|
Delaware
|
| |
7374
|
| |
88-1068854
|
|
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization)
|
| |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number)
|
| |
(IRS Employer
Identification Number)
|
|
Alan Baratz
D-Wave Quantum Inc.
3033 Beta Avenue
Burnaby, British Columbia V5G 4M9
Canada
Tel: (604) 630-1428
|
| |
Michael M. Mills, Jr.
Holland & Knight LLP
100 North Tampa Street
Suite 4100
Tampa, Florida 33602
Tel: (813) 227-8500
|
|
Large accelerated filer
|
| |
☐
|
| |
Accelerated filer
|
| |
☐
|
|
Non-accelerated filer
|
| |
☒
|
| |
Smaller reporting company
|
| |
☐
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
Emerging Growth Company
|
| |
☒
|

|
•
|
the expected benefits of the Merger (as defined below);
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s future growth and innovations;
|
|
•
|
the increased adoption of quantum computing solutions and expansion of related market opportunities and use cases;
|
|
•
|
the estimated total addressable market (“TAM”) for quantum computing and expectations regarding product development and
functionality;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s financial and business performance following the Merger, including financial projections and business
metrics;
|
|
•
|
changes in D-Wave Quantum’s strategy, future operations, financial position, estimated revenues and losses, projected costs,
prospects and plans;
|
|
•
|
the ability of D-Wave Quantum’s products and services to meet customers’ compliance and regulatory needs;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to attract and retain qualified employees and management;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to develop and maintain its brand and reputation;
|
|
•
|
developments and projections relating to D-Wave Quantum’s products, competitors and industry;
|
|
•
|
the impact of the current economic environment due to inflation, increased interest rates, Ukraine/Russia conflict, and any
evolutions thereof;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s expectations regarding its ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection and not infringe
on the rights of others;
|
|
•
|
expectations regarding the time during which we will be an emerging growth company under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups
Act (the ‘‘JOBS Act”);
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s future capital requirements and sources and uses of cash;
|
|
•
|
statements regarding the reseller agreement with Davidson Technologies, Inc. (“Davidson”), and Davidson’s and D-Wave’s
collaboration on an initiative to support classified quantum-hybrid applications;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to obtain funding for its operations and future growth; and
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s business, expansion plans and opportunities.
|
|
•
|
anticipated trends, growth rates, and challenges in companies that are engaged in the business of quantum computing, such as
D-Wave Quantum, and in the markets in which they operate;
|
|
•
|
the risk that D-Wave Quantum’s securities will not maintain a listing on the NYSE;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to recognize the anticipated benefits of the Merger, which may be affected by, among other things,
competition and the ability of D-Wave Quantum to grow and achieve and maintain profitability following the Merger;
|
|
•
|
risks related to the uncertainty of the unaudited prospective forecasted financial information;
|
|
•
|
risks related to the performance of D-Wave Quantum’s business and the timing of expected business or financial milestones;
|
|
•
|
unanticipated technological or project development challenges, including with respect to the cost and or timing thereof;
|
|
•
|
the performance of D-Wave Quantum’s products and services;
|
|
•
|
the effects of competition on D-Wave Quantum’s business;
|
|
•
|
changes in the business of D-Wave Quantum and D-Wave Quantum’s market, financial, political and legal conditions;
|
|
•
|
the risk that D-Wave Quantum will need to raise additional capital to execute its business plan, which may not be available
on acceptable terms or at all;
|
|
•
|
the risk that D-Wave Quantum may never achieve or sustain profitability;
|
|
•
|
the risk that D-Wave Quantum is unable to secure or protect its intellectual property;
|
|
•
|
changes in applicable laws or regulations;
|
|
•
|
the effect of the current economic environment due to inflation, increased interest rates, Ukraine/Russia conflict,
geopolitical events, natural disasters, wars, terrorist acts or a combination of these factors on D-Wave Quantum’s business and the economy in general;
|
|
•
|
the ability of D-Wave Quantum to execute its business model, including market acceptance of its planned products and
services;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to raise capital, including under the Purchase Agreement (as defined below) with Lincoln Park
Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”);
|
|
•
|
D-Wace Quantum’s ability to obtain funds under the Term Loan (as defined below);
|
|
•
|
the possibility that D-Wave Quantum may be negatively impacted by other economic, business, and/or competitive factors;
|
|
•
|
risks stemming from inflation;
|
|
•
|
any changes to applicable tax laws, including U.S. tax laws; and
|
|
•
|
other risks and uncertainties described in this prospectus, including those under the section titled “Risk Factors.”
|
|
•
|
The sale or issuance of Common Shares to Lincoln Park may cause dilution and the sale of the Common Shares by Lincoln Park
that it acquires pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, or the perception that such sales may occur, could cause the price of Common Shares to decrease. In addition, certain of the Selling Securityholders purchased, or are able to
purchase, Common Shares at prices that are well below the current trading price of the Common Shares. As a result, the Selling Securityholders may effect sales of Common Shares well below prices significantly below the current market
price, which could cause market prices to decline further.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum is in its growth stage which makes it difficult to forecast its future results of operations and its funding
requirements.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum has a history of losses and expects to incur significant expenses and continuing losses for the foreseeable
future.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may be unable to maintain a listing on the NYSE, and such a delisting will likely make it more difficult for
us to raise capital on favorable terms in the future, would likely have a negative effect on the price of our securities and would impair your ability to sell or purchase our shares when you wish to do so.
|
|
•
|
If D-Wave Quantum does not adequately fund its research and development efforts or use research and development teams
effectively or build a sufficient number of annealing quantum computer production systems, it may not be able to achieve its technological goals, meet customer and market demand, or compete effectively and D-Wave Quantum’s business
and operating results may be harmed.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum depends on its ability to retain existing senior management and other key employees and qualified, skilled
personnel and to attract new individuals to fill these roles as needed. If D-Wave Quantum is unable to do so, such failure could adversely affect its business, results of operations and financial condition.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum expects to require additional capital to pursue its business objectives, growth strategy and respond to
business opportunities, challenges or unforeseen circumstances, and it may be unable to raise capital or additional financing when needed on acceptable terms, or at all.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s industry is competitive on a global scale, from both quantum and classical competitors, and D-Wave Quantum
may not be successful in competing in this industry or establishing and maintaining confidence in its long-term business prospects among current and future partners and customers, which would materially harm its reputation, business,
results of operations and financial condition.
|
|
•
|
Any cybersecurity-related attack, significant data breach or disruption of the information technology systems,
infrastructure, network, third-party processors or platforms on which D-Wave Quantum relies could damage D-Wave Quantum’s reputation and adversely affect its business and financial results.
|
|
•
|
Market adoption of cloud-based online quantum computing platform solutions is relatively new and unproven and may not grow
as D-Wave Quantum expects and, even if market demand increases, the demand for D-Wave Quantum’s QCaaS may not increase, or certain customers may be reluctant to use a cloud-based QCaaS for applications, all of which may harm D-Wave
Quantum’s business and results of operations.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may, in the future, be adversely affected by continuation or worsening of the global COVID-19 pandemic,
various COVID-19 strains or future pandemics.
|
|
•
|
Unfavorable conditions in D-Wave Quantum's industry or the global economy, including uncertain geopolitical conditions such
as inflation, recessions and war, among others, could limit D-Wave Quantum's ability to grow the business and negatively affect D-Wave Quantum's results of operations.
|
|
•
|
System failures, interruptions, delays in service, catastrophic events, inadequate infrastructure and resulting
interruptions in the availability or functionality of D-Wave Quantum’s products and services could harm its reputation or subject D-Wave Quantum to significant liability, and adversely affect its business, financial condition and
operating results.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may be unable to obtain, maintain and protect its intellectual property or prevent third parties from making
unauthorized use of its intellectual property, which could cause it to lose the competitive advantage resulting from its intellectual property.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s patent applications may not result in issued patents or its patent rights may be contested, circumvented,
invalidated or limited in scope, any of which could have a material adverse effect on D-Wave Quantum’s ability to prevent others from interfering with the commercialization of its products and services.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may face patent infringement and other intellectual property claims that could be costly to defend and may
result in injunctions and significant damage awards or other costs. If third parties claim that D-Wave Quantum infringes upon or otherwise violates their intellectual property rights, D-Wave Quantum’s business could be adversely
affected.
|
|
•
|
If the Merger's benefits do not meet the expectations of investors or securities analysts, the market price of D-Wave
Quantum’s securities may decline.
|
|
•
|
Uncertainty about the effect of the Merger may affect D-Wave Quantum’s ability to retain key employees, integrate
management structures and may materially impact the management, strategy and results of its operation as a combined company.
|
|
•
|
Financial projections with respect to D-Wave Quantum may not prove to be reflective of actual financial results.
|
|
•
|
The historical financial results of D-Wave Quantum and unaudited pro forma financial information included elsewhere in this
prospectus may not be indicative of what D-Wave Quantum's actual financial position or results of operations would have been if it were a public company.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may be required to take write-downs or write-offs, or D-Wave Quantum may be subject to restructuring,
impairment or other charges that could have a significant negative effect on D-Wave Quantum’s financial condition, results of operations and the price of D-Wave Quantum’s securities, which could cause you to lose some or all of your
investment.
|
|
•
|
The price of D-Wave Quantum's Common Shares has been and may continue to be volatile or may decline regardless of our
operating performance.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may amend the terms of the Warrants in a manner that may be adverse to holders with the approval by the
holders of at least a majority of the then outstanding Warrants.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum may issue additional Common Shares or other equity securities without your approval, which would dilute your
ownership interests and may depress the market price of the Common Shares.
|
|
•
|
The D-Wave Quantum Charter contains anti-takeover provisions that could adversely affect the rights of our stockholders.
|
|
•
|
16,965,849 shares reserved under the 2022 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2022 Plan”);
|
|
•
|
8,036,455 shares reserved under the 2022 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”);
|
|
•
|
2,889,282 Common Shares underlying D-Wave Warrants;
|
|
•
|
26,053,126 Common Shares underlying Warrants; and
|
|
•
|
11,949,501 Common Shares underlying outstanding D-Wave Options.
|
|
|
| |
March 31,
|
| |
December 31,
|
|
(In thousands of U.S. dollars, except share and per share
data)
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
|
Assets
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Current assets:
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Cash
|
| |
$8,988
|
| |
$7,065
|
|
Trade accounts receivable, net
|
| |
542
|
| |
757
|
|
Inventories
|
| |
2,240
|
| |
2,196
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets
|
| |
3,142
|
| |
3,907
|
|
Total current assets
|
| |
$14,912
|
| |
$13,925
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
| |
2,041
|
| |
2,294
|
|
Operating lease right-of-use assets
|
| |
8,927
|
| |
9,133
|
|
Intangible assets, net
|
| |
228
|
| |
244
|
|
Other noncurrent assets
|
| |
1,351
|
| |
1,351
|
|
Total assets
|
| |
$27,459
|
| |
$26,947
|
|
Liabilities and stockholders’ (deficit) equity
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Trade accounts payable
|
| |
5,608
|
| |
3,756
|
|
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities
|
| |
9,859
|
| |
8,640
|
|
Loans payable, current
|
| |
790
|
| |
1,671
|
|
Deferred revenue, current
|
| |
1,827
|
| |
1,781
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
| |
18,084
|
| |
15,848
|
|
Warrant liabilities
|
| |
1,254
|
| |
1,892
|
|
Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion
|
| |
7,165
|
| |
7,301
|
|
Loans payable, noncurrent
|
| |
8,260
|
| |
7,811
|
|
Deferred revenue, noncurrent
|
| |
9
|
| |
9
|
|
Total liabilities
|
| |
$34,772
|
| |
$32,861
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 11)
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Stockholders’ (deficit) equity:
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Common stock par value $0.0001 per share; 675,000,000
shares authorized at March 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively; 127,173,552 shares and 113,335,530 shares issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively.
|
| |
12
|
| |
11
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
| |
404,501
|
| |
381,274
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
| |
(401,405)
|
| |
(376,797)
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss
|
| |
(10,421)
|
| |
(10,402)
|
|
Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity
|
| |
$(7,313)
|
| |
$(5,914)
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity
|
| |
$27,459
|
| |
$26,947
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Year ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
|
Revenue
|
| |
$1,583
|
| |
$1,713
|
| |
$7,173
|
| |
$6,279
|
| |
$5,160
|
|
Cost of revenue
|
| |
1,162
|
| |
616
|
| |
2,923
|
| |
1,750
|
| |
915
|
|
Total gross profit
|
| |
421
|
| |
1,097
|
| |
4,250
|
| |
4,529
|
| |
4,245
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Research and development
|
| |
10,915
|
| |
6,802
|
| |
32,101
|
| |
25,401
|
| |
20,411
|
|
General and administrative
|
| |
11,296
|
| |
3,646
|
| |
21,539
|
| |
11,897
|
| |
11,587
|
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
2,900
|
| |
1,600
|
| |
10,068
|
| |
6,179
|
| |
3,714
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
| |
25,111
|
| |
12,048
|
| |
63,708
|
| |
43,477
|
| |
35,712
|
|
Loss from operations
|
| |
(24,690)
|
| |
(10,951)
|
| |
(59,458)
|
| |
(38,948)
|
| |
(31,467)
|
|
Other income (expense), net:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Interest expense
|
| |
(454)
|
| |
(525)
|
| |
(4,633)
|
| |
(1,728)
|
| |
(5,257)
|
|
Government assistance
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
7,167
|
| |
12,027
|
|
Non-cash interest income on SIF
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
5,673
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Gain on debt extinguishment
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
—
|
| |
3,873
|
|
Gain on settlement of warrant liability
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
—
|
| |
7,836
|
|
Gain on investment in marketable securities
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
1,163
|
| |
—
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities
|
| |
638
|
| |
—
|
| |
6,173
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Lincoln Park Purchase Agreement issuance costs
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
(629)
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Other income (expense), net
|
| |
(102)
|
| |
(181)
|
| |
1,345
|
| |
801
|
| |
2,969
|
|
Total other income (expense), net
|
| |
82
|
| |
(706)
|
| |
7,929
|
| |
7,403
|
| |
21,448
|
|
Net loss
|
| |
$(24,608)
|
| |
$(11,657)
|
| |
$(51,529)
|
| |
$(31,545)
|
| |
$(10,019)
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
| |
$(0.20)
|
| |
$(0.09)
|
| |
$(0.43)
|
| |
$(0.25)
|
| |
$(0.08)
|
|
Weighted-average shares * used in computing net loss per
share, basic and diluted
|
| |
123,144,097
|
| |
125,385,841
|
| |
119,647,777
|
| |
125,342,746
|
| |
127,161,731
|
|
Comprehensive loss:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Net loss
|
| |
$(24,608)
|
| |
$(11,657)
|
| |
$(51,529)
|
| |
$(31,545)
|
| |
$(10,019)
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax
|
| |
(19)
|
| |
(70)
|
| |
41
|
| |
15
|
| |
(82)
|
|
Net comprehensive loss
|
| |
$(24,627)
|
| |
$(11,727)
|
| |
$(51,488)
|
| |
$(31,530)
|
| |
$(10,101)
|
Weighted-average shares have been retroactively restated to give effect to the Merger.
