false2023FY0001818502oneP10Yone yearone year15200018185022023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-3100018185022023-06-30iso4217:USD0001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-03-22xbrli:shares0001818502us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2024-03-220001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMember2024-03-2200018185022023-12-3100018185022022-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares0001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-3100018185022022-01-012022-12-3100018185022021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2020-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-3100018185022020-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMemberus-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMembersrt:RestatementAdjustmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMembersrt:RestatementAdjustmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502srt:RestatementAdjustmentMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-3100018185022021-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:LimitedLiabilityCompanyPreferredUnitMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:TreasuryStockCommonMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-07-20xbrli:pure0001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-01-012023-02-160001818502opfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:OhioAndTexasMember2023-12-310001818502srt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001818502srt:MinimumMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:ComputerSoftwareIntangibleAssetMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Member2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Member2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Member2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Member2023-12-3100018185022021-07-200001818502opfi:TaxBenefitMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ExistingEquityHoldersMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ExistingEquityHoldersMember2022-12-31opfi:segment0001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-07-202021-07-200001818502us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMember2021-07-202021-07-2000018185022021-07-202021-07-200001818502opfi:OppFiUnitsConversionMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-07-202021-07-200001818502opfi:OppFiUnitsConversionMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:ClassVVotingStockMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:ExistingEquityHoldersMember2021-07-200001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2020-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetNotPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:RecencyDelinquencyMemberus-gaap:FinancingReceivables30To59DaysPastDueMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivables60To89DaysPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetNotPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMemberus-gaap:FinancingReceivables30To59DaysPastDueMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivables60To89DaysPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetNotPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:RecencyDelinquencyMemberus-gaap:FinancingReceivables30To59DaysPastDueMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivables60To89DaysPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberopfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:RecencyDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetNotPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMemberus-gaap:FinancingReceivables30To59DaysPastDueMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivables60To89DaysPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancingReceivablesEqualToGreaterThan90DaysPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FinancialAssetPastDueMemberopfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:ContractualDelinquencyMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:LeaseholdsAndLeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:LeaseholdsAndLeaseholdImprovementsMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2021-06-292021-06-2900018185022022-10-10opfi:office_facility0001818502us-gaap:LetterOfCreditMember2022-10-1000018185022023-04-300001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheAMaturingApril2024OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheAMaturingApril2024OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheAMaturingApril2024OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheAMaturingApril2024OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheBMaturingJune2026OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheBMaturingJune2026OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheBMaturingJune2026OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheBMaturingJune2026OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMemberus-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheCMaturingJuly2027OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheCMaturingJuly2027OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheCMaturingJuly2027OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheCMaturingJuly2027OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2025GrayRockSPVLLCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2025GrayRockSPVLLCMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2025GrayRockSPVLLCMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2025GrayRockSPVLLCMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMemberopfi:FinancedInsurancePremiumOppFiLLCJuly2023Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMemberopfi:FinancedInsurancePremiumOppFiLLCJuly2023Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMemberopfi:FinancedInsurancePremiumOppFiLLCJuly2023Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMemberopfi:FinancedInsurancePremiumOppFiLLCJune2024Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMemberopfi:FinancedInsurancePremiumOppFiLLCJune2024Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMemberopfi:SpeIiLlcMember2018-01-012018-12-31opfi:option0001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2018-01-012018-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2018-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2020-05-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2020-05-012020-05-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2023-02-162023-02-160001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SecuredDebtMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2022OppFiLLCMember2018-08-130001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingJanuary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIIILLCMember2018-01-230001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingJanuary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIIILLCMember2020-01-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingJanuary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIIILLCMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Member2020-01-312020-01-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingOctober2023OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-06-130001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingOctober2023OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-06-140001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingJune2025OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-06-142022-06-140001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheAMaturingJune2025OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-06-140001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditTrancheBMaturingJune2025OpportunityFundingSPEVLLCOpportunityFundingSPEVIILLCMember2022-06-140001818502opfi:AAndRCreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2023-07-190001818502opfi:AAndRCreditAgreementTrancheBMaturingJuly2027Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2023-07-190001818502opfi:AAndRCreditAgreementTrancheCMaturingJuly2027Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2023-07-190001818502opfi:AAndRCreditAgreementTrancheCMaturingJuly2027Memberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2023-07-192023-07-190001818502opfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMemberopfi:AAndRCreditAgreementMemberus-gaap:LineOfCreditMember2023-07-192023-07-190001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2023OpportunityFundingSPEVILLCMember2019-04-300001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2019-08-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2021-09-300001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Memberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2019-08-012019-08-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Memberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2021-12-312021-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2022-03-312022-03-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2022-03-312022-03-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingFebruary2024OpportunityFundingSPEIVLLCSalaryTapFundingSPELLCMember2022-09-010001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMember2022-12-140001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingDecember2026OpportunityFundingSPEIXLLCMemberopfi:SecuredOvernightFinancingRateSOFRMember2022-12-142022-12-140001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:RevolvingLineOfCreditMaturingApril2025GrayRockSPVLLCMember2022-04-150001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2018-11-300001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2020-04-300001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Member2021-03-222021-03-220001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMemberopfi:LondonInterbankOfferedRateLIBOR1Member2021-03-232021-03-230001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2021-03-302021-03-300001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberopfi:TermLoanMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2022-03-31opfi:installment0001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2022-08-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2023-08-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:NotesPayableOtherPayablesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:OtherLongTermDebtMember2020-04-130001818502opfi:PaycheckProtectionProgramCARESActMemberopfi:ExtinguishmentOfDebtPrincipalMember2021-09-132021-09-130001818502opfi:ExtinguishmentOfDebtInterestMemberopfi:PaycheckProtectionProgramCARESActMember2021-09-132021-09-130001818502opfi:TermLoanMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:WarrantUnitsMember2021-07-190001818502opfi:WarrantUnitsMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-31opfi:day0001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Member2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2021-01-012021-12-3100018185022021-07-19opfi:classopfi:vote0001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-060001818502us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionOneMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheTwoMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionOneMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionOneMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheThreeMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionOneMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheOneMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionTwoMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheTwoMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionTwoMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheThreeMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionTwoMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheOneMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionTwoMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionThreeMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheTwoMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionThreeMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheOneMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionThreeMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EarnoutUnitsTrancheThreeMemberopfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsMemberopfi:EarnoutUnitsOptionThreeMember2021-07-200001818502opfi:EquityIncentivePlan2021Memberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:EquityIncentivePlan2021Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:EquityIncentivePlan2021Memberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberopfi:EquityIncentivePlan2021Memberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:EquityIncentivePlan2021Memberus-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:EmployeesAndOfficersMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberopfi:EmployeesAndOfficersMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheTwoMemberopfi:EmployeesAndOfficersMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502srt:DirectorMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-07-200001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-07-202021-07-200001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:ProfitUnitInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:ProfitUnitInterestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:ProfitUnitInterestMember2020-12-310001818502opfi:ProfitUnitInterestMember2021-12-310001818502opfi:NonVestedUnitsMember2020-12-310001818502opfi:NonVestedUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:NonVestedUnitsMember2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:ShareBasedCompensationAwardTrancheOneMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:DomesticCountryMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:StateAndLocalJurisdictionMember2022-12-3100018185022021-07-202023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:CarryingReportedAmountFairValueDisclosureMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:EstimateOfFairValueFairValueDisclosureMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputDiscountRateMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:MeasurementInputServicingFeeMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:MeasurementInputServicingFeeMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputDefaultRateMember2022-12-310001818502opfi:MeasurementInputAccruedInterestRateMember2023-12-310001818502opfi:MeasurementInputAccruedInterestRateMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMember2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPrepaymentRateMember2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputRiskFreeInterestRateMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:MeasurementInputExpectedTermMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputPriceVolatilityMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:MeasurementInputExercisePriceMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:MeasurementInputFairValuePerShareMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:MeasurementInputFairValuePerShareMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:MeasurementInputFairValuePerShareMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:MeasurementInputFairValuePerShareMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2021-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:WarrantMemberopfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2023-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001818502us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Member2022-12-3100018185022021-11-182021-11-180001818502us-gaap:SubordinatedDebtMember2021-03-290001818502us-gaap:SubordinatedDebtMemberus-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:SubordinatedDebtMemberus-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:SubordinatedDebtMemberus-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:RelatedPartyMemberopfi:ManagementFeeAgreementTerminationMember2020-08-012020-08-310001818502opfi:ElexusMckayMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:ElexusMckayMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:ElexusMckayMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberstpr:TXus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:FL2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberstpr:VAus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberstpr:TXus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMemberstpr:FL2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:GeographicConcentrationRiskMemberstpr:VAus-gaap:FinanceReceivablesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502srt:ScenarioPreviouslyReportedMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsExcludingEarnoutUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsExcludingEarnoutUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:RetainedOppFiUnitsExcludingEarnoutUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PublicWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1150Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:PrivatePlacementWarrantsExercisePrice1500Memberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:UnderwriterWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:UnderwriterWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:UnderwriterWarrantsMemberus-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestEarnoutUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestEarnoutUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestEarnoutUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001818502opfi:NoncontrollingInterestUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001818502opfi:JocelynMooreMember2023-01-012023-12-310001818502opfi:JocelynMooreMember2023-10-012023-12-310001818502opfi:JocelynMooreMember2023-12-3100018185022023-10-012023-12-31
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
__________________________________________________________________
FORM 10-K
__________________________________________________________________
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023
OR
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from__________to__________
Commission File Number 001-39550
__________________________________________________________________
OppFi Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
__________________________________________________________________
| | | | | |
Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of Incorporation or organization) | 85-1648122 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
130 E. Randolph Street. Suite 3400 Chicago, IL (Address of principal executive offices) | 60601 (Zip Code) |
(312) 212-8079
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Not Applicable
(Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report)
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of Each Class | | Trading Symbol(s) | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share | | OPFI | | New York Stock Exchange |
| Warrants, each whole warrant exercisable for one share of Class A common stock, each at an exercise price of $11.50 per share | | OPFI WS | | New York Stock Exchange |
__________________________________________________________________
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ☐No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ☐No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | | Smaller reporting company | ☒ |
| | | Emerging growth company | ☒ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant's executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of shares of voting and non-voting common equity of the registrant held by non-affiliates of the registrant on June 30, 2023, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was $30,369,239 based on a $2.04 closing price per share as reported on the New York Stock Exchange on such date.
As of March 22, 2024, there were 110,917,817 shares of common stock, including 19,311,623 shares of Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, 0 shares of Class B common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, and 91,606,194 shares of Class V common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K includes references to portions of the registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement for the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (“Definitive Proxy Statement”). The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2023.
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY NOTE CONCERNING FACTORS THAT MAY AFFECT FUTURE RESULTS
This Annual Report includes “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. All statements, other than statements of historical fact included in this Form 10-K including, without limitation, statements in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” regarding the Company’s financial position, business strategy and the plans and objectives of management for future operations, are forward-looking statements. Words such as “expect,” "estimate," "project," "budget," "forecast," "anticipate," "intend," "plan," "may," "will," "could," "should," "believes," "predicts," "potential," "possible," "continue,"and variations and similar words and expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. Such forward-looking statements relate to future events or future performance, but reflect management’s current beliefs, based on information currently available and involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expected and projected.
A number of factors could cause actual events, performance or results to differ materially from the events, performance and results discussed in the forward-looking statements. Factors that may cause such differences include, but are not limited to the impact of general economic conditions, including economic slowdowns, inflation, interest rate changes, recessions, and tightening of credit markets on our business; the impact of challenging macroeconomic and marketplace conditions, including lingering effects of COVID-19 on our business; the impact of stimulus or other government programs; whether we will be successful in obtaining declaratory relief against the Commissioner of the Department of Financial Protection and Innovation for the State of California; whether we will be subject to AB 539; whether our bank partners will continue to lend in California and whether our financing sources will continue to finance the purchase of participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners in California; the impact that events involving financial institutions or the financial services industry generally, such as actual concerns or events involving liquidity, defaults, or non-performance, may have on our business; risks related to the material weakness in our internal controls over financial reporting; our ability to grow and manage growth profitably and retain our key employees; risks related to new products; risks related to evaluating and potentially consummating acquisitions; concentration risk; changes in applicable laws or regulations; the possibility that we may be adversely affected by other economic, business, and/or competitive factors; risks related to management transitions; risks related to the restatement of our financial statements and any accounting deficiencies or weaknesses related thereto and other risks contained in the section captioned “Risk Factors”. Except as expressly required by applicable securities law, the Company disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this section to “OppFi” or the “Company” refers to Opportunity Financial, LLC (“OppFi-LLC”) and its subsidiaries prior to the consummation of the Business Combination, or to OppFi Inc. and its subsidiaries from and after the Business Combination. OppFi’s business and the industry in which OppFi operates is subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in the section titled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this report. These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in the estimates made by the independent parties and by OppFi.
On July 20, 2021 (“Closing Date”), OppFi completed a business combination pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement (“Business Combination Agreement”), dated as of February 9, 2021, by and among FG New America Acquisition Corp. (“FGNA”), OppFi-LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, OppFi Shares, LLC (“OFS”), a Delaware limited liability company, and Todd Schwartz (“Members’ Representative”), in his capacity as the representative of the members of OppFi-LLC (“Members”) immediately prior to the closing (“Closing”) of the transactions contemplated by the Business Combination Agreement (“Business Combination”). At the Closing, FGNA changed its name to “OppFi Inc.” OppFi’s Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”) and redeemable warrants exercisable for Class A Common Stock (“Public Warrants”) are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbols “OPFI” and “OPFI WS,” respectively.
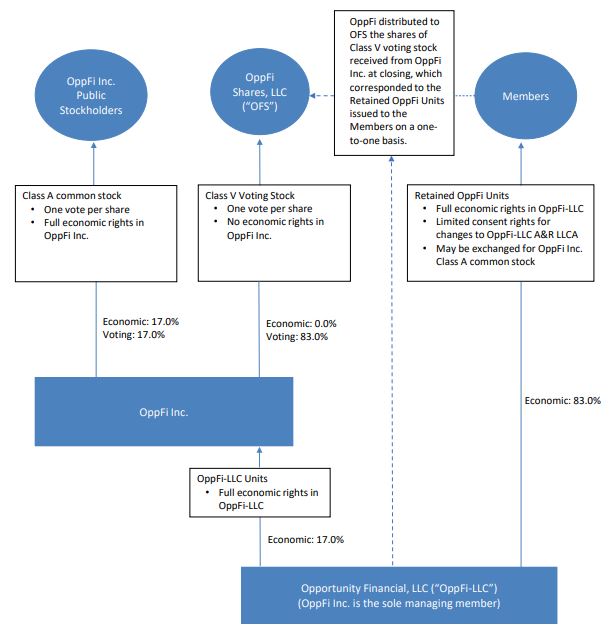
Following the Closing, OppFi is organized in an “Up-C” structure in which substantially all of the assets and the business of the Company are held by OppFi-LLC and its subsidiaries, and OppFi’s only direct assets consist of Class A common units of OppFi-LLC (“OppFi Units”). As of December 31, 2023, OppFi owned approximately 17.0% of the OppFi Units and controls OppFi-LLC as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC in accordance with the terms of the Third Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of OppFi-LLC (“OppFi A&R LLCA”). All remaining OppFi Units (“Retained OppFi Units”) are beneficially owned by the Members. Each Retained OppFi Unit held by the Members may be exchanged, subject to certain conditions, for either one share of Class A Common Stock or, at the election of OppFi, in its capacity as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC, the cash equivalent of the market value of one share of Class A Common Stock, pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Third Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of OppFi-LLC (the “Exchange Rights”). OFS holds a controlling voting interest in OppFi through its ownership of shares of Class V common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of OppFi (“Class V Voting Stock”) in an amount equal to the number of Retained OppFi Units and therefore has the ability to control OppFi-LLC. Each share of Class V Voting Stock entitles OFS to one vote per share at any annual or special meeting of the stockholders of OppFi, voting together with the holders of Class A Common Stock as a single class, but the shares of Class V Voting Stock do not entitle OFS to any economic rights in OppFi.
The following diagram illustrates the ownership structure of OppFi as of December 31, 2023.
Company Overview
OppFi is a tech-enabled, mission-driven specialty finance platform that broadens the reach of community banks to extend credit access to everyday Americans. Through transparency, responsible lending, financial inclusion, and an excellent customer experience, the Company supports consumers, who are turned away by mainstream options, to build better financial health. OppFi’s primary mission is to facilitate financial inclusion and credit access to the 63 million everyday Americans who are credit marginalized, through its products and an unwavering commitment to its customers. Unlike payday loans and similar credit products that typically do not provide transparency, fairness, and ability to repay guidelines, OppFi is dedicated to offering the best possible product and service through its platform. The average installment loan facilitated by OppFi with its OppLoans platform is approximately $1,500, payable in installments and for an average contractual term of 11 months. Payments are reported to the three major credit bureaus. OppFi’s dedication to borrowers is further evidenced by the OppFi TurnUp Program, which is described below and most importantly, by its strong customer satisfaction ratings.
OppFi’s platform provides one of the highest rated customer experiences in the industry and powers banks to offer credit products. Customers on OppFi’s platform benefit from a highly automated, transparent, efficient, and fully digital experience. The banks that work with OppFi benefit from its turn-key, outsourced marketing, data science, and proprietary technology to digitally acquire, underwrite and service these consumers. From inception through December 31, 2023, OppFi has facilitated more than $5.8 billion in gross loan issuance covering more than 3.4 million loans.
OppFi’s primary product is offered by its OppLoans platform. Customers on this platform are generally U.S. consumers, who are employed, have bank accounts, and earn median wages. Some have experienced a hardship or emergency and need a loan; others are struggling to make ends meet; while others have unplanned expenses. When these consumers apply for a loan through a bank, they are often rejected due to their credit score.
The OppFi platform is a mobile-optimized online application where eligible applicants, at their request, are able to opt into the OppFi TurnUp Program. This program helps these applicants find more affordable credit options by checking the market voluntarily on their behalf for sub-36% annual percentage rate, or APR products offered by traditional, mainstream lenders. If any lower cost products are identified, OppFi displays the offers from the applicable lenders and consumers can choose to finish their application at another lender’s website. At that point, the applicant leaves OppFi’s website. If no mainstream credit options are available with an APR of less than 36%, the application is processed through OppFi’s underwriting platform which utilizes machine learning, bank-approved, proprietary algorithms. This process is designed to allow for maximum value and benefit to be realized by all parties.
OppFi collects and calculates more than 500 attributes on loan applications for use in underwriting decisions. These attributes are based on data from credit bureaus, bank transactions and loan applications. Using this information, OppFi generates a proprietary score in combination with scores generated from third party providers. The proprietary score determines the exact loan terms to be offered to an applicant.
OppFi’s platform offers consumers a streamlined application experience that is simple, easy and transparent. Approximately 89% of OppFi’s underwriting decisions were automated, during the year ended December 31, 2023. Most applicants receive their funds either the same business day or the next business day after they are approved. Qualified customers who apply and are approved by 1:00 pm ET on a business day are eligible for funding on the same day their applications are approved.
This process provides consumers with access to fair, transparent credit as well as an opportunity to build financial health over time through our standard reporting to the three major credit bureaus. Installment loans through the OppFi platform have an average contractual length of 11 months. These loans have no fees (neither origination, nor late, nor insufficient funds). Customers are offered transparent and flexible repayment options, including allowing customers to make payments for their full-term, as well as allowing them to prepay their loans with no penalties.
In pursuit of its mission to provide financial inclusion to everyday Americans, OppFi focuses not only on facilitating access to credit but also offering education to build financial health. OppU, a financial education initiative, provides free, standards-aligned courses intended to teach financial literacy. With OppU, both customers and non-customers can learn what it takes to build credit as well as how to budget and manage their finances.
OppFi also currently services customers for its SalaryTap and OppFi Card products. SalaryTap is a payroll deduction secured installment loan product. OppFi Card is an alternative to traditional credit cards. OppFi previously conducted strategic reviews of SalaryTap and OppFi Card. OppFi is no longer accepting applications for these products and only servicing existing customers. Neither product contributes meaningfully to OppFi’s results. As of December 31, 2022, the OppFi Card portfolio was classified as held for sale. In May 2023, the Company made the decision to wind down the OppFi Card business; accordingly, the Company has discontinued its marketing of the OppFi Card portfolio for sale. The OppFi Card portfolio has been reclassified from held for sale to held for investment.
OppFi believes that it has achieved significant scale with the OppLoans product. As of December 31, 2023, OppFi had served more than 1 million unique customers since its inception. OppFi’s net promoter score (NPS) was 79 for the year ended December 31, 2023 and is reflective of its commitment to providing a best-in-class customer service experience. NPS is a score that measures the likelihood of users to recommend a company’s products or services to others, and ranges from a low of negative 100 to high of positive 100, and benchmark scores can vary significantly by industry. A score greater than zero represents a company having more promoters than detractors. OppFi maintained an A- rating from the Better Business Bureau (BBB) and a 4.5/5.0 star rating with more than 4,100 Trustpilot reviews, as of December 31, 2023.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, total revenue was approximately $509 million and $453 million, respectively, representing period-over-period total revenue growth of approximately 12%. OppFi generated net income of approximately $39 million and $3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Market Opportunity
Significant Percentage of U.S. Consumers Are Credit Marginalized, Have Non-Prime Credit, Lack Sufficient Savings, and Live Paycheck-to-Paycheck
Approximately 63 million U.S. consumers are credit marginalized, according to a study published by PYMNTS and Sezzle in 2023. This represents approximately 25% of the population. The study defined “credit marginalized” as those consumers who have been rejected for a credit product at least once in the past year. Of these consumers, approximately 50% have either a credit score below 650 or no credit score and approximately 46% live paycheck-to-paycheck with issues paying bills. More broadly, according to a report published by Bankrate in 2024, 56% percent of U.S. adults cannot afford to pay for a $1,000 emergency expense from their savings. In addition, according to research by PYMNTS published in 2024, six out of 10 U.S. consumers live paycheck-to-paycheck.
OppFi facilitates credit access to historically underserved consumers. Generally, these consumers are in need of fair, affordable, transparent and flexible credit products to cover everyday expenses and cash shortfalls, but traditional banks and credit providers are largely unwilling to service these consumers due to low FICO scores or similar factors. Many top lenders use the FICO score among other quantifiable metrics and qualifying rules to determine a potential borrower’s creditworthiness, and these criteria often result in adverse selection—potentially overlooking consumers who are otherwise willing and able to repay while simultaneously accepting consumers who are not.
Traditional Banks Have Been Slow to Adopt Digital Technology for Consumer Lending.
Traditional banks, which have historically played a substantial role in consumer credit markets, have often been slow to adapt to digital adoption among consumers. There are approximately 4,600 Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) insured institutions, many of which have legacy technology and lack sufficient mobile solutions in today’s digital era. Unlike larger institutions, smaller firms often lack many of the resources needed to fund and develop effective platform digitization. OppFi believes the performance of its platform through the COVID-19 pandemic has given OppFi’s existing and prospective bank partners important new data points to underpin their growing confidence in our solution.
Consumer Lenders Offering Small Personal Loans Require Higher APRs to Break Even.
Loan interest is inclusive of the time value of money, credit risk, and expenses incurred to originate, service and collect a loan. While the former expenses are variable with the amount of the credit and the creditworthiness of the borrower, the latter are largely fixed. These fixed costs are tied to the loan application itself. In the case of smaller-sized consumer loans, these fixed costs are representatively large relative to loan amount; therefore, smaller loans require higher interest rates than larger loans. According to a report published in 2020 by the Federal Reserve, break-even APRs are quite high for small loan amounts. Based on data in the report, a loan amount of $2,530 is necessary to break even at a 36% APR, and the trend is even more pronounced for smaller loan amounts. The required break-even APR shrinks and flattens for larger loans; however, the implication is that the loan comes with a longer period of indebtedness and a higher overall interest payment over the life of the loan, which is often far worse for OppFi’s target customers who either lack access to this larger loan or lack the willingness or ability to repay larger loan amounts. Additionally, break-even APRs tend to be much higher for small loan amounts than for large loan amounts, with a $594 loan requiring an APR of 103.5% for a lender to break even and a loan amount of $2,530 being necessary for a lender to break even at an APR of 36%, according to the research study by the Federal Reserve. As a result, such economics often result in credit-challenged consumers being unable to qualify for credit. The average APR for a loan facilitated on the OppLoans platform over the past three years has been approximately 155%, which has not changed significantly from year to year.
OppLoans Platform
OppFi has determined that alternative metrics outside of FICO scores can be used reliably to determine a consumer’s true ability and willingness to repay. Many non-bank lenders utilize non-FICO based alternative methods to determine creditworthiness. Applicants are evaluated based on metrics such as consistency of income, types of previous loans, previous repayment patterns and employment status, among many others. OppFi believes these nontraditional methods more accurately identify those consumers who are willing and able to repay loans, while simultaneously avoiding the issuance of loans to those consumers who may have received a loan that they cannot afford or do not intend to repay.
Highlights
•Simple interest installment loans. With its OppLoans platform, OppFi facilitates the issuance of fair, transparent, digital specialty finance products structured to rebuild financial health for the approximately 63 million U.S. consumers that are credit marginalized. Customers are provided with industry-leading features and protections, including: simple interest, installment loans with no balloon payments, no ancillary fees (neither origination, nor late, nor insufficient funds), and no prepayment penalties. In addition, OppFi reports payment history to the major credit bureaus.
•Easy, digital application and rapid approval. After the approximately five-minute application process submitted through OppFi’s fully digital platform, consumers typically receive quick credit decisions. Approximately 88% of all credit decisions were automated in the year ended December 31, 2023.
•Same-day funding service. OppFi offers a same-day funding service in collaboration with its partner banks. Qualified customers who apply and are approved by 1:00 pm ET on a business day are eligible for funding on the same day their applications are approved.
•Tech-driven decisioning. OppFi’s tech stack uses machine learning and real-time data analytics to generate credit decisions. In contrast to traditional credit providers, OppFi does not take in account traditional credit scores and instead uses alternative data to assist in identifying borrowers who have the ability to repay.
•OppFi TurnUp Program. After an application is submitted, the OppFi TurnUp Program helps eligible applicants find more affordable credit options by checking the market voluntarily on their behalf for sub-36% APR products offered by traditional, mainstream lenders. If any lower cost products are identified, OppFi displays the offers from the applicable lenders and consumers can choose to finish their application at another lender’s website. At that point, the applicant leaves OppFi’s website. If no mainstream credit options are available with an APR of less than 36%, the application is processed through OppFi’s underwriting platform which utilizes machine learning, bank-approved, proprietary algorithms. This process is designed to allow for maximum value and benefit to be realized by all parties.
•Loan flexibility. Loans through the OppFi platform are typically used to finance items such as car repairs, medical bills, housing costs, and education expenses. This flexibility helps foster loyalty as customers receive the help they need and the opportunity to rebuild their credit, with the goal of ultimately graduating to mainstream credit products.
•Customer Advocates. OppFi’s Customer Advocate team combines customer service with collections. Customer Advocates serve customers by providing easy-to-understand information so that customers can make informed, financially responsible decisions. Customer Advocates are rewarded for both their outstanding customer service as well as their collections. OppFi’s standard operating procedures, outbound dialer/email/SMS solutions, and associated controls are designed to ensure compliance with unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practice regulations, or UDAAPs; fair lending laws; the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, or TCPA; the federal Fair Debt Collection Practices Act, or FDCPA; and the Federal Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing, or CAN-SPAM, Act. The Customer Advocate team works with delinquent customers to quickly re-establish a positive payment history by providing flexible pathways out of delinquency for customers who are able to pay. Proactive outreach via email and text messages encourages delinquent customers to visit OppFi’s online portal or to call the Customer Advocate team to set up customized payment arrangements. These inbound calls are prioritized and routed to the appropriate team member based on delinquency status and customer request.
When capacity exists, OppFi also outbound dials delinquent customers. The dialing strategy and pace prioritizes customers by delinquency ordered least to most delinquent while also maximizing Customer Advocate efficiency to ensure high service levels for inbound calls. After a customer is charged off, OppFi utilizes a mix of internal recoveries and third party collection companies to contact the customer via email, SMS, and outbound dialing to resolve the account. Charged-off customers, who are unable or unwilling to pay off their balance in full, are offered targeted settlements, based on outstanding balance amounts and duration of repayment. There are a variety of programs in place in order to prevent customers from entering delinquency at all, including:
•no prepayment penalties;
•borrower’s assistance program allowing customers to remain in good standing regardless of payment status and reduce accrued interest if they are affected by natural and/or man-made disasters, such as a pandemic (including COVID-19);
•temporary and permanent hardship programs for customers experiencing longer-term inability to pay, such as job loss; and
•One-time payment deferment to end of loan term.
•Social impact relationships. As part of OppFi’s commitment to help customers build a better financial path through more resources, education and support, OppFi maintains relationships with a suite of social impact-focused organizations whose services customers can access for free. OppFi seeks to add relationships with organizations that share its social impact mission. Current relationships include Zogo, SpringFour, and Experian Boost®.
OppFi’s Competitive Advantages
Digitally-Native Solution
Consumers are increasingly shifting towards digital products and services. OppFi has successfully serviced the non-prime consumer with its fully digital platform, driven by a scalable and modern technology stack, as well as proprietary risk models that are continually developed through iterative data collection and analytics. This platform provides OppFi with exceptional scalability, cost efficiency, marketing effectiveness, customization, and a best-in-class customer experience. OppFi believes that this digital foundation creates a significant and durable advantage over traditional banks and credit providers who have been slow to adapt legacy technology into modern digitally native solutions, as well as higher-cost alternatives, such as bank overdraft fees, tribal lenders, payday and title loans, lease-to-own services.
In addition, due to OppFi’s digital nature, as its bank partners’ originations grow, OppFi achieves greater operating leverage. OppFi’s model is primarily driven by a tech-enabled platform that does not require significant increases in operating overhead to support its bank partners’ origination growth. Additionally, as OppFi serves consumers across the United States without brick-and-mortar stores, OppFi does not have any costs associated with physical stores and the personnel needed to operate them.
Bank Partner Model
Bank partners use the OppFi platform to provide loan products to consumers where OppFi facilitates the process and the loan products are funded directly by the bank. OppFi ended its direct lending program during 2023 and exclusively utilized a bank partner model as of December 31, 2023.
The bank partner model leverages OppFi’s marketing and servicing expertise and the banks’ broad national presence to facilitate credit access in 38 states, as of December 31, 2023. OppFi manages many aspects of the loan life cycle on behalf of its bank partners, including customer acquisition, underwriting and loan servicing. This relationship allows OppFi’s bank partners to leverage OppFi’s digital acquisition, machine learning underwriting and highly-rated customer service capabilities, which they would otherwise need to develop in-house. OppFi’s bank partners use their own capital to originate loans. OppFi’s bank partners are FinWise Bank (Finwise), First Electronic Bank (FEB), and Capital Community Bank (CCB).
In the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 98% of OppFi’s net originations were generated from loans originated by its bank partners and facilitated by the OppFi platform. OppFi’s bank partner FEB began originating loans on the OppFi platform in May 2020 and OppFi’s bank partner CCB began originating loans on the OppFi platform in October 2020.
OppFi has entered into separate agreements with each of its three bank partners. OppFi’s agreements with its bank partners are nonexclusive, generally have 60-month terms and certain agreements automatically renew, subject to certain early termination provisions and minimum fee amounts, and do not include any minimum origination obligations or origination limits. OppFi’s bank partners generally retain approval rights on all aspects of the program and are primarily responsible for regulatory and compliance oversight.
Under the bank partner model, OppFi is compensated by the bank partner as a service provider for OppFi’s role in delivering the technology and services to the bank partner to facilitate origination and servicing of loans throughout each loan’s lifecycle. Customers who meet the underwriting criteria for multiple bank partners are referred to a specific bank partner randomly based on a computer algorithm and volume targets set with each bank partner. OppFi’s bank partners generally hold loans originated on our platform for typically two to three days following origination. OppFi acquires certain participation rights in such loans. OppFi and its bank partners each pay or reimburse each other for certain fees and costs that are immaterial in amount.
The economic difference to OppFi in loans originated via the bank partnership model as compared to the direct origination model are immaterial and generally result from a minimal program fee paid to OppFi for each origination as well as increased compliance costs for OppFi, which collectively have an insignificant impact on OppFi’s customer lifetime value. During 2023, OppFi shifted completely to the bank partner model as the percentage of Total Net Originations by OppFi’s bank partners increased from 95% for the year ended December 31, 2022 to 98% for the year ended December 31, 2023. OppFi has shifted to the bank partner model because its bank partners operate under federal law, which allows them to lend nationally based on their state domicile and facilitates a national product offering for the consumer while also streamlining regulatory requirements and compliance infrastructure.
Technology, Engineering Talent and Product Architecture
Technology is essential to OppFi’s core operations. OppFi utilizes modern technology solutions including sophisticated analytics tools, machine learning models and cloud-based computing to offer a smooth and engaging digital experience on the front-end and a constantly evolving real time decisioning engine on the back-end. In order to build and maintain these proprietary, innovative and secure products, OppFi commits substantial resources to identifying, employing, and retaining talented and mission-driven technology-focused professionals and engineers. OppFi believes that its platform architecture and the talent retained to continually evolve provides OppFi with a competitive edge over its more traditional credit competitors.
Proprietary, Data Driven Decisioning and Risk Models
OppFi’s underwriting platform takes a holistic approach to evaluating potential customers across traditional, nontraditional, banking history, and income/employment data to make decisions on each credit application. The models ignore traditional credit scores, instead relying on internally developed scoring and analytics to identify the creditworthiness of each application. Machine learning-based risk models are custom built to effectively evaluate risk and provide customized credit product solutions for each credit application. The platform considers applicant data such as available bank balance trends, volatility of income, and bank-approved fraud scores amongst others to predict repayment ability, and leverages this with real-time Instant Bank Verification, or IBV, response data.
Multi-Sided Ecosystem
OppFi generates value for all potential parties on its platform. Consumers gain access to fair, transparent credit that is structured to rebuild financial health, Bank partners benefit from OppFi’s turn-key, outsourced marketing and digital acquisition and servicing, data, and proprietary technology. OppFi’s nationwide presence allows it to increase awareness, directly contributing to organic growth, as well as the growth and success of bank partners. Customers have proven to be loyal and highly satisfied, which in turn drives additional growth through referrals.
Integrated and Efficient Multi-Channel Marketing Approach
OppFi utilizes an integrated multi-channel marketing strategy to reach potential customers. For the year ended December 31, 2023, approximately 18.3% of loans originated on the OppFi platform were generated by search engine optimization, email marketing, and customer referrals. In addition, approximately 74.2% of loans originated on the OppFi platform were derived through key strategic partners who are compensated with a negotiated fixed unit price per loan funded or fixed percent of principal dollars funded. Approximately 7.5% of loans originated on the OppFi platform were sourced from direct mail marketing channels. OppFi has created unique capabilities to effectively identify and attract qualified customers, which supports its long-term growth objectives at target customer acquisition costs. Marketing costs from OppFi’s strategic partner channel are based on fixed price agreements, while marketing costs for direct mail and other direct channels can vary based on the number of customers that ultimately apply and obtain loans. OppFi’s mix of new and refinanced loans also impacts its average acquisition cost. OppFi believes this approach allows it to focus on higher quality, lower cost customer acquisition while maximizing reach and enhancing awareness of OppFi’s platform. OppFi continues to invest in new marketing channels, which it believes will provide OppFi with further competitive advantages and support its ongoing growth.
Commitment to Customer Service
OppFi is nationally recognized for its exceptional customer service. OppFi maintained a 4.5/5.0 star rating on Trustpilot with more than 4,100 reviews, making OppLoans one of the top consumer-rated financial platforms online, and an A- rating from the Better Business Bureau (BBB), as of December 31, 2023. In addition, OppFi has a Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 79 for the year ended December 31, 2023. Financial education is also important, which is why OppFi launched its own online financial education portal —OppU. Customers and non-customers can use OppU to learn about building credit and budgeting, as well as how to better manage finances. OppFi continuously works to improve customer satisfaction by evaluating information from website analytics, customer surveys and Customer Advocate feedback. OppFi’s teams receive training on a regular basis and are monitored for quality assurance. OppFi believes customers who wish to access credit again via its platform, or who refer a potential customer to OppFi, often do so because of OppFi’s dedication to customer service and industry-leading product features and protections.
OppFi’s Growth Strategy
OppFi anticipates leveraging organic and inorganic opportunities to achieve long-term profitable growth. By leveraging its deep knowledge of the credit market for everyday Americans, OppFi believes it has a significant runway to further scale and gain market share for its core OppLoans platform by executing on its multi-channel marketing strategy that utilizes partners, affiliates, email, direct mail, referral, and SEO. OppFi also seeks to evaluate and test new products or features that can increase its reach to the 63 million credit marginalized U.S. consumers. OppFi is evaluating corporate development opportunities to diversify its overall business by potentially acquiring businesses in adjacent categories, inclusive of new customer types and new products that fit OppFi’s mission. OppFi expects to accelerate profitable growth by driving core product volume, serving more non-prime consumers with strategic marketing and credit enhancements, and expanding into new customer and product types via acquisitions.
Competition
Consumer lending is a vast and competitive market, and the OppFi platform competes in varying degrees with all other sources of unsecured consumer credit, including banks, non-bank lenders (including retail-based lenders) and digital specialty finance platforms. Because personal loans often serve as a replacement for credit cards, the OppFi platform competes with the convenience and ubiquity that credit cards represent.
OppFi competes with a variety of tech-enabled specialty finance companies that aim to help banks with the digital transformation of their business, particularly with respect to all-digital lending. This includes new products from legacy bank technology providers as well as newer companies focused entirely on lending software infrastructure for banks. OppFi may also face competition from banks or companies that have not previously competed in the consumer lending market, including companies with large and experienced data science teams and access to vast amounts of consumer-related information that could be used in the development of their own credit risk models.
OppFi believes it competes favorably based on the following competitive factors:
•Constantly improving models;
•Compelling loan offers from bank partners to consumers;
•Automated and user-friendly loan application process;
•Cloud-native, multi-tenant architecture;
•Combination of technology and customer acquisition for bank partners;
•Robust and diverse loan funding program; and
•Brand recognition and trust.
Available Information
Our website address is www.oppfi.com. Our annual report on Form 10-K, annual proxy statements, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), are available through the investor relations page of our website free of charge as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). Our proxy statements and reports may also be obtained directly from the SEC's Internet website at www.sec.gov. Our website and the information contained therein or connected thereto are not incorporated into or deemed a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Government Regulation
OppFi and the loans made through its platform by its bank partners are subject to extensive and complex rules and regulations and examination by various federal, state and local government authorities. Failure to comply with any of the applicable rules and regulations may result in, among other things, revocation of required licenses or registration, loss of approved status, effective voiding or rescission of the loan contracts, reduction of allowable interest, class action lawsuits, administrative enforcement actions and civil and criminal liability. While compliance with such requirements is at times complicated by OppFi’s novel business model and an evolving regulatory environment, OppFi believes it is, at a minimum, in substantial compliance with these rules and regulations.
Several state and federal agencies have the ability to regulate aspects of OppFi’s business. For example, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”) has supervisory and enforcement authority over OppFi and the Federal Trade Commission has jurisdiction to investigate aspects of its business, including with respect to marketing practices. The Dodd-Frank Act, as well as many state statutes, provide a mechanism for the CFPB and state attorneys general to investigate OppFi. In addition, as a result of OppFi’s relationships with its current bank partners, OppFi is subject to oversight by federal banking agencies, including the FDIC. As a service provider to banks, we are subject to examination and enforcement authority of the prudential bank regulators that supervise our bank partners under the Bank Service Company Act. Further, OppFi is subject to inspections, examinations, supervision and regulation by applicable agencies in each state in which OppFi is licensed or in which our borrowers reside. Regulatory oversight of OppFi’s business may change over time. By way of example, in California the DFPI is considered a “mini-CFPB” agency, because it seeks to emulate the CFPB with respect to its enforcement and supervisory capabilities as well as require additional state registration for certain covered persons. OppFi expects that regulatory examinations by both federal and state agencies will continue, and there can be no assurance that the results of such examinations will not have a material adverse effect on OppFi.
Below, OppFi summarizes several of the material federal lending, servicing and related laws applicable to its business. Many states have laws and regulations that are similar to the federal consumer protection laws referred to below, but the degree and nature of such laws and regulations, and their applicability to us and our products, vary from state to state.
Federal Lending and Related Laws
Truth in Lending Act
The Truth in Lending Act, or TILA, and Regulation Z, which implements it, require creditors to provide consumers with uniform, understandable information concerning certain terms and conditions of their loan and credit transactions, and to comply with certain lending practice requirements and restrictions. These rules apply to loans facilitated through OppFi’s platform, and OppFi assists with compliance as part of the services OppFi provides to its bank partners. or closed-end credit transactions, required disclosures include, among others, providing the annual percentage rate, the finance charge, the amount financed, the number of payments, the amount of the monthly payment, the presence and amount of certain fees, and the presence of certain contractual terms. TILA also regulates the advertising of credit and gives borrowers, among other things,
certain rights regarding updated disclosures and the treatment of credit balances. OppFi, on behalf of the applicable bank partner, provides applicants with a TILA disclosure when applicants complete their loan applications on its platform.
If the applicant’s request is not fully funded and the applicant chooses to accept a lesser amount offered, OppFi provides an updated TILA disclosure on behalf of the applicable bank partner. OppFi also seeks to comply with TILA’s disclosure requirements related to credit advertising and, to the extent that OppFi holds or services loans, TILA’s requirements related to treatment of credit balances for closed-end loans. OppFi also can facilitate the origination of a limited number of credit card accounts through its platform. In connection with such accounts, TILA requires the provision of certain solicitation and account-opening disclosures. TILA also imposes requirements on the terms of credit card accounts, and the process of originating and servicing such accounts.
Equal Credit Opportunity Act
The Equal Credit Opportunity Act, or ECOA, prohibits creditors from discriminating against credit applicants on the basis of race, color, sex, age (provided that the applicant has the capacity to enter into a binding contract), religion, national origin, marital status, the fact that all or part of the applicant’s income derives from any public assistance program, or the fact that the applicant has in good faith exercised any right under the federal Consumer Credit Protection Act or certain state laws. Regulation B, which implements ECOA, restricts creditors from requesting certain types of information from loan applicants or engaging in certain loan-related practices, and from using advertising or making statements that would discourage on a prohibited basis a reasonable person from making or pursuing an application. These requirements apply to bank partners for loans facilitated through its platform as well as to OppFi as a service provider that assists in the process. OppFi abides by policies and procedures implemented by its bank partners to comply with ECOA’s provisions prohibiting discouragement and discrimination. ECOA also requires creditors to provide applicants with timely notices of adverse action taken on credit applications, including disclosing to applicants who have been declined their rights and the reason for their having been declined. On behalf of its bank partners, OppFi provides prospective borrowers who apply for a loan through its platform but are denied credit with an adverse action notice in compliance with applicable requirements. The current Presidential Administration has indicated an increased focus (likely through the CFPB and its enforcement of ECOA and Regulation B) on equality in credit availability and pricing, as compared to the prior Administration. It is unclear at this point how or if such increased focus will impact OppFi’s business or operations or those of its bank partners.
Fair Credit Reporting Act
The federal Fair Credit Reporting Act, or FCRA, as amended by the Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act, and administered by the CFPB, promotes the accuracy, fairness, and privacy of information in the files of consumer reporting agencies. FCRA requires consent or a permissible purpose to obtain a consumer credit report and requires that persons who report loan payment information to credit bureaus do so accurately and resolve disputes regarding reported information timely. FCRA also imposes disclosure requirements on creditors who take adverse action on credit applications based on information contained in a credit report.
Under FCRA, certain information must be provided to applicants whose credit applications are not approved or who are offered credit at an interest rate higher than other borrowers on the basis of a report obtained from a consumer reporting agency, promptly update any credit information reported to a credit reporting agency about a customer and have a process by which customers may inquire about credit information furnished by OppFi to a consumer reporting agency. OppFi and its bank partners have a permissible purpose for obtaining credit reports on potential borrowers, and OppFi also obtains explicit consent from borrowers to obtain such reports. As part of its loan servicing activities, OppFi accurately reports loan payment and delinquency information to appropriate consumer reporting agencies. OppFi provides timely adverse action notices when required on behalf of each bank partner on its platform that includes all the required disclosures. OppFi also has processes in place to ensure that consumers are given “opt-out” opportunities, as required by the FCRA, regarding the sharing of their personal information. OppFi has also implemented an identity theft prevention program, as required by FCRA and its implementing regulations.
Fair Debt Collection Practices Act
The federal Fair Debt Collection Practices Act, or FDCPA, provides guidelines and limitations on the conduct of certain debt collectors in connection with the collection of consumer debts. The FDCPA limits certain communications with third parties, imposes notice and debt validation requirements, and prohibits threatening, harassing or abusive conduct in the course of debt collection. The FDCPA primarily applies to third-party debt collectors, meaning parties collecting on behalf of another, and debt collection laws of certain states also impose similar requirements more broadly on creditors who collect their own debts. In addition, the CFPB prohibits unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices, or UDAAPs in debt collection, including
first-party debt collection. In addition, on October 30, 2020, the CFPB issued a final rule implementing requirements of the FDCPA and a second final rule on debt collection focused on consumer disclosures on December 18, 2020, which took effect on November 30, 2021. The CFPB also issued a second final rule on debt collection focused on consumer disclosures on December 18, 2020, which also took effect on November 30, 2021. OppFi uses its internal collection team and professional third-party debt collection agents to collect delinquent accounts. Any third-party debt collection agents OppFi uses are required to comply with the FDCPA and all other applicable laws in collecting delinquent accounts of borrowers. While its internal servicing team is not subject to the formal requirements of the FDCPA in most cases, OppFi has established policies intended to substantially comply with the collection practice requirements under the FDCPA as a means of complying with more general UDAAP standards.
