File No. 2-40341
811-2192
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM N-1A
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933 [X]
Pre-Effective Amendment No. [__]
Post-Effective Amendment No. 70 [X]
and/or
REGISTRATION STATEMENT UNDER THE INVESTMENT COMPANY ACT OF 1940 [X]
Amendment No. 70 [X]
(Check appropriate box or boxes.)
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Inc.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Charter)
c/o The Dreyfus Corporation
200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) (Zip Code)
Registrant's Telephone Number, including Area Code: (212) 922-6000
John Pak, Esq.
200 Park Avenue
New York, New York 10166
(Name and Address of Agent for Service)
It is proposed that this filing will become effective (check appropriate box)
__ immediately upon filing pursuant to paragraph (b)
X on October 1, 2014 pursuant to paragraph (b)
____ days after filing pursuant to paragraph (a)(1)
__ on (date) pursuant to paragraph (a)(1)
____ days after filing pursuant to paragraph (a)(2)
__ on (date) pursuant to paragraph (a)(2) of Rule 485
If appropriate, check the following box:
__ this post-effective amendment designates a new effective date for a previously filed post-effective amendment.

The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Inc.
|
|
Prospectus October 1, 2014 |
||
|
Class |
Ticker |
|
A |
DTCAX |
|
C |
DTCCX |
|
I |
DRTCX |
|
Z |
DRTHX |
|
As with all mutual funds, the Securities and Exchange Commission has not approved or disapproved |
|
Contents
See back cover.
Fund Summary
The fund seeks to provide capital growth, with current income as a secondary goal.
This table describes the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shares of the fund. You may qualify for sales charge discounts if you and your family invest, or agree to invest in the future, at least $50,000 in certain funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. More information about these and other discounts is available from your financial professional and in the Shareholder Guide section beginning on page 8 of this prospectus and in the How to Buy Shares section and the Additional Information About How to Buy Shares section beginning on page II-1 and page III-1, respectively, of the fund's Statement of Additional Information.
|
Shareholder Fees (fees paid directly from your investment) | ||||
|
Class A |
Class C |
Class I |
Class Z | |
|
Maximum sales charge (load) imposed on purchases |
5.75 |
none |
none |
none |
|
Maximum deferred sales charge (load) |
none* |
1.00 |
none |
none |
|
Annual Fund Operating Expenses (expenses that you pay each year as percentage of the value of your investment) | ||||
|
Class A |
Class C |
Class I |
Class Z | |
|
Management fees |
.75 |
.75 |
.75 |
.75 |
|
Distribution (12b-1) fees |
none |
.75 |
none |
none |
|
Other expenses (including shareholder services fees) |
.47 |
.49 |
.16 |
.26 |
|
Total annual fund operating expenses |
1.22 |
1.99 |
.91 |
1.01 |
*Class A shares bought without an initial sales charge as part of an investment of $1 million or more may be charged a deferred sales charge of 1.00% if redeemed within one year.
Example
The Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the fund's operating expenses remain the same. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
|
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
|
Class A |
$692 |
$940 |
$1,207 |
$1,967 |
|
Class C |
$302 |
$624 |
$1,073 |
$2,317 |
|
Class I |
$93 |
$290 |
$504 |
$1,120 |
|
Class Z |
$103 |
$322 |
$558 |
$1,236 |
You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares:
|
1 Year |
3 Years |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
|
Class A |
$692 |
$940 |
$1,207 |
$1,967 |
|
Class C |
$202 |
$624 |
$1,073 |
$2,317 |
|
Class I |
$93 |
$290 |
$504 |
$1,120 |
|
Class Z |
$103 |
$322 |
$558 |
$1,236 |
1
Portfolio Turnover
The fund pays transaction costs, such as commissions, when it buys and sells securities (or "turns over" its portfolio). A higher portfolio turnover may indicate higher transaction costs and may result in higher taxes when fund shares are held in a taxable account. These costs, which are not reflected in annual fund operating expenses or in the Example, affect the fund's performance. During the most recent fiscal year, the fund's portfolio turnover rate was 34.37% of the average value of its portfolio.
To pursue its goals, the fund, under normal circumstances, invests at least 80% of its net assets in the common stocks of companies that, in the opinion of the fund's management, meet traditional investment standards and conduct their business in a manner that contributes to the enhancement of the quality of life in America.
The fund's investment strategy combines a disciplined investment process that consists of computer modeling techniques, fundamental analysis and risk management with a social investment process. In selecting stocks, the portfolio managers begin by using computer models to identify and rank stocks within an industry or sector, based on several characteristics, including value, growth and financial profile.
Next, based on fundamental analysis, the portfolio managers designate the most attractive of the higher ranked securities as potential purchase candidates, drawing on a variety of sources, including company management and internal as well as Wall Street research.
The portfolio managers then evaluate each stock to determine whether the company enhances the quality of life in America by considering its record in the areas of protection and improvement of the environment and the proper use of our natural resources, occupational health and safety, consumer protection and product purity and equal employment opportunity.
The portfolio managers then further examine the companies determined to be eligible for purchase, by industry or sector, and select investments from those companies the portfolio managers consider to be the most attractive based on financial considerations.
An investment in the fund is not a bank deposit. It is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) or any other government agency. It is not a complete investment program. The fund's share price fluctuates, sometimes dramatically, which means you could lose money.
· Risks of stock investing. Stocks generally fluctuate more in value than bonds and may decline significantly over short time periods. There is the chance that stock prices overall will decline because stock markets tend to move in cycles, with periods of rising prices and falling prices. The market value of a stock may decline due to general market conditions or because of factors that affect the particular company or the company's industry.
· Social investment risk. A socially responsible investment criteria may limit the number of investment opportunities available to the fund, and as a result, at times the fund's returns may be lower than those funds that are not subject to such special investment considerations.
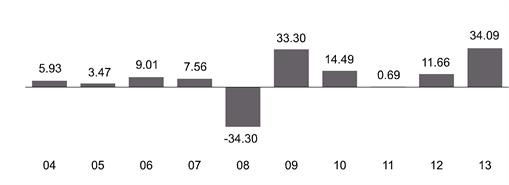
The following bar chart and table provide some indication of the risks of investing in the fund. The bar chart shows changes in the performance of the fund's Class Z shares from year to year. The table compares the average annual total returns of the fund's shares to those of a broad measure of market performance. The fund's past performance (before and after taxes) is not necessarily an indication of how the fund will perform in the future. Sales charges, if any, are not reflected in the bar chart, and if those charges were included, returns would have been less than those shown. More recent performance information may be available at www.dreyfus.com.
2
|
Year-by-Year Total Returns as of 12/31 each year (%) Class Z | |
|
|
Best Quarter Worst Quarter |
The year-to-date total return of the fund's Class Z shares as of June 30, 2014 was 8.36%.
After-tax performance is shown only for Class Z shares. After tax performance of the fund's other share classes will vary. After-tax returns are calculated using the historical highest individual federal marginal income tax rates, and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on the investor's tax situation and may differ from those shown, and the after-tax returns shown are not relevant to investors who hold their shares through tax-deferred arrangements such as 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts.
|
Average Annual Total Returns (as of 12/31/13) | |||
|
1 Year |
5 Years |
10 Years | |
|
Class Z returns before taxes |
34.09% |
18.13% |
6.86% |
|
Class Z returns after taxes on distributions |
32.83% |
17.81% |
6.70% |
|
Class Z returns after taxes on distributions and sale of fund shares |
20.07% |
15.91% |
5.99% |
|
Class A returns before taxes |
26.11% |
16.44% |
5.95% |
|
Class C returns before taxes |
31.79% |
17.00% |
5.80% |
|
Class I returns before taxes |
34.26% |
18.30% |
6.93% |
|
S&P 500 Comp Stock Price Index |
32.37% |
17.93% |
7.40% |
The fund's investment adviser is The Dreyfus Corporation (Dreyfus). Investment decisions for the fund are made by the Active Equity Team of Mellon Capital Management Corporation (Mellon Capital), an affiliate of Dreyfus. The team members are C. Wesley Boggs, Warren Chiang, CFA and Ronald Gala, CFA, each of whom serves as portfolio manager of the fund. The team has managed the fund since May 2012. Mr. Boggs is a vice president and senior portfolio manager at Mellon Capital. Mr. Chiang is a managing director of active equity strategies at Mellon Capital. Mr. Gala is a director and senior portfolio manager at Mellon Capital. Each member of the team is also an employee of Dreyfus.
In general, for each share class, the fund's minimum initial investment is $1,000 and the minimum subsequent investment is $100. You may sell (redeem) your shares on any business day by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or by visiting www.dreyfus.com. If you invested in the fund through a third party, such as a bank, broker-dealer or financial adviser, or in a 401(k) or other retirement plan, you may mail your request to sell shares to Dreyfus Institutional Department, P.O. Box 9882, Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8082. If you invested directly through the fund, you may mail your request to sell shares to Dreyfus Shareholder Services, P.O. Box 9879, Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8079. If you are an Institutional Direct accountholder, please contact your BNY Mellon relationship manager for instructions.
The fund's distributions are taxable as ordinary income or capital gains, except when your investment is through an IRA, 401(k) plan or other tax-advantaged investment plan (in which case you may be taxed upon withdrawal of your investment from such account).
3
If you purchase shares through a broker-dealer or other financial intermediary (such as a bank), the fund and its related companies may pay the intermediary for the sale of fund shares and related services. These payments may create a conflict of interest by influencing the broker-dealer or other intermediary and your salesperson to recommend the fund over another investment. Ask your salesperson or visit your financial intermediary's website for more information.
4
Fund Details
The fund seeks to provide capital growth, with current income as a secondary goal. To pursue its goals, the fund, under normal circumstances, invests at least 80% of its net assets in the common stocks of companies that, in the opinion of the fund's management, meet traditional investment standards determined as described below and conduct their business in a manner that contributes to the enhancement of the quality of life in America.
The fund's investment strategy combines a disciplined investment process that consists of computer modeling techniques, fundamental analysis and risk management with a social investment process. In selecting stocks, the portfolio managers begin by using computer models to identify and rank stocks within an industry or sector, based on several characteristics, including:
· value, or how a stock is priced relative to its perceived intrinsic worth
· growth, in this case the sustainability or growth of earnings
· financial profile, which measures the financial health of the company
Next, based on fundamental analysis, the portfolio managers designate the most attractive of the higher ranked securities as potential purchase candidates, drawing on a variety of sources, including company management and internal as well as Wall Street research.
The portfolio managers manage risk by diversifying across companies, industries and sectors, seeking to dilute the potential adverse impact from a decline in value of any one stock, industry or sector.
The portfolio managers then evaluate each stock considered to be a potential purchase candidate, by industry or sector, to determine whether the company enhances the quality of life in America by considering its record in the areas of:
· protection and improvement of the environment and the proper use of our natural resources
· occupational health and safety
· consumer protection and product purity
· equal employment opportunity
The portfolio managers use publicly available information, including reports prepared by "watchdog" groups and governmental agencies, as well as information obtained from research vendors, the media and the companies themselves, to assist them in the social screening process. Because there are few generally accepted standards for the portfolio managers to use in the evaluation, the portfolio managers will determine which research tools to use. The portfolio managers do not currently examine:
· corporate activities outside the U.S.
· nonbusiness activities
· secondary implications of corporate activities (such as the activities of a client or customer of the company being evaluated)
Consistent with its consumer protection screen, the fund will not purchase shares in a company that manufactures tobacco products.
If the portfolio managers determine that a company fails to meet the fund's social criteria, the stock will not be purchased, or if it is already owned, it will be sold as soon as reasonably possible, consistent with the best interests of the fund. If the portfolio managers' assessment does not reveal a negative pattern of conduct in these social areas, the company's stock is eligible for purchase or retention.
The portfolio managers then further examine the companies determined to be eligible for purchase, by industry or sector, and select investments from those companies the portfolio managers consider to be the most attractive based on financial considerations. If there is more than one company to choose from, the portfolio managers can select stocks of
5
companies that are considered to have records that exhibit positive accomplishments in the fund's areas of social concern.
The fund normally focuses on large-cap growth stocks. The portfolio managers may emphasize different types of growth-oriented stocks (such as those with pure growth characteristics or those that also have favorable value characteristics) and different market capitalizations within the large-capitalization range (such as mega cap or the low end of the large-capitalization range) as market conditions warrant. The fund also may invest in value-oriented stocks, mid-cap stocks and small-cap stocks. The fund also may invest in common stocks of foreign companies whose U.S. operations are evaluated in accordance with the social screens set forth above.
The fund also typically sells a stock when the portfolio managers believe there is a more attractive alternative, the stock's valuation is excessive or there are deteriorating fundamentals, such as a loss of competitive advantage, a failure in management execution or deteriorating capital structure.
An investment in the fund is not a bank deposit. It is not insured or guaranteed by the FDIC or any other government agency. It is not a complete investment program. The value of your investment in the fund will fluctuate, sometimes dramatically, which means you could lose money.
· Risks of stock investing. Stocks generally fluctuate more in value than bonds and may decline significantly over short time periods. There is the chance that stock prices overall will decline because stock markets tend to move in cycles, with periods of rising prices and falling prices. The market value of a stock may decline due to general market conditions that are not related to the particular company, such as real or perceived adverse economic conditions, changes in the general outlook for corporate earnings, changes in interest or currency rates, or adverse investor sentiment generally. A security's market value also may decline because of factors that affect the particular company, such as management performance, financial leverage, and reduced demand for the company's products or services, or factors that affect the company's industry, such as labor shortages or increased production costs and competitive conditions within an industry.
· Social investment risk. A socially responsible investment criteria may limit the number of investment opportunities available to the fund, and as a result, at times the fund's returns may be lower than those funds that are not subject to such special investment considerations.
In addition to the principal risks described above, the fund is subject to the following additional risks that are not anticipated to be principal risks of investing in the fund:
· Growth stock risk. Investors often expect growth companies to increase their earnings at a certain rate. If these expectations are not met, investors can punish the stocks inordinately, even if earnings do increase. In addition, growth stocks may lack the dividend yield that may cushion stock prices in market downturns.
· Value stock risk. Value stocks involve the risk that they may never reach their expected full market value, either because the market fails to recognize the stock's intrinsic worth or the expected value was misgauged. They also may decline in price even though in theory they are already undervalued.
· Market sector risk. The fund may significantly overweight or underweight certain companies, industries or market sectors, which may cause the fund's performance to be more or less sensitive to developments affecting those companies, industries or sectors.
· Other potential risks. The fund may lend its portfolio securities to brokers, dealers and other financial institutions. In connection with such loans, the fund will receive collateral from the borrower equal to at least 100% of the value of loaned securities. If the borrower of the securities fails financially, there could be delays in recovering the loaned securities or exercising rights to the collateral.
Under adverse market conditions, the fund could invest some or all of its assets in U.S. Treasury securities and money market securities. Although the fund would do this for temporary defensive purposes, it could reduce the benefit from any upswing in the market. During such periods, the fund may not achieve its investment objectives.
The investment adviser for the fund is The Dreyfus Corporation, 200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166. Founded in 1947, Dreyfus manages approximately $253 billion in 167 mutual fund portfolios. For the past fiscal year, the fund paid Dreyfus a management fee at the annual rate of 0.75% of the fund's average daily net assets. A discussion regarding the basis for the board's approving the fund's management agreement with Dreyfus is available in the fund's semiannual report for the six-month period ended November 30, 2013. Dreyfus is the primary mutual fund business of
6
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (BNY Mellon), a global financial services company focused on helping clients manage and service their financial assets, operating in 35 countries and serving more than 100 markets. BNY Mellon is a leading investment management and investment services company, uniquely focused to help clients manage and move their financial assets in the rapidly changing global marketplace. BNY Mellon has $28.5 trillion in assets under custody and administration and $1.6 trillion in assets under management. BNY Mellon is the corporate brand of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation. BNY Mellon Investment Management is one of the world's leading investment management organizations, and one of the top U.S. wealth managers, encompassing BNY Mellon's affiliated investment management firms, wealth management services and global distribution companies. Additional information is available at www.bnymellon.com.
The Dreyfus asset management philosophy is based on the belief that discipline and consistency are important to investment success. For each fund, Dreyfus seeks to establish clear guidelines for portfolio management and to be systematic in making decisions. This approach is designed to provide each fund with a distinct, stable identity.
Investment decisions for the fund are made by the Active Equity Team of Mellon Capital. The team members are C. Wesley Boggs, Warren Chiang, CFA and Ronald Gala, CFA, each of whom serves as portfolio manager of the fund and all of whom are jointly and primarily responsible for managing the fund's portfolio. The team has managed the fund since May 2012. Mr. Boggs is a vice president and senior portfolio manager at Mellon Capital, where he has been employed since 1993. He has also been employed by Dreyfus since 2007. Mr. Chiang is a managing director of active equity strategies at Mellon Capital, where he has been employed since 1997. He has also been employed by Dreyfus since 2007. Mr. Gala is a director and senior portfolio manager at Mellon Capital and has been employed by other current or predecessor BNY Mellon entities since 1993. He has also been employed by Dreyfus since 1998. There are no limitations on the role of a team member with respect to making investment decisions for the fund.
The fund's Statement of Additional Information (SAI) provides additional portfolio manager information, including compensation, other accounts managed and ownership of fund shares.
MBSC Securities Corporation (MBSC), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Dreyfus, serves as distributor of the fund and of the other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. Any Rule 12b-1 fees and shareholder services fees, as applicable, are paid to MBSC for financing the sale and distribution of fund shares and for providing shareholder account service and maintenance, respectively. Dreyfus or MBSC may provide cash payments out of its own resources to financial intermediaries that sell shares of funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds or provide other services. Such payments are separate from any sales charges, 12b-1 fees and/or shareholder services fees or other expenses that may be paid by a fund to those intermediaries. Because those payments are not made by fund shareholders or the fund, the fund's total expense ratio will not be affected by any such payments. These payments may be made to intermediaries, including affiliates, that provide shareholder servicing, sub-administration, recordkeeping and/or sub-transfer agency services, marketing support and/or access to sales meetings, sales representatives and management representatives of the financial intermediary. Cash compensation also may be paid from Dreyfus' or MBSC's own resources to intermediaries for inclusion of a fund on a sales list, including a preferred or select sales list or in other sales programs. These payments sometimes are referred to as "revenue sharing." From time to time, Dreyfus or MBSC also may provide cash or non-cash compensation to financial intermediaries or their representatives in the form of occasional gifts; occasional meals, tickets or other entertainment; support for due diligence trips; educational conference sponsorships; support for recognition programs; technology or infrastructure support; and other forms of cash or non-cash compensation permissible under broker-dealer regulations. In some cases, these payments or compensation may create an incentive for a financial intermediary or its employees to recommend or sell shares of the fund to you. Please contact your financial representative for details about any payments they or their firm may receive in connection with the sale of fund shares or the provision of services to the fund.
The fund, Dreyfus and MBSC have each adopted a code of ethics that permits its personnel, subject to such code, to invest in securities, including securities that may be purchased or held by the fund. Each code of ethics restricts the personal securities transactions of employees, and requires portfolio managers and other investment personnel to comply with the code's preclearance and disclosure procedures. The primary purpose of the respective codes is to ensure that personal trading by employees does not disadvantage any fund managed by Dreyfus or its affiliates.
7
Shareholder Guide
The fund is designed primarily for people who are investing through a third party, such as a bank, broker-dealer or financial adviser, or in a 401(k) or other retirement plan. Third parties with whom you open a fund account may impose policies, limitations and fees that are different from those described in this prospectus. Consult a representative of your plan or financial institution for further information.
This prospectus offers Class A, C, I and Z shares of the fund.
Your financial representative may receive different compensation for selling one class of shares than for selling another class. It is important to remember that any contingent deferred sales charge (CDSC) or Rule 12b-1 fees have the same purpose as the front-end sales charge: to compensate the distributor for concessions and expenses it pays to dealers and financial institutions in connection with the sale of fund shares. A CDSC is not charged on fund shares acquired through the reinvestment of fund dividends. Because the Rule 12b-1 fee is paid out of the fund's assets on an ongoing basis, over time it will increase the cost of your investment and may cost you more than paying other types of sales charges.
The different classes of fund shares represent investments in the same portfolio of securities, but the classes are subject to different expenses and will likely have different share prices. When choosing a class, you should consider your investment amount, anticipated holding period, the potential costs over your holding period and whether you qualify for any reduction or waiver of the sales charge.
A complete description of these classes follows. You should review these arrangements with your financial representative before determining which class to invest in.
Class A Shares
When you invest in Class A shares, you pay the public offering price, which is the share price, or net asset value (NAV), plus the initial sales charge that may apply to your purchase. The amount of the initial sales charge is based on the size of your investment, as the following table shows. We also describe below how you may reduce or eliminate the initial sales charge (see "Sales Charge Reductions and Waivers"). Class A shares are subject to an annual shareholder services fee of .25% paid to the fund's distributor for shareholder account service and maintenance.
Since some of your investment goes to pay an up-front sales charge when you purchase Class A shares, you purchase fewer shares than you would with the same investment in Class C shares. Nevertheless, you are usually better off purchasing Class A shares, rather than Class C shares, and paying an up-front sales charge if you:
· plan to own the shares for an extended period of time, since the ongoing Rule 12b-1 fees on Class C shares may eventually exceed the cost of the up-front sales charge; and
· qualify for a reduced or waived sales charge
If you invest $1 million or more (and are not eligible to purchase Class I shares), Class A shares will always be the most advantageous choice. Shareholders who received Class A shares in exchange for Class T shares of the fund may be eligible for lower sales charges. See the SAI for further details.
8
|
Total Sales Load -- Class A Shares | ||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of Offering |
As a % of Net Asset Value per Share |
|
Less than $50,000 |
5.75 |
6.10 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.50 |
3.63 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.50 |
2.56 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
No sales charge applies on investments of $1 million or more, but a CDSC of 1% may be imposed on certain redemptions of such shares within one year of the date of purchase.
Sales Charge Reductions and Waivers
To receive a reduction or waiver of your initial sales charge, you must let your financial intermediary or the fund know at the time you purchase shares that you qualify for such a reduction or waiver. If you do not let your financial intermediary or the fund know that you are eligible for a reduction or waiver, you may not receive the reduction or waiver to which you are otherwise entitled. In order to receive a reduction or waiver, you may be required to provide your financial intermediary or the fund with evidence of your qualification for the reduction or waiver, such as records regarding shares of certain Dreyfus Funds held in accounts with that financial intermediary and other financial intermediaries. Additional information regarding reductions and waivers of sales loads is available, free of charge, at www.dreyfus.com and in the SAI.
You can reduce your initial sales charge in the following ways:
· Rights of accumulation. You can count toward the amount of your investment your total account value in all share classes of the fund and certain other Dreyfus Funds that are subject to a sales charge. For example, if you have $1 million invested in shares of certain other Dreyfus Funds that are subject to a sales charge, you can invest in Class A shares of any fund without an initial sales charge. We may terminate or change this privilege at any time on written notice.
· Letter of intent. You can sign a letter of intent, in which you agree to invest a certain amount (your goal) in the fund and certain other Dreyfus Funds over a 13-month period, and your initial sales charge will be based on your goal. A 90-day back-dated period can also be used to count previous purchases toward your goal. Your goal must be at least $50,000, and your initial investment must be at least $5,000. The sales charge will be adjusted if you do not meet your goal.
· Combine with family members. You can also count toward the amount of your investment all investments in certain other Dreyfus Funds, in any class of shares that is subject to a sales charge, by your spouse and your children under age 21 (family members), including their rights of accumulation and goals under a letter of intent. Certain other groups may also be permitted to combine purchases for purposes of reducing or eliminating sales charges. See "How to Buy Shares" in the SAI.
Class A shares may be purchased at NAV without payment of a sales charge by the following individuals and entities:
· full-time or part-time employees, and their family members, of Dreyfus or any of its affiliates
· board members of Dreyfus and board members of the Dreyfus Family of Funds
· full-time employees, and their family members, of financial institutions that have entered into selling agreements with the fund's distributor
· "wrap" accounts for the benefit of clients of financial institutions, provided they have entered into an agreement with the fund's distributor specifying operating policies and standards
· qualified separate accounts maintained by an insurance company; any state, county or city or instrumentality thereof; and charitable organizations investing $50,000 or more in fund shares and charitable remainder trusts, provided that such Class A shares are purchased directly through the fund's distributor
· investors who purchase Class A shares directly through the fund's distributor, and either (i) have, or whose spouse or minor children have, beneficially owned shares and continuously maintained an open account with the distributor in a Dreyfus-managed fund since on or before February 28, 2006, or (ii) such purchase is for a self-directed investment account that may or may not be subject to a transaction fee
9
· investors who participate in a self-directed investment brokerage account program offered by a financial intermediary that has entered into an agreement with the fund's distributor. Financial intermediaries offering self-directed investment brokerage accounts may or may not charge their customers a transaction fee
· investors with the cash proceeds from the investor's exercise of stock options and/or disposition of stock related to employment-based stock plans, whether invested in the fund directly or indirectly through an exchange from a Dreyfus money market fund, provided that the proceeds are processed through an entity that has entered into an agreement with the fund's distributor specifically relating to administering employment-based stock plans. Upon establishing the account in the fund or the Dreyfus money market fund, the investor and the investor's spouse and minor children become eligible to purchase Class A shares of the fund at NAV, whether or not the investor uses the proceeds of the employment-based stock plan to establish the account
· members of qualified affinity groups who purchase Class A shares directly through the fund's distributor, provided that the qualified affinity group has entered into an affinity agreement with the distributor
· investors who have continuously owned shares of the fund since before the imposition of a sales load
· charitable organizations investing $50,000 or more in fund shares and charitable remainder trusts, provided that such Class A shares are purchased directly through the fund's distributor
· employees participating in qualified or non-qualified employee benefit plans, including pension, profit-sharing and other deferred compensation plans, whether established by corporations, partnerships, non-profit entities, trade or labor unions, or state and local governments (Retirement Plans), but not including IRAs, IRA "Rollover Accounts" or IRAs set up under Simplified Employee Pension Plans (SEP-IRAs), Salary Reduction Simplified Employee Pension Plans (SARSEPs) or Savings Incentive Match Plans for Employees (SIMPLE IRAs)
· shareholders in Dreyfus-sponsored IRA rollover accounts funded with the distribution proceeds from Retirement Plans or a Dreyfus-sponsored 403(b)(7) plan, provided that, in the case of a Retirement Plan, the rollover is processed through an entity that has entered into an agreement with the fund's distributor specifically relating to processing rollovers. Upon establishing the Dreyfus-sponsored IRA rollover account in the fund, the shareholder becomes eligible to make subsequent purchases of Class A shares of the fund at NAV in such account
Class C Shares
Since you pay no initial sales charge, an investment of less than $1 million in Class C shares buys more shares than the same investment would in Class A shares. However, Class C shares are subject to an annual Rule 12b-1 fee of .75% and an annual shareholder services fee of .25%.. Because the Rule 12b-1 fees are paid out of the fund's assets attributable to Class C shares on an ongoing basis, over time these fees will increase the cost of your investment and may cost you more than paying other types of sales charges, such as the initial sales charge on Class A shares. Class C shares redeemed within one year of purchase are subject to a 1% CDSC.
Because Class A shares will always be a more favorable investment than Class C shares for investments of $1 million or more, the fund will generally not accept a purchase order for Class C shares in the amount of $1 million or more. While the fund will take reasonable steps to prevent investments of $1 million or more in Class C shares, it may not be able to identify such investments made through certain financial intermediaries or omnibus accounts.
Class I Shares
Since you pay no initial sales charge, an investment of less than $1 million in Class I shares buys more shares than the same investment would in a class of shares subject to an initial sales charge. There is also no CDSC imposed on redemptions of Class I shares, and you do not pay any ongoing service or distribution fees.
Class I shares may be purchased by:
· bank trust departments, trust companies and insurance companies that have entered into agreements with the fund's distributor to offer Class I shares to their clients
· institutional investors acting in a fiduciary, advisory, agency, custodial or similar capacity for Retirement Plans and SEP-IRAs that have entered into agreements with the fund's distributor to offer Class I shares to such plans
· law firms or attorneys acting as trustees or executors/administrators
· foundations and endowments that make an initial investment in the fund of at least $1 million
· sponsors of college savings plans that qualify for tax-exempt treatment under Section 529 of the Internal Revenue Code, that maintain an omnibus account with the fund and do not require shareholder tax reporting or 529 account support responsibilities from the fund's distributor
10
· advisory fee-based accounts offered through financial intermediaries who, depending on the structure of the selected advisory platform, make Class I shares available
· certain institutional clients of a BNY Mellon investment advisory subsidiary, provided that such clients are approved by Dreyfus
· unaffiliated investment companies approved by the fund's distributor
Institutions purchasing fund shares on behalf of their clients determine whether Class I shares will be available for their clients. Accordingly, the availability of Class I shares of the fund will depend on the policies of the institutional investor.
Class Z Shares
Since you pay no initial sales charge, Class Z shares generally are offered only to shareholders of the fund who are holders of an account in the fund which existed on August 30, 1999 and continues to exist at the time of the current purchase of Class Z shares. Class Z shares are subject to an annual shareholder services fee of up to .25% to reimburse the fund's distributor for shareholder account service and maintenance expenses related to Class Z shares.
CDSC Waivers
The fund's CDSC on Class A and C shares may be waived in the following cases:
· permitted exchanges of shares, except if shares acquired by exchange are then redeemed within the period during which a CDSC would apply to the initial shares purchased
· redemptions made within one year of death or disability of the shareholder
· redemptions due to receiving required minimum distributions from retirement accounts upon reaching age 70½
· redemptions made through the fund's Automatic Withdrawal Plan, if such redemptions do not exceed 12% of the value of the account annually
· redemptions by Retirement Plans
Dreyfus calculates fund NAVs as of the close of trading on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) (usually 4:00 p.m. Eastern time) on days the NYSE is open for regular business. Your order will be priced at the next NAV calculated after your order is received in proper form by the fund's transfer agent or other authorized entity. When calculating NAVs, Dreyfus values equity investments on the basis of market quotations or official closing prices. Dreyfus generally values fixed-income investments based on values supplied by an independent pricing service approved by the fund's board. The pricing service's procedures are reviewed under the general supervision of the board. If market quotations or official closing prices or valuations from a pricing service are not readily available, or are determined not to reflect accurately fair value, the fund may value those investments at fair value as determined in accordance with procedures approved by the fund's board. Fair value of investments may be determined by the fund's board, its pricing committee or its valuation committee in good faith using such information as it deems appropriate under the circumstances. Under certain circumstances, the fair value of foreign equity securities will be provided by an independent pricing service. Using fair value to price investments may result in a value that is different from a security's most recent closing price and from the prices used by other mutual funds to calculate their net asset values. Foreign securities held by a fund may trade on days when the fund does not calculate its NAV and thus may affect the fund's NAV on days when investors will not be able to purchase or sell (redeem) fund shares.
Investments in certain types of thinly traded securities may provide short-term traders arbitrage opportunities with respect to the fund's shares. For example, arbitrage opportunities may exist when trading in a portfolio security or securities is halted and does not resume, or the market on which such securities are traded closes before the fund calculates its NAV. If short-term investors in the fund were able to take advantage of these arbitrage opportunities, they could dilute the NAV of fund shares held by long-term investors. Portfolio valuation policies can serve to reduce arbitrage opportunities available to short-term traders, but there is no assurance that such valuation policies will prevent dilution of the fund's NAV by short-term traders. While the fund has a policy regarding frequent trading, it too may not be completely effective to prevent short-term NAV arbitrage trading, particularly in regard to omnibus accounts. Please see "Shareholder Guide — General Policies" for further information about the fund's frequent trading policy.
Orders to buy and sell shares received by an authorized entity (such as a bank, broker-dealer or financial adviser, or 401(k) or other retirement plan that has entered into an agreement with the fund's distributor) by the close of trading on the NYSE and transmitted to the distributor or its designee by the close of its business day (usually 5:15 p.m. Eastern time) will be based on the NAV determined as of the close of trading on the NYSE that day.
11
How to Buy Shares
By Mail.
Regular Accounts. To open a regular account, complete an application and mail it, together with a check payable to The Dreyfus Family of Funds, to the appropriate address below. To purchase additional shares in a regular account, mail a check payable to The Dreyfus Family of Funds (with your account number on your check), together with an investment slip, to the appropriate address below.
IRA Accounts. To open an IRA account or make additional investments in an IRA account, be sure to specify the fund name and the year for which the contribution is being made. When opening a new account include a completed IRA application, and when making additional investments include an investment slip. Make checks payable to The Dreyfus Family of Funds, and mail to the appropriate address below.
Mailing Address. If you are investing directly through the fund, mail to:
Dreyfus Shareholder Services
P.O. Box 9879
Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8079
If you are investing through a third party, such as a bank, broker-dealer or financial adviser, or in a 401(k) or other retirement plan, mail to:
Dreyfus Institutional Department
P.O. Box 9882
Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8082
If you are applying for an Institutional Direct account, please contact your BNY Mellon relationship manager for mailing instructions.
Electronic Check or Wire. To purchase shares in a regular or IRA account by wire or electronic check, please call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) for more information.
Telephone or Online. To purchase additional shares by telephone or online, you can call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or visit www.dreyfus.com to request your transaction. In order to do so, you must have elected the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege on your account application or a Shareholder Services Form. See "Services for Fund Investors — Wire Redemption and Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privileges" for more information. Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for online services.
Automatically. You may purchase additional shares in a regular or IRA account by selecting one of Dreyfus' automatic investment services made available to the fund on your account application or service application. See "Services for Fund Investors."
The minimum initial and subsequent investment for regular accounts is $1,000 and $100, respectively. The minimum initial investment for IRAs is $750, with no minimum subsequent investment. The minimum initial investment for education savings accounts is $500, with no minimum subsequent investment. Subsequent investments made through Dreyfus TeleTransfer are subject to a $100 minimum and a $150,000 maximum. All investments must be in U.S. dollars. Third-party checks, cash, travelers' checks or money orders will not be accepted. You may be charged a fee for any check that does not clear.
How to Sell Shares
You may sell (redeem) shares at any time. Your shares will be sold at the next NAV calculated after your order is received in proper form by the fund's transfer agent or other authorized entity. Any certificates representing fund shares being sold must be returned with your redemption request. Your order will be processed promptly and you will generally receive the proceeds within a week.
To keep your CDSC as low as possible, each time you request to sell shares we will first sell shares that are not subject to a CDSC, and then those subject to the lowest charge. The CDSC is based on the lesser of the original purchase cost or the current market value of the shares being sold, and is not charged on fund shares you acquired by reinvesting your fund dividends. As described above in this prospectus, there are certain instances when you may qualify to have the CDSC waived. Consult your financial representative or refer to the SAI for additional details.
Before selling shares recently purchased by check, Dreyfus TeleTransfer or Automatic Asset Builder, please note that:
· if you send a written request to sell such shares, the fund may delay sending the proceeds for up to eight business days following the purchase of those shares
12
· the fund will not process wire, telephone, online or Dreyfus TeleTransfer redemption requests for up to eight business days following the purchase of those shares
By Mail.
Regular Accounts. To redeem shares in a regular account by mail, send a letter of instruction that includes your name, your account number, the name of the fund, the share class, the dollar amount to be redeemed and how and where to send the proceeds. Mail your request to the appropriate address below.
IRA Accounts. To redeem shares in an IRA account by mail, send a letter of instruction that includes all of the same information for regular accounts and indicate whether the distribution is qualified or premature and whether the 10% TEFRA should be withheld. Mail your request to the appropriate address below.
Mailing Address. If you invested directly through the fund, mail to:
Dreyfus Shareholder Services
P.O. Box 9879
Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8079
If you invested through a third party, such as a bank, broker-dealer or financial adviser, or in a 401(k) or other retirement plan, mail to:
Dreyfus Institutional Department
P.O. Box 9882
Providence, Rhode Island 02940-8082
If you are an Institutional Direct accountholder, please contact your BNY Mellon relationship manager for mailing instructions.
A medallion signature guarantee is required for some written sell orders. These include:
· amounts of $10,000 or more on accounts whose address has been changed within the last 30 days
· requests to send the proceeds to a different payee or address
· amounts of $100,000 or more
A medallion signature guarantee helps protect against fraud. You can obtain one from most banks or securities dealers, but not from a notary public. For joint accounts, each signature must be guaranteed. Please call to ensure that your medallion signature guarantee will be processed correctly.
Telephone or Online. To redeem shares by telephone or online, call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or, for regular accounts, visit www.dreyfus.com to request your transaction. Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for online services.
By calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only), you may speak to a Dreyfus representative and request that redemption proceeds be paid by check and mailed to your address of record (maximum $250,000 per day). For redemption requests made online through www.dreyfus.com or through Dreyfus Express® automated account access system, there is a $100,000 per day limit.
If the fund has your bank account information on file, you may request a wire via the Wire Redemption Privilege ($1,000 minimum) or electronic check via the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege ($500 minimum) and proceeds will be wired or sent by electronic check, as applicable, to your bank account. See "Services for Fund Investors — Wire Redemption and Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privileges" for more information.
Automatically. You may sell shares in a regular account by completing a Dreyfus Automatic Withdrawal Form which you can obtain by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only), visiting www.dreyfus.com or contacting your financial representative. For instructions on how to establish automatic withdrawals to sell shares in an IRA account, please call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or contact your financial representative. See "Services for Fund Investors — Automatic Services."
The fund and the fund's transfer agent are authorized to act on telephone or online instructions from any person representing himself or herself to be you and reasonably believed by the fund or the transfer agent to be genuine. You may be responsible for any fraudulent telephone or online order as long as the fund or the fund's transfer agent (as applicable) takes reasonable measures to confirm that the instructions are genuine.
13
The fund reserves the right to reject any purchase or exchange request in whole or in part. All shareholder services and privileges offered to shareholders may be modified or terminated at any time, except as otherwise stated in the fund's SAI. Please see the fund's SAI for additional information on buying and selling shares, privileges and other shareholder services.
The fund is designed for long-term investors. Frequent purchases, redemptions and exchanges may disrupt portfolio management strategies and harm fund performance by diluting the value of fund shares and increasing brokerage and administrative costs. As a result, Dreyfus and the fund's board have adopted a policy of discouraging excessive trading, short-term market timing and other abusive trading practices (frequent trading) that could adversely affect the fund or its operations. Dreyfus and the fund will not enter into arrangements with any person or group to permit frequent trading.
The fund also reserves the right to:
· change or discontinue fund exchanges, or temporarily suspend exchanges during unusual market conditions
· change its minimum or maximum investment amounts
· delay sending out redemption proceeds for up to seven days (generally applies only during unusual market conditions or in cases of very large redemptions or excessive trading)
· "redeem in kind," or make payments in securities rather than cash, if the amount redeemed is large enough to affect fund operations (for example, if it exceeds 1% of the fund's assets)
· refuse any purchase or exchange request, including those from any individual or group who, in Dreyfus' view, is likely to engage in frequent trading
More than four roundtrips within a rolling 12-month period generally is considered to be frequent trading. A roundtrip consists of an investment that is substantially liquidated within 60 days. Based on the facts and circumstances of the trades, the fund may also view as frequent trading a pattern of investments that are partially liquidated within 60 days.
Transactions made through Automatic Withdrawal Plans, Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privileges, automatic investment plans (including Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®), automatic non-discretionary rebalancing programs, and minimum required retirement distributions generally are not considered to be frequent trading. For employer-sponsored benefit plans, generally only participant-initiated exchange transactions are subject to the roundtrip limit.
Dreyfus monitors selected transactions to identify frequent trading. When its surveillance systems identify multiple roundtrips, Dreyfus evaluates trading activity in the account for evidence of frequent trading. Dreyfus considers the investor's trading history in other accounts under common ownership or control, in other Dreyfus Funds and BNY Mellon Funds and, if known, in non-affiliated mutual funds and accounts under common control. These evaluations involve judgments that are inherently subjective, and while Dreyfus seeks to apply the policy and procedures uniformly, it is possible that similar transactions may be treated differently. In all instances, Dreyfus seeks to make these judgments to the best of its abilities in a manner that it believes is consistent with shareholder interests. If Dreyfus concludes the account is likely to engage in frequent trading, Dreyfus may cancel or revoke the purchase or exchange on the following business day. Dreyfus may also temporarily or permanently bar such investor's future purchases into the fund in lieu of, or in addition to, canceling or revoking the trade. At its discretion, Dreyfus may apply these restrictions across all accounts under common ownership, control or perceived affiliation.
Fund shares often are held through omnibus accounts maintained by financial intermediaries, such as brokers and retirement plan administrators, where the holdings of multiple shareholders, such as all the clients of a particular broker, are aggregated. Dreyfus' ability to monitor the trading activity of investors whose shares are held in omnibus accounts is limited. However, the agreements between the distributor and financial intermediaries include obligations to comply with the terms of this prospectus and to provide Dreyfus, upon request, with information concerning the trading activity of investors whose shares are held in omnibus accounts. If Dreyfus determines that any such investor has engaged in frequent trading of fund shares, Dreyfus may require the intermediary to restrict or prohibit future purchases or exchanges of fund shares by that investor.
Certain retirement plans and intermediaries that maintain omnibus accounts with the fund may have developed policies designed to control frequent trading that may differ from the fund's policy. At its sole discretion, the fund may permit such intermediaries to apply their own frequent trading policy. If you are investing in fund shares through an intermediary (or in the case of a retirement plan, your plan sponsor), please contact the intermediary for information on the frequent trading policies applicable to your account.
To the extent the fund significantly invests in foreign securities traded on markets that close before the fund calculates its NAV, events that influence the value of these foreign securities may occur after the close of these foreign markets and before the fund calculates its NAV. As a result, certain investors may seek to trade fund shares in an effort to
14
benefit from their understanding of the value of these foreign securities at the time the fund calculates its NAV (referred to as price arbitrage). This type of frequent trading may dilute the value of fund shares held by other shareholders. The fund has adopted procedures designed to adjust closing market prices of foreign equity securities under certain circumstances to reflect what it believes to be their fair value.
To the extent the fund significantly invests in thinly traded securities, certain investors may seek to trade fund shares in an effort to benefit from their understanding of the value of these securities (referred to as price arbitrage). Any such frequent trading strategies may interfere with efficient management of the fund's portfolio to a greater degree than funds that invest in highly liquid securities, in part because the fund may have difficulty selling these portfolio securities at advantageous times or prices to satisfy large and/or frequent redemption requests. Any successful price arbitrage may also cause dilution in the value of fund shares held by other shareholders.
Although the fund's frequent trading and fair valuation policies and procedures are designed to discourage market timing and excessive trading, none of these tools alone, nor all of them together, completely eliminates the potential for frequent trading.
Small Account Policy
If your account falls below $500, the fund may ask you to increase your balance. If it is still below $500 after 45 days, the fund may close your account and send you the proceeds.
The fund earns dividends, interest and other income from its investments, and distributes this income (less expenses) to shareholders as dividends. The fund also realizes capital gains from its investments, and distributes these gains (less any losses) to shareholders as capital gain distributions. The fund normally pays dividends and capital gain distributions annually. Fund dividends and capital gain distributions will be reinvested in the fund unless you instruct the fund otherwise. There are no fees or sales charges on reinvestments.
Distributions paid by the fund are subject to federal income taxes, and may also be subject to state or local taxes (unless you are investing through a tax-advantaged retirement account). For federal tax purposes, in general, certain fund distributions, including distributions of short-term capital gains, are taxable as ordinary income. Other fund distributions, including dividends from certain U.S. companies and certain foreign companies and distributions of long-term capital gains, generally are taxable as qualified dividends and capital gains, respectively.
High portfolio turnover and more volatile markets can result in significant taxable distributions to shareholders, regardless of whether their shares have increased in value. The tax status of any distribution generally is the same regardless of how long you have been in the fund and whether you reinvest your distributions or take them in cash.
If you buy shares of a fund when the fund has realized but not yet distributed income or capital gains, you will be "buying a dividend" by paying the full price for the shares and then receiving a portion back in the form of a taxable distribution.
Your sale of shares, including exchanges into other funds, may result in a capital gain or loss for tax purposes. A capital gain or loss on your investment in the fund generally is the difference between the cost of your shares and the amount you receive when you sell them.
The tax status of your distributions will be detailed in your annual tax statement from the fund. Because everyone's tax situation is unique, please consult your tax adviser before investing.
Automatic Services
Buying or selling shares automatically is easy with the services described below. With each service, you select a schedule and amount, subject to certain restrictions. If you purchase shares through a third party, the third party may impose different restrictions on these services and privileges, or may not make them available at all. For information, call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or your financial representative.
Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder® permits you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 and maximum of $150,000 per transaction) at regular intervals selected by you. Fund shares are purchased by transferring funds from the bank account designated by you.
Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan permits you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 per transaction) automatically through a payroll deduction.
15
Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit permits you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 and maximum of $50,000 per transaction) automatically from your federal employment, Social Security or other regular federal government check.
Dreyfus Dividend Sweep permits you to automatically reinvest dividends and distributions from the fund into another Dreyfus Fund (not available for IRAs).
Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege permits you to exchange at regular intervals your fund shares for shares of other Dreyfus Funds.
Dreyfus Automatic Withdrawal Plan permits you to make withdrawals (minimum of $50) on a specific day each month, quarter or semi-annual or annual period, provided your account balance is at least $5,000. Any CDSC will be waived, as long as the amount of any withdrawal does not exceed on an annual basis 12% of the greater of the account value at the time of the first withdrawal under the plan, or at the time of the subsequent withdrawal.
Fund Exchanges
Generally, you can exchange shares worth $500 or more (no minimum for retirement accounts) into shares of the same class, or another class in which you are eligible to invest, of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. You can request your exchange by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or your financial representative. If you are an Institutional Direct accountholder, please contact your BNY Mellon relationship manager for instructions. Be sure to read the current prospectus for any fund into which you are exchanging before investing. Any new account established through an exchange generally will have the same privileges as your original account (as long as they are available). There is currently no fee for exchanges, although you may be charged a sales load when exchanging into any fund that has one.
Your exchange request will be processed on the same business day it is received in proper form, provided that each fund is open at the time of the request. If the exchange is accepted at a time of day after one or both of the funds is closed (i.e., at a time after the NAV for the fund has been calculated for that business day), the exchange will be processed on the next business day. See the SAI for more information regarding exchanges.
Wire Redemption and Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privileges
To redeem shares from your Dreyfus Fund account with a phone call (for regular or IRA accounts) or online (for regular accounts only), use the Wire Redemption Privilege or the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege. To purchase additional shares of your Dreyfus Fund account with a phone call (for regular or IRA accounts) or online (for regular accounts only), use the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege. You can set up the Wire Redemption Privilege and Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege on your account by providing bank account information and following the instructions on your application or, if your account has already been established, a Shareholder Services Form which you can obtain by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only), visiting www.dreyfus.com or by contacting your financial representative. Shares held in an education savings account may not be redeemed through the Wire Redemption or Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privileges. Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for the Wire Redemption or Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privileges initiated online.
Account Statements
Every Dreyfus Fund investor automatically receives regular account statements. You will also be sent a yearly statement detailing the tax characteristics of any dividends and distributions you have received.
Reinvestment Privilege
If you redeem Class A shares of the fund, you can reinvest in the same account of the fund up to the number of Class A shares you redeemed at the current share price without paying a sales charge. If you paid a CDSC, it will be credited back to your account. This privilege may be used only once and your reinvestment request must be received in writing by the fund within 45 days of the redemption.
Dreyfus Express® Voice-Activated Account Access
You can check your Dreyfus account balances, get fund price and performance information, order documents and much more, by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) and using the Dreyfus Express® Voice-Activated System. You may also be able to purchase fund shares and/or transfer money between your Dreyfus Funds using Dreyfus Express®. Certain requests require the services of a representative.
16
These financial highlights describe the performance of the fund's shares for the fiscal periods indicated. "Total return" shows how much your investment in the fund would have increased (or decreased) during each period, assuming you had reinvested all dividends and distributions. These financial highlights have been derived from the fund's financial statements, which have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, whose report, along with the fund's financial statements, is included in the annual report, which is available upon request.
|
|
Year Ended May 31, | ||||
|
Class A Shares |
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
2011 |
2010 |
|
Per Share Data ($): |
|
|
| ||
|
Net asset value, beginning of period |
12.76 |
10.24 |
10.61 |
8.36 |
7.08 |
|
Investment Operations: |
|
|
| ||
|
Investment income--neta |
.10 |
.13 |
.05 |
.03 |
.03 |
|
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments |
2.45 |
2.46 |
(.38) |
2.24 |
1.25 |
|
Total from Investment Operations |
2.55 |
2.59 |
(.33) |
2.27 |
1.28 |
|
Distributions: |
|
|
| ||
|
Dividends from investment income--net |
(.14) |
(.05) |
(.04) |
(.02) |
- |
|
Dividends from net realized gain on investments |
(.35) |
(.02) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total Distributions |
(.49) |
(.07) |
(.04) |
(.02) |
- |
|
Net asset value, end of period |
14.82 |
12.76 |
10.24 |
10.61 |
8.36 |
|
Total Return (%)b |
20.37 |
25.47 |
(3.13) |
27.18 |
18.08 |
|
Ratios/Supplemental Data (%): |
|
|
| ||
|
Ratio of total expenses to average net assets |
1.22 |
1.25 |
1.31 |
1.39 |
1.35 |
|
Ratio of net expenses to average net assets |
1.22 |
1.25 |
1.31 |
1.39 |
1.35 |
|
Ratio of net investment income to average net assets |
.70 |
1.11 |
.46 |
.32 |
.40 |
|
Portfolio Turnover Rate |
34.37 |
48.33 |
64.12 |
50.46 |
35.17 |
|
Net Assets, end of period ($ x 1,000) |
24,320 |
17,562 |
14,469 |
15,154 |
13,252 |
|
aBased on average shares outstanding at each month end. | |||||
|
bExclusive of sales charge. | |||||
|
|
Year Ended May 31, | ||||
|
Class C Shares |
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
2011 |
2010 |
|
Per Share Data ($): |
|
|
| ||
|
Net asset value, beginning of period |
11.72 |
9.43 |
9.80 |
7.75 |
6.63 |
|
Investment Operations: |
|
|
| ||
|
Investment income (loss)--neta |
(.01) |
.04 |
(.03) |
(.03) |
(.03) |
|
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments |
2.23 |
2.27 |
(.34) |
2.08 |
1.17 |
|
Total from Investment Operations |
2.22 |
2.31 |
(.37) |
2.05 |
1.14 |
|
Distributions: |
|
|
| ||
|
Dividends from investment income--net |
(.07) |
- |
- |
- |
(.02) |
|
Dividends from net realized gain on investments |
(.35) |
(.02) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total Distributions |
(.42) |
(.02) |
- |
- |
(.02) |
|
Net asset value, end of period |
13.52 |
11.72 |
9.43 |
9.80 |
7.75 |
|
Total Return (%)b |
19.33 |
24.55 |
(3.78) |
26.45 |
17.16 |
|
Ratios/Supplemental Data (%): |
|
|
| ||
|
Ratio of total expenses to average net assets |
1.99 |
2.00 |
2.05 |
2.00 |
2.09 |
|
Ratio of net expenses to average net assets |
1.99 |
2.00 |
2.05 |
2.00 |
2.09 |
|
Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets |
(.07) |
.35 |
(.27) |
(.29) |
(.39) |
|
Portfolio Turnover Rate |
34.37 |
48.33 |
64.12 |
50.46 |
35.17 |
|
Net Assets, end of period ($ x 1,000) |
5,800 |
4,332 |
3,313 |
2,944 |
2,652 |
|
aBased on average shares outstanding at each month end. | |||||
|
bExclusive of sales charge. | |||||
17
|
|
Year Ended May 31, | ||||
|
Class I Shares |
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
2011 |
2010 |
|
Per Share Data ($): |
|
|
| ||
|
Net asset value, beginning of period |
12.95 |
10.39 |
10.77 |
8.48 |
7.23 |
|
Investment Operations: |
|
| |||
|
Investment income--neta |
.14 |
.17 |
.09 |
.08 |
.06 |
|
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments |
2.48 |
2.51 |
(.38) |
2.28 |
1.27 |
|
Total from Investment Operations |
2.62 |
2.68 |
(.29) |
2.36 |
1.33 |
|
Distributions: |
|
| |||
|
Dividends from investment income--net |
(.18) |
(.10) |
(.09) |
(.07) |
(.08) |
|
Dividends from net realized gain on investments |
(.35) |
(.02) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total Distributions |
(.53) |
(.12) |
(.09) |
(.07) |
(.08) |
|
Net asset value, end of period |
15.04 |
12.95 |
10.39 |
10.77 |
8.48 |
|
Total Return (%) |
20.65 |
25.98 |
(2.72) |
27.87 |
18.43 |
|
Ratios/Supplemental Data (%): |
|
| |||
|
Ratio of total expenses to average net assets |
.91 |
.90 |
.92 |
.89 |
1.01 |
|
Ratio of net expenses to average net assets |
.91 |
.90 |
.92 |
.89 |
1.01 |
|
Ratio of net investment income to average net assets |
1.01 |
1.46 |
.86 |
.83 |
.71 |
|
Portfolio Turnover Rate |
34.37 |
48.33 |
64.12 |
50.46 |
35.17 |
|
Net Assets, end of period ($ x 1,000) |
8,629 |
4,558 |
2,766 |
2,043 |
1,651 |
|
aBased on average shares outstanding at each month end. | |||||
|
|
Year Ended May 31, | ||||
|
Class Z Shares |
2014 |
2013 |
2012 |
2011 |
2010 |
|
Per Share Data ($): |
|
|
| ||
|
Net asset value, beginning of period |
12.94 |
10.38 |
10.76 |
8.48 |
7.22 |
|
Investment Operations: |
|
| |||
|
Investment income--neta |
.13 |
.15 |
.07 |
.07 |
.05 |
|
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments |
2.47 |
2.51 |
(.38) |
2.27 |
1.28 |
|
Total from Investment Operations |
2.60 |
2.66 |
(.31) |
2.34 |
1.33 |
|
Distributions: |
|
| |||
|
Dividends from investment income--net |
(.16) |
(.08) |
(.07) |
(.06) |
(.07) |
|
Dividends from net realized gain on investments |
(.35) |
(.02) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Total Distributions |
(.51) |
(.10) |
(.07) |
(.06) |
(.07) |
|
Net asset value, end of period |
15.03 |
12.94 |
10.38 |
10.76 |
8.48 |
|
Total Return (%) |
20.50 |
25.80 |
(2.86) |
27.61 |
18.40 |
|
Ratios/Supplemental Data (%): |
|
| |||
|
Ratio of total expenses to average net assets |
1.01 |
1.03 |
1.07 |
1.03 |
1.10 |
|
Ratio of net expenses to average net assets |
1.01 |
1.03 |
1.07 |
1.03 |
1.10 |
|
Ratio of net investment income to average net assets |
.91 |
1.32 |
.71 |
.68 |
.60 |
|
Portfolio Turnover Rate |
34.37 |
48.33 |
64.12 |
50.46 |
35.17 |
|
Net Assets, end of period ($ x 1,000) |
283,351 |
255,298 |
221,387 |
247,051 |
210,701 |
|
aBased on average shares outstanding at each month end. | |||||
18
NOTES
19
NOTES
20
NOTES
21
For More Information
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Inc.
SEC file number: 811-2192
More information on this fund is available free upon request, including the following:
Annual/Semiannual Report
Describes the fund's performance, lists portfolio holdings and contains a letter from the fund's manager discussing recent market conditions, economic trends and fund strategies that significantly affected the fund's performance during the last fiscal year. The fund's most recent annual and semiannual reports are available at www.dreyfus.com.
Statement of Additional Information (SAI)
Provides more details about the fund and its policies. A current SAI is available at www.dreyfus.com and is on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The SAI is incorporated by reference (and is legally considered part of this prospectus).
Portfolio Holdings
Dreyfus funds generally disclose their complete schedule of portfolio holdings monthly with a 30-day lag at www.dreyfus.com under Products and Performance. Complete holdings as of the end of the calendar quarter are disclosed 15 days after the end of such quarter. Dreyfus money market funds generally disclose their complete schedule of holdings daily. The schedule of holdings for a fund will remain on the website until the fund files its Form N-Q or Form N-CSR for the period that includes the dates of the posted holdings.
A complete description of the fund's policies and procedures with respect to the disclosure of the fund's portfolio securities is available in the fund's SAI and at www.dreyfus.com.
To Obtain Information
By telephone. Call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only)
By mail.
The Dreyfus Family of Funds
144 Glenn Curtiss Boulevard
Uniondale, NY 11556-0144
By E-mail. Send your request to info@dreyfus.com
On the Internet. Certain fund documents can be viewed online or downloaded from:
SEC: http://www.sec.gov
Dreyfus: http://www.dreyfus.com
You can also obtain copies, after paying a duplicating fee, by visiting the SEC's Public Reference Room in Washington, DC (for information, call 1-202-551-8090) or by E-mail request to publicinfo@sec.gov, or by writing to the SEC's Public Reference Section, Washington, DC 20549-1520.
This prospectus does not constitute an offer or solicitation in any state or jurisdiction in which, or to any person to whom, such offering or solicitation may not lawfully be made.
Printed on recycled paper.
50% post-consumer.
Process chlorine free.
Vegetable-based ink.


|
© 2014 MBSC Securities Corporation |
|
STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
November 15, 2013, as revised or amended, December 1, 2013, February 1, 2014,
March 1, 2014, April 1, 2014, May 1, 2014,
June 1, 2014, August 1, 2014, September 1, 2014, September 11, 2014 and October 1, 2014
This Statement of Additional Information (SAI), which is not a prospectus, supplements and should be read in conjunction with the current prospectus of each fund listed below, as such prospectuses may be revised from time to time. To obtain a copy of a fund's prospectus, please call your financial adviser, or write to the fund at 144 Glenn Curtiss Boulevard, Uniondale, New York 11556-0144, visit www.dreyfus.com, or call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only).
The most recent annual report and semi-annual report to shareholders for each fund (other than Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund) are separate documents supplied with this SAI, and the financial statements, accompanying notes and report of the independent registered public accounting firm appearing in the annual report are incorporated by reference into this SAI. All classes of a fund have the same fiscal year end and prospectus date. Capitalized but undefined terms used in this SAI are defined in the Glossary at the end of this SAI.
|
Fund |
Abbreviation |
Share Class/Ticker |
Fiscal Year End* |
Prospectus Date |
|
CitizensSelect Funds |
CSF |
April 30th |
September 1st | |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
CSPMMF |
Class A/CZAXX |
||
|
Class B/CZBXX |
||||
|
Class C/CZCXX |
||||
|
Class D/CZDXX |
||||
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
CSTMMF |
Class A/CEAXX |
||
|
Class B/CEBXX |
||||
|
Class C/CECXX |
||||
|
Class D/CEDXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Cash Management |
DCM |
Administrative/ DACXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DMCXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DICXX |
||||
|
Investor/DVCXX |
||||
|
Participant/DPCXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management Funds |
DGCMF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management |
DGCM |
Administrative/ DAGXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DGMXX |
||||
|
Institutional /DGCXX |
||||
|
Investor/DGVXX |
||||
|
Participant/DPGXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management |
DGPCM |
Administrative/ DAPXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DRPXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DIPXX |
||||
|
Investor/DVPXX |
||||
|
Participant/DGPXX |
|
|
|
Fund |
Abbreviation |
Share Class/Ticker |
Fiscal Year End* |
Prospectus Date |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Funds |
ICAF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
DICAF |
Administrative Advantage/DDTXX |
April 30th |
September 1st |
|
Participant Advantage/DPTXX |
||||
|
Institutional Advantage/DADXX |
||||
|
Investor Advantage/DIVXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Funds |
IPMMF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund |
DIPMMF |
Prime/N/A |
March 31st |
August 1st |
|
Reserve/DRSXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund |
DIPPMMF |
N/A |
March 31st |
August 1st |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Funds |
IRF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
DIRMF |
Institutional/DSVXX |
December 31st |
May 1st |
|
Hamilton/DSHXX |
||||
|
Agency/DRGXX |
||||
|
Premier/DERXX |
||||
|
Classic/DLSXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund |
DIRTF |
Institutional/DNSXX |
December 31st |
May 1st |
|
Hamilton/DHLXX |
||||
|
Agency/DGYXX |
||||
|
Premier/DRRXX |
||||
|
Classic/DSSXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund |
DIRTPF |
Institutional/DUPXX |
December 31st |
May 1st |
|
Hamilton/DHMXX |
||||
|
Premier/DMEXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Investment Grade Funds, Inc. |
DIGF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
DIASF |
Investor/DIAVX |
July 31st |
December 1st |
|
Class I/DIASX |
||||
|
Class Y/DAIYX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
DITIF |
Class A/DRITX |
July 31st |
December 1st |
|
Class C/DTECX |
||||
|
Class I/DITIX |
||||
|
Class Y/DITYX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
DSTIF |
Class D/DSTIX |
July 31st |
December 1st |
|
Class P/DSHPX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Inc. |
DLA |
Class 1/DLAXX |
December 31st |
May 1st |
|
Class 2/DLATX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
DMCMP |
Administrative/ DAMXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DRAXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DIMXX |
||||
|
Investor/DVMXX |
||||
|
Participant/DMPXX |
|
Fund |
Abbreviation |
Share Class/Ticker |
Fiscal Year End* |
Prospectus Date |
|
Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management |
DNYMCM |
Administrative/ DAYXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Institutional/DIYXX |
||||
|
Investor/DVYXX |
||||
|
Participant/DPYXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Opportunity Funds |
DOF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
DNRF |
Class A/DNLAX |
September 30th |
February 1st |
|
Class C/DLDCX |
||||
|
Class I/DLDRX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund*** |
DSBEMEF |
Class A/DOFAX |
October 31st |
September 11th |
|
Class C/DOFCX |
||||
|
Class I/DOFIX |
||||
|
Class Y/DOFYX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund*** |
DSBGEF |
Class A/DBGAX |
October 31st |
September 11th |
|
Class C/DBGCX |
||||
|
Class I/DBGIX |
||||
|
Class Y/DBGYX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund*** |
DSBUSEF |
Class A/DOUAX |
October 31st |
September 11th |
|
Class C/DOUCX |
||||
|
Class I/DOUIX |
||||
|
Class Y/DOUYX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Premier Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
PSIMBF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
DSIMBF |
Class A/DMBAX |
March 31st |
August 1st |
|
Class D/DSIBX |
||||
|
Class I/DIMIX |
||||
|
Class Y/DMYBX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund** |
SDBF |
Class D/DSDDX |
November 30th |
April 1st |
|
Class I/DSIDX |
||||
|
Class Y/DSYDX |
||||
|
Class Z/DSIGX |
|
Fund |
Abbreviation |
Share Class/Ticker |
Fiscal Year End* |
Prospectus Date |
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management Funds |
DTECMF |
|||
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
DTECM |
Administrative/ DEAXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Institutional/DEIXX |
||||
|
Investor/DEVXX |
||||
|
Participant/DEPXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
DCAAMT |
Administrative/ DFAXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Institutional/DIIXX |
||||
|
Investor/DAIXX |
||||
|
Participant/DFPXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
DNYAMT |
Administrative/ DDVXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Classic/DLCXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DYIXX |
||||
|
Investor/DYVXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management |
DTACM |
Administrative/ DTAXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DYAXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DTRXX |
||||
|
Investor/DTVXX |
||||
|
Participant/DTPXX |
||||
|
Premier/DYPXX |
||||
|
Select/DTSXX |
||||
|
Service/DSRXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management |
DTPCM |
Administrative/ DARXX |
January 31st |
June 1st |
|
Agency/DSAXX |
||||
|
Institutional/DIRXX |
||||
|
Investor/DVRXX |
||||
|
Participant/DPRXX |
||||
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund, Inc. |
WDMMF |
DWDXX |
October 31st |
March 1st |
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
DF |
DREVX |
December 31st |
May 1st |
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Inc. |
DTCF |
Class A/DTCAX |
May 31st |
October 1st |
|
Class C/DTCCX |
||||
|
Class I/DRTCX |
||||
|
Class Z/DRTHX |
||||
* Certain information provided in this SAI is indicated to be as of the end of a fund's last fiscal year or during a fund's last fiscal year. The term "last fiscal year" means the most recently completed fiscal year, except that, for funds with fiscal years ended July 31st and September 30th, "last fiscal year" means the fiscal year ended in 2013.
** Effective November 15, 2013, the fund changed its name from Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Government Fund and adopted a multi-class structure.
*** As this fund commenced operations on September 15, 2014, no information is provided in respect of a previous fiscal year.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART I
PART II
PART III
|
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT DISTRIBUTION PLANS, SERVICE PLANS AND SHAREHOLDER SERVICES PLANS |
|
|
INVESTMENT TECHNIQUES AND RISKS |
|
|
Taxable Investments (municipal or other tax-exempt funds only) |
|
PART I
Information About Each Board Member's Experience, Qualifications, Attributes or Skills
Board members for the funds, together with information as to their positions with the funds, principal occupations and other board memberships during the past five years, are shown below. The address of each board member is 200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166.
Independent Board Members
|
Name |
Principal Occupation During Past 5 Years |
Other Public Company Board Memberships During Past 5 Years |
|
Joseph S. DiMartino |
Corporate Director and Trustee |
CBIZ (formerly, Century Business Services, Inc.), a provider of outsourcing functions for small and medium size companies, Director (1997 - present) The Newark Group, a provider of a national market of paper recovery facilities, paperboard mills and paperboard converting plants, Director (2000 - 2010) Sunair Services Corporation, a provider of certain outdoor-related services to homes and businesses, Director (2005 - 2009) |
|
Whitney I. Gerard |
Partner in the law firm of Chadbourne & Parke LLP |
N/A |
|
Nathan Leventhal |
Chairman of the Avery Fisher Artist Program Commissioner, NYC Planning Commission |
Movado Group, Inc., Director (2003 - present) |
I-1
|
Robin A. Melvin |
Board Member, Illinois Mentoring Partnership, non-profit organization dedicated to increasing the quantity and quality of mentoring services in Illinois (2013 - present) Director, Boisi Family Foundation, a private family foundation that supports youth-serving organizations that promote the self sufficiency of youth from disadvantaged circumstances (1995 - 2012) |
N/A |
|
Roslyn M. Watson |
Principal, Watson Ventures, Inc., a real estate investment company (1993 - present) |
N/A |
|
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
Principal, The Wiley Group, a firm specializing in strategy and business development |
CBIZ (formerly, Century Business Services, Inc.), a provider of outsourcing functions for small and medium size companies, Director (2008 - present) |
1 Each of the Independent Board Members serves on the board's audit, nominating, compensation and litigation committees.
I-2
Interested Board Members
|
Name |
Principal Occupation During Past 5 Years |
Other Public Company Board Memberships During Past 5 Years |
|
J. Charles Cardona¹ 1955 Board Member |
President and a Director of the Manager Executive Vice President of the Distributor President of Dreyfus Institutional Services Division |
N/A |
|
Gordon J. Davis² |
Partner in the law firm of Venable LLP (2012 - present) Partner in the law firm of Dewey & LeBoeuf LLP (1994 - 2012) |
Consolidated Edison, Inc., a utility company, Director (1997 - present) The Phoenix Companies, Inc., a life insurance company, Director (2000 - present) |
|
Isabel P. Dunst³ |
Partner in the law firm of Hogan Lovells LLP |
N/A |
1 Mr. Cardona is deemed to be an Interested Board Member of all of the funds because of his positions with the Manager and its affiliates. Mr. Cardona does not serve on the board's audit, nominating, compensation or litigation committees.
2 Mr. Davis is deemed to be an Interested Board Member of DF, DIGF, DLA, DTCF and WDMMF as a result of his affiliation with Venable LLP, which provides legal services to these funds. Mr. Davis does not serve as a member of the board's audit committees, and Mr. Davis is not a member of the nominating, compensation or litigation committees of the boards of DF, DIGF, DLA, DTCF and WDMMF.
3 Ms. Dunst is deemed to be an Interested Board Member of all the funds because the law firm in which she is a partner provides legal services to BNY Mellon and certain of its affiliates, but not the Manager or the funds. Ms. Dunst is not involved in these representations. Ms. Dunst does not serve on the board's audit, nominating, compensation or litigation committees.
The following table shows the year each board member joined each fund's board.
|
Independent Board Members |
Interested Board Members | ||||||||
|
Fund |
Joseph S. DiMartino |
Whitney I. Gerard |
Nathan Leventhal |
Robin A. Melvin |
Roslyn M. Watson |
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
J. Charles Cardona |
Gordon J. Davis |
Isabel P. Dunst |
|
CSF |
2002 |
2008 |
2013 |
2014 |
2014 |
2013 |
2014 |
2013 |
2014 |
|
DCM |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
DGCMF |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
ICAF |
2002 |
2003 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
IPMMF |
1997 |
2003 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
IRF |
2008 |
2008 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DIGF |
1995 |
1993 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DLA |
1995 |
1973 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DMCMP |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
DNYMCM |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
DOF |
2000 |
2003 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
PSIMBF |
1995 |
1989 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
I-3
|
Independent Board Members |
Interested Board Members | ||||||||
|
Fund |
Joseph S. DiMartino |
Whitney I. Gerard |
Nathan Leventhal |
Robin A. Melvin |
Roslyn M. Watson |
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
J. Charles Cardona |
Gordon J. Davis |
Isabel P. Dunst |
|
SDBF |
1995 |
1989 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DTECMF |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
DTACM |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
DTPCM |
1995 |
2014 |
2014 |
2010 |
2010 |
2007 |
2014 |
2014 |
1991 |
|
WDMMF |
1995 |
1989 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DF |
1995 |
1973 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
|
DTCF |
1995 |
2003 |
2009 |
2014 |
2014 |
2009 |
2014 |
2012 |
2014 |
Each board member, except for Mr. Cardona, has been a Dreyfus Family of Funds board member for over fifteen years. Additional information about each board member follows (supplementing the information provided in the table above) that describes some of the specific experiences, qualifications, attributes or skills that each board member possesses which the board believes has prepared them to be effective board members. The board believes that the significance of each board member's experience, qualifications, attributes or skills is an individual matter (meaning that experience that is important for one board member may not have the same value for another) and that these factors are best evaluated at the board level, with no single board member, or particular factor, being indicative of board effectiveness. However, the board believes that board members need to have the ability to critically review, evaluate, question and discuss information provided to them, and to interact effectively with fund management, service providers and counsel, in order to exercise effective business judgment in the performance of their duties; the board believes that its members satisfy this standard. Experience relevant to having this ability may be achieved through a board member's educational background; business, professional training or practice (e.g., medicine, accounting or law), public service or academic positions; experience from service as a board member (including the board for the funds) or as an executive of investment funds, public companies or significant private or not-for-profit entities or other organizations; and/or other life experiences. The charter for the board's nominating committee contains certain other factors considered by the committee in identifying and evaluating potential board member nominees. To assist them in evaluating matters under federal and state law, the board members are counseled by their independent legal counsel, who participates in board meetings and interacts with the Manager, and also may benefit from information provided by the Manager's counsel; counsel to the funds and to the board have significant experience advising funds and fund board members. The board and its committees have the ability to engage other experts as appropriate. The board evaluates its performance on an annual basis.
Independent Board Members
· Joseph S. DiMartino – Mr. DiMartino has been the Chairman of the Board of the funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds for over 15 years. From 1971 through 1994, Mr. DiMartino served in various roles as an employee of Dreyfus (prior to its acquisition by a predecessor of BNY Mellon in August 1994 and related management changes), including portfolio manager, President, Chief Operating Officer and a director. He ceased being an employee or director of Dreyfus by the end of 1994. From January 1995 to November 1997, Mr. DiMartino served as Chairman of the Board of The Noel Group, a public buyout firm; in that capacity, he helped manage, acquire, take public and liquidate a number of operating companies. From 1986 to 2010, Mr. DiMartino served as a Director of the Muscular Dystrophy Association.
· Whitney I. Gerard – Mr. Gerard is a partner in the law firm of Chadbourne & Parke LLP, where his practice focuses on the representation and counseling of international companies and individuals doing business and/or engaged in litigation in the United States.
· Nathan Leventhal – Mr. Leventhal was previously a Commissioner of the New York City Planning Commission. Previously, Mr. Leventhal served in a number of senior positions in New York City Government, including Fiscal Director of the Human Resources Administration and Chief of Staff to Mayor John V. Lindsay, Deputy Mayor to Mayor Ed Koch, and Transition Chairman for both Mayors David Dinkins and Michael Bloomberg. Mr. Leventhal is a former partner in the law firm Poletti Freidin Prashker Feldman & Gartner. In the not-for-profit sector, Mr. Leventhal served as President of Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts and Chairman of the Avery Fisher Artist Program; he is now President Emeritus of Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts.
I-4
· Robin A. Melvin – Ms. Melvin currently serves as a Board member of Illinois Mentoring Partnership, a non-profit organization dedicated to increasing the quantity and quality of mentoring services in Illinois. Ms. Melvin served as a Director of the Boisi Family Foundation, a private family foundation that supports organizations serving the needs of youth from disadvantaged circumstances, from 1995 to 2012. In that role she also managed the Boisi Family Office, providing the primary interface with all investment managers, legal advisors and other service providers to the family. She has also served in various roles with MENTOR, a national non-profit youth mentoring advocacy organization, including Executive Director of the New York City affiliate, Vice President of the national affiliate network, Vice President of Development, and, immediately prior to her departure, Senior Vice President in charge of strategy. Prior to that, Ms. Melvin was an investment banker with Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.
· Roslyn M. Watson – Ms. Watson has been a business entrepreneur in commercial and residential real estate for over 15 years. Ms. Watson currently serves as President and Founder of Watson Ventures, Inc. a real estate development investment firm, and her current board memberships include American Express Bank, FSB, The Hyams Foundation, Inc., Pathfinder International and Simmons College. Previously, she held various positions in the public and private sectors, including General Manager for the Massachusetts Port Authority. She has received numerous awards, including the Woman of Achievement award from the Boston Big Sister Association and the Working Woman of the Year Award from Working Woman Magazine.
· Benaree Pratt Wiley – Ms. Wiley is a Principal of The Wiley Group, a firm specializing in personnel strategy, talent management and leadership development primarily for global insurance and consulting firms. Prior to that, Ms. Wiley served as the President and Chief Executive Officer of The Partnership, Inc., a talent management organization for multicultural professionals in the greater Boston region. Ms. Wiley currently serves on the board of Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts. She has also served on the boards of several public companies and charitable organizations, including serving as chair of the advisory board of PepsiCo African-American.
Interested Board Members
· J. Charles Cardona – Mr. Cardona is the President and a Director of Dreyfus and the Chief Executive Officer of BNY Mellon Cash Investment Strategies, a division of Dreyfus. Mr. Cardona is an Executive Vice President of the Distributor. He also serves as President of the Institutional Services Division of the Distributor. He joined the Institutional Services Division in 1985 with management responsibility for all Institutional Operations and Client Service units. Prior to joining the Institutional Services Division, he served as Assistant Director of Sales and Services in Dreyfus Retail Division of the Distributor, which he joined in 1981.
· Gordon J. Davis – Mr. Davis is a partner in the law firm of Venable LLP where his practice focuses on complex real estate, land use development and related environmental matters; state and municipal authorities and financings; and cultural and not-for-profit organizations. Prior to joining the firm in 2012, Mr. Davis was a partner in the law firm of Dewey & LeBoeuf LLP from 1994 until 2012. Mr. Davis also served as a Commissioner and member of the New York City Planning Commission, and as Commissioner of Parks and Recreation for the City of New York. Mr. Davis was a co-founder of the Central Park Conservancy and the founding Chairman of Jazz at the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts in New York City. He has also served as President of Lincoln Center. Mr. Davis also served on the board of Dreyfus (prior to its acquisition by a predecessor of BNY Mellon in August 1994 and related management changes). He currently serves as a Director of The Phoenix Companies, Inc., a life insurance company.
· Isabel P. Dunst – Ms. Dunst has been practicing law for almost 40 years. Half of her career was spent at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, including serving as the Deputy General Counsel, the senior career legal position. Ms. Dunst has been a partner for approximately 20 years in the Washington based international law firm of Hogan Lovells, which she joined in 1990.
I-5
The boards' audit, nominating, compensation, litigation and pricing committees met during the funds' last fiscal years as indicated below:
|
Fund |
Audit |
Nominating |
Compensation |
Litigation |
Pricing |
|
CSF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DCM |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DGCMF |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
ICAF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
IPMMF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
IRF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DIGF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DLA |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DMCMP |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DNYMCM |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DOF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
PSIMBF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
SDBF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DTECMF |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DTACM |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DTPCM |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
WDMMF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
DTCF |
4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Board Members' and Officers' Fund Share Ownership
The table below indicates the dollar range of each board member's ownership of fund shares and shares of other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds for which he or she is a board member, in each case as of December 31, 2013.
|
Independent Board Members |
Interested Board Members | ||||||||
|
Fund |
Joseph S. DiMartino |
Whitney I. Gerard |
Nathan Leventhal |
Robin A. Melvin |
Roslyn M. Watson |
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
Gordon J. Davis |
Isabel P. Dunst |
J. Charles Cardona |
|
CSF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DCM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DGCM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DGPCM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DICAF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIPMMF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIPPMMF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIRMF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIRTF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIRTPF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DIASF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DSTIF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DLA |
None |
Over $100,000 |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DMCMP |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DNYMCM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
I-6
|
Independent Board Members |
Interested Board Members | ||||||||
|
Fund |
Joseph S. DiMartino |
Whitney I. Gerard |
Nathan Leventhal |
Robin A. Melvin |
Roslyn M. Watson |
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
Gordon J. Davis |
Isabel P. Dunst |
J. Charles Cardona |
|
DNRF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DSIMBF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
SDBF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DTECM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DCAAMT |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DNYAMT |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DTACM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DTPCM |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
WDMMF |
None |
$1,001-$10,000 |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DF |
None |
$10,001- $50,000 |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
None |
N/A |
|
Aggregate holdings of funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds for which responsible as a board member |
Over $100,000 |
Over $100,000 |
None |
Over $100,000 |
$50,001-$100,000 |
$50,001-$100,000 |
$50,001-$100,000 |
None |
N/A |
Board members and officers, as a group, owned less than 1% of each class of each fund's voting securities outstanding on September 5, 2014.
As of December 31, 2013, none of the board members or their immediate family members owned securities of the Manager, any Sub-Advisers, the Distributor or any person (other than a registered investment company) directly or indirectly controlling, controlled by or under common control with the Manager, any Sub-Advisers or the Distributor.
Annual retainer fees and meeting attendance fees are allocated among the funds on the basis of net assets, with the Chairman of the Boards, Joseph S. DiMartino, receiving an additional 25% of such compensation. Mr. Cardona will receive no compensation from the funds for serving as a director. The funds reimburse board members for their expenses. The funds do not have a bonus, pension, profit-sharing or retirement plan. Each emeritus board member is entitled to receive an annual retainer of one-half the amount paid as a retainer at the time the board member became emeritus and a per meeting attended fee of one-half the amount paid to board members.
The aggregate amount of fees and expenses* received from the funds by each current board member for the funds' last fiscal years, and by all funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds for which such person was a board member during 2013, were as follows:
I-7
|
Independent Board Members | ||||||
|
Fund |
Joseph S. DiMartino* |
Whitney I. Gerard |
Nathan Leventhal |
Robin A. Melvin |
Roslyn M. Watson |
Benaree Pratt Wiley |
|
CSF |
$17,644 |
$14,116 |
$8,083 |
$116 |
$116 |
$7,333 |
|
DCM |
$17,912 |
N/A |
N/A |
$14,330 |
$14,330 |
$14,330 |
|
DGCMF |
$14,144 |
N/A |
N/A |
$11,315 |
$11,315 |
$11,315 |
|
ICAF |
$73,640 |
$58,912 |
$58,912 |
$6,039 |
$6,039 |
$57,845 |
|
IPMMF |
$39,321 |
$31,457 |
$31,457 |
$1,400 |
$1,400 |
$31,008 |
|
IRF |
$24,608 |
$19,686 |
$19,686 |
N/A |
N/A |
$19,466 |
|
DIGF |
$9,087 |
$7,259 |
$6,673 |
N/A |
N/A |
$6,148 |
|
DLA |
$4,251 |
$3,401 |
$3,401 |
N/A |
N/A |
$3,363 |
|
DMCMP |
$336 |
N/A |
N/A |
$269 |
$269 |
$269 |
|
DNYMCM |
$270 |
N/A |
N/A |
$216 |
$216 |
$216 |
|
DOF |
$137 |
$110 |
$101 |
N/A |
N/A |
$94 |
|
PSIMBF |
$7,313 |
$5,851 |
$5,851 |
$4,709 |
$4,709 |
$5,828 |
|
SDBF |
$621 |
$497 |
$497 |
N/A |
N/A |
$192 |
|
DTECMF |
$1,823 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,458 |
$1,458 |
$1,458 |
|
DTACM |
$11,905 |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,524 |
$9,524 |
$9,524 |
|
DTPCM |
$22,360 |
N/A |
N/A |
$17,888 |
$17,888 |
$17,888 |
|
WDMMF |
$1,454 |
$1,163 |
$1,163 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,057 |
|
DF |
$5,577 |
$4,462 |
$4,462 |
N/A |
N/A |
$4,404 |
|
DTCF |
$5,135 |
$4,108 |
$4,108 |
$3,797 |
$3,797 |
$4,096 |
|
Total compensation from the funds and fund complex (**) |
$1,084,688 |
$193,750 |
$329,717 |
$511,000 (98) |
$220,000 (41) |
$393,467 |
I-8
|
Interested Board Members |
Emeritus Board Members | |||||||
|
Fund |
J. Charles Cardona |
Gordon J. Davis |
Isabel P. Dunst |
Clifford L. Alexander |
Lyle E. Gramley1 |
Arthur A. Hartman |
George L. Perry |
Philip Toia1 |
|
CSF |
N/A |
$8,083 |
$116 |
$11,890 |
N/A |
$11 |
$52 |
$25 |
|
DCM |
N/A |
N/A |
$14,330 |
N/A |
$2,867 |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,863 |
|
DGCMF |
N/A |
N/A |
$11,315 |
N/A |
$2,221 |
N/A |
N/A |
$7,821 |
|
ICAF |
N/A |
$59,217 |
$6,039 |
$49,187 |
N/A |
$19,914 |
$63,416 |
$1,318 |
|
IPMMF |
N/A |
$31,594 |
$1,400 |
$28,141 |
N/A |
$9,644 |
$33,048 |
$182 |
|
IRF |
N/A |
$19,758 |
N/A |
$17,202 |
N/A |
$5,696 |
$19,686 |
N/A |
|
DIGF |
N/A |
$6,829 |
N/A |
$7,248 |
N/A |
$2,678 |
$7,267 |
N/A |
|
DLA |
N/A |
$3,413 |
N/A |
$3,013 |
N/A |
$993 |
$3,401 |
N/A |
|
DMCMP |
N/A |
N/A |
$269 |
N/A |
$53 |
N/A |
N/A |
$201 |
|
DNYMCM |
N/A |
N/A |
$216 |
N/A |
$43 |
N/A |
N/A |
$145 |
|
DOF |
N/A |
$4 |
N/A |
$91 |
N/A |
$32 |
$110 |
N/A |
|
PSIMBF |
N/A |
$5,858 |
$4,709 |
$2,040 |
N/A |
$1,039 |
$2,275 |
$535 |
|
SDBF |
N/A |
$498 |
N/A |
$478 |
N/A |
$147 |
$197 |
N/A |
|
DTECMF |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,458 |
N/A |
$286 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,009 |
|
DTACM |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,524 |
N/A |
$1,922 |
N/A |
N/A |
$6,489 |
|
DTPCM |
N/A |
N/A |
$17,888 |
N/A |
$3,609 |
N/A |
N/A |
$12,125 |
|
WDMMF |
N/A |
$237 |
N/A |
$1,230 |
N/A |
$425 |
$1,212 |
N/A |
|
DF |
N/A |
$4,479 |
N/A |
$3,873 |
N/A |
$1,329 |
$4,462 |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
N/A |
$4,112 |
$3,797 |
$1,312 |
N/A |
$573 |
$1,455 |
$685 |
|
Total compensation from the funds and fund complex (**) |
N/A |
$279,717 |
$55,000 (10) |
$299,533 (42) |
$11,000 (10) |
$48,750 |
$170,500 |
$174,390 (57) |
* Amounts shown do not include the cost of office space, secretarial services and health benefits for the Chairman of the Boards and expenses reimbursed to board members for attending board meetings.
** Represents the number of separate portfolios comprising the investment companies in the fund complex, including the funds, for which the board member served in 2013.
