by the adoption of new government regulations requiring stricter standards. Our ability to anticipate changes in regulatory standards and to respond with new and enhanced products on a timely basis will be a significant factor in our ability to grow and to remain competitive. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to achieve the technological advances that may be necessary for us to remain competitive or that certain of our products or services will not become obsolete.
Changes in current environmental legislation and enforcement could have an adverse impact on the sale of our environmental control systems and products and on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our business is primarily driven by capital spending, clean air rules, plant upgrades by our customers to comply with laws and regulations governing the discharge of pollutants into the environment or otherwise relating to the protection of the environment or human health. These laws include, but are not limited to, United States federal statutes such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act of 1976, the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, the Clean Water Act, the Clean Air Act, the Clean Air Interstate Rule, and the regulations implementing these statutes, as well as similar laws and regulations at state and local levels and in other countries. These United States laws and regulations may change and other countries may not adopt similar laws and regulations. Our business may be adversely impacted to the extent that environmental regulations are repealed, amended, implementation dates are delayed, or to the extent that regulatory authorities reduce enforcement.
Changes in laws or regulations or the manner of their interpretation or enforcement could adversely impact our financial performance and restrict our ability to operate our business or execute our strategies.
New laws or regulations, or changes in existing laws or regulations, or the manner of their interpretation or enforcement, could increase our cost of doing business and restrict our ability to operate our business or execute our strategies. In particular, there is continued uncertainty with respect to United States trade policies, treaties, government regulations and tariffs. Any changes the Biden administration makes to United States administrative policy could result in changes to existing trade agreements, greater restrictions on free trade generally and significant increases in tariffs on goods imported into the United States, particularly tariffs on products manufactured in Mexico and China, among other possible changes. A trade war or other governmental action related to tariffs or international trade agreements, and any resulting negative sentiments towards the United States as a result thereof, would likely have an adverse effect on our international operations or upon our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
18
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The market price of our common stock may be volatile or may decline regardless of our operating performance and investors may not be able to resell shares they purchase at their purchase price.
The stock market has experienced and may in the future experience volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The market price of our common stock has experienced, and may continue to experience, substantial volatility. During 2023, the sales price of our common stock on the NASDAQ ranged from $10.68 to $21.43 per share. We expect our common stock to continue to be subject to fluctuations. Broad market and industry factors may adversely affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. Factors that could cause fluctuation in the common stock price may include, among other things:
The realization of any of these risks and other factors beyond our control could cause the market price of our common stock to decline significantly.
We are not currently paying dividends and cannot make assurances that we will pay dividends on our common stock and our indebtedness could limit our ability to pay dividends.
The timing, declaration, amount and payment of future dividends to our stockholders fall within the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on many factors, including our financial condition, results of operations and capital requirements, as well as applicable legal or regulatory constraints, industry practice and other business considerations that our Board of Directors considers relevant. We have not paid a cash dividend on our common stock in recent years and currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to finance the operations, growth and development of our business into the foreseeable future.
Our ability to issue preferred stock could adversely affect the rights of holders of our common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation authorizes us to issue up to 10,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series on terms that may be determined at the time of issuance by our Board of Directors. Accordingly, we may issue shares of any series of preferred stock that would rank senior to our common stock as to voting or dividend rights or rights upon our liquidation, dissolution or winding up.
Certain provisions in our charter documents have anti-takeover effects.
Certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of us. Such provisions, including those limiting who may call special stockholders’ meetings, together with the possible issuance of our preferred stock without stockholder approval, may make it more difficult for other persons, without the approval of our Board of Directors, to make a tender offer or otherwise acquire substantial amounts of our common stock or to launch other takeover attempts that a stockholder might consider to be in such stockholder’s best interest.
19
Risks Related to Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. If we are unable to develop and maintain adequate internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results in a timely manner, which may adversely affect investor confidence in us and materially and adversely affect our business.
Under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, we are required to include in each of our Annual Reports on Form 10-K a report containing our management’s assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting and an attestation report of our independent auditor. These laws, rules and regulations continue to evolve and could become increasingly stringent in the future. We have undertaken actions to enhance our ability to comply with the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, including, but not limited to, the engagement of consultants, the documentation of existing controls and the implementation of new controls or modification of existing controls as deemed appropriate.
We continue to devote substantial time and resources to the documentation and testing of our controls, and to plan for and the implementation of remedial efforts in those instances where remediation is indicated.
As disclosed in Item 9A. “Controls and Procedures” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we have material weaknesses in our control environment with regard to management’s review of revenue recognition for contracts and balance sheet reconciliations. These material weaknesses could result in a misstatement of account balances or disclosures that would result in a material misstatement to the annual or interim financial statements that would not be prevented or detected.
To address these material weaknesses, we have developed a remediation plan that includes reinforcing the importance of adherence to Company policies regarding control performance and related documentation with control owners, strengthening existing training programs for control owners, and developing monitoring activities to validate the performance of controls by control owners. As of December 31, 2023, these remediation efforts are ongoing.
The actions that we are taking are subject to ongoing senior management review, as well as Audit Committee oversight. We will not be able to conclude whether the steps we are taking will fully remediate the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting until we have completed our remediation efforts and subsequent evaluation of their effectiveness. Until these material weaknesses are remediated, we plan to continue to perform additional analyses and other procedures to ensure that our consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP.
If we continue to have material weaknesses in our internal controls, or, if we fail to develop and maintain adequate internal controls in the future, including remediating any material weaknesses or deficiencies in our internal controls, we could be subject to regulatory actions, civil or criminal penalties or stockholder litigation. In addition, failure to maintain adequate internal controls could result in financial statements that do not accurately reflect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. We believe that the out-of-pocket costs, the diversion of management’s attention from running our day-to-day operations and operational changes caused by the need to comply with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 will continue to be significant.
There are inherent limitations in all internal control systems over financial reporting, and misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
While we continue to take action to ensure compliance with the internal control, disclosure control and other requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder by the SEC, there are inherent limitations in our ability to control all circumstances. Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, do not expect that our internal controls and disclosure controls can prevent all errors and all frauds. A control system, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. In addition, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and the benefit of controls must be evaluated in relation to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Further, controls can be circumvented by individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more persons or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, a control may be inadequate because of changes in conditions or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Because of inherent limitations in a cost-effective control system, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected.
If we are not able to establish and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting, including any failure to implement required new or improved controls, or if we experience difficulties in their implementation, our business, financial condition and
20
operating results could be harmed. We can give no assurances that any additional material weaknesses will not arise in the future due to our failure to implement and maintain adequate internal control over financial reporting.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
The Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) recognizes the critical importance of maintaining the trust and confidence of our customers, clients, business partners and employees. The Board is actively involved in oversight of the Company’s risk management program, and cybersecurity represents an important component of the Company’s overall approach to enterprise risk management (“ERM”). The Company’s cybersecurity policies, standards, and processes are being integrated into the Company’s ERM program and based on recognized frameworks and industry standards, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the International Organization for Standardization and other applicable industry standards. In general, the Company seeks to address cybersecurity risks through a comprehensive, cross-functional approach that is focused on preserving the confidentiality, security, and availability of Company and customer systems, information, and products.
The Company has engaged third-party cybersecurity service providers and leverages leading technologies and expertise to monitor, maintain, and provide 24/7 managed detection and response capabilities for coordination, escalation and remediation of alerts associated with information technology systems utilized by the Company.
Risk Management and Strategy
The Company engages in the periodic assessment and testing of the Company’s policies, standards, processes and practices that are designed to address cybersecurity threats and incidents. These efforts include a wide range of activities, including audits, assessments, tabletop exercises, threat modeling, vulnerability testing and other exercises focused on evaluating the effectiveness of our cybersecurity measures and planning. The results of such assessments, audits and reviews are reported to the Audit Committee and the Board, and the Company adjusts its cybersecurity program as necessary based on the information provided by these assessments, audits, and reviews.
Governance
The Board, in coordination with the Audit Committee, oversees the Company’s ERM process, including the management of risks arising from cybersecurity threats. The Board and the Audit Committee each receive regular presentations and reports on cybersecurity risks, which address a wide range of topics including recent developments, evolving standards, vulnerability assessments, and third-party and independent reviews. The Board and the Audit Committee also receive prompt and timely information regarding any cybersecurity incident that meets established reporting thresholds, as well as ongoing updates regarding any such incident until it has been addressed. On an annual basis, the Board and the Audit Committee discuss the Company’s approach to cybersecurity risk management with the Company's Vice President of Information Technology (the "VP of IT").
The VP of IT reports to the Chief Financial and Strategy Officer and is the head of the Company’s cybersecurity team. Through ongoing communications, the VP of IT and the Executive Leadership Team, which includes our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, and Chief Administrative and Legal Officer, monitor the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation of cybersecurity threats and incidents in real time and report such threats and incidents to the Audit Committee when appropriate.
The VP of IT has served in various roles in information technology and information security for over 25 years, including leading the cybersecurity programs for three public companies. The VP of IT holds undergraduate and graduate degrees in business and has attained multiple cybersecurity certifications including Certified Information Security Manager.
Cybersecurity threats, including those as a result of any previous cybersecurity incidents, have not materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including its business strategy, results of operations or financial condition. For more information on our cybersecurity related risks, refer to "Part I, Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
21
Item 2. Properties
The Company has 30 principal operating facilities across 12 states and nine countries. The Company’s executive offices are located in Dallas, Texas. We maintain our facilities in good operating condition, and we believe they are suitable and adequate for the purposes for which they are intended to conduct business. Our current capacity, with limited capital additions, is expected to be sufficient to meet production requirements for the near future. It is anticipated that most leases coming due in the near future will be renewed at expiration. The property we own is subject to collateral mortgages to secure the amounts owed under the Credit Facility. Information on the number and location of principal operating facilities by segment was as follows as of December 31, 2023.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Location of Facilities |
||||
Segment |
|
Owned |
|
|
Leased |
|
|
States |
|
Countries |
||
Engineered Systems Segment |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
Arizona, California, Connecticut, Florida, New York, Ohio, Texas |
|
United States, The Netherlands, Canada, India, United Arab Emirates, Singapore, United Kingdom, People's Republic of China, South Korea |
Industrial Process Solutions Segment |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
California, Indiana, Michigan, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, Tennessee |
|
United States, United Kingdom, The Netherlands, People's Republic of China |
Corporate |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
Ohio, Texas |
|
United States |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
See Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements contained in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information regarding legal proceedings in which we are involved.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
22
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
Our common stock is traded on The Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol “CECO.”
Performance Graph
The following graph sets forth the cumulative total return to CECO’s stockholders during the five years ended December 31, 2023, as well as the following indices: Russell 2000 Index, Standard and Poor’s (“S&P”) 600 Small Cap Industrial Machinery Index, and S&P 500 Index. The following graph assumes $100 was invested on December 31, 2018, including the reinvestment of dividends, in each category.
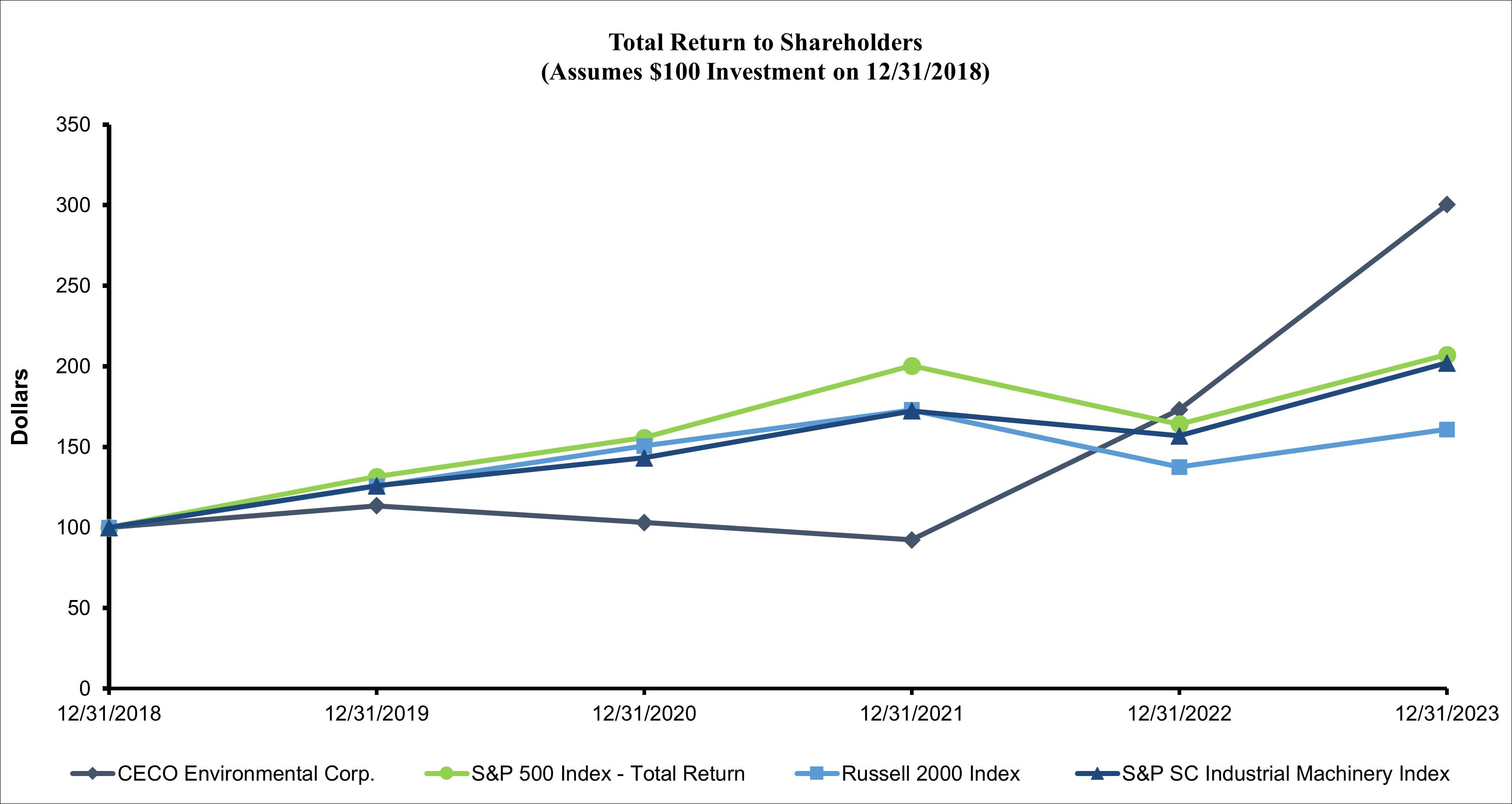
Dividends
The timing, declaration, amount and payment of future dividends to our stockholders fall within the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on many factors, including our financial condition, results of operations and capital requirements, as well as applicable legal or regulatory constraints, industry practice and other business considerations that our Board of Directors considers relevant. We have not paid a cash dividend on our common stock in recent years and currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to finance the operations, growth and development of our business into the foreseeable future, or for other uses such as the continuation of our share repurchase program. Payment of dividends is also subject to the continuing compliance with our financial covenants under our Credit Facility.