|
Assumed Average Purchase Price Per Share
|
| |
Number of Common
Shares that may be Issued
in this Offering
if Full Purchases Made
under the Purchase
Agreement(1)
|
| |
Proceeds from the Sale of
Common Shares to Lincoln Park
Under the Purchase Agreement(2)
|
|
$14.00
|
| |
9,292,857
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$13.00
|
| |
10,007,692
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$12.00
|
| |
10,841,666
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$11.00
|
| |
11,827,272
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$10.00
|
| |
13,010,000
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$9.00
|
| |
14,455,555
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$8.00
|
| |
16,262,500
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$7.00
|
| |
18,585,714
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
Assumed Average Purchase Price Per Share
|
| |
Number of Common
Shares that may be Issued
in this Offering
if Full Purchases Made
under the Purchase
Agreement(1)
|
| |
Proceeds from the Sale of
Common Shares to Lincoln Park
Under the Purchase Agreement(2)
|
|
$6.00
|
| |
21,683,333
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$5.00
|
| |
26,020,000
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$4.00
|
| |
32,525,000
|
| |
$150,000,000
|
|
$3.00
|
| |
35,000,000
|
| |
$124,900,000
|
|
$2.00
|
| |
35,000,000
|
| |
$89,900,000
|
|
$1.98(3)
|
| |
35,000,000
|
| |
$89,200,000
|
|
$1.00(4)
|
| |
35,000,000
|
| |
$54,900,000
|
|
(1)
|
Excludes the 381,540 Commitment Shares previously issued to Lincoln Park.
|
|
(2)
|
Includes the $19.9 million in proceeds previously received from issuing Common Shares to Lincoln Park.
|
|
(3)
|
The closing price of our Common Shares on July 6, 2023.
|
|
(4)
|
The Floor Price under the Purchase Agreement.
|
|
•
|
holders of Common Shares’ proportionate ownership interest in D-Wave Quantum would decrease;
|
|
•
|
the amount of cash available per share, including for payment of dividends (if any) in the future, may decrease;
|
|
•
|
the relative voting strength of each previously outstanding share of Common Shares may be diminished; and
|
|
•
|
the market price of the Common Shares may decline.
|
|
•
|
effectively manage organizational change;
|
|
•
|
design scalable processes;
|
|
•
|
accelerate and/or refocus research and development activities;
|
|
•
|
expand supply chain and distribution capacity, and ultimately expand manufacturing capacity;
|
|
•
|
increase sales and marketing efforts;
|
|
•
|
scale and manage our professional services;
|
|
•
|
broaden customer-support and services capabilities;
|
|
•
|
maintain or increase operational efficiencies;
|
|
•
|
scale support operations in a cost-effective manner;
|
|
•
|
implement appropriate operational and financial systems; and
|
|
•
|
maintain effective financial disclosure controls and procedures.
|
|
•
|
large, well-established tech companies that generally compete in all of our markets, including Google, Quantinuum, IBM,
Microsoft and AWS;
|
|
•
|
countries such as China, Russia, Canada, the United States, Australia and the United Kingdom, and those in the European Union
as of the date of this prospectus and we believe additional countries in the future;
|
|
•
|
less-established public and private companies with competing technology, including companies located outside the United
States;
|
|
•
|
existing or new entrants seeking to enter the quantum annealing space; and
|
|
•
|
new or emerging entrants seeking to develop competing technologies.
|
|
•
|
our inability to enter into agreements with suppliers on commercially reasonable terms, or at all;
|
|
•
|
difficulties of suppliers ramping up their supply of materials to meet our requirements;
|
|
•
|
a significant increase in the price of one or more components, including due to industry consolidation occurring within one
or more component supplier markets or as a result of decreased production capacity at manufacturers;
|
|
•
|
any reductions or interruption in supply, including due to technological problems, equipment malfunctions, regulatory actions
or disruptions on our global supply chain as a result of large scale public health restrictions or geopolitical factors, which we have experienced, and may in the future experience;
|
|
•
|
financial problems of either contract manufacturers or component suppliers;
|
|
•
|
significantly increased freight charges, or raw material costs and other expenses associated with our business;
|
|
•
|
a failure to develop our supply chain management capabilities and recruit and retain qualified professionals;
|
|
•
|
a failure to adequately authorize procurement of inventory;
|
|
•
|
a failure to adequately maintain our or our suppliers’ manufacturing equipment; or
|
|
•
|
a failure to appropriately cancel, reschedule, or adjust our requirements based on our business needs.
|
|
•
|
lack of familiarity and burdens and complexity involved with complying with multiple, conflicting and changing foreign laws,
standards, regulatory requirements, tariffs, export controls and other barriers;
|
|
•
|
difficulties in ensuring compliance with countries’ multiple, conflicting and changing privacy, data security, international
trade, customs and sanctions laws;
|
|
•
|
differing technology standards; and
|
|
•
|
new and uncertain protection for intellectual property rights in some countries.
|
|
•
|
use of resources that are needed in other areas of our business;
|
|
•
|
in the case of an acquisition, implementation or remediation of controls, procedures and policies of the acquired company;
|
|
•
|
in the case of an acquisition, difficulty integrating the accounting systems and operations of the acquired company,
including potential risks to our corporate culture;
|
|
•
|
in the case of an acquisition, coordination of product, engineering and selling and marketing functions, including
difficulties and additional expenses associated with supporting legacy services and products and hosting infrastructure of the acquired company, as applicable, difficulties associated with supporting new products or services, difficulty
converting the customers of the acquired company onto our platform and difficulties associated with contract terms, including disparities in the revenues, licensing, support or professional services model of the acquired company;
|
|
•
|
in the case of an acquisition, retention and integration of employees from the acquired company;
|
|
•
|
in the case of an acquisition, past intellectual property infringement or data security issues arising from the acquired
company;
|
|
•
|
unforeseen costs or liabilities;
|
|
•
|
adverse effects on our existing business relationships with customers as a result of the acquisition or investment;
|
|
•
|
the possibility of adverse tax consequences;
|
|
•
|
litigation or other claims arising in connection with the acquired company or investment; and
|
|
•
|
in the case of foreign acquisitions, the need to integrate operations across different cultures and languages and to address
the particular economic, currency, political and regulatory risks associated with specific countries.
|
|
•
|
be expensive and time consuming to defend;
|
|
•
|
cause us to cease making, licensing or using our platform or products that incorporate the challenged intellectual property;
|
|
•
|
require us to modify, redesign, reengineer or rebrand our platform or products, if feasible;
|
|
•
|
cause significant delays in introducing new or enhanced services or technology;
|
|
•
|
divert management’s attention and resources; or
|
|
•
|
require us to enter into royalty or licensing agreements in order to obtain the right to use a third party’s intellectual
property.
|
|
•
|
actual or anticipated fluctuations in its revenue or other operating metrics;
|
|
•
|
changes in the financial guidance provided to the public or D-Wave Quantum’s failure to meet this guidance;
|
|
•
|
failure of securities analysts to initiate or maintain coverage of D-Wave Quantum, changes in financial estimates by any
securities analysts who follow D-Wave Quantum, or its failure to meet the estimates or the expectations of investors;
|
|
•
|
changes in accounting standards, policies, guidelines, interpretations, or principles;
|
|
•
|
the economy as a whole and market conditions in its industry;
|
|
•
|
rumors and market speculation involving D-Wave Quantum or other companies in its industry;
|
|
•
|
announcements by D-Wave Quantum or its competitors of significant innovations, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint
ventures, or capital commitments;
|
|
•
|
new laws or regulations or new interpretations of existing laws or regulations applicable to its business;
|
|
•
|
lawsuits threatened or filed against us;
|
|
•
|
other events or factors, including those resulting from war, incidents of terrorism, or responses to these events;
|
|
•
|
the expiration of contractual lock-up or market standoff agreements; and
|
|
•
|
sales of additional Common Shares by D-Wave Quantum or its stockholders.
|
|
•
|
provisions that authorize its board of directors, without action by its stockholders, to issue additional Common Shares and
preferred stock with preferential rights determined by its board of directors;
|
|
•
|
provisions that permit only a majority of its board of directors, the chairperson of the board of directors or the chief
executive officer to call stockholder meetings and therefore do not permit stockholders to call special meetings of the stockholders;
|
|
•
|
provisions generally eliminating stockholders’ ability to act by written consent;
|
|
•
|
provisions requiring a two-thirds super majority vote to remove a director; and
|
|
•
|
provisions requiring certain amendments to our governing documents be made by a two-thirds super majority vote.
|
|
•
|
allocation of expenses to and among different jurisdictions;
|
|
•
|
changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities;
|
|
•
|
expected timing and amount of the release of any tax valuation allowances;
|
|
•
|
tax effects of stock-based compensation;
|
|
•
|
costs related to intercompany restructurings;
|
|
•
|
changes in tax laws, tax treaties, regulations or interpretations thereof; or
|
|
•
|
lower than anticipated future earnings in jurisdictions where we have lower statutory tax rates and higher than anticipated
future earnings in jurisdictions where we have higher statutory tax rates.
|
|
•
|
actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly financial results or the quarterly financial results of companies
perceived to be similar to it;
|
|
•
|
changes in the market’s expectations about our operating results;
|
|
•
|
success of competitors;
|
|
•
|
our operating results failing to meet the expectation of securities analysts or investors in a particular period;
|
|
•
|
changes in financial estimates and recommendations by securities analysts concerning D-Wave Quantum or the industries in
which D-Wave Quantum operates;
|
|
•
|
operating and share price performance of other companies that investors deem comparable to D-Wave Quantum;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum’s ability to market new and enhanced products and technologies on a timely basis;
|
|
•
|
changes in laws and regulations affecting our business;
|
|
•
|
our ability to meet compliance requirements;
|
|
•
|
commencement of, or involvement in, litigation involving D-Wave Quantum;
|
|
•
|
changes in D-Wave Quantum’s capital structure, such as future issuances of securities or the incurrence of additional debt;
|
|
•
|
the volume of Common Shares available for public sale;
|
|
•
|
any changes in our board of directors or management;
|
|
•
|
sales of substantial amounts of Common Shares by our directors, executive officers or significant stockholders or the
perception that such sales could occur; and
|
|
•
|
general economic and political conditions such as recessions, interest rates, international currency fluctuations and acts of
war or terrorism. See “—Risks Related to D-Wave Quantum’s Business and Industry”
|
|
•
|
the requirement that a majority of our board of directors consist of “independent directors” as defined under the rules of
the NYSE;
|
|
•
|
the requirement that we have a compensation committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written
charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities;
|
|
•
|
the requirement that we have a nominating and corporate governance committee that is composed entirely of independent
directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities; and
|
|
•
|
the requirement for an annual performance evaluation of the compensation and nominating and corporate governance committees.
|
|
•
|
16,965,849 shares reserved under the 2022 Plan;
|
|
•
|
8,036,455 shares reserved under the ESPP;
|
|
•
|
2,889,282 Common Shares underlying outstanding D-Wave Warrants;
|
|
•
|
26,053,126 Common Shares underlying outstanding Warrants; and
|
|
•
|
11,949,501 Common Shares underlying outstanding D-Wave Options.
|
|
•
|
the accompanying notes to the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statements of operations;
|
|
•
|
the historical unaudited financial statements of DPCM as of and for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and the related notes
included elsewhere in this prospectus;
|
|
•
|
the historical audited consolidated financial statements of D-Wave Quantum for the year ended December 31, 2022 and the
related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus; and
|
|
•
|
the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included
elsewhere in this prospectus and the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contained in D-Wave Quantum’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31,
2022, filed with the SEC on April 18, 2023.