1 Messrs. Gramley and Toia receive compensation from the funds for attending board meetings in an advisory role although not board members or emeritus board members of the funds.
|
Name |
Principal Occupation During Past 5 Years |
Number of Other Investment Companies (Portfolios) for which serves as an Officer |
|
Bradley J. Skapyak |
Chief Operating Officer and a director of the Manager since June 2009; Chairman of the Transfer Agent since May 2011 and Executive Vice President of the Distributor since June 2007; from April 2003 to June 2009, head of the Investment Accounting and Support Department of the Manager |
69 (142) |
I-9
|
Name |
Principal Occupation During Past 5 Years |
Number of Other Investment Companies (Portfolios) for which serves as an Officer |
|
J. Charles Cardona2 |
President and a Director of the Manager; Executive Vice President of the Distributor; President of Dreyfus Institutional Services Division |
12 (19) |
|
James Windels3 |
Director – Mutual Fund Accounting of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
John Pak |
Deputy General Counsel, Investment Management of BNY Mellon since August 2014; Chief Legal Officer of the Manager since August 2012; from March 2005 to July 2012, Managing Director of Deutsche Bank, Deputy Global Head of Deutsche Asset Management Legal and Regional Head of Deutsche Asset Management Americas Legal |
70 (167) |
|
Janette E. Farragher |
Assistant General Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
Kiesha Astwood |
Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
James Bitetto |
Managing Counsel of BNY Mellon and Secretary of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Joni Lacks Charatan |
Managing Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
Joseph M. Chioffi |
Managing Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
John B. Hammalian |
Senior Managing Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
Sarah S. Kelleher |
Senior Counsel of BNY Mellon since March 2013; from August 2005 to March 2013, Associate General Counsel, Third Avenue Management |
70 (167) |
I-10
|
Name |
Principal Occupation During Past 5 Years |
Number of Other Investment Companies (Portfolios) for which serves as an Officer |
|
Jeff S. Prusnofsky |
Senior Managing Counsel of BNY Mellon |
70 (167) |
|
Richard S. Cassaro |
Senior Accounting Manager – Money Market and Municipal Bond Funds of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Gavin C. Reilly |
Tax Manager of the Investment Accounting and Support Department of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Robert S. Robol4 |
Senior Accounting Manager – Fixed Income Funds of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Robert Salviolo |
Senior Accounting Manager – Equity Funds of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Robert Svagna5 |
Senior Accounting Manager – Equity Funds of the Manager |
70 (167) |
|
Matthew D. Connolly |
Anti-Money Laundering Compliance Officer of the Distributor since October 2011; from March 2010 to September 2011, Global Head, KYC Reviews and Director, UBS Investment Bank; until March 2010, AML Compliance Officer and Senior Vice President, Citi Global Wealth Management |
65 (162) |
|
Joseph W. Connolly |
Chief Compliance Officer of the Manager and the Dreyfus Family of Funds |
70 (167) |
1 With respect to IRF, each officer has held his or her respective position with the fund since 2008, except for John Pak, Bradley Skapyak and Matthew Connolly and Mmes. Farragher, Astwood and Kelleher, whose dates are as shown above. With respect to CSF, each officer has held his or her respective position with the fund since the date shown above, except Mr. Robol and Mr. Svagna (please see notes 4 & 5).
2 Mr. Cardona is an officer with respect to IRF, IPMMF and ICAF only, a position he has held since 2000 with respect to IPMMF, 2002 with respect to ICAF, and 2008 with respect to IRF.
3 With respect to ICAF, Mr. Windels has held the position with the fund since 2002.
4 Mr. Robol has held this position since 2002 with respect to DF and DLA, 2003 with respect to WDMMF, DICAF and CSF, and 2005 with respect to DTCF, DOF, SDBF, DF, DIGF, IPMMF and PSIMBF.
5 Mr. Svagna has held this position since 2002 with respect to DOF, PSIMBF, DTCF and DF, and 2005 with respect to WDMMF, IPMMF, DIGF, CSF, DLA and SDBF.
The address of each officer is 200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166.
I-11
CERTAIN PORTFOLIO MANAGER INFORMATION
(not applicable to money market funds)
The following table lists the funds' portfolio managers, if any, who are in addition to the primary portfolio managers listed in the prospectus. See the prospectus for a list of, and certain other information regarding, the primary portfolio manager(s) for your fund.
|
Fund |
Additional Portfolio Managers |
|
DIASF |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
N/A |
|
DSTIF |
N/A |
|
DSBEMEF |
N/A |
|
DSBGEF |
N/A |
|
DSBUSEF |
N/A |
|
DNRF |
N/A |
|
DSIMBF |
N/A |
|
SDBF |
N/A |
|
DF |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
N/A |
The following table lists the number and types of accounts (including the funds) advised by each fund's primary portfolio manager(s) and assets under management in those accounts as of the end of the last fiscal year of the funds they manage. If a portfolio manager is a primary portfolio manager for multiple funds with different fiscal year ends, information is provided as of the most recent last fiscal year end of the relevant funds, unless otherwise indicated.
|
Primary |
Registered Investment Companies |
Total Assets Managed |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
Total Assets Managed |
Other Accounts |
Total Assets Managed |
|
Robert Bayston |
5 |
$1.5B |
4 |
$65.2M |
83 |
$9.2B |
|
C. Wesley Boggs1 |
12 |
$1.7B |
17 |
$665M |
45 |
$7.2B |
|
David Bowser |
4 |
$1.5B |
6 |
$880.7M |
159 |
$21.5B |
|
Jeffrey Burger |
7 |
$3.2B |
1 |
$52M |
304 |
$916M |
|
Thomas Casey |
8 |
$4.5B |
None |
N/A |
224 |
$2.1B |
|
Warren Chiang1 |
12 |
$1.7B |
17 |
$665M |
45 |
$7.2B |
|
Sean P. Fitzgibbon |
14 |
$4.6B |
5 |
$377.9M |
21 |
$3.4B |
|
Ronald Gala1 |
12 |
$1.7B |
17 |
$665M |
45 |
$7.2B |
|
Peter D. Goslin1 |
12 |
$1.7B |
17 |
$665M |
45 |
$7.2B |
|
David Horsfall |
5 |
$1.5B |
9 |
$1.5B |
159 |
$22.2B |
|
Barry K. Mills |
13 |
$5.5B |
3 |
$214.4M |
19 |
$1.4B |
|
Nate Pearson |
3 |
$466.7M |
None |
N/A |
None |
N/A |
|
David M. Sealy |
13 |
$5.5B |
3 |
$214.4M |
19 |
$1.4B |
|
Elizabeth Slover |
13 |
$5.0B |
3 |
$215.6M |
18 |
$1.3B |
|
Robin Wehbe |
13 |
$5.0B |
3 |
$215.6M |
18 |
$1.3B |
1 Because Messrs. Boggs, Chiang, Gala and Goslin became primary portfolio managers of Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund as of September 15, 2014, their information is as of April 30, 2014.
I-12
The following table provides information on accounts managed (included within the table above) by each primary portfolio manager that are subject to performance-based advisory fees. If a portfolio manager is a primary portfolio manager for multiple funds with different fiscal year ends, information is provided as of the most recent last fiscal year end of the relevant funds, unless otherwise indicated.
|
Primary |
Type of Account |
Number of Accounts |
Total Assets of Accounts |
|
Robert Bayston |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
C. Wesley Boggs1 |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
2 |
$12.3M |
|
Other Accounts |
10 |
$1.8B | |
|
David Bowser |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Jeffrey Burger |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Thomas Casey |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Warren Chiang1 |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
2 |
$12.3M |
|
Other Accounts |
10 |
$1.8B | |
|
Sean P. Fitzgibbon |
Other Accounts |
2 |
$184.3M |
|
Ronald Gala1 |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
2 |
$12.3M |
|
Other Accounts |
10 |
$1.8B | |
|
Peter D. Goslin1 |
Other Pooled Investment Vehicles |
2 |
$12.3M |
|
Other Accounts |
10 |
$1.8B | |
|
David Horsfall |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Barry K. Mills |
Other Accounts |
2 |
$17.0M |
|
Nate Pearson |
None |
N/A |
N/A |
|
David M. Sealy |
Other Accounts |
2 |
$17.0M |
|
Elizabeth Slover |
Other |
2 |
$16.9M |
|
Robin Wehbe |
Other |
2 |
$16.9M |
1 Because Messrs. Boggs, Chiang, Gala and Goslin became primary portfolio managers of Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund as of September 15, 2014, their information is as of April 30, 2014.
I-13
The following table lists the dollar range of fund shares beneficially owned by the primary portfolio manager(s) as of the end of the fund's last fiscal year, unless otherwise indicated.
|
Primary Portfolio Manager |
Fund |
Dollar Range of Fund Shares Beneficially Owned |
|
Robert Bayston |
DIASF |
None |
|
C. Wesley Boggs |
DTCF |
None |
|
DSBEMEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBGEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBUSEF1 |
None | |
|
David Bowser |
DSTIF |
None |
|
DITIF |
None | |
|
SDBF |
None | |
|
Jeffrey Burger |
DSIMBF |
None |
|
Thomas Casey |
DSIMBF |
None |
|
Warren Chiang |
DTCF |
None |
|
DSBEMEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBGEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBUSEF1 |
None | |
|
Sean P. Fitzgibbon |
DF |
None |
|
Ronald Gala |
DTCF |
None |
|
DSBEMEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBGEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBUSEF1 |
None | |
|
Peter D. Goslin |
DSBEMEF1 |
None |
|
DSBGEF1 |
None | |
|
DSBUSEF1 |
None | |
|
David Horsfall |
DIASF |
None |
|
DITIF |
None | |
|
DSTIF |
None | |
|
SDBF |
None | |
|
Barry K. Mills |
DF |
None |
|
Nate Pearson |
DIASF |
None |
|
David M. Sealy |
DF |
$1-$10,000 |
|
Elizabeth Slover |
DNRF |
None |
|
Robin Wehbe |
DNRF |
None |
1 Messrs. Boggs, Chiang, Gala and Goslin became primary portfolio managers of Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund as of September 15, 2014, and on that date they did not own shares of the respective funds.
I-14
For each fund's last three fiscal years, the management fees payable by the fund, the reduction, if any, in the amount of the fee paid due to fee waivers and/or expense reimbursements by the Manager and the net fees paid by the fund were as follows:
|
2014 Fiscal Year |
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year | |||||||
|
Fund |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
|
CSPMMF |
$236,888 |
$236,888 |
$0 |
$215,860 |
$215,860 |
$0 |
$257,147 |
$257,147 |
$0 |
|
CSTMMF |
$375,371 |
$375,371 |
$0 |
$409,421 |
$409,421 |
$0 |
$483,916 |
$483,916 |
$0 |
|
DCM |
$53,248,889 |
$25,313,773 |
$27,935,116 |
$54,439,256 |
$8,239,182 |
$46,200,074 |
$56,959,947 |
$13,983,868 |
$42,976,079 |
|
DGCM |
$32,868,448 |
$25,315,802 |
$7,552,646 |
$36,715,743 |
$15,424,011 |
$21,291,732 |
$42,668,618 |
$23,455,744 |
$19,212,874 |
|
DGPCM |
$9,396,749 |
$9,038,719 |
$358,030 |
$9,442,530 |
$7,281,319 |
$2,161,211 |
$8,804,862 |
$7,951,811 |
$853,051 |
|
DICAF |
$38,753,690 |
$13,228,205 |
$25,525,485 |
$30,691,988 |
$395,541 |
$30,296,447 |
$41,866,154 |
$759,599 |
$41,106,555 |
|
DIPMMF |
$8,420,863 |
$312,288 |
$8,108,575 |
$8,476,789 |
$252,925 |
$8,223,864 |
$10,147,226 |
$268,964 |
$9,878,262 |
|
DIPPMMF |
$1,212,320 |
$1,212,320 |
$0 |
$1,285,708 |
$1,285,708 |
$0 |
$1,158,101 |
$1,158,101 |
$0 |
|
DMCMP |
$850,661 |
$850,661 |
$0 |
$1,531,961 |
$887,292 |
$644,669 |
$1,827,368 |
$1,019,544 |
$807,824 |
|
DSIMBF |
$2,554,166 |
$554,844 |
$1,999,322 |
$2,919,117 |
$280,497 |
$2,638,620 |
$2,739,028 |
$0 |
$2,739,028 |
|
DNYMCM |
$859,584 |
$859,584 |
$0 |
$986,831 |
$683,140 |
$303,691 |
$1,407,300 |
$805,394 |
$601,906 |
|
DTECM |
$4,418,584 |
$3,585,525 |
$833,059 |
$4,939,221 |
$1,952,624 |
$2,986,597 |
$5,629,894 |
$2,012,265 |
$3,617,629 |
|
DCAAMT |
$918,431 |
$918,431 |
$0 |
$897,829 |
$828,268 |
$69,561 |
$766,890 |
$482,283 |
$284,607 |
|
DNYAMT |
$225,312 |
$225,312 |
$0 |
$286,045 |
$226,252 |
$59,793 |
$313,103 |
$251,532 |
$61,571 |
|
DTACM |
$36,555,979 |
$33,494,613 |
$3,061,366 |
$37,434,261 |
$24,009,302 |
$13,424,959 |
$30,864,938 |
$27,357,914 |
$3,507,024 |
|
DTPCM |
$68,996,653 |
$68,996,653 |
$0 |
$57,035,249 |
$57,035,249 |
$0 |
$47,239,366 |
$47,239,366 |
$0 |
|
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year |
2011 Fiscal Year | |||||||
|
Fund |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
Fee payable |
Reduction in fee |
Net fee paid |
|
DIRMF |
$4,306,890 |
$2,377,795 |
$1,929,095 |
$4,307,122 |
$84,720 |
$4,222,402 |
$7,199,375 |
$85,530 |
$7,113,845 |
|
DIRTF |
$1,700,637 |
$1,700,637 |
$0 |
$1,756,683 |
$87,865 |
$1,668,818 |
$2,021,092 |
$676,757 |
$1,344,335 |
|
DIRTPF |
$1,152,797 |
$1,152,797 |
$0 |
$1,184,450 |
$651,403 |
$533,047 |
$1,360,273 |
$768,729 |
$591,544 |
|
DLA1 |
$4,305,595 |
$4,305,595 |
$0 |
$11,567,285 |
$11,437,508 |
$129,777 |
$22,019,827 |
$20,153,414 |
$1,866,413 |
|
DF2 |
$7,891,236 |
$0 |
$7,891,236 |
$6,573,652 |
$0 |
$6,573,652 |
$6,637,722 |
$0 |
$6,637,722 |
|
SDBF |
$588,525 |
$322,166 |
$266,359 |
$751,962 |
$51,059 |
$700,903 |
$871,236 |
$0 |
$871,236 |
|
WDMMF |
$1,408,506 |
$1,408,506 |
$0 |
$1,657,813 |
$1,657,813 |
$0 |
$2,218,759 |
$2,218,759 |
$0 |
|
DIASF |
$1,141,102 |
$0 |
$1,141,102 |
$938,177 |
$0 |
$938,177 |
$585,505 |
$0 |
$585,505 |
|
DITIF |
$5,266,511 |
$54,718 |
$5,211,793 |
$5,072,250 |
$0 |
$5,072,250 |
$5,353,661 |
$0 |
$5,353,661 |
|
DSTIF |
$1,254,668 |
$488,090 |
$766,578 |
$1,294,966 |
$0 |
$1,294,966 |
$1,287,343 |
$0 |
$1,287,343 |
|
DNRF |
$212,391 |
$88,733 |
$123,658 |
$190,499 |
$59,095 |
$131,404 |
$231,609 |
$5,819 |
$225,790 |
1 As compensation for its services to the fund, the fund has agreed to pay the Manager a monthly management fee, as a percentage of the fund's average daily net assets, at the following annual rate: .50% up to $1.5 billion; .48% between $1.5 billion and $2 billion; .47% between $2 billion and $2.5 billion; and .45% over $2.5 billion.
2 As compensation for its services to the fund, the fund has agreed to pay the Manager a monthly management fee, as a percentage of the fund's average daily net assets, at the following annual rate: .65% up to $1.5 billion; .625% between $1.5 billion and $2 billion; .60% between $2 billion and $2.5 billion; and .55% over $2.5 billion.
I-15
SALES LOADS, CDSCS AND DISTRIBUTOR'S COMPENSATION
The following table lists, for each of the last three fiscal years, the total commissions on sales of Class A shares (sales loads) and the total CDSCs on redemptions of all classes of shares (as applicable), along with corresponding amounts of each retained by the Distributor.
|
Fund |
2014 Fiscal Year |
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year | |
|
DSIMBF |
Total commissions (A shares) |
$7,277 |
$13,535 |
$5,584 |
|
Commission amount retained |
$4,183 |
$3,142 |
$2,951 | |
|
Total CDSCs |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 | |
|
CDSC amount retained |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 | |
|
DTCF |
||||
|
Total commissions (A shares) |
$26,249 |
$49,100 |
$7,984 | |
|
Commission amount retained |
$2,978 |
$8,256 |
$5,266 | |
|
Total CDSCs |
$51 |
$113 |
$984 | |
|
CDSC amount retained |
$51 |
$113 |
$984 |
|
Fund |
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year |
2011 Fiscal Year | |
|
DITIF |
||||
|
Total commissions (A shares) |
$105,071 |
$32,620 |
$34,158 | |
|
Commission amount retained |
$9,015 |
$12,118 |
$337 | |
|
Total CDSCs |
$3,696 |
$10,675 |
$21,042 | |
|
CDSC amount retained |
$3,696 |
$10,675 |
$21,042 | |
|
DSTIF |
||||
|
Total commissions (A shares) |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A | |
|
Commission amount retained |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A | |
|
Total CDSCs |
N/A |
$34 |
$976 | |
|
CDSC amount retained |
N/A |
$34 |
$976 | |
|
DNRF |
||||
|
Total commissions (A shares) |
$104,521 |
$19,687 |
$12,221 | |
|
Commission amount retained |
$10,277 |
$4,106 |
$9,480 | |
|
Total CDSCs |
$35 |
$258 |
$1,254 | |
|
CDSC amount retained |
$35 |
$258 |
$1,254 | |
The amounts paid by each fund to the Distributor under the fund's Plan or Plans, as applicable, for services described in Part II of this SAI under "Distribution Plans, Service Plans and Shareholder Services Plans" for the fund's last fiscal year were as follows:
|
Fund |
Plan |
Class |
Amount |
Printing and Implementation and Operation of Plan |
Amount Reimbursed to Fund Pursuant to Undertaking in Effect |
Total Amount |
|
CSPMMF |
12b-1 |
Class C |
$60,307 |
N/A |
N/A |
$60,307 |
|
Class D |
$207,794 |
N/A |
N/A |
$207,794 | ||
|
Administration |
Class B |
$217,310 |
N/A |
N/A |
$217,310 |
I-16
|
Class C |
$60,307 |
N/A |
N/A |
$60,307 | ||
|
Class D |
$79,921 |
N/A |
N/A |
$79,921 | ||
|
Omnibus |
Class A |
$93,873 |
N/A |
N/A |
$93,873 | |
|
Class B |
$86,924 |
N/A |
N/A |
$86,924 | ||
|
Class C |
$24,123 |
N/A |
N/A |
$24,123 | ||
|
Class D |
$31,968 |
N/A |
N/A |
$31,968 | ||
|
CSTMMF |
12b-1 |
Class C |
$23,140 |
N/A |
N/A |
$23,140 |
|
Class D |
$3,043 |
N/A |
N/A |
$3,043 | ||
|
Administration |
Class B |
$380,516 |
N/A |
N/A |
$380,516 | |
|
Class C |
$23,139 |
N/A |
N/A |
$23,139 | ||
|
Class D |
$1,170 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,170 | ||
|
Omnibus |
Class A |
$213,347 |
N/A |
N/A |
$213,347 | |
|
Class B |
$152,303 |
N/A |
N/A |
$152,303 | ||
|
Class C |
$9,253 |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,253 | ||
|
Class D |
$468 |
N/A |
N/A |
$468 | ||
|
DCM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$1,291,822 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,291,822 | |
|
Agency |
$95,158 |
N/A |
N/A |
$95,158 | ||
|
Investor |
$6,043,006 |
N/A |
N/A |
$6,043,006 | ||
|
Participant |
$3,324,827 |
N/A |
N/A |
$3,324,827 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$352,179 |
N/A |
N/A |
$352,179 | |
|
DGCM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$724,388 |
N/A |
N/A |
$724,388 | |
|
Agency |
$60,607 |
N/A |
N/A |
$60,607 | ||
|
Investor |
$4,630,846 |
N/A |
N/A |
$4,630,846 | ||
|
Participant |
$810,420 |
N/A |
N/A |
$810,420 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$219,714 |
N/A |
N/A |
$219,714 | |
|
DGPCM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$541,836 |
N/A |
N/A |
$541,836 | |
|
Agency |
$8,429 |
N/A |
N/A |
$8,429 | ||
|
Investor |
$1,373,911 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,373,911 | ||
|
Participant |
$845,794 |
N/A |
N/A |
$845,794 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$44,222 |
N/A |
N/A |
$44,222 | |
|
DICAF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Administrative Advantage |
$368,890 |
N/A |
N/A |
$368,890 | |
|
Participant Advantage |
$278,731 |
N/A |
N/A |
$278,731 | ||
|
Investor Advantage |
$34,730 |
N/A |
N/A |
$34,730 | ||
|
DIPMMF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Reserve |
$329,863 |
N/A |
N/A |
$329,863 | |
|
DIPPMMF |
||||||
|
None |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A | |
|
DIRMF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Hamilton |
$723,149 |
N/A |
N/A |
$723,149 |
I-17
|
Agency |
$22,021 |
N/A |
N/A |
$22,021 | ||
|
Premier |
$1,247,029 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,247,029 | ||
|
Classic |
$1,017,645 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,017,645 | ||
|
DIRTF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Hamilton |
$81,252 |
N/A |
N/A |
$81,252 | |
|
Agency |
$4,849 |
N/A |
N/A |
$4,849 | ||
|
Premier |
$2,054,124 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,054,124 | ||
|
Classic |
$1,168,253 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,168,253 | ||
|
DIRTPF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Hamilton |
$4,824 |
N/A |
N/A |
$4,824 | |
|
Premier |
$1,051,626 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,051,626 | ||
|
DIASF |
||||||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Investor |
$130,326 |
N/A |
N/A |
$130,326 | |
|
DITIF |
||||||
|
Distribution Plan |
Class C |
$308,704 |
N/A |
N/A |
$308,704 | |
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class A |
$2,361,467 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,361,467 | |
|
Class C |
$102,928 |
N/A |
N/A |
$102,928 | ||
|
DSTIF |
||||||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class D |
$499,778 |
N/A |
N/A |
$499,778 | |
|
Class P |
$2,611 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,611 | ||
|
DLA |
||||||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class 1 |
$1,788,284 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,788,284 | |
|
DMCMP |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$75,923 |
N/A |
N/A |
$75,923 | |
|
Agency |
$1 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1 | ||
|
Investor |
$459,852 |
N/A |
N/A |
$459,852 | ||
|
Participant |
$64,122 |
N/A |
N/A |
$64,122 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$7,032 |
N/A |
N/A |
$7,032 | |
|
DNYMCM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$8,605 |
N/A |
N/A |
$8,605 | |
|
Investor |
$745,370 |
N/A |
N/A |
$745,370 | ||
|
Participant |
$15,447 |
N/A |
N/A |
$15,447 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$2,343 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,343 | |
|
DNRF |
||||||
|
Distribution Plan |
Class C |
$27,467 |
N/A |
N/A |
$27,467 | |
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class A |
$49,249 |
N/A |
N/A |
$49,249 | |
|
Class C |
$9,156 |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,156 | ||
|
DSIMBF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Class D |
$421,774 |
N/A |
N/A |
$421,774 | |
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class A |
$149,876 |
N/A |
N/A |
$149,876 | |
|
SDBF |
||||||
|
Service Plan |
Class D |
$329 |
N/A |
N/A |
$329 | |
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class Z |
$110,471 |
N/A |
N/A |
$110,471 |
I-18
|
DTECM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$64,080 |
N/A |
N/A |
$64,080 | |
|
Investor |
$1,069,560 |
N/A |
N/A |
$1,069,560 | ||
|
Participant |
$139,775 |
N/A |
N/A |
$139,775 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$336,638 |
N/A |
N/A |
$336,638 | |
|
DCAAMT |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$2,666 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,666 | |
|
Investor |
$593,871 |
N/A |
N/A |
$593,871 | ||
|
Participant |
$140,337 |
N/A |
N/A |
$140,337 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$221 |
N/A |
N/A |
$221 | |
|
DNYAMT |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$4,421 |
N/A |
N/A |
$4,421 | |
|
Classic |
$7,803 |
N/A |
N/A |
$7,803 | ||
|
Investor |
$77,027 |
N/A |
N/A |
$77,027 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$308 |
N/A |
N/A |
$308 | |
|
DTACM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$623,288 |
N/A |
N/A |
$623,288 | |
|
Agency |
$17,134 |
N/A |
N/A |
$17,134 | ||
|
Investor |
$5,867,098 |
N/A |
N/A |
$5,867,098 | ||
|
Participant |
$2,130,107 |
N/A |
N/A |
$2,130,107 | ||
|
Select |
$43,241 |
N/A |
N/A |
$43,241 | ||
|
Service |
$61,577 |
N/A |
N/A |
$61,577 | ||
|
Premier |
$83,326 |
N/A |
N/A |
$83,326 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$191,367 |
N/A |
N/A |
$191,367 | |
|
DTPCM |
||||||
|
Services Plan |
Administrative |
$650,716 |
N/A |
N/A |
$650,716 | |
|
Agency |
$19,493 |
N/A |
N/A |
$19,493 | ||
|
Investor |
$9,305,973 |
N/A |
N/A |
$9,305,973 | ||
|
Participant |
$12,130,658 |
N/A |
N/A |
$12,130,658 | ||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Institutional |
$27,884 |
N/A |
N/A |
$27,884 | |
|
WDMMF |
||||||
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
$690,608 |
N/A |
N/A |
$690,608 | ||
|
DF |
||||||
|
None |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A | |
|
DTCF |
||||||
|
Distribution Plan |
Class C |
$38,738 |
N/A |
N/A |
$38,738 | |
|
Shareholder Services Plan |
Class A |
$52,287 |
N/A |
N/A |
$52,287 | |
|
Class C |
$12,913 |
N/A |
N/A |
$12,913 | ||
|
Class Z |
$222,850 |
N/A |
N/A |
$222,850 |
I-19
OFFERING PRICE
(Class A shares only)
Set forth below is an example of the method of computing the offering price of each fund's Class A shares, if applicable. The example assumes a purchase of Class A shares aggregating less than $50,000 subject to the schedule of sales charges set forth in the fund's prospectus at a price based upon the NAV of a Class A share at the close of business on the last business day of the fund's last fiscal year. Certain purchases are not subject to a sales charge or are subject to a different sales charge than the one shown below. See the prospectus and "How to Buy Shares" in Part II of this SAI.
|
Fund |
NAV Per Share |
Sales Charge as a Percentage of Offering Price and NAV Per Share |
Per Share Sales Charge |
Per Share Offering Price to Public |
|
DITIF |
$13.59 |
4.50% of offering price (4.71% of NAV per share) |
$0.64 |
$14.23 |
|
DNRF |
$29.66 |
5.75% of offering price (6.10% of NAV per share) |
$1.81 |
$31.47 |
|
DSBEMEF |
$12.50 |
5.75% of offering price (6.10% of NAV per share) |
$0.76 |
$13.26 |
|
DSBGEF |
$12.50 |
5.75% of offering price (6.10% of NAV per share) |
$0.76 |
$13.26 |
|
DSBUSEF |
$12.50 |
5.75% of offering price (6.10% of NAV per share) |
$0.76 |
$13.26 |
|
DSIMBF |
$13.05 |
2.5% of offering price (2.6% of NAV per share) |
$0.33 |
$13.38 |
|
DTCF |
$14.82 |
5.75% of offering price (6.10% of NAV per share) |
$0.90 |
$15.72 |
RATINGS OF MUNICIPAL OBLIGATIONS
(money market funds)
The average distribution of investments (at value) in Municipal Obligations (including notes) by ratings for the last fiscal year, computed on a monthly basis, for each fund that focuses its investments in Municipal Obligations was as follows:
|
Fitch |
Moody's |
S&P |
DMCMP |
DNYMCM |
DTECM |
DCAAMT |
DNYAMT |
|
F-1+/F-1 |
VMIG 1/MIG 1, P-1 |
SP-1+/SP-1, A1+/A1 |
85.9% |
77.5% |
96.1% |
97.0% |
71.7% |
|
F-2+/F-2 |
VMIG 2/MIG 2, P-2 |
SP-2+/SP-2, A2+/A2 |
5.6% |
6.0% |
- |
1.9% |
8.8% |
|
AAA/AA |
Aaa/Aa |
AAA/AA |
3.6% |
3.6% |
3.9% |
0.5% |
1.0% |
|
Not Rated |
Not Rated |
Not Rated |
4.9%* |
12.9%* |
- |
0.6%* |
18.5%* |
|
Total |
100.0% |
100.0% |
100.0% |
100.0% |
100.0% | ||
*Those securities which are not rated have been determined by the Manager to be of comparable quality to securities in the F-1/MIG 1/SP-1/rating category.
RATINGS OF MUNICIPAL BONDS
The average distribution of investments (at value) in Municipal Bonds (including notes) by ratings for the last fiscal year, computed on a monthly basis, for each fund that focuses its investments in Municipal Bonds was as follows:
I-20
|
Fitch |
Moody's |
S&P |
DSIMBF |
|
Fitch |
Moody's |
S&P |
DSIMBF |
|
AAA |
Aaa |
AAA |
22.2% |
|
AA |
Aa |
AA |
46.3% |
|
A |
A |
A |
24.6% |
|
BBB |
Baa |
BBB |
5.5% |
|
BB |
Ba |
BB |
0.5% |
|
B |
B |
B |
0.0% |
|
CCC |
Caa |
CCC |
0.0% |
|
CC |
Ca |
CC |
0.0% |
|
F-1/F-1+ |
VMIG 1/MIG 1/P-1 |
SP-1/A-1 |
0.9% |
|
Not Rated |
Not Rated |
Not Rated |
0.0% |
|
Total |
100.0% | ||
RATINGS OF CORPORATE DEBT SECURITIES
The average distribution of investments (at value) in corporate debt securities (excluding any preferred stock, convertible preferred stock or convertible bonds) by ratings for the last fiscal year, computed on a monthly basis, for each fund that focuses its investments in corporate debt securities was as follows:
|
Fitch |
Moody's |
DITIF |
DSTIF |
|
AAA |
Aaa |
73.6% |
60.0% |
|
AA |
Aa |
5.3% |
4.4% |
|
A |
A |
12.7% |
12.4% |
|
BBB |
Baa |
24.1% |
19.2% |
|
BB |
Ba |
4.8% |
3.5% |
|
B |
B |
1.4% |
0.5% |
|
CCC |
Caa |
0.0% |
0.0% |
|
Not Rated |
Not Rated |
0.0% |
0.0% |
|
Total |
121.9%* |
100.0% | |
*The fund also held convertible preferred stocks rated AA/Aa (0.5%).
SECURITIES OF REGULAR BROKERS OR DEALERS
A fund may acquire securities issued by one or more of its "regular brokers or dealers," as defined in Rule 10b-1 under the 1940 Act. Rule 10b-1 provides that a "regular broker or dealer" is one of the ten brokers or dealers that, during the fund's last fiscal year: (1) received the greatest dollar amount of brokerage commissions from participating, either directly or indirectly, in the fund's portfolio transactions, (2) engaged as principal in the largest dollar amount of the fund's portfolio transactions or (3) sold the largest dollar amount of the fund's securities. The following is a list of the issuers of the securities, and the aggregate value per issuer, of a fund's regular brokers or dealers held by such fund as of the end of its last fiscal year:
|
Fund |
Regular Broker or Dealer |
Aggregate Value Per Issuer |
|
CSPMMF |
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$15,000,000 |
|
Bank of Nova Scotia |
$15,000,000 | |
|
RBS Securities Inc. |
$12,000,000 | |
|
RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
$5,000,000 | |
|
Credit Suisse (USA) Inc. |
$5,000,000 | |
|
CSTMMF |
N/A |
N/A |
I-21
|
DCM |
RBS Securities Inc. |
$780,000,000 |
|
RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
$50,000,000 | |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$663,000,000 | |
|
Lloyds Securities Inc. |
$1,000,000,000 | |
|
Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. |
$400,000,000 | |
|
Rabo Securities USA, Inc. |
$939,412,000 | |
|
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$2,240,000,000 | |
|
DGCM |
Cowen & Company, LLC |
$1,425,000,000 |
|
RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
$550,000,000 | |
|
Bank of Nova Scotia |
$500,000,000 | |
|
Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. |
$55,000,000 | |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$85,000,000 | |
|
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
$150,000,000 | |
|
DGPCM |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DICAF |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DIPMMF |
Bank of Nova Scotia |
$350,000,000 |
|
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$300,000,000 | |
|
Lloyds Securities Inc. |
$300,000,000 | |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$291,000,000 | |
|
UBS Securities LLC |
$150,000,000 | |
|
RBS Securities Inc. |
$100,000,000 | |
|
DIPPMMF |
RBS Securities Inc. |
$170,000,000 |
|
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$55,000,000 | |
|
Lloyds Securities Inc. |
$55,000,000 | |
|
DIRMF |
RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
$125,000,000 |
|
Lloyds Capital Markets Corp. |
$140,000,000 | |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$115,988,000 | |
|
HSBC Securities (USA) Inc. |
$65,000,000 | |
|
DIRTF |
Citigroup Inc. |
$100,000,000 |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$75,000,000 | |
|
Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. |
$150,000,000 | |
|
Goldman, Sachs & Co. |
$76,000,000 | |
|
DIRTPF |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DIASF |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
$18,510,000 |
|
Citigroup Inc. |
$7,196,000 | |
|
Bank of America NA |
$5,838,000 | |
|
Morgan Stanley |
$7,645,000 | |
|
Goldman, Sachs & Co. |
$6,108,000 | |
|
HSBC Securities (USA) Inc. |
$4,690,000 | |
|
Credit Suisse (USA) Inc. |
$199,000 | |
|
DSTIF |
Citigroup Inc. |
$2,187,000 |
I-22
|
Bank of America NA |
$2,296,000 | |
|
Goldman, Sachs & Co. |
$4,062,000 | |
|
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
$2,005,000 | |
|
Morgan Stanley |
$1,877,000 | |
|
HSBC Securities (USA) Inc. |
$926,000 | |
|
Credit Suisse (USA) Inc. |
$197,000 | |
|
DLA |
HSBC Securities (USA) Inc. |
$40,000,000 |
|
RBC Securities Inc. |
$15,000,000 | |
|
Citigroup Inc. |
$35,000,000 | |
|
Credit Suisse (USA) Inc. |
$30,000,000 | |
|
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$64,991,000 | |
|
UBS Securities LLC |
$35,000,000 | |
|
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$35,000,000 | |
|
DMCMP |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DNYMCM |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DNRF |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DSIMBF |
N/A |
N/A |
|
SDBF |
Bank of America NA |
$2,209,000 |
|
Goldman, Sachs & Co. |
$1,613,000 | |
|
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
$987,000 | |
|
Morgan Stanley |
$1,060,000 | |
|
DTECM |
RBC Capital Markets, LLC |
$62,000,000 |
|
DCAAMT |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DNYAMT |
N/A |
N/A |
|
DTACM |
Credit Agricole Cheuvreux North America, Inc. |
$2,115,000,000 |
|
Cowen & Company, LLC |
$1,425,000,000 | |
|
RBC Securities Inc. |
$700,000,000 | |
|
TD Wealth Management Services Inc. |
$425,000,000 | |
|
RBC Capital Markets Corp. |
$400,000,000 | |
|
Credit Suisse (USA) Inc. |
$250,000,000 | |
|
Bank of Nova Scotia |
$200,000,000 | |
|
Citigroup Inc. |
$140,000,000 | |
|
Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. |
$125,000,000 | |
|
DTPCM |
N/A |
N/A |
|
WDMMF |
Barclays Capital Inc. |
$22,000,000 |
|
Cowen & Company, LLC |
$10,000,000 | |
|
RBS Securities Inc. |
$10,000,000 | |
|
DF |
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
$33,304,000 |
|
Wells Fargo & Co. |
$32,202,000 | |
|
Bank of America NA |
$37,144,000 |
I-23
|
Citigroup Inc. |
$21,296,000 | |
|
DTCF |
N/A |
N/A |
The aggregate amounts of commissions paid by each fund for brokerage commissions and spreads or concessions on principal transactions (none of which were paid to affiliates) for its last three fiscal years were as follows:
|
Fund |
2014 Fiscal Year |
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year | |||
|
Commissions |
Spreads/ |
Commissions |
Spreads/ |
Commissions |
Spreads/ | |
|
CSPMMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
CSTMMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DCM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DGCM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DGPCM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DICAF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DIPMMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DIPPMMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DMCMP |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DNYMCM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DSIMBF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DTCF |
$76,461 |
$0 |
$117,982 |
$0 |
$162,145 |
$0 |
|
DTECM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DCAAMT |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DNYAMT |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DTACM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DTPCM |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
Fund |
2013 Fiscal Year |
2012 Fiscal Year |
2011 Fiscal Year | |||
|
Commissions |
Spreads/ |
Commissions |
Spreads/ |
Commissions |
Spreads/ | |
|
DIRMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DIRTF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DIRTPF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DLA |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DF |
$783,165 |
$502 |
$697,804 |
$21,592 |
$1,176,427 |
$311,543 |
|
SDBF |
$986 |
$0 |
$242 |
$0 |
$258 |
$0 |
|
WDMMF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DIASF |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
$0 |
|
DITIF |
$23,132 |
$0 |
$6,145 |
$0 |
$51,411 |
$0 |
|
DSTIF |
$11,102 |
$0 |
$8,375 |
$0 |
$14,025 |
$0 |
|
DNRF |
$13,385 |
$7,338 |
$15,636 |
$7,426 |
$15,949 |
$10,660 |
The following table provides an explanation of any material difference in the commissions or spreads/concessions paid by a fund in either of the two fiscal years preceding the last fiscal year.
I-24
|
Fund |
Reason for Any Material Difference in Commissions or Spreads/Concessions |
|
CSPMMF |
N/A |
|
CSTMMF |
N/A |
|
DCM |
N/A |
|
DGCM |
N/A |
|
DGPCM |
N/A |
|
DICAF |
N/A |
|
DIPMMF |
N/A |
|
DIPPMMF |
N/A |
|
DIRMF |
N/A |
|
DIRTF |
N/A |
|
DIRTPF |
N/A |
|
DIASF |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
N/A |
|
DSTIF |
N/A |
|
DLA |
N/A |
|
DMCMP |
N/A |
|
DNYMCM |
N/A |
|
DNRF |
N/A |
|
DSIMBF |
N/A |
|
SDBF |
N/A |
|
DTECM |
N/A |
|
DCAAMT |
N/A |
|
DNYAMT |
N/A |
|
DTACM |
N/A |
|
DTPCM |
N/A |
|
WDMMF |
N/A |
|
DF |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
The fund decreased trading activity from 2012 to 2014. |
The aggregate amount of transactions during each fund's last fiscal year in securities effected on an agency basis through a broker-dealer for, among other things, research services and the commissions and concessions related to such transactions were as follows:
I-25
|
Fund |
Transactions |
Related Commissions/Concessions |
|
CSPMMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
CSTMMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DCM |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DICAF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIPMMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIPPMMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIRMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIRTF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIRTPF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DIASF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DSTIF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DLA |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DMCMP |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DNYMCM |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DNRF |
$7,329,816 |
$8,122 |
|
DSIMBF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DTECM |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DCAAMT |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DNYAMT |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DTACM |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DTPCM |
$0 |
N/A |
|
WDMMF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DF |
$798,791,924 |
$566,856 |
|
SDBF |
$0 |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
$213,755,995 |
$15,565 |
PORTFOLIO TURNOVER VARIATION
(not applicable to money market funds)
Each fund's portfolio turnover rate for up to five fiscal years is shown in the prospectus. The following table provides an explanation of any significant variation in a fund's portfolio turnover rates over the last two fiscal years (or any anticipated variation in the portfolio turnover rate from that reported for the last fiscal year).
|
Fund |
Reason for Any Significant Portfolio Turnover Rate Variation, or Anticipated Variation |
|
DIASF |
N/A |
|
DITIF |
N/A |
|
DSTIF |
The fund increased trading activity as a result of the market environment. |
|
DNRF |
N/A |
|
DSIMBF |
N/A |
|
SDBF |
N/A |
|
DF |
N/A |
|
DTCF |
N/A |
I-26
The following persons are known by each fund to own of record 5% or more of the indicated class of the fund's outstanding voting securities. A shareholder who beneficially owns, directly or indirectly, more than 25% of a fund's voting securities may be deemed to "control" (as defined in the 1940 Act) the fund. All information for a fund is as of the date indicated for the first listed class.
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
August 4, 2014 |
CSPMMF |
Class A |
Citizens Bank |
69.5311% |
|
National Financial Services LLC |
30.3235% | |||
|
Class B |
Citizens Bank |
44.1986% | ||
|
Citizens Investment Services |
26.7467% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
15.7928% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
12.7296% | |||
|
Class C |
Citizens Bank |
78.0214% | ||
I-27
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
National Financial Services LLC |
21.8322% | |||
|
Class D |
National Financial Services LLC |
100.0000% | ||
|
August 4, 2014 |
CSTMMF |
Class A |
Citizens Bank |
96.8122% |
|
Class B |
Citizens Bank |
86.3230% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
8.3918% | |||
|
Class C |
Citizens Bank |
90.1705% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
9.8295% | |||
|
Class D |
National Financial Services LLC |
100.0000% | ||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DCM |
Administrative |
American Enterprise Investment Services |
64.5238% |
I-28
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Bost & Co. |
13.1067% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
7.3098% | |||
|
Agency |
Mellon Financial Corporation |
86.0816% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
9.9059% | |||
|
Institutional |
Boston & Co. |
45.5925% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
17.1754% | |||
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
49.4419% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
36.5483% | |||
|
Participant |
Pershing LLC |
22.0525% | ||
I-29
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
First Republic Bank |
20.7636% | |||
|
Vantagetrust |
19.2168% | |||
|
ICMA Retirement Corporation |
9.9711% | |||
|
WTRISC Co IRA Omnibus Account |
7.9883% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
6.4726% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DGCM |
Administrative |
Hare & Co. |
29.7086% |
|
Pershing LLC |
24.2384% | |||
|
Agency |
Hare & Co. |
99.4291% | ||
|
Institutional |
Bost & Co. |
46.0946% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
22.1660% | |||
I-30
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
59.1701% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
23.4197% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
5.9321% | |||
|
Union Bank Trust Nominee |
5.7899% | |||
|
Participant |
Hare & Co. |
32.7085% | ||
|
Pershing LLC |
31.7045% | |||
|
BNP Paribas Prime Brokerage, Inc. |
5.1698% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DGPCM |
Administrative |
Hare & Co. |
6.6618% |
|
Museum of Contemporary Art |
5.7813% | |||
|
Agency |
Hare & Co. |
99.9992% |
I-31
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Institutional |
Bost & Co. |
69.4295% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
24.7563% | |||
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
50.9997% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
21.0878% | |||
|
Participant |
First Republic Bank |
36.4301% | ||
|
Jefferies LLC |
31.8878% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
20.3738% | |||
|
Pershing LLC |
9.5933% | |||
|
August 4, 2014 |
DICAF |
Administrative Advantage |
Amalgamated Bank |
86.2468% |
I-32
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Hare & Co. |
13.6653% | |||
|
Participant Advantage |
JP Morgan Clearing Corporation |
55.5330% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
21.8578% | |||
|
Wilmington Trust RISC Trustee |
11.7667% | |||
|
Jefferies LLC |
10.8425% | |||
|
Institutional Advantage |
Hare & Co. |
27.8502% | ||
|
Boston & Co. |
18.8528% | |||
|
JP Morgan Clearing Corporation (GAMA) |
8.1078% | |||
|
Chicago Mercantile Exchange Inc. Chicago, IL 60606-7431 |
7.9806% | |||
|
Merrill Lynch Pierce Fenner & Smith Charlotte, NC 28202-2191 |
7.2131% |
I-33
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Investor Advantage |
Hare & Co. |
49.2157% | ||
|
Wells Fargo Bank |
15.4208% | |||
|
Reliannce Trust Company FBO Various Clients PO Box 48529 Atlanta, GA 30362-1529 |
13.2767% | |||
|
Mid Atlantic Trust Company |
11.4850% | |||
|
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, |
7.8755% | |||
|
July 3, 2014 |
DIPMMF |
Prime |
UTIMCO |
32.3854% |
|
Boston & Co. |
21.2920% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
19.1414% | |||
|
Kuwait Investment Authority |
15.9384% | |||
|
Reserve |
Comerica Bank |
99.9996% |
I-34
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
DIPPMMF |
Bost & Co. |
74.3704% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
25.6296% | |||
|
April 8, 2014 |
DIRMF |
Institutional |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
67.5264% |
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
32.1832% | |||
|
Hamilton |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
39.5545% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
30.4271% | |||
|
M&T Trust Company of Delaware |
28.5956% | |||
|
Agency |
Hare & Co. |
100% | ||
|
Premier |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
69.8546% | ||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
17.4695% | |||
|
Mac & Co. |
9.6421% | |||
I-35
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Classic |
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
16.8578% | ||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
9.3981% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
6.0533% | |||
|
April 8, 2014 |
DIRTF |
Institutional |
Wells Fargo Bank |
51.5866% |
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
23.7553% | |||
|
Mac & Co. |
21.8749% | |||
|
Hamilton |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
49.9725% | ||
|
Bost & Co. |
31.2785% | |||
|
Suecia Holding Corporation |
14.1201% | |||
|
Agency |
Hare & Co. |
100% | ||
|
Premier |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
81.9601% |
I-36
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Mac & Co. |
16.3678% | |||
|
Classic |
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
23.4527% | ||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
14.7711% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
10.1799% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
7.5752% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
5.7639% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon As Agent For |
5.0486% | |||
|
April 8, 2014 |
DIRTPF |
Institutional |
Mac & Co. |
55.9095% |
|
SEI Private Trust Company |
25.7968% | |||
|
The Bank of New York Mellon |
11.3138% | |||
I-37
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Bost & Co. |
6.3121% | |||
|
Hamilton |
Bost & Co. |
48.7877% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
24.9975% | |||
|
David Blank |
20.0378% | |||
|
Jerry J. Limoncelli and Alice R. Limoncelli |
6.1697% | |||
|
Premier |
Mac & Co. |
84.4272% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
14.8541% | |||
|
November 4, 2013 |
DIASF |
Class I |
SEI Private Trust Company |
84.7961% |
|
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. Cust |
5.8759% | |||
|
Investor |
American Enterprise Investment Services |
25.5046% | ||
I-38
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Charles Schwab & Company Inc. |
20.1452% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
7.2077% | |||
|
Class Y |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation |
100.0000% | ||
|
November 4, 2013 |
DITIF |
Class A |
National Financial Services LLC |
10.2122% |
|
Charles Schwab & Company Inc. |
8.5879% | |||
|
Pershing Division Transfer Department |
7.2064% | |||
|
Class C |
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
30.4020% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
18.3195% | |||
|
First Clearing, LLC |
8.4527% | |||
|
LPL Financial Corporation |
6.7736% | |||
|
Pershing LLC |
6.5090% |
I-39
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
UBS WM USA |
6.1856% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
5.9038 | |||
|
Class I |
Wells Fargo Bank |
20.4403% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
18.4560% | |||
|
Mac & Co. |
17.4996% | |||
|
SEI Private Trust Company |
9.6265% | |||
|
Class Y |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation |
100.0000% | ||
|
November 4, 2013 |
DSTIF |
Class D |
National Financial Services LLC |
9.8355% |
|
Charles Schwab & Company Inc. |
8.9372% | |||
|
Pershing LLC |
8.3239% | |||
|
Class P |
Raymond James & Associates Inc. |
48.9558% | ||
I-40
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
National Financial Services LLC |
23.1201% | |||
|
Crowell, Weedon & Co. |
17.9856% | |||
|
April 8, 2014 |
DLA |
Class 1 |
None |
N/A |
|
Class 2 |
Pershing LLC |
74.5152% | ||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
16.4261% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DMCMP |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
93.6330% |
|
Agency |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation |
99.9036% | ||
|
Institutional |
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
29.6593% | ||
|
Bost & Co. |
29.6139% | |||
|
The Private Bank & Trust Company |
19.0447% | |||
|
UBS WM USA |
14.9978% | |||
I-41
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
90.1951% | ||
|
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
5.8981% | |||
|
Participant |
First Republic Bank |
79.2330% | ||
|
Pershing LLC |
11.6798% | |||
|
Deborah A. Ice |
8.2997% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DNYMCM |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
70.2305% |
|
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
29.7694% | |||
|
Institutional |
Bost & Co. |
87.0527% | ||
|
JP Morgan Clearing Corporation (GAMA) |
6.3072% | |||
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
90.2759% | ||
|
Participant |
First Republic Bank |
46.5305% | ||
I-42
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
J.A. Levin Group Inc. |
21.7330% | |||
|
Alyne L. Model |
18.3539% | |||
|
Glenn A. Aigen & Melissa E. Aigen |
5.7468% | |||
|
Pershing LLC |
5.0723% | |||
|
January 3, 2014 |
DNRF |
Class A |
American Enterprise Investment Services |
18.6278% |
|
First Clearing, LLC |
12.1270% | |||
|
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
10.4293% | |||
|
UBS WM USA |
9.0121% | |||
|
Pershing LLC |
5.5680% | |||
|
Class C |
American Enterprise Investment Services |
21.6493% | ||
|
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
17.8415% | |||
|
First Clearing, LLC |
16.8539% | |||
I-43
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Pershing LLC |
13.9535% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
5.9563% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
5.1890% | |||
|
Class I |
First Clearing, LLC |
36.9504% | ||
|
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
21.4905% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
16.9814% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
12.1689% | |||
|
July 3, 2014 |
DSIMBF |
Class A |
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
23.9464% |
|
American Enterprise Investment Services |
21.8521% | |||
|
UBS WM USA |
19.0341% | |||
|
Stephens Inc. |
7.5523% |
I-44
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
First Clearing, LLC |
6.9544% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
6.4439% | |||
|
Class D |
Pershing LLC |
9.1687% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
6.5385% | |||
|
Class I |
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
37.8328% | ||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
34.0859% | |||
|
First Clearing, LLC |
17.6950% | |||
|
Class Y |
SEI Private Trust Company |
99.0131% | ||
|
March 6, 2014 |
SDBF |
Class D |
Pershing LLC |
33.1149% |
|
St. Nicholas Music Inc. |
20.0104% | |||
I-45
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Class I |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation |
100.0000% | ||
|
Class Y |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation |
100.0000% | ||
|
Class Z |
Pershing LLC |
12.2615% | ||
|
Charles Schwab & Company Inc. |
11.0717% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DTECM |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
62.5942% |
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
30.8332% | |||
|
Institutional |
Boston & Co. |
32.6265% | ||
|
Pershing LLC |
10.5666% | |||
|
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
9.6496% | |||
|
Wells Fargo Bank |
7.9147% | |||
|
Bank of Hawaii |
6.2337% | |||
I-46
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
48.8262% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
38.7520% | |||
|
Participant |
Pershing LLC |
61.6181% | ||
|
Saturn & Co. |
17.5562% | |||
|
Laba & Co. |
11.1297% | |||
|
Bayterra & Co. |
8.0524% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DCAAMT |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
100.0000% |
|
Institutional |
Capinco |
51.4543% | ||
|
UBS WM USA |
14.8940% | |||
|
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
11.8135% | |||
|
Wells Fargo Securities, LLC |
8.2499% |
I-47
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Wells Fargo Bank |
5.6801% | |||
|
Trust Management Network LLC |
5.4002% | |||
|
Investor |
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
89.9590% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
7.9606% | |||
|
Participant |
First Republic Bank |
97.7912% | ||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DNYAMT |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
100.0000% |
|
Classic |
The Bank of New York Mellon |
98.1270% | ||
|
Institutional |
Hare & Co. |
55.9449% | ||
|
UBS WM USA |
14.7496% | |||
|
Mac & Co. |
11.7549% | |||
I-48
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Marcus Adler Gloves |
5.4950% | |||
|
Investor |
Mac & Co. |
86.8873% | ||
|
Pershing LLC |
6.7290% | |||
|
SEI Private Trust Company |
5.2949% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DTACM |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
26.7910% |
|
Bost & Co. |
21.5483% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
8.6380% | |||
|
Institutional |
Boston & Co. |
45.7274% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
16.6241% | |||
|
State Street Bank & Trust |
14.4244% | |||
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
30.0729% |
I-49
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Mellon Financial Corporation |
26.7390% | |||
|
Hare & Co. |
21.3495% | |||
|
Bank of Utah |
7.1009% | |||
|
Peoples United Bank |
5.4306% | |||
|
Bank of Hawaii |
5.0056% | |||
|
Participant |
Hare & Co. |
55.1532% | ||
|
Jefferies LLC |
29.7661% | |||
|
Select |
Hare & Co. |
72.2151% | ||
|
Band & Co. |
27.7849% | |||
|
Service |
Hare & Co. |
76.6354% |
I-50
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Reliance Trust Co. II |
19.3452% | |||
|
May 8, 2014 |
DTPCM |
Administrative |
Pershing LLC |
78.7176% |
|
Hare & Co. |
11.9039% | |||
|
First Republic Bank |
7.0126% | |||
|
Agency |
Hare & Co. |
18.3254% | ||
|
Cadence Bank |
14.4807% | |||
|
CTCNA |
11.9724% | |||
|
Howard Jeffrey Fogel Trust |
7.6454% | |||
|
Myles R. Itkin & Francis R. Itkin |
6.8154% | |||
|
Anne B. Keating |
5.9685% | |||
|
Institutional |
Boston & Co. |
43.3146% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
33.3659% |
I-51
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Pershing LLC |
5.1968% | |||
|
Investor |
Pershing LLC |
32.4285% | ||
|
Hare & Co. |
13.4822% | |||
|
Participant |
First Republic Bank |
14.5284% | ||
|
Saturn & Co. |
12.3465% | |||
|
Harvest MLP Income Fund II LLC |
11.7401% | |||
|
Typhoonbass and Co. |
11.0887% | |||
|
Stifel, Nicolaus & Co. Inc. |
8.5289% | |||
|
February 4, 2014 |
WDMMF |
First Clearing, LLC |
5.9252% | |
|
April 8, 2014 |
DF |
The Vanguard Fiduciary Trust Company |
18.8793% | |
I-52
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
September 5, 2014 |
DTCF |
Class A |
Pershing LLC |
12.9958% |
|
LPL Financial |
9.6488% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
6.0854% | |||
|
Class C |
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
36.9314% | ||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
29.9901% | |||
|
First Clearing, LLC |
6.8255% | |||
|
Class I |
SEI Private Trust Company |
45.9842% | ||
|
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Incorporated |
16.1914% | |||
|
Morgan Stanley & Company |
14.1526% | |||
|
First Clearing, LLC |
7.5086% | |||
|
National Financial Services LLC |
5.3390% |
I-53
|
Date |
Fund |
Class |
Name & Address |
Percent Owned |
|
Class Z |
None |
Certain shareholders of a fund may from time to time own or control a significant percentage of the fund's shares ("Large Shareholders"). Large Shareholders may include, for example, institutional investors, funds of funds, affiliates of the Manager, and discretionary advisory clients whose buy-sell decisions are controlled by a single decision-maker, including separate accounts and/or funds managed by the Manager or its affiliates. Large Shareholders may redeem all or a portion of their shares of a fund at any time or may be required to redeem all or a portion of their shares in order to comply with applicable regulatory restrictions (including, but not limited to, restrictions that apply to U.S. banking entities and their affiliates, such as the Manager). Redemptions by Large Shareholders of their shares of a fund may force the fund to sell securities at an unfavorable time and/or under unfavorable conditions, or sell more liquid assets of the fund, in order to meet redemption requests. These sales may adversely affect a fund's NAV and may result in increasing the fund's liquidity risk, transaction costs and/or taxable distributions.
I-54
PART II
See "Additional Information About How to Buy Shares" in Part III of this SAI for general information about the purchase of fund shares.
Cash Management Funds. Institutions purchasing shares of each fund have agreed to transmit copies of the fund's prospectuses and all relevant fund materials, including proxy materials, to each individual or entity for whose account the shares were purchased, to the extent required by law.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. The fund is sold exclusively to Citizens, and certain other institutional investors, acting for themselves, or in a fiduciary, advisory, agency, brokerage, custodial or similar capacity. Fund shares may not be purchased directly by individuals, although Citizens, and certain other approved institutions, may purchase shares for accounts maintained by individuals. Generally, investors will be required to open a single master account with the fund for all purposes. In certain cases, the fund may require investors to maintain separate master accounts for shares held by the investor (i) for its own account, for the account of other institutions and for accounts for which the institution acts as a fiduciary, and (ii) for accounts for which the investor acts in some other capacity. These omnibus accounts will be registered in nominee name for the benefit of the clients of Citizens or other approved institutions purchasing fund shares. Citizens and other approved institutions will provide omnibus account services pursuant to an agreement with the fund. Such services may include aggregating and processing purchase and redemption requests, transmitting funds for the purchase of shares to the fund, transmitting redemption proceeds to redeeming beneficial owners of the shares, maintaining records of fund shares transactions, preparing shareholder statements, and such other related services as the fund may reasonably request, other than those provided pursuant to the fund's Administrative Services Plan.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. The minimum initial investment for each class is $1 billion, unless the investor has invested at least $1 billion in the aggregate among any classes of shares of one of these two funds, in which case there would be no minimum initial investment amount for the other fund, or the investor has, in the opinion of the Distributor, adequate intent and availability of funds to reach a future aggregate level of investment of $1 billion among any classes of shares of these funds.
Cash Management Funds, CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. The minimum initial investment requirements apply to fund board members who elect to have all or a portion of their compensation for serving in that capacity automatically invested in the fund.
There is no minimum for subsequent purchases.
Funds other than the Cash Management Funds, CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. The minimum initial investment for each fund, except Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund (Class I), Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2), Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund (Class P) and the Institutional Money Funds, is $1,000 for full-time or part-time employees of the Manager or any of its affiliates, directors of the Manager, board members of a fund advised by the Manager, or the spouse or minor child of any of the foregoing. The minimum initial investment for each fund, except Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund (Class I), Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2), Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund (Class A), Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund (Class P) and the Institutional Money Funds, is $50 for full-time or part-time employees of the Manager or any of its affiliates who elect to have a portion of their pay directly deposited into their fund accounts.
Shares of each fund, except Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund (Class I), Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2), Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund (Class P) and the Institutional Money Funds, are offered without regard to the minimum initial or subsequent investment requirements to investors purchasing fund shares through wrap fee accounts or other fee based programs.
II-1
Shares of each fund, except Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund (Class I), Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2), Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund (Class A), Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund (Class P) and the Institutional Money Funds, are offered without regard to the minimum initial investment requirements to fund board members who elect to have all or a portion of their compensation for serving in that capacity automatically invested in the fund.
Each fund, except Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2), Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and the Institutional Money Funds, reserves the right to offer fund shares without regard to minimum purchase requirements to government-sponsored programs or to employees participating in certain Retirement Plans or other programs where contributions or account information can be transmitted in a manner and form acceptable to the fund.
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund's and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund's minimum initial investment requirement will be waived in connection with investments in the fund by other funds managed by the Manager.
Information Pertaining to Purchase Orders
Holders of Classic shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management who received their shares in exchange for Classic shares of the BNY Hamilton New York AMT-Free Municipal Money Fund ("New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund") in connection with the reorganization of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund also may purchase additional Classic shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management by check, wire or Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege, or through Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®, Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan or Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit Privilege as described under "Additional Information About Shareholder Services" in Part III of this SAI.
Holders of Classic shares of Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund or Classic shares of Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund who received their shares in exchange for Classic shares of the relevant BNY Hamilton Fund in connection with the reorganization of BNY Hamilton Funds may purchase additional Classic shares of the relevant fund by check, wire or Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege or through Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®, Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan or Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit Privilege as described under "Additional Information About Shareholder Services" in Part III of this SAI.
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. Orders for shares placed between 3:00 p.m. and 5:00 p.m. will not be accepted and executed, and notice of the purchase order being rejected will be given to the institution placing the order, and any funds received will be returned promptly to the sending institution.
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management (Classic shares only). The Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege is offered to holders of Classic shares who received their shares in exchange for Classic shares of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund in connection with the reorganization of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund.
Funds other than the Cash Management Funds. You may purchase shares of each fund except Dreyfus Liquid Assets (Class 2) and the Institutional Money Funds (excluding Classic shares) by telephone or online if you have supplied the necessary information on the Account Application or have filed a Shareholder Services Form with the Transfer Agent. The proceeds will be transferred between the bank account designated in one of these documents and your fund account. Only a bank account maintained in a domestic financial institution which is an ACH member may be so designated.
Information Regarding the Offering of Share Classes
Funds other than the Cash Management Funds. The share classes of each fund with more than one class are offered as described in the relevant fund's prospectus and as follows:
On March 13, 2012, outstanding Class B shares of Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund converted to Class A shares.
II-2
On March 13, 2012, outstanding Class B shares of Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund converted to Class D shares.
Class I shares of Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund are offered to certain other funds in The Dreyfus Family of Funds.
Holders of Class I shares of The Dreyfus Third Century Fund who have held their shares since June 5, 2003 may continue to purchase Class I shares of the fund for their existing accounts whether or not they would otherwise be eligible to do so.
Class Z shares of The Dreyfus Third Century Fund are offered to those shareholders of the fund whose fund account existed on August 30, 1999 and continues to exist at the time of purchase of the Class Z shares. In addition, certain broker-dealers and other financial institutions maintaining accounts in the fund on August 30, 1999 may open new accounts in Class Z shares of the fund on behalf of Retirement Plans and "wrap accounts" or similar programs. Class Z shares generally are not available for new accounts.
Class 2 shares of Dreyfus Liquid Assets are offered only to clients of certain Service Agents that have entered into an agreement with the Distributor. Class 2 shares may not be purchased directly by individuals, although Service Agents may purchase shares for accounts maintained by individuals.
Prior to February 4, 2009, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund offered Class T shares.
General information about the public offering price of Class A shares of the Multi-Class Funds can be found in Part III of this SAI under "Additional Information About How to Buy Shares—Class A." The public offering price for Class A shares of each of Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund is the net asset value per share of that class, plus a sales load as shown below:
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of |
As a % of net asset value |
Dealers' reallowance as |
|
Less than $100,000 |
2.50 |
2.60 |
2.25 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
2.00 |
2.10 |
1.75 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
1.50 |
1.50 |
1.25 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
0.75 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
____________________________
* Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
II-3
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of |
As a % of net asset value |
Dealers' reallowance as |
|
Less than $50,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
4.25 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.00 |
4.17 |
3.75 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.00 |
3.09 |
2.75 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.50 |
2.56 |
2.25 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
1.75 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
____________________________
*Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
Class A shares of Multi-Class Funds, including Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, purchased without an initial sales load as part of an investment of $1,000,000 or more may be assessed at the time of redemption a 1% CDSC if redeemed within one year of purchase. The Distributor may pay Service Agents an up-front commission of up to 1% of the net asset value of Class A shares purchased by their clients as part of a $1,000,000 or more investment in Class A shares that are subject to a CDSC. If the Service Agent waives receipt of such commission, the CDSC applicable to such Class A shares will not be assessed at the time of redemption.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Reduced sales loads apply to any purchase of Class A shares of the fund by you and any related Purchaser where the aggregate investment including such purchase is $100,000 or more. If, for example, you previously purchased and still hold Eligible Shares, or combination thereof, with an aggregate current value of $90,000 and subsequently purchase Class A shares of the fund having a current value of $20,000, the sales load applicable to the subsequent purchase would be reduced to 2.0% of the offering price. All present holdings of Eligible Shares may be combined to determine the current offering price of the aggregate investment in ascertaining the sales load applicable to each subsequent purchase.
See "Additional Information About How to Redeem Shares" in Part III of this SAI for general information about the redemption of fund shares.
|
Fund |
Services* |
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Redemption through an Authorized Entity |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege |
II-4
|
Fund |
Services* |
|
CitizenSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
Redemption through Compatible Automated Facilities Wire Redemption Privilege |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege (Classic shares only) |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
Checkwriting Privilege (Class A only)** |
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets |
Checkwriting Privilege (Class 1 only) |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege |
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege (certain Classic shares only)*** |
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund |
Checkwriting Privilege |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Checkwriting Privilege (Class A and D only) |
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
Checkwriting Privilege (Class D and Z only) |
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege |
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege |
____________________________
* Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for online services.
** Investors beneficially owning Institutional shares as of the date such shares were redesignated Class I shares and who continuously held fund shares since that date also are eligible for the Checkwriting Privilege.
*** The Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege is offered to holders of Classic shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management who received their shares in exchange for Classic shares of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund in connection with the reorganization of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund. There is a $100,000 per day limit on redemption requests made online through www.dreyfus.com or through the Dreyfus Express® voice-activated account access system.
II-5
Cash Management Funds and Institutional Money Funds. Each fund ordinarily will make payment for shares on the same or next business day after receipt by Dreyfus Investments Division or other authorized entity of a redemption request in proper form.
Cash Management Funds. Except for Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management (Classic shares), by using this privilege the investor authorizes the Transfer Agent to act on telephone redemption instructions from any person representing himself or herself to be an authorized representative of the investor, and reasonably believed by the Transfer Agent to be genuine. Redemption proceeds will be transferred by Federal Reserve wire only to a bank that is a member of the Federal Reserve System.
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management (Classic shares only). For holders of Classic shares who received their shares in exchange for Classic shares of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund in connection with the reorganization of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund, there is a $100,000 per day limit on redemption requests made online through www.dreyfus.com or through the Dreyfus Express® voice-activated account access system.
Institutional Money Funds (excluding Classic shares). By using this privilege the investor authorizes the fund and the Transfer Agent to act on telephone redemption instructions from any person representing himself or herself to be an authorized representative of the investor, and reasonably believed by the fund or the Transfer Agent to be genuine. Redemption proceeds will be transferred by Federal Reserve wire only to a bank that is a member of the Federal Reserve System.
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. The fund reserves the right to refuse any request made by telephone and may limit the amount involved or the number of telephone redemptions. This privilege may be modified or terminated at any time by the Transfer Agent or the fund. Shares for which certificates have been issued may not be redeemed by telephone.
II-6
The following shareholder services apply to the funds. See "Additional Information About Shareholder Services" in Part III of this SAI for more information.
|
Fund |
Services* |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
Fund Exchanges |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund† |
Fund Exchanges1 |
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
Fund Exchanges3 |
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets |
Fund Exchanges5 |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
Fund Exchanges |
II-7
|
Fund |
Services* |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
Fund Exchanges9 |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Fund Exchanges10 |
______________________
* Class Y shares (offered by certain funds) only have the Fund Exchanges shareholder service, as described below. Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for online services.
† Citizens and other approved institutions may not make these services available.
1 Prime shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund may be exchanged for shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, and shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund may be exchanged for Prime shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund. For holders of Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, shares may be exchanged for shares of a corresponding class of any of the Dreyfus Cash Management Funds.
2 For holders of shares of both Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, the privilege operates between Prime shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and shares of Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund (or vice versa). Holders of shares of Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund may purchase, in exchange for shares of one class of the fund, shares of a corresponding class of any of the Dreyfus Cash Management Funds.
3 For Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, Class D and Class P shares may be exchanged for shares of any class of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds open to direct investment by individuals.
4 For Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, applies only to Class D shares.
5 Holders of Class 2 shares of Dreyfus Liquid Assets should contact their Service Agent for information.
6 For Dreyfus Liquid Assets, applies only to Class 1 shares.
7 Holders of Classic shares may purchase, in exchange for Classic shares, shares of certain funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds of which the investor is a shareholder.
8 For Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, applies only to Classic shares received in exchange for Classic shares of the relevant BNY Hamilton Fund in connection with the reorganization of such BNY Hamilton Fund. Available only to holders of Classic Shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management who received their shares in exchange for Classic Shares of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund in connection with the reorganization of the New York AMT-Free Predecessor Fund.
9 Investor shares and Class I shares may be exchanged for shares of any class of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds open to direct investment by individuals.
10 Class D shares may be exchanged for shares of any class of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds open to direct investment by individuals.
Cash Management Funds. Shares of one class of a fund may be exchanged for shares of the same class of another fund or of Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund. In addition, Classic Shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management may be exchanged for shares of certain other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. An investor who wishes to redeem shares of one class of shares and purchase shares of another class of shares of a fund identified above should contact Dreyfus Investments Division by calling 1-800-346-3621.
II-8
Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege
Cash Management Funds. Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege permits an investor to purchase, in exchange for shares of one class of a fund, shares of the same class of another fund or of Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund. In addition, holders of Classic Shares of Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management may purchase, in exchange for Classic Shares, shares of certain other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds of which the investor is a shareholder.
DISTRIBUTION PLANS, SERVICE PLANS AND SHAREHOLDER SERVICES PLANS
The following Plans apply to the funds. See "Additional Information About Distribution Plans, Service Plans and Shareholder Services Plans" in Part III of this SAI for more information about the Plans.
|
Fund |
Class(es)* |
Plan (12b-1 or servicing)** |
Key Features*** |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
Class C |
Distribution Plan (12b-1) |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.25% for distributing, advertising and marketing this class of shares. The Distributor may pay all or a part of the fees paid pursuant to the Distribution Plan to Citizens or other approved institutions that have purchased this class of shares for the benefit of others. |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
Class D |
Distribution Plan (12b-1) |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.65% for distributing, advertising and marketing this class of shares. The Distributor may pay all or a part of the fees paid pursuant to the Distribution Plan to Citizens or other approved institutions that have purchased this class of shares for the benefit of others. |
II-9
|
Fund |
Class(es)* |
Plan (12b-1 or servicing)** |
Key Features*** |
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Agency |
Service Plan (12b-1) |
The fund pays the Distributor fees as disclosed in the prospectus for distributing these classes of shares, for advertising and marketing and for providing certain services to shareholders of these classes, including answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. Pursuant to the Plan, the Distributor may make payments to Service Agents in respect to these services. Generally, a Service Agent may provide holders of these shares a consolidated statement, checkwriting privileges, automated teller machine access, and bill paying services. |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
Class C |
Distribution Plan |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.75% for distributing these shares. The Distributor may pay one or more Service Agents in respect of advertising, marketing and other distribution services, and determines the amounts, if any, to be paid to Service Agents and the basis on which such payments are made. |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
Class A |
Shareholder Services Plan (servicing) |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.25% for the provision of certain services to the shareholders of these classes. Services may include personal services relating to shareholder accounts, such as answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. Pursuant to the Plan, the Distributor may make payments to certain Service Agents in respect of these services. |
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Class Z |
Shareholder Services Plan (servicing) |
The fund reimburses the Distributor an amount not to exceed 0.25% for certain allocated expenses of providing personal services and/or |
II-10
|
Fund |
Class(es)* |
Plan (12b-1 or servicing)** |
Key Features*** |
|
Management |
maintaining shareholder accounts; these services may include personal services relating to shareholder accounts, such as answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. | ||
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund |
N/A |
Shareholder Services Plan (servicing) |
The fund reimburses the Distributor an amount not to exceed 0.25% for certain allocated expenses of providing personal services and/or maintaining shareholder accounts; these services may include personal services relating to shareholder accounts, such as answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. |
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
Class D |
Shareholder Services Plan (servicing) |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.20% for the provision of certain services to the shareholders of this class. Services may include personal services relating to shareholder accounts, such as answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. The Distributor may make payments to certain Service Agents in respect of these services. |
II-11
|
Fund |
Class(es)* |
Plan (12b-1 or servicing)** |
Key Features*** |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Class D |
Service Plan |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.10% for distributing these shares, servicing shareholder accounts and advertising and marketing. The Distributor may pay one or more Service Agents in respect of shares owned by shareholders with whom the Service Agent has a servicing relationship or for whom the Service Agent is the dealer or holder of record and determines the amounts, if any, to be paid to Service Agents and the basis on which such payments are made. Pursuant to the Plan, Class D shares bear (i) the costs of preparing, printing and distributing prospectuses and SAIs used other than for regulatory purposes or distribution to existing shareholders, and (ii) the costs associated with implementing and operating the Plan (such as costs of printing and mailing service agreements), the aggregate of such amounts not to exceed in any fiscal year of the fund the greater of $100,000 or .005%. |
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
Class D |
Service Plan |
The fund pays the Distributor 0.25% for distributing these shares, servicing shareholder accounts and advertising and marketing. The Distributor may pay one or more Service Agents in respect of shares owned by shareholders with whom the Service Agent has a servicing relationship or for whom the Service Agent is the dealer or holder of record and determines the amounts, if any, to be paid to Service Agents and the basis on which such payments are made. |
II-12
|
Fund |
Class(es)* |
Plan (12b-1 or servicing)** |
Key Features*** |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
Administrative Advantage |
Service Plan |
The fund pays the Distributor fees as disclosed in the prospectus for distributing these shares, for advertising and marketing and for providing certain services to shareholders of these classes. Services include answering shareholder inquiries regarding the fund and providing reports and other information, and services related to the maintenance of shareholder accounts. The Distributor may make payments to certain Service Agents in respect of these services. Generally, the Service Agent will provide (1) holders of Administrative Advantage, Investor Advantage or Participant Advantage shares with a consolidated statement; (2) holders of Investor Advantage or Participant Advantage shares checkwriting privileges; and (3) holders of Participant Advantage shares with automated teller machine access and bill paying services. Generally, the Service Agent may provide holders of Reserve, Hamilton, Agency, Premier or Classic shares a consolidated statement, checkwriting privileges, automated teller machine access and bill paying services. |
______________
* As applicable to the funds listed (not all funds have all classes shown).
** The parenthetical indicates whether the Plan is pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act or is a type of servicing plan not adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1.
*** Amounts expressed as an annual rate as a percentage of the value of the average daily net assets attributable to the indicated class of fund shares or the fund, as applicable.
II-13
INVESTMENTS, INVESTMENT TECHNIQUES AND RISKS
The following charts, which supplement and should be read together with the information in the prospectus, indicate some of the specific investments and investment techniques applicable to your fund. Additional policies and restrictions are described in the prospectus and below in the next section (see "Investment Restrictions"). See "Additional Information About Investments, Investment Techniques and Risks" in Part III of this SAI for more information, including important risk disclosure, about the investments and investment techniques applicable to your fund.
Funds other than Money Market Funds
|
Fund |
Equity Securities1 |
IPOs |
U.S. Government Securities2 |
Corporate Debt Securities |
High Yield and Lower-Rated Securities3 |
Zero Coupon, Pay-in-Kind and Step-Up Securities |
Inflation-Indexed Securities (other than TIPS) |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
|||||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
1 Except as otherwise noted, (1) includes common and preferred stock, convertible securities and warrants and (2) each fund is limited to investing 5% of its net assets in warrants, except that this limitation does not apply to warrants purchased by a fund that are sold in units with, or attached to, other securities. The Dreyfus Third Century Fund may not purchase warrants in excess of 2% of its net assets. Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund, The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund are not subject to (2).
For The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated, includes common stock and convertible securities.
II-14
2 For Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, see "Money Market Instruments" below.
3 Each of Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund may invest up to 20% of its assets in fixed income securities rated below investment grade and as low as Caa by Moody's or CCC by S&P or Fitch or the unrated equivalent as determined by the Adviser.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund may invest up to up to 5% of its assets in fixed-income securities rated below investment grade or the unrated equivalent as determined by the Adviser.
|
Fund |
Variable |
Loans |
Mortgage-Related Securities |
Asset- |
Collateralized Debt Obligations |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
|||||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
||||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
|||||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
II-15
|
Fund |
Municipal Securities4 |
Funding Agreements |
REITs |
Money Market Instruments5 |
Foreign |
Emerging Markets |
Depositary Receipts |
Sovereign Debt Obligations and Brady Bonds |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
||||||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
ü |
ü7 |
ü |
4 Each of Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund currently intends to invest no more than 25% of its assets in municipal securities; however, this percentage may be varied from time to time without shareholder approval.
5 Includes short-term U.S. Government securities, bank obligations, repurchase agreements and commercial paper. Except for Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, generally (1) when the Adviser determines that adverse market conditions exist, a fund may adopt a temporary defensive position and invest up to 100% of its assets in money market instruments, and (2) a fund also may purchase money market instruments when it has cash reserves or in anticipation of taking a market position. The Dreyfus Third Century Fund also may invest in corporate bonds under such circumstances but is limited to bank obligations issued in this country and those issued in dollar denominations by the foreign branches of U.S. banks. In addition, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund each may invest in money market instruments as part of its investment strategy.
For Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, from time to time, on a temporary basis other than for temporary defensive purposes (but not to exceed 20% of the value of the fund's net assets) or for temporary defensive purposes, the fund may invest in taxable short-term investments ("Taxable Investments") consisting of: notes of issuers having, at the time of purchase, a quality rating within the two highest grades of a Rating Agency; obligations of the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities; commercial paper rated not lower than P-1 by Moody's, A-1 by S&P or F-1 by Fitch; certificates of deposit of U.S. domestic banks, including foreign branches or domestic banks, with assets of $1 billion or more; time deposits; bankers' acceptances and other short-term obligations and repurchase agreements in respect of any of the foregoing. Under normal market conditions, the fund anticipates that not more than 5% of the value of its total assets will be invested in any one category of Taxable Investments.
II-16
6 Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund each may invest up to 30% of its total assets in fixed-income securities of foreign issuers, including those of issuers in emerging markets.
7 Does not include foreign government obligations and securities of supranational entities.
II-17
|
Fund |
Eurodollar and Yankee Dollar Investments |
Investment Companies |
ETFs |
Exchange-Traded |
Futures Transactions |
Options Transactions8 |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü9 |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
ü |
ü |
8 Each of Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated (1) is limited to investing 5% of its assets, represented by the premium paid, in the purchase of call and put options and (2) may write (i.e., sell) covered call and put option contracts to the extent of 20% of the value of its net assets at the time such option contracts are written.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund also may purchase and sell options in respect of specific commodities (or baskets of specific commodities) or commodity indices. An option on a commodity index is similar to an option in respect of specific commodities, except that settlement does not occur by delivery of the commodities comprising the index. Instead, the option holder receives an amount of cash if the closing level of the index upon which the option is based is greater than in the case of a call, or less than in the case of a put, the exercise price of the option. Thus, the effectiveness of purchasing or writing index options will depend upon price movements in the level of the index rather than the price of a particular commodity. The fund also may purchase cash-settled options on commodity index swaps in pursuit of its investment objective. Index swaps involve the exchange by the fund with another party of cash flows based upon the performance of an index or a portion of an index of securities, which usually includes dividends, or commodities. A cash-settled option on a swap gives the purchaser the right, but not the obligation, in return for the premium paid, to receive an amount of cash equal to the value of the underlying swap as of the exercise date.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund may only write (i.e., sell) covered call option contracts on securities owned by the fund to the extent of 20% of the value of its net assets at the time such option contracts are written and may purchase call options only to close out open positions.
9 Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund may invest in commodity futures contracts and options thereon. A commodity futures contract is an agreement between two parties, in which one party agrees to buy a commodity, such as an energy, agricultural or metal commodity, from the other party at a later date at a price and quantity agreed-upon when the contract is made. The commodities which underlie commodity futures contracts may be subject to additional economic and non-economic variables, such as drought, floods, weather, livestock disease, embargoes, tariffs, and international economic, political and regulatory developments. These factors may have a larger impact on commodity prices and commodity-linked instruments, including futures contracts than on traditional securities. Certain commodities are also subject to limited pricing flexibility
II-18
because of supply and demand factors. Others are subject to broad price fluctuations as a result of the volatility of the prices for certain raw materials and the instability of supplies of other materials. These additional variables may create additional investment risks which subject the fund's investments to greater volatility than investments in traditional securities. Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund currently intends to limit the amount of its assets invested in commodity futures and options thereon to no more than 10% of its assets, represented by the liquidation value of the contract.
|
Fund |
Swap Transactions |
Credit Linked Securities |
Credit Derivatives |
Structured Securities and Hybrid Instruments10 |
Participatory Notes |
Custodial Receipts |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü (municipal securities only) | |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü11 |
ü12 |
||||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü (municipal securities only) | |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü (municipal securities only) | ||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü (municipal securities only) | |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
|||||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
||||||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
10 For Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, structured notes only.
11 To a limited extent, the fund may gain exposure to the commodity markets by investing in commodity swap agreements, including swap agreements on commodity indexes and specific commodities. For example, an investment in a commodity swap agreement may involve the exchange of floating-rate interest payments for the total return on a commodity index. In a total return commodity swap, the fund will receive the price appreciation of a commodity index, a portion of the index, or a single commodity in exchange for paying an agreed-upon fee. If the commodity swap is for one period, the fund may pay a fixed fee, established at the outset of the swap. However, if the term of the commodity swap is more than one period, with interim swap payments, the fund may pay an adjustable or floating fee. With a "floating" rate, the fee may be pegged to a base rate, such as LIBOR, and is adjusted each period. Therefore, if interest rates increase over the term of the swap contract, the fund may be required to pay a higher fee at each swap reset date.
II-19
12 The fund also may invest in structured securities or hybrid instruments whose return is based on, or otherwise determined by reference to, a commodity, commodity index or commodity-related instrument.
|
Fund |
Foreign Currency Transactions |
Commodities |
Short-Selling13 |
Lending Portfolio Securities |
Borrowing Money14 |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
ü |
ü |
13 Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated (1) will not sell securities short if, after effect is given to any such short sale, the total market value of all securities sold short would exceed 25% of the value of the fund's net assets (also applies to Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund and Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund) and (2) at no time will more than 15% of the value of the fund's net assets be in deposits on short sales against the box. Additionally, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated may not make a short sale which results in the fund having sold short in the aggregate more than 5% of the outstanding securities of any class of issuer.
14 Each of Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund currently intends to borrow money only for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes in an amount up to 15% of the value of its total assets (including the amount borrowed) valued at the lesser of cost or market, less liabilities (not including the amount borrowed) at the time the borrowing is made.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund each currently intends to borrow money only for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes; however, these funds, along with Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, may borrow for investment purposes on a secured basis through entering into reverse repurchase agreements.
II-20
|
Fund |
Borrowing Money for Leverage14 |
Reverse Repurchase Agreements |
Forward Commitments |
Forward Roll Transactions |
Illiquid Securities |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
ü | ||||
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund |
ü |
|
Fund |
U.S. Government Securities15 |
Repurchase Agreements16 |
Bank Obligations17 |
Participation Interests |
Floating and Variable Rate Obligations |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
II-21
|
Fund |
U.S. Government Securities15 |
Repurchase Agreements16 |
Bank Obligations17 |
Participation Interests |
Floating and Variable Rate Obligations |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund |
ü |
ü18 |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management |
ü |
ü | |||
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
15 CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund may invest only in securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund normally invests only in U.S. Treasury securities backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government and in repurchase agreements, including tri-party repurchase agreements, collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities and other securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund normally invests only in U.S. Treasury securities backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government.
II-22
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management may invest only in securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities supported by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury.
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management may invest in U.S. Treasury securities only.
For Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, see the definition of Money Fund Taxable Investments following this chart.
16 For the funds other than the Cash Management Funds, except with respect to Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, these repurchase agreements may be collateralized by securities other than U.S. Government securities, such as corporate bonds, asset-backed securities and privately-issued mortgage-related securities, of investment grade or below investment grade credit quality, and equity securities ("credit and/or equity collateral").
Dreyfus Cash Management may engage in repurchase agreement transactions that are collateralized by credit and/or equity collateral. Repurchase agreement transactions engaged in by Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management will be collateralized only by U.S. Treasury securities and securities issued by the GNMA.
17 Normally, Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund each invests at least 25% of its assets in domestic or dollar-denominated foreign bank obligations.
For Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, see the definition of Money Fund Taxable Investments following this chart.
18 These repurchase agreements must be collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities, except that up to 20% of the fund's net assets may consist of repurchase agreements collateralized by other securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government.
II-23
|
Fund |
Asset-Backed |
Commercial |
Investment Companies |
Municipal |
Foreign Securities20 |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management |
ü |
|
|||
|
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
ü |
||||
|
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management |
ü |
II-24
|
Fund |
Asset-Backed |
Commercial |
Investment Companies |
Municipal |
Foreign Securities20 |
|
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management |
|||||
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
19 Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus and Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management may invest without limitation, and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management may invest up to 20% of its assets, in Municipal Obligations, including certain private activity bonds, the income from which is subject to the AMT, if the Adviser determines that their purchase is consistent with the fund's investment objective. Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management will not purchase Municipal Obligations the income from which is subject to the AMT. If New York Municipal Obligations are at any time unavailable for investment by Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management or Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, or, if California Municipal Obligations are at any time unavailable for investment by Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, the fund will invest temporarily in other Municipal Obligations.
Each of Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management may invest only in those Municipal Obligations which are rated in one of the two highest rating categories for debt obligations by at least two Rating Agencies (or one Rating Agency if the instrument was rated by only one Rating Agency) or, if unrated, are of comparable quality as determined in accordance with procedures established by the board.
20 Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund may invest only in securities issued by foreign branches of domestic banks, domestic and foreign branches of foreign banks and commercial paper issued by foreign issuers.
II-25
|
Fund |
Illiquid Securities |
Borrowing Money21 |
Reverse Repurchase Agreements |
Forward Commitments |
Interfund Borrowing |
Lending Portfolio Securities22 |
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü23 |
|
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü | ||
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
||
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|
|
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management |
ü |
ü |
ü |
|||
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
ü |
21 Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund
II-26
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund each currently intends to borrow money for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes. However, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund each may borrow for investment purposes on a secured basis through entering into reverse repurchase agreements.
22 Other than pursuant to the Interfund Borrowing and Lending Program.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund will only receive collateral consisting of cash or U.S. Treasury securities or, for Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund only, cash equivalents or other high quality liquid debt securities. Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund will only receive collateral consisting of cash, cash equivalents, U.S. Government securities or other high quality liquid debt securities.