Holders
The approximate number of registered stockholders of record of our common stock as of February 26, 2024 was 248, although there is a larger number of beneficial owners.
23
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
The following table provides information about our purchases of our equity securities for the quarter ended December 31, 2023.
|
|
Issuer's Purchases of Equity Securities |
|
|||||||||||||
Period (amounts in thousands, except per share data) |
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased 1 |
|
|
Average Price Paid per Share |
|
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
|
|
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
|
||||
October 1, 2023 - October 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
13,000 |
|
November 1, 2023 - November 30, 2023 |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,000 |
|
||
December 1, 2023 - December 31, 2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,000 |
|
Total |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
(1) On May 10, 2022, the Board of Directors authorized a $20.0 million share repurchase program as described within Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. The program expires on April 30, 2025.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Not applicable.
Item 6. [Reserved]
24
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Management’s discussion and analysis (“MD&A”) should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, which include additional information about our accounting policies, practices and the transactions underlying our financial results. The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes including various claims and contingencies related to lawsuits, taxes, environmental and other matters arising during the normal course of business. We apply our best judgment, our knowledge of existing facts and circumstances and actions that we may undertake in the future in determining the estimates that affect our consolidated financial statements. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis using our historical experience, as well as other factors we believe appropriate under the circumstances, such as current economic conditions, and adjust or revise our estimates as circumstances change. As future events and their effects cannot be determined with precision, actual results may differ from these estimates.
Overview
Business Overview
CECO is a leading environmentally focused, diversified industrial company, serving the broad landscape of industrial air, industrial water and energy transition markets globally by providing innovative technology and application expertise. We help companies grow their business with safe, clean, and more efficient solutions that help protect people, the environment and industrial equipment. Our solutions improve air and water quality, optimize emissions management, and increase the energy and process efficiency for highly engineered applications in power generation, midstream and downstream hydrocarbon processing and transport, chemical processing, electric vehicle production, polysilicon fabrication, semiconductor and electronics production, battery production and recycling, specialty metals, aluminum and steel production, beverage can manufacturing, and industrial and produced water and wastewater treatment, and a wide range of other industrial end markets.
Industry Trends and Corporate Strategy
We are a global corporation with worldwide operations. As a global business, our operations are affected by worldwide, regional and industry-specific economic factors, wherever we operate or do business. Our geographic and industry diversity, and the breadth of our product and services portfolio, have helped mitigate the impact of any one industry or the economy of any single country on our consolidated operating results.
We believe growth for our products and services is driven by the increase in demand for air quality and water treatment solutions, the energy transition, a shift towards cleaner sources of fuel such as natural gas, hydrogen, nuclear, and renewable sources, and increased awareness of our customers about corporate social responsibility and interest to procure equipment and solutions that protects employees, the environment and their industrial equipment.
With a shift to cleaner, more environmentally responsible power generation, power providers and industrial power consumers are building new facilities that use cleaner fuels. In developed markets, natural gas is the largest source of electricity generation. We supply product offerings throughout the entire natural gas value chain and believe expansion will drive growth within our Engineered Systems segment for our gas separation & filtration, pressure products, acoustical equipment , water treatment solutions and DeNOx SCR systems for natural-gas-fired power plants. Increases in global natural gas, installed miles of new pipeline, including future CO2 and hydrogen pipelines, and liquified natural gas ("LNG") demand and supply all stand to drive the need for our products.
We also believe there is a growing demand to control and reduce air and water emissions from industrial facilities for which our pollution control equipment will serve. In 2021, the US Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act with $550 billion of new federal spending aimed at rebuilding roads and bridges, climate resilience, and other environmental initiatives. Similar investments are being made in many other countries in which we do business. As industrial capital expenditures grow, corporations are seeking to do so with a smaller environmental impact. These regulatory and economic tailwinds coupled with shareholder pressure on companies to improve their sustainability and reduce their global carbon footprint serve as catalysts for a growing set of opportunities for our portfolio of equipment and solutions.
We continue to focus on increasing revenues and profitability in developing markets, where environmental awareness and associated regulatory standards are increasing, while continuing to strengthen and expand our product offerings and channels in our domestic market of the United States. Our enterprise strategy consists of a combined operational strategy and capital allocation strategy.
25
Our operational strategy is implemented through our technology and application-based platforms aligned around target customers and end markets where our solutions are particularly valuable. Core elements of our operational strategy are commercial and operational excellence, margin expansion, recurring revenue growth, cash flow generation, product management, and project management execution.
Our capital allocation strategy supports the growth and value creation generated by our operational strategy. We will focus our capital deployment on building out our leading industrial air solutions portfolio, advancing our emerging industrial water treatment position, and supporting our customers as they make the transition to cleaner more sustainable forms of energy, while also shifting our portfolio mix towards businesses with more recurring revenue and more predictable cash flows, strong secular growth trends and less cyclicality.
Market Pressures
The senior management team monitors and manages the Company’s ability to operate effectively as the result of market pressures. In particular, we are currently experiencing shortages of raw materials and inflationary pressures for certain materials and labor. We have secured raw materials from existing and alternate suppliers and have taken other mitigating actions to mitigate supply disruptions; however, we cannot guarantee that we can continue to do so in the future. In this event, our business, results and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Operations Overview
We operate our segments and the underlying platforms serving their respective niche end markets. Our platforms are structured to win in their target markets with a core focus on understanding customer needs and providing best-in-class solutions. Our business model provides scalable efficiencies enabling us to serve our customers with a variety of products that we typically classify into three categories: make-to-order, configure-to-order, and engineer-to-order. For our project-based platforms, we leverage third-party subcontract fabrication partners in a global network to execute for our customers world-wide. Our platforms are focused on sales, application engineering, product management, project management, and supply chain execution for our customers.
Our operations management team has distinct industry expertise coupled with strong leadership skills resulting in a customer-first mindset across the business. Our operations management team works closely with our Chief Executive Officer on global fulfillment strategies, operational excellence, resource allocation, and employee development.
Within our segments we have monthly business reviews to ensure we are serving customers, achieving our operating plan, and executing on strategic growth initiatives. These reviews include, but are not limited to pipeline reviews, quotation reviews, project management reviews, financial performance, manufacturing scorecards, safety, and customer feedback. In these reviews we focus on metrics such as quality, customer satisfaction, on-time-delivery, lead-times, price, inflation, project margins, backlog, and above all, safety.
In support of the segments, centralized teams provide back-office functions for scale, efficiency, and compliance. These key functions include: accounting, treasury, tax, payroll, human resources and total rewards management, legal, information technology, marketing, and internal control over financial reporting. We have excellent collaboration between our platforms and our centralized service teams ensuring optimal efficiency and alignment on growth and improvement initiatives.
Our reportable segments are:
26
Our contracts are obtained either through competitive bidding or as a result of negotiations with our customers. Contract terms offered by us are generally dependent on the complexity and risk of the project as well as the resources that will be required to complete the project. Our focus is on increasing our operating margins as well as our gross margin percentage, which translates into stronger operating results.
Our cost of sales is principally driven by a number of factors, including material and subcontract prices and labor cost and availability. Changes in these factors may have a material impact on our overall gross profit margins.
We break down costs of sales into five categories, as follows:
In general, subcontracts are the highest percentage of costs and also the most flexible followed by labor, material, and equipment. Due to the project nature and global orientation of several of our platforms, leveraging subcontract fabrication partners close to our customers increases our ability to meet customer delivery expectations at market competitive pricing. In periods where orders are infrequent, we do not have to maintain the fixed cost of a manufacturing plant. Across our various product lines, the relative relationships of these cost categories change and cause variations in gross margin percentage. Material and labor costs can increase quickly, which also reduces gross margin percentage. As material cost inflation occurs, the Company seeks to pass this cost onto our customers as price increases.
Selling and administrative expense principally includes sales and engineering payroll and related fringes, advertising and marketing expenditures as well as all corporate and administrative functions and other costs that support our operations. The majority of these expenses are fixed. An advantage of our operating model is that as revenue grows, we have significant operating leverage on our fixed selling and administrative cost structure.
Note Regarding Use of Non-GAAP Financial Measures
The Company’s consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). These GAAP financial statements include certain charges the Company believes are not indicative of its core ongoing operational performance.
As a result, the Company provides financial information in this MD&A that was not prepared in accordance with GAAP and should not be considered as an alternative to the information prepared in accordance with GAAP. The Company provides this supplemental non-GAAP financial information, because the Company’s management utilizes it to evaluate its ongoing financial performance and the Company believes it provides greater transparency to investors as supplemental information to its GAAP results.
The Company has provided the non-GAAP financial measures including non-GAAP operating income, non-GAAP operating margin, and non-GAAP net income as a result of the adjustment for items that the Company believes are not indicative of its ongoing operations. These items include charges associated with the Company’s acquisitions, and the items described below in “Consolidated Results.” The Company believes that evaluation of its financial performance compared with prior and future periods can be enhanced by a presentation of results that exclude the impact of these items. The Company has incurred substantial expense and generated substantial income associated with acquisitions. While the Company cannot predict the exact timing or amounts of such charges, it does expect to treat these charges as special items in its future presentation of non-GAAP results.
27
Results of Operations
Consolidated Results
Our consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 are as follows:
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in millions) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net sales |
|
$ |
544.8 |
|
|
$ |
422.6 |
|
|
$ |
324.1 |
|
Cost of goods sold |
|
|
373.8 |
|
|
|
294.4 |
|
|
|
223.2 |
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
171.0 |
|
|
$ |
128.2 |
|
|
$ |
100.9 |
|
Percent of sales |
|
|
31.4 |
% |
|
|
30.3 |
% |
|
|
31.1 |
% |
Selling and administrative expenses |
|
$ |
122.9 |
|
|
$ |
93.4 |
|
|
$ |
81.8 |
|
Percent of sales |
|
|
22.6 |
% |
|
|
22.1 |
% |
|
|
25.2 |
% |
Amortization and earnout expenses |
|
|
8.2 |
|
|
|
6.8 |
|
|
|
7.8 |
|
Acquisition and integration expenses |
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
Executive transition expenses |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Restructuring expenses |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
Operating income |
|
$ |
34.6 |
|
|
$ |
22.2 |
|
|
$ |
9.9 |
|
Percent of sales |
|
|
6.4 |
% |
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
|
3.1 |
% |
Other income (expense), net |
|
$ |
0.4 |
|
|
$ |
6.9 |
|
|
$ |
(2.2 |
) |
Interest expense |
|
|
(13.4 |
) |
|
|
(5.4 |
) |
|
|
(3.0 |
) |
Income before income taxes |
|
$ |
21.5 |
|
|
$ |
23.7 |
|
|
$ |
4.7 |
|
Income tax expense |
|
|
7.0 |
|
|
|
5.4 |
|
|
|
2.7 |
|
Net income |
|
$ |
14.5 |
|
|
$ |
18.3 |
|
|
$ |
2.0 |
|
Noncontrolling interest |
|
|
(1.6 |
) |
|
|
(0.8 |
) |
|
|
(0.6 |
) |
Net income attributable to CECO Environmental Corp. |
|
$ |
12.9 |
|
|
$ |
17.4 |
|
|
$ |
1.4 |
|
Non-GAAP Measures
To compare operating performance between the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 the Company has adjusted GAAP operating income to exclude (1) amortization of intangible assets, and earnout expenses, (2) restructuring expenses primarily relating to severance, facility exits, and associated legal expenses, (3) acquisition and integration expenses, which include legal, accounting, and other expenses, (4) executive transition expenses, including severance for the Company's former executives, fees and expenses incurred in the search, for and hiring, of new executives and (5) intangible asset impairment. See “Note Regarding Use of Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above. The following tables present the reconciliation of GAAP operating income and GAAP operating margin to non-GAAP operating income and non-GAAP operating margin, and GAAP net income to non-GAAP net income.