|
|
•
|
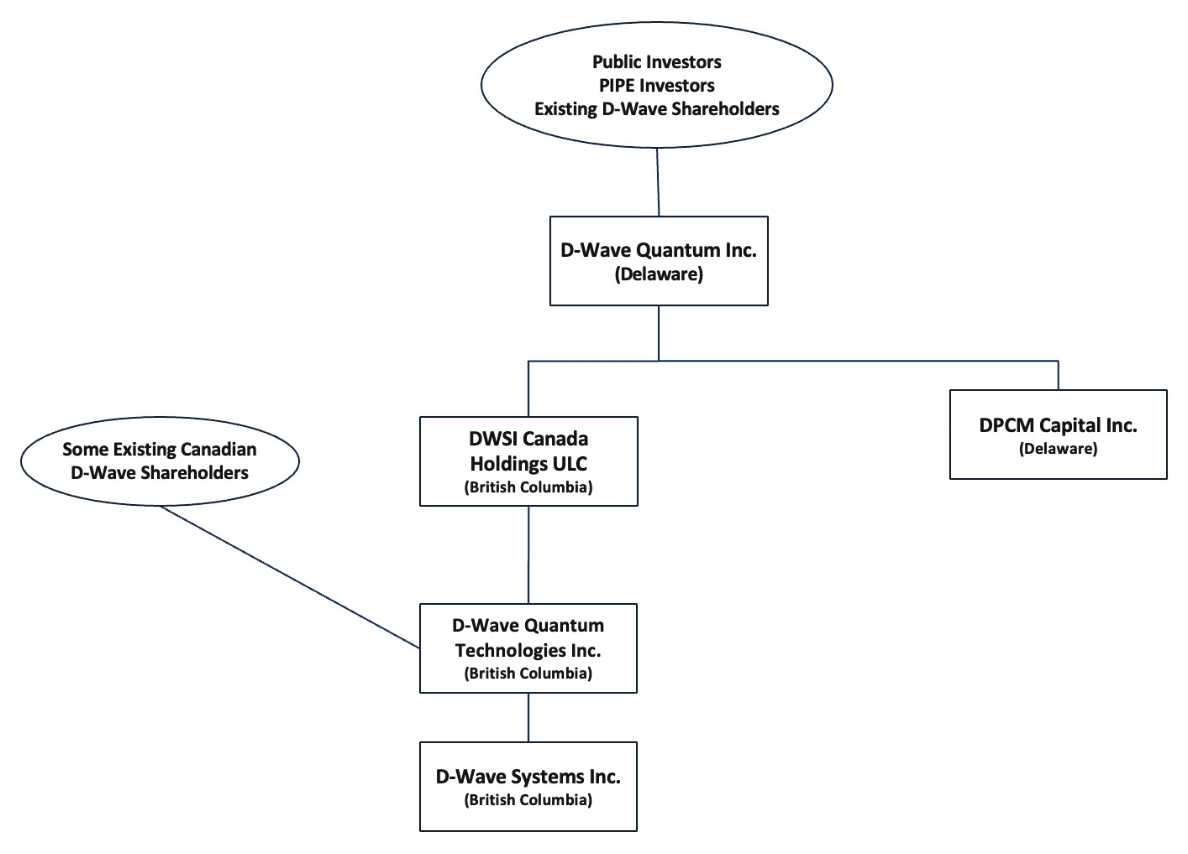
On the Closing Date, the DPCM Merger was consummated;
|
|
•
|
At the Effective Time, (a) each issued and outstanding share of DPCM Class A Common Stock (other than any shares of DPCM
Class A Common Stock or shares of DPCM’s Class B Common Stock held in DPCM’s treasury or owned by D-Wave or any other wholly-owned subsidiary of D-Wave or DPCM immediately prior to the Effective Time (the “Excluded Shares”)) and after
giving effect to the right of the holders of DPCM Class A Common Stock to redeem all or a portion of their DPCM Class A Common Stock was automatically converted into and exchanged for the right to receive from the depositary, for each
share of DPCM Class A Common Stock, a number of Common Shares equal to the Exchange Ratio and (b) each issued and outstanding share of DPCM Class B Common Stock (other than any Excluded Shares) was automatically converted into and
exchanged for the right to receive from the depositary, one Common Share;
|
|
•
|
Immediately following the DPCM Merger, the parties proceeded to effect the Arrangement on the terms and subject to the
conditions set forth in the statutory plan of arrangement under the Business Corporations Act (British Columbia) (the “Plan of Arrangement”) and the Transaction Agreement or made at the direction of the Supreme Court of British Columbia
(the “Court”) in accordance with the final order of the Court pursuant to Section 291 of the Business Corporations Act (British Columbia), in a form acceptable to D-Wave and DPCM, each acting reasonably, approving the Arrangement with
the prior written consent of DPCM and D-Wave, each such consent not to be unreasonably withheld, conditioned, or delayed. Pursuant to the Plan of Arrangement, (i) CallCo acquired a portion of the issued and outstanding D-Wave Shares
from certain holders in exchange for Common Shares (the “D-Wave Quantum Share Exchange”), (ii) CallCo contributed such D-Wave Shares to ExchangeCo in exchange for shares of ExchangeCo’s non-par value common stock, (iii) following the
D-Wave Quantum Share Exchange, ExchangeCo acquired the remaining issued and outstanding D-Wave Shares from the remaining holders of D-Wave Shares in exchange for Exchangeable Shares and (iv) as a result of the foregoing, D-Wave Systems
became a wholly-owned subsidiary of ExchangeCo. The holders of the Exchangeable Shares have certain rights as specified in the Exchangeable Share Support Agreement and the Voting and Exchange Trust Agreement, including the right to
exchange Exchangeable Shares for Common Shares;
|
|
•
|
Immediately following the consummation of the DPCM Merger, pursuant to the Plan of Arrangement, each outstanding D-Wave Share
was automatically converted into and exchanged for the right to receive a number of Common Shares or Exchangeable Shares equal to, in the aggregate, the Per Share D-Wave Stock Consideration (as defined in the Transaction Agreement);
|
|
•
|
Concurrently with the execution of the Transaction Agreement, the PIPE Investors entered into the PIPE Subscription
Agreements, pursuant to which, among other things, each PIPE Investor subscribed to and agreed to purchase on the Closing Date, and D-Wave Quantum agreed to issue and sell to each such PIPE Investor on the Closing Date, the PIPE Shares;
and
|
|
•
|
On June 16, 2022, we entered into the Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park pursuant to which Lincoln Park has agreed to
purchase from us, at our option, up to $150,000,000 of Common Shares from time to time over a 36-month period following the Commencement Date. The Purchase Agreement is subject to certain limitations, including the Floor Price
Limitation, the Beneficial Ownership Limitation and
|
|
•
|
the filing and effectiveness of this registration statement. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to the Offering—The terms of the
Purchase Agreement limit the amount of Common Shares we may sell to Lincoln Park and the trading price of the Common Shares may decline as a result of the sale of Common Shares pursuant to the Purchase Agreement or under the Resale
Registration Statement, each of which may limit our ability to utilize the Purchase Agreement to enhance our cash resources”. Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, we also agreed to pay Lincoln Park the Commitment Fee of $2,625,000. We
paid the Commitment Fee entirely in Common Shares, in two tranches consisting of 127,180 and 254,360 Common Shares issued on August 5, 2022 and August 25, 2022, respectively.
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Systems’ existing stockholders have the majority of the voting interest in the combined company;
|
|
•
|
The combined company’s board of directors has seven board members consisting of one board member designated by DPCM, three
board members retained from the D-Wave Systems board, and three additional independent board members;
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Systems’ senior management comprises all the senior management of the combined company; and
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Systems’ operations comprises the ongoing operations of the combined company.
|
|
|
| |
Historical
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|||
|
|
| |
DPCM Capital, Inc
January 1, 2022 –
August 5, 2022
|
| |
D-Wave Quantum Inc.
Year Ended
December 31, 2022
|
| |
Transaction
Accounting
Adjustments
|
| |
|
| |
D-Wave Quantum Inc.
Pro Forma
|
| |
|
|
Revenue
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$7,173
|
| |
$—
|
| |
|
| |
$7,173
|
| |
|
|
Cost of Revenue
|
| |
—
|
| |
2,923
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
2,923
|
| |
|
|
Total gross profit
|
| |
—
|
| |
4,250
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
4,250
|
| |
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Research and development
|
| |
—
|
| |
32,101
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
32,101
|
| |
|
|
General and administrative
|
| |
3,366
|
| |
21,539
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
24,905
|
| |
|
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
—
|
| |
10,068
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
10,068
|
| |
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
| |
3,366
|
| |
63,708
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
67,074
|
| |
|
|
Loss from operations
|
| |
(3,366)
|
| |
(59,458)
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
(62,824)
|
| |
|
|
Other income (expense):
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Interest expense
|
| |
—
|
| |
(4,633)
|
| |
855
|
| |
(a)
|
| |
(3,778)
|
| |
|
|
Non-cash interest income on SIF
|
| |
—
|
| |
5,673
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
5,673
|
| |
|
|
Reduction of deferred underwriting fees
|
| |
235
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
235
|
| |
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities
|
| |
2,687
|
| |
6,173
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
8,860
|
| |
|
|
Lincoln Park Purchase Agreement issuance costs
|
| |
—
|
| |
(629)
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
(629)
|
| |
|
|
Interest earned on marketable securities held in Trust
Account
|
| |
786
|
| |
—
|
| |
(786)
|
| |
(b)
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
|
Other income, net
|
| |
—
|
| |
1,345
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
1,345
|
| |
|
|
Total other income, net
|
| |
3,708
|
| |
7,929
|
| |
69
|
| |
|
| |
11,706
|
| |
|
|
Net income (loss) before taxes
|
| |
$342
|
| |
$(51,529)
|
| |
$69
|
| |
|
| |
$(51,118)
|
| |
|
|
Provision for income taxes
|
| |
(147)
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
|
| |
(147)
|
| |
|
|
Net income (loss)
|
| |
$195
|
| |
$(51,529)
|
| |
$69
|
| |
|
| |
$(51,265)
|
| |
|
|
Net loss per share, basic and diluted
|
| |
|
| |
$(0.43)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
$(0.46)
|
| |
(c)
|
|
Net income per share, Class A common stock, basic and
diluted
|
| |
$0.01
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Net income per share, Class B common stock, basic and
diluted
|
| |
$0.01
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
| |
|
| |
119,647,777
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
110,620,638
|
| |
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding, Class A common
stock, basic and diluted
|
| |
30,000,000
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding, Class B common
stock, basic and diluted
|
| |
7,500,000
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
(a)
|
Reflects the removal of interest expense on a loan with PSP as it is assumed that the loan would have not been entered into
if the Merger had occurred on January 1, 2022.
|
|
(b)
|
Reflects the elimination of interest income on marketable securities held in the Trust Account.
|
|
(c)
|
Reflects the pro forma basic and diluted earnings per share amounts presented in the unaudited pro forma condensed combined
statement of operations based upon the number of Common Shares outstanding at the closing of the Merger, assuming the Merger occurred on January 1, 2022. As the unaudited pro forma condensed combined statement of operations is in a loss
position, anti-dilutive instruments were not included in the calculation of the diluted weighted-average number of common shares outstanding (the anti-dilutive instruments are described below).
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31, 2022
|
|
(In thousands, except per share data)
|
| |
|
|
Numerator:
|
| |
|
|
Pro forma net loss
|
| |
$(51,265)
|
|
|
| |
|
|
Denominator:
|
| |
|
|
Public Stockholders
|
| |
1,347
|
|
PIPE investors
|
| |
5,817
|
|
Lincoln Park
|
| |
536
|
|
Sponsor shares
|
| |
2,769
|
|
Additional Former Class B Holder shares
|
| |
247
|
|
D-Wave shareholders
|
| |
99,905
|
|
Pro forma weighted-average shares outstanding, basic and diluted
|
| |
110,621
|
|
Pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share(1)
|
| |
$(0.46)
|
|
(1)
|
Because basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding are the same in a net loss position, combined pro forma net loss
per share excludes public warrants as converted to common shares of 14,420,065, private warrants as converted to common shares of 11,633,060, D-Wave Systems warrant shares as converted to common shares of 2,889,282, and options to
purchase common stock as converted to common shares of 13,689,638.
|
|
•
|
Volkswagen has investigated multiple use cases, including a commercial application that required live access to a quantum
processor. During Web Summit 2019 in Lisbon, Volkswagen’s Quantum Shuttle project combined live Android data from buses, live traffic data, and access to a D-Wave hybrid solver through Leap to optimize bus routes in real time.
|
|
•
|
SavantX, a quantum analytics company, worked with the Port of Los Angeles to create a quantum application specific to the
port’s third largest terminal - Pier 300 - to optimize cargo handling and truck scheduling using D-Wave’s annealing quantum computer. With the application, truck drivers are directed
|
|
•
|
Pattison Food Group, a western Canadian grocery retailer, successfully used our hybrid solver service in Leap, which
incorporates the Advantage quantum processing unit (“QPU”), to find solutions to optimization problems in grocery logistics. The company was able to reduce the time needed for one optimization task from 25 hours to less than two minutes
per week. Although the gain from the time savings is significant, the real value is in allowing this business optimization process, previously done weekly, to be done in real time, providing optimal solutions to ever-changing inputs and
conditions. Pattison Food Group is now looking to apply our hybrid quantum capability to other challenges across its business.
|
|
•
|
BBVA, a global financial institution, along with financial quantum applications partner Multiverse Computing, set out to
identify management strategies that yield the highest Sharpe ratio—a metric reflecting the rate of return at a given level of risk. An algorithmic solver was used to find the optimal solution to a cost function equation that describes
the risk, return, and transaction costs associated with a given portfolio. Utilizing D-Wave’s hybrid solver service, BBVA was able to find the maximum value at the lowest risk in 171 seconds, even with 10382 possible portfolios. In
comparison, existing solutions either took an entire day or failed to find a solution.
|
|
•
|
Volkswagen identified a commercial optimization application, the binary paint shop problem, which was run on D-Wave’s hybrid
solver service. The solver outperformed four purely classical methods on problem sizes at commercial scale (N=3,000). In a separate project, similar inputs were tested using a leading ion trap system, which failed to find any commercial
solution.
|
|
•
|
Professional services accelerate QCaaS: Our model features a professional-services-enabled approach for application discovery
and proof-of-concept development, and a QCaaS model for recurring revenue as applications move to production. This model enables us to capture professional services revenue in the first half of the customer journey and recurring QCaaS
revenue in the second half once the application has been built and validated.