23 For Dreyfus Government Cash Management, loans of portfolio securities may not exceed 20% of the value of the fund's total assets (including the value of all assets received as collateral for the loan).
For Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, from time to time, on a temporary basis other than for temporary defensive purposes (but not to exceed 20% of the value of the fund's net assets) or for temporary defensive purposes, the fund may invest in taxable short-term investments ("Money Fund Taxable Investments") consisting of: notes of issuers having, at the time of purchase, a quality rating within the two highest grades of a Rating Agency; obligations of the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities; commercial paper rated not lower than P-1 by Moody's, A-1 by S&P or F-1 by Fitch; certificates of deposit of U.S. domestic banks, including foreign branches of domestic banks, with assets of $1 billion or more; time deposits; bankers' acceptances and other short-term bank obligations; and repurchase agreements in respect of any of the foregoing. Except for temporary defensive purposes, at no time will more than 20% of the value of the fund's net assets be invested in Money Fund Taxable Investments and, with respect to Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, Municipal Obligations the interest from which gives rise to a preference item for the purpose of the AMT. When Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management or Dreyfus New York Cash Management has adopted a temporary defensive position, including when acceptable New York Municipal Obligations are unavailable for investment by Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management or Dreyfus New York Cash Management, more than 20% of the fund's net assets may be invested in securities that are not exempt from New York State and New York City income tax. When Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management has adopted a temporary defensive position, including when acceptable California Municipal Obligations are unavailable for investment by Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, more than 20% of the fund's net assets may be invested in securities that are not exempt from California State income tax. Under normal market conditions, each fund anticipates that not more than 5% of the value of its total assets will be invested in any one category of Money Fund Taxable Investments.
"Fundamental Policies" may not be changed without approval of the holders of a majority of the fund's outstanding voting securities (as defined in the 1940 Act). "Nonfundamental Policies" may be changed at any time, without shareholder approval, by a vote of a majority of the board members and in compliance with applicable law and regulatory policy.
Except as may be otherwise disclosed in the prospectus, each fund's investment objective is a Fundamental Policy. For each of Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, the fund's policy with respect to the investment of at least 80% of its net assets is a Fundamental Policy (see "Policies Related to Fund Names" below). Additionally, as a matter of Fundamental Policy, each fund, as indicated, may not (with respect to Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, except as described below or as otherwise permitted by the
II-27
1940 Act, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors, each fund, as indicated, may not):
1. Purchase of Other Securities
Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Purchase common stocks, preferred stocks, warrants or other equity securities, or purchase corporate bonds or debentures, state bonds, municipal bonds or industrial revenue bonds.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Purchase securities other than Municipal Obligations and Money Fund Taxable Investments as those terms are defined herein and in the prospectus, except that Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management may invest in investment companies.
2. Borrowing
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Borrow money, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits borrowing to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets).
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management. Except as otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act, or interpretations or modifications by, or exemptive or other relief from, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors, borrow money, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits borrowing to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets).
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Borrow money, except from banks for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes in an amount up to 15% of the value of the fund's total assets (including the amount borrowed) based on the lesser of cost or market, less liabilities (not including the amount borrowed) at the time the borrowing is made. While borrowings exceed 5% of the value of the fund's total assets, the fund will not make any additional investments.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Borrow money, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits borrowing to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets). For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the entry into options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices shall not constitute borrowing.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Borrow money, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits borrowing to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets). For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the entry into options, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices shall not constitute borrowing.
3. Commodities
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Invest in physical commodities or physical commodities contracts.
II-28
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Invest in commodities.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Invest in commodities, except that the fund may purchase and sell futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund. Invest in commodities, except that the fund may purchase and sell options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices. (This restriction shall not prohibit the fund, subject to restrictions described in its prospectus and this SAI, from purchasing, selling or entering into futures contracts, options on futures contracts, foreign currency forward contracts, foreign currency options, or any interest rate, securities-related or foreign currency-related hedging instrument, including swap agreements and other derivative instruments, subject to compliance with any applicable provisions of the federal securities or commodities law.)
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Invest in physical commodities or physical commodities contracts, except that the fund may purchase and sell options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices and enter into swap agreements and other derivative instruments.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Purchase and sell commodities, except that the fund may purchase and sell options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Purchase or sell physical commodities, except that the fund may purchase and sell options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices, and enter into swap agreements and other derivative instruments that are commodities or commodity contracts.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Invest in physical commodities or commodities contracts, except that the fund may purchase and sell options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices and enter into swap agreements and other derivative instruments.
4. Issuer Diversification
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any single issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, or its agencies or instrumentalities and securities of other investment companies may be purchased, without regard to any such limitation.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. With respect to 75% of its total assets, purchase securities of an issuer (other than the U.S. Government, its agencies, instrumentalities or authorities or repurchase agreements collateralized by U.S. Government securities and other investment companies), if: a) such purchase would cause more than 5% of the fund's total assets taken at market value to be invested in the securities of such issuer; or b) such purchase would at the time result in more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer being held by the fund.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund and Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund. Invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any single issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be
II-29
invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, or its agencies or instrumentalities may be purchased, without regard to any such limitation.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Invest more than 5% of the market value of its net assets in the securities of any one issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, or its agencies or instrumentalities may be purchased, without regard to such limitation.
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any one issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested without regard to any such limitation.
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund. Invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any single issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities may be purchased, without regard to any such limitation.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets. Invest more than 15% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank or invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any one issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested without regard to any such limitation. Notwithstanding the foregoing, to the extent required by rules of the SEC, the fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase the securities of any issuer if such purchase would cause more than 5% of the value of its total assets to be invested in securities of such issuer (except securities of the U.S. Government or any instrumentality thereof).
Dreyfus Cash Management and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Invest more than 15% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank, or invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any other issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested without regard to any such limitations. Notwithstanding the foregoing, to the extent required by the rules of the SEC, the fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Hold more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of any single issuer. This Fundamental Policy applies only with respect to 75% of the fund's total assets.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase the securities of any issuer if such purchase would cause the fund to hold more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer.
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Invest more than 15% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank, or invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any other issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities may be purchased, without regard to any such limitations. Notwithstanding the foregoing, to the extent required by the rules of the SEC, the fund will not invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any one bank, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested without regard to such limitation.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus. Invest more than 5% of its assets in the obligations of any issuer, except that up to 25% of the value of the fund's total assets may be invested, and securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities may be purchased, without regard to any such limitation.
II-30
5. Industry Concentration
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities or as otherwise permitted by the SEC.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued by banks or issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities or as otherwise permitted by the SEC.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. The natural resources sector, in general, is not considered an industry for purposes of this Fundamental Policy.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities or as otherwise permitted by the SEC. Securities issued or guaranteed by governments other that the U.S. Government or by foreign supranational entities are not considered to be the securities of issuers in a single industry for purposes of this Fundamental Policy.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry; provided that there shall be no such limitation on the purchase of Municipal Bonds and, for temporary defensive purposes, securities issued by banks and obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, industrial development bonds, where the payment of principal and interest is the ultimate responsibility of companies with the same industry, are grouped together as an "industry."
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Invest less than 25% of its total assets in securities issued by banks or invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of issuers in any other industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. Notwithstanding the foregoing, for temporary defensive purposes the fund may invest less than 25% of its assets in bank obligations.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund. Invest less than 25% of its total assets in securities issued by banks or invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any other industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. Notwithstanding the foregoing, for temporary defensive purposes the fund may invest less than 25% of its assets in bank obligations.
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Invest less than 25% of its total assets in securities issued by banks or invest more than 25% in the securities of issuers in any other industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. Notwithstanding
II-31
the foregoing, for temporary defensive purposes the fund may invest less than 25% of its assets in bank obligations.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets. Invest less than 25% of its assets in obligations issued by banks or invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of issuers in any other industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. Notwithstanding the foregoing, for temporary defensive purposes the fund may invest less than 25% of its assets in bank obligations.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Concentrate its investments in any particular industry or industries, except that the fund may invest up to 25% of the value of its total assets in a single industry.
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no such limitation on investments in obligations issued and guaranteed by the U.S. Government.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Invest more than 25% of the value of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of Municipal Obligations (other than Municipal Obligations backed only by assets and revenues of non-governmental issuers) and obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities.
Dreyfus Cash Management. Invest less than 25% of its assets in securities issued by banks or invest more than 25% of its assets in the securities of issuers in any other industry, provided that there shall be no limitation on the purchase of obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities. Notwithstanding the foregoing, for temporary defensive purposes the fund may invest less than 25% of its assets in bank obligations.
Dreyfus Government Cash Management and Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no such limitation on investments in obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus and Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management. Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no such limitation on the purchase of Municipal Obligations and, for temporary defensive purposes, obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities.
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no such limitation on the purchase of Municipal Obligations and, for temporary defensive purposes, securities issued by banks and obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities.
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Invest more than 25% of its total assets in the securities of issuers in any single industry, provided that there shall be no such limitation on investments in obligations issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government.
6. Loans
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund and Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Lend any securities or make loans to others, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets). For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
II-32
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Make loans to others, except through the purchase of debt obligations and the entry into repurchase agreements; however, the fund may lend its portfolio securities in an amount not to exceed 33-1/3% of the value of its total assets. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Lend any securities or make loans to others, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets) or as otherwise permitted by the SEC. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund. Lend any securities or make loans to others, if, as a result, more than 33-1/3% of its total assets would be lent to others, except that this limitation does not apply to the purchase of debt obligations and the entry into repurchase agreements. However, the fund may lend its portfolio securities in an amount not to exceed 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Lend any securities or make loans to others, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets), and except as otherwise permitted by interpretations or modifications by, or exemptive or other relief from, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Lend securities or make loans to others, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets), or interpretations or modifications by, or exemptive or other relief from, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets. Make loans to others or lend any securities, except as otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets), or interpretations or modifications by, or exemptive or other relief from, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management. Except as otherwise permitted by the 1940 Act, or interpretations or modifications by, or exemptive or other relief from, the SEC or other authority with appropriate jurisdiction, and disclosed to investors, lend any securities or make loans to others, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act (which currently limits such loans to no more than 33-1/3% of the value of the fund's total assets). For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, the purchase of debt obligations (including acquisitions of loans, loan participations or other forms of debt instruments) and the entry into repurchase
II-33
agreements shall not constitute loans by the fund. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made according to guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Make loans to others, except through the purchase of debt obligations referred to in the prospectus. However, the fund may lend its portfolio securities in an amount not to exceed 33-1/3% of the value of its total assets. Any loans of portfolio securities will be made in accordance with guidelines established by the SEC and the board.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Make loans to others, except through the purchase of qualified debt obligations and the entry into repurchase agreements referred to herein and in the prospectus.
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Make loans to others except through the purchase of debt obligations referred to in the prospectus.
7. Short Sales; Margin
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Purchase securities on margin, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Purchase securities on margin, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, and options on futures contracts.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management, Dreyfus Liquid Assets and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Purchase securities on margin.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Purchase or sell securities on margin.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase securities on margin, but the fund may obtain such short-term credit as may be necessary for the clearance of purchases and sales of securities.
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Sell securities short or purchase securities on margin.
8. Pledging Assets
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus and Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to secure borrowings for temporary or emergency purposes.
9. Puts; Calls
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Write or purchase put or call options or combinations thereof.
10. Real Estate; Oil and Gas
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, or oil, gas or other mineral leases or exploration or development programs.
II-34
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity. Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, or oil, gas or other mineral leases or exploration or development programs, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that invest or deal in real estate or REITs and may acquire and hold real estate or interests therein through exercising rights or remedies with regard to such securities.
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Purchase or sell real estate, REIT securities, commodities, or oil and gas interests.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Purchase or sell real estate, commodities or commodity contracts, or oil and gas interests, but this shall not prevent the fund from purchasing and selling options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, or oil, gas or other mineral leases or exploration or development programs, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that invest or deal in real estate. In particular, the fund may purchase mortgage-backed securities and REIT securities.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, or oil, gas or other mineral leases or exploration or development programs, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that invest in or deal in real estate.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Purchase or sell real estate, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that invest or deal in real estate or REITs and may acquire and hold real estate or interests therein through exercising rights or remedies with regard to such securities.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase, hold or deal in commodities or commodity contracts, in oil, gas, or other mineral exploration or development programs, or in real estate but this shall not prohibit the fund from investing, consistent with Nonfundamental Policy No. 5 below, in securities of companies engaged in oil, gas or mineral investments or activities. This limitation shall not prevent the fund from investing in securities issued by a REIT, provided that such trust is not permitted to invest in real estate or in interests other than mortgages or other security interests.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Purchase, hold or deal in real estate, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that invest or deal in real estate or REITs.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Purchase or sell real estate, REIT securities, commodities, or oil and gas interests, but the fund may purchase and sell securities that are secured by real estate or issued by companies that deal in real estate.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Purchase or sell real estate, REIT securities, commodities or commodity contracts, or oil and gas interests, but this shall not prevent the fund from investing in Municipal Obligations secured by real estate or interests therein.
II-35
11. Senior Securities
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act), except insofar as the fund may be deemed to have issued a senior security by reason of borrowing money in accordance with the fund's borrowing policies. For purposes of this Fundamental Policy, collateral, escrow, or margin or other deposits with respect to the making of short sales, the purchase or sale of futures contracts or options, and the writing of options on securities are not deemed to be an issuance of a senior security.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund and Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act), except insofar as the fund may be deemed to have issued a senior security by reason of borrowing money in accordance with the fund's borrowing policies.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act), except to the extent the activities permitted by Fundamental Policy Nos. 2 and 10 and Nonfundamental Policy No. 3 may be deemed to give rise to a senior security.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act), except to the extent the activities permitted by Fundamental Policy Nos. 2 and 3 and Nonfundamental Policy Nos. 3 and 9 may be deemed to give rise to a senior security.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Borrow money or issue any senior security, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act), except to the extent the activities permitted by Fundamental Policy Nos. 2 and 3 and Nonfundamental Policy No. 3 may be deemed to give rise to a senior security.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Issue any senior security (as such term is defined in Section 18(f) of the 1940 Act).
12. Short Sales
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Sell securities short or purchase securities on margin, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Sell any security short or engage in the purchase and sale of put, call, straddle, or spread options or combinations thereof, or in writing such options, except that the fund may write and sell covered call option contracts on securities owned by the fund up to, but not in excess of, 20% of the market value of its net assets at the time such option contracts are written. The fund may also purchase call options for the purpose of terminating its outstanding obligations with respect to securities upon which covered call option contracts have been written. In connection with the writing of covered call options, the fund may pledge assets to an extent not greater than 20% of the market value of its total net assets at the time such options are written.
13. Underwriting
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Underwrite the securities of other issuers.
II-36
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund and The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Act as an underwriter of securities of other issuers, except to the extent the fund may be deemed an underwriter under the Securities Act by virtue of disposing of portfolio securities.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Act as an underwriter of securities of other issuers, except to the extent the fund may be deemed an underwriter under the Securities Act in connection with the purchase and sale of portfolio securities.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Underwrite the securities of other issuers, except that the fund may bid separately or as part of a group for the purchase of Municipal Bonds directly from an issuer for its own portfolio to take advantage of the lower purchase price available, and except to the extent the fund may be deemed an underwriter under the Securities Act by virtue of disposing of portfolio securities.
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Underwrite the securities of other issuers, except that the fund may bid separately or as part of a group for the purchase of Municipal Obligations directly from an issuer for its own portfolio to take advantage of the lower purchase price available.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Act as an underwriter of securities of other issuers, except that the fund may bid separately or as part of a group for the purchase of Municipal Obligations directly from an issuer for its own portfolio to take advantage of the lower purchase price available, and except to the extent the fund may be deemed an underwriter under the Securities Act by virtue of disposing of portfolio securities.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Act as an underwriter of securities of other issuers.
14. Investing for Control
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control.
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management. Purchase more than 10% of the voting securities of any issuer (this Fundamental Policy applies only with respect to 75% of the fund's assets) or invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Invest in the securities of a company for the purpose of exercising management or control, but the fund will vote the securities it owns in its portfolio as a shareholder in accordance with its views.
15. Purchase Securities of Other Investment Companies
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Invest in securities of other investment companies, except as they may be acquired as part of a merger, consolidation or acquisition of assets.
II-37
16. Other
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase securities of any company having less than three years' continuous operating history (including that of any predecessors) if such purchase would cause the value of the fund's investments in all such securities to exceed 5% of the value of its net assets.
With respect to Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, for purposes of industry concentration determinations, municipal securities, where the payment of principal and interest for such securities is derived solely from a specific project, are grouped together as an "industry."
With respect to Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, for purposes of industry concentration determinations, industrial development bonds, where the payment of principal and interest is the ultimate responsibility of companies within the same industry, are grouped together as an "industry."
In addition to the Fundamental Policies described above, the following Fundamental Policies also apply to The Dreyfus Third Century Fund:
· The fund's special considerations described in the prospectus will not be changed without shareholder approval. The board may from time to time without shareholder approval adopt additional criteria or restrictions governing the fund's investments if the board determines that the new criteria or restrictions are consistent with the fund's objective of investing in a socially responsible manner. Any such new criteria or restrictions would not be fundamental policies of the fund and could be subsequently terminated or changed by the board at any time without shareholder approval.
· The fund may not purchase or retain the securities of any issuer if officers or board members of the fund or of the Manager, who own beneficially more than 1/2 of 1% of the securities of such issuer, together own beneficially more than 5% of the securities of such issuer.
· The fund may not purchase from or sell to any of its officers or board members, or firms of which any of them are members, any securities (other than capital stock of the fund), but such persons or firms may act as brokers for the fund for customary commissions.
· The fund may not purchase warrants in excess of 2% of the value of its net assets. Such warrants shall be valued at fair market value, except that warrants acquired by the fund in units or attached to securities shall be deemed to be without value, for purposes of this restriction only.
Except for Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, references to "commodities" or "commodity contracts" in the Fundamental Policies described above are to physical commodities or contracts in respect of physical commodities, typically natural resources or agricultural products, and are not intended to refer to instruments that are strictly financial in nature and are not related to the purchase or delivery of physical commodities.
As a Nonfundamental Policy, which may be changed at any time, without shareholder approval, by a vote of a majority of the board members and in compliance with applicable law and regulatory policy, each fund, as indicated, may not:
1. Investing for Control
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Invest in the securities of a company for the purpose of exercising management or control, but the fund will vote the securities it owns in its portfolio as a shareholder
II-38
in accordance with its views.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Invest in the securities of a company for the purpose of management or the exercise of control, but the fund votes the securities it owns in its portfolio as a shareholder in accordance with its own views.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Invest in companies for the purpose of exercising control.
2. Margin
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Purchase securities on margin, except for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, and options on futures contracts, and except that effecting short sales will be deemed not to constitute a margin purchase for purposes of this Nonfundamental Policy.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Purchase securities on margin, except for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Purchase securities on margin, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in futures, including those relating to indices, and options on futures or indices.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Purchase securities on margin, except for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, options on futures contracts, swap agreements and other derivative instruments, and except that affecting short sales will be deemed no to constitute a margin purchase for purposes of this Nonfundamental Policy.
3. Pledging Assets
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. Pledge, mortgage, hypothecate or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management, Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Pledge, mortgage or hypothecate its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued, forward commitment or delayed-delivery basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with writing covered put and call options and collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to permitted transactions.
II-39
Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to facilitate engaging in repurchase agreement transactions.
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund. Pledge, mortgage or hypothecate its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with writing covered put and call options and collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Pledge, mortgage or hypothecate its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to effecting short sales of securities, the purchase of securities on a when-issued, forward commitment or delayed-delivery basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with the entry into options, forward contracts, futures contracts, options on futures contracts, swap agreements and other derivative instruments.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with the purchase of securities on a when-issued or delayed-delivery basis and collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those related to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Pledge, mortgage or hypothecate its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with writing covered put and call options and collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to options, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings; to facilitate engaging in repurchase agreement transactions; and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued, forward commitment or delayed-delivery basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to permitted transactions.
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued, forward commitment or delayed-delivery basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to permitted transactions.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Pledge, hypothecate, mortgage or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings; to facilitate engaging in repurchase agreement transactions; and in connection with the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis.
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. Pledge, mortgage, hypothecate or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis and in connection with writing covered put and call options and margin arrangements with respect to options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund and Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund. Pledge, mortgage, hypothecate or otherwise encumber its
II-40
assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings; to facilitate engaging in repurchase agreement transactions; and to the extent related to the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Pledge, mortgage, hypothecate or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Pledge, mortgage, hypothecate or otherwise encumber its assets, except to the extent necessary to secure permitted borrowings and to the extent related to the purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward commitment basis and the deposit of assets in escrow in connection with writing covered put and call options and collateral and initial or variation margin arrangements with respect to options, forward contracts, futures contracts, including those relating to indices, and options on futures contracts or indices.
4. Purchase Securities of Other Investment Companies
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Invest in securities of other investment companies, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. Purchase securities of other investment companies, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. Purchase any securities issued by any investment company, except to the extent permitted under the 1940 Act.
5. Illiquid Investments
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. Enter into repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice or purchase securities which are illiquid if, in the aggregate, more than 5% of the value of the fund's net assets would be so invested.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Enter into repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice or purchase securities which are illiquid if, in the aggregate, more than 5% of the value of the fund's total assets would be so invested.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund, The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated and The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund. Enter into repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice or purchase securities which are illiquid if, in the aggregate, more than 15% of the value of the fund's net assets would be so invested.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Enter into repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice or purchase securities which are illiquid (which securities could include participation interests (including municipal lease/purchase agreements) that are not subject to the demand feature described in the fund's prospectus, and floating and variable rate demand obligations as to which the
II-41
fund cannot exercise the demand feature described in the fund's prospectus on less than seven days' notice and as to which there is no secondary market), if, in the aggregate, more than 15% of its net assets would be so invested.
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus, Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management, Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management. Enter into repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice or purchase securities which are illiquid if, in the aggregate, more than 5% of the value of the fund's net assets would be so invested.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Purchase securities which are illiquid if, in the aggregate, more than 5% of the value of the fund's net assets would be so invested.
6. Margin
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management and Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management. Purchase securities on margin, except for use of short-term credit necessary for clearance of purchases and sales of portfolio securities, but the fund may make margin deposits in connection with transactions in options, forward contracts, futures contracts, and options on futures contracts, and except that effecting short sales will be deemed not to constitute a margin purchase for purposes of this Nonfundamental Policy.
7. Short Sales
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Sell securities short.
8. Investment in Other than Municipal Bonds
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. Purchase securities other than Municipal Bonds and taxable investments and those arising out of transactions in futures and options or as otherwise provided in the fund's prospectus.
9. Puts/Calls
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Write or purchase put or call options or combinations thereof, except that the fund may purchase and sell "obligations with puts attached" in accordance with its stated investment policies.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund and Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund. Purchase, sell or write puts, calls or combinations thereof, except as described in its prospectus and this SAI.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. Write or purchase put or call options or combinations thereof.
10. Other
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Enter into repurchase agreements.
Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management. Purchase common stocks, preferred stocks, warrants or other equity securities.
II-42
With respect to Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus and Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management, notwithstanding Fundamental Policies Nos. 1, 8 and 10, and with respect to Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management, notwithstanding Fundamental Policies Nos. 1 and 10 and Nonfundamental Policy No. 1, each fund reserves the right to enter into interest rate futures contracts and municipal bond index futures contracts, and any options that may be offered in respect thereof, subject to the restrictions then in effect of the SEC and the CFTC and to the receipt or taking, as the case may be, of appropriate consents, approvals and other actions from or by those regulatory bodies. In any event, no such contracts or options will be entered into until a general description of the terms thereof are set forth in a subsequent prospectus and statement of additional information, the registration statement with respect to which has been filed with the SEC and has become effective.
With respect to each fund, if a percentage restriction is adhered to at the time of investment, a later change in percentage resulting from a change in values or assets will not constitute a violation of such restriction, except as otherwise required by the 1940 Act. With respect to the funds' policies pertaining to borrowing, however, if borrowings exceed 33-1/3% of the value of a fund's total assets as a result of a change in values or assets, the fund must take steps to reduce such borrowings within three days (not including Sundays and holidays) thereafter at least to the extent of such excess.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund, Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund and Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund have adopted policies prohibiting them from operating as funds-of-funds in reliance on Section 12(d)(1)(F) or Section 12(d)(1)(G) of the 1940 Act.
Policies Related to Fund Names
Under normal circumstances, Dreyfus Government Cash Management invests solely in securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities, and repurchase agreements; Dreyfus Government Prime Cash Management invests solely in securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities; Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management invests solely in securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government and repurchase agreements collateralized by such securities; and Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management invests solely in securities issued or guaranteed as to principal and interest by the U.S. Government. Each of the following funds invests, under normal circumstances, at least 80% of its net assets, plus any borrowings for investment purposes (for funds that may borrow for investment purposes), in the instruments described below (or other instruments with similar economic characteristics). Each fund has adopted a policy to provide its shareholders with at least 60 days' prior notice of any change in its policy to so invest its assets (except for certain funds that have adopted such policy as a Fundamental Policy as indicated above).
|
Fund |
Investment |
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
U.S. Treasury securities |
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
California Municipal Obligations |
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
Two separate tests: (1) inflation-indexed securities and (2) investment grade securities |
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
Fixed-income securities of U.S. and foreign issuers rated investment grade or the unrated equivalent as determined by the Manager |
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
Municipal Obligations |
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
Stocks of companies in the natural resources and natural resources related sectors |
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
New York Municipal Obligations |
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
Bonds (or other instruments with similar economic characteristics) |
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Municipal Bonds |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
Common stocks and other equity securities of companies |
II-43
|
Fund |
Investment |
|
organized or with their principal place of business, or majority of assets or business, in emerging market countries | |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
Common stocks and other equity securities |
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
Common stocks and other equity securities of U.S. companies |
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
Tax exempt Municipal Obligations |
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund
Each fund ordinarily declares dividends from its net investment income on each business day, which is every day the NYSE or, with respect to CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund, CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund, Dreyfus Liquid Assets and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund only, the Transfer Agent is open for business.
II-44
INFORMATION ABOUT THE FUNDS' ORGANIZATION AND STRUCTURE
Each fund is an open-end management investment company. Listed below are the forms of organization of each fund company, its corresponding fund series (if any), the dates of organization and each fund's subclassification as "diversified" or "non-diversified" under the 1940 Act. The fund companies (in bold) listed below are either Maryland corporations or Massachusetts business trusts. If one or more funds are listed in italics thereunder, then such fund company is a "series" company, and investments are made through, and shareholders invest in, the fund series shown. References in this SAI to a "fund" generally refer to the series of a series company; if no such funds are listed under a bold fund company name, then it is not organized as a series company and the term "fund" refers to such fund company. A fund may not change its subclassification from "diversified" to "non-diversified" without approval of the holders of a majority of the fund's outstanding securities (as defined in the 1940 Act).
|
Name |
State of Organization* |
Date of Organization** |
Diversification Classification |
|
CitizensSelect Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 14, 1993 |
|
|
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Cash Management |
Massachusetts |
May 22, 1987 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 22, 1987 |
|
|
Dreyfus Government Cash Management |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Government |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 21, 1993 |
|
|
Dreyfus Institutional Cash Advantage Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 21, 1993 |
|
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Money Market Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Preferred Plus Money Market Fund |
Diversified |
II-45
|
Name |
State of Organization* |
Date of Organization** |
Diversification Classification |
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Funds |
Massachusetts |
January 10, 2008*** |
|
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Money Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Treasury Prime Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Investment Grade Funds, Inc. |
Maryland |
June 26, 1992 |
|
|
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund |
Non-diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Liquid Assets, Inc. |
Maryland |
September 6, 1973 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus Municipal Cash Management Plus |
Massachusetts |
September 12, 1990 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus New York Municipal Cash Management |
Massachusetts |
September 12, 1990 |
Non-diversified |
|
Dreyfus Opportunity Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 21, 1993 |
|
|
Dreyfus Natural Resources Fund |
Non-diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Emerging Markets Equity Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta Global Equity Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Strategic Beta U.S. Equity Fund |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Premier Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Massachusetts |
October 29, 1986 |
|
|
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund |
Non-diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund |
Massachusetts |
September 19, 1986 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management Funds |
Massachusetts |
May 22, 1987 |
|
|
Dreyfus California AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Non-diversified |
II-46
|
Name |
State of Organization* |
Date of Organization** |
Diversification Classification |
|
Dreyfus New York AMT-Free Municipal Cash Management |
Non-diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management |
Diversified | ||
|
Dreyfus Treasury & Agency Cash Management |
Massachusetts |
June 4, 1986 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus Treasury Prime Cash Management |
Massachusetts |
February 16, 1987 |
Diversified |
|
Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund, Inc. |
Maryland |
February 2, 1989 |
Diversified |
|
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated |
Maryland |
January 2, 1947 |
Diversified |
|
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund, Inc. |
Delaware |
May 6, 1971 |
Diversified |
* On May 22, 1987, each of Dreyfus Cash Management, Dreyfus Government Cash Management Funds and Dreyfus Tax Exempt Cash Management Funds was reorganized from a Maryland corporation
** As a result of legal requirements relating to the formation of Massachusetts business trusts, there may have been a significant period of time between the dates of organization and commencement of operations for funds organized in this structure, during which time no business or other activities were conducted.
*** Prior to Dreyfus Institutional Reserves Funds commencing operations, the fund participated in a tax-free reorganization where each series of the fund received the assets of a corresponding series of BNY Hamilton Funds.
CERTAIN EXPENSE ARRANGEMENTS AND OTHER DISCLOSURES
Cash Management Funds. The Manager has agreed that if in any fiscal year the aggregate expenses of each fund, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest on borrowings and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed 1-1/2% of the value of the fund's average net assets for the fiscal year, the fund may deduct from the payment to be made to the Manager under the fund's agreement with the Manager, or the Manager will bear, such excess expense. Such deduction or payment, if any, will be estimated on a daily basis, and reconciled and effected or paid, as the case may be, on a monthly basis.
Dreyfus Inflation Adjusted Securities Fund, Dreyfus Intermediate Term Income Fund, Dreyfus Short Term Income Fund and Dreyfus Worldwide Dollar Money Market Fund. The Manager has agreed that if in any fiscal year the aggregate expenses of the fund, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest on borrowings and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed the expense limitation of any state having jurisdiction over the fund, the fund may deduct from the payment to be made to the Manager under the fund's agreement with the Manager, or the Manager will bear, such excess expense to the extent required by state law. Such deduction or payment, if any, will be estimated daily, and reconciled and effected or paid, as the case may be, on a monthly basis.
Dreyfus Liquid Assets. The Manager has agreed that if in any fiscal year the fund's aggregate expenses, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed 1% of the value of the fund's average net assets for the fiscal year, the Manager will refund to the fund, or bear, the excess over 1%. Such expense reimbursement, if any, will be estimated, reconciled and paid on a monthly basis.
II-47
Dreyfus Short Duration Bond Fund. The Manager has agreed that if in any fiscal year the aggregate expenses of the fund, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest on borrowings and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed 1-1/2% of the average value of the fund's net assets for the fiscal year, the fund may deduct from the payment to be made to the Manager under the fund's agreement with the Manager, or the Manager will bear, such excess expense. Such deduction or payment, if any, will be estimated daily, and reconciled and effected or paid, as the case may be, on a monthly basis.
Dreyfus Short-Intermediate Municipal Bond Fund. The Manager has agreed that if in any fiscal year the aggregate expenses of the fund, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest on borrowings and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed, with respect to Class D shares, 1-1/2% of the value of the fund's average net assets attributable to Class D shares for the fiscal year, the fund may deduct from the payment to be made to the Manager under the fund's agreement with the Manager, or the Manager will bear, such excess expense. Such deduction or payment, if any, will be estimated daily, and reconciled and effected or paid, as the case may be, on a monthly basis.
The Dreyfus Fund Incorporated. The Manager has agreed that if the aggregate expenses of the fund, exclusive of taxes and brokerage commissions but including the management fee, exceed 1% of the value of the fund's average daily net assets for any full fiscal year, the Manager will bear such expenses or refund to the fund the amount of such excess.
The Dreyfus Third Century Fund. The Manager has agreed that if, in any fiscal year, the aggregate expenses of the fund, exclusive of taxes, brokerage, interest and (with the prior written consent of the necessary state securities commissions) extraordinary expenses, but including the management fee, exceed, with respect to Class Z of the fund, 1-1/2% of the average value of the fund's net assets attributable to its Class Z shares, the fund may deduct from the fees to be paid to the Manager, or the Manager will bear, the excess expense. For each fiscal year of the fund, the Manager will pay or bear such excess on a pro rata basis in proportion to the relative fees otherwise payable pursuant to the fund's agreement with the Manager. Such deduction or payment, if any, will be estimated, reconciled and effected or paid, as the case may be, on a monthly basis and will be limited to the amount of fees otherwise payable to the Manager under the fund's agreement with the Manager.
CitizensSelect Prime Money Market Fund and CitizensSelect Treasury Money Market Fund. The fund has adopted an Administrative Services Plan with respect to Class B, Class C and Class D shares. Pursuant to the plan, each fund pays Citizens or other approved institutions for the provision of certain services to the holders of such shares a fee at the annual rate of 0.25% of the value of the average daily net assets of Class B, Class C and Class D shares. These services may include: providing beneficial owners with statements showing their positions in the fund; mailing periodic reports, prospectuses and other fund communications to beneficial owners; withholding taxes on non-resident alien accounts; disbursing income dividends and capital gain distributions; reinvesting dividends and distributions; preparing and delivering to beneficial owners, and state and federal authorities, including the IRS and the SEC, such information respecting dividends and distributions paid by the fund as may be required by law, rule or regulation; withholding on dividends and distributions as may be required by state or federal authorities from time to time; receiving, tabulating, and transmitting proxies executed by beneficial owners; and providing such other related services as the fund may reasonably request.
A written quarterly report of the amounts expended under the plan, and the purposes for which such expenditures were incurred, must be made to the fund's board for its review. In addition, the plan provides that material amendments must be approved by the board and by the board members who are not "interested persons" (as defined in the 1940 Act) of the fund and have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the plan or in any agreements entered into in connection with the plan, by vote cast in person at a meeting called for the purpose of considering such amendments. The plan is subject to annual approval by such vote of the board members cast in person at a meeting called for the purpose of voting on the plan. As to each class of shares, the plan is terminable at any time by vote of a majority of the board members who are not "interested persons" of the fund and who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the plan or in any agreements entered into in connection with the plan.
II-48
COUNSEL AND INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Stroock & Stroock & Lavan LLP, 180 Maiden Lane, New York, New York 10038-4982, as counsel for the funds, has rendered its opinion as to certain legal matters regarding the due authorization and valid issuance of the shares being sold pursuant to the funds' prospectuses.
Ernst & Young LLP, 5 Times Square, New York, New York 10036-6530, an independent registered public accounting firm, has been selected to serve as the independent registered public accounting firm for the funds.
II-49
RISKS OF INVESTING IN STATE MUNICIPAL SECURITIES
The following information constitutes only a brief summary, does not purport to be a complete description, and is based on information drawn from official statements relating to securities offerings of the specified state or states (each, the "State" or the "Commonwealth") and various local agencies available as of the date of this SAI. While the relevant fund(s) have not independently verified this information, the fund(s) have no reason to believe that such information is not correct in all material respects.
Economy. California's economy, the nation's largest and one of the largest and most diverse in the world, has major sectors in high technology, trade, entertainment, agriculture, manufacturing, government, tourism, construction and services. During the recent recession, the State experienced the most significant economic downturn since the Great Depression of the 1930s. As a result, State tax revenues declined precipitously, resulting in large budget gaps and occasional cash shortfalls during 2008 through 2011. The State enacted and has maintained significant spending reductions since that period. Despite these significant budgetary improvements, there remain a number of material risks and pressures that threaten the State's financial condition, including the need to repay billions of dollars of obligations that were deferred to balance budgets during the economic downturn.
Various economic indicators suggest that the national economy experienced an uneven expansion in 2013, with a strong third quarter, and growth likely muted in the fourth quarter by the federal government shutdown. Following an annual growth rate of 1.1% in the first quarter of 2013, U.S. gross domestic product grew by 2.5% in the second quarter of 2013 and 4.1% in the third quarter of 2013—the tenth consecutive quarter of growth. The national recovery is expected to pick up in 2014 and 2015. The California economy also continued to experience a gradual and broadening recovery, which spread to more sectors of the economy in 2013. Continued growth in the high-technology sector, international trade and tourism are being supplemented by better residential construction and real estate conditions. Personal income increased in thirteen of the fifteen quarters through the third quarter of 2013, with decreases only in the fourth quarter of 2011 and the first quarter of 2013. Personal income is projected to grow 2.2% in 2013, 5.7% in 2014 and 5.3% in 2015.
California's nonfarm payroll jobs grew by 391,700 between December 2012 and December 2013. During the first six months of 2013, payroll jobs grew by 82,800, or by 13,800 jobs per month on average. During the last six months of 2013, payroll jobs grew by 152,900, or by 25,500 jobs per month on average. The State unemployment rate reached a high of 12.4% in late 2010. The unemployment rate improved thereafter, falling to 8.0% in February 2014. In comparison, the national unemployment rate was 6.7% in February 2014. Industry employment is forecast to expand 2.1% and 2.4% in 2013 and 2014, respectively, and 2.5% growth is projected for 2015.
After hitting a low of close to 200,000 units (seasonally-adjusted and annualized) in the middle of 2007, sales of existing single-family homes have rebounded to above 400,000 units annually. The State median sales price rose to $438,040 in December 2013, an increase of almost 20% over December 2012 (but still 26% below the pre-recession peak). California issued 83,000 residential building permits in 2013, 42.6% more than were issued in 2012, but still only 39% of the 213,000 permits issued in 2004. The number of California homes going into foreclosure dropped to an eight-year low in the fourth quarter of 2013 to 18,120. That was down 10.8% from the prior quarter, and down 52.6% from the fourth quarter of 2012. Foreclosures peaked at 135,431 in the first quarter of 2009. The declining rate of foreclosures was likely due in part to the new state foreclosure laws which took effect at the beginning of calendar year 2013.
Population. California's 2013 estimated population was 38.2 million residents, which represented 12% of the total United States population. The State's population is expected to reach 38.55 million by July 2014 and 38.90 million by July 2015. California's population is highly concentrated in metropolitan areas. By July 2018, the State is expected to have added another 1.8 million people for a total population of over 40 million residents.
II-50
State Indebtedness and Other Obligations
The State Treasurer is responsible for the sale of debt obligations of the State and its various authorities and agencies. The State has always paid when due the principal of and interest on its general obligation bonds, general obligation commercial paper notes, lease-purchase debt and short-term obligations, including Revenue Anticipation Notes ("RANs") and revenue anticipation warrants ("RAWs"). State agencies and authorities also can issue revenue obligations for which the State General Fund has no liability.
General Obligation Bonds. The State Constitution prohibits the creation of general obligation indebtedness of the State unless a bond law is approved by a majority of the electorate voting at a general election or a direct primary. General obligation bond acts provide that debt service on such bonds shall be appropriated annually from the State General Fund and all debt service on general obligation bonds is paid from the State General Fund. Under the State Constitution, debt service on general obligation bonds is the second charge to the State General Fund after the application of monies in the State General Fund to the support of the public school system and public institutions of higher education. Certain general obligation bond programs receive revenues from sources other than the sale of bonds or the investment of bond proceeds.
As of February 1, 2014, the State had outstanding approximately $80.52 billion aggregate principal amount of long-term general obligation bonds, of which $75.19 billion was payable primarily from the State General Fund and $5.33 billion was payable from other revenue sources. As of February 1, 2014, there were unused voter authorizations for the future issuance of approximately $28.29 billion of long-term general obligation bonds. Of this unissued amount, approximately $706.21 million is for bonds payable from other revenue sources.
The Legislature has placed on the statewide election ballot on June 3, 2014 a measure to approve $600 million of general obligation bonds to finance rental housing programs for military veterans. This measure also would cancel $600 million of existing authorizations from 2008 that are payable primarily from mortgage payments made by veteran homeowners. A ballot measure also is scheduled to be submitted to the voters at the statewide election in November 2014 (rescheduled from 2012) to approve the issuance of $11.14 billion in general obligation bonds for a wide variety of purposes relating to improvement of California's water supply systems, drought relief, and groundwater protection. Additional bond measures may be included on future election ballots, but any proposed bond measure must first be approved by a 2/3 vote of the Legislature or placed on the ballot through the initiative process.
The State is permitted to issue as variable rate indebtedness up to 20% of the aggregate amount of long-term general obligation bonds outstanding. As of February 1, 2014, the State had outstanding approximately $4.03 billion in variable rate general obligation bonds (which includes a portion of the Economic Recovery Bonds ("ERBs") described below), representing about 5.0% of the State's total outstanding general obligation bonds as of that date.
Under State law, except for the ERBs and certain indexed floating rate bonds without credit enhancement, the State must pay the principal and interest of any general obligation bonds that are subject to optional or mandatory tender, and which are not remarketed or, if applicable, purchased by financial institutions which provide liquidity support. The State has not entered into any interest rate hedging contracts in relation to any of its variable rate general obligation bonds. The State has no auction rate bonds outstanding.
Commercial Paper Program. Pursuant to legislation enacted in 1995, voter-approved general obligation indebtedness may be issued either as long-term bonds or, for some but not all bond issuances, as commercial paper notes. Commercial paper notes may be renewed or may be refunded by the issuance of long-term bonds. The State issues long-term general obligation bonds from time to time to retire its general obligation commercial paper notes. Commercial paper notes are deemed outstanding upon authorization by the respective finance committees, whether or not such notes are actually issued. A total of approximately $1.73 billion principal amount of commercial paper is now authorized under agreements with various banks. A total of approximately $892.33 million of commercial paper was outstanding as of March 3, 2014.
Bank Arrangements. In connection with the letters of credit or other credit facilities obtained by the State in connection with variable rate obligations and the commercial paper program, the State has entered into a number of reimbursement agreements or other credit agreements with a variety of financial institutions. As of April 9, 2014, the State had a total par amount of $4.31 billion of bank arrangements available.
II-51
Lease-Revenue Debt. In addition to general obligation bonds, the State builds and acquires capital facilities through the use of lease-revenue borrowing. Under these arrangements, the State Public Works Board ("SPWB"), another State or local agency or a joint powers authority issues bonds to pay for the construction of facilities such as office buildings, university buildings or correctional institutions. These facilities are leased to a State agency or the University of California ("UC") under a long-term lease that provides the source of payment of the debt service on the lease-revenue bonds. In some cases, there is not a separate bond issue, but a trustee directly creates certificates of participation in the State's lease obligation, which are then marketed to investors. Certain of the lease-revenue financings are supported by special funds rather than the State General Fund. The State had approximately $10.24 billion in State General Fund-supported lease-revenue obligations outstanding as of February 1, 2014. The SPWB, which is authorized to sell lease-revenue bonds, had approximately $5.87 billion in authorized and unissued bonds as of February 1, 2014.
Non-Recourse Debt. Certain State agencies and authorities issue revenue obligations for which the State General Fund has no liability. Revenue bonds represent obligations payable from State revenue-producing enterprises and projects, which are not payable from the State General Fund, and conduit obligations payable only from revenues paid by private users of facilities financed by the revenue bonds. The enterprises and projects include transportation projects, various public works projects, public and private educational facilities, housing, health facilities and pollution control facilities. State agencies and authorities had approximately $55.6 billion aggregate principal amount of revenue bonds and notes, which are non-recourse to the State General Fund outstanding as of June 30, 2013.
Build America Bonds. In February 2009, the U.S. Congress enacted certain new municipal bond provisions as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act in February 2009 ("ARRA"), which allowed municipal issuers such as the State to issue "Build America Bonds" ("BABs") for new infrastructure investments. BABs are bonds whose interest is subject to federal income tax, but pursuant to ARRA the U.S. Treasury was to repay the issuer an amount equal to 35% of the interest cost on any BABs issued during 2009 and 2010. The BAB subsidy payments from general obligation bonds are State General Fund revenues to the State, while subsidy payments for lease-revenue bonds are deposited into a fund which is made available to the SPWB for any lawful purpose. In neither instance are the subsidy payments specifically pledged to repayment of the BABs to which they relate. The cash subsidy payment with respect to the BABs, to which the State is entitled, is treated by the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS") as a refund of a tax credit and such refund may be offset by the Department of the Treasury by any liability of the State payable to the federal government. As of March 26, 2014 the State has received all BABs cash subsidy payments to which it has been entitled, without offset.
Between April 2009 and through December 2010, the State issued a significant amount of BABs, including $13.54 billion of general obligation bonds and $551 million of lease revenue bonds. $149.62 million of the SPWB BABs were redeemed in November 2013. The aggregate amount of the subsidy payments to be received from Fiscal Year 2013-14 through the maturity of these bonds (mostly 20 to 30 years) is approximately $8.3 billion for the general obligation BABs and $223 million for the lease revenue BABs.
Starting in March 1, 2013, the BAB subsidy payments were reduced as part of a government-wide "sequestration" of expenditures. The reduction of the BAB subsidy payment is presently scheduled to continue until 2024, although the U.S. Congress can terminate or modify it sooner, or extend it. Each BAB subsidy payment was reduced by 8.7% for the federal Fiscal Year 2013 (ended September 30, 2013). This resulted in a reduction of approximately $15.65 million from the $367.40 million of total subsidies the State had been scheduled to receive between October 1, 2012 and September 30, 2013 for both general obligation and SPWB BABs. The IRS has announced that the sequestration reduction for federal Fiscal Year 2014 (starting October 1, 2013) will be 7.2%, resulting in a reduction of approximately $26.20 million in subsidies from a total of $363.86 million expected to be received during that period. (The sequestration percentage is recalculated for each fiscal year.) None of the BAB subsidy payments are pledged to pay debt service, so this reduction would not affect the State's ability to pay all of its general obligation and lease revenue BABs on time, nor have any material impact on the State General Fund.
Economic Recovery Bonds. The California Economic Recovery Bond Act ("Proposition 57"), which was approved by voters at the Statewide primary election in March 2004, authorized the issuance of up to $15 billion of ERBs to finance the negative State General Fund reserve balance as of June 30, 2004 and other State General Fund obligations undertaken prior to that time. Repayment of the ERBs is secured by a pledge of revenues from a 1/4¢ increase in the State's sales and use tax that started July 1, 2004, but also is secured by the State's full faith and credit
II-52
because the ERBs were approved by voters as general obligation bonds. The entire authorized amount of ERBs was issued in three sales, in May and June 2004, and in February 2008. No further ERBs can be issued under Proposition 57, except for refunding bonds. In 2009, the State issued refunding ERBs to restructure the program in response to a drop in taxable sales caused by the recent severe recession, and in 2011 for debt service savings.
Three different sources of funds are required to be applied to the early retirement (generally by purchase or redemption) of ERBs: (i) all proceeds from the dedicated quarter cent sales tax in excess of the amounts needed, on a semi-annual basis, to pay debt service and other required costs of the bonds, (ii) all proceeds from the sale of specified surplus state property, and (iii) 50% of each annual deposit, up to $5 billion in the aggregate, of deposits in the Budget Stabilization Account ("BSA"). As of December 31, 2013, funds from these sources have been used for early retirement of approximately $5.36 billion of bonds during Fiscal Years 2005-06 through 2012-13, including $472 million which was transferred from the BSA in Fiscal Year 2006-07 and $1.023 billion transferred from the BSA in Fiscal Year 2007-08. The State accumulated approximately $330 million in excess special sales tax and $8 million from the sale of surplus state property up to January 1, 2014. The State will use these moneys to retire ERBs during the next six months.
The Governor suspended the BSA transfers in each of Fiscal Years 2008-09 through 2013-14 due to the condition of the State General Fund. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget proposes the resumption of the BSA transfer in Fiscal Year 2014-15, which will provide an estimated $1.59 billion of additional funds for early retirement of ERBs. It currently is estimated that by June 30, 2015 all of the ERBs will have been paid or provision for their payment will have been made through creation of escrow accounts.
Tobacco Settlement Revenue Bonds. In 1998, the State signed the Master Settlement Agreement (the "MSA") with the four major cigarette manufacturers (the "PMs") for payment of approximately $25 billion (subject to adjustment) over 25 years. Under the MSA, half of the money will be paid to the State and half to local governments. Payments continue in perpetuity, but the specific amount to be received by the State and local governments is subject to adjustment under the MSA, including reduction of the PMs' payments for decreases in cigarette shipment volumes by the PMs, payments owed to certain previously settled states and certain other types of offsets.
In 2003, two separate sales of these assets financed with revenue bonds (the "2003 Bonds") produced about $4.75 billion in proceeds which were transferred to the State General Fund. In 2005 and 2007, the State refunded all of the original 2003 Bonds, generating additional proceeds of approximately $1.783 billion, which were also transferred to the State General Fund. This credit enhancement mechanism was applied to only the second 2003 sale of bonds and was continued when those bonds were refunded in 2005 and 2013 (the "2005 Bonds" and the "2013 Bonds"). This credit enhancement mechanism only applies to the outstanding principal amount of approximately $2.7 billion of 2005 Bonds and 2013 Bonds.
One of the reserve funds relating to the 2005 Bonds was used to make required debt service interest payments on the 2005 Bonds in 2011 and 2012 in part due to the withholding related to the declining tobacco consumption and disputes over declining PM market share. The total amount of the draws was approximately $7.94 million. In April 2013, the reserve fund was replenished in full following the disbursements of the non-participating manufacturer settlement funds and receipt of the scheduled tobacco settlement revenues. As of January 1, 2014, the amount of the two reserve funds relating to the 2005 Bonds was approximately $253.3 million. If, in any future year tobacco settlement revenues are less than required debt service payments on the 2005 Bonds and 2013 Bonds in such year, additional draws on the reserve funds with respect to the 2005 Bonds and 2013 Bonds will be required. Future revenues in excess of debt service requirements, if any, will be used to replenish the reserve funds of the bonds. Although the State cannot predict the amount of future tobacco settlement revenues, if the current trends continue, the amount of tobacco settlement revenues may be insufficient to pay debt service on the 2005 Bonds and 2013 Bonds, and the Governor would be required to request an appropriation from the State General Fund. The Legislature, however, is not obligation to grant such a request.
Future Issuance Plans. Since 2006, a significant amount of new general obligation bonds, lease revenue bonds and Proposition 1A bonds have been authorized by voters and/or the Legislature. These authorizations led to a substantial increase in the amount of State General Fund-supported debt outstanding, from $44.85 billion as of July 1, 2006 to $85.42 billion as of February 1, 2014, while still leaving current authorized and unissued bonds of about $33.45 billion. In 2009 and 2010, over $35.07 billion of general obligation bonds, lease-revenue bonds and Proposition 1A bonds were sold.
II-53
Following the record bond issuance levels in calendar years 2009 and 2010, bond issuance for new money general obligation bonds has substantially decreased as departments work to manage their existing bond cash balances. In calendar years 2011 and 2012, $8.0 billion of new money general obligation and lease-revenue bonds were sold. In addition, $5.8 billion of refunding general obligation and lease-revenue bonds were sold. In calendar year 2013, $6.04 billion of new money general obligation and lease-revenue bonds were sold, and $4.42 billion of refunding general obligation and lease-revenue bonds were sold. Based on estimates from the 2014-15 Governor's Budget and the Department of Finance (the "DOF"), approximately $4.48 billion of new money general obligation bonds (some of which may initially be in the form of commercial paper notes) and approximately $1.41 billion of lease-revenue bonds will be issued in calendar year 2014.
With the continued issuance of authorized but unissued new bond sales to occur in the future, the ratio of debt service on general obligation and lease-revenue supported by the State General Fund, to annual State General Fund revenues and transfers, can be expected to increase in future years. Based on the revenue estimates contained in the 2014-15 Governor's Budget and bond issuance estimates, the State General Fund debt ratio is estimated to equal approximately 7.46% in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and 7.43% in Fiscal Year 2014-15. The total offset for general obligation bond debt service is estimated to equal approximately $1.39 billion for Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $1.46 billion for Fiscal Year 2014-15, which will decrease the debt ratio to 6.07% and 6.03% in Fiscal Years 2013-14 and 2014-15, respectively.
Cash Flow Borrowings and Management. The majority of State General Fund revenues are received in the latter part of the State's fiscal year, whereas State General Fund expenditures occur more evenly throughout the fiscal year. The State's cash flow management program customarily addresses this timing difference by making use of internal borrowing and by issuing short-term notes in the capital markets. External borrowing is typically done with RANs that are payable not later than the last day of the fiscal year in which they are issued. The State has issued RANs in all but one fiscal year since the mid-1980s; such RANs have always been paid at maturity. RANs must mature prior to the end of the fiscal year of issuance. If additional external cash flow borrowings are required, the State has issued RAWs, which can mature in a subsequent fiscal year. RANs and RAWs are both payable from any unapplied revenues in the State General Fund on their maturity date, subject to the prior application of such money in the State General Fund to pay certain priority payments in the general areas of education, general obligation debt service, State employee wages and benefits and other specified State General Fund reimbursements.
The State entered Fiscal Years 2012-13 and 2013-14 in a stronger cash position than it had in some prior years. Timely enactment of the 2012 Budget Act allowed the State to carry out its regular cash management borrowing with RANs early in the year without the need for interim RANs for the first time in three years. The State issued approximately $10 billion of RANs on August 23, 2012, which were all repaid when due. The State's cash management plan in Fiscal Year 2013-14 consists primarily of internal borrowing from special funds and issuance of RANs in the amount of $5.5 billion.
Ratings. The current ratings of the State's general obligation bonds are "A1" from Moody's, "A" from Fitch and "A" from S&P.
The Budget and Appropriations Process. The State's fiscal year begins on July 1 and ends on June 30. The annual budget is proposed by the Governor by January 10 of each year for the next fiscal year. Under State law, the annual proposed budget cannot provide for projected expenditures in excess of projected revenues and balances available from prior fiscal years. Following the submission of the proposed budget, the Legislature takes up the proposal. The Balanced Budget Amendment ("Proposition 58"), which was approved by voters in March 2004, requires the State to adopt and maintain a balanced budget and establish an additional reserve, and restricts future long-term deficit-related borrowing.
The primary source of the annual expenditure authorizations is the Budget Act as approved by the Legislature and signed by the Governor. Pursuant to Proposition 25, enacted on November 2, 2010, and effective immediately, the Budget Act (or other appropriation bills and "trailer bills" which are part of a budget package) must be approved by a majority vote of each House of the Legislature. (This was a reduction from a requirement for a two-thirds vote.) The Governor may reduce or eliminate specific line items in the Budget Act or any other appropriations bill without vetoing the entire bill. Such individual line-item vetoes are subject to override by a two-thirds majority vote of each House of the Legislature. Appropriations also may be included in legislation other than the Budget Act. Continuing
II-54
appropriations, available without regard to fiscal year, may also be provided by statute or the State Constitution. Funds necessary to meet an appropriation are not required to be in the State Treasury at the time an appropriation is enacted; revenues may be appropriated in anticipation of their receipt.
The State General Fund. The monies of the State are segregated into the State General Fund and over 1,000 other funds, including special, bond and other funds. The State General Fund consists of revenues received by the State Treasury and not required by law to be credited to any other fund, as well as earnings from the investment of State monies not allocable to another fund. The State General Fund is the principal operating fund for the majority of governmental activities and is the depository of most of the major revenue sources of the State. The State General Fund may be expended as a consequence of appropriation measures enacted by the Legislature and approved by the Governor, as well as appropriations pursuant to various constitutional authorizations and initiative statutes.
The Special Fund for Economic Uncertainties. The Special Fund for Economic Uncertainties ("SFEU") is funded with State General Fund revenues and was established to protect the State from unforeseen revenue reductions and/or unanticipated expenditure increases. Amounts in the SFEU may be transferred by the State to the State General Fund as necessary to meet cash needs of the State General Fund. The State is required to return monies so transferred without payment of interest as soon as there are sufficient monies in the State General Fund. At the end of each fiscal year, the State is required to transfer from the SFEU to the State General Fund any amount necessary to eliminate any deficit in the State General Fund. In certain circumstances, monies in the SFEU may be used in connection with disaster relief. For budgeting and general accounting purposes, any appropriation made from the SFEU is deemed an appropriation from the State General Fund. For year-end reporting purposes, the State is required to add the balance in the SFEU to the balance in the State General Fund so as to show the total monies then available for State General Fund purposes.
The Budget Stabilization Account. Proposition 58, approved in March 2004, created the BSA. Beginning with Fiscal Year 2006-07, a specified portion of estimated annual State General Fund revenues (reaching a ceiling of 3% by Fiscal Year 2008-09) will be transferred into the BSA no later than September 30 of each fiscal year, unless the transfer is suspended or reduced. These transfers will continue until the balance in the BSA reaches $8 billion or 5% of the estimated State General Fund revenues for that fiscal year, whichever is greater. The annual transfer requirement will go back into effect whenever the balance falls below the $8 billion or the 5% target. Since 2007, the State has been authorized to transfer funds from the BSA back into the State General Fund. Proposition 58 also provides that one-half of the annual transfers shall be used to retire ERBs, until a total of $5 billion has been used for that purpose. A total of $1.495 billion of the $5 billion amount has been applied to the retirement of ERBs.
Governor Brown suspended the State General Fund transfer to the BSA in Fiscal Years 2011- 12, 2012-13, and 2013-14. In addition, the previous Governor suspended the State General Fund transfer to the BSA for Fiscal Years 2008-09 through 2010-11. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget proposes a transfer of $3.182 billion to the BSA, half of which ($1.59 billion) will be used to retire ERBs, with the other half remaining in the BSA as a "rainy day" budgetary reserve.
Inter-Fund Borrowings. Inter-fund borrowing is used to meet temporary imbalances of receipts and disbursements in the State General Fund. If State General Fund revenue is or will be exhausted, the State may direct the transfer of all or any part of the monies not needed in special funds to the State General Fund. All money so transferred must be returned to the special fund from which it was transferred as soon as there is sufficient money in the State General Fund to do so. Transfers cannot be made which will interfere with the objective for which such special fund was created, or from certain specific funds. In general, when moneys transferred to the State General Fund in any fiscal year from any special fund pursuant to the inter-fund borrowing mechanism exceed 10% of the total additions to such special fund, interest must be paid on such excess. This provision does not apply to temporary borrowings from the BSA or other accounts within the State General Fund. As of June 30, 2013, there was approximately $2.435 billion of loans from the SFEU and other internal sources to the State General Fund (compared to almost $9.593 billion owed at June 30, 2012 and $8.165 billion at June 30, 2011). The 2014-15 Governor's Budget projects that such loans will total approximately $976.6 million as of June 30, 2014.
State Appropriations Limit. The State is subject to an annual appropriations limit imposed by the State Constitution (the "Appropriations Limit"). The Appropriations Limit does not restrict appropriations to pay debt service on
II-55
voter-authorized bonds or appropriations from funds that do not derive their proceeds from taxes. There are other various types of appropriations excluded from the Appropriations Limit, including appropriations required to comply with mandates of courts or the federal government, appropriations for qualified capital outlay projects, appropriations for tax refunds, appropriations of revenues derived from any increase in gasoline taxes and motor vehicle weight fees above January 1, 1990 levels, and appropriation of certain special taxes imposed by initiative. The Appropriations Limit may be exceeded in cases of emergency.
The Appropriations Limit in each year is based on the limit for the prior year, adjusted annually for changes in State per capita personal income and changes in population, and adjusted, when applicable, for any transfer of financial responsibility of providing services to or from another unit of government or any transfer of the financial source for the provisions of services from tax proceeds to non-tax proceeds. The Appropriations Limit is tested over consecutive two-year periods. Any excess of the aggregate "proceeds of taxes" received over such two-year period above the combined Appropriations Limits for those two years is divided equally between transfers to K-14 school districts and refunds to taxpayers. The DOF projects appropriations subject to limitation to be approximately $10.80 billion, $14.64 billion and $10.79 billion under the Appropriations Limit in Fiscal Years 2012-13, 2013-14 and 2014-15, respectively.
Pension Trusts. The principal retirement systems in which the State participates are California Public Employees' Retirement System ("CalPERS") and the California State Teachers' Retirement System ("CalSTRS"). CalPERS administers the Public Employees' Retirement Fund ("PERF"), which is a multiple-employer defined benefit retirement plan. In addition to PERF, CalPERS also administers various other defined benefit plans. As of June 30, 2013, PERF had 334,083 active and inactive program members and 538,719 total members. The estimated payroll for State employees covered by PERF for Fiscal Year 2011-12 was approximately $15.68 billion. The State's contribution to CalPERS, through the PERF, has increased from $3.00 billion in Fiscal Year 2007-08 to an estimated $3.69 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14, with an estimated $4.01 billion for Fiscal Year 2014-15.
In March 2011, the CalPERS Board reviewed the discount rate assumption as a result of recent changes to the CalPERS asset allocation, and adopted once again the use of a 7.75% discount rate (investment return) assumption. At its March 14, 2012, meeting, the CalPERS Board voted to lower the investment earnings assumption to 7.50% commencing for actuarial valuations dated June 30, 2011, which DOF estimated would result in an increase in the State's total contribution for Fiscal Year 2012-13 of approximately $304 million (of which approximately $173 million would be payable from the State General Fund). The investment return for the PERF in Fiscal Years 2010-11, 2011-12 and 2012-13 was 21.7%, 0.1% and 13.8%, respectively. On January 13, 2014, CalPERS reported a 16.2% return on investments for calendar year 2013.
CalSTRS administers an employee benefit trust fund created to administer the State Teachers' Retirement Plan ("STRP"). STRP is a cost-sharing, multi-employer, defined benefit plan that provides for retirement, disability and survivor benefits to teachers and certain other employees of the California public school system. As of June 30, 2013, the STRP's defined benefit program included 1,660 contributing employers, 599,219 active and inactive program members and 868,493 total members. State contributions to CalSTRS have increased from $501 million in Fiscal Year 2007-08 to $779 million in Fiscal Year 2013-14, with an estimated $843 million for Fiscal Year 2014-15.
According to CalSTRS, the biggest source of funding of STRP's defined benefit program is investment returns, and in calculating the actuarial value of assets, contributions for the past year are added to the actuarial value of assets at the end of the prior year; benefits and expenses are subtracted; an assumed rate of return is added and a portion of market value gains and losses are added or subtracted. The assumed investment rate of return on STRP's defined benefit program assets (net of investment and administrative expenses) and the assumed interest to be paid on refunds of member accounts (4.5% in 2013) are based in part on an inflation assumption of 3.0%. The market value of STRP's defined benefit program's investment portfolio as of November 30, 2013 was $176.4 billion. The investment return reported by CalSTRS in Fiscal Years 2010-11, 2011-12 and 2012-13 was 23.1%, 1.84% and 13.8%, respectively.
Despite positive investment returns in 2013, CalPERS and CalSTRS still face large unfunded future liabilities. The most recent actuarial valuation of CalPERS, based on data through June 30, 2012, showed an accrued unfunded liability allocable to State employees of $28.2 billion on an actuarial value of assets basis, and $45.5 billion on a market value basis. CalSTRS reported the unfunded accrued liability of STRP's defined benefit program at June 30, 2013 at $73.7 billion on an actuarial value of assets basis, and $74.4 billion on a market value basis. State General Fund contributions to CalPERS and CalSTRS are estimated in the 2014-15 Governor's Budget to be approximately
II-56
$2.3 billion and $1.4 billion, respectively. These combined contributions represent approximately 3.5% of all State General Fund expenditures for Fiscal Year 2014-15. Recent actions by CalPERS to revise its smoothing and amortization policies also is expected to result in more rapid increases in State retirement contributions starting in Fiscal Year 2015-16.
Pension System Reform. On August 31, 2012, the Legislature approved a comprehensive pension reform package affecting State and local government, which the Governor signed into law on September 12, 2012. The reform package implements lower defined-benefit formulas with higher retirement ages for new employees hired on or after January 1, 2013, and includes provisions to increase current employee contributions. These reforms do not change the State's statutory contribution rate to CalSTRS and will not likely have a material effect on State contributions in the short term. However, additional employee contributions, limits on pensionable compensation, and higher retirement ages for new members will reduce pressure on the system's unfunded liabilities and potentially State contribution levels in the long term.
In a preliminary actuarial analysis, CalPERS noted savings to the State of $10.3 billion to $12.6 billion over the next 30 years due primarily to increased employee contributions and, as the workforce turns over, lower benefit formulas that will gradually reduce normal costs. The reform also directs savings from additional employee contributions to be used toward additional payments on the State's unfunded liability. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget includes an additional $108.4 million ($73.8 million from the State General Fund) directed toward the State's unfunded pension liability to reflect the savings resulting from increased employee contributions under the reform legislation.
Health and Human Services. The State provides welfare benefits to certain adults and children living in California. These benefits generally take the form of cash payments to beneficiaries or programs pursuant to which beneficiaries receive food or employment assistance. Many of these programs are funded with a combination of federal, State and local funds. The federal government pays a substantial portion of welfare benefit costs, subject to a requirement that states provide significant matching funds. Federal law imposes detailed eligibility and programmatic requirements in order for states to be entitled to receive federal funds. Federal law also imposes time limits on program availability for individuals and establishes certain work requirements. The primary federal law establishing funding and eligibility standards is The Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act of 1996. Significant elements of this law include: (i) Temporary Assistance for Needy Families ("TANF"), a block grant program; and (ii) the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program at the federal level (referred to as "CalFresh" in California). The California Work Opportunity and Responsibility to Kids ("CalWORKs") contains time limits on receipt of welfare aid. The centerpiece of CalWORKs is the linkage of eligibility to work participation requirements. The CalWORKs caseload projections are 545,647 and 529,367 cases in Fiscal Years 2013-14 and 2014-15, respectively. Since CalWORKs' inception in January 1998, caseload is estimated to have declined by approximately 17.4%.
The State's required expenditures under federal law are referred to as "Maintenance of Effort" or "MOE." California's required MOE is generally equal to 75% of federal Fiscal Year 1994 historic expenditures. However, in order to qualify for that level of MOE, the State is required to demonstrate a 50% work participation rate among all families. The federal government determined that the State failed to meet this requirement for federal Fiscal Years 2007 through 2010, and the State is therefore subject to a penalty. The federal government waived the penalty for federal Fiscal Year 2007, but required the State to increase the required MOE to 80% of federal Fiscal Year 1994 historic expenditures. As a result, the State was required to increase its MOE expenditure by approximately $180 million. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget continues to reflect this increase in MOE spending. Currently, the State is seeking relief from the 2008, 2009 and 2010 penalties. If the State is unsuccessful, and the State is unable to provide an acceptable corrective compliance plan, penalties (currently estimated to be $47.7 million, $113.6 million, and $179.7 million for federal Fiscal Years 2008, 2009, and 2010, respectively) may be imposed, which would be payable in future years. In Fiscal Years 2013-14 and 2014-15, $541.7 million and $544.9 million, respectively, in federal TANF is estimated to be transferred to the California Student Aid Commission to offset State General Fund costs in Cal Grants.
Health Care. Medi-Cal, the State's Medicaid program, is a health care entitlement program for low-income individuals and families who receive public assistance or otherwise lack health care coverage. Federal law requires Medi-Cal to provide a set of basic services such as doctor visits, hospital inpatient and outpatient care, hospice and early periodic screening, diagnosis and treatment. Also, federal matching funds are available if the State chooses to provide any of numerous optional benefits. The federal government pays for half of the cost of providing most
II-57
Medi-Cal services in California, including optional benefits. Approximately 6.3 million Medi-Cal beneficiaries (more than half of the people receiving Medi-Cal benefits and services) are currently enrolled in managed care plans. Average monthly caseload in Medi-Cal is projected to be 9.2 million in Fiscal Year 2013-14. Caseload is expected to increase in Fiscal Year 2014-15 by approximately 900,000 (10.2%) to 10.1 million people.
Federal health care reform under the ARRA expands the health insurance exchange, which is a new marketplace in which individuals who do not have access to public coverage or affordable employer coverage can purchase insurance and access federal tax credits, and also provides for the expansion of Medicaid by simplifying rules affecting eligibility, enrollment, and retention and providing an optional expansion to adults with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. Specified rate increases are required for primary care for two years beginning January 1, 2013, and California was prohibited from restricting eligibility primarily for the Medi-Cal and Healthy Families programs before the new coverage requirements go into effect in 2014. Medi-Cal expenditures are estimated to be $69.7 billion ($16.2 billion State General Fund) in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $73.5 billion ($16.9 billion from the State General Fund) in Fiscal Year 2014-15. Health care reform may result in a significant net increase of State General Fund program costs in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and beyond. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget sets aside $124 million and $250.8 million from the State General Fund in Fiscal Years 2013-14 and 2014-2015, respectively, for the costs of expanded eligibility and enhanced benefits under federal health care reform.
Unemployment Insurance. The Unemployment Insurance ("UI") program is a federal-state program that provides weekly UI payments to eligible workers who lose their jobs through no fault of their own. The regular unemployment program is funded by unemployment tax contributions paid by employers for each covered worker. Due to the high rate of State unemployment, the employer contributions are not sufficient to cover the cost of the benefits to claimants. The State reported that the UI Fund had a deficit of $10.2 billion at the end of 2012, and projected that, absent changes to the UI Fund financing structure, the UI Fund would have a deficit of $9.7 billion at the end of 2013 and $8.8 billion at the end of 2014.
Commencing in January 2009, the State began to fund deficits in the UI Fund through a federal loan to support benefit payments. Pursuant to federal law, if the State is unable to repay the loan within the same year it is taken, state funds must be used to pay the annual interest payments on the borrowed funds. Interest payments of $303.5 million and $308.2 million were made in 2011 and 2012, respectively. Given the condition of the State General Fund in those years, loans were authorized from the Unemployment Compensation Disability Fund to the State General Fund to pay the UI interest expense. The interest payment for September 2013 of $259 million was paid from the State General Fund. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget proposes $231.6 million from the State General Fund to make the 2014 interest payment. Interest will continue to accrue and be payable annually until the principal on the UI loan is repaid. The interest due after Fiscal Year 2014-15 will depend on a variety of factors, including the actual amount of the federal loan outstanding and the interest rate imposed by the federal government.
Local Governments. The primary units of local government in the State are the 58 counties, which are responsible for the provision of many basic services, including indigent health care, welfare, jails and public safety in unincorporated areas. There also are 482 incorporated cities and thousands of special districts formed for education, utility and other services. The fiscal condition of local governments has been constrained since the enactment of "Proposition 13" in 1978, which reduced and limited the future growth of property taxes and limited the ability of local governments to impose "special taxes" (those devoted to a specific purpose) without two-thirds voter approval. Counties, in particular, have had fewer options to raise revenues than many other local government entities and have been required to maintain many services.
The 2004 Budget Act, related legislation and the enactment of Proposition 1A in 2004 and Proposition 22 in 2010, dramatically changed the State-local fiscal relationship. These constitutional and statutory changes implemented an agreement negotiated between the Governor and local government officials (the "State-local agreement") in connection with the 2004 Budget Act. One change relates to the reduction of the vehicle license fee ("VLF") rate from 2% to 0.65% (1.15% in Fiscal Years 2009-10 and 2010-11) of the market value of the vehicle. In order to protect local governments, which have previously received all VLF revenues, the reduction in VLF revenue to cities and counties from this rate change was replaced by an increase in the amount of property tax that they receive. This worked to the benefit of local governments because the backfill amount annually increases in proportion to the growth in property tax revenues, which has historically grown at a higher rate than VLF revenues, although property tax revenues have declined over the past two years. This arrangement continued without change in the 2014-15 Governor's Budget.
II-58
The Amended 2009 Budget Act authorized the State to exercise its authority under Proposition 1A to borrow an amount equal to about 8% of local property tax revenues, or $1.9 billion, which must be repaid within three years. State law was also enacted to create a securitization mechanism for local governments to sell their right to receive the State's payment obligations to a local government operated joint powers agency ("JPA"). The JPA sold bonds in a principal amount of $1.895 billion in November 2009 to pay the participating local governments their full property tax allocations when they normally would receive such allocations. Pursuant to Proposition 1A, the State is required to repay the local government borrowing (which in turn will be used to repay the bonds of the JPA) in June 2013, from the State General Fund. Proposition 22, however, supersedes Proposition 1A and completely prohibits any future borrowing by the State from local government funds, and generally prohibits the Legislature from making changes in local government funding sources. Allocation of local transportation funds cannot be changed without an extensive process. Proposition 1A borrowing incurred as part of the Amended 2009 Budget Act was not affected by Proposition 22.
Trial Courts. Prior to legislation enacted in 1997, local governments provided the majority of funding for the State's trial court system. The legislation consolidated trial court funding at the State level in order to streamline the operation of the courts, provide a dedicated revenue source and relieve fiscal pressure on the counties. In addition, legislation enacted in 2008 provides California's court system with increased fees and fines to expand and repair its infrastructure to address significant caseload increases and reduce delays. The fees raised by this legislation are intended to support up to $5 billion in lease-revenue bonds, of which $1.2 billion has been issued to date through the SPWB. Additional legislative authorization is required prior to the issuance of such lease-revenue bonds. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget includes $54.2 million in court construction funds to support the new Long Beach Courthouse service fee payment. The service fees are subject to appropriation by the Legislature and are expected to total approximately $2 billion over a period of 35 years.
The State's trial court system will receive approximately $1.9 billion in State resources in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $2.0 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, as well as $499 million in resources from counties in each fiscal year. The 2013 Budget Act included a State General Fund augmentation of $60 million to support the State's trial court system and the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Governor's Budget includes an additional $100 million in ongoing State General Fund resources. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget also includes $123.6 million for fifteen court construction projects, including $101.7 million from lease revenue bonds, with debt service expected to be paid from future court construction revenues.
Proposition 98. On November 8, 1988, voters approved Proposition 98, a combined initiative constitutional amendment and statute called the "Classroom Instructional Improvement and Accountability Act." Proposition 98 changed State funding of public education primarily by guaranteeing K-14 schools a minimum share of State General Fund revenues. Any amount not funded by local property taxes is funded by the State General Fund. Proposition 98 (as modified by Proposition 111, enacted on June 5, 1990), guarantees K-14 schools a certain variable percentage of State General Fund revenues, based on certain factors including cost of living adjustments, enrollment and per capita income and revenue growth.
Legislation adopted prior to the end of Fiscal Year 1988-89, implementing Proposition 98, determined the K-14 schools' funding guarantee to be 40.7% of the State General Fund tax revenues, based on Fiscal Year 1986-87 appropriations. However, that percentage has been adjusted to approximately 39.5% to account for a subsequent redirection of local property taxes that directly affected the share of State General Fund revenues to schools. Proposition 98 permits the Legislature by two-thirds vote of both Houses, with the Governor's concurrence, to suspend the minimum funding formula for a one-year period. Proposition 98 also contains provisions transferring certain excess State tax revenues to K-14 schools, but no such transfers were made in Fiscal Year 2012-13 or Fiscal Year 2013-14 and none are expected to be made for Fiscal Year 2014-15.
The 2014-15 Governor's Budget continues to include the additional tax revenues generated by the passage of the Proposition 30 in November 2012, which requires that additional tax revenues generated by temporary increases in personal income tax and sales and use tax rates be deposited into a newly created Education Protection Account ("EPA"). The funds deposited into the EPA offset $7.2 billion in base Proposition 98 guarantee costs that would have otherwise been funded by the State General Fund in Fiscal Year 2014-15. In addition to those revenues, the passage of Proposition 39, the California Clean Energy Jobs Act, will provide a $726 million increase in the Proposition 98 minimum guarantee. Of this amount, $355 million will be transferred to the Clean Energy Jobs Creation Fund in support of energy efficiency related activities in public schools and community colleges.
II-59
The 2014-15 Governor's Budget Proposition 98 guarantee level includes changes in revenues and "rebenching" of the guarantee (i.e., a change in the minimum guarantee percentage of State General Fund revenues). The major changes in revenues are the inclusion of the revenues generated from Proposition 30 and Proposition 39, the on-going increase in local tax revenues resulting from the elimination of redevelopment agencies and the distribution of cash assets previously held by redevelopment agencies ("RDAs"). In addition to these major changes, an overall increase in personal income tax, sales and use tax, and base local property tax revenues, result in an increase in the Proposition 98 minimum guarantee over the 2013 Budget Act levels. For Fiscal Year 2013-14, the Proposition 98 guarantee is estimated to be $56.8 billion, which is a $1.5 billion increase over the 2013 Budget Act level. Proposition 98 funding in Fiscal Year 2014-15 is projected to be $61.6 billion. Of this amount, the State General Fund share in Fiscal Year 2014-15 is $45.1 billion, including $7.2 billion in EPA revenues.
Constraints on the Budget Process. Over the years, a number of laws and Constitutional amendments have been enacted that restrict the use of State General Fund or special fund revenues, or otherwise limit the Legislature's and Governor's discretion in enacting budgets. More recently, a new series of Constitutional amendments have affected the budget process. These include Proposition 58, approved in 2004, which requires the adoption of a balanced budget and restricts future borrowing to cover budget deficits, Proposition 1A, approved in 2004, which limits the Legislature's power over local revenue sources, Proposition IA, approved in 2006, which limits the Legislature's ability to use sales taxes on motor vehicle fuels for any purpose other than transportation, and Propositions 30 and 39, which were passed in November 2012.
Proposition 58 (Balanced Budget Amendment). Proposition 58, approved in 2004, requires the State to enact a balanced budget, establish a special reserve in the State General Fund and restricts future borrowing to cover budget deficits. As a result, the State may have to take more immediate actions to correct budgetary shortfalls. Beginning with the budget for Fiscal Year 2004-05, Proposition 58 requires the Legislature to pass a balanced budget and provides for mid-year adjustments in the event that the budget falls out of balance. The balanced budget determination is made by subtracting expenditures from all available resources, including prior-year balances.
Proposition 58 also requires that a special reserve (the BSA) be established in the State General Fund. The BSA is funded by annual transfers of specified amounts from the State General Fund, unless suspended or reduced by the Governor or until a specified maximum amount has been deposited. Proposition 58 also prohibits certain future borrowing to cover budget deficits. This restriction applies to general obligation bonds, revenue bonds, and certain other forms of long-term borrowing. The restriction does not apply to certain other types of RANs or RAWs currently used by the State or inter-fund borrowings.
Local Government Finance (Proposition 1A of 2004). Approved in 2004, Proposition 1A amended the State Constitution to reduce the Legislature's authority over local government revenue sources by placing restrictions on the State's access to local governments' property, sales, and VLF revenues as of November 3, 2004. Beginning with Fiscal Year 2008-09, the State was able to borrow up to 8% of local property tax revenues, but only if the Governor proclaimed such action was necessary due to a severe State fiscal hardship and two-thirds of both houses of the Legislature approved the borrowing. The amount borrowed is required to be paid back within three years. The State also will not be able to borrow from local property tax revenues for more than two fiscal years within a period of 10 fiscal years. In addition, the State cannot reduce the local sales tax rate or restrict the authority of local governments to impose or change the distribution of the Statewide local sales tax. The provisions of Proposition 1A allowing the State to borrow money from local governments from time to time have been deleted by Proposition 22 of 2010, which permanently prohibits any future such borrowing.
Proposition 1A further requires the State to reimburse cities, counties, and special districts for mandated costs incurred prior to Fiscal Year 2004-05 over a term of years. The 2012 Budget Act deferred payment of these claims through the 2014-15 Fiscal Year and refinances the balance owed over the remaining payment period. The remaining estimated cost of claims for mandated costs incurred prior to Fiscal Year 2004-05 is $900 million. The Amended 2009 Budget Act authorized the State to exercise its Proposition 1A borrowing authority. This borrowing generated $1.998 billion that was be used to offset State General Fund costs for a variety of court, health, corrections and K-12 programs. Pursuant to Proposition 1A, the State was required to repay the local government borrowing no later than June 15, 2013. The 2012 Budget Act included $2.1 billion to fully retire the outstanding obligations, with interest, to be paid from the State General Fund, and repayment was made in June 2013.
II-60
Proposition 1A also prohibits the State from mandating activities on cities, counties or special districts without providing for the funding needed to comply with the mandates. The 2013 Budget Act suspends mandates subject to Proposition 1A until Fiscal Year 2014-15. The total estimated back cost owed on the suspended mandates is approximately $888 million. That amount would be payable if the Legislature chose to individually fund all suspended mandates.
Proposition 49 (After School Education Funding). An initiative statute, called the "After School Education and Safety Program of 2002," was approved by the voters in 2002, and requires the State to expand funding for before and after school programs in public elementary and middle schools. This increase was first triggered in Fiscal Year 2006-07, which increased funding for these programs to $550 million. These funds are part of the Proposition 98 minimum-funding guarantee for K-14 education and can only be reduced in certain low revenue years.
Transportation Financing (Proposition 1A of 2006). On November 7, 2006, voters approved Proposition 1A to protect Proposition 42 transportation funds from any further suspensions. The new measure modified the constitutional provisions of Proposition 42 in a manner similar to Proposition 1A of 2004, so that if such suspension occurs, the amount owed by the State General Fund must be repaid to the Transportation Investment Fund within three years, and only two such suspensions can be made within any ten-year period. The Budget Acts for Fiscal Years 2006-07 through 2010-11 all fully funded the Proposition 42 transfer and partially repaid two earlier suspensions (in Fiscal Years 2003-04 and 2004-05). The 2011 Budget Act included an elimination of the State sales tax rate on gasoline and an increase in gasoline excise taxes, effectively removing the revenue subject to these restrictions from the tax system. However, consistent with the requirements of Proposition 1A of 2006, the 2014-15 Governor's Budget includes $81 million in 2013-14 and $83 million in 2014-15 to repay a portion of past suspensions. The final payment of $85 million is scheduled for 2015-16.
Local Government Funds (Proposition 22 of 2010). On November 2, 2010, voters approved Proposition 22, which supersedes some parts of Proposition 1A, prohibiting any future action by the Legislature to take, reallocate or borrow money raised by local governments for local purposes, and also prohibits changes in the allocation of property taxes among local governments designed to aid State finances. Proposition 22 also supersedes Proposition 1A in that it prohibits the State from borrowing sales taxes or excise taxes on motor vehicle fuels or changing the allocations of those taxes among local governments except pursuant to specified procedures involving public notices and hearings. Any law enacted after October 29, 2009 inconsistent with Proposition 22 is repealed. Passage of this measure jeopardized an estimated $850 million in State General Fund relief in Fiscal Year 2010-11, an amount which would grow to over $1 billion by Fiscal Year 2013-14.
Increases in Taxes or Fees (Proposition 26 of 2010). On November 2, 2010, voters approved this measure, which revises provisions in the State's Constitution dealing with tax increases. The measure specifies that a two-thirds vote of both houses of the Legislature is required for any increase in any tax on any taxpayer, eliminating the current practice where a tax increase coupled with a tax reduction is treated as being able to be adopted by majority vote. Furthermore, any increase in a fee beyond the amount needed to provide the specific service or benefit is deemed a tax requiring two-thirds vote. Finally, any tax or fee adopted after January 1, 2010 with a majority vote which would have required a two-thirds vote if Proposition 26 were in place would be repealed after one year from the election date unless readopted by the necessary two-thirds vote.
The Schools and Local Public Safety Protection Act of 2012 (Proposition 30). On November 6, 2012, voters approved Proposition 30, which provided temporary increases in personal income tax rates for high-income taxpayers and a temporary increase in the State sales tax rate, and specified that the additional revenues will support K-14 public schools and community colleges as part of the Proposition 98 guarantee. Proposition 30 also placed into the State Constitution the current statutory provisions transferring 1.0625% of the State sales tax to local governments to fund the "realignment" program for many services including housing criminal offenders.
The California Clean Energy Jobs Act (Proposition 39). On November 6, 2012, voters approved Proposition 39 thereby amending state statutes governing corporation taxes by reversing a provision adopted in 2009 giving corporations an option on how to calculate the portion of worldwide income attributable to California. By requiring corporations to base their state tax liability on sales in California, it is estimated that State revenues would be increased by $600 to $900 million per year starting in Fiscal Year 2013-14. The measure also, for five years,
II-61
dedicates up to an estimated $550 million per year from this increased income to funding of projects that create energy efficiency and clean energy jobs in California.
Tax Revenues. DOF reported that total revenues for March 2014 were $459 million above the 2014-15 Governor's Budget forecast of $6.07 billion. Fiscal Year 2014 year-to-date revenues are $1.44 billion above the expected $64.76 billion.
Tax revenues in Fiscal Year 2013-14 are estimated to total $100.1 billion. Of this amount personal income tax accounts for $64.29 billion (65.8%), sales and use tax accounts for $22.92 billion (22.7%), corporation tax accounts for $7.97 billion (8.0%), insurance tax accounts for $2.1 billion (2.1%), "other" taxes (inheritance and gift taxes, cigarette taxes, alcoholic beverage taxes, horse racing license fees, trailer coach license fees) accounts for $459 million (.46%). Tax revenues in Fiscal Year 2014-15 are projected to total $106.1 billion. Of this amount personal income tax accounts for $69.76 billion (64.2%), sales and use tax accounts for $24.07 billion (22.9%), corporation tax accounts for $8.68 billion (8.2%), insurance tax accounts for $2.30 billion (2.1%), "other" taxes (inheritance and gift taxes, cigarette taxes, alcoholic beverage taxes, horse racing license fees, trailer coach license fees) accounts for $463 million (.44%).