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in millions) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Operating income as reported in accordance with GAAP |
|
$ |
34.6 |
|
|
$ |
22.2 |
|
|
$ |
9.9 |
|
Operating margin in accordance with GAAP |
|
|
6.4 |
% |
|
|
5.3 |
% |
|
|
3.1 |
% |
Amortization and earnout expenses |
|
|
8.2 |
|
|
|
6.8 |
|
|
|
7.8 |
|
Acquisition and integration expenses |
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
Executive transition expenses |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Restructuring expenses |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
Non-GAAP operating income |
|
$ |
48.1 |
|
|
$ |
34.8 |
|
|
$ |
19.1 |
|
Non-GAAP operating margin |
|
|
8.8 |
% |
|
|
8.2 |
% |
|
|
5.9 |
% |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in millions) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net income as reported in accordance with GAAP |
|
$ |
12.9 |
|
|
$ |
17.4 |
|
|
$ |
1.4 |
|
Amortization and earnout expenses |
|
|
8.2 |
|
|
|
6.8 |
|
|
|
7.8 |
|
Acquisition and integration expenses |
|
|
2.5 |
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
0.8 |
|
Executive transition expenses |
|
|
1.5 |
|
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Restructuring expenses |
|
|
1.3 |
|
|
|
0.1 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
Foreign currency remeasurement |
|
|
(1.0 |
) |
|
|
(1.3 |
) |
|
|
2.0 |
|
Tax (benefit) expense of adjustments |
|
|
1.2 |
|
|
|
(2.8 |
) |
|
|
(2.8 |
) |
Non-GAAP net income |
|
$ |
26.6 |
|
|
$ |
25.9 |
|
|
$ |
9.8 |
|
Non-GAAP net income as a percentage of sales |
|
|
4.9 |
% |
|
|
6.1 |
% |
|
|
3.0 |
% |
28
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Consolidated net sales in 2023 were $544.8 million compared with $422.6 million in 2022, an increase of $122.2 million or 28.9%. The increase was led by increases of $88.2 million in our separation, filtration and industrial water businesses and $21.2 million in our thermal acoustics technologies. Approximately 58.2%, or $71.1 million, of the increase in net sales is attributable to organic revenue growth, defined as revenue recorded subsequent to the twelve-month period post-acquisition date, while $51.1 million is attributable to acquisitions that have occurred during the preceding twelve-month period.
Gross profit increased by $42.8 million, or 33.4%, to $171.0 million in 2023 compared with $128.2 million in 2022. The increase in gross profit was primarily attributable to the increase in sales volume as described above. Gross profit as a percentage of sales increased to 31.4% in 2023 compared with 30.3% in 2022 due to higher project margin mix executed during the year and price increases. We continue to experience shortages of raw materials and inflationary pressures for certain materials and labor. We have secured additional raw materials from existing and alternate suppliers and have taken other mitigating actions to mitigate supply disruptions, such as implementing price increases and applying material surcharges, we cannot guarantee that we can continue to do so in the future. In this event, our business, results and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Orders booked were $582.8 million in 2023 compared with $526.6 million in 2022. This $56.2 million increase is primarily attributable to recent acquisitions.
Selling and administrative expenses were $122.9 million in 2023 compared with $93.4 million in 2022. The increase is primarily attributed to acquisitions during 2023, as well as increased investment to support our revenue growth and increased backlog. Selling and administrative expenses as a percentage of sales were flat, with 22.6% in 2023 compared with 22.1% in 2022.
Amortization and earnout expenses were $8.2 million in 2023 and $6.8 million in 2022. The increase in expense is attributable to an increase of $0.9 million in definite lived asset amortization due to recent acquisitions and $0.5 million in earnout expense. See Note 7 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion on earnout expenses.
Acquisitions and integration expenses related to various merger and acquisition diligence activities, which include legal, accounting and banking expenses, were $2.5 million in 2023, as compared with $4.5 million in 2022. The decrease is due to the timing of acquisition activity. See Note 14 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion on recent acquisitions.
Executive transition expenses were $1.5 million in 2023 compared to $1.2 million in 2022. These expenses related to fees and other expenses incurred in the search for and hiring of new executives, specifically the Chief Administrative and Legal Officer and Chief Finance and Strategy Officer for 2022 and Chief Operating Officer and Chief Accounting Officer for 2023.
Restructuring expenses were $1.4 million in 2023 compared to $0.1 million in 2022. These expenses related to severance, facility exits, and associated legal expenses, primarily as it relates to the exit of certain operations in China at the end of 2023.
Operating income for 2023 was $34.6 million, an increase of $12.4 million from $22.2 million in 2022. Operating income as a percentage of sales for 2023 was 6.4% compared with 5.3% for 2022. The increase in operating income is primarily attributable to increases in net organic sales and gaining operating leverage.
Non-GAAP operating income was $48.1 million in 2023 and $34.8 million in 2022. The increase in non-GAAP operating income is primarily attributable to the increase in net organic sales and improved operating leverage. Non-GAAP operating income as a percentage of sales for 2023 was 8.8% compared with 8.2% for 2022.
Other income for 2023 was $0.4 million compared to $6.9 million in 2022. The decrease in other income was primarily attributable to net foreign currency transaction losses in the current year based on changes in exchange rates at our foreign subsidiaries.
Interest expense increased to $13.4 million in 2023 from $5.4 million in 2022. The increase in interest expense is primarily due to higher interest rates and increased debt balances to fund acquisitions.
Income tax expense was $7.0 million and $5.4 million in 2023 and 2022, respectively. The effective tax rate for 2023 was 32.6% compared with 22.9% in 2022. Income tax expense and the effective tax rate for 2023 were affected by changes in valuation allowances, and the net impact of global intangible low-taxed income ("GILTI") and foreign-derived intangible income ("FDII"), as well as certain permanent differences including state income taxes, non-deductible incentive stock-based compensation, and differences in tax rates among the jurisdictions in which we operate.
29
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
See the Management Discussion and Analysis section of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022 for a discussion of our consolidated results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021.
Business Segments
The Company’s operations are organized and reviewed by management along its product lines and end markets that the segment serves and are presented in two reportable segments. The results of the segments are reviewed through the “Income from operations” line on the Consolidated Statements of Income. The amounts presented in the Net Sales table below and in the following comments regarding our net sales at the reportable business segment level exclude both intra-segment and inter-segment net sales. The Income from Operations table and corresponding comments regarding operating income at the reportable segment level include both intra-segment and inter-segment operating income.
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net Sales (less intra-, inter-segment sales) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(table only in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems Segment |
|
$ |
380,108 |
|
|
$ |
263,224 |
|
|
$ |
186,926 |
|
Industrial Process Solutions Segment |
|
|
164,737 |
|
|
|
159,403 |
|
|
|
137,214 |
|
Total net sales |
|
$ |
544,845 |
|
|
$ |
422,627 |
|
|
$ |
324,140 |
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Income from Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
(table only in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
59,846 |
|
|
$ |
36,200 |
|
|
$ |
25,770 |
|
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
21,630 |
|
|
|
22,705 |
|
|
|
15,054 |
|
Corporate and Other (1) |
|
|
(46,907 |
) |
|
|
(36,744 |
) |
|
|
(30,967 |
) |
Total income from operations |
|
$ |
34,569 |
|
|
$ |
22,161 |
|
|
$ |
9,857 |
|
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
Engineered Systems segment
Our Engineered Systems segment net sales increased $116.9 million to $380.1 million in 2023 compared with $263.2 million in 2022, an increase of 44.4%. The increase is broad-based, led by increases of $88.2 million in our separation, filtration and industrial water businesses and $21.2 million in our thermal acoustics technologies. Approximately 56.6%, or $66.2 million, of the increase in net sales is attributable to organic revenue growth, while $50.7 million is attributable to acquisitions that have occurred during the preceding twelve-month period.
Operating income for the Engineered Systems segment increased $23.6 million to $59.8 million for 2023 compared with $36.2 million in 2022, an increase of 65.2%. The increase in operating income in primarily attributable to higher gross profit related to increased sales.
Industrial Process Solutions segment
Our Industrial Process Solutions segment net sales increased $5.3 million to $164.7 million in 2023 compared with $159.4 million in 2022, an increase of 3.3%. The increase is primarily attributable to an increase of $4.7 million in our duct fabrication and installation businesses. Approximately 62.3%, or $3.3 million, of the increase in net sales is attributable to organic revenue growth, while $2.0 million is attributable to acquisitions that have occurred during the preceding twelve-month period.
Operating income was $21.6 million in 2023 compared with $22.7 million in 2022. The decrease is primarily attributable to $1.0 million of restructuring expenses incurred in 2023.
30
Corporate and Other segment
Operating expense for the Corporate and Other segment increased $10.2 million to $46.9 million for 2023 compared with $36.7 million for 2022. The increase is primarily attributable to inflationary increases in wages and services, as well as increased headcount in order to support our revenue growth.
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021
See the Management Discussion and Analysis section of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022 for a discussion of business segment results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2022 compared to the year ended December 31, 2021.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
When we undertake large jobs, our working capital objective is to make these projects self-funding. We work to achieve this by obtaining initial down payments, progress billing contracts, when possible, utilizing extended payment terms from material suppliers, and paying sub-contractors after payment from our customers, which is an industry practice. Our investment in net working capital is funded by cash flow from operations and by our revolving line of credit.
At December 31, 2023, the Company had working capital of $78.3 million, compared with $94.0 million at December 31, 2022. The ratio of current assets to current liabilities was 1.39 to 1.00 at December 31, 2023 as compared with a ratio of 1.64 to 1.00 at December 31, 2022.
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, cash and cash equivalents totaled $54.8 million and $45.5 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, $38.5 million and $31.7 million, respectively, of our cash and cash equivalents were held by non-U.S. subsidiaries, as well as being denominated in foreign currencies.
Debt consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Outstanding borrowings under Credit Facility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
– Term loan |
|
$ |
112,424 |
|
|
$ |
41,309 |
|
– Revolving Credit Loan |
|
|
17,300 |
|
|
|
61,300 |
|
Total outstanding borrowings under the Credit Facility |
|
|
129,724 |
|
|
|
102,609 |
|
Outstanding borrowings under the joint venture term debt |
|
|
8,855 |
|
|
|
10,083 |
|
Unamortized debt discount |
|
|
(1,296 |
) |
|
|
(1,488 |
) |
Total outstanding borrowings |
|
|
137,283 |
|
|
|
111,204 |
|
Less: current portion |
|
|
(10,488 |
) |
|
|
(3,579 |
) |
Total debt, less current portion |
|
$ |
126,795 |
|
|
$ |
107,625 |
|
In 2023, the Company made repayments of $44.0 million on the revolving credit line and $1.2 million on the joint venture term debt, with net borrowings of $71.1 million on the term loan.
Credit Facility
The Company's outstanding borrowings in the United States consist of a senior secured term loan and a senior secured revolver loan with sub-facilities for letters of credit, swing-line loans and multi-currency loans (collectively, the "Credit Facility").
On October 30, 2023, the Company entered into Amendment No. 4 to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement. Pursuant to this amendment, the lenders provided an additional term loan in the aggregate principal amount of $75.0 million.
Under the terms of the Credit Facility, the Company is required to maintain certain financial covenants, including the maintenance of a Consolidated Net Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Credit Facility). In the third quarter of 2023, the Company entered into an Elevated Ratio Period resulting in a maximum Consolidated Net Leverage Ratio of 4.00 through June 30, 2024, after which time it will decrease to 3.50 until the end of the term of the Credit Facility.
31
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company was in compliance with all related financial and other restrictive covenants under the Credit Facility.
Joint Venture Debt
On March 7, 2022, the Company's Effox-Flextor-Mader, Inc. joint venture ("EFM JV") entered into a loan agreement secured by the assets of the EFM JV in the aggregate principal amount of $11.0 million for the acquisition of General Rubber, LLC ("GRC"), as further described in Note 14 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Foreign Debt
In addition, the Company has a number of bank guarantee facilities and bilateral lines of credit in various foreign countries currently supported by cash, letters of credit or pledged assets and collateral under the Credit Facility. The Credit Facility allows letters of credit and bank guarantee issuances of up to $65.0 million from the bilateral lines of credit secured by pledged assets and collateral under the Credit Facility.
See Note 8 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on the Company’s debt facilities.
Total unused credit availability under our Credit Facility and other non-U.S. credit facilities and agreements, exclusive of any potential asset base limitations, is as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
(dollars in millions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Credit Facility, revolving loans |
|
$ |
140.0 |
|
|
$ |
140.0 |
|
Draw down |
|
|
(17.3 |
) |
|
|
(61.3 |
) |
Letters of credit open |
|
|
(13.3 |
) |
|
|
(18.9 |
) |
Total unused credit availability |
|
$ |
109.4 |
|
|
$ |
59.8 |
|
Amount available based on borrowing limitations |
|
$ |
99.8 |
|
|
$ |
59.8 |
|
Overview of Cash Flows and Liquidity
|
|
For the year ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Total operating cash flow provided by operating activities |
|
$ |
44,647 |
|
|
$ |
29,649 |
|
|
$ |
13,298 |
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(56,486 |
) |
|
|
(48,257 |
) |
|
|
(2,083 |
) |
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
21,144 |
|
|
|
38,176 |
|
|
|
(15,556 |
) |
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(442 |
) |
|
|
(4,978 |
) |
|
|
(1,475 |
) |
Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
$ |
8,863 |
|
|
$ |
14,590 |
|
|
$ |
(5,816 |
) |
Operating Activities
In 2023, $44.6 million of cash was provided by operating activities compared with $29.6 million provided by operating activities in 2022, an increase of $15.0 million. Cash flow from operating activities in 2023 had a favorable impact year-over-year primarily due to changes in net working capital.
In 2022, $29.6 million of cash was provided by operating activities compared with $13.2 million in 2021, an increase of $16.4 million. Cash flow from operating activities in 2022 had a favorable impact year-over-year primarily due to increases in net earnings, partially offset by increases in net working capital.
Investing Activities
In 2023, $56.5 million of cash was used in investing activities, which consisted of $48.1 for current year acquisitions and $8.4 million for acquisition of property and equipment.
In 2022, $48.3 million of cash was used in investing activities, which consisted of $44.9 for current year acquisitions and $3.4 million for acquisition of property and equipment.