Privacy and Data Security Laws
The federal Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, or GLBA, includes limitations on financial institutions’ disclosure of nonpublic personal information about a consumer to nonaffiliated third parties, in certain circumstances requires financial institutions to limit the use and further disclosure of nonpublic personal information by nonaffiliated third parties to whom they disclose such information and requires financial institutions to disclose certain privacy policies and practices with respect to information sharing with affiliated and unaffiliated entities as well as to safeguard personal customer information. OppFi collects and uses a wide variety of information to help ensure the integrity of its services and to provide features and functionality to its customers. This aspect of OppFi’s business, including the collection, use, and protection of the information OppFi acquires from its own services as well as from third-party sources, is subject to laws and regulations in the United States. Accordingly, OppFi publishes its privacy policies and terms of service, which describe its practices concerning the use, transmission, and disclosure of information. OppFi has a detailed privacy policy, which complies with GLBA and is accessible from every page of its website. OppFi maintains consumers’ personal information securely, and OppFi does not sell, rent or share such information with third parties for marketing purposes unless previously agreed to by the consumer. In addition, OppFi takes measures to safeguard the personal information of borrowers and investors and protect against unauthorized access to this information. As OppFi’s business continues to expand, and as state and federal laws and regulations continue to be passed and their interpretations continue to evolve, additional laws and regulations may become relevant to OppFi.
Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act
In response to the prior financial crisis, the Dodd-Frank Act was enacted as extensive and significant legislation with consumer protection provisions. Among other things, the Dodd-Frank Act created the CFPB, which commenced operations in July 2011 and has significant authority to implement and enforce federal consumer financial laws, such as the TILA and ECOA. The CFPB is authorized to prevent “unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices” through its regulatory, supervisory and enforcement authority. The CFPB also engages in consumer financial education, requests data and promotes the availability of financial services to underserved customers and communities. The CFPB has regulatory and enforcement powers over most providers of consumer financial products and services, including OppFi. It also has supervisory and examination powers over certain providers of consumer financial products and services, including large banks, payday lenders, “larger participants” in certain financial services markets defined by CFPB regulation, and non-bank entities determined to present a risk to consumers after notice and an opportunity to respond.
The CFPB has imposed, and will continue to impose, restrictions on lending practices, including with respect to the terms of certain loans. OppFi and its bank partners are subject to the CFPB’s enforcement authority, which could increase under new CFPB leadership. The CFPB may request reports concerning OppFi’s organization, business conduct, markets and activities. In addition, the CFPB may, in connection with its supervisory authority, also conduct on-site examinations of its and its bank partners’ businesses on a periodic basis, subject to whether the applicable bank partner satisfies the assets threshold for CFPB supervision. If the CFPB were to conclude that OppFi’s loan origination assistance or servicing activities, or any loans originated by its bank partners on its platform, violate applicable consumer protection laws or regulations, OppFi could be subject to a formal or informal inquiry, investigation and/or enforcement action. Formal enforcement actions are generally made public, which carries reputational risk. In addition, the market price of the Class A Common Stock could decline as a result of the initiation of a CFPB investigation of OppFi or even the perception that such an investigation could occur, even in the absence of any finding by the CFPB that OppFi has violated any state or federal law. As of the date hereof, OppFi is not subject to any enforcement actions by the CFPB.
For more information regarding the CFPB and the CFPB rules to which OppFi is subject or may become subject, see “Risk Factors” included elsewhere in this report.
Federal Trade Commission Act
Under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, OppFi and its bank partners are prohibited from engaging in unfair and deceptive acts and practices. The FTC is the primary regulator enforcing this prohibition, and in recent years the FTC has been focused on practices of nonbank financial institutions. Based on publicly available actions, the FTC’s primary focus has been with respect to marketing and disclosure practices. For instance, in September 2020, the FTC filed a complaint against a collection firm for illegal debt collection practices including use of deceptive robocalling and misrepresenting their association with a law firm.
Electronic Fund Transfer Act and NACHA Rules
The federal Electronic Fund Transfer Act, or EFTA, provides guidelines and restrictions on the electronic transfer of funds from consumers’ bank accounts. Under EFTA, and Regulation E that implements it, OppFi must obtain consumer consents prior to receiving preauthorized electronic transfer of funds from consumers’ bank accounts, and its bank partners may not condition an extension of credit on the borrower’s agreement to repay the loan through preauthorized (recurring) electronic fund transfers. In addition to compliance with federal laws, transfers performed by ACH electronic transfers are subject to detailed timing and notification rules and guidelines administered by NACHA. While NACHA guidelines are not laws, failure to comply with them may nevertheless result in commercial harm to OppFi’s business. All transfers of funds related to its operations conform to the EFTA, its regulations and NACHA guidelines. As part of OppFi’s servicing activities, OppFi obtains necessary electronic authorization from borrowers and investors for such transfers in compliance with applicable rules. The loans offered on OppFi’s platform by its bank partners must also comply with the requirement that a loan cannot be conditioned on the borrower’s agreement to repay the loan through preauthorized (recurring) electronic fund transfers.
Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act
The federal Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act, or ESIGN, and similar state laws, particularly the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act, or UETA, authorize the creation of legally binding and enforceable agreements utilizing electronic records and signatures. ESIGN and UETA require businesses that want to use electronic records or signatures in consumer transactions and provide disclosures to consumers (otherwise required to be “in writing” in electronic form), to obtain the consumer’s consent to receive information electronically. When a consumer registers on its platform, OppFi obtains his or her consent to transact business electronically, receive electronic disclosures and maintain electronic records in compliance with ESIGN and UETA requirements, and OppFi maintains electronic signatures and records in a manner intended to support enforceability of relevant consumer agreements and consents.
Federal Marketing Regulations
The Telephone Consumer Protection Act, or TCPA, generally prohibits robocalls, including those calls made using an auto-dialer or prerecorded or artificial voice calls made to a wireless telephone without the prior express consent of the called party (or prior express written consent, if messages constitute telemarketing). In addition, the FTC Telemarketing Sales Rule implements the FTC’s Do-Not-Call Registry and imposes numerous other requirements and limitations in connection with telemarketing. OppFi’s policies address the requirements of the TCPA as well as FTC Telemarketing Sales Rule and other laws limiting telephone outreach. Furthermore, OppFi does not engage in certain activities covered by the TCPA, such as using an automated dialer.
The Federal Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing, or CAN-SPAM, Act makes it unlawful to send certain electronic mail messages that contain false or deceptive information and provide other protections for email users. CAN-SPAM also requires the need to provide a functioning mechanism that allows the recipient to opt-out of receiving future commercial e-mail messages from the sender of such messages. OppFi’s email communications with all consumers are formulated to comply with the CAN-SPAM Act.
Servicemembers Civil Relief Act
Under the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act, or SCRA, there are limits on interest rates chargeable to military personnel and civil judicial proceedings against them, and there are limitations on its ability to collect on a loan to servicemembers on active duty originated prior to the servicemember entering active duty status and, in certain cases, for a period of time thereafter. The SCRA allows military members to suspend or postpone certain civil obligations so that the military member can devote his or her full attention to military duties. The SCRA requires OppFi to adjust the interest rate charged on loans to borrowers who qualify for and request relief. If a borrower with an outstanding loan qualifies for SCRA protection the interest rate on their loan (including certain fees) will be reduced to 6% for the duration of the borrower’s active duty. During this
period, any interest holder in the loan will not receive the difference between 6% and the loan’s original interest rate. As part of the services OppFi provides, and in compliance with SCRA, OppFi requires the borrower to send it a written request and a copy of the borrower’s mobilization orders to obtain an interest rate reduction on a loan due to military service. Other protections offered to servicemembers under the SCRA, including protections related to the collection of loans, do not require the servicemember to take any particular action, such as submitting military orders, to claim benefits.
Military Lending Act
Under the Military Lending Act, certain members of the armed forces serving on active duty and their dependents must be identified and be provided with certain protections when becoming obligated on a consumer credit transaction. These protections include: a limit on the Military Annual Percentage Rate (an all-in cost-of-credit measure which is the same as the APR for loans facilitated on its platform) of 36%, certain required disclosures before origination, a prohibition on charging prepayment penalties and a prohibition on arbitration agreements and certain other loan agreement terms. As part of the services OppFi provides, OppFi ensures compliance with the requirements of the Military Lending Act, where applicable.
Bank Secrecy Act, USA PATRIOT Act, and U.S. Sanctions Laws
Under the Bank Secrecy Act, the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act, or USA PATRIOT ACT, and certain U.S. sanctions laws, OppFi’s bank partners are required to maintain anti-money laundering (“AML”), customer due diligence and record-keeping policies and procedures, which OppFi performs on behalf of its bank partners, and to avoid doing business with sanctioned persons or entities or engaging in types of sanctioned activity in certain jurisdictions. OppFi has implemented an AML program designed to prevent its platform from being used to facilitate money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activity. OppFi’s AML program is designed to prevent its platform from being used to facilitate money laundering and from conducting business in countries, or with persons or entities, included on designated lists promulgated by the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Controls (“OFAC”) and equivalent foreign authorities. OppFi’s AML compliance program includes policies, procedures, reporting protocols, and internal controls, including the designation of an AML compliance officer, and is designed to address these legal and regulatory requirements and to assist in managing risk associated with money laundering and terrorist financing. With respect to new borrowers, OppFi applies the customer identification and verification program rules and screen names against the list of specially designated nationals maintained by OFAC.
Bankruptcy Code
Under the Bankruptcy Code, OppFi is in certain circumstances prohibited by the automatic stay, reorganization plan and discharge provisions, among others, in seeking enforcement of debts against parties who have filed for bankruptcy protection. OppFi’s policies are designed to support compliance with the Bankruptcy Code as OppFi services and collects loans.
Small Dollar Loan Rule
In 2017, the CFPB issued a rule regulating small dollar loans which applies to lenders (such as our bank partners) making covered loans, defined as: (i) consumer loans with a term of 45 days or less; (ii) longer-term consumer balloon payment loans; and (iii) consumer loans that exceed 45 days in term with a “cost of credit” that exceeds 36% APR in which the lender obtains a leveraged payment mechanism (i.e., the lender has the right to transfer money from a consumer’s account). As proposed, the rule (a) included fairly significant requirements for lenders to undertake specific underwriting processes referred to as ability-to-pay determinations before making a loan; (b) made it an unfair and abusive practice for a lender to make a third attempt to withdraw payment from a consumer’s account in connection with loans that have terms of 45 days or less where two consecutive attempts to withdraw payments from the account failed due to a lack of sufficient funds, unless the lender obtains new and specific authorization from the consumer; and (c) required lenders to provide consumers with written notice before making their first attempt to withdraw payment from a borrower’s account and before subsequent attempts that involve different dates, amounts, or payment channels.
The CFPB rescinded portions of the rule requiring an ability-to-pay determination in 2020. In October 2022, the Fifth Circuit Court of Appeals issued its opinion in Community Financial Services Association of America, et al. v. CFPB (CFSA v. CFPB) invalidating the CFPB’s Payday, Vehicle-Title, and Certain High-Cost Installment Loans rule (Small-Dollar Rule). The three-member panel decision called into question the future viability of the CFPB by declaring unconstitutional the regulator’s funding mechanism. The CFPB appealed the case to the United States Supreme Court, which heard oral arguments in October 2023. Enforcement of the rule is stayed, pending resolution of the litigation.
OppFi believes the rule is common sense legislation and good for the industry. It is possible the rule, when enforced, could impact OppFi’s business or require it to obtain additional borrower consents or make additional disclosures on behalf of its bank partners. Also, if the ability-to-pay determination is re-inserted by the CFPB, OppFi could be required to take additional actions in connection with loan transactions made on behalf of its bank partners.
State Lending Regulations
State Usury Limitations
With respect to bank partners that are FDIC-insured, state banks originating loans on our platform, which represent the vast majority of loans originated or national banks or federal savings banks originating loans on our platform, federal case law and relevant regulatory guidance (including FDIC advisory opinion 92-47) permit depository institutions to “export” requirements regarding interest rates and certain fees considered to be “interest” under federal law from the state or U.S. territory where the bank is located for all loans originated from such state, regardless of the usury limitations imposed by the state law of the borrower’s residence or other states with which the loan may have a geographic nexus, unless the state has chosen to opt out of the exportation regime. OppFi believes, however, if a state or U.S. territory in which one of our bank partners operate opted out of rate exportation, judicial interpretations support the view that such opt outs would apply only to loans “made” in those states. OppFi believes that the “opt-out” of any state would not affect the ability of its platform to benefit from the exportation of rates. If a loan made through OppFi’s platform by a bank partner were deemed to be subject to the usury laws of a state or U.S. territory that had opted-out of the exportation regime, if the loan were not originated in a manner that permitted exportation of interest rate requirements from the state OppFi and its bank partners believed applied at the time of origination, if the loan bore interest or certain fees in excess of the amounts permitted by the state in which the loan was “made” for exportation purposes (or was otherwise in violation of such state’s relevant usury and fee laws) or if the interest exportation authority were determined not to apply to a loan under any particular circumstances, OppFi, its bank partners, or subsequent holders of such loans could become subject to fines, penalties and possible forfeiture of amounts charged to borrowers, and OppFi could decide not to permit bank partners to originate loans in that jurisdiction through its platform or its bank partners or loan investors could choose not to continue doing business with OppFi in such jurisdiction or more broadly, which could adversely impact its growth.
There have also been recent judicial decisions that could affect the collectability of loans sold by OppFi’s bank partners after origination and the exposure of loan purchasers to potential fines or other penalties for usury violations. See the section titled “Risk Factors” for more information about recent case law developments.
State Disclosure and Lending Practice Requirements
The loans originated on OppFi’s platform by its bank partners may be subject to state laws and regulations that impose requirements related to loan disclosures and terms, credit discrimination, credit reporting, debt collection, and unfair or deceptive business practices. OppFi’s ongoing compliance program seeks to comply with these requirements.
State Licensing/Registration
OppFi holds licenses, registrations, and similar filings so that OppFi can conduct business, including providing referral services and origination assistance to lenders on its platform and servicing and collecting loans, in all states and the District of Columbia where its activities require such licensure, registration or filing. Licenses granted by the regulatory agencies in various states are subject to periodic renewal and may be revoked or suspended for failure to comply with applicable state and federal laws and regulations. In addition, as the product offerings of OppFi or its bank partners change, as states enact new licensing requirements or amend existing licensing laws or regulations, or as states regulators or courts adjust their interpretations of licensing statutes and regulations, OppFi may be required to obtain additional licenses. OppFi is also typically required to complete an annual report (or its equivalent) to each state’s regulator. The statutes also typically subject OppFi to the supervisory and examination authority of state regulators.
State licensing statutes impose a variety of requirements and restrictions, including:
•record-keeping requirements;
•collection and servicing practices;
•requirements governing electronic payments, transactions, signatures and disclosures;
•examination requirements;
•surety bond and minimum net worth requirements;
•financial reporting requirements;
•notification requirements for changes in principal officers, stock ownership or corporate control; and
•restrictions on advertising and other loan solicitation activity, as well as restrictions on loan referral or similar practices.
Compliance
OppFi reviews its policies and procedures to ensure compliance with applicable regulatory laws and regulations applicable to OppFi and its bank partners. OppFi has built its systems and processes with controls in place in order to permit its policies and procedures to be followed on a consistent basis. For example, to ensure proper controls are in place to maintain compliance with the consumer protection related laws and regulations, OppFi has developed a compliance management system consistent with the regulatory expectations published by governmental agencies. While no compliance program can assure that there will never be violations, or alleged violations, of applicable laws, OppFi believes that its compliance management system is reasonably designed and managed to minimize compliance-related risks.
Intellectual Property
OppFi protects its intellectual property through a combination of trademarks, domain names and trade secrets, as well as through confidentiality agreements, its information security infrastructure and restrictions on access to or use of its proprietary technology.
OppFi has trademark registrations in the United States in its names and its logo. OppFi will pursue additional trademark registrations to the extent OppFi believes it will be beneficial. OppFi also has registered domain names for websites that OppFi uses in its business. OppFi may be subject to third party claims from time to time with respect to its intellectual property.
Additionally, OppFi relies upon unpatented trade secrets and confidential know-how and continuing technological innovation to develop and maintain its competitive position. OppFi also enters into confidentiality and intellectual property rights agreements with its employees, consultants, contractors and bank partners. Under such agreements, OppFi’s employees, consultants and contractors are subject to invention assignment provisions designed to protect its proprietary information and ensure its ownership in intellectual property developed pursuant to such agreements.
For additional information about its intellectual property and associated risks, see the section titled “Risk Factors-Risks Related to OppFi’s Business and Industry.”
Employees and Human Capital
OppFi believes it has built something very special in terms of its company culture. Building a great place to work for the best talent was a priority for OppFi from day one. It is not an accident that OppFi has received numerous best place to work awards in its Chicago headquarters.
OppFi has brought together a remarkable diversity of thinkers. The members of OppFi’s management team come from diverse backgrounds with varying ethnicities, education backgrounds, genders and ages. As the focal point of its human capital strategy, OppFi attracts and recruits diverse, exceptionally talented, experienced and motivated employees.
As of December 31, 2023, OppFi had approximately 445 full-time employees. OppFi also engages contractors and consultants as needed to support its operations. None of OppFi’s employees are represented by a labor union or subject to a collective bargaining agreement. OppFi has not experienced any work stoppages, and OppFi considers its relations with its employees to be good.
Corporate Information
FGNA was incorporated in the State of Delaware on June 24, 2020 as a special purpose acquisition company under the name FG New America Acquisition Corp. OppFi-LLC is a Delaware limited liability company formed on December 3, 2015.
On October 2, 2020, FGNA completed its IPO. On the Closing Date, the Business Combination with OppFi was consummated, resulting in the combined company being organized in an “Up-C” structure, and FGNA as the registrant changed its name to “OppFi Inc.” OppFi is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Investing in our securities involves risks. You should consider carefully the risks and uncertainties described below, together with all of the other information in this Annual Report, including the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and notes to the financial statements included herein, before deciding whether to purchase our securities. If any of these risks actually occur, our business, results of operations, financial condition, and prospects could be materially and adversely affected. Unless otherwise indicated, references in these risk factors to our business being harmed will include harm to our business, reputation, brand, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. In such event, the market price of our securities could decline, and you could lose all or part of your investment. We may face additional risks and uncertainties that are not presently known to us, or that we currently deem immaterial, which may also impair our business or financial condition.
Summary of Risk Factors Related to Our Business
The following is a summary of the risk factors our business faces. The list below is not exhaustive, and investors should read this “Risk Factors” section in full. Some of the risks we face include:
• we are a rapidly growing company with a relatively limited operating history, which may result in increased risks, uncertainties, expenses and difficulties, and makes it difficult to evaluate our future prospects;
• our revenue growth rate and financial performance in recent periods may not be indicative of future performance and such growth may slow over time;
• if we fail to effectively manage our growth, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected;
• we may not be able to maintain or increase our profitability in the future;
• we may experience fluctuations in our quarterly operating results;
• if we are unable to continue to improve our machine learning models or if these models contain errors or are otherwise ineffective, our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected;
• if our bank partners were to cease or limit operations with us or if we are unable to attract and onboard new bank partners, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected;
• our sales and onboarding process of new bank partners could take longer than expected, leading to fluctuations or variability in expected revenues and results of operations;
• our business may be adversely affected by economic conditions and other factors that we cannot control;
• decreased demand for loans as a result of increased savings or income could result in a loss of revenues or decline in profitability if we are unable to successfully adapt to such changes;
• our models have not yet been extensively tested during down-cycle economic conditions. If our models do not accurately reflect a borrower’s credit risk in such economic conditions, the performance of loans facilitated on our platform may be worse than anticipated;
• our business is subject to a wide range of laws and regulations, many of which are evolving, and changes in such laws and regulations or the enforcement of such laws and regulations, and/or failure or perceived failure to comply with such laws and regulations, could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations;
• substantially all of our revenue is derived from a single loan product, and it is thus particularly susceptible to fluctuations in the unsecured personal loan market. We also do not currently offer a broad suite of products that bank partners may find desirable;
• if we are unable to manage the risks related to new products and service offerings that we offer, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected;
• if we are unable to maintain diverse and robust sources of capital to fund loans originated by us on our platform in certain states or fund our purchase of participation rights in the economic interests of loans originated by our bank partners on our platform, then our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected;
• we rely on borrowings under our corporate and warehouse credit facilities to fund certain aspects of our operations, and any inability to meet our obligations as they come due or to comply with various covenants could harm our business;
• if we fail to establish and maintain proper and effective internal controls over financial reporting, as a public company, our ability to produce accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, investors may lose confidence in financial reporting and the trading price of our securities may decline;
• it may be difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property rights, and we may not be able to ensure their protection;
• if loans originated by us or loans originated by our bank partners and facilitated by our platform are found to violate the laws of one or more states, whether at origination or after sale by the originating bank partner, such loans may be unenforceable or otherwise impaired, and we or other program participants may be subject to, among other things, fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations;
• if we are unsuccessful in preventing the California Department of Financial Protection and Innovation (“DFPI”) from enforcing the interest rate caps set forth in the California Financing Law, as amended by the Fair Access to Credit Act, a/k/a AB 539 (“CFL”), against loans that are originated by our bank partners on our platform and serviced through our technology and service platform, our bank partners’ ability to originate loans on our platform in California could suffer, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition;
• if loans facilitated through our platform for one or more bank partners are subject to successful challenge that the bank partner was not the “true lender,” such loans may be unenforceable, subject to rescission, or otherwise impaired, we or other program participants may be subject to fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations;
• litigation, regulatory actions and compliance issues could subject us to significant fines, penalties, judgments, remediation costs and/or requirements resulting in increased expenses;
• as a holding company, our only asset is our interest in OppFi-LLC, and we depend on OppFi-LLC to pay our expenses, and based on our tax structure, we may be required to satisfy our liabilities under the Tax Receivable Agreement, which could be substantial; and
• a minority share position may reduce the influence that our non-affiliate stockholders have on our management.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
We are a rapidly growing company with a relatively limited operating history, which may result in increased risks, uncertainties, expenses and difficulties, and makes it difficult to evaluate our future prospects.
We were founded in 2012 and have experienced rapid growth in recent years. Our limited operating history may make it difficult to make accurate predictions about our future performance. Assessing our business and future prospects may also be difficult because of the risks and difficulties we face. These risks and difficulties include our ability to:
• improve the effectiveness and predictiveness of our machine learning models;
• maintain and increase the volume of loans facilitated by our specialty finance platform;
• enter into new and maintain existing bank partnerships;
• successfully maintain diverse and robust sources of capital to fund loans originated by us on our platform in certain states or fund our purchase of participation rights in the economic interests of loans originated by our bank partners on our platform;
• successfully fund a sufficient quantity of our borrower loan demand with low cost bank funding to help keep interest rates offered to borrowers competitive;
• successfully build our brand and protect our reputation from negative publicity;
• increase the effectiveness of our marketing strategies, including our direct consumer marketing initiatives;
• continue to expand the number of potential borrowers;
• successfully adjust our proprietary machine learning models, products and services in a timely manner in response to changing macroeconomic conditions and fluctuations in the credit market;
• respond to general economic conditions, including economic slowdowns, inflation, interest rate changes, recessions and tightening of credit markets;
• comply with and successfully adapt to complex and evolving regulatory environments;
• protect against increasingly sophisticated fraudulent borrowing and online theft;
• successfully compete with companies that are currently in, or may in the future enter, the business of providing online lending services to financial institutions or consumer financial services to borrowers;
• enter into new markets and introduce new products and services;
• effectively secure and maintain the confidentiality of the information received, accessed, stored, provided and used across our systems;
• successfully obtain and maintain funding and liquidity to support continued growth and general corporate purposes;
• attract, integrate and retain qualified employees; and
• effectively manage and expand the capabilities of our operations teams, outsourcing relationships and other business operations.
If we are not able to timely and effectively address these risks and difficulties as well as those described elsewhere in this “Risk Factors” section, our business and results of operations may be harmed.
Our revenue growth rate and financial performance in recent periods may not be indicative of future performance and such growth may slow over time.
We have grown rapidly over the last several years, and our recent revenue growth rate and financial performance may not be indicative of our future performance. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, our revenue was approximately $350.6 million, $452.9 million and $508.9 million, respectively, representing year-over-year revenue growth of approximately 29% from 2021 to 2022 and 12% from 2022 to 2023. You should not rely on our revenue for any previous quarterly or annual period as any indication of our revenue or revenue growth in future periods. As we grow our business, our revenue growth rates may slow, or our revenue may decline, in future periods for a number of reasons, which may include slowing demand for our platform offerings and services, increasing competition, a decrease in the growth of the overall credit market, changes in the regulatory environment, which could lead to increasing regulatory costs and challenges, and our failure to capitalize on growth opportunities. Further, we believe our growth over the last several years has been driven in large part by our machine learning models and our continued improvements to our machine learning models. Future incremental improvements to our machine learning models may not lead to the same level of growth as in past periods. In addition, we believe our growth over the last several years has been driven in part by our ability to rapidly streamline and automate the loan application and origination process on our platform. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, our auto-approval rate was approximately 51.6%, 65.3% and 71.9%, respectively, representing a year-over-year increase of approximately 26.6% from 2021 to 2022 and 10.1% from 2022 to 2023. See the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for more information on how we define auto-approval rate. We expect the auto-approval rate on our platform to level off and remain relatively constant in the long term, and to the extent we expand our loan offerings beyond unsecured personal loans, we expect that such percentage may decrease in the short term. As a result of these factors, our revenue growth rates may slow, and our financial performance may be adversely affected.
If we fail to effectively manage our growth, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Over the last several years, we have experienced rapid growth and fluctuations in our business and the total net originations on our platform, and we expect to continue to experience growth and fluctuations in the future. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, total net originations on our platform were approximately $595.1 million, $752.9 million, $747.8 million, respectively, representing a year-over-year increase of approximately 26.5% from 2021 to 2022 and a year-over-year decrease of approximately 0.7% from 2022 to 2023. See the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for more information on how we define total net originations. This rapid growth has placed, and may continue to place, significant demands on our management, processes and operational, technological and financial resources. Our ability to manage our growth effectively and to integrate new employees and technologies into our existing business will require us to continue to retain, attract, train, motivate and manage employees and expand our operational, technological and financial infrastructure. Continued growth could strain our ability to develop and improve our operational, technological, financial and management controls, enhance our reporting systems and procedures,
recruit, train and retain highly skilled personnel and maintain user satisfaction. Any of the foregoing factors could negatively affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to maintain or increase our profitability in the future.
For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, we experienced net income of approximately $89.8 million, $3.3 million and $39.5 million, respectively, representing a year-over-year decrease of approximately 96% from 2021 to 2022 and a year-over-year increase of approximately 1,082% from 2022 to 2023. We intend to continue to expend significant funds to continue to develop and improve our proprietary machine learning models, improve our marketing efforts to increase the number of borrowers on our platform, enhance the features and overall user experience of our platform, expand the types of loan offerings on our platform and otherwise continue to grow our business, and we may not be able to increase our revenue enough to offset these significant expenditures. We may incur significant losses in the future for a number of reasons, including the other risks described in this section, and unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications and delays, macroeconomic conditions, including economic slowdowns, interest rate changes, recessions, inflation and tightening of credit markets, poor performance of loan vintages, and other unknown events. Any failure to increase our revenue sufficiently to keep pace with our investments and other expenses could prevent us from maintaining or improving profitability on a consistent basis. If we are unable to successfully address these risks and challenges as we encounter them, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We may experience fluctuations in our quarterly operating results.
Our quarterly results of operations, including the levels of our revenue, net income and other key metrics, are likely to vary significantly in the future, and period-to-period comparisons of our results of operations may not be meaningful. Accordingly, the results for any one quarter are not necessarily an accurate indication of future performance. Our quarterly financial results may fluctuate due to a variety of factors, many of which are outside of our control. Factors that may cause fluctuations in our quarterly financial results include:
• our ability to improve the effectiveness and predictiveness of our machine learning models;
• our ability to maintain relationships with existing bank partners and our ability to attract new bank partners;
• our ability to maintain or increase loan volumes, and improve loan mix and the channels through which the loans, bank partners and loan funding are sourced;
• general economic conditions, including economic slowdowns, recessions and tightening of credit markets, including due the failures of banks or other financial institutions, the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and any governmental response to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic;
• improvements to our machine learning models that negatively impact transaction volume, such as lower approval rates;
• the timing and success of new products and services;
• the effectiveness of our direct marketing and other marketing channels;
• the amount and timing of operating expenses related to maintaining and expanding our business, operations and infrastructure, including acquiring new and maintaining existing bank partners and investors and attracting borrowers to our platform;
• our cost of borrowing money and access to loan and participation right funding sources;
• the number and extent of loans facilitated on our platform that are subject to loan modifications and/or temporary assistance due to disasters or emergencies;
• the number and extent of prepayments of loans facilitated on our platform;
• changes in the fair value of assets and liabilities on our balance sheet;
• network outages or actual or perceived security breaches;
• our involvement in litigation or regulatory enforcement efforts (or the threat thereof) or those that impact our industry generally;
• the length of the onboarding process related to acquisitions of new bank partners;
• changes in laws and regulations that impact our business; and
• changes in the competitive dynamics of our industry, including consolidation among competitors or the development of competitive products by larger well-funded incumbents.
In addition, we experience significant seasonality in the demand for loans on our platform, which is generally lower in the first quarter. This seasonal slowdown is primarily attributable to high loan demand around the holidays in the fourth quarter and the general increase in borrowers’ available cash flows in the first quarter, including cash received from tax refunds, which temporarily reduces borrowing needs. While our growth has obscured this seasonality in our overall financial results, we expect our results of operations to continue to be affected by such seasonality in the future. In light of these factors, results for any period should not be relied upon as being indicative of performance in future periods.
If we are unable to continue to improve our machine learning models or if our machine learning models contain errors or are otherwise ineffective, our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
Our ability to attract customers to our platform and increase the number of loans facilitated on our platform will depend in large part on our ability to effectively evaluate a borrower’s creditworthiness and likelihood of default and, based on that evaluation, offer competitively priced loans and higher approval rates. Further, our overall operating efficiency and margins will depend in large part on our ability to maintain a high degree of automation in the loan application process and achieve incremental improvements in the degree of automation. If our models fail to adequately predict the creditworthiness of borrowers due to the design of our models or programming or other errors, and our models do not detect and account for such errors, or any of the other components of our credit decision process fails, we and our bank partners may experience higher than forecasted loan losses. Any of the foregoing could result in sub-optimally priced loans, incorrect approvals or denials of loans, or higher than expected loan losses, which in turn could adversely affect our ability to attract new borrowers and bank partners to our platform, increase the number of loans facilitated on our platform or maintain or increase the average size of loans facilitated on our platform.
Our models also target and optimize other aspects of the lending process, such as borrower acquisition, fraud detection, default timing, loan stacking, prepayment timing and fee optimization, and our continued improvements to such models have allowed us to facilitate loans inexpensively and virtually instantly, with a high degree of consumer satisfaction and with an insignificant impact on loan performance. However, such applications of our models may prove to be less predictive than we expect, or than they have been in the past, for a variety of reasons, including inaccurate assumptions or other errors made in constructing such models, incorrect interpretations of the results of such models and failure to timely update model assumptions and parameters. Additionally, such models may not be able to effectively account for matters that are inherently difficult to predict and beyond our control, such as macroeconomic conditions, credit market volatility and interest rate fluctuations, which often involve complex interactions between a number of dependent and independent variables and factors. Material errors or inaccuracies in such models could lead us to make inaccurate or sub-optimal operational or strategic decisions, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, errors or inaccuracies in our models could result in any person exposed to the credit risk of loans facilitated on our platform, whether it be us, our bank partners or our sources of capital, experiencing higher than expected losses or lower than desired returns, which could impair our ability to retain existing or attract new bank partners and sources of capital, reduce the number, or limit the types, of loans bank partners and sources of capital are willing to fund, and limit our ability to increase commitments under our credit facilities. Any of these circumstances could reduce the number of loans facilitated on our platform and harm our ability to maintain diverse and robust sources of capital and could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Continuing to improve the accuracy of our models is central to our business strategy. While we believe that continuing to improve the accuracy of our models is key to our long-term success, those improvements could, from time to time, lead us to reevaluate the risks associated with certain borrowers, which could in turn cause us to lower approval rates or increase interest rates for any borrowers identified as a higher risk, either of which could negatively impact our growth and results of operations in the short term.
If our existing bank partners were to cease or limit operations with us or if we are unable to attract and onboard new bank partners, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Approximately 95% and 98% of our net originations were generated from loans originated by our bank partners and facilitated by our platform in the years ended December 31, 2022 and December 31, 2023, respectively. Our primary bank partners FinWise, First Electronic Bank (“FEB”) and Capital Community Bank (“CCB”) began originating loans on the OppFi platform in January 2018, May 2020 and October 2020, respectively. FinWise accounted for approximately 36.2% and 34.2% of the net originations facilitated by our platform during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2023, respectively, and similar percentages of our net revenues. FEB accounted for approximately 43.2% and 45.2% of the net originations facilitated by our platform during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2023, respectively, and similar percentages of our net revenues. CCB accounted for approximately 15.6% and 18.3% of the net originations facilitated by our platform during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2023, respectively, and similar percentages of our net revenues. Our bank partners retain a certain
portion of the economic interests in these originated loans on their own balance sheets and sell participation rights in the remainder of the economic interests in these originated loans to us, which we in turn sell to our special purpose finance entities.
We have entered into separate agreements with each of our three primary bank partners. Our agreements with our bank partners are nonexclusive, generally have 60-month terms and certain agreements automatically renew, subject to certain early termination provisions and minimum fee amounts, and do not include any minimum origination obligations or origination limits. The current term of our agreements with FinWise, FEB and CCB expire on February 1, 2026, November 1, 2024, and April 17, 2025, respectively, unless renewed.
Our bank partners could decide to stop working with us, terminate our agreements with them early upon the occurrence of certain events, ask to modify their agreement terms in a cost prohibitive manner when their agreement is up for renewal or enter into exclusive or more favorable relationships with our competitors. Further, even during the term of our arrangements, our bank partners could choose to reduce the volume of loans facilitated on our platform that they choose to originate. In addition, regulators may require that they terminate or otherwise limit their business with us; impose regulatory pressure limiting their ability to do business with us; or directly examine and assess our records, risk controls and compliance programs as they relate to our interactions with bank partners (and thereafter limit or prohibit future business between that bank partner and us). For example, in spite of federal law permitting state-chartered banks to enter into loans with interest rates allowed in their chartering states, the DFPI has sought to limit the interest rates of loans made by our bank partners on our platform in the State of California, which could have an impact on our bank partners’ ability to originate loans on our platform in California. We could in the future have disagreements or disputes with any of our bank partners, which could negatively impact or threaten our relationship with them. In our agreements with bank partners, we make certain representations and warranties and covenants concerning our compliance with specific policies of a bank partner, our compliance with certain procedures and guidelines related to laws and regulations applicable to our bank partners, as well as the services to be provided by us. If those representations and warranties were not accurate when made or if we fail to perform a covenant, we may be liable for any resulting damages, including potentially any losses associated with impacted loans, and our reputation and ability to continue to attract new bank partners would be adversely affected. Additionally, our bank partners may engage in mergers, acquisitions or consolidations with each other, our competitors or with third parties, any of which could be disruptive to our existing and prospective relationships with our bank partners. If the bank partners listed above or any of our future bank partners were to stop working with us, suspend, limit, or cease their operations, or otherwise terminate their relationship with us, the number of loans facilitated through our platform could decrease and our revenue and revenue growth rates could be adversely affected. We also may be unable to reach agreements with or timely onboard any new bank partners, and our results of operations could be adversely affected.
The sales and onboarding process of new bank partners could take longer than expected, leading to fluctuations or variability in expected revenues and results of operations.
Our sales and onboarding process with new bank partners can be long and typically takes between three to six months. As a result, our revenues and results of operations may vary significantly from period to period. Prospective bank partners are often cautious in making decisions to implement our platform and related services because of the risk management alignment and regulatory uncertainties related to their use of our machine learning models, including their oversight, model governance and fair lending compliance obligations associated with using such models. In addition, prospective banks undertake an extensive diligence review of our platform, compliance and servicing activities before choosing to partner with us. Further, the implementation of our machine learning underwriting model often involves adjustments to the bank partner’s software and/or hardware platform or changes in their operational procedures, which may involve significant time and expense to implement. Delays in onboarding new bank partners can also arise while prospective bank partners complete their internal procedures to approve expenditures and test and accept our applications. Consequently, we face difficulty predicting the quarter in which new bank partners will begin using our platform and the volume of fees we will receive, which can lead to fluctuations in our revenues and results of operations.
Our business has been, and may continue to be, adversely affected by economic conditions and other factors that we cannot control.
Uncertainty and negative trends in general economic conditions, including significant tightening of credit markets, historically have created a difficult operating environment for our industry. Many factors, including factors that are beyond our control, may impact our results of operations or financial condition and our overall success by affecting a borrower’s willingness to incur loan obligations or willingness or capacity to make payments on their loans. These factors include interest rates, levels of inflation, unemployment levels, conditions in the housing market, immigration policies, gas prices, energy costs, government shutdowns, trade wars and delays in tax refunds, as well as events such as natural disasters, acts of war, terrorism, catastrophes and pandemics.
Many new consumers on our platform have limited or no credit history. Accordingly, such borrowers have historically been, and may in the future become, disproportionately affected by adverse macroeconomic conditions, such as economic slowdowns, inflation, interest rate changes, recessions and the disruption and uncertainty caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
In addition, major medical expenses, divorce, death or other issues that affect borrowers could affect a borrower’s willingness or ability to make payments on their loans. Increasing inflation and interest rates may also cause borrowers to allocate more of their income to necessities, thereby potentially increasing their risk of default by reducing their ability to make loan payments. If borrowers default on loans facilitated on our platform, the cost to service these loans may also increase without a corresponding increase in our servicing fees or other related fees and the value of the loans held on our balance sheet could decline. Higher default rates by these borrowers may lead to lower demand by our bank partners and institutional investors to fund loans facilitated by our platform, which would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
During periods of economic slowdown or recession, our sources of capital may reduce the level of participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners on our platform that they will fund our purchase of, or the amounts of loans originated by us that they will fund, or demand terms that are less favorable to us to compensate for any increased risks. A reduction in the volume of the loans that can be facilitated by our platform due to our sources of capital would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic and other related adverse economic events led to a significant increase in unemployment, comparable, and at times surpassing, the unemployment rates during the peak of the financial crisis in 2008. The increase in the unemployment rate could increase the delinquency rate of loans facilitated on our platform or increase the rate of borrowers declaring bankruptcy. If we are unable to improve our machine learning platform to account for events like the COVID-19 pandemic and the resulting rise in unemployment, or if our machine learning platform is unable to more successfully predict the creditworthiness of potential borrowers compared to other lenders, then our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
In addition, personal loans are dischargeable in a bankruptcy proceeding involving a borrower without the need for the borrower to file an adversary claim. The discharge of a significant amount of personal loans facilitated by our platform could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations, including by causing our bank partners to stop working with us, suspend, limit, or cease their operations, or otherwise terminate their relationship with us.
The COVID-19 pandemic harmed our growth rate and any future outbreaks or pandemics could also harm our growth rate and our business, financial condition and results of operations, including the credit risk of our customers.
The COVID-19 pandemic caused extreme societal, economic and financial market volatility, resulting in business shutdowns, an unprecedented reduction in economic activity and significant dislocation to businesses, the capital markets and the broader economy. In particular, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the finances of borrowers on our platform has been profound, as many have been, and will likely continue to be, impacted by unemployment, reduced earnings and/or elevated economic disruption and insecurity.
The extent to which the COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact our business and results of operations will depend on future developments that are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted. An extended period of economic disruption as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic or any future pandemics or epidemics could have a material negative impact on our business, results of operations and financial condition, though the full extent and duration is uncertain. To the extent the COVID-19 pandemic or any future outbreak or pandemic adversely affects our business and financial results, it is likely to also have the effect of heightening many of the other risks described in this “Risk Factors” section.
Decreased demand for loans as a result of increased savings or income could result in a loss of revenues or decline in profitability if we are unable to successfully adapt to such changes.
The demand for the loan products facilitated on our platform in the markets we serve could decline due to a variety of factors, such as regulatory restrictions that reduce borrower access to particular products, the availability of competing or alternative products, or changes in borrowers’ financial conditions, particularly increases in income or savings, such as recent government stimulus programs. For instance, an increase in state or federal minimum wage requirements, a decrease in individual income tax rates or an increase in tax credits, could decrease demand for our loans. Additionally, a change in focus from borrowing to saving would reduce demand. Should we fail to adapt to a significant change in borrowers’ demand for, or access to, the loan products facilitated on our platform, our revenues could decrease significantly. Even if we make adaptations or introduce new products to fulfill borrower demand, borrowers may resist or may reject products whose adaptations make them less attractive or less available. Such decreased demand could have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Our models have not yet been extensively tested during down-cycle economic conditions. If our models do not accurately reflect a borrower’s credit risk in such economic conditions, the performance of loans facilitated on our platform may be worse than anticipated.
The performance of loans facilitated by our platform is significantly dependent on the effectiveness of our proprietary models used to evaluate a borrower’s credit profile and likelihood of default. While our models have been refined and updated to account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the bulk of the data gathered and the development of our models have largely occurred during a period of sustained economic growth, and our models have not been extensively tested during a down-cycle economy or recession and have not been tested at all during a down-cycle economy or recession without significant levels of government assistance. For example, during the year ended December 31, 2021, despite the outbreak and effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, our models indicated that the credit risk of our loan applicants remained flat during this period and government stimulus programs had positive effects on the credit performance of loans facilitated on our platform during this period. This positive performance continued through the middle of 2021. As the effects of stimulus wore off in the second half of 2021, it took time for the models to recognize the shift in loan performance. There is no assurance that our models can continue to accurately predict loan performance under adverse economic conditions, or that our models will be able to recognize future changes in credit performance before the effects or any such changes have an impact on the fair value of the finance receivables on our balance sheet. If our models are unable to accurately reflect the credit risk of loans under such economic conditions, we may experience greater than expected losses on such loans, which would harm our reputation and erode the trust we have built with our bank partners and capital sources. In addition, the fair value of the loans on our balance sheet may decline. Any of these factors could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Substantially all of our revenue is derived from a single loan product, and we are thus particularly susceptible to fluctuations in the unsecured personal loan market. We also do not currently offer a broad suite of products that bank partners may find desirable.
While we previously expanded the type of loan products offered on our platform to include SalaryTap, our payroll deduction secured installment loan product, and our OppFi Card credit card product, we are not currently accepting applications for new SalaryTap loans or OppFi Card accounts on our platform. All loan originations facilitated through our platform are currently unsecured personal installment loans. The market for unsecured personal loans has grown rapidly in recent years, and it is unclear to what extent such market will continue to grow, if at all. A wide variety of factors could impact the market for unsecured personal loans, including macroeconomic conditions, competition, regulatory developments and other developments in the credit market. For example, FICO has changed its methodology in calculating credit scores in a manner that potentially penalizes borrowers who take out personal loans to pay off or consolidate credit card debt. This change could negatively affect the overall demand for personal loans. Our success will depend in part on the continued growth of the unsecured personal loan market, and if such market does not further grow or grows more slowly than we expect, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
In addition, bank partners may in the future seek partnerships with competitors that are able to offer them a broader array of credit products. Over time, in order to preserve and expand our relationships with our existing bank partners, and enter into new bank partnerships, it may become increasingly important for us to be able to offer a wider variety of products than we currently provide. We are also susceptible to competitors that may intentionally underprice their loan products, even if such pricing practices lead to losses. Such practices by competitors would negatively affect the overall demand for personal loans facilitated on our platform.
Further, because such personal loans are unsecured, there is a risk that borrowers will not prioritize repayment of such loans, particularly in any economic downcycle. To the extent borrowers have or incur other indebtedness that is secured, such as a mortgage, a home equity line of credit or an auto loan, borrowers may choose to repay obligations under such secured indebtedness before repaying their loans facilitated on our platform. In addition, borrowers may not view loans facilitated on our platform, which were originated through an online platform, as having the same significance as other credit obligations arising under more traditional circumstances, such as loans originated by banks or other commercial financial institutions on other platforms. Any of the forgoing could lead to higher default rates and decreased demand by our bank partners and capital sources to fund loans facilitated by our platform, which would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
For the years ended December 31, 2021, 2022 and 2023, we experienced losses, which we refer to as net charge-offs, as a percentage of average receivables on the installment loans portfolio of 37.5%, 61.9% and 55.4%, respectively. See the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for more information on net charge-offs as a percentage of average receivables. When a loan facilitated on our platform is charged off, the cost to service these loans may increase without a corresponding increase in our servicing fees or other related fees and the value of the loans held on our balance sheet may decline. Higher default rates may also lead to lower demand by our bank partners and
capital sources to fund loans facilitated by our platform, which would adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are also more susceptible to the risks of changing and increased regulations and other legal and regulatory actions targeted towards the unsecured personal loan market. It is possible that regulators may view unsecured personal loans as high risk for a variety of reasons, including that borrowers will not prioritize repayment of such loans due to the unsecured nature of such loans or because existing laws and regulations may not sufficiently address the benefits and corresponding risks related to nonbank financial institutions and their digital specialty finance platforms. Further, courts and/or regulators could change their interpretation or application of state and federal consumer financial protection laws for the unsecured personal loan product class given hardships borrowers experience or actual or perceived lack of borrower disclosure or understanding of loan terms. If we are unable to manage the risks associated with the unsecured personal loan market, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We have developed and may develop in the future new loan products and services offerings, and if we are unable to manage the related risks, our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We may develop new loan products in the future. New initiatives are inherently risky, as each involves unproven business strategies, new regulatory requirements and new financial products and services with which we, and in some cases our bank partners, have limited or no prior development or operating experience. Launching new products can be capital intensive, and it can take time to determine both an appropriate market fit and profitable unit. New products, once launched, may never achieve scale in a target market or achieve significant profitability, such as our SalaryTap loans or OppFi Card products for which we are not currently accepting new applications.