Proposition 30 provides for an increase in the personal income tax rate of 1.0% for joint filing taxpayers with income above $500,000 and equal to or below $600,000; 2.0% increase for incomes above $600,000 and equal to or below $1,000,000; and 3.0% increase for incomes above $1,000,000. Tax rates for single filers will start at incomes one half those for joint filers. It is estimated that the additional revenue from the addition of the three new tax brackets was, or will be, $3.4 billion in Fiscal Year 2011-12, $5.4 billion in Fiscal Year 2012-13, $5.6 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $5.7 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15. Proposition 30 also added a 0.25% additional sales tax rate from January 1, 2013 through December 31, 2016, with 1.0625% of the sales tax rate dedicated to local governments. The 1.0625% of the sales tax rate was expected to generate $5.88 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $6.31 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15.
Special Fund Revenues. The State Constitution and statutes specify the uses of certain revenue. Such receipts are accounted for in various special funds. In general, special fund revenues comprise three categories of income: (i) receipts from tax levies, which are allocated to specified functions such as motor vehicle taxes and fees and certain taxes on tobacco products; (ii) charges for special services to specific functions, including such items as business and professional license fees; and (iii) rental royalties and other receipts designated for particular purposes (e.g., oil and gas royalties). Motor vehicle related taxes and fees are projected to account for approximately 26% of all special fund revenues in Fiscal Year 2014-15. Principal sources of this income are motor vehicle fuel taxes, registration and weight fees and VLFs. In Fiscal Year 2014-15, $11.8 billion is projected to come from the ownership or operation of motor vehicles. About $4.4 billion of this revenue is projected to be returned to local governments. The remainder will be available for various State programs related to transportation and services to vehicle owners.
The economic downturn of the last few years adversely affected the State's budget situation. Despite the economy's gradual recovery, in 2011, the State faced $20 billion in expected annual gaps between its revenues and spending for the ensuing several years. The State's fiscal challenges were exacerbated by unprecedented levels of debts, deferrals and budgetary obligations accumulated over the prior decade.
The State has enacted and maintained significant spending reductions since 2011. Despite these significant budgetary improvements, there remain a number of material risks and pressures that threaten the State's financial condition, including the need to repay billions of dollars of obligations that were deferred to balance budgets during the economic downturn. With the significant spending cuts enacted over the past three years and new temporary revenues, the State's budget now is projected to remain balanced within the projection period ending in Fiscal Year 2016-17. Risks to the budget, however, still remain. Potential cost increases associated with actions to reduce the federal deficit, federal government actions, court decisions, the pace of the economic recovery, an aging population and rising health care and pension costs all threaten the ability of the State to achieve and maintain a balanced budget over the long term. Another threat is the overhang of billions of dollars of obligations which were deferred to balance budgets during the economic downturn. In addition, the State's revenues (particularly taxes on capital gains) can be volatile and correlates to overall economic conditions.
II-62
Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget. The Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget, including the 2013 Budget Act, which was enacted on June 27, 2013, provided a multi-year State General Fund plan that was balanced. It projected a $1.1 billion reserve by the end of Fiscal Year 2013-14, and continued to pay down budgetary debt from past years. For the first time in several years, corrective measures were not necessary to avoid a year-end deficit in the fiscal year just ended. State General Fund revenues and transfers for Fiscal Year 2013-14 were projected at $97.1 billion, a decrease of $1.1 billion (1.1%) compared with revised estimates for Fiscal Year 2012-13. State General Fund expenditures for Fiscal Year 2013-14 were projected at $96.3 billion, an increase of $0.6 billion (0.6%) compared with revised estimates for Fiscal Year 2012-13.
The Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget built a $1.1 billion reserve principally by using the following steps which reduced State General Fund expenditures: suspending four newly identified State mandates ($111 million), continuing the use of miscellaneous State highway account revenues to pay for transportation bond debt service ($67 million), extending the hospital quality assurance fee ($310 million), extending the gross premiums tax on Medi-Cal managed care plans ($166 million), and applying sales tax on Medi-Cal managed care plans ($305 million). Certain of these actions raised revenues in special funds which offset State General Fund costs.
As enacted, the Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget has the following significant components by major program area:
1. Proposition 98. Proposition 98 funding of $55.3 billion is provided for Fiscal Year 2013-14, of which $39.1 billion was funded from the State General Fund.
2. Higher Education. Total funding of $25.4 billion for all major segments of Higher Education, including $13.1 billion from the State General Fund and local property taxes for the California Community Colleges. The remaining funds include special and bond funds.
3. Health and Human Services. Total State funding of $46 billion, including $28.1 billion from the State General Fund. The remaining funding will be provided from special and bond funds.
4. Prison Funding. Total state funding of $11.2 billion, including $8.9 billion from the State General Fund, for the California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation.
5. Redevelopment Agencies. The elimination of RDAs was projected to offset $1.5 billion of Proposition 98 costs in Fiscal Year 2013-14, of which $824 million was from property taxes that will be distributed to local school districts, and $707 million was from distribution of excess RDA cash.
6. Other Revenues and Transfers. The Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget reflected a delay in repayment of approximately $1 billion of loans scheduled for repayment in Fiscal Year 2013-14 (as projected in the 2012 Budget Act). Additionally, the 2013 Budget Act authorized a $500 million loan to the State General Fund from the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund (Cap and Trade).
7. Health Care Reform. The Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget included $195.6 million for costs relating to implementation of federal health care reforms. State General Fund net costs of expanded eligibility and enhanced benefits under health care reform were estimated to increase to approximately $700 million in Fiscal Years 2014-15 and 2015- 16.
8. Unemployment Insurance Interest Repayment. In Fiscal Year 2013-14, the interest payment of $261.5 million was to be paid from the State General Fund.
The 2013 Budget Act also revised various estimates involving the State General Fund beginning balance, revenues and expenditures for Fiscal Year 2012-13. The 2013 Budget Act projected a positive State General Fund reserve balance of $254 million for Fiscal Year 2012-13, compared to the positive balance of $948 million estimated when the 2012 Budget Act was enacted. State General Fund revenues and transfers for Fiscal Year 2012-13 were projected at a revised $98.2 billion, which was $2.3 billion higher than the estimate of $95.9 billion when the 2012 Budget Act was enacted. State General Fund expenditures for Fiscal Year 2012-13 were projected at $95.7 billion, an increase of $4.3 billion compared with the estimate of $91.3 billion when the 2012 Budget Act was enacted.
II-63
Proposed Fiscal Year 2014-2015 Budget. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget, released on January 9, 2014, proposes a multi-year plan that is balanced and continues to pay down budgetary debt from past years. State General Fund revenues and transfers for Fiscal Year 2014-15 are projected to be $104.5 billion, an increase of $4.4 billion (4.3%) compared with revised estimates for Fiscal Year 2013-14. State General Fund expenditures for Fiscal Year 2014-15 are projected at $106.8 billion, an increase of $8.3 billion (8.5%) compared with revised estimates for Fiscal Year 2013-14.
For the first time since Fiscal Year 2007-08, the Governor will allow full funding of the BSA during Fiscal Year 2014-15. Pursuant to Proposition 58 of 2004, the State will set aside 3% of estimated State General Fund revenues, estimated at about $3.2 billion, in the BSA. Under Proposition 58, half this amount will remain in the BSA, and half will be transferred to a redemption account to retire ERBs. Under the State's budgeting procedures, the $1.6 billion transferred to the BSA for "rainy day" purposes will be reflected as a reduction of revenues and transfers, while the $1.6 billion used to retire ERBs will be reflected as an expenditure of State General Fund resources. The Legislature cannot reduce or suspend the transfer to the BSA, but can increase the transfer. The Governor can modify the transfer up to June 1, 2014.
The 2014-15 Governor's Budget has the following other major components:
1. Proposition 98. Proposes funding of $61.6 billion for Fiscal Year 2014-15, of which $45.1 billion is from the State General Fund. When combined with State General Fund increases of $3.7 billion in Fiscal Years 2012-13 and 2013-14, the 2014-15 Governor's Budget proposes a $9.7 billion increase in the State General Fund investment in K-14 education compared to the Fiscal Year 2013-14 Budget.
2. Higher Education. Proposes total State funding of $12.8 billion for all major segments of Higher Education, including $12.4 billion from the State General Fund (both Non-Proposition 98 and Proposition 98), an increase of $1.2 billion State General Fund from revised estimates for Fiscal Year 2013-14. The remaining funds include special and bond funds.
3. Health and Human Services. Proposes $48.1 billion, including $28.8 billion from the State General Fund and $19.3 billion from special funds, for these programs.
4. Implementation of the Affordable Care Act. Proposes $7.6 billion, including $250.8 million from the State General Fund, to implement federal health care reform, which started in January 2014.
5. Prison Funding. Proposes total State funding of $12.0 billion, including $9.6 billion from the State General Fund and $2.4 billion from special funds, for the Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation.
6. Redevelopment Agency Dissolution Savings. Proposes Proposition 98 General Fund savings of $1.1 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $785 million in Fiscal Year 2014-15. This reflects the receipt of a like amount of property tax revenues in each fiscal year by K-12 schools and community colleges.
7. Payment of Interest on Unemployment Insurance Fund Debt. Proposes $231.6 million from the State General Fund to make the 2014 interest payment on the outstanding loan from the federal unemployment account. Interest will continue to accrue and be payable annually until the principal on the loan is repaid. The principal amount of the federal loan is projected to be $8.8 billion at the end of 2014 compared to $9.7 billion at the end of 2013.
8. Cash Management. Cash flow needs will be managed through internal and external borrowing. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget projects the need for $3.5 billion in RANs, compared with $5.5 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14.
9. Reserve Policy. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget proposes a constitutional amendment to appear on the November 2014 ballot which would significantly amend the existing rainy day fund requirements established by Proposition 58.
II-64
The 2014-15 Governor's Budget also revised various estimates involving the State General Fund beginning balance, revenues and expenditures for Fiscal Year 2013-14. The 2014-15 Governor's Budget projected a positive State General Fund reserve balance of $3.26 billion for Fiscal Year 2013-14, compared to the positive balance of $1.1 billion estimated when the 2013 Budget Act was enacted. State General Fund revenues and transfers for Fiscal Year 2013-14 are projected at a revised $100.1 billion, which is $3.0 billion higher than the estimate of $97.1 billion when the 2013 Budget Act was enacted. State General Fund expenditures for Fiscal Year 2013-14 are projected at $98.5 billion, an increase of $2.2 billion compared with the estimate of $96.3 billion when the 2013 Budget Act was enacted.
The State is a party to numerous legal proceedings. The following describes litigation matters that are pending with service of process on the State accomplished and have been identified by the State as having a potentially significant fiscal impact upon State revenues or expenditures. The State makes no representation regarding the likely outcome of these matters.
Action Challenging Cap and Trade Program Auctions. In California Chamber of Commerce, et al. v. California Air Resources Board, business interests and a taxpayer challenge the authority of the California Air Resources Board to conduct auctions under the State's cap and trade program and allege that the auction revenues are an unconstitutional tax under the California Constitution. A second lawsuit raising substantially similar claims, Morning Star Packing Co., et al. v. California Air Resources Board has been filed has been filed and consolidated with the Chamber of Commerce matter. The trial court ruled for the California Air Resources Board, finding that it had the authority to conduct the auctions, and that the auction does not constitute an unconstitutional tax. Petitioners filed notices of appeal.
Actions Challenging School Financing. In Robles-Wong, et al. v. State of California and California Teachers Association Complaint in Intervention, plaintiffs challenge the constitutionality of the State's "education finance system." Plaintiffs, consisting of 62 minor school children, various school districts, the California Association of School Administrators, the California School Boards Association and the California Teachers Association, allege the State has not adequately fulfilled its constitutional obligation to support its public schools, and seek an order enjoining the State from continuing to operate and rely on the current financing system and to develop a new education system that meets constitutional standards as declared by the court. It is currently unknown what the fiscal impact of this matter might be upon the State General Fund. In a related matter, Campaign for Quality Education et al. v. State of California, plaintiffs also challenge the constitutionality of the State's education finance system. The court issued a ruling that there was no constitutional right to a particular level of school funding. The court allowed plaintiffs to amend their complaint with respect to alleged violation of plaintiffs' right to equal protection. Plaintiffs in each of these matters elected not to amend, and both matters were dismissed. Plaintiffs in each matter have appealed those dismissals.
In California School Boards Association v. State of California, the plaintiff has filed an amended complaint that challenges the use of block grant funding to pay for education mandates in the 2012 Budget Act and associated trailer bills. The amended complaint also contends that recent changes to the statutes that control how education mandates are directed and funded violate the requirements of the California Constitution that the State pay local school districts for the costs of state mandated programs. If the court declares that the State has failed to properly pay for mandated educational programs, the State will be limited in the manner in which it funds education going forward.
Actions Challenging Statutes Which Reformed California Redevelopment Law. In California Redevelopment Association, et al. v. Matosantos, et al., the California Supreme Court upheld the validity of legislation dissolving all local RDAs and invalidated a second law that would have permitted existing RDAs to convert themselves into a new form of RDA and continue to exist, although they would have to pay higher fees to school, fire and transit districts to do so. A second case challenging the constitutionality of these statutes, City of Cerritos, et al. v. State of California, raises the same theories advanced in Matosantos, and also contains various other procedural challenges. On January 27, 2012, the trial court denied plaintiffs' motion for a preliminary injunction. Plaintiffs appealed. Plaintiff's request to stay portions of the legislation was denied by the appellate court.
II-65
There are over 100 pending actions that challenge implementation of the statutory process for winding down the affairs of the RDAs. Some of the pending cases challenge the provision that requires successor agencies to the former RDAs to remit certain property tax revenues or other funds that the successor agency had received, or face a penalty. Some of the pending cases include: City of National City et al. v. Matosantos, Morgan Hill Economic Development Corporation, et al. v. Office of State Controller, et al., Inland Valley Development Agency v. Chiang, City of Union City v. Matosantos, City of Orange, et al. v. State of California Department of Finance, et al., City of Bellflower et al. v. Matosantos et al., City of Walnut v. Matosantos, City of Lancaster v. Matosanto, City of San Diego, et al. v. Matosantos, et al., County of Orange v. Matosantos, City of Irvine v. Matosantos, City of Emeryville, et al. v. Matosantos and League of California Cities et al. v. Matosantos et al. In Affordable Housing Coalition v. Sandoval plaintiffs argue that all former RDAs had obligations to pay for affordable housing that should be funded going forward on an implied contracts theory. A motion for class action status in this matter was denied.
Another challenge has been filed by plaintiffs who insured bonds issued by now dissolved RDAs. In Syncora Guarantee Inc., et al v. State of California, et al, plaintiffs allege that the governing legislation constitutes an impairment of contract and a taking of property without just compensation, in violation of both the U.S. and California Constitutions. The trial court denied plaintiffs' request for injunctive relief, including an order requiring the tax revenues remitted by the successor agencies to local taxing entities be returned and held in trust for the bondholders until the bonds are paid.
Action Regarding Furlough of State Employees. In several cases, petitioners challenged the former Governor's executive orders issued in December 2008, July 2009 and July 2010 directing the furlough without pay of State employees. On October 4, 2010, the California Supreme Court, ruling in three consolidated cases, upheld the validity of the two day per month furloughs implemented by the Governor's December 2008 order on the ground that the Legislature had ratified these furloughs in enacting the revisions to the 2008 Budget Act. (Professional Engineers in California Government ("PECG"), et al. v. Schwarzenegger, et al.)
Most of the remaining cases that challenge the two furlough orders issued in July 2009 and/or July 2010 have been dismissed or settled. The pending cases include the following:
Two cases challenge the furloughs of certain categories of employees, such as those paid from funds other than the State General Fund or who otherwise assert a claim not to be furloughed on a basis outside of the rationale of the Supreme Court's decision. These two cases are PECG v. Schwarzenegger, et al. and California Association of Professional Scientists v. Schwarzenegger, et al. The trial court granted the petition, in part, finding that two furloughed days in March 2011 were unlawful for certain employees. The State appealed.
In Horton v. Brown, et al., plaintiff asserts a class action on behalf of all gubernatorial and certain other appointees. The complaint alleges that such appointees were exempt from civil service rules, and therefore should not have been furloughed. The trial court granted the State's motion to strike certain claims and the appellate court rejected the plaintiff's appeal. Because the putative class is limited, any fiscal impact on the State General Fund is expected to be modest. In PECG, et al. v. Brown et al., PECG challenges the implementation of the 2012 furlough program, for the period of July 1, 2012 through June 2013, alleging an unlawful impairment of contractual rights in the bargaining agreement. The trial court ruled for the State and petitioners filed a notice of appeal. In Vent v. Brown, et al., an individual state employee challenges both Governor Schwarzenegger's furlough order and the 2012 furlough program and seeks back pay for herself and other attorneys employed by the State.
Action Challenging Use of Mortgage Settlement Proceeds. In National Asian American Coalition, et al. v. Brown, et al., three non-profit organizations allege that approximately $369 million received by the State in 2012 in connection with the nationwide settlement between states and certain mortgage servicers was deposited in a special fund intended to provide assistance to California homeowners, but that such settlement monies were instead used for other purposes in the Fiscal Year 2012-13 budget. The plaintiffs allege the use of the settlement monies was inconsistent with the terms of the settlement agreement and California law, and seek to compel state officials to return the monies to the special fund.
Tax Refund Cases. Six actions have been filed contending that the Legislature's modification of part of the State's tax code that implemented the double-weighting of the sales factor in California's apportionment of income formula for the taxation of multistate business entities, is invalid and/or unconstitutional. Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc.,
II-66
et. al. v. Franchise Tax Board; Gillette Company and Subsidiaries v. Franchise Tax Board; Proctor & Gamble Manufacturing Company & Affiliates v. Franchise Tax Board; Sigma-Aldrich, Inc. and Affiliates v. Franchise Tax Board; RB Holdings (USA), Inc. v. Franchise Tax Board and Jones Apparel Group v. Franchise Tax Board, now consolidated in one matter, collectively referred to as Gillette Company v. Franchise Tax Board. The trial court ruled for the State in each of these matters, but the appellate court ruled in favor of the taxpayers. The California Supreme Court granted the State's petition for review. If the Gillette taxpayers are ultimately successful in their suit for refund, the vast majority of the revenue loss may not occur for several years, but could reach an estimated $750 million.
A pending case challenges the imposition of limited liability company fees by the Franchise Tax Board. Bakersfield Mall LLC v. Franchise Tax Board was filed as a purported class action on behalf of all limited liability companies operating solely in California and is pending in the trial court. A second lawsuit that is virtually identical to Bakersfield Mall has been filed, and also seeks to proceed as a class action. CA-Centerside II, LLC v. Franchise Tax Board. The cases are coordinated for hearing, but the coordination trial judge denied the plaintiffs' joint motion for class certification and plaintiffs appealed. If this order is reversed and the cases proceed as class actions, the claimed refunds could be significant (in excess of $500 million).
Lucent Technologies, Inc. v. State Board of Equalization ("Lucent I"), a tax refund case, involves the interpretation of certain statutory sales and use tax exemptions for "custom-written" computer software and licenses to use computer software. A second case, Lucent Technologies, Inc. v. State Board of Equalization ("Lucent II"), involving the same issue but for different tax years than in the Lucent I matter, has been consolidated with the Lucent I case. In a similar case, Nortel Networks Inc. v. State Board of Equalization, the trial court ruled in favor of plaintiff and the ruling was affirmed on appeal. The adverse ruling in Nortel, unless limited in scope by a decision in the Lucent matters, if applied to other similarly situated taxpayers, could have a significant negative impact, in the range of approximately $300 million annually, on tax revenues. In the Lucent matters, the trial court granted plaintiffs' motion for summary judgment and denied the Board of Equalization's motion for summary judgment.
Harley Davidson, Inc. and Subsidiaries v. California Franchise Tax Board and Abercrombie & Fitch Co. & Subsidiaries v. California Franchise Tax Board both challenge the constitutionality of a State tax code provision, allowing intrastate unitary businesses the option to report their income on a separate rather than combined basis. The trial court in Harley Davidson sustained a motion to dismiss on this issue without leave to amend; the issue is now pending on appeal. Trial in Abercrombie is set for February 2015. Should this provision be invalidated, a significant amount of otherwise apportionable income from multi-state unitary businesses would be removed from the State's taxing power. At this time, it is unknown what future fiscal impact a potential adverse ruling would actually have on corporation taxes (including potentially rebates of previously collected taxes and reduced future tax revenue) because of the uncertainty regarding the number of businesses which currently pay the tax and how taxation on those companies would change as a result of an adverse ruling. However, the fiscal impact could be significant. The Harley Davidson case also raises the issue raised in the Gillette case regarding modification of the apportionment formula for multi-state businesses; resolution of this issue in Harley Davidson has been deferred to await the outcome of the issue in Gillette.
A pending bankruptcy matter, In re Washington Mutual Inc., involves a taxpayer claim to a refund. The disputed issues involve, among others, the taxpayer's use of certain investment vehicles to shelter millions of dollars of income from taxation. In the event the issues are decided adversely to the State, the matter could result in a significant refund of up to approximately $400 million. The parties are discussing settlement and planned to submit a settlement proposal to the court for approval in May 2014.
Environmental Matters. In the Matter of Leviathan Mine, Alpine County, California, Regional Water Quality Control Board, Lahontan Region, State of California, the State, as owner of the Leviathan Mine, is a party through the Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board (the "Board"), which is the State entity potentially responsible for performing certain environmental remediation at the Leviathan Mine site. Also a party is Atlantic Richfield Company ("ARCO"), the successor in interest to the mining company that caused certain pollution of the mine site. The Leviathan Mine site is listed on the Environmental Protection Agency Superfund List, and both remediation costs and costs for natural resource damages may be imposed on the State. The Board has undertaken certain remedial action at the mine site, but the Environmental Protection Agency's decision on the interim and final remedies are pending. ARCO filed a complaint on November 9, 2007, against the State, the State Water Resources Control Board, and the Board (Atlantic Richfield Co. v. State of California). ARCO seeks to recover past and future
II-67
costs, based on the settlement agreement, the State's ownership of the property, and the State's allegedly negligent past cleanup efforts. The October 2012 trial date for this matter was been postponed until June 2014 to permit the parties to continue settlement negotiations. It is possible these matters could result in a potential loss to the State in the hundreds of millions of dollars.
In Pacific Lumber, et al. v. State of California, plaintiffs are seeking injunctive relief and damages against defendants State Water Resources Council, North Coast Water Quality Control Board, and the State of California for the alleged breach of the Headwaters Agreement, which involved the sale of certain timberlands by plaintiffs to federal and State agencies. The plaintiffs allege that the State's environmental regulation of their remaining timberlands constitute a breach of the prior agreement. The State denies plaintiffs' claims. The current plaintiffs are successors in interest to the original plaintiffs who are debtors in a bankruptcy proceeding, and have alleged in that proceeding that the value of the litigation ranges from $626 million to $639 million in the event liability is established. It is currently unknown what the fiscal impact of this matter might be upon the State General Fund. The trial court granted the State's motion for summary judgment and the appellate court affirmed. Plaintiff's petition for review was denied by the California Supreme Court.
In Consolidated Suction Dredge Mining Cases (Karuk Tribe v. DFG), environmental and mining interests challenge the State's regulation of suction dredge gold mining. After initially prohibiting such mining except pursuant to a permit, the Legislature subsequently placed a moratorium on all suction dredging. The cases have been consolidated for hearing by the court. One of these matters, The New 49'ERS, Inc. et al. v. California Department of Fish and Game, claims that federal law preempts and prohibits State regulation of suction dredge mining on federal land. Plaintiffs, who have pled a class action but have yet to seek certification, claim that as many as 11,000 claims, at a value of $500,000 per claim, have been taken.
In City of Colton v. American Professional Events, Inc. et al, two defendants involved in a liability action for contaminated ground water have filed cross complaints seeking indemnification from the State and the Regional Water Quality Control Board in an amount of up to $300 million. In a related action, Emhart Industries v. Regional Water Quality Control Board, another defendant in an action involving liability for contaminated groundwater seeks indemnification from the State and the Regional Water Quality Control Board in an amount up to $300 million.
Escheated Property Claims. In Taylor v. Chiang, plaintiffs claim that the State's unclaimed property program violates the U.S. Constitution and various federal and State laws. They assert that the State has an obligation to pay interest on private property that has escheated to the State, and that failure to do so constitutes an unconstitutional taking of private property. Although the case is styled as a class action, no class has been certified. Plaintiffs also assert that for the escheated property that has been disposed of by the State, plaintiffs are entitled to recover, in addition to the proceeds of such sale, any difference between the sale price and the property's highest market value during the time the State held it; the State asserts that such claims for damages are barred by the Eleventh Amendment. The district court ruled against plaintiffs in a related action, Suever v. Connell. The Ninth Circuit affirmed and the U.S. Supreme Court denied review. Meanwhile, the Taylor plaintiffs amended their complaint to allege that the Controller applies certain notice requirements in ways that violate State and federal law, and the district court granted the State's motion to dismiss plaintiffs' claims. Plaintiffs have appealed this ruling.
Action Seeking Damages for Alleged Violations of Privacy Rights. In Gail Marie Harrington-Wisely, et al. v. State of California, et al., plaintiffs seek damages for alleged violations of prison visitors' rights resulting from the Department of Corrections' use of a body imaging machine to search visitors entering State prisons for contraband. This matter has been certified as a class action. The trial court granted judgment in favor of the State. Plaintiffs' appeal has been dismissed and the trial court denied plaintiff's motion for attorneys' fees. The parties agreed to a stipulated judgment and dismissed the case subject to further review if the Department of Corrections decides to use similar technology in the future. Plaintiffs have filed another appeal. If plaintiffs were successful in obtaining an award of damages for every use of the body-imaging machine, damages could be as high as $3 billion.
The plaintiff in Gilbert P. Hyatt v. Franchise Tax Board was subject to an audit by the Finance Tax Board involving a claimed change of residence from California to Nevada. Plaintiff alleges a number of separate torts involving privacy rights and interference with his business relationships arising from the audit. The trial court ruled that plaintiff had not established a causal relation between the audit and the loss of his licensing business with Japanese companies; the Nevada Supreme Court denied review of this ruling. The economic damages claim exceeds $500 million. On the remaining claims, the jury awarded damages of approximately $387 million, including punitive
II-68
damages, plus interest and attorneys' fees, for a total of approximately $490 million. The total judgment with interest is currently approximately $600 million. The State appealed and the Nevada Supreme Court has granted a stay of execution on the judgment pending appeal. The State will vigorously pursue its appeal of this unprecedented award.
Action Regarding Special Education. Plaintiffs in Morgan Hill Concerned Parents Assoc. v. California Department of Education challenge the oversight and operation by the California Department of Education ("CDE") of the federal Individuals with Disabilities Education Act ("IDEA"). The complaint alleges that CDE has failed to monitor, investigate, and enforce the IDEA. Under the IDEA, local school districts are responsible for delivering special education directly to eligible students. The complaint seeks injunctive and declaratory relief, and asks the court to retain jurisdiction to monitor the operation of the IDEA by the State.
Actions Seeking Medi-Cal Reimbursements and Fees. In Orinda Convalescent Hospital, et al. v. Department of Health Services, plaintiffs challenge a quality assurance fee ("QAF") charged to certain nursing facilities and a Medi-Cal reimbursement methodology applicable to such facilities that were enacted in 2004, alleging violations of federal Medicaid law, the federal and State constitutions and State law. Funds assessed under the QAF are made available, in part, to enhance federal financial participation in the Medi-Cal program. Plaintiffs seek a refund of fees paid. On March 25, 2011, the trial court ruled the QAF is properly characterized as a "tax" rather than a "fee." Trial then proceeded on plaintiffs' claims for refund amounts. The QAF amounts collected from all providers to date total nearly $2 billion, and California has received additional federal financial participation based on its imposition and collection of the QAF. An adverse ruling could negatively affect the State's receipt of federal funds. The trial court ruled for the State, finding that the QAF is constitutionally valid. Plaintiffs appealed.
A series of federal court cases challenging State legislation requiring reductions in Medi-Cal were argued before the U.S. Supreme Court last year and remanded to the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals, where they remain in mediation. In Independent Living Center of Southern California, et al. v. Shewry, et al., California Pharmacists Association, et al. v. Maxwell-Jolly, et al. and Managed Pharmacy Care, et al. v. Maxwell-Jolly, et al., the district court enjoined certain of the reductions and the Ninth Circuit affirmed. After the U.S. Supreme Court heard argument but before it decided the cases, DHCS reached an agreement with the federal government under which DHCS withdrew most of its pending requests for approvals of the reductions. The U.S. Supreme Court vacated the judgment and remanded the matters to the Ninth Circuit for further review in light of the federal government's intervening action approving the State's plan to implement the rate reductions. The parties are currently mediating their remaining claims regarding the reductions.
In California Medical Association, et al. v. Shewry, et al., professional associations representing Medi-Cal providers seek to enjoin implementation of the Medi-Cal rate reductions planned to go into effect on July 1, 2008, alleging that the legislation violates Medicaid requirements, State laws and regulations and the California Constitution. The trial court denied plaintiffs' motion for a preliminary injunction, plaintiffs filed an appeal, which was dismissed at their request. Plaintiffs have indicated that they will file an amended petition seeking the retrospective relief the Ninth Circuit awarded in the Independent Living Center case, above, after final disposition of that case. The matter is stayed pending final resolution in the Independent Living Center matter. A final decision adverse to the State in this matter could result in costs to the State General Fund of $508.2 million.
In California Pharmacists Association, et al. v. Maxwell-Jolly, et al., Medi-Cal pharmacy providers filed a suit challenging reimbursement rates, including the DHCS' use of reduced published average wholesale price data to establish reimbursement rates. The district court granted a request for preliminary judgment in part, and denied it in part, with respect to the DHCS' reimbursement rate methodology. Plaintiffs filed a motion seeking to modify the district court ruling, and both parties filed notices of appeal to the Ninth Circuit. The parties have requested mediation. At this time it is unknown what fiscal impact this case would have on the State General Fund.
In Centinela Freeman Emergency Medical Associates, et al. v. David Maxwell-Jolly, et al., filed as a class action on behalf of emergency room physicians and emergency department groups, plaintiffs claim that Medi-Cal rates for emergency room physicians are below the cost of providing care. Plaintiffs seek damages and injunctive relief, based on alleged violations of the federal Medicaid requirements, State law and the federal and State Constitutions. The trial court granted the petition of the plaintiffs and ordered the DHCS to conduct an annual review of
II-69
reimbursement rates for physicians and dentists. A final decision in this matter adverse to the State could result in costs to the State General Fund of $250 million.
In Sierra Medical Services Alliance, et al. v. Maxwell-Jolly, et al., emergency medical transportation companies challenge legislation, which sets Medi-Cal reimbursement rates paid for medical transportation services. Plaintiffs seek damages and injunctive relief. The case was stayed pending the outcome of a petition for certiorari filed with the United States Supreme Court in other Medi-Cal rate cases. At this time it is unknown what fiscal impact this case would have on the State General Fund.
In California Hospital Association v. Maxwell-Jolly, et al., plaintiff challenges limits on Medi-Cal reimbursement rates for hospital services enacted in 2008, and which were to take effect October 1, 2008 or March 1, 2009, as allegedly violating federal law. Plaintiff seeks to enjoin the implementation of the limits. This matter is currently stayed. At this time it is unknown what fiscal impact this matter may have on the State General Fund.
Medicaid providers and beneficiaries filed four law suits against both the State and the federal government, seeking to enjoin a set of rate reductions that were approved by the federal government in October 2011 with an effective date of June 1, 2011. Managed Pharmacy Care, et al., v. Sebelius, California Medical Assoc., et al., v. Douglas, California Medical Transportation Assoc. Inc., v. Douglas and California Hospital Association, et al., v. Douglas. The district court entered a series of preliminary injunctions to prevent the rate reductions from taking effect. Both the federal government and DHCS appealed to the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. The Ninth Circuit reversed the district court, vacated the preliminary injunctions and remanded the case. The Ninth Circuit denied plaintiffs' petitions for rehearing and request for a stay. The U.S. Supreme Court also has denied plaintiffs' petitions for rehearing and requests for a stay. Plaintiffs filed two petitions for certiorari in the United States Supreme Court challenging the Ninth Circuit's decision. The United States Supreme Court denied plaintiffs' petitions for certiorari.
Prison Healthcare Reform. The adult prison health care delivery system includes medical health care, mental health care and dental health care. There are two significant cases pending in federal district courts challenging the constitutionality of prison health care. Plata v. Brown is a class action regarding the adequacy of medical health care, and Coleman v. Brown is a class action regarding mental health care. A third case, Armstrong v. Brown is a class action on behalf of inmates with disabilities alleging violations of the Americans with Disabilities Act and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act. In Plata the district court appointed a receiver, who took office in April 2006, to run and operate the medical health care portion of the health care delivery system. The Plata Receiver and the Special Master appointed by the Coleman court, joined by the court representative appointed by the Armstrong court, meet routinely to coordinate efforts in these cases. To date, ongoing costs of remedial activities have been incorporated into the State's budget process. However, at this time, it is unknown what future financial impact this litigation may have on the State General Fund.
In Plata and Coleman, a three-judge panel was convened to consider plaintiffs' motion for a prisoner-release order. The motions alleged that prison overcrowding was the primary cause of unconstitutional medical and mental health care. After a trial, the panel issued a prisoner release order and ordered the State to prepare a plan for the reduction of approximately 40,000 prisoners over two years. The State filed its prisoner-reduction plan with the three-judge panel and filed an appeal in the U.S. Supreme Court. The U.S. Supreme Court affirmed the prisoner release order.
On January 7, 2013, the State moved to terminate the Coleman matter arguing that the prison mental health-care system is constitutional. The district court denied the State's motion and the State appealed. In January 2013, the State also moved to vacate the three-judge panel's prisoner-release order arguing that further population reductions are unnecessary in order for the State to provide appropriate health care to the prison population. The three-judge panel denied the State's motion and ordered the State to meet the court-ordered reduction by December 31, 2013. The State requested a stay of the order, which was denied by the U.S. Supreme Court. The State's request for review of the court-ordered reduction was also denied by the United States Supreme Court. On February 10, 2014, a three judge panel issued its order granting the State a two-year extension to meet the final population-reduction benchmark. The order requires the State to comply, in part, through a combination of additional in-state capacity in county jails, community correctional facilities, and a private prison, and through newly enacted programs, including the development of additional measures regarding reforms to state penal and sentencing laws designed to reduce the prison population.
II-70
Actions Regarding Proposed Sale of State-Owned Properties. Two taxpayers filed a lawsuit seeking to enjoin the sale of State-owned office properties, which was originally scheduled to close in December 2010, on the grounds that the sale of certain of the buildings that house appellate court facilities required the approval of the Judicial Council, which had not been obtained, and that the entire sale constituted a gift of public funds in violation of the California Constitution and a waste of public funds in violation of State law. Epstein, et al. v. Schwarzenegger, et al. Plaintiffs' request for a preliminary injunction was denied. In a second action filed after the State decided not to proceed with the sale, and now coordinated with the Epstein matter, the prospective purchaser seeks to compel the State to proceed with the sale of the State-owned properties, or alternatively, for damages for breach of contract. California First, LP v. California Department of General Services, et al. The trial court denied the State's motion for judgment on the pleadings, in which the State asserted that the plaintiff should not be permitted to pursue claims for damages. The parties have stipulated to bifurcate the matters for trial and to stay the Epstein matter pending trial of the California First matter.
High-Speed Rail Litigation. In Tos, et al. v. California High-Speed Rail Authority, et al., petitioners claim that the defendant has not complied with the State's high-speed rail bond act in approving plans for the high-speed rail system. In Tos, the trial court ruled that the State's plan for funding the high-speed rail project did not comply with certain requirements in the bond act, and ordered the High-Speed Rail Authority to rescind the plan. Respondents' motion for judgment on the pleadings on petitioners' remaining claims was denied by the trial court on March 4, 2014. On March 7, 2014, the trial court stayed further proceedings in Tos to permit the State to seek review of the ruling, and on March 21, 2014, the respondents filed a writ of petition with the appellate court. In High-Speed Rail Authority, et al. v. All Persons Interested, etc., the High-Speed Rail Authority is seeking to validate issuance of the bonds authorized for the high-speed rail system. The trial court denied validation of the bonds. Respondents in Tos and plaintiffs in the validation action filed a petition from the judgment in the validation action and the order in Tos requiring the Authority to rescind the funding plan, and the trial court transferred the proceeding to the appellate court. On February 14, 2014, the appellate court granted an alternative writ and stayed the trial court's order in Tos directing the Authority to rescind the funding plan. Briefing was scheduled to be concluded by April 1, 2014. In the event of a ruling adverse to the State in these pending matters that delays or prevents issuance of the bonds, it is possible that the federal government may require the State to reimburse federal funds provided for the high-speed rail project. The potential amount of any such reimbursement cannot be determined at this time.
Actions Regarding State Mandates. In Santa Clarita Valley Sanitation District of Los Angeles County v. California Commission on State Mandates, et al., the plaintiff asserts that certain orders issued by the regional water quality control board regarding treatment of wastewater impose additional state-mandated costs that must be reimbursed by the State. Plaintiff alleges the cost of compliance with the orders would be over $250 million.
U.S. Economy. The U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis estimates that real U.S. gross domestic product ("GDP") contracted 2.1% in the first quarter of calendar year 2014, the first such decrease since the first quarter of 2011 and the steepest decline since the first quarter of 2009, when the economy was still in recession. Unusually harsh winter weather likely was the chief cause of the contraction, but other contributing factors include a pullback in production because of excess inventory and a decline in residential construction. Additionally, the impact of the Affordable Care Act on healthcare spending in the first quarter of 2014 was less than expected. However, the steep decline in the first quarter of calendar year 2014 was followed by a rebound in economic activity, including an increase in private sector hiring. The Division of the Budget ("DOB") now estimates real U.S. GDP growth of 1.4% for calendar year 2014 and 2.9% in 2015. U.S. Personal income growth of 3.8% and 5.0% is projected for 2014 and 2015, respectively, following growth of 2.0% for 2013. The Federal Reserve is still expected to complete the gradual tapering of the growth of its historically large balance sheet by October 2014. The Federal Reserve, however, is not expected to begin raising its short-term interest rate target until the second quarter of 2015.
There are significant risks to this forecast. In today's highly interdependent global economy, it is difficult to foresee domestic growth achieving normal rates for a recovery without strong stimulus from vigorous export and single-family home demand, yet neither is anticipated over the near-term. Global economic growth continues to stall as
II-71
regional conflicts flare, while U.S. households continue to favor apartment rentals over homeownership. Slower than anticipated global growth could result in slower export growth, which could in turn result in weaker corporate profits and investment, and thus fewer jobs. The prospect of international conflict has kept energy prices volatile, which, along with equity price volatility, presents risk to household spending. Finally, the response of global financial markets to the unwinding of central bank accommodative policies remains a risk.
State Economy. New York is the third most populous state in the nation and has a relatively high level of personal wealth. The State's economy is diverse, with a comparatively large share of the nation's financial activities, information, education, and health services employment, and a very small share of the nation's farming and mining activity. The State's location and its air transport facilities and natural harbors have made it an important link in international commerce. Travel and tourism constitute an important part of the economy. Like the rest of the nation, New York has a declining proportion of its workforce engaged in manufacturing, and an increasing proportion engaged in service industries.
The State's private sector labor market has continued to perform well, exhibiting robust growth in professional and business services, private educational services, and tourism-related leisure and hospitality services. Real estate and construction activity also remains strong. Nonagricultural employment is estimated to have grown 1.6% in Fiscal Year 2013-14, and is projected to grow 1.3% in each of Fiscal Years 2014-15 and 2015-16. State wage growth of 4.5% and 4.6% is projected for Fiscal Years 2014-15 and 2015-16, following growth of 4.0% in Fiscal Year 2013-14. Total personal income growth of 4.4% and 5.0% is projected for Fiscal Years 2014-15 and 2015-16, respectively, following 3.0% growth for Fiscal Year 2013-14.
The recent weakening in several national economic indicators is a risk to the New York forecast going forward. State labor market growth has held up well so far, but a weaker than projected labor market could result in lower wages, as well as lower household spending. As the nation's financial capital, financial market volatility poses a particularly large degree of uncertainty for New York. Events over the past year have demonstrated how sensitive markets can be to shifting expectations surrounding Federal Reserve policy. The resulting market gyrations are likely to have a larger impact on the State economy than on the nation as a whole. Should financial and real estate markets be weaker than expected, taxable capital gains realizations could be negatively affected.
The City of New York. The fiscal demands on the State may be affected by the fiscal health of New York City, which relies in part on State aid to balance its budget and meet its cash requirements. The State's finances also may be affected by the ability of the City, and its related issuers, to market securities successfully in the public credit markets.
Other Localities. Certain localities outside the City have experienced financial problems and have requested and received additional State assistance during the last several years. While a relatively infrequent practice, deficit financing has become more common in recent years. Between 2004 and March 2014, the State Legislature authorized 24 bond issuances to finance local government operating deficits. In addition, the State has periodically enacted legislation to create oversight boards in order to address deteriorating fiscal conditions within a locality. The potential impact on the State of any future requests by localities for additional oversight or financial assistance is not included in the projections of the State's receipts and disbursements for Fiscal Year 2013-14 or thereafter.
Like the State, local governments must respond to changing political, economic and financial influences over which they have little or no control, but which can adversely affect their financial condition. For example, the State or federal government may reduce (or in some cases eliminate) funding of local programs, thus requiring local governments to pay these expenditures using their own resources. Similarly, past cash flow problems for the State have resulted in delays in State aid payments to localities. In some cases, these delays have necessitated short-term borrowing at the local level. Other factors that have had, or could have, an impact on the fiscal condition of local governments and school districts include: the loss of temporary federal stimulus funding; recent State aid trends, constitutional and statutory limitations on the imposition by local governments and school districts of property, sales and other taxes; and for some communities, the significant upfront costs for rebuilding and clean-up in the wake of a natural disaster. Localities also may face unanticipated problems resulting from certain pending litigation, judicial decisions and long-range economic trends. Other large-scale potential problems, such as declining urban populations, declines in the real property tax base, increasing pension, health care and other fixed costs, or the loss of skilled manufacturing jobs may also adversely affect localities and necessitate requests for State assistance.
II-72
Special Considerations. The State's financial plan is subject to many complex economic, social, financial, political, and environmental risks and uncertainties, many of which are outside the ability of the State to control. DOB believes that the projections of receipts and disbursements are based on reasonable assumptions, but there can be no assurance that actual results will not differ materially and adversely from these projections. In certain fiscal years, actual receipts collections have fallen substantially below the levels forecasted. The State's financial plan is based on numerous assumptions, including but not limited to: (i) the condition of the national and State economies and the concomitant receipt of economically sensitive tax receipts in the amounts projected; (ii) the extent, if any, to which wage and benefit increases for State employees exceed projected annual costs; (iii) the realization of the projected rate of return for pension fund assets and current assumptions with respect to wages for State employees affecting the State's required pension fund contributions; (v) the willingness and ability of the federal government to provide the aid contemplated in a financial plan; (vi) the ability of the State to implement cost reduction initiatives, including the reduction in State agency operations, and the success with which the State controls expenditures; and (vii) the ability of the State and its public authorities to market securities successfully in the public credit markets.
Federal Funding. The State receives a substantial amount of federal aid for health care, education, transportation and other governmental purposes, as well as federal funding to address response to and recovery from severe weather events. Any reductions in federal funding levels could have a materially adverse impact on the State's financial plan. The Federal Budget Control Act ("BCA") of 2011 imposed annual caps on federal discretionary spending over a ten-year period. The specific spending reductions necessary for Congress to live within the caps will be decided through the annual federal budget process, so the magnitude of impact on federal funds for the State has yet to be determined. Further, if additional deficit reduction is not enacted, the BCA directs that savings be achieved through sequestration of funding, with across-the-board cuts to federal discretionary programs and lower discretionary caps. The DOB estimates that State and local governments could lose approximately $5 billion in federal funding over a multi-year period from these additional federal deficit reduction measures. In addition, the State's financial plan may be adversely affected by other actions taken by the federal government, including audits, disallowances, and changes to federal participation rates or other Medicaid rules.
Health Insurance Company Conversions. State law permits a health insurance company to convert its organizational status from a not-for-profit to a for-profit corporation (a "health care conversion"), subject to a number of terms, conditions and approvals. The State is entitled to proceeds from the monetization of a health service corporation under a health care conversion and such proceeds must be used by the State for health-care related expenses. In recent years, the State's financial plan has counted on proceeds from health care conversions ($175 million in Fiscal Year 2013-14 and $300 million annually in each of the three subsequent fiscal years), which have not been realized. For planning purposes, the State's financial plan no longer counts on health care conversion proceeds.
Labor Settlements. The State's financial plan continues to include a State General Fund reserve to cover the costs of a pattern settlement for unsettled union contracts prior to Fiscal Year 2010-11. There can be no assurance that this reserve will fully fund these unsettled contracts. In addition, the State's ability to fund all future agreements in Fiscal Year 2014-15 and beyond depends on the achievement of balanced budgets in those years.
Pension Amortization. Under legislation enacted in August 2010, the State and local governments may amortize a portion of their annual pension costs beginning in Fiscal Year 2010-11. Amortization temporarily reduces the pension costs that must be paid by public employers in a given fiscal year, but results in higher costs overall when repaid with interest. The legislation enacted a formula to set an amortization threshold rate for each year. The amortization rate may increase or decrease by up to one percentage point annually. Pension contribution costs in excess of the amortization rate may be amortized.
For Fiscal Year 2014-15, the graded contribution rates for the New York State and Local Employees Retirement System ("ERS") and the Fire Retirement System ("PFRS") will be 13.5% and 21.5%, respectively. For both ERS and PFRS, DOB projects the Fiscal Year 2015-16 graded rates will be equal to, or more than, the normal contribution rates. As such, continued amortization is not expected. Furthermore, DOB projects the graded rates will exceed the normal contribution rates in Fiscal Years 2016-17 through 2019-20. In these years, contributions that exceed the normal contributions will be used to pay the outstanding cost of prior year amortizations, as required by statute. These projections are based on projected market returns and numerous actuarial assumptions. The next five-year experience study is scheduled to take place in 2015 and could change these projections materially.
II-73
Storm Recovery. In recent years, New York has sustained damage from three powerful storms that crippled entire regions. In August 2011, Hurricane Irene disrupted power and caused extensive flooding to various New York State counties. In September 2011, Tropical Storm Lee caused flooding in additional counties and, in some cases, exacerbated the damage caused by Hurricane Irene two weeks earlier. Little more than one year later, on October 29, 2012, Superstorm Sandy struck the East Coast, causing widespread infrastructure damage and economic losses to the greater New York region. The frequency and intensity of these storms presents economic and financial risks to the State. State claims for reimbursement for the costs of the immediate response are in process, and both recovery and future mitigation efforts have begun, largely supported by federal funds. In January 2013, the federal government approved approximately $60 billion in federal disaster aid for general recovery, rebuilding and mitigation activity nationwide. New York anticipates receiving approximately one-half of this amount over the coming years for response, recovery and mitigation costs. There can be no assurance that all anticipated federal disaster aid described above will be provided to the State and its affected entities, or that such federal disaster aid will be provided on the expected schedule.
The State accounts for all budgeted receipts and disbursements that support programs and other administrative costs of running State government within the All Governmental Funds type. The All Governmental Funds, comprised of funding supported by State Funds and Federal Funds, provides the most comprehensive view of the financial operations of the State. State Funds includes the State General Fund and other State-supported funds including State Special Reserve Funds, Capital Projects Funds and Debt Service Funds. The State General Fund is the principal operating fund of the State and is used to account for all financial transactions except those required to be accounted for in another fund. It is the State's largest fund and receives almost all State taxes and other resources not dedicated to particular purposes.
Fiscal Year 2012-13 Results. The State ended Fiscal Year 2012-13 in balance on a cash basis in the State General Fund, and maintained a closing balance of $1.61 billion, consisting of $1.1 billion in the Tax Stabilization Reserve, $175 million in the Rainy Day Reserve, $93 million in the Community Projects Fund, $21 million in the Contingency Reserve, $77 million reserved for potential retroactive labor settlements, and $113 million in an undesignated fund balance. The Fiscal Year 2012-13 closing balance was $177 million less than prior year's closing balance, which largely reflects the use of designated resources to address costs associated with retroactive labor agreements.
State General Fund receipts, including transfers from other funds, totaled $58.8 billion in Fiscal Year 2012-13. Total receipts during Fiscal Year 2012-13 were $1.9 billion (3.3%) higher than in the prior fiscal year. Total tax receipts were $1.5 billion higher than the previous fiscal year, mainly due to growth in personal income tax collections ($1.0 billion) and business tax collections ($493 million).
State General Fund disbursements, including transfers to other funds, totaled $59.0 billion in Fiscal Year 2012-13, $2.5 billion (4.4%) higher than in the prior fiscal year. This reflects expected growth in various local assistance programs, including education and Medicaid, both of which are subject to an annual cap; increased personal service costs associated with retroactive labor settlements; and increased transfers in support of debt service payments.
All Funds receipts for Fiscal Year 2012-13 totaled $133.2 billion, an increase of $511 million over the prior year's results. Annual growth in tax receipts and miscellaneous receipts was partly offset by a decline in federal grants. All Funds disbursements for Fiscal Year 2012-13 totaled $133.1 billion, a decrease of $407 million over Fiscal Year 2011-12 results. The State ended Fiscal Year 2012-13 with an All Funds cash balance of $3.9 billion.
Fiscal Year 2013-14 Results. The State ended Fiscal Year 2013-14 in balance on a cash basis in the State General Fund, and maintained a closing balance of $2.24 billion, consisting of $1.1 billion in the Tax Stabilization Reserve, $350 million in the Rainy Day Reserve, $87 million in the Community Projects Fund, $21 million in the Contingency Reserve, $45 million reserved for potential retroactive labor settlements, $58 million that has been transferred to a fiduciary fund to account for proceeds realized from a settlement between J.P. Morgan and the State, and $543 million in an undesignated fund balance. The Fiscal Year 2013-14 closing balance was $625 million
II-74
greater than the Fiscal Year 2012-13 closing balance, reflecting an increase in the level of available resources to the State.
State General Fund receipts, including transfers from other funds, totaled $61.9 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14, an increase of $3.1 billion (5.2%) from the prior fiscal year. Tax receipts, including the transfer of tax receipts to the State General Fund after payment of debt service, were $3.2 billion (5.8%) higher than in the prior fiscal year, reflecting an increase in all major tax categories. Miscellaneous receipts and federal grants were $347 million lower than the prior fiscal year, reflecting one-time receipts from settlements during Fiscal Year 2012-13. Non-tax transfers were $242 million greater than the prior fiscal year, due to the timing of certain transactions.
State General Fund disbursements, including transfers to other funds, totaled $61.2 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14, an increase of $2.3 billion (3.9%) from the prior fiscal year. This reflects expected growth in various local assistance programs, including education and Medicaid; increased transfers in support of capital projects and debt service payments; partly offset by reduced costs for agency operations.
All Funds receipts for Fiscal Year 2013-14 totaled $137.7 billion, an increase of $4.5 billion over the prior year's results. All Funds tax receipts during Fiscal Year 2013-14 were $3.4 billion higher than receipts collected during the prior year, with 80% of the growth attributable to higher personal income tax collections ($2.7 billion), due largely to strength in withholding as a result of a strong bonus season in the financial sector, as well as higher extension payments due to taxpayers accelerating income into the 2012 tax year in order to avoid increased federal rates in 2013. All Funds disbursements for Fiscal Year 2013-14 totaled $137.5 billion, an increase of $4.4 billion over Fiscal Year 2012-2013 results. The State ended Fiscal Year 2013-14 with an All Funds cash balance of $4.0 billion.
Fiscal Year 2014-15 Enacted Budget Financial Plan
The Fiscal Year 2014-15 Enacted Budget (the "Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget") provides for balanced operations on a cash basis in the State General Fund, as required by law. The Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget reflects savings from the continuation of spending controls and cost containment measures put in place in prior years. Funding for agency operations is generally expected to remain level across the financial plan period (excluding the timing of cash disbursements in Fiscal Year 2013-14). Statutory reserves are expected to remain at the same level as Fiscal Year 2013-14.
At the time the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget was enacted, State General Fund receipts, including transfers from other funds, were expected to total $63.0 billion, an annual increase of $1.1 billion (31.8%). Tax collections, including transfers of tax receipts to the State General Fund after payment of debt service, were expected to total $58.0 billion, an increase of $236 million (0.4%). Non-tax transfers to the State General Fund were expected to total $1.2 billion, an increase of $262 million, largely due to the timing of transfers from other funds and changes in the level of resources expected to be available from other funds. At the time the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget was enacted, All Funds receipts were projected to total $141.6 billion, an increase of 2.9% from Fiscal Year 2013-14 results.
At the time the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget was enacted, State General Fund disbursements, including transfers to other funds, were expected to total $63.1 billion, an increase of $1.9 billion (3.1%) from Fiscal Year 2013-14 spending levels. The State's annual pension payment was expected to increase by $50 million. This growth, which was partly offset by the pre-payment of certain obligations in Fiscal Year 2013-14, reflects increased normal costs and repayment of amounts amortized in prior years. The State expects to continue to amortize pension costs in excess of the amortization thresholds established in law. At the time the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget was enacted, State General Fund transfers to other funds were expected to total $8.1 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, a decrease of $993 million from Fiscal Year 2013-14. The annual change is attributable to the prepayment in Fiscal Year 2013-14 of debt service due in Fiscal Year 2014-15 and reduced State General Fund support for capital projects spending due to the timing of available bond proceeds. The Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget reserved $363 million for debt management purposes in Fiscal Year 2014-15, unchanged from the level currently reserved in Fiscal Year 2013-14.
At the time the Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget was enacted, DOB projected that the State will end Fiscal Year 2014-15 with a State General Fund cash balance of $2.1 billion, a decrease of $180 million from the Fiscal Year 2013-14 closing balance. In part, the reduction in the balance includes the transfer of funds received in Fiscal Year 2013-14
II-75
related to legal settlements to a new fiduciary fund, the Mortgage Settlement Proceeds Trust Fund ($58 million), and the use of excess resources from Fiscal Year 2013-14 ($43 million). These declines are partly offset by an $8 million increase in amounts set aside for the potential costs of prior-year labor agreements. The State's financial plan continues to set aside money in the State General Fund balance to cover the costs of potential retroactive labor settlements with unions that have not agreed to terms for contract periods prior to April 2011. This amount is calculated based on the "pattern" settlement for Fiscal Year 2007-08 through Fiscal Year 2010-11, and is expected to be reduced as labor agreements for prior periods are reached with unsettled unions.
Update to Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget. As of September 2014, DOB estimates that the State will end Fiscal Year 2014-15 with a sizeable State General Fund cash-basis surplus due to a series of unbudgeted financial settlements reached with several banks and insurance companies in the first four months of the current fiscal year. DOB expects that a formal plan for use of these funds in connection with the proposed budget for Fiscal Year 2015-16. As a result, State General Fund receipts are now expected to total $67.2 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, an increase of $4.2 billion from the enacted Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget. State General Fund disbursements are expected to total $63.2 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, an increase of $29 million from the enacted Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget. DOB expects the State to end Fiscal Year 2014-15 with a State General Fund closing balance of $6.2 billion, an increase of $4.2 billion from the enacted Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget.
Through June 2014, State General Fund receipts totaled $18.8 billion, $2.0 billion higher than projections in the enacted Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget, reflecting higher tax collections ($1.3 billion) and higher miscellaneous receipts ($730 million). Through June 2014, State General Fund disbursements totaled $15.9 billion, $638 million lower than projections in the enacted Fiscal Year 2014-15 Budget, reflecting lower than anticipated spending in local assistance ($567 million) and agency operations ($134 million), offset by higher State General Fund transfers to other funds ($63 million).
The State authorizes the State General Fund to borrow resources temporarily from the State's Short Term Investment Pool ("STIP") for up to four months, or to the end of the fiscal year, whichever period is shorter. Based on current information, DOB expects that the State will have sufficient liquidity to make payments as they become due throughout Fiscal Year 2014-15, but that the State General Fund may, from time to time, need to borrow resources temporarily from other funds in STIP. The State continues to reserve money on a quarterly basis for debt service payments that are financed with State General Fund resources. Money to pay debt service on bonds secured by dedicated receipts, including personal income tax bonds, continues to be set aside as required by law and bond covenants. As of March 31, 2014, the total outstanding balance of loans from STIP was $2.244 billion, an increase of $450 million from STIP's outstanding loan balance as of March 31, 2013.
General. The State is one of the largest issuers of municipal debt, ranking second among the states, behind California, in the amount of debt outstanding. The State ranks fifth in the U.S. in debt per capita, behind Connecticut, Massachusetts, Hawaii and New Jersey. As of March 31, 2014, total State-related debt outstanding totaled $55.2 billion excluding capital leases and mortgage loan commitments, equal to approximately 5.2% of New York personal income. Total debt service is projected at $5.6 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, of which $1.1 billion is paid from the State General Fund through transfers, and $4.6 billion from other State funds. The State General Fund transfer finances debt service payments on general obligation and service contract bonds. Debt service is paid directly from other State funds for the State's revenue bonds.
Financing activities of the State include general obligation debt and State-guaranteed debt, to which the full faith and credit of the State has been pledged, as well as lease-purchase and contractual-obligation financing, moral obligation and other financing through public authorities and municipalities, where the State's legal obligation to make payments to those public authorities and municipalities for their debt service is subject to annual appropriation by the Legislature. The State has never defaulted on any of its general obligation indebtedness or its obligations under lease-purchase or contractual-obligation financing arrangements and has never been called upon to make any direct payments pursuant to its guarantees.
II-76
Limitations on State-Supported Debt. The Debt Reform Act of 2000 limits outstanding State-supported debt to no greater than 4% of New York State personal income, and debt service on State-supported debt to no greater than 5% of All Funds receipts. The limits apply to all State-supported debt issued after April 1, 2000. Bond caps are legal authorizations to issue bonds to finance the State's capital projects. As the bond cap for a particular programmatic purpose is reached, subsequent legislative changes are required to raise the statutory cap to the level necessary to meet the bondable capital needs, as permitted by a single or multi-year appropriation.
For Fiscal Year 2012-13, the State was in compliance with the statutory caps based on calendar year 2012 personal income and Fiscal Year 2012-13 debt outstanding. DOB expects that debt outstanding and debt service in Fiscal Year 2013-14 will continue to remain below permitted limits. Based on the most recent forecasts, the available room under the debt outstanding cap is expected to decline from $3.3 billion in Fiscal Year 2013-14 to $421 million in Fiscal Year 2016-17. This includes the estimated impact of the bond-financed portion of capital commitment levels included in DOB's 10-year capital planning projections.
Variable Rate Obligations and Related Agreements. State statutory law authorizes issuers of State-supported debt to issue a limited amount of variable rate obligations and, subject to various statutory restrictions, enter into a limited amount of interest rate exchange agreements. State law limits the use of debt instruments which result in a variable rate exposure to no more than 15% of total outstanding State-supported debt, and limits the use of interest rate exchange agreements to a total notional amount of no more than 15% of total State-supported outstanding debt. As of March 31, 2014, State-supported debt in the amount of $52.5 billion was outstanding, resulting in a variable rate exposure cap and interest rate exchange agreement cap of approximately $8 billion each. As of March 31, 2014, both amounts are less than the statutory cap of 15%.
As of March 31, 2014, the State's authorized issuers had entered into a notional amount of $2.0 billion of interest rate exchange agreements that are subject to the interest rate exchange agreement cap, or 3.8% of total debt outstanding. Overall, the State's swap exposure is expected to decline from 3.8% to 2.7% in Fiscal Year 2017-18. The State currently has no plans to increase its swap exposure, and may take further actions to reduce swap exposures commensurate with variable rate restructuring efforts.
General Obligation Bond Programs. General obligation debt is currently authorized by the State for transportation, environment and housing purposes. Transportation-related bonds are issued for State highway and bridge improvements, and mass transportation, rail, aviation, canal, port and waterway programs and projects. Environmental bonds are issued to fund environmentally sensitive land acquisitions, air and water quality improvements, municipal non-hazardous waste landfill closures and hazardous waste site cleanup projects. As of March 31, 2014, approximately $3.2 billion of general obligation bonds were outstanding.
Lease-Purchase and Contractual-Obligation Financing Programs. Lease-purchase and contractual-obligation financing arrangements with public authorities and municipalities has been used primarily by the State to finance the State's bridge and highway programs, State University of New York and City University of New York buildings, health and mental hygiene facilities, prison construction and rehabilitation and various other State capital projects.
Legislation included in the Fiscal Year 2013-14 Enacted Budget created a new Sales Tax Revenue Bond program. This new bonding program will replicate certain credit features of existing revenue bonds and is expected to provide the State with increased efficiencies and a lower cost of borrowing. The legislation created the Sales Tax Revenue Bond Tax Fund, a sub-fund within the General Debt Service Fund that provides for the payment of these bonds. The Sales Tax Revenue Bonds are secured by dedicated revenues consisting of 1 cent of the State's 4 cent sales and use tax receipts. Such sales tax receipts in excess of debt service requirements will be transferred to the State General Fund. The first Sales Tax Revenue Bond issuance occurred in October 2013, and it is anticipated that the Sales Tax Revenue Bonds will be used interchangeably with personal income tax revenue bonds to finance State capital needs. As of March 31, 2014, $960 million of Sales Tax Revenue Bonds were outstanding. Based on current projections and anticipated coverage requirements, the State expects to issue approximately $1.2 billion of Sales Tax Revenue Bonds annually over the next four years.
II-77
Ratings. The current ratings of the State's general obligation bonds are "Aa1" from Moody's, "AA" from S&P and "AA+" from Fitch.
Fiscal Year 2014-15 State Supported Borrowing Plan. Spending on capital projects is projected to total $9.4 billion in Fiscal Year 2014-15, which includes $928 million in "off-budget spending" directly from bond proceeds held by public authorities. Overall, capital spending in Fiscal Year 2014-15 is projected to increase by $290 million (3%) from Fiscal Year 2013-14. In Fiscal Year 2014-15, transportation spending is projected to total $4.5 billion, which represents 48% of total capital spending, with education comprising the next largest share at 19%. In Fiscal Year 2014-15, the State plans to finance 57% of capital projects spending with long-term debt. Federal aid is expected to fund 18% of the State's Fiscal Year 2014-15 capital spending, primarily for transportation. State cash resources will finance the remaining 25% of capital spending.
Debt issuances of $4.8 billion are planned to finance new capital project spending in Fiscal Year 2014-15, an increase of $946 million (25%) from the prior fiscal year, which increase is primarily attributable to a delay in the sale of bonds from Fiscal Year 2013-14 until Fiscal Year 2014-15. The bond issuances will finance capital commitments for transportation infrastructure ($1.3 billion), education ($1.8 billion), mental hygiene and health care facilities ($716 million), economic development ($4377 million), the environment ($285 million), and State facilities and equipment ($317 million). Over the next four years, new debt issuances are projected to total $21.0 billion. New issuances are primarily for transportation infrastructure ($5.9 billion), education facilities ($8.0 billion), economic development ($2.3 billion), the environment ($1.2 billion), mental hygiene and health care facilities ($2.3 billion), and State facilities and equipment ($1.4 billion).
Pension and Retirement Systems
The State's retirement systems comprise the ERS and the PFRS. State employees made up about 32% of total membership during Fiscal Year 2013-14. There were 3,029 other public employers participating in the State's retirement systems, including all cities and counties (except New York City), most towns, villages and school districts (with respect to non-teaching employees) and many public authorities. As of March 31, 2014, approximately 644,000 persons were members and approximately 422,000 pensioners or beneficiaries were receiving benefits. The State Constitution considers membership in any State pension or retirement system to be a contractual relationship, the benefits of which shall not be diminished or impaired.
Assets are held by the Common Retirement Fund (the "CRF") for the exclusive benefit of members, pensioners and beneficiaries. Investments are made by the Comptroller as trustee of the CRF. Net assets available for benefits as of March 31, 2014 were $181.3 billion (including $5.3 billion in receivables, which consist of employer contributions, member contributions, member loans, accrued interest and dividends, investment sales and other miscellaneous receivables), an increase of $17.1 billion (10.4%) from prior fiscal year's level of $164.2 billion. The increase in net assets available for benefits year-over-year reflects, in large part, equity market performance. The CRF's net assets gained 13.02% during Fiscal Year 2013-14.
The present value of anticipated benefits for current members, retirees, and beneficiaries increased from $204.5 billion on April 1, 2013 to $216.4 billion (including $101.5 billion for current retirees and beneficiaries) on April 1, 2014. It is anticipated that the net assets, plus future actuarially determined contributions, will be sufficient to pay for the anticipated benefits of current members, retirees and beneficiaries. Actuarially determined contributions are calculated using actuarial assets and the present value of anticipated benefits. Actuarial assets differed from net assets on April 1, 2014 in that amortized cost was used instead of market value for bonds and mortgages, and the non-fixed investments utilized a smoothing method. Actuarial assets increased from $155.4 billion on April 1, 2013 to $171.7 billion on April 1, 2014. The funded ratio, as of April 1, 2014, calculated in August 2014 using the entry age normal funding method and actuarial assets, was 92%.
An amendment to the laws adopted in 2010 authorized the State and participating employers to amortize a portion of their annual pension costs during periods when actuarial contribution rates exceed thresholds established by the statute. Amortized amounts must be paid by State and participating employers in equal annual installments over a ten-year period, and employers may prepay these amounts at any time without penalty. Employers are required to pay interest on the amortized amount at a rate determined annually by the Comptroller that is comparable to taxable fixed income investments of a comparable duration. The interest rate on the amount an employer chooses to
II-78
amortize in a particular rate year will be the rate for that year and will be fixed for the duration of the ten-year repayment period. Should the employer choose to amortize in the next rate year, the interest rate on that amortization will be the rate set for that year, which may be different from the previous rate year. For amounts amortized in Fiscal Year 2010-11, the Comptroller set an interest rate of 5%. For amounts amortized in Fiscal Year 2011-12, the interest rate was 3.75%. For amounts amortized in Fiscal Years 2012-13 and 2013-14, the interest rate was 3.00% and 3.67%, respectively. The first payment is due in the fiscal year following the decision to amortize pension costs. When contribution rates fall below legally specified levels and all outstanding amortizations have been paid, employers that elected to amortize will be required to pay additional monies into reserve funds, specific to each employer, which will be used to offset their contributions in the future. These reserve funds will be invested separately from pension assets. Over time, it is expected that this will reduce the budgetary volatility of employer contributions. As of March 31, 2014, the amortized amount receivable, including accrued interest, for the 2011 amortization is $187.78 million from the State and $31.71 million from 45 participating employers; the amortized amount receivable, including accrued interest, for the 2012 amortization is $467.67 million from the State and $171.90 million from 118 participating employers; and, the amortized amount receivable, including accrued interest, for the 2013 amortization is $712.36 million from the State and $337.54 million from 136 participating employers.
The estimated State payment (including Judiciary) for Fiscal Year 2014-15 is approximately $2.83 billion. Multiple prepayments to date (including interest credit) have reduced this amount by approximately $1.081 billion. If the State (including Judiciary) opts to amortize the maximum amount permitted, it would reduce the required March 1, 2015 payment by $742.5 million. Amounts amortized are treated as receivables for purposes of calculating assets of the CRF.
General. The legal proceedings listed below involve State finances and programs and miscellaneous civil rights, real property, contract and other tort claims in which the State is a defendant and the potential monetary claims against the State are deemed to be material, generally in excess of $100 million. These proceedings could adversely affect the State's finances in the current fiscal year or thereafter. Adverse developments in the proceedings could affect the ability of the State to maintain a balanced budget. The State believes that any budget will include sufficient reserves to offset the costs associated with the payment of judgments that may be required during the current fiscal year. There can be no assurance, however, that adverse decisions in legal proceedings against the State would not exceed the amount of all potential budget resources available for the payment of judgments.
Real Property Claims. There are several cases in which Native American tribes have asserted possessory interests in real property or sought monetary damages as a result of claims that certain transfers of property from the tribes or the predecessors-in-interest in the 18th and 19th centuries were illegal.
In Oneida Indian Nation of New York v. State of New York, the plaintiff, alleged successors-in-interest to the historic Oneida Indian Nation, sought a declaration that they held a current possessory interest in approximately 250,000 acres of lands that the tribe sold to the State in a series of transactions that took place between 1795 and 1846, money damages, and the ejectment of the State and Madison and Oneida Counties from all publicly-held lands in the claim area. In 1998, the United States intervened in support of plaintiff. During the pendency of this case, significant decisions were rendered by the United States Supreme Court and the Second Circuit Court of Appeals which changed the legal landscape pertaining to ancient land claims: City of Sherrill v. Oneida Indian Nation of New York and Cayuga Indian Nation of New York v. Pataki. Taken together, these cases have made clear that the equitable doctrines of laches, acquiescence, and impossibility can bar ancient land claims.
Relying on these decisions, in Oneida Indian Nation et al. v. County of Oneida et al., the Second Circuit Court of Appeals dismissed the Oneida land claim. On October 17, 2011, the U.S. Supreme Court denied plaintiffs' petition for certiorari. On May 16, 2013, the State, Madison and Oneida Counties, and the Oneida Indian Nation signed a settlement agreement covering many issues. In part, the agreement would place a cap on the amount of land the tribe could reacquire and have taken into trust for its benefit by the United States. The agreement has been approved by the State Legislature, and was approved by the federal court on March 4, 2014. There are two cases challenging the settlement agreement. In Matter of Town of Verona, et al. v. Cuomo, et al., the plaintiffs are citizen taxpayers, voters and two towns. The defendants answered and moved for summary judgment, which was granted on June 27, 2014. Plaintiffs have filed a notice of appeal. In Schulz v. New York State Executive, et al., plaintiff seeks a
II-79
declaratory judgment that the New York Gaming Act, the New York Tax Free Zones Act, and the Oneida, St. Regis Mohawk and Seneca Nation settlement agreements violate various provisions of the State Constitution. In a decision, order and judgment dated April 10, 2014, the court disposed of some of the constitutional challenges to the statutes and ordered that plaintiff serve the tribes and the Counties of Madison and Oneida within thirty days. The counties dispute whether they were properly served and the tribes appear to have invoked immunity from suit such that none of those parties answered the amended complaint by June 16, 2014 as directed by the court.
In Canadian St. Regis Band of Mohawk Indians, et al. v. State of New York, et al., plaintiffs seek ejectment and monetary damages for their claim that approximately 15,000 acres in Franklin and St. Lawrence Counties were illegally transferred from their predecessors-in-interest. The defendants' motion for judgment on the pleadings, relying on the decisions in Sherrill, Cayuga and Oneida, was granted in great part through decisions on July 8, 2013 and July 23, 2013, holding that all claims are dismissed except for claims over the area known as the Hogansburg Triangle and a right of way claim against Niagara Mohawk, which will now proceed through discovery and additional motion practice. On May 21, 2013, the State, Franklin and St. Lawrence Counties, and the tribe signed an agreement resolving a gaming exclusivity dispute, which agreement provides that the parties will work towards a mutually agreeable resolution of the tribe's land claim. The land claim was stayed through at least October 8, 2014 to allow for settlement negotiations. On May 28, 2014, the State, the New York Power Authority and St. Lawrence County signed a memorandum of understanding with the St. Regis Mohawk Tribe endorsing a general framework for a settlement, subject to further negotiation. The memorandum of understanding does not address all claims by all parties and will require a formal written settlement agreement. Any formal settlement agreement will also require additional local, State and Congressional approval.
In Shinnecock Indian Nation v. State of New York, et al., plaintiff seeks ejectment, monetary damages, and declaratory and injunctive relief for its claim that approximately 3,600 acres in the Town of Southampton were illegally transferred from its predecessors-in-interest. On December 5, 2006, the District Court granted defendants' motion to dismiss, based on the Sherrill and Cayuga decisions. Plaintiff moved for reconsideration before the District Court and also appealed to the Second Circuit Court of Appeals. The motion for reconsideration has been withdrawn, but a motion to amend the complaint remains pending in the district court and stayed through at least October 1, 2014. The Shinnecock appeal to the Second Circuit also remains stayed.
Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement. In 1998, the attorneys general of 46 states, including New York, and several territories (collectively the "Settling States") and the then four largest United States tobacco manufacturers (the "Original Participating Manufacturers" or "OPMs"), entered into a Master Settlement Agreement (the "MSA") to resolve cigarette smoking-related litigation between the Settling States and the OPMs. Approximately 30 additional tobacco companies have entered into the settlement (the "Subsequent Participating Manufacturers" or "SPMs" and together, the "Participating Manufacturers" or "PMs"). The MSA released the PMs from past and present smoking-related claims by the Settling States, and provided for a continuing release of future smoking-related claims, in exchange for certain payments to be made to the Settling States, and the imposition of certain tobacco advertising and marketing restrictions among other things.
Arbitration Related to Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement. The PMs also have brought a nationwide arbitration proceeding against the Settling States (excluding Montana). The MSA provides that each year, in perpetuity, the PMs pay the Settling States a base payment, subject to certain adjustments, to compensate for financial harm suffered by the Settling States due to smoking-related illness. In order to keep the base payment under the MSA, each Settling State must pass and diligently enforce a statute that requires tobacco manufacturers who are not party to the MSA ("Non-Participating Manufacturers" or "NPMs") to deposit in escrow an amount roughly equal to the amount that PMs pay per pack sold. New York's allocable share of the total base payment is approximately 12.8% of the total, or approximately $800 million annually.
The arbitration proceeding brought by the PMs asserts that the Settling States involved failed to diligently enforce their escrow statutes in 2003. The PMs seek a downward adjustment of the payment due in that year (an "NPM Adjustment") which would serve as a credit against future payments. Any such claim for NPM Adjustment for years prior to 2003 was settled in 2003. The PMs have raised the same claim for years 2004-2006, but none of those years is yet in arbitration. The arbitration panel has thus far ruled, among other things, that the Settling States involved have the burden of proof in establishing diligent enforcement of the escrow statutes and that the 2003 settlement of prior NPM Adjustment claims does not preclude the PMs from basing their claim for a 2003 NPM
II-80
Adjustment on 2002 NPM sales. A hearing on issues common to all states took place in Chicago on April 16-24, 2012. State-specific hearings commenced in May 2012. New York's diligent enforcement hearings took place on June 25-29, 2012. The last state-specific diligent enforcement hearing took place on May 21-24, 2013. New York was found to have diligently enforced its qualifying statute in 2003 and, thus, is not subject to an NPM Adjustment for 2003.
In December 2012, the PMs and certain states (collectively the "Signatory Parties") agreed to a term sheet purportedly settling the NPM Adjustment disputes for 2003-2012. New York and certain other states and territories rejected the term sheet. The Signatory Parties then sought the approval of the panel in order to obtain an early release of MSA annual payments currently being held in a disputed payments account. The non-joining states then objected to approval of the term sheet. Under the MSA reallocation provision, every state is either "diligent" or "not diligent" and only "diligent" states are exempt from the NPM Adjustment. For every state found diligent, its allocable share of the NPM Adjustment is shifted to any remaining non-diligent states. The non-joining states sought to have the joining states treated as non-diligent for purposes of allocation of the NPM Adjustment. The panel held a status conference on January 22, 2013, and a hearing of March 7, 2013, to discuss the term sheet. On March 13, 2013, the panel issued a Partial Stipulated Settlement Award ("Partial Award") based on the provisions of the term sheet. In so doing, the Panel deemed the 20 states (collectively the "Signatory States") "diligent" for purposes of allocation of the NPM Adjustment. The panel also established a mechanism for reallocating any NPM Adjustment among non-diligent states that alters the terms of the MSA itself. Thus, if has the State been found to have been "not diligent" in its enforcement of its escrow statute in 2003, it would have exposure not only for its share of the NPM Adjustment but also for its proportionate share of the NPM Adjustment attributable to the Signatory States. The State, as well as several other states, has moved in its state court to vacate or modify the Partial Award notwithstanding the panel's finding. New York's motion has been adjourned several times. The six states that were found "not diligent" are all actively pursuing motions to vacate or modify the Partial Award as well as to vacate the panel's findings. Courts in two of the non-prevailing states, Missouri and Pennsylvania, have issued decisions vacating and/or modifying the Panel's Partial Award to the extent that the Award unfairly harms each of those states by having the Signatory States deemed diligent for purposes of allocation of the NPM Adjustment. Each of these courts held that the Signatory States should be deemed non-diligent for purposes of allocation of the NPM Adjustment. The court in Maryland denied the State's motion to vacate or modify the Partial Award. Courts in the remaining states challenging the Partial Award have not yet ruled. The PMs have indicated their intent to bring a nationwide NPM Adjustment Arbitration for sales year 2004 against New York and the other states that rejected the term sheet.
West Valley Litigation. In State of New York, et al. v. The United States of America, et al., the parties have sought to resolve the relative responsibilities of the State and federal governments for the cost of remediating the Western New York Nuclear Service Center (the "Center" or "Site"), located in West Valley, New York. The Center was established by the State in the 1960s in response to a federal call to commercialize the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel from power reactors. The private company that had leased the Site ceased operations in 1972, leaving behind two disposal areas and lagoons, highly contaminated buildings, and 600,000 gallons of liquid high level radioactive waste ("HLRW") generated by reprocessing activities.
Congress enacted the West Valley Demonstration Project Act in 1980, directing the federal government to solidify the HLRW and transport it to a federal repository, decontaminate and decommission the facilities and dispose of the low-level waste. The Act directed the State to pay 10% of those clean-up costs. However, for many years the two governments disputed what additional cleanup is needed; which cleanup activities are covered by the Act; who bears the long-term responsibility for maintaining, repairing or replacing and monitoring and tanks or other facilities that are decommissioned in place at the Site; and who pays for the offsite disposal fee for the solidified HLRW. The combined federal and State cost expenditures to date amount to approximately $2.6 billion. The State's expenditures at the Center are now approaching $320 million.
In order to resolve these disputes, the State filed suit in December 2006, seeking a declaration: (1) that the federal government is liable under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) for the State's cleanup costs and for damages to the State's natural resources, and a judgment reimbursing the State for these costs and damages, (2) of the scope of the federal government's responsibilities under the Act to decontaminate and decommission the Site and for further Site monitoring and maintenance, and (3) that the federal government is responsible under the Nuclear Waste Policy Act for paying the fees for disposal of
II-81
solidified HLRW at the Site. After commencement of the action, the parties engaged in court-ordered mediation, as a result of which a consent decree was approved and entered on August 17, 2010 resolving several key claims in the litigation.
The consent decree identifies a specific cost share for each government for specified facilities and known areas of contamination, and sets forth a process for determining cost shares for contamination that may be identified in the future. The consent decree does not select or advocate the selection of any particular cleanup program for the Site- cleanup decisions are being made via the ongoing Environmental Impact Statement process. The consent decree also does not resolve two claims raised in the State's lawsuit—the State's natural resource damages claim and its Nuclear Waste Policy Act claim. The first claim, which the federal government has agreed to toll, will be pursued by the NYS Department of Environmental Conservation and the Attorney General's office. Regarding the latter claim, the State asserts that the federal government bears sole responsibility for the cost of disposing of the remaining HLRW waste at the Site at a federal repository once one becomes available. This claim was neither settled nor dismissed and remains in litigation. Pursuant to an agreed briefing schedule, the parties submitted to the court their opening and responsive briefs for competing motions to dismiss the Nuclear Waste Policy Act claim. On November 20, 2013, the court issued an order granting the State's motion to dismiss this claim for lack of ripeness, and denying the United States' motion to dismiss to the extent it sought a ruling on alternative grounds.
Medicaid Nursing Home Rate Methodology. In Kateri Residence v. Novello and several other cases, the plaintiffs challenge several nursing home rate methodologies, including the "reserve bed patient day adjustment," which regulates payments to nursing homes when long term care patients are receiving off-site care. The trial court granted partial summary judgment to plaintiffs in Kateri, holding that the methodology was improper. The appellate court affirmed trial court's partial summary judgment decision on interlocutory appeal and remanded the case to trial court for further proceedings. The Court of Appeals denied leave to appeal on the grounds that the decision was not final. The trial court directed the defendant to re-compute Medicaid rates for the plaintiff's facilities, and that re-computation was completed in October 2013. The parties are presently conducting discovery. Plaintiffs have brought a motion, returnable March 5, 2014, to compel payment of the impacted Medicaid rates computed thus far by Department of Health staff, resulting from application of the reserve bed day methodology. On June 3, 2014, the court granted this motion to the extent of directing payment of $6.5 million out of the $49 million sought by plaintiff. Plaintiffs also brought a motion to consolidate over two hundred additional Medicaid rate cases into the present case, which was returnable May 16, 2014. The motion has been fully briefed, and awaits argument and decision.
Metropolitan Transportation Authority. In several cases, the plaintiffs challenged the constitutionality of a 2009 law that imposed certain taxes and fees, including a regional payroll tax, in that portion of the State lying within the Metropolitan Commuter Transportation District. The revenues derived from this statute are intended to assist the MTA, which a State commission concluded was facing substantial financial pressure. The plaintiffs seek judgments declaring that the enactment the 2009 law violates various State constitutional provisions. Some of the plaintiffs also sought judgments declaring that the enactment of the 2009 law violated provisions of State law requiring that the MTA be self-sustaining. Those cases include Hampton Transportation Ventures, Inc. et al. v. Silver et al., William Floyd Union Free School District v. State, Town of Brookhaven v. Silver, et al., Town of Southampton and Town of Southold v. Silver, Town of Huntington v. Silver, Mangano v. Silver, Town of Smithtown v. Silver and Vanderhoef v. Silver. Suffolk County, Westchester County, the Orange County Chamber of Commerce, and a number of additional towns and a village also joined the Mangano case as plaintiffs. All of those cases have been resolved on the merits in favor of the defendants and are concluded.
School Aid. In Maisto v. State of New York (formerly identified as Hussein v. State of New York), plaintiffs seek a judgment declaring that the State's system of financing public education violates the Constitution on the ground that it fails to provide a sound basic education. In a decision and order dated July 21, 2009 the trial court denied the State's motion to dismiss the action. The State appealed this decision, which was upheld by the appellate court on January 13, 2011. On May 6, 2011, defendants were granted leave to appeal to the Court of Appeals. On June 26, 2012, the Court of Appeals denied the State's motion to dismiss. Depositions were conducted and the discovery deadline was May 3, 2013. Trial is scheduled for December 8, 2014.
In Aristy-Farer, et al. v. The State of New York, et al., commenced February 6, 2013, plaintiffs seek a judgment declaring that the statutory provisions linking payment of State school aid increases for Fiscal Year 2012-2013 to
II-82
submission by local school districts of approvable teacher evaluation plans violates certain provisions of the State Constitution because implementation of the statutes would prevent students from receiving a sound basic education. Plaintiffs moved for a preliminary injunction enjoining the defendants from taking any actions to carry out the statutes to the extent that they would reduce payment of certain State aid disbursements to the City of New York pending a final determination. The State opposed this motion. By order dated February 19, 2013, the trial court granted the motion for preliminary injunction. The State appealed. On May 21, 2013, the appellate court denied plaintiffs motion for a stay pending appeal. As a result, plaintiffs have agreed to vacate their preliminary injunction and the State will withdraw its appeal. On April 7, 2014, the trial court denied the State's motion to dismiss. The State has appealed. By decision dated August 12, 2014, the trial granted a motion to consolidate Aristy-Farer with New Yorkers for Student Educational Rights.
In New York State United Teachers, et al. v. The State of New York, et al., commenced February 20, 2013, plaintiffs seek a judgment declaring that certain statutes that imposes a limitation on the tax that school districts can levy on the real property subject to tax within their borders violates certain provisions of the State Constitution because implementation of the statutes would prevent students from receiving a sound basic education and impair the right of plaintiffs to substantially control school district finances. Plaintiffs also seek injunctive relief barring application of the statutory tax cap to local education funding. Defendants' motion to dismiss the amended complaint was returnable on December 12, 2013. After argument before Judge O'Connor, the case was reassigned to Judge Devine, who agreed to rehear argument. Argument was delayed pending another motion by plaintiffs to amend the complaint. Upon Judge Devine's appointment to the Appellate Division, the case was reassigned to Acting Supreme Court Justice Richard Platkin who shortly thereafter recused himself at the request of the plaintiff. Justice Patrick McGrath was then assigned and the various motions are pending before him.
In New Yorkers for Students Educational Rights v. New York, the organizational plaintiff and several individual plaintiffs filed suit on February 11, 2014 claiming that the State is not meeting its constitutional obligation to fund schools in New York City and throughout the State to provide students with an opportunity for a sound basic education. Among other things, plaintiffs specifically allege that the State is not meeting its funding obligations for New York City schools under the Court of Appeals' 2006 decision in Campaign for Fiscal Equity ("CFE") v. New York and also challenge legislation conditioning increased funding for New York City schools on the timely adoption of a teacher evaluation plan. Plaintiffs seek a judgment declaring that the State has failed to comply with CFE, that the State has failed to comply with the constitutional requirement to provide funding for public schools across the State, and that the gap elimination adjustment and caps on State aid and local property tax increases are unconstitutional. They seek an injunction requiring the State to eliminate the gap elimination adjustments and caps on State aid and local property tax increases, to reimburse New York City for the funding that was withheld for failure to timely adopt a teacher evaluation plan, to provide greater assistance, services and accountability, to appoint an independent commission to determine the cost of providing students the opportunity for a sound basic education, and to revise State aid formulas. On May 30, 2014, the State filed a motion to dismiss all claims. That motion is returnable on September 15, 2014. On June 24, 2014, plaintiffs moved for a preliminary injunction seeking to restrain defendants from enforcing three of the four statutory provisions challenged in the underlying action. On August 8, 2014, the trial court granted defendants' motion to transfer the preliminary injunction application, but denied that part of the motion which sought to transfer the entire action.