32
Financing Activities
Financing activities in 2023 provided cash of $21.1 million, which consisted primarily of $27.1 million of net borrowings under the Credit Facility, used to finance current year acquisitions, as well as $1.4 million of proceeds from employee stock purchase plan and exercise of stock options. This was partially offset by $2.1 million of earnout payments, $1.7 million in distributions to non-controlling interest, $1.2 million of deferred consideration for acquisitions, $0.9 million in payments on our capital leases, and $0.4 million of financing fees.
Financing activities in 2022 provided cash of $38.2 million, which consisted primarily of $39.3 million net borrowings on our revolving credit line and $11.0 million borrowings of joint venture term debt, both of which were used to finance current year acquisitions. These were partially offset by $3.1 million paydown of our term debt, $7.0 million for the repurchase and retirement of our common stock, $1.4 million in distributions to non-controlling interest, and $0.6 million in payments on our capital leases.
Our primary sources of liquidity are cash generated from operations and borrowing availability under the Credit Facility. We believe that cash flows from operating activities, together with our existing cash and borrowings available under our Credit Facility, will be sufficient for at least the next twelve months to fund our current anticipated uses of cash. After that, our ability to fund these expected uses of cash and to comply with the financial covenants under our debt agreements will depend on the results of future operations, performance and cash flow. Our ability to fund these expected uses from the results of future operations will be subject to prevailing economic conditions and to financial, business, regulatory, legislative and other factors, many of which are beyond our control.
Our material cash requirements included (i) debt repayments under with respect to our Credit Facility and joint venture term debt, (ii) interest expense, (iii) purchase obligations for costs associated with uncompleted sales contracts, (iv) operating and capital lease obligations and (v) contingent liabilities related to acquisitions, including earnout liabilities and retention payments.
We are party to many contractual obligations involving commitments to make payments to third parties, and such commitments require a material amount of cash. The following table summarizes the Company’s material cash requirements from known contractual obligations as of December 31, 2023:
|
|
Payments Due by Period |
|
|||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) |
|
Total |
|
|
Less than 1 |
|
|
1-3 years |
|
|
3-5 years |
|
|
More than |
|
|||||
Term Loan Debt, including joint venture debt |
|
$ |
121,279 |
|
|
$ |
10,488 |
|
|
$ |
107,023 |
|
|
$ |
3,768 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
Revolving Credit Loan |
|
|
17,300 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
17,300 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Interest expense (estimated) |
|
|
26,825 |
|
|
|
11,154 |
|
|
|
15,344 |
|
|
|
328 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Purchase obligations (1) |
|
|
109,957 |
|
|
|
109,957 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Operating lease obligations |
|
|
16,938 |
|
|
|
4,363 |
|
|
|
6,372 |
|
|
|
2,723 |
|
|
|
3,480 |
|
Capital lease obligations |
|
|
6,409 |
|
|
|
925 |
|
|
|
1,905 |
|
|
|
1,983 |
|
|
|
1,596 |
|
Liabilities related to acquisitions (2) |
|
|
3,700 |
|
|
|
1,115 |
|
|
|
2,585 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Totals |
|
$ |
302,408 |
|
|
$ |
138,001 |
|
|
$ |
150,529 |
|
|
$ |
8,802 |
|
|
$ |
5,076 |
|
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in conformity with GAAP. Preparation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions affecting the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and related contingent liabilities. Critical accounting estimates or assumptions are those where the nature of the estimates or assumptions is material given the level of subjectivity and judgment necessary to account for uncertain matters, and the potential impact of the estimates and assumptions on financial condition or operating performance is material. We consider the estimates discussed below to be critical to the understanding of our financial statements. Actual results may differ from our estimates and assumptions, and any such differences could be material to our consolidated financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
A substantial portion of our revenue is derived from fixed-price contracts. We account for a contract after it has been approved by all parties to the arrangement, the rights of the parties are identified, payment terms are identified, the contract has commercial substance and collectability of consideration is probable.
33
We recognize revenue as performance obligations are satisfied. A significant amount of our revenue is recognized over a period of time as we perform under the contract because control of the work in process transfers continuously to the customer. For performance obligations to deliver products with continuous transfer of control to the customer, revenue is recognized based on the extent of progress towards completion of the performance obligation. Progress is measured based on the ratio of costs incurred to date to the total estimated costs to complete the performance obligation. For these contracts, the cost-to-cost measure best depicts the continuous transfer of goods or services to the customer.
The judgments and estimates involved include management’s ability to accurately estimate the contracts’ progress to completion at each financial reporting period. In addition, certain contracts are highly dependent on the work of contractors and other subcontractors participating in a project, over which we have no or limited control, and their performance on such project could have an adverse effect on the profitability of our contracts. Delays resulting from these contractors and subcontractors, changes in the scope of the project, weather, and labor availability also can have an effect on a contract’s profitability. Changes to job performance, job conditions, and estimated profitability may result in revisions to contract revenue and costs and are recognized in the period in which the revisions are made.
Provisions for estimated losses on uncompleted contracts are made in the period in which such losses are determined. No provision for estimated losses on uncompleted contracts was needed at December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Inventories
The Company’s inventories are valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value using the first-in, first-out inventory costing method. Inventory quantities are regularly reviewed and provisions for excess or obsolete inventory are recorded primarily based on our forecast of future demand and market conditions. Significant unanticipated changes to our forecasts could require a change in the provision for excess or obsolete inventory.
Long-lived assets
Property, plant and equipment and finite life intangible assets are reviewed whenever events or changes in circumstances occur that indicate possible impairment. If such events or changes in circumstances occur, our impairment review is based on an undiscounted cash flow analysis at the lowest level at which cash flows of the long-lived assets are largely independent of other groups of our assets and liabilities. This analysis requires management judgment with respect to changes in technology, the continued success of product lines, and future volume, revenue and expense growth rates. We also review business plans for possible impairment. Impairment occurs when the carrying value of the assets exceeds the future undiscounted cash flows expected to be earned by the use of the asset or asset group. When impairment is indicated, the estimated future cash flows are then discounted to determine the estimated fair value of the asset or asset group and an impairment charge is recorded for the difference between the carrying value and the estimated fair value.
Additionally, we review the remaining useful lives of assets to determine whether events and circumstances warrant a revision to the remaining period of depreciation or amortization. If the estimate of a long-lived asset’s remaining useful life is changed, the remaining carrying amount of the asset is depreciated/amortized prospectively over that revised remaining useful life.
We complete an impairment assessment of the Company's indefinite life intangible assets on an annual basis, or more often as circumstances require. As a part of its annual assessment, we first qualitatively assess whether current events or changes in circumstances lead to a determination that it is more likely than not (defined as a likelihood of more than 50 percent) that the fair value of an asset is less than its carrying amount. If there is a qualitative determination that the fair value of a particular asset is more likely than not greater than its carrying value, we do not need to proceed to the quantitative estimated fair value test for that asset. If this qualitative assessment indicates a more likely than not potential that the asset may be impaired, the estimated fair value is determined by the relief from royalty method. If the estimated fair value of an asset is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recorded for the amount by which the carrying value of the asset exceeds its estimated fair value.
During 2023, 2022, and 2021, our annual impairment test indicated no impairment of our indefinite-lived tradenames. Accordingly, we recognized no impairment charges in our financial results for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021. For additional information on impairment testing results, see Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Goodwill
We complete a goodwill impairment assessment on an annual basis as of October 1, or more often as circumstances require, on a reporting unit level, at or below the operating segment level. As a part of the annual assessment, we first qualitatively assess whether current events or changes in circumstances lead to a determination that it is more likely than not (defined as a likelihood of more than
34
50 percent) that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If there is a qualitative determination that the fair value of a particular reporting unit is more likely than not greater than its carrying value, we do not need to quantitatively test for goodwill impairment for that reporting unit. If this qualitative assessment indicates a more likely than not potential that the asset may be impaired, the estimated fair value is calculated using a weighting of the income method and the market method. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recorded.
We base our measurement of the fair value of a reporting unit using a 50/50 weighting of the income method and the market method. The income method is based on a discounted future cash flow approach that uses the significant assumptions of projected revenue, projected operational profit, terminal growth rates, and the cost of capital. Projected revenue, projected operational profit and terminal growth rates are significant assumptions because they are three primary drivers of the projected cash flows in the discounted future cash flow approach. Cost of capital is a significant assumption as it is the discount rate used to calculate the current fair value of those projected cash flows. The market method is based on financial multiples of comparable companies and applies a control premium. Significant estimates in the market approach include identifying similar companies with comparable business factors such as size, growth, profitability, risk and return on investment and assessing comparable revenue and operating income multiples in estimating the fair value of a reporting unit. Based on the analysis, the resultant estimated fair value of all of the reporting units exceeded their carrying value as of December 31, 2023. For additional information on goodwill impairment testing results, see Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are determined using the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”), Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 740, “Income Taxes”. Income tax expense includes federal, state and foreign income taxes.
Deferred income taxes are provided using the asset and liability method whereby deferred tax assets are recognized for deductible temporary differences and operating loss and tax credit carry-forwards and deferred tax liabilities are recognized for taxable temporary differences. Temporary differences are the differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases and are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted for the effects of changes in tax laws and rates on the date of enactment. Tax credits and other incentives reduce income tax expense in the year the credits are claimed.
Management must assess the need to accrue or disclose uncertain tax positions for proposed potential adjustments from various federal, state and foreign tax authorities who regularly audit the Company in the normal course of business. In making these assessments, management must often analyze complex tax laws of multiple jurisdictions, including many foreign jurisdictions. The accounting guidance prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We record the related interest expense and penalties, if any, as tax expense in the tax provision.
Management must assess the realizability of the Company’s deferred tax assets. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities (including the impact of available carryback and carry forward periods), projected future taxable income, and tax-planning strategies in making this assessment. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income during the carryforward period are reduced.
The Company has made an accounting policy election to record the U.S. income tax effect of future global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) inclusions in the period in which they arise, rather than establishing deferred taxes with respect to the expected future tax liabilities associated with future GILTI inclusion.
Certain of the Company’s undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries are not permanently reinvested. A liability has been recorded for the deferred taxes on such undistributed foreign earnings. The amount is attributable primarily to the foreign withholding taxes that would become payable should the Company repatriate cash held in its foreign operations.
Other significant accounting policies
Other significant accounting policies, not involving the same level of uncertainties as those discussed above, are nevertheless important to an understanding of our financial statements. See Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, Summary of
35
Significant Accounting Policies, which discusses accounting policies that must be selected by us when there are acceptable alternatives.
New Accounting Pronouncements
For information regarding recent accounting pronouncements, see Note 1 to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this annual report on Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to certain market risks, primarily changes in interest rates. Market risk is the potential loss arising from adverse changes in market rates and prices, such as foreign currency exchange and interest rates. For the Company, these exposures are primarily related to changes in interest rates. The amount of interest expense may increase because a substantial portion of our borrowings is at variable rates of interest, which, if interest rates increase, could result in higher interest expense. We do not currently hold any derivatives or other financial instruments purely for trading or speculative purposes.
The carrying value of the Company’s total long-term debt and current maturities of long-term debt at December 31, 2023 was $138.6 million. Market risk was estimated as the potential decrease (increase) in future earnings and cash flows resulting from a hypothetical 10% increase (decrease) in the Company’s estimated weighted average borrowing rate at December 31, 2023. Most of the interest on the Company’s debt is indexed to SOFR market rates. The estimated annual impact of a hypothetical 10% change in the estimated weighted average borrowing rate at December 31, 2023 is $1.2 million.
The Company has wholly-owned subsidiaries in several countries, including in the Netherlands, Canada, the People’s Republic of China, United Kingdom, Singapore, India, United Arab Emirates and South Korea. In the past, we have not hedged our foreign currency exposure. Future changes in exchange rates may positively or negatively impact our revenues, operating expenses and earnings. Transaction gains (losses) included in “Other income (expense), net” line of the Consolidated Statements of Income were $1.2 million, $6.3 million, and $(3.1) million in 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively.
36
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The Consolidated Financial Statements of CECO Environmental Corp. and subsidiaries for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 and other data are included in this report following the signature page of this report and incorporated into this Item 8 by reference:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (BDO USA, P.C., Cincinnati, Ohio, PCAOB # |
|
F-1 |
|
F-3 |
|
|
F-4 |
|
|
F-5 |
|
|
F-6 |
|
|
F-7 |
|
|
F-8 |
|
|
F-9 |
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) are controls and other procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and made known to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
In connection with the preparation of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2023. Based on that evaluation, our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2023, as a result of the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting discussed below, which are currently being remediated.
The management of the Company does not expect that its disclosure controls and procedures will prevent all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision-making can be faulty, and that breakdowns can occur due to simple errors or mistakes. The design of any system of controls is based in part upon certain assumptions regarding the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The management of the Company is responsible for the preparation and accuracy of the financial statements and other information included in this report. Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial and Strategy Officer, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) (the “Framework”) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2023, its internal control over financial reporting was not effective based on the Framework, as a result of the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting discussed below.
Notwithstanding these material weaknesses, management believes that the consolidated financial statements included in this report present fairly, in all material respects, the Company’s financial condition, results of operations and cash flows for each of the periods presented in this report in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
37
Material Weaknesses in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Revenue Recognition
As previously reported, we identified a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting relating to management’s review of its revenue recognition for contracts recognized over time isolated to our Engineered Systems segment. Specifically, management did not retain appropriate documentation supporting the review of over time revenue recognition for customer contracts within the Engineered Systems segment.
Balance Sheet Reconciliations
As previously reported, we identified a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting relating to management’s review of balance sheet reconciliations for certain divisions within our Engineered Systems segment. Specifically, management did not review the reconciliations prepared for balance sheet accounts for certain divisions within the Engineered Systems segment as required by Company policy.
These material weaknesses did not result in any material misstatement in our interim or audited financial statements or disclosures, and there were no changes required to any of our previously released interim or audited consolidated financial statements.