|
|
•
|
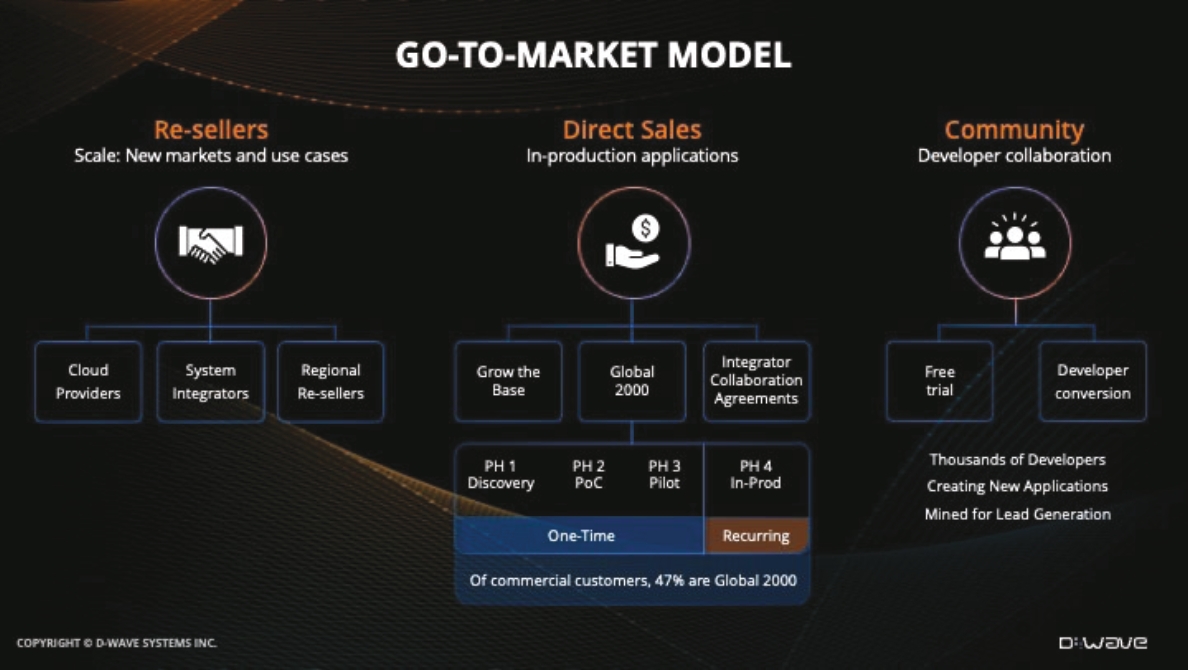
Three-pronged go-to-market model: Our go-to-market model—across direct sales,
re-sellers and developers—extends our ability to scale sales.
|
|
•
|
Our direct sales strategy involves: (1) growing our existing customer base by
accelerating the path from pre-production to in-production application deployment on Leap, our quantum cloud service; and (2) acquiring net new customers using D-Wave Launch, a services-enabled journey to the adoption of quantum
technology. For direct to enterprise sales, we sell through a four-phased customer engagement that we call D-Wave Launch. We describe phase 1 as our discovery phase. In this phase, our professional services organization works with
customers to identify one or more applications that are valuable for their business and that could be run on one of our quantum hybrid solvers. We describe phase 2 as our proof of concept (“PoC”) phase. In this phase, again our
professional services organization works with the customer to build out an actual software implementation and we begin to run the software on the Leap quantum cloud service to test if the implementation works correctly and if the
customer begins to see early business value. We describe phase 3 as our pilot deployment phase. In this phase, we expand the implementation to support running the application at business scale. For example: in the case of delivery
scheduling, we would add more vehicles to the model, for example from 10 to 100 trucks. Or in the case of a portfolio optimization problem, we would add additional portfolios to test the performance of the quantum hybrid solver at
larger business size problems. We describe phase 4 as putting the quantum hybrid application into full production. In this phase, our customer is running the problem in their environment while connected to the Leap quantum cloud
service, at full scale, deriving additional business benefits beyond those identified in earlier phases. Phases 1-3 are considered non-recurring revenue per application as they are phases that the customer moves through to get to full
production (phase 4). Phase 4 represents recurring revenue as the application in full production consumes QCaaS resources to run the full production application on an ongoing basis. As an application consumes QCaaS resources, D-Wave
recognizes the revenue. See “—Our Quantum Computers, Developer Tools and Quantum Hybrid Solvers Delivered via QCaaS—D-Wave Launch™ on-board to quantum computing program”.
|
|
•
|
Our partner strategy involves: (1) expanding our reach by enabling AWS customers to
purchase Leap and other services through AWS Marketplace; (2) creating new markets and unlocking new use cases via systems consultants and integrators such as Deloitte and Accenture; and (3) building an ecosystem of global re-sellers
such as NEC and regional re-sellers such as Strangeworks and Sigma-i. For our partner-led strategy, we work with system integrators, independent software vendors, and cloud providers to resell our Leap quantum cloud service around the
globe to scale our business.
|
|
•
|
Our developer strategy involves: (1) providing access to a free trial of Leap, our
quantum cloud service; (2) driving developer product usage, quantum application development, and community engagement to maximize developer conversions (from free to paid); and (3) lead generation, i.e., engaging our developer base for
potential new enterprise customer accounts. We do this by offering free, unlimited access to our Leap quantum cloud service platform. In this platform, users have unlimited “always on” access to demos, code samples, training materials,
an integrated developer environment, and a community forum. Initially, they also receive up to one minute of free use of the actual QPUs and additional free time on the quantum hybrid solvers. Because of the speed of the QPU, one minute
of QPU time is equal to running between 400 and 4000 different problems. Developers who attach their GitHub account to their Leap sign ups continue to receive one free minute monthly. There is currently no limit to the ability to
receive an additional one minute of free time each month, assuming developers continue to open source their work and associate their GitHub account. To date, more than 34,000 developers have joined our ecosystem.
|
|
•
|
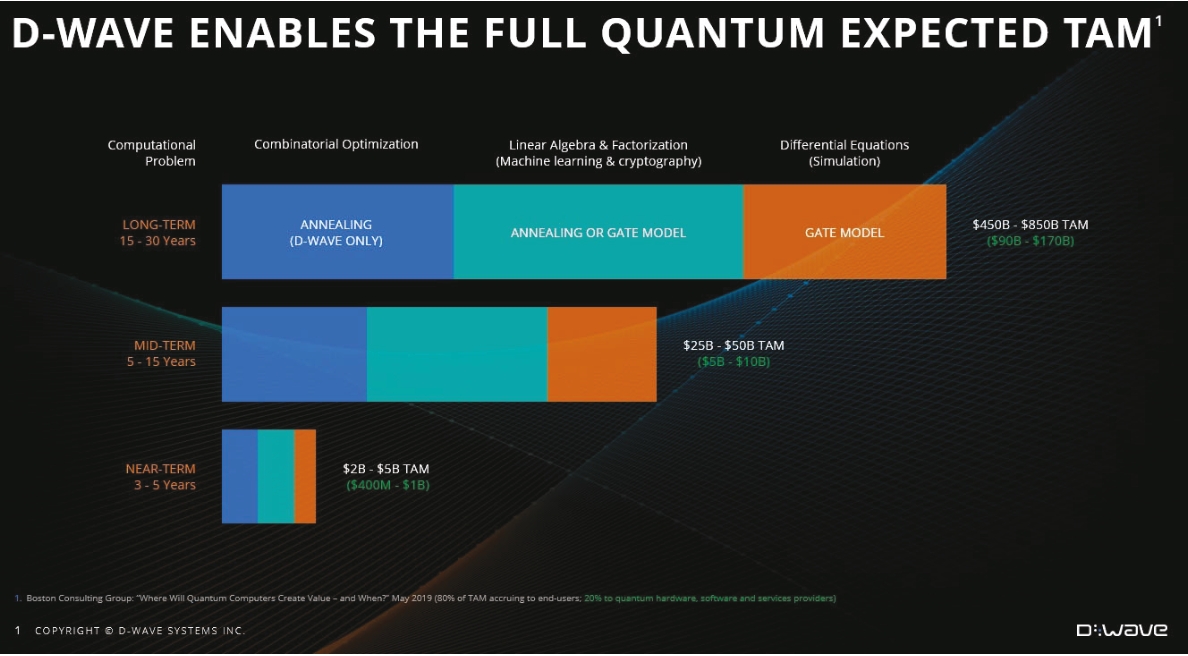
Win the fast-growing optimization market: Quantum annealing is uniquely suited for
solving optimization problems and, as noted above, this problem class is anticipated to comprise $22 billion to $42 billion of the longer-term quantum computing TAM that is available to hardware, software and service providers. As the
only company in the world offering quantum annealing, we’ll continue to leverage this competitive position and acquire additional customers with optimization use cases across multiple verticals, including financial services,
manufacturing/logistics, mobility, and life sciences/pharmaceuticals.
|
|
•
|
Direct sales, recurring revenue and expanding partner strategy: We’re pursuing
multiple revenue streams from our three-pronged go-to-market model. Our main line of business—cloud service—has seen significant year-over-year growth, which we anticipate will continue. Specifically, between 2018, when we introduced
our Leap cloud service, and the end of 2022, cloud revenue has grown at a compound annual growth rate of 37 percent. We have two types of cloud revenue contracts: large, multiyear engagements and smaller, recurring contracts that are
often multi-month in duration. We continue to acquire net new customers through the D-Wave Launch program and further drive recurring QCaaS revenue by moving existing customers from their pre-production journey into production
applications. We recognize professional services revenue from phase 1 (discovery) and phase 2 (PoC) of Launch projects, with many customers initially contracting for both. We’re seeing more than 80 percent of phase 1 (discovery)
projects convert into phase 2 (PoC) projects, demonstrating early customer value and continued engagement and retention. We also intend to expand our channel partner and reseller relationships to identify new geographies, customers, and
use cases, all of which could potentially utilize our products. We’ve also seen that as businesses identify and build use cases, customers learn more about quantum computing and begin to explore alternative use cases, yielding
additional professional services and QCaaS revenues.
|
|
•
|
Grow our existing user base and developer ecosystem: Our developer ecosystem is a
source of innovation for new quantum applications, extended brand awareness, and new use case discovery. We plan to continue to drive developer community engagement and product adoption to grow the ecosystem.
|
|
•
|
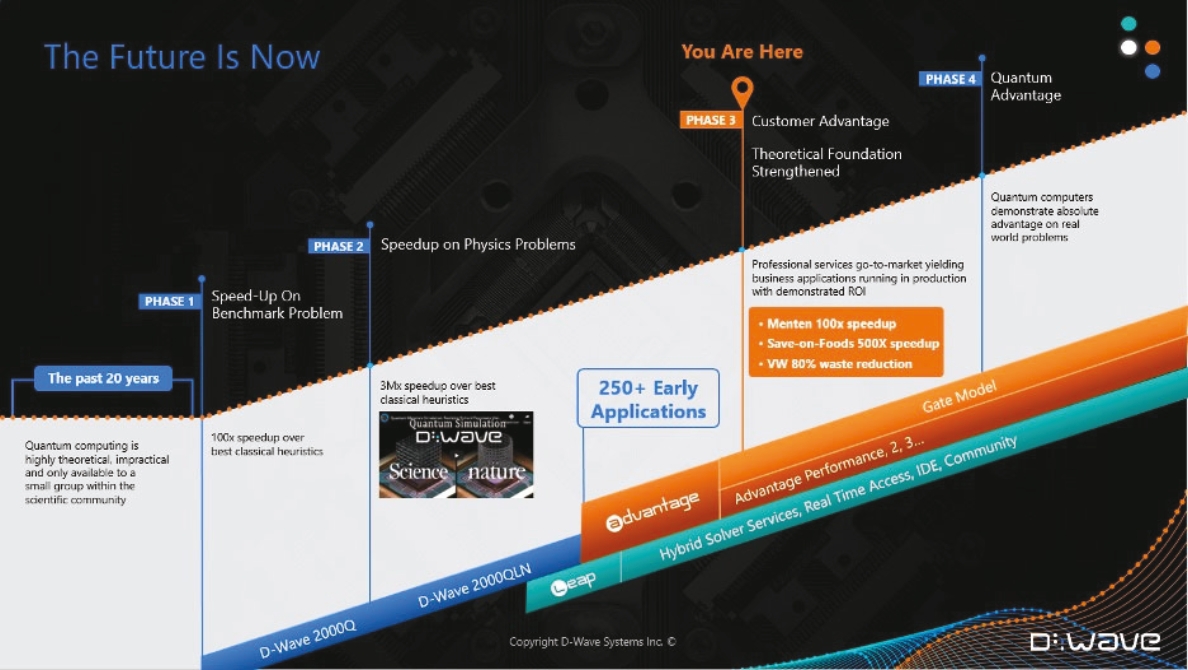
Demonstrate the power of our quantum technology through benchmarking: Our annealing
quantum computers have outperformed the best classical computers in several specific use cases. As noted in a recent peer-reviewed paper published in Nature Communications, our systems demonstrated a solution to a problem three million
times faster than the best-known classical approaches on an application in quantum materials simulation. In the context of real-world applications, our customers have shown material efficiency improvements in solving business problems
(for example, up to 500 times faster for Pattison Food Group, as described above).
|
|
•
|
Pursue the cutting edge and push the boundaries of quantum knowledge: We plan to
continue to create new knowledge in the quantum space that shows the power of our scientific and technological approaches and pushes the frontiers of quantum information science. We have an active research program that focuses on
quantifying the increases in performance we achieve with increasingly coherent quantum systems. And we’ve seen promising new results on interesting physics problems, currently in peer-review, because of even greater coherence in our
systems.
|
|
•
|
Continue to invest in our differentiated quantum annealing technology: As discussed
above, while our technology approach encompasses both annealing and gate-model technologies, we are the only company that builds and delivers annealing quantum computers. Our extensive
intellectual property portfolio around our annealing systems and 10-year head start in superconducting expertise give us a first-mover advantage,
|
|
•
|
Build and deliver a unified quantum platform that offers solutions for broad quantum use
cases for customers: The intersection of systems, software, services and tools is familiar to us. We’re utilizing our integrated engineering expertise to build a cross-platform quantum service with both annealing and gate-model
systems that we believe will be the first and only quantum computing offering to impact full product lifecycles across multiple industries.
|
|
•
|
Extend our track record of continuous innovation, execution, and operational excellence:
We have a strong track record of innovation in building and delivering quantum annealing systems to market. From the D-Wave One, D-Wave Two, D-Wave 2X, D-Wave 2000Q, D-Wave 2000Q LN, Advantage and Advantage Performance Update to the
forthcoming Advantage 2 system, we have demonstrated a relentless pursuit of increased qubit count, coherence (qubit quality), qubit connectivity, and performance. This has resulted in a rapid increase in the complexity of problems our
customers are able to solve. We plan to continue this trajectory and focus on driving additional improvements in coherence and connectivity in our annealing systems to further expand the universe of solvable problems, while utilizing
this expertise to build our gate-model system.