Sales Tax. There are several cases challenging the State's authority to collect taxes on cigarettes sold on Indian reservations. In Oneida Indian Nation of New York v. Paterson, et al. (and four consolidated cases), plaintiffs seek judgments declaring that their federal rights are violated by the State's imposition of an excise tax on cigarettes sold by the plaintiffs to non-tribal members. In four of the five cases, the trial court denied plaintiffs' motions for preliminary injunctions, but granted a stay of enforcement pending plaintiffs' appeal. In the fifth case, the trial court granted the plaintiff's motion for a preliminary injunction. On May 9, 2011, the Second Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the trial court's order denying the plaintiffs' motions for preliminary injunctions, and vacated the trial court's order granting the motion for a preliminary injunction, vacated all stays pending appeal, and remanded the cases to the various trial courts for further proceedings consistent with the court's opinion. The State moved for summary judgment in two cases. The plaintiffs moved for voluntary dismissal without prejudice in these cases. On January 9, 2012, the district court in one of the two cases granted plaintiff's motion for summary dismissal without prejudice and denied the State's motion for summary judgment as moot. Arguments in the second case were heard on December 20, 2011. On January 9, 2012, the trial court in the first case granted plaintiff's motion for voluntary dismissal without prejudice and denied the defendants' motion for summary judgment as moot.
II-83
In July 2011, plaintiffs commenced Akwesasne Convenience Store Association et al. v. State of New York against the State of New York and other defendants, seeking a declaration that the statutory voucher system impermissibly burdens Indian commerce and is preempted by federal law and further seeking to enjoin the implementation, administration or enforcement of the system. The court denied plaintiffs' request for a temporary restraining order and, by decision dated August 18, 2011, also denied plaintiffs' subsequent motion for a preliminary injunction. Plaintiffs appealed to the appellate court, which denied plaintiffs' motion for a preliminary injunction pending appeal on September 14, 2011. The appeal is pending. By decision dated August 2, 2012, the trial court granted defendants' motion for summary judgment dismissing the complaint and denied plaintiffs' cross motion for summary judgment. Plaintiffs appealed directly to the Court of Appeals by notice of appeal filed on October 12, 2012. On January 15, 2013, the Court of Appeals transferred the appeal.
Insurance Department Assessments. In New York Insurance Association, Inc. v. State, several insurance companies and an association of insurance companies seek a declaration that certain assessments issued against the plaintiff insurance companies by the Insurance Department violate State statutes as well as the and the State and U.S. Constitutions. The plaintiff insurance companies argue, among other things, that these assessments constitute an unlawful tax because they include amounts for items that are not the legitimate direct and indirect costs of the Insurance Department. Depositions have been completed. The note of issue was filed on June 3, 2013. The parties moved for summary judgment, and the motions were submitted on March 25, 2014.
II-84
PART III
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT HOW TO BUY SHARES
See the prospectus and "How to Buy Shares" in Part II of this SAI to determine which sections of the discussion below apply to your fund.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Information Regarding the Offering of Share Classes" in Part II of this SAI or in the prospectus, fund shares may be purchased through the Distributor or Service Agents that have entered into service agreements with the Distributor. The initial investment must be accompanied by the Account Application. If required information is missing from your Account Application, it may be rejected. If an account is established pending receipt of requested information, it may be restricted to liquidating transactions only and closed if requested information is not received within specified time frames. Subsequent purchase requests may be sent directly to the Transfer Agent or your Service Agent or as otherwise described in the prospectus. Shares of the funds will only be issued against full payment. You will be charged a fee if a check used to purchase fund shares is returned unpayable. Effective July 1, 2011 the funds issue shares in book entry form only and no longer issue share certificates.
Each fund reserves the right to reject any purchase order. No fund will establish an account for a "foreign financial institution," as that term is defined in Treasury rules implementing Section 312 of the USA PATRIOT Act. Foreign financial institutions include: foreign banks (including foreign branches of U.S. depository institutions); foreign offices of U.S. securities broker-dealers, futures commission merchants and mutual funds; non-U.S. entities that, if they were located in the United States, would be securities broker-dealers, futures commission merchants or mutual funds; and non-U.S. entities engaged in the business of currency dealer or exchanger or money transmitter. No fund will accept cash, travelers' checks or money orders as payment for shares.
Service Agents may impose certain conditions on their clients which are different from those described in the prospectus and this SAI and, to the extent permitted by applicable regulatory authority, may charge their clients direct fees. You should consult your Service Agent in this regard. As discussed under "Management Arrangements—Distributor" in Part III of this SAI, Service Agents may receive revenue sharing payments from Dreyfus or the Distributor. The receipt of such payments could create an incentive for a Service Agent to recommend or sell fund shares instead of other mutual funds where such payments are not received. Please contact your Service Agent for details about any payments it may receive in connection with the sale of fund shares or the provision of services to a fund.
The Code imposes various limitations on the amount that may be contributed to certain Retirement Plans or government sponsored programs. These limitations apply with respect to participants at the Retirement Plan level and, therefore, do not directly affect the amount that may be invested in a fund by a Retirement Plan or government sponsored programs. Participants and plan sponsors should consult their tax advisors for details.
Each fund reserves the right to vary further the initial and subsequent investment minimum requirements at any time.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Investment Minimums" in Part II of this SAI, shares of each fund are offered without regard to the minimum initial investment requirements to fund board members who elect to have all or a portion of their compensation for serving in that capacity automatically invested in the fund.
The funds reserve the right to waive any small account policies that are described in the prospectus.
III-1
Purchase of Institutional Money Funds and Cash Management Funds (not applicable to Institutional Direct accounts)
In addition to the purchase information which may be described in "How to Buy Shares—Purchase of Institutional Money Funds" in Part II of this SAI, shares may be purchased by wire, by telephone or through a compatible automated interface or trading system. All payments should be made in U.S. dollars and, to avoid fees and delays, should be drawn only on U.S. banks. To place an order by telephone or to determine whether their automated facilities are compatible with the fund, investors should call Dreyfus Investments Division at 1-800-346-3621.
Certain funds may, at their discretion, permit the purchases of shares through an "in-kind" exchange of securities. Any securities exchanged must meet the investment objective, policies and limitations of the fund, must have a readily ascertainable market value, must be liquid and must not be subject to restrictions on resale. The market value of any securities exchanged, plus any cash, must be at least equal to the fund's minimum initial investment. Shares purchased in exchange for securities generally cannot be redeemed for fifteen days following the exchange in order to allow time for the transfer to settle.
Securities accepted by a fund will be valued in the same manner as the fund values its assets. Any interest earned on the securities following their delivery to the fund and prior to the exchange will be considered in valuing the securities. All interest, dividends, subscription or other rights attached to the securities become the property of the fund, along with the securities. The exchange of securities for fund shares may be a taxable transaction to the shareholder. For further information about "in-kind" purchases, call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only).
Information Pertaining to Purchase Orders
For certain institutions that have entered into agreements with the Distributor, payment for the purchase of shares of funds other than money market funds may be transmitted, and must be received by the Transfer Agent, within three business days after the order is placed. If such payment is not received within three business days after the order is placed, the order may be canceled and the institution could be held liable for resulting fees and/or losses.
Federal Funds (money market funds only). Shares of each fund are sold on a continuous basis at the NAV per share next determined after an order and Federal Funds are received by the Transfer Agent or other entity authorized to receive orders on behalf of the fund. If you do not remit Federal Funds, your payment must be converted into Federal Funds. This usually occurs within one business day of receipt of a bank wire and within two business days of receipt of a check drawn on a member bank of the Federal Reserve System. Checks drawn on banks which are not members of the Federal Reserve System may take considerably longer to convert into Federal Funds. Prior to receipt of Federal Funds, your money will not be invested in the fund.
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege. Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, you may purchase fund shares by telephone or online if you have supplied the necessary information on the Account Application or have filed a Shareholder Services Form with the Transfer Agent. The proceeds will be transferred between the bank account designated in one of these documents and your fund account. Only a bank account maintained in a domestic financial institution which is an ACH member may be so designated.
Dreyfus TeleTransfer purchase orders may be made at any time. If purchase orders are received prior to the time as of which the fund calculates its NAV (as described in the prospectus) on any day the Transfer Agent and the NYSE are open for regular business, fund shares will be purchased at the public offering price determined on that day. If purchase orders are made after the time as of which the fund calculates its NAV on any day the Transfer Agent and the NYSE are open for regular business, or made on Saturday, Sunday or any fund holiday (e.g., when the NYSE is not open for business) fund shares will be purchased at the public offering price determined on the next bank business day following such purchase order. To qualify to use the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege, the initial payment for purchase of shares must be drawn on, and redemption proceeds paid to, the same bank and account as are designated on the Account Application or Shareholder Services Form on file. If the proceeds of a particular redemption are to be sent to an account at any other bank, the request must be in writing and signature-guaranteed as described below under "Additional Information About How to Redeem Shares—Share Certificates; Medallion
III-2
Signature Guarantees." See "Additional Information About How to Redeem Shares—Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege" below for more information. Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege enables investors to make regularly scheduled investments and may provide investors with a convenient way to invest for long-term financial goals, but does not guarantee a profit and will not protect an investor against loss in a declining market.
Reopening an Account. You may reopen an account in a fund that you previously closed without filing a new Account Application during the calendar year the account is closed or during the following calendar year, provided the information in the old Account Application is still applicable. During the second calendar year after your account was closed, you may be eligible to reopen such account for part of that calendar year. Please call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or contact your financial representative for availability or options before seeking to invest in such account. You cannot at any time reopen an account that you closed in a fund, or in a share class of a fund, that previously was closed to new investment accounts.
Multi-Class Funds. When purchasing shares of a Multi-Class Fund, you must specify which class is being purchased. In many cases, neither the Distributor nor the Transfer Agent will have the information necessary to determine whether a quantity discount or reduced sales charge is applicable to a purchase. You or your Service Agent must notify the Distributor whenever a quantity discount or reduced sales charge is applicable to a purchase and must provide the Distributor with sufficient information at the time of purchase to verify that each purchase qualifies for the privilege or discount.
Service Agents may receive different levels of compensation for selling different classes of shares of the Multi-Class Funds.
Class A. Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Class A" in Part II of this SAI, and as described below with respect to: (a) Class A shares of a Multi-Class Fund that is an equity fund purchased by shareholders who beneficially owned Class A shares of such fund on November 30, 1996; and (b) Class T shares exchanged for Class A shares, the public offering price for Class A shares of each Multi-Class Fund that is an equity fund is the NAV per share of that class plus a sales load as shown below:
|
Total Sales Load*—Class A Shares | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of offering |
As a % of NAV |
Dealers' reallowance as a % |
|
Less than $50,000 |
5.75 |
6.10 |
5.00 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
3.75 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.50 |
3.63 |
2.75 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.50 |
2.56 |
2.25 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
1.75 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
____________________________
*Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
The public offering price for Class A shares of a Multi-Class Fund that is an equity fund purchased by shareholders who beneficially owned Class A shares of such fund on November 30, 1996 is the NAV per share of that class plus a sales load as shown below:
III-3
|
Total Sales Load*—Class A Shares | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of offering |
As a % of NAV |
Dealers' reallowance as a % |
|
Less than $50,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
4.25 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.00 |
4.17 |
3.75 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.00 |
3.09 |
2.75 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.50 |
2.56 |
2.25 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
1.75 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
____________________________
*Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
Effective February 4, 2009 (the "Exchange Date"), Class T shares are no longer offered by any Multi-Class Fund. Holders of Class T shares of a Multi-Class Fund as of the Exchange Date received automatically, in exchange for their Class T shares of a fund, Class A shares of the fund having an aggregate NAV equal to the aggregate value of the shareholder's Class T shares. For shareholders of a Multi-Class Fund who received Class A shares of the fund in exchange for their Class T shares of the fund on the Exchange Date, the public offering price for Class A shares of the fund is the NAV per share of Class A of the fund plus a sales load as shown below:
|
Total Sales Load*—Class A Shares | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of offering |
As a % of NAV |
Dealers' reallowance as a % |
|
Less than $50,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
4.00 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.00 |
4.17 |
3.50 |
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.00 |
3.09 |
2.50 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
1.75 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
1.50 |
1.52 |
1.25 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
____________________________
*Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Class A" in Part II of this SAI, the public offering price for Class A shares of each Multi-Class Fund that is a bond fund is the NAV per share of that class plus a sales load as shown below:
|
Total Sales Load*—Class A Shares | |||
|
Amount of Transaction |
As a % of offering |
As a % of NAV |
Dealers' reallowance as a % |
|
Less than $50,000 |
4.50 |
4.71 |
4.25 |
|
$50,000 to less than $100,000 |
4.00 |
4.17 |
3.75 |
III-4
|
$100,000 to less than $250,000 |
3.00 |
3.09 |
2.75 |
|
$250,000 to less than $500,000 |
2.50 |
2.56 |
2.25 |
|
$500,000 to less than $1,000,000 |
2.00 |
2.04 |
1.75 |
|
$1,000,000 or more |
-0- |
-0- |
-0- |
___________________________
*Due to rounding, the actual sales load you pay may be more or less than that calculated using these percentages.
Class A shares of a Multi-Class Fund purchased without an initial sales load as part of an investment of $1,000,000 or more may be assessed at the time of redemption a 1% CDSC if redeemed within one year of purchase. The Distributor may pay Service Agents an up-front commission of up to 1% of the NAV of Class A shares purchased by their clients as part of a $1,000,000 or more investment in Class A shares that are subject to a CDSC. If the Service Agent waives receipt of such commission, the CDSC applicable to such Class A shares will not be assessed at the time of redemption.
The scale of sales loads applies to purchases of Class A shares made by any Purchaser.
· Class A Shares Offered at NAV. Full-time employees of member firms of FINRA and full-time employees of other financial institutions which have entered into an agreement with the Distributor pertaining to the sale of fund shares (or which otherwise have a brokerage-related or clearing arrangement with a FINRA member firm or financial institution with respect to the sale of such shares) may purchase Class A shares for themselves directly or pursuant to an employee benefit plan or other program (if fund shares are offered to such plans or programs), or for their spouses or minor children, at NAV without a sales load, provided they have furnished the Distributor with such information as it may request from time to time in order to verify eligibility for this privilege. This privilege also applies to full-time employees of financial institutions affiliated with FINRA member firms whose full-time employees are eligible to purchase Class A shares at NAV. In addition, Class A shares are offered at NAV to full-time or part-time employees of Dreyfus or any of its affiliates or subsidiaries, directors of Dreyfus, board members of a fund advised by Dreyfus or its affiliates, or the spouse or minor child of any of the foregoing. Further, a charitable organization investing $50,000 or more in fund shares and a charitable remainder trust (each as defined in Section 501(c)(3) of the Code) may purchase Class A shares at NAV without payment of a sales charge, provided that such Class A shares are purchased directly through the Distributor. Any such charitable organization or charitable remainder trust that held Class A shares of a fund as of July 15, 2011, and continues to hold such Class A shares, may purchase additional Class A shares of the fund at NAV without a sales load whether or not purchasing such shares directly through the Distributor. Additional information about purchasing Class A shares at NAV is in the prospectus.
A shareholder purchasing fund shares through a Service Agent may no longer be eligible to purchase fund shares at NAV without a sales load, if the nature of the shareholder's relationship, and/or the services the shareholder receives from, the Service Agent changes. Please consult your Service Agent for further details.
· Dealer Reallowance. The dealer reallowance provided with respect to Class A shares may be changed from time to time but will remain the same for all dealers. The Distributor, at its own expense, may provide additional promotional incentives to dealers that sell shares of funds advised or administered by Dreyfus which are sold with a sales load, such as Class A shares. In some instances, these incentives may be offered only to certain dealers who have sold or may sell significant amounts of such shares. See "Management Arrangements—Distributor" below.
· Right of Accumulation. Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Buy Shares—Right of Accumulation" in Part II of this SAI, reduced sales loads apply to any purchase of Class A shares by you and any related Purchaser where the aggregate investment including such purchase is $50,000 or more. If, for example, you previously purchased and still hold Eligible Shares, or combination thereof, with an
III-5
aggregate current market value of $40,000 and subsequently purchase Class A shares of such fund having a current value of $20,000, the sales load applicable to the subsequent purchase would be the sales load in effect for a transaction in the range of $50,000 to less than $100,000. All present holdings of Eligible Shares may be combined to determine the current offering price of the aggregate investment in ascertaining the sales load applicable to each subsequent purchase.
To qualify for reduced sales loads, at the time of purchase you or your Service Agent must notify the Distributor if orders are made by wire or the Transfer Agent if orders are made by mail. The reduced sales load is subject to confirmation of your holdings through a check of appropriate records.
· Conversion of All Class B Shares. Effective as of the Effective Date, each Multi-Class Fund offering Class B shares converted its outstanding Class B shares to Class A shares of the fund (or, for certain funds, Class D shares of the fund—see "How to Buy Shares" in Part II of this SAI). Class B shares are no longer offered by the funds and have been terminated as a separately designated class of each fund. On the Effective Date, holders of Class B shares of a fund received Class A shares (or, as applicable, Class D shares) of the fund having an aggregate NAV equal to the aggregate NAV of the shareholder's Class B shares. Each fund's Class A shares (or, as applicable, Class D shares) have a lower total annual expense ratio than the fund's Class B shares. No front-end sales load or CDSC was imposed in connection with the conversion. Any subsequent investments in a fund's Class A shares by holders of Class A shares that were converted from Class B shares will be subject to the front-end sales load applicable to the fund's Class A shares.
Class C. The public offering price for Class C shares is the NAV per share of that class. No initial sales charge is imposed at the time of purchase. A CDSC is imposed, however, on redemptions of Class C shares made within the first year of purchase. See "Additional Information About How to Redeem Shares—Contingent Deferred Sales Charge—Multi-Class Funds—Class C" below.
Class I. The public offering price for Class I shares is the NAV per share of that class.
Shareholders who received Class I shares of a fund in exchange for Class Y shares of a corresponding Acquired Fund as a result of the reorganization of such series may continue to purchase Class I shares of any fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds whether or not they would otherwise be eligible to do so. Additional information about eligibility to purchase Class I shares is in the prospectus and may be in Part II of this SAI.
Institutions effecting transactions in Class I shares for the accounts of their clients may charge their clients direct fees in connection with such transactions.
Class Y. The public offering price for Class Y shares is the NAV per share of that class. Class Y shares of a fund have established an exchange privilege between Class Y shares of other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds, as well as between Class R shares of Dreyfus AMT-Free Municipal Reserves and Dreyfus Money Market Reserves.
All Other Funds and Share Classes. The public offering price is the NAV per share of the class.
Under certain circumstances, shares of a fund with more than one class may be converted from one class of shares to another class of shares of the same fund. The aggregate dollar value of the shares of the class received upon any such conversion will equal the aggregate dollar value of the converted shares on the date of the conversion. An investor whose fund shares are converted from one class to another class will not realize taxable gain or loss as a result of the conversion.
Federal regulations require that you provide a certified taxpayer identification number ("TIN") upon opening or reopening an account. See the Account Application for further information concerning this requirement. Failure to furnish a certified TIN could subject you to a $50 penalty imposed by the IRS.
III-6
Frequent Purchases and Exchanges (non-money market funds only)
The funds are intended to be long-term investment vehicles and are not designed to provide investors with a means of speculating on short-term market movements. A pattern of frequent purchases and exchanges can be disruptive to efficient portfolio management and, consequently, can be detrimental to a fund's performance and its shareholders. If fund management determines that an investor is following an abusive investment strategy, it may reject any purchase request, or terminate the investor's exchange privilege, with or without prior notice. Such investors also may be barred from purchasing shares of other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. Accounts under common ownership or control may be considered as one account for purposes of determining a pattern of excessive or abusive trading. In addition, a fund may refuse or restrict purchase or exchange requests for fund shares by any person or group if, in the judgment of fund management, the fund would be unable to invest the money effectively in accordance with its investment objective and policies or could otherwise be adversely affected or if the fund receives or anticipates receiving simultaneous orders that may significantly affect the fund. If an exchange request is refused, the fund will take no other action with respect to the fund shares until it receives further instructions from the investor. While a fund will take reasonable steps to prevent excessive short-term trading deemed to be harmful to the fund, it may not be able to identify excessive trading conducted through certain financial intermediaries or omnibus accounts.
Transactions made through Automatic Withdrawal Plans, Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privileges, automatic investment plans (including Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®), automatic non-discretionary rebalancing programs, minimum required retirement distributions and investments through certain third party programs for individual investors approved by the fund generally are not considered to be frequent trading. For employer-sponsored benefit plans, generally only participant-initiated exchange transactions are subject to the roundtrip limit.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT HOW TO REDEEM SHARES
See the prospectus or "How to Redeem Shares" in Part II of this SAI for fund-specific and other information about the redemption of fund shares.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares" in Part II of this SAI, each fund ordinarily will make payment for all shares redeemed within seven days after receipt by the Transfer Agent of a redemption request in proper form, except as provided by the rules of the SEC. However, if you have purchased fund shares by check, by Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege or through Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®, and subsequently submit a written redemption request to the Transfer Agent, you will receive proceeds from the redemption once a sufficient period of time has passed to reasonably ensure that the purchase check (including a certified or cashier's check) has cleared (normally eight business days). For a money market fund, the fund may delay the redemption of such shares for such period; for a fund other than a money market fund, the fund may delay sending the redemption proceeds for such period. In addition, the fund will not honor redemption checks under the Checkwriting Privilege, and will reject requests to redeem shares by wire or telephone, online or pursuant to the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege, for eight business days after receipt by the Transfer Agent of the purchase check, the Dreyfus TeleTransfer purchase or the Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder order against which such redemption is requested. These procedures will not apply if your shares were purchased by wire payment, or if you otherwise have a sufficient collected balance in your account to cover the redemption request. Fund shares will not be redeemed until the Transfer Agent has received your Account Application.
If you hold shares of more than one class of a fund with more than one class, any request for redemption must specify the class of shares being redeemed. If you fail to specify the class of shares to be redeemed or if you own fewer shares of the class than specified to be redeemed, the redemption request may be delayed until the Transfer Agent receives further instructions from you or your Service Agent.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares" in Part II of this SAI, the Wire Redemption Privilege, Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege and the Telephone Exchange Privilege authorize the Transfer Agent to act on telephone (including over the Dreyfus Express® voice-activated account access system), letter or online instructions from any person representing himself or herself to be you, or a representative of your Service Agent, and reasonably believed by the Transfer Agent to be genuine. The fund will require the Transfer Agent to employ reasonable procedures, such as requiring a form of personal identification, to confirm that instructions are genuine
III-7
and, if it does not follow such procedures, the fund or the Transfer Agent may be liable for any losses due to unauthorized or fraudulent instructions. Neither the fund nor the Transfer Agent will be liable for following telephonic instructions reasonably believed to be genuine.
During times of drastic economic or market conditions, you may experience difficulty in contacting the Transfer Agent by telephone or online to request a redemption or exchange of fund shares. In such cases, you should consider using the other redemption procedures described herein. Use of these other redemption procedures may result in your redemption request being processed at a later time than it would have been if telephonic redemption had been used. During the delay the NAV of non-money market funds may fluctuate.
Certain funds will deduct a redemption fee as described in the relevant funds' prospectuses. Subject to the exceptions described in a fund's prospectus, shares held for less than the 60-day holding period will be subject to the fund's redemption fee, whether held directly in your name or indirectly through an intermediary, such as a broker, bank, investment adviser, recordkeeper for Retirement Plan participants or any other third party. If you hold your shares through an intermediary's omnibus account, the intermediary is responsible for imposing the fee and remitting the fee to the fund.
The redemption fee will be charged and retained by a fund on shares sold before the end of the required holding period. The fund will use the "first-in, first-out" method to determine the holding period for the shares sold. Under this method, shares held the longest will be redeemed or exchanged first. The holding period commences on the day after your purchase order is effective. For example, the holding period for shares purchased on October 31 (trade date) begins on November 1 and ends on the 59th day, which is December 29. Thus, if you redeemed these shares on December 29, you would be assessed the fee, but you would not be assessed the fee if you redeemed on or after December 30.
A redemption fee generally is collected by deduction from the redemption proceeds, but may be imposed by billing you if the fee is not imposed as part of the redemption transaction.
A fund may postpone the effective date of the assessment of the redemption fee on the underlying shareholder accounts within an omnibus account if an intermediary requires additional time to collect the fund's redemption fee.
The fund may impose the redemption fee at the plan level for employee benefit plans that hold shares on behalf of a limited number of employees. Plan sponsors of such benefit plans that opt to impose redemption fees at the employee account level, rather than at the plan level, must enter into agreements with Dreyfus that obligate the sponsor to collect and remit redemption fees at the employee level and to provide to the fund, at its request, shareholder identity and transaction information.
The funds' prospectuses contain information on transactions for which the redemption fee is waived. The funds reserve the right to exempt additional transactions from the redemption fee.
Contingent Deferred Sales Charge—Multi-Class Funds
Class C. A CDSC of 1% payable to the Distributor is imposed on any redemption of Class C shares within one year of the date of purchase. No CDSC will be imposed to the extent that the NAV of the Class C shares redeemed does not exceed (i) the current NAV of Class C shares of the fund acquired through reinvestment of fund dividends or capital gain distributions, plus (ii) increases in the NAV of your Class C shares above the dollar amount of all your payments for the purchase of Class C shares held by you at the time of redemption.
If the aggregate value of Class C shares redeemed has declined below their original cost as a result of the fund's performance, a CDSC may be applied to the then-current NAV rather than the purchase price.
In determining whether a CDSC is applicable to a redemption, the calculation will be made in a manner that results in the lowest possible rate. It will be assumed that the redemption is made first of amounts representing Class C shares acquired pursuant to the reinvestment of dividends and distributions; then of amounts representing the increase in NAV of Class C shares above the total amount of payments for the purchase of Class C shares made
III-8
during the preceding year; and finally, of amounts representing the cost of shares held for the longest period.
For example, assume an investor purchased 100 shares of the fund at $10 per share for a cost of $1,000. Subsequently, the shareholder acquired five additional shares through the reinvestment of fund dividends. Within a year after the purchase the investor decided to redeem $500 of the investment. Assuming at the time of the redemption the NAV had appreciated to $12 per share, the value of the investor's shares would be $1,260 (105 shares at $12 per share). The CDSC would not be applied to the value of the reinvested dividend shares and the amount which represents appreciation ($260). Therefore, $240 of the $500 redemption proceeds ($500 minus $260) would be charged at a rate of 1% for a total CDSC of $2.40.
Waiver of CDSC. The CDSC may be waived in connection with (a) redemptions made within one year after the death or disability, as defined in Section 72(m)(7) of the Code, of the shareholder, (b) redemptions by employees participating in Retirement Plans or other programs, (c) redemptions as a result of a combination of any investment company with the fund by merger, acquisition of assets or otherwise, (d) a distribution following retirement under a tax-deferred retirement plan or upon attaining age 70½ in the case of an IRA or Keogh plan or custodial account pursuant to Section 403(b) of the Code and (e) redemptions pursuant to the Automatic Withdrawal Plan, as described under "Additional Information About Shareholder Services—Automatic Withdrawal Plan" in Part III of this SAI. If a fund's board determines to discontinue the waiver of the CDSC, the disclosure herein will be revised appropriately. Any fund shares subject to a CDSC which were purchased prior to the termination of such waiver will have the CDSC waived as provided in the fund's prospectus or this SAI at the time of the purchase of such shares.
To qualify for a waiver of the CDSC, at the time of redemption you must notify the Transfer Agent or your Service Agent must notify the Distributor. Any such qualification is subject to confirmation of your entitlement.
Redemption Through an Authorized Entity
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares—Redemption Through an Authorized Entity" in Part II of this SAI, redemption orders received by an Authorized Entity by the close of trading on the floor of the NYSE on any business day and transmitted to the Distributor or its designee in accordance with the Authorized Entity's agreement with the Distributor are effected at the price determined as of the close of trading on the floor of the NYSE on that day. Otherwise, the shares will be redeemed at the next determined NAV. It is the responsibility of the Authorized Entity to transmit orders on a timely basis. The Authorized Entity may charge the shareholder a fee for executing the order. This repurchase arrangement is discretionary and may be withdrawn at any time.
Certain funds provide redemption checks ("Checks") automatically upon opening an account, unless you specifically refuse the Checkwriting Privilege by checking the applicable "No" box on the Account Application. Checks will be sent only to the registered owner(s) of the account and only to the address of record. The Checkwriting Privilege may be established for an existing account by a separate signed Shareholder Services Form. The Account Application or Shareholder Services Form must be manually signed by the registered owner(s). Checks are drawn on your fund account and, except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares—Checkwriting Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, may be made payable to the order of any person in the amount of $500 or more. When a Check is presented to the Transfer Agent for payment, the Transfer Agent, as your agent, will cause the fund to redeem a sufficient number of full and fractional shares in your account to cover the amount of the Check. Potential fluctuations in the NAV of a non-money market fund should be considered in determining the amount of a Check. Dividends are earned until the Check clears. After clearance, a copy of the Check will be returned to you. You generally will be subject to the same rules and regulations that apply to checking accounts, although the election of this privilege creates only a shareholder-transfer agent relationship with the Transfer Agent.
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares—Checkwriting Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, Checks are free but the Transfer Agent will impose a fee for stopping payment of a Check upon your request or if the Transfer Agent cannot honor a Check due to insufficient funds or other valid reason. If the amount of the Check is greater than the value of the shares in your account, the Check will be returned marked "insufficient funds." Checks should not be used to close your account.
III-9
You should date your Checks with the current date when you write them. Please do not postdate your Checks. If you do, the Transfer Agent will honor, upon presentment, even if presented before the date of the Check, all postdated Checks which are dated within six months of presentment for payment if they are otherwise in good order. If you hold shares in a Dreyfus sponsored IRA account, you may be permitted to make withdrawals from your IRA account using checks furnished to you for this purpose.
Except with respect to money market funds, the Checkwriting Privilege will be terminated immediately, without notice, with respect to any account which is, or becomes, subject to backup withholding on redemptions. Any Check written on an account which has become subject to backup withholding on redemptions will not be honored by the Transfer Agent. Institutional Direct accounts are not eligible for the Checkwriting Privilege.
Except as may be otherwise described under "How to Redeem Shares—Wire Redemption Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, by using this privilege, you authorize the fund and the Transfer Agent to act on telephone, letter or online redemption instructions from any person representing himself or herself to be you, or a representative of your Service Agent, and reasonably believed by the fund or the Transfer Agent to be genuine. Ordinarily, a fund other than a money market fund will initiate payment for shares redeemed pursuant to the Wire Redemption Privilege on the next business day if the Transfer Agent receives a redemption request in proper form prior to the time as of which the fund calculates its NAV (as described in the prospectus); for a money market fund that receives a redemption request in proper form prior to the time as of which the fund calculates its NAV, payment will be initiated the same day and the shares will not receive the dividend declared on that day.
Except as may be otherwise described under "How to Redeem Shares—Wire Redemption Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, redemption proceeds ($1,000 minimum) will be transferred by Federal Reserve wire only to the commercial bank account specified by you on the Account Application or Shareholder Services Form, or to a correspondent bank if your bank is not a member of the Federal Reserve System. Fees ordinarily are imposed by such bank and borne by the investor. Immediate notification by the correspondent bank to your bank is necessary to avoid a delay in crediting the funds to your bank account. To change the commercial bank or account designated to receive redemption proceeds, a written request must be sent to the Transfer Agent. In most circumstances, this request must be signed by each shareholder, with each signature guaranteed as described below under "Share Certificates; Medallion Signature Guarantees." Shares held in an Education Savings Account may not be redeemed through the Wire Redemption Privilege.
Redemption through Compatible Automated Facilities
Certain funds make available to institutions the ability to redeem shares through compatible automated interface or trading system facilities. Investors desiring to redeem shares in this manner should call Dreyfus Investments Division at 1-800-346-3621 to determine whether their automated facilities are compatible and to receive instructions for redeeming shares in this manner.
Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege
Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares—Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege" in Part II of this SAI, you may request by telephone (for regular accounts or IRAs) or online (for regular accounts only) that redemption proceeds ($500 minimum) be transferred between your fund account and your bank account. Except as may be otherwise described in "How to Redeem Shares—Transaction Fees" in Part II of this SAI or in the prospectus, transaction fees do not apply to Dreyfus TeleTransfer redemptions. Only a bank account maintained in a domestic financial institution which is an ACH member may be designated. You should be aware that if you have selected the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege, any request for a Dreyfus TeleTransfer transaction will be effected through the ACH system unless more prompt transmittal specifically is requested. Redemption proceeds will be on deposit in your account at an ACH member bank ordinarily two business days after receipt of the redemption request. Shares held in an Education Savings Account may not be redeemed through the Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege. See "Additional Information About How to Buy Shares—Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege" above.
III-10
Upon written request, you may reinvest up to the number of Class A shares of a Multi-Class Fund you have redeemed, within 45 days of redemption, at the then-prevailing NAV without a sales load, or reinstate your account for the purpose of exercising Fund Exchanges. Upon reinstatement, if such shares were subject to a CDSC, your account will be credited with an amount equal to the CDSC previously paid upon redemption of the shares reinvested. The Reinvestment Privilege may be exercised only once.
Share Certificates; Medallion Signature Guarantees
Share Certificates. Effective July 1, 2011 each fund issues shares in book entry form only and no longer issues share certificates. Any certificates representing fund shares to be redeemed must be submitted with the redemption request. Written redemption requests must be signed by each shareholder, including each holder of a joint account, and each signature must be guaranteed. Signatures on endorsed certificates submitted for redemption also must be guaranteed as described below.
Medallion Signature Guarantees. The Transfer Agent has adopted standards and procedures pursuant to which signature-guarantees in proper form generally will be accepted from participants in the NYSE Medallion Signature Program, the Securities Transfer Agents Medallion Program (STAMP) or the Stock Exchanges Medallion Program (SEMP). Guarantees must be signed by an authorized signatory of the guarantor. No other types of signature guarantees will be accepted. The Transfer Agent may request additional documentation from corporations, executors, administrators, trustees or guardians, and may accept other suitable verification arrangements from foreign investors, such as consular verification. For more information with respect to signature-guarantees, please call one of the telephone numbers listed on the cover.
Each fund has committed itself to pay in cash all redemption requests by any fund shareholder of record, limited in amount during any 90-day period to the lesser of $250,000 or 1% of the value of the fund's net assets at the beginning of such period. Such commitment is irrevocable without the prior approval of the SEC. In the case of requests for redemption from the fund in excess of such amount, the fund's board reserves the right to make payments in whole or in part in securities or other assets of the fund in case of an emergency or any time a cash distribution would impair the liquidity of the fund to the detriment of the existing shareholders. In such event, the securities would be valued in the same manner as the fund's portfolio is valued. If the recipient sells such securities, brokerage charges would be incurred.
The right of redemption may be suspended or the date of payment postponed (a) during any period when the NYSE is closed (other than customary weekend and holiday closings), (b) when the SEC determines that trading in the markets a fund ordinarily utilizes is restricted, or when an emergency exists as determined by the SEC so that disposal of the fund's investments or determination of its NAV is not reasonably practicable, or (c) for such other periods as the SEC by order may permit to protect fund shareholders.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT SHAREHOLDER SERVICES
See "Shareholder Services" in Part II of this SAI to determine which sections of the discussion below apply to your fund.
Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder, the Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan and Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit Privilege enable investors to make regularly scheduled investments and may provide these investors with a convenient way to invest for long-term financial goals, but do not guarantee a profit and will not protect an investor against loss in a declining market.
Shareholder Services Forms and prospectuses of the funds may be obtained by visiting www.dreyfus.com or by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only). To modify or terminate your participation in a service, call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only). Except as otherwise stated, the shareholder services described below may be
III-11
modified or terminated at any time.
You should obtain and review the prospectus of the fund and class, if applicable, into which an exchange is being made. Upon exchanging into a new account, the following shareholder services and privileges, as applicable, will be automatically carried over to the fund into which the exchange is made: Fund Exchanges, Checkwriting Privilege, Dreyfus TeleTransfer Privilege, Wire Redemption Privilege and the dividends and distributions payment options (except Dreyfus Dividend Sweep) selected by you.
The funds reserve the right to reject any exchange request in whole or in part. Fund Exchanges and the Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege are available to investors resident in any state in which shares of the fund being acquired may legally be sold. Shares may be exchanged only between accounts having certain identical identifying designations. The Fund Exchanges service or the Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege may be modified or terminated at any time upon notice to shareholders.
Fund Exchanges. Except as may be otherwise described in "Shareholder Services" in Part II of this SAI, you or clients of certain Service Agents may purchase, in exchange for shares of a fund, shares of the same class, or another class in which you are eligible to invest, of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. Fund exchanges are subject to any redemption fee applicable to the fund from which you are exchanging, as described in such fund's prospectus. You should review carefully the current prospectus of the fund from which your shares were exchanged and, if applicable, into which shares are exchanged to determine the sales load or CDSC chargeable upon the redemption of the shares and for information on conversion features. Shares of funds purchased by exchange will be purchased on the basis of relative NAV per share as follows:
A. Exchanges for shares of funds offered without a sales load will be made without a sales load.
B. Shares of funds purchased without a sales load may be exchanged for shares of other funds sold with a sales load, and the applicable sales load will be deducted.
C. Shares of funds purchased with a sales load may be exchanged without a sales load for shares of other funds sold without a sales load.
D. Shares of funds purchased with a sales load, shares of funds acquired by a previous exchange from shares purchased with a sales load and additional shares acquired through reinvestment of dividends or distributions of any such funds (collectively referred to herein as "Purchased Shares") may be exchanged for shares of other funds sold with a sales load (referred to herein as "Offered Shares"), but if the sales load applicable to the Offered Shares exceeds the maximum sales load that could have been imposed in connection with the Purchased Shares (at the time the Purchased Shares were acquired), without giving effect to any reduced loads, the difference may be deducted.
E. Shares of funds subject to a CDSC that are exchanged for shares of another fund will be subject to the higher applicable CDSC of the two funds, and, for purposes of calculating CDSC rates and conversion periods, if any, will be deemed to have been held since the date the shares being exchanged were initially purchased.
To accomplish an exchange under item D above, you or your Service Agent acting on your behalf must notify the Transfer Agent of your prior ownership of fund shares and your account number. Any such exchange is subject to confirmation of your holdings through a check of appropriate records.
You also may exchange your Class A or Class C shares of a Multi-Class Fund that are subject to a CDSC for shares of the Worldwide Dollar Fund. The shares so purchased will be held in an Exchange Account. Exchanges of shares from an Exchange Account only can be made into certain other funds managed or administered by Dreyfus. No CDSC is charged when an investor exchanges into an Exchange Account; however, the applicable CDSC will be imposed when shares are redeemed from an Exchange Account or other applicable fund account. Upon redemption, the applicable CDSC will be calculated without regard to the time such shares were held in an Exchange Account. See "How to Redeem Shares" in Part II of this SAI. Redemption proceeds for Exchange Account shares are paid by federal wire or check only. Exchange Account shares also are eligible for the Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege and the Automatic Withdrawal Plan, each of which is described below.
III-12
As of the Effective Date, holders of Class A shares of a fund or the General Fund received by conversion from Class B shares, and holders of shares of the Worldwide Dollar Fund received in a prior exchange for a fund's Class B shares, may exchange such shares for Class A shares or no-load shares or classes of other funds managed or administered by Dreyfus, without the imposition of a front-end sales load or CDSC.
Except as may be otherwise described in "Shareholder Services" in Part II of this SAI or in the prospectus, to request an exchange, you, or a Service Agent acting on your behalf, may give exchange instructions to the Transfer Agent in writing, by telephone or online. Except as may be otherwise described in "Shareholder Services" in Part II of this SAI, by using this privilege, you authorize the fund and the Transfer Agent to act on telephone or online instructions (including over the Dreyfus Express® voice-activated account access system) from any person representing himself or herself to be you or a representative of your Service Agent and reasonably believed by the fund or the Transfer Agent to be genuine. Exchanges may be subject to limitations as to the amount involved or the number of exchanges permitted. Shares issued in certificate form are not eligible for telephone or online exchange. Unless otherwise stated in the prospectus, no fees currently are charged to shareholders directly in connection with exchanges, although the funds reserve the right, upon not less than 60 days' written notice, to charge shareholders a nominal administrative fee in accordance with rules promulgated by the SEC.
Exchanges of Class I, Class R or Class Y shares held by a Retirement Plan may be made only between the investor's Retirement Plan account in one fund and such investor's Retirement Plan account in another fund.
When establishing a new account by exchange, the shares being exchanged must have a value of at least the minimum initial investment required for the fund into which the exchange is being made (and the investor must otherwise be eligible to invest in the class of shares being purchased). For the BASIC funds, the shares being exchanged must have a current value of at least $1,000.
During times of drastic economic or market conditions, Fund Exchanges may be temporarily suspended without notice, and exchange requests may be treated based on their separate components¾redemption orders with a simultaneous request to purchase the other fund's shares. In such a case, the redemption request would be processed at the fund's next determined NAV, but the purchase order would be effective only at the NAV next determined after the fund being purchased receives the proceeds of the redemption, which may result in the purchase being delayed.
Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege. Dreyfus Auto-Exchange Privilege, which is available for existing accounts only, permits you to purchase (on a semi-monthly, monthly, quarterly or annual basis), in exchange for shares of a fund, shares of the same class, or another class in which you are eligible to invest, of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds of which you are a shareholder. The amount you designate, which can be expressed either in terms of a specific dollar or share amount ($100 minimum), will be exchanged automatically on the first and/or fifteenth day of the month according to the schedule you have selected. With respect to Class I or Class R shares held by a Retirement Plan, exchanges may be made only between the investor's Retirement Plan account in one fund and such investor's Retirement Plan account in another fund. Shares will be exchanged on the basis of relative NAV as described above under "Fund Exchanges." Enrollment in or modification or cancellation of this privilege is effective three business days following notification by you. Shares held under IRAs and Retirement Plans are eligible for this privilege. Exchanges of IRA shares may be made between IRA accounts and from regular accounts to IRA accounts, but not from IRA accounts to regular accounts. With respect to Retirement Plan accounts, exchanges may be made only among those accounts. Shares in certificate form are not eligible for this privilege.
Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder®
Dreyfus Automatic Asset Builder® permits you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 and a maximum of $150,000 per transaction) at regular intervals selected by you. Fund shares are purchased by transferring funds from the bank account designated by you.
Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit Privilege
Dreyfus Government Direct Deposit Privilege enables you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 and maximum of $50,000 per transaction) by having federal salary, Social Security, or certain veterans', military or other payments from the U.S. Government automatically deposited into your fund account. When selecting this service
III-13
for a fund other than a money market fund, you should consider whether Direct Deposit of your entire payment into a fund with a fluctuating NAV may be appropriate for you.
Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan permits you to purchase fund shares (minimum of $100 per transaction) automatically on a regular basis. Depending upon your employer's direct deposit program, you may have part or all of your paycheck transferred to your existing Dreyfus account electronically through the ACH system at each pay period. To establish a Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan account, you must file an authorization form with your employer's payroll department. It is the sole responsibility of your employer to arrange for transactions under the Dreyfus Payroll Savings Plan. Shares held through a Retirement Plan are not eligible for this privilege.
Dreyfus Dividend Sweep. Dreyfus Dividend Sweep allows you to invest automatically your dividends or dividends and capital gain distributions, if any, from a fund in shares of the same class, or another class in which you are eligible to invest, of another fund in the Dreyfus Family of Funds. Shares held through a Retirement Plan are not eligible for this privilege. Identically registered existing IRA accounts are eligible for this privilege. Shares of the other funds purchased pursuant to this privilege will be purchased on the basis of relative NAV per share as follows:
A. Dividends and distributions paid by a fund may be invested without a sales load in shares of other funds offered without a sales load.
B. Dividends and distributions paid by a fund that does not charge a sales load may be invested in shares of other funds sold with a sales load, and the applicable sales load will be deducted.
C. Dividends and distributions paid by a fund that charges a sales load may be invested in shares of other funds sold with a sales load (Offered Shares), but if the sales load applicable to the Offered Shares exceeds the maximum sales load charged by the fund from which dividends or distributions are being swept (without giving effect to any reduced loads), the difference may be deducted.
D. Dividends and distributions paid by a fund may be invested in shares of other funds that impose a CDSC and the applicable CDSC, if any, will be imposed upon redemption of such shares.
Dreyfus Dividend ACH. Dreyfus Dividend ACH permits you to transfer electronically dividends or dividends and capital gain distributions, if any, from a fund to a designated bank account. Only an account maintained at a domestic financial institution which is an ACH member may be so designated. Banks may charge a fee for this service.
The Automatic Withdrawal Plan permits you to request withdrawal of a specified dollar amount (minimum of $50) on a specific day each month, quarter or semi-annual or annual period if you have a $5,000 minimum account. Automatic Withdrawal Plan transactions that fall on a non-business day generally will be processed on the next business day. However, when the next business day is part of a new month, the transaction will be processed on the previous business day. For example, if you request that Automatic Withdrawal Plan transactions be processed on the 30th day of each month, and June 30th falls on a Sunday, the transaction will be processed on June 28th.
Withdrawal payments are the proceeds from sales of fund shares, not the yield on the shares. If withdrawal payments exceed reinvested dividends and distributions, your shares will be reduced and eventually may be depleted. The Automatic Withdrawal Plan may be established by completing a Dreyfus Automatic Withdrawal Form which you can obtain by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only), visiting www.dreyfus.com or contacting your financial representative. For instructions on how to establish automatic withdrawals to sell shares in an IRA account, please call 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only) or contact your financial representative. Shares for which share certificates have been issued may not be redeemed through the Automatic Withdrawal Plan.
No CDSC with respect to Class C shares will be imposed on withdrawals made under the Automatic Withdrawal Plan, provided that any amount withdrawn under the plan does not exceed on an annual basis 12% of the greater of (1) the account value at the time of the first withdrawal under the Automatic Withdrawal Plan or (2) the account
III-14
value at the time of the subsequent withdrawal. Withdrawals with respect to Class C shares under the Automatic Withdrawal Plan that exceed such amounts will be subject to a CDSC. Withdrawals of Class A shares subject to a CDSC under the Automatic Withdrawal Plan will be subject to any applicable CDSC. Purchases of additional Class A shares where the sales load is imposed concurrently with withdrawals of Class A shares generally are undesirable.
Certain Retirement Plans, including Dreyfus-sponsored retirement plans, may permit certain participants to establish an automatic withdrawal plan from such Retirement Plans. Participants should consult their Retirement Plan sponsor and tax advisor for details. Such a withdrawal plan is different than the Automatic Withdrawal Plan.
Letter of Intent¾Class A Shares
By submitting a Letter of Intent form, you become eligible for the reduced sales load on purchases of Class A shares based on the total number of shares of Eligible Shares purchased by you and any related Purchaser within a period of up to 13-months pursuant to the terms and conditions set forth in the Letter of Intent. Eligible Shares purchased within 90 days prior to the submission of the Letter of Intent ("Pre-LOI Purchases") may be used to equal or exceed the amount specified in the Letter of Intent. A minimum initial purchase of $5,000 is required. You can obtain a Letter of Intent form by calling 1-800-DREYFUS (inside the U.S. only).
Each purchase you make from the date you submit the Letter of Intent until the earlier of (i) the date you fulfill the terms of the Letter of Intent by purchasing the minimum investment specified in the Letter of Intent (the "LOI Purchase Commitment") or (ii) the end of the 13-month period following the date you submit the Letter of Intent will be at the public offering price applicable to a single transaction in the amount of the LOI Purchase Commitment. The Transfer Agent will hold in escrow 5% of the minimum amount indicated in the Letter of Intent, which may be used for payment of a higher sales load if you do not fulfill the LOI Purchase Commitment. When you fulfill the LOI Purchase Commitment, the escrowed amount will be released and additional shares representing such amount will be credited to your account. In addition, when you fulfill the LOI Purchase Commitment, the Pre-LOI Purchases will be adjusted to reflect the sales load applicable to the LOI Purchase Commitment. The adjustment will be made in the form of additional shares credited to your account at the then-current offering price applicable to a single purchase in the amount of the LOI Purchase Commitment. If, however, total purchases at the end of the 13-month period are less than the LOI Purchase Commitment, the offering price of the shares you purchased (including shares representing the escrowed amount) during the 13-month period will be adjusted to reflect the sales load applicable to the aggregate purchases you actually made (which will reduce the number of shares in your account), unless you have redeemed the shares in your account, in which case the Transfer Agent, as attorney-in-fact pursuant to the terms of the Letter of Intent, will redeem an appropriate number of Class A shares of the fund held in escrow to realize the difference between the sales load actually paid and the sales load applicable to the aggregate purchases actually made and any remaining shares will be credited to your account. Submitting a Letter of Intent does not bind you to purchase, or the fund to sell, the full amount indicated at the sales load in effect at the time of signing, but you must complete the intended purchase to obtain the reduced sales load. At the time you purchase Class A shares, you must indicate your intention to do so under a Letter of Intent. Purchases pursuant to a Letter of Intent will be made at the then-current NAV plus the applicable sales load in effect at the time such Letter of Intent was submitted.
Corporate Pension/Profit-Sharing and Retirement Plans
A fund may make available to corporations a variety of prototype pension and profit-sharing plans, including a 401(k) Salary Reduction Plan. In addition, certain funds make available Keogh Plans, IRAs (including regular IRAs, spousal IRAs for a non-working spouse, Roth IRAs, SEP-IRAs and rollover IRAs), Education Savings Accounts and 403(b)(7) Plans. Plan support services also are available.
If you wish to purchase fund shares in conjunction with a Keogh Plan, a 403(b)(7) Plan, an IRA, including a SEP-IRA, or an Education Savings Account, you may request from the Distributor forms for adoption of such plans. Shares may be purchased in connection with these plans only by direct remittance to the entity acting as custodian. Such purchases will be effective when payments received by the Transfer Agent are converted into Federal Funds. Purchases for these plans may not be made in advance of receipt of funds.
The entity acting as custodian for Keogh Plans, 403(b)(7) Plans, IRAs or Education Savings Accounts may charge a
III-15
fee, payment of which could require the liquidation of shares. All fees charged are described in the appropriate form. You should read the prototype retirement plan and the appropriate form of custodial agreement for further details on eligibility, service fees and tax implications, and should consult a tax advisor.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT DISTRIBUTION PLANS, SERVICE PLANS AND SHAREHOLDER SERVICES PLANS
See "Distribution Plans, Service Plans and Shareholder Services Plans" in Part II of this SAI for more information about the Plan(s) adopted by your fund.
Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act, which is applicable to certain Plans, provides, among other things, that an investment company may bear expenses of distributing its shares only pursuant to a plan adopted in accordance with the Rule. For each fund that has adopted a Plan pursuant to Rule 12b-1, the board believes that there is a reasonable likelihood that the Plan will benefit the fund and the class(es) of fund shares to which the Plan applies.
A written quarterly report of the amounts expended under a fund's Plan, and the purposes for which such expenditures were incurred, must be made to the fund's board for its review. For a Plan adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1, the Plan provides that it may not be amended to increase materially the costs that holders of the fund's applicable class(es) of shares may bear pursuant to the Plan without the approval of the holders of such shares; other material amendments of the Plan must be approved by the board and by the board members who are not "interested persons" (as defined in the 1940 Act) of the fund and have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Plan or in any agreements entered into in connection with the Plan, by vote cast in person at a meeting called for the purpose of considering such amendments. For a Plan not adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1, the Plan provides that material amendments to the Plan must be approved by the board and by the board members who are not "interested persons" (as defined in the 1940 Act) of the fund and have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Plan or in any agreements entered into in connection with the Plan, by vote cast in person at a meeting called for the purpose of considering such amendments. Each Plan is subject to annual approval by such vote of the board members cast in person at a meeting called for the purpose of voting on the Plan. As to the relevant class of fund shares (if applicable), the Plan is generally terminable at any time by vote of a majority of the board members who are not "interested persons" with respect to the fund and have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Plan or in any agreements related to the Plan or, for a Plan adopted pursuant to Rule 12b-1, by vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of such class.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT INVESTMENTS, INVESTMENT TECHNIQUES AND RISKS
See the prospectus and "Investments, Investment Techniques and Risks" and "Investment Restrictions" in Part II of this SAI to determine which policies and risks apply to your fund.
The Funds of Funds invest in Underlying Funds and, therefore, the following descriptions of investments, investment techniques and risks apply to the Underlying Funds, as applicable. To the extent a Fund of Fund's Underlying Funds invest as described below, the effect of investment risks generally would be experienced similarly for the Fund of Funds.
All Funds other than Money Market Funds
Equity securities include common stocks and certain preferred stocks, convertible securities and warrants. Equity securities fluctuate in value, often based on factors unrelated to the value of the issuer of the securities, and such fluctuations can be pronounced. Changes in the value of a fund's investments will result in changes in the value of its shares and thus the fund's total return to investors.
Investing in equity securities poses risks specific to an issuer as well as to the particular type of company issuing the equity securities. For example, equity securities of small- or mid-capitalization companies tend to have more abrupt or erratic price swings than equity securities of larger, more established companies because, among other reasons,
III-16
they trade less frequently and in lower volumes and their issuers typically are more subject to changes in earnings and prospects in that they are more susceptible to changes in economic conditions, may be more reliant on singular products or services and are more vulnerable to larger competitors. Equity securities of these types of companies may have a higher potential for gains, but also may be subject to greater risk of loss. If a fund, together with other investment companies and other clients advised by the Adviser and its affiliates, owns significant positions in portfolio companies, depending on market conditions, the fund's ability to dispose of some or all positions at a desirable time may be adversely affected. While common stockholders usually have voting rights on a number of significant matters, other types of equity securities, such as preferred stock, common limited partnership units and limited liability company interests, may not ordinarily have voting rights.
An investment in securities of companies that have no earnings or have experienced losses is generally based on a belief that actual or anticipated products or services will produce future earnings. If the anticipated event is delayed or does not occur, or if investor perception about the company changes, the company's stock price may decline sharply and its securities may become less liquid.
Investing in equity securities also poses risks specific to a particular industry, market or sector, such as technology, financial services, consumer goods or natural resources (e.g., oil and gas). To some extent, the prices of equity securities tend to move by industry, market or sector. When market conditions favorably affect, or are expected to favorably affect, an industry, the share prices of the equity securities of companies in that industry tend to rise. Conversely, negative news or a poor outlook for a particular industry can cause the share prices of such securities of companies in that industry to decline quickly.
Common Stock. Stocks and similar securities, such as common limited partnership units and limited liability company interests, represent shares of ownership in a company. After other claims are satisfied, common stockholders and other common equity owners participate in company profits on a pro-rata basis; profits may be paid out in dividends or reinvested in the company to help it grow. Increases and decreases in earnings are usually reflected in a company's common equity securities, so common equity securities generally have the greatest appreciation and depreciation potential of all corporate securities. Common stock may be received upon the conversion of convertible securities.
Preferred Stock. Preferred stock is a form of equity ownership in a corporation. Generally, preferred stock has a specified dividend and ranks after bonds and before common stocks in its claim on income for dividend payments and on assets should the company be liquidated. The market value of preferred stock generally increases when interest rates decline and decreases when interest rates rise, but, as with debt securities, also is affected by the issuer's ability or perceived ability to make payments on the preferred stock. While most preferred stocks pay a dividend, a fund may purchase preferred stock where the issuer has omitted, or is in danger of omitting, payment of its dividend. Such investments would be made primarily for their capital appreciation potential. Certain classes of preferred stock are convertible, meaning the preferred stock is convertible into shares of common stock of the issuer. Holding convertible preferred stock can provide a steady stream of dividends and the option to convert the preferred stock to common stock.
Certain convertible preferred stocks may offer enhanced yield features. These preferred stocks may feature a mandatory conversion date and may have a capital appreciation limit expressed in terms of a stated price. Other types of convertible securities may be designed to provide the investor with high current income with some prospect of future capital appreciation and may have some built-in call protection. Investors may have the right to convert such securities into shares of common stock at a preset conversion ratio or hold them until maturity. Upon maturity they may convert into either cash or a specified number of shares of common stock.
Trust preferred securities are preferred stocks issued by a special purpose trust subsidiary backed by subordinated debt of the corporate parent. These securities typically bear a market rate coupon comparable to interest rates available on debt of a similarly rated company. Holders of trust preferred securities have limited voting rights to control the activities of the trust and no voting rights with respect to the parent company.
Convertible Securities. Convertible securities include bonds, debentures, notes, preferred stocks or other securities that may be converted or exchanged (by the holder or by the issuer) into shares of the underlying common stock (or cash or securities of equivalent value) at a stated exchange ratio or predetermined price (the conversion price).
III-17
Convertible securities have characteristics similar to both equity and fixed-income securities. Convertible securities generally are subordinated to other similar but non-convertible securities of the same issuer, although convertible bonds, as corporate debt obligations, enjoy seniority in right of payment to all equity securities, and convertible preferred stock is senior to common stock of the same issuer. Because of the subordination feature, however, convertible securities typically have lower ratings than similar non-convertible securities.
Although to a lesser extent than with fixed-income securities, the market value of convertible securities tends to decline as interest rates increase and, conversely, tends to increase as interest rates decline. In addition, because of the conversion feature, the market value of convertible securities tends to vary with fluctuations in the market value of the underlying common stock. A unique feature of convertible securities is that as the market price of the underlying common stock declines, convertible securities tend to trade increasingly on a yield basis, and so may not experience market value declines to the same extent as the underlying common stock. When the market price of the underlying common stock increases, the prices of the convertible securities tend to rise as a reflection of the value of the underlying common stock. While no securities investments are without risk, investments in convertible securities generally entail less risk than investments in common stock of the same issuer.
Convertible securities provide for a stable stream of income with generally higher yields than common stocks, but there can be no assurance of current income because the issuers of the convertible securities may default on their obligations. A convertible security, in addition to providing fixed-income, offers the potential for capital appreciation through the conversion feature, which enables the holder to benefit from increases in the market price of the underlying common stock. There can be no assurance of capital appreciation, however, because securities prices fluctuate. Convertible securities generally offer lower interest or dividend yields than non-convertible securities of similar quality because of the potential for capital appreciation.
Synthetic Convertible Securities. So-called "synthetic convertible securities" are comprised of two or more different securities, each with its own market value, whose investment characteristics, taken together, resemble those of convertible securities. An example is a non-convertible debt security and a warrant or option. The "market value" of a synthetic convertible is the combined value of its fixed-income component and its convertible component. For this reason, the values of a synthetic convertible and a true convertible security may respond differently to market fluctuations.
Warrants and Stock Purchase Rights. Warrants or stock purchase rights ("rights") give the holder the right to subscribe to equity securities at a specific price for a specified period of time. Warrants and rights are subject to the same market risk as stocks, but may be more volatile in price. A fund's investment in warrants and rights will not entitle it to receive dividends or exercise voting rights, provide no rights with respect to the assets of the issuer and will become worthless if not profitably exercised before the expiration date. Warrants, rights or other non-income producing equity securities may be received in connection with a fund's investments in corporate debt securities (further described below), or restructuring of investments. Bonds with warrants attached to purchase equity securities have many characteristics of convertible bonds and their prices may, to some degree, reflect the performance of the underlying stock.
IPOs. An IPO is a corporation's first offering of stock to the public. Shares are given a market value reflecting expectations for the corporation's future growth. Special rules of FINRA apply to the distribution of IPOs. Corporations offering IPOs generally have limited operating histories and may involve greater investment risk. Special risks associated with IPOs may include a limited number of shares available for trading, unseasoned trading, lack of investor knowledge of the company, and limited operating history, all of which may contribute to price volatility. The limited number of shares available for trading in some IPOs may make it more difficult for a fund to buy or sell significant amounts of shares without an unfavorable impact on prevailing prices. In addition, some IPOs are involved in relatively new industries or lines of business, which may not be widely understood by investors. Some of the companies involved in new industries may be regarded as developmental stage companies, without revenues or operating income, or the near-term prospects of such. Foreign IPOs are subject to foreign political and currency risks. Many IPOs are issued by undercapitalized companies of small or microcap size. The prices of these companies' securities can be very volatile, rising and falling rapidly, sometimes based solely on investor perceptions rather than economic reasons.
III-18
Fixed-income securities include interest-bearing securities, such as corporate debt securities. Interest-bearing securities are investments which promise a stable stream of income, although the prices of fixed rate fixed-income securities are inversely affected by changes in interest rates and, therefore, are subject to interest rate risk, as well as the risk of unrelated market price fluctuations. Fixed-income securities may have various interest rate payment and reset terms, including fixed rate, floating or adjustable rate, zero coupon, contingent, deferred, payment in kind and auction rate features. Floating rate instruments, the rates of which adjust periodically by reference to another measure, such as the market interest rate, are generally less sensitive to interest rate changes than fixed rate instruments, although the value of floating rate loans and other floating rate securities may decline if their interest rates do not rise as quickly, or as much, as general interest rates or as expected. Certain securities, such as those with interest rates that fluctuate directly or indirectly based on multiples of a stated index, are designed to be highly sensitive to changes in interest rates and can subject the holders thereof to extreme reductions of yield and possibly loss of principal. Certain fixed-income securities may be issued at a discount from their face value or purchased at a price less than their stated face amount or at a price less than their issue price plus the portion of "original issue discount" previously accrued thereon, i.e., purchased at a "market discount." The amount of original issue discount and/or market discount on certain obligations may be significant, and accretion of market discount together with original issue discount, will cause a fund to realize income prior to the receipt of cash payments with respect to these securities. To maintain its qualification as a regulated investment company and avoid liability for federal income taxes, a fund may be required to distribute such income accrued with respect to these securities and may have to dispose of portfolio securities under disadvantageous circumstances in order to generate cash to satisfy these distribution requirements.
Failure of an issuer to make timely interest or principal payments, or a decline or perception of a decline in the credit quality of a fixed-income security (known as credit risk), can cause the security's price to fall, potentially lowering a fund's share price. The values of fixed-income securities also may be affected by changes in the credit rating of the issuer. Once the rating of a portfolio security has been changed, a fund will consider all circumstances deemed relevant in determining whether to continue to hold the security. Fixed-income securities rated below investment grade by the Rating Agencies may be subject to greater risks with respect to the issuing entity and to greater market fluctuations (and not necessarily inversely with changes in interest rates) than certain lower yielding, higher-rated fixed-income securities. See "High Yield and Lower-Rated Securities" below for a discussion of those securities and see "Rating Categories" below for a general description of the Rating Agencies' ratings.
As a measure of a fixed-income security's cash flow, duration is an alternative to the concept of "term to maturity" in assessing the price volatility associated with changes in interest rates (known as interest rate risk). Generally, the longer the duration, the more volatility an investor should expect. For example, the market price of a bond with a duration of three years would be expected to decline 3% if interest rates rose 1%. Conversely, the market price of the same bond would be expected to increase 3% if interest rates fell 1%. The market price of a bond with a duration of six years would be expected to increase or decline twice as much as the market price of a bond with a three-year duration. Duration is a way of measuring a security's maturity in terms of the average time required to receive the present value of all interest and principal payments as opposed to its term to maturity. The maturity of a security measures only the time until final payment is due; it does not take account of the pattern of a security's cash flows over time, which would include how cash flow is affected by prepayments and by changes in interest rates. Incorporating a security's yield, coupon interest payments, final maturity and option features into one measure, duration is computed by determining the weighted average maturity of a bond's cash flows, where the present values of the cash flows serve as weights. In computing the duration of a fund, the Adviser will estimate the duration of obligations that are subject to features such as prepayment or redemption by the issuer, put options retained by the investor or other imbedded options, taking into account the influence of interest rates on prepayments and coupon flows.
Average weighted maturity is the length of time, in days or years, until the securities held by a fund, on average, will mature or be redeemed by their issuers. The average maturity is weighted according to the dollar amounts invested in the various securities by the fund. In general, the longer a fund's average weighted maturity, the more its share price will fluctuate in response to changing interest rates. For purposes of calculating average effective portfolio maturity, a security that is subject to redemption at the option of the issuer on a particular date (the "call date") which is prior to the security's stated maturity may be deemed to mature on the call date rather than on its stated
III-19
maturity date. The call date of a security will be used to calculate average effective portfolio maturity when the Adviser reasonably anticipates, based upon information available to it, that the issuer will exercise its right to redeem the security. The Adviser may base its conclusion on such factors as the interest rate paid on the security compared to prevailing market rates, the amount of cash available to the issuer of the security, events affecting the issuer of the security, and other factors that may compel or make it advantageous for the issuer to redeem a security prior to its stated maturity.
When interest rates fall, the principal on certain fixed-income securities, including mortgage-backed and certain asset-backed securities (discussed below), may be prepaid. The loss of higher yielding underlying mortgages and the reinvestment of proceeds at lower interest rates can reduce a fund's potential price gain in response to falling interest rates, reduce the fund's yield, or cause the fund's share price to fall. This is known as prepayment risk. Conversely, when interest rates rise, the effective duration of a fund's fixed rate mortgage-related and other asset-backed securities may lengthen due to a drop in prepayments of the underlying mortgages or other assets. This is known as extension risk and would increase the fund's sensitivity to rising interest rates and its potential for price declines.
U.S. Government Securities. U.S. Government securities are issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities. U.S. Government securities include Treasury bills, Treasury notes and Treasury bonds, which differ in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance. Treasury bills have initial maturities of one year or less; Treasury notes have initial maturities of one to ten years; and Treasury bonds generally have initial maturities of greater than ten years. Some obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies and instrumentalities are supported by the full faith and credit of the Treasury; others by the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury; others by discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase certain obligations of the agency or instrumentality; and others only by the credit of the agency or instrumentality. These securities bear fixed, floating or variable rates of interest. While the U.S. Government currently provides financial support to such U.S. Government-sponsored agencies or instrumentalities, no assurance can be given that it will always do so, since it is not so obligated by law. A security backed by the Treasury or the full faith and credit of the United States is guaranteed only as to timely payment of interest and principal when held to maturity. Neither the market value nor a fund's share price is guaranteed.
TIPS are issued by the Treasury and are designed to provide investors a long-term investment vehicle that is not vulnerable to inflation. The interest rate paid by TIPS is fixed, while the principal value rises or falls semi-annually based on changes in a published Consumer Price Index. Thus, if inflation occurs, the principal and interest payments on the TIPS are adjusted accordingly to protect investors from inflationary loss. During a deflationary period, the principal and interest payments decrease, although the TIPS' principal will not drop below its face value at maturity. In exchange for the inflation protection, TIPS generally pay lower interest rates than typical Treasury securities. Only if inflation occurs will TIPS offer a higher real yield than a conventional Treasury bond of the same maturity. The secondary market for TIPS may not be as active or liquid as the secondary market for conventional Treasury securities. Principal appreciation and interest payments on TIPS generally will be taxed annually as ordinary interest income or original issue discount for federal income tax calculations. As a result, any appreciation in principal generally will be counted as income in the year the increase occurs, even though the investor will not receive such amounts until the TIPS are sold or mature. Principal appreciation and interest payments will be exempt from state and local income taxes. See also "Inflation-Indexed Securities" below.
Many states grant tax-free status to dividends paid to shareholders of a fund from interest income earned by that fund from direct obligations of the U.S. Government, subject in some states to minimum investment requirements that must be met by the fund. Investments in securities issued by the GNMA or FNMA, bankers' acceptances, commercial paper and repurchase agreements collateralized by U.S. Government securities do not generally qualify for tax-free treatment.
On August 5, 2011, S&P lowered its long-term sovereign credit rating for the United States of America to "AA+" from "AAA." The value of shares of a fund that may invest in U.S. Government obligations may be adversely affected by S&P's downgrade or any future downgrades of the U.S. Government's credit rating. While the long-term impact of the downgrade is uncertain, it could, for example, lead to increased volatility in the short-term.
Corporate Debt Securities. Corporate debt securities include corporate bonds, debentures, notes and other similar
III-20
instruments, including certain convertible securities. Debt securities may be acquired with warrants attached to purchase additional fixed-income securities at the same coupon rate. A decline in interest rates would permit a fund to buy additional bonds at the favorable rate or to sell the warrants at a profit. If interest rates rise, the warrants would generally expire with no value. Corporate income-producing securities also may include forms of preferred or preference stock, which may be considered equity securities. The rate of interest on a corporate debt security may be fixed, floating or variable, and may vary inversely with respect to a reference rate such as interest rates or other financial indicators. The rate of return or return of principal on some debt obligations may be linked or indexed to the level of exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and a foreign currency or currencies. Such securities may include those whose principal amount or redemption price is indexed to, and thus varies directly with, changes in the market price of certain commodities, including gold bullion or other precious metals.
Ratings of Securities; Unrated Securities. Subsequent to its purchase by a fund, an issue of rated securities may cease to be rated or its rating may be reduced below any minimum that may be required for purchase by a fund. Neither event will require the sale of such securities by the fund, but the Adviser will consider such event in determining whether the fund should continue to hold the securities. In addition, it is possible that a Rating Agency might not timely change its ratings of a particular issue to reflect subsequent events. To the extent the ratings given by a Rating Agency for any securities change as a result of changes in such organizations or their rating systems, a fund will attempt to use comparable ratings as standards for its investments in accordance with its investment policies.
A fund may purchase unrated securities, which are not rated by a Rating Agency but that the Adviser determines are of comparable quality to the rated securities in which the fund may invest. Unrated securities may be less liquid than comparable rated securities, because dealers may not maintain daily markets in such securities and retail markets for many of these securities may not exist. As a result, a fund's ability to sell these securities when, and at a price, the Adviser deems appropriate may be diminished. Investing in unrated securities involves the risk that the Adviser may not accurately evaluate the security's comparative credit rating. To the extent that a fund invests in unrated securities, the fund's success in achieving its investment objective(s) may depend more heavily on the Adviser's credit analysis than if the fund invested exclusively in rated securities.
High Yield and Lower-Rated Securities. Fixed-income securities rated below investment grade, such as those rated Ba by Moody's or BB by S&P and Fitch, and as low as those rated Caa/CCC by Rating Agencies at the time of purchase (commonly known as "high yield" or "junk" bonds), or, if unrated, deemed to be of comparable quality by the Adviser, though higher yielding, are characterized by higher risk. See "Rating Categories" below for a general description of securities ratings. These securities may be subject to certain risks with respect to the issuing entity and to greater market fluctuations than certain lower yielding, higher-rated securities. These securities generally are considered by the Rating Agencies to be, on balance, predominantly speculative with respect to the issuer's ability to make principal and interest payments in accordance with the terms of the obligation and generally will involve more credit risk than securities in the higher rating categories. The ratings of Rating Agencies represent their opinions as to the quality of the obligations which they undertake to rate. It should be emphasized, however, that ratings are relative and subjective and are not absolute standards of quality and, although ratings may be useful in evaluating the safety or interest and principal payments, they do not evaluate the market value risk of such obligations. Although these ratings may be an initial criterion for selection of portfolio investments, the Adviser also will evaluate these securities and the ability of the issuers of such securities to pay interest and principal based upon financial and other available information. The success of a fund's investments in lower-rated securities may be more dependent on the Adviser's credit analysis than might be the case for investments in higher-rated securities.
Bond prices generally are inversely related to interest rate changes; however, bond price volatility also may be inversely related to coupon. Accordingly, below investment grade securities may be relatively less sensitive to interest rate changes than higher quality securities of comparable maturity, because of their higher coupon. This higher coupon is what the investor receives in return for bearing greater credit risk. The higher credit risk associated with below investment grade securities potentially can have a greater effect on the value of such securities than may be the case with higher quality issues of comparable maturity, and will be a substantial factor in a fund's relative share price volatility.
The prices of these securities can fall dramatically in response to negative news about the issuer or its industry. The market values of many of these securities also tend to be more sensitive to general economic conditions than are
III-21
higher-rated securities and will fluctuate over time. Companies that issue certain of these securities often are highly leveraged and may not have available to them more traditional methods of financing. Therefore, the risk associated with acquiring the securities of such issuers generally is greater than is the case with the higher-rated securities. These securities may be particularly susceptible to economic downturns. For example, during an economic downturn or a sustained period of rising interest rates, highly leveraged issuers of these securities may not have sufficient revenues to meet their interest payment obligations. The issuer's ability to service its debt obligations also may be affected adversely by specific corporate developments, forecasts, or the unavailability of additional financing. The risk of loss because of default by the issuer is significantly greater for the holders of these securities because such securities generally are unsecured and often are subordinated to other creditors of the issuer. It is likely that an economic recession also would disrupt severely the market for such securities and have an adverse impact on their value.
Because there is no established retail secondary market for many of these securities, it may be anticipated that such securities could be sold only to a limited number of dealers or institutional investors. To the extent a secondary trading market for these securities does exist, it generally is not as liquid as the secondary market for higher-rated securities. The lack of a liquid secondary market may have an adverse impact on market price and yield and a fund's ability to dispose of particular issues when necessary to meet the fund's liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as a deterioration in the creditworthiness of the issuer. The lack of a liquid secondary market for certain securities also may make it more difficult for a fund to obtain accurate market quotations for purposes of valuing the fund's portfolio and calculating its NAV. Adverse conditions could make it difficult at times for a fund to sell certain securities or could result in lower prices than those used in calculating the fund's NAV. Adverse publicity and investor perceptions, whether or not based on fundamental analysis, may decrease the values and liquidity of these securities. In such cases, the Adviser's judgment may play a greater role in valuation because less reliable, objective data may be available.
Certain funds may invest in these securities when their issuers will be close to, or already have entered, reorganization proceedings. As a result, it is expected that these securities will cease or will have ceased to meet their interest payment obligations, and accordingly would trade in much the same manner as an equity security. Consequently, a fund would intend to make such investments on the basis of potential appreciation in the price of these securities, rather than any expectation of realizing income. Reorganization entails a complete change in the structure of a business entity. An attempted reorganization may be unsuccessful, resulting in substantial or total loss of amounts invested. If reorganization is successful, the value of securities of the restructured entity may depend on numerous factors, including the structure of the reorganization, the market success of the entity's products or services, the entity's management, and the overall strength of the marketplace.
High yield, lower-rated securities acquired during an initial offering may involve special risks because they are new issues. A fund will not have any arrangement with any person concerning the acquisition of such securities.
Distressed and Defaulted Securities. Investing in securities that are the subject of bankruptcy proceedings or in default or at risk of being in default as to the repayment of principal and/or interest at the time of acquisition by a fund ("Distressed Securities") is speculative and involves significant risks.
A fund may make such investments when, among other circumstances, the Adviser believes it is reasonably likely that the issuer of the Distressed Securities will make an exchange offer or will be the subject of a plan of reorganization pursuant to which the fund will receive new securities in return for the Distressed Securities. There can be no assurance, however, that such an exchange offer will be made or that such a plan of reorganization will be adopted. In addition, a significant period of time may pass between the time at which a fund makes its investment in Distressed Securities and the time that any such exchange offer or plan of reorganization is completed, if at all. During this period, it is unlikely that the fund would receive any interest payments on the Distressed Securities, the fund would be subject to significant uncertainty whether the exchange offer or plan of reorganization will be completed and the fund may be required to bear certain extraordinary expenses to protect and recover its investment. A fund also will be subject to significant uncertainty as to when, in what manner and for what value the obligations evidenced by the Distressed Securities will eventually be satisfied (e.g., through a liquidation of the obligor's assets, an exchange offer or plan of reorganization involving the Distressed Securities or a payment of some amount in satisfaction of the obligation). Even if an exchange offer is made or plan of reorganization is adopted with respect to Distressed Securities held by a fund, there can be no assurance that the securities or other assets received by the fund
III-22
in connection with the exchange offer or plan of reorganization will not have a lower value or income potential than may have been anticipated when the investment was made, or no value. Moreover, any securities received by a fund upon completion of an exchange offer or plan of reorganization may be restricted as to resale. Similarly, if a fund participates in negotiations with respect to any exchange offer or plan of reorganization with respect to an issuer of Distressed Securities, the fund may be restricted from disposing of such securities for a period of time. To the extent that a fund becomes involved in such proceedings, the fund may have a more active participation in the affairs of the issuer than that assumed generally by an investor.
Zero Coupon, Pay-In-Kind and Step-Up Securities. Zero coupon securities are issued or sold at a discount from their face value and do not entitle the holder to any periodic payment of interest prior to maturity or a specified redemption date or cash payment date. Zero coupon securities also may take the form of notes and bonds that have been stripped of their unmatured interest coupons, the coupons themselves and receipts or certificates representing interests in such stripped debt obligations and coupons. Zero coupon securities issued by corporations and financial institutions typically constitute a proportionate ownership of the issuer's pool of underlying Treasury securities. A zero coupon security pays no interest to its holders during its life and is sold at a discount to its face value at maturity. The amount of any discount varies depending on the time remaining until maturity or cash payment date, prevailing interest rates, liquidity of the security and perceived credit quality of the issuer. Pay-in-kind securities generally pay interest through the issuance of additional securities. Step-up coupon bonds are debt securities that typically do not pay interest for a specified period of time and then pay interest at a series of different rates. The amount of any discount on these securities varies depending on the time remaining until maturity or cash payment date, prevailing interest rates, liquidity of the security and perceived credit quality of the issuer. The market prices of these securities generally are more volatile and are likely to respond to a greater degree to changes in interest rates than the market prices of securities that pay cash interest periodically having similar maturities and credit qualities. In addition, unlike bonds that pay cash interest throughout the period to maturity, a fund will realize no cash until the cash payment date unless a portion of such securities are sold and, if the issuer defaults, the fund may obtain no return at all on its investment. Federal income tax law requires the holder of a zero coupon security or of certain pay-in-kind or step-up bonds to accrue income with respect to these securities prior to the receipt of cash payments. To maintain its qualification as a regulated investment company and avoid liability for federal income taxes, a fund may be required to distribute such income accrued with respect to these securities and may have to dispose of portfolio securities under disadvantageous circumstances in order to generate cash to satisfy these distribution requirements.
The credit risk factors pertaining to high-yield, lower-rated securities (discussed above) also apply to lower-rated zero coupon, pay-in-kind and step-up securities. In addition to the risks associated with the credit rating of the issuers, the market prices of these securities may be very volatile during the period no interest is paid.
Inflation-Indexed Securities. Inflation-indexed securities, such as TIPS, are fixed-income securities whose value is periodically adjusted according to the rate of inflation. Two structures are common. The Treasury and some other issuers utilize a structure that accrues inflation into the principal value of the bond. Most other issuers pay out the Consumer Price Index accruals as part of a semi-annual coupon.
Inflation-indexed securities issued by the Treasury have varying maturities and pay interest on a semi-annual basis equal to a fixed percentage of the inflation-adjusted principal amount. If the periodic adjustment rate measuring inflation falls, the principal value of inflation-index bonds will be adjusted downward, and consequently the interest payable on these securities (calculated with respect to a smaller principal amount) will be reduced. Repayment of the original bond principal upon maturity (as adjusted for inflation) is guaranteed in the case of Treasury inflation-indexed bonds, even during a period of deflation. However, the current market value of the bonds is not guaranteed and will fluctuate. Other inflation-related bonds may or may not provide a similar guarantee. If a guarantee of principal is not provided, the adjusted principal value of the bond repaid at maturity may be less than the original principal amount.
The periodic adjustment of U.S. inflation-indexed securities is tied to the Consumer Price Index for Urban Consumers ("CPI-U"), which is calculated monthly by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The CPI-U is a measurement of changes in the cost of living, made up of components such as housing, food, transportation and energy. Inflation-indexed securities issued by a foreign government are generally adjusted to reflect a comparable inflation index calculated by that government. There can be no assurance that the CPI-U or any foreign inflation
III-23
index will accurately measure the real rate of inflation in the prices of goods and services. Moreover, there can be no assurance that the rate of inflation in a foreign country will be correlated to the rate of inflation in the United States.
The value of inflation-indexed securities is expected to change in response to changes in real interest rates. Real interest rates in turn are tied to the relationship between nominal interest rates and the rate of inflation. Therefore, if the rate of inflation rises at a faster rate than nominal interest rates, real interest rates might decline, leading to an increase in value of inflation-indexed securities. In contrast, if nominal interest rates increase at a faster rate than inflation, real interest rates might rise, leading to a decrease in value of inflation-index securities. Any increase in the principal amount of an inflation-indexed security generally will be considered taxable ordinary income, even though investors do not receive their principal until maturity. While these securities are expected to be protected from long-term inflationary trends, short-term increases in inflation may lead to a decline in value. If interest rates rise due to reasons other than inflation (for example, due to changes in currency exchange rates), investors in these securities may not be protected to the extent that the increase is not reflected in the security's inflation measure.
Variable and Floating Rate Securities. Variable and floating rate securities provide for adjustment in the interest rate paid on the obligations. The terms of such obligations typically provide that interest rates are adjusted based upon an interest or market rate adjustment as provided in the respective obligations. The adjustment intervals may be regular, and range from daily up to annually, or may be event-based, such as based on a change in the prime rate. Variable rate obligations typically provide for a specified periodic adjustment in the interest rate, while floating rate obligations typically have an interest rate which changes whenever there is a change in the external interest or market rate. Because of the interest rate adjustment feature, variable and floating rate securities provide a fund with a certain degree of protection against rises in interest rates, although the fund will participate in any declines in interest rates as well. Generally, changes in interest rates will have a smaller effect on the market value of variable and floating rate securities than on the market value of comparable fixed-income obligations. Thus, investing in variable and floating rate securities generally allows less opportunity for capital appreciation and depreciation than investing in comparable fixed-income securities.
Variable Rate Demand Notes. Variable rate demand notes include master demand notes, which are obligations that permit a fund to invest fluctuating amounts, at varying rates of interest, pursuant to direct arrangements between the fund, as lender, and the borrower. These obligations permit daily changes in the amounts borrowed. Because these obligations are direct lending arrangements between the lender and borrower, it is not contemplated that such instruments generally will be traded, and there generally is no established secondary market for these obligations, although they are redeemable on demand at face value, plus accrued interest. Accordingly, where these obligations are not secured by letters of credit or other credit support arrangements, the fund's right to redeem is dependent on the ability of the borrower to pay principal and interest on demand. Such obligations frequently are not rated by credit rating agencies. Changes in the credit quality of banks or other financial institutions providing any credit support or liquidity enhancements could cause losses to the fund.
Floating and Inverse Floating Rate Debt Instruments. The interest rate on a floating rate debt instrument ("floater") is a variable rate which is tied to another interest rate, such as a prime rate or Treasury bill rate. The interest rate on an inverse floating rate debt instrument moves or resets in the opposite direction from the market rate of interest to which the inverse floater is indexed or inversely to a multiple of the applicable index. An inverse floating rate debt instrument may exhibit greater price volatility than a fixed rate obligation of similar credit quality, and investing in these instruments involves leveraging which may magnify gains or losses.
Loans. Senior secured loans ("Senior Loans") typically hold a first lien priority and, like other types of loans, pay interest at rates that are determined daily, monthly, quarterly or semi-annually on the basis of a floating base lending rate plus a premium or credit spread. These base lending rates are primarily LIBOR and secondarily the prime rate offered by one or more major U.S. banks and the certificate of deposit rate or other base lending rates used by commercial lenders. As short-term interest rates increase, interest payable to a fund from its investments in loans is likely to increase, and as short-term interest rates decrease, interest payable to the fund from its investments in loans is likely to decrease. To the extent a fund invests in loans with a base lending rate floor, the fund's potential for decreased income in a flat or falling rate environment may be mitigated, but the fund may not receive the benefit of increased coupon payments if the relevant interest rate increases but remains below the base lending rate floor.
III-24
Loans in which a fund may invest are typically made to U.S. and, to a limited extent, non-U.S. corporations, partnerships and other business entities that operate in various industries and geographical regions (a "Borrower"). Borrowers may obtain loans to, among other reasons, refinance existing debt and for acquisitions, dividends, leveraged buyouts and general corporate purposes. Subordinated loans generally have the same characteristics as Senior Loans except that such loans are subordinated in payment and/or lower in lien priority to first lien holders or may be unsecured.
Senior Loans hold the most senior position in the capital structure of a Borrower, are secured with specific collateral and have a claim on the assets and/or stock of the Borrower that is senior to that held by unsecured creditors, subordinated debt holders and stockholders of the Borrower. Typically, in order to borrow money pursuant to a Senior Loan, a Borrower will, for the term of the Senior Loan, pledge collateral, including, but not limited to: (i) working capital assets, such as accounts receivable and inventory, (ii) tangible fixed assets, such as real property, buildings and equipment, (iii) intangible assets, such as trademarks and patent rights (but excluding goodwill) and (iv) security interests in shares of stock of subsidiaries or affiliates. In the case of Senior Loans made to non-public companies, the company's shareholders or owners may provide collateral in the form of secured guarantees and/or security interests in assets that they own. In many instances, a Senior Loan may be secured only by stock in the Borrower or its subsidiaries. Collateral may consist of assets that may not be readily liquidated, and there is no assurance that the liquidation of such assets would satisfy fully a Borrower's obligations under a Senior Loan.