We cannot be sure that we will be able to develop, commercially market and achieve market acceptance of any new products and services that we may offer. In addition, our investment of resources to develop new products and services may either be insufficient or result in expenses that are excessive in light of revenue actually derived from these new products and services. If the profile or behavior of loan applicants using any new products and services is different from that of those currently served by our existing loan products, our machine learning models may not be able to accurately evaluate the credit risk of such borrowers, and our bank partners and capital sources may in turn experience higher levels of delinquencies or defaults. Failure to accurately predict demand or growth with respect to our new products and services could have an adverse impact on our reputation and business, and there is always risk that new products and services will be unprofitable, will increase our costs, decrease operating margins or take longer than anticipated to achieve target margins. In addition, any new products or services may raise new and potentially complex regulatory compliance obligations, which would increase our costs and may cause us to change our business in unexpected ways. Further, our development efforts with respect to these initiatives could distract management from current operations and will divert capital and other resources from our existing business.
We may also have difficulty with securing adequate funding for any such new loan products and services, and if we are unable to do so, our ability to develop and grow these new offerings and services will be impaired. If we are unable to effectively manage the foregoing risks, our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our reputation and brand are important to our success, and if we are unable to continue developing our reputation and brand, our ability to retain existing and attract new bank partners, our ability to attract borrowers to our platform and our ability to maintain and improve our relationship with regulators of our industry could be adversely affected.
We believe maintaining a strong brand and trustworthy reputation is critical to our success and our ability to attract borrowers to our platform, attract new bank partners and maintain good relations with regulators and existing bank partners. Factors that affect our brand and reputation include: perceptions of machine learning, our industry and our company, including the quality and reliability of our machine learning enabled underwriting platform; the accuracy of our machine learning models; perceptions regarding the application of machine learning to consumer lending specifically; our loan funding programs; changes to our platform; our ability to effectively manage and resolve borrower complaints; collection practices; privacy and security practices; litigation; regulatory activity; and the overall user experience of our platform. Negative publicity or negative public perception of these factors, even if inaccurate, could adversely affect our brand and reputation.
For example, consumer advocacy groups, politicians and certain government and media reports have, in the past, advocated governmental action to prohibit or severely restrict consumer loan arrangements where banks contract with a third- arty platform such as ours to provide origination assistance services to bank customers. Such criticism has frequently been levied in the context of payday loan marketers, though other entities operating programs through which loans similar to loans facilitated on our platform are originated have also faced criticism. The perceived improper use of a bank charter by these entities has been challenged by both governmental authorities and private litigants, in part because of the higher rates and fees a bank is permitted to charge consumers in certain payday and small-dollar specialty finance programs relative to non-bank
lenders. State regulators have made statements in the past threatening regulatory action against us related to loans originated on our platform by state chartered-banks, and such statements and the perception of possible regulatory action could adversely affect our reputation and the willingness of bank partners to originate loans on our platform. Bank regulators have also required banks to exit third-party programs that the regulators determined involved unsafe and unsound practices or present other risks to the bank. We believe the payday or “small-dollar” loans that have been subject to more frequent criticism and challenge are fundamentally different from loans facilitated on our platform in many ways, including that loans facilitated on our platform typically have lower interest rates, longer terms and amortize over their life. If we are nevertheless associated with such payday or small-dollar consumer loans, or if we are associated with increased criticism of non-payday loan programs involving relationships between bank originators and specialty finance platforms and program managers, demand for loans facilitated on our platform could significantly decrease, which could cause our bank partners to reduce their origination volumes or terminate their arrangements with us, impede our ability to attract new bank partners or delay the onboarding of bank partners, impede our ability to attract capital sources or reduce the number of potential borrowers who use our platform. In addition, the increased focus on environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) issues could damage our reputation or prospects if customers, prospective customers, investors or third parties assigning ESG ratings to us are of the opinion that our practices, including without limitation our lending practices, are not sufficiently robust from an ESG perspective. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Any negative publicity or public perception of loans facilitated on our platform or other similar consumer loans or the consumer lending service we provide may also result in us being subject to more restrictive interpretation or application of laws and regulations and potential investigations and enforcement actions. We may also become subject to additional lawsuits, including class action lawsuits, or other challenges such as government enforcement or arbitration, against our bank partners or us for loans originated by our bank partners on our platform or loans we service or have serviced, which we have been subject to in the past. See the section titled “Risk Factors—We have been in the past and may in the future be subject to federal and state regulatory inquiries regarding our business” for more information. If there are changes in the laws or in the interpretation or enforcement of existing laws affecting consumer loans similar to those offered on our platform, or our marketing and servicing of such loans, or if we become subject to such lawsuits, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
Machine learning and related technologies are subject to public debate and heightened regulatory scrutiny, particularly when used in connection with obtaining financial services. Any negative publicity or negative public perception of machine learning could negatively impact demand for our platform, hinder our ability to attract new bank partners. From time to time, certain advocacy groups have made claims that unlawful or unethical discriminatory effects may result from the use of machine learning technology by various companies. Such claims, whether or not accurate, and whether or not concerning us or our machine learning enabled underwriting platform, may harm our ability to attract prospective borrowers to our platform, retain existing and attract new bank partners and achieve regulatory acceptance of our business.
Harm to our reputation can also arise from many other sources, including employee or former employee misconduct, misconduct by outsourced service providers or other counterparties, failure by us or our bank partners to meet minimum standards of service and quality, and inadequate protection of borrower information and compliance failures and claims. If we are unable to protect our reputation, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
If we do not compete effectively in our target markets, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be harmed.
The specialty finance industry is highly competitive and increasingly dynamic as new entrants and emerging technologies continue to enter into the marketplace. With the introduction of new technologies and the influx of new entrants, competition may persist and intensify in the future, which could have an adverse effect on our operations or business.
Our inability to compete effectively could result in reduced loan volumes, reduced average size of loans facilitated on our platform, reduced fees, increased marketing and borrower acquisition costs or the failure of our platform to achieve or maintain more widespread market acceptance, any of which could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Specialty finance is a broad and competitive market, and we compete to varying degrees with other sources of unsecured consumer credit. This can include banks and non-bank financial institutions, such as online platforms. Because personal loans often serve as a replacement for credit cards, we also compete with the convenience and ubiquity that credit cards represent. Many of our competitors operate with different business models, such as lending-as-a-service or point-of-sale lending, have different cost structures or regulatory obligations, or participate selectively in different market segments. They may ultimately prove more successful or more adaptable to new regulatory, economic, technological and other developments, including utilizing new data sources or credit models. We may also face competition from banks or companies that have not previously competed in the consumer lending market, including companies with access to vast amounts of consumer-related information that could be used in the development of their own credit risk models. Our current or potential competitors may be better at
developing new products due to their large and experienced data science and engineering teams, who are able to respond more quickly to new technologies. Many of our current or potential competitors have significantly more resources, such as financial, technical and marketing resources, than we do and may be able to devote greater resources to the development, promotion, sale and support of their platforms and distribution channels. We face competition in areas such as compliance capabilities, commercial financing terms and costs of capital, interest rates and fees (and other financing terms) available to consumers from our bank partners, approval rates, model efficiency, speed and simplicity of loan origination, ease-of-use, marketing expertise, service levels, products and services, technological capabilities and integration, borrower experience, brand and reputation. Our competitors may also have longer operating histories, lower costs of capital, more extensive borrower bases, more diversified products and borrower bases, operational efficiencies, more versatile or extensive technology platforms, greater brand recognition and brand loyalty, broader borrower and partner relationships, more extensive and/or more diversified source of capital than we have, and more extensive product and service offerings than we have. Furthermore, our existing and potential competitors may decide to modify their pricing and business models to compete more directly with us. Our ability to compete will also be affected by our ability to provide our bank partners with a commensurate or more extensive suite of loan products than those offered by our competitors. In addition, current or potential competitors, including digital specialty finance platforms and existing or potential bank partners, may also acquire or form strategic alliances with one another, which could result in our competitors being able to offer more competitive loan terms due to their access to lower-cost capital. Such acquisitions or strategic alliances among our competitors or potential competitors could also make our competitors more adaptable to a rapidly evolving regulatory environment. To stay competitive, we may need to increase our regulatory compliance expenditures or our ability to compete may be adversely affected.
Our industry is driven by constant innovation. We utilize machine learning, which is characterized by extensive research efforts and rapid technological progress. If we fail to anticipate or respond adequately to technological developments, our ability to operate profitably could suffer. There can be no assurance that research, data accumulation and development by other companies will not result in products superior to those we develop or that any technologies, products or services we develop will be preferred to any existing or newly-developed technologies, products or services. If we are unable to compete with such companies or fail to meet the need for innovation in our industry, the use of our platform could stagnate or substantially decline, or our loan products could fail to maintain or achieve more widespread market acceptance, which could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If we are unable to manage the risks associated with fraudulent activity, our brand and reputation, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Fraud is prevalent in the financial services industry and is likely to increase as perpetrators become more sophisticated. Although we have not experienced any material business or reputational harm as a result of fraudulent activity in the past, we are subject to the risk of fraudulent activity associated with borrowers and third parties handling borrower information. In the event of losses arising out of fraudulent loan applications, we may also be contractually obligated to indemnify our bank partners or capital sources for such losses. Fraud rates could also increase in a downcycle economy. We use several identity and fraud detection tools, including tools provided by third-party vendors and our proprietary machine learning models, to predict and otherwise validate or authenticate applicant-reported data and data derived from third-party sources. We have historically had very low levels of fraud rates; however, the possibility of fraudulent or other malicious activities and human error or malfeasance cannot be eliminated entirely and will evolve as new and emerging technology is deployed, including the increasing use of personal mobile and computing devices that are outside of our network and control environments. Moreover, if our efforts are insufficient to accurately detect and prevent fraud, the level of fraud-related losses of loans facilitated on our platform could increase, which would decrease confidence in our platform. In addition, our bank partners, our sources of capital or we may not be able to recover amounts disbursed on loans made in connection with inaccurate statements, omissions of fact or fraud, which could erode the trust in our brand and negatively impact our ability to attract new bank partners and our sources of capital.
High profile fraudulent activity also could negatively impact our brand and reputation. In addition, significant increases in fraudulent activity could lead to regulatory intervention, which could increase our costs and also negatively impact our brand and reputation. Further, if there is any increase in fraudulent activity that increases the need for human intervention in screening loan application data, the level of automation on our platform could decline and negatively affect our unit economics. If we are unable to manage these risks, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We depend on our key personnel and other highly skilled personnel, and if we fail to attract, retain and motivate our personnel, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our success significantly depends on the continued service of our senior management team, including Todd Schwartz, our Chief Executive Officer, Pamela Johnson, our Chief Financial Officer, and other highly skilled personnel. Our success also depends on our ability to identify, hire, develop, motivate and retain highly qualified personnel for all areas of our organization.
Competition for highly skilled personnel, including engineering and data analytics personnel, is extremely intense, including in Chicago where our headquarters is located. We have experienced, and expect to continue to face, difficulty identifying and hiring qualified personnel in many areas, especially as we pursue our growth strategy, and we may be required to pay increasingly higher wages to hire and retain adequate personnel. Further, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, a large and increasing number of companies have adopted permanent work-from-home policies, which further increases the challenges associated with hiring and retaining qualified personnel. We may not be able to hire or retain such personnel at compensation or flexibility levels consistent with our existing compensation and salary structure and policies. Many of the companies with which we compete for experienced employees have greater resources than we have and may be able to offer more attractive terms of employment. In particular, candidates making employment decisions, specifically in high-technology industries, often consider the value of any equity they may receive in connection with their employment. Any significant volatility in the price of our securities may adversely affect our ability to attract or retain highly skilled technical, financial and marketing personnel.
In addition, we invest significant time and expense in training our employees, which increases their value to competitors who may seek to recruit them. If we fail to retain our employees, we could incur significant expenses in hiring and training their replacements. While we are in the process of training their replacements, the quality of our services and our ability to serve our bank partners, investors and borrowers whose loans we service may suffer, resulting in an adverse effect on our business.
Security breaches of borrowers’ confidential information that we store may harm our reputation, adversely affect our results of operations and expose us to liability.
We are increasingly dependent on information technology systems and infrastructure to operate our business. In the ordinary course of our business, we collect, process, transmit and store large amounts of sensitive information, including personal information, credit information and other sensitive data of borrowers and potential borrowers. It is critical that we do so in a manner designed to maintain the confidentiality, integrity and availability of such sensitive information. We have made commitments to our bank partners as it relates to data security and information technology. We also have arrangements in place with certain of our third-party vendors that require us to share consumer information. We have outsourced elements of our operations (including elements of our information technology infrastructure) to third parties, and as a result, we manage a number of third-party vendors who may have access to our computer networks and sensitive or confidential information. In addition, many of those third parties may in turn subcontract or outsource some of their responsibilities to other third parties. As a result, our information technology systems, including the functions of third parties that are involved or have access to those systems, is large and complex, with many points of entry and access. While all information technology operations are inherently vulnerable to inadvertent or intentional security breaches, incidents, attacks and exposures, the size, complexity, accessibility and distributed nature of our information technology systems, and the large amounts of sensitive information stored on those systems, make such systems potentially vulnerable to unintentional or malicious, internal and external attacks. Any vulnerabilities can be exploited from inadvertent or intentional actions of our employees, third-party vendors, bank partners, loan investors or by malicious third parties. Attacks of this nature are increasing in their frequency, levels of persistence, sophistication and intensity, and are being conducted by sophisticated and organized groups and individuals with a wide range of motives (including, but not limited to, industrial espionage) and expertise, including organized criminal groups, “hacktivists,” nation states and others. In addition to the extraction of sensitive information, such attacks could include the deployment of harmful malware, ransomware, denial-of-service attacks, social engineering and other means to affect service reliability and threaten the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information and systems. In addition, the prevalent use of mobile devices increases the risk of data security incidents. Further, our shift to a more flexible remote working environment could increase the risk of a security breach. Significant disruptions of our, our bank partners’ and third-party vendors’ and/or other business partners’ information technology systems or other similar data security incidents could adversely affect our business operations and result in the loss, misappropriation, or unauthorized access, use or disclosure of, or the prevention of access to, sensitive information, which could result in financial, legal, regulatory, business and reputational harm to us.
Because techniques used to obtain unauthorized access or to sabotage systems change frequently and generally are not recognized until they are launched against a target, we and our vendors may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. In addition, many governments have enacted laws requiring companies to notify individuals of data security breaches involving their personal data. These mandatory disclosures regarding a security breach are costly to implement and often lead to widespread negative publicity following a breach, which may cause borrowers and potential borrowers to lose confidence in the effectiveness of our data security measures on our platform. Any security breach, whether actual or perceived, would harm our reputation and ability to attract new borrowers to our platform.
We also face indirect technology, cybersecurity and operational risks relating to our borrowers, bank partners, investors, vendors and other third parties with whom we do business or upon whom we rely to facilitate or enable our business activities, including vendors, payment processors, and other parties who have access to confidential information due to our agreements with them. In addition, any security compromise in our industry, whether actual or perceived, or information technology system disruptions, whether from attacks on our technology environment or from computer malware, natural disasters, terrorism, war and telecommunication and electrical failures, could interrupt our business or operations, harm our reputation, erode borrower
confidence, negatively affect our ability to attract new borrowers, or subject us to third-party lawsuits, regulatory fines or other action or liability, which could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Like other financial services firms, we have been and continue to be the subject of actual or attempted unauthorized access, mishandling or misuse of information, computer viruses or malware, and cyber-attacks that could obtain confidential information, destroy data, disrupt or degrade service, sabotage systems or cause other damage, distributed denial of service attacks, data breaches and other infiltration, exfiltration or other similar events.
While we regularly monitor data flow inside and outside the company, attackers have become very sophisticated in the way they conceal access to systems, and we may not be aware that we have been attacked. Any event that leads to unauthorized access, use or disclosure of personal information or other sensitive information that we or our vendors maintain, including our own proprietary business information and sensitive information such as personal information regarding borrowers, loan applicants or employees, could disrupt our business, harm our reputation, compel us to comply with applicable federal and/or state breach notification laws and foreign law equivalents, subject us to time consuming, distracting and expensive litigation, regulatory investigation and oversight, mandatory corrective action, require us to verify the correctness of database contents, or otherwise subject us to liability under laws, regulations and contractual obligations, including those that protect the privacy and security of personal information. This could result in increased costs to us and result in significant legal and financial exposure and/or reputational harm. In addition, any failure or perceived failure by us or our vendors to comply with our privacy, confidentiality or data security-related legal or other obligations to our bank partners or other third parties, actual or perceived security breaches, or any security incidents or other events that result in the unauthorized access, release or transfer of sensitive information, which could include personally identifiable information, may result in governmental investigations, enforcement actions, regulatory fines, litigation, or public statements against us by advocacy groups or others, and could cause our bank partners and other third parties to lose trust in us or we could be subject to claims by our bank partners and other third parties that we have breached our privacy- or confidentiality-related obligations, which could harm our business and prospects. Moreover, data security incidents and other inappropriate access can be difficult to detect, and any delay in identifying them may lead to increased harm of the type described above. There can be no assurance that our security measures intended to protect our information technology systems and infrastructure will successfully prevent service interruptions or security incidents. For example, in December 2018, we were made aware of a software error by a vendor that displayed mismatched consumer data on a prepopulated form, which affected fewer than 100 participants on our platform. The vendor system was patched and we made changes to our systems designed to prevent similar issues in the future. However, we cannot provide any assurance that similar vulnerabilities will not arise in the future as we continue to expand the features and functionalities of our platform and introduce new loan products on our platform, and we expect to continue investing substantially to protect against security vulnerabilities and incidents.
We maintain errors, omissions, and cyber liability insurance policies covering certain security and privacy damages. However, we cannot be certain that our coverage will continue to be available on economically reasonable terms or will be available in sufficient amounts to cover one or more large claims, or that an insurer will not deny coverage as to any future claim, or that any insurer will be adequately covered by reinsurance or other risk mitigants or that any insurer will offer to renew policies at an affordable rate or offer such coverage at all in the future. The successful assertion of one or more large claims against us that exceed available insurance coverage, or the occurrence of changes in our insurance policies, including premium increases or the imposition of large deductible or co-insurance requirements, could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we are unable to manage the risks related to our loan servicing and collections obligations, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Loans facilitated on our platform are not secured by any collateral, guaranteed or insured by any third party or backed by any governmental authority. As a result, we are limited in our ability to collect on such loans on behalf of ourselves and our bank partners if a borrower is unwilling or unable to repay them. We handle in-house substantially all of the servicing activities for loans facilitated on our platform, including collection activities, which requires that we hire and train significant numbers of servicing personnel. For more information about our collections procedures and experience handling collections, see the section titled “Business—Customer Advocates and Collections Arrangements.” Our need for servicing personnel may vary over time and there is no assurance that we will be able to hire and train appropriate servicing personnel when necessary. For example, during periods of increased delinquencies caused by economic downturns or otherwise, it is important that our servicing personnel are proactive and consistent in contacting a borrower to bring a delinquent balance current and ultimately avoid the related loan becoming charged off, which in turn makes it extremely important that the servicing personnel are properly staffed and trained to take prompt and appropriate action. If the servicing personnel are unable to maintain a high quality of service, or fulfill their servicing obligations at all due to resource constraints resulting from the increased delinquencies, it could result in increased delinquencies and charge-offs on the loans, which could decrease fees payable to us, cause our bank partners to decrease the volume of loans facilitated on our platform and erode trust in our platform.
In addition, loan servicing is a highly regulated activity. Errors in our servicing activities or failures to comply with our servicing obligations could affect our internal and external reporting of the loans that we service, adversely affect our business and reputation and expose us to liability to borrowers, bank partners or capital sources. In addition, the laws and regulations governing these activities are subject to change. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic certain states prohibited or restricted collection activities. If we are unable to comply with such laws and regulations, we could lose one or more of our licenses or authorizations, become subject to greater scrutiny by regulatory agencies, or become subject to sanctions or litigation, which may have an adverse effect on our ability to perform our servicing obligations or make our platform available to borrowers in particular states. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, we charge our bank partners and capital sources a fixed percentage servicing fee based on the outstanding balance of loans serviced. If we fail to efficiently service such loans and the costs incurred exceed the servicing fee charged, our results of operations would be adversely affected.
The soundness of other financial institutions or the financial services industry generally, such as actual concerns or events involving liquidity, defaults or non-performance, may adversely affect us.
Actual events involving limited liquidity, defaults, non-performance or other adverse developments that affect financial institutions for the financial services industry generally, or concerns or rumors about any events of these kinds, have in the past and may in the future lead to market-wide liquidity problems. For example, on March 10, 2023, the FDIC took control and was appointed receiver of Silicon Valley Bank (“SVB”), and on March 12, 2023, the FDIC took control and was appointed receiver of Signature Bank, in each case due primarily to liquidity concerns related to those institutions. We did not have any direct exposure to SVB or Signature Bank at such time. However, if other banks and financial institutions enter receivership or become insolvent in the future in response to financial conditions affecting the banking system and financial markets, our ability to access our existing cash, including cash held at financial institutions in excess of the FDIC insured limit, cash equivalents and investments and conduct our business operations may be threatened. In addition, investor concerns regarding the U.S. or international financial systems could result in less demand for our services and less favorable commercial financing terms, including higher interest rates or costs and tighter financial and operating covenants, or systemic limitations on access to credit and liquidity sources, thereby making it more difficult for us to acquire financing on acceptable terms or at all or be able to provide loans to our customers. Any decline in available funding or access to our cash and liquidity resources could, among other risks, adversely impact our ability to meet our operating expenses, financial obligations or fulfill our other obligations, or result in breaches of our financial and/or contractual obligations. Any of these impacts, or any other impacts resulting from the factors described above or other related or similar factors not described above, could have material adverse impacts on our liquidity and our current and/or projected business operations and financial condition and results of operations.
Borrowers may prepay a loan at any time without penalty, which could reduce our servicing fees and deter our bank partners and investors from investing in loans facilitated by our platform.
Borrowers may decide to prepay all or a portion of the remaining principal amount on loans facilitated by our platform at any time without penalty. If the entire or a significant portion of the remaining unpaid principal amount of a loan is prepaid, we would not receive a servicing fee or we would receive a significantly lower servicing fee associated with such prepaid loan. Prepayments may occur for a variety of reasons. If prepayments increase, the amount of our servicing fees would decline, which could harm our business and results of operations. If a significant volume of prepayments occur that our models do not accurately predict, returns targeted by us, our bank partners and our capital sources would be adversely affected and our ability to attract new bank partners and capital sources would be negatively affected.
Our marketing efforts and brand promotion activities may not be effective, which could adversely affect our ability to grow our business.
Promoting awareness of our platform is important to our ability to grow our business, attract new bank partners and increase the number of potential borrowers on our platform. We believe that the importance of brand recognition will increase as competition in the consumer lending industry expands. Successful promotion of our brand will depend largely on the effectiveness of marketing efforts and the overall user experience of our bank partners and potential borrowers on our platform, which factors are outside our control. The marketing channels that we employ may also become more crowded and saturated by other specialty finance platforms, which may decrease the effectiveness of our marketing campaigns and increase borrower acquisition costs. Also, the methodologies, policies and regulations applicable to marketing channels may change. For example, internet search engines could revise their methodologies, which could adversely affect borrower volume from organic ranking and paid search. Search engines may also implement policies that restrict the ability of companies such as us to advertise their services and products, which could prevent us from appearing in a favorable location or any location in the organic rankings or paid search results when certain search terms are used by the consumer.
Our brand promotion activities may not yield increased revenues. If we fail to successfully build trust in our platform and the performance and predictability of loans facilitated on our platform, we may lose existing bank partners to our competitors or be unable to attract new bank partners and capital sources, which in turn would harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. Even if our marketing efforts result in increased revenue, we may be unable to recover our marketing costs through increases in loan volume, which could result in a higher borrower acquisition cost per account. Any incremental increases in loan servicing costs, such as increases due to greater marketing expenditures, could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Unfavorable outcomes in legal proceedings may harm our business and results of operations.
We are, and may in the future become, subject to litigation, claims, examinations, investigations, legal and administrative cases and proceedings, whether civil or criminal, or lawsuits by governmental agencies or private parties, which may affect our results of operations. These claims, lawsuits, and proceedings could involve labor and employment, discrimination and harassment, commercial disputes, intellectual property rights (including patent, trademark, copyright, trade secret, and other proprietary rights), class actions, general contract, tort, defamation, data privacy rights, antitrust, common law fraud, government regulation, or compliance, alleged securities and law violations or other investor claims, and other matters. Due to the consumer-oriented nature of our business and the application of certain laws and regulations, participants in our industry are regularly named as defendants in litigation alleging violations of federal and state laws and regulations and liability for common law torts, including fraud. Many of these legal proceedings involve alleged violations of consumer protection laws. In addition, we are, and may in the future become, subject to litigation, claims, examinations, investigations, legal and administrative cases and proceedings related to the loans facilitated on our platform.
In particular, specialty finance programs that involve originations by a bank in reliance on origination-related services being provided by specialty finance platforms and/or program managers are subject to potential litigation and government enforcement claims based on “rent-a-charter” or “true lender” theories, particularly where such programs involve the subsequent sale of such loans or interests therein to the platform. See the section titled “Risk Factors —If loans facilitated through our platform for one or more bank partners were subject to successful challenge that the bank partner was not the “true lender,” such loans may be unenforceable, subject to rescission or otherwise impaired, we or other program participants may be subject to fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business and results of operations” below. In addition, loans originated by banks (which are exempt from certain state requirements), followed by the sale, assignment, or other transfer to non-banks of such loans or interests therein are subject to potential litigation and government enforcement claims based on the theory that transfers of loans from banks to non-banks do not transfer the ability to enforce contractual terms such as interest rates and fees which banks may charge, but non-banks may not. See “—If loans originated by us or loans originated by our bank partners were found to violate the laws of one or more states, whether at origination or after sale by the originating bank partner, loans facilitated through our platform may be unenforceable or otherwise impaired, we or other program participants may be subject to, among other things, fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business and results of operations” below. If we were subject to such litigation or enforcement, then any unfavorable results of pending or future legal proceedings may result in contractual damages, usury related claims, fines, penalties, injunctions, the unenforceability, rescission or other impairment of loans originated on our platform or other censure that could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Even if we adequately address the issues raised by an investigation or proceeding or successfully defend a third-party lawsuit or counterclaim, we may have to devote significant financial and management resources to address these issues, which could harm our business, financial condition, reputation and results of operations.
Recent financial, political and other events may increase the level of regulatory scrutiny on nonbank financial institutions. Regulatory bodies may enact new laws or promulgate new regulations or view matters or interpret laws and regulations differently than they have in the past, or commence investigations or inquiries into our business practices. Any such investigations or inquiries, whether or not accurate or warranted, or whether concerning us or one of our competitors, could negatively affect our brand and reputation and the overall market acceptance of and trust in our platform. Any of the foregoing could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may evaluate and potentially consummate acquisitions, which could require significant management attention, consume our financial resources, disrupt our business and adversely affect our financial results.
Our success will depend, in part, on our ability to grow our business. In some circumstances, we may determine to do so through the acquisition of complementary businesses and technologies rather than through internal development. The identification of suitable acquisition candidates can be difficult, time-consuming, and costly, and we may not be able to successfully complete identified acquisitions. In the future, we may acquire, assets or businesses. The risks we face in connection with acquisitions include:
• diversion of management time and focus from operating our business to addressing acquisition integration challenges;
• utilization of our financial resources for acquisitions or investments that may fail to realize the anticipated benefits;
• inability of the acquired technologies, products or businesses to achieve expected levels of revenue, profitability, productivity or other benefits;
• coordination of technology, product development and sales and marketing functions and integration of administrative systems;
• transition of the acquired company’s borrowers to our systems;
• retention of employees from the acquired company;
• regulatory risks, including maintaining good standing with existing regulatory bodies or receiving any necessary approvals, as well as being subject to new regulators with oversight over an acquired business;
• attracting financing;
• cultural challenges associated with integrating employees from the acquired company into our organization;
• the need to implement or improve controls, procedures and policies at a business that prior to the acquisition may have lacked effective controls, procedures and policies;
• potential write-offs of loans or intangibles or other assets acquired in such transactions that may have an adverse effect on our results of operations in a given period;
• liability for activities of the acquired company before the acquisition, including patent and trademark infringement claims, violations of laws, commercial disputes, tax liabilities and other known and unknown liabilities;
• assumption of contractual obligations that contain terms that are not beneficial to us, require us to license or waive intellectual property or increase our risk for liability; and
• litigation, regulatory criticisms, customer claims or other liabilities in connection with the acquired company.
Our failure to address these risks or other problems encountered in connection with any future acquisitions and investments could cause us to fail to realize the anticipated benefits of these acquisitions or investments, cause us to incur unanticipated liabilities and harm our business generally. Future acquisitions could also result in dilutive issuances of the combined company’s equity securities, the incurring of debt, contingent liabilities, amortization expenses or the write-off of goodwill, any of which could harm our financial condition.
Our business is subject to the risks of natural disasters and other catastrophic events, and to interruption by man-made problems, any of which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Significant natural disasters or other catastrophic events, such as earthquakes, fires, hurricanes, blizzards, or floods (many of which are becoming more acute and frequent as a result of climate change), or interruptions by strikes, crime, terrorism, epidemics, pandemics, cyber-attacks, computer viruses, internal or external system failures, telecommunications failures, power outages or increased risk of cybersecurity breaches due to a swift transition to remote work brought about by a catastrophic event, could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on the global economy and consumer confidence. In addition, it is possible that continued widespread remote work arrangements may have a negative impact on our operations, the execution of our business plans, the productivity and availability of key personnel and other employees necessary to conduct our business, or otherwise cause operational failures. There is no guarantee that we will be as effective while working remotely because our team is dispersed and employees may have less capacity to work due to increased personal obligations (such as childcare, eldercare, or caring for family members who become sick). Additionally, remote work arrangements may make it more difficult to scale our operations efficiently, as the recruitment, onboarding and training of new employees may be prolonged or delayed. We continue to operate using a hybrid remote working model. If a natural disaster, power outage, connectivity issue, or other event occurred that impacted our employees’ ability to work remotely, it may be difficult or, in certain cases, impossible, for us to continue our business for a substantial period of time. The increase in remote working may also result in privacy, data protection, data security, and fraud risks.
In addition, acts of war and other armed conflicts, disruptions in global trade, travel restrictions and quarantines, terrorism and other civil, political and geo-political unrest could cause disruptions in our business and lead to interruptions, delays or loss of critical data. Any of the foregoing risks may be further increased if our business continuity plans prove to be inadequate and there can be no assurance that both personnel and non-mission critical applications can be fully operational after a declared disaster within a defined recovery time. If our personnel, systems or data centers are impacted, we may suffer
interruptions and delays in our business operations. In addition, to the extent these events impact the ability of borrowers to timely repay their loans, our business could be negatively affected.
We may not maintain sufficient business interruption or property insurance to compensate us for potentially significant losses, including potential harm to our business that may result from interruptions in our ability to provide our financial products and services.
Risks Related to Our Financial Reporting and Risk Management
If our estimates or judgments relating to our critical accounting policies prove to be incorrect or financial reporting standards or interpretations change, our results of operations could be adversely affected.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States requires our management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported and disclosed in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. We base our estimates and assumptions on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. The results of these estimates form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets, liabilities, and equity, and the amount of revenue and expenses that are not readily apparent from other sources. Significant assumptions and estimates used in preparing our consolidated financial statements include those related to fair value determinations, stock-based compensation and consolidation of variable interest entities, as well as tax matters. Our results of operations may be adversely affected if our assumptions change or if actual circumstances differ from those in our assumptions, which could cause our results of operations to fall below the expectations of industry or financial analysts and investors, resulting in a decline in the trading price of the our securities.
Additionally, we regularly monitor our compliance with applicable financial reporting standards and review new pronouncements and drafts thereof that are relevant to us. As a result of new standards, or changes to existing standards, and changes in their interpretation, we might be required to change our accounting policies, alter our operational policies and implement new or enhance existing systems so that they reflect new or amended financial reporting standards, or we may be required to restate our published financial statements. Such changes to existing standards or changes in their interpretation may have an adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition, and profit and loss, or cause an adverse deviation from our revenue and operating profit and loss target, which may negatively impact our results of operations.
The determination of the fair values of our finance receivables portfolio involves unobservable inputs that can be highly subjective and may prove to be materially different than the actual economic outcome.
We began utilizing the fair value option for our finance receivables (other than SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables, which are carried at amortized cost) effective January 1, 2021. The fair values of our finance receivables are determined using discounted cash flow analyses that factor in estimated losses and prepayments over the estimated duration of the underlying assets. Loss and prepayment assumptions are determined using historical loss data and include appropriate consideration of recent trends and anticipated future performance. Valuations are highly dependent upon the reasonableness of our assumptions and estimates and the predictability of the relationships that drive the results of our valuation methodologies. A variety of factors including, but not limited to, estimated customer default rates, the timing of expected payments, utilization rates on our line of credit accounts, estimated costs to service the finance receivables, prepayment rates, discount rates, and valuations of comparable portfolios may ultimately affect the fair values of our loans and finance receivables. Modifications to our assumptions due to the passage of time and more information becoming available could result in material changes to our fair value calculations. These changes to fair value could adversely affect our results of operations. Additionally, under the fair value option, these changes are generally recorded directly to the income statement, which may make our financial statements less comparable to others in the industry that do not record their loan balances under the fair value option.
We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting and determined that our disclosure controls and procedures were ineffective as of December 31, 2023. If we are unable to remediate these material weaknesses, or if we identify additional material weaknesses in the future or otherwise fail to establish and maintain proper and effective internal control over financial reporting as a public company, our ability to produce accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, investors may lose confidence in our financial reporting and the trading price of our securities may decline.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time period specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that the information required to be disclosed by us in such reports is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer or persons performing similar functions, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
We have identified a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting relating to information technology general controls (“ITGCs”) associated with our financially relevant information systems. We determined that the Company’s user access controls designed to ensure appropriate segregation of duties, adequate restriction of users and privileged access to our financially relevant information systems were not operating effectively and that the Company’s user access control designed to ensure appropriate segregation of duties was also not designed effectively. Due to the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, we have also concluded our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2023.
As further described in “Item 9A. Controls and Procedures,” we are taking the necessary steps to remediate the material weakness and believe that compensating controls are in place and operating effectively to mitigate the risks associated with the identified material weakness as it is being remediated. However, as the reliability of the internal control process requires repeatable execution, the successful on-going remediation of this material weakness will require on-going review and evidence of effectiveness prior to concluding that the controls are effective. We cannot guarantee that these initiatives will ultimately have the intended effects. While we have implemented a variety of steps to remediate this material weakness, this material weakness will not be considered remediated until our remediation plan has been fully implemented, the applicable controls operate for a sufficient period of time, and we have concluded, through testing, that the newly implemented and enhanced controls are operating effectively.
Further, other weaknesses in our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting have been discovered in the past and may be discovered in the future. On December 6, 2022, the Audit Committee (the “Audit Committee”) of our Board of Directors concluded that certain of our prior financial statements should no longer be relied upon due to a misapplication of accounting guidance in connection with the Company's calculations of diluted earnings per share for such periods. In connection with such misapplication, management subsequently identified a deficiency in controls related to the design of its control to contemplate all the relevant authoritative accounting guidance when considering securities of a subsidiary that are convertible into its parent entity’s common stock in the calculation of earnings per share and further concluded such deficiency represented a material weakness. Our remediation plan included steps to design and implement new controls as well as expand training related to the accounting considerations for complex financing transactions, and we have since concluded that this material weakness has been remediated.
As a public company, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“the Sarbanes-Oxley Act”), and the rules and regulations of the applicable listing standards of the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”). We expect that the requirements of these rules and regulations will continue to increase our legal, accounting, and financial compliance costs, make some activities more difficult, time-consuming, and costly, and place significant strain on our personnel, systems, and resources.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires, among other things, that we maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. However, as an emerging growth company, an attestation of an independent registered public accounting firm will initially not be required. We are continuing to develop and refine our disclosure controls and other procedures. We are also continuing to improve our internal control over financial reporting. In order to maintain and improve the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting, we have expended, and anticipate that we will continue to expend, significant resources, including accounting-related costs, and significant management oversight. Our current controls and any new controls that we develop may become inadequate because of changes in conditions in our business. We may need to upgrade our legacy information technology systems; implement additional financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures; and hire additional accounting and finance staff. If we are unable to hire the additional accounting and finance staff necessary to comply with these requirements, we may need to retain additional outside consultants. If we or, if required, our independent registered public accounting firm, are unable to conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, investors may lose confidence in our financial reporting, which could negatively impact the price of our securities.
Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to compliance initiatives applicable to public companies, including compliance with Section 404 and the evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting within the prescribed timeframe, as well as the remediation of the material weakness that we have identified. We cannot assure you that there will not be additional material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting now or in the future and we may discover additional deficiencies in existing systems and controls that we may not be able to remediate in an efficient or timely manner. In the event that we are not able to remediate our existing material weakness, or if we identify additional deficiencies, we may be required to further restate our financial statements and our results of operations and financial condition could be negatively affected.
Any failure to maintain internal control over financial reporting could severely inhibit our ability to accurately report our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. If we are unable to conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if our independent registered public accounting firm determines that we have a material weakness in
our internal control over financial reporting, investors may lose confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports, the market price of our securities could decline, and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by the NYSE, the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Failure to remedy any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, or to implement or maintain other effective control systems required of public companies, could also restrict our future access to the capital markets.
We may face litigation and other risks as a result of the material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting.
As a result of the material weakness identified in our financial reporting, the restatement of certain of our financial statements, the change in accounting for our diluted earnings per share, and other matters, we face potential for litigation or other disputes which may include, among others, claims invoking the federal and state securities laws, contractual claims or other claims arising from the restatement of our financial statements, material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, and the preparation of our financial statements. We have no knowledge of any such litigation or dispute resulting from the material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. However, we can provide no assurance that litigation or disputes will not arise in the future. Any such litigation or dispute, whether successful or not, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If our risk management framework does not effectively identify and control our risks, we could suffer unexpected losses or be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our risk management processes and procedures seek to appropriately balance risk and return and mitigate risks. We have established processes and procedures intended to identify, measure, monitor and control the types of risk to which we are subject, including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, strategic risk, operational risk, cybersecurity risk and reputational risk. Credit risk is the risk of loss that arises when a loan obligor fails to meet the terms of a loan repayment obligation, the loan enters default, and if uncured results in financial loss of remaining principal and interest to the investor. Our exposure to credit risk mainly arises from our lending activities. Market risk is the risk of loss due to changes in external market factors, such as interest rates, asset prices, and foreign exchange rates. Liquidity risk is the risk that financial condition or overall safety and soundness are adversely affected by an inability, or perceived inability, to meet obligations (e.g., current and future cash flow needs) and support business growth. We actively monitor our liquidity position. Strategic risk is the risk from changes in the business environment, ineffective business strategies, improper implementation of decisions or inadequate responsiveness to changes in the business and competitive environment.
Our management is responsible for defining the priorities, initiatives, and resources necessary to execute our strategic plan, the success of which is regularly evaluated by our Board. Operational risk is the risk of loss arising from inadequate or failed internal processes, controls, people (e.g., human error or misconduct) or systems (e.g., technology problems), business continuity or external events (e.g., natural disasters), compliance, reputational, regulatory, or legal matters and includes those risks as they relate directly to us, fraud losses attributed to applications and any associated fines and monetary penalties as a result, transaction processing, or employees, as well as to third parties with whom we contract or otherwise do business. Operational risk is one of the most prevalent forms of risk in our risk profile. We strive to manage operational risk by establishing policies and procedures to accomplish timely and efficient processing, obtaining periodic internal control attestations from management, conducting internal process risk control self-assessments and audit reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls.
In order to be effective, among other things, our enterprise risk management capabilities must adapt and align to support any new product or loan features, capability, strategic development, or external change. Cybersecurity risk is the risk of a malicious technological attack intended to impact the confidentiality, availability, or integrity of our systems and data, including, but not limited to, sensitive client data. Our technology and information security teams rely on a layered system of preventive and detective technologies, practices, and policies to detect, mitigate, and neutralize cybersecurity threats. In addition, our information security team and third-party consultants regularly assesses our cybersecurity risks and mitigation efforts. Cyberattacks can also result in financial and reputational risk.
Reputational risk is the risk arising from possible negative perceptions of us, whether true or not, among our current and prospective members, counterparties, employees, and regulators. The potential for either enhancing or damaging our reputation is inherent in almost all aspects of business activity. We manage this risk through our commitment to a set of core values that emphasize and reward high standards of ethical behavior, maintaining a culture of compliance, and by being responsive to member and regulatory requirements.
Risk is inherent in our business, and therefore, despite our efforts to manage risk, there can be no assurance that we will not sustain unexpected losses. We could incur substantial losses and our business operations could be disrupted to the extent our business model, operational processes, control functions, technological capabilities, risk analyses, and business/product knowledge do not adequately identify and manage potential risks associated with our strategic initiatives. There also may be
risks that exist, or that develop in the future, that we have not appropriately anticipated, identified or mitigated, including when processes are changed or new products and services are introduced. If our risk management framework does not effectively identify and control our risks, we could suffer unexpected losses or be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our projections are subject to significant risks, assumptions, estimates and uncertainties. As a result, our projected revenues, market share, expenses and profitability may differ materially from our expectations.
We operate in a rapidly changing and competitive industry and our projections will be subject to the risks and assumptions made by management with respect to our industry. Operating results are difficult to forecast because they generally depend on a number of factors, including the competition we face and our ability to attract and retain bank partners. Additionally, our business may be affected by reductions in consumer borrowing, spending and investing from time to time as a result of a number of factors which may be difficult to predict. This may result in decreased revenue levels, and we may be unable to adopt measures in a timely manner to compensate for any unexpected shortfall in income. This inability could cause our operating results in a given quarter to be higher or lower than expected. These factors make creating accurate forecasts and budgets challenging and, as a result, we may fall materially short of our forecasts and expectations, which could cause the price of our securities to decline and investors to lose confidence in us.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property and Platform Development
It may be difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property rights, and we may not be able to ensure their protection.
Our ability to operate our platform depends, in part, upon our proprietary technology. We may be unable to protect our proprietary technology effectively, which would allow competitors to duplicate our machine learning models or machine learning enabled underwriting platform and adversely affect our ability to compete with them. We rely on a combination of copyright, trade secret, trademark laws and other rights, as well as confidentiality procedures, contractual provisions and our information security infrastructure to protect our proprietary technology, processes and other intellectual property. We do not currently have patent protection on our intellectual property. The steps we take to protect our intellectual property rights may be inadequate. For example, a third party may attempt to reverse engineer or otherwise obtain and use our proprietary technology without our consent. The pursuit of a claim against a third party for infringement of our intellectual property could be costly, and there can be no guarantee that any such efforts would be successful. Our failure to secure, protect and enforce our intellectual property rights could adversely affect our brand and adversely impact our business.
Our proprietary technology, including our machine learning models, may actually or may be alleged to infringe upon third-party intellectual property, and we may face intellectual property challenges from such other parties. We may not be successful in defending against any such challenges or in obtaining licenses to avoid or resolve any intellectual property disputes. If we are unsuccessful, such claim or litigation could result in a requirement that we pay significant damages or licensing fees, or we could in some circumstances be required to make changes to our business to avoid such infringement, which would negatively impact our financial performance. We may also be obligated to indemnify parties or pay substantial settlement costs, including royalty payments, in connection with any such claim or litigation and to modify applications or refund fees, which could be costly. Even if we were to prevail in such a dispute, any litigation regarding our intellectual property could be costly and time consuming and divert the attention of our management and key personnel from our business operations.
Moreover, it has become common in recent years for individuals and groups to purchase intellectual property assets for the sole purpose of making claims of infringement and attempting to extract settlements from companies such as ours. Even in instances where we believe that claims and allegations of intellectual property infringement against us are without merit, defending against such claims is time consuming and expensive and could result in the diversion of time and attention of our management and employees. In addition, although in some cases a third party may have agreed to indemnify us for such costs, such indemnifying party may refuse or be unable to uphold its contractual obligations. In other cases, our insurance may not cover potential claims of this type adequately or at all, and we may be required to pay monetary damages, which may be significant.
Furthermore, our technology may become obsolete or inadequate, and there is no guarantee that we will be able to successfully develop, obtain or use new technologies to adapt our models and systems to compete with other technologies as they develop. If we cannot protect our proprietary technology from intellectual property challenges, or if our technology becomes obsolete or inadequate, our ability to maintain our model and systems, facilitate loans or perform our servicing obligations on the loans could be adversely affected.
Any significant disruption in our platform could prevent us from processing loan applicants and servicing loans, reduce the effectiveness of our machine learning models and result in a loss of bank partners or borrowers.
In the event of a system outage or other event resulting in data loss or corruption, our ability to process loan applications, service loans or otherwise facilitate loans on our platform would be adversely affected. We also rely on facilities, components, and services supplied by third parties, including data center facilities and cloud storage services. We currently rely on multiple providers of cloud infrastructure services, including Salesforce and Amazon Web Services, for our platform. In the event that our service agreement with one or more third party providers is terminated, or there is a lapse of service, interruption of internet service provider connectivity or damage to the third party data centers, we could experience interruptions in access to our platform as well as delays and additional expense in the event we must secure alternative cloud infrastructure services. Any interference or disruption of our technology and underlying infrastructure or our use of third-party services could adversely affect our relationships with our bank partners and the overall user experience of our platform. Also, as our business grows, we may be required to expand and improve the capacity, capability and reliability of our infrastructure. If we are not able to effectively address capacity constraints, upgrade our systems as needed and continually develop our technology and infrastructure to reliably support our business, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Additionally, in the event of damage or interruption, our insurance policies may not adequately compensate us for any losses incurred. Our disaster recovery plan has not been tested under actual disaster conditions, and we may not have sufficient capacity to recover all data and services in the event of an outage or other event resulting in data loss or corruption. These factors could prevent us from processing or posting payments on the loans, damage our brand and reputation, divert our employees’ attention, subject us to liability and cause borrowers to abandon our business, any of which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our platform and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical, and if our software contains undetected errors, our business could be adversely affected.