|
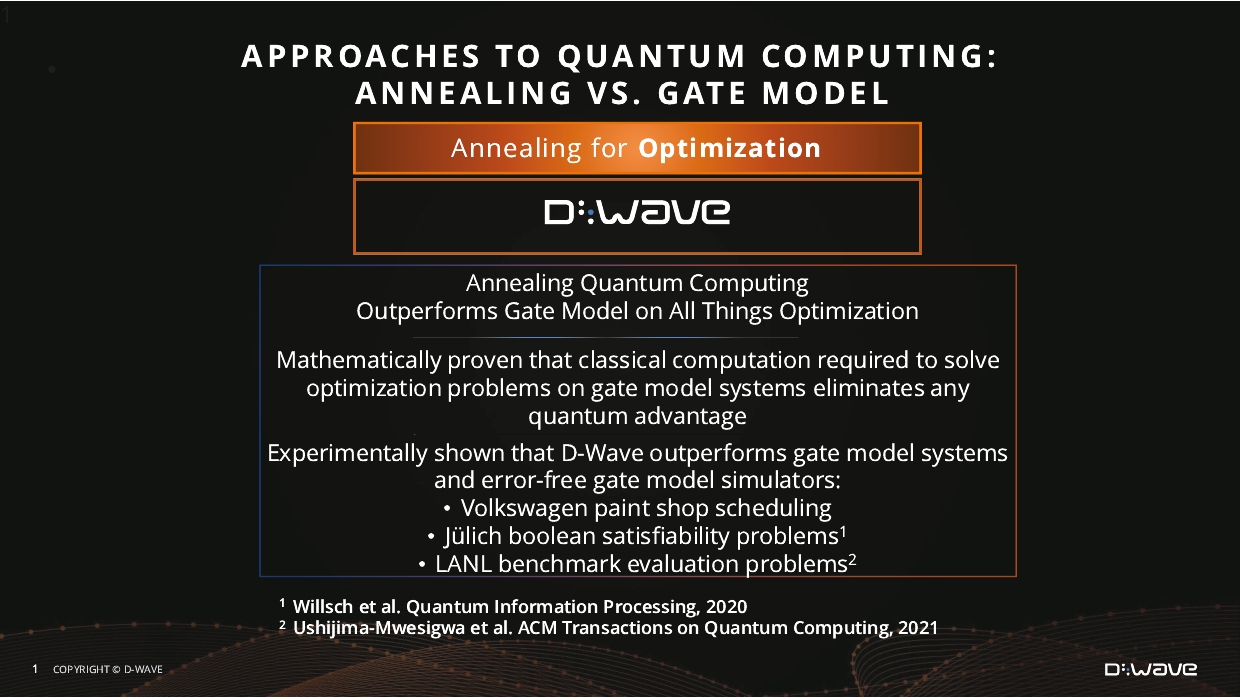
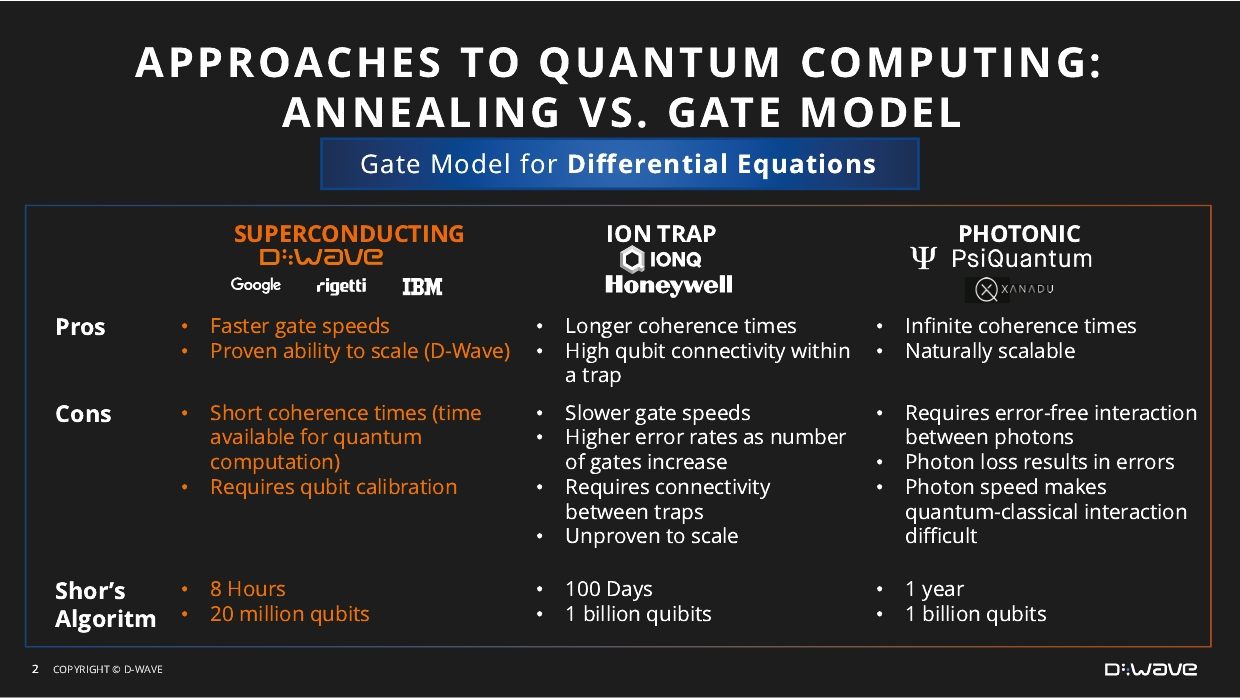
|
•
|
Quantum annealing: Heavily inspired by physics and uniquely effective at solving
challenging, ubiquitous optimization problems, quantum annealing is the first and only approach to date that delivers large-scale quantum computing and is a core of our product platform.
|
|
•
|
Gate-model computation: Heavily inspired by classical digital computation,
gate-model computation replaces classical registers of bits with qubits and performs a series of single and multiqubit operations, or gates, on the registers to run a computation. This includes superconducting, ion trap, and photonic
approaches to quantum computing.
|
|
•
|
Scaling the quantum system: In addition to the growing number of qubits and couplers, and the increasing complexity of
problems our quantum computers can handle, other notable improvements we’ve made while transitioning from the D-Wave 2000Q to the Advantage quantum system (released in October 2020) include the following:
|
|
•
|
Increasing the number of qubits from 2,000 to 5,000 (2.5 times)
|
|
•
|
Increasing connectivity between qubits from 6 to 15 (2.5 times)
|
|
•
|
Increasing problem precision (the precision to which a problem can be posed) by two times
|
|
•
|
Reducing problem latency by 60 percent
|
|
•
|
An updated processor design that increased problem precision
|
|
•
|
Improvements in system control enabled faster anneal times
|
|
•
|
An increased yield of qubits and couplers that allows more complex problems to be solved
|
|
•
|
Gate-model quantum computing (“GMQC”) theory has matured considerably since 2004.
|
|
•
|
Over the past 20 years, we have accrued considerable experience and intellectual property in quantum systems engineering,
including cryogenics, environmental control, input/output and filtering, and scalable control and readout of superconducting devices. This can be directly brought to bear on building scalable GMQC technology.
|
|
•
|
We have developed a mature superconducting VLSI design and manufacturing capability that can immediately be employed for our
gate-model program. This is the only physical implementation of a quantum computing technology that can be utilized for both quantum annealing and gate-model computers.
|
|
•
|
Power consumption and refrigeration: Our quantum computers draw 12 kilowatts of nominal power and have used the same-sized
dilution refrigerators for cooling since the 2010 release of the original D-Wave One system. The refrigerators’ cryocoolers require the bulk of this power to provide cooling to 4 kelvin. While the computational power of our systems has
dramatically increased with each product generation, the power requirements have remained the same and are expected to do so for at least the next two system product generations. This contrasts with competitors that are using and
developing massive dilution refrigerators, which will require increasingly more power to continue with technology development.
|
|
•
|
The superconducting gate-model approach uses the same basic underlying technology as that found in our qubits. Still, there
are significant differences in the details of the implementations, levels of integration, and the performance achieved to date, particularly in optimization and material simulation.
|
|
•
|
The ion trap approach uses the state of atoms trapped in electric fields that are manipulated by electric fields and lasers
for qubits. Current ion trap systems are in the range of about 20 qubits. While technologies such as optical interconnects have been proposed to connect many ion trap QPUs with high connectivity,
this level of integration has not yet been demonstrated at a large enough scale to be used for business-sized problems, and early customer comparisons suggest that such technology is not commercially viable.
|
|
•
|
The photonic approach uses photons of light for qubits. These technologies are in the development stage, with little detail
available on their level of integration or roadmaps.
|
|
|
| |
Three Months ended March 31*,
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
|
Revenue
|
| |
$1,583
|
| |
$1,713
|
| |
$7,173
|
| |
$6,279
|
| |
$5,160
|
|
Cost of revenue
|
| |
1,162
|
| |
616
|
| |
2,923
|
| |
1,750
|
| |
915
|
|
Total gross profit
|
| |
421
|
| |
1,097
|
| |
4,250
|
| |
4,529
|
| |
4,245
|
|
Operating expenses:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Research and development
|
| |
10,915
|
| |
6,802
|
| |
32,101
|
| |
25,401
|
| |
20,411
|
|
General and administrative
|
| |
11,296
|
| |
3,646
|
| |
21,539
|
| |
11,897
|
| |
11,587
|
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
2,900
|
| |
1,600
|
| |
10,068
|
| |
6,179
|
| |
3,714
|
|
Total operating expenses
|
| |
25,111
|
| |
12,048
|
| |
63,708
|
| |
43,477
|
| |
35,712
|
|
Loss from operations
|
| |
(24,690)
|
| |
(10,951)
|
| |
(59,458)
|
| |
(38,948)
|
| |
(31,467)
|
|
Other income (expense), net:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Interest expense
|
| |
(454)
|
| |
(525)
|
| |
(4,633)
|
| |
(1,728)
|
| |
(5,257)
|
|
Government assistance
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
7,167
|
| |
12,027
|
|
Non-cash interest income on SIF
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
5,673
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Gain on debt extinguishment
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
3,873
|
|
Gain on settlement of warrant liability
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
7,836
|
|
Gain on investment in marketable securities
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
1,163
|
| |
—
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities
|
| |
638
|
| |
—
|
| |
6,173
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Lincoln Park Purchase Agreement issuance costs
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
(629)
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Other income (expense), net
|
| |
(102)
|
| |
(181)
|
| |
1,345
|
| |
801
|
| |
2,969
|
|
Total other income (expense), net
|
| |
$82
|
| |
$(706)
|
| |
$7,929
|
| |
$7,403
|
| |
$21,448
|
|
Net loss
|
| |
$(24,608)
|
| |
$(11,657)
|
| |
$(51,529)
|
| |
$(31,545)
|
| |
$(10,019)
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of tax
|
| |
(19)
|
| |
(70)
|
| |
41
|
| |
15
|
| |
(82)
|
|
Net comprehensive loss
|
| |
$(24,627)
|
| |
$(11,727)
|
| |
$(51,488)
|
| |
$(31,530)
|
| |
$(10,101)
|
|
*
|
Our results of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2023 and 2022 are unaudited.
|
|
•
|
An increase in personnel-related costs of $0.3 million related to higher salaries; and
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.3 million related to stock-based compensation expense.
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Research and development
|
| |
$10,915
|
| |
$6,802
|
| |
$4,113
|
| |
60%
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
General and administrative
|
| |
$11,296
|
| |
$3,646
|
| |
$7,650
|
| |
210%
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
$2,900
|
| |
$1,600
|
| |
$1,300
|
| |
81%
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
| |
$454
|
| |
$525
|
| |
$(71)
|
| |
(14)%
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended March 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities
|
| |
$638
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$638
|
| |
100%
|
|
|
| |
Three months ended - March 31st
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Other income (expense), net
|
| |
$(102)
|
| |
$(181)
|
| |
$79
|
| |
(44)%
|
|
•
|
An increase in personnel-related costs of $0.5 million associated with the growth of our QCaaS revenue;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.3 million related to stock-based compensation expense;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.1 million related to the maintenance and repair of our quantum systems; and
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.1 million related to the increase of depreciation of our quantum systems.
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Research and development
|
| |
$32,101
|
| |
$25,401
|
| |
$6,700
|
| |
26%
|
|
•
|
An increase of $2.8 million in stock-based compensation expense primarily relating to new stock option and restricted stock
unit awards;
|
|
•
|
An increase in personnel-related costs of $1.5 million relating to higher salaries and an increase in headcount;
|
|
•
|
An increase in research and development expenditures of $1.5 million resulting from a reduction in Scientific Research and
Experimental Development expenditure credits during the year due to the Company’s loss of Canadian Controlled Private Corporation (“CCPC”) status after becoming a public company;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.6 million in wafer fabrication costs due to increased activity demands; and
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.3 million associated with the increase in third party professional services for various research and
development initiatives as we continue to develop new products and enhance existing products, services and technologies.
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
General and administrative
|
| |
$21,539
|
| |
$11,897
|
| |
$9,642
|
| |
81%
|
|
•
|
An increase of $4.5 million in third party professional services from legal and accounting consultants, including
$0.2 million in transfer agent fees;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $1.5 million in stock-based compensation due to the issuance of stock option and restricted stock unit awards;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $2.1 million in personnel-related expenses due to an increase in headcount and higher salaries;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $1.2 million related to the increase in Directors and Officers insurance costs;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.3 million related to an increase from software licensing fees; and
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.1 million related to other operating costs.
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
$10,068
|
| |
$6,179
|
| |
$3,889
|
| |
63%
|
|
•
|
An increase of $2.8 million in stock-based compensation due to the issuance of stock option and restricted stock unit awards;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.9 million in personnel-related costs resulting from an increase in headcount and higher salaries;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.4 million in public relations, advertising, and marketing costs;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.3 million in other expenses; with
|
|
•
|
The above increases partially offset by a decrease of $0.5 million in promotion and conference costs.