A Borrower must comply with various restrictive covenants contained in a loan agreement or note purchase agreement between the Borrower and the holders of a loan (the "Loan Agreement"). In a typical loan, an agent (the "Agent Bank") administers the terms of the Loan Agreement. In such cases, the Agent Bank is normally responsible for the collection of principal and interest payments from the Borrower and the apportionment of these payments to the credit of all institutions that are parties to the Loan Agreement. A fund will generally rely upon the Agent Bank or an intermediate participant to receive and forward to the fund its portion of the principal and interest payments on the loan. Additionally, a fund normally will rely on the Agent Bank and the other loan investors to use appropriate credit remedies against the Borrower. The Agent Bank is typically responsible for monitoring compliance with covenants contained in the Loan Agreement based upon reports prepared by the Borrower. The Agent Bank may monitor the value of any collateral and, if the value of the collateral declines, may accelerate the loan, may give the Borrower an opportunity to provide additional collateral or may seek other protection for the benefit of the participants in the loan. The Agent Bank is compensated by the Borrower for providing these services under a Loan Agreement, and such compensation may include special fees paid upon structuring and funding the Senior Loan and other fees paid on a continuing basis. With respect to loans for which the Agent Bank does not perform such administrative and enforcement functions, the Adviser may perform such tasks on a fund's behalf, although a collateral bank will typically hold any collateral on behalf of the fund and the other loan investors pursuant to the applicable Loan Agreement.
In the process of buying, selling and holding loans, a fund may receive and/or pay certain fees. These fees are in addition to interest payments received and may include facility fees, commitment fees, amendment fees, commissions and prepayment penalty fees. When a fund buys a loan it may receive a facility fee and when it sells a loan it may pay a facility fee. On an ongoing basis, a fund may receive a commitment fee based on the undrawn portion of the underlying line of credit portion of a loan. In certain circumstances, a fund may receive a prepayment penalty fee upon the prepayment of a loan by a Borrower. Other fees received by a fund may include covenant waiver fees, covenant modification fees or other amendment fees.
Offerings of Senior Loans and other loans in which a fund may invest generally are not registered with the SEC, or any state securities commission, and are not listed on any national securities exchange. Because there is less readily available or reliable information about most loans than is the case for many other types of securities, the Adviser will rely primarily on its own evaluation of a Borrower's credit quality rather than on any available independent sources. Therefore, a fund investing in loans will be particularly dependent on the analytical abilities of the Adviser. No active trading market may exist for some loans, which may make it difficult to value them. Some loans may be subject to restrictions on resale. In some cases, negotiations involved in disposing of indebtedness may require weeks to complete. Any secondary market for loans may be subject to irregular trading activity, wide bid/ask spreads and extended trade settlement periods, which may impair the ability of a seller to realize full value and thus cause a material decline in a fund's net asset value. In addition, a fund may not be able to readily dispose of its loans at prices that approximate those at which the fund could sell such loans if they were more widely-traded and, as a
III-25
result of such illiquidity, the fund may have to sell other investments or engage in borrowing transactions if necessary to raise cash to meet its obligations. If a fund's investments are focused on loans, a limited supply or relative illiquidity of loans may adversely affect a fund's yield.
The settlements of secondary market purchases of Senior Loans in the ordinary course, on a settlement date beyond the period expected by loan market participants (i.e., T+7 for par loans and T+20 for distressed loans, in other words more than seven or twenty business days beyond the trade date, respectively), are subject to the delayed compensation mechanics prescribed by the Loan Syndications and Trading Association (''LSTA''). For par loans, for example, income accrues to the buyer of the loan (the ''Buyer'') during the period beginning on the last date by which the loan purchase should have settled (T+7) to and including the actual settlement date. Should settlement of a par loan purchased in the secondary market be delayed beyond the T+7 period prescribed by the LSTA, the Buyer is typically compensated for such delay through a payment from the seller of the loan (this payment may be netted from the wire released on settlement date for the purchase price of the loan paid by the Buyer). In brief, the adjustment is typically calculated by multiplying the notional amount of the trade by the applicable margin in the Loan Agreement pro rated for the number of business days (calculated using a year of 360 days) beyond the settlement period prescribed by the LSTA, plus any amendment or consent fees that the Buyer should have received. Furthermore, the purchase of a Senior Loan in the secondary market is typically negotiated and finalized pursuant to a binding trade confirmation, and, therefore, the risk of non-delivery of the security to the fund is reduced or eliminated.
A fund may purchase and retain in its portfolio loans where the Borrower has experienced, or may be perceived to be likely to experience, credit problems, including involvement in or recent emergence from bankruptcy court proceedings or other forms of debt restructuring. Such investments may provide opportunities for enhanced income, although they also will be subject to greater risk of loss. At times, in connection with the restructuring of a loan either outside of bankruptcy court or in the context of bankruptcy court proceedings, a fund may determine or be required to accept equity securities or junior credit securities in exchange for all or a portion of a loan. A fund may from time to time participate on ad-hoc committees formed by creditors to negotiate with the management of financially troubled Borrowers and may incur legal fees as a result of such participation. In addition, such participation may restrict the fund's ability to trade in or acquire additional positions in a particular security when it might otherwise desire to do so. Participation by a fund also may expose the fund to potential liabilities under bankruptcy or other laws governing the rights of creditors and debtors.
Loans are usually rated below investment grade and may also be unrated. As a result, the risks associated with investing in loans are similar to the risks of fixed-income securities rated below investment grade, although Senior Loans are senior and secured, in contrast to other fixed-income securities rated below investment grade, which are often subordinated and/or unsecured. Any specific collateral used to secure a loan, however, may decline in value or become illiquid, which would adversely affect the loan's value. Loans are subject to a number of risks described elsewhere in this SAI section titled "Fixed-Income Securities," including non-payment of principal and interest, liquidity risk and the risk of investing in fixed-income securities rated below investment grade.
Investing in loans is subject to legislative risk. If legislation or state or federal regulations impose additional requirements or restrictions on the ability of financial institutions to make loans, the availability of Senior Loans and other types of loans for investment by a fund may be adversely affected. In addition, such requirements or restrictions could reduce or eliminate sources of financing for certain issuers. This would increase the risk of default. If legislation or federal or state regulations require financial institutions to increase their capital requirements, this may cause financial institutions to dispose of loans that are considered highly levered transactions. If a fund attempts to sell a loan at a time when a financial institution is engaging in such a sale, the price the fund could receive for the loan may be adversely affected.
Subordinated loans generally are subject to similar risks as those associated with investments in Senior Loans, except that such loans are subordinated in payment and/or lower in lien priority to first lien holders or may be unsecured. In the event of default on a subordinated loan, the first priority lien holder has first claim to the underlying collateral of the loan. These loans are subject to the additional risk that the cash flow of the Borrower and property securing the loan or debt, if any, may be insufficient to meet scheduled payments after giving effect to the senior unsecured or senior secured obligations of the Borrower. This risk is generally higher for subordinated unsecured loans or debt that is not backed by a security interest in any specific collateral. Subordinated loans generally have greater price volatility than Senior Loans and may be less liquid.
III-26
The Adviser and/or its affiliates may participate in the primary and secondary market for loans. Because of limitations imposed by applicable law, the presence of the Adviser and/or the Adviser's affiliates in the loan market may restrict a fund's ability to acquire certain loans, or affect the timing or price of such acquisitions. Also, because the Adviser, in the course of investing fund assets in loans, may have access to material non-public information regarding a Borrower, the ability of a fund or funds advised by such Adviser to purchase or sell publicly-traded securities of such Borrowers may be restricted. Conversely, because of the financial services and asset management activities of the Adviser and/or its affiliates, the Adviser may not have access to material non-public information regarding the Borrower to which other lenders have access.
Participation Interests and Assignments. Loans may be originated, negotiated and structured by a syndicate of lenders ("Co-Lenders"), consisting of commercial banks, thrift institutions, insurance companies, financial companies or other financial institutions one or more of which acts as Agent Bank. Co-Lenders may sell such securities to third parties called "Participants." A fund investing in such securities may participate as a Co-Lender at origination or acquire an interest in the security (a "participation interest") from a Co-Lender or a Participant. Co-Lenders and Participants interposed between a fund and the Borrower, together with the Agent Bank(s), are referred herein as "Intermediate Participants." A participation interest gives a fund an undivided interest in the security in the proportion that the fund's participation interest bears to the total principal amount of the security. These instruments may have fixed, floating or variable rates of interest.
A fund may purchase a participation interest in a portion of the rights of an Intermediate Participant, which would not establish any direct relationship between the fund and the Borrower. The fund would be required to rely on the Intermediate Participant that sold the participation interest not only for the enforcement of the fund's rights against the Borrower but also for the receipt and processing of payments due to the fund under the security. The fund would have the right to receive payments of principal, interest and any fees to which it is entitled only from the Intermediate Participant and only upon receipt of the payments from the Borrower. The fund generally will have no right to enforce compliance by the Borrower with the terms of the Loan Agreement nor any rights of set-off against the Borrower, and the fund may not directly benefit from any collateral supporting the obligation in which it has purchased the participation interest. Because it may be necessary to assert through an Intermediate Participant such rights as may exist against the Borrower, in the event the Borrower fails to pay principal and interest when due, the fund may be subject to delays, expenses and risks that are greater than those that would be involved if the fund would enforce its rights directly against the Borrower. Moreover, under the terms of a participation interest, a fund may be regarded as a creditor of the Intermediate Participant (rather than of the Borrower), so that the fund may also be subject to the risk that the Intermediate Participant may become insolvent. In the event of the insolvency of the Intermediate Participant, the fund may be treated as a general creditor of the Intermediate Participant and may not benefit from any set-off between the Intermediate Participant and the Borrower. Certain participation interests may be structured in a manner designed to avoid purchasers being subject to the credit risk of the Intermediate Participant, but even under such a structure, in the event of the Intermediate Participant's insolvency, the Intermediate Participant's servicing of the participation interests may be delayed and the assignability of the participation interest impaired. Similar risks may arise with respect to the Agent Bank if, for example, assets held by the Agent Bank for the benefit of a fund were determined by the appropriate regulatory authority or court to be subject to the claims of the Agent Bank's creditors. In such case, the fund might incur certain costs and delays in realizing payment in connection with the participation interest or suffer a loss of principal and/or interest. Further, in the event of the bankruptcy or insolvency of the Borrower, the obligation of the Borrower to repay the loan may be subject to certain defenses that can be asserted by such Borrower as a result of improper conduct by the Agent Bank or Intermediate Participant.
A fund may invest in the underlying loan to the Borrower through an assignment of all or a portion of such loan ("Assignments") from a third party. When the fund purchases Assignments from Co-Lenders it will acquire direct rights against the Borrower on the loan. Because Assignments are arranged through private negotiations between potential assignees and potential assignors, however, the rights and obligations acquired by the fund as the purchaser of an Assignment may differ from, and be more limited than, those held by the assigning Co-Lender.
A fund may have difficulty disposing of participation interests and Assignments because to do so it will have to sell such securities to a third party. Because there is no established secondary market for such securities, it is anticipated that such securities could be sold only to a limited number of institutional investors. The lack of an established secondary market may have an adverse impact on the value of such securities and the fund's ability to dispose of
III-27
particular participation interests or Assignments when necessary to meet the fund's liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as a deterioration in the creditworthiness of the Borrower. The lack of an established secondary market for participation interests and Assignments also may make it more difficult for the fund to assign a value to these securities for purposes of valuing the fund's portfolio and calculating its NAV.
Mortgage-Related Securities. Mortgage-related securities are a form of derivative collateralized by pools of residential or commercial mortgages. Pools of mortgage loans are assembled as securities for sale to investors by various governmental, government-related and private organizations. These securities may include complex instruments such as collateralized mortgage obligations ("CMOs") and stripped mortgage-backed securities, mortgage pass-through securities, interests in REMICs, adjustable rate mortgage loans, or other kinds of mortgage-backed securities, including those with fixed, floating and variable interest rates; interest rates based on multiples of changes in a specified index of interest rates; interest rates that change inversely to changes in interest rates; and those that do not bear interest.
Mortgage-related securities are subject to credit, prepayment and interest rate risk, and may be more volatile and less liquid, and more difficult to price accurately, than more traditional debt securities. Although certain mortgage-related securities are guaranteed by a third party (such as a U.S. Government agency or instrumentality with respect to government-related mortgage-backed securities) or otherwise similarly secured, the market value of the security, which may fluctuate, is not secured. Mortgage-backed securities issued by private issuers, whether or not such securities are subject to guarantees or another form of credit enhancement, may entail greater risk than securities directly or indirectly guaranteed by the U.S. Government. The market value of mortgage-related securities depends on, among other things, the level of interest rates, the securities' coupon rates and the payment history of the mortgagors of the underlying mortgages.
Mortgage-related securities generally are subject to credit risks associated with the performance of the underlying mortgage properties and to prepayment risk. In certain instances, the credit risk associated with mortgage-related securities can be reduced by third party guarantees or other forms of credit support. Improved credit risk does not reduce prepayment risk, which is unrelated to the rating assigned to the mortgage-related security. Prepayment risk may lead to pronounced fluctuations in value of the mortgage-related security. If a mortgage-related security is purchased at a premium, all or part of the premium may be lost if there is a decline in the market value of the security, whether resulting solely from changes in interest rates or from prepayments on the underlying mortgage collateral (the rates of which are highly dependent upon changes in interest rates, as discussed below). Mortgage loans are generally partially or completely prepaid prior to their final maturities as a result of events such as sale of the mortgaged premises, default, condemnation or casualty loss. Because these securities may be subject to extraordinary mandatory redemption in whole or in part from such prepayments of mortgage loans, a substantial portion of such securities may be redeemed prior to their scheduled maturities or even prior to ordinary call dates. Extraordinary mandatory redemption without premium could also result from the failure of the originating financial institutions to make mortgage loans in sufficient amounts within a specified time period. The ability of issuers of mortgage-backed securities to make payments depends on such factors as rental income, occupancy levels, operating expenses, mortgage default rates, taxes, government regulations and appropriation of subsidies.
Certain mortgage-related securities, such as inverse floating rate CMOs, have coupons that move inversely to a multiple of a specific index, which may result in a form of leverage. As with other interest-bearing securities, the prices of certain mortgage-related securities are inversely affected by changes in interest rates. However, although the value of a mortgage-related security may decline when interest rates rise, the converse is not necessarily true, since in periods of declining interest rates the mortgages underlying the security are more likely to be prepaid. For this and other reasons, a mortgage-related security's stated maturity may be shortened by unscheduled prepayments on the underlying mortgages, and, therefore, it is not possible to predict accurately the security's return to a fund. Moreover, with respect to certain stripped mortgage-backed securities, if the underlying mortgage securities experience greater than anticipated prepayments of principal, a fund may fail to fully recoup its initial investment even if the securities are rated in the highest rating category by a nationally recognized statistical rating organization. During periods of rapidly rising interest rates, prepayments of mortgage-related securities may occur at slower than expected rates. Slower prepayments effectively may lengthen a mortgage-related security's expected maturity, which generally would cause the value of such security to fluctuate more widely in response to changes in interest rates. Were the prepayments on a fund's mortgage-related securities to decrease broadly, the fund's effective duration, and thus sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations, would increase. Commercial real property loans, however,
III-28
often contain provisions that reduce the likelihood that such securities will be prepaid. The provisions generally impose significant prepayment penalties on loans and in some cases there may be prohibitions on principal prepayments for several years following origination.
Residential Mortgage-Related Securities. Residential mortgage-related securities representing participation interests in pools of one- to four-family residential mortgage loans issued or guaranteed by governmental agencies or instrumentalities, such as the GNMA, the FNMA and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation ("FHLMC"), or issued by private entities, have been issued using a variety of structures, including multi-class structures featuring senior and subordinated classes. Some mortgage-related securities have structures that make their reactions to interest rate changes and other factors difficult to predict, making their value highly volatile.
Mortgage-related securities issued by GNMA include Ginnie Maes which are guaranteed as to the timely payment of principal and interest by GNMA and such guarantee is backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. Ginnie Maes are created by an "issuer," which is a Federal Housing Administration ("FHA") approved mortgagee that also meets criteria imposed by GNMA. The issuer assembles a pool of FHA, Farmers' Home Administration or Veterans' Administration ("VA") insured or guaranteed mortgages which are homogeneous as to interest rate, maturity and type of dwelling. Upon application by the issuer, and after approval by GNMA of the pool, GNMA provides its commitment to guarantee timely payment of principal and interest on the Ginnie Maes backed by the mortgages included in the pool. The Ginnie Maes, endorsed by GNMA, then are sold by the issuer through securities dealers. Ginnie Maes bear a stated "coupon rate" which represents the effective FHA-VA mortgage rate at the time of issuance, less GNMA's and the issuer's fees. GNMA is authorized under the National Housing Act to guarantee timely payment of principal and interest on Ginnie Maes. This guarantee is backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. GNMA may borrow Treasury funds to the extent needed to make payments under its guarantee. When mortgages in the pool underlying a Ginnie Mae are prepaid by mortgagors or by result of foreclosure, such principal payments are passed through to the certificate holders. Accordingly, the life of the Ginnie Mae is likely to be substantially shorter than the stated maturity of the mortgages in the underlying pool. Because of such variation in prepayment rates, it is not possible to predict the life of a particular Ginnie Mae. Payments to holders of Ginnie Maes consist of the monthly distributions of interest and principal less GNMA's and the issuer's fees. The actual yield to be earned by a holder of a Ginnie Mae is calculated by dividing interest payments by the purchase price paid for the Ginnie Mae (which may be at a premium or a discount from the face value of the certificate). Monthly distributions of interest, as contrasted to semi-annual distributions which are common for other fixed interest investments, have the effect of compounding and thereby raising the effective annual yield earned on Ginnie Maes.
Mortgage-related securities issued by FNMA, including FNMA Guaranteed Mortgage Pass-Through Certificates (also known as "Fannie Maes"), are solely the obligations of FNMA and are not backed by or entitled to the full faith and credit of the U.S. Government. Fannie Maes are guaranteed as to timely payment of principal and interest by FNMA. Mortgage-related securities issued by FHLMC include FHLMC Mortgage Participation Certificates (also known as "Freddie Macs" or "PCs"). Freddie Macs are not guaranteed by the U.S. Government or by any Federal Home Loan Bank and do not constitute a debt or obligation of the U.S. Government or of any Federal Home Loan Bank. Freddie Macs entitle the holder to timely payment of interest, which is guaranteed by FHLMC. FHLMC guarantees either ultimate collection or timely payment of all principal payments on the underlying mortgage loans. When FHLMC does not guarantee timely payment of principal, FHLMC may remit the amount due on account of its guarantee of ultimate payment of principal at any time after default on an underlying mortgage, but in no event later than one year after it becomes payable.
In September 2008, the Treasury and the Federal Housing Finance Agency ("FHFA") announced that FNMA and FHLMC had been placed in conservatorship. Since that time, FNMA and FHLMC have received significant capital support through Treasury preferred stock purchases, as well as Treasury and Federal Reserve purchases of their mortgage-backed securities. The FHFA and the U.S. Treasury (through its agreement to purchase FNMA and FHLMC preferred stock) have imposed strict limits on the size of their mortgage portfolios. While the mortgage-backed securities purchase programs ended in 2010, the Treasury continued its support for the entities' capital as necessary to prevent a negative net worth through at least 2012. When a credit rating agency downgraded long-term U.S. Government debt in August 2011, the agency also downgraded FNMA and FHLMC's bond ratings, from AAA to AA+, based on their direct reliance on the U.S. Government (although that rating did not directly relate to their mortgage-backed securities). From the end of 2007 through the first quarter of 2014, FNMA and FHLMC required
III-29
Treasury support of approximately $187.5 billion through draws under the preferred stock purchase agreements. However, they have paid $203 billion in senior preferred dividends to Treasury over the same period. FNMA did not require any draws from Treasury from the fourth quarter of 2011 through the second quarter of 2014. Similarly, FHLMC did not require any draws from Treasury from the first quarter of 2012 through the second quarter of 2014. In April 2014, FHFA projected that FNMA and FHLMC would require no additional draws from Treasury through the end of 2015. However, FHFA also conducted a stress test mandated by the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, enacted on July 21, 2010 (the "Dodd-Frank Act"), which suggested that in a "severely adverse scenario" additional Treasury support of between $84.4 billion and $190 billion (depending on the treatment of deferred tax assets) might be required. No assurance can be given that the Federal Reserve or the Treasury will ensure that FNMA and FHLMC remain successful in meeting their obligations with respect to the debt and mortgage-backed securities that they issue.
In addition, the problems faced by FNMA and FHLMC, resulting in their being placed into federal conservatorship and receiving significant U.S. Government support, have sparked serious debate among federal policymakers regarding the continued role of the U.S. Government in providing liquidity for mortgage loans. In December 2011, Congress enacted the Temporary Payroll Tax Cut Continuation Act of 2011 which, among other provisions, requires that FNMA and FHLMC increase their single-family guaranty fees by at least 10 basis points and remit this increase to the Treasury with respect to all loans acquired by FNMA or FHLMC on or after April 1, 2012 and before January 1, 2022. Serious discussions among policymakers continue, however, as to whether FNMA and FHLMC should be nationalized, privatized, restructured or eliminated altogether. FNMA reported in the second quarter of 2014 that there was "significant uncertainty regarding the future of our company, including how long the company will continue to exist in its current form, the extent of our role in the market, what form we will have, and what ownership interest, if any, our current common and preferred stockholders will hold in us after the conservatorship is terminated and whether we will continue to exist following conservatorship." FHLMC faces similar uncertainty about its future role. FNMA and FHLMC also are the subject of several continuing legal actions and investigations over certain accounting, disclosure or corporate governance matters, which (along with any resulting financial restatements) may continue to have an adverse effect on the guaranteeing entities.
Commercial Mortgage-Related Securities. Commercial mortgage-related securities generally are multi-class debt or pass-through certificates secured by mortgage loans on commercial properties. These mortgage-related securities generally are constructed to provide protection to holders of the senior classes against potential losses on the underlying mortgage loans. This protection generally is provided by having the holders of subordinated classes of securities ("Subordinated Securities") take the first loss if there are defaults on the underlying commercial mortgage loans. Other protection, which may benefit all of the classes or particular classes, may include issuer guarantees, reserve funds, additional Subordinated Securities, cross-collateralization and over-collateralization. Commercial lending, however, generally is viewed as exposing the lender to a greater risk of loss than one- to four-family residential lending. Commercial lending, for example, typically involves larger loans to single borrowers or groups of related borrowers than residential one- to four-family mortgage loans. In addition, the repayment of loans secured by income-producing properties typically is dependent upon the successful operation of the related real estate project and the cash flow generated therefrom. Consequently, adverse changes in economic conditions and circumstances are more likely to have an adverse impact on mortgage-related securities secured by loans on certain types of commercial properties than those secured by loans on residential properties. The risks that recovery or repossessed collateral might be unavailable or inadequate to support payments on commercial mortgage-related securities may be greater than is the case for non-multifamily residential mortgage-related securities.
Subordinated Securities. Subordinated Securities, including those issued or sponsored by commercial banks, savings and loan institutions, mortgage bankers, private mortgage insurance companies and other non-governmental issuers, have no governmental guarantee, and are subordinated in some manner as to the payment of principal and/or interest to the holders of more senior mortgage-related securities arising out of the same pool of mortgages. The holders of Subordinated Securities typically are compensated with a higher stated yield than are the holders of more senior mortgage-related securities. On the other hand, Subordinated Securities typically subject the holder to greater risk than senior mortgage-related securities and tend to be rated in a lower rating category, and frequently a substantially lower rating category, than the senior mortgage-related securities issued in respect of the same pool of mortgages. Subordinated Securities generally are likely to be more sensitive to changes in prepayment and interest rates and the market for such securities may be less liquid than is the case for traditional fixed-income securities and senior mortgage-related securities.
III-30
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs) and Multi-Class Pass-Through-Securities. CMOs are multiclass bonds backed by pools of mortgage pass-through certificates or mortgage loans. CMOs may be collateralized by: (1) Ginnie Mae, Fannie Mae, or Freddie Mac pass-through certificates; (2) unsecuritized mortgage loans insured by the FHA or guaranteed by the Department of Veterans' Affairs; (3) unsecuritized conventional mortgages; (4) other mortgage-related securities; or (5) any combination thereof.
Each class of CMOs, often referred to as a "tranche," is issued at a specific coupon rate and has a stated maturity or final distribution date. Principal prepayments on collateral underlying a CMO may cause it to be retired substantially earlier than the stated maturities or final distribution dates. The principal and interest on the underlying mortgages may be allocated among the several classes of a series of a CMO in many ways. One or more tranches of a CMO may have coupon rates which reset periodically at a specified increment over an index or market rate, such as LIBOR (or sometimes more than one index). These floating rate CMOs typically are issued with lifetime caps on the coupon rate thereon. Inverse floating rate CMOs constitute a tranche of a CMO with a coupon rate that moves in the reverse direction to an applicable index or market rate such as LIBOR. Accordingly, the coupon rate thereon will increase as interest rates decrease. Inverse floating rate CMOs are typically more volatile than fixed or floating rate tranches of CMOs.
Many inverse floating rate CMOs have coupons that move inversely to a multiple of the applicable indexes. The effect of the coupon varying inversely to a multiple of an applicable index creates a leverage factor. Inverse floating rate CMOs based on multiples of a stated index are designed to be highly sensitive to changes in interest rates and can subject the holders thereof to extreme reductions of yield and loss of principal. The markets for inverse floating rate CMOs with highly leveraged characteristics at times may be very thin. The ability of a fund to dispose of positions in such securities will depend on the degree of liquidity in the markets for such securities. It is impossible to predict the amount of trading interest that may exist in such securities, and therefore the future degree of liquidity. It should be noted that inverse floaters based on multiples of a stated index are designed to be highly sensitive to changes in interest rates and can subject the holders thereof to extreme reductions of yield and loss of principal.
As CMOs have evolved, some classes of CMO bonds have become more prevalent. The planned amortization class ("PAC") and targeted amortization class ("TAC"), for example, were designed to reduce prepayment risk by establishing a sinking-fund structure. PAC and TAC bonds assure to varying degrees that investors will receive payments over a predetermined period under varying prepayment scenarios. Although PAC and TAC bonds are similar, PAC bonds are better able to provide stable cash flows under various prepayment scenarios than TAC bonds because of the order in which these tranches are paid.
Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities. Stripped mortgage-backed securities are created by segregating the cash flows from underlying mortgage loans or mortgage securities to create two or more new securities, each with a specified percentage of the underlying security's principal or interest payments. Mortgage securities may be partially stripped so that each investor class receives some interest and some principal. When securities are completely stripped, however, all of the interest is distributed to holders of one type of security, known as an interest-only security ("IO") and all of the principal is distributed to holders of another type of security known as a principal-only security ("PO"). IOs and POs can be created in a pass-through structure or as tranches of a CMO. The yields to maturity on IOs and POs are very sensitive to the rate of principal payments (including prepayments) on the related underlying mortgage assets. If the underlying mortgage assets experience greater than anticipated prepayments of principal, a fund may not fully recoup its initial investment in IOs. Conversely, if the underlying mortgage assets experience less than anticipated prepayments of principal, the yield on POs could be materially and adversely affected.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgage Loans ("ARMs"). ARMs eligible for inclusion in a mortgage pool will generally provide for a fixed initial mortgage interest rate for a specified period of time, generally for either the first three, six, twelve, thirteen, thirty-six, or sixty scheduled monthly payments. Thereafter, the interest rates are subject to periodic adjustment based on changes in an index. ARMs typically have minimum and maximum rates beyond which the mortgage interest rate may not vary over the lifetime of the loans. Certain ARMs provide for additional limitations on the maximum amount by which the mortgage interest rate may adjust for any single adjustment period. Negatively amortizing ARMs may provide limitations on changes in the required monthly payment. Limitations on monthly payments can result in monthly payments that are greater or less than the amount necessary to amortize a negatively amortizing ARM by its maturity at the interest rate in effect during any particular month.
III-31
Private Entity Securities. Mortgage-related securities may be issued by commercial banks, savings and loan institutions, mortgage bankers, private mortgage insurance companies and other non-governmental issuers. Timely payment of principal and interest on mortgage-related securities backed by pools created by non-governmental issuers often is supported partially by various forms of insurance or guarantees, including individual loan, title, pool and hazard insurance. The insurance and guarantees are issued by government entities, private insurers and the mortgage poolers. There can be no assurance that the private insurers or mortgage poolers can meet their obligations under the policies, so that if the issuers default on their obligations the holders of the security could sustain a loss. No insurance or guarantee covers a fund or the price of a fund's shares. Mortgage-related securities issued by non-governmental issuers generally offer a higher rate of interest than government-agency and government-related securities because there are no direct or indirect government guarantees of payment.
Other Mortgage-Related Securities. Other mortgage-related securities include securities other than those described above that directly or indirectly represent a participation in, or are secured by and payable from, mortgage loans on real property, including a CMO tranche which collects any cash flow from collateral remaining after obligations to the other tranches have been met. Other mortgage-related securities may be equity or debt securities issued by agencies or instrumentalities of the U.S. Government or by private originators of, or investors in, mortgage loans, including savings and loan associations, homebuilders, mortgage banks, commercial banks, investment banks, partnerships, trusts and special purpose entities of the foregoing.
Asset-Backed Securities. Asset-backed securities are a form of derivative instrument. Non-mortgage asset-backed securities are securities issued by special purpose entities whose primary assets consist of a pool of loans, receivables or other assets. Payment of principal and interest may depend largely on the cash flows generated by the assets backing the securities and, in certain cases, supported by letters of credit, surety bonds or other forms of credit or liquidity enhancements. The value of these asset-backed securities also may be affected by the creditworthiness of the servicing agent for the pool of assets, the originator of the loans or receivables or the financial institution providing the credit support.
The securitization techniques used for asset-backed securities are similar to those used for mortgage-related securities, including the issuance of securities in senior and subordinated classes (see "Mortgage-Related Securities—Commercial Mortgage-Related Securities" and "—Subordinated Securities" above). These securities include debt securities and securities with debt-like characteristics. The collateral for these securities has included home equity loans, automobile and credit card receivables, boat loans, computer leases, airplane leases, mobile home loans, recreational vehicle loans and hospital account receivables. Other types of asset-backed securities may be developed in the future. The purchase of non-mortgage asset-backed securities raises considerations peculiar to the financing of the instruments underlying such securities.
Asset-backed securities present certain risks of mortgage-backed securities, such as prepayment risk, as well as risks that are not presented by mortgage-backed securities. Primarily, these securities may provide a less effective security interest in the related collateral than do mortgage-backed securities. Therefore, there is the possibility that recoveries on the underlying collateral may not, in some cases, be available to support payments on these securities.
Collateralized Debt Obligations. Collateralized debt obligations ("CDOs") are securitized interests in pools of—generally non-mortgage—assets. Assets called collateral usually are comprised of loans or other debt instruments. A CDO may be called a collateralized loan obligation (CLO) or collateralized bond obligation (CBO) if it holds only loans or bonds, respectively. Investors bear the credit risk of the collateral. Multiple tranches of securities are issued by the CDO, offering investors various maturity and credit risk characteristics. Tranches are categorized as senior, mezzanine and subordinated/equity, according to their degree of credit risk. If there are defaults or the CDO's collateral otherwise underperforms, scheduled payments to senior tranches take precedence over those of mezzanine tranches, and scheduled payments to mezzanine tranches take precedence over those to subordinated/equity tranches. Senior and mezzanine tranches are typically rated, with the former receiving ratings of A to AAA/Aaa and the latter receiving ratings of B to BBB/Baa. The ratings reflect both the credit quality of underlying collateral as well as how much protection a given tranche is afforded by tranches that are subordinate to it.
III-32
Municipal Securities Generally. "Municipal securities" are debt securities or other obligations issued by states, territories and possessions of the United States and the District of Columbia and their political subdivisions, agencies and instrumentalities, or multistate agencies and authorities, and certain other specified securities, the interest from which generally is, in the opinion of bond counsel to the issuer, exempt from federal and, with respect to municipal securities in which certain funds invest, the personal income taxes of a specified state (referred to in this SAI as Municipal Bonds, Municipal Obligations, State Municipal Bonds or State Municipal Obligations, as applicable—see "Glossary" below). Municipal securities generally include debt obligations issued to obtain funds for various public purposes and include certain industrial development bonds issued by or on behalf of public authorities. Municipal securities are classified as general obligation bonds, revenue bonds and notes. General obligation bonds are secured by the issuer's pledge of its full faith, credit and taxing power for the payment of principal and interest. Revenue bonds are payable from the revenue derived from a particular facility or class of facilities or, in some cases, from the proceeds of a special excise or other specific revenue source, but not from the general taxing power. Tax-exempt industrial development bonds, in most cases, are revenue bonds that do not carry the pledge of the credit of the issuing municipality, but generally are guaranteed by the corporate entity on whose behalf they are issued. Notes are short-term instruments which are obligations of the issuing municipalities or agencies and are sold in anticipation of a bond issuance, collection of taxes or receipt of other revenues. Issues of municipal commercial paper typically represent short-term, unsecured, negotiable promissory notes. These obligations are issued by agencies of state and local governments to finance seasonal working capital needs of municipalities or to provide interim construction financing and are paid from general revenues of municipalities or are refinanced with long-term debt. In most cases, municipal commercial paper is backed by letters of credit, lending agreements, note repurchase agreements or other credit facility agreements offered by banks or other institutions. Municipal securities include municipal lease/purchase agreements which are similar to installment purchase contracts for property or equipment issued by municipalities.
A fund's investments in municipal securities may include investments in U.S. territories or possessions such as Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands. A fund's investments in a territory or possession could be affected by economic, legislative, regulatory or political developments affecting issuers in the territory or possession. For example, Puerto Rico, like many other states and U.S. municipalities, experienced a significant downturn during the recent recession and continues to face significant fiscal challenges, including persistent government deficits, underfunded public pensions, sizable debt service obligations and a high unemployment rate. As a result, many Rating Agencies have downgraded Puerto Rico's various municipal issuers, including the Commonwealth itself and its general obligation debt, or placed them on "negative watch." If the economic situation in Puerto Rico persists or worsens, the volatility, credit quality and performance of a fund holding securities of issuers in Puerto Rico could be adversely affected.
Municipal securities bear fixed, floating or variable rates of interest, which are determined in some instances by formulas under which the municipal security's interest rate will change directly or inversely to changes in interest rates or an index, or multiples thereof, in many cases subject to a maximum and minimum. Certain municipal securities are subject to redemption at a date earlier than their stated maturity pursuant to call options, which may be separated from the related municipal security and purchased and sold separately. The purchase of call options on specific municipal securities may protect a fund from the issuer of the related municipal security redeeming, or other holder of the call option from calling away, the municipal security before maturity. The sale by a fund of a call option that it owns on a specific municipal security could result in the receipt of taxable income by the fund.
The municipal securities market is not subject to the same level of regulation as other sectors of the U.S. capital markets due to broad exemptions under the federal securities laws for municipal securities. As a result, there may be less disclosure, including current audited financial information, available about municipal issuers than is available for issuers of securities registered under the Securities Act.
For a fund that invests less than 50% of its assets in municipal securities, dividends received by shareholders on fund shares which are attributable to interest income received by the fund from municipal securities generally will be subject to federal income tax. While, in general, municipal securities are tax exempt securities having relatively low yields as compared to taxable, non-municipal securities of similar quality, certain municipal securities are taxable obligations, offering yields comparable to, and in some cases greater than, the yields available on other
III-33
permissible investments.
For the purpose of diversification under the 1940 Act, the identification of the issuer of municipal securities depends on the terms and conditions of the security. When the assets and revenues of an agency, authority, instrumentality or other political subdivision are separate from those of the government creating the subdivision and the security is backed only by the assets and revenues of the subdivision, such subdivision would be deemed to be the sole issuer. Similarly, in the case of an industrial development bond, if the bond is backed only by the assets and revenues of the non-governmental user, then such non-governmental user would be deemed to be the sole issuer. If, however, in either case, the creating government or some other entity guarantees a security, such a guaranty would be considered a separate security and would be treated as an issue of such government or other entity.
Municipal securities include certain private activity bonds (a type of revenue bond issued by or on behalf of public authorities to raise money to finance various privately operated or public facilities and for which the payment of principal and interest is dependent solely on the ability of the facility's user to meet its financial obligations and the pledge, if any, of real and personal property so financed as security for such payment), the income from which is subject to AMT. Taxable municipal securities also may include remarketed certificates of participation. Certain funds may invest in these municipal securities if the Adviser determines that their purchase is consistent with a fund's investment objective. A municipal or other tax-exempt fund that invests substantially all of its assets in Municipal Bonds may invest more than 25% of the value of the fund's total assets in Municipal Bonds which are related in such a way that an economic, business or political development or change affecting one such security also would affect the other securities (e.g., securities the interest upon which is paid from revenues of similar types of projects, or securities whose issuers are located in the same state). A fund that so invests its assets may be subject to greater risk as compared to municipal or other tax-exempt funds that do not follow this practice.
Municipal securities may be repayable out of revenue streams generated from economically related projects or facilities or whose issuers are located in the same state. Sizable investments in these securities could increase risk to a fund should any of the related projects or facilities experience financial difficulties. An investment in a fund that focuses its investments in securities issued by a particular state or entities within that state may involve greater risk than investments in certain other types of municipal funds. You should consider carefully the special risks inherent in a fund's investment in such municipal securities. If applicable, you should review the information in "Risks of Investing in State Municipal Securities" in Part II of this SAI, which provides a brief summary of special investment considerations and risk factors relating to investing in municipal securities of a specific state.
The yields on municipal securities are dependent on a variety of factors, including general economic and monetary conditions, money market factors, conditions in the municipal securities market, size of a particular offering, maturity of the obligation and rating of the issue. The achievement of the investment objective of a municipal or other tax-exempt fund is dependent in part on the continuing ability of the issuers of municipal securities in which the fund invests to meet their obligations for the payment of principal and interest when due. Municipal securities historically have not been subject to registration with the SEC, although there have been proposals which would require registration in the future. Issuers of municipal securities, like issuers of corporate securities, may declare bankruptcy, and obligations of issuers of municipal securities are subject to the provisions of bankruptcy, insolvency and other laws affecting the rights and remedies of creditors. Many such bankruptcies historically have been of smaller villages, towns, cities and counties, but in November 2011 Jefferson County, Alabama (the state's most populous county) became the subject of what was then the largest municipal bankruptcy ever in the U.S., at over $4 billion in total indebtedness, surpassing in size the 1994 bankruptcy of Orange County, California. Other prominent municipal bankruptcies have followed. In July 2013, Detriot, Michigan filed for bankruptcy. With an estimated $18 to $20 billion in total indebtedness, it became the largest municipal bankruptcy in the U.S. The obligations of municipal issuers may become subject to laws enacted in the future by Congress or state legislatures, or referenda extending the time for payment of principal and/or interest, or imposing other constraints upon enforcement of such obligations or upon the ability of municipalities to levy taxes. There is also the possibility that, as a result of litigation or other conditions, the ability of any municipal issuer to pay, when due, the principal of and interest on its municipal securities may be materially affected.
Certain provisions in the Code relating to the issuance of municipal securities may reduce the volume of municipal securities qualifying for federal tax exemption. One effect of these provisions could be to increase the cost of the municipal securities available for purchase by a fund and thus reduce available yield. Shareholders should consult
III-34
their tax advisors concerning the effect of these provisions on an investment in such a fund. Proposals that may restrict or eliminate the income tax exemption for interest on municipal securities may be introduced in the future. If any such proposal were enacted that would reduce the availability of municipal securities for investment by a fund so as to adversely affect fund shareholders, the fund would reevaluate its investment objective and policies and submit possible changes in the fund's structure to shareholders for their consideration. If legislation were enacted that would treat a type of municipal securities as taxable, a fund would treat such security as a permissible Taxable Investment or, with respect to a money market fund, Money Fund Taxable Investment (in each case, as discussed below), within the applicable limits set forth herein.
Instruments Related to Municipal Securities. The following is a description of certain types of investments related to municipal securities in which some funds may invest. A fund's use of certain of the investment techniques described below may give rise to taxable income.
· Floating and Variable Rate Demand Notes and Bonds. Floating and variable rate demand notes and bonds are tax exempt obligations ordinarily having stated maturities in excess of one year, but which permit the holder to demand payment of principal at any time, or at specified intervals. Variable rate demand notes include master demand notes. See "Fixed-Income Securities—Variable and Floating Rate Securities" above.
· Tax Exempt Participation Interests. A participation interest in municipal securities (such as industrial development bonds and municipal lease/purchase agreements) purchased from a financial institution gives a fund an undivided interest in the municipal security in the proportion that the fund's participation interest bears to the total principal amount of the municipal security. These instruments may have fixed, floating or variable rates of interest and generally will be backed by an irrevocable letter of credit or guarantee of a bank. For certain participation interests, a fund will have the right to demand payment, on not more than seven days' notice, for all or any part of the fund's participation interest in the municipal security, plus accrued interest. As to these instruments, a fund intends to exercise its right to demand payment only upon a default under the terms of the municipal security, as needed to provide liquidity to meet redemptions, or to maintain or improve the quality of its investment portfolio. See also "Fixed-Income Securities—Participation Interests and Assignments" above.
· Municipal Lease Obligations. Municipal lease obligations or installment purchase contract obligations (collectively, "lease obligations") have special risks not ordinarily associated with general obligation or revenue bonds. Leases and installment purchase or conditional sale contracts (which normally provide for title to the leased asset to pass eventually to the government issuer) have evolved as a means for governmental issuers to acquire property and equipment without meeting the constitutional and statutory requirements for the issuance of debt. Although lease obligations do not constitute general obligations of the municipality for which the municipality's taxing power is pledged, a lease obligation ordinarily is backed by the municipality's covenant to budget for, appropriate and make the payments due under the lease obligation. However, lease obligations in which a fund may invest may contain "non-appropriation" clauses which provide that the municipality has no obligation to make lease or installment purchase payments in future years unless money is appropriated for such purpose on a yearly basis. Although "non-appropriation" lease obligations are secured by the leased property, disposition of the property in the event of foreclosure might prove difficult. Certain lease obligations may be considered illiquid. Determination as to the liquidity of such securities is made in accordance with guidelines established by the board. Pursuant to such guidelines, the board has directed the Adviser to monitor carefully a fund's investment in such securities with particular regard to: (1) the frequency of trades and quotes for the lease obligation; (2) the number of dealers willing to purchase or sell the lease obligation and the number of other potential buyers; (3) the willingness of dealers to undertake to make a market in the lease obligation; (4) the nature of the marketplace trades, including the time needed to dispose of the lease obligation, the method of soliciting offers and the mechanics of transfer; and (5) such other factors concerning the trading market for the lease obligation as the Adviser may deem relevant. In addition, in evaluating the liquidity and credit quality of a lease obligation that is unrated, the board has directed the Adviser to consider: (1) whether the lease can be canceled; (2) what assurance there is that the assets represented by the lease can be sold; (3) the strength of the lessee's general credit (e.g., its debt, administrative, economic and financial characteristics); (4) the likelihood that the municipality will discontinue appropriating funding for the
III-35
leased property because the property is no longer deemed essential to the operations of the municipality (e.g., the potential for an "event of non-appropriation"); (5) the legal recourse in the event of failure to appropriate; and (6) such other factors concerning credit quality as the Adviser may deem relevant.
· Tender Option Bonds. A tender option bond is a municipal security (generally held pursuant to a custodial arrangement) having a relatively long maturity and bearing interest at a fixed rate substantially higher than prevailing short-term tax exempt rates, that has been coupled with the agreement of a third party, such as a bank, broker-dealer or other financial institution, pursuant to which such institution grants the security holders the option, at periodic intervals, to tender their securities to the institution and receive the face value thereof. As consideration for providing the option, the financial institution receives periodic fees equal to the difference between the municipal security's fixed coupon rate and the rate, as determined by a remarketing or similar agent at or near the commencement of such period, that would cause the securities, coupled with the tender option, to trade at par on the date of such determination. Thus, after payment of this fee, the security holder effectively holds a demand obligation that bears interest at the prevailing short-term tax exempt rate. In certain instances and for certain tender option bonds, the option may be terminable in the event of a default in payment of principal or interest on the underlying municipal security and for other reasons. The funds expect to be able to value tender option bonds at par; however, the value of the instrument will be monitored to assure that it is valued at fair value. The quality of the underlying creditor or of the third party provider of the tender option, as the case may be, as determined by the Adviser, must be equivalent to the quality standard prescribed for the fund. In addition, the Adviser monitors the earning power, cash flow and other liquidity ratios of the issuers of such obligations.
· Pre-Refunded Municipal Securities. The principal and interest on pre-refunded municipal securities are no longer paid from the original revenue source for the securities. Instead, the source of such payments is typically an escrow fund consisting of U.S. Government securities. The assets in the escrow fund are derived from the proceeds of refunding bonds issued by the same issuer as the pre-refunded municipal securities. Issuers of municipal securities use this advance refunding technique to obtain more favorable terms with respect to bonds that are not yet subject to call or redemption by the issuer. For example, advance refunding enables an issuer to refinance debt at lower market interest rates, restructure debt to improve cash flow or eliminate restrictive covenants in the indenture or other governing instrument for the pre-refunded municipal securities. However, except for a change in the revenue source from which principal and interest payments are made, the pre-refunded municipal securities remain outstanding on their original terms until they mature or are redeemed by the issuer.
· Mortgage-Related and Asset-Backed Municipal Securities. Mortgage-backed municipal securities are municipal securities of issuers that derive revenues from mortgage loans on multiple family residences, retirement housing or housing projects for low- to moderate-income families. Certain of such securities may be single family mortgage revenue bonds issued for the purpose of acquiring from originating financial institutions notes secured by mortgages on residences located within the issuer's boundaries. Non-mortgage asset-based securities are securities issued by special purpose entities whose primary assets consist of a pool of loans, receivables or other assets. See "Fixed-Income Securities—Mortgage-Related Securities" and "Fixed-Income Securities—Asset-Backed Securities" above.
· Custodial Receipts. Custodial receipts represent the right to receive certain future principal and/or interest payments on municipal securities which underlie the custodial receipts. A number of different arrangements are possible. A fund also may purchase directly from issuers, and not in a private placement, municipal securities having characteristics similar to custodial receipts. These securities may be issued as part of a multi-class offering and the interest rate on certain classes may be subject to a cap or floor. See "Derivatives—Custodial Receipts" below.
· Indexed and Inverse Floating Rate Municipal Securities. Indexed rate municipal securities are securities that pay interest or whose principal amount payable upon maturity is based on the value of an index of interest rates. Interest and principal payable on certain securities also may be based on relative changes among particular indexes. So-called "inverse floating obligations" or "residual interest bonds" ("inverse floaters") are derivative instruments created by depositing municipal securities in a trust which divides the bond's income stream into two parts: (1) a short-term variable rate demand note; and (2) a residual interest
III-36
bond (the inverse floater) which receives interest based on the remaining cash flow of the trust after payment of interest on the note and various trust expenses. The interest rate on the inverse floater varies inversely with a floating rate (which may be reset periodically by a "Dutch" auction, a remarketing agent or by reference a short-term tax-exempt interest rate index), usually moving in the opposite direction as the interest on the variable rate demand note.
A fund may either participate in structuring an inverse floater or purchase an inverse floater in the secondary market. When structuring an inverse floater, a fund will transfer to a trust fixed rate municipal securities held in the fund's portfolio. The trust then typically issues the inverse floaters and the variable rate demand notes that are collateralized by the cash flows of the fixed rate municipal securities. In return for the transfer of the municipal securities to the trust, the fund receives the inverse floaters and cash associated with the sale of the notes from the trust. For accounting purposes, a fund treats these transfers as part of a secured borrowing or financing transaction (not a sale), and the interest payments and related expenses due on the notes issued by the trusts and sold to third parties as expenses and liabilities of the fund. Inverse floaters purchased in the secondary market are treated as the purchase of a security and not as a secured borrowing or financing transaction. Synthetically created inverse floating rate bonds evidenced by custodial or trust receipts are securities that have the effect of providing a degree of investment leverage, since they may increase or decrease in value in response to changes in market interest rates at a rate that is a multiple of the rate at which fixed rate securities increase or decrease in response to such changes.
An investment in inverse floaters may involve greater risk than an investment in a fixed rate municipal security. Because changes in the interest rate on the other security or index inversely affect the residual interest paid on the inverse floater, the value of an inverse floater is generally more volatile than that of a fixed rate municipal security. Inverse floaters have interest rate adjustment formulas which generally reduce or, in the extreme, eliminate the interest paid to a fund when short-term interest rates rise, and increase the interest paid to the fund when short-term interest rates fall. Investing in inverse floaters involves leveraging which may magnify the fund's gains or losses. Although volatile, inverse floaters typically offer the potential for yields exceeding the yields available on fixed rate municipal securities with comparable credit quality, coupon, call provisions and maturity. These securities usually permit the investor to convert the floating rate to a fixed rate (normally adjusted downward), and this optional conversion feature may provide a partial hedge against rising rates if exercised at an opportune time. Investments in inverse floaters may be illiquid.
· Zero Coupon, Pay-In-Kind and Step-Up Municipal Securities. Zero coupon municipal securities are issued or sold at a discount from their face value and do not entitle the holder to any periodic payment of interest prior to maturity or a specified redemption date or cash payment date. Zero coupon securities also may take the form of municipal securities that have been stripped of their unmatured interest coupons, the coupons themselves and receipts or certificates representing interest in such stripped debt obligations and coupons. Pay-in-kind municipal securities generally pay interest through the issuance of additional securities. Step-up municipal securities typically do not pay interest for a specified period of time and then pay interest at a series of different rates. See "Fixed-Income Securities—Zero Coupon, Pay-In-Kind and Step-Up Securities."
· Special Taxing Districts. Some municipal securities may be issued in connection with special taxing districts. Special taxing districts are organized to plan and finance infrastructure development to induce residential, commercial and industrial growth and redevelopment. The bond financing methods, such as tax increment finance, tax assessment, special services district and Mello-Roos bonds, generally are payable solely from taxes or other revenues attributable to the specific projects financed by the bonds without recourse to the credit or taxing power of related or overlapping municipalities. They often are exposed to real estate development-related risks and can have more taxpayer concentration risk than general tax-supported bonds, such as general obligation bonds. Further, the fees, special taxes or tax allocations and other revenues that are established to secure such financings generally are limited as to the rate or amount that may be levied or assessed and are not subject to increase pursuant to rate covenants or municipal or corporate guarantees. The bonds could default if development failed to progress as anticipated or if larger taxpayers failed to pay the assessments, fees and taxes as provided in the financing plans of the districts.
III-37
· Stand-By Commitments. Under a stand-by commitment, a fund obligates a broker, dealer or bank to repurchase, at the fund's option, specified securities at a specified price prior to such securities' maturity date and, in this respect, stand-by commitments are comparable to put options. The exercise of a stand-by commitment, therefore, is subject to the ability of the seller to make payment on demand. The funds will acquire stand-by commitments solely to facilitate portfolio liquidity and do not intend to exercise their rights thereunder for trading purposes. A fund may pay for stand-by commitments if such action is deemed necessary, thus increasing to a degree the cost of the underlying municipal security and similarly decreasing such security's yield to investors. Gains realized in connection with stand-by commitments will be taxable. For a fund that focuses its investments in New Jersey Municipal Bonds, the fund will acquire stand-by commitments only to the extent consistent with the requirements for a "qualified investment fund" under the New Jersey Gross Income Tax Act.
· Structured Notes. Structured notes typically are purchased in privately negotiated transactions from financial institutions and, therefore, may not have an active trading market. When a fund purchases a structured note, it will make a payment of principal to the counterparty. Some structured notes have a guaranteed repayment of principal while others place a portion (or all) or the principal at risk. The possibility of default by the counterparty or its credit provider may be greater for structured notes than for other types of money market instruments.
Taxable Investments (municipal or other tax-exempt funds only). From time to time, on a temporary basis other than for temporary defensive purposes (but not to exceed 20% of the value of the fund's net assets) or for temporary defensive purposes, a fund may invest in taxable short-term investments (Taxable Investments, as defined in Part II of this SAI under "Investments, Investments Techniques and Risks"). Dividends paid by a fund that are attributable to income earned by the fund from Taxable Investments will be taxable to investors. When a fund invests for temporary defensive purposes, it may not achieve its investment objective(s).
Funding Agreements. In a funding agreement (sometimes referred to as a Guaranteed Interest Contract or "GIC"), a fund contributes cash to a deposit fund of an insurance company's general account, and the insurance company then credits the fund, on a monthly basis, guaranteed interest that is based on an index. This guaranteed interest will not be less than a certain minimum rate. Because the principal amount of a funding agreement may not be received from the insurance company on seven days' notice or less, the agreement is considered to be an illiquid investment.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
A REIT is a corporation, or a business trust that would otherwise be taxed as a corporation, which meets the definitional requirements of the Code. The Code permits a qualifying REIT to deduct dividends paid, thereby effectively eliminating corporate level federal income tax and making the REIT a pass-through vehicle for federal income tax purposes. To meet the definitional requirements of the Code, a REIT must, among other things, invest substantially all of its assets in interests in real estate (including mortgages and other REITs) or cash and government securities, derive most of its income from rents from real property or interest on loans secured by mortgages on real property, and distribute to shareholders annually a substantial portion of its otherwise taxable income.
REITs are characterized as equity REITs, mortgage REITs and hybrid REITs. Equity REITs invest primarily in the fee ownership or leaseshold ownership of land and buildings and derive their income primarily from rental income. Equity REITs also can realize capital gains (or losses) by selling properties that have appreciated (or depreciated) in value. Mortgage REITs can make construction, development or long-term mortgage loans and are sensitive to the credit quality of the borrower. Mortgage REITs derive their income from interest payments on such loans. Hybrid REITs combine the characteristics of both equity and mortgage REITs, generally by holding both ownership interests and mortgage interests in real estate. The value of securities issued by REITs is affected by tax and regulatory requirements and by perceptions of management skill. They also are subject to heavy cash flow dependency, defaults by borrowers or tenants, self-liquidation and the possibility of failing to qualify for tax-free status under the Code or to maintain exemption from the 1940 Act. A fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of expenses, including management fees, paid by each REIT in which it invests in addition to the expenses of the fund.
III-38
When the Adviser determines that adverse market conditions exist, a fund may adopt a temporary defensive position and invest up to 100% of its assets in money market instruments, including U.S. Government securities, bank obligations, repurchase agreements and commercial paper. During such periods, the fund may not achieve its investment objective(s). A fund also may purchase money market instruments when it has cash reserves or in anticipation of taking a market position.
Investing in money market instruments is subject to certain risks. Money market instruments (other than certain U.S. Government securities) are not backed or insured by the U.S. Government, its agencies or its instrumentalities. Accordingly, only the creditworthiness of an issuer, or guarantees of that issuer, support such instruments.
Bank Obligations. See "Bank Obligations" below under "Money Market Funds."
Repurchase Agreements. See "Repurchase Agreements" below under "Money Market Funds."
Commercial Paper. Commercial paper represents short-term, unsecured promissory notes issued in bearer form by banks or bank holding companies, corporations and finance companies used to finance short-term credit needs and may consist of U.S. dollar-denominated obligations of domestic issuers and foreign currency-denominated obligations of domestic or foreign issuers. Commercial paper may be backed only by the credit of the issuer or may be backed by some form of credit enhancement, typically in the form of a guarantee by a commercial bank. Commercial paper backed by guarantees of foreign banks may involve additional risk due to the difficulty of obtaining and enforcing judgments against such banks and the generally less restrictive regulations to which such banks are subject.
Foreign securities include the securities of companies organized under the laws of countries other than the United States and those issued or guaranteed by governments other than the U.S. Government or by foreign supranational entities. They also include securities of companies whose principal trading market is in a country other than the United States or of companies (including those that are located in the United States or organized under U.S. law) that derive a significant portion of their revenue or profits from foreign businesses, investments or sales, or that have a majority of their assets outside the United States. They may be traded on foreign securities exchanges or in the foreign over-the-counter markets. Supranational entities include international organizations designated or supported by governmental entities to promote economic reconstruction or development and international banking institutions and related government agencies. Examples include the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (the World Bank), the European Coal and Steel Community, the Asian Development Bank and the InterAmerican Development Bank. Obligations of the World Bank and certain other supranational organizations are supported by subscribed but unpaid commitments of member countries. There is no assurance that these commitments will be undertaken or complied with in the future.
Investing in the securities of foreign issuers, as well as instruments that provide investment exposure to foreign securities and markets, involves risks that are not typically associated with investing in U.S. dollar-denominated securities of domestic issuers. Investments in foreign issuers may be affected by changes in currency rates (i.e., affecting the value of assets as measured in U.S. dollars), changes in foreign or U.S. laws or restrictions applicable to such investments and in exchange control regulations (e.g., currency blockage). A decline in the exchange rate of the currency (i.e., weakening of the currency against the U.S. dollar) in which a portfolio security is quoted or denominated relative to the U.S. dollar would reduce the value of the portfolio security. A change in the value of such foreign currency against the U.S. dollar also will result in a change in the amount of income available for distribution. If a portion of a fund's investment income may be received in foreign currencies, such fund will be required to compute its income in U.S. dollars for distribution to shareholders, and therefore the fund will absorb the cost of currency fluctuations. After the fund has distributed income, subsequent foreign currency losses may result in the fund having distributed more income in a particular fiscal period than was available from investment income, which could result in a return of capital to shareholders. In addition, if the exchange rate for the currency in which a fund receives interest payments declines against the U.S. dollar before such income is distributed as dividends to shareholders, the fund may have to sell portfolio securities to obtain sufficient cash to enable the fund to pay such dividends. Commissions on transactions in foreign securities may be higher than those for similar transactions on
III-39
domestic stock markets, and foreign custodial costs are higher than domestic custodial costs. In addition, clearance and settlement procedures may be different in foreign countries and, in certain markets, such procedures have on occasion been unable to keep pace with the volume of securities transactions, thus making it difficult to conduct such transactions.
Foreign securities markets generally are not as developed or efficient as those in the United States. Securities of some foreign issuers are less liquid and more volatile than securities of comparable U.S. issuers. Similarly, volume and liquidity in most foreign securities markets are less than in the United States and, at times, volatility of price can be greater than in the United States.
Because evidences of ownership of foreign securities usually are held outside the United States, additional risks of investing in foreign securities include possible adverse political and economic developments, seizure or nationalization of foreign deposits and adoption of governmental restrictions that might adversely affect or restrict the payment of principal and interest on the foreign securities to investors located outside the country of the issuer, whether from currency blockage, exchange control regulations or otherwise. Foreign securities held by a fund may trade on days when the fund does not calculate its NAV and thus may affect the fund's NAV on days when shareholders have no access to the fund.
Emerging Markets. Investments in, or economically tied to, emerging market countries may be subject to potentially higher risks than investments in companies in developed countries. Risks of investing in emerging markets and emerging market securities include (in addition to those described above): less social, political and economic stability; less diverse and mature economic structures; the lack of publicly available information, including reports of payments of dividends or interest on outstanding securities; certain national policies that may restrict a fund's investment opportunities, including restrictions on investment in issuers or industries deemed sensitive to national interests; local taxation; the absence of developed structures governing private or foreign investment or allowing for judicial redress for injury to private property; the absence until recently, in certain countries, of a capital structure or market-oriented economy; the possibility that recent favorable economic developments in certain countries may be slowed or reversed by unanticipated political or social events in these countries; restrictions that may make it difficult or impossible for a fund to vote proxies, exercise shareholder rights, pursue legal remedies, and obtain judgments in foreign courts; the risk of uninsured loss due to lost, stolen, or counterfeit stock certificates; possible losses through the holding of securities in domestic and foreign custodial banks and depositories; heightened opportunities for governmental corruption; large amounts of foreign debt to finance basic governmental duties that could lead to restructuring or default; and heavy reliance on exports that may be severely affected by global economic downturns.
The purchase and sale of portfolio securities in certain emerging market countries may be constrained by limitations as to daily changes in the prices of listed securities, periodic trading or settlement volume and/or limitations on aggregate holdings of foreign investors. In certain cases, such limitations may be computed based upon the aggregate trading by or holdings of a fund, its Adviser and its affiliates and their respective clients and other service providers. A fund may not be able to sell securities in circumstances where price, trading or settlement volume limitations have been reached.
Economic conditions, such as volatile currency exchange rates and interest rates, political events and other conditions may, without prior warning, lead to government intervention and the imposition of "capital controls." Countries use these controls to restrict volatile movements of capital entering (inflows) and exiting (outflows) their country to respond to certain economic conditions. Such controls are mainly applied to short-term capital transactions to counter speculative flows that threaten to undermine the stability of the exchange rate and deplete foreign exchange reserves. Capital controls include the prohibition of, or restrictions on, the ability to transfer currency, securities or other assets in such a way that may adversely affect the ability of a fund to repatriate its income and capital. These limitations may have a negative impact on the fund's performance and may adversely affect the liquidity of the fund's investment to the extent that it invests in certain emerging market countries. Some emerging market countries may have fixed or managed currencies which are not free-floating against the U.S. dollar. Further, certain emerging market countries' currencies may not be internationally traded. Certain of these currencies have experienced a steady devaluation relative to the U.S. dollar. If a fund does not hedge the U.S. dollar value of securities it owns denominated in currencies that are devalued, the fund's NAV will be adversely affected. Many emerging market countries have experienced substantial, and in some periods, extremely high rates of inflation for many years. Inflation and rapid fluctuations in inflation rates have had, and may continue to have, adverse effects
III-40
on the economies and securities markets of certain of these countries. Further, the economies of emerging market countries generally are heavily dependent upon international trade and, accordingly, have been and may continue to be adversely affected by trade barriers, exchange controls, managed adjustments in relative currency values and other protectionist measures imposed or negotiated by the countries with which they trade.
Certain funds may invest in companies organized or with their principal place of business, or majority of assets or business, in pre-emerging markets, also known as frontier markets. The risks associated with investments in frontier market countries include all the risks described above for investments in foreign securities and emerging markets, although the risks are magnified for frontier market countries. Because frontier markets are among the smallest, least mature and least liquid of the emerging markets, investments in frontier markets generally are subject to a greater risk of loss than investments in developed markets or traditional emerging markets. Frontier market countries have smaller economies, less developed capital markets, more political and economic instability, and more governmental limitations on foreign investments than typically found in more developed countries, and frontier markets typically have greater market volatility, lower trading volume and greater risk of a market shutdown than more developed markets. Frontier markets are more prone to economic shocks associated with political and economic risks than are emerging markets generally. Many frontier market countries may be dependent on commodities, foreign trade or foreign aid.
Certain Asian Emerging Market Countries. The performance of a fund that concentrates its investments in Asian emerging market countries is expected to be closely tied to social, political and economic conditions within Asia and to be more volatile than the performance of more geographically diversified funds. Many Asian economies are characterized by over-extension of credit, frequent currency fluctuation, devaluations and restrictions, rising unemployment, rapid fluctuations in inflation, reliance on exports and less efficient markets. Currency devaluation in one Asian country can have a significant effect on the entire region. The legal systems in many Asian countries are still developing, making it more difficult to obtain and/or enforce judgments.
Furthermore, increased political and social unrest in some Asian countries could cause economic and market uncertainty throughout the region. The auditing and reporting standards in some Asian emerging market countries may not provide the same degree of shareholder protection or information to investors as those in developed countries. In particular, valuation of assets, depreciation, exchange differences, deferred taxation, contingent liability and consolidation may be treated differently than under the auditing and reporting standards of developed countries.
Certain Asian emerging market countries are undergoing a period of growth and change which may result in trading volatility and difficulties in the settlement and recording of securities transactions, and in interpreting and applying the relevant law and regulations. The securities industries in these countries are comparatively underdeveloped. Stockbrokers and other intermediaries in Asian emerging market countries may not perform as well as their counterparts in the United States and other more developed securities markets. Certain Asian emerging market countries may require substantial withholding on dividends paid on portfolio securities and on realized capital gains. There can be no assurance that repatriation of the fund's income, gains or initial capital from these countries can occur.
Investing in Russia and other Eastern European Countries. Many formerly communist, eastern European countries have experienced significant political and economic reform over the past decade. However, the democratization process is still relatively new in a number of the smaller states and political turmoil and popular uprisings remain threats. Investments in these countries are particularly subject to political, economic, legal, market and currency risks. The risks include uncertain political and economic policies and the risk of nationalization or expropriation of assets, short-term market volatility, poor accounting standards, corruption and crime, an inadequate regulatory system, unpredictable taxation, the imposition of capital controls and/or foreign investment limitations by a country and the imposition of sanctions on an Eastern European country by other countries, such as the U.S. Adverse currency exchange rates are a risk, and there may be a lack of available currency hedging instruments.
These securities markets, as compared to U.S. markets, have significant price volatility, less liquidity, a smaller market capitalization and a smaller number of exchange-traded securities. A limited volume of trading may result in difficulty in obtaining accurate prices and trading. There is little publicly available information about issuers. Settlement, clearing and registration of securities transactions are subject to risks because of insufficient registration systems that may not be subject to effective government supervision. This may result in significant delays or
III-41
problems in registering the transfer of shares. It is possible that a fund's ownership rights could be lost through fraud or negligence. While applicable regulations may impose liability on registrars for losses resulting from their errors, it may be difficult for a fund to enforce any rights it may have against the registrar or issuer of the securities in the event of loss of share registration.
Political risk in Russia remains high, and steps that Russia may take to assert its geopolitical influence may increase the tensions in the region and affect economic growth. Russia's economy is heavily dependent on exportation of natural resources, which may be particularly vulnerable to economic sanctions by other countries during times of political tension or crisis.
In response to recent political and military actions undertaken by Russia, the United States and certain other countries, as well as the European Union, have instituted economic sanctions against certain Russian individuals and companies. The political and economic situation in Russia, and the current and any future sanctions or other government actions against Russia, may result in the decline in the value and liquidity of Russian securities, devaluation of Russian currency, a downgrade in Russia's credit rating, the inability to freely trade sanctioned companies (either due to the sanctions imposed or related operational issues) and/or other adverse consequences to the Russian economy, any of which could negatively impact a fund's investments in Russian securities. Sanctions could result in the immediate freeze of Russian securities, impairing the ability of a fund to buy, sell, receive or deliver those securities. Both the current and potential future sanctions or other government actions against Russia also could result in Russia taking counter measures or retaliatory actions, which may impair further the value or liquidity of Russian securities and negatively impact a fund. Any or all of these potential results could lead Russia's economy into a recession.
Depositary Receipts and New York Shares. Securities of foreign issuers in the form of ADRs, EDRs and GDRs and other forms of depositary receipts may not necessarily be denominated in the same currency as the securities into which they may be converted. ADRs are receipts typically issued by a U.S. bank or trust company which evidence ownership of underlying securities issued by a foreign corporation. EDRs are receipts issued in Europe, and GDRs are receipts issued outside the United States typically by non-U.S. banks and trust companies that evidence ownership of either foreign or domestic securities. Generally, ADRs in registered form are designed for use in the U.S. securities markets, EDRs in bearer form are designed for use in Europe, and GDRs in bearer form are designed for use outside the United States. New York Shares are securities of foreign companies that are issued for trading in the United States. New York Shares are traded in the United States on national securities exchanges or in the over-the-counter market.
Depositary receipts may be purchased through "sponsored" or "unsponsored" facilities. A sponsored facility is established jointly by the issuer of the underlying security and a depositary. A depositary may establish an unsponsored facility without participation by the issuer of the deposited security. Holders of unsponsored depositary receipts generally bear all the costs of such facilities, and the depositary of an unsponsored facility frequently is under no obligation to distribute shareholder communications received from the issuer of the deposited security or to pass through voting rights to the holders of such receipts in respect of the deposited securities. Purchases or sales of certain ADRs may result, indirectly, in fees being paid to the Depositary Receipts Division of The Bank of New York Mellon, an affiliate of the Manager, by brokers executing the purchases or sales.
Securities of foreign issuers that are represented by ADRs or that are listed on a U.S. securities exchange or traded in the U.S. over-the-counter markets are not subject to many of the special considerations and risks discussed in the prospectus and this SAI that apply to foreign securities traded and held abroad. A U.S. dollar investment in ADRs or shares of foreign issuers traded on U.S. exchanges may be impacted differently by currency fluctuations than would an investment made in a foreign currency on a foreign exchange in shares of the same issuer.
Sovereign Debt Obligations. Investments in sovereign debt obligations involve special risks which are not present in corporate debt obligations. The foreign issuer of the sovereign debt or the foreign governmental authorities that control the repayment of the debt may be unable or unwilling to repay principal or interest when due, and a fund may have limited recourse in the event of a default. During periods of economic uncertainty, the market prices of sovereign debt, and the NAV of a fund, to the extent it invests in such securities, may be more volatile than prices of U.S. debt issuers. In the past, certain foreign countries have encountered difficulties in servicing their debt obligations, withheld payments of principal and interest and declared moratoria on the payment of principal and interest on their sovereign debt.
III-42
A sovereign debtor's willingness or ability to repay principal and pay interest in a timely manner may be affected by, among other factors, its cash flow situation, the extent of its foreign currency reserves, the availability of sufficient foreign exchange, the relative size of the debt service burden, the sovereign debtor's policy toward principal international lenders and local political constraints. Sovereign debtors may also be dependent on expected disbursements from foreign governments, multilateral agencies and other entities to reduce principal and interest arrearages on their debt. The failure of a sovereign debtor to implement economic reforms, achieve specified levels of economic performance or repay principal or interest when due may result in the cancellation of third party commitments to lend funds to the sovereign debtor, which may further impair such debtor's ability or willingness to service its debts.
Moreover, no established secondary markets may exist for many of the sovereign debt obligations in which a fund may invest. Reduced secondary market liquidity may have an adverse effect on the market price and a fund's ability to dispose of particular instruments when necessary to meet its liquidity requirements or in response to specific economic events such as a deterioration in the creditworthiness of the issuer. Reduced secondary market liquidity for certain sovereign debt obligations also may make it more difficult for a fund to obtain accurate market quotations for purposes of valuing its portfolio. Market quotations are generally available on many sovereign debt obligations only from a limited number of dealers and may not necessarily represent firm bids of those dealers or prices of actual sales.
Sovereign Debt Obligations of Emerging Market Countries. Investing in foreign government obligations and the sovereign debt of emerging market countries creates exposure to the direct or indirect consequences of political, social or economic changes in the countries that issue the securities or in which the issuers are located. The ability and willingness of sovereign obligors in emerging market countries or the governmental authorities that control repayment of their external debt to pay principal and interest on such debt when due may depend on general economic and political conditions within the relevant country. Certain countries in which a fund may invest have historically experienced, and may continue to experience, high rates of inflation, high interest rates, exchange rate trade difficulties and extreme poverty and unemployment. Many of these countries also are characterized by political uncertainty or instability. Additional factors which may influence the ability or willingness to service debt include a country's cash flow situation, the availability of sufficient foreign exchange on the date a payment is due, the relative size of its debt service burden to the economy as a whole and its government's policy towards the International Monetary Fund, the World Bank and other international agencies. The ability of a foreign sovereign obligor to make timely payments on its external debt obligations also will be strongly influenced by the obligor's balance of payments, including export performance, its access to international credits and investments, fluctuations in interest rates and the extent of its foreign reserves. A governmental obligor may default on its obligations. If such an event occurs, a fund may have limited legal recourse against the issuer and/or guarantor. In some cases, remedies must be pursued in the courts of the defaulting party itself, and the ability of the holder of foreign sovereign debt securities to obtain recourse may be subject to the political climate in the relevant country. In addition, no assurance can be given that the holders of commercial bank debt will not contest payments to the holders of other foreign sovereign debt obligations in the event of default under their commercial bank loan agreements. Sovereign obligors in emerging market countries are among the world's largest debtors to commercial banks, other governments, international financial organizations and other financial institutions. These obligors, in the past, have experienced substantial difficulties in servicing their external debt obligations, which led to defaults on certain obligations and the restructuring of certain indebtedness. Restructuring arrangements have included, among other things, reducing and rescheduling interest and principal payments by negotiating new or amended credit agreements or converting outstanding principal and unpaid interest to Brady Bonds (discussed below), and obtaining new credit to finance interest payments. Holders of certain foreign sovereign debt securities may be requested to participate in the restructuring of such obligations and to extend further loans to their issuers. There can be no assurance that the Brady Bonds and other foreign sovereign debt securities in which a fund may invest will not be subject to similar restructuring arrangements or to requests for new credit which may adversely affect the fund's holdings. Obligations of the World Bank and certain other supranational organizations are supported by subscribed but unpaid commitments of member countries. There is no assurance that these commitments will be undertaken or complied with in the future.
Brady Bonds. "Brady Bonds" are securities created through the exchange of existing commercial bank loans to public and private entities in certain emerging markets for new bonds in connection with debt restructurings. In light of the history of defaults of countries issuing Brady Bonds on their commercial bank loans, investments in
III-43
Brady Bonds may be viewed as speculative. Brady Bonds may be fully or partially collateralized or uncollateralized, are issued in various currencies (but primarily in U.S. dollars) and are actively traded in over-the-counter secondary markets. Brady Bonds with no or limited collateralization of interest or principal payment obligations have increased credit risk, and the holders of such bonds rely on the willingness and ability of the foreign government to make payments in accordance with the terms of such Brady Bonds. U.S. dollar-denominated collateralized Brady Bonds, which may be fixed rate bonds or floating rate bonds, generally are collateralized by Treasury zero coupon bonds having the same maturity as the Brady Bonds. One or more classes of securities ("structured securities") may be backed by, or represent interests in, Brady Bonds. The cash flow on the underlying instruments may be apportioned among the newly-issued structured securities to create securities with different investment characteristics such as varying maturities, payment priorities and interest rate provisions, and the extent of the payments made with respect to structured securities is dependent on the extent of the cash flow on the underlying instruments. See "Derivatives—Structured Securities" below.
Eurodollar and Yankee Dollar Investments. Eurodollar instruments are bonds of foreign corporate and government issuers that pay interest and principal in U.S. dollars generally held in banks outside the United States, primarily in Europe. Yankee Dollar instruments are U.S. dollar-denominated bonds typically issued in the United States by foreign governments and their agencies and foreign banks and corporations. Eurodollar Certificates of Deposit are U.S. dollar-denominated certificates of deposit issued by foreign branches of domestic banks; Eurodollar Time Deposits are U.S. dollar-denominated deposits in a foreign branch of a U.S. bank or in a foreign bank; and Yankee Certificates of Deposit are U.S. dollar-denominated certificates of deposit issued by a U.S. branch of a foreign bank and held in the United States. These investments involve risks that are different from investments in securities issued by U.S. issuers, including potential unfavorable political and economic developments, foreign withholding or other taxes, seizure of foreign deposits, currency controls, interest limitations or other governmental restrictions which might affect payment of principal or interest.
The 1940 Act, subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, limits a fund's investment in securities issued by registered and unregistered investment companies, including exchange-traded funds (discussed below), subject to certain exceptions (including those that apply for a Fund of Funds' investment in Underlying Funds), currently is limited to: (1) 3% of the total voting stock of any one investment company; (2) 5% of the fund's total assets with respect to any one investment company; and (3) 10% of the fund's total assets in the aggregate. As a shareholder of another investment company, a fund would bear, along with other shareholders, its pro rata portion of the other investment company's expenses, including advisory fees. These expenses would be in addition to the advisory fees and other expenses that the fund bears directly in connection with its own operations. A fund also may invest its uninvested cash reserves or cash it receives as collateral from borrowers of its portfolio securities in connection with the fund's securities lending program, in shares of one or more money market funds advised by the Manager. Such investments will not be subject to the limitations described above.
Private Investment Funds. As with investments in registered investment companies, if a fund invests in a private investment fund, such as a "hedge fund" or private equity fund, the fund will be charged its proportionate share of the advisory fees, including any incentive compensation and other operating expenses, of the private investment fund. These fees, which can be substantial, would be in addition to the advisory fees and other operating expenses incurred by the fund. In addition, private investment funds are not registered with the SEC and may not be registered with any other regulatory authority. Accordingly, they are not subject to certain regulatory requirements and oversight to which registered issuers are subject. There may be very little public information available about their investments and performance. Moreover, because sales of shares of private investment funds are generally restricted to certain qualified purchasers, such shares may be illiquid and it could be difficult for the fund to sell its shares at an advantageous price and time. Finally, because shares of private investment funds are not publicly traded, a fair value for the fund's investment in these companies typically will have to be determined under policies approved by the board.
Exchange-Traded Funds and Similar Exchange-Traded Products (ETFs)
Although certain ETFs are actively managed, most ETFs are designed to provide investment results that generally correspond to the price and yield performance of the component securities or commodities of a benchmark index.
III-44
These ETFs may include S&P Depositary Receipts ("SPDRs"), DIAMONDS, Nasdaq-100 Index Tracking Stock (also referred to as "Nasdaq-100 Shares") and iShares exchange-traded funds ("iShares"), such as iShares Russell 2000 Growth Index Fund. ETFs usually are units of beneficial interest in an investment trust or represent undivided ownership interests in a portfolio of securities or commodities. For an ETF designed to correspond to a securities index benchmark, the ETF's portfolio typically consists of all or substantially all of the component securities of, and in substantially the same weighting as, the relevant benchmark index. The benchmark indexes of SPDRs, DIAMONDS and Nasdaq-100 Shares are the S&P 500 Stock Index, the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the Nasdaq-100 Index, respectively. The benchmark index for iShares varies, generally corresponding to the name of the particular iShares fund. ETFs are listed on an exchange, and shares are generally purchased and sold in the secondary market at market price. At times, the market price may be at a premium or discount to the ETF's NAV. Because shares of ETFs trade on an exchange, they may be subject to trading halts on the exchange.
The values of ETFs are subject to change as the values of their respective component securities or commodities fluctuate according to market volatility. Investments in ETFs that are designed to correspond to an index of securities involve certain inherent risks generally associated with investments in a portfolio of such securities, including the risk that the general level of securities prices may decline, thereby adversely affecting the value of ETFs invested in by a fund. Similarly, investments in ETFs that are designed to correspond to commodity returns involve certain inherent risks generally associated with investment in commodities. Moreover, investments in ETFs designed to correspond to indexes of securities may not exactly match the performance of a direct investment in the respective indexes to which they are intended to correspond due to the temporary unavailability of certain index securities in the secondary market or other extraordinary circumstances, such as discrepancies with respect to the weighting of securities.
Exchange-traded notes ("ETNs") are senior, unsecured, unsubordinated debt securities whose returns are linked to the performance of a particular market benchmark or strategy minus applicable fees. ETNs are traded on an exchange (e.g., the NYSE) during normal trading hours. However, investors can also hold the ETN until maturity. At maturity, the issuer pays to the investor a cash amount equal to the principal amount, subject to adjustment for the market benchmark or strategy factor.
ETNs do not make periodic coupon payments or provide principal protection. ETNs are subject to credit risk, and the value of the ETN may drop due to a downgrade in the issuer's credit rating, despite the underlying market benchmark or strategy remaining unchanged. The value of an ETN may also be influenced by time to maturity, level of supply and demand for the ETN, volatility and lack of liquidity in underlying assets, changes in the applicable interest rates, changes in the issuer's credit rating and economic, legal, political or geographic events that affect the referenced underlying asset. When a fund invests in an ETN, it will bear its proportionate share of any fees and expenses borne by the ETN. These fees and expenses generally reduce the return realized at maturity or upon redemption from an investment in an ETN; therefore, the value of the index underlying the ETN must increase significantly in order for an investor in an ETN to receive at least the principal amount of the investment at maturity or upon redemption. A fund's decision to sell ETN holdings may be limited by the availability of a secondary market.
Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs)
An investment in MLPs involves risks that differ from an investment in common stock. Investing in MLPs involves certain risks related to investing in the underlying assets of the MLPs.
An MLP generally has two classes of partners, the general partner and the limited partners who hold common units. MLP common units represent an equity ownership interest in a partnership, providing limited voting rights and entitling the holder to a share of the company's success through distributions and/or capital appreciation. The general partner normally controls the MLP through an equity interest plus units that are subordinated to the common (publicly traded) units for an initial period and then only converting to common if certain financial tests are met. As a motivation for the general partner to successfully manage the MLP and increase cash flows, the terms of most MLPs typically provide that the general partner receives a larger portion of the net income as distributions reach higher target levels. As cash flow grows, the general partner receives a greater interest in the incremental income compared to the interest of limited partners.
III-45
Unlike stockholders of a corporation, common unit holders do not elect directors annually and generally have the right to vote only on certain significant events, such as mergers, a sale of substantially all of the assets, removal of the general partner or material amendments to the partnership agreement. MLPs are required by their partnership agreements to distribute a large percentage of their current operating earnings. Common unit holders generally have first right to a minimum quarterly distribution prior to distributions to the convertible subordinated unit holders or the general partner (including incentive distributions). Common unit holders typically have arrearage rights if the minimum quarterly distribution is not met. In the event of liquidation, MLP common unit holders have first right to the partnership's remaining assets after bondholders, other debt holders, and preferred unit holders have been paid in full. MLP common units trade on a national securities exchange or over-the-counter. MLP common units and other equity securities can be affected by macroeconomic and other factors affecting the stock market in general, expectations of interest rates, investor sentiment towards MLPs or its business sector, changes in a particular issuer's financial condition, or unfavorable or unanticipated poor performance of a particular issuer (in the case of MLPs, generally measured in terms of distributable cash flow). Prices of common units of individual MLPs and other equity securities can also be affected by fundamentals unique to the partnership or company, including earnings power and coverage ratios.
The benefit derived from a fund's investment in MLPs is largely dependent on the MLPs being treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A change in current tax law, or a change in the business of a given MLP, could result in an MLP being treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, which would result in such MLP being required to pay U.S. federal income tax on its taxable income. Thus, if any of the MLPs owned by a fund were treated as corporations for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the after-tax return to the fund with respect to its investment in such MLPs would be materially reduced, which could cause a decline in the value of the fund's shares.
Some limited liability companies ("LLCs") may be treated as MLPs for federal income tax purposes. Similar to MLPs, these LLCs typically do not pay federal income tax at the entity level and are required by their operating agreements to distribute a large percentage of their current operating earnings. In contrast to MLPs, these LLCs have no general partner and there are no incentives that entitle management or other unit holders to increased percentages of cash distributions as distributions reach higher target levels. In addition, LLC common unit holders typically have voting rights with respect to the LLC, whereas MLP common units have limited voting rights.
Depending on the fund, derivatives may be used for a variety of reasons, including to (1) hedge to seek to mitigate certain market, interest rate or currency risks; (2) to manage the maturity or the interest rate sensitivity (sometimes called duration) of fixed-income securities; (3) to provide a substitute for purchasing or selling particular securities to reduce portfolio turnover, to seek to obtain a particular desired return at a lower cost to a fund than if the fund had invested directly in an instrument yielding the desired return, such as when a fund "equitizes" available cash balances by using a derivative instrument to gain exposure to relevant equity investments or markets consistent with its investment objective and policies, or for other reasons; or (4) to seek to increase potential returns. Generally, a derivative is a financial contract whose value depends upon, or is derived from, the value of an underlying asset, reference rate or index, and may relate to stocks, bonds, interest rates, currencies or currency exchange rates and related indexes. Derivatives may provide a cheaper, quicker or more specifically focused way to invest than "traditional" securities would. Examples of derivative instruments include options contracts, futures contracts, options on futures contracts, forward contracts, swap agreements, credit derivatives, structured securities and participatory notes. Whether or not a fund may use some or all of these derivatives varies by fund. In addition, a fund's portfolio managers may decide not to employ some or all of these strategies, and there is no assurance that any derivatives strategy used by the fund will succeed.
Derivatives can be volatile and involve various types and degrees of risk, depending upon the characteristics of the particular derivative and the portfolio as a whole. Derivatives permit a fund to increase or decrease the level of risk, or change the character of the risk, to which its portfolio is exposed in much the same way as the fund can increase or decrease the level of risk, or change the character of the risk, of its portfolio by making investments in specific securities. However, derivatives may entail investment exposures that are greater than their cost would suggest, meaning that a small investment in derivatives could have a large potential impact on the fund's performance. Derivatives involve greater risks than if a fund had invested in the reference obligation directly.
III-46
An investment in derivatives at inopportune times or when market conditions are judged incorrectly may lower return or result in a loss. A fund could experience losses if its derivatives were poorly correlated with underlying instruments or the fund's other investments or if the fund were unable to liquidate its position because of an illiquid secondary market. The market for many derivatives is, or suddenly can become, illiquid. Changes in liquidity may result in significant, rapid and unpredictable changes in the prices for derivatives.
Derivatives may be purchased on established exchanges or through privately negotiated transactions referred to as over-the-counter derivatives. Exchange-traded derivatives, primarily futures contracts and options, generally are guaranteed by the clearing agency that is the issuer or counterparty to such derivatives. This guarantee usually is supported by a variation margin payment system operated by the clearing agency in order to reduce overall credit risk. As a result, unless the clearing agency defaults, there is relatively little counterparty credit risk associated with derivatives purchased on an exchange. In contrast, no clearing agency guarantees over-the-counter derivatives. Therefore, each party to an over-the-counter derivative bears the risk that the counterparty will default. Accordingly, the Adviser will consider the creditworthiness of counterparties to over-the-counter derivatives in the same manner as it would review the credit quality of a security to be purchased by a fund. Over-the-counter derivatives are less liquid than exchange-traded derivatives since the other party to the transaction may be the only investor with sufficient understanding of the derivative to be interested in bidding for it. Derivatives that are considered illiquid will be subject to a fund's limit on illiquid investments.