Our platform and internal systems rely on software that is highly technical and complex. In addition, our platform and internal systems depend on the ability of such software to store, retrieve, process and manage high volumes of data. The software on which we rely has contained, and may now or in the future contain, undetected errors or bugs. Some errors may only be discovered after the code has been released for external or internal use. Errors or other design defects within the software on which we rely may result in failure to accurately predict a loan applicant’s creditworthiness, failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations, approval of sub-optimally priced loans, incorrectly displayed interest rates to applicants or borrowers, or incorrectly charged interest to borrowers or fees to bank partners or capital sources, failure to detect fraudulent activity on our platform, a negative experience for consumers or bank partners, delayed introductions of new features or enhancements, or failure to protect borrower data or our intellectual property. Any errors, bugs or defects discovered in the software on which we rely could result in harm to our reputation, loss of consumers or bank partners, increased regulatory scrutiny, fines or penalties, loss of revenue or liability for damages, any of which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Some aspects of our business processes include open source software, and any failure to comply with the terms of one or more of these open source licenses could negatively affect our business.
We incorporate open source software into processes supporting our business. Such open source software may include software covered by licenses like the GNU General Public License and the Apache License. The terms of various open source licenses have not been interpreted by U.S. courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that limits our use of the software, inhibits certain aspects of our systems and negatively affects our business operations.
Some open source licenses contain requirements that we make source code available at no cost for modifications or derivative works we create based upon the type of open source software we use.
We may face claims from third parties claiming ownership of, or demanding the release or license of, such modifications or derivative works (which could include our proprietary source code) or otherwise seeking to enforce the terms of the applicable open source license. If portions of our proprietary models are determined to be subject to an open source license, or if the license terms for the open source software that we incorporate change, we could be required to publicly release the affected portions of our source code, re-engineer all or a portion of our model or change our business activities, any of which could negatively affect our business operations and potentially our intellectual property rights. If we were required to publicly disclose any portion of our proprietary models, it is possible we could lose the benefit of trade secret protection for our models.
In addition to risks related to license requirements, the use of open source software can lead to greater risks than the use of third-party commercial software, as open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or controls on the origin of the software. Use of open source software may also present additional security risks because the public availability of such software may make it easier for hackers and other third parties to determine how to breach our website and systems that rely on open source software. Many of the risks associated with the use of open source software cannot be eliminated and could adversely affect our business.
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
We rely on strategic relationships with loan aggregators to attract applicants to our platform, and if we cannot maintain effective relationships with loan aggregators or successfully replace their services, or if loan aggregators begin offering competing products, our business could be adversely affected.
A significant number of consumers that apply for a loan on Opploans.com learn about and access Opploans.com through the website of a loan aggregator, typically with a hyperlink from such loan aggregator’s website to a landing page on our website. For example, in 2021, 2022 and 2023, approximately 18.5%, 22.8% and 21.3%, respectively, of our net loan issuances were derived from traffic from our top three loan aggregators. Our agreements with these loan aggregators generally provide that either party may terminate the agreement immediately upon a material breach of any provision of the agreement or at any time, with or without cause, by providing advance written notice. Even during the term of the agreements, loan aggregators may not be required to display offers from Opploans.com or prohibited from working with our competitors or from offering competing services. There is also no assurance that our top loan aggregators will continue to contract with us on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
While we are planning to move towards more direct acquisition channels, we anticipate that we will continue to depend in significant part on relationships with loan aggregators to maintain and grow our business. Our current agreements with these loan aggregators do not require them to display offers from lenders on Opploans.com nor prohibit them from working with our competitors or from offering competing services. Further, there is no assurance that a loan aggregator will renew its contract with us on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Our competitors may be effective in providing incentives to loan aggregators to favor their products or services or in reducing the volume of loans facilitated through our platform. Loan aggregators may not perform as expected under our agreements with them, and we may have disagreements or disputes with them, which could adversely affect our brand and reputation. If we cannot successfully enter into and maintain effective strategic relationships with loan aggregators, our business could be adversely affected.
In addition, the limited information such loan aggregators collect from applicants does not always allow us to offer rates to applicants that we would otherwise be able to through direct applicant traffic to Opploans.com. Typically, the rates offered to borrowers who come to Opploans.com directly are lower and more competitive than those rates offered through aggregators. In the event we do not successfully optimize direct traffic, our ability to attract borrowers would be adversely affected.
Such loan aggregators also face litigation and regulatory scrutiny for their part in the consumer lending ecosystem, and as a result, their business models may require fundamental change or may not be sustainable in the future. For example, loan aggregators are increasingly required to be licensed as loan brokers or lead generators in many states, subjecting them to increased regulatory supervision and more stringent business requirements. While we require loan aggregators to make certain disclosures in connection with our bank partners’ offers and restrict how loan aggregators may display such loan offers, loan aggregators may nevertheless alter or even remove these required disclosures without notifying us, which may result in liability to us. Further, we do not have control over any content on loan aggregator websites, and it is possible that our brand and reputation may be adversely affected by being associated with such content. An unsatisfied borrower could also seek to bring claims against us based on the content presented on a loan aggregator’s website. Such claims could be costly and time consuming to defend and could distract management’s attention from the operation of the business.
Our proprietary machine learning models rely in part on the use of loan applicant and borrower data and other third-party data, and if we lose the ability to use such data, or if such data contain inaccuracies, our business could be adversely affected.
We rely on our proprietary models, which are statistical models built using a variety of data-sets. Our models rely on a wide variety of data sources, including data collected from applicants and borrowers, credit bureau data and our credit experience gained through monitoring the payment performance of borrowers over time. Under our agreements with our bank partners, we receive licenses to use data collected from loan applicants and borrowers. If we are unable to access and use data collected from applicants and borrowers, data received from credit bureaus, repayment data collected as part of our loan servicing activities, or other third-party data used in our models, or our access to such data is limited, our ability to accurately evaluate potential borrowers, detect fraud and verify applicant data would be compromised. Any of the foregoing could negatively impact the accuracy of our pricing decisions, the degree of automation in our loan application process and the volume of loans facilitated on our platform.
Third-party data sources on which we rely include the consumer reporting agencies regulated by the CFPB and other alternative data sources. Such data is electronically obtained from third parties and used in our models to price applicants and in our fraud model to verify the accuracy of applicant-reported information. Data from national credit bureaus and other consumer reporting agencies and other information that we receive from third parties about an applicant or borrower may be inaccurate or
may not accurately reflect the applicant or borrower’s creditworthiness for a variety of reasons, including inaccurate reporting by creditors to the credit bureaus, errors, staleness or incompleteness. For example, loan applicants’ credit scores may not reflect such applicants’ actual creditworthiness because the credit scores may be based on outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate consumer reporting data, including, as a consequence of us utilizing credit reports for a specific period of time after issuance before such reports are deemed to be outdated. Similarly, the data taken from an applicant’s credit report may also be based on outdated, incomplete or inaccurate consumer reporting data. Although we use numerous third-party data sources and multiple credit factors within our proprietary models, which helps mitigate this risk, it does not eliminate the risk of an inaccurate individual report.
Further, although we attempt to verify the income, employment and education information provided by certain selected applicants, we cannot guarantee the accuracy of applicant information. Our fraud model relies in part on data we receive from a number of third-party verification vendors, data collected from applicants, and our experience gained through monitoring the performance of borrowers over time. Information provided by borrowers may be incomplete, inaccurate or intentionally false. Applicants may also misrepresent their intentions for the use of loan proceeds. We do not verify or confirm any statements by applicants as to how loan proceeds are to be used after loan funding. If an applicant supplied false, misleading or inaccurate information and our fraud detection processes do not flag the application, repayments on the corresponding loan may be lower, in some cases significantly lower, than expected, leading to losses for the bank partner or investor.
In addition, if third party data used to train and improve our models is inaccurate, or access to such third-party data is limited or becomes unavailable to us, our ability to continue to improve our models would be adversely affected. Any of the foregoing could result in sub-optimally and inefficiently priced loans, incorrect approvals or denials of loans, or higher than expected loan losses, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on third-party vendors and if such third parties do not perform adequately or terminate their relationships with us, our costs may increase and our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our success depends in part on our relationships with third-party vendors. In some cases, third-party vendors are one of a limited number of sources. For example, we rely on national consumer reporting agencies, such as Clarity Services, Inc., a part of Experian, for a large portion of the data used in our models. In addition, we rely on third-party verification technologies and services that are critical to our ability to maintain a high level of automation on our platform. In addition, because we are not a bank, we cannot belong to or directly access the Automated Clearing House (“ACH”) payment network. As a result, we rely on one or more banks with access to the ACH payment network to process collections on loans facilitated on our platform. See the section titled “Risk Factors—Regulators and payment processors are scrutinizing certain online lenders’ access to the ACH system to disburse and collect loan proceeds and repayments, and any interruption or limitation on our ability to access this critical system would materially adversely affect our business.” Most of our vendor agreements are terminable by either party without penalty and with little notice. If any of our third-party vendors terminates its relationship with us or refuses to renew its agreement with us on commercially reasonable terms, we would need to find an alternate provider, and may not be able to secure similar terms or replace such providers in an acceptable timeframe. We also rely on other software and services supplied by vendors, such as communications, analytics and internal software, and our business may be adversely affected to the extent such software and services do not meet our expectations, contain errors or vulnerabilities, are compromised or experience outages. Any of these risks could increase our costs and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Further, any negative publicity related to any of our third-party partners, including any publicity related to quality standards or safety concerns, could adversely affect our reputation and brand, and could potentially lead to increased regulatory or litigation exposure.
We incorporate technology from third parties into our platform. We cannot be certain that our licensors are not infringing the intellectual property rights of others or that the suppliers and licensors have sufficient rights to the technology in all jurisdictions in which we may operate. Some of our license agreements may be terminated by our licensors for convenience. If we are unable to obtain or maintain rights to any of this technology because of intellectual property infringement claims brought by third parties against our suppliers and licensors or against us, or if we are unable to continue to obtain the technology or enter into new agreements on commercially reasonable terms, our ability to develop our platform containing that technology could be severely limited and our business could be harmed. Additionally, if we are unable to obtain necessary technology from third parties, we may be forced to acquire or develop alternate technology, which may require significant time and effort and may be of lower quality or performance standards. This would limit and delay our ability to provide new or competitive loan products or service offerings and increase our costs. If alternate technology cannot be obtained or developed, we may not be able to offer certain functionality as part of our platform and service offerings, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Failure by our third-party vendors or our failure to comply with legal or regulatory requirements or other contractual requirements could have an adverse effect on our business.
We have significant vendors that provide us with a number of services to support our platform. If any third-party vendors fail to comply with applicable laws and regulations, fail to comply with their contractual requirements, including failure to maintain adequate systems addressing privacy and data protection and security, or suffer disruptions in, or otherwise fail to provide, contracted services, we could be subject to regulatory enforcement actions or litigation and suffer economic and reputational harm that could harm our business. Further, we may incur significant costs to resolve any such failures to comply with applicable laws and regulations or contractual requirements or to resolve any disruptions in service or failure to provide contracted services, which could adversely affect our business.
The CFPB and each of the prudential bank regulators that supervise our bank partners have issued guidance stating that institutions under their supervision may be held responsible for the actions of the companies with which they contract. As a service provider to those supervised entities, we must ensure we perform our obligations in accordance with applicable laws and contractual requirements and have implemented an adequate vendor management program for our own vendors. We or our bank partners could be adversely impacted to the extent we or our vendors fail to comply with the legal requirements applicable to the particular products or services being offered. Our use of third-party vendors is subject to increasing regulatory attention.
The CFPB and the prudential bank regulators have also issued regulatory guidance that has focused on the need for financial institutions to perform increased due diligence and ongoing monitoring of third-party vendor relationships, thus increasing the scope of management involvement in connection with using third-party vendors. Moreover, if regulators conclude that we or our bank partners have not met the standards for oversight of our third-party vendors or their third-party vendors, our bank partners could terminate their relationship with us or we or our bank partners could be subject to enforcement actions, civil monetary penalties, supervisory orders to cease and desist or other remedial actions, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, as a service provider to banks, we are subject to examination and enforcement authority of the prudential bank regulators that supervise our bank partners under the Bank Service Company Act. If we fail to comply with requirements applicable to us by applicable law or contract, our bank partners could terminate their relationship with us or we or our bank partners could be subject to enforcement actions, civil monetary penalties, supervisory orders to cease and desist or other remedial actions, which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If loans originated by us or loans originated by our bank partners were found to violate the laws of one or more states, whether at origination or after sale of participation rights by the originating bank partner, loans facilitated through our platform may be unenforceable or otherwise impaired, we or other program participants may be subject to, among other things, fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business and results of operations.
When establishing the interest rates and fees (including the amounts of certain fees constituting interest under federal banking laws related to interest rate exportation, such as origination fees, late fees and non-sufficient funds fees) that are charged to borrowers on loans originated through our platform and how such interest rates and fees are structured, our bank partners rely on certain authority under federal law to export the interest rate and fees permitted by the state where each bank partner is located to borrowers in other states. Further, certain of our bank partners and capital sources rely on the ability of subsequent holders of loans to continue charging such rates and fees and to enforce other contractual terms that the applicable bank partners was permitted under federal and applicable state banking laws to charge and enforce at the time of origination following such subsequent holder’s acquisition of the loans. The current annual percentage rates of the installment loans facilitated through our platform, for the year ended December 31, 2023 typically range from approximately 59% to 160%. In some states, the interest rates of certain loans facilitated on our platform exceed the maximum interest rate permitted for consumer loans made by non-bank lenders to borrowers residing in, or that have nexus to, such states. In addition, the rate structures for loans facilitated on our platform may not be permissible in all states for non-bank lenders and/or the amount or structures of certain fees charged in connection with loans facilitated on our platform may not be permissible in all states for non-bank lenders.
Usury, fee, and disclosure related claims involving loans facilitated on our platform may be raised in multiple ways. Program participants may face litigation, government enforcement or other challenge, for example, based on claims that bank lenders did not establish loan terms that were permissible in the state they were located or did not correctly identify the home or host state in which they were located for purposes of interest exportation authority under federal law. Alternatively, we or our capital sources may face litigation, government enforcement, or other challenge, for example, based on claims that rates and fees were lawful at origination and through any period during which the originating bank partner retained the loan and interests therein, but that subsequent purchasers were unable to enforce the loan pursuant to its contracted-for terms, or that certain disclosures were not provided at origination because while such disclosures are not required of banks they may be required of non-bank lenders.
In Madden v. Midland Funding, LLC, 786 F.3d 246 (2d Cir. 2015), cert. denied, 136 S.Ct. 2505 (June 27, 2016), for example, the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit held that the non-bank purchaser of defaulted credit card
debt could not rely on preemption standards under the National Bank Act applicable to the originator of such debt in defense of usury claims. Madden addressed circumstances under which a defaulted extension of credit under a consumer credit card account was assigned, following default, to a non-bank debt buyer that then attempted to collect the loan and to continue charging interest at the contracted-for rate. The debtor filed a suit claiming, among other claims, that the rate charged by the non-bank collection entity exceeded the usury rates allowable for such entities under New York usury law. Reversing a lower court decision, the Second Circuit held that preemption standards under the National Bank Act applicable to the bank that issued the credit card were not available to the non-bank debt buyer as a defense to usury claims. Following denial of a petition for rehearing by the Second Circuit, the defendant sought review by the United States Supreme Court. Following the United States Supreme Court’s request that the Solicitor General file a brief setting forth the government’s position on whether the Supreme Court should hear the case in 2016, the Solicitor General filed its brief recommending that the petition for a writ of certiorari be denied for certain vehicle suitability reasons, although the Solicitor General’s brief concluded that the Second Circuit’s decision was substantively incorrect as a matter of law. The Supreme Court denied certiorari on June 27, 2016, such that the Second Circuit’s decision remains binding on federal courts in the Second Circuit (which include all federal courts in New York, Connecticut, and Vermont). Upon remand to the District Court for consideration of additional issues, including whether a choice of law provision in the debtor’s credit card agreement was enforceable to displace New York usury law and class certification, the parties settled the matter in 2019.
The scope and validity of the Second Circuit’s Madden decision remain subject to challenge and clarification. For example, the Colorado Administrator of the Colorado Uniform Consumer Credit Code, or the UCCC, reached a settlement with respect to complaints against two digital specialty finance platforms whose business includes the use of bank partners and sale of loans to investors. The complaints included, among other claims, allegations, grounded in the Second Circuit’s Madden decision, that the rates and fees for certain loans could not be enforced lawfully by non-bank purchasers of bank-originated loans. Under the settlement, these banks and nonbank partners committed to, among other things, limit the annual percentage rates, or APR, on loans to Colorado consumers to 36% and take other actions. The nonbanks also agreed to obtain and maintain a Colorado lending license. In Colorado, this settlement might provide a helpful model for what constitutes an acceptable bank partnership model. However, the settlement may also invite other states to initiate their own actions, and set their own regulatory standards through enforcement.
As noted above, federal prudential regulators have also taken actions to address the Madden decision. On May 29, 2020, the OCC issued a final rule clarifying that, when a national bank or savings association sells, assigns, or otherwise transfers a loan, interest permissible before the transfer continues to be permissible after the transfer. That rule took effect on August 3, 2020. Similarly, the FDIC finalized on June 25, 2020 its 2019 proposal declaring that the interest rate for a loan is determined when the loan is made, and will not be affected by subsequent events. On July 29, 2020, California, New York and Illinois filed suit in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California to enjoin enforcement of the OCC rule (Case No. 20-CV-5200) and, similarly in the same court, on August 20, 2020 California, Illinois, Massachusetts, Minnesota, New Jersey, New York, North Carolina, and the District of Columbia sought to enjoin enforcement of the FDIC rule (Case No. 20-CV-5860), in each case related to permissible interest rates post-loan transfer on the grounds that the OCC and FDIC exceeded their authority when promulgating those rules. In 2022, the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California dismissed these challenges; however, there can be no assurance that these regulations will not be challenged in the future.
There are factual distinctions between our program and the circumstances addressed in the Second Circuit’s Madden decision, as well as the circumstances in the Colorado UCCC settlement and similar cases. As noted above, there are also bases on which the Madden decision’s validity might be subject to challenge or the Madden decision may be addressed by federal regulation or legislation. Nevertheless, there can be no guarantee that a Madden-like claim will not be brought successfully against us or our program participants.
If a borrower or any state agency were to successfully bring a claim against us, our bank partners or our capital sources for a state usury law or fee restriction violation and the rate or fee at issue on the loan was impermissible under applicable state law, we, our bank partners or our capital sources may face various commercial and legal repercussions, including that such parties would not receive the total amount of interest expected, and in some cases, may not receive any interest or principal, may hold loans that are void, voidable, rescindable, or otherwise impaired or may be subject to monetary, injunctive or criminal penalties. Were such repercussions to apply to us, we may suffer direct monetary loss or may be a less attractive candidate for bank partners or capital sources to enter into or renew relationships; and were such repercussions to apply to our bank partners, such parties could be discouraged from using our platform. We may also be subject to payment of damages in situations where we agreed to provide indemnification, as well as fines and penalties assessed by state and federal regulatory agencies. Litigation or enforcement decisions might also affect our decision to continue operating in any particular state.
If loans facilitated through our platform for one or more bank partners were subject to successful challenge that the bank partner was not the “true lender,” such loans may be unenforceable, subject to rescission or otherwise impaired, we or other program participants may be subject to fines, judgments and penalties, and/or our commercial relationships may suffer, each of which would adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Loans facilitated on our platform by our bank partners are originated in reliance on the fact that our bank partners are the “true lenders” for such loans. That true lender status determines various loan program details and how we operate our business, including that we do not hold licenses required solely for being the party that extends credit to consumers, and that loans facilitated on our platform by our bank partners may involve interest rates and structures (and certain fees and fees structures) permissible at origination only because the loan terms and lending practices are permissible only when the lender is a bank, and/or the disclosures provided to borrowers would be accurate and compliant only if the lender is a bank. Many state consumer financial regulatory requirements, including usury restrictions (other than the restrictions of the state in which a bank partner originating a particular loan is located) and many licensing requirements and substantive requirements under state consumer credit laws, are treated as inapplicable to loans facilitated on our platform by our bank partners based on principles of federal preemption or express exemptions provided in relevant state laws for certain types of financial institutions or loans they originate.
Certain recent litigation and regulatory enforcement has challenged, or is currently challenging, the characterization of bank partners as the “true lender” in connection with programs involving origination and/or servicing relationships between a bank partner and specialty finance platforms or program manager. As noted above, the Colorado Administrator has entered into a settlement agreement with certain banks and nonbanks that addresses this true lender issue. Specifically, the settlement agreement sets forth a safe harbor indicating that a bank that is a party to the settlement may lend in excess of Colorado’s usury rate for nonbanks if certain specific terms and conditions are met. Further, States have enacted, and additional states may enact, laws that seek to deem certain entities to be the lender of a loan and prohibit any evasion or circumvention of state laws regulating consumer lending. For example, in 2021 Maine adopted a law that, among other things, may deem an entity to be the lender of a loan if it (a) holds, acquires or maintains the “predominant economic interest in the loan” or (b) markets, arranges or facilitates the loan and holds the right to purchase the loan or interest in the loan, or (c) based on the totality of the circumstances, appears to be the lender, and the transaction is structured to evade certain statutory requirements. States and consumers could bring lawsuits challenging whether our bank partners that originated through our platform are the “true lenders” and whether the interest rates, fees, and structures of loans originated through our platform comply with federal and state law. For example, in April 2021, the Washington, DC Attorney General filed a lawsuit against us for allegedly deceptively marketing high-cost loans with interest rates above the Washington, DC usury cap. The usury claim was based on an allegation that we and not our partner bank, FinWise, was the “true lender” of these loans, and we were therefore in violation of the district’s usury laws. FinWise has ceased originating loans in Washington D.C. and as a result, we have ceased doing business in Washington, DC. In November 2021, we entered into a Consent Judgment and Order (“Settlement”) with the DC Attorney General to resolve all matters in dispute related to this lawsuit. We deny the allegations in the lawsuit and deny that we violated any law or engaged in any deceptive or unfair practices. The lawsuit was resolved to avoid the expense of protracted litigation, which is often expensive, time-consuming, disruptive to our operations, distracting to management and may involve payment of damages. As part of the settlement, we agreed to, among other things, refrain from certain business activities in the District of Columbia, pay $250,000 to the District of Columbia and provide refunds to certain District of Columbia consumers.
We note that the OCC on October 27, 2020, issued a final rule to address the “true lender” issue for lending transactions involving a national bank. For certain purposes related to federal banking law, including the ability of a national bank to “export” interest-related requirements from the state from which they lend, the rule would treat a national bank as the “true lender” if it is named as the lender in the loan agreement or funds the loan. In June 2021, Congress utilized a procedure under the Congressional Review Act to repeal the OCC’s “true lender” rule. Repeal of the “true lender” rule under the CRA prevents the OCC from issuing any substantially similar rule unless subsequently authorized by law to do so. The OCC rule did not apply to state-chartered banks and there can be no assurance that the FDIC will issue a similar rule applicable to state-chartered banks. While we do not anticipate any material changes to our business model as a result of the repeal of the OCC’s “true lender” rule because (i) the banks with whom we partner are state chartered, FDIC regulated banks and are the lenders under such loans, and (ii) the repeal of the OCC’s “true lender” rule does not have direct implications on the rules finalized by the OCC and FDIC last year around the continued validity of the “valid when made doctrine,” we cannot be certain that the repeal of such rule, or the restrictions on the OCC implementing a similar rule without statutory approval, will not have a material effect on our business or our industry.
We, our bank partners and similarly situated parties could become subject to challenges like that presented by the Colorado settlement and, if so, we could face penalties and/or loans facilitated on our platform by our bank partners may be void, voidable, or otherwise impaired in a manner that may have adverse effects on our operations (directly, or as a result of adverse impact on our relationships with our bank partners, institutional investors or other commercial counterparties).
There can be no assurance that the Colorado Administrator or other regulators or customers will not make assertions similar to those made in its present actions with respect to the loans facilitated by our platform in the future. It is also possible that other state agencies or regulators could make similar assertions. If a court or a state or federal enforcement agency were to determine that we, rather than our bank partners, are the “true lender” for loans originated on our platform by our bank partners, and if for this reason (or any other reason) the loans were deemed subject to and in violation of certain state consumer finance
laws, we could be subject to fines, damages, injunctive relief (including required modification or discontinuation of our business in certain areas) and other penalties or consequences, and the loans could be rendered void or unenforceable in whole or in part, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If we are unable to successfully challenge the position of the DFPI that we are subject to the CFL, our bank partners’ ability to originate loans in California could suffer, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In February 2022, the DFPI informed us that the commissioner of the DFPI had taken the position that we are the “true lenders” for certain loans (“Program Loans”) originated by our federally-insured state-chartered bank partners serviced through the OppFi technology and service platform pursuant to a contractual arrangement with each such bank (“Program”), and as such we would be subject to the CFL, which would apply an interest rate cap of 36% to certain of the Program Loans. On March 7, 2022, we filed a lawsuit seeking a declaration that the interest rate caps set forth in the CFL do not apply to Program Loans and injunctive relief against the commissioner of the DFPI, preventing the DFPI from enforcing interest rate caps under the CFL against us based on activities related to the Program.
While we believe that Program Loans made through the OppFi platform pursuant to the Program are constitutionally and statutorily exempt from the CFL because the Program Loans are made by state-chartered banks located in Utah and because federal law permits state-chartered banks to export the interest rates allowed in their chartering state to any other state in the country, we cannot assure you that we will prevail in our action against the DFPI or that we will not otherwise be unable to prevent the DFPI from enforcing interest rate caps under the CFL against us. As of December 31, 2023, more than 5% of our finance receivables portfolio was related to loans originated in the State of California, and if we become subject to the CFL interest rate cap of 36%, our bank partners’ ability to originate Program Loans in California could suffer. This could have an adverse effect on our relationships with our bank partners and financing sources, who may choose not to finance our purchase of participation interests in loans originated by our bank partners on our platform in California, and our ability to maintain and grow our finance receivables portfolio, and potentially subject us to fines damages, and other penalties or consequences, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Regulators and payment processors are scrutinizing certain online lenders’ access to the ACH system to disburse and collect loan proceeds and repayments, and any interruption or limitation on our ability to access this critical system would materially adversely affect our business.
When making loans, we typically use the ACH system to deposit loan proceeds into borrowers’ bank accounts. This includes loans originated by our bank partners. We also depend on the ACH system to collect amounts due on loans by withdrawing funds from borrowers’ bank accounts when the borrower has provided authorization to do so. ACH transactions are processed through banks and may involve other payment processors, and if these banks or payment processors cease to provide ACH processing services or are not allowed to do so, we would have to materially alter, or possibly discontinue, some or all of our business if alternative ACH processors or other payment mechanisms are not available.
In the past, heightened regulatory scrutiny by the U.S. Department of Justice, the FDIC and other regulators has caused some banks and ACH payment processors to cease doing business with consumer lenders who are operating legally, without regard to whether those lenders are complying with applicable laws, simply to avoid the risk of heightened scrutiny or even litigation. These actions have reduced the number of banks and payment processors that provide ACH payment processing services to companies such as ours, could conceivably make it increasingly difficult to find bank partners and payment processors in the future and/or could lead to significantly increased costs for these services. If we are unable to maintain access to needed services on favorable terms, we would have to materially alter, or possibly discontinue, some or all of our business if alternative processors are not available.
If we lost access to the ACH system because our payment processor was unable or unwilling to access the ACH system on our behalf, we would experience a significant reduction in borrower loan payments. Although we would notify borrowers that they would need to make their loan payments via physical check, debit card or other method of payment a large number of borrowers would likely go into default because they are expecting us to arrange automated payment processing through ACH system. Similarly, if regulatory changes limited our access to the ACH system or reduced the number of times ACH transactions could be re-presented, we would experience higher losses.
Our offshore service providers involve inherent risks which could result in harm to our business.
We have and may in the future engage outsourcing partners that provide offshore customer-facing activities. These international activities are subject to inherent risks that are beyond our control, including:
•risks related to government regulation or required compliance with local laws;
•local licensing and reporting obligations;
•difficulties in developing, staffing and simultaneously managing a number of varying foreign operations as a result of distance, language and cultural differences;
•different, uncertain, overlapping or more stringent local laws and regulations;
•political and economic instability, tensions, security risks and changes in international diplomatic and trade relations;
•state or federal regulations that restrict offshoring of business operational functions or require offshore partners to obtain additional licenses, registrations or permits to perform services on our behalf;
•geopolitical events, including natural disasters, public health issues, epidemics or pandemics, acts of war, and terrorism;
•the impact of, and response of local governments to, the COVID-19 pandemic;
•compliance with applicable U.S. laws and foreign laws related to consumer protection, intellectual property, privacy, data security, corruption, money laundering, and export/trade control;
•misconduct by our outsourcing partners and their employees or even unsubstantiated allegations of misconduct;
•risks due to lack of direct involvement in hiring and retaining personnel; and
•potentially adverse tax developments and consequences.
Violations of the complex foreign and U.S. laws, rules and regulations that apply to our international operations and offshore activities of our service providers may result in heightened regulatory scrutiny, fines, criminal actions or sanctions against us, our directors, our officers or our employees, as well as restrictions on the conduct of our business and reputational damage.
Risks Related to Our Regulatory Environment
Litigation, regulatory actions and compliance issues could subject us to significant fines, penalties, judgments, remediation costs and/or requirements resulting in increased expenses.
In the ordinary course of business, we have been named as a defendant in various legal actions, including class action lawsuits and other litigation. Generally, this litigation arises from the dissatisfaction of a consumer with the products or services offered on our platform. All such legal actions are inherently unpredictable and, regardless of the merits of the claims, litigation is often expensive, time-consuming, disruptive to our operations, and distracting to management. In addition, certain actions may include claims for indeterminate amounts of damages. Our involvement in any such matter also could cause significant harm to our or our bank partners’ reputations and divert management attention from the operation of our business, even if the matters are ultimately determined in our favor. If resolved against us, legal actions could result in significant verdicts and judgments, injunctive relief, equitable relief, and other adverse consequences that may affect our financial condition and how we operate our business, including our decision to continue operating in certain states.
In addition, a number of participants in the consumer financial services industry, ourselves included, have been the subject of putative class action lawsuits, state attorney general actions and other state regulatory enforcement actions and federal regulatory enforcement actions, including actions relating to alleged unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices, violations of state licensing and lending laws, including state usury and disclosure laws and allegations of noncompliance with various state and federal laws and regulations relating to originating, servicing and collecting consumer finance loans and other consumer financial services and products. The current regulatory environment of increased regulatory compliance efforts and enhanced regulatory enforcement has resulted in us undertaking significant time-consuming and expensive operational and compliance improvement efforts, and in some cases litigation to assert our rights under existing laws, which may delay or preclude our or our bank partners’ ability to provide certain new products and services. There is no assurance that these regulatory matters or other factors will not, in the future, affect how we conduct our business and, in turn, have a material adverse effect on our business. In particular, legal proceedings brought under state consumer protection statutes or under several of the various federal consumer financial protection statutes may result in a separate fine assessed for each statutory and regulatory violation or substantial damages from class action lawsuits, potentially in excess of the amounts we earned from the underlying activities.
Some of our agreements used in the course of our business include arbitration clauses. If our arbitration agreements were to become unenforceable for any reason, we could experience an increase to our consumer litigation costs and exposure to potentially damaging class action lawsuits, with a potential material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We contest our liability and the amount of damages, as appropriate, in each pending matter. The outcome of pending and future matters could be material to our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially adversely affect our business.
In addition, from time to time, through our operational and compliance controls, we identify compliance issues that require us to make operational changes and, depending on the nature of the issue, result in financial remediation to impacted borrowers. These self-identified issues and voluntary remediation payments could be significant, depending on the issue and the number of borrowers impacted, and could generate litigation or regulatory investigations that subject us to additional risk.
We are subject to or facilitate compliance with a variety of federal, state, and local laws, including those related to consumer protection, privacy and loan financings, and if we fail to comply with such laws, our business could be adversely affected.
We must comply with regulatory regimes or facilitate compliance with regulatory regimes on behalf of our bank partners that are independently subject to federal and/or state oversight by bank regulators, including those applicable to our referral and marketing services, consumer credit transactions, loan servicing and collection activities and the purchase and sale of whole loans and other related transactions. Certain state laws generally regulate interest rates and other charges and require certain disclosures. In addition, other federal and state laws may apply to the origination, servicing and collection of loans originated on our platform or the purchase and sale of whole loans or participation rights. In particular, certain laws, regulations and rules we or our bank partners are subject to include:
• state lending laws and regulations that require certain parties to hold licenses or other government approvals or filings in connection with specified activities, and impose requirements related to loan disclosures and terms, fees and interest rates, credit discrimination, credit reporting, servicemember relief, debt collection, repossession, unfair or deceptive business practices and consumer protection, as well as other state laws relating to privacy, information security, conduct in connection with data breaches and money transmission;
• the Truth-in-Lending Act and Regulation Z promulgated thereunder, and similar state laws, which require certain disclosures to borrowers regarding the terms and conditions of their loans and credit transactions, require creditors to comply with certain lending practice restrictions, limit the ability of a creditor to impose certain loan terms and impose disclosure requirements in connection with credit card origination;
• the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and Regulation B promulgated thereunder, and similar state fair lending laws, which prohibit creditors from discouraging or discriminating against credit applicants on the basis of race, color, sex, age, religion, national origin, marital status, the fact that all or part of the applicant’s income derives from any public assistance program or the fact that the applicant has in good faith exercised any right under the federal Consumer Credit Protection Act;
• the Fair Credit Reporting Act and Regulation V promulgated thereunder, imposes certain obligations on users of consumer reports and those that furnish information to consumer reporting agencies, including obligations relating to obtaining consumer reports, using consumer reports, taking adverse action on the basis of information from consumer reports, addressing risks of identity theft and fraud and protecting the privacy and security of consumer reports and consumer report information;
• Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, which prohibits unfair and deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce, and Section 1031 of the Dodd-Frank Act, which prohibits unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices in connection with any consumer financial product or service, and analogous state laws prohibiting unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices;
• the Credit Practices Rule which prohibits lenders from using certain contract provisions that the Federal Trade Commission has found to be unfair to consumers, requires lenders to advise consumers who co-sign obligations about their potential liability if the primary obligor fails to pay and prohibits certain late charges;
• the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act and similar state debt collection laws, which provide guidelines and limitations on the conduct of third-party debt collectors (and some limitation on creditors collecting their own debts) in connection with the collection of consumer debts;
• the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and Regulation P promulgated thereunder, which includes limitations on financial institutions’ disclosure of nonpublic personal information about a consumer to nonaffiliated third parties, in certain circumstances requires financial institutions to limit the use and further disclosure of nonpublic personal information by nonaffiliated third parties to whom they disclose such information and requires financial institutions to disclose certain privacy notices and practices with respect to information sharing with affiliated and unaffiliated entities as well as to safeguard personal borrower information, and other privacy laws and regulations;
• state financial privacy laws in California, Vermont and a limited number of other states that require financial institutions to obtain opt-in consent before sharing a consumer’s nonpublic financial information with nonaffilaited third parties;
• limited provisions of the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), including provisions enforceable by California’s new privacy agency and its Department of Justice that require specific privacy policy disclosures and give
consumers the right to opt out of the sale or sharing of personal information for certain behavioral advertising purposes, and which also includes a private right of action for negligent data breaches, all of which are subject to civil and administrative penalties and statutory damages (for private right of action) assessed on a per-consumer or per-incident basis, in addition to actual damages and injunctive relief;
• the Bankruptcy Code, which limits the extent to which creditors may seek to enforce debts against parties who have filed for bankruptcy protection;
• the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act, which allows military members to suspend or postpone certain civil obligations, requires creditors to reduce the interest rate to 6% on loans to military members under certain circumstances, and imposes restrictions on enforcement of loans to servicemembers, so that the military member can devote his or her full attention to military duties;
• the Military Lending Act, which requires those who lend to “covered borrowers”, including members of the military and their dependents, to only offer Military APRs (a specific measure of all-in-cost-of-credit) under 36%, prohibits arbitration clauses in loan agreements, and prohibits certain other loan agreement terms and lending practices in connection with loans to military servicemembers, among other requirements, and for which violations may result in penalties including voiding of the loan agreement;
• the Electronic Fund Transfer Act and Regulation E promulgated thereunder, which provide guidelines and restrictions on the electronic transfer of funds from consumers’ bank accounts, including a prohibition on a creditor requiring a consumer to repay a credit agreement in preauthorized (recurring) electronic fund transfers and disclosure and authorization requirements in connection with such transfers;
• the Telephone Consumer Protection Act and the regulations promulgated thereunder, which impose various consumer consent requirements and other restrictions in connection with telemarketing activity and other communication with consumers by phone, fax or text message, and which provide guidelines designed to safeguard consumer privacy in connection with such communications;
• the federal Controlling the Assault of Non-Solicited Pornography and Marketing Act of 2003 and the Telemarketing Sales Rule and analogous state laws, which impose various restrictions on marketing conducted use of email, telephone, fax or text message;
• the Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act and similar state laws, particularly the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act, which authorize the creation of legally binding and enforceable agreements utilizing electronic records and signatures and which require creditors and loan servicers to obtain a consumer’s consent to electronically receive disclosures required under federal and state laws and regulations;
• the Right to Financial Privacy Act and similar state laws enacted to provide the financial records of financial institution customers a reasonable amount of privacy from government scrutiny;
• the Bank Secrecy Act and the USA PATRIOT Act, which relate to compliance with anti-money laundering, borrower due diligence, transaction monitoring and reporting and record-keeping policies and procedures;
• the Executive Orders and regulations promulgated by the Office of Foreign Assets Control under the U.S. Treasury Department related to the administration and enforcement of sanctions against foreign jurisdictions and persons that threaten U.S. foreign policy and national security goals, primarily to prevent targeted jurisdictions and persons from accessing the U.S. financial system; and
• federal and state securities laws, including, among others, the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, the Exchange Act, the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, or the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 (referred to as the IAA) and the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the Investment Company Act, rules and regulations adopted under those laws, and similar state laws and regulations, which govern how we offer, sell and transact in our loan financing products; and other state-specific and local laws and regulations.
We may not always have been, and may not always be, in compliance with these and other applicable laws, regulations and rules. Compliance with these requirements is also costly, time-consuming and limits our operational flexibility. Even if we believe we are in compliance with applicable laws, regulators may assert that we are not in compliance with such laws, and we have and may in the future be required to seek redress against regulators through legal action or otherwise, which could be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, Congress, the states and regulatory agencies, as well as local municipalities, could further regulate the consumer financial services industry in ways that make it more difficult or costly for us to offer our platform and related services or facilitate the origination of loans for our bank partners. These laws also are often subject to changes that could severely limit the operations of our business model. For example, in July 2021, a bill was reintroduced in the U.S. Senate that would create a national cap of 36% APR on most consumer loans, and 18 states and Washington, D.C. have
enacted interest rate caps on certain types of consumer loans. Although the proposed national rate cap may never be enacted into law, if such a bill were to be enacted, it would greatly restrict the number of loans that could be funded through our platform. In another example, in June 2023, Colorado enacted a law to opt out from interest rate preemption afforded state-chartered banks with respect to installment loans made in Colorado, pursuant to the Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control Act of 1980. The law becomes effective July 1, 2024. Iowa and Puerto Rico also have exercised this opt out. Other states and jurisdictions are considering similar legislation. If other states or jurisdictions adopt similar legislation, it may limit the interest rates that could be charged on new loans made in such states by state chartered banks that originate loans on our platform and may restrict the number of loans that could be funded through our platform. Further, changes in the regulatory application or judicial interpretation of the laws and regulations applicable to financial institutions also could impact the manner in which we conduct our business. The regulatory environment in which financial institutions operate has become increasingly complex, and following the financial crisis that began in 2008 and the financial distress experienced by many consumer as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, supervisory efforts to apply relevant laws, regulations and policies have become more intense. Additionally, states are increasingly introducing and, in some cases, passing laws that restrict interest rates and APRs on loans similar to the loans made on our platform. For example, in California the DFPI is considered a “mini-CFPB” because it has sought to increase oversight over bank partnership relationships and strengthen state consumer protection authority of state regulators to police debt collections and unfair, deceptive or abusive acts and practices. Additionally, voter referendums have been introduced and, in some cases, passed restrictions on interest rates and/or APRs. If such legislation or bills were to be propagated, or state or federal regulators seek to restrict regulated financial institutions such as our bank partners from engaging in business us in certain ways, our bank partners’ ability to originate loans in certain states could be greatly reduced, and as a result, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be adversely affected.
Where applicable, we seek to comply with state broker, credit service organization, small loan, finance lender, servicing, collection, money transmitter and similar statutes. Nevertheless, if we are found to not comply with applicable laws, we could lose one or more of our licenses or authorizations, become subject to greater scrutiny by other state regulatory agencies, face other sanctions or be required to obtain a license in such jurisdiction, which may have an adverse effect on our ability to continue to facilitate loans, perform our servicing obligations or make our platform available to consumers in particular states, which may harm our business. Further, failure to comply with the laws and regulatory requirements applicable to our business and operations may, among other things, limit our ability to collect all or part of the principal of or interest on loans facilitated on our platform. In addition, non-compliance could subject us to civil penalties, damages, revocation of required licenses, class action lawsuits, administrative enforcement actions and civil and criminal liability, all of which would harm our business.
Internet-based loan origination processes may give rise to greater risks than paper-based processes and may not always be allowed under state law.
We use the internet to obtain application information and distribute certain legally required notices to applicants and borrowers, and to obtain electronically signed loan documents in lieu of paper documents with actual borrower signatures. These processes may entail greater risks than would paper-based loan origination processes, including risks regarding the sufficiency of notice for compliance with consumer protection laws, risks that borrowers may challenge the authenticity of loan documents, and risks that despite internal controls, unauthorized changes are made to the electronic loan documents. In addition, our software could contain “bugs” that result in incorrect calculations or disclosures or other non-compliance with federal or state laws or regulations. If any of those factors were to cause any loans, or any of the terms of the loans, to be unenforceable against our borrowers, or impair our ability to service loans, the performance of the underlying promissory notes could be adversely affected.
If we are found to be operating without having obtained necessary state or local licenses, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Certain states have adopted laws regulating and requiring licensing by parties that engage in certain activities regarding consumer finance transactions, including facilitating and assisting such transactions in certain circumstances. Furthermore, certain states and localities have also adopted laws requiring licensing for consumer debt collection or servicing and/or purchasing or selling consumer loans. While we believe we have obtained all necessary licenses, the application of some consumer finance licensing laws to our platform and the related activities we perform is unclear. In addition, state licensing requirements may evolve over time, including, in particular, recent trends toward increased licensing requirements and regulation of parties engaged in loan solicitation activities. States also maintain licensing requirements pertaining to the transmission of money, and certain states may broadly interpret such licensing requirements to cover loan servicing and the transmission of funds to investors. If we were found to be in violation of applicable state licensing requirements by a court or a state, federal, or local enforcement agency, we could be subject to fines, damages, injunctive relief (including required modification or discontinuation of our business in certain areas), criminal penalties and other penalties or consequences, and the loans originated by our bank partners on our platform could be rendered void or unenforceable in whole or in part, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
The CFPB has sometimes taken expansive views of its authority to regulate consumer financial services, creating uncertainty as to how the agency’s actions or the actions of any other new agency could impact our business.
The CFPB, which commenced operations in July 2011, has broad authority to create and modify regulations under federal consumer financial protection laws, such as Regulation Z (implementing the Truth in Lending Act), Regulation B (implementing ECOA), Regulation V (implementing the Fair Credit Reporting Act), and Regulation E (implementing the Electronic Fund Transfer Act), among other regulations, and to enforce compliance with those laws. The CFPB supervises banks, thrifts and credit unions with assets over $10 billion and examines certain of our bank partners. Further, the CFPB is charged with the examination and supervision of certain participants in the consumer financial services market, including short-term, small dollar lenders, and larger participants in other areas of financial services. The CFPB is also authorized to prevent “unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices” through its rulemaking, supervisory and enforcement authority. To assist in its enforcement, the CFPB maintains an online complaint system that allows consumers to log complaints with respect to various consumer finance products, including our loan products. This system could inform future CFPB decisions with respect to its regulatory, enforcement or examination focus. The CFPB may also request reports concerning our organization, business conduct, markets and activities and conduct on-site examinations of our business on a periodic basis if the CFPB were to determine or suspect, as a result of information provided through its complaint system, that we were engaging in activities that pose risks to consumers.
Only one digital specialty finance platforms has ever received a no-action letter from the CFPB with respect to ECOA compliance as it pertains to underwriting applicants for unsecured non-revolving credit, and there continues to be uncertainty about the future of the CFPB and as to how its strategies and priorities, including in both its examination and enforcement processes, will impact our business and our results of operations going forward. In addition, evolving views regarding the use of alternative variables and machine learning in assessing credit risk and/or stated focus of the Administration and CFPB leadership on fair lending could result in the CFPB taking actions that result in requirements to alter or cease offering affected financial products and services, making them less attractive and restricting our ability to offer them. The CFPB could also implement rules that restrict our effectiveness in servicing our financial products and services. Although we have committed resources to enhancing our compliance programs, any actions by the CFPB (or other regulators) against us, our bank partners or our competitors could discourage the use of our services or those of our bank partners, which could result in reputational harm, a loss of bank partners, borrowers or capital sources, or discourage the use of our or their services and adversely affect our business. If the CFPB changes regulations or modifies through supervision or enforcement past regulatory guidance or interprets existing regulations in a different or stricter manner than they have been interpreted in the past by us, the industry or other regulators, our compliance costs and litigation exposure could increase materially. This is particularly true with respect to the application of ECOA and Regulation B to credit risk models that rely upon alternative variables and machine learning, an area of law where regulatory guidance is currently uncertain and still evolving, and for which there are not well-established regulatory norms for establishing compliance. If future regulatory or legislative restrictions or prohibitions are imposed that affect our ability to offer certain of our products or that require us to make significant changes to our business practices, and if we are unable to develop compliant alternatives with acceptable returns, these restrictions or prohibitions could have a material adverse effect on our business. If the CFPB, or another regulator, were to issue a consent decree or other similar order against us or our competitors, this could also directly or indirectly affect our results of operations.