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
| |
$(4,633)
|
| |
$(1,728)
|
| |
$(2,905)
|
| |
168%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Government assistance
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$7,167
|
| |
$(7,167)
|
| |
(100)%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Non-cash interest income on SIF
|
| |
$5,673
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$5,673
|
| |
100%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Gain on investment in marketable securities
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$1,163
|
| |
$(1,163)
|
| |
-100%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities
|
| |
$6,173
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$6,173
|
| |
100%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Lincoln Park Purchase Agreement issuance costs
|
| |
$(629)
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$(629)
|
| |
100%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Other income, net
|
| |
$1,345
|
| |
$801
|
| |
$544
|
| |
68%
|
|
•
|
An increase of $1.4 million in professional services revenue related to the completion of certain customer deliverables of
our remote systems;
|
|
•
|
An increase of $0.1 million in our QCaaS revenue; with
|
|
•
|
The above increases partially offset by a decrease of $0.4 million in other revenue mainly due to the completion of a
customer contract during the year ended December 31, 2020.
|
|
•
|
An increase of personnel-related costs of $0.9 million associated with providing services as a result of the growth of our
professional services and our QCaaS offerings during the year ended December 31, 2021;
|
|
•
|
Offset by a reduction of $0.1 million in other costs during the year ended December 31, 2021.
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Research and development
|
| |
$25,401
|
| |
$20,411
|
| |
$4,990
|
| |
24%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
General and administrative
|
| |
$11,897
|
| |
$11,587
|
| |
$310
|
| |
3%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Sales and marketing
|
| |
$6,179
|
| |
$3,714
|
| |
$2,465
|
| |
66%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Interest expense
|
| |
$(1,728)
|
| |
$(5,257)
|
| |
$3,529
|
| |
(67)%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Government assistance
|
| |
$7,167
|
| |
$12,027
|
| |
$(4,860)
|
| |
(40)%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Gain on debt extinguishment
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$3,873
|
| |
$(3,873)
|
| |
(100)%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Gain on settlement of warrant liability
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$7,836
|
| |
$(7,836)
|
| |
(100)%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Gain on investment in marketable securities
|
| |
$1,163
|
| |
$—
|
| |
$1,163
|
| |
100%
|
|
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
| |
Change
|
||||||
|
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
| |
Amount
|
| |
%
|
|
|
| |
(In thousands, except percentages)
|
|||||||||
|
Other income, net
|
| |
$801
|
| |
$2,969
|
| |
$(2,168)
|
| |
(73)%
|
|
|
| |
Three Months Ended March 31,
|
| |
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
|
| |
2023
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2022
|
| |
2021
|
| |
2020
|
|
Net cash (used in) provided by:
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Operating Activities
|
| |
$(13,574)
|
| |
$(9,509)
|
| |
$(45,226)
|
| |
$(34,800)
|
| |
$(29,287)
|
|
Investing Activities
|
| |
(76)
|
| |
(144)
|
| |
(498)
|
| |
(1,999)
|
| |
(789)
|
|
Financing Activities
|
| |
15,592
|
| |
17,872
|
| |
43,265
|
| |
24,913
|
| |
43,144
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash
equivalents
|
| |
(19)
|
| |
(41)
|
| |
41
|
| |
34
|
| |
(13)
|
|
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents
|
| |
$1,923
|
| |
$8,178
|
| |
$(2,418)
|
| |
$(11,852)
|
| |
$13,055
|
|
|
| |
Payments due by period (3)
|
||||||||||||
|
|
| |
Total
|
| |
Less than
1 year
|
| |
1 - 3 year
|
| |
4 - 5 year
|
| |
More than
5 years
|
|
Lease commitment(1)
|
| |
$14,227
|
| |
$1,533
|
| |
$2,478
|
| |
$2,367
|
| |
$7,849
|
|
Promissory note – related party(2)
|
| |
420
|
| |
420
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
$—
|
|
Total
|
| |
$14,647
|
| |
$1,953
|
| |
$2,478
|
| |
$2,367
|
| |
$7,849
|
|
(1)
|
Includes operating lease liabilities for certain of our offices and facilities.
|
|
(2)
|
Promissory notes – related party are described in Note 13, Promissory note – related party
of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included herein.
|
|
(3)
|
Excludes the Venture Loan entered into on March 3, 2022 by and between the Borrowers, and PSPIB, as the loan has since been
repaid.
|
|
•
|
identify the contract with the customers
|
|
•
|
identify the performance obligations;
|
|
•
|
determine the transaction price;
|
|
•
|
allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations; and
|
|
•
|
recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
|
|
•
|
Alan E. Baratz, President, Chief Financial Officer and Director;
|
|
•
|
John M. Markovich, Chief Financial Officer; and
|
|
•
|
Victoria Brydon, Chief People Officer
|
|
Name and Principal
Position
|
| |
Year
|
| |
Salary
($)
|
| |
Stock
Awards
($)(1)
|
| |
Option
Awards
($)(2)
|
| |
Non-Equity
Incentive Plan
Compensation
($)(3)
|
| |
All Other
Compensation
($)(4)
|
| |
Total
($)
|
|
Alan E. Baratz
President & Chief Executive Officer,
Director
|
| |
2022
|
| |
491,667
|
| |
10,050,000
|
| |
—
|
| |
273,333
|
| |
1,348
|
| |
10,816,348
|
| |
2021
|
| |
450,000
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
144,000
|
| |
1,329
|
| |
595,329
|
||
|
John M. Markovich(5)
Chief Financial Officer
|
| |
2022
|
| |
350,000
|
| |
3,517,500
|
| |
—
|
| |
144,000
|
| |
51
|
| |
4,011,551
|
| |
2021
|
| |
118,834
|
| |
—
|
| |
5,161,080
|
| |
30,294
|
| |
—
|
| |
5,310,208
|
||
|
Victoria Brydon
Chief People Officer
|
| |
2022
|
| |
191,528
|
| |
818,432
|
| |
537,600
|
| |
60,871
|
| |
122
|
| |
1,608,553
|
|
(1)
|
The amounts reported in this column reflect the grant date fair value of restricted share unit awards made under the 2022 Plan
(as defined below) to the NEOs listed in this table, computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718 for stock-based compensation transactions. Assumptions used in the calculation of these amounts are included in note 2 to our audited
consolidated financial statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022.
|
|
(2)
|
The amounts reported in this column reflect the grant date fair value of stock option awards made under the 2022 Plan and 2020
Plan (as defined below) to the NEOs, computed in accordance with ASC 718 for stock-based compensation transactions. Assumptions used in the calculation of these amounts are included in note 12 to our audited consolidated financial
statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022. These amounts do not reflect the actual economic value that will be realized by the NEO upon the vesting of the stock options, the exercise of
the stock options, or the sale of the Common Shares underlying such stock options.
|
|
(3)
|
For 2022, the amounts reported in this column reflect annual cash incentive earned by each NEO determined by the Company’s
Compensation Committee.
|
|
(4)
|
For 2022 and 2021, the amounts reported in this column represent life insurance premiums paid by D-Wave for the benefit of the
NEOs and represent a reimbursement to Dr. Baratz for tax accounting expenses.
|
|
(5)
|
Mr. Markovich commenced employment on August 20, 2021.
|
|
|
| |
Option Awards
|
| |
Stock Awards
|
||||||||||||
|
Name
|
| |
Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Options (#)
Exercisable(1)
|
| |
Number of
Securities
Underlying
Unexercised
Options (#)
Unexercisable(1)
|
| |
Option
Exercise
Price ($)
|
| |
Option
Expiration
Date
|
| |
Number of
Shares or
Units of
Stock That
Have Not
Vested
(#)
|
| |
Market
Value of
Shares or
Units of
Stock That
Have Not
Vested
($)(8)
|
|
Alan E. Baratz
|
| |
2,920,208
|
| |
—
|
| |
0.81
|
| |
5/5/2030
|
| |
2,500,000(5)
|
| |
3,600,000
|
|
John M. Markovich
|
| |
500,498
|
| |
1,000,888(2)
|
| |
0.82
|
| |
8/20/2031
|
| |
875,000(6)
|
| |
1,260,000
|
|
Victoria Brydon
|
| |
159,283
|
| |
—
|
| |
0.81
|
| |
5/05/30
|
| |
203,590(7)
|
| |
293,170
|
| |
68,666
|
| |
37,648(3)
|
| |
0.81
|
| |
5/05/30
|
| | | | ||||
| |
—
|
| |
120,000(4)
|
| |
10.07
|
| |
8/18/32
|
| |
|
| |
|
||
|
(1)
|
Except as otherwise noted, these amounts represent Common Shares issuable upon exercise of previously granted options of
D-Wave Systems, following the Merger.
|
|
(2)
|
The remaining portion of the option vests in equal monthly installments on the 20th of each month through August 20, 2025.
|
|
(3)
|
The remaining portion of the option vests in equal monthly installments on the 5th of each month through May 5, 2024.
|
|
(4)
|
The option vested as to 30,000 shares on February 16, 2023, with the remaining portion of the option vesting in equal monthly
installments on the 16th of each month through February 16, 2026.
|
|
(5)
|
1,000,000 of these restricted share units vest at a rate of 50% on the first and second anniversaries of the grant date of
October 27, 2022. 1,500,000 of these restricted share units vest at a rate of 50% on the first anniversary and then 25% on each of the second and third anniversaries of the grant date of October 27, 2022.
|
|
(6)
|
875,000 of these restricted shares vest at a rate of 50% on the first anniversary of the grant date and then 25% on each of
the second and third anniversaries of the grant date of October 27, 2022.
|
|
(7)
|
203,590 of these restricted shares will vest at a rate of 50% on the first anniversary of the grant date and then 25% on each
of the second and third anniversaries of the grant date of October 27, 2022.
|
|
(8)
|
The market value of these shares is based on the closing price of D-Wave Quantum on December 30, 2022 ($1.44 per share).
|
|
Name
|
| |
Fees
Earned or
Paid in
Cash
($)(1)
|
| |
Stock Awards
($)(2)
|
| |
All Other
Compensation
($)
|
| |
Total
($)
|
|
Amy Cappellanti-Wolf
|
| |
48,333
|
| |
146,814
|
| |
—
|
| |
195,147
|
|
Emil Michael
|
| |
35,833
|
| |
116,664
|
| |
—
|
| |
152,497
|
|
Michael Rogers
|
| |
42,500
|
| |
146,814
|
| |
—
|
| |
189,314
|
|
Steven M. West
|
| |
60,833
|
| |
116,664
|
| |
—
|
| |
177,497
|
|
Roger Biscay
|
| |
45,833
|
| |
146,814
|
| |
—
|
| |
192,647
|
|
Eduard van Gelderen(3)
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
(1)
|
Cash retainers were prorated from August 2022 through May 2023.
|
|
(2)
|
RSUs awarded and vest 100% at the Annual Meeting.
|
|
(3)
|
Mr. van Gelderen was not eligible to be compensated for his board position.
|
|
Name
|
| |
Shares Underlying
Options
Outstanding
at Fiscal
Year End
(#)
|
| |
Stock Awards
Outstanding
at Fiscal
Year End
(#)(1)
|
|
Amy Cappellanti-Wolf
|
| |
—
|
| |
36,521
|
|
Emil Michael
|
| |
—
|
| |
29,021
|
|
Michael Rogers
|
| |
—
|
| |
36,521
|
|
Steven M. West
|
| |
311,973
|
| |
29,021
|
|
Roger Biscay
|
| |
—
|
| |
36,521
|
|
Eduard van Gelderen(2)
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
(1)
|
RSUs awarded and vest 100% at the Annual Meeting.
|
|
(2)
|
Mr. van Gelderen was not eligible to be compensated for his board position.
|
|
Name
|
| |
Age
|
| |
Position
|
|
Executive Officers
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Alan Baratz
|
| |
68
|
| |
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director
|
|
John M. Markovich
|
| |
67
|
| |
Chief Financial Officer
|
|
Victoria Brydon
|
| |
49
|
| |
Chief People Officer
|
|
Diane Nguyen
|
| |
38
|
| |
General Counsel and Corporate Secretary
|
|
Non-Employee Directors
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Steven M. West
|
| |
67
|
| |
Chair
|
|
Emil Michael
|
| |
50
|
| |
Director
|
|
Roger Biscay
|
| |
55
|
| |
Director
|
|
Amy Cappellanti-Wolf
|
| |
58
|
| |
Director
|
|
Michael Rogers
|
| |
59
|
| |
Director
|
|
Ziv Ehrenfeld
|
| |
48
|
| |
Director
|
|
Phillip Adam Smalley III
|
| |
51
|
| |
Director
|
|
•
|
the Class I directors are Alan Baratz and Ziv Ehrenfeld and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to
be held in 2023;
|
|
•
|
the Class II directors are Emil Michael, Amy Cappellanti-Wolf and Adam Smalley and their terms will expire at the annual
meeting of stockholders to be held in 2024; and
|
|
•
|
the Class III directors are Steven M. West, Michael Rogers and Roger Biscay and their terms will expire at the annual meeting
of stockholders to be held in 2025.
|
|
•
|
helping the board of directors oversee corporate accounting and financial reporting processes;
|
|
•
|
managing the selection, engagement, qualifications, independence and performance of a qualified firm to serve as the
independent registered public accounting firm to audit the financial statements;
|
|
•
|
discussing the scope and results of the audit with the independent registered public accounting firm, and reviewing, with
management and the independent accountants, the interim and year-end operating results;
|
|
•
|
developing procedures for employees to submit concerns anonymously about questionable accounting or audit matters;
|
|
•
|
reviewing related person transactions;
|
|
•
|
obtaining and reviewing a report by the independent registered public accounting firm at least annually that describes
internal quality control procedures, any material issues with such procedures and any steps taken to deal with such issues when required by applicable law; and
|
|
•
|
approving or, as permitted, pre-approving, audit and permissible non-audit services to be performed by the independent
registered public accounting firm.
|
|
•
|
reviewing and approving the compensation of the chief executive officer, other executive officers and senior management;
|
|
•
|
administering the equity incentive plans and other benefit programs;
|
|
•
|
reviewing, adopting, amending and terminating incentive compensation and equity plans, severance agreements, profit sharing
plans, bonus plans, change-of-control protections and any other compensatory arrangements for the executive officers and other senior management; and
|
|
•
|
reviewing and establishing general policies relating to compensation and benefits of the employees, including the overall
compensation philosophy.