Some derivatives may involve leverage (e.g., an instrument linked to the value of a securities index may return income calculated as a multiple of the price movement of the underlying index). This economic leverage will increase the volatility of these instruments as they may increase or decrease in value more quickly than the underlying security, index, futures contract, currency or other economic variable. Pursuant to regulations and/or published positions of the SEC, a fund may be required to segregate permissible liquid assets, or engage in other measures approved by the SEC or its staff, to "cover" the fund's obligations relating to its transactions in derivatives. For example, in the case of futures contracts or forward contracts that are not contractually required to cash settle, a fund must set aside liquid assets equal to such contracts' full notional value (generally, the total numerical value of the asset underlying a future or forward contract at the time of valuation) while the positions are open. With respect to futures contracts or forward contracts that are contractually required to cash settle, however, a fund is permitted to set aside liquid assets in an amount equal to the fund's daily marked-to-market net obligation (i.e., the fund's daily net liability) under the contracts, if any, rather than such contracts' full notional value. By setting aside assets equal to only its net obligations under cash-settled derivatives, a fund may employ leverage to a greater extent than if the fund were required to segregate assets equal to the full notional value of such contracts. Requirements to maintain cover might impair a fund's ability to sell a portfolio security, meet redemption requests or other current obligations, or make an investment at a time when it would otherwise be favorable to do so, or require that the fund sell a portfolio security at a disadvantageous time.
Successful use of certain derivatives may be a highly specialized activity that requires skills that may be different than the skills associated with ordinary portfolio securities transactions. If the Adviser is incorrect in its forecasts of market factors, or a counterparty defaults, investment performance would diminish compared with what it would have been if derivatives were not used. Successful use of derivatives by a fund also is subject to the Adviser's ability to predict correctly movements in the direction of the relevant market and, to the extent the transaction is entered into for hedging purposes, to ascertain the appropriate correlation between the securities or position being hedged and the price movements of the corresponding derivative position. For example, if a fund enters into a derivative position to hedge against the possibility of a decline in the market value of securities held in its portfolio and the prices of such securities instead increase, the fund will lose part or all of the benefit of the increased value of securities which it has hedged because it will have offsetting losses in the derivative position.
Options and futures contracts prices can diverge from the prices of their underlying instruments. Options and futures contracts prices are affected by such factors as current and anticipated short-term interest rates, changes in volatility of the underlying instrument, and the time remaining until expiration of the contract, which may not affect the prices of the underlying instruments in the same way. Imperfect correlation may also result from differing levels of demand in the options and futures markets and the securities markets, from structural differences in how options and futures and securities are traded, or from imposition of daily price fluctuation limits or trading halts. A fund may purchase or sell options and futures contracts with a greater or lesser value than any securities it wishes to hedge or intends to purchase in order to attempt to compensate for differences in volatility between the contract and
III-47
the securities, although this may not be successful in all cases. If price changes in a fund's options or futures positions used for hedging purposes are poorly correlated with the investments the fund is attempting to hedge, the options or futures positions may fail to produce anticipated gains or result in losses that are not offset by gains in other investments.
The funds, except the CPO Fund, have claimed exclusions from the definition of the term "commodity pool operator" pursuant to Regulation 4.5 under the CEA and, therefore, are not subject to registration or regulation as a CPO under the CEA. Although the Manager has been registered as a "commodity trading advisor" and "commodity pool operator" with the National Futures Association since December 19, 2012 and January 1, 2013, respectively, the Manager relies on the exemption in Regulation 4.14(a)(8) to provide commodity interest trading advice to the funds that rely on Regulation 4.5 exclusion.
The funds, except the CPO Fund, may be limited in their ability to use commodity futures or options thereon, engage in certain swap transactions or make certain other investments (collectively, "commodity interests") if such funds continue to claim the exclusion from the definition of CPO. In order to be eligible to continue to claim this exclusion, if a fund uses commodity interests other than for bona fide hedging purposes (as defined by the CFTC), the aggregate initial margin and premiums required to establish those positions (after taking into account unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such positions and excluding the amount by which options are "in-the-money" at the time of purchase) may not exceed 5% of the fund's NAV, or, alternatively, the aggregate net notional value of those positions, as determined at the time the most recent position was established, may not exceed 100% of the fund's NAV (after taking into account unrealized profits and unrealized losses on any such positions). In addition to meeting one of the foregoing trading limitations, a fund may not market itself as a commodity pool or otherwise as a vehicle for trading in the commodity futures, commodity options or swaps markets. Even if a fund's direct use of commodity interests complies with the trading limitations described above, the fund may have indirect exposure to commodity interests in excess of such limitations. Such exposure may result from the fund's investment in other investment vehicles, including investment companies that are not managed by the Manager or one of its affiliates, certain securitized vehicles that may invest in commodity interests and/or non-equity REITs that may invest in commodity interests (collectively, "underlying funds"). Because the Manager may have limited or no information as to the commodity interests in which an underlying fund invests at any given time, the CFTC has issued temporary no-action relief permitting registered investment companies, such as the funds, to continue to rely on the exclusion from the definition of CPO. The Manager, on behalf of the funds, has filed the required notice to claim this no-action relief. In order to rely on the temporary no-action relief, the Manager must meet certain conditions and the funds must otherwise comply with the trading and market limitations described above with respect to their direct investments in commodity interests.
The CPO Fund no longer claims an exclusion from the definition of CPO and, as a result, is not subject to the trading and marketing limitations discussed above with respect to their use of commodity interests. In accordance with CFTC guidance, the Manager, and not the CPO Fund, has registered as a CPO with the NFA and will operate the CPO Fund in compliance with applicable CFTC regulations, in addition to all applicable SEC regulations. On August 13, 2013, the CFTC adopted final rules (the "Harmonization Rules") with respect to the compliance obligations of advisers to registered investment companies that are registered as CPOs, such as the CPO Fund. Under the Harmonization Rules, the Manager will be deemed to have fulfilled its disclosure, reporting and recordkeeping obligations under applicable CFTC regulations with respect to the CPO Fund by complying with comparable SEC regulations, subject to certain notice filings with the NFA and disclosures in the CPO Fund's prospectus.
If a fund, except the CPO Fund, were to invest in commodity interests in excess of the trading limitations discussed above and/or market itself as a vehicle for trading in the commodity futures, commodity options or swaps markets, the fund would withdraw its exclusion from the definition of CPO and the Manager would become subject to regulation as a CPO, and would need to comply with the Harmonization Rules, with respect to that fund, in addition to all applicable SEC regulations.
It is possible that developments in the derivatives markets, including potential government regulation, could adversely affect the ability to terminate existing derivatives positions or to realize amounts to be received in such transactions.
Futures Transactions. A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy and sell a security or other
III-48
asset for a set price on a future date. When a fund sells a futures contract, it incurs an obligation to deliver a specified amount of the obligation underlying the futures contract at a specified time in the future for an agreed upon price. With respect to index futures, no physical transfer of the securities underlying the index is made. Rather, the parties settle by exchanging in cash an amount based on the difference between the contract price and the closing value of the index on the settlement date. An option on a futures contract gives the holder of the option the right to buy from or sell to the writer of the option a position in a futures contract at a specified price on or before a specified expiration date. When a fund writes an option on a futures contract, it becomes obligated, in return for the premium paid, to assume a position in a futures contract at a specified exercise price at any time during the term of the option. If the fund has written a call option, it assumes a short futures position. If the fund has written a put option, it assumes a long futures position. When a fund purchases an option on a futures contract, it acquires the right, in return for the premium it pays, to assume a position in a futures contract (a long position if the option is a call and a short position if the option is a put). The purchase of futures or call options on futures can serve as a long hedge, and the sale of futures or the purchase of put options on futures can serve as a short hedge. Writing call options on futures contracts can serve as a limited short hedge, using a strategy similar to that used for writing call options on securities or indexes. Similarly, writing put options on futures contracts can serve as a limited long hedge.
Futures contracts are traded on exchanges, so that, in most cases, either party can close out its position on the exchange for cash, without delivering the security or other asset. Although some futures contracts call for making or taking delivery of the underlying securities or other asset, generally these obligations are closed out before delivery by offsetting purchases or sales of matching futures contracts (same exchange, underlying asset, and delivery month). Closing out a futures contract sale is effected by purchasing a futures contract for the same aggregate amount of the specific type of financial instrument with the same delivery date. If an offsetting purchase price is less than the original sale price, a fund realizes a capital gain, or if it is more, a fund realizes a capital loss. Conversely, if an offsetting sale price is more than the original purchase price, a fund realizes a capital gain, or if it is less, a fund realizes a capital loss. Transaction costs also are included in these calculations.
Engaging in these transactions involves risk of loss to a fund which could adversely affect the value of the fund's net assets. No assurance can be given that a liquid market will exist for any particular contract at any particular time. Many futures exchanges and boards of trade limit the amount of fluctuation permitted in futures contract prices during a single trading day. Once the daily limit has been reached in a particular contract, no trades may be made that day at a price beyond that limit or trading may be suspended for specified periods during the trading day. Futures contract prices could move to the limit for several consecutive trading days with little or no trading, thereby preventing prompt liquidation of futures positions and potentially leading to substantial losses.
A fund may engage in futures transactions in foreign markets to the extent consistent with applicable law and the fund's ability to invest in foreign securities. Foreign futures markets may offer advantages such as trading opportunities or arbitrage possibilities not available in the United States. Foreign markets, however, may have greater risk potential than domestic markets. For example, some foreign exchanges are principal markets so that no common clearing facility exists and an investor may look only to the broker for performance of the contract. In addition, any profits that a fund might realize in trading could be eliminated by adverse changes in the currency exchange rate, or the fund could incur losses as a result of those changes.
Futures contracts and options on futures contracts include those with respect to securities, securities indexes, interest rates and foreign currencies and Eurodollar contracts, to the extent a fund can invest in the underlying reference security, instrument or asset.
Security Futures Contract. A security future obligates a fund to purchase or sell an amount of a specific security at a future date at a specific price.
Index Futures Contract. An index future obligates a fund to pay or receive an amount of cash based upon the change in value of the index based on the prices of the securities that comprise the index.
Interest Rate Futures Contract. An interest rate future obligates a fund to purchase or sell an amount of a specific debt security at a future date at a specific price (or, in some cases, to settle an equivalent amount in cash).
Foreign Currency Futures Contract. A foreign currency future obligates a fund to purchase or sell an amount of a
III-49
specific currency at a future date at a specific price.
Eurodollar Contracts. A Eurodollar contract is a U.S. dollar-denominated futures contract or option thereon which is linked to the LIBOR, although foreign currency-denominated instruments are available from time to time. Eurodollar futures contracts enable purchasers to obtain a fixed rate for the lending of funds and sellers to obtain a fixed rate for borrowings. Certain funds might use Eurodollar futures contracts and options thereon to hedge against changes in LIBOR, to which many interest rate swaps and fixed-income instruments are linked.
Options. A call option gives the purchaser of the option the right to buy, and obligates the writer to sell, the underlying security, securities or other asset at the exercise price at any time during the option period, or at a specific date. Conversely, a put option gives the purchaser of the option the right to sell, and obligates the writer to buy, the underlying security, securities or other asset at the exercise price at any time during the option period, or at a specific date. A fund receives a premium from writing an option which it retains whether or not the option is exercised.
A covered call option written by a fund is a call option with respect to which the fund owns the underlying security or otherwise covers the transaction such as by segregating permissible liquid assets. The principal reason for writing covered call options is to realize, through the receipt of premiums, a greater return than would be realized on the underlying securities alone.
Options may be traded on U.S. or, to the extent a fund may invest in foreign securities, foreign securities exchanges or in the over-the-counter market. There is no assurance that sufficient trading interest to create a liquid secondary market on a securities exchange will exist for any particular option or at any particular time, and for some options no such secondary market may exist. A liquid secondary market in an option may cease to exist for a variety of reasons. In the past, for example, higher than anticipated trading activity or order flow, or other unforeseen events, at times have rendered certain of the clearing facilities inadequate and resulted in the institution of special procedures, such as trading rotations, restrictions on certain types of orders or trading halts or suspensions in one or more options. There can be no assurance that similar events, or events that may otherwise interfere with the timely execution of customers' orders, will not recur. In such event, it might not be possible to effect closing transactions in particular options. If, as a covered call option writer, a fund is unable to effect a closing purchase transaction in a secondary market, it will not be able to sell the underlying security until the option expires or it delivers the underlying security upon exercise or it otherwise covers its position.
Purchases or sales of options on exchanges owned by The NASDAQ OMX Group, Inc. may result, indirectly, in a portion of the transaction and other fees assessed on options trading being paid to The Bank of New York Mellon, an affiliate of the Manager, as the result of an arrangement between The NASDAQ OMX Group, Inc. and The Bank of New York Mellon.
Call and put options in which a fund may invest include the following, in each case, to the extent that a fund can invest in such securities or instruments (or securities underlying an index, in the case of options on securities indexes).
Options on Securities. Call and put options on specific securities (or groups or "baskets" of specific securities), including equity securities (including convertible securities), U.S. Government securities, municipal securities, mortgage-related securities, asset-backed securities, foreign sovereign debt, corporate debt securities or Eurodollar instruments, convey the right to buy or sell, respectively, the underlying securities at prices which are expected to be lower or higher than the current market prices of the securities at the time the options are exercised.
Options on Securities Indexes. An option on an index is similar to an option in respect of specific securities, except that settlement does not occur by delivery of the securities comprising the index. Instead, the option holder receives an amount of cash if the closing level of the index upon which the option is based is greater in the case of a call, or less, in the case of a put, than the exercise price of the option. Thus, the effectiveness of purchasing or writing index options will depend upon price movements in the level of the index rather than the price of a particular security.
Foreign Currency Options. Call and put options on foreign currency convey the right to buy or sell the underlying currency at a price which is expected to be lower or higher than the spot price of the currency at the time the option is exercised or expires.
III-50
Swap Transactions. Swap agreements involve the exchange by a fund with another party of their respective commitments to pay or receive payments at specified dates based upon or calculated by reference to changes in specified prices or rates (e.g., interest rates in the case of interest rate swaps) based on a specified amount (the "notional") amount. Some swaps are, and more in the future will be, centrally cleared. Swaps that are centrally cleared are subject to the creditworthiness of the clearing organizations involved in the transaction. For example, a fund could lose margin payments it has deposited with a clearing organization as well as the net amount of gains not yet paid by the clearing organization if the clearing organization breaches its agreement with the fund or becomes insolvent or goes into bankruptcy. In the event of bankruptcy of the clearing organization, the fund may be entitled to the net amount of gains the fund is entitled to receive plus the return of margin owed to it only in proportion to the amount received by the clearing organization's other customers, potentially resulting in losses to the fund. Swap agreements also may be two party contracts entered into primarily by institutional investors for periods ranging from a few weeks to more than one year.
Swap agreements will tend to shift investment exposure from one type of investment to another. For example, if a fund agreed to exchange payments in U.S. dollars for payments in a foreign currency, the swap agreement would tend to decrease the fund's exposure to U.S. interest rates and increase its exposure to foreign currency and interest rates. Depending on how they are used, swap agreements may increase or decrease the overall volatility of a fund's investments and its share price and yield.
Most swap agreements entered into are cash settled and calculate the obligations of the parties to the agreement on a "net basis." Thus, a fund's current obligations (or rights) under a swap agreement generally will be equal only to the net amount to be paid or received under the agreement based on the relative values of the positions held by each party to the agreement (the "net amount"). A fund's current obligations under a swap agreement will be accrued daily (offset against any amounts owed to the fund) and any accrued but unpaid net amounts owed to a swap counterparty will be covered by the segregation of permissible liquid assets of the fund. A fund will enter into swap agreements only with counterparties that meet certain standards of creditworthiness (generally, such counterparties would have to be eligible counterparties under the terms of the Manager's repurchase agreement guidelines).
A swap option is a contract (sometimes called "swaptions") that gives a counterparty the right (but not the obligation) in return for payment of a premium, to enter into a new swap agreement or to shorten, extend, cancel or otherwise modify an existing swap agreement, at some designated future time on specified terms. A cash-settled option on a swap gives the purchaser the right, in return for the premium paid, to receive an amount of cash equal to the value of the underlying swap as of the exercise date. These options typically are entered into with institutions, including securities brokerage firms. Depending on the terms of the particular option agreement, a fund generally will incur a greater degree of risk when it writes a swap option than it will incur when it purchases a swap option. When a fund purchases a swap option, it risks losing only the amount of the premium it has paid should it decide to let the option expire unexercised. However, when a fund writes a swap option, upon exercise of the option the fund will become obligated according to the terms of the underlying agreement.
The swaps market has been an evolving and largely unregulated market. It is possible that developments in the swaps market, including new regulatory requirements, could limit or prevent a fund's ability to utilize swap agreements or options on swaps as part of its investment strategy, terminate existing swap agreements or realize amounts to be received under such agreements, which could negatively affect the fund. As discussed above, some swaps currently are, and more in the future will be, centrally cleared, which affects how swaps are transacted. In particular, the Dodd-Frank Act, has resulted in new clearing and exchange-trading requirements for swaps and other over-the-counter derivatives. The Dodd-Frank Act also requires the CFTC and/or the SEC, in consultation with banking regulators, to establish capital requirements for swap dealers and major swap participants as well as requirements for margin on uncleared derivatives, including swaps, in certain circumstances that will be clarified by rules proposed by the CFTC and/or the SEC. In addition, the CFTC and the SEC are reviewing the current regulatory requirements applicable to derivatives, including swaps, and it is not certain at this time how the regulators may change these requirements. For example, some legislative and regulatory proposals would impose limits on the maximum position that could be held by a single trader in certain contracts and would subject certain derivatives transactions to new forms of regulation that could create barriers to certain types of investment activity. Other provisions would expand entity registration requirements; impose business conduct, reporting and disclosure requirements on dealers, recordkeeping on counterparties such as the funds; and require banks to move some derivatives trading units to a non-guaranteed (but capitalized) affiliate separate from the deposit-taking bank or divest them altogether. While some provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act have either already been implemented
III-51
through rulemaking by the CFTC and/or the SEC or must be implemented through future rulemaking by those and other federal agencies, and any regulatory or legislative activity may not necessarily have a direct, immediate effect upon the funds, it is possible that, when compliance with these rules is required, they could potentially limit or completely restrict the ability of a fund to use certain derivatives as a part of its investment strategy, increase the cost of entering into derivatives transactions or require more assets of the fund to be used for collateral in support of those derivatives than is currently the case. Limits or restrictions applicable to the counterparties with which a fund engages in derivative transactions also could prevent the funds from using derivatives or affect the pricing or other factors relating to these transactions, or may change the availability of certain derivatives.
Specific swap agreements (and options thereon) include currency swaps; index swaps; interest rate swaps (including interest rate locks, caps, floors and collars); credit default swaps; and total return swaps (including equity swaps), in each case, to the extent that a fund can invest in the underlying reference security, instrument or asset (or fixed-income securities, in the case of interest rate swaps, or securities underlying an index, in the case of index swaps).
Currency Swap Transactions. A currency swap agreement involves the exchange of principal and interest in one currency for the same in another currency.
Index Swap Transactions. An index swap agreement involves the exchange of cash flows associated with a securities or other index.
Interest Rate Swap Transactions. An interest rate swap agreement involves the exchange of cash flows based on interest rate specifications and a specified principal amount, often a fixed payment for a floating payment that is linked to an interest rate.
An interest rate lock transaction (which may also be known as a forward rate agreement) is a contract between two parties to make or receive a payment at a future date determined on the basis of a specified interest rate or yield of a particular security (the "contracted interest rate") over a predetermined time period, with respect to a stated notional amount. These transactions typically are entered as a hedge against interest rate changes. One party to the contract locks in the contracted interest rate to seek to protect against an interest rate increase, while the other party seeks to protect against a possible interest rate decline. The payment at maturity is determined by the difference between the contracted interest rate and the then-current market interest rate.
In an interest rate cap one party receives payments at the end of each period in which a specified interest rate on a specified principal amount exceeds an agreed rate; conversely, in an interest rate floor one party may receive payments if a specified interest rate on a specified principal amount falls below an agreed rate. Caps and floors have an effect similar to buying or writing options. Interest rate collars involve selling a cap and purchasing a floor, or vice versa, to protect a fund against interest rate movements exceeding given minimum or maximum levels.
Credit Default Swap Transactions. Credit default swap agreements and similar agreements may have as reference obligations debt securities that are or are not currently held by a fund. The protection "buyer" in a credit default contract may be obligated to pay the protection "seller" an up front payment or a periodic stream of payments over the term of the contract provided generally that no credit event on a reference obligation has occurred. If a credit event occurs, the seller generally must pay the buyer the "par value" (full notional value) of the swap in exchange for an equal face amount of deliverable obligations of the reference entity described in the swap, or the seller may be required to deliver the related net cash amount, if the swap is cash settled.
Total Return Swap Transactions. In a total return swap agreement one party makes payments based on a set rate, either fixed or variable, while the other party makes payments based on the return of an underlying asset, which includes both the income it generates and any capital gains, and recovers any capital losses from the first party. The underlying reference asset of a total return swap may include an equity index, loans or bonds.
Contracts for Difference. A contract for difference ("CFD") is a contract between two parties, typically described as "buyer" and "seller," stipulating that the seller will pay to the buyer the difference between the current value of an asset and its value in the future. (If the difference is negative, then the buyer instead pays the seller.) In effect, CFDs are financial derivatives that allow a fund to take advantage of values moving up (long positions) or values moving down (short positions) on underlying assets. For example, when applied to equities, a CFD is an equity
derivative
III-52
equity
derivative that allows a fund to obtain investment exposure to share price movements, without the need for ownership of the underlying shares. CFDs are over-the-counter derivative instruments that are subject to the credit risk of the counterparty. Because CFDs are not traded on an exchange and may not have an expiration date, CFDs generally are illiquid.
Credit Linked Securities. Credit linked securities are issued by a limited purpose trust or other vehicle that, in turn, invests in a derivative instrument or basket of derivative instruments, such as credit default swaps or interest rate swaps, to obtain exposure to certain fixed-income markets or to remain fully invested when more traditional income producing securities are not available. Like an investment in a bond, an investment in these credit linked securities represents the right to receive periodic income payments (in the form of distributions) and payment of principal at the end of the term of the security. However, these payments are conditioned on the issuer's receipt of payments from, and the issuer's potential obligations to, the counterparties to certain derivative instruments entered into by the issuer of the credit linked security. For example, the issuer may sell one or more credit default swaps entitling the issuer to receive a stream of payments over the term of the swap agreements provided that no event of default has occurred with respect to the referenced debt obligation upon which the swap is based. If a default occurs, the stream of payments may stop and the issuer would be obligated to pay the counterparty the par (or other agreed upon value) of the referenced debt obligation.
Credit Derivatives. Credit derivative transactions include those involving default price risk derivatives and credit spread derivatives. Default price risk derivatives are linked to the price of reference securities or loans after a default by the issuer or borrower, respectively. Credit spread derivatives are based on the risk that changes in credit spreads and related market factors can cause a decline in the value of a security, loan or index. Credit derivatives may take the form of options, swaps, credit-linked notes and other over-the-counter instruments. The risk of loss in a credit derivative transaction varies with the form of the transaction. For example, if a fund purchases a default option on a security, and if no default occurs with respect to the security, the fund's loss is limited to the premium it paid for the default option. In contrast, if there is a default by the grantor of a default option, a fund's loss will include both the premium it paid for the option and the decline in value of any underlying security that the default option hedged (if the option was entered into for hedging purposes). If a fund is a buyer of credit protection in a credit default swap agreement and no credit event occurs, the fund recovers nothing if the swap is held through its termination date. However, if a credit event occurs, the fund may elect to receive the full notional value of the swap in exchange for an equal face amount of deliverable obligations of the reference entity that may have little or no value. As a seller of credit protection, a fund generally receives an upfront payment or a fixed rate of income throughout the term of the swap, which typically is between six months and three years, provided that there is no credit event. If a credit event occurs, generally the seller must pay the buyer the full notional value of the swap in exchange for an equal face amount of deliverable obligations of the reference entity that may have little or no value. Unlike credit default swaps, credit-linked notes are funded balance sheet assets that offer synthetic credit exposure to a reference entity in a structure designed to resemble a synthetic corporate bond or loan. Credit-linked notes are frequently issued by special purpose vehicles that would hold some form of collateral securities financed through the issuance of notes or certificates to a fund. The fund receives a coupon and par redemption, provided there has been no credit event of the reference entity. The vehicle enters into a credit swap with a third party in which it sells default protection in return for a premium that subsidizes the coupon to compensate the fund for the reference entity default risk. A fund will enter into credit derivative transactions only with counterparties that meet certain standards of creditworthiness (generally, such counterparties would have to be eligible counterparties under the terms of the Manager's repurchase agreement guidelines).
Structured Securities and Hybrid Instruments
Structured Securities. Structured securities are securities whose cash flow characteristics depend upon one or more indexes or that have embedded forwards or options or securities where a fund's investment return and the issuer's payment obligations are contingent on, or highly sensitive to, changes in the value of underlying assets, indexes, interest rates or cash flows ("embedded index"). When a fund purchases a structured security, it will make a payment of principal to the counterparty. Some structured securities have a guaranteed repayment of principal while others place a portion (or all) of the principal at risk. Guarantees are subject to the risk of default by the counterparty or its credit provider. The terms of such structured securities normally provide that their principal and/or interest payments are to be adjusted upwards or downwards (but not ordinarily below zero) to reflect changes in the embedded index while the structured securities are outstanding. As a result, the interest and/or principal
III-53
payments that may be made on a structured security may vary widely, depending upon a variety of factors, including the volatility of the embedded index and the effect of changes in the embedded index on principal and/or interest payments. The rate of return on structured securities may be determined by applying a multiplier to the performance or differential performance of the embedded index. Application of a multiplier involves leverage that will serve to magnify the potential for gain and the risk of loss. Structured securities may be issued in subordinated and unsubordinated classes, with subordinated classes typically having higher yields and greater risks than an unsubordinated class. Structured securities may not have an active trading market, which may have an adverse impact on a fund's ability to dispose of such securities when necessary to meet the fund's liquidity needs or in response to a specific economic event such as a deterioration in the creditworthiness of the issuer. The lack of an active trading market also may make it more difficult for a fund to obtain accurate market quotations for purposes of valuing the fund's portfolio and calculating its NAV.
Hybrid Instruments. A hybrid instrument can combine the characteristics of securities, futures and options. For example, the principal amount or interest rate of a hybrid instrument could be tied (positively or negatively) to the price of a benchmark, e.g., currency, securities index or another interest rate. The interest rate or the principal amount payable at maturity of a hybrid security may be increased or decreased, depending on changes in the value of the benchmark. Hybrids can be used as an efficient means of pursuing a variety of investment strategies, including currency hedging, duration management and increased total return. Hybrids may not bear interest or pay dividends. The value of a hybrid or its interest rate may be a multiple of a benchmark and, as a result, may be leveraged and move (up or down) more steeply and rapidly than the benchmark. These benchmarks may be sensitive to economic and political events, such as currency devaluations, which cannot be readily foreseen by the purchaser of a hybrid. Under certain conditions, the redemption value of a hybrid could be zero. Thus, an investment in a hybrid may entail significant market risks that are not associated with a similar investment in a traditional, U.S. dollar-denominated bond that has a fixed principal amount and pays a fixed rate or floating rate of interest.
Exchange-Linked Notes. Exchange-linked notes ("ELNs") are debt instruments that differ from a more typical fixed-income security in that the final payout is based on the return of the underlying equity, which can be a single stock, basket of stocks, or an equity index. Usually, the final payout is the amount invested times the gain in the underlying stock(s) or index times a note-specific participation rate, which can be more or less than 100%. Most ELNs are not actively traded on the secondary market and are designed to be kept to maturity. However, the issuer or arranger of the notes may offer to buy back the ELNs, although the buy-back price before maturity may be below the original amount invested. As a result, ELNs generally are considered illiquid.
ELNs are generally subject to the same risks as the securities to which they are linked. If the linked securities decline in value, the ELN may return a lower amount at maturity. ELNs involve further risks associated with purchases and sales of notes, including any applicable exchange rate fluctuations and a decline in the credit quality of the note's issuer. ELNs are frequently secured by collateral. If an issuer defaults, the fund would look to any underlying collateral to recover its losses. Ratings of issuers of ELNs refer only to the issuers' creditworthiness and the related collateral. They provide no indication of the potential risks of the linked securities.
Participation Notes. Participation notes are issued by banks or broker-dealers and are designed to replicate the performance of certain equity or debt securities or markets. Participation notes are a type of derivative which generally is traded over-the-counter. The performance results of participation notes will not replicate exactly the performance of the securities or markets that the notes seek to replicate due to transaction costs and other expenses. Risks of investing in participation notes include the same risks associated with a direct investment in the underlying security or market the notes seek to replicate. Participation notes constitute general unsecured contractual obligations of the banks or broker-dealers that issue them, and a fund is relying on the creditworthiness of such banks or broker-dealers and has no rights under a participation note against the issuers of the assets underlying such participation notes, including any collateral supporting a loan participation note.
Custodial Receipts. Custodial receipts, which may be underwritten by securities dealers or banks, represent the right to receive certain future principal and/or interest payments on a basket of securities which underlie the custodial receipts, or, in some cases, the payment obligation of a third party that has entered into an interest rate swap or other arrangement with the custodian. Underlying securities may include U.S. Government securities, municipal securities or other types of securities in which a fund may invest. A number of different arrangements are possible.
III-54
In a typical custodial receipt arrangement, an issuer or a third party owner of securities deposits such securities obligations with a custodian in exchange for custodial receipts. These custodial receipts are typically sold in private placements and are designed to provide investors with pro rata ownership of a portfolio of underlying securities. For certain securities law purposes, custodial receipts may not be considered obligations of the underlying securities held by the custodian. As a holder of custodial receipts, a fund will bear its proportionate share of the fees and expenses charged to the custodial account. Although under the terms of a custodial receipt a fund typically would be authorized to assert its rights directly against the issuer of the underlying obligation, the fund could be required to assert through the custodian bank those rights as may exist against the underlying issuers. Thus, in the event an underlying issuer fails to pay principal and/or interest when due, the fund may be subject to delays, expenses and risks that are greater than those that would have been involved if the fund had purchased a direct obligation of the issuer. In addition, in the event that the custodial account in which the underlying securities have been deposited is determined to be an association taxable as a corporation, instead of a non-taxable entity, the yield on the underlying securities would be reduced in recognition of any taxes paid.
Certain custodial receipts may be synthetic or derivative instruments that have interest rates that reset inversely to changing short-term rates and/or have embedded interest rate floors and caps that require the issuer to pay an adjusted interest rate if market rates fall below or rise above a specified rate. Because some of these instruments represent relatively recent innovations, and the trading market for these instruments is less developed than the markets for more traditional types of instruments, it is uncertain how these instruments will perform under different economic and interest-rate scenarios. Also, because these instruments may be leveraged, their market values may be more volatile than other types of fixed-income instruments and may present greater potential for capital gain or loss. The possibility of default by an issuer or the issuer's credit provider may be greater for these derivative instruments than for other types of instruments.
Combined Transactions. Certain funds may enter into multiple transactions, including multiple options, futures, swap, currency and/or interest rate transactions, and any combination of options, futures, swaps, currency and/or interest rate transactions ("combined transactions"), instead of a single transaction, as part of a single or combined strategy when, in the opinion of the Adviser, it is in the best interests of the fund to do so. A combined transaction will usually contain elements of risk that are present in each of its component transactions. Although combined transactions are normally entered into based on the Adviser's judgment that the combined strategies will reduce risk or otherwise more effectively achieve the desired portfolio management goal, it is possible that the combination will instead increase such risks or hinder achievement of the portfolio management objective.
Future Developments. A fund may take advantage of opportunities in derivatives transactions which are not presently contemplated for use by the fund or which are not currently available but which may be developed, to the extent such opportunities are both consistent with the fund's investment objective and legally permissible for the fund. Before a fund enters into such transactions or makes any such investment, the fund will provide appropriate disclosure in its prospectus or this SAI.
Investments in foreign currencies, including investing directly in foreign currencies, holding financial instruments that provide exposure to foreign currencies, or investing in securities that trade in, or receive revenues in, foreign currencies, are subject to the risk that those currencies will decline in value relative to the U.S. dollar.
Depending on the fund, foreign currency transactions could be entered into for a variety of purposes, including: (1) to fix in U.S. dollars, between trade and settlement date, the value of a security a fund has agreed to buy or sell; (2) to hedge the U.S. dollar value of securities the fund already owns, particularly if it expects a decrease in the value of the currency in which the foreign security is denominated; or (3) to gain or reduce exposure to the foreign currency for investment purposes. Foreign currency transactions may involve, for example, a fund's purchase of foreign currencies for U.S. dollars or the maintenance of short positions in foreign currencies. A short position would involve the fund agreeing to exchange an amount of a currency it did not currently own for another currency at a future date in anticipation of a decline in the value of the currency sold relative to the currency the fund contracted to receive. A fund may engage in cross currency hedging against price movements between currencies, other than the U.S. dollar, caused by currency exchange rate fluctuations. In addition, a fund might seek to hedge against changes in the value of a particular currency when no derivative instruments on that currency are available or such
III-55
derivative instruments are more expensive than certain other derivative instruments. In such cases, the fund may hedge against price movements in that currency by entering into transactions using derivative instruments on another currency or a basket of currencies, the values of which the Adviser believes will have a high degree of positive correlation to the value of the currency being hedged. The risk that movements in the price of the derivative instrument will not correlate perfectly with movements in the price of the currency being hedged is magnified when this strategy is used.
Currency hedging may substantially change a fund's exposure to changes in currency exchange rates and could result in losses if currencies do not perform as the Adviser anticipates. There is no assurance that a fund's currency hedging activities will be advantageous to the fund or that the Adviser will hedge at an appropriate time.
The cost of engaging in foreign currency exchange contracts for the purchase or sale of a specified currency at a specified future date ("forward contracts") varies with factors such as the currency involved, the length of the contract period and the market conditions then prevailing. Because forward contracts are usually entered into on a principal basis, no fees or commissions are involved. Generally, secondary markets do not exist for forward contracts, with the result that closing transactions can be made for forward contracts only by negotiating directly with the counterparty to the contract. As with other over-the-counter derivatives transactions, forward contracts are subject to the credit risk of the counterparty.
Currency exchange rates may fluctuate significantly over short periods of time. They generally are determined by the forces of supply and demand in the foreign exchange markets and the relative merits of investments in different countries, actual or perceived changes in interest rates and other complex factors, as seen from an international perspective. Currency exchange rates also can be affected unpredictably by intervention, or failure to intervene, by U.S. or foreign governments or central banks, or by currency controls or political developments in the United States or abroad.
The value of derivative instruments on foreign currencies depends on the value of the underlying currency relative to the U.S. dollar. Because foreign currency transactions occurring in the interbank market might involve substantially larger amounts than those involved in the use of foreign currency derivative instruments, a fund could be disadvantaged by having to deal in the odd lot market (generally consisting of transactions of less than $1 million) for the underlying foreign currencies at prices that are less favorable than for round lots.
There is no systematic reporting of last sale information for foreign currencies or any regulatory requirement that quotations available through dealers or other market sources be firm or revised on a timely basis. Quotation information generally is representative of very large transactions in the interbank market and thus might not reflect odd-lot transactions where rates might be less favorable. The interbank market in foreign currencies is a global, round-the-clock market.
Settlement of transactions involving foreign currencies might be required to take place within the country issuing the underlying currency. Thus, a fund might be required to accept or make delivery of the underlying foreign currency in accordance with any U.S. or foreign regulations regarding the maintenance of foreign banking arrangements by U.S. residents and might be required to pay any fees, taxes and charges associated with such delivery assessed in the issuing country.
Commodities are assets that have tangible properties, such as oil, metals, livestock or agricultural products. Historically, commodity investments have had a relatively high correlation with changes in inflation and a relatively low correlation to stock and bond returns. Commodity-related instruments provide exposure, which may include long and/or short exposure, to the investment returns of physical commodities that trade in commodities markets, without investing directly in physical commodities. A fund may invest in commodity-related securities and other instruments, such as certain ETFs, that derive value from the price movement of commodities, or some other readily measurable economic variable dependent upon changes in the value of commodities or the commodities markets. However, the ability of a fund to invest directly in commodities and certain commodity-related securities and other instruments is subject to significant limitations in order to enable the fund to maintain its status as a regulated investment company under the Code.
III-56
The value of commodity-related instruments may be affected by changes in overall market movements, volatility of the underlying benchmark, changes in interest rates or factors affecting a particular industry or commodity, such as drought, floods, weather, livestock disease, acts of terrorism, embargoes, tariffs and international economic, political and regulatory developments. The value of commodity-related instruments will rise or fall in response to changes in the underlying commodity or related index. Investments in commodity-related instruments may be subject to greater volatility than non-commodity based investments. A liquid secondary market may not exist for certain commodity-related instruments, and there can be no assurance that one will develop. Commodity-related instruments also are subject to credit and interest rate risks that in general affect the values of debt securities.
A fund may make short sales as part of its investment strategy, to hedge positions (such as to limit exposure to a possible market decline in the value of portfolio securities), for duration and risk management, to maintain portfolio flexibility or to seek to enhance returns. A short sale involves the sale of a security that a fund does not own in the expectation of purchasing the same security (or a security exchangeable therefor) at a later date and at a lower price. To complete a short sale transaction and make delivery to the buyer, the fund must borrow the security. The fund is obligated to replace the borrowed security to the lender, which is accomplished by a later purchase of the security by the fund. Until the security is replaced, the fund is required to pay the lender any dividends or interest accruing during the period of the loan. To borrow the security, the fund also may have to pay a fee to the lender, which would increase the cost to the fund of the security it sold short. The fund will incur a loss as a result of a short sale if the price of the security increases between the date of the short sale and the date on which the fund replaces the borrowed security. The fund will realize a gain if the security declines in price between those two dates. In certain cases, purchasing a security to cover a short position can itself cause the price of the security to rise, thereby exacerbating any loss, especially in an environment where others are taking the same actions. Short positions in stocks involve more risk than long positions in stocks because the maximum sustainable loss on a stock purchased is limited to the amount paid for the stock plus the transaction costs, whereas there is no maximum attainable price on the shorted stock. In theory, stocks sold short have unlimited risk. The amount of any gain will be decreased and the amount of any loss will be increased by any interest, premium and transaction charges or other costs a fund may be required to pay in connection with the short sale. A fund may not always be able to borrow a security the fund seeks to sell short at a particular time or at an acceptable price.
A fund also may make short sales "against the box," in which the fund enters into a short sale of a security it owns or has the immediate and unconditional right to acquire at no additional cost at the time of the sale.
When a fund makes a short sale, it must leave the proceeds thereof with the broker and deposit with, or pledge to, the broker an amount of cash or liquid securities sufficient under current margin regulations to collateralize its obligation to replace the borrowed securities that have been sold. Until a fund closes its short position or replaces the borrowed security, the fund will: (1) segregate permissible liquid assets in an amount that, together with the amount provided as collateral, is at least equal to the current value of the security sold short; or (2) otherwise cover its short position through offsetting positions. Short-selling is considered "leverage" and may involve substantial risk.
Fund portfolio securities may be lent to brokers, dealers and other financial institutions needing to borrow securities to complete certain transactions. In connection with such loans, a fund would remain the owner of the loaned securities and continue to be entitled to payments in amounts equal to the interest, dividends or other distributions payable on the loaned securities. A fund also has the right to terminate a loan at any time. Any voting rights that accompany the loaned securities generally pass to the borrower of the securities, but the fund retains the right to recall a security and may then exercise the security's voting rights. In order to vote the proxies of securities out on loan, the securities must be recalled prior to the established record date. A fund may recall the loan to vote proxies if a material issue affecting the fund's investment is to be voted upon. Subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, an investment company is limited in the amount of portfolio securities it may loan to 33-1/3% of its total assets (including the value of all assets received as collateral for the loan). Except as may be otherwise described in "Investments, Investment Techniques and Risks" in Part II of this SAI, a fund will receive collateral consisting of cash, cash equivalents, U.S. Government securities or irrevocable letters of credit, which will
III-57
be maintained at all times in an amount equal to at least 100% of the current market value of the loaned securities. If the collateral consists of a letter of credit or securities, the borrower will pay the fund a loan premium fee. If the collateral consists of cash, the fund will reinvest the cash and pay the borrower a pre-negotiated fee or "rebate" from any return earned on the investment. A fund may participate in a securities lending program operated by the Lending Agent. The Lending Agent will receive a percentage of the total earnings of the fund derived from lending its portfolio securities. Should the borrower of the securities fail financially, the fund may experience delays in recovering the loaned securities or exercising its rights in the collateral. Loans are made only to borrowers that are deemed by the Adviser to be of good financial standing. In a loan transaction, a fund will also bear the risk of any decline in value of securities acquired with cash collateral. A fund will minimize this risk by limiting the investment of cash collateral to money market funds advised by the Manager, repurchase agreements or other high quality instruments with short maturities, in each case to the extent it is a permissible investment for the fund.
The 1940 Act, subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, permits an investment company to borrow in an amount up to 33-1/3% of the value of its total assets. Such borrowings may be for temporary or emergency purposes or for leveraging. If borrowings are for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes, when such borrowings exceed 5% of the value of a fund's total assets the fund will not make any additional investments.
Borrowing Money for Leverage. Leveraging (buying securities using borrowed money) exaggerates the effect on NAV of any increase or decrease in the market value of a fund's investments. These borrowings will be subject to interest costs which may or may not be recovered by appreciation of the securities purchased; in certain cases, interest costs may exceed the return received on the securities purchased. For borrowings for investment purposes, the 1940 Act requires a fund to maintain continuous asset coverage (total assets including borrowings, less liabilities exclusive of borrowings) of 300% of the amount borrowed. If the required coverage should decline as a result of market fluctuations or other reasons, the fund may be required to sell some of its portfolio securities within three days to reduce the amount of its borrowings and restore the 300% asset coverage, even though it may be disadvantageous from an investment standpoint to sell securities at that time. A fund also may be required to maintain minimum average balances in connection with such borrowing or pay a commitment or other fee to maintain a line of credit; either of these requirements would increase the cost of borrowing over the stated interest rate.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. Reverse repurchase agreements may be entered into with banks, broker/dealers or other financial institutions. This form of borrowing involves the transfer by a fund of an underlying debt instrument in return for cash proceeds based on a percentage of the value of the security. The fund retains the right to receive interest and principal payments on the security. At an agreed upon future date, the fund repurchases the security at principal plus accrued interest. As a result of these transactions, the fund is exposed to greater potential fluctuations in the value of its assets and its NAV per share. These borrowings will be subject to interest costs which may or may not be recovered by appreciation of the securities purchased; in certain cases, interest costs may exceed the return received on the securities purchased. To the extent a fund enters into a reverse repurchase agreement, the fund will segregate permissible liquid assets at least equal to the aggregate amount of its reverse repurchase obligations, plus accrued interest, in certain cases, in accordance with SEC guidance. The SEC views reverse repurchase transactions as collateralized borrowings by a fund.
Forward Commitments. The purchase or sale of securities on a forward commitment (including "TBA" (to be announced)), when-issued or delayed-delivery basis, means delivery and payment take place at a future date at a predetermined price and/or yield. Typically, no interest accrues to the purchaser until the security is delivered. When purchasing a security on a forward commitment basis, a fund assumes the risks of ownership of the security, including the risk of price and yield fluctuations, and takes such fluctuations into account when determining its NAV. Purchasing securities on a forward commitment, when-issued or delayed-delivery basis can involve the additional risk that the yield available in the market when the delivery takes place actually may be higher than that obtained in the transaction itself. The sale of securities on a forward commitment or delayed-delivery basis involves the risk that the prices available in the market on the delivery date may be greater than those obtained in the sale transaction.
Debt securities purchased on a forward commitment, when-issued or delayed-delivery basis are subject to changes
III-58
in value based upon the perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and changes, real or anticipated, in the level of interest rates (i.e., appreciating when interest rates decline and depreciating when interest rates rise). Securities purchased on a forward commitment, when-issued or delayed-delivery basis may expose a fund to risks because they may experience declines in value prior to their actual delivery. A fund will make commitments to purchase such securities only with the intention of actually acquiring the securities, but the fund may sell these securities or dispose of the commitment before the settlement date if it is deemed advisable as a matter of investment strategy. A fund would engage in forward commitments to increase its portfolio's financial exposure to the types of securities in which it invests. If the fund is fully or almost fully invested when forward commitment purchases are outstanding, such purchases may result in a form of leverage. Leveraging the portfolio in this manner will increase the fund's exposure to changes in interest rates and may result in greater potential fluctuation in the value of the fund's net assets and its NAV per share. A fund will segregate permissible liquid assets at least equal at all times to the amount of the fund's purchase commitments.
Forward Roll Transactions. In a forward roll transaction, a fund sells a security, such as a mortgage-related security, to a bank, broker-dealer or other financial institution and simultaneously agrees to purchase a similar security from the institution at a later date at an agreed upon price. During the period between the sale and purchase, the fund will not be entitled to receive interest and principal payments on the securities sold by the fund. Proceeds of the sale typically will be invested in short-term instruments, particularly repurchase agreements, and the income from these investments, together with any additional fee income received on the sale, will be expected to generate income for the fund exceeding the yield on the securities sold. Forward roll transactions involve the risk that the market value of the securities sold by the fund may decline below the purchase price of those securities. A fund will segregate permissible liquid assets at least equal to the amount of the repurchase price (including accrued interest).
In a mortgage "dollar roll" transaction, a fund sells mortgage-related securities for delivery in the current month and simultaneously contracts to purchase substantially similar securities on a specified future date. The mortgage-related securities that are purchased will be of the same type and will have the same interest rate as those securities sold, but generally will be supported by different pools of mortgages with different prepayment histories than those sold. A fund forgoes principal and interest paid during the roll period on the securities sold in a dollar roll, but the fund is compensated by the difference between the current sales price and the lower prices of the future purchase, as well as by any interest earned on the proceeds of the securities sold. The dollar rolls entered into by a fund normally will be "covered." A covered roll is a specific type of dollar roll for which there is an offsetting cash position or a cash equivalent security position that matures on or before the forward settlement date of the related dollar roll transaction. Covered rolls are not treated as borrowings or other senior securities and will be excluded from the calculation of a fund's borrowings.
Illiquid Securities Generally. The 1940 Act, subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, limits funds other than money market funds to 15% of net assets in illiquid securities. Illiquid securities, which are securities that cannot be sold or disposed of in the ordinary course of business within seven days at approximately the value ascribed to them by a fund, may include securities that are not readily marketable, such as securities that are subject to legal or contractual restrictions on resale that do not have readily available market quotations, repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice and certain privately negotiated derivatives transactions and securities used to cover such derivatives transactions. As to these securities, there is a risk that, should a fund desire to sell them, a ready buyer will not be available at a price the fund deems representative of their value, which could adversely affect the value of a fund's net assets.
Section 4(2) Paper and Rule 144A Securities. "Section 4(2) paper" consists of commercial obligations issued in reliance on the so-called "private placement" exemption from registration afforded by Section 4(2) of the Securities Act. Section 4(2) paper is restricted as to disposition under the federal securities laws, and generally is sold to institutional investors that agree that they are purchasing the paper for investment and not with a view to public distribution. Any resale by the purchaser must be pursuant to registration or an exemption therefrom. Section 4(2) paper normally is resold to other institutional investors through or with the assistance of the issuer or investment dealers who make a market in the Section 4(2) paper, thus providing liquidity. "Rule 144A securities" are securities that are not registered under the Securities Act but that can be sold to qualified institutional buyers in accordance with Rule 144A under the Securities Act. Rule 144A securities generally must be sold to other qualified
III-59
institutional buyers. If a particular investment in Section 4(2) paper or Rule 144A securities is not determined to be liquid, that investment will be included within the percentage limitation on investment in illiquid securities. Investing in Rule 144A securities could have the effect of increasing the level of fund illiquidity to the extent that qualified institutional buyers become, for a time, uninterested in purchasing these securities from a fund or other holders. Liquidity determinations with respect to Section 4(2) paper and Rule 144A securities will be made by the fund's board or by the Adviser pursuant to guidelines established by the board. The fund's board or the Adviser will consider availability of reliable price information and other relevant information in making such determinations.
A fund's classification as a "non-diversified" investment company means that the proportion of the fund's assets that may be invested in the securities of a single issuer is not limited by the 1940 Act. The 1940 Act generally requires a "diversified" investment company, with respect to 75% of its total assets, to invest not more than 5% of such assets in securities of a single issuer. Since a relatively high percentage of a fund's assets may be invested in the securities of a limited number of issuers or industries, the fund may be more sensitive to changes in the market value of a single issuer or industry. However, to meet federal tax requirements, at the close of each quarter a fund may not have more than 25% of its total assets invested in any one issuer and, with respect to 50% of its total assets, not more than 5% of its total assets invested in any one issuer. These limitations do not apply to U.S. Government securities or investments in certain other investment companies.
Investments in the Technology Sector
The technology sector has been among the most volatile sectors of the stock market. Many technology companies involve greater risks because their revenues and earnings tend to be less predictable (and some companies may be experiencing significant losses) and their share prices tend to be more volatile. Certain technology companies may have limited product lines, markets or financial resources, or may depend on a limited management group. In addition, these companies are strongly affected by worldwide technological developments, and their products and services may not be economically successful or may quickly become outdated. Investor perception may play a greater role in determining the day-to-day value of technology stocks than it does in other sectors. Investments made in anticipation of future products and services may decline dramatically in value if the anticipated products or services are delayed or cancelled.
Investments in the Real Estate Sector
An investment in securities of real estate companies may be susceptible to adverse economic or regulatory occurrences affecting that sector. An investment in real estate companies, while not an investment in real estate directly, involves risks associated with the direct ownership of real estate. These risks include: declines in the value of real estate; risks related to general and local economic conditions; possible lack of availability of mortgage funds; overbuilding; extended vacancies of properties; increased competition; increases in property taxes and operating expenses; changes in zoning laws; losses due to costs resulting from the clean-up of environmental problems; liability to third parties for damages resulting from environmental problems; casualty or condemnation losses; limitations on rents; changes in neighborhood values and the appeal of properties to tenants; changes in interest rates; financial condition of tenants, buyers and sellers of real estate; and quality of maintenance, insurance and management services.
An economic downturn could have a material adverse effect on the real estate markets and on real estate companies.
Real property investments are subject to varying degrees of risk. The yields available from investments in real estate depend on the amount of income and capital appreciation generated by the related properties. Income and real estate values may also be adversely affected by such factors as applicable laws (e.g., the Americans with Disabilities Act and tax laws), interest rate levels and the availability of financing. If the properties do not generate sufficient income to meet operating expenses, including, where applicable, debt service, ground lease payments, tenant improvements, third party leasing commissions and other capital expenditures, the income and ability of the real estate company to make payments of any interest and principal on its debt securities will be adversely affected. In addition, real property may be subject to the quality of credit extended and defaults by borrowers and tenants. The performance of the economy in each of the regions and countries in which the real estate owned by a portfolio company is located affects occupancy, market rental rates and expenses and, consequently, has an impact on the
III-60
income from such properties and their underlying values.
The financial results of major local employers also may have an impact on the cash flow and value of certain properties. In addition, certain real estate investments are relatively illiquid and, therefore, the ability of real estate companies to vary their portfolios promptly in response to changes in economic or other conditions is limited. A real estate company may also have joint venture investments in certain of its properties and, consequently, its ability to control decisions relating to such properties may be limited.
Investments in the Infrastructure Sector
Infrastructure companies are subject to a variety of factors that may affect their business or operations including high interest costs in connection with capital construction programs, costs associated with environmental and other regulations, the level of government spending on infrastructure projects, the effects of economic slowdown and surplus capacity, increased competition from other providers of services, uncertainties concerning the availability of fuel at reasonable prices, the effects of energy conservation policies and other factors. Infrastructure companies may also be subject to regulation by various governmental authorities and may also be affected by governmental regulation of rates charged to customers, service interruption due to environmental, operational or other mishaps, and the imposition of special tariffs and changes in tax laws, regulatory policies and accounting standards. Changes in law or regulations or general changes in market sentiment towards infrastructure assets may be difficult to predict or respond to, which may adversely affect the operations of infrastructure companies. Certain infrastructure companies may operate in limited areas, have few sources of revenue or face intense competition.
Some infrastructure companies' assets are not movable, which creates the risk that an event may occur in the region of the company's asset that may impair the performance of that asset and the performance of the issuer. Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, flood, lightning, hurricanes and wind or other man-made disasters, terrorist attacks or political activities could result in substantial damage to the facilities of companies located in the affected areas, and significant volatility in the products or services of infrastructure companies could adversely impact the prices of infrastructure companies' securities. Any destruction or loss of an infrastructure asset may have a major impact on the infrastructure company. Failure by the infrastructure company to carry adequate insurance or to operate the asset appropriately could lead to significant losses and damages.
Infrastructure companies' revenues may also be impacted by a number of factors, including a decrease in the number of users of the asset, inability to meet user demand, failure to efficiently maintain and operate infrastructure assets, failure of customers or counterparties to pay their contractual obligations, difficulties in obtaining financing for construction programs during inflationary periods or the inability to complete a project within budget. In addition, infrastructure assets can be highly leveraged, which makes such companies more susceptible to changes in interest rates. The market value of infrastructure companies also may decline in value in times of higher inflation rates.
Other factors that may affect the operations of infrastructure companies include changes in technology that could render the way in which a company delivers a product or service obsolete, significant changes to the number of ultimate end-users of a company's products, increased susceptibility to terrorist acts or political actions, and risks of environmental damage due to a company's operations or an accident.
Investments in the Natural Resources Sector
Many companies in the natural resources sector may experience more price volatility than securities of companies in other industries. Some of the commodities that these industries use or provide are subject to limited pricing flexibility because of supply and demand factors. Others are subject to broad price fluctuations as a result of the volatility of the prices for certain raw materials and the instability of supplies of other materials. These factors can affect the profitability of companies in the natural resources sector and, as a result, the value of their securities. To the extent a fund invests in the securities of companies with substantial natural resource assets, the fund will be exposed to the price movements of natural resources.
The money market funds attempt to increase yields by trading to take advantage of short-term market variations. This policy is expected to result in high portfolio turnover but should not adversely affect a fund since the funds
III-61
usually do not pay brokerage commissions when purchasing short-term obligations. The value of the portfolio securities held by a fund will vary inversely to changes in prevailing interest rates and, therefore, are subject to the risk of market price fluctuations. Thus, if interest rates have increased from the time a security was purchased, such security, if sold, might be sold at a price less than its cost. Similarly, if interest rates have declined from the time a security was purchased, such security, if sold, might be sold at a price greater than its purchase cost. In any event, if a security was purchased at face value and held to maturity and was paid in full, no gain or loss would be realized. The values of fixed-income securities also may be affected by changes in the credit rating or financial condition of the issuing entities.
If, subsequent to its purchase by a fund, (a) a portfolio security ceases to be rated in the highest rating category by at least two rating organizations (or one rating organization if the instrument was rated by only one such organization) or the board determines that it is no longer of comparable quality or (b) the Adviser becomes aware that any portfolio security not so highly rated or any unrated security has been given a rating by any rating organization below the rating organization's second highest rating category, the board will reassess promptly whether such security continues to present minimal credit risks and will cause the fund to take such action as it determines is in the best interest of the fund and its shareholders; provided that the reassessments required by clauses (a) and (b) are not required if the portfolio security is disposed of or matures within five business days of the specified event and, in the case of events specified in clause (b), the board is subsequently notified of the Adviser's actions. To the extent the ratings given by a Rating Agency for securities change as a result of changes in such organizations or their rating systems, a fund will attempt to use comparable ratings as standards for its investments in accordance with the investment policies described in such fund's prospectus and this SAI. The ratings of the Rating Agencies represent their opinions as to the quality of the securities which they undertake to rate. It should be emphasized, however, that ratings are relative and subjective and are not absolute standards of quality. Although these ratings may be an initial criterion for selection of portfolio investments, the Adviser also will evaluate these securities and the creditworthiness of the issuers of such securities based upon financial and other available information.
Treasury securities include Treasury bills, Treasury notes and Treasury bonds that differ in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance. Treasury bills have initial maturities of one year or less; Treasury notes have initial maturities of one to ten years; and Treasury bonds generally have initial maturities of greater than ten years.
U.S. Government securities are issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government or its agencies or instrumentalities. Some obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies and instrumentalities are supported by the full faith and credit of the Treasury; others by the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury; others by discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase certain obligations of the agency or instrumentality; and others only by the credit of the agency or instrumentality. These securities bear fixed, floating or variable rates of interest. Interest rates may fluctuate based on generally recognized reference rates or the relationship of rates. While the U.S. Government currently provides financial support to such U.S. Government-sponsored agencies or instrumentalities, no assurance can be given that it will always do so, since it is not so obligated by law. A security backed by the Treasury or the full faith and credit of the United States is guaranteed only as to timely payment of interest and principal when held to maturity. Neither the market value nor a fund's share price is guaranteed.
Many states grant tax-free status to dividends paid to shareholders of a fund from interest income earned by that fund from direct obligations of the U.S. Government, subject in some states to minimum investment requirements that must be met by the fund. Investments in securities issued by the GNMA or FNMA, bankers' acceptances, commercial paper and repurchase agreements collateralized by U.S. Government securities do not generally qualify for tax-free treatment.
A repurchase agreement is a contract under which a fund would acquire a security for a relatively short period subject to the obligation of the seller, typically a bank, broker/dealer or other financial institution, to repurchase and
III-62
the fund to resell such security at a fixed time and at a price higher than the purchase price (representing the fund's cost plus interest). The repurchase agreement thereby determines the yield during the purchaser's holding period, while the seller's obligation to repurchase is secured by the value of the underlying security. The fund's custodian or sub-custodian engaged in connection with tri-party repurchase agreement transactions will have custody of, and will segregate, securities acquired by the fund under a repurchase agreement. In connection with its third party repurchase transactions, a fund will engage only eligible sub-custodians that meet the requirements set forth in Section 17(f) of the 1940 Act. The value of the underlying securities (or collateral) will be at least equal at all times to the total amount of the repurchase obligation, including the interest factor. The fund bears a risk of loss if the other party to the repurchase agreement defaults on its obligations and the fund is delayed or prevented from exercising its rights to dispose of the collateral securities. This risk includes the risk of procedural costs or delays in addition to a loss on the securities if their value should fall below their repurchase price. Repurchase agreements are considered by the staff of the SEC to be loans by the fund that enters into them. Repurchase agreements could involve risks in the event of a default or insolvency of the other party to the agreement, including possible delays or restrictions upon a fund's ability to dispose of the underlying securities. A fund may engage in repurchase agreement transactions that are collateralized by U.S. Government securities (which are deemed to be "collateralized fully" pursuant to the 1940 Act) or, for certain funds, to the extent consistent with the fund's investment policies, collateralized by securities other than U.S. Government securities ("credit and/or equity collateral"). Transactions that are collateralized fully enable the fund to look to the collateral for diversification purposes under the 1940 Act. Conversely, transactions secured with credit and/or equity collateral require the fund to look to the counterparty to the repurchase agreement for determining diversification. Because credit and/or equity collateral is subject to certain credit, liquidity, market and/or other additional risks that U.S. Government securities are not subject to, the amount of collateral posted in excess of the principal value of the repurchase agreement is expected to be higher in the case of repurchase agreements secured with credit and/or equity collateral compared to repurchase agreements secured with U.S. Government securities. In an attempt to reduce the risk of incurring a loss on a repurchase agreement, a fund will require that additional securities be deposited with it if the value of the securities purchased should decrease below resale price. See "Fixed-Income Securities—High Yield and Lower-Rated Securities" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds" for a discussion of certain risks of collateral rated below investment grade. The funds may jointly enter into one or more repurchase agreements in accordance with an exemptive order granted by the SEC pursuant to Section 17(d) of the 1940 Act and Rule 17d-1 thereunder. Any joint repurchase agreements must be collateralized fully by U.S. Government securities.
Bank obligations include certificates of deposit ("CDs"), time deposits ("TDs"), bankers' acceptances and other short-term obligations issued by domestic or foreign banks or thrifts or their subsidiaries or branches and other banking institutions. CDs are negotiable certificates evidencing the obligation of a bank to repay funds deposited with it for a specified period of time. TDs are non-negotiable deposits maintained in a banking institution for a specified period of time (in no event longer than seven days) at a stated interest rate. Bankers' acceptances are credit instruments evidencing the obligation of a bank to pay a draft drawn on it by a customer. These instruments reflect the obligation both of the bank and the drawer to pay the face amount of the instrument upon maturity. The other short-term obligations may include uninsured, direct obligations bearing fixed, floating or variable interest rates. TDs and CDs may be issued by domestic or foreign banks or their subsidiaries or branches. A fund may purchase CDs issued by banks, savings and loan associations and similar institutions with less than $1 billion in assets, the deposits of which are insured by the FDIC, provided the fund purchases any such CD in a principal amount of no more than an amount that would be fully insured by the Deposit Insurance Fund administered by the FDIC. Interest payments on such a CD are not insured by the FDIC. A fund would not own more than one such CD per such issuer.
Domestic commercial banks organized under federal law are supervised and examined by the Comptroller of the Currency and are required to be members of the Federal Reserve System and to have their deposits insured by the FDIC. Domestic banks organized under state law are supervised and examined by state banking authorities but are members of the Federal Reserve System only if they elect to join. In addition, state banks whose CDs may be purchased by a fund are insured by the FDIC (although such insurance may not be of material benefit to the fund, depending on the principal amount of the CDs of each bank held by the fund) and are subject to federal examination and to a substantial body of federal law and regulation. As a result of federal and state laws and regulations, domestic branches of domestic banks whose CDs may be purchased by the fund generally, among other things, are
III-63
required to maintain specified levels of reserves and are subject to other supervision and regulation designed to promote financial soundness. However, not all of such laws and regulations apply to the foreign branches of domestic banks.
Obligations of foreign subsidiaries or branches of domestic banks may be general obligations of the parent banks in addition to the issuing subsidiary or branch, or may be limited by the terms of a specific obligation and governmental regulation. Such obligations and obligations of foreign banks or their subsidiaries or branches are subject to different risks than are those of domestic banks. These risks include foreign economic and political developments, foreign governmental restrictions that may adversely affect payment of principal and interest on the obligations, foreign exchange controls, seizure of assets, declaration of a moratorium and foreign withholding and other taxes on interest income. Foreign subsidiaries and branches of domestic banks and foreign banks are not necessarily subject to the same or similar regulatory requirements that apply to domestic banks, such as mandatory reserve requirements, loan limitations, and accounting, auditing and financial recordkeeping requirements. In addition, less information may be publicly available about a foreign subsidiary or branch of a domestic bank or about a foreign bank than about a domestic bank.
Obligations of U.S. branches of foreign banks may be general obligations of the parent bank in addition to the issuing branch, or may be limited by the terms of a specific obligation or by federal or state regulation as well as governmental action in the country in which the foreign bank has its head office. A U.S. branch of a foreign bank with assets in excess of $1 billion may or may not be subject to reserve requirements imposed by the Federal Reserve System or by the state in which the branch is located if the branch is licensed in that state. In addition, federal branches licensed by the Comptroller of the Currency and branches licensed by certain states may be required to: (1) pledge to the regulator, by depositing assets with a designated bank within the state, a certain percentage of their assets as fixed from time to time by the appropriate regulatory authority; and (2) maintain assets within the state in an amount equal to a specified percentage of the aggregate amount of liabilities of the foreign bank payable at or through all of its agencies or branches within the state.
In view of the foregoing factors associated with the purchase of CDs and TDs issued by foreign subsidiaries or branches of domestic banks, or by foreign banks or their branches or subsidiaries, the Adviser carefully evaluates such investments on a case-by-case basis.
To the extent a money market fund's investments are concentrated in the banking industry, the fund will have correspondingly greater exposure to the risk factors which are characteristic of such investments. Sustained increases in interest rates can adversely affect the availability or liquidity and cost of capital funds for a bank's lending activities, and a deterioration in general economic conditions could increase the exposure to credit losses. In addition, the value of and the investment return on the fund's shares could be affected by economic or regulatory developments in or related to the banking industry, which industry also is subject to the effects of competition within the banking industry as well as with other types of financial institutions. A fund, however, will seek to minimize its exposure to such risks by investing only in debt securities which are determined to be of the highest quality.
Floating and Variable Rate Obligations
Floating and variable rate demand notes and bonds are obligations ordinarily having stated maturities in excess of 397 days but which permit the holder to demand payment of principal at any time, or at specified intervals not exceeding 397 days, in each case upon not more than 30 days' notice. Frequently these obligations are secured by letters of credit or other credit support arrangements secured by banks. Variable rate demand notes include master demand notes (see "Fixed-Income Securities—Variable and Floating Rate Securities " above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds").
A participation interest purchased from a financial institution gives a fund an undivided interest in a security in the proportion that the fund's participation interest bears to the total principal amount of the security. If the participation
III-64
interest is unrated, or has been given a rating below that which is permissible for purchase by the fund, the participation interest will be backed by an irrevocable letter of credit or guarantee of a bank, or the payment obligation otherwise will be collateralized by U.S. Government securities, or, in the case of unrated participation interests, the Adviser must have determined that the instrument is of comparable quality to those instruments in which the fund may invest. See "Fixed-Income Securities—Participation Interests and Assignments" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
A fund may purchase asset-backed securities, which are securities issued by special purpose entities whose primary assets consist of a pool of mortgages, loans, receivables or other assets. Payment of principal and interest may depend largely on the cash flows generated by the assets backing the securities and, in certain cases, supported by letters of credit, surety bonds or other forms of credit or liquidity enhancements. The value of these asset-backed securities also may be affected by the creditworthiness of the servicing agent for the pool of assets, the originator of the loans or receivables or the financial institution providing the credit support.
Commercial paper represents short-term, unsecured promissory notes issued to finance short-term credit needs. The commercial paper purchased by a fund will consist only of direct obligations issued by domestic and foreign entities. The other corporate obligations in which a fund may invest consist of high quality, U.S. dollar-denominated short-term bonds and notes (which may include variable rate master demand notes).
See "Investment Companies" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
Foreign securities may include U.S. dollar-denominated securities issued by foreign subsidiaries or foreign branches of domestic banks, domestic and foreign branches of foreign banks, foreign government obligations and commercial paper issued by foreign issuers. Foreign government obligations may include securities issued or guaranteed by foreign governments or any of their political subdivisions, agencies or instrumentalities and debt obligations of supranational entities. Supranational entities include organizations designated or supported by governmental entities to promote economic reconstruction or development and international banking institutions and related government agencies. Examples include the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (the World Bank), the European Coal and Steel Community, the Asian Development Bank and the InterAmerican Development Bank.
A fund investing in foreign securities, including foreign government obligations, may be subject to additional investment risks with respect to these securities or obligations that are different in some respects from those incurred by a money market fund which invests only in debt obligations of U.S. domestic issuers. See, as applicable, "Foreign Securities" and "Foreign Securities—Sovereign Debt Obligations" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
See "Fixed-Income Securities—Municipal Securities—Municipal Securities Generally" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
Derivative Products. The value of certain derivative products is tied to underlying municipal securities. A fund investing in derivative products will purchase only those derivative products that are consistent with its investment objective and policies and comply with the quality, maturity, liquidity and diversification standards of Rule 2a-7 under the 1940 Act. The principal types of derivative products include tax exempt participation interests, tender option bonds and custodial receipts (see " Fixed-Income Securities—Municipal Securities—Instruments Related to Municipal Securities" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds") and structured notes (see "Derivative Instruments—Structured Securities and Hybrid Instruments—Structured Securities" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds").
III-65
Stand-By Commitments. See "Fixed-Income Securities—Municipal Securities—Stand-By Commitments" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
Taxable Investments (municipal or other tax-exempt funds only)
From time to time, on a temporary basis other than for temporary defensive purposes (but not to exceed 20% of the value of the fund's net assets) or for temporary defensive purposes, a fund may invest in taxable short-term investments (Money Fund Taxable Investments, as defined in Part II of this SAI). Dividends paid by a fund that are attributable to income earned by the fund from Money Fund Taxable Investments will be taxable to investors. When a fund invests for temporary defensive purposes, it may not achieve its investment objective(s). If a fund purchases Money Fund Taxable Investments, it will value them using the amortized cost method and comply with the provisions of Rule 2a-7 relating to purchases of taxable instruments.
The 1940 Act, subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, limits money market funds to 5% of total assets in illiquid securities. Illiquid securities, which are securities that cannot be sold or disposed of in the ordinary course of business within seven days at approximately the value ascribed to them by a fund, may include securities that are not readily marketable, such as securities that are subject to legal or contractual restrictions on resale that do not have readily available market quotations, and repurchase agreements providing for settlement in more than seven days after notice. As to these securities, there is a risk that, should a fund desire to sell them, a ready buyer will not be available at a price the fund deems representative of their value, which could adversely affect the value of a fund's net assets. See "Illiquid Securities—Section 4(2) Paper and Rule 144A Securities" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
The 1940 Act, subject to a fund's own more restrictive limitations, if applicable, permits an investment company to borrow in an amount up to 33-1/3% of the value of its total assets. Such borrowings may be for temporary or emergency purposes or for leveraging. If borrowings are for temporary or emergency (not leveraging) purposes, when such borrowings exceed 5% of the value of a fund's total assets the fund will not make any additional investments.
Reverse Repurchase Agreements. See "Borrowing Money—Reverse Repurchase Agreements" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
Forward Commitments. The purchase of portfolio securities on a forward commitment (including "TBA" (to be announced)), when-issued or delayed-delivery basis means that delivery and payment take place in the future after the date of the commitment to purchase. See "Borrowing Money—Forward Commitments" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds."
Interfund Borrowing and Lending Program. Pursuant to an exemptive order issued by the SEC, a fund may lend money to, and/or borrow money from, certain other funds advised by the Manager or its affiliates. All interfund loans and borrowings must comply with the conditions set forth in the exemptive order, which are designed to ensure fair and equitable treatment of all participating funds. A fund's participation in the Interfund Borrowing and Lending Program must be consistent with its investment policies and limitations. A fund will borrow through the Interfund Borrowing and Lending Program only when the costs are equal to or lower than the costs of bank loans, and will lend through the Program only when the returns are higher than those available from an investment in repurchase agreements. Interfund loans and borrowings are normally expected to extend overnight, but can have a maximum duration of seven days. Loans may be called on one day's notice. Any delay in repayment to a lending fund could result in a lost investment opportunity or additional borrowing costs.
The funds have no intention currently or for the foreseeable future to lend portfolio securities. To the extent a fund would seek to lend portfolio securities (see "Lending Portfolio Securities" above under "All Funds other than Money Market Funds"), the fund's shareholders would be notified within a reasonable time prior to such activity occurring.
III-66
The following is a description of certain ratings assigned by S&P, Moody's, Fitch and DBRS.
An S&P issue credit rating is a forward-looking opinion about the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to a specific financial obligation, a specific class of financial obligations or a specific financial program (including ratings on medium-term note programs and commercial paper programs). It takes into consideration the creditworthiness of guarantors, insurers or other forms of credit enhancement on the obligation and takes into account the currency in which the obligation is denominated. The opinion reflects S&P's view of the obligor's capacity and willingness to meet its financial commitments as they come due, and may assess terms, such as collateral security and subordination, which could affect ultimate payment in the event of default.
Issue credit ratings can be either long-term or short-term. Short-term ratings are generally assigned to those obligations considered short-term in the relevant market. In the U.S., for example, that means obligations with an original maturity of no more than 365 days¾including commercial paper. Short-term ratings also are used to indicate the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to put features on long-term obligations. The result is a dual rating, in which the short-term rating addresses the put feature, in addition to the usual long-term rating. Medium-term notes are assigned long-term ratings.
Long-Term Issue Credit Ratings. Issue credit ratings are based, in varying degrees, on S&P's analysis of the following considerations: likelihood of payment¾capacity and willingness of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on an obligation in accordance with the terms of the obligation; nature of and provisions of the obligation; and protection afforded by, and relative position of, the obligation in the event of bankruptcy, reorganization or other arrangement under the laws of bankruptcy and other laws affecting creditors' rights.
Issue ratings are an assessment of default risk, but may incorporate an assessment of relative seniority or ultimate recovery in the event of default. Junior obligations are typically rated lower than senior obligations, to reflect the lower priority in bankruptcy, as noted above. (Such differentiation may apply when an entity has both senior and subordinated obligations, secured and unsecured obligations, or operating company and holding company obligations.)
An obligation rated "AAA" has the highest rating assigned by S&P. The obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is extremely strong.
An obligation rated "AA" differs from the highest-rated obligations only to a small degree. The obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is very strong.
An obligation rated "A" is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher-rated categories. However, the obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is still strong.
An obligation rated "BBB" exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
Obligations rated "BB," "B," "CCC," "CC" and "C" are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. "BB" indicates the least degree of speculation and "C" the highest. While such obligations will likely have some quality and protective characteristics, these may be outweighed by large uncertainties or major exposures to adverse conditions.
An obligation rated "BB" is less vulnerable to nonpayment than other speculative issues. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial or economic conditions which could lead to the obligor's inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
An obligation rated "B" is more vulnerable to nonpayment than obligations rated "BB," but the obligor currently has
III-67
the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation. Adverse business, financial or economic conditions will likely impair the obligor's capacity or willingness to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
An obligation rated "CCC" is currently vulnerable to nonpayment, and is dependent upon favorable business, financial and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation. In the event of adverse business, financial or economic conditions, the obligor is not likely to have the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
An obligation rated "CC" is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment.
A "C" rating is assigned to obligations that are currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment, obligations that have payment arrearages allowed by the terms of the documents or obligations of an issuer that is the subject of a bankruptcy petition or similar action which have not experienced a payment default. Among others, the "C" rating may be assigned to subordinated debt, preferred stock or other obligations on which cash payments have been suspended in accordance with the instrument's terms or when preferred stock is the subject of a distressed exchange offer, whereby some or all of the issue is either repurchased for an amount of cash or replaced by other instruments having a total value that is less than par.
An obligation rated "D" is in payment default. The "D" rating category is used when payments on an obligation, including a regulatory capital instrument, are not made on the date due even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless S&P believes that such payments will be made during such grace period. The "D" rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of similar action if payments on an obligation are jeopardized. An obligation's rating is lowered to "D" upon completion of a distressed exchange offer, whereby some or all of the issue is either repurchased for an amount of cash or replaced by other instruments having a total value that is less than par.
Note: The ratings from "AA" to "CCC" may be modified by the addition of a plus (+) or minus (-) sign to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
An "NR" indicates that no rating has been requested, that there is insufficient information on which to base a rating, or that S&P does not rate a particular obligation as a matter of policy.
Short-Term Issue Credit Ratings. A short-term obligation rated "A-1" is rated in the highest category by S&P. The obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is strong. Within this category, certain obligations are designated with a plus sign (+). This indicates that the obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on these obligations is extremely strong.
A short-term obligation rated "A-2" is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher rating categories. However, the obligor's capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is satisfactory.
A short-term obligation rated "A-3" exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
A short-term obligation rated "B" is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. Ratings of "B-1," "B-2," and "B-3" may be assigned to indicate finer distinctions within the "B" category. The obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation; however, it faces major ongoing uncertainties which could lead to the obligor's inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
A short-term obligation rated "B-1" is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, but the obligor has a relatively stronger capacity to meet its financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
A short-term obligation rated "B-2" is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, and the obligor has an average speculative-grade capacity to meet its financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
III-68
A short-term obligation rated "B-3" is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, and the obligor has a relatively weaker capacity to meet its financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
A short-term obligation rated "C" is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
A short-term obligation rated "D" is in payment default. The "D" rating category is used when payments on an obligation, including a regulatory capital instrument, are not made on the date due even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless S&P believes that such payments will be made during such grace period. The "D" rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of a similar action if payments on an obligation are jeopardized.
Municipal Short-Term Note Ratings Definitions. An S&P U.S. municipal note rating reflects S&P's opinion about the liquidity factors and market access risks unique to the notes. Notes due in three years or less will likely receive a note rating. Notes with an original maturity of more than three years will most likely receive a long-term debt rating. In determining which type of rating, if any, to assign, S&P analysis will review the following considerations: amortization schedule¾the larger the final maturity relative to other maturities, the more likely it will be treated as a note; and source of payment¾the more dependent the issue is on the market for its refinancing, the more likely it will be treated as a note.
Note rating symbols are as follows:
SP-1 Strong capacity to pay principal and interest. An issue determined to possess a very strong capacity to pay debt service is given a plus (+) designation.
SP-2 Satisfactory capacity to pay principal and interest, with some vulnerability to adverse financial and economic changes over the term of the notes.
SP-3 Speculative capacity to pay principal and interest.
Long-Term Obligation Ratings and Definitions. Moody's long-term obligation ratings are opinions of the relative credit risk of fixed-income obligations with an original maturity of one year or more. They address the possibility that a financial obligation will not be honored as promised. Such ratings reflect both the likelihood of default and any financial loss suffered in the event of default.
Obligations rated "Aaa" are judged to be of the highest quality, with minimal credit risk.
Obligations rated "Aa" are judged to be of high quality and are subject to very low credit risk.
Obligations rated "A" are considered upper-medium grade and are subject to low credit risk.
Obligations rated "Baa" are subject to moderate credit risk. They are considered medium-grade and as such may possess certain speculative characteristics.
Obligations rated "Ba" are judged to have speculative elements and are subject to substantial credit risk.
Obligations rated "B" are considered speculative and are subject to high credit risk.
Obligations rated "Caa" are judged to be of poor standing and are subject to very high credit risk.
Obligations rated "Ca" are highly speculative and are likely in, or very near, default, with some prospect of recovery of principal and interest.
Obligations rated "C" are the lowest rated class of bonds and are typically in default, with little prospect for recovery of principal or interest.
III-69
Note: Moody's appends numerical modifiers 1, 2, and 3 to each generic rating classification from Aa through Caa. The modifier 1 indicates that the obligation ranks in the higher end of its generic rating category; the modifier 2 indicates a mid-range ranking and the modifier 3 indicates a ranking in the lower end of that generic rating category.
Short-Term Ratings. Moody's short-term ratings are opinions of the ability of issuers to honor short-term financial obligations. Ratings may be assigned to issuers, short-term programs or to individual short-term debt instruments. Such obligations generally have an original maturity not exceeding thirteen months, unless explicitly noted.
Moody's employs the following designations to indicate the relative repayment ability of rated issuers:
|
P-1 |
Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-1 have a superior ability to repay short-term debt obligations. |
|
P-2 |
Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-2 have a strong ability to repay short-term debt obligations. |
|
P-3 |
Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-3 have an acceptable ability to repay short-term debt obligations. |
|
NP |
Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Not Prime do not fall within any of the Prime rating categories. |
U.S. Municipal Short-Term Debt and Demand Obligation Ratings.
Short-Term Obligation Ratings. There are three rating categories for short-term municipal obligations that are considered investment grade. These ratings are designated as Municipal Investment Grade ("MIG") and are divided into three levels—MIG 1 through MIG 3. In addition, those short-term obligations that are of speculative quality are designated SG, or speculative grade. MIG ratings expire at the maturity of the obligation.
|
MIG 1 |
This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by established cash flows, highly reliable liquidity support, or demonstrated broad-based access to the market for refinancing. |
|
MIG 2 |
This designation denotes strong credit quality. Margins of protection are ample, although not as large as in the preceding group. |
|
MIG 3 |
This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Liquidity and cash flow protection may be narrow, and market access for refinancing is likely to be less well-established. |
|
SG |
This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Debt instruments in this category may lack sufficient margins of protection. |
Demand Obligation Ratings. In the case of variable rate demand obligations ("VRDOs"), a two-component rating is assigned; a long- or short-term debt rating and a demand obligation rating. The first element represents Moody's evaluation of the degree of risk associated with scheduled principal and interest payments. The second element represents Moody's evaluation of the degree of risk associated with the ability to receive purchase price upon demand ("demand feature"), using a variation of the MIG rating scale, the Variable Municipal Investment Grade or VMIG rating.
When either the long- or short-term aspect of a VRDO is not rated, that piece is designated NR, e.g., Aaa/NR or NR/VMIG 1.
VMIG rating expirations are a function of each issue's specific structural or credit features.
|
VMIG 1 |
This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by the superior short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand. |
|
VMIG 2 |
This designation denotes strong credit quality. Good protection is afforded by the strong short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely |
III-70
|
payment of purchase price upon demand. | |
|
VMIG 3 |
This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Adequate protection is afforded by the satisfactory short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand. |
|
SG |
This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Demand features rated in this category may be supported by a liquidity provider that does not have an investment grade short-term rating or may lack the structural and/or legal protections necessary to ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand. |
Corporate Finance Obligations — Long-Term Rating Scales. Ratings of individual securities or financial obligations of a corporate issuer address relative vulnerability to default on an ordinal scale. In addition, for financial obligations in corporate finance, a measure of recovery given default on that liability also is included in the rating assessment. This notably applies to covered bond ratings, which incorporate both an indication of the probability of default and of the recovery given a default of this debt instrument.
The relationship between issuer scale and obligation scale assumes an historical average recovery of between 30%–50% on the senior, unsecured obligations of an issuer. As a result, individual obligations of entities, such as corporations, are assigned ratings higher, lower or the same as that entity's issuer rating.
Highest credit quality: "AAA" ratings denote the lowest expectation of credit risk. They are assigned only in cases of exceptionally strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
Very high credit quality: "AA" ratings denote expectations of very low credit risk. They indicate very strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is not significantly vulnerable to foreseeable events.
High credit quality: "A" ratings denote expectations of low credit risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered strong. This capacity may, nevertheless, be more vulnerable to adverse business or economic conditions than is the case for higher ratings.
Good credit quality: "BBB" ratings indicate that expectations of credit risk are currently low. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
Speculative: "BB" ratings indicate an elevated vulnerability to credit risk, particularly in the event of adverse changes in business or economic conditions over time; however, business or financial alternatives may be available to allow financial commitments to be met.
Highly speculative: "B" ratings indicate that material credit risk is present.
Substantial credit risk: "CCC" ratings indicate that substantial credit risk is present.
Very high levels of credit risk: "CC" ratings indicate very high levels of credit risk.
Exceptionally high levels of credit risk: "C" indicates exceptionally high levels of credit risk.
Defaulted obligations typically are not assigned "D" ratings, but are instead rated in the "B" to "C" rating categories, depending upon their recovery prospects and other relevant characteristics. This approach better aligns obligations that have comparable overall expected loss but varying vulnerability to default and loss.
Note: The modifiers "+" or "-" may be appended to a rating to denote relative status within major rating categories. Such suffixes are not added to the "AAA" obligation rating category, or to corporate finance obligation ratings in the categories below "B."
III-71
Structured, Project & Public Finance Obligations — Long-Term Rating Scales. Ratings of structured finance, project finance and public finance obligations on the long-term scale, including the financial obligations of sovereigns, consider the obligations' relative vulnerability to default. These ratings are typically assigned to an individual security or tranche in a transaction and not to an issuer.
Highest credit quality: "AAA" ratings denote the lowest expectation of default risk. They are assigned only in cases of exceptionally strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
Very high credit quality: "AA" ratings denote expectations of very low default risk. They indicate very strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is not significantly vulnerable to foreseeable events.
High credit quality: "A" ratings denote expectations of low default risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered strong. This capacity may, nevertheless, be more vulnerable to adverse business or economic conditions than is the case for higher ratings.
Good credit quality: "BBB" ratings indicate that expectations of default risk are currently low. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
Speculative: "BB" ratings indicate an elevated vulnerability to default risk, particularly in the event of adverse changes in business or economic conditions over time.
Highly speculative: "B" ratings indicate that material default risk is present, but a limited margin of safety remains. Financial commitments are currently being met; however, capacity for continued payment is vulnerable to deterioration in the business and economic environment.
Substantial credit risk: "CCC" indicates that default is a real possibility.
Very high levels of credit risk: "CC" indicates that default of some kind appears probable.
Exceptionally high levels of credit risk: "C" indicates that default appears imminent or inevitable.
Default: "D" indicates a default. Default generally is defined as one of the following: failure to make payment of principal and/or interest under the contractual terms of the rated obligation; the bankruptcy filings, administration, receivership, liquidation or other winding-up or cessation of the business of an issuer/obligor; or the coercive exchange of an obligation, where creditors were offered securities with diminished structural or economic terms compared with the existing obligation.
Short-Term Ratings Assigned to Obligations in Corporate, Public and Structured Finance. A short-term issuer or obligation rating is based in all cases on the short-term vulnerability to default of the rated entity or security stream and relates to the capacity to meet financial obligations in accordance with the documentation governing the relevant obligation. Short-term ratings are assigned to obligations whose initial maturity is viewed as "short-term" based on market convention. Typically, this means up to 13 months for corporate, sovereign and structured obligations, and up to 36 months for obligations in U.S. public finance markets.
Highest short-term credit quality: "F1" indicates the strongest intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments; may have an added "+" to denote any exceptionally strong credit feature.
Good short-term credit quality: "F2" indicates good intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments.