We have been in the past and may in the future be subject to federal and state regulatory inquiries regarding our business, which may cause significant harm to our reputation, lead to investigations and enforcement actions from regulatory agencies or litigants, and divert management attention and resources from the operation of our business.
We have, from time to time in the normal course of our business, received, and may in the future receive or be subject to, inquiries or investigations by state and federal regulatory agencies and bodies such as the CFPB, state attorneys general, state financial regulatory agencies, such as the DFPI, and other state or federal agencies or bodies regarding our platform, including the marketing of loans for lenders, underwriting and pricing of consumer loans for our bank partners, our fair lending compliance program and licensing and registration requirements. We have addressed these inquiries directly and engaged in open dialogue with regulators. For example, the CFPB has issued a civil investigative demand, or CID, to us, as a result of a consumer complaint, the stated purpose of which is to determine whether our lending practices violated any consumer financial laws with respect to the Military Lending Act. We have responded to the CFPB to refute the number of affected consumers, and on August 25, 2021 we received notification from the staff of the CFPB that the CFPB had completed its investigation and does not intend to recommend that the CFPB take enforcement action against us.
We have also received inquiries from state regulatory agencies regarding requirements to obtain licenses from or register with those states, including in states where we have determined that we are not required to obtain such a license or be registered with the state, and we expect to continue to receive such inquiries. Any such inquiries or investigations could involve substantial time and expense to analyze and respond to, could divert management’s attention and other resources from running our business, has and could in the future lead to public enforcement actions or lawsuits and fines, penalties, injunctive relief, and the need to obtain additional licenses that we do not currently possess. For example, in the case of the inquiry initiated by
the DFPI with respect to Program Loans, we have sought declaratory and injunctive relief in response to action by the DFPI, the outcome of which is uncertain at this time. Our involvement in any such matters, whether tangential or otherwise and even if the matters are ultimately determined in our favor, could also cause significant harm to our reputation, lead to additional investigations and enforcement actions from other agencies or litigants, and further divert management attention and resources from the operation of our business. As a result, the outcome of legal and regulatory actions arising out of any state or federal inquiries we receive could be material to our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
The collection, processing, storage, use and disclosure of personal data could give rise to liabilities as a result of existing or new governmental regulation, conflicting legal requirements or differing views of personal privacy rights.
We receive, transmit and store a large volume of personally identifiable information and other sensitive data from applicants and borrowers. There are federal, state and foreign laws regarding privacy and the storing, sharing, use, disclosure and protection of personally identifiable information and sensitive data. Specifically, cybersecurity and data privacy issues, particularly with respect to personally identifiable information are increasingly subject to legislation and regulations to protect the privacy and security of personal information that is collected, processed and transmitted. For example, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act or the GLBA includes limitations on financial institutions’ disclosure of nonpublic personal information about a consumer to nonaffiliated third parties, in certain circumstances requires financial institutions to limit the use and further disclosure of nonpublic personal information by nonaffiliated third parties to whom they disclose such information and requires financial institutions to disclose certain privacy notices and practices with respect to information sharing with affiliated and unaffiliated entities as well as to safeguard personal borrower information. Financial privacy laws in some states provide additional limitations on the use of nonpublic personal information, including requiring opt-in consent before it can be disclosed to nonaffiliated entities. In addition, the California Consumer Privacy Act, or the CCPA, which went into effect on January 1, 2020 and applies to employees, business contacts, job applicants, and certain personal data not subject to the GLBA, requires, among other things, that covered companies provide detailed disclosures to California residents and afford California residents rights to access, delete and correct their personal information as well as the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information or the disclosure of their personal information to third parties for cross-context behavioral advertising. Additionally, other U.S. states are proposing and enacting laws and regulations that impose obligations similar to the CCPA or that otherwise involve significant obligations and restrictions. Compliance with current and future borrower privacy data protection and information security laws and regulations could result in higher compliance, technical or operating costs. Further, any actual or perceived violations of these laws and regulations may require us to change our business practices, data infrastructure or operational structure, address legal claims and regulatory investigations and proceedings and sustain monetary penalties and/or other harms to our business. We could also be adversely affected if new legislation or regulations are adopted or if existing legislation or regulations are modified such that we are required to alter our systems or change our business practices or privacy policies.
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) and many state attorneys general are interpreting existing federal and state consumer protection laws to impose evolving standards for the collection, use, dissemination and security of personally identifiable information, including financial information. For instance, the FTC published an advance notice of proposed rulemaking on commercial surveillance and data security in 2022 and may implement new trade regulation rules or other regulatory alternatives relating to the ways in which companies (1) collect, aggregate, protect, use, analyze, and retain consumer data, as well as (2) transfer, share, sell, or otherwise monetize that data in ways that are unfair or deceptive in the coming years. Privacy laws require us to publish statements describing how we handle personal information and choices individuals may have concerning the way we handle their personal information. Violating individuals’ privacy rights, publishing false or misleading information about security practices, or failing to take appropriate steps to keep individuals’ personal information secure may constitute unfair or deceptive acts or practices in violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act. Federal regulators, state attorneys general and plaintiffs’ attorneys have been and will likely continue to be active in this space, and if we do not comply with existing or new laws and regulations related to personally identifiable information, we could be subject to criminal or civil sanctions.
In addition, there has been a noticeable increase in class actions in the U.S. where plaintiffs have utilized a variety of laws, including state wiretapping laws, in relation to the use of tracking technologies, such as cookies and pixels. Actual, potential, or perceived violations of such laws could result in regulatory investigations, fines, orders to cease/change our use of such technologies and processing of personal data, as well as civil claims including class actions, reputational damage and ongoing compliance costs, any of which could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
As the regulatory framework for machine learning technology evolves, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected.
The regulatory framework for machine learning technology, particularly when used in connection with the offering of financial services, is developing and being discussed by several regulatory agencies, including the CFPB. It is possible that in
the coming years ahead, new laws and regulations will be adopted in the United States, or existing laws and regulations may be interpreted in new ways, both of which could affect the operation of our platform and the way in which we use machine learning technology, including with respect to fair lending laws. Further, the cost to comply with such laws or regulations could be significant and would increase our operating expenses, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If we are required to register under the Investment Company Act, our ability to conduct business could be materially adversely affected.
The Investment Company Act contains substantive legal requirements that regulate the manner in which “investment companies” are permitted to conduct their business activities. In general, an “investment company” is a company that holds itself out as an investment company or holds more than 40% of the total value of its assets (minus cash and government securities) in “investment securities.” We believe we are not an investment company. We do not hold ourselves out as an investment company. We understand, however, that the loans held on our balance sheet could be viewed by the SEC or its staff as “securities,” which could in turn cause the SEC or its staff to view Opportunity Financial, LLC or an affiliate as an “investment company” subject to regulation under the Investment Company Act. We believe that we have never been an investment company because, among other reasons, we are primarily engaged in the business of providing a specialty finance platform to banks. If we were ever deemed to be in non-compliance with the Investment Company Act, we could also be subject to various penalties, including administrative or judicial proceedings that might result in censure, fine, civil penalties, cease-and-desist orders or other adverse consequences, as well as private rights of action, any of which could materially adversely affect our business.
Anti-money laundering, anti-terrorism financing, anti-corruption and economic sanctions laws could have adverse consequences for us.
We maintain a compliance program designed to enable us to comply with all applicable anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing laws and regulations, including the Bank Secrecy Act and the USA PATRIOT Act and U.S. economic sanctions laws administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control. This program includes policies, procedures, processes and other internal controls designed to identify, monitor, manage and mitigate the risk of money laundering and terrorist financing and engaging in transactions involving sanctioned countries persons and entities. These controls include procedures and processes to detect and report suspicious transactions, perform borrower due diligence, respond to requests from law enforcement, and meet all recordkeeping and reporting requirements related to particular transactions involving currency or monetary instruments. We are also subject to anti-corruption and anti-bribery and similar laws, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended, or the FCPA, the U.S. domestic bribery statute contained in 18 U.S.C. § 201, and the U.S. Travel Act, which prohibit companies and their employees and agents from promising, authorizing, making, or offering improper payments or other benefits to government officials and others in the private sector in order to influence official action, direct business to any person, gain any improper advantage, or obtain or retain business. We have implemented an anti-corruption policy to ensure compliance with these anti-corruption and anti-bribery laws. No assurance is given that our programs and controls will be effective to ensure compliance with all applicable anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism financing and anti-corruption laws and regulations, and our failure to comply with these laws and regulations could subject us to significant sanctions, fines, penalties, contractual liability to our bank partners or institutional investors, and reputational harm, all of which could harm our business.
Risks Related to Loan Funding and Indebtedness
Our warehouse facilities expose us to certain risks, and we can provide no assurance that we will be able to access the whole loan sales markets, or secured warehouse credit facilities, in the future, which may require us to seek more costly financing.
We have funded, and may in the future fund, certain loans on our balance sheet and our purchase of participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners by selling such loans or participation interests to warehouse special purpose entities, or SPEs, which loan and participation rights sales are partially financed with associated warehouse credit facilities from financial institutions. Concurrently, the SPE borrows money from financial institutions pursuant to credit and security agreements. The lines of credit borrowed by the SPEs are each secured by the pool of loans and participation rights owned by the applicable SPE.
During periods of financial disruption, such as the financial crisis that began in 2008 and the COVID-19 pandemic that began in early 2020, the credit market constrained, and this could continue or occur again in the future. In addition, other matters, such as (i) accounting standards applicable to the foregoing transactions and (ii) capital and leverage requirements applicable to banks and other regulated financial institutions, could result in decreased investor demand, or increased competition from other institutions that undertake similar transactions. In addition, compliance with certain regulatory
requirements, including the Dodd-Frank Act, the Investment Company Act and the so-called “Volcker Rule,” may affect the type of transactions that we are able to complete.
If it is not possible or economical for us to engage in whole loan or participation rights sales in the future, we would need to seek alternative financing to support our loan funding programs and to meet our existing debt obligations. Such funding may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. If the cost of such loan funding mechanisms were to be higher than that of our whole loan and participation right sales, the fair value of the loans and participation rights would likely be reduced, which would negatively impact our results of operations. If we are unable to access such financing, our ability to originate loans and acquire participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners and our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity would be materially adversely affected.
If we are unable to maintain diverse and robust sources of capital, our growth prospects, business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our business depends on maintaining diverse and robust sources of capital to originate loans facilitated on our platform in certain states and to acquire participation rights in loans that our bank partners originate using our platform. We currently have committed financing agreements with two non-banks lenders and one commercial bank. We cannot be sure that these funding sources will continue to be available on reasonable terms or at all beyond the current maturity dates of our existing credit facilities. See the section “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” for more information.
Events of default or breaches of financial, performance or other covenants, or worse than expected performance of certain pools of loans underpinning our credit facilities, could reduce or terminate our access to funding from such facilities. Loan performance is dependent on a number of factors, including the predictiveness of our models and social and economic conditions. The availability and capacity of sources of capital also depends on many factors that are outside of our control, such as credit market volatility and regulatory reforms. In the event that we do not maintain adequate sources of capital, we may not be able to maintain the necessary levels of funding to retain current loan volume, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In connection with our credit facilities, we make representations and warranties concerning the loans or participation rights sold, and if such representations and warranties are not accurate when made, we could be required to repurchase such loans or participation rights.
Under our credit facilities we make numerous representations and warranties concerning the characteristics of the loans facilitated on our platform, or participation rights with respect thereto, sold and transferred in connection with such transactions, including representations and warranties that the loans meet the eligibility requirements of those facilities. If those representations and warranties were not accurate when made, we may be required to repurchase the underlying loans or participation rights. Failure to repurchase so-called ineligible receivables when required could constitute an event of default or termination event under our credit facilities. Historically, we have not had to repurchase loans or participations rights as a result of inaccurate representations or warranties related to loans facilitated on our platform. While only a small number of loans or participation rights have been historically repurchased by us, there can be no assurance that we would have adequate cash or other qualifying assets available to make such repurchases if and when required. Such repurchases could be limited in scope, relating to small pools of loans or participation rights, or significant in scope, across multiple pools of loans or participation rights. If we were required to make such repurchases and if we do not have adequate liquidity to fund such repurchases, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We rely on borrowings under our corporate and warehouse credit facilities to fund certain aspects of our operations, and any inability to meet our obligations as they come due or to comply with various covenants could harm our business.
Our corporate credit facilities consist of term loans and revolving loan facilities that we have drawn on to finance our operations and for other corporate purposes. As of December 31, 2023, we had approximately $333 million outstanding principal under these term loans and revolving credit facilities. These borrowings are generally secured by all the assets of the company that have not otherwise been sold or pledged to secure our structured finance facilities, such as assets belonging to our SPEs. These credit agreements contain operating and financial covenants, including customary limitations on the incurrence of certain indebtedness and liens, restrictions on certain transactions and limitations on distributions and stock repurchases. We have in the past, and may in the future, fail to comply with certain operating or financial covenants in our credit agreements, requiring a waiver from our lenders. Our ability to comply with or renegotiate these covenants may be affected by events beyond our control, and breaches of these covenants could result in a default under such agreements and any future financial agreements into which we may enter. If we were to default on our credit obligations and such defaults were not waived, our lenders may require repayment of any outstanding debt and terminate their agreements with us.
In addition, we, through our SPEs, have entered into warehouse credit facilities to partially finance the origination of loans by us on our platform or the purchase of participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners through our
platform, which credit facilities are secured by the loans or participation rights. We generally hold these loans or participation rights on our balance sheet until we can liquidate them. As of December 31, 2023, outstanding borrowings under these warehouse credit facilities were $283 million. See the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” for more information about our term loans and revolving loan facilities.
Our warehouse credit facilities impose operating and financial covenants on the SPEs, and under certain events of default, the lenders could require that all outstanding borrowings become immediately due and payable or terminate their agreements with us. We have in the past, and may in the future, fail to comply with certain operating or financial covenants in our credit facilities, requiring waivers from our lenders. If we are unable to repay our obligations at maturity or in the event of default, the borrowing SPEs may have to liquidate the loans or participation rights held as collateral at an inopportune time or price or, if the lender liquidated the loans or participation rights, the SPE, and in certain situations we, would have to pay any amount by which the original purchase price exceeded their sale price. An event of default would negatively impact our ability to originate loans on our platform and purchase participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners on our platform and require us to rely on alternative funding sources, which might increase our costs or which might not be available when needed. If we were unable to arrange new or alternative methods of financing on favorable terms, we might have to curtail our specialty finance programs, which could have an adverse effect on our and our bank partners’ ability or willingness to originate new loans, which in turn would have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Some of our borrowings carry a floating rate of interest linked to the London Inter-bank Offered Rate, or LIBOR. On July 27, 2017, the United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority (“FCA”), announced that it intended to stop persuading or compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. In response, the Alternative Reference Rates Committee (“ARRC”), made up of financial and capital market institutions, was convened to address the replacement of LIBOR in the U.S. The ARRC identified a potential successor to LIBOR in the Term Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“TSOFR”) and has crafted a plan to facilitate the transition. In March 2022, the Adjustable Interest Rate (LIBOR) Act (the “LIBOR Act”) was enacted, providing that LIBOR-based contracts that lack practicable replacement benchmarks will automatically transition to the applicable reference rates recommended by the Federal Reserve. In December 2022, the Federal Reserve issued a Final Rule establishing benchmark replacements based on TSOFR. However, the ICE Benchmark Administration (“IBA”), the authorized and regulated administrator of LIBOR, expects to continue publishing some LIBOR tenors until June 2023 and may be compelled to continue publishing other tenors under a different methodology after the FCA completes a consultation and makes a final determination on the matter (expected in 2023). While our agreements generally include alternative rates to LIBOR, if a change in indices results in interest rate increases on our debt, debt service requirements will increase, which could adversely affect our cash flow and results of operations. We do not expect a materially adverse change to our financial condition or liquidity as a result of any such changes or any other reforms to LIBOR that may be enacted in the United States, the United Kingdom or elsewhere.
Changes in interest rates could adversely affect our performance.
Our results of operations depend to a great extent on our net interest and loan related income, which is related to the difference between the interest rates earned on interest-earning assets such as loans and investment securities, and the interest rates paid on interest-bearing liabilities such as borrowings under our credit facilities. We are exposed to interest rate risk because our interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities do not react uniformly or concurrently to changes in interest rates. The interest rates of borrowings under some of our credit facilities are based on floating interest rates and are sensitive to factors that are beyond our control, including domestic and international economic conditions and the policies of various governmental and regulatory agencies, including the Federal Reserve. The monetary policies of the Federal Reserve, implemented through open market operations, the federal funds rate targets, the discount rate for banking borrowings and reserve requirements, affect prevailing interest rates. For instance, between August 2019 and March 2020, the Federal Open Market Committee of the Federal Reserve Board decreased its target range for short-term interest rates by 200 basis points, while between March 2022 and December 2023, it raised interest rates by 525 basis points and indicated that further changes may occur in 2024. A material change in any of these policies could affect the cost of borrowings under our credit facilities which in turn could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may need to raise additional funds in the future, including through equity, debt or convertible debt financings, to support business growth and those funds may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all.
We intend to continue to make investments to support our business growth and may require additional funds to respond to business challenges, including the need to develop new loan products, enhance our models, improve our operating infrastructure, or acquire complementary businesses and technologies. Accordingly, we may need to engage in equity, debt or convertible debt financings to secure additional funds. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities or securities convertible into equity securities, the combined company’s stockholders may experience dilution. Debt financing, if available,
may involve covenants restricting our operations or our ability to incur additional debt. Any debt or additional equity financing that we raise may contain terms that are not favorable to us or our stockholders.
If we are unable to obtain adequate financing or on terms satisfactory to us when we require it, we may be unable to pursue certain business opportunities and our ability to continue to support our business growth and to respond to business challenges could be impaired and our business may be harmed.
Risks Related to Ownership of our Securities
Having a minority share position may reduce the influence of stockholders on the management of the Company.
At December 31, 2023, (i) the Company’s public stockholders owned approximately 17.0% of the Company’s Common Stock and the Members owned approximately 83.0% of the Company’s Common Stock. The ownership percentage does not take into account (i) the Warrants; (ii) the issuance of any shares under the OppFi Inc. 2021 Equity Incentive Plan or the OppFi Inc. 2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan; or (iii) any shares of Class A Common Stock that may be repurchased pursuant to the Repurchase Program (as defined below). To the extent that any shares of Class A Common Stock are issued upon exercise of the Warrants or pursuant to our incentive plan or employee stock purchase plan, current stockholders may experience substantial dilution, and to the extent any shares of Class A Common Stock are repurchased pursuant to the Repurchase Program, the relative ownership interest of the Members will increase. This dilution, or increase in the relative ownership interest of the Members could, among other things, further limit the ability of our current stockholders to influence management of our company.
There can be no assurance that we will be able to comply with the continued listing standards of the NYSE.
Our Class A Common Stock and Public Warrants are currently listed on the NYSE. If the NYSE delists our Class A Common Stock from trading on its exchange for failure to meet the listing standards, we and our stockholders could face significant adverse consequences including:
• a limited availability of market quotations for our securities;
• reduced liquidity for our securities;
• a determination that our Class A Common Stock is a “penny stock,” which will require brokers trading in our Class A Common Stock to adhere to more stringent rules and possibly result in a reduced level of trading activity in the secondary trading market for our securities;
• a limited amount of news and analyst coverage; and
• decreased ability to issue additional securities or obtain additional financing in the future.
The National Securities Markets Improvement Act of 1996, which is a federal statute, prevents or preempts the states from regulating the sale of certain securities, which are referred to as “covered securities.” Because our Class A Common Stock and Public Warrants are listed on the NYSE, they are covered securities. Although the states are preempted from regulating the sale of our securities, the federal statute does allow the states to investigate companies if there is a suspicion of fraud, and, if there is a finding of fraudulent activity, then the states can regulate or bar the sale of covered securities in a particular case. While we are not aware of a state, other than the state of Idaho, having used these powers to prohibit or restrict the sale of securities issued by blank check companies, certain state securities regulators view blank check companies unfavorably and might use these powers, or threaten to use these powers, to hinder the sale of securities of blank check companies in their states. Further, if we were no longer listed on the NYSE, our securities would not be covered securities and we would be subject to regulation in each state in which we offer our securities, including in connection with our initial business combination.
Future resales of Class A Common Stock may cause the market price of our securities to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 66.4 million Retained OppFi-LLC Units (“Initial Shares”) may be exchanged for shares of our Class A Common Stock by the Members pursuant to the Members’ Exchange Rights, and may be sold without any contractual restriction by the Members. Pursuant to the lock-up restrictions agreed to in connection with the Investor Rights Agreement, beginning on the nine month anniversary of the Closing (unless earlier waived by the Company in its capacity as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC), or with respect to the Earnout Units, on such later date the Earnout Units are earned in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement, all of the Retained OppFi-LLC Units held by the Members may be exchanged, upon the exercise of such Members’ Exchange Rights, for either one share of Class A Common Stock or, at the election of the Company in its capacity as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC, the cash equivalent of the market value of one share of Class A Common Stock, pursuant to the terms and conditions of the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA. Assuming the full exercise of the Exchange Rights by all of the Members (including with respect to the Initial Shares and the Earnout Units), the Members will own 83.0% of our Class A Common Stock.
Except with respect to the restrictions described above, the Members will not be restricted from selling the shares of Class A Common Stock held by them following their exercise of Exchange Rights, other than by applicable securities laws. As such, sales of a substantial number of shares of Class A Common Stock in the public market could occur at any time. These sales, or the perception in the market that the holders of a large number of shares intend to sell shares, could cause the market price of our securities to decline or increase the volatility in the market price of our securities.
The amount and frequency of our share repurchases may fluctuate, and we cannot guarantee that we will continue to repurchase shares of our Class A Common Stock , or that it will enhance long-term stockholder value. Share repurchases could also increase the volatility of the trading price of our stock and will diminish our cash reserves.
In January 2022, we announced a program to repurchase up to $20.0 million in the aggregate of shares of Class A Common Stock (“Repurchase Program”). The Repurchase Program expired in December 2023. As of the expiration, we had purchased approximately $2.5 million of shares of Class A Common Stock under the Repurchase Program. There can be no guarantee that the Board will approve a new share repurchase program. Any decision to approve a new share repurchase program will be made by the Board from time to time based on the Board's evaluation of the best interests of the Company and our stockholders.
We cannot guarantee that any additional shares of Class A Common Stock will be repurchased under a new repurchase program or that it will enhance long-term stockholder value. The timing and amount of any repurchases will depend on market conditions and other requirements. A new repurchase program could affect the trading price of our securities and increase volatility, and any announcement of a pause in, or termination of, a program may result in a decrease in the trading price of our securities. In addition, a new repurchase program could diminish our cash reserves.
There is no guarantee that the Warrants will ever be in the money, and they may expire worthless and the terms of our Warrants may be amended.
The exercise price for our Warrants (other than the $15 Exercise Price Warrants) is $11.50 per share of Class A Common Stock, and the exercise price of the $15 Exercise Price Warrants is $15.00 per share of Class A Common Stock. There is no guarantee that the Warrants will ever be in the money prior to their expiration, and as such, the Warrants may expire worthless.
Our only significant asset is our ownership interest in OppFi-LLC and the ownership may not be sufficient to pay dividends or make distributions or loans to enable us to pay any dividends on our Class A Common Stock or satisfy our other financial obligations.
We have no direct operations and no significant assets other than our ownership interest in OppFi-LLC. We depend on OppFi-LLC for distributions, loans and other payments to generate the funds necessary to meet our financial obligations, including our expenses as a publicly traded company and to pay any dividends with respect to our Class A Common Stock. The financial condition and operating requirements of OppFi-LLC may limit our ability to obtain cash from OppFi-LLC. The earnings from, or other available assets of, OppFi-LLC may not be sufficient to pay dividends or make distributions or loans to enable us to pay any dividends on our Class A Common Stock or satisfy our other financial obligations.
We may be required to take write-downs or write-offs, restructuring and impairment or other charges that could negatively affect our financial condition, results of operations and our stock price.
As a result of factors beyond our control, we may be forced to write-down or write-off assets, restructure our operations, or incur impairment or other charges that could result in our reporting losses. Unexpected risks may arise and previously known risks may materialize. Even though these charges may be non-cash items and not have an immediate impact on our liquidity, the fact that we report charges of this nature could contribute to negative market perceptions about us or our securities.
The historical financial results of OppFi-LLC included in this Annual Report may not be indicative of what our actual financial position or results of operations would have been.
The historical financial results of OppFi included in this Annual Report that include periods prior to the Business Combination do not necessarily reflect the financial condition, results of operations or cash flows we would have achieved as a combined company during the periods presented or those that we will achieve in the future. This is primarily the result of the following factors: (i) we have incurred additional ongoing costs as a result of the Business Combination, including costs related to public company reporting, investor relations and other compliance related costs; and (ii) our capital structure is also different from that reflected in OppFi-LLC’s historical financial statements. Our financial condition and future results of operations could be materially different from amounts reflected in its historical financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report, so it may be difficult for investors to compare our future results to historical results or to evaluate our relative performance or trends in our business.
Our Certificate of Incorporation (“Charter”) includes a forum selection clause, which could discourage claims or limit stockholders’ ability to make a claim against us, our directors, officers, other employees or stockholders.
The Charter includes a forum selection clause. The charter provides that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware shall, to the fullest extent permitted by law, be the sole and exclusive forum for any stockholder (including a beneficial owner) to bring any: (i) derivative action or proceeding; (ii) action asserting a claim of breach of fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers or other employees to us or our stockholders; (iii) action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL or the charter or bylaws; or (iv) action asserting a claim against us, our directors, officers or employees governed by the internal affairs doctrine, except for, as to each of (i) through (iv) above, any claim (A) as to which the Court of Chancery determines that there is an indispensable party not subject to the jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery (and the indispensable party does not consent to the personal jurisdiction of the Court of Chancery within ten days following the determination), (B) that is vested in the exclusive jurisdiction of a court or forum other than the Court of Chancery, (C) for which the Court of Chancery does not have subject matter jurisdiction, or (D) any action arising under the Securities Act as to which the Court of Chancery and the federal district court for the District of Delaware shall have concurrent jurisdiction. Unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal district courts of the United States of America shall be the sole and exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under federal securities laws, including the Securities Act. Under the Securities Act, federal and state courts have concurrent jurisdiction over all suits brought to enforce any duty or liability created by the Securities Act, and stockholders cannot waive compliance with the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder. Accordingly, there is uncertainty as to whether a court would enforce such a forum selection provision as written in connection with claims arising under the Securities Act. This forum selection clause may also discourage claims or limit stockholders’ ability to submit claims in a judicial forum that they find favorable and may result in additional costs for a stockholder seeking to bring a claim. While we believe the risk of a court declining to enforce this forum selection clause is low, if a court were to determine the forum selection clause to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs in conjunction with our efforts to resolve the dispute in an alternative jurisdiction, which could have a negative impact on our results of operations and financial condition. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the forum selection clause will not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Exchange Act or any other claim for which the federal district courts of the United States of America shall be the exclusive forum.
Unanticipated changes in effective tax rates or adverse outcomes resulting from examination of our income or other tax returns could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We will be subject to income taxes in the United States, and our domestic tax liabilities will be subject to the allocation of expenses in differing jurisdictions. Our future effective tax rates could be subject to volatility or adversely affected by a number of factors, including:
• changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities;
• expected timing and amount of the release of any tax valuation allowances;
• tax effects of stock-based compensation;
• costs related to intercompany restructurings;
• changes in tax laws, regulations or interpretations thereof; and
• lower than anticipated future earnings in jurisdictions where we have lower statutory tax rates and higher than anticipated future earnings in jurisdictions where we have higher statutory tax rates.
In addition, we may be subject to audits of our income, sales and other transaction taxes by U.S. federal and state authorities. Outcomes from these audits could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
A market for our securities may not continue, which would adversely affect the liquidity and price of our securities.
The price of our securities may fluctuate. An active trading market for our securities may never develop or, if developed, it may not be sustained. In addition, the price of our securities can vary due to general economic conditions and forecasts, our general business condition and the release of our financial reports. Additionally, if our securities become delisted from the NYSE for any reason, and are quoted on the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board, an inter-dealer automated quotation system for equity securities that is not a national securities exchange, the liquidity and price of our securities may be more limited. You may be unable to sell your securities unless a market for such securities can be sustained.
The trading price of our securities could be volatile and subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control. Any of the factors listed below could have a material adverse effect on any investment in our securities which may trade at prices significantly below the price you paid for them. In these circumstances, the trading price of our securities may not recover and may experience a further decline.
If an active market for our securities develops and continues, the trading price of our securities could be volatile and subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control. Any of the factors listed below could adversely effect on your investment in our securities and our securities may trade at prices significantly below the price you paid for them. In these circumstances, the trading price of our securities may not recover and may experience a further decline.
Factors affecting the trading price of our securities may include:
• actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly financial results or the quarterly financial results of companies perceived to be similar to us;
• changes in the market’s expectations about our operating results;
• the public’s reaction to our press releases, our other public announcements and our filings with the SEC;
• speculation in the press or investment community;
• success of competitors;
• our operating results failing to meet the expectation of securities analysts or investors in a particular period;
• changes in financial estimates and recommendations by securities analysts concerning the post-combination company or the market in general;
• operating and stock price performance of other companies that investors deem comparable to the post-combination company;
• our ability to market new and enhanced products on a timely basis;
• changes in laws and regulations affecting our business;
• commencement of, or involvement in, litigation involving the post-combination company;
• changes in the post-combination company’s capital structure, such as future issuances of securities or the incurrence of additional debt;
• the volume of shares of our Class A Common Stock available for public sale;
• any major change in our Board or management;
• sales of substantial amounts of Class A Common Stock by our directors, officers or significant stockholders or the perception that such sales could occur; and
• general economic and political conditions such as recessions, interest rates, inflation, monetary policy changes, fuel prices, international currency fluctuations and acts of war or terrorism.
Broad market and industry factors may materially harm the market price of our securities irrespective of our operating performance. The stock market in general and the NYSE have experienced price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of the particular companies affected. The trading prices and valuations of these stocks, and of our securities, may not be predictable. A loss of investor confidence in the market for the stocks of other companies that investors perceive to be similar to us could depress our stock price regardless of our business, prospects, financial conditions or results of operations. For example, the volatility resulting from the failures of SVB and Signature Bank particularly impacted the price of securities issued by financial institutions and participants in the financial services industry generally, including ours. A decline in the market price of our securities also could adversely affect our ability to issue additional securities and our ability to obtain additional financing in the future.
In the past, securities class action litigation has often been initiated against companies following periods of volatility in their stock price. This type of litigation could result in substantial costs and divert our management’s attention and resources and could also require us to make substantial payments to satisfy judgments or to settle litigation.
Our quarterly operating results may fluctuate significantly and could fall below the expectations of securities analysts and investors due to seasonality and other factors, some of which are beyond our control, resulting in a decline in our stock price.
Our quarterly operating results may fluctuate significantly because of several factors, including:
• profitability of our products, especially in new markets and due to seasonal fluctuations;
• changes in interest rates;
• impairment of assets;
• macroeconomic conditions, including inflation and interest rate changes, both nationally and locally;
• negative publicity relating to our products;
• changes in consumer preferences and competitive conditions; and
• expansion to new markets.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us our business, or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our Class A Common Stock adversely, then the price and trading volume of our securities could decline.
The trading market for our securities will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market, or our competitors. Securities and industry analysts do not currently, and may never, publish research on us. If no securities or industry analysts commence coverage of us, our stock price and trading volume would likely be negatively impacted. If any of the analysts who may cover us change their recommendation regarding our stock adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, the price of our securities would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us were to cease coverage of us or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
We may be unable to obtain additional financing to fund our operations and growth.
We may require additional financing to fund our operations or growth. We cannot assure you that such financing will be available on acceptable terms, if at all. The failure to secure additional financing could adversely affect our continued development or growth. None of our officers, directors or stockholders are required to provide any financing to us.
Changes in laws, regulations or rules, or a failure to comply with any laws, regulations or rules, may adversely affect our business.
We are subject to laws, regulations and rules enacted by national, regional and local governments and the NYSE. In particular, we are required to comply with certain SEC, NYSE and other legal or regulatory requirements. Compliance with, and monitoring of, applicable laws, regulations and rules may be difficult, time consuming and costly. Those laws, regulations or rules and their interpretation and application may also change from time to time and those changes could adversely affect our business, investments and results of operations. In addition, a failure to comply with applicable laws, regulations or rules, as interpreted and applied, could adversely affect our business.
A recent ruling by the Court of Chancery in Delaware introduced uncertainty as to whether Section 242(b)(2) of the Delaware General Corporation Law (the “DGCL”) required a separate vote in favor of at least a majority of the outstanding shares of Class A Common Stock, in addition to a vote in favor of at least a majority of the outstanding shares of Class A and Class B Common Stock, voting together as a single class, to properly authorize an increase or decrease in the aggregate number of authorized shares of such Class A Common Stock. At a special meeting of the stockholders of the Company held on July 16, 2021 (the “Special Meeting”), a majority of the then-outstanding shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock, voting together as a single class, voted to approve the Company’s Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, which, among other things, increased the authorized capital stock from 401,000,000 shares, consisting of 380,000,000 shares of Class A Common Stock, 20,000,000 shares of Class B Common Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.0001 per share, to 501,000,000 shares, consisting of 500,000,000 shares of common stock, including (i) 379,000,000 shares of Class A Common Stock, (ii) 6,000,000 shares of Class B Common Stock, and (iii) 115,000,000 shares of Class V Voting Stock and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock by creating an additional 100,000,000 shares of common stock (the “Capitalization Amendment”). Notwithstanding the fact that the proxy statement relating to the Special Meeting did not disclose that a separate vote of the Class A Common Stock was required, a majority of the then-outstanding shares of Class A Common Stock voted in favor of the Capitalization Amendment. Accordingly, we do not believe that the Delaware ruling applies to us. However, if the Court of Chancery in Delaware were to determine that this ruling does apply to us, this or any other failure to comply with applicable laws, regulations or rules, as interpreted and applied, could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations and, with respect to the Capitalization Amendment, require us to seek relief with the Delaware Court of Chancery.
We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of NYSE rules and, as a result, are exempt from certain corporate governance requirements.
So long as Schwartz Capital Group, LTHS Capital Group, or TGS Capital Group (f/k/a Todd Schwartz Capital Group), and any of their respective permitted transferees (collectively, the “SCG Holders”) and their affiliates maintain holdings of more than 50% of the voting power of our capital stock, we will be a “controlled company” within the meaning of NYSE
corporate governance standards. Under these standards, a company need not comply with certain corporate governance requirements, including the requirements that:
• a majority of our board of directors consist of “independent directors” as defined under NYSE rules;
• the requirement that we have a compensation committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities;
• we have a nominating and corporate governance committee that is composed entirely of independent directors with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities, or otherwise have director nominees selected by vote of a majority of the independent directors; and
• the requirement for an annual performance evaluation of the nominating and corporate governance and compensation committees.
We have relied on certain of these exemptions. As a result, our board of directors would not be required to consist of a majority of independent directors, and our compensation committee and nominating and corporate governance committee would not consist entirely of independent directors and will not be subject to annual performance evaluations. If we are no longer eligible to rely on the controlled company exception, we will comply with all applicable NYSE corporate governance requirements, but we will be able to rely on phase-in periods for certain of these requirements in accordance with NYSE rules. Accordingly, our stockholders may not have the same protections afforded to stockholders of companies that are subject to all NYSE corporate governance requirements.
The SCG Holders and their affiliates will have significant influence or control and their interests may conflict with those of other stockholders.
The SCG Holders and their affiliates collectively hold 83.0% of total voting power of all outstanding shares of Common Stock, voting together as a single class. Additionally, the Company has entered into the Investor Rights Agreement, pursuant to which the SCG Holders’ Representative has the right to nominate five directors to the Board.
The Investor Rights Agreement also provides that at each meeting at which directors are to be elected, the Company shall take such necessary action to include in the slate of nominees recommended by the Board for election as directors (i) five directors chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 50% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors, (ii) four directors chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 40% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors, (iii) three directors chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 30% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors, (iv) three directors chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 30% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors, (v) two directors chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 20% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors and (vi) one director chosen by the SCG Holders’ Representative as long as the SCG Holders have at least of 5% of the voting power entitled to vote in the election of directors.
As such, the SCG Holders and their affiliates will have significant influence over the election of the members of our Board and thereby may significantly influence our policies and operations, including the appointment of management, future issuances of our Class A Common Stock or other securities, the payment of dividends, if any, the incurrence or modification of debt, amendments to our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, and the entering into of extraordinary transactions, and the SCG Holders’ interests may not in all cases be aligned with those of other stockholders.
In the event of a conflict between our interests and the interests of the SCG Holders and their affiliates, we have adopted policies and procedures, specifically a Code of Ethics and a Related Party Transactions Policy, to identify, review, consider and approve such conflicts of interest. In general, if an affiliate of a director, executive officer or significant stockholder, including the SCG Holders and their affiliates, intends to engage in a transaction involving us, that director, executive officer or significant stockholder must report the transaction for consideration and approval by our audit committee. However, there are no assurances that our efforts and policies to eliminate the potential impacts of conflicts of interest will be effective.
We may amend the terms of the Warrants in a manner that may be adverse to holders of Public Warrants with the approval by the holders of at least 50% of the then-outstanding Warrants. As a result, the exercise price of your Warrants could be increased, the exercise period could be shortened and the number of shares of our Class A Common Stock purchasable upon exercise of a Warrant could be decreased, all without your approval.
Our Warrants have been issued under a Warrant Agreement between the Warrant Agent, and us. The Warrant Agreement provides that the terms of the Warrants may be amended without the consent of any holder to cure any ambiguity or correct any defective provision, but requires the approval by the holders of at least 50% of the then outstanding Public Warrants to make any change that adversely affects the interests of the registered holders of Public Warrants. Accordingly, we may amend the
terms of the Public Warrants in a manner adverse to a holder if holders of at least 50% of the then outstanding Public Warrants approve of such amendment. Although our ability to amend the terms of the Public Warrants with the consent of at least 50% of the then outstanding Public Warrants is unlimited, examples of such amendments could be amendments to, among other things, increase the exercise price of the Warrants, convert the Warrants into cash or stock (at a ratio different than initially provided), shorten the exercise period or decrease the number of shares of Class A Common Stock purchasable upon exercise of a Warrant.
We may redeem unexpired Public Warrants prior to their exercise at a time that is disadvantageous to the holders of outstanding Public Warrants, thereby making the Public Warrants worthless.
We have the ability to redeem outstanding Public Warrants at any time after they become exercisable and prior to their expiration, at a price of $0.01 per Public Warrant, provided that the last reported sales price of our Class A Common Stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) for any 20 trading days within a 30 trading-day period ending on the third trading day prior to the date on which we give proper notice of redemption and provided certain other conditions are met. If and when the Public Warrants become redeemable by us, we may not exercise our redemption right if the issuance of shares of Class A Common Stock upon exercise of the Public Warrants is not exempt from registration or qualification under applicable state blue sky laws or we are unable to effect registration or qualification. We will use our best efforts to register or qualify the shares of Class A Common Stock under the blue-sky laws of the state of residence in those states in which the Public Warrants were offered by us in the IPO. Redemption of the outstanding Public Warrants could force the holders of outstanding Public Warrants to (i) exercise their Public Warrants and pay the exercise price therefor at a time when it may be disadvantageous to do so, (ii) sell their Public Warrants at the then-current market price when they might otherwise wish to hold Public Warrants or (iii) accept the nominal redemption price which, at the time the outstanding Public Warrants are called for redemption, is likely to be substantially less than the market value of your Public Warrants. None of the Private Placement Warrants will be redeemable by us so long as they are held by the Sponsor or its permitted transferees, or the Underwriters and their permitted transferees, respectively.
Warrants are exercisable for our Class A Common Stock, which would increase the number of shares eligible for future resale in the public market and result in dilution to our stockholders.
We have outstanding (i) Public Warrants to purchase 11,887,500 shares of Class A Common Stock, (ii) Private Placement Unit Warrants to purchase 231,250 shares of Class A Common Stock, (iii) Underwriter Warrants to purchase 59,437 shares of Class A Common Stock, (iv) Founder Warrants to purchase 2,248,750 shares of Class A Common Stock, and (v) $15 Exercise Price Warrants to purchase 912,500 shares of Class A Common Stock. The shares of Class A Common Stock issuable upon exercise of our Warrants will result in dilution to the then existing holders of Class A Common Stock and increase the number of shares eligible for resale in the public market. Sales of substantial numbers of shares Class A Common Stock in the public market could adversely affect the market price of our Class A Common Stock.
Anti-takeover provisions contained in the Charter and Amended and Restated Bylaws, as well as provisions of Delaware law, could impair a takeover attempt.
The Charter contains provisions that may discourage unsolicited takeover proposals that stockholders may consider to be in their best interests. These provisions provide, among other things, that the Company shall not engage in any business combination (as such term is defined in the Charter), at any point in time at which the Class A Common Stock is registered under Section 12(b) or 12(g) of the Exchange Act, with any interested stockholder (which, as defined in the Charter, shall not include SCG or any of its affiliates, or any person that acquires (other than in a registered public offering) directly from SCG or any of its successors, any “group”, or any member of any such group, of which such persons are a member of under Rule 13d-5 of the Exchange Act beneficial ownership of fifteen percent (15%) or more of the then outstanding voting stock of the Company) for a period of three years following the time that such stockholder became an interested stockholder, unless: (i) prior to such time, the Board approved either the business combination or the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; or (ii) upon consummation of the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the Company outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, excluding for purposes of determining the voting stock outstanding (but not the outstanding voting stock owned by the interested stockholder) those shares owned by (A) persons who are directors and also officers of the Company and (B) employee stock plans in which employee participants do not have the right to determine confidentially whether shares held subject to the plan will be tendered in a tender or exchange offer; (iii) at or subsequent to such time, the applicable business combination is approved by the Board and authorized at an annual or special meeting of stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least 66 2/3% of the outstanding voting stock of the Company that is not owned by the interested stockholder; or (iv) the stockholder became an interested stockholder inadvertently and (A) as soon as practicable divested itself of ownership of sufficient shares so that the stockholder ceased to be an interested stockholder and (B) was not, at any time within the three-year period immediately prior to a business combination between the Company and such stockholder, an interested stockholder but for the inadvertent acquisition of ownership, which provision of the Charter may
only be amended by the affirmative vote of at least 66 2/3% of all then outstanding shares of Class A Common Stock of the Company.
Together these provisions may make more difficult the removal of management and may discourage transactions that otherwise could involve payment of a premium over prevailing market prices for our securities.
We are an emerging growth company within the meaning of the Securities Act, and if we take advantage of certain exemptions from disclosure requirements available to emerging growth companies, this could make our securities less attractive to investors and may make it more difficult to compare our performance with other public companies.
We are an “emerging growth company” within the meaning of the Securities Act, as modified by the JOBS Act, and we may take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies including, but not limited to, not being required to comply with the auditor internal controls attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes- Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. As a result, our stockholders may not have access to certain information they may deem important. We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years, although circumstances could cause us to lose that status earlier, including if the market value of our Class A Common Stock held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of any June 30 before that time, in which case we would no longer be an emerging growth company as of the following December 31. We cannot predict whether investors will find our securities less attractive because we will rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our securities less attractive as a result of our reliance on these exemptions, the trading prices of our securities may be lower than they otherwise would be, there may be a less active trading market for our securities and the trading prices of our securities may be more volatile.
Further, Section 102(b)(1) of the JOBS Act exempts emerging growth companies from being required to comply with new or revised financial accounting standards until private companies (that is, those that have not had a Securities Act registration statement declared effective or do not have a class of securities registered under the Exchange Act) are required to comply with the new or revised financial accounting standards. The JOBS Act provides that a company can elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such an election to opt out is irrevocable. We have elected not to opt out of such extended transition period which means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public or private companies, we, as an emerging growth company, can adopt the new or revised standard at the time private companies adopt the new or revised standard. This may make comparison of our financial statements with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
Additionally, we are a “smaller reporting company” as defined in Item 10(f)(1) of Regulation S-K. Smaller reporting companies may take advantage of certain reduced disclosure obligations, including, among other things, providing only two years of audited financial statements. We will remain a smaller reporting company until the last day of the fiscal year in which (1) the market value of our Common Stock held by non-affiliates exceeds $250 million as of the prior June 30th, and (2) our annual revenues exceeded $100 million during such completed fiscal year and the market value of our Common Stock held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the prior June 30th. To the extent we take advantage of such reduced disclosure obligations, it may also make comparison of our financial statements with other public companies difficult or impossible.
Our only principal asset is our interest in OppFi-LLC, and accordingly we depend on distributions from OppFi-LLC to pay distributions, taxes, other expenses, and make any payments required to be made by us under the Tax Receivable Agreement.
We are a holding company and have no material assets other than our ownership of the OppFi-LLC Units. We are not expected to have independent means of generating revenue or cash flow, and our ability to pay our taxes, operating expenses, and pay any dividends in the future, if any, will be dependent upon the financial results and cash flows of OppFi-LLC. There can be no assurance that OppFi-LLC will generate sufficient cash flow to distribute funds to us or that applicable state law and contractual restrictions, including negative covenants under debt instruments, will permit such distributions. If OppFi-LLC does not distribute sufficient funds to us to pay our taxes or other liabilities, we may default on contractual obligations or have to borrow additional funds. In the event that we are required to borrow additional funds it could adversely affect our liquidity and subject us to additional restrictions imposed by lenders.