|
|
•
|
identifying and evaluating candidates, including the nomination of incumbent directors for reelection and nominees
recommended by stockholders, to serve on the board of directors;
|
|
•
|
considering and making recommendations to the board of directors regarding the composition and chairmanship of the committees
of the board of directors;
|
|
•
|
developing and making recommendations to the board of directors regarding corporate governance guidelines and matters,
including in relation to corporate social responsibility; and
|
|
•
|
overseeing periodic evaluations of the performance of the board of directors, including its individual directors and
committees.
|
|
•
|
for any transaction from which the director derives an improper personal benefit;
|
|
•
|
for any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law;
|
|
•
|
for any unlawful payment of dividends or redemption of shares; or
|
|
•
|
for any breach of a director’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders.
|
|
•
|
675,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, and
|
|
•
|
20,000,000 preferred stock, par value $0.0001 per share.
|
|
•
|
before such date, the board of directors of the corporation approved either the business combination or the transaction that
resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder;
|
|
•
|
upon completion of the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested
stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction began, excluding for purposes of determining the voting stock outstanding (but not the outstanding voting stock owned by the
interested stockholder) those shares owned (i) by persons who are directors and also officers and (ii) employee stock plans in which employee participants do not have the right to determine confidentially whether shares held subject to
the plan will be tendered in a tender or exchange offer; or
|
|
•
|
on or after such date, the business combination is approved by the board of directors and authorized at an annual or special
meeting of the stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least 662/3% of the outstanding voting stock that is not owned by the interested stockholder.
|
|
•
|
any merger or consolidation involving the corporation and the interested stockholder;
|
|
•
|
any sale, transfer, pledge or other disposition of 10% or more of the assets of the corporation involving the interested
stockholder;
|
|
•
|
subject to certain exceptions, any transaction that results in the issuance or transfer by the corporation of any stock of
the corporation to the interested stockholder;
|
|
•
|
any transaction involving the corporation that has the effect of increasing the proportionate share of the stock or any class
or series of the corporation beneficially owned by the interested stockholder; and
|
|
•
|
the receipt by the interested stockholder of the benefit of any loans, advances, guarantees, pledges or other financial
benefits by or through the corporation.
|
|
•
|
any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to the corporation or its stockholders;
|
|
•
|
any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law;
|
|
•
|
unlawful payments of dividends or unlawful stock repurchases or redemptions; and
|
|
•
|
any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit.
|
|
(a)
|
in case of a cash dividend or other distribution declared on the Common Shares, in an amount in cash, payable in United
States dollars, for each Exchangeable Share equal to the cash dividend or other distribution declared on each Common Share multiplied by the relevant Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio on the D-Wave Quantum Dividend Declaration Date;
|
|
(b)
|
in the case of a stock or share dividend or other distribution declared on the Common Shares to be paid in Common Shares, by
the issue or transfer by ExchangeCo of such number of Exchangeable Shares for each Exchangeable Share as is equal to the number of Common Shares to be paid on each Common Share multiplied by the relevant Exchangeable Share Exchange
Ratio on the D-Wave Quantum Dividend Declaration Date; or
|
|
(c)
|
in the case of a dividend or other distribution declared on the Common Shares in property other than cash or Common Shares,
in such type and amount of property for each Exchangeable Share as is the same as or economically equivalent (as determined by the board of directors of ExchangeCo) and adjusted for the relevant Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio to the
type and amount of property declared as a dividend or other distribution on each Common Share.
|
|
(a)
|
pay any dividends or other distributions to any shares ranking junior to the Exchangeable Shares with respect to the payment
of dividends or other distributions (other than to common shares of ExchangeCo), provided that ExchangeCo may pay stock or share dividends payable in common shares of ExchangeCo or any such other shares ranking junior to the
Exchangeable Shares, as the case may be;
|
|
(b)
|
redeem or purchase or make any capital distribution in respect of common shares of ExchangeCo or any other shares ranking
equally or junior to the Exchangeable Shares with respect to the payment of dividends or the distribution of assets in the event of the liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of ExchangeCo, whether voluntary or involuntary, or any other
distribution of the assets of ExchangeCo among its shareholders for the purpose of winding up its affairs; or
|
|
(c)
|
issue any Exchangeable Shares or any other shares of ExchangeCo ranking equally with, or superior to, the Exchangeable
Shares, other than, in each case, by way of stock or share dividend to the holders of such Exchangeable Shares.
|
|
(a)
|
the aggregate number of Exchangeable Shares issued and outstanding (other than Exchangeable Shares held by D-Wave Quantum and
its affiliates) is less than 5% of the number of Exchangeable Shares issued on the Effective Date (as such number of shares may be adjusted as deemed appropriate by the board of directors of ExchangeCo in certain circumstances set forth
in the Exchangeable Share Provisions) and provided that the exercise of such redemption right does not result in any shareholder being in violation of Canadian pension regulations that restrict it from owning more than 30% of the
securities that vote for the election of directors of D-Wave Quantum (including, for greater certainty, the 30% Rule), in which case the board of directors of ExchangeCo may accelerate such Redemption Date to such date as it may
determine, upon at least 30 days’ prior written notice to the holders of the Exchangeable Shares and the Trustee;
|
|
(b)
|
(i) any person acquires, directly or indirectly, any voting security of D-Wave Quantum, immediately after such acquisition,
directly or indirectly owns, or exercises control and direction over, voting securities representing more than 50% of the total voting power of all of the then outstanding voting securities of D-Wave Quantum; (ii) the shareholders of
D-Wave Quantum approve a merger, consolidation, recapitalization or reorganization of D-Wave Quantum, other than any such transaction which would result in the holders of outstanding voting securities of D-Wave Quantum immediately prior
to such transaction directly or indirectly owning, or exercising control and direction over, voting securities representing more than 50% of the total voting power of all of the voting securities of the surviving entity outstanding
immediately after such transaction; (iii) the shareholders of D-Wave Quantum approve a liquidation of D-Wave Quantum; (iv) D-Wave Quantum sells or disposes of all or substantially all of its assets; (v) D-Wave Quantum distributes
securities or other property, by way of dividend, distribution, reorganization, spin-off, split-off or other similar event, to all holders of Common Shares that constitutes, prior to the date of distribution, business securities or
assets (including equity interests of affiliates or investees of D-Wave Quantum) with a fair market value (as determined by the board of directors of D-Wave Quantum in its good faith judgment) equal to 10% or more of the fair market
value of, or that constitutes
|
|
(a)
|
not take any action that will result in the declaration or payment of any dividend or make any other distribution on the
Common Shares unless (i) ExchangeCo shall simultaneously, declare or pay, as the case may be, an equivalent dividend or other distribution economically equivalent thereto (as determined in accordance with the Exchangeable Share
Provisions) on the Exchangeable Shares (an “Equivalent Dividend”), (ii) if the dividend is a cash dividend or other distribution, receive sufficient money or other assets from D-Wave Quantum (through any intermediary entities) to enable
the due declaration and the due and punctual payment, in accordance with applicable law and the Exchangeable Share Provisions, of any such Equivalent Dividend, and (iii) if the dividend or other distribution is a stock or share dividend
or distribution of stock or shares, have sufficient but unissued securities available to enable the due declaration and the due and punctual payment, in accordance with applicable law and the Exchangeable Share Provisions, of any such
Equivalent Dividend; or, if the board of directors of ExchangeCo so chooses, in its sole discretion, as an alternative to taking any of the actions described above, ExchangeCo shall adjust the Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio in
accordance with the Exchangeable Share Provisions, provided however that the Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio shall only be so adjusted to the extent that the board of directors of ExchangeCo determines in good faith and in its sole
discretion that ExchangeCo would be liable for any unrecoverable tax as a result of taking any of the actions described in this paragraph and determines to adjust the Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio in lieu of taking any such action;
|
|
(b)
|
advise ExchangeCo sufficiently in advance of the declaration of any dividend or other distribution on the Common Shares and
take all such other actions as are reasonably necessary or desirable, in cooperation with ExchangeCo, to ensure that the respective declaration date, record date and payment date for equivalent dividends on the Exchangeable Shares are
the same as those for any corresponding dividends or other distributions on the Common Shares;
|
|
(c)
|
ensure that the record date for any dividend or other distribution declared on the Common Shares is not less than 10 business
days after the declaration date of such dividend or declaration;
|
|
(d)
|
take all such actions and do all things as are reasonably necessary or desirable to enable and permit ExchangeCo, in
accordance with applicable law, to pay the Liquidation Amount, the Retraction Price or the Redemption Price to the holders of the Exchangeable Shares in the event of a liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of ExchangeCo, whether
voluntary or involuntary, the delivery of a Retraction Request by a holder of Exchangeable Shares or a redemption of Exchangeable Shares by ExchangeCo;
|
|
(e)
|
take all such actions and do all such things as are reasonably necessary or desirable to enable and permit the Trustee, in
accordance with applicable law, to perform its obligations under the Voting and Exchange Trust Agreement, including, without limitation, all such actions and all such things as are reasonably necessary or desirable to enable and permit
the Trustee in its capacity as trustee under the Voting and Exchange Trust Agreement to exercise such number of votes in respect of a meeting of D-Wave Quantum Shareholders as is equal to the aggregate number of Exchangeable Shares
outstanding on an as-converted to D-Wave Quantum Shares basis at the relevant time (other than those held by D-Wave Quantum and its affiliates) multiplied by the Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio;
|
|
(f)
|
take all such actions and do all things as are reasonably necessary or desirable to enable and permit D-Wave Quantum or
CallCo, as the case may be, in accordance with applicable law, to perform its obligations arising upon the exercise by it of the Liquidation Call Right, the Retraction Call Right, the Change of Law Call Right or the Redemption Call
Right;
|
|
(g)
|
take all such actions and do all such things as are reasonably necessary or desirable to enable and permit D-Wave Quantum, in
accordance with applicable law, to perform its obligations in connection with a Retraction Request and redemption by ExchangeCo pursuant to the Exchangeable Share Provisions; and
|
|
(h)
|
not exercise its vote as a shareholder of ExchangeCo to initiate the voluntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of
ExchangeCo or any other distribution of the assets of ExchangeCo for the purpose of winding up its affairs, nor take any action or omit to take any action that is designed to result in the liquidation, dissolution or winding up of
ExchangeCo or any other distribution of the assets of ExchangeCo among its shareholders for purpose of winding up its affairs, without the prior approval of the holders of the Exchangeable Shares in accordance with the Exchangeable
Share Provisions as long as any Exchangeable Shares are outstanding.
|
|
(a)
|
D-Wave Quantum will not without the prior approval of ExchangeCo and the prior approval of the holders of the Exchangeable
Shares given in accordance with the Exchangeable Share Provisions:
|
|
(i)
|
issue or distribute Common Shares (or securities exchangeable for or convertible into or carrying rights to acquire Common
Shares) to the holders of all or substantially all of the then outstanding Common Shares by way of stock dividend or other distribution, other than an issue of Common Shares (or securities exchangeable for or convertible into or
carrying rights to acquire Common Shares) to holders of Common Shares (A) who exercise an option to receive dividends in Common Shares (or securities exchangeable for or convertible into or carrying rights to acquire Common Shares) in
lieu of receiving cash dividends, or (B) pursuant to any dividend reinvestment plan or scrip dividend or similar arrangement; or issue or distribute rights, options or warrants to the holders of all or substantially all of the then
outstanding Common Shares entitling them to subscribe for or to purchase Common Shares (or securities exchangeable for or convertible into or carrying rights to acquire Common Shares); or
|
|
(ii)
|
issue or distribute to the holders of all or substantially all of the then outstanding Common Shares (A) shares or securities
of D-Wave Quantum of any class (other than Common Shares or securities convertible into or exchangeable for or carrying rights to acquire Common Shares), (B) rights, options, warrants or other assets other than those referred to in
clause (a)(ii) above, (C) evidence of indebtedness of D-Wave Quantum or (D) assets of D-Wave Quantum, unless, in each case, the economic equivalent on a per share basis of such rights, options, warrants, securities, shares, evidences of
indebtedness or other assets is issued or distributed by ExchangeCo simultaneously to holders of the Exchangeable Shares including, without limitation, an adjustment to the Exchangeable Share Exchange Ratio in accordance with the terms
of the Exchangeable Share Provisions.
|
|
(b)
|
D-Wave Quantum shall not without the prior approval of ExchangeCo and the prior approval of the holders of the Exchangeable
Shares given in accordance with the Exchangeable Share Provisions:
|
|
(i)
|
subdivide, redivide or change the then outstanding Common Shares into a greater number of Common Shares; or
|
|
(ii)
|
reduce, combine, consolidate or change the then outstanding Common Shares into a lesser number of Common Shares; or
|
|
(iii)
|
reclassify or otherwise change Common Shares or effect an amalgamation, merger, reorganization or other transaction affecting
Common Shares; unless, in each case, the same or an economically equivalent change is simultaneously made to, or in the rights of the holders of, the Exchangeable Shares.
|
|
(c)
|
D-Wave Quantum shall ensure that the record date for any event referred to in (a) and (b) above, or (if no record date is
applicable for such event) the effective date for any such event, is not less than five business days after the date on which such event is declared or announced by D-Wave Quantum (with contemporaneous notification thereof by D-Wave
Quantum to ExchangeCo).
|
|
•
|
1% of the total number of Common Shares then outstanding; or
|
|
•
|
the average weekly reported trading volume of the Common Shares during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a
notice on Form 144 with respect to the sale.
|
|
•
|
the issuer of the securities that was formerly a shell company has ceased to be a shell company;
|
|
•
|
the issuer of the securities is subject to the reporting requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act;
|
|
•
|
the issuer of the securities has filed all Exchange Act reports and material required to be filed, as applicable, during the
preceding 12 months (or such shorter period that the issuer was required to file such reports and materials), other than Form 8-K reports; and
|
|
•
|
at least one year has elapsed from the time that the issuer filed current Form 10 type information with the SEC, which was
filed by D-Wave Quantum on August 10, 2022, reflecting its status as an entity that is not a shell company.
|
|
•
|
the amounts involved exceeded or will exceed $120,000; and
|
|
•
|
any of D-Wave Quantum’s current directors, executive officers or holders of more than 5% of D-Wave Quantum’s capital stock,
or any member of the immediate family of, or person sharing the household with, the foregoing persons, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest.