Fair short-term credit quality: "F3" indicates that the intrinsic capacity for timely payment of financial commitments is adequate.
Speculative short-term credit quality: "B" indicates minimal capacity for timely payment of financial commitments, plus heightened vulnerability to near term adverse changes in financial and economic conditions.
High short-term default risk: "C" indicates that default is a real possibility.
III-72
Restricted default: "RD" indicates an entity that has defaulted on one or more of its financial commitments, although it continues to meet other financial obligations. Applicable to entity ratings only.
Default: "D" indicates a broad-based default event for an entity, or the default of a specific short-term obligation.
Long Term Obligations. The DBRS long-term rating scale provides an opinion on the risk of default. That is, the risk that an issuer will fail to satisfy its financial obligations in accordance with the terms under which an obligation has been issued. Ratings are based on quantitative and qualitative considerations relevant to the issuer, and the relative ranking of claims. All ratings categories other than AAA and D also contain subcategories "(high)" and "(low)." The absence of either a "(high)" or "(low)" designation indicates the rating is in the middle of the category.
Long-term debt rated "AAA" is considered to be of the highest credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is exceptionally high and unlikely to be adversely affected by future events.
Long-term debt rated "AA" is considered to be of superior credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is considered high. Credit quality differs from AAA only to a small degree. Unlikely to be significantly vulnerable to future events.
Long-term debt rated "A" is considered to be of good credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is substantial, but of lesser credit quality than AA. May be vulnerable to future events, but qualifying negative factors are considered manageable.
Long-term debt rated "BBB" is considered to be of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of financial obligations is considered acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events.
Long-term debt rated "BB" is considered to be of speculative, non-investment-grade credit quality. The capacity for the payment of future obligations is uncertain. Vulnerable to future events.
Long-term debt rated "B" is considered to be of highly speculative credit quality. There is a high level of uncertainty as to the capacity to meet financial obligations.
Long-term debt rated "CCC," "CC" or "C" is of very highly speculative credit quality. In danger of defaulting on financial obligations. There is little difference between these three categories, although CC and C ratings are normally applied to obligations that are seen as highly likely to default, or subordinated to obligations rated in the CCC to B range. Obligations in respect of which default has not technically taken place but is considered inevitable may be rated in the C category.
A "D" rating implies a financial obligation has not been met or it is clear that a financial obligation will not met in the near future or a debt instrument has been subject to a distressed exchange. A downgrade to D may not immediately follow an insolvency or restructuring filing as grace periods or extenuating circumstances may exist.
Commercial Paper and Short Term Debt. The DBRS short-term debt rating scale provides an opinion on the risk that an issuer will not meet its short-term financial obligations in a timely manner. Ratings are based on quantitative and qualitative considerations relevant to the issuer and the relative ranking of claims. The R-1 and R-2 rating are further denoted by the subcategories "(high)," "(middle)" and "(low)."
Short-term debt rated "R-1 (high)" is considered to be of the highest credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is exceptionally high. Unlikely to be adversely affected by future events.
Short-term debt rated "R-1 (middle)" is considered to be of superior credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is very high. Differs from R-1 (high) by a relatively modest degree. Unlikely to be significantly vulnerable to future events.
Short-term debt rated "R-1 (low)" is considered to be of good credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is substantial. Overall strength is not as favorable as higher rating
III-73
categories. May be vulnerable to future events, but qualifying negative factors are considered manageable.
Short-term debt rated "R-2 (high)" is considered to be at the upper end of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events.
Short-term debt rated "R-2 (middle)" is considered to be of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events or may be exposed to other factors that could reduce credit quality.
Short-term debt rated "R-2 (low)" is considered to be at the lower end of adequate credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is acceptable. May be vulnerable to future events. A number of challenges are present that could affect the issuer's ability to meet such obligations.
Short-term debt rated "R-3" is considered to be at the lowest end of adequate credit quality. There is a capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due. May be vulnerable to future events and the certainty of meeting such obligations could be impacted by a variety of developments.
Short-term debt rated "R-4" is considered to be of speculative credit quality. The capacity for the payment of short-term financial obligations as they fall due is uncertain.
Short-term debt rated "R-5" is considered to be of highly speculative credit quality. There is a high level of uncertainty as to the capacity to meet short-term financial obligations as they fall due.
A security rated "D" implies that a financial obligation has not been met or it is clear that a financial obligation will not met in the near future, or a debt instrument has been subject to a distressed exchange. A downgrade to D may not immediately follow an insolvency or restructuring filing as grace periods, other procedural considerations or extenuating circumstances may exist.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE BOARD
Boards' Oversight Role in Management
The boards' role in management of the funds is oversight. As is the case with virtually all investment companies (as distinguished from operating companies), service providers to the funds, primarily the Manager and its affiliates, have responsibility for the day-to-day management of the funds, which includes responsibility for risk management (including management of investment risk, valuation risk, issuer and counterparty credit risk, compliance risk and operational risk). As part of their oversight, the boards, acting at their scheduled meetings, or the Chairman, acting between board meetings, regularly interacts with and receives reports from senior personnel of the Manager and its affiliates, service providers, including the Manager's Chief Investment Officer (or a senior representative of his office), the funds' and the Manager's Chief Compliance Officer and portfolio management personnel. The boards' audit committee (which consists of all Independent Board Members) meets during its regularly scheduled and special meetings, and between meetings the audit committee chair is available to the funds' independent registered public accounting firm and the funds' Chief Financial Officer. The boards also receive periodic presentations from senior personnel of Dreyfus and its affiliates regarding risk management generally, as well as periodic presentations regarding specific operational, compliance or investment areas, such as business continuity, anti-money laundering, personal trading, valuation, credit, investment research and securities lending. As warranted, the boards also receive informational reports from the boards' independent legal counsel (and, if applicable, separate counsel to the fund) regarding regulatory compliance and governance matters. The boards have adopted policies and procedures designed to address certain risks to the funds. In addition, the Manager and other service providers to the funds have adopted a variety of policies, procedures and controls designed to address particular risks to the funds. Different processes, procedures and controls are employed with respect to different types of risks. However, it is not possible to eliminate all of the risks applicable to the funds, and the boards' risk management oversight is subject to inherent limitations.
Board Composition and Leadership Structure
The 1940 Act requires that at least 40% of the board members be Independent Board Members and as such are not
III-74
affiliated with the Manager. To rely on certain exemptive rules under the 1940 Act, a majority of the funds' board members must be Independent Board Members, and for certain important matters, such as the approval of investment advisory agreements or transactions with affiliates, the 1940 Act or the rules thereunder require the approval of a majority of the Independent Board Members. Currently, except as noted in Part I of this SAI, all of the funds' board members, including the Chairman of the Boards, are Independent Board Members. The boards have determined that their leadership structure, in which the Chairman of the Boards is not affiliated with the Manager, is appropriate in light of the specific characteristics and circumstances of the funds, including, but not limited to: (i) the services that the Manager and its affiliates provide to the funds and potential conflicts of interest that could arise from these relationships; (ii) the extent to which the day-to-day operations of the funds are conducted by fund officers and employees of the Manager and its affiliates; and (iii) the boards' oversight role in management of the funds.
Additional Information About the Boards and Their Committees
Board members are elected to serve for an indefinite term. The boards have standing audit, nominating, compensation, litigation and pricing committees. The functions of the audit committees are (i) to oversee the funds' accounting and financial reporting processes and the audits of the funds' financial statements and (ii) to assist in the boards' oversight of the integrity of the funds' financial statements, the funds' compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and the independent registered public accounting firm's qualifications, independence and performance. The nominating committees are responsible for selecting and nominating persons as members of the boards for election or appointment by the boards and for election by shareholders. In evaluating potential nominees, including any nominees recommended by shareholders, a committee takes into consideration various factors listed in the nominating committee charter. The nominating committees will consider recommendations for nominees from shareholders submitted to the Secretary of the Dreyfus Family of Funds, c/o The Dreyfus Corporation Legal Department, 200 Park Avenue, 7th Floor East, New York, New York 10166, which include information regarding the recommended nominee as specified in the nominating committee charter. The function of the compensation committees is to establish appropriate compensation for serving on the boards. The litigation committee seeks to address any potential conflicts of interest between the funds and the Manager in connection with any potential or existing litigation or other legal proceeding relating to securities held by a fund and held or otherwise deemed to have a beneficial interest held by the Manager or its affiliate. The boards (other than the boards of the money market funds) also have standing pricing committees comprised of any one board member; the function of the pricing committee is to assist in valuing fund investments.
The Manager is a wholly-owned subsidiary of BNY Mellon. Dreyfus is the primary mutual fund business of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation, a global financial services company focused on helping clients manage and service their financial assets, operating in 36 countries and serving more than 100 markets. BNY Mellon is a leading investment management and investment services company, uniquely focused to help clients manage and move their financial assets in the rapidly changing global marketplace. BNY Mellon Investment Management is one of the world's leading investment management organizations, and one of the top U.S. wealth managers, encompassing BNY Mellon's affiliated investment management firms, wealth management services and global distribution companies. Additional information is available at www.bnymellon.com.
Pursuant to a management or advisory agreement applicable to each fund, the Manager generally maintains office facilities on behalf of the funds, and furnishes statistical and research data, clerical help, data processing, bookkeeping and internal auditing and certain other required services to the funds (including, when a fund does not have a separate administration agreement, accounting and administration services).
As further described below under "Distributor," Dreyfus may pay the Distributor or financial intermediaries for shareholder or other services from Dreyfus' own assets, including past profits but not including the management fee paid by the funds. The Distributor may use part or all of such payments to pay Service Agents. Dreyfus also may make such advertising and promotional expenditures, using its own resources, as it from time to time deems appropriate.
III-75
See the prospectus to determine if any of the information about Sub-Advisers (below and elsewhere in this SAI) applies to your fund.
For funds with one or more Sub-Advisers, the Manager or the fund has entered into a Sub-Advisory Agreement with each Sub-Adviser. A Sub-Adviser provides day-to-day investment management of a fund's portfolio (or a portion thereof allocated by the Manager), and certain related services.
The following is a list of persons (to the extent known by the fund) who are deemed to control each Sub-Adviser by virtue of ownership of stock or other interests of the Sub-Adviser. Companies listed are in the asset management or other financial services business. For Alcentra, CenterSquare, Mellon Capital, Newton, Standish, TBCAM and Walter Scott, which are all subsidiaries of BNY Mellon, see "The Manager" above for ownership information.
CCM: Andrew S. Cupps
Channing: Rodney B. Herenton/Herenton Capital Management, LLC, Wendell E. Mackey and Eric T. McKissack
EAM: Montie L. Weisenberger, Travis Prentice, Joshua Moss, Frank Hurst, Derek Gaertner, Byron Roth and CR Financial Holdings, Inc.
Geneva: Amy S. Croen, William A. Priebe, Michelle Picard, Kris Amborn, William S. Priebe, Lindsay K. Priebe, Linda J. Priebe, William S. Priebe and Lindsay K. Priebe Living Trust dated 01/27/06 (William S. Priebe and Lindsay K. Priebe, Trustees) and Priebe Living Trust dated 04/01/98 (William A. Priebe and Linda J. Priebe, Trustees). Effective on or about October 1, 2014, Geneva will become a wholly-owned subsidiary of Henderson Global Investors (North America) Inc.
Granite: Geoffrey Edelstein, Robert Foran, Bradley Slocum, Gary Rolle, Joshua Shaskan, Jeffrey Hoo, Edward Han, Peter Lopez, Douglas Morse, Richard Passafiume and Erik Rolle
Hamon: Hugh Simon, Hamon Investment Holdings Limited, Hamon Investment Holdings Ltd., Simon Associates Ltd. and The Hamon Investment Group Pte Limited; Hamon also is an affiliate of BNY Mellon
Iridian: David L. Cohen, Harold J. Levy, Jeffrey Elliott, Lane Steven Bucklan, Arovid Associates LLC, Alhero LLC and LLMD LLC
Kayne: Stephen Rigali, Robert Schwartzkopf, Jeannine Vanian, Douglas Foreman, Virtus Partners, Inc. and Virtus Investment Partners, Inc. ("Virtus")
Kingsford Capital: Brian M. Cooney, Louis W. Corrigan, Kelly A. Mazzucco and Michael I. Wilkins
Lombardia: George Castro, Leslie Waite, Fernando Inzunza, Alvin Marley, Kelly Ko, Wendell Williams, Alvin Polit and Lombardia Capital Partners, Inc.
Neuberger Berman: Robert Conti, Joseph Amato, Bradley Tank, Jason Ainsworth, James Dempsey, Neuberger Berman Holdings LLC, Lehman Brothers Holdings Inc., Neuberger Berman Group LLC and NBSH Acquisition, LLC
Nicholas: Catherine C. Somhegyi Nicholas, Arthur E. Nicholas and Nicholas Investment Partners, LLC
Owl Creek: Jeffrey A. Altman, Daniel E. Krueger, Jeffrey F. Lee and Daniel J. Sapadin
Perella: Daniel J. Arbess, Tarek F. Abdel-Meguid, Sandra M. Haas, Aaron F. Hood, Joseph R. Perella, Andrew N. Siegel, Perella Weinberg Partners Capital Management GP LLC, Perella Weinberg Partners Group LP, Perella Weinberg Partners LLC, PWP Group GP LLC, PWP MC LP and NoCo A L.P.
III-76
RHJ: Thomas McDowell, Carl Obeck, Thuong-Thao Buu-Hoan, Timothy Todaro and Cara Thome
Riverbridge: Andrew Turner, Mark A. Thompson, Rick Moulton, Jonathan Little, Richard Potter, Colin Sharp, Ernesto Bertarelli, Donata Bertarelli, Northill US Holdings, Inc., Northill Jersey Holdings LP, Northill Capital (Jersey) LP, Northill Capital Holdings Limited, Donata Bertarelli Northill Discretionary Trust, NCT Limited, Ernesto Bertarelli Northill Discretionary Trust, Northill Purpose Trust, NC PT Limited, Landmark LP and LM (GP) Limited
Sarofim & Co.: Fayez S. Sarofim, Raye White and The Sarofim Group, Inc.
Sirios: John F. Brennan, Jr. and Sirios Associates, L.L.C.
Standard Pacific: G. Douglas Dillard, Raj Venkatesan, SPH GP, LLC and Standard Pacific Partners, L.P.
TOBAM: David Bellaiche, Yves Choueifaty, Tristan A. Froidure, Maylis Lhotellier, Christophe Roehri, TOBAM Holding Company and TOBEMP
TS&W: Horace Whitworth, Cheryl Mounce, Lawrence Gibson, Herbert Thomson, Frank Reichel, Lori Anderson, Jessica Thompson, Aidan Riordan, Old Mutual (US) Holdings, Inc., OM Group (UK) Limited, Old Mutual plc and TS&W Investment GP LLC
Union Point: The principal owner of Union Point Advisors, LLC is Christopher Aristides, who owns his interests indirectly through one or more intermediate entities.
Walthausen: John B. Walthausen
EACM, a wholly-owned subsidiary of BNY Mellon, has been engaged as the Portfolio Allocation Manager for certain funds as described in the prospectus. EACM is responsible for evaluating and recommending Sub-Advisers for these funds. It is expected that differences in investment returns among the portions of a fund managed by different Sub-Advisers will cause the actual percentage of the fund's assets managed by each Sub-Adviser to vary over time.
Portfolio Managers and Portfolio Manager Compensation
See the prospectus to determine which portions of the information provided below apply to your fund.
For funds other than money market funds, an Affiliated Entity or the Sub-Adviser(s), as applicable, provide the funds with portfolio managers who are authorized by the board to execute purchases and sales of securities. For the TBCAM Stock Funds, portfolio managers are employed by the Manager. Portfolio managers are compensated by the company that employs them, and are not compensated by the funds. Each fund's portfolio managers are listed in Part I of this SAI.
The following provides information about the compensation policies for portfolio managers.
Alcentra. Alcentra's compensation arrangements include a fixed salary, discretionary cash bonus and a number of long term incentive plans that are structured to align an employee's interest with the firm's longer term goals. Portfolio managers are compensated in line with portfolio performance, rather than the growth of assets under management. Other factors that may be taken into consideration include asset selection and trade execution and management of portfolio risk.
CCM. Through Andrew Cupps' ownership of the firm, he participates directly in the revenue of the firm, which is determined by the performance of the firm's accounts, including the relevant funds, and the assets under management by the firm. He also is compensated with a base salary.
CenterSquare. The portfolio managers' compensation is comprised of a market-based salary and incentive
III-77
compensation, including both annual and long-term retention incentive awards. Portfolio managers' incentive opportunities are 100% discretionary and are pre-established for each individual based upon competitive industry compensation benchmarks.
In addition to annual incentives, portfolio managers also are eligible to participate in CenterSquare's Long Term Incentive Cash Award Plan. This plan provides for an annual award, payable to participants (generally to senior level executives) 50% in deferred cash and 50% in BNY Mellon Restricted Stock. These awards have a three-year cliff vest, with the participant becoming 100% vested on the third anniversary of the grant date, provided the employee remains an employee of the company. The deferred cash portion is generally invested by CenterSquare in affiliated mutual funds.
Channing. Total compensation is comprised of (1) base salaries, (2) performance bonuses, (3) equity participations, where applicable, and (4) benefits. For investment professionals, the bonus component is determined based on equal weighting of four factors: firm performance, product performance, individual performance and management discretion. Channing has a stock incentive program where key employees may be allocated phantom equity, with an intended five-year growth trajectory (20% each year) into ownership stakes.
EACM. Employees at EACM, including investment professionals (e.g., portfolio managers), generally receive two forms of compensation: a base salary and a discretionary annual bonus (based on the firm's profitability and their performance). The discretionary bonus is based upon an individual's overall performance, with as much emphasis (for the relevant personnel) on contribution to the risk monitoring and quality control areas as there is on generating superior performance. Personal performance and firm performance are roughly equally weighted. As part of EACM's retention plan for key management personnel, a portion of each annual bonus pool also is invested in an offshore fund of hedge funds managed by EACM and vests over a period of three years.
EAM. Portfolio managers at EAM are paid a base salary in line with industry benchmarks and participate in EAM's revenue share plan. Portfolio managers also are compensated by distribution of profits based on ownership.
Geneva. Geneva's investment professionals have significant short and long-term financial incentives. In general, the compensation plan is based on pre-defined, objective, measurable investment performance and performance goals that are ambitious, but attainable.
The compensation structure for Geneva's investment professionals consists of four primary elements. There is a competitive base salary together with a short-term incentive bonus plan. In addition, there are two further incentive-based packages for senior investment professionals that reward staff on both individual and team performance, reflecting profitable asset growth. "Profitable asset growth" refers to the increase in Geneva's revenues generated less the increase in costs. It is typically calculated per team on a calendar year basis. Members of the relevant team receive a share of this growth, which is typically paid over a three year period. Managers are also granted an award in a long-term incentive program that is based on several factors, including the profitability of Geneva's parent company.
Granite. Compensation of portfolio managers at Granite includes base compensation and revenue-based and performance-based compensation for each team (Small Cap and Large Cap) and, if principals, a profits interest in Granite. The overall compensation structure is reviewed annually for market competitiveness with an objective of offering compensation structures in the top third as compared to industry peers. Portfolio managers, and other key investment personnel, have membership interests in Granite and are evaluated on an annual basis to determine additional allocations of membership interests. Such interests entitle the members to distribution of profits as well as certain liquidity features. The interests effectively vest over a determined time period so as to provide a retention incentive.
Hamon. Portfolio manager compensation is comprised of a market-based salary and an annual incentive plan. Under the annual incentive plan, portfolio managers may receive a bonus of up to two times their annual salary, at the discretion of management. In determining the amount of the bonus, significant consideration is given to the portfolio manager's investment portfolio performance over a one-year period (weighted 75%) and a three-year period (weighted 25%) compared to peer groups and relevant indexes. Other factors considered are individual qualitative performance, asset size and revenue growth of the product and funds managed by the portfolio manager.
III-78
Iridian. Iridian's compensation structure includes the following components: base salary, 401(k) retirement plan, and annual bonus if warranted by the overall financial success of the firm. Bonuses are based on performance.
Kayne. Kayne's compensation structure includes a base salary, an incentive bonus opportunity and a benefits package.
Base Salary. Kayne pays each of its portfolio managers a fixed base salary, which is designed to be competitive in light of the individual's experience and responsibilities. Kayne management uses compensation survey results of investment industry compensation conducted by an independent third party in evaluating competitive market compensation for its investment management professionals.
Incentive Bonus. Incentive bonus pools at Kayne are based upon individual firm profits and in some instances overall Virtus profitability. Individual payments are assessed using comparisons of actual investment performance with specific peer group or index measures established at the beginning of each calendar year. Performance of a fund managed is measured over one-, three and five-year periods. Generally, an individual manager's participation is based on the performance of the funds/accounts managed as weighted roughly by total assets in each of these funds/accounts. In certain instances, comparison of portfolio risk factors to peer or index risk factors, as well as achievement of qualitative goals, also may be components of the individual payment potential. The short-term incentive payment is generally paid in cash, but a portion may be made in Virtus Restricted Stock Units.
Other Benefits. Portfolio managers at Kayne also are eligible to participate in broad-based plans offered generally to employees of Virtus and its affiliates, including 401(k), health and other employee benefit plans. While portfolio manager compensation contains a performance component, this component is adjusted by Kayne to reward investment personnel for managing within the stated framework and for not taking unnecessary risk.
Kingsford Capital. Portfolio managers receive a salary plus a discretionary bonus and retirement contribution.
Lombardia. Lombardia's compensation packages for its portfolio managers are comprised of base salaries and performance bonuses. For performance bonuses, each investment professional is evaluated by Lombardia's compensation committee using a combination of quantitative and subjective factors. The quantitative weight is 65% and the subjective weight is 35%. The quantitative measure is based on an internal attribution report broken down by analyst and focused on stock selection. Given that each of Lombardia's products has a stock picking strategy, Lombardia believes that this is the best measure of added value. Lombardia's compensation committee then considers three factors: (i) new idea generation, (ii) teamwork and (iii) work ethic. New idea generation is intended to capture the quality and frequency of new idea generation. This factor credits or penalizes ideas that do not make it into the portfolios. Teamwork and work ethic will be measured both within individual teams and across the organization. The compensation of Alvin W. Marley, a 25% owner of the firm, also is based on overall firm profitability.
Mellon Capital. The primary objectives of the Mellon Capital compensation plans are to:
· Motivate and reward superior investment and business performance
· Motivate and reward continued growth and profitability
· Attract and retain high-performing individuals critical to the on-going success of Mellon Capital
· Create an ownership mentality for all plan participants
Cash compensation is comprised primarily of a market-based base salary and (variable) incentives (cash and deferred). Base salary is determined by the employees' experience and performance in the role, taking into account the ongoing compensation benchmark analyses. Base salary is generally a fixed amount that may change as a result of an annual review, upon assumption of new duties, or when a market adjustment of the position occurs. Funding for the Mellon Capital Annual and Long Term Incentive Plan is through a pre-determined fixed percentage of overall Mellon Capital profitability. Therefore, all bonus awards are based initially on Mellon Capital's financial performance. Annual incentive opportunities are pre-established for each individual, expressed as a percentage of base salary ("target awards"). These targets are derived based on a review of competitive market data for each
III-79
position annually. Annual awards are determined by applying multiples to this target award. Awards are 100% discretionary. Factors considered in awards include individual performance, team performance, investment performance of the associated portfolio(s) (including both short and long term returns) and qualitative behavioral factors. Other factors considered in determining the award are the asset size and revenue growth/retention of the products managed (if applicable). Awards are paid partially in cash with the balance deferred through the Long Term Incentive Plan.
Participants in the Long Term Incentive Plan have a high level of accountability and a large impact on the success of the business due to the position's scope and overall responsibility. This plan provides for an annual award, payable in cash after a three-year cliff vesting period, as well as a grant of BNY Mellon Restricted Stock for senior level roles.
The same methodology described above is used to determine portfolio manager compensation with respect to the management of mutual funds and other accounts. Mutual fund portfolio managers are also eligible for the standard retirement benefits and health and welfare benefits available to all Mellon Capital employees. Certain portfolio managers may be eligible for additional retirement benefits under several supplemental retirement plans that Mellon Capital provides to restore dollar-for-dollar the benefits of management employees that had been cut back solely as a result of certain limits due to tax laws. These plans are structured to provide the same retirement benefits as the standard retirement benefits. In addition, mutual fund portfolio managers whose compensation exceeds certain limits may elect to defer a portion of their salary and/or bonus under the BNY Mellon Deferred Compensation Plan for Employees.
Neuberger Berman. Neuberger Berman's compensation philosophy is one that focuses on rewarding performance and incentivizing its employees. Neuberger Berman also is focused on creating a compensation process that is fair, transparent, and competitive with the market. Compensation for portfolio managers is more heavily weighted on the variable portion of total compensation and reflects individual performance, overall contribution to the team, collaboration with colleagues across Neuberger Berman and, most importantly, overall investment performance. The bonus for a portfolio manager is determined by using a formula which may or may not contain a discretionary component. The discretionary component is determined on the basis of a variety of criteria including investment performance (including the pre-tax three-year track record in order to emphasize long-term performance), utilization of central resources (including research, sales and operations/support), business building to further the longer term sustainable success of the investment team, effective team/people management and overall contribution to the success of Neuberger Berman. In addition, compensation of portfolio managers at other comparable firms is considered, with an eye toward remaining competitive with the market. The terms of long-term retention incentives at Neuberger Berman are as follows:
Employee-Owned Equity. An integral part of the management buyout of Neuberger Berman in 2009 was implementing an equity ownership structure which embodies the importance of incentivizing and retaining key investment professionals. The senior portfolio managers on the mutual fund teams are key shareholders in the equity ownership structure. On a yearly basis over the subsequent five years, the equity ownership allocations will be re-evaluated and re-allocated based on performance and other key metrics. A set percentage of employee equity and preferred stock is subject to vesting.
Contingent Compensation Plan. Neuberger Berman also has established the Neuberger Berman Group Contingent Compensation Plan pursuant to which a certain percentage of an employee's compensation is deemed contingent and vests over a three-year period. Under the plan, most participating employees who are members of mutual fund investment teams will receive a cash return on their contingent compensation with a portion of such return being determined based on the team's investment performance, as well as the performance of a portfolio of other investment funds managed by Neuberger Berman Group investment professionals.
Restrictive Covenants. Portfolio managers who have received equity interests have agreed to certain restrictive covenants, which impose obligations and restrictions with respect to confidential information and employee and client solicitation.
Certain portfolio managers may manage products other than mutual funds, such as high-net-worth separate accounts. For the management of these accounts, a portfolio manager may generally receive a percentage of pre-tax revenue determined on a monthly basis less certain deductions (e.g., a "finder's fee" or "referral fee" paid to a third party).
III-80
The percentage of revenue a portfolio manager receives will vary based on certain revenue thresholds.
Newton. Portfolio manager compensation is primarily comprised of a market-based salary, annual cash bonus and participation in the Newton Long Term Incentive Plan. The level of variable compensation (annual cash bonus and Newton Long Term Incentive Plan) ranges from 0% of base salary to in excess of 200% of base salary, depending upon corporate profits, team performance and individual performance. The annual cash bonus is discretionary. Portfolio manager awards are heavily weighted towards their investment performance relative to both benchmarks and peer comparisons and individual qualitative performance. Awards also are reviewed against market data from industry compensation consultants such as McLagan Partners to ensure comparability with competitors. The portfolio managers also are eligible to participate, at the discretion of management, in the Newton Long Term Incentive Plan. This plan provides for an annual cash award that vests after four years. The value of the award may change during the vesting period based upon changes in Newton's operating income. Portfolio managers also are eligible to join the BNY Mellon Group Personal Pension Plan. Employer contributions are invested in individual member accounts. The value of the fund is not guaranteed and fluctuates based on market factors.
Nicholas. Portfolio managers are partners of the firm. Nicholas' compensation structure for its portfolio managers specifically aligns their goals with that of Nicholas' clients, rewards investment performance and promotes teamwork through their partnership in the firm. Portfolio managers typically receive a base salary and, as partners of the firm, proportionately share in the aggregate profits of Nicholas. In addition to cash compensation, portfolio managers receive a benefit package.
Owl Creek. Portfolio managers are partners of Owl Creek. As partners of the firm, they are entitled to receive allocations of a portion of the firm's net profits. In addition, partners receive base salaries and may be eligible for discretionary bonuses. A portion of the partners' compensation is subject to vesting.
Perella. Members of the investment team are compensated primarily from the net revenues they generate. Individual compensation is determined by the portfolio manager in conjunction with the head of Asset Management. Generally, investment team members are paid a base salary and a discretionary bonus that is dependent upon performance and other factors. All partners are given an equity interest in the adviser.
RHJ. Compensation of portfolio managers at RHJ includes base compensation and bonus. In addition, Messrs. Holtz and Lipsker participate in revenues generated by the strategies they manage.
Riverbridge. Riverbridge has three levels of compensation for investment team members. Investment team members are compensated with a base compensation believed to be industry competitive relative to their level of responsibility. The second level of compensation is predicated on the overall performance of the investment team and individual contributions to the team. The chief investment officer makes a qualitative evaluation of the performance of the individual team member that contemplates contributions made for the current year and considers contributions made during the course of the last several years. Evaluation factors include, but are not limited to, the performance of the relevant funds and other accounts managed relative to expectations for how those funds and accounts should have performed, given their objective, policies, strategies and limitations, and the market environment during the measurement period. This performance factor is not based on the value of assets held in the portfolio strategy. Additional factors considered include quality of research conducted, contributions made to the overall betterment of the investment team and contribution to the betterment of the firm. The actual variable compensation may be more or less than the target amount, based on how well the individual satisfies the objectives stated above. Multi-year time periods are used to evaluate the individual performance of investment team members. Riverbridge stresses superior long-term performance and accordingly benchmarks portfolio managers' performance against comparable peer managers and the appropriate strategy benchmark. The third level of compensation is ownership in the firm.
Sarofim & Co. The portfolio managers are compensated through (i) payment of a fixed annual salary and discretionary annual bonus that may be based on a number of factors, including fund performance, the performance of other accounts and the overall performance of Sarofim & Co. over various time frames, including one-year, two-year and three-year periods, and (ii) the possible issuance of stock options. The fixed annual salary amounts and the discretionary annual bonus amounts constitute the largest component of the portfolio managers' compensation, and these amounts are determined annually through a comprehensive review process pursuant to which executive officers and the members of Sarofim & Co.'s board of directors review and consider the accomplishments and
III-81
development of each portfolio manager, especially with respect to those client accounts involving the portfolio manager. A lesser component of the portfolio managers' compensation results from the possible issuance of stock options. Portfolio managers are sometimes granted stock options and incentive stock options to acquire shares of the capital stock of The Sarofim Group, Inc., the ultimate corporate parent of Sarofim & Co. The decisions as to whether to issue such options and to whom the options are to be issued are made in conjunction with the annual salary and bonus review process, and the options are issued pursuant to a stock option plan adopted by The Sarofim Group, Inc. The options are not based on the particular performance or asset value of any particular client account or of all client accounts as a group, but rather the performance and accomplishments of the individual to whom the option is to be granted. There are various aspects of the review process that are designed to provide objectivity, but, in the final analysis, the evaluation is a subjective one that is based upon a collective overall assessment. There are, however, no specified formulas or benchmarks tied to the particular performance or asset value of any particular client account or of all client accounts as a group.
Sirios. Investment professionals receive a fixed base salary and a discretionary bonus based on individual and overall performance. In addition, senior investment professionals may receive a percentage of the incentive fee paid by certain clients.
Standard Pacific. Mr. Venkatesan receives a salary and retirement contribution and participates in firm profits.
Standish. The portfolio managers' compensation is comprised primarily of a market-based salary and an incentive compensation plan (annual and long-term). Funding for the Standish Incentive Plan is through a pre-determined fixed percentage of overall company profitability. Therefore, all bonus awards are based initially on Standish's overall performance as opposed to the performance of a single product or group. All investment professionals are eligible to receive incentive awards. Cash awards are payable in the February month end pay of the following year. Most of the awards granted have some portion deferred for three years in the form of deferred cash, BNY Mellon equity, interests in investment vehicles (consisting of investments in a range of Standish products), or a combination of the above. Individual awards for portfolio managers are discretionary, based on both individual and multi-sector product risk adjusted performance relative to both benchmarks and peer comparisons over one year, three year and five year periods. Also considered in determining individual awards are team participation and general contributions to Standish. Individual objectives and goals are also established at the beginning of each calendar year and are taken into account. Portfolio managers whose compensation exceeds certain levels may elect to defer portions of their base salaries and/or incentive compensation pursuant to BNY Mellon's Elective Deferred Compensation Plan.
TBCAM. TBCAM's rewards program was designed to be market competitive and align its compensation with the goals of its clients. This alignment is achieved through an emphasis on deferred awards which incentivizes its investment personnel to focus on long-term alpha generation. The following factors encompass its investment professional awards program: base salary, annual cash bonus, long-term incentive plan, deferred cash, BNY Mellon restricted stock, TBCAM restricted shares and a franchise dividend pool (i.e., if a team meets a pre-established contribution margin, any excess contribution is shared by the team and TBCAM and is paid out in both cash and long-term incentives).
Incentive compensation awards are generally subject to management discretion and pool funding availability. Funding for TBCAM annual and long-term incentive plans is through a pre-determined fixed percentage of overall TBCAM profitability. Awards are paid in cash on an annual basis; however, some portfolio managers may receive a portion of their annual incentive award in deferred vehicles.
Awards for select senior portfolio managers are based on a two-stage model: an opportunity range based on the current level of business and an assessment of long-term business value. A significant portion of the opportunity awarded is structured and based upon the one-, three- and five-year (three-year and five-year weighted more heavily) pre-tax performance of the portfolio manager's accounts relative to the performance of the appropriate peer groups.
TOBAM. The salary of each employee is determined by his or her background and seniority in the firm. Bonuses are based on the contribution of the employee to the firm's annual results. Once a year, after an individual performance review, the monthly salary is revised, and bonuses are decided by the executive committee. All
III-82
employees with at least six months of seniority have the opportunity to become shareholders of the firm and, as such, are directly concerned with the profits of the firm and the dividends distributed. All primary portfolio managers are shareholders of TOBAM.
TS&W. For each portfolio manager, TS&W's compensation structure includes the following components: base salary, annual bonus, deferred profit sharing and the ability to participate in a voluntary income deferral plan.
Base Salary. Each portfolio manager is paid a fixed base salary, which varies among portfolio managers depending on the experience and responsibilities of the portfolio manager as well as the strength or weakness of the employment market at the time the portfolio manager is hired or upon any renewal period.
Bonus. Each portfolio manager is eligible to receive an annual bonus. Targeted bonus amounts vary among portfolio managers based on the experience level and responsibilities of the portfolio manager. Bonus amounts are discretionary and tied to overall performance versus individual objectives. Performance versus peer groups and benchmarks are taken into consideration. For capacity constrained products, like small cap value, the small cap portfolio manager has an incentive program tied to the revenue generated in that product area.
Deferred Profit Sharing. All employees are eligible to receive annual profit sharing contributions under a qualified profit sharing plan, subject to IRS limitations. Discretionary contributions are made on an annual basis at the sole discretion of TS&W.
Deferred Compensation Plan. Portfolio managers meeting certain requirements also are eligible to participate in a voluntary, nonqualified deferred compensation plan that allows participants to defer a portion of their income on a pre-tax basis and potentially earn tax-deferred returns.
Equity Plan. Key employees may be awarded deferred TS&W equity grants. In addition, key employees may purchase TS&W equity directly.
Union Point. Union Point compensation can include a combination of salary, bonus and equity ownership of the firm which may be determined based on performance and other factors.
Walter Scott. Compensation generally consists of a competitive base salary and entitlement to annual profit share. In addition, all staff qualify for retirement benefits, life assurance and health insurance. All staff are eligible to participate in the firm's annual profit share, which is a fixed percentage of pre-incentive operating profits. This is the sole source of incentive compensation. Investment, operations, compliance and client service staff are all focused upon the same goals of providing superior performance and service to clients. Success in these goals drives the firm's profits and therefore the profit share.
For senior staff, the majority of annual compensation is the profit share. An element of this is deferred via a long-term incentive plan, largely invested in a long-term global equity fund for which Walter Scott is the investment adviser and in BNY Mellon stock. Both have a deferral period which vests on a pro-rata basis over four years.
Walter Scott's compensation structure is designed to promote fair and equal treatment of all clients. The remuneration and nominations committee of Walter Scott's governing board determines the salary and profit share allocation based on the overall performance of the firm.
Walthausen. All members of Walthausen have common stock ownership in the firm. This is a founding principle of the firm, which Walthausen believes maximizes the alignment of goals for the firm and its clients. As the firm grows, Walthausen intends to expand ownership to new team members after an initial review period. Walthausen's compensation structure consists of base salary, bonus and profit sharing. Each member of the investment team receives a base salary which is commensurate with past experience and role within the firm. Bonuses are similarly awarded based on team performance and firm profitability. As the firm grows, Walthausen intends to allocate profits across ownership levels.
Certain Conflicts of Interest with Other Accounts
Portfolio managers may manage multiple accounts for a diverse client base, including mutual funds, separate
III-83
accounts (assets managed on behalf of private clients or institutions such as pension funds, insurance companies and foundations), private funds, bank collective trust funds or common trust accounts and wrap fee programs that invest in securities in which a fund may invest or that may pursue a strategy similar to a fund's component strategies ("Other Accounts").
Potential conflicts of interest may arise because of an Adviser's or portfolio manager's management of a fund and Other Accounts. For example, conflicts of interest may arise with both the aggregation and allocation of securities transactions and allocation of limited investment opportunities, as an Adviser may be perceived as causing accounts it manages to participate in an offering to increase the Adviser's overall allocation of securities in that offering, or to increase the Adviser's ability to participate in future offerings by the same underwriter or issuer. Allocations of bunched trades, particularly trade orders that were only partially filled due to limited availability, and allocation of investment opportunities generally, could raise a potential conflict of interest, as an Adviser may have an incentive to allocate securities that are expected to increase in value to preferred accounts. IPOs, in particular, are frequently of very limited availability. A potential conflict of interest may be perceived to arise if transactions in one account closely follow related transactions in a different account, such as when a fund purchase increases the value of securities previously purchased by the Other Account or when a sale in one account lowers the sale price received in a sale by a second account. Conflicts of interest may also exist with respect to portfolio managers who also manage performance-based fee accounts, which could give the portfolio managers an incentive to favor such Other Accounts over the corresponding funds such as deciding which securities to allocate to a fund versus the performance-based fee account. Additionally, portfolio managers may be perceived to have a conflict of interest if there are a large number of Other Accounts, in addition to a fund, that they are managing on behalf of an Adviser. The Advisers periodically review each portfolio manager's overall responsibilities to ensure that he or she is able to allocate the necessary time and resources to effectively manage the fund. In addition, an Adviser could be viewed as having a conflict of interest to the extent that the Adviser or its affiliates and/or portfolio managers have a materially larger investment in Other Accounts than their investment in the fund.
Other Accounts may have investment objectives, strategies and risks that differ from those of the relevant fund. In addition, the funds, as registered investment companies, are subject to different regulations than certain of the Other Accounts and, consequently, may not be permitted to engage in all the investment techniques or transactions, or to engage in such techniques or transactions to the same degree, as the Other Accounts. For these or other reasons, the portfolio managers may purchase different securities for the fund and the Other Accounts, and the performance of securities purchased for the fund may vary from the performance of securities purchased for Other Accounts. The portfolio managers may place transactions on behalf of Other Accounts that are directly or indirectly contrary to investment decisions made for the fund, which could have the potential to adversely impact the fund, depending on market conditions. In addition, if a fund's investment in an issuer is at a different level of the issuer's capital structure than an investment in the issuer by Other Accounts, in the event of credit deterioration of the issuer, there may be a conflict of interest between the fund's and such Other Accounts' investments in the issuer. If an Adviser sells securities short, it may be seen as harmful to the performance of any funds investing "long" in the same or similar securities whose market values fall as a result of short-selling activities.
BNY Mellon and its affiliates, including the Manager, Sub-Advisers affiliated with the Manager and others involved in the management, sales, investment activities, business operations or distribution of the funds, are engaged in businesses and have interests other than that of managing the funds. These activities and interests include potential multiple advisory, transactional, financial and other interests in securities, instruments and companies that may be directly or indirectly purchased or sold by the funds or the funds' service providers, which may cause conflicts that could disadvantage the funds.
BNY Mellon and its affiliates may have deposit, loan and commercial banking or other relationships with the issuers of securities purchased by the funds. BNY Mellon has no obligation to provide to the Adviser or the funds, or effect transactions on behalf of the funds in accordance with, any market or other information, analysis, or research in its possession. Consequently, BNY Mellon (including, but not limited to, BNY Mellon's central Risk Management Department) may have information that could be material to the management of the funds and may not share that information with relevant personnel of the Adviser. Accordingly, in making investment decisions for a fund, the Adviser does not seek to obtain or use material inside information that BNY Mellon may possess with respect to such issuers. However, because an Adviser, in the course of investing fund assets in loans (as described above), may have access to material non-public information regarding a Borrower, the ability of a fund or funds advised by
III-84
such Adviser to purchase or sell publicly-traded securities of such Borrowers may be restricted.
Code of Ethics. The funds, the Manager, the Sub-Advisers and the Distributor each have adopted a Code of Ethics that permits its personnel, subject to such respective Code of Ethics, to invest in securities, including securities that may be purchased or held by a fund. The Code of Ethics subjects the personal securities transactions of employees to various restrictions to ensure that such trading does not disadvantage any fund. In that regard, portfolio managers and other investment personnel employed by the Manager or an Affiliated Entity or a Sub-Adviser affiliated with the Manager must preclear and report their personal securities transactions and holdings, which are reviewed for compliance with the Code of Ethics and also are subject to the oversight of BNY Mellon's Investment Ethics Committee. Portfolio managers and other investment personnel may be permitted to purchase, sell or hold securities which also may be or are held in fund(s) they manage or for which they otherwise provide investment advice.
The Distributor, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Dreyfus, located at 200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166, serves as each fund's distributor on a best efforts basis pursuant to an agreement, renewable annually, with the fund or the corporation or trust of which it is a part. The Distributor also serves as distributor for the other funds in the Dreyfus Family of Funds and BNY Mellon Funds Trust.
Depending on your fund's distribution arrangements and share classes offered, not all of the language below may be applicable to your fund (see the prospectus and "How to Buy Shares" in Part II of this SAI to determine your fund's arrangements and share classes).
The Distributor compensates from its own assets certain Service Agents for selling Class A shares subject to a CDSC and Class C shares at the time of purchase. The proceeds of the CDSCs and fees pursuant to a fund's 12b-1 Plan, in part, are used to defray the expenses incurred by the Distributor in connection with the sale of the applicable class of a fund's shares. The Distributor also may act as a Service Agent and retain sales loads and CDSCs and 12b-1 Plan fees. For purchases of Class A shares subject to a CDSC and Class C shares, the Distributor generally will pay Service Agents on new investments made through such Service Agents a commission of up to 1% of the NAV of such shares purchased by their clients.
The Distributor may pay Service Agents that have entered into agreements with the Distributor a fee based on the amount invested in fund shares through such Service Agents by employees participating in Retirement Plans, or other programs. Generally, the Distributor may pay such Service Agents a fee of up to 1% of the amount invested through the Service Agents. The Distributor, however, may pay Service Agents a higher fee and reserves the right to cease paying these fees at any time. The Distributor will pay such fees from its own funds, other than amounts received from a fund, including past profits or any other source available to it. Sponsors of such Retirement Plans or the participants therein should consult their Service Agent for more information regarding any such fee payable to the Service Agent.
Dreyfus or the Distributor may provide additional cash payments out of its own resources to financial intermediaries that sell shares of a fund or provide other services (other than Class Y shares). Such payments are separate from any sales charges, 12b-1 fees and/or shareholder services fees or other expenses paid by the fund to those intermediaries. Because those payments are not made by you or the fund, the fund's total expense ratio will not be affected by any such payments. These additional payments may be made to Service Agents, including affiliates, that provide shareholder servicing, sub-administration, recordkeeping and/or sub-transfer agency services, marketing support and/or access to sales meetings, sales representatives and management representatives of the Service Agent. Cash compensation also may be paid from Dreyfus' or the Distributor's own resources to Service Agents for inclusion of a fund on a sales list, including a preferred or select sales list or in other sales programs. These payments sometimes are referred to as "revenue sharing." From time to time, Dreyfus or the Distributor also may provide cash or non-cash compensation to Service Agents in the form of: occasional gifts; occasional meals, tickets or other entertainment; support for due diligence trips; educational conference sponsorships; support for recognition programs; technology or infrastructure support; and other forms of cash or non-cash compensation permissible under broker-dealer regulations. In some cases, these payments or compensation may create an incentive for a Service Agent to recommend or sell shares of a fund to you. In addition, the Distributor may provide additional and differing compensation from its own assets to certain of its employees who promote the sale of select funds to certain Service Agents, who in turn may recommend such funds to their clients. In some cases, these payments may
III-85
create an incentive for the employees of the Distributor to promote a fund for which the Distributor provides a higher level of compensation. Please contact your Service Agent for details about any payments it may receive in connection with the sale of fund shares or the provision of services to a fund.
Transfer and Dividend Disbursing Agent and Custodian
The Transfer Agent, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Dreyfus, located at 200 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10166, is each fund's transfer and dividend disbursing agent. Pursuant to a transfer agency agreement with the funds, the Transfer Agent arranges for the maintenance of shareholder account records for the funds, the handling of certain communications between shareholders and the funds and the payment of dividends and distributions payable by the funds. For these services, the Transfer Agent receives a monthly fee computed on the basis of the number of shareholder accounts it maintains for each fund during the month, and is reimbursed for certain out-of-pocket expenses. The funds, other than the Index Funds, also may make payments to certain financial intermediaries, including affiliates, who provide sub-administration, recordkeeping and/or sub-transfer agency services to beneficial owners of fund shares.
The Custodian, an affiliate of the Manager, located at One Wall Street, New York, New York 10286, serves as custodian for the investments of the funds. The Custodian has no part in determining the investment policies of the funds or which securities are to be purchased or sold by the funds. Pursuant to a custody agreement applicable to each fund, the Custodian holds each fund's securities and keeps all necessary accounts and records. For its custody services, the Custodian receives a monthly fee based on the market value of each fund's assets held in custody and receives certain securities transaction charges.
Funds' Compliance Policies and Procedures
The funds have adopted compliance policies and procedures pursuant to Rule 38a-1 under the 1940 Act that cover, among other matters, certain compliance matters relevant to the management and operations of the funds.
See the prospectus and "Investments, Investment Techniques and Risks" in Part II of this SAI to determine which sections of the discussion below apply to your fund.
Valuation of Portfolio Securities (funds other than money market funds)
A fund's equity securities, including option contracts (but not including investments in other open-end registered investment companies), generally are valued at the last sale price on the day of valuation on the securities exchange or national securities market on which such securities primarily are traded. Securities listed on NASDAQ markets generally will be valued at the official closing price. If there are no transactions in a security, or no official closing prices for a NASDAQ market-listed security on that day, the security will be valued at the average of the most recent bid and asked prices. Bid price is used when no asked price is available. Open short positions for which there is no sale price on a given day are valued at the lowest asked price. Investments in other open-end investment companies are valued at their reported NAVs each day, except that shares of ETFs generally are valued at the last sale price on the day of valuation on the securities exchange on which the shares are primarily traded.
Substantially all of a fund's debt securities and instruments generally will be valued, to the extent possible, by one or more independent pricing services (the "Service") approved by the board. When, in the judgment of the Service, quoted bid prices for investments are readily available and are representative of the bid side of the market, these investments are valued at the mean between the quoted bid prices (as obtained by the Service from dealers in such securities) and asked prices (as calculated by the Service based upon its evaluation of the market for such securities). The value of other debt securities and instruments is determined by the Service based on methods which include consideration of: yields or prices of securities of comparable quality, coupon, maturity and type; indications as to values from dealers; and general market conditions. The Service's procedures are reviewed by fund officers under the general supervision of the board. Overnight and certain other short-term debt securities and instruments (excluding Treasury bills) will be valued by the amortized cost method, which approximates value, unless a Service provides a valuation for such security or, in the opinion of the board or a committee or other persons designated by
III-86
the board, the amortized cost method would not represent fair value.
Market quotations of foreign securities in foreign currencies and any fund assets or liabilities initially expressed in terms of foreign currency are translated into U.S. dollars at the spot rate, and foreign currency forward contracts are valued using the forward rate obtained from a Service approved by the board. If a fund has to obtain prices as of the close of trading on various exchanges throughout the world, the calculation of the fund's NAV may not take place contemporaneously with the determination of prices of certain of the fund's portfolio securities. Fair value of foreign equity securities may be determined with the assistance of a pricing service using correlations between the movement of prices of foreign securities and indexes of domestic securities and other appropriate indicators, such as closing market prices of relevant ADRs and futures contracts. The valuation of a security based on this fair value process may differ from the security's most recent closing price and from the prices used by other mutual funds to calculate their NAVs. Foreign securities held by a fund may trade on days that the fund is not open for business, thus affecting the value of the fund's assets on days when fund investors have no access to the fund.
Generally, over-the-counter option contracts and interest rate, credit default, total return and equity swap agreements, and options thereon, will be valued by the Service. Equity-linked instruments, such as contracts for difference, will be valued by the Service based on the value of the underlying reference asset(s). Futures contracts will be valued at the most recent settlement price. Restricted securities, as well as securities or other assets for which recent market quotations or official closing prices are not readily available or are determined by a fund not to reflect accurately fair value (such as when the value of a security has been materially affected by events occurring after the close of the exchange or market on which the security is principally traded (for example, a foreign exchange or market) but before the fund calculates its NAV), or which are not valued by the Service, are valued at fair value as determined in good faith based on procedures approved by the board. Fair value of investments may be determined by the board or its pricing committee or the fund's valuation committee using such information as it deems appropriate. The factors that may be considered when fair valuing a security include fundamental analytical data, the nature and duration of restrictions on disposition, an evaluation of the forces that influence the market in which the securities are purchased and sold, and public trading in similar securities of the issuer or comparable issuers. The valuation of a security based on fair value procedures may differ from the prices used by other mutual funds to calculate their NAVs.
Valuation of Portfolio Securities (money market funds only)
In the case of a money market fund that uses amortized cost pricing to value its portfolio securities, the valuation of the fund's portfolio securities is based upon their amortized cost which does not take into account unrealized gains or losses. This involves valuing an instrument at its cost and thereafter assuming a constant amortization to maturity of any discount or premium, regardless of the impact of fluctuating interest rates on the market value of the instrument. While this method provides certainty in valuation, it may result in periods during which value, as determined by amortized cost, is higher or lower than the price the fund would receive if it sold the instrument. Boards overseeing money market funds have established, as a particular responsibility within the overall duty of care owed to fund investors, procedures reasonably designed to stabilize the funds' price per share as computed for the purpose of purchases and redemptions at $1.00. Such procedures include review of the funds' portfolio holdings by the board, at such intervals as it may deem appropriate, to determine whether the funds' NAV calculated by using available market quotations or market equivalents (including valuations obtained from a Service) deviates from $1.00 per share based on amortized cost. Other investments and assets will be valued at fair value as determined in good faith by the board.
Fund shares are sold on a continuous basis. Except as otherwise described in the prospectus, NAV per share of each fund and each class of a Multi-Class Fund is determined as of the close of trading on the floor of the NYSE (usually 4:00 p.m., Eastern time) on each day the NYSE is open for regular business. For purposes of determining NAV, certain options and futures contracts may be valued 15 minutes after the close of trading on the floor of the NYSE. The NAV per share of a fund is computed by dividing the value of the fund's net assets (i.e., the value of its assets less liabilities) by the total number of shares of such fund outstanding.
Fund expenses and fees, including management fees and fees pursuant to Plans (reduced by the fund's expense
III-87
limitation, if any), are accrued daily and taken into account for the purpose of determining the NAV of a fund's shares. For funds with more than one class of shares, because of the differences in operating expenses incurred by each class of shares of a fund, the per share NAV of each class of shares of the fund will differ. The NAV of each class of a fund with more than one class of shares is computed by dividing the value of the fund's net assets represented by such class (i.e., the value of its assets less liabilities) by the total number of shares of such class outstanding.
Except as may be otherwise described in "Certain Expense Arrangements and Other Disclosures" in Part II of this SAI, all expenses incurred in the operation of the series of a fund company are borne by the fund company. Expenses attributable to a particular series of a fund company are charged against the assets of that series; other expenses of the fund company are allocated among the series on the basis determined by the board, including, but not limited to, proportionately in relation to the net assets of each series. In addition, each class of shares of a fund with more than one class bears any class specific expenses allocated to such class, such as expenses related to the distribution and/or shareholder servicing of such class.
NYSE and Transfer Agent Closings
The holidays (as observed) on which both the NYSE and the Transfer Agent are closed currently are: New Year's Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, Presidents' Day, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving and Christmas. In addition, the NYSE is closed on Good Friday.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ABOUT DIVIDENDS AND DISTRIBUTIONS
Dividends automatically are reinvested in additional shares of the fund from which they were paid at NAV without a sales load (if applicable), or, at your option, paid in cash. If a fund investor elects to receive dividends and distributions in cash, and the investor's dividend or distribution check is returned to the fund as undeliverable or remains uncashed for six months, the fund reserves the right to reinvest such dividends or distributions and all future dividends and distributions payable to you in additional fund shares at NAV. No interest will accrue on amounts represented by uncashed distribution or redemption checks.
For a fund that declares dividends each business day, if you redeem all shares in your account at any time during a month, all dividends to which you are entitled will be paid to you along with the proceeds of the redemption. If an omnibus accountholder indicates in a partial redemption request that a portion of any accrued dividends to which such account is entitled belongs to an underlying accountholder who has redeemed all shares in his or her account, such portion of the accrued dividends will be paid to the omnibus accountholder along with the proceeds of the redemption.
Dividends and distributions among share classes in the same fund may vary due to the different expenses of such share classes.
Funds Other Than Money Market Funds
Any dividend or distribution paid shortly after an investor's purchase of fund shares may have the effect of reducing the aggregate NAV of the shares below the cost of the investment. Such a dividend or distribution would be a return of capital in an economic sense, although taxable as stated in the prospectus and this SAI. In addition, the Code provides that if a shareholder holds shares of a fund for six months or less and has (or is deemed to have) received a capital gain distribution with respect to such shares, any loss incurred on the sale of such shares will be treated as long-term capital loss to the extent of the capital gain distribution received or deemed to have been received. The Code further provides that if a shareholder holds shares of a municipal or other tax-exempt fund for six months or less and has received an exempt-interest dividend with respect to such shares, any loss incurred on the sale of such shares generally will be disallowed to the extent of the exempt-interest dividend received.
A fund may make distributions on a more frequent basis than is described in its prospectus to comply with the distribution requirements of the Code, in all events in a manner consistent with the provisions of the 1940 Act. A fund may not make distributions from net realized securities gains unless capital loss carryovers, if any, have been utilized or have expired.
III-88
For a bond fund that declares dividends daily (see Part II of this SAI under "Dividends and Distributions"), dividends accrue beginning one day after the date of purchase and through the date a redemption is effective. When determining a fund's dividend rate on a weekend or holiday, the fund will use the dividend rate on the business day following the weekend or holiday. All expenses are accrued daily and deducted before declaration of dividends to shareholders.
Dividends accrue beginning on the date of purchase (provided purchase payments are received by wire prior to the time as of which the fund calculates its NAV on such day (as described in the prospectus)) and through the day prior to the date a redemption is effective. A fund's earnings for Saturdays, Sundays and holidays are declared as dividends on the preceding business day. Dividends usually are paid on the last calendar day of each month. All expenses are accrued daily and deducted before declaration of dividends to shareholders.
Dividends from net realized short-term capital gains, if any, generally are declared and paid once a year, but the funds may make distributions on a more frequent basis to comply with the distribution requirements of the Code, in all events in a manner consistent with the provisions of the 1940 Act. A fund will not make distributions from net realized capital gains unless capital loss carryovers, if any, have been utilized or have expired. The funds do not expect to realize any long-term capital gains or losses.
See the prospectus and "Investment Policies and Restrictions" in Part II of this SAI to determine which sections of the discussion below apply to your funds.
The following is only a general summary of some of the important federal income tax considerations generally affecting the funds and their shareholders. No attempt is made to present a complete explanation of the federal tax treatment of the funds' activities or, except to the extent specifically addressed herein, to discuss state and local tax matters affecting the funds or their shareholders. Shareholders are urged to consult their own tax advisors for more detailed information concerning the tax implications of investments in the funds.
Each fund intends to qualify for treatment as a regulated investment company ("RIC") under Subchapter M of the Code and intends to continue to so qualify if such qualification is in the best interests of its shareholders. As a RIC, a fund will pay no federal income tax on its net investment income and net realized capital gains to the extent that such income and gains are distributed to shareholders in accordance with applicable provisions of the Code. To qualify as a RIC, a fund must, among other things: (a) derive in each taxable year (the "gross income test") at least 90% of its gross income from (i) dividends, interest, payments with respect to securities loans and gains from the sale or other disposition of stocks, securities or foreign currencies or other income (including but not limited to gains from options, futures or forward contracts) derived with respect to its business of investing in such stocks, securities or currencies, and (ii) net income from interests in "qualified publicly traded partnerships" ("QPTPs," as defined below); (b) diversify its holdings (the "asset diversification test") so that, at the end of each quarter of the taxable year, (i) at least 50% of the market value of the fund's assets is represented by cash and cash items (including receivables), U.S. Government securities, the securities of other RICs and other securities, with such other securities of any one issuer limited for the purposes of this calculation to an amount not greater than 5% of the value of the fund's total assets and not greater than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer, and (ii) not more than 25% of the value of its total assets is invested in the securities (other than U.S. Government securities or the securities of other RICs) of a single issuer, two or more issuers that the fund controls and that are engaged in the same, similar or related trades or businesses or one or more QPTPs; and (c) distribute with respect to each taxable year at least 90% of the sum of its investment company taxable income (determined without regard to the dividends paid deduction) and net tax-exempt interest income, if any, for such year.
In general, for purposes of the gross income test described above, income derived from a partnership will be treated as qualifying income only to the extent such income is attributable to items of income of the partnership that would be qualifying income if realized by a RIC. However, as noted above, 100% of the net income derived from an interest in a QPTP is qualifying income for purposes of the gross income test. A QPTP is defined as a partnership
III-89
(i) interests in which are traded on an established securities market or readily tradable on a secondary market or the substantial equivalent thereof and (ii) that derives at least 90% of its gross income from certain enumerated passive income sources described in Code section 7704(d), but does not include a partnership that derives 90% of its gross income from sources described in Code section 851(b)(2)(A). Although income from a QPTP is qualifying income for purposes of the gross income test, investment in QPTPs cannot exceed 25% of a fund's assets.
Gains from foreign currencies (including foreign currency options, foreign currency swaps, foreign currency futures and foreign currency forward contracts) currently constitute qualifying income for purposes of the gross income test. However, the Treasury has the authority to issue regulations (possibly with retroactive effect) treating a RIC's foreign currency gains as non-qualifying income for purposes of the gross income test to the extent that such income is not directly related to the RIC's principal business of investing in stock or securities.
A fund's investment in MLPs may qualify as an investment in (1) a QPTP, (2) a "regular" partnership, (3) a "passive foreign investment company" (a "PFIC") or (4) a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The treatment of particular MLPs for U.S. federal income tax purposes will affect the extent to which a fund can invest in MLPs. The U.S. federal income tax consequences of a fund's investments in "PFICs" and "regular" partnerships are discussed in greater detail below. Some amounts received by a fund with respect to certain investments in MLPs will likely be treated as a return of capital because of accelerated deductions available with respect to the activities of such MLPs. On the disposition of an investment in such an MLP, the fund will likely realize taxable income in excess of economic gain with respect to that asset (or, if the fund does not dispose of the MLP, the fund likely will realize taxable income in excess of cash flow with respect to the MLP in a later period), and the fund must take such income into account in determining whether the fund has satisfied its distribution requirements. The fund may have to borrow or liquidate securities to satisfy its distribution requirements and to meet its redemption requests, even though investment considerations might otherwise make it undesirable for the fund to sell securities or borrow money at such time.
A RIC that fails the gross income test for a taxable year shall nevertheless be considered to have satisfied the test for such year if (i) the RIC satisfies certain procedural requirements, and (ii) the RIC's failure to satisfy the gross income test is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect. However, in such case, a tax is imposed on the RIC for the taxable year in which, absent the application of the above cure provision, it would have failed the gross income test equal to the amount by which (x) the RIC's non-qualifying gross income exceeds (y) one-ninth of the RIC's qualifying gross income, each as determined for purposes of applying the gross income test for such year.
A RIC that fails the asset diversification test as of the end of a quarter shall nevertheless be considered to have satisfied the test as of the end of such quarter in the following circumstances. If the RIC's failure to satisfy the asset diversification test at the end of the quarter is due to the ownership of assets the total value of which does not exceed the lesser of (i) one percent of the total value of the RIC's assets at the end of such quarter and (ii) $10,000,000 (a "de minimis failure"), the RIC shall be considered to have satisfied the asset diversification test as of the end of such quarter if, within six months of the last day of the quarter in which the RIC identifies that it failed the asset diversification test (or such other prescribed time period), the RIC either disposes of assets in order to satisfy the asset diversification test, or otherwise satisfies the asset diversification test.
In the case of a failure to satisfy the asset diversification test at the end of a quarter under circumstances that do not constitute a de minimis failure, a RIC shall nevertheless be considered to have satisfied the asset diversification test as of the end of such quarter if (i) the RIC satisfies certain procedural requirements; (ii) the RIC's failure to satisfy the asset diversification test is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect; and (iii) within six months of the last day of the quarter in which the RIC identifies that it failed the asset diversification test (or such other prescribed time period), the RIC either disposes of the assets that caused the asset diversification failure, or otherwise satisfies the asset diversification test. However, in such case, a tax is imposed on the RIC, at the highest prescribed corporate income tax rate, on the net income generated by the assets that caused the RIC to fail the asset diversification test during the period for which the asset diversification test was not met. In all events, however, such tax will not be less than $50,000.
If a fund were to fail to qualify as a RIC in any taxable year, the fund would be subject to tax on its taxable income at corporate rates, and all distributions from current or accumulated earnings and profits, including any distributions of net tax-exempt income and net long-term capital gains, would be taxable to shareholders as ordinary income. Some portions of such distributions may be eligible for the dividends received deduction in the case of corporate
III-90
shareholders and may be eligible for a preferential maximum tax rate in respect of "qualified dividends" in the case of shareholders taxed as individuals, provided in both cases, the shareholder meets certain holding period and other requirements in respect of the fund's shares (as described below). In addition, a fund could be required to recognize unrealized gains, pay substantial taxes and interest and make substantial distributions before requalifying as a RIC that is accorded special tax treatment.
A nondeductible excise tax at a rate of 4% will be imposed on the excess, if any, of a fund's "required distribution" over its actual distributions in any calendar year. Generally, the required distribution is 98% of a fund's ordinary income for the calendar year plus 98.2% of its capital gain net income, determined under prescribed rules for this purpose, recognized during the one-year period ending on October 31st of such year (or December 31st of that year if the fund is permitted to so elect and so elects) plus undistributed amounts from prior years. Each fund generally intends to make distributions sufficient to avoid imposition of the excise tax, although there can be no assurance that it will be able to do so.
Although in general the passive loss rules of the Code do not apply to RICs, such rules do apply to a RIC with respect to items attributable to an interest in a QPTP. A fund's investments in partnerships, including in QPTPs, may result in a fund being subject to state, local or foreign income, franchise or withholding tax liabilities.
Taxation of Fund Distributions (Funds Other Than Municipal or Other Tax-Exempt Funds)
For federal income tax purposes, distributions of investment income generally are taxable as ordinary income to the extent of the distributing fund's earnings and profits, regardless of whether you receive your distributions in cash or have them reinvested in additional fund shares. Taxes on distributions of capital gains are determined by how long a fund owned the investments that generated them, rather than how long a shareholder has owned his or her shares. In general, a fund will recognize long-term capital gain or loss on assets it has owned (or is deemed to have owned) for more than one year, and short-term capital gain or loss on investments it has owned (or is deemed to have owned) for one year or less. Distributions of "net capital gain," that is, the excess of net long-term capital gains over net short-term capital losses, that are properly characterized by the fund as capital gain dividends ("capital gain dividends") will generally be taxable to a shareholder receiving such distributions as long-term capital gain. Long-term capital gains are generally taxable to individuals at a maximum rate of 20%, with lower rates potentially applicable to taxpayers depending on their income levels. These rates may increase depending on whether legislation is or has been enacted, and, if so, in what form. Distributions of net short-term capital gains that exceed net long-term capital losses will generally be taxable as ordinary income. The determination of whether a distribution is from capital gains is generally made taking into account available net capital loss carryforwards, if any. If a RIC has a "net capital loss" (that is, capital losses in excess of capital gains) for a taxable year, that portion of the RIC's net capital loss consisting of the excess (if any) of the RIC's net short-term capital losses over its net long-term capital gains is treated as a short-term capital loss arising on the first day of the RIC's next taxable year, and that portion of the RIC's net capital loss consisting of the excess (if any) of the RIC's net long-term capital losses over its net short-term capital gains is treated as a long-term capital loss arising on the first day of the RIC's next taxable year. Any such capital losses of a RIC may be carried forward to succeeding taxable years of the RIC without limitation. Net capital loss carryforwards of a RIC arising in taxable years of the RIC beginning on or before December 22, 2010 (the date of enactment of the Regulated Investment Company Modernization Act of 2010) may be applied against any net realized capital gains of the RIC in each succeeding year, or until their respective expiration dates, whichever is first.
Distributions are taxable to shareholders even if they are paid from income or gains earned by a fund before a shareholder's investment (and thus were included in the price the shareholder paid for his or her shares). If a shareholder buys shares of a fund when the fund has realized but not distributed income or capital gains, the shareholder will be "buying a dividend" by paying full price for the shares and then receiving a portion back in the form of a taxable distribution. Distributions are taxable regardless of whether shareholders receive them in cash or in additional shares. Distributions declared and payable by a fund during October, November or December to shareholders of record on a date in any such month and paid by the fund during the following January generally will be treated for federal tax purposes as paid by the fund and received by shareholders on December 31st of the year in which the distributions are declared rather than the calendar year in which they are received. A fund may elect to retain its net capital gain or a portion thereof for investment and be taxed at corporate rates on the amount retained. In such case, the fund may designate its retained amount as undistributed capital gains in a notice to its shareholders who will be treated as if each received a distribution of his or her pro rata share of such gain, with the result that
III-91
each shareholder in the fund will (i) be required to report his or her pro rata share of such gain on his or her tax return as long-term capital gain, (ii) receive a refundable tax credit for his or her pro rata share of the tax paid by the fund on the gain and (iii) increase the tax basis for his or her shares in the fund by an amount equal to the deemed distribution less the tax credit.
In general, dividends (other than capital gain dividends) paid by a fund to U.S. individual shareholders may be eligible for preferential tax rates applicable to long-term capital gain to the extent that the fund's income consists of dividends paid by U.S. corporations and certain "qualified foreign corporations" on shares that have been held by the fund for at least 61 days during the 121-day period commencing 60 days before the shares become ex-dividend. Dividends paid on shares held by a fund will not be taken into account in determining the applicability of the preferential maximum tax rate to the extent that the fund is under an obligation (pursuant to a short sale or otherwise) to make related payments with respect to positions in substantially similar or related property. Dividends paid by REITs are not generally eligible for the preferential maximum tax rate. Further, a "qualified foreign corporation" does not include any foreign corporation, which for its taxable year in which its dividend was paid, or the preceding taxable year, is a PFIC (discussed below). In order to be eligible for the preferential rate, the shareholder in the fund must have held his or her shares in the fund for at least 61 days during the 121-day period commencing 60 days before the fund shares become ex-dividend. Additional restrictions on a shareholder's qualification for the preferential rate may apply.
In general, dividends (other than capital gain dividends) paid by a fund to U.S. corporate shareholders may be eligible for the dividends received deduction to the extent that the fund's income consists of dividends paid by U.S. corporations (other than REITs) on shares that have been held by the fund for at least 46 days during the 91-day period commencing 45 days before the shares become ex-dividend. Dividends paid on shares held by a fund will not be taken into account for this purpose if the stock on which the dividend is paid is considered to be "debt-financed" (generally, acquired with borrowed funds), or to the extent that the fund is under an obligation (pursuant to a short sale or otherwise) to make related payments with respect to positions in substantially similar or related property. Moreover, the dividend received deduction may be disallowed or reduced if the corporate shareholder fails to satisfy the foregoing holding period and other requirements with respect to its shares of the fund or by application of the Code.
If a fund makes a distribution that is or is considered to be in excess of its current and accumulated "earnings and profits" for the relevant period, the excess distribution will be treated as a return of capital to the extent of a shareholder's tax basis in his or her shares, and thereafter as capital gain. A return of capital is not taxable, but it reduces a shareholder's basis in his or her shares, thus reducing any loss or increasing any gain on a subsequent taxable disposition by the shareholder of such shares.
An additional 3.8% Medicare tax is imposed on certain net investment income (including ordinary dividends and capital gain distributions received from a RIC and net gains from redemptions or other taxable dispositions of RIC shares) of U.S. individuals, estates and trusts. The tax applies to the lesser of (i) such net investment income (or, in the case of an estate or trust, its undistributed net investment income), and (ii) the excess, if any, of such person's "modified adjusted gross income" (or, in the case of an estate or trust, its "adjusted gross income") over a threshold amount.
Sale, Exchange or Redemption of Shares
A sale, exchange or redemption of shares in a fund will give rise to a gain or loss. Any gain or loss realized upon a taxable disposition of shares will be treated as long-term capital gain or loss if the shares have been held for more than 12 months. Otherwise, the gain or loss on the taxable disposition of fund shares will be treated as short-term capital gain or loss.
However, any loss realized upon a taxable disposition of fund shares held for six months or less will be treated as long-term, rather than short-term, to the extent of any capital gain dividends received (or deemed received) by the shareholder with respect to the shares. Further, all or a portion of any loss realized upon a taxable disposition of fund shares will be disallowed if other substantially identical shares of the fund are purchased (including by means of a dividend reinvestment plan) within 30 days before or after the disposition. In such a case, the basis of the newly purchased shares will be adjusted to reflect the disallowed loss.
III-92
As discussed below under "Funds Investing in Municipal Securities," any loss realized upon a taxable disposition of shares in a municipal or other tax-exempt fund that have been held for six months or less will be disallowed to the extent of any exempt-interest dividends received (or deemed received) by the shareholder with respect to the shares. This loss disallowance rule, however, does not apply with respect to a regular dividend paid by a RIC which declares exempt-interest dividends on a daily basis in an amount equal to at least 90% of its net tax-exempt interest and distributes such dividends on a monthly or more frequent basis.
Generally, if a shareholder sells or redeems shares of a fund within 90 days of their original acquisition, the shareholder cannot claim a loss on the original shares attributable to the amount of their load charge if the load charge is reduced or waived on a future purchase of shares of any fund (on account of the prior load charge), but instead is required to reduce the basis of the original shares by the amount of their load charge and carry over that amount to increase the basis of the newly acquired fund shares. This rule applies only if the acquisition of the new fund shares occurs on or before January 31 of the calendar year following the year in which the original shares were sold or redeemed.
If a shareholder recognizes a loss with respect to a fund's shares of $2 million or more for an individual shareholder or $10 million or more for a corporate shareholder, the shareholder must file with the IRS a disclosure statement on Form 8886. Direct shareholders of portfolio securities are in many cases excepted from this reporting requirement, but under current guidance, shareholders of a RIC are not excepted. Future guidance may extend the current exception from this reporting requirement to shareholders of most or all RICs. The fact that a loss is reportable under these regulations does not affect the legal determination of whether the taxpayer's treatment of the loss is proper. Shareholders should consult their tax advisors to determine the applicability of the applicable regulations in light of their individual circumstances.
The funds (or their administrative agent) are required to report to the IRS and furnish to fund shareholders the cost basis information and holding period for fund shares purchased on or after January 1, 2012, and redeemed on or after that date. The funds will permit fund shareholders to elect from among several IRS-accepted cost basis methods, including average cost. In the absence of an election by a shareholder, the funds will use the average cost method with respect to that shareholder. The cost basis method a shareholder elects may not be changed with respect to a redemption of shares after the settlement date of the redemption. Fund shareholders should consult with their tax advisors to determine the best IRS-accepted cost basis method for their tax situation and to obtain more information about how the cost basis reporting rules apply to them.
Funds that invest in foreign securities may own shares in certain foreign entities that are treated as PFICs for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A fund that owns shares of a PFIC may be subject to U.S. federal income tax (including interest charges) on distributions received from the PFIC or gains from a disposition of shares in the PFIC. To avoid this treatment, each fund owning PFIC shares may make an election to mark the gains (and to a limited extent losses) in a PFIC "to market" as though it had sold and repurchased its holdings in the PFIC on the last day of the fund's taxable year. Such gains and losses are treated as ordinary income and loss. Alternatively, a fund may in certain cases elect to treat a PFIC as a "qualified electing fund" (a "QEF"), in which case the fund will be required to include in its income annually its share of the QEF's income and net capital gains, regardless of whether the fund receives any distribution from the QEF. If the QEF incurs a loss for a taxable year, the loss will not pass through to the fund and, accordingly, cannot offset other income and/or gains of the fund. A fund may not be able to make the QEF election with respect to many PFICs because of certain requirements that the PFICs would have to satisfy.
The mark-to-market and QEF elections may accelerate the recognition of income (without the receipt of cash) and increase the amount required to be distributed by a fund to avoid taxation. Making either of these elections therefore may require a fund to liquidate investments (including when it is not advantageous to do so) to meet its distribution requirements, which also may accelerate the recognition of gain and affect the fund's total return. Dividends paid by PFICs generally will not be eligible to be treated as qualified dividend income.
Investment income that may be received by a fund from sources within foreign countries may be subject to foreign
III-93
withholding and other taxes. Tax treaties between the United States and certain countries may reduce or eliminate such taxes. If more than 50% of the value of a fund's total assets at the close of its taxable year consists of stock or securities of foreign corporations, or if at least 50% of the value of a fund's total assets at the close of each quarter of its taxable year is represented by interests in other RICs (as is the case for a Fund of Funds), that fund may elect to "pass through" to its shareholders the amount of foreign taxes paid or deemed paid by that fund. If that fund so elects, each of its shareholders would be required to include in gross income, even though not actually received, his or her pro rata share of the foreign taxes paid or deemed paid by that fund, but would be treated as having paid his or her pro rata share of such foreign taxes and would therefore be allowed to either deduct such amount in computing taxable income or use such amount (subject to various Code limitations) as a foreign tax credit against federal income tax (but not both). For purposes of the foreign tax credit limitation rules of the Code, each shareholder would treat as foreign source income his or her pro rata share of such foreign taxes plus the portion of dividends received from the fund representing income derived from foreign sources. No deduction for foreign taxes could be claimed by an individual shareholder who does not itemize deductions. In certain circumstances, a shareholder that (i) has held shares of the fund for less than a specified minimum period during which it is not protected from risk of loss or (ii) is obligated to make payments related to the dividends will not be allowed a foreign tax credit for foreign taxes deemed imposed on dividends paid on such shares. Additionally, the fund must also meet this holding period requirement with respect to its foreign stocks and securities in order for "creditable" taxes to flow-through. Each shareholder should consult his or her own tax advisor regarding the potential application of foreign tax credits.
Gains or losses attributable to fluctuations in exchange rates between the time a fund accrues income or receivables or expenses or other liabilities denominated in a foreign currency and the time that fund actually collects such income or receivables or pays such liabilities are generally treated as ordinary income or loss. Similarly, gains or losses on foreign currency forward contracts and the disposition of debt securities denominated in a foreign currency, to the extent attributable to fluctuations in exchange rates between the acquisition and disposition dates, also are treated as ordinary income or loss.
A fund's investments in options, futures contracts, forward contracts, swaps and derivatives, as well as any of its other hedging, short sale or similar transactions, may be subject to one or more special tax rules (including notional principal contract, constructive sale, straddle, wash sale, short sale and other rules), the effect of which may be to accelerate income to the fund (including, potentially, without a corresponding receipt of cash with which to make required distributions), defer fund losses, cause adjustments in the holding periods of fund securities, convert capital gains into ordinary income, render dividends that would otherwise be eligible for the dividends received deduction or preferential rates of taxation ineligible for such treatment, convert long-term capital gains into short-term capital gains and convert short-term capital losses into long-term capital losses. These rules could therefore affect the amount, timing and character of distributions to shareholders of a fund. In addition, because the tax rules applicable to derivative financial instruments are in some cases uncertain under current law, an adverse determination or future guidance by the IRS with respect to these rules (which determination or guidance could be retroactive) may affect whether a fund has made sufficient distributions, and otherwise satisfied the applicable requirements, to maintain its qualification as a RIC and avoid fund-level taxation.
Payments with Respect to Securities Loans
A fund's participation in loans of securities may affect the amount, timing and character of distributions to shareholders. With respect to any security subject to a securities loan, any (i) amounts received by a fund in place of dividends earned on the security during the period that such security was not directly held by a fund may not give rise to qualified dividend income and (ii) withholding taxes accrued on dividends during the period that such security was not directly held by a fund will not qualify as a foreign tax paid by such fund and therefore cannot be passed through to shareholders even if the fund meets the requirements described in "Non-U.S. Taxes," above.
Securities Issued or Purchased at a Discount and Payment-in-Kind Securities
A fund's investments, if any, in securities issued or purchased at a discount, as well as certain other securities (including zero coupon obligations and certain redeemable preferred stock), may require the fund to accrue and
III-94
distribute income not yet received. Similarly, a fund's investment in payment-in-kind securities will give rise to income which is required to be distributed even though the fund receives no payment in cash on the security during the year. In order to generate sufficient cash to make its requisite distributions, a fund may be required to borrow money or sell securities in its portfolio that it otherwise would have continued to hold.
Inflation-Indexed Treasury Securities
The taxation of inflation-indexed Treasury securities is similar to the taxation of conventional bonds. Both interest payments and the difference between original principal and the inflation-adjusted principal generally will be treated as interest or original issue discount income subject to taxation. Interest payments generally are taxable when received or accrued. The inflation adjustment to the principal generally is subject to tax in the year the adjustment is made, not at maturity of the security when the cash from the repayment of principal is received. Accordingly, as in the case of securities issued or purchased at a discount and zero coupon obligations, a fund's investments in inflation-indexed Treasury securities may require the fund to accrue and distribute income not yet received. Decreases in the indexed principal in a given year generally (i) will reduce the amount of interest income otherwise includible in income for that year in respect of the Treasury security, (ii) to the extent not treated as an offset to current income under (i), will constitute an ordinary loss to the extent of prior year inclusions of interest, original issue discount and market discount in respect of the security that exceed ordinary losses in respect of the security in such prior years, and (iii) to the extent not treated as an offset to current income under (i) or an ordinary loss under (ii), can be carried forward as an ordinary loss to reduce interest, original issue discount and market discount in respect of the security in subsequent taxable years. If inflation-indexed Treasury securities are sold prior to maturity, capital losses or gains generally are realized in the same manner as traditional debt instruments. Special rules apply in respect of inflation-indexed Treasury securities issued with more than a prescribed de minimis amount of discount or premium.
Certain Higher-Risk and High Yield Securities
Certain funds may invest in lower-quality fixed-income securities, including debt obligations of issuers not currently paying interest or that are in default. Investments in debt obligations that are at risk of or are in default present special tax issues for a fund. Tax rules are not entirely clear on the treatment of such debt obligations, including as to whether and to what extent a fund should recognize market discount on such a debt obligation, when a fund may cease to accrue interest, original issue discount or market discount, when and to what extent a fund may take deductions for bad debts or worthless securities and how a fund shall allocate payments received on obligations in default between principal and interest. These and other related issues would be addressed by each fund if it invests in such securities as part of the fund's efforts to ensure that it distributes sufficient income to preserve its status as a RIC and does not become subject to U.S. federal income or excise tax.
Funds Investing in Municipal Securities (Municipal or Other Tax-Exempt Funds)
It is anticipated that substantially all of the ordinary dividends to be paid by municipal or other tax-exempt funds that invest substantially all of their assets in U.S. municipal securities will constitute "exempt-interest dividends." Such exempt-interest dividends will be exempt from federal income taxes. It is possible, however, that a portion of the income dividends from such funds will not be exempt from federal income taxes. Municipal or other tax-exempt funds may realize capital gains from the sale or other disposition of municipal securities or other securities. Distributions by such funds of capital gains will be treated in the same manner as capital gains as described under "Taxation of Fund Distributions." Recipients of Social Security and/or certain railroad retirement benefits who receive dividends from municipal bond or other tax-exempt funds may have to pay taxes on a portion of their benefits. Shareholders will receive a Form 1099-DIV, Form 1099-INT or other IRS forms, as required, reporting the taxability of all dividends. Certain municipal or other tax-exempt funds may invest in municipal securities the income from which is subject to AMT. Such funds will advise shareholders of the percentage of dividends, if any, which should be included in the computation of AMT.
Because the ordinary dividends of municipal or other tax-exempt funds are expected to be exempt-interest dividends, any interest on money a shareholder of such a fund borrows that is directly or indirectly used to purchase shares in the fund will not be deductible. Further, entities or persons that are "substantial users" (or persons related to "substantial users") of facilities financed by private activity bonds or industrial development bonds should consult their tax advisors before purchasing shares of these funds. The income from such bonds may not be tax-exempt for
III-95
such substantial users. There also may be collateral federal income tax consequences regarding the receipt of exempt-interest dividends by shareholders such as S corporations, financial institutions and property and casualty insurance companies. A shareholder falling into any such category should consult its tax advisor concerning its investment in a fund that is intended to generate exempt-interest dividends.
As a general rule, any loss realized upon a taxable disposition of shares in a municipal or other tax-exempt fund that have been held for six months or less will be disallowed to the extent of any exempt-interest dividends received (or deemed received) by the shareholder with respect to the shares. This loss disallowance rule, however, does not apply with respect to a regular dividend paid by a RIC which declares exempt-interest dividends on a daily basis in an amount equal to at least 90% of its net tax-exempt interest and distributes such dividends on a monthly or more frequent basis.
If at least 50% of the value of a fund's total assets at the close of each quarter of its taxable year is represented by interests in other RICs (such as a Fund of Funds), the fund may pass through to its shareholders its exempt interest income in the form of dividends that are exempt from federal income tax.
Proposals have been and may be introduced before Congress that would restrict or eliminate the federal income tax exemption of interest on municipal securities. If such a proposal were enacted, the availability of such securities for investment by a fund that would otherwise invest in tax-exempt securities and the value of such a fund's portfolio would be affected. In that event, such a fund would reevaluate its investment objective and policies.
The treatment under state and local tax law of dividends from a fund that invests in municipal securities may differ from the federal income tax treatment of such dividends under the Code.
Investing in Mortgage Entities
Special tax rules may apply to the investments by a fund in entities which invest in or finance mortgage debt. Such investments include residual interests in REMICs and interests in a REIT which qualifies as a taxable mortgage pool under the Code or has a qualified REIT subsidiary that is a taxable mortgage pool under the Code. Although it is the practice of each fund not to make such investments, there is no guarantee that a fund will be able to avoid an inadvertent investment in REMIC residual interests or a taxable mortgage pool.
Such investments may result in a fund receiving excess inclusion income ("EII") in which case a portion of its distributions will be characterized as EII and shareholders receiving such distributions, including shares held through nominee accounts, will be deemed to have received EII. This can result in the funds being required to pay tax on the portion of its EII that is allocated to disqualified organizations, including certain cooperatives, agencies or instrumentalities of a government or international organization, and tax-exempt organizations that are not subject to tax on unrelated business taxable income ("UBTI"). In addition, such amounts generally cannot be offset by net operating losses, will be treated as UBTI to tax-exempt organizations that are not disqualified organizations, and will be subject to a 30% withholding tax for shareholders who are not U.S. persons, notwithstanding any otherwise applicable exemptions or rate reductions in any relevant tax treaties.
Special tax consequences also apply where charitable remainder trusts invest in RICs that invest directly or indirectly in residual interests in REMICs or in taxable mortgage pools. Furthermore, any investment in residual interests of a REMIC can create complex tax consequences to both a fund and its shareholders, especially if a fund has state or local governments or other tax-exempt organizations as shareholders.
Under current law, each fund serves to "block" (that is, prevent the attribution to shareholders of) UBTI from being realized by its tax-exempt shareholders (including, among others, individual retirement accounts, 401(k) accounts, Keogh plans, pension plans and certain charitable entities). Notwithstanding the foregoing, a tax-exempt shareholder could realize UBTI by virtue of its investment in a fund if shares in the fund constitute debt-financed property in the hands of the tax-exempt shareholder within the meaning of Section 514(b) of the Code. As noted above, a tax-exempt shareholder may also recognize UBTI if a fund recognizes EII derived from direct or indirect investments in residual interests in REMICs or taxable mortgage pools. If a charitable remainder annuity trust or a charitable remainder unitrust (each as defined in Section 664 of the Code) has UBTI for a taxable year, a 100%
III-96
excise tax on the UBTI is imposed on the trust.