OppFi-LLC will continue to be treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes and, as such, generally will not be subject to any entity- level U.S. federal income tax. Instead, taxable income will be allocated, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, to the holders of OppFi-LLC Units. Accordingly, we are required to pay U.S. federal income taxes on our allocable share of the net taxable income of OppFi-LLC. Under the terms of the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA, OppFi-LLC is obligated to
make tax distributions to holders of OppFi-LLC Units (including us) calculated at certain assumed rates. In addition to tax expenses, we will also incur expenses related to our operations, including our payment obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement, which could be significant and some of which will be reimbursed by OppFi-LLC (excluding payment obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement). We intend to cause OppFi-LLC to make ordinary distributions and tax distributions to the holders of OppFi-LLC Units on a pro rata basis in amounts sufficient to cover all applicable taxes, relevant operating expenses, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement and dividends, if any, declared by us. However, as discussed below, OppFi-LLC’s ability to make such distributions may be subject to various limitations and restrictions, including, but not limited to, retention of amounts necessary to satisfy the obligations of OppFi-LLC and its subsidiaries and restrictions on distributions that would violate any applicable restrictions contained in OppFi-LLC’s debt agreements, or any applicable law, or that would have the effect of rendering OppFi-LLC insolvent. To the extent we are unable to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement for any reason, such payments will be deferred and will accrue interest until paid, provided, however, that nonpayment for a specified period and/or under certain circumstances may constitute a material breach of a material obligation under the Tax Receivable Agreement and therefore accelerate payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement, which could be substantial.
Additionally, although OppFi-LLC generally will not be subject to any entity-level U.S. federal income tax, it may be liable under certain federal income tax legislation for adjustments to its tax return, absent an election to the contrary. In the event OppFi-LLC’s calculations of taxable income are incorrect, OppFi-LLC and/or its members, including us, in later years may be subject to material liabilities pursuant to this federal income tax legislation and its related guidance.
We anticipate that the distributions we receive from OppFi-LLC may, in certain periods, exceed our actual liabilities and our obligations to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement. The Board, in its sole discretion (and in compliance with our credit facilities), will make any determination from time to time with respect to the use of any such excess cash so accumulated, which may include, among other uses, to pay dividends on our Class A Common Stock. We will have no obligation to distribute such cash (or other available cash other than any declared dividend) to our stockholders. We may, if necessary, undertake ameliorative actions, which may include pro rata or non-pro rata reclassifications, combinations, subdivisions or adjustments of outstanding OppFi-LLC Units, to maintain one-for-one parity between OppFi-LLC Units held by us and shares of our Class A Common Stock.
Pursuant to the Tax Receivable Agreement, we are required to pay to the Members and/or the exchanging holders of Retained OppFi-LLC Units, as applicable, 90% of the net income tax savings that we realize as a result of increases in tax basis in our assets related to the Business Combination and the future exchange of the Retained OppFi-LLC Units for shares of Class A Common Stock (or cash) pursuant to the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA and tax benefits related to entering into the Tax Receivable Agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement, and those payments may be substantial.
In connection with the Business Combination, the Members were deemed for U.S. federal (and applicable state and local) income tax purposes to have sold to us OppFi-LLC Units and may in the future exchange their OppFi-LLC Units, together with the cancelation of an equal number of shares of Class V Voting Stock, for shares of our Class A Common Stock (or cash) pursuant to the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA, subject to certain conditions and transfer restrictions as set forth therein and in the Investor Rights Agreement. These sales and exchanges are expected to result in increases in our allocable share of the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of OppFi-LLC. These increases in tax basis may increase (for income tax purposes) depreciation and amortization deductions allocable to us and therefore reduce the amount of income or franchise tax that we would otherwise be required to pay in the future had such sales and exchanges never occurred.
We have entered into the Tax Receivable Agreement, which generally provides for the payment by us of 90% of certain net tax benefits, if any, that we realize (or in certain cases are deemed to realize) as a result of these increases in tax basis and tax benefits related to the transactions contemplated under the Business Combination Agreement and the exchange of Retained OppFi-LLC Units for Class A Common Stock (or cash) pursuant to the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA and tax benefits related to entering into the Tax Receivable Agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement. These payments are our obligation and not of OppFi-LLC. The actual increase in our allocable share of OppFi-LLC’s tax basis in its assets, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of exchanges, the market price of the Class A Common Stock at the time of the exchange and the amount and timing of the recognition of our income. While many of the factors that will determine the amount of payments that we will make under the Tax Receivable Agreement are outside of our control, we expect that the payments we will make under the Tax Receivable Agreement will be substantial and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
Any payments we make under the Tax Receivable Agreement will generally reduce the amount of overall cash flow that might have otherwise been available to us. To the extent that we are unable to make timely payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement for any reason, the unpaid amounts will be deferred and will accrue interest until paid; however, nonpayment for a
specified period and/or under certain circumstances may constitute a material breach of a material obligation under the Tax Receivable Agreement and therefore accelerate payments due under the Tax Receivable Agreement, as further described below. Furthermore, our future obligation to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement could make us a less attractive target for an acquisition, particularly in the case of an acquirer that cannot use some or all of the tax benefits that may be deemed realized under the Tax Receivable Agreement.
Increases in our income tax rates, changes in income tax laws or disagreements with tax authorities can adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Increases in our income tax rates or other changes in income tax laws in the United States or any particular jurisdiction in which we operate could reduce our after-tax income from such jurisdiction and adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. Existing tax laws in the United States have been and could in the future be subject to significant change. For example, in December 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“TCJA”) was signed into law in the United States which provided for significant changes to then-existing tax laws and subsequent legislation (such as the enactment of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act in March 2020) modifying certain TCJA provisions and additional guidance issued by the IRS pursuant to the TCJA may continue to impact us in future periods. Additional changes in the U.S. tax regime, including changes in how existing tax laws are interpreted or enforced, can adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We will also be subject to regular reviews, examinations and audits by the IRS and other taxing authorities with respect to income and non-income-based taxes. Economic and political pressures to increase tax revenues in jurisdictions in which we operate, or the adoption of new or reformed tax legislation or regulation, may make resolving tax disputes more difficult and the final resolution of tax audits and any related litigation can differ from our historical provisions and accruals, resulting in an adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Tax Risks Related to Our Tax Structure and Taxes
Although we may be entitled to tax benefits relating to additional tax depreciation or amortization deductions as a result of the tax basis step-up we receive in connection with the exchanges of Retained OppFi-LLC Units into our Class A Common Stock and related transactions, we are required to pay the Members 90% of these tax benefits under the Tax Receivable Agreement.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 66.4 million Initial Shares may be exchanged for shares of our Class A Common Stock by the Members pursuant to the Members’ Exchange Rights, and may be sold without any contractual restriction by the Members. Pursuant to the lock-up restrictions agreed to into in connection with the Investor Rights Agreement, beginning on the nine month anniversary of the Closing (unless earlier waived by the Company in its capacity as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC), or with respect to the Earnout Units, on such later date the Earnout Units are earned in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement, each Retained OppFi-LLC Unit (other than the Initial Shares) held by the Members may be exchanged, upon the exercise of such Members’ Exchange Rights, for either one share of Class A Common Stock or, at the election of the Company in its capacity as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC, the cash equivalent of the market value of one share of Class A Common Stock, pursuant to the terms and conditions of the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA. The deemed exchanges in the business combination and any exchanges pursuant to the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA, are expected to result in increases in our allocable share of the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of OppFi-LLC. These increases in tax basis may increase (for tax purposes) depreciation and amortization deductions and therefore reduce the amount of income or franchise tax that we would otherwise be required to pay in the future, although the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) or any applicable foreign, state or local tax authority may challenge all or part of that tax basis increase, and a court could sustain such a challenge.
At the Closing, we entered into the Tax Receivable Agreement, which generally provides for the payment by us to holders of Retained OppFi-LLC Units of 90% of certain tax benefits, if any, that we realize as a result of these increases in tax basis and of certain other tax benefits related to entering into the Tax Receivable Agreement, including income or franchise tax benefits attributable to payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement. These payment obligations pursuant to the Tax Receivable Agreement are the obligation of the Company and not of OppFi-LLC. The actual increase in our allocable share of OppFi-LLC’s tax basis in its assets, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of exchanges, the market price of shares of our Class A Common Stock at the time of the exchange, the extent to which such exchanges are taxable and the amount and timing of our income. Because none of the foregoing factors are known at this time, we cannot determine the amounts (if any) that would be payable under the Tax Receivable Agreement. However, we expect that as a result of the possible size and frequency of the exchanges and the resulting increases in the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of OppFi-LLC, the payments that we expect to make under the Tax Receivable Agreement will be substantial and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition. The payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement are not conditioned upon continued ownership of the Company by the holders of units.
The Members will not be required to reimburse us for any excess payments that may previously have been made under the Tax Receivable Agreement, for example, due to adjustments resulting from examinations by taxing authorities. Rather, excess payments made to such holders will be netted against payments otherwise to be made, if any, after the determination of such excess. As a result, in certain circumstances we could make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement in excess of our actual income or franchise tax savings, which could materially impair our financial condition.
In certain cases, payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement may be accelerated or significantly exceed the actual benefits we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the Tax Receivable Agreement.
Payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement will be based on the tax reporting positions that we determine, and the IRS or another taxing authority may challenge all or any part of the tax basis increases, as well as other tax positions that we take, and a court may sustain such a challenge. In the event that any tax benefits initially claimed by us are disallowed, the Members and the exchanging holders will not be required to reimburse us for any excess payments that may previously have been made under the Tax Receivable Agreement, for example, due to adjustments resulting from examinations by the IRS or other taxing authorities. Rather, excess payments made to such holders will be applied against and reduce any future cash payments otherwise required to be made by us, if any, after the determination of such excess. However, a challenge to any tax benefits initially claimed by us may not arise for a number of years following the initial time of such payment and, even if challenged earlier, such excess cash payment may be greater than the amount of future cash payments that we might otherwise be required to make under the terms of the Tax Receivable Agreement and, as a result, there might not be future cash payments against which such excess can be applied. As a result, in certain circumstances we could make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement in excess of our actual income or franchise tax savings, which could materially impair our financial condition.
Moreover, the Tax Receivable Agreement provides that, in the event that we exercise our right to early termination of the Tax Receivable Agreement, or in the event of a change of control of the Company or we are more than 90 days late in making of a payment due under the Tax Receivable Agreement, the Tax Receivable Agreement will terminate, and we are required to make a lump-sum payment to the Members equal to the present value of all forecasted future payments that would have otherwise been made under the Tax Receivable Agreement, which lump-sum payment would be based on certain assumptions, including those relating to our future taxable income. The change of control payment to the Members could be substantial and could exceed the actual tax benefits that we receive as a result of acquiring units from owners of OppFi-LLC because the amounts of such payments would be calculated assuming that we would have been able to use the potential tax benefits each year for the remainder of the amortization periods applicable to the basis increases, and that tax rates applicable to us would be the same as they were in the year of the termination.
Decisions made in the course of running our business, such as with respect to mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes in control, may influence the timing and amount of payments that are received by the other holders of Retained OppFi-LLC Units under the Tax Receivable Agreement. For example, the earlier disposition of assets following an exchange or acquisition transaction will generally accelerate payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement and increase the present value of such payments, and the disposition of assets before an exchange or acquisition transaction will increase an existing owner’s tax liability without giving rise to any rights of holders of Retained OppFi-LLC Units to receive payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement.
There may be a material negative effect on our liquidity if the payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement exceed the actual income or franchise tax savings that we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the Tax Receivable Agreement or if distributions to us by OppFi-LLC are not sufficient to permit us to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement after we have paid taxes and other expenses. Furthermore, our obligations to make payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement could make us a less attractive target for an acquisition, particularly in the case of an acquirer that cannot use some or all of the tax benefits that are deemed realized under the Tax Receivable Agreement. We may need to incur additional indebtedness to finance payments under the Tax Receivable Agreement to the extent our cash resources are insufficient to meet our obligations under the Tax Receivable Agreement as a result of timing discrepancies or otherwise which may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
We may not be able to realize all or a portion of the tax benefits that are expected to result from the acquisition of Retained OppFi-LLC Units from OppFi-LLC Members.
Pursuant to the Tax Receivable Agreement, the Company will share tax savings resulting from (A) the amortization of the anticipated step-up in tax basis in OppFi-LLC’s assets as a result of (i) the business combination and (ii) the exchange of Retained OppFi-LLC Units that were received in connection with the Business Combination, for shares of Class A Stock pursuant to the OppFi-LLC A&R LLCA and (B) certain other related transactions with the Members. The amount of any such tax savings attributable to the payment of cash to the Members in the business combination and the exchanges contemplated by the Exchange Agreement will be paid 90% to the Members and retained 10% by the Company. Any such amounts payable will only be due once the relevant tax savings have been realized by the Company. Our ability to realize, and benefit from, these tax
savings depends on a number of assumptions, including that we will earn sufficient taxable income each year during the period over which the deductions arising from any such basis increases and payments are available and that there are no adverse changes in applicable law or regulations. If our actual taxable income were insufficient to fully utilize such tax benefits or there were adverse changes in applicable law or regulations, we may be unable to realize all or a portion of these expected benefits and our cash flows and stockholders’ equity could be negatively affected.
Taxing authorities may successfully assert that we should have collected or in the future should collect sales and use, gross receipts, value added or similar taxes and may successfully impose additional obligations on us, and any such assessments or obligations could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The application of indirect taxes, such as sales and use tax, value-added tax, goods and services tax, business tax and gross receipts tax, to platform businesses is a complex and evolving issue. Many of the fundamental statutes and regulations that impose these taxes were established before the adoption and growth of the Internet and e-commerce. Significant judgment is required on an ongoing basis to evaluate applicable tax obligations and as a result amounts recorded are estimates and are subject to adjustments. In many cases, the ultimate tax determination is uncertain because it is not clear how new and existing statutes might apply to our business.
In addition, governments are increasingly looking for ways to increase revenue, which has resulted in discussions about tax reform and other legislative action to increase tax revenue, including through indirect taxes. For example, on November 6, 2018, voters in San Francisco approved “Proposition C,” which authorizes San Francisco to impose additional taxes on businesses in San Francisco that generate a certain level of gross receipts, and in January 2022, the California assembly introduced legislation proposing a statewide tax on business that generate gross receipts of over $2 million. Such taxes would adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We may face various indirect tax audits in various U.S. jurisdictions. In certain jurisdictions, we collect and remit indirect taxes. However, tax authorities may raise questions about or challenge or disagree with our calculation, reporting or collection of taxes and may require us to collect taxes in jurisdictions in which we do not currently do so or to remit additional taxes and interest, and could impose associated penalties and fees. For example, after the U.S. Supreme Court decision in South Dakota v. Wayfair Inc., certain states have adopted, or started to enforce, laws that may require the calculation, collection and remittance of taxes on sales in their jurisdictions, even if we do not have a physical presence in such jurisdictions. A successful assertion by one or more tax authorities requiring us to collect taxes in jurisdictions in which we do not currently do so or to collect additional taxes in a jurisdiction in which we currently collect taxes, could result in substantial tax liabilities, including taxes on past sales, as well as penalties and interest, could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. Although we have reserved for potential payments of possible past tax liabilities in our financial statements, if these liabilities exceed such reserves, our financial condition will be harmed.
As a result of these and other factors, the ultimate amount of tax obligations owed may differ from the amounts recorded in our financial statements and any such difference may adversely impact our results of operations in future periods in which we change our estimates of our tax obligations or in which the ultimate tax outcome is determined.
Changes in U.S. tax laws could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, or the Tax Act contains significant changes to U.S. tax law, including a reduction in the corporate tax rate and a transition to a new territorial system of taxation. The primary impact of the new legislation on our provision for income taxes was a reduction of the future tax benefits of our deferred tax assets as a result of the reduction in the corporate tax rate. The impact of the Tax Act will likely be subject to ongoing technical guidance and accounting interpretation, which we will continue to monitor and assess. As we expand the scale of our business activities, any changes in the U.S. taxation of such activities may increase our effective tax rate and harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy
We confront substantial cybersecurity risks driven by various factors. These risks are rooted in the wide range of systems we must safeguard against cyberattacks, further exacerbated by the complexity and technical sophistication of our products and systems. Additionally, our reliance on third-party products, services, and components adds complexity to our risk landscape.
In response, we have adopted a cybersecurity program to manage cybersecurity risks, prioritizing the protection of data entrusted to us by our customers and other stakeholders. We employ various mechanisms, controls, technologies, and processes aimed at assessing, identifying, and managing these risks.
Our cybersecurity program is rooted in industry best practices, drawing upon frameworks established by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (“NIST”), the International Organization for Standardization, and other relevant industry standards. This does not mean that we meet any particular technical standards, specifications, or requirements, but only that we use these standards as a guide to help us design and assess our program.
Our policies, standards, processes, and practices for assessing, identifying, and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats are integrated into our overall risk management program. Regular cybersecurity risk assessments are conducted, leveraging both internal and external sources of information to drive alignment on initiatives aimed at enhancing security controls. We maintain a cybersecurity incident response plan that identifies the activities and escalation processes to be implemented upon detection of a cybersecurity incident, and we regularly test and evaluate the effectiveness of such plan.
Technical safeguards undergo periodic assessment and enhancement designed to protect information systems from cybersecurity threats, utilizing vulnerability assessments, threat intelligence, and incident response experience. Our policies also mandate that our employees contribute to our security efforts. We regularly remind our employees of the importance of handling and protecting customer and employee data through quarterly security training and testing, aimed at enhancing employee awareness and improving their ability to detect and respond to cybersecurity threats.
Additionally, controls have been implemented that are designed to identify and mitigate cybersecurity threats associated with our use of third-party service providers. Certain providers undergo security risk assessments upon onboarding and upon detection of an increase in their risk profile. Our risk assessments utilize various inputs, including information supplied by the providers and third parties. Furthermore, we mandate that our providers meet appropriate security requirements, controls, and responsibilities. We also investigate security incidents impacting our third-party providers as necessary.
Our cybersecurity policies, standards, processes and practices are regularly assessed by external consultants and auditors. These assessments include a variety of activities including information security maturity assessments, audits and independent reviews of our information security control environment and operating effectiveness. For example, for the last three years, we conducted an independent cyber security risk assessment to assess our cybersecurity maturity against the NIST cybersecurity framework. The results of significant assessments are reported to management and our Audit Committee. Cybersecurity processes are adjusted based on the information provided from these assessments.
For more information on our cybersecurity risks that may materially affect us, please refer to the section titled “Risk Factors – Security breaches of borrowers’ confidential information that we store may harm our reputation, adversely affect our results of operations and expose us to liability – and – If our risk management framework does not effectively identify and control our risks, we could suffer unexpected losses or be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.” While to date we have not identified any breaches from known cybersecurity threats, including as a result of any prior cybersecurity incidents, that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect us, including our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, the sophistication of cybersecurity threats continues to increase, and the preventative actions we take to reduce the risk of cybersecurity incidents and protect our systems and information may be insufficient. Accordingly, no matter how well our program is designed or implemented, we will not be able to anticipate all security breaches, and we may not be able to implement effective preventive measures against such security breaches in a timely manner, which could result in substantial expenses and reputational damage.
Cybersecurity Governance
Our Board of Directors and management are actively involved in the oversight of our risk management program, with cybersecurity representing a critical component to ensure alignment with our strategic objectives. The Audit Committee directly
oversee and regularly review our cybersecurity program, receiving periodic reports from our Chief Information Security Officer (“CISO”) on various matters including risk assessment results, progress of risk reduction initiatives, feedback from external auditors, control maturity assessments, and relevant internal and industry cybersecurity incidents.
While our Board of Directors has overall responsibility for the oversight of our enterprise-wide risk management, of which cybersecurity risk management is one component, our management team is responsible for day-to-day risk management, including the implementation of our cybersecurity program. We have established an information security council (the “Information Security Council”), with full participation from our senior management team, to serve as the steward of our information security program. Designed to meet quarterly or more frequently as needed, the council reviews security performance metrics, stays abreast of industry trends and regulatory changes, and evaluates progress on security initiatives. The council plays a crucial role in promoting a culture of security awareness and ensuring OppFi remains resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Our corporate information security organization manages and continually enhances a robust enterprise security structure with the goal of averting cybersecurity incidents while increasing our system resilience to minimize the business impact should an incident occur. Led by our CISO, who reports to the Chief Technology Officer (“CTO”), our corporate information security organization is composed of seasoned professionals, some holding certifications such as Certified Information Systems Security Professional or Certified Information Security Manager. Our CTO has served in various leadership roles in information technology for over 20 years, including a nine-year tenure as the Chief Technology Officer at a fintech company. He holds a bachelor's degree in computer engineering and a master's degree in information systems. Our CISO, with over 20 years of leadership experience in IT and security, was a CISO at a financial services company before joining OppFi. She has an MBA and a master's degree in Computer Information Systems and is a Certified Information Security Manager (CISM). Additionally, both the CISO and CTO are members of the Information Security Council, providing regular updates to our senior management team regarding our cybersecurity program, mitigation strategy, and progress.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
OppFi’s corporate headquarters is located in Chicago, Illinois and consists of approximately 79,928 square feet under a lease that expires in 2030. We sublease 10,481 square feet to a subtenant under a three-year lease that expires on August 31, 2025. OppFi believes that its facilities are adequate for its current needs and that, if necessary, additional facilities will be available to accommodate the expansion of its business. We do not own any real property.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
See “Legal contingencies” of Note 14 to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER
MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information and Stockholders
The Company’s Class A Common Stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “OPFI.” As of March 22, 2024, there were 32 stockholders of record of our Class A Common Stock and 1 stockholder of record of our Class V Voting Stock. In addition to holders of record of our Class A Common Stock, we believe there is a substantially greater number of “street name” holders or beneficial holders whose Class A Common Stock is held of record by banks, brokers, and other financial institutions.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared nor paid cash dividends on our common stock, and do not currently have any plans to declare or pay any dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. The declaration of cash dividends in the future is subject to the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on a number of factors, including our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, and other relevant factors.
Stock Performance Graph
As a “smaller reporting company,” as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act, and pursuant to Instruction 6 to Item 201(e) of Regulation S-K, we are not required to provide this information.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
None.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
On January 6, 2022, OppFi announced that its Board of Directors (“Board”) had authorized the Repurchase Program. The Repurchase Program expired in December 2023. There was no repurchase activity during the fourth quarter of 2023.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
Information relating to equity compensation plans will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement for the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
ITEM 6. [RESERVED]
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION
OVERVIEW
OppFi is a tech-enabled, mission-driven specialty finance platform that broadens the reach of community banks to extend credit access to everyday Americans. The Company’s platform powers banks to offer accessible lending products through its proprietary technology and top-rated customer experience. OppFi’s primary mission is to facilitate financial inclusion and credit access to the 63 million everyday Americans who are credit marginalized with digital specialty finance products and an unwavering commitment to its customers.
OppFi works with banks to facilitate short-term credit options for everyday Americans who lack access to mainstream financial products. OppFi’s specialty finance platform focuses on helping these consumers rebuild their financial health. Customers on OppFi’s platform benefit from a highly automated, transparent, efficient, and fully digital experience. The banks that work with OppFi benefit from its turn-key, outsourced marketing, data science, and proprietary technology to digitally acquire, underwrite and service these consumers.
OppFi’s primary products are offered by its OppLoans platform. Customers on this platform are U.S. consumers, who are employed, have bank accounts, and generally earn median wages. The average installment loan facilitated by OppFi is approximately $1,500, payable in installments and with an average contractual term of 11 months. Neither SalaryTap nor OppFi Card contributed meaningfully to OppFi’s results during the year ended December 31, 2023.
On the Closing Date, OppFi completed the Business Combination. At the Closing, FGNA changed its name to “OppFi Inc.” OppFi’s Class A Common Stock and Public Warrants are listed on the NYSE under the symbols “OPFI” and “OPFI WS,” respectively.
Unless the context otherwise requires, all references in this section to “OppFi” or the “Company” refer OppFi-LLC and its subsidiaries prior to the Closing, or to OppFi Inc. and its subsidiaries from and after the Closing. See Item 1. “Business” for more information.
HIGHLIGHTS
Our financial results as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023 are summarized below:
•Basic and diluted loss per share of $0.06 and $0.06 for the year ended December 31, 2023, respectively;
•Adjusted earnings per share (“Adjusted EPS”)(1) of $0.51 for the year ended December 31, 2023;
•Ending receivables increased 4% to $416.5 million from $402.2 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively;
•Total revenue increased 12% to $508.9 million from $452.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively;
•Net income of $39.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, an increase of $36.1 million from $3.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022; and
•Adjusted net income (“Adjusted Net Income”)(1) of $43.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, an increase of $38.4 million from $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
(1) Adjusted EPS and Adjusted Net Income are not prepared in accordance with the United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”). For information regarding our uses and definitions of these measures and for reconciliations to the most directly comparable United States GAAP measures, see the section titled “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” below.
Key Performance Metrics
We regularly review the following key metrics to evaluate our business, measure our performance, identify trends affecting our business, formulate financial projections, and make strategic decisions, which may also be useful to an investor. The following tables and related discussion set forth key financial and operating metrics for the Company’s operations as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
The key performance metrics presented are for the OppLoans product only and exclude the SalaryTap and OppFi Card products. Prior period metrics currently presented may differ slightly than previously reported due to the exclusion of SalaryTap and OppFi Card.
Total Net Originations
We measure originations to assess the growth trajectory and overall size of our loan portfolio. There is a direct correlation between origination growth and revenue growth. We include both bank partner originations as well as those originated by us directly. OppFi ended its direct lending program during 2023 and exclusively utilizes a bank partner model, as of December 31, 2023. Loans are considered to be originated when the contract is signed between us and the prospective borrower. The vast majority of our originations ultimately disburse to a borrower, but disbursement timing lags that of originations. Originations may be useful to an investor because they help understand the growth trajectory of our revenues.
The following table presents total net originations (defined as gross originations net of transferred balance on refinanced loans), percentage of net originations by bank partners, and percentage of net originations by new loans for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Total net originations | | $ | 747,839 | | $ | 752,918 | | $ | (5,079) | | | (0.7) | % |
| Percentage of net originations by bank partners | | 97.7 | % | | 94.6 | % | | N/A | | 3.3 | % |
| Percentage of net originations by new loans | | 43.6 | % | | 51.2 | % | | N/A | | (14.8) | % |
Net originations decreased to $747.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from $752.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Despite greater application volume, the 0.7% decrease was driven by relatively tighter credit standards with the qualified rate (defined as qualified applications over total applications) dropping year over year.
Total net originations by our bank partners increased to 97.7% for the year ended December 31, 2023 from 94.6% for the year ended December 31, 2022. The 3.3% increase is due to our origination mix continuing to shift towards a servicing / facilitation model for bank partners from a direct origination model.
Total net originations of new loans as percentage of total loans decreased to 43.6% for the year ended December 31, 2023 from 51.2% for the year ended December 31, 2022. The decrease is a result of credit adjustments midway through 2022 causing a lower qualified rate on new loans as well as marketing campaigns targeting email engagement rates in the refinance population.
Ending Receivables
Ending receivables are defined as the unpaid principal balances of loans at the end of the reporting period. The following table presents ending receivables as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Ending receivables | | $ | 416,463 | | | $ | 402,180 | | | $ | 14,283 | | | 3.6 | % |
Ending receivables increased to $416.5 million as of December 31, 2023 from $402.2 million as of December 31, 2022. The 3.6% increase was primarily driven by a higher receivables balance to begin the year in 2023 relative to 2022 as well as a healthier portfolio leading to less charge-offs year over year.
Average Yield
Average yield represents interest income from the period as a percent of average receivables. Receivables are defined as the unpaid principal balances of loans. The following table presents average yield for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | % |
| Average yield | | 127.3 | % | | 120.0 | % | | 6.1 | % |
Average yield increased to 127.3% for the year ended December 31, 2023 from 120.0% for the year ended December 31, 2022. The 6.1% increase was driven by a decrease in delinquent loans in the portfolio that were not accruing interest and a decrease in enrollment in our hardship and assistance programs, which provide payment relief due to natural disasters, loss of income, increase in expenses, or other unpredictable events such as COVID-19, as well as a relative shift away from states with lower interest rates.
Net Charge-Offs as a Percentage of Average Receivables
Net charge-offs as a percentage of average receivables represents total charge-offs from the period less recoveries as a percent of average receivables. Receivables are defined as the unpaid principal balances of loans. Our charge-off policy is based on a review of delinquent finance receivables on a loan by loan basis. Finance receivables are charged off at the earlier of the time
when accounts reach 90 days past due on a recency basis, when we receive notification of a customer bankruptcy, or when finance receivables are otherwise deemed uncollectible.
The following table presents net charge-offs as a percentage of average receivables for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | % |
| Net charge-offs as % of average receivables | | 55.4 | % | | 61.9 | % | | (10.5) | % |
Net charge-offs as a percentage of average receivables decreased by 10.5% to 55.4% for the year ended December 31, 2023 from 61.9% for the year ended December 31, 2022. The decrease for the year ended December 31, 2023 is a combination of the lower quality loans originated prior to credit adjustments midway through 2022 having charged off and higher quality loans being originated following the credit adjustments.
Auto-Approval Rate
Auto-approval rate is calculated by taking the number of approved loans that are not decisioned by a loan advocate or underwriter (auto-approval) divided by the total number of loans approved. The following table presents auto approval rate for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | % |
| Auto-approval rate | | 71.9 | % | | 65.3 | % | | 10.1 | % |
Auto-approval rate increased by 10.1% for the year ended December 31, 2023 to 71.9% from 65.3% for the year ended December 31, 2022, driven by the continued application of algorithmic automation projects that streamline frictional steps of the origination process.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The following table presents our consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands, except number of shares and per share data).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Interest and loan related income | | $ | 505,430 | | | $ | 451,448 | | | $ | 53,982 | | | 12.0 | % |
| Other revenue | | 3,519 | | | 1,411 | | | 2,108 | | | 149.4 | |
| Total revenue | | 508,949 | | | 452,859 | | | 56,090 | | | 12.4 | |
| Change in fair value of finance receivables | | (231,419) | | | (233,959) | | | 2,540 | | | (1.1) | |
| Provision for credit losses on finance receivables | | (4,348) | | | (1,940) | | | (2,408) | | | 124.1 | |
| Net revenue | | 273,182 | | | 216,960 | | | 56,222 | | | 25.9 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and marketing | | 46,222 | | | 54,407 | | | (8,185) | | | (15.0) | |
| Customer operations | | 41,559 | | | 42,314 | | | (755) | | | (1.8) | |
| Technology, products, and analytics | | 39,161 | | | 33,439 | | | 5,722 | | | 17.1 | |
| General, administrative, and other | | 53,135 | | | 57,980 | | | (4,845) | | | (8.4) | |
| Total expenses before interest expense | | 180,077 | | | 188,140 | | | (8,063) | | | (4.3) | |
| Interest expense | | 46,750 | | | 35,162 | | | 11,588 | | | 33.0 | |
| Total expenses | | 226,827 | | | 223,302 | | | 3,525 | | | 1.6 | |
| Income (loss) from operations | | 46,355 | | | (6,342) | | | 52,697 | | | 830.9 | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liabilities | | (4,976) | | | 9,352 | | | (14,328) | | | (153.2) | |
| Other income | | 431 | | | 53 | | | 378 | | | 713.2 | |
| Income before income taxes | | 41,810 | | | 3,063 | | | 38,747 | | | 1265.0 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | | 2,331 | | | (277) | | | 2,608 | | | 941.5 | |
| Net income | | 39,479 | | | 3,340 | | | 36,139 | | | 1082.0 | |
| Less: net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interest | | 40,484 | | | (3,758) | | | 44,242 | | | 1177.3 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to OppFi Inc. | | $ | (1,005) | | | $ | 7,098 | | | $ | (8,103) | | | (114.2) | % |
| | | | | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share attributable to OppFi Inc.: | | | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.51 | | | | | |
| Diluted | | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.05 | | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | 16,391,199 | | 13,913,626 | | | | |
| Diluted | | 16,391,199 | | 84,256,084 | | | | |
Total Revenue
Total revenue consists mainly of revenue earned from interest on receivables from outstanding loans based on the interest method. We also earn revenue from referral fees related primarily to our turn-up program, which represented 0.3% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Total revenue increased by $56.1 million, or 12.4%, to $508.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from $452.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase was due to higher average receivables balances throughout the year as well as stronger payment activity driving a higher yield on the balances.
Change in Fair Value and Provision for Credit Losses on Finance Receivables
Commencing on January 1, 2021, we elected the fair value option on the OppLoans installment product. To derive the fair value, we generally utilize discounted cash flow analyses that factor in estimated losses and prepayments over the estimated duration of the underlying assets. Loss and prepayment assumptions are determined using historical loss data and include appropriate consideration of recent trends and anticipated future performance. Future cash flows are discounted using a rate of return that we believe a market participant would require based on the risk characteristics of the loans. We did not elect the fair value option on our SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables, which are carried at amortized cost, net of allowance for credit losses.
Change in fair value consists of gross charge-offs incurred in the period on the OppLoans installment product, net of recoveries, plus the change in the fair value on the installment loans portfolio. Change in fair value totaled $231.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, which was comprised of $220.9 million of net charge-offs and a fair market value adjustment of $10.5 million, down from $234.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, which was comprised of $232.3 million of net charge-offs and a fair market value adjustment of $1.7 million. The fair value mark decreased primarily due to an increase in the default rate, partially offset by an increase in the weighted average interest rate of the portfolio.
Provision for credit losses on finance receivables consists of gross charge-offs incurred in the period, net of recoveries, plus the change in allowance for credit losses for our SalaryTap and OppFi Card products. Provision for credit losses on finance receivables increased by $2.4 million to $4.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, from $1.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Provision for credit losses on finance receivables for the year ended December 31, 2023 increased due to higher charge-offs throughout the year, particularly due to the OppFi Card portfolio.
Net Revenue
Net revenue is equal to total revenue less the change in fair value and total provision costs. Total net revenue increased by $56.2 million, or 25.9%, to $273.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from $217.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was mainly due to the increase in total revenue.
Expenses
Expenses include costs related to salaries and employee benefits, interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs, sales and marketing, customer operations, technology, products, and analytics, and general, administrative, and other expenses.
Expenses increased by $3.5 million, or 1.6%, to $226.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from $223.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. The increase in expenses was primarily related to elevated interest expense as a result of increased debt draws to support higher receivables balances and a rising interest rate environment and higher professional fees related to accounting, legal, and staffing matters. The increase was partially offset by lower direct marketing costs resulting from lower total originations as well as a relative shift in originations towards lower-cost refinance loans. Despite the overall increase in expenses, expenses as a percent of total revenue decreased from 49.3% to 44.6% for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022.
Income (Loss) from Operations
Income (loss) from operations is the difference between net revenue and expenses. Total income from operations increased by $52.7 million to $46.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from loss from operations of $6.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was due to higher net revenue outweighing higher total expenses for the year ended December 31, 2023 as a result of the reasons discussed above.
Change in Fair Value of Warrant Liabilities
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities totaled $(5.0) million for the year ended December 31, 2023 and $9.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. These warrant liabilities arose with respect to warrants issued in connection with the initial public offering of FGNA and is subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date.
Other Income
Other income totaled $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 and $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. For the year ended December 31, 2023, other income includes the $0.3 million in income related to the Company subleasing one floor of its office space and $0.1 million from the gain on partial loan forgiveness of the secured borrowing payable. For the year ended December 31, 2022, other income includes the income related to the Company subleasing one floor of its office space.
Income Before Income Taxes
Income before income taxes is the sum of income (loss) from operations, the change in fair value of warrant liabilities, and other income. Income before income tax increased by $38.7 million to $41.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 from $3.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
Income Tax Expense (Benefit)
OppFi Inc. recorded an income tax expense of $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, an increase of $2.6 million from income tax benefit of $0.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. This increase was largely attributed to the change in fair value of warrant liabilities.
Net Income
Net income increased by $36.1 million to $39.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, from $3.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 for all of the reasons stated above.
Net (Loss) Income Attributable to OppFi Inc.
Net loss attributable to OppFi Inc. was $1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, down from net income attributable to OppFi Inc. of $7.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Net (loss) income attributable to OppFi Inc. represents the income solely attributable to stockholders of OppFi Inc. As a result of the Company’s Up-C structure, the underlying income or expense components that are attributable to OppFi Inc. are generally expense items related to OppFi Inc.’s status as a public company, the income or expense for the change in fair value of warrant liabilities related to the Company’s warrants, and the Company’s approximate percentage interest in the non-controlling interest. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the underlying income or expense components that are attributable to OppFi Inc. include the loss on change in fair value of warrant liabilities of $5.0 million, tax expense of $2.1 million, general and administrative expense of $0.6 million, and board fees of $0.4 million, for total loss attributable to OppFi Inc. of $8.1 million. The loss also includes OppFi Inc.’s percentage interest in the income attributable to non-controlling interest of $7.1 million, for net loss attributable to OppFi Inc. of $1.0 million. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the underlying income or expense components that are attributable to OppFi Inc. include the gain on change in fair value of warrant liabilities of $9.4 million and tax benefit of $0.3 million, partially offset by payroll and stock compensation expense of $0.8 million, general and administrative expense of $0.7 million, and board fees of $0.4 million, for total income attributable to OppFi Inc. of $7.8 million. The income also includes OppFi Inc.’s percentage interest in the loss attributable to non-controlling interest of $0.7 million, for net income attributable to OppFi Inc. of $7.1 million.
Diluted Earnings per Share
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company’s outstanding shares of Class V Voting Stock were excluded in computing the diluted earnings per share as the inclusion of these shares would have had an antidilutive effect under the if-converted method. Under the if-converted method, shares of the Company’s Class V Voting Stock are assumed to be exchanged, together with OppFi Units, into shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock as of the beginning of the period. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company’s outstanding shares of Class V Voting Stock were included in computing the diluted earnings per share as the inclusion of these shares had a dilutive effect under the if-converted method.
Condensed Balance Sheets
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
The following table presents our condensed balance sheet as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and restricted cash | | $ | 73,943 | | | $ | 49,670 | | | $ | 24,273 | | | 48.9 | % |
| Finance receivables at fair value | | 463,320 | | | 457,296 | | | 6,024 | | | 1.3 | |
| Finance receivables at amortized cost, net | | 110 | | | 643 | | | (533) | | | (82.9) | |
| Other assets | | 64,170 | | | 72,230 | | | (8,060) | | | (11.2) | |
| Total assets | | $ | 601,543 | | | $ | 579,839 | | | $ | 21,704 | | | 3.7 | % |
| Liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | $ | 26,448 | | | $ | 29,558 | | | $ | (3,110) | | | (10.5) | % |
| Other liabilities | | 40,086 | | | 42,183 | | | (2,097) | | | (5.0) | |
| Total debt | | 334,116 | | | 347,060 | | | (12,944) | | | (3.7) | |
| Warrant liabilities | | 6,864 | | | 1,888 | | | 4,976 | | | 263.6 | |
| Total liabilities | | 407,514 | | | 420,689 | | | (13,175) | | | (3.1) | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | | 194,029 | | | 159,150 | | | 34,879 | | | 21.9 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 601,543 | | | $ | 579,839 | | | $ | 21,704 | | | 3.7 | % |
Total cash and restricted cash increased by $24.3 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 driven by an increase in received payments relative to originations. Finance receivables at fair value increased by $6.0 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 due to strength in issuance volume and decrease in charge-offs throughout the second half of the year. Finance receivables at amortized cost, net decreased by $0.5 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 due to the continued rundown of OppFi Card and SalaryTap finance receivables. Other assets decreased by $8.1 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 mainly due to a decrease in property, equipment, and software of $3.7 million, a decrease in the operating lease right of use asset of $1.4 million, and a decrease in the deferred tax asset of $1.0 million.
Current liabilities decreased by $3.1 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 driven by a decrease in accounts payable of $1.9 million and a decrease in accrued expenses of $1.2 million. Other liabilities decreased by $2.1 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 driven by a decrease in the operating lease liability of $1.5 million and a decrease in the tax receivable agreement liability of $0.6 million. Total debt decreased by $12.9 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 driven by a decrease in utilization of revolving lines of credit of $12.0 million, paydown of the secured borrowing payable of $0.8 million, and a decrease in notes payable of $0.2 million. Warrant liabilities increased by $5.0 million due to the increase in the valuation of the warrants as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022. Total stockholders’ equity increased by $34.9 million as of December 31, 2023 compared to December 31, 2022 driven by net income and stock-based compensation.
NON-GAAP FINANCIAL MEASURES
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022
We believe that the provision of non-GAAP financial measures in this report, including Adjusted EPS, Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted EBT, and Adjusted Net Income can provide useful measures for period-to-period comparisons of our business and useful information to investors and others in understanding and evaluating our operating results. However, non-GAAP financial measures are not calculated in accordance with GAAP measures, should not be considered an alternative to any measure of financial performance calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP, and may not be comparable to the non-GAAP financial measures of other companies.
Adjusted EBT, Adjusted Net Income, and Adjusted EBITDA
Adjusted EBT is a non-GAAP measure defined as our GAAP net income (loss) adjusted to eliminate the effect of certain items as shown below, including provision for income taxes, debt issuance cost amortization, other addbacks and one-time expenses and sublease income. Adjusted Net Income is a non-GAAP measure defined as our Adjusted EBT less pro forma taxes for comparison purposes. We believe that Adjusted EBT and Adjusted Net Income are important measures because they allow management, investors, and our board of directors to evaluate and compare our operating results from period-to-period by making the adjustments described below.
Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP measure defined as our Adjusted Net Income adjusted for the items as shown below, including pro forma and business (non-income) taxes, depreciation and amortization, and interest expense. We believe that Adjusted EBITDA is an important measure because it allows management, investors, and our board of directors to evaluate and compare our operating results from period-to-period by making the adjustments described below. In addition, it provides a useful measure for period-to-period comparisons of our business, as it removes the effect of taxes, certain non-cash items, variable charges, and timing differences.
Adjusted EBITDA excludes certain expenses that are required in accordance with GAAP because they are non-recurring items (such as severance), non-cash expenditures (such as depreciation and amortization, changes in the fair value of warrant liabilities, and expenses related to stock compensation), or are not related to our underlying business performance (such as interest expense). We believe these adjustments provide investors with a comparative view of expenses that the Company expects to incur on an ongoing basis.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | | Year Ended December 31, | | Variance |
| (unaudited) | | 2023 | | 2022 | | % |
| Net income | | $ | 39,479 | | | $ | 3,340 | | | 1082.0 | % |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | | 2,331 | | | (277) | | | 941.5 | |
| Debt issuance cost amortization | | 2,428 | | | 2,372 | | | 2.4 | |
| Other addbacks and one-time expenses, net(a) | | 12,790 | | | 1,180 | | | 983.9 | |
| Sublease income | | (318) | | | (53) | | | 500.0 | |
| Adjusted EBT | | 56,710 | | | 6,562 | | | 764.2 | |
| Less: pro forma taxes(b) | | (13,361) | | | (1,586) | | | 742.4 | |
| Adjusted net income | | 43,349 | | | 4,976 | | | 771.2 | |
| Pro forma taxes(b) | | 13,361 | | | 1,586 | | | 742.4 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 12,735 | | | 13,581 | | | (6.2) | |
| Interest expense | | 44,322 | | | 32,789 | | | 35.2 | |
| Business (non-income) taxes | | 917 | | | 934 | | | (1.8) | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | 114,684 | | | $ | 53,866 | | | 112.9 | % |
| | | | | | |
| Adjusted earnings per share | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 0.06 | | | |
| Weighted average diluted shares outstanding | | 85,051,304 | | 84,256,084 | | |
| | | | | | |
| (a) For the year ended December 31, 2023, other addbacks and one-time expenses, net of $12.8 million included a $5.0 million expense related to the change in fair value of the warrant liabilities, $4.1 million in expenses related to provision for credit losses on the OppFi Card finance receivables, $4.1 million in expenses related to stock-based compensation, $1.5 million in expenses related to corporate development, $0.9 million in expenses related to severance and retention, $0.3 million in expenses related to legal fees, a $(3.0) million addback related to the reclassification of OppFi Card finance receivables from assets held for sale to assets held for investment at amortized cost, and a $(0.1) million addback related to partial forgiveness of the secured borrowing payable. For the year ended December 31, 2022, other addbacks and one-time expenses, net of $1.2 million included a $(9.4) million addback related to the change in fair value of the warrant liabilities, a $3.6 million expense related to the impairment of OppFi Card finance receivables as a result of their reclassification as held for sale, $3.4 million in expenses related to stock-based compensation, $3.0 million in expenses related to severance and retention, a $0.5 million expense related to the impairment of the operating lease right of use asset, and $0.1 million in expenses related to legal fees. |
| (b) Assumes the entire Company is a C-Corp with a tax rate of 23.56% for the year ended December 31, 2023 and a tax rate of 24.17% for the year ended December 31, 2022, reflecting the U.S. federal statutory rate of 21% and a blended statutory rate for state income taxes, in order to allow for a comparison with other publicly traded companies. |
Adjusted Earnings Per Share
Adjusted EPS is defined as adjusted net income divided by weighted average diluted shares outstanding, which represent shares of both classes of common stock outstanding, excluding 25,500,000 shares related to earnout obligations and including the impact of restricted stock units, performance stock units, and the employee stock purchase plan. We believe that presenting Adjusted EPS is useful to investors and others because, due to the Company’s Up-C structure, Basic EPS calculated on a GAAP basis excludes a large percentage of the Company’s outstanding shares of common stock, which are Class V Voting Stock, and Diluted EPS calculated on a GAAP basis excludes dilutive securities, including Class V Voting Stock, in any period in which the Company reports a loss as dilutive securities are considered to be antidilutive. Shares of the Company’s Class V Voting Stock may be exchanged, together with OppFi Units, into shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock. We believe that presenting Adjusted EPS is useful to investors and others because it presents the Company’s Adjusted Net Income on a per share basis based on the shares of the Company’s common stock that would be issued but for, and can be issued as a result of, the Company’s Up-C structure, excluding the forfeitable earnout shares from the Company’s Business Combination. The earnout shares issued in the Business Combination are excluded from the calculation of Adjusted EPS because such earnout shares are subject to potential forfeiture pending the achievement (if any) of certain earnout targets pursuant to the terms of the Business Combination, and we believe that, until such shares are forfeited or no longer subject to forfeiture, it is useful to investors and others to provide per share earnings information based only on those shares that are not subject to forfeiture.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (unaudited) | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Weighted average Class A common stock outstanding | 16,391,199 | | 13,913,626 |
| Weighted average Class V voting stock outstanding | 93,857,926 | | 95,724,487 |
| Elimination of earnouts at period end | (25,500,000) | | (25,500,000) |
| Dilutive impact of restricted stock units | 261,595 | | 105,928 |
| Dilutive impact of performance stock units | 40,584 | | 9,492 |
| Dilutive impact of employee stock purchase plan | — | | 2,551 |
| Weighted average diluted shares outstanding | 85,051,304 | | 84,256,084 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | Year Ended
December 31, 2023 | | Year Ended
December 31, 2022 |
| (unaudited) | $ | | Per Share | | $ | | Per Share |
| Weighted average diluted shares outstanding | | | 85,051,304 | | | | 84,256,084 |
| Net income | $ | 39,479 | | | $ | 0.46 | | | $ | 3,340 | | | $ | 0.04 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 2,331 | | | 0.03 | | | (277) | | | — | |
| Debt issuance cost amortization | 2,428 | | | 0.03 | | | 2,372 | | | 0.03 | |
| Other addbacks and one-time expenses, net | 12,790 | | | 0.15 | | | 1,180 | | | 0.01 | |
| Sublease income | (318) | | | — | | | (53) | | | — | |
| Adjusted EBT | 56,710 | | | 0.67 | | | 6,562 | | | 0.08 | |
| Less: pro forma taxes | (13,361) | | | (0.16) | | | (1,586) | | | (0.02) | |
| Adjusted net income | 43,349 | | | $ | 0.51 | | | 4,976 | | | $ | 0.06 | |
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
To date, the funds received from operating income and our ability to obtain lending commitments have provided the liquidity necessary for us to fund our operations.