|
|
Stockholder
|
| |
Common Shares
|
| |
Total Purchase Price
|
|
PSP(1)
|
| |
4,362,397
|
| |
$30,000,000
|
|
Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC(2)
|
| |
727,066
|
| |
$5,000,000
|
|
Emil Michael(3)
|
| |
36,353
|
| |
$250,000
|
|
(1)
|
PSP beneficially owns more than 5% of D-Wave Quantum’s capital stock.
|
|
(2)
|
Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC beneficially owns more than 5% of D-Wave Quantum’s capital stock.
|
|
(3)
|
Emil Michael is a member of the D-Wave Quantum board of directors.
|
|
•
|
the benefits to D-Wave Quantum;
|
|
•
|
the impact on a director’s independence in the event the related person is a director, immediate family member of a director
or an entity in which a director is a partner, shareholder or executive officer;
|
|
•
|
the availability of other sources for comparable products or services;
|
|
•
|
the terms of the transaction; and
|
|
•
|
the terms available to unrelated third parties or to employees generally.
|
|
•
|
each person who is known to be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of the outstanding Common Shares;
|
|
•
|
each of the Company’s current named executive officers, directors and director nominees; and
|
|
•
|
all current executive officers and directors of the Company as a group.
|
|
Beneficial Owner
|
| |
Number of Common
Shares
|
| |
% of Total Voting
Power
|
|
Directors and Executive Officers of
D-Wave Quantum(1)
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
Alan Baratz(2)
|
| |
2,920,208
|
| |
2.2%
|
|
John M. Markovich(2)
|
| |
750,692
|
| |
*
|
|
Victoria Brydon
|
| |
270,701
|
| |
*
|
|
Diane Nguyen
|
| |
75,706
|
| |
*
|
|
Steven M. West(3)
|
| |
390,655
|
| |
*
|
|
Emil Michael(4)
|
| |
14,437,489
|
| |
10.3%
|
|
Roger Biscay
|
| |
36,521
|
| |
*
|
|
Amy Cappellanti-Wolf
|
| |
36,521
|
| |
*
|
|
Michael Rogers
|
| |
36,521
|
| |
*
|
|
Ziv Ehrenfeld
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
Phillip Adam Smalley III
|
| |
—
|
| |
—
|
|
All Directors and Executive Officers
of D-Wave Quantum as a Group (11 individuals)(5)
|
| |
18,955,014
|
| |
13.2%
|
|
Five Percent Holders of D-Wave
Quantum
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
PSP(6)
|
| |
59,431,311
|
| |
46.4%
|
|
CDPM Sponsor Group, LLC(7)
|
| |
14,401,136
|
| |
10.3%
|
|
BDC Capital Inc. (8)
|
| |
9,424,713
|
| |
7.4%
|
|
The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (9)
|
| |
7,939,146
|
| |
6.2%
|
|
*
|
Less than one percent.
|
|
(1)
|
Unless otherwise noted, the business address of each of the following entities or individuals is D-Wave Quantum Inc., 3033
Beta Avenue, Burnaby, British Columbia V5G 4M9, Canada.
|
|
(2)
|
Consists of Common Shares underlying D-Wave Options.
|
|
(3)
|
Includes Common Shares held by Emerging Company Partners LLC, an entity controlled by Steven M. West and Common Shares
underlying D-Wave Options.
|
|
(4)
|
Includes Common Shares of which each of the Sponsor and the Emil Michael Living Trust dated 7/28/2017 (the “Trust”) is the record holder and 11,633,061 Common Shares underlying Warrants issued to the Sponsor in the Merger in exchange for Private Warrants, which Warrants were exercisable as of September 4,
2022. Mr. Michael is the manager of the Sponsor and the trustee of the Trust, and, as such, has voting and dispositive power over the securities held by the Sponsor and the Trust and may be deemed to have beneficial ownership of such
securities. Mr. Michael disclaims beneficial ownership of such securities except to the extent of his pecuniary interest therein.
|
|
(5)
|
Includes Common Shares underlying D-Wave Options, Warrants and Exchangeable Shares.
|
|
(6)
|
Based on Schedule 13G filed on February 14, 2023 in which PSP reported that, as of December 31, 2022, it had sole voting power
and sole dispositive power over 59,431,311 Common Shares and Common Shares underlying Exchangeable Shares. PSP is a Canadian Crown corporation with a share capital created by a special act of Legislature in Canada on September 14, 1999.
All the shares of PSP are held by the President of Treasury Board on behalf of his Majesty in Right of Canada, in accordance with the Public Sector Pension Investment Board Act, S.C. 1999, c.34, as amended from time to time. Deborah K.
Orida, the CEO of PSP, has authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by PSP. The business address for PSP is 1250 René-Lévesque Boulevard West, Suite 1400, Montréal, Québec, Canada H3B 5E9. On September 26, 2022, D-Wave Quantum
and PSP entered into the PSP Side Letter Agreement (as described in the section entitled “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions).
|
|
(7)
|
Consists of Common Shares of which the Sponsor is the record holder and 11,633,061 Common Shares underlying Warrants issued to
the Sponsor in the Merger in exchange for Private Warrants, which Warrants were exercisable as of September 4, 2022. Mr. Michael is the manager of the Sponsor, and as such has voting and dispositive power over the securities held by the
Sponsor and may be deemed to have beneficial ownership of such securities. Mr. Michael disclaims beneficial ownership of such securities except to the extent of his pecuniary interest therein.
|
|
(8)
|
Consists of Common Shares held of record by BDC Capital Inc. (“BDC”). BDC is a
wholly-owned subsidiary of the Business Development Bank of Canada, which is itself wholly-owned by the federal government of Canada. Jerôme Nycz, Executive Vice-President, BDC, and Karl Reckziegel, Senior Vice-President, Direct
Investments, BDC, have authority to vote and dispose of the shares held by BDC. The business address of the foregoing persons is 5 Place Ville Marie, Suite 300, Montreal Quebec (Canada) H3B 5E7.
|
|
(9)
|
Based on the Form 3 filed on March 3, 2023 in which The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (“GSG”)
and its affiliates Broad Street Principal Investments, L.L.C., Bridge Street Opportunity Advisors, L.L.C., Bridge Street 2014, L.P., Stone Street 2014 Holdings, L.P., MBD Advisors, L.L.C., MBD 2014, L.P., 2014 Employee Offshore
Aggregator, L.P. (collectively, the “GS Entities”) and Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC (“GS”), a wholly owned subsidiary of GSG, reported their balance of
Common Shares as of August 5, 2022. Affiliates of GSG are the general partner, managing general partner or investment manager, as applicable, of the GS Entities. Each of GS and GSG disclaims beneficial ownership of the equity interests
and the shares described above held directly or indirectly by the GS Entities, except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein, if any. The address of each of GS, GSG, and the GS Entities, except for 2014 Employee Offshore
Aggregator, L.P. and Stone Street 2014 Holdings, L.P. is 200 West Street, New York, NY 10282. The address of each of 2014 Employee Offshore Aggregator, L.P. and Stone Street 2014 Holdings, L.P. is P.O. Box 309 Ugland Hourse, George
Town, Cayman Islands.
|
|
Selling Stockholder
|
| |
Common Shares
Beneficially Owned Before
this Offering
|
| |
Percentage of Outstanding
Common Shares
Beneficially Owned Before
this Offering
|
| |
Common Shares to be Sold
in this Offering Assuming
the Company issues the
Maximum Number of
Common Shares Under the
Purchase Agreement
|
| |
Percentage of Outstanding
Common Shares
Beneficially Owned After
this Offering
|
|
Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC(1)
|
| |
298,900(2)
|
| |
*
|
| |
35,000,000(3)
|
| |
*
|
|
*
|
Represents less than 1% of the outstanding Common Shares (including the Exchangeable Shares) and/or assumes all Common Shares
registered hereunder have been resold by Lincoln Park.
|
|
(1)
|
Josh Scheinfeld and Jonathan Cope, the Managing Members of Lincoln Park Capital, LLC, are deemed to be beneficial owners of
all of the Common Shares owned by Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC. Messrs. Cope and Scheinfeld have shared voting and investment power over the Common Shares being offered under the prospectus in connection with the transactions
contemplated under the Purchase Agreement. Lincoln Park Capital, LLC is not a licensed broker dealer or an affiliate of a licensed broker dealer.
|
|
(2)
|
Represents shares previously issued to Lincoln Park under the Purchase Agreement, all of which are covered by the First LP
Registration Statement. We have excluded from the number of shares beneficially owned by Lincoln Park prior to the offering all of the Common Shares that Lincoln Park may be required to purchase on or after the date of this prospectus
pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, because the issuance of such Common Shares is solely at our discretion and is subject to certain conditions, the satisfaction of all of which are outside of Lincoln Park’s control, including the
registration statement of which this prospectus is a part becoming and remaining effective. Furthermore, under the terms of the Purchase Agreement, issuances and sales of Common Shares to Lincoln Park are subject to certain limitations
on the amounts we may sell to Lincoln Park at any time, including the Beneficial Ownership Limitation. See the description under the heading “Lincoln Park Transaction” for more information about the Purchase Agreement.
|
|
(3)
|
Represents an aggregate of 35,000,000 Common Shares that may be sold by us under this prospectus. Depending on the price per
Common Share at which we sell our shares to Lincoln Park pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, we may need to sell to Lincoln Park under the Purchase Agreement more or less Common Shares than are offered under this prospectus in order to
receive aggregate gross proceeds equal to the $150,000,000 total commitment available to us under the Purchase Agreement. If we choose to sell more Common Shares than are offered under this prospectus, we must first register for resale
under the Securities Act such additional Common Shares. The number of Common Shares ultimately offered for resale by Lincoln Park is dependent upon the number of Common Shares we sell to Lincoln Park under the Purchase Agreement.
|
|
•
|
banks, insurance companies or other financial institutions;
|
|
•
|
persons subject to the alternative minimum tax;
|
|
•
|
tax-exempt organizations;
|
|
•
|
controlled foreign corporations, passive foreign investment companies and corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid
United States federal income tax;
|
|
•
|
partnerships or other entities treated as pass-through entities for United States federal income tax purposes;
|
|
•
|
dealers in securities or currencies;
|
|
•
|
traders in securities that elect to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for their securities holdings;
|
|
•
|
persons that own, or are deemed to own, more than five percent of our common stock, except to the extent specifically set
forth below;
|
|
•
|
real estate investment trusts or regulated investment companies;
|
|
•
|
certain former citizens or long-term residents of the United States;
|
|
•
|
persons who hold our Common Shares as part of a straddle, hedge, conversion, constructive sale, or other integrated security
transaction; or
|
|
•
|
persons who do not hold our Common Shares as a capital asset (within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code).
|
|
•
|
an individual who is a citizen or resident of the U.S., as determined for U.S. federal income tax purposes;
|
|
•
|
a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized in the
U.S. or under the laws of the U.S., any state thereof or the District of Columbia;
|
|
•
|
an estate, the income of which is includible in gross income for U.S. federal income tax purposes regardless of its source;
or
|
|
•
|
a trust if: (i) a court within the U.S. is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one
or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust; or (ii) it has a valid election in effect under applicable U.S. Treasury regulations to be treated as a domestic trust.
|
|
•
|
such gain is effectively connected with the non-U.S. holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States (and,
if required by an applicable income tax treaty, is attributable to a permanent establishment or fixed base maintained by the non-U.S. holder in the United States);
|
|
•
|
you are an individual who is present in the U.S. for 183 or more days in the taxable year of the disposition and certain
other conditions are met; or
|
|
•
|
D-Wave Quantum is or has been a “United States real property holding corporation” (“USRPHC”) for U.S. federal income tax
purposes at any time during the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of disposition or the period that the non-U.S. holder held the Common Shares, and the non-U.S. holder has owned, directly or constructively, more than 5%
of the Common Shares at any time during the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of disposition or the period that the non-U.S. holder held the Common Shares.
|
|
•
|
ordinary brokers’ transactions;
|
|
•
|
transactions involving cross or block trades;
|
|
•
|
through brokers, dealers, or underwriters who may act solely as agents;
|
|
•
|
“at the market” into an existing market for the Common Shares;
|
|
•
|
in other ways not involving market makers or established business markets, including direct sales to purchasers or sales
effected through agents;
|
|
•
|
in privately negotiated transactions; or
|
|
•
|
any combination of the foregoing.
|
|
•
|
the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part lapses for any reason (including,
without limitation, the issuance of a stop order), or any required prospectus supplement and accompanying prospectus are unavailable for the resale by Lincoln Park of Common Shares offered hereby, and such lapse or unavailability
continues for a period of ten consecutive business days or for more than an aggregate of 30 business days in any 365-day period;
|
|
•
|
suspension by our principal market of Common Shares from trading for a period of one business day (other than in connection
with a general suspension of trading on such market);
|
|
•
|
the delisting of the Common Shares from the NYSE (or nationally recognized successor thereto), provided, however, that the
Common Shares is not immediately thereafter trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market, The Nasdaq Global Market, The Nasdaq Global Select Market, the NYSE American, the NYSE Arca, the OTC Bulletin Board, the OTCQX operated by the OTC Markets
Group, Inc., the OTCQB operated by the OTC Markets Group, Inc. or such other nationally recognized trading market (or nationally recognized successor to any of the foregoing);
|
|
•
|
the failure of our transfer agent to issue to Lincoln Park Common Shares within three business days after the applicable date
on which Lincoln Park is entitled to receive such shares;
|
|
•
|
any breach of the representations or warranties or covenants contained in the Purchase Agreement or Registration Rights
Agreement that has or could have a material adverse effect on us and, in the case of a breach of a covenant that is reasonably curable, that is not cured within five business days;
|
|
•
|
any voluntary or involuntary participation or threatened participation in insolvency or bankruptcy proceedings by or against
us;
|
|
•
|
a court of competent jurisdiction enters an order or decree under any bankruptcy law that (i) is for relief against us in an
involuntary case, (ii) appoints a Custodian for us or for all or substantially all of our property, or (iii) orders the liquidation of us or our subsidiaries; or
|
|
•
|
if at any time we are not eligible to transfer Common Shares electronically as DWAC shares.
|
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | |
| | | ||
|
Consolidated Financial Statements:
|
| |
|
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | | ||
| | |