Remediation Efforts to Address Material Weaknesses
Management is committed to maintaining a strong internal control environment. In response to the identified material weaknesses, management, with the oversight of the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors, has taken actions toward the remediation of the material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting, including reinforcing the importance of adherence to Company policies regarding control performance and related documentation with control owners, strengthening existing training programs for control owners, and developing monitoring activities to validate the performance of controls by control owners. As of December 31, 2023, management has reinforced policies through training sessions as well as ongoing communications, and implemented incremental monitoring activities, but remediation efforts are ongoing.
The Company anticipates the actions described above and resulting improvements in controls will strengthen the Company’s processes, procedures and controls related to management’s review of over time revenue recognition and balance sheet reconciliations and will address the related material weaknesses. However, the material weaknesses cannot be considered remediated until the applicable controls have operated for a sufficient period of time, and management has concluded, through testing, that the controls are operating effectively.
There are inherent limitations on the effectiveness of any system of internal controls and procedures, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of the controls and procedures. Accordingly, even effective internal controls and procedures can only provide reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued their attestation report on our internal control over financial reporting. The report is included below under the heading “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Except as noted above with respect to our ongoing remediation efforts, there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act) during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2023 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
38
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and Board of Directors
CECO Environmental Corp.
Dallas, Texas
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited CECO Environmental Corp.’s (the “Company’s”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the “COSO criteria”). In our opinion, the Company did not maintain, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the COSO criteria.
We do not express an opinion or any other form of assurance on management’s statements referring to any corrective actions taken by the Company after the date of management’s assessment.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and accumulated other comprehensive loss, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes and our report dated March 5, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Item 9A, Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit of internal control over financial reporting in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Material weaknesses regarding management’s review of its revenue recognition for contracts recognized over time in the Engineered Systems segment and review of balance sheet reconciliations have been identified and described in management’s assessment. These material weaknesses were considered in determining the nature, timing, and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the 2023 financial statements, and this report does not affect our report dated March 5, 2024 on those financial statements.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
39
/s/
March 5, 2024
40
Item 9B. Other Information
Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plans
(b)
During the three months ended December 31, 2023, no director or officer of the Company
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
41
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information called for by this Item 10 of Part III of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference to the information set forth in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Exchange Act within 120 days from December 31, 2023 (the “Proxy Statement”). Reference is also made to the information appearing in Item 1 of Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the caption “Business— Executive Officers of CECO.”
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information called for by this Item 11 of Part III of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information called for by this Item 12 of Part III of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
EQUITY COMPENSATION PLAN INFORMATION
December 31, 2023 |
|
(a) |
|
|
(b) |
|
|
(c) |
|
|||
Plan Category |
|
Number of securities |
|
|
Weighted-average |
|
|
Number of securities |
|
|||
Equity compensation plans approved by security |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2007 Equity Incentive Plan 1 |
|
|
30,600 |
|
|
$ |
12.10 |
|
|
|
— |
|
2017 Equity and Incentive Plan 2 |
|
|
188,207 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
2021 Equity and Incentive Plan 3 |
|
|
1,107,794 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
1,597,135 |
|
2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan 4 |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
1,180,156 |
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders 5 |
|
|
1,238,691 |
|
|
$ |
10.85 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
|
2,565,292 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,777,291 |
|
|
42
The information called for by this Item 13 of Part III of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information called for by this Item 14 of Part III of Form 10-K is incorporated by reference to the Proxy Statement.
43
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
1. Financial statements are set forth in this report following the signature page of this report.
2. Financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or because the required information is shown in the financial statements or in the notes thereto.
3. Exhibit Index. The exhibits listed below, as part of Form 10-K, are numbered in conformity with the numbering used in Item 601 of Regulation S-K and relate to SEC File No. 0-07099, unless otherwise indicated.
Exhibit Number |
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
44
^10.11 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.13 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.14 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.16 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.17 |
|
|
|
|
|
†10.18 |
|
|
|
|
|
†10.19 |
|
|
|
|
|
†10.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
†10.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
*†10.22 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.23 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.26 |
|
|
|
|
|
45
^10.27 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.28 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.29 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.30 |
|
|
|
|
|
^10.31 |
|
|
|
|
|
*†^10.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
*^10.33 |
|
|
|
|
|
*^10.34 |
|
|
|
|
|
*21.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
*23.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
*31.1 |
|
Rule 13(a)/15d-14(a) Certification by Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
|
*31.2 |
|
Rule 13(a)/15d-14(a) Certification by Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
|
*32.1 |
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer (18 U.S. Section 1350) |
|
|
|
*32.2 |
|
Certification of Chief Financial Officer (18 U.S. Section 1350) |
|
|
|
97.1 |
|
CECO Environmental Corp. Compensation Recovery Policy |
|
|
|
*101.INS |
|
Inline XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
*101.SCH |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document with Embedded Linkbase Documents |
|
|
|
*104 |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
|
|
|
* Filed or furnished herewith
^ Management contracts or compensation plans or arrangement
† Schedules and exhibits have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. The Company hereby undertakes to furnish on a supplemental basis a copy of any omitted schedule or exhibit upon request by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
Not applicable.
46
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. |
|
|
|
By: |
/S/ PETER JOHANSSON |
|
Peter Johansson |
|
Chief Financial and Strategy Officer |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated:
Principal Executive Officer:
/S/ TODD GLEASON |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Todd Gleason Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
|
|
|
|
Principal Financial Officer: |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ PETER JOHANSSON |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Peter Johansson Chief Financial and Strategy Officer |
|
|
|
|
|
Principal Accounting Officer: |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ KIRIL KOVACHEV |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Kiril Kovachev Chief Accounting Officer |
|
|
Directors: |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ JASON DEZWIREK |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Jason DeZwirek Chairman of the Board and Director |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ ROBERT E. KNOWLING JR |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Robert E. Knowling Jr. Director |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ CLAUDIO A. MANNARINO |
|
March 5, 2024 |
Claudio A. Mannarino Director |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ MUNISH NANDA |
|
March 5, 2024
|
Munish Nanda Director |
|
|
|
||
/S/ VALERIE GENTILE SACHS |
|
March 5, 2024
|
Valerie Gentile Sachs Director |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ LAURIE A. SIEGEL |
|
March 5, 2024
|
Laurie A. Siegel Director |
|
|
|
|
|
/S/ RICHARD F. WALLMAN |
|
March 5, 2024
|
Richard F. Wallman Director |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and Board of Directors
CECO Environmental Corp.
Dallas, Texas
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of CECO Environmental Corp. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and accumulated other comprehensive loss, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) and our report dated March 5, 2024 expressed an adverse opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Over Time Revenue Recognition Using the Cost-to-Cost Measure
As described in Notes 1 and 15 to the Company’s consolidated financial statements, the Company derives a significant portion of its revenues from fixed-price contracts within the Engineered Systems and Industrial Process Solutions segments. The revenue for such contracts is recognized over a period of time based on the extent of progress towards completion of the performance obligation, which is measured based on the ratio of costs incurred to date to total estimated costs to complete the performance obligation. Changes in these estimates can have a material impact on the amount of revenue recognized each period.
We identified the accuracy of revenue recognized over time for open contracts as a critical audit matter. The determination of estimated cost and progress to completion requires management to make significant estimates and assumptions, which includes an analysis of total estimated labor, material and subcontract costs, historical experience, current performance to date and the conditions to complete each contract. This analysis requires significant management judgment, which affects the amount of revenue recognized
F-1
by the Company. Auditing these complex judgments and assumptions involves especially challenging auditor judgment due to the nature and extent of audit evidence available and effort required to address these matters.
The primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter included:
/s/ BDO USA, P.C.
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2008.
Cincinnati, Ohio
March 5, 2024
F-2
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(dollars in thousands, except share data) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts receivable, net of allowances of $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Costs and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Inventories, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property, plant and equipment, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Right-of-use assets from operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangible assets – finite life, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangible assets – indefinite life |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred charges and other assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current portion of debt |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accounts payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Income taxes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Debt, less current portion |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred income tax liability, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Shareholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Preferred stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Common stock, $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Capital in excess of par value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total CECO shareholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Noncontrolling interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total shareholders' equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-3
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in thousands, except share and per share data) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Cost of sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Gross profit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Selling and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Amortization and earnout expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Acquisition and integration expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Executive transition expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Restructuring expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income from operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Interest expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income before income taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income tax expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Noncontrolling interest |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net income attributable to CECO Environmental Corp. |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-4
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net income |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Other comprehensive income, net of tax: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Translation gain (loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Minimum pension liability adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Comprehensive income |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-5
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capital in |
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
excess of |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
Treasury Stock |
|
|
Noncontrolling |
|
|
Shareholders' |
|
|||||||||||||||
(in thousands) |
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
par value |
|
|
Loss |
|
|
Loss |
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Interest |
|
|
Equity |
|
|||||||||
Balance January 1, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2021 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercise of stock options |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|||
Restricted stock units issued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Share-based compensation earned |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|||
Common stock repurchase and retirement (See Note 9) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Adjustment for minimum pension liability, net of tax of $ |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||
Translation loss |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Noncontrolling interest distribution |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Balance December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercise of stock options |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|||
Restricted stock units issued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Share-based compensation earned |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||||
Common stock repurchase and retirement (See Note 9) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Adjustment for minimum pension liability, net of tax of $ |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Translation loss |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
Noncontrolling interest distribution |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Fair value of noncontrolling interest equity issued (See Note 14) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Balance December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
Net income for the year ended December 31, 2023 |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercise of stock options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||||
Restricted stock units issued |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Share-based compensation earned |
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|||
Adjustment for minimum pension liability, net of tax of $ |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||
Translation gain |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
|
||
Noncontrolling interest distribution |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Balance December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-6
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
(dollars in thousands) |
|
Translation |
|
|
Minimum pension |
|
|
Accumulated other |
|
|||
Balance January 1, 2021 |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
2021 activity |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Balance December 31, 2021 |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
2022 activity |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Balance December 31, 2022 |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
2023 activity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance December 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-7
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(dollars in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net income |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Unrealized foreign currency (gain) loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Fair value adjustments to earnout liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Earnout payments |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Loss (gain) on sale of property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Amortization of debt discount |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Share-based compensation expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Bad debt expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Inventory reserve expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deferred income tax (benefit) expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Accounts receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Cost and estimated earnings of billings on uncompleted contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deferred charges and other assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accounts payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income taxes payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Acquisitions of property and equipment |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net proceeds from sale of assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash paid for acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Borrowings on revolving credit lines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Repayments on revolving credit lines |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Borrowings of long-term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Repayments of long-term debt |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Repayments of notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Deferred financing fees paid |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred consideration paid for acquisitions |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Payments on capital leases and sale-leaseback financing liability |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Earnout payments |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan and exercise of stock options |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Distributions to non-controlling interest |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Common stock repurchases |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Cash paid (received) during the period for: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Interest |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Income taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
||
The notes to consolidated financial statements are an integral part of the above statements.
F-8
CECO ENVIRONMENTAL CORP. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
Nature of business— CECO Environmental Corp. and its consolidated subsidiaries (“CECO,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” or “our”) is a leading environmentally focused, diversified industrial company, serving the broad landscape of industrial air, industrial water and energy transition markets globally providing innovative technology and application expertise. CECO helps companies grow their business with safe, clean, and more efficient solutions that help protect people, the environment and industrial equipment. CECO solutions improve air and water quality, optimize emissions management, and increase the energy and process efficiency for highly engineered applications in power generation, midstream and downstream hydrocarbon processing and transport, chemical processing, electric vehicle production, polysilicon fabrication, semiconductor and electronics production, battery production and recycling, specialty metals, aluminum and steel production, beverage can manufacturing, and industrial and produced water and wastewater treatment, and a wide range of other industrial end markets.
Principles of consolidation—The consolidated financial statements include the Company and its controlled subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Unless indicated, all balances within tables are in thousands except per share amounts.
Use of estimates—The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Significant estimates and assumptions reflected in the financial statements relate to and include, but are not limited to, the estimates of contracts' progress to completion used in the recognition of revenue over time, inventory valuation, the estimated useful lives of fixed assets and intangible assets, fair values of long-lived assets and goodwill, and deferred tax assets.
Cash equivalents—The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of
The following table provides a reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash reported within the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Restricted cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accounts receivable—Receivables are generally uncollateralized customer obligations due under normal terms requiring payment generally within
Inventories—The Company’s inventory is valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value, using the first-in, first-out inventory costing method. Inventory quantities are regularly reviewed and provisions for excess or obsolete inventory are recorded based on the Company’s forecast of future demand and market conditions. Significant unanticipated changes to the Company’s forecasts could require a change in the provision for excess or obsolete inventory.
Property, plant and equipment—Property, plant and equipment are carried at the cost of acquisition or construction and depreciated over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Depreciation and amortization are provided using the straight-line method in amounts sufficient to amortize the cost of the assets over their estimated useful lives (buildings and improvements—generally to
F-9
machinery and equipment—generally to
Intangible assets— Indefinite life intangible assets are comprised of tradenames, while finite life intangible assets are comprised of technology, customer lists, and tradenames. Finite life intangible assets are amortized on a straight line or accelerated basis over their estimated useful lives of to
Long-lived assets—Property, plant and equipment and finite life intangible assets are reviewed whenever events or changes in circumstances occur that indicate possible impairment. If events or changes in circumstances occur that indicate possible impairment, the impairment review is based on an undiscounted cash flow analysis at the lowest level at which cash flows of the long-lived assets are largely independent of other groups of assets and liabilities. This analysis requires management judgment with respect to changes in technology, the continued success of product lines, and future volume, revenue and expense growth rates. The Company conducts annual reviews for idle and underutilized equipment, and review business plans for possible impairment. Impairment occurs when the carrying value of the assets exceeds the future undiscounted cash flows expected to be earned by the use of the asset or asset group. When impairment is indicated, the estimated future cash flows are then discounted to determine the estimated fair value of the asset or asset group and an impairment charge is recorded for the difference between the carrying value and the estimated fair value.