Maturities of our financing facilities are staggered over three years to help minimize refinance risk.
The following table presents our unrestricted cash and undrawn debt as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Unrestricted cash | | $ | 31,791 | | | $ | 16,239 | |
| Undrawn debt | | $ | 192,333 | | | $ | 136,800 | |
As of December 31, 2023, OppFi had $31.8 million in unrestricted cash, an increase of $15.6 million from December 31, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, OppFi had an additional $192.3 million of unused debt capacity under its financing facilities for future availability, representing a 37% overall undrawn capacity, an increase from $136.8 million as of December 31, 2022. The increase in undrawn debt was driven primarily by the increase in capacity of the revolving credit agreement with affiliates of Atalaya Capital Management in July 2023. Including total financing commitments of $525.0 million, and cash on the balance sheet of $73.9 million, OppFi had approximately $598.9 million in funding capacity as of December 31, 2023.
We believe that our unrestricted cash, undrawn debt and funds from operating income will be sufficient to meet our liquidity needs for at least the next 12 months from the date of this Annual Report. Our future capital requirements will depend on multiple factors, including our revenue growth, aggregate receivables balance, interest expense, working capital requirements, cash provided by and used in operating, investing and financing activities and capital expenditures.
To the extent our unrestricted cash balances, funds from operating income and funds from undrawn debt are insufficient to satisfy our liquidity needs in the future, we may need to raise additional capital through equity or debt financing and may not be able to do so on terms acceptable to it, if at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital when needed, our results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely impacted.
Cash Flows
The following table presents cash provided by (used in) operating, investing and financing activities during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | | Change |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | $ | 296,146 | | | $ | 243,297 | | | $ | 52,849 | | | 21.7 | % |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | (244,292) | | | (317,244) | | | 72,952 | | | (23.0) | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | | (27,581) | | | 61,255 | | | (88,836) | | | (145.0) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and restricted cash | | $ | 24,273 | | | $ | (12,692) | | | $ | 36,965 | | | 291.2 | % |
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $296.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023. This was an increase of $52.8 million when compared to net cash provided by operating activities of $243.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022. Cash provided by operating activities increased mainly due to higher net income and less gain from the change in fair value of warrant liabilities compared to the prior year.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $244.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023. This was a decrease of $73.0 million when compared to net cash used in investing activities of $317.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, mainly due to lower finance receivables originated and acquired and higher finance receivables repaid and recovered.
Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities was $27.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023. This was an increase of $88.8 million when compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $61.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to an increase in member distributions and net payments of senior debt and notes payable, partially offset by a decrease in net payments of secured borrowings payable.
Financing Arrangements
Our corporate credit facilities consist of term loans and revolving loan facilities that we have drawn on to finance our operations and for other corporate purposes. These borrowings are generally secured by all the assets of OppFi-LLC that have not otherwise been sold or pledged to secure our structured finance facilities, such as assets belonging to certain of the special purpose entity subsidiaries of OppFi-LLC (“SPEs”). In addition, we, through our SPEs, have entered into warehouse credit facilities to partially finance the origination of loans by us on our platform or the purchase of participation rights in loans originated by our bank partners through our platform, which credit facilities are secured by the loans or participation rights. See Note 18, Subsequent Events, in the notes to the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion regarding the Company’s revolving credit agreement with UMB Bank, N.A.
The following is a summary of OppFi’s borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Borrowing | | December 31, | | December 31, | | Interest Rate as of | | Maturity |
| Purpose | | Borrower(s) | | Capacity | | 2023 | | 2022 | | December 31, 2023 | | Date |
| Secured borrowing payable | | Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 756 | | | 15.00 | % | | — |
| Senior debt | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC; Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC (Tranche A) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 37,500 | | | SOFR plus 7.36% | | April 2024 |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC (Tranche B) | | $ | 125,000 | | | $ | 103,400 | | | $ | 121,647 | | | SOFR plus 6.75% | | June 2026 |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC (Tranche C) | | $ | 125,000 | | | $ | 37,500 | | | $ | — | | | SOFR plus 7.50% | | July 2027 |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC; SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | SOFR plus 0.11% plus 3.85% | | February 2024 |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC | | $ | 150,000 | | | $ | 93,871 | | | $ | 91,871 | | | SOFR plus 7.50% | | December 2026 |
| Revolving line of credit | | Gray Rock SPV, LLC | | $ | 75,000 | | | $ | 48,442 | | | $ | 44,716 | | | SOFR plus 7.25% | | April 2025 |
| Total revolving lines of credit | | | $ | 475,000 | | | $ | 283,213 | | | $ | 295,734 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Term loan, net | | OppFi-LLC | | $ | 50,000 | | | $ | 49,454 | | | $ | 48,954 | | | LIBOR plus 10.00% | | March 2025 |
| Total senior debt | | | | $ | 525,000 | | | $ | 332,667 | | | $ | 344,688 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Notes payable | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financed insurance premium | | OppFi-LLC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,616 | | | 7.07 | % | | July 2023 |
| Financed insurance premium | | OppFi-LLC | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | — | | | 9.70 | % | | June 2024 |
| Total notes payable | | | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,616 | | | | | |
| | |
LIBOR Transition
In July 2017, the FCA, which regulates LIBOR, announced its intention to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. On December 31, 2021, IBA, the administrator of LIBOR, announced plans to cease publication for all USD LIBOR tenors (except the one- and two-week tenors, which ceased on December 31, 2021) on June 30, 2023. The Federal Reserve Board and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York have identified the SOFR as its preferred alternative to LIBOR in derivatives and other financial contracts. Each of our credit facilities, except for the senior secured multi-draw term loan, provided for the replacement of LIBOR as discussed above in “Financing Arrangements.” As of December 31, 2023, all of our LIBOR-based credit facilities, except for the senior secured multi-draw term loan, have been transitioned to the SOFR. As of December 31, 2023, the senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement was subject to the synthetic LIBOR rates until the senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement is amended. The replacement of LIBOR did not have any material effect on our liquidity or the financial terms of our credit facilities.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires OppFi to make estimates and judgments that affect reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses and related disclosures. OppFi bases estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under current circumstances, results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of certain assets and liabilities that are not readily available from other sources. Estimates are evaluated on an ongoing basis. To the extent that there are differences between OppFi’s estimates and actual results, OppFi’s future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows will be affected.
Accounting policies, as described in detail in the notes to the Company’s consolidated financial statements, are an integral part of the OppFi’s consolidated financial statements. A thorough understanding of these accounting policies is essential when reviewing OppFi’s reported results of operations and financial position. Management believes that the critical accounting policies and estimates listed below require OppFi to make difficult, subjective, or complex judgments about matters that are inherently uncertain:
–Valuation of installment finance receivables accounted for under the fair value option; and
–Valuation of the public and private warrants.
Fair value is the price that could be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants as of the measurement date. Fair value is determined using different inputs and assumptions based upon the instrument being valued. Where observable market prices from transactions for identical assets or liabilities are not available, we identify market prices for similar assets or liabilities. If observable market prices are unavailable or impracticable to obtain for any such similar assets or liabilities, we look to other modeling techniques, which often incorporate unobservable inputs which are inherently subjective and require significant judgment. Fair value estimates requiring significant judgments are determined using various inputs developed by management with the appropriate skills, understanding and knowledge of the underlying asset or liability to ensure the development of fair value estimates is reasonable. In certain cases, our assessments, with respect to assumptions market participants would make, may be inherently difficult to determine, and the use of different assumptions could result in material changes to these fair value measurements.
Installment Finance Receivables: To derive the fair value, the Company generally utilizes discounted cash flow analyses that factor in estimated losses and prepayments over the estimated duration of the underlying assets. Loss and prepayment assumptions are determined using historical loss data and include appropriate consideration of recent trends and anticipated future performance. Future cash flows are discounted using a rate of return that the Company believes a market participant would require.
The following describes the primary inputs to the discounted cash flow analyses that require significant judgment:
•Discount rate: The discount rate utilized in the discounted cash flow analyses reflects our estimate of the rate of return that a market participant would require when investing in financial instruments with similar risk and return characteristics.
•Servicing cost: The servicing cost percentage that is applied to portfolio’s expected cash flows reflects our estimate of the amount we would incur to service the underlying assets over the assets’ remaining lives. Servicing costs are derived from an internal analysis of our cost structure considering the characteristics of our installment finance receivables and have been benchmarked against observable information on comparable assets in the marketplace.
•Remaining life: Remaining life is the time weighted average of the remaining contractual loan term divided by the principal balance at the measurement date. The timing of estimated principal payments is impacted by scheduled amortization of loans, charge-offs, and prepayments.
•Default rate: The default rate reflects our estimate of principal payments that will not be repaid over the remaining life of an installment finance receivable. Charge-off expectations are developed using the historical performance of our installment finance receivable portfolio but also incorporate discretionary adjustments based on our expectations of future credit performance.
•Prepayment rate: The prepayment rate is the estimated percentage of principal payments that will occur earlier than contractually required over the remaining life of an installment finance receivable. Prepayments accelerate the timing of principal repayment and reduce interest payments. Prepayment rates in our discounted cash flow models are developed using historical results but may also incorporate discretionary adjustments based on our expectations of future performance.
Warrants: OppFi holds public and private placement warrants that are recorded as a liability on the consolidated balance sheets. These liabilities are subjected to remeasurement at each balance sheet date and are recorded at fair value. We value Public Warrants at market price based on the observable traded price in the marketplace. For Private Placement Warrants, Private Units Warrants and Underwriter Warrants, we estimate the fair value using a Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model. This model utilizes observable inputs such as risk-free interest rate and common stock price and unobservable inputs, including expected volatility and dividend yield. These inputs may be influenced by several factors that can change significantly and are difficult to predict. These estimates are inherently risky and require significant judgment on the part of management.
Changes in these estimates, that are likely to occur from period to period, or the use of different estimates that the Company could have reasonably used in the current period, would have a material impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations or liquidity.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
As a “smaller reporting company,” as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act, and pursuant to Item 305(e) of Regulation S-K, we are not required to provide this information.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
| | | | | |
| Index to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
| |
Auditor name: RSM US LLP; Firm ID: (49); Auditor location: Raleigh, North Carolina | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of OppFi Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of OppFi Inc. and its subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity/members’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively, the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ RSM US LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2014.
Raleigh, North Carolina
March 27, 2024
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | | | 2022 |
| Assets | | | | | |
Cash(1) | $ | 31,791 | | | | | $ | 16,239 | |
| Restricted cash(1) | 42,152 | | | | 33,431 |
| Total cash and restricted cash | 73,943 | | | | 49,670 |
| Finance receivables at fair value(1) | 463,320 | | | | 457,296 |
Finance receivables at amortized cost, net of allowance for credit losses of $346 and $96 as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 110 | | | | 643 |
| Settlement receivable(1) | 1,904 | | | | 2,000 |
| Assets held for sale | — | | | | 550 |
| Debt issuance costs, net(1) | 3,834 | | | | 4,049 |
| Property, equipment and software, net | 10,292 | | | | 14,039 |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 12,180 | | | | 13,587 |
| Deferred tax asset | 25,777 | | | | 26,758 |
| Other assets(1) | 10,183 | | | | 11,247 |
| Total assets | $ | 601,543 | | | | | $ | 579,839 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | | | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts payable(1) | $ | 4,442 | | | | | $ | 6,338 | |
| Accrued expenses(1) | 22,006 | | | | 23,220 |
| Operating lease liabilities | 15,061 | | | | 16,558 |
| Secured borrowing payable(1) | — | | | | 756 |
| Senior debt, net(1) | 332,667 | | | | 344,688 |
| Notes payable | 1,449 | | | | 1,616 |
| Warrant liabilities | 6,864 | | | | 1,888 |
| Tax receivable agreement liability | 25,025 | | | | 25,625 |
| Total liabilities | 407,514 | | | | 420,689 |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 14) | | | | | |
| Stockholders' equity: | | | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value (1,000,000 shares authorized with no shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | — | | | | — |
Class A common stock, $0.0001 par value (379,000,000 shares authorized with 19,554,774 shares issued and 18,850,860 shares outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 15,464,480 shares issued and 14,760,566 shares outstanding as of December 31, 2022) | 2 | | | | 2 |
Class B common stock, $0.0001 par value (6,000,000 shares authorized with no shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | — | | | | — |
Class V voting stock, $0.0001 par value (115,000,000 shares authorized with 91,898,193 and 94,937,285 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | 9 | | | | 9 |
| Additional paid-in capital | 76,480 | | | | 65,501 |
| Accumulated deficit | (63,591) | | | | (63,546) |
Treasury stock at cost, 703,914 shares as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | (2,460) | | | | (2,460) |
| Total OppFi Inc.'s stockholders' equity (deficit) | 10,440 | | | | (494) |
| Noncontrolling interest | 183,589 | | | | 159,644 |
| Total stockholders' equity | 194,029 | | | | 159,150 |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 601,543 | | | | | $ | 579,839 | |
| | | | | |
| (1) Includes amounts in consolidated variable interest entities ("VIEs") presented separately in the table below. | | | |
| | | | | |
| Continued on next page | | | | | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets - Continued
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| The following table summarizes the consolidated assets and liabilities of VIEs, which are included in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The assets below may only be used to settle obligations of VIEs and are in excess of those obligations. |
| | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | | | 2022 |
| Assets of consolidated VIEs, included in total assets above | | | | | |
| Cash | $ | 368 | | | | | $ | — | |
| Restricted cash | 32,782 | | | | | 24,577 | |
| Total cash and restricted cash | 33,150 | | | | | 24,577 | |
| Finance receivables at fair value | 417,138 | | | | | 417,476 | |
| Settlement receivable | 1,904 | | | | | 2,000 | |
| Debt issuance costs, net | 3,834 | | | | | 4,049 | |
| Other assets | 7 | | | | | 108 | |
| Total assets | $ | 456,033 | | | | | $ | 448,210 | |
| Liabilities of consolidated VIEs, included in total liabilities above | | | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 5 | | | | | $ | 109 | |
| Accrued expenses | 3,614 | | | | | 3,428 | |
| Secured borrowing payable | — | | | | | 756 | |
| Senior debt, net | 283,213 | | | | | 295,734 | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 286,832 | | | | | $ | 300,027 | |
| | | | | |
| See notes to consolidated financial statements. | | | | | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Revenue: | | | | | |
| Interest and loan related income | $ | 505,430 | | | $ | 451,448 | | | $ | 349,029 | |
| Other revenue | 3,519 | | | 1,411 | | | 1,539 | |
| 508,949 | | | 452,859 | | | 350,568 | |
| Change in fair value of finance receivables | (231,419) | | | (233,959) | | | (85,960) | |
| Provision for credit losses on finance receivables | (4,348) | | | (1,940) | | | (929) | |
| Net revenue | 273,182 | | | 216,960 | | | 263,679 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | |
| Salaries and employee benefits | 60,680 | | | 59,976 | | | 65,049 | |
| Direct marketing costs | 50,562 | | | 58,294 | | | 52,462 | |
| Interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs | 46,750 | | | 35,162 | | | 24,119 | |
| Interest expense - related party | — | | | — | | | 137 | |
| Professional fees | 18,027 | | | 12,940 | | | 18,838 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 12,735 | | | 13,581 | | | 10,282 | |
| Technology costs | 12,543 | | | 13,054 | | | 10,064 | |
| Payment processing fees | 10,439 | | | 10,418 | | | 7,480 | |
| Occupancy | 4,431 | | | 4,441 | | | 3,781 | |
| Lower of cost or market adjustment on transfer of finance receivables from held for sale to held for investment | (2,983) | | | — | | | — | |
| Impairment of assets held for sale | — | | | 3,571 | | | — | |
| Management fees - related party | — | | | — | | | 350 | |
| General, administrative and other | 13,643 | | | 11,865 | | | 13,860 | |
| Total expenses | 226,827 | | | 223,302 | | | 206,422 | |
| Income (loss) from operations | 46,355 | | | (6,342) | | | 57,257 | |
| Other (expense) income: | | | | | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liabilities | (4,976) | | | 9,352 | | | 26,405 | |
| Gain on forgiveness of Paycheck Protection Program loan | — | | | — | | | 6,444 | |
| Other income | 431 | | | 53 | | | — | |
| Income before income taxes | 41,810 | | | 3,063 | | | 90,106 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 2,331 | | | (277) | | | 311 | |
| Net income | 39,479 | | | 3,340 | | | 89,795 | |
| Less: net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interest | 40,484 | | | (3,758) | | | 64,241 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to OppFi Inc. | $ | (1,005) | | | $ | 7,098 | | | $ | 25,554 | |
| | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share attributable to OppFi Inc.: | | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per common share: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 1.93 | |
| Diluted | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | 0.48 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | |
| Basic | 16,391,199 | | 13,913,626 | | | 13,218,119 |
| Diluted | 16,391,199 | | 84,256,084 | | | 84,474,039 |
| | | | | |
| See notes to consolidated financial statements. | | | | | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity / Members’ Equity
(in thousands, except share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Total |
| Preferred Units | Class A Common Stock | Class V Voting Stock | Additional Paid- | Accumulated | Treasury | Noncontrolling | Stockholders' Equity / |
| Units | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | in Capital | Earnings (Deficit) | Stock | Interest | Members' Equity |
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | 41,102,500 | $ | 6,660 | | — | $ | — | | — | $ | — | | $ | 352 | | $ | 92,320 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 99,332 | |
| Effects of adopting fair value option | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 69,435 | — | — | 69,435 |
| Net income before transaction | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 44,970 | — | — | 44,970 |
| Profit interest compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | 229 | — | — | — | 229 |
| Member contribution | — | 200 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 200 |
| Member distributions | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (50,241) | — | (783) | (51,024) |
| Warrant units exercised | 486,852 | — | 486,852 | — | (486,852) | — | 5,517 | — | — | — | 5,517 |
| Reverse recapitalization | (41,589,352) | (6,860) | 12,977,690 | 1 | 96,987,093 | 10 | 52,830 | (252,791) | — | 148,693 | (58,117) |
| Exchange of Class V shares | — | — | 161,767 | — | (161,767) | — | 233 | 30 | — | (263) | — |
| Issuance of common stock under equity incentive plan | — | — | 5,175 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Stock-based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,511 | — | — | — | 2,511 |
| Net income after transaction | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 25,554 | — | 19,271 | 44,825 |
| Balance, December 31, 2021 | — | — | 13,631,484 | 1 | 96,338,474 | 10 | 61,672 | (70,723) | — | 166,918 | 157,878 |
| Exchange of Class V shares | — | — | 1,401,189 | 1 | (1,401,189) | (1) | 2,128 | 79 | — | (2,207) | — |
| Issuance of common stock under equity incentive plan | — | — | 387,180 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan | — | — | 44,627 | — | — | — | 125 | — | — | — | 125 |
| Stock-based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3,354 | — | — | — | 3,354 |
| Purchase of treasury stock | — | — | (703,914) | — | — | — | — | — | (2,460) | — | (2,460) |
| Member distributions | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,309) | (1,309) |
| Tax receivable agreement | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,778) | — | — | — | (1,778) |
| Net income (loss) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 7,098 | — | (3,758) | 3,340 |
| Balance, December 31, 2022 | — | — | 14,760,566 | 2 | | 94,937,285 | 9 | | 65,501 | | (63,546) | | (2,460) | | 159,644 | | 159,150 | |
| Exchange of Class V shares | — | | — | | 3,039,092 | | — | | (3,039,092) | | — | | 5,349 | | 960 | | — | | (6,309) | | — | |
| Issuance of common stock under equity incentive plan | — | | — | | 979,216 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan | — | | — | | 189,622 | | — | | — | | — | | 328 | | — | | — | | — | | 328 | |
| Exercise of stock options | — | | — | | 18,651 | | — | | — | | — | | 59 | | — | | — | | — | | 59 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 4,067 | | — | | — | | — | | 4,067 | |
| Tax withholding on vesting of restricted stock units | — | | — | | (136,287) | | — | | — | | — | | (280) | | — | | — | | — | | (280) | |
| Member distributions | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (10,230) | | (10,230) | |
| Tax receivable agreement | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 459 | | — | | — | | — | | 459 | |
| Deferred tax asset | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 997 | | — | | — | | — | | 997 | |
| Net (loss) income | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (1,005) | | — | | 40,484 | | 39,479 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, December 31, 2023 | — | | $ | — | | 18,850,860 | | $ | 2 | | 91,898,193 | | $ | 9 | | $ | 76,480 | | $ | (63,591) | | $ | (2,460) | | $ | 183,589 | | $ | 194,029 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| See notes to consolidated financial statements. | | | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 39,479 | | | $ | 3,340 | | | $ | 89,795 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Change in fair value of finance receivables | 231,419 | | | 233,959 | | | 85,960 | |
| Provision for credit losses on finance receivables | 4,348 | | | 1,940 | | | 929 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 12,735 | | | 13,581 | | | 10,282 | |
| Debt issuance cost amortization | 2,428 | | | 2,372 | | | 2,310 | |
| Stock-based compensation and profit interest expense | 4,067 | | | 3,354 | | | 3,012 | |
| Loss on disposition of equipment | 3 | | | 1 | | | 6 | |
| Lower of cost or market adjustment on transfer of finance receivables from held for sale to held for investment | (2,983) | | | — | | | — | |
| Impairment loss on assets held for sale | — | | | 3,571 | | | — | |
| Impairment of right of use asset | — | | | 465 | | | — | |
| Tax receivable agreement liability adjustment | 163 | | | (36) | | | 296 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 1,667 | | | (553) | | | (544) | |
| Change in fair value of warrant liabilities | 4,976 | | | (9,352) | | | (26,405) | |
| Change in fair value of warrant units | — | | | — | | | 4,208 | |
| Gain on forgiveness of debt | (113) | | | — | | | — | |
| Gain on forgiveness of Paycheck Protection Program loan | — | | | — | | | (6,444) | |
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | (2,258) | | | (5,148) | | | (2,751) | |
| Settlement receivable | 96 | | | (2,000) | | | — | |
| Operating lease, net | (90) | | | (7) | | | — | |
| Other assets | 3,478 | | | 2,453 | | | (4,969) | |
| Accounts payable | (1,896) | | | 238 | | | 3,437 | |
| Accrued expenses | (1,373) | | | (4,881) | | | 8,224 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 296,146 | | | 243,297 | | | 167,346 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Finance receivables originated and acquired | (721,287) | | | (738,413) | | | (587,639) | |
| Finance receivables repayments | 485,986 | | | 434,419 | | | 402,542 | |
| Purchases of equipment and capitalized technology | (8,991) | | | (13,250) | | | (14,373) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (244,292) | | | (317,244) | | | (199,470) | |
| | | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Member distributions | (10,230) | | | (1,309) | | | (51,024) | |
| Member contributions | — | | | — | | | 200 | |
| Payments to Opportunity Financial, LLC unit holders | — | | | — | | | (91,646) | |
| Cash received in reverse capitalization | — | | | — | | | 91,857 | |
| Payment of capitalized transaction costs | — | | | — | | | (21,591) | |
| Net (payments) advances of secured borrowing payable | (643) | | | (21,687) | | | 6,418 | |
| Net (payments) advances of senior debt | (12,522) | | | 92,734 | | | 120,943 | |
| Net payments of notes payable | (2,581) | | | (1,627) | | | — | |
| Payment of subordinated debt - related party | — | | | — | | | (4,000) | |
| Payment for debt issuance costs | (1,712) | | | (4,521) | | | (2,328) | |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 328 | | | 125 | | | — | |
| Exercise of stock options | 59 | | | — | | | — | |
| Payments of tax withholdings on vesting of restricted stock units | (280) | | | — | | | — | |
| Repurchases of common stock | — | | | (2,460) | | | — | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (27,581) | | | 61,255 | | | 48,829 | |
| | | | | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and restricted cash | 24,273 | | | (12,692) | | | 16,705 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash and restricted cash | | | | | |
| Beginning | 49,670 | | | 62,362 | | | 45,657 | |
| Ending | $ | 73,943 | | | $ | 49,670 | | | $ | 62,362 | |
| | | | | |
| Continued on next page | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - Continued |
| (in thousands) |
|
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Interest paid on borrowed funds | $ | 43,725 | | | $ | 32,086 | | | $ | 22,041 | |
| Income taxes paid | $ | 73 | | | $ | 356 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | |
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash activities | | | | | |
| Non-cash change from adopting the fair value option on finance receivables | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 69,435 | |
| Adjustments to additional paid-in capital as a result of tax receivable agreement | $ | 459 | | | $ | (1,778) | | | $ | — | |
| Adjustments to additional paid-in capital as a result of adjustment to deferred tax asset | $ | 997 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Operating lease right of use asset recognized | $ | 159 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Operating lease liability recognized | $ | 159 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Operating lease right of use asset recognized from adoption of ASU 2016-02 | $ | — | | | $ | 15,459 | | | $ | — | |
| Operating lease liability recognized from adoption of ASU 2016-02 | $ | — | | | $ | 17,972 | | | $ | — | |
| Reclassification of finance receivables held for sale to held for investment | $ | 2,637 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Reclassification of finance receivables at amortized cost to assets held for sale | $ | — | | | $ | 550 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Prepaid insurance financed with promissory notes | $ | 2,414 | | | $ | 3,243 | | | $ | — | |
| Warrant liabilities recognized in the reverse recapitalization | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 37,645 | |
| Additional paid-in capital recognized in the reverse capitalization | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 78,468 | |
| Conversion of warrant unit liability to additional paid-in capital | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 5,517 | |
| Forgiveness of Paycheck Protection Program loan | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 6,444 | |
| | | | | |
| See notes to consolidated financial statements. | | | | | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1. Organization and Nature of Operations
OppFi Inc. (“OppFi”), formerly FG New America Acquisition Corp. (“FGNA”), collectively with its subsidiaries (“Company”), is a tech-enabled, mission-driven specialty finance platform that broadens the reach of community banks to extend credit access to everyday Americans. OppFi’s primary products are offered by its installment loan product, OppLoans. OppFi’s products also include its payroll deduction secured installment loan product, SalaryTap, and credit card product, OppFi Card.
On July 20, 2021 (“Closing Date”), the Company completed a business combination pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement (“Business Combination Agreement”), dated as of February 9, 2021, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC (“OppFi-LLC”), a Delaware limited liability company, OppFi Shares, LLC (“OFS”), a Delaware limited liability company, and Todd Schwartz (“Members’ Representative”), in his capacity as the representative of the members of OppFi-LLC (“Members”) immediately prior to the closing (“Closing”). The transactions contemplated by the Business Combination Agreement are referred to herein as the “Business Combination.” At the Closing, FGNA changed its name to “OppFi Inc.” OppFi’s Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class A Common Stock”) and redeemable warrants exercisable for Class A Common Stock (“Public Warrants”) are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbols “OPFI” and “OPFI WS,” respectively.
Following the Closing, the Company is organized in an “Up-C” structure in which substantially all of the assets and the business of the Company are held by OppFi-LLC and its subsidiaries, and OppFi’s only direct assets consist of Class A common units of OppFi-LLC (“OppFi Units”). As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, OppFi owned approximately 17.0% and 13.5% of the OppFi Units, respectively, and controls OppFi-LLC as the sole manager of OppFi-LLC in accordance with the terms of the Third Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of OppFi-LLC (“OppFi A&R LLCA”). All remaining OppFi Units (“Retained OppFi Units”) are beneficially owned by the Members. OFS holds a controlling voting interest in OppFi through its ownership of shares of Class V common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of OppFi (“Class V Voting Stock”) in an amount equal to the number of Retained OppFi Units and therefore has the ability to control OppFi-LLC.
Note 2. Significant Accounting Policies
Overview: The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of OppFi and OppFi-LLC with its subsidiaries: Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VIII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC, OppWin BPI, LLC (f/k/a Opportunity Funding SPE X, LLC), OppWin, LLC, Opportunity Manager, LLC, Opportunity Financial Card Company, LLC, OppWin Card, LLC, SalaryTap, LLC, OppWin SalaryTap, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC and Gray Rock SPV LLC.
On April 26, 2023, Opportunity Funding SPE X, LLC changed its name to OppWin BPI, LLC.
In 2017, OppFi-LLC entered into a preferred return agreement with Midtown Madison Management LLC, an unrelated third party, which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC acquires receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin LLC, and the third party receives a future preferred economic interest in these assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is being accounted for as a secured borrowing payable and the entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt. During the period from January 1, 2023 through February 16, 2023, the Company paid principal balance totaling $0.6 million. The remaining principal of $0.1 million was forgiven. On February 16, 2023, OppFi-LLC terminated the preferred return agreement.
In 2018, OppFi-LLC entered into a credit agreement with Ares Agent Services L.P., which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC uses the proceeds from the credit facility to acquire receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt. On December 14, 2022, the borrowings under this credit agreement were paid in full. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the credit agreement.
In 2019, OppFi-LLC entered into a credit agreement with BMO Harris Bank N.A, an unrelated third party, which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC uses the proceeds from the credit facility to acquire receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt. OppFi-LLC provides a financial guaranty in connection with this credit agreement.
On September 30, 2021, the credit agreement with BMO Harris Bank N.A. was amended to require OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, as amended, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC uses the proceeds from the existing credit facility to acquire receivables from SalaryTap, LLC and OppWin SalaryTap, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. SalaryTap, LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt. On February 15, 2023, the Company terminated the credit agreement upon the end of the revolving commitment period.
In 2019, OppFi-LLC entered into a credit agreement with Midtown Madison Management LLC which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC uses the proceeds from the credit facility to acquire receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt.
On October 13, 2021, the credit agreement with Midtown Madison Management, LLC was amended to add Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary, as an additional borrower. Under the terms of the agreement, as amended, Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC uses the proceeds from the existing credit facility to acquire receivables from Opportunity Financial Card Company, LLC and OppWin Card, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement.
On July 19, 2023, OppFi-LLC and Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC (“OF V Borrower”) entered into an Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement (the “A&R Credit Agreement”), which amended and restated that certain Revolving Credit Agreement, dated as of April 15, 2019 (as previously amended, supplemented or otherwise modified, the “Prior Credit Agreement”), by and among OppFi-LLC, OF V Borrower, Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, the other credit parties and guarantors thereto, Midtown Madison Management LLC as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the lenders party thereto. The A&R Credit Agreement amended the Prior Credit Agreement to, among other things, remove Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC as a borrower and remove the concept of pledging OppFi Card receivables under the A&R Credit Agreement, including removing OppWin Card, LLC as a seller.
In 2019, OppFi-LLC entered into a credit agreement with Ares Agent Services, L.P., an unrelated third party, which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC uses the proceeds from the credit facility to acquire receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt. On June 22, 2022, the borrowings under this revolving line of credit agreement were paid in full. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the revolving credit agreement.
On April 15, 2022, OppFi-LLC entered into agreements with Midtown Madison Management LLC, an unrelated third party, and Gray Rock SPV LLC, an entity formed by third-party investors for the purpose of purchasing participation interests in receivables from Gray Rock Finance LLC. Under the terms of the agreements, OppFi-LLC serves as the servicer of these financial assets. As the servicer, OppFi-LLC is subject to various financial covenants, such as minimum tangible net worth, liquidity and debt-to-equity ratio. OppFi-LLC also entered into a total return swap transaction with Midtown Madison Management LLC, providing credit protection related to a reference pool of consumer receivables financed by Midtown Madison Management LLC.
On December 14, 2022, OppFi-LLC entered into a credit agreement with UMB Bank, N.A., an unrelated third party, which required OppFi-LLC to create a bankruptcy protected entity named Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly owned subsidiary. Under the terms of the agreement, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC uses the proceeds from the credit facility to acquire receivables from OppFi-LLC and OppWin, LLC, and the lender receives first priority lien on all of the entity’s assets. OppFi-LLC continues to service the assets in accordance with the terms of the agreement but is required to maintain a backup servicing agreement. This transaction is accounted for as senior debt in which this bankruptcy protected entity holds all assets on its balance sheet, which collateralize the debt.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
OppFi-LLC has entered into bank partnership arrangements with certain Utah-chartered banks (“Banks”) insured by the FDIC. Under the terms and conditions of the agreement, the Banks originate finance receivables based on criteria provided by OppFi-LLC. After an initial holding period, OppFi-LLC has committed to acquire the participation rights to the finance receivables originated by the Banks. To facilitate these relationships, OppFi-LLC formed OppWin, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly-owned subsidiary of OppFi-LLC; OppWin SalaryTap, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly-owned subsidiary of OppFi-LLC; OppWin Card, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly-owned subsidiary of OppFi-LLC; and OppWin BPI, LLC, a Delaware Limited Liability Company and a wholly-owned subsidiary of OppFi-LLC.
OppWin, LLC acquires the participation rights in the economic interest in installment finance receivables originated by the Banks. Subsequently, OppWin, LLC sells these rights to SPEs, which in turn, pledge the participation rights to their respective lenders.
OppWin SalaryTap, LLC acquires the participation rights in the economic interest in the SalaryTap finance receivables originated by the Banks. Subsequently, OppWin SalaryTap, LLC sells these rights to SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, which in turn, pledges the participation rights to its respective lenders.
OppWin Card, LLC acquires the participation rights in the economic interest in the OppFi Card finance receivables originated by the Banks.
OppWin BPI, LLC acquires the participation rights in the economic interest in installment finance receivables originated by the Banks. Subsequently, OppWin BPI, LLC sells these rights to Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, which in turn, pledges the participation rights to its lender.
The Company accounts for the participation rights as finance receivables. As part of these bank partnership arrangements, the Banks have the ability to retain a percentage of the finance receivables they have originated. OppFi-LLC’s economic interest and acquired participation rights are reduced by the percentage retained by the Banks.
Basis of presentation: The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and include the accounts of OppFi Inc. and OppFi-LLC with its wholly-owned subsidiaries and consolidated VIEs. In the opinion of the Company’s management, the consolidated financial statements include all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for the fair statement of the results and financial position for the periods presented.
The Business Combination was accounted for as a reverse recapitalization in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 805, Business Combinations. Under this method, FGNA was treated as the “acquired” company, and OppFi-LLC, as the accounting acquirer, was assumed to have issued equity for the net assets of FGNA, accompanied by a recapitalization.
Principles of consolidation: The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the above named entities. Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VIII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, and Gray Rock SPV LLC are special purpose entities holding finance receivables secured by lenders under a credit or preferred return agreement.
The Company determines whether it is the primary beneficiary of a VIE based on a qualitative assessment to determine if the Company or another party, if any, has the power to direct activities of the VIE and the obligation to absorb losses and/or receive its benefits. The Company considers the activities that most significantly impact the VIE's economic performance and determine whether the Company or another party, if any, has the power to direct these activities of the VIE. The Company also considers the nature, purpose and activities of the VIE and the Company’s involvement, including exposure to loss, with the VIE.
OppFi has identified Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE VIII, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, and Gray Rock SPV LLC as VIEs. OppFi-LLC is the sole equity member of all of the aforementioned entities, except for SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC and Gray Rock SPV LLC. SalaryTap, LLC is the sole equity member of SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC. While Gray Rock SPV LLC is not owned by OppFi-LLC, Gray Rock SPV LLC was determined to be a VIE. The Company directs the activities of the VIEs that most significantly impact economic performance. Additionally, the Company has the obligation to absorb losses of the VIEs that could potentially be significant. As the primary beneficiary of the VIEs, the Company has consolidated the financial statements of the VIEs. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Segments: Segments are defined as components of an enterprise for which discrete financial information is available and evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker ("CODM") in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. OppFi’s Chief Executive Officer is considered to be the CODM. The CODM reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for purposes of allocating resources and evaluating financial performance. The Company’s operations constitute a single reportable segment.
Use of estimates: The preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and operations and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period.
The judgements, assumptions, and estimates used by management are based on historical experience, management’s experience and qualitative factors. The areas subject to significant estimation techniques include, but are not limited to, the determination of fair value of installment finance receivables and warrants, the adequacy of the allowance for credit losses on finance receivables, valuation allowance of deferred tax assets, stock-based compensation expense and income tax provision. For the aforementioned estimates, it is reasonably possible the recorded amounts or related disclosures could significantly change in the near future as new information is available.
Revenue recognition: The Company recognizes finance charges on installment and SalaryTap contracts based on the interest method. Under this method, interest is earned over the lives of the installment and SalaryTap finance receivables to produce constant rates of interest (yields). Fees for returned payments approximate the cost of services provided and are recognized as incurred, assuming collectability is reasonably assured.
For OppFi Card finance receivables, interest is earned on unpaid balance, inclusive of previously outstanding balance and interest and fees, at the conclusion of the monthly billing cycle. Card-related fees, with the exception of the annual fee, are recognized as incurred. Annual fee revenue is amortized straight-line over the course of 12 months.
The Company discontinues and reverses the accrual of interest income on installment and SalaryTap finance receivables at the earlier of 60 days past due based on a recency basis or 90 days past due based on a contractual basis. The accrual of income is not resumed until the account is current on a recency or contractual basis, at which time management considers collectability to be probable.
Cash: The Company classifies all cash accounts which are not subject to withdrawal restrictions or penalties as cash. All cash accounts are held in financially insured institutions, which may at times exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced losses in such accounts. Management believes the Company’s exposure to credit risk is minimal for these accounts.
Restricted cash: Restricted cash consists of the following: (1) cash required to be held on reserve by the Company’s vendors for purposes of loan processing or funding; (2) cash required to be held in blocked accounts held by the VIEs; and (3) cash required to be held on deposit in connection with the bank partnership arrangements. All cash accounts are held in financially insured institutions, which may at times exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced losses in such accounts. Management believes the Company’s exposure to credit risk is minimal for these accounts.
CSO arrangements: In Texas and Ohio, OppFi-LLC previously arranged for consumers to obtain finance receivable products from independent third-party lenders as part of the Credit Access Business and Credit Service Organization programs (collectively, the “CSO Program”). For the consumer finance receivable products originated by the third-party lenders under the CSO Program, the lenders were responsible for providing the criteria by which the consumer's application was underwritten and, if approved, determining the amount of the finance receivable. When a consumer executed an agreement with OppFi-LLC under the CSO Program, OppFi-LLC agreed, for a fee payable to OppFi-LLC by the consumer, to provide certain services to the consumer, one of which was to guarantee the consumer's obligation to repay the finance receivable obtained by the consumer from the third-party lender if the consumer failed to do so. The guarantees represented an obligation to purchase specific finance receivables that are delinquent, secured by a collateral account established in favor of the respective lenders. The Company discontinued the CSO Program in Ohio and Texas on April 23, 2019 and March 19, 2021, respectively. No new finance receivables were originated through this program in Ohio and Texas after such dates.
Participation rights purchase obligations: OppFi-LLC has entered into bank partnership arrangements with certain Banks insured by the FDIC. Under the terms and conditions of the bank partnership agreements, the Banks originate finance receivables based on criteria provided by OppFi-LLC. The issuing Bank earns interest during an initial hold period and owns the economic interest in the finance receivables. After the initial holding period, OppFi-LLC is committed to acquire participation rights in the economic interest in the finance receivables originated by the Banks, net of bank partnership retention, plus accrued interest (“Participation Rights”). OppFi-LLC also provides certain services for these receivables in its capacity of sub-servicer pursuant to the terms of the servicing agreement between the Bank and OppFi-LLC. To facilitate these relationships, OppFi-LLC formed OppWin, LLC, OppWin SalaryTap, LLC, OppWin Card, LLC, and OppWin BPI, LLC,
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
which acquire the Participation Rights and sell these rights to certain of the other OppFi subsidiaries, which in turn, pledge the Participation Rights to their respective lenders. The Company accounts for the Participation Rights as a finance receivable. As part of these bank partnership arrangements, the Banks have the ability to retain a percentage of the finance receivables they have originated, and OppFi-LLC’s Participation Rights are reduced by the percentage of the finance receivables retained by the Banks.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, gross finance receivables originated through the bank partnership arrangements totaled 97% and 94%, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the unpaid principal balance of finance receivables outstanding for purchase was $14.5 million and $11.2 million, respectively.
Finance receivables: On January 1, 2021, the Company elected the fair value option on its installment finance receivables upon adoption of ASU 2016-13. Accordingly, the related finance receivables are carried at fair value in the consolidated balance sheets and the changes in fair value are included in the consolidated statements of operations. To derive the fair value, the Company generally utilizes discounted cash flow analyses that factor in estimated losses and prepayments over the estimated duration of the underlying assets. Loss and prepayment assumptions are determined using historical loss data and include appropriate consideration of recent trends and anticipated future performance. Future cash flows are discounted using a rate of return that the Company believes a market participant would require. Accrued interest and fees are included in “Finance receivables at fair value” in the consolidated balance sheets. Interest income is included in “Interest and loan related income, net” in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company did not elect the fair value option on its SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables. Accordingly, the related finance receivables are carried at amortized cost, net of allowance for credit losses and unearned fees.
Loan origination costs: With the election of the fair value option, loan origination costs related to the origination of installment finance receivables recognized at fair value are expensed when incurred. Direct costs incurred for the origination of these finance receivables included underwriting fees, employee salaries and benefits directly related to the origination of the loan and program fees. Loan origination costs also included direct costs incurred for directly acquiring a customer.
Allowance for credit losses on finance receivables at amortized cost: Effective January 1, 2021, the Company adopted ASU 2016-13. Under the current expected credit losses methodology, the Company determines the allowance for credit losses and records a provision for credit losses considering all anticipated credit losses over the remaining expected life of its SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables. The Company uses competitive research and considers qualitative factors, such as changes to regulatory requirements, general economic conditions and other events impacting the credit quality of the portfolio for determining the anticipated credit losses of its SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables. While management uses the best information available to make its evaluation, future adjustments to the allowance may be necessary if there are significant changes in any of the factors.
The Company’s charge-off policy is based on a review of delinquent finance receivables on a loan by loan basis. Finance receivables are charged off at the earlier of the time when accounts reach 90 days past due on a recency basis, when the Company receives notification of a customer bankruptcy, or is otherwise deemed uncollectible.
Delinquency: The Company determines the past due status on a recency basis, which is defined as the last time a qualifying payment is made on an account. Finance receivables are considered delinquent at 30 days or more past due.
Troubled debt restructurings: As the terms of the receivables are typically not renegotiated and settlement offers are not typically made until after a receivable stops accruing interest income (up to 60 days delinquent), the only receivables considered to be impaired, or troubled debt restructurings, are: 1) those receivables where a settlement offer is made after receivables cease accruing interest, which may result in a modification of contractual terms, 2) the Company has received notification that a borrower is working with a third party to settle debt on his/her behalf and 3) customers who have entered into the Company’s short-term or long-term hardship programs. As of December 31, 2022, management determined the balance of troubled debt restructuring receivables to be immaterial to the consolidated financial statements as a whole. As such, substantially all disclosures relating to impaired finance receivables, and troubled debt restructuring, have been omitted from these consolidated financial statements.
Settlement receivable: In accordance with the Company’s credit agreement with UMB Bank, N.A., customer payments are collected by the Company and then deposited into a commercial bank account held by UMB Bank, N.A. on behalf of the Company until the Company settled with UMB Bank, N.A. The Company did not record an allowance for doubtful accounts against the settlement receivable as potential write-offs are deemed immaterial.
Assets held for sale: Assets held for sale are assets which management has the intent to sell in the foreseeable future, and are carried at the lower of aggregate cost or fair value, less estimated costs to sell, in the period in which the held for sale criteria are met and every subsequent period until the asset is sold. The carrying amount of the asset is adjusted for subsequent
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
increases or decreases in its fair value, less estimated cost to sell, except that any subsequent increase cannot exceed the cumulative loss previously recognized. Such assets are not depreciated or amortized while they are classified as held for sale. Realized gains and losses on the sale of the asset are recognized when the asset is sold and are determined by the difference between the sale proceeds and the carrying value of the asset. Assets classified as held for sale as of December 31, 2022 comprised the Company’s OppFi Card finance receivables; as a result, the Company recognized the impairment loss of assets held for sale totaling $3.6 million. In May 2023, the Company made the decision to wind down the OppFi Card business; accordingly, the Company has discontinued its marketing of the OppFi Card finance receivables for sale. The OppFi Card finance receivables no longer meet the held for sale criteria and have been reclassified from held for sale to held for investment, which is included in finance receivables at amortized cost in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023. Upon transfer of the Company’s OppFi Card finance receivables from held for sale to held for investment, the Company reversed its previously recorded valuation allowance on being held for sale totaling $2.3 million and established an allowance for credit losses on being held for investment totaling $2.6 million.