Additionally, the Company evaluates the remaining useful life each reporting period to determine whether events and circumstances warrant a revision to the remaining period of depreciation or amortization. If the estimate of a long-lived asset’s remaining useful life is changed, the remaining carrying amount of the asset is amortized prospectively over that revised remaining useful life.
The Company completes an impairment assessment annually as of October 1 of its indefinite life intangible assets, or more often as circumstances require. As a part of its annual assessment, typically, the Company first qualitatively assesses whether current events or changes in circumstances lead to a determination that it is more likely than not, as defined as a likelihood of more than 50 percent, that the fair value of an asset is less than its carrying amount. If there is a qualitative determination that the fair value of a particular asset is more likely than not greater than its carrying value, the Company does not need to proceed to the quantitative estimated fair value test for that asset. If this qualitative assessment indicates a more likely than not potential that the asset may be impaired, the estimated fair value is determined by the relief from royalty method. If the estimated fair value of an asset is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recorded for the amount by which the carrying value of the asset exceeds its estimated fair value.
Goodwill—The Company completes an impairment assessment annually as of October 1, or more often as circumstances require, of its goodwill on a reporting unit level, at or below the operating segment level. As a part of its annual assessment, the Company first qualitatively assesses whether current events or changes in circumstances lead to a determination that it is more likely than not, defined as a likelihood of more than 50 percent, that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If there is a qualitative determination that the fair value of a particular reporting unit is more likely than not greater than its carrying value, the Company does not need to quantitatively test for goodwill impairment for that reporting unit. If this qualitative assessment indicates a more likely than not potential that the asset may be impaired, the estimated fair value is determined using a weighting of the income method and the market method. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recorded.
Deferred financing costs—Deferred financing costs are amortized to interest expense over the life of the related loan. In fiscal 2021, the Company entered into Amendment No.2 to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “Credit Facility”). The Credit Facility amended the Company’s existing Amendment No. 1 to Second Amended and Restated Agreement. In connection with the Credit Facility, the Company incurred $
Revenue recognition—A significant portion of the Company's revenue is derived from fixed-price contracts. The Company accounts for a contract after it has been approved by all parties to the arrangement, the rights of the parties are identified, payment terms are identified, the contract has commercial substance and collectability of consideration is probable.
For each contract, the Company assesses the goods and services promised to a customer and identifies a performance obligation for each distinct promised good or service.
F-10
price for each contract based on the consideration the Company expects to receive for the products or services being provided under the contract.
The Company recognizes revenue as performance obligations are satisfied and the customer obtains control of the products and services. A significant amount of the Company's revenue is recognized over a period of time as the Company performs under the contract because control of the work in process transfers continuously to the customer. For performance obligations to deliver products with continuous transfer of control to the customer, revenue is recognized based on the extent of progress towards completion of the performance obligation. Progress is measured based on the ratio of costs incurred to date to the total estimated costs to complete the performance obligation. For these contracts, the cost-to-cost measure best depicts the continuous transfer of goods or services to the customer. Annual revenue recognized over a period of time is approximately 70% of total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021.
For contracts where the duration is short, total contract revenue is insignificant, or control does not continuously transfer to the customer, revenues are recognized at the point in time control passes to the customer, which occurs generally upon shipment of product. Annual revenue recognized at a point in time is approximately 30% of total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021.
Progress payments are generally made over the duration of the contract. Shipping and handling activities after control of the products has transferred to the customer are considered fulfillment activities. Sales taxes are recorded on a net basis.
Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities — Contract assets consist of costs and earnings in excess of billings, costs incurred for contracts recognized at a point in time, and retainage. Costs and earnings in excess of billings represent the estimated value of unbilled work for contracts with performance obligations recognized over time and are separately classified as current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Costs incurred for contracts recognized at a point in time are classified within inventories as work-in-process. Retainage represents a portion of the contract billings that have been billed, but for which the contract allows the customer to retain a portion of the billed amount until final settlement. Retainage is not considered to be a significant financing component because the intent is to protect the customer. Retainage is classified within accounts receivable and deferred charges and other assets depending on when it is due. Almost all of the Company’s contract assets are classified as current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts are current liabilities, which relate to fixed-price contracts recognized over time, and represents payments in advance of performing the related contract work. Billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts is not considered to be a significant financing component because it is generally used to meet working capital demands that can be higher in the early stages of a contract. Contract liabilities, classified in accounts payable and accrued expenses in the Consolidated Balance Sheets, include advance payments received from customers for which revenue has not been recognized for contracts where revenue is recognized at a point in time. Contract liabilities are reduced when the associated revenue from the contract is recognized, which is generally within one year.
As of the beginning of the prior year period, or January 1, 2022, costs and estimated earnings in excess of billings on uncompleted contracts and billings in excess of costs and estimated earnings on uncompleted contracts were $
The revenue streams within the Company are consistent with those disclosed for the Company's reportable segments. See Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on product offerings and segments.
Provisions for estimated losses on uncompleted contracts are made in the period in which such losses are determined. Changes to job performance, job conditions, and estimated profitability may result in revisions to contract revenue and costs and are recognized in the period in which the revisions are made. There was
Cost of sales—Cost of sales amounts include materials, subcontract costs, direct labor and associated benefits, inbound freight charges, purchasing and receiving, inspection, warehousing, and depreciation.
Claims—Change orders arise when the scope of the original project is modified for any of a variety of reasons. The Company will negotiate the extent of the modifications, its expected costs and recovery with the customer. Costs related to change orders are added
F-11
to the expected total cost of the project. In cases where contract revenues are assured beyond a reasonable doubt to be increased in excess of the expected costs of the change order, incremental profit also is recognized on the contract. Such assurance is generally only achieved when the customer approves in writing the scope and pricing of the change order. Change orders that are in dispute are effectively handled as claims.
Claims are amounts in excess of the agreed contract price that the Company seeks to collect from customers or others for customer-caused delays, errors in specifications and designs, contract terminations, change orders in dispute or unapproved as to both scope and price. Costs attributable to claims are treated as contract costs as incurred.
The Company recognizes certain significant claims for recovery of incurred costs when it is probable that the claim will result in additional contract revenue and when the amount of the claim can be reliably estimated. When the customer or other parties agree in writing to the amount of the claim to be recovered by the Company, the amount of the claim becomes contractual and is accounted for as an increase in the contract’s total estimated revenue and estimated cost. As actual costs are incurred and revenues are recognized over time, a corresponding percentage of the revised total estimated profit will therefore be recognized.
Should it become probable that the claim will not result in additional contract revenue, the Company removes the related contract revenues from its previous estimate of total revenues, which effectively reduces the estimated profit margin on the job and negatively impacts profit for the period.
Pre-contract costs—Pre-contract costs are not significant and are primarily internal costs. As most of the Company’s contracts are one year or less, the Company expenses all pre-contract costs as incurred regardless of whether or not the bids are successful. A majority of the Company's business is obtained through a bidding process and this activity is on-going with multiple bids in process at any one time. These costs consist primarily of engineering, sales and project manager wages, fringes and general corporate overhead.
Selling and administrative expenses—Selling and administrative expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Income include sales and administrative wages and associated benefits, selling and office expenses, professional fees, bad debt expense and depreciation. Selling and administrative expenses are charged to expense as incurred. Selling and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021 included $
Acquisition and integration expenses—Acquisition and integration expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Income are related to acquisition activities, which include, legal, accounting, and other expenses.
Amortization and earnout expenses—Amortization and earnout expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Income include amortization of intangible assets, and changes to earnout and contingent compensation amounts related to acquisitions.
Restructuring expenses—Restructuring expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Income include expenses related to ongoing restructuring programs to reduce operating costs in the future. Within restructuring expenses are charges related to severance, facility exit, legal and property, plant and equipment impairment. The Company’s policy is to recognize restructuring expenses in accordance with the accounting rules related to exit or disposal activities.
Product warranties—The Company’s warranty reserve is to cover the products sold. The warranty accrual is based on historical claims information. The warranty reserve is reviewed and adjusted as necessary on a quarterly basis and is presented within Note 7.
Research and development—Although not technically defined as research and development, a significant amount of time, effort and expense is devoted to custom engineering which qualifies products for specific customer applications, developing proprietary process technology and partnering with customers to develop new products.
Income taxes - Income taxes are determined using the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”), Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 740, “Income Taxes”. Income tax expense includes federal, state and foreign income taxes.
Deferred income taxes are provided using the asset and liability method whereby deferred tax assets are recognized for deductible temporary differences and operating loss and tax credit carry-forwards and deferred tax liabilities are recognized for taxable temporary differences. Temporary differences are the differences between the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases and are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the year in which those temporary differences are
F-12
expected to be recovered or settled. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are adjusted for the effects of changes in tax laws and rates on the date of enactment. Tax credits and other incentives reduce income tax expense in the year the credits are claimed.
Management must assess the need to accrue or disclose uncertain tax positions for proposed potential adjustments from various federal, state and foreign tax authorities who regularly audit the Company in the normal course of business. In making these assessments, management must often analyze complex tax laws of multiple jurisdictions, including many foreign jurisdictions. The accounting guidance prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company records the related interest expense and penalties, if any, as tax expense in the tax provision.
Management must assess the realizability of the Company’s deferred tax assets. In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities (including the impact of available carryback and carry forward periods), projected future taxable income, and tax-planning strategies in making this assessment. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income during the carryforward period are reduced.
The Company has made an accounting policy election to record the U.S. income tax effect of future global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) inclusions in the period in which they arise, rather than establishing deferred taxes with respect to the expected future tax liabilities associated with future GILTI inclusion.
Certain of the Company’s undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries are not permanently reinvested. A liability has been recorded for the deferred taxes on such undistributed foreign earnings. The amount is attributable primarily to the foreign withholding taxes that would become payable should the Company repatriate cash held in its foreign operations.
Earnings per share—The following table reconciles the numerators and denominators used to calculate basic and diluted earnings per share for 2023, 2022 and 2021.
|
|
For the Year Ended December 31 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
(table only in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Numerator (for basic and diluted earnings per share) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net income attributable to CECO Environmental Corp. |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Denominator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Basic weighted-average shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Common stock equivalents arising from stock options and restricted stock awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Options and unvested restricted stock units are included in the computation of diluted earnings per share using the treasury stock method. For 2023, 2022 and 2021, outstanding options and unvested restricted stock units of
Once a restricted stock award vests, it is included in the computation of weighted average shares outstanding for purposes of basic and diluted earnings per share.
Foreign Currency Translation—The functional currencies of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are their local currencies and their books and records are maintained in the local currency. The assets and liabilities of these foreign subsidiaries are translated into United States Dollars (“USD”) based on the end-of period exchange rates and the resultant translation adjustments are reported in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss in Shareholders’ Equity on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Income and expenses are translated into USD at average exchange rates in effect during the period.
Transactions denominated in other than the local currency are remeasured into the local currency and the resulting exchange gains or losses are included in “Other (expense) income, net” line of the Consolidated Statements of Income. Transaction gains (losses) were $
F-13
Accounting Standards Adopted in 2023
On January 1, 2023, the beginning of the Company's fiscal year, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2021-08, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Accounting for Contract Assets and Contract Liabilities from Contracts with Customers, which addresses how an acquirer should recognize and measure revenue contracts acquired in a business combination. The adoption of ASU 2021-08 did not have a material impact on the Company's Consolidated Financial Statements.
Accounting Standards to be Adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which addresses income tax disclosure requirements, primarily around the disclosure of the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of the standard will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which addresses segment disclosure requirements, primarily the disclosure of significant segment expenses. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of the standard will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The Company's financial instruments consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, receivables and certain other assets, and accounts payable, which approximate fair value at December 31, 2023 and 2022, due to their short-term nature or variable, market-driven interest rates.
The fair value of the debt issued under the Credit Facility and joint venture term loan was $
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company had cash and cash equivalents of $
Concentrations of credit risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to credit risk consist principally of cash and cash equivalents, and accounts receivable. The Company maintains cash and cash equivalents with various major financial institutions. The Company perform periodic evaluations of the financial institutions in which its cash is invested. Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade and contract receivables are limited due to the large number of customers and various geographic areas. Additionally, the Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers’ financial condition.
Accounts receivable consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Accounts receivable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Allowance for credit losses |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total accounts receivable |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accounts receivable, net as of the beginning of the prior year period, or January 1, 2022, were $
Balances billed, but not paid by customers under retainage provisions in contracts, amounted to approximately $
F-14
Provision for credit losses was $
Inventories consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Raw materials |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Work in process |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Finished goods |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Obsolescence allowance |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total inventories |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Property, plant and equipment consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Land, building and improvements |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Machinery and equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Property, plant and equipment, gross |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less accumulated depreciation |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Property, plant and equipment, net |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Depreciation expense was $
(table only in thousands) |
|
Engineered Systems |
|
|
Industrial Process Solutions |
|
|
Totals |
|
|||
Balance of goodwill at December 31, 2021 |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Acquisitions |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Foreign currency translation |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Balance of goodwill at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Acquisitions |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign currency translation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance of goodwill at December 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company has an aggregate amount of goodwill acquired of $
The Company’s indefinite lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 consisted of the following:
|
|
Tradenames |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Balance beginning of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Foreign currency adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Balance end of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-15
The Company completes an impairment assessment of its goodwill and indefinite life intangible assets annually as of October 1, or more often as circumstances require, at the reporting unit level.
The Company bases its measurement of the fair value of a reporting unit using a 50/50 weighting of the income method and the market method. The income method is based on a discounted future cash flow approach that uses the significant assumptions of projected revenue, projected operational profit, terminal growth rates, and the cost of capital. Projected revenue and operational profit, and terminal growth rates were determined to be significant assumptions because they are three primary drivers of the projected cash flows in the discounted future cash flow approach. Cost of capital was also determined to be a significant assumption as it is the discount rate used to calculate the current fair value of those projected cash flows. The market method is based on financial multiples of comparable companies and applies a control premium. Significant estimates in the market approach include identifying similar companies with comparable business factors such as size, growth, profitability, risk and return on investment and assessing comparable revenue and operating income multiples in estimating the fair value of a reporting unit. Based on this analysis, the estimated fair value of all of the Company's reporting units exceeded their carrying value as of October 1, 2023. There was
The Company also performed an impairment analysis for all indefinite life intangible assets, which consists of tradenames, as of October 1, 2023. The Company based its measurement of the fair value of the indefinite life intangible assets utilizing the relief from royalty method. The significant assumptions used under the relief from royalty method are projected revenue, royalty rates, terminal growth rates, and the cost of capital. Projected revenue, royalty rates and terminal growth rates were determined to be significant assumptions because they are three primary drivers of the projected royalty cash flows in the relief from royalty method. Cost of capital was also determined to be a significant assumption as it is the discount rate used to calculate the current fair value of those projected royalty cash flows. Changes in any of the significant assumptions used can materially affect the expected cash flows, and such impacts can result in material non-cash impairment charges. Under this approach, the estimated fair value of the indefinite life intangible assets exceeded their carrying value for segments as of the testing date. Accordingly, the Company recognized no impairment charges in its financial results for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
As described above, the fair value measurement methods used in the Company’s goodwill and indefinite life intangible assets impairment analyses utilizes a number of significant unobservable inputs or Level 3 assumptions. These assumptions include, among others, projections of the Company's future operating results, the implied fair value of these assets using an income approach by preparing a discounted cash flow analysis and other subjective assumptions.
The Company’s finite lived intangible assets consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
Cost |
|
|
Accum. |
|
|
Cost |
|
|
Accum. |
|
||||
Technology |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Customer lists |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Tradenames |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Foreign currency adjustments |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total finite life intangible assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Amortization expense of finite life intangible assets was $
Accrued expenses consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Compensation and related benefits |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Accrued warranty |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Contract liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Short-term operating lease liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total accrued expenses |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-16
The activity in the Company’s earnout liability consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Earnout accrued at beginning of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Fair value of earnout at acquisition date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Fair value adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Payments and other |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Earnout accrued at end of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Current portion, recorded within Accrued expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Non-current portion, recorded within Other liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
As additional consideration in the acquisition of Kemco Systems Co., LLC ("Kemco"), the former owners of Kemco are entitled to earn-out payments up to $
As additional consideration in the acquisition of Malvar Engineering Limited, including its subsidiaries Arkanum Management Limited and Wakefield Acoustics Limited (collectively, "Wakefield"), the former owners of Wakefield were entitled to earn-out payments based upon specified financial results through July 31, 2023. Based on projections at the acquisition date, the Company estimated the fair value of the earn-out to be $
As additional consideration in the acquisition of Compass Water Solutions, Inc. ("Compass"), the former owners of Compass were entitled to earn-out payments based upon specified financial results through April 30, 2023. Based on projections at the acquisition date of May 3, 2022, the Company estimated the fair value of the earnout to be $
Debt consisted of the following:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Outstanding borrowings under Credit Facility (defined below) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
– Term loan |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
– Revolving Credit Loan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total outstanding borrowings under Credit Facility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding borrowings under the joint venture term debt |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Unamortized debt discount |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total outstanding borrowings |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Less: current portion |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total debt, less current portion |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Scheduled principal payments under the Credit Facility and joint venture term debt are $
Credit Facility
On December 17, 2021, the Company entered into Amendment No. 2 to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “Credit Facility”). The Credit Facility amended and restated the Company’s prior credit agreement. Pursuant to the Credit Facility, the
F-17
lenders provided a term loan in the aggregate principal amount of $
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, $
At the Company’s option, revolving loans and the term loans accrue interest at a per annum rate based on (a) either the highest of (i) the federal funds rate plus
Interest on Base Rate loans is payable quarterly in arrears on the last day of each calendar quarter and at maturity. Interest on Term SOFR rate loans is payable on the last date of each applicable Interest Period (as defined in the agreement), but in no event less than once every three months and at maturity. The weighted average stated interest rate on outstanding borrowings was
Under the terms of the Credit Facility, the Company is required to maintain certain financial covenants, including the maintenance of a Consolidated Net Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Credit Facility). In the third quarter of 2023, the Company entered into an Elevated Ratio Period resulting in a maximum Consolidated Net Leverage Ratio of
The Company has granted a security interest in substantially all of its assets to secure its obligations pursuant to the Credit Facility. The Company’s obligations under the Credit Facility are guaranteed by the Company’s U.S. subsidiaries and such guaranty obligations are secured by a security interest on substantially all the assets of such subsidiaries, including certain real property. The Company’s obligations under the Credit Agreement may also be guaranteed by the Company’s material foreign subsidiaries to the extent no adverse tax consequences would result to the Company.
In connection with the Credit Facility, the Company paid $
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company was in compliance with all related financial and other restrictive covenants under the Credit Facility.
Joint Venture Debt
On March 7, 2022, the Company's Effox-Flextor-Mader, Inc. joint venture ("EFM JV") entered into a loan agreement secured by the assets of the EFM JV in the aggregate principal amount of $
F-18
Foreign Debt
Share-Based Compensation
The Company’s 2021 Equity and Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2021 Plan”) was approved by the Company’s stockholders on May 25, 2021 which replaced the 2017 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2017 Plan”).
On July 6, 2020, in connection with the appointment of the Chief Executive Officer, the Company granted its Chief Executive Officer approximately
Share-based compensation expense for stock options and restricted stock awards under these plans was $
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) was approved by shareholders on June 11, 2020. The ESPP is administered by the Compensation Committee. The ESPP allows employees to purchase shares of common stock at a
The aggregate maximum number of shares of the Company’s common stock that may be granted under the ESPP is
The Company recognized employee stock purchase plan expense of $
Stock Options
The estimated weighted-average fair value of stock options was determined using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model at the grant date based on the following assumptions:
Expected Volatility: The Company utilizes a volatility factor based on the Company’s historical stock prices for a period of time equal to the expected term of the stock option utilizing weekly price observations.
F-19
Expected Term: Due to limited historical exercise data, the Company utilizes the simplified method of determining the expected term based on the vesting schedules and terms of the stock options.
Risk-Free Interest Rate: The risk-free interest rate factor utilized is based upon the implied yields currently available on U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues over the expected term of the stock options.
The fair value of stock options is recorded as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting periods (which approximates the requisite service period) of the options and forfeitures are accounted for when they occur.
Information related to all stock options under the 2021 Plan, 2017 Plan and 2007 Plan, and the 2020 Inducement Awards for 2023, 2022 and 2021 is shown in the tables below:
(Shares in thousands) |
|
Shares |
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Weighted |
|
Aggregate |
|
|||
Outstanding at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Forfeitures |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding and expected to vest at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
(Shares in thousands) |
|
Shares |
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Weighted |
|
Aggregate |
|
|||
Outstanding at December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Forfeitures |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding and expected to vest at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
(Shares in thousands) |
|
Shares |
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
Weighted |
|
Aggregate |
|
|||
Outstanding at December 31, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Forfeitures |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Exercised |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding and expected to vest at December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
The Company received $
Restricted Stock Awards
Information related to restricted stock awards under the 2021 Plan, 2017 Plan, 2007 Plan, and the 2020 Inducement Awards for 2023, 2022 and 2021 is shown in the table below. The fair value of restricted stock awards is based on the price of the stock in the open market on the date of the grant, and the fair value of performance-based restricted stock units is determined by using the Monte Carlo
F-20
valuation model. The fair value of the restricted stock awards is recorded as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the vesting periods of the awards and forfeitures are accounted for when they occur.
(Shares in thousands) |
|
Shares |
|
|
Weighted |
|
||
Nonvested at December 31, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Nonvested at December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Nonvested at December 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Nonvested at December 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||
The fair value of awards vested and released during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $
Unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested shares of stock options, restricted stock and performance units was $
Common Stock Repurchase
On May 10, 2022, the Company's Board of Directors authorized a share repurchase program under which the Company may purchase up to $
On August 3, 2021, the Company's Board of Directors authorized a share repurchase program under which CECO may purchase up to $
Dividends
The Company's dividend policy and the payment of cash dividends under that policy are subject to the Board of Director’s continuing determination that the dividend policy and the declaration of dividends are in the best interest of the Company’s stockholders. Future dividends and the dividend policy may be changed at the Company’s discretion at any time. Payment of dividends is also subject to the continuing compliance with financial covenants under the Credit Facility. The Company has not paid a cash dividend on its common stock in any of the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 or 2021.
The Company sponsors a non-contributory defined benefit pension plan for certain union employees. The accrual of future benefits for all participants who are non-union employees was frozen effective December 31, 2008. The plan is funded in accordance with the funding requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974.
F-21
The following tables set forth the plan changes in benefit obligations, plan assets and funded status on the measurement dates:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Change in projected benefit obligation: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Actuarial loss (gain) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Benefits paid |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Projected benefit obligation at end of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Change in plan assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Actual return on plan assets |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Benefits paid |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Fair value of plan assets at end of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Funded status at end of year |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations for the year ended December 31: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Discount rate |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
|||
The funded status as of December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, was $
The details of net periodic benefit cost for pension benefits included in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Income are as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Interest cost |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Expected return on plan assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Amortization of net loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net periodic benefit (expense) income |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive income:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net (gain) loss |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Amortization of net actuarial loss |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Total recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost and other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit costs
|
|
December 31, |
||||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
|
2021 |
Discount Rate |
|
|
|
|||
Expected return on assets |
|
|
|
|||
The basis of the long-term rate of return assumption reflects the current asset mix for the pension plan of approximately
Benefits under the plan is not based on wages and, therefore, future wage adjustments have no effect on the projected benefit obligation.
F-22
During 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Company updated the mortality tables (RP-2021 Total Mortality Table, RP-2020 Total Mortality Table, and RP-2019 Total Mortality Table for each respective year) in the underlying assumptions used to determine the benefit obligation.
Pension plan assets are invested in trusts comprised primarily of investments in various debt and equity funds. A fiduciary committee establishes the target asset mix and monitors asset performance. The expected rate of return on assets includes the determination of a real rate of return for equity and fixed income investment applied to the portfolio based on their relative weighting, increased by an underlying inflation rate.
The Company's
|
|
Target |
|
Percentage of |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Asset Category: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|||
Equity securities |
|
|
|
|||
Debt securities |
|
|
|
|||
Total |
|
|
|
|||
Estimated pension plan cash obligations are $
Fair Value Measurements of Pension Plan Assets
Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for pension assets measured at fair value:
Cash and cash equivalents: Cash and cash equivalents consist primarily of cash on deposit in money market funds. Cash and cash equivalents are stated at cost, which approximates fair value.
Equity securities: Equity securities consist of various managed funds that invest primarily in common stocks. These securities are valued at the net asset value of shares held by the plan at year end. The net asset value is calculated based on the underlying shares and investments held by the funds.
Debt securities: Debt securities consist of U.S. government and agency securities, corporate bonds and notes, and managed funds that invest in fixed income securities. U.S governmental and agency securities are valued at closing prices reported in the active market in which the individual securities are traded. Corporate bonds and notes are valued using market inputs including benchmark yields, reported trades, broker/dealer quotes, issuer spreads, two-sided markets, benchmark securities, bids, offers and reference data including market research publications. Inputs may be prioritized differently at certain times based on market conditions. Managed funds are valued at the net asset value of shares held by the plan at year end. The net asset value is calculated based on the underlying investments held by the fund.
The preceding methods described may produce a fair value calculation that may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. Furthermore, although the Company believes its valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with other market participants, the use of different methodologies or assumptions to determine the fair value of certain financial instruments could result in a different fair value measurement at the reporting date.
The Company’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment and may affect the valuation of the fair value of assets and liabilities and their placement within the fair value hierarchy levels.
The levels assigned to the defined benefit plan assets as of December 31, 2023, are summarized in the tables below:
(table only in thousands) |
|
Level 1 |
|
|
Level 2 |
|
|
Level 3 |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
Pension assets, at fair value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Debt securities |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
F-23
The levels assigned to the defined benefit plan assets as of December 31, 2022, are summarized in the tables below:
(table only in thousands) |
|
Level 1 |
|
|
Level 2 |
|
|
Level 3 |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
Pension assets, at fair value: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Equity securities |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Debt securities |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Total assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The Company contributes to a number of multiemployer defined benefit pension plans under the terms of collective-bargaining agreements that cover its union-represented employees. The risks of participating in these multiemployer plans are different from single-employer plans in the following aspects:
The Company’s participation in these plans for the year ended December 31, 2023, is outlined in the table below. The “EIN/Pension Plan Number” column provides the Employer Identification Number and the three-digit plan number, if applicable. Unless otherwise noted, the most recent Pension Protection Act zone status available in 2023 is for the plan’s year-end at December 31, 2022. The zone status is based on information that the Company received from the plan and is certified by the plan’s actuary. Among other factors, plans in the red zone are generally less than 65% funded, plans in the yellow zone are less than 80% funded, and plans in the green zone are at least 80% funded. The “FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented” column indicates plans for which a financial improvement plan (FIP) or a rehabilitation plan (RP) is either pending or has been implemented. The last column lists the expiration date(s) of the collective-bargaining agreement(s) to which the plans are subject.
Pension Fund |
|
EIN/Pension |
|
Pension |
|
FIF/RP Status |
|
Surcharge |
|
Expiration |
Sheet Metal Workers’ National Pension Fund |
|
|
|
FIF: Yes - |
|
|
||||
Sheet Metal Workers Local 224 Pension Plan |
|
|
|
FIF: Yes - Implemented |
|
|
n/a |
|||
Sheet Metal Workers Local No. 177 Pension Fund |
|
|
|
|
|
Kirk and Blum was listed in the Sheet Metal Workers Local No. 177 Pension Fund’s Form 5500 as providing more than five percent of total contributions for the year ended December 31, 2022. The Company was not listed in any of the other plans’ Forms 5500 as providing more than five percent of the total contributions for the plans and plan years. At the date the financial statements were issued, Forms 5500 were not available for the plan years ended December 31, 2023.
The Company has no current intention of withdrawing from any plan and, therefore,
Amounts charged to pension expense under the above plans including the multi-employer plans totaled $
The Company has a 401(k) savings retirement plan for employees of certain of its subsidiaries.
F-24
The lease accounting guidance under ASC 842 establishes a right-of-use (“ROU”) model that requires a lessee to record a ROU asset and a lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with terms longer than 12 months. The Company's leasing activity is primarily related to buildings used for manufacturing, warehousing, sales, and administrative activities. The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Many of the Company's lease agreements contain renewal options; however, the Company does not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities for renewal periods unless it is determined that lease renewal is reasonably certain at inception or when a triggering event occurs. Some of the Company's lease agreements contain rent escalation clauses, free-rent periods, or other lease concessions. The Company recognizes its minimum rental expense on a straight-line basis based on the fixed components of a lease arrangement. Variable lease costs represent amounts that are not fixed in nature and are not tied to an index or rate, and are recognized as incurred. The Company's variable lease costs are not material.
In determining its ROU assets and lease liabilities, the Company applies a discount rate to the minimum lease payments within each lease agreement. ASC 842 requires the Company to use the rate of interest that a lessee would have to pay to borrow on a collateralized basis over a similar term an amount equal to the lease payments in a similar economic environment. When the Company cannot readily determine the discount rate implicit in the lease agreement, it utilizes its fully collateralized incremental borrowing rate. To estimate its specific incremental borrowing rates the Company considers, among other factors, interest rates on its existing credit facilities, risk-free rates, the types of assets being leased, and the term of the leases.
The components of lease expense were as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Operating lease cost (a) |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Finance lease cost: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Amortization of right-of-use assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Interest on lease liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total finance lease cost |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total lease cost |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
(a) includes variable lease costs which are immaterial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases was as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating cash flows from operating leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Operating cash flows from finance leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Financing cash flows from finance leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Right of use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
F-25
Supplemental balance sheet information related to leases was as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Operating leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Right-of-use assets from operating leases |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Operating lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total operating lease liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Finance leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total finance lease liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Weighted-average remaining lease term were as follows:
|
|
December 31, |
||
|
|
2023 |
|
2022 |
Operating leases |
|
|
||
Finance leases |
|
|
||
Weighted-average discount rate |
|
|
|
|
Operating leases |
|
|
||
Finance leases |
|
|
||
As of December 31, 2023, maturities of lease liabilities were as follows:
(table only in thousands) |
|
Operating Leases |
|
|
Finance Leases |
|
||
2024 |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
2025 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2026 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2027 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2028 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Thereafter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total minimum lease payments |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Less imputed interest |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Lease liability |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Legal Proceedings
Asbestos cases
The Company's subsidiary, Met-Pro, beginning in 2002 began to be named in asbestos-related lawsuits filed against a large number of industrial companies including, in particular, those in the pump and fluid handling industries. In management’s opinion, the complaints typically have been vague, general and speculative, alleging that Met-Pro, along with the numerous other defendants, sold unidentified asbestos-containing products and engaged in other related actions which caused injuries (including death) and loss to the plaintiffs. Counsel has advised that more recent cases typically allege more serious claims of mesothelioma. The Company’s insurers have hired attorneys who, together with the Company, are vigorously defending these cases. Many cases have been dismissed after the plaintiff fails to produce evidence of exposure to Met-Pro’s products. In those cases, where evidence has been produced, the Company’s experience has been that the exposure levels are low and the Company’s position has been that its products were not a cause of death, injury or loss. The Company has been dismissed from or settled a large number of these cases. Cumulative settlement
F-26
payments from 2002 through December 31, 2023 for cases involving asbestos-related claims were $
Based upon the most recent information available to the Company regarding such claims, there were a total of 313 cases pending against the Company as of December 31, 2023 (with Illinois, New York, Pennsylvania and West Virginia having the largest number of cases), as compared with
Other
The Company is also involved in legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of its business.
The final outcome and impact of open matters, and related claims and investigations that may be brought in the future, are subject to many variables, and cannot be predicted. In accordance with ASC 450, “Contingencies,” and related guidance, the Company records reserves for estimated losses relating to claims and lawsuits when available information indicates that a loss is probable and the amount of the loss, or range of loss, can be reasonably estimated. The Company expenses legal costs as they are incurred.
The Company is
Income before income taxes was generated in the United States and globally as follows:
(in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Domestic |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Certain of the Company’s undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries are not permanently reinvested, as management intends to repatriate foreign-held cash as needed to meet domestic cash needs for operating, investing, and financing activities. A liability of $
Income tax expense (benefit) consisted of the following for the years ended December 31:
(in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Federal |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
State |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deferred: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Federal |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
State |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Foreign |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
F-27
The income tax expense (benefit) differs from the statutory rate due to the following:
(in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Tax expense at statutory rate |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Increase (decrease) in tax resulting from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
State income tax, net of federal benefit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Other permanent differences |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
||
Impact of rate differences and adjustments |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
United States tax credits and incentives |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Foreign tax credits and incentives |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Change in valuation allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Foreign withholding taxes on repatriation of foreign earnings |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Earnout expense (income) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Equity compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Excess compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Provision-to-return adjustments |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Investment in joint venture |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net effect GILTI and FDII |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Deferred income taxes reflect the future tax consequences of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes and tax credit carry forwards. The net deferred tax liabilities consisted of the following at December 31:
(in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Gross deferred tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued expenses |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Reserves on assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Share-based compensation awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Minimum pension |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net operating loss carry-forwards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Tax credit carry-forwards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Investment in joint venture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Research and development costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total gross deferred tax assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Valuation allowances |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gross deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Depreciation |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Goodwill and intangibles |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Prepaid expenses and inventory |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Withholding tax on unremitted foreign earnings |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Leases |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Revenue recognition |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Other |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net deferred tax liabilities |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
As of December 31, 2023, state and local net operating loss carry forwards total $
F-28
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities (including the impact of available carryback and carry forward periods), projected future taxable income, and tax-planning strategies in making this assessment. Based on this assessment, management believes it is more likely than not that the Company will realize the benefits of these deductible differences, net of the existing valuation allowances at December 31, 2023. The amount of the deferred tax assets considered realizable, however, could be reduced in the near term if estimates of future taxable income during the carryforward period are reduced.
The Company accounts for uncertain tax positions pursuant to FASB ASC Topic 740. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than
(in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Balance as of January 1, |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Additions for tax positions taken in prior years |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Balance as of December 31, |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense. The reserve for uncertain tax positions includes $
Kemco Systems Co., LLC
On August 23, 2023, the Company acquired
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including accounts receivable of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Right-of-use assets from operating leases |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Other liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
The Company acquired technology, customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Kemco accounted for $
F-29
Transcend Solutions
On March 31, 2023, the Company acquired
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including cash of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
The Company acquired technology, customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Transcend accounted for $
Malvar Engineering Limited
On January 10, 2023, the Company acquired
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including accounts receivable of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred income tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
The Company acquired customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Wakefield accounted for $
F-30
DS21 Co., Ltd.
On September 19, 2022, the Company acquired
DS21 is a South Korean-based design and manufacturing firm specializing in innovative water and wastewater treatment solutions. The addition of DS21 advances the Company's leadership position in niche oily water and produced water treatment, demineralization water treatment and ultra-pure water supply applications within the Company's Engineered Systems segment.
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including cash of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Other liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company acquired customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
Western Air Ducts Ltd.
On June 22, 2022, the Company acquired
Western Air Ducts is a leading European supplier of dust and fume extraction solutions, providing consultation, design, manufacturing, installation, and service. The acquisition diversifies and expands the Company's industrial air product offerings within the Industrial Process Solutions segment.
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including cash of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred income tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company acquired customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
Compass Water Solutions, Inc.
On May 3, 2022, the Company acquired
F-31
Compass is a leading global supplier of membrane-based industrial water and wastewater treatment systems that help customers achieve regulatory compliance of water discharge at the lowest lifecycle cost. The acquisition diversifies and expands the Company's industrial water product offerings within the Engineered Systems segment.
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including cash of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred income tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company acquired customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
General Rubber LLC
On March 7, 2022, the Company, through the EFM JV, acquired
GRC engineers and manufactures non-metallic expansion joints and flow control products including rubber expansion joints, ducting expansion joints, and industrial pinch and duck bill valves, serving the industrial water and wastewater markets. The acquisition diversifies and expands the EFM JV product offerings within the Engineered Systems segment.
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
Current assets (including cash of $ |
|
$ |
|
|
Property and equipment |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Intangible - finite life |
|
|
|
|
Total assets acquired |
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities assumed |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred income tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Net assets acquired |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Company acquired customer lists and tradename intangible assets valued at $
The Company has finalized the valuation of assets acquired and liabilities assumed related to the 2022 acquisitions. The purchase accounting related to the 2023 acquisitions is subject to final adjustment, primarily for the valuation of intangible assets pending final valuation results for such assets and tax balances for the further assessment of the acquiree’s tax positions. These preliminary estimates and assumptions could change significantly during the purchase price measurement period as the Company finalizes the valuation of assets acquired and liabilities assumed. These changes could result in material variances in the Company's future financial results, including variances in the estimated purchase price, fair values recorded and expenses associated with these items.
Goodwill recognized represents value the Company expects to be created by combining the various operations of the acquired businesses with the Company’s operations, including the expansion into markets within existing business segments, access to new customers and potential cost savings and synergies. Goodwill related to these acquisitions is not deductible for tax purposes.
F-32
Acquisition and integration expenses on the Consolidated Statements of Income are related to acquisition activities, which include retention, legal, accounting, banking, and other expenses.
The following unaudited pro forma financial information represents the Company’s results of operations as if these acquisitions had occurred at the beginning of the fiscal year prior to the acquisition:
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands, except per share data) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Net income attributable to CECO Environmental Corp. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
||
Earnings per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
The pro forma results have been prepared for informational purposes only and include adjustments to amortize acquired intangible assets with finite life, reflect additional interest expense on debt used to fund the acquisition, and to record the income tax consequences of the pro forma adjustments. These pro forma results do not purport to be indicative of the results of operations that would have occurred had the purchase been made as of the beginning of the periods presented or of the results of operations that may occur in the future.
The Company’s operations are organized and reviewed by management along its product lines or end markets that the segment serves and are presented in
The Company’s reportable segments are organized as groups of similar products and services, as described as follows:
Engineered Systems segment: The Company's Engineered Systems segment serves the power generation, hydrocarbon processing, water/wastewater treatment, oily water separation and treatment, marine and naval vessels, and midstream oil and gas sectors. The Company seeks to address the global demand for environmental and equipment protection solutions with its highly engineered platforms including emissions management, fluid bed cyclones, thermal acoustics, separation and filtration, and dampers and expansion joints.
Industrial Process Solutions segment: The Company's Industrial Process Solutions segment serves the broad industrial sector with solutions for air pollution and contamination control, fluid handling, and process filtration in applications such as aluminum beverage can production, automobile production, food and beverage processing, semiconductor fabrication, electronics production, steel and aluminum mill processing, wood manufacturing, desalination, and aquaculture markets. The Company assists customers in maintaining clean and safe operations for employees, reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste for customers, and meeting regulatory standards for toxic emissions, fumes, volatile organic compounds, and odor elimination through its platforms including duct fabrication and installation, industrial air, and fluid handling.
The financial segment information is as follows:
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Net Sales (less intra-, inter-segment sales) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Income from Operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Corporate and Other (1) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income from operations |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
F-33
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Property and Equipment Additions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Corporate and Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Property and equipment additions |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|||
Depreciation and Amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Corporate and Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Depreciation and amortization |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Identifiable Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Corporate and Other (2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Identifiable assets |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
2023 |
|
|
2022 |
|
||
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Goodwill |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Intra-segment and Inter-segment Revenues
The Company has divisions that sell to each other within segments (intra-segment sales) and between segments (inter-segment sales), as follows:
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2023 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less Inter-Segment Sales |
|
|
||||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
Total Sales |
|
|
Intra-Segment |
|
|
Industrial Process Solutions |
|
|
Engineered Systems |
|
|
Net Sales to |
|
|||||
Net Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
- |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Total net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||
F-34
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2022 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less Inter-Segment Sales |
|
|
||||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
Total Sales |
|
|
Intra-Segment |
|
|
Industrial Process Solutions |
|
|
Engineered Systems |
|
|
Net Sales to |
|
|||||
Net Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Total net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less Inter-Segment Sales |
|
|
||||||||||
(table only in thousands) |
|
Total Sales |
|
|
Intra-Segment |
|
|
Industrial Process Solutions |
|
|
Engineered Systems |
|
|
Net Sales to |
|
|||||
Net Sales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Engineered Systems segment |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Industrial Process Solutions segment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Total net sales |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
||
For 2023, 2022, and 2021, sales outside the United States accounted for approximately
F-35