Property and equipment: Furniture, equipment, and leasehold improvements are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization of furniture, equipment, and leasehold improvements are computed under both straight-line and accelerated methods for financial reporting and income tax purposes, respectively, based on the estimated useful lives of the assets generally as follows: furniture and fixtures - 5 years; office equipment - 3 years; and leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the useful life of the assets or the term of the lease.
Capitalized technology: Software development costs related to internal use software are incurred in three stages of development: the preliminary project stage, the application development stage, and the post-implementation stage. Costs incurred during the preliminary project and post-implementation stages are expensed as incurred. Costs incurred during the application development stage that meet the criteria for capitalization are capitalized and amortized, when the software is ready for its intended use, using the straight-line basis, over the estimated useful life of the software, which is generally two years. The Company capitalized software costs associated with application development totaling $8.6 million and $12.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Amortization expense, which is included in depreciation and amortization on the consolidated statements of operations, totaled $12.0 million, $12.7 million, and $9.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Leases: The Company determines if an arrangement is or contains a lease at its inception. Right-of-use (“ROU”) assets and lease liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. The discount rate used to determine the commencement date present value of lease payments is typically the incremental borrowing rate, as most of the leases do not provide an implicit rate. Lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Variable lease payment amounts that cannot be determined at the commencement of the lease, such as increases in lease payments that do not depend on changes in index rates or payments based on usage, are not included in the ROU assets or lease liabilities and are expensed as incurred. The Company has elected to combine lease and non-lease components for the purpose of calculating ROU assets and lease liabilities, to the extent the non-lease components are fixed. Non-lease components that are not fixed are expensed as incurred as variable lease payments. Additionally, the Company has elected not to recognize ROU assets and lease liabilities that arise from short-term leases, defined as having an initial term of twelve months or less, from the consolidated balance sheets. Operating leases are included in operating lease right-of-use assets and operating lease liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets.
Debt issuance costs: Debt issuance costs are capitalized and amortized based on the contractual terms of the related debt agreements using the interest method for fixed-term debt and the straight-line method for all other debt.
Transfer and servicing of financial assets: After a transfer of financial assets, an entity recognizes the financial and servicing assets it controls and the liabilities it has incurred, derecognizes financial assets when control has been surrendered, and derecognizes liabilities when extinguished. The transfers of assets for debt purposes have been accounted for as secured and senior borrowings and the related assets and borrowings are retained on the consolidated balance sheets and no gain or loss has been recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
Warrants: Public Warrants, $11.50 Exercise Price Warrants, $15 Exercise Price Warrants, Private Placement Warrants and Underwriter Warrants do not meet the criteria for equity treatment, due to a provision in the warrant agreement governing such warrants (“Warrant Agreement”) related to certain tender or exchange offer provisions, each warrant must be recorded as a liability. Accordingly, the Company classifies each warrant as a liability at its fair value. This liability is subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date. With each such re-measurement, the warrant liability will be adjusted to fair value, with the change in fair value recognized in the Company’s statement of operations. The Public Warrants are valued at market price based on the observable traded price in an active market. The Company utilizes a Black-Scholes-Merton (“Black- Scholes”) option-pricing model to value the outstanding private placement warrants (“Private Placement Warrants”) issued in connection with FGNA’s initial public offering (“IPO”) at each reporting period.
Tax receivable agreement liability: In connection with the Business Combination, OppFi entered into the Tax Receivable Agreement ("TRA") with the Members and the Members’ Representative. The TRA provides for payment to the Members of 90% of the U.S. federal, state and local income tax savings realized by the Company as a result of the increases in tax basis and
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
certain other tax benefits related to the transactions contemplated under the Business Combination Agreement and the exchange of Retained OppFi Units for Class A Common Stock or cash. OppFi-LLC will have in effect an election under Section 754 of the Internal Revenue Code effective for each taxable year in which an exchange of Retained OppFi Units occurs. The remaining 10% cash tax savings resulting from the basis adjustments will be retained by the Company.
In general, cash tax savings result in a year when the tax liability of the Company for the year, computed without regard to the deductions attributable to the amortization or depreciation of the basis increase and other deductions that arise in connection with the payment of the cash consideration under the TRA or the exchange of Retained OppFi Units for Class A Common Stock, would be more than the tax liability for the year taking into account such deductions. Payments under the TRA will not be due until the Company is able to reduce an actual cash tax liability by the amortization of the basis increase on a filed tax return. The payments under the TRA are expected to be substantial.
The Company accounts for the effects of the basis increases as follows:
•the Company records an increase in deferred tax assets for the income tax effects of the increases in tax basis based on enacted federal and state income tax rates at the date of the exchange;
•the Company evaluates the ability to realize the full benefit represented by the deferred tax asset based on an analysis that will consider expectations of future earnings among other things. If the Company determines that the full benefit is not likely to be realized, a valuation allowance is established to reduce the amount of the deferred tax assets to an amount that is likely to be realized.
The Company records obligations under the TRA at the gross undiscounted amount of the expected future payments as an increase to liabilities and the realizable deferred tax asset with an offset to additional paid-in capital and/or tax benefit.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company’s liability related to its expected obligations under the TRA was $25.0 million with a corresponding deferred tax asset of $5.9 million; the remaining $19.0 million and $0.1 million were recorded to additional paid-in capital and tax benefit, respectively. As of December 31, 2022, the Company’s liability related to its expected obligations under the TRA was $25.6 million with a corresponding deferred tax asset of $6.2 million; the remaining $19.4 million was recorded to additional paid-in capital.
Loss contingencies: Loss contingencies, including claims and legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business, are recorded as liabilities when the likelihood of loss is probable and an amount or range of loss can be reasonably estimated. Management does not believe there are such matters that will have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Stock-based compensation: The Company established the OppFi Inc. 2021 Equity Incentive Plan (“Plan”), which provides for the grant of restricted stock unit awards, incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units awards, performance units, performance shares, cash-based awards, and other stock-based awards to employees, non-employee directors, officers, and consultants. The Company measures stock-based compensation expense based on the fair value of awards as determined on the date of the grant. The Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense over the requisite service period. The Company accounts for forfeitures when they occur. The Company uses a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the estimated fair value of stock options. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model requires estimates of highly subjective assumptions, which affect the fair value of stock options. The fair value of restricted stock units and performance stock units is estimated using the market price of the Company’s Class A Common Stock on the date of grant.
Income taxes: OppFi-LLC is organized as a partnership for U.S. income tax purposes, and therefore is not subject to tax on its earnings, as the taxable income and deductions are passed to the Members who are responsible for income tax based upon their allocable share of OppFi-LLC's income. Following the Closing, the Company’s consolidated financial statements include the accounts of OppFi and OppFi-LLC. OppFi is subject to corporate income taxes in the United States based upon its activities and its allocable share of taxable income from OppFi-LLC at the federal and state level, therefore the amount of income taxes recorded prior to the Closing are not representative of the expenses expected in the future.
The computation of the effective tax rate and provision at each period requires the use of certain estimates and significant judgment including, but not limited to, the expected operating income for the year, projections of the proportion of income that is subject to tax, and permanent differences between the Company’s GAAP earnings and taxable income. The estimates used to compute the provision for income taxes may change throughout the year as new events occur, additional information is obtained or as tax laws and regulations change. Accordingly, the effective tax rate for future periods may vary.
The Company accounts for income taxes pursuant to the asset and liability method which requires the recognition of current tax liabilities or receivables for the amount of taxes it estimates are payable or refundable for the current year, deferred tax assets
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and their respective tax bases of assets and liabilities and the expected benefits of net operating loss and credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in operations in the period enacted. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more likely than not that a portion or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income and the reversal of deferred tax liabilities during the period in which related temporary differences become deductible.
The benefit of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in the Company’s income tax returns is recognized in the financial statements if such positions are more likely than not of being sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. Differences between tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return and the benefit recognized and measured pursuant to the interpretation are referred to as “unrecognized benefits.” A liability is recognized (or amount of net operating loss carryover or amount of tax refundable is reduced) for an unrecognized tax benefit because it represents a potential future obligation to the taxing authority for a tax position that was not recognized. Interest costs and related penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are required to be calculated, if applicable, and are recognized as general, administrative, and other expenses.
Government regulation: The Company is subject to complex regulation, supervision and licensing under various federal, state, local statutes, ordinances, regulations, rules and guidance. The Company must comply with federal laws as well as regulations adopted to implement those laws. In July 2010, the U.S. Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Act, and Title X of the Dodd-Frank Act created the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”), which regulates U.S. consumer financial products and services, including consumer loans offered by the Company. The CFPB has regulatory, supervisory and enforcement powers over providers of consumer financial products and services, including explicit supervisory authority to examine and require registration of such providers.
Treasury stock: The Company accounts for treasury stock under the cost method and includes treasury stock as a component of stockholders’ equity on the consolidated balance sheets. The Company accounts for the reissuance of treasury stock on the first-in, first out method. The Company did not reissue or retire treasury stock during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Earnings (loss) per share: Basic earnings (loss) per share available to common stockholders is computed by dividing the net income (loss) attributable to OppFi by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share available to common stockholders is computed using the treasury stock method, which gives effect to potentially dilutive common stock equivalents of OppFi outstanding during the period, and the if-converted method, which gives effect to both the potentially dilutive common stock equivalents outstanding during the period as well as an assumed full exchange of OppFi Units into Class A Common Stock of OppFi as of the beginning of the period. The if-converted method would also give effect to conversion of the Earnout Units in periods they would be deemed to vest. For the if-converted method, earnings are also adjusted to reflect all income of OppFi-LLC inuring to the benefit of OppFi and taxed accordingly. In periods in which the Company reports a net loss attributable to OppFi, diluted loss per share available to common stockholders would be the same as basic loss per share available to common stockholders, since dilutive common shares are not assumed to have been issued if their effect is anti-dilutive.
Noncontrolling interests: Noncontrolling interests are held by the Members, who retained 83.0% and 86.5% of the economic ownership percentage of OppFi-LLC as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 810, Consolidation, the Company classifies the noncontrolling interests as a component of stockholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheets. Additionally, the Company has presented the net income attributable to the Company and the noncontrolling ownership interests separately in the consolidated statements of operations.
Fair value disclosure: ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, established a fair value hierarchy for valuation inputs that gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs. Fair value measurements are determined based on the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability.
ASC 820 provides a framework for measuring fair value under generally accepted accounting principles. Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In determining fair value, the Company uses various methods including market, income and cost approaches. Based on these approaches, the Company often utilizes certain assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, including assumptions about risk and or the risks inherent in the inputs to the valuation technique. These inputs can be readily observable, market corroborated, or generally unobservable inputs. The Company utilizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Based on the nature of the inputs used in the valuation techniques, the Company is required to provide the following information according to the fair
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
value hierarchy. The fair value hierarchy ranks the quality and reliability of the information used to determine fair values. Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value will be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
Level 1 - Valuations for assets and liabilities traded in active exchange markets, such as the NYSE. Valuations are obtained from readily available pricing sources for market transactions involving identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2 - Valuations for assets and liabilities traded in less-active dealer or broker markets. Valuations are obtained from third-party pricing services for identical or similar assets or liabilities.
Level 3 - Valuations for assets and liabilities that are derived from other valuation methodologies, including option-pricing models, discounted cash flow models and similar techniques, and not based on market exchange, dealer, or broker traded transactions. Level 3 valuations incorporate certain assumptions and projections in determining the fair value assigned to such assets or liabilities.
Emerging growth company: The Company is an emerging growth company as defined under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (“Jobs Act”). The Company is permitted to delay the adoption of new or revised accounting pronouncements applicable to public companies until such pronouncements apply to private companies. This may make comparison of the Company’s financial statements with another public company which is neither an emerging growth company nor an emerging growth company which has opted out of using the extended transition period difficult or impossible because of the potential differences in accounting standards used.
Accounting pronouncements issued and adopted: In March 2022, the FASB issued ASU No. 2022-02, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326): Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures. The purpose of ASU No. 2022-02 is to provide guidance on troubled debt restructuring accounting model for creditors that have adopted Topic 326. Additionally, the guidance expands on vintage disclosure requirements. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within the annual reporting period. The adoption of ASU No. 2022-02 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Accounting pronouncements issued and not yet adopted: In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting. The purpose of ASU 2020-04 is to provide optional guidance for a period of time related to accounting for reference rate reform on financial reporting. It is intended to reduce the potential burden of reviewing contract modifications related to discontinued rates. The amendments and expedients in this update are effective as of March 12, 2020 through December 31, 2022 and may be elected by topic. In December 2022, the FASB issued ASU 2022-06, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Deferral of the Sunset Date of Topic 848, which defers the sunset date of Topic 848 to December 31, 2024. The purpose of ASU No. 2022-06 is to defer the effective date of the provisions of ASU 2020-04 from December 31, 2022 to December 31, 2024. The Company is currently evaluating the impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures. The purpose of ASU 2023-07 is to provide guidance on new segment disclosures, including significant segment expenses. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2023 and, interim periods within the annual reporting period beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures. The purpose of ASU 2023-09 is to provide guidance on the enhanced income tax disclosure requirements. The guidance requires an entity to disclose specific categories in the effective tax rate reconciliation as well as provide additional information for reconciling items that meet a quantitative threshold. Further, the ASU requires certain disclosures of state versus federal income tax expense and taxes paid. The standard is intended to benefit investors by providing more detailed income tax disclosures that would be useful in making capital allocation decisions. The guidance is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2024. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Note 3. Business Combination
On the Closing Date, OppFi completed the Business Combination with OppFi-LLC pursuant to the Business Combination Agreement. Pursuant to ASC 805, the Business Combination was accounted for as a reverse recapitalization, where FGNA was treated as the “acquired” company and OppFi-LLC, as the accounting acquirer. OppFi-LLC was assumed to have issued equity for the net assets of FGNA, accompanied by a recapitalization. Under this method of accounting, the pre-Business Combination consolidated financial statements of the Company are the historical financial statements of OppFi-LLC. The net assets, consisting of cash, prepaid expenses, accounts payable, and warrant liability, of FGNA were stated at fair value, with no goodwill or other intangible assets recorded in accordance with GAAP and are consolidated with OppFi-LLC’s financial statements on the Closing Date.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
At the Closing, (i) OppFi-LLC transferred to the Company 12,977,690 OppFi Units, which was equal to the number of shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding as of immediately prior to the Closing (after giving effect to redemptions by FGNA’s public stockholders prior to the Closing and the conversion of FGNA’s Class B common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (“Class B Common Stock”)), (ii) FGNA contributed the Cash Consideration (as defined below) to OppFi-LLC in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement, which was distributed to the Members, and (iii) FGNA issued 96,987,093 shares of newly authorized Class V Voting Stock, which number of shares of Class V Voting Stock was equal to the number of Retained OppFi Units.
The aggregate value of the consideration paid to the Members in the Business Combination was approximately $806.5 million, after giving effect to the estimated purchase price adjustments as set forth in the Business Combination Agreement, consisting of: (i) cash consideration in the amount of $91.6 million (“Cash Consideration”), equal to the cash remaining in FGNA’s trust account as of immediately prior to the Closing and (ii) 96,987,093 shares of Class V Voting Stock.
Immediately after giving effect to the Business Combination, there were 12,977,690 issued and outstanding shares of Class A Common Stock (giving effect to shares redeemed in connection with the Business Combination and 3,443,750 shares of Class A Common Stock issued upon the conversion of the Class B Common Stock). Shortly after, and as a result of the Business Combination, a lender converted its OppFi Units, resulting in an additional 486,852 shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding for a total of 13,464,542 shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding. On the business day following the Closing, FGNA’s public units automatically separated into their component securities upon consummation of the Business Combination and, as a result, no longer trade as a separate security and were delisted from the NYSE.
In connection with the Closing, on the Closing Date, 25,500,000 Retained OppFi Units (“Earnout Units”) held by the Members, and an equal number of shares of Class V Voting Stock distributed to OFS in connection with the Business Combination, are subject to certain restrictions and potential forfeiture pending the achievement (if any) of certain earnout targets pursuant to the terms of the Business Combination Agreement. But for restrictions related to a lock-up (transfer restrictions) and forfeiture (earnout criteria), as such restrictions are more specifically set forth in the Investor Rights Agreement entered into at the Closing, by and among the Company, certain founder holders of FGNA, the Members, the Members’ Representative and/or the OppFi A&R LLCA, as applicable, the Earnout Units have all other economic and voting rights of the other units of OppFi-LLC. With respect to transfers, the Earnout Units are subject to a lock-up until the later of the end of the lock-up period applicable to other OppFi Units or until such Earnout Units are earned in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement. With respect to distributions (other than tax distributions, which in respect of such Earnout Units are treated the same as any other OppFi Unit in accordance with the OppFi A&R LLCA) in relation to the Earnout Units, such distributions (other than tax distributions) are held back until the Earnout Units are earned. If an Earnout Unit is not earned, and therefore forfeited, related distributions are distributed to the other holders of units at such time.
In connection with the Business Combination, the Company incurred direct and incremental costs of approximately $30.6 million, consisting primarily of investment banking, legal, accounting and other professional fees. Of these costs, $21.6 million were recorded as a reduction of additional paid-in capital in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, $0.8 million were recorded as a prepaid expense and included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets, and $8.2 million were expensed as professional fees in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
As a result of the Business Combination, OppFi organized as a C corporation, owns an equity interest in OppFi-LLC in what is commonly referred to as an “Up-C” structure. OppFi-LLC is treated as a partnership for U.S. federal and state income tax purposes. Accordingly, for U.S. federal and state income tax purposes, all income, losses, and other tax attributes pass through to the members’ income tax returns, and no U.S. federal and state and local provision for income taxes has been recorded for these entities in the consolidated financial statements.
As a result of the Up-C structure, noncontrolling interests are held by the Members who retained 88.2% of the economic ownership percentage of OppFi-LLC as of the Closing. As of the Closing, OppFi held a 11.8% ownership interest in OppFi-LLC. The Company classifies the noncontrolling interests as a component of stockholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheets.
In connection with the Business Combination, OppFi entered into the TRA with the Members and the Members’ Representative. The TRA provides for payment to the Members of 90% of the U.S. federal, state and local income tax savings realized by the Company as a result of the increases in tax basis and certain other tax benefits related to the transactions contemplated under the Business Combination Agreement and the exchange of Retained OppFi Units for Class A Common Stock or cash.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
The Company recorded a net deferred tax asset of $24.3 million for the difference between the book value and tax basis of the Company’s investment in OppFi-LLC at the time of the Business Combination. The Company has assessed the realizability of their deferred tax assets and in that analysis has considered the relevant positive and negative evidence available to determine whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all the deferred tax assets will be realized.
Note 4. Finance Receivables
Finance receivables at fair value: The components of installment finance receivables at fair value as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Unpaid principal balance of finance receivables - accrual | $ | 384,587 | | | $ | 369,643 | |
| Unpaid principal balance of finance receivables - non-accrual | 31,876 | | | 32,537 | |
| Unpaid principal balance of finance receivables | $ | 416,463 | | | $ | 402,180 | |
| | | |
| Finance receivables at fair value - accrual | $ | 444,120 | | | $ | 436,552 | |
| Finance receivables at fair value - non-accrual | 1,135 | | | 4,944 | |
| Finance receivables at fair value, excluding accrued interest and fees receivable | 445,255 | | | 441,496 | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | 18,065 | | | 15,800 | |
| Finance receivables at fair value | $ | 463,320 | | | $ | 457,296 | |
| | | |
| Difference between unpaid principal balance and fair value | $ | 28,792 | | | $ | 39,316 | |
The Company’s policy is to discontinue and reverse the accrual of interest income on installment finance receivables at the earlier of 60 days past due on a recency basis or 90 days past due on a contractual basis. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the aggregate unpaid principal balance of installment finance receivables 90 days or more past due was $15.2 million and $17.6 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the fair value of installment finance receivables 90 days or more past due was $0.5 million and $2.7 million, respectively.
Changes in the fair value of installment finance receivables at fair value for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 457,296 | | | $ | 383,890 | | | $ | 289,166 | |
| Originations | 719,503 | | | 731,159 | | | 581,412 | |
| Repayments | (484,325) | | | (428,957) | | | (401,638) | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | 2,265 | | | 5,163 | | | 2,727 | |
| Charge-offs, net (1) | (220,895) | | | (232,266) | | | (103,385) | |
| Adjustment to fair value | — | | | — | | | (1,817) | |
| Net change in fair value (1) | (10,524) | | | (1,693) | | | 17,425 | |
| Balance at the end of the period | $ | 463,320 | | | $ | 457,296 | | | $ | 383,890 | |
| | | | | |
| (1) Included in "Change in fair value of finance receivables" in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. |
Finance receivables at amortized cost, net: The Company’s finance receivables measured at amortized cost comprised of its SalaryTap and OppFi Card finance receivables. In May 2023, the Company reclassified its OppFi Card finance receivables from assets held for sale to held for investment when the OppFi Card finance receivables no longer met the held for sale
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
criteria. As of December 31, 2022, the Company’s OppFi Card finance receivables were classified as assets held for sale, which was included in assets held for sale in the consolidated balance sheets as of such date.
The components of finance receivables measured at amortized cost were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Finance receivables | $ | 454 | | | $ | 730 | |
| Accrued interest and fees | 2 | | | 9 | |
| Allowance for credit losses | (346) | | | (96) | |
| Finance receivables at amortized cost, net | $ | 110 | | | $ | 643 | |
Changes in the allowance for credit losses on finance receivables measured at amortized cost for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Beginning balance | $ | 96 | | | $ | 803 | | | $ | 55,031 | |
| Effects of adopting fair value option | — | | | — | | | (55,031) | |
| Provision for credit losses on finance receivables | 4,348 | | | 1,940 | | | 929 | |
| Finance receivables charged off | (4,144) | | | (2,653) | | | (126) | |
| Recoveries of charge offs | 46 | | | 6 | | | — | |
| Ending balance | $ | 346 | | | $ | 96 | | | $ | 803 | |
The following is an assessment of the credit quality of finance receivable measured at amortized cost and presents the recency and contractual delinquency by year of origination as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | Revolving charge accounts | | Total |
| Recency delinquency | | | | | | | | | |
| Current | $ | — | | | $ | 35 | | | $ | 73 | | | $ | 244 | | | $ | 352 | |
| Delinquency | | | | | | | | | |
| 30-59 days | — | | | 3 | | | 1 | | | 16 | | | 20 | |
| 60-89 days | — | | | 1 | | | 11 | | | 9 | | | 21 | |
| 90+ days | — | | | — | | | — | | | 61 | | | 61 | |
| Total delinquency | — | | | 4 | | | 12 | | | 86 | | | 102 | |
| Finance receivables | $ | — | | | $ | 39 | | | $ | 85 | | | $ | 330 | | | $ | 454 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Contractual delinquency | | | | | | | | | |
| Current | $ | — | | | $ | 32 | | | $ | 46 | | | $ | 244 | | | $ | 322 | |
| Delinquency | | | | | | | | | |
| 30-59 days | — | | | 3 | | | 8 | | | 16 | | | 27 | |
| 60-89 days | — | | | 2 | | | 9 | | | 9 | | | 20 | |
| 90+ days | — | | | 2 | | | 22 | | | 61 | | | 85 | |
| Total delinquency | — | | | 7 | | | 39 | | | 86 | | | 132 | |
| Finance receivables | $ | — | | | $ | 39 | | | $ | 85 | | | $ | 330 | | | $ | 454 | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2022 |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | 2020 | | Total |
| Recency delinquency | | | | | | | |
| Current | $ | 155 | | | $ | 475 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 638 | |
| Delinquency | | | | | | | |
| 30-59 days | 5 | | | 40 | | | — | | | 45 | |
| 60-89 days | 12 | | | 35 | | | — | | | 47 | |
| 90+ days | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total delinquency | 17 | | | 75 | | | — | | | 92 | |
| Finance receivables | $ | 172 | | | $ | 550 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 730 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Contractual delinquency | | | | | | | |
| Current | $ | 148 | | | $ | 429 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 585 | |
| Delinquency | | | | | | | |
| 30-59 days | 5 | | | 39 | | | — | | | 44 | |
| 60-89 days | 15 | | | 44 | | | — | | | 59 | |
| 90+ days | 4 | | | 38 | | | — | | | 42 | |
| Total delinquency | 24 | | | 121 | | | — | | | 145 | |
| Finance receivables | $ | 172 | | | $ | 550 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 730 | |
In accordance with the Company’s income recognition policy, finance receivables in non-accrual status as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 were $30 thousand and $0.1 million, respectively.
Note 5. Property, Equipment and Software, Net
Property, equipment and software consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Capitalized technology | | $ | 55,405 | | | $ | 46,760 | |
| Furniture, fixtures and equipment | | 3,964 | | | 3,680 | |
| Leasehold improvements | | 979 | | | 979 | |
| Total property, equipment and software | | 60,348 | | | 51,419 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (50,056) | | | (37,380) | |
| Property, equipment and software, net | | $ | 10,292 | | | $ | 14,039 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $12.7 million, $13.6 million and $10.3 million, respectively.
Note 6. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Accrued payroll and benefits | | $ | 8,900 | | | $ | 8,646 | |
| Accrual for services rendered and goods purchased | | 6,899 | | | 8,589 | |
| Accrued interest | | 2,794 | | | 2,196 | |
| Other | | 3,413 | | | 3,789 | |
| Total | | $ | 22,006 | | | $ | 23,220 | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 7. Leases
The Company leases its office facilities under a non-cancelable operating lease agreement with an unrelated party through September 2030. The lease agreement includes non-lease components, such as common area maintenance and reimbursements for real estate taxes, which are expensed as incurred as variable lease payments. The lease agreement also includes options to extend or terminate the lease agreement. The Company is not reasonably certain that it will extend or terminate the lease agreement; as such, lease payments do not take into account these options. The Company’s lease agreement does not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. In connection with the lease agreement, the Company executed a letter of credit in the amount of $1.8 million. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no outstanding balances on the letter of credit.
On October 10, 2022, the Company entered into a sublease agreement with a third-party to sublease one of its office facilities through August 2025. The sublease agreement includes options for the sublessee to extend or terminate the lease agreement. The Company is not reasonably certain that the sublessee will extend or terminate the lease agreement; as such, lease payments do not take into account these options. The Company’s sublease agreement does not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. Under the terms of the sublease agreement, the third-party provides the Company with an irrevocable letter of credit in the amount $0.1 million. The Company is entitled to draw on the letter of credit in the event of any default under the terms of the sublease agreement. The Company expects to receive $0.9 million over the term of the sublease agreement. The remaining balances of deferred lease revenue as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 were $0.5 million and $0.8 million, respectively, which will be recognized over the remaining lease term of approximately 20 months. The sublease agreement did not relieve the Company of its primary obligation under its lease agreement. The sublease income to be earned was determined to be less than the costs associated with the primary lease held by the Company. As a result, the Company recorded an impairment expense of $0.5 million on the lease commencement date to adjust its operating lease right-of-use asset, which was included in general, administrative and other in the consolidated statement of operations.
In April 2023, the Company entered into a lease agreement under a non-cancelable operating lease agreement with an unrelated party through May 31, 2024. The lease provides for monthly lease payments of $12 thousand. The lease agreement does not include options to extend or terminate the lease agreement. The Company is not reasonably certain that it will extend or terminate the lease agreement; as such, lease payments do not take into account these options. The Company’s lease agreement does not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants. The Company recognized a right-of-use asset of $0.2 million and lease liability of $0.2 million related to this lease agreement.
The components of total lease cost for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Operating lease cost | $ | 2,347 | | | $ | 2,043 | |
| Variable lease expense | 1,983 | | | 2,271 | |
| Short-term lease cost | 71 | | | 98 | |
| Sublease income | (318) | | | (53) | |
| Total lease cost | $ | 4,083 | | | $ | 4,359 | |
Supplemental cash flow information related to the leases for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: | | | |
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 2,647 | | | $ | 2,271 | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new lease liabilities | | | |
| Operating leases | $ | 159 | | | $ | 465 | |
The aggregate weighted-average remaining lease term and weighted-average discount rate as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (in years) | | 6.7 | | 7.8 |
| Weighted-average discount rate | | 5 | % | | 5 | % |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Future minimum operating leases as of December 31, 2023 are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| Year | | Amount |
| 2024 | | $ | 2,470 | |
| 2025 | | 2,482 | |
| 2026 | | 2,557 | |
| 2027 | | 2,633 | |
| 2028 | | 2,712 | |
| Thereafter | | 4,938 | |
| Total lease payments | | 17,792 | |
| Less: imputed interest | | (2,731) | |
| Operating lease liabilities | | $ | 15,061 | |
Disclosures under ASC 840, Leases
Rent expense, which is included in occupancy expense in the consolidated statements of operations, totaled $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2021.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 8. Borrowings
The following is a summary of the Company’s outstanding borrowings as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, including borrowing capacity as of December 31, 2023 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purpose | | Borrower | | Borrowing Capacity | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Interest Rate as of December 31, 2023 | | Maturity Date |
| Secured borrowing payable | | Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 756 | | | 15.00% | | — | (1) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Senior debt, net | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC; Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC (Tranche A) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 37,500 | | | SOFR plus 7.36% | | April 2024 | (2) |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC (Tranche B) | | 125,000 | | | 103,400 | | | 121,647 | | | SOFR plus 6.75% | | June 2026 | (3) |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC (Tranche C) | | 125,000 | | | 37,500 | | | — | | | SOFR plus 7.50% | | July 2027 | |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC; SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC | | — | | | — | | | — | | | SOFR plus 0.11% plus 3.85% | | February 2024 | (4) |
| Revolving line of credit | | Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC | | 150,000 | | | 93,871 | | | 91,871 | | | SOFR plus 7.50% | | December 2026 | |
| Revolving line of credit | | Gray Rock SPV LLC | | 75,000 | | | 48,442 | | | 44,716 | | | SOFR plus 7.25% | | April 2025 | |
| Total revolving lines of credit | | 475,000 | | | 283,213 | | | 295,734 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Term loan, net | | OppFi-LLC | | 50,000 | | | 49,454 | | | 48,954 | | | LIBOR plus 10.00% | | March 2025 | |
| Total senior debt, net | | | | $ | 525,000 | | | $ | 332,667 | | | $ | 344,688 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Notes payable | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financed insurance premium | | OppFi-LLC | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,616 | | | 7.07% | | July 2023 | |
| Financed insurance premium | | OppFi-LLC | | 1,449 | | | 1,449 | | | — | | | 9.70% | | June 2024 | |
| Total notes payable | | | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,616 | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Maturity date as of December 31, 2022 and for the subsequent period until the secured borrowing payable was paid in full and terminated in February 2023. (2) Maturity date as of December 31, 2022 and for the subsequent period until Tranche A of this revolving line of credit was terminated in July 2023. (3) Borrower included Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC until the revolving line of credit was amended in July 2023. (4) Maturity date as of December 31, 2022 and for the subsequent period until the revolving line of credit was terminated in February 2023. |
Secured borrowing payable: During 2017, Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC entered into a preferred return agreement with Midtown Madison Management LLC. Per the terms of the agreement, the finance receivables are grouped into quarterly pools. Collections are distributed on a pro rate basis after the payout of expenses to back-up servicer, servicer and other relevant parties. This agreement is secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC. The receivables are transferred to Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC and OppWin LLC by OppFi-LLC, which has provided representations and warranties in connection with such sale. The agreement is subject to various financial covenants.
During 2018, the preferred return agreement was amended. Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC sells a 97.5% interest of certain unsecured finance receivables to the unrelated third party. Per the revised agreement, the unrelated third party earns a preferred return of 15% and a performance fee after the preferred return has been satisfied. The initial agreement expired August 1, 2018 and was then extended for one year. The agreement provides for two consecutive options to renew the purchase period for eighteen months. The unrelated third party exercised the first option, which provides a $65.0 million purchase commitment by the unrelated third party. After satisfaction of the purchase commitment, the agreement provides for a third option for an additional $100.0 million purchase commitment.
In May 2020, the preferred return agreement was amended. Midtown Madison Management LLC exercised the option, which provided an additional $100.0 million purchase commitment, resulting in a total $165.0 million purchase commitment by the unrelated third party. Prior to the expiration of the second option in December 2021, Midtown Madison Management LLC extended the purchase period indefinitely to the time at which Opportunity Funding SPE II, LLC purchases equal or exceed the purchase commitment. As of December 31, 2022, $165.0 million of finance receivables had been purchased with an active secured borrowing balance of $0.8 million.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
On February 16, 2023, the borrowings under this secured borrowing payable were paid in full, of which borrowings totaling $0.1 million were forgiven. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the preferred return agreement. As of December 31, 2023, there is no secured borrowing balance.
Total interest expense related to secured borrowings, which is included in interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs in the consolidated statements of operations, was $10 thousand, $1.3 million and $2.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Additionally, the Company has capitalized $0.2 million in debt issuance costs related to secured borrowings. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no amortized debt issuance costs related to secured borrowings. For the year ended December 31, 2021, amortized debt issuance costs related to secured borrowing, which is included in interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs in the consolidated statements of operations, were $29 thousand. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no unamortized debt issuance costs related to secured borrowings.
Senior debt:
Corporate credit agreement
On August 13, 2018, OppFi-LLC entered into a corporate credit agreement with BMO Harris Bank N.A., which provided a maximum available amount of $10.0 million. Interest was payable monthly. The facility was secured by OppFi-LLC’s assets and certain brokerage assets made available by the Schwartz Capital Group (SCG), a related party. The agreement was subject to various financial covenants. On August 6, 2020, the corporate credit agreement was amended, and the maturity date was extended to February 2022.
On March 23, 2021, the borrowings under this revolving credit agreement were paid in full. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the revolving credit agreement.
Revolving line of credit - Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC
On January 23, 2018, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement with Ares Agent Services, L.P. that provides maximum borrowings of $75.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC. OppFi-LLC provides certain representations and warranties. The line of credit agreement is subject to a borrowing base threshold and various financial covenants, including maintaining a minimum tangible net worth and maximum senior debt to equity.
On January 31, 2020, the revolving line of credit agreement was amended to increase the aggregate commitment to $175.0 million. The amendment also changed the interest rate to one-month LIBOR plus 6% with a 2% LIBOR floor. The agreement matures in January 2024.
On December 14, 2022, the borrowings under this revolving credit agreement were paid in full. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the revolving credit agreement.
Revolving line of credit - Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC
In April 2019, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement with Midtown Madison Management LLC (“OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement”) that provides maximum borrowings of $75.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC. OppFi-LLC provides certain representations and warranties related to the debt. The line of credit agreement is subject to a borrowing base and various financial covenants, including maintaining a minimum tangible net worth and restrictions related to dividend payments.
On October 13, 2021, OppFi-LLC, certain of the OppFi subsidiaries and the other credit parties and guarantors thereto entered into Amendment No. 6 to Revolving Credit Agreement and Other Credit Documents (“Atalaya Amendment”), which amends the OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement. The Atalaya Amendment amends the OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement to, among other things, add Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC as an additional borrower under the OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement, permit the pledge of OppFi Card receivables under the OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement, and extend the maturity date of the OppFi-LLC Midtown Credit Agreement to April 15, 2024.
On June 14, 2022, this revolving credit agreement was amended to, among other things, increase the size of the facility from $75.0 million to $200.0 million, and extend the revolving period for an additional three years to June 14, 2025 with a maturity date on June 14, 2026. Under the amendment, this revolving credit agreement was bifurcated into two tranches: Tranche A, in amount of $75.0 million, and Tranche B, in an amount of $125.0 million. The amendment also replaced the use of Adjusted LIBOR Rate with Term Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) as the benchmark interest rate for Tranche B.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
On July 19, 2023, OppFi-LLC and Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC entered into an Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement (the “A&R Credit Agreement”), which amended and restated the revolving credit agreement. The A&R Credit Agreement amended the revolving credit agreement to, among other things, increase the size of the facility from$200.0 million to $250.0 million, remove Opportunity Funding SPE VII, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and indirect wholly owned subsidiary of OppFi-LLC, as a borrower and remove the concept of pledging OppFi Card receivables under the A&R Credit Agreement, including removing OppWin Card, LLC as a seller. The $250.0 million of availability under the A&R Credit Agreement is comprised of $125.0 million under the existing Tranche B and $125.0 million under a new Tranche C. In addition, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC may request, at any time during the Tranche C commitment period, one (1) increase in the Tranche C committed amount in an amount equal to $25.0 million, resulting in an aggregate Tranche C commitment equal to $150.0 million. Loans under Tranche C bear interest at the Term Secured Overnight Financing Rate plus 7.5% with a commitment period until July 19, 2026 and a maturity date of July 19, 2027. A portion of the proceeds of the A&R Credit Agreement were used to repay in full the outstanding Tranche A loans under the prior revolving credit agreement.
Revolving line of credit - Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC
In April 2019, Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement with Ares Agent Services, L.P. that provides maximum borrowings of $50.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC. OppFi-LLC provides certain representations and warranties related to the debt. The line of credit agreement is subject to a borrowing base and various financial covenants, including maintaining a minimum tangible net worth and restrictions related to dividend payments.
On June 22, 2022, the borrowings under this revolving line of credit agreement were paid in full. Subsequent to repayment, OppFi-LLC terminated the revolving credit agreement.
Revolving line of credit - Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC and SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC
In August 2019, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement with BMO Harris Bank N.A. that provides maximum borrowings of $25.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC. OppFi-LLC provides certain representations and warranties related to the debt, as well as an unsecured guaranty. The line of credit agreement is subject to a borrowing base and various financial covenants, including maintaining a minimum tangible net worth and restrictions related to dividend payments.
On September 30, 2021, the revolving line of credit agreement was amended to increase the aggregate commitment to $45.0 million. The amended agreement added SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC as an additional borrower to the facility. SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC pledges SalaryTap receivables as eligible collateral. The amendment also changed the interest rate from LIBOR plus 4.25% to LIBOR plus 3.85% with a 0.40% LIBOR floor, and the amended agreement matures in February 2024.
On March 31, 2022, this revolving credit agreement was amended to bear interest in accordance with the SOFR at a per annum rate equal to the applicable SOFR rate plus a credit spread adjustment of 0.11% plus 3.85%.
On September 1, 2022, this revolving credit agreement was amended to decrease the aggregate commitment from $45.0 million to $7.5 million.
On February 15, 2023, the Company terminated the revolving line of credit agreement upon the end of the revolving commitment period.
Revolving line of credit - Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC
On December 14, 2022, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement with UMB Bank N.A. that provides maximum borrowings of $150.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC. OppFi-LLC provides certain representations and warrants related to the debt. The line of credit agreement is subject to a borrowing base and various financial covenants, including maintaining a minimum tangible net worth and restrictions related to dividend payments. This revolving credit agreement to bear interest in accordance with the SOFR at a per annum rate equal to the applicable SOFR rate plus a credit spread adjustment of 7.50%.
Revolving line of credit - Gray Rock SPV LLC
On April 15, 2022, Gray Rock SPV LLC entered into a revolving line of credit agreement that provides maximum borrowings of $75.0 million. Interest is payable monthly. Borrowings are secured by the assets of Gray Rock SPV LLC. The revolving line of credit agreement contains a financial covenant restricting dividend payments.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Term loan, net
In November 2018, OppFi-LLC entered into a $25.0 million senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement with Midtown Madison Management LLC (“OppFi-LLC Midtown Term Loan Agreement”), which is secured by a senior secured claim on OppFi-LLC’s assets and a second lien interest in the receivables owned by Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V, LLC, and Opportunity Funding SPE VI, LLC. Interest is payable monthly. The loan agreement is subject to various financial covenants. Per the terms of the loan agreement, OppFi-LLC had issued warrants to the lender. In April 2020, OppFi-LLC exercised an option to increase the facility commitment amount to $50.0 million.
On March 23, 2021, the senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement was amended to decrease the interest rate from LIBOR plus 14% to LIBOR plus 10% and extend the maturity date to March 23, 2025. On March 30, 2021, OppFi-LLC drew the remaining $35.0 million available commitment.
On June 30, 2023, LIBOR was phased out. As such, the senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement is subject to the synthetic LIBOR rates until the senior secured multi-draw term loan agreement is amended.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the outstanding balances of $50.0 million and $50.0 million were net of unamortized debt issuance costs of $0.5 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
Certain of the Company’s foregoing credit facilities that consist of term loans and revolving loan facilities are subject to provisions that provide for a cross-default in the event certain covenants under the relevant agreements are breached.
Total interest expense related to the Company’s senior debt, which is included in interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs in the consolidated statements of operations, was $44.2 million, $31.4 million and $19.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Additionally, the Company has capitalized $14.0 million and $12.2 million, respectively in debt issuance costs in connection with the Company’s senior debt for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. Amortized debt issuance costs associated with the Company’s senior debt, which is included in interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs in the consolidated statements of operations, were $2.4 million, $2.4 million and $2.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, unamortized debt issuance costs associated with the Company’s senior debt totaled $4.3 million and $5.1 million of which $3.8 million and $4.0 million related to the revolving line of credit, respectively, and $0.5 million and $1.0 million related to the term loan, respectively.
Notes payable: In March 2022, OppFi entered into a financing agreement for the financing of insurance premiums totaling $0.3 million payable in ten monthly installments of $28 thousand through December 23, 2022. As of December 31, 2022, the borrowing under this note payable was paid in full.
In August 2022, OppFi entered into a financing agreement for the financing of insurance premiums totaling $2.9 million payable in eleven monthly installments of $0.3 million through July 15, 2023. As of December 31, 2023, the borrowing under this note payable was paid in full.
In August 2023, OppFi entered into a financing agreement for the financing of insurance premiums totaling $2.4 million payable in ten monthly installments of $0.2 million through June 15, 2024.
Total interest expense related to notes payable, which is included in interest expense and amortized debt issuance costs in the consolidated statements of operations, was $0.1 million and $44 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Other debt: On April 13, 2020, OppFi-LLC obtained an unsecured loan in the amount of $6.4 million from BMO Harris Bank N.A. in connection with the U.S. Small Business Administration’s (“SBA”) Paycheck Protection Program (“PPP Loan”). Pursuant to the Paycheck Protection Program, all or a portion of the PPP Loan was forgivable if OppFi used the proceeds of the PPP Loan for its payroll costs and other expenses in accordance with the requirements of the Paycheck Protection Program. OppFi-LLC used the proceeds of the PPP Loan for payroll costs and other covered expenses. On November 14, 2020, OppFi-LLC submitted the forgiveness application to the SBA.
On September 13, 2021, the Company was notified that the SBA had forgiven repayment of the entire PPP Loan, which consisted of $6.4 million in principal and $0.1 million of accrued interest. The Company recorded the entire amount of the forgiven principal and accrued interest as other income in its statement of operations during the year ended December 31, 2021. The SBA reserves the right to audit any PPP Loan, for eligibility and other criteria, regardless of size. These audits may occur after forgiveness has been granted. In accordance with the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act (“CARES Act”), all borrowers are required to maintain their PPP loan documentation for six years after the PPP Loan was forgiven and to provide that documentation to the SBA upon request.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2023, required payments for all borrowings, excluding revolving lines of credit, for each of the next five years are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| Year | | Amount |
| 2024 | | $ | 1,449 | |
| 2025 | | 50,000 | |
| 2026 | | — | |
| 2027 | | — | |
| 2028 | | — | |
| Total | | $ | 51,449 | |
Note 9. Warrants
Warrant units: In November 2018, in conjunction with OppFi-LLC entering into a senior secured multi-draw term loan, OppFi-LLC issued warrant units to the lender.
Prior to the Closing, the lender exercised the warrant units; accordingly, the warrant unit liability was remeasured to fair value. The fair value of the warrant unit liability was $5.5 million and was reclassified to additional paid-in capital. After the lender exercised the warrant units, there were no warrant units outstanding thereafter.
Public Warrants: As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were 11,887,500 Public Warrants outstanding. Each whole Public Warrant entitles the registered holder to purchase one whole share of Class A Common Stock at a price of $11.50 per share. Pursuant to the Warrant Agreement, a holder of Public Warrants may exercise its warrants only for a whole number of shares of Class A Common Stock. This means that only a whole warrant may be exercised at any given time by a warrant holder. The Public Warrants will expire on July 20, 2026, five years after the Closing Date, at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, or earlier upon redemption or liquidation.
The Company may redeem the Public Warrants under the following conditions:
•In whole and not in part;
•At a price of $0.01 per warrant;
•Upon not less than 30 days’ prior written notice of redemption (“30-day redemption period”) to each warrant holder; and
•If, and only if, the reported last sale price of the Class A Common Stock equals or exceeds $18.00 per share for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending three business days before the Company sends the notice of redemption to the warrant holders.
The last of the redemption criterion discussed above prevent a redemption call unless there is at the time of the call a significant premium to the exercise price of the Public Warrants. If the foregoing conditions are satisfied and the Company issues a notice of redemption of the Public Warrants, each warrant holder will be entitled to exercise its warrant prior to the scheduled redemption date. However, the price of the Class A Common Stock may fall below the $18.00 redemption trigger price (as adjusted for stock splits, stock dividends, reorganizations, recapitalizations and the like) as well as the $11.50 warrant exercise price after the redemption notice is issued.
Private Placement Warrants: As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were 3,451,937 Private Placement Warrants outstanding, all of which are non-redeemable and may be exercised on a cashless basis so long as they continue to be held by their initial holders or their permitted transferees. The Private Placement Warrants are comprised of 2,539,437 warrants to purchase Class A Common Stock at $11.50 per share (“$11.50 Exercise Price Warrants”) and 912,500 warrants to purchase Class A Common Stock at $15.00 per share (“$15 Exercise Price Warrants”). The $11.50 Exercise Price Warrants expire simultaneously with the Public Warrants, except for certain of the $11.50 Exercise Price Warrants held by underwriters in the IPO (“Underwriter Warrants”) that expire on September 29, 2025 so long as they continue to be held by their initial holders or their permitted transferees. The $15 Exercise Price Warrants expire on July 20, 2031, ten years after the Closing Date, at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, so long as they continue to be held by their initial holders or their permitted transferees, and otherwise expire simultaneously with the Public Warrants.
Warrant liabilities: The Company recorded warrant liabilities of $6.9 million and $1.9 million in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The fair value of the Public Warrants increased by $3.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 and decreased by $6.9 million and $19.3 million, for the years ended December 31, 2022 and
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
2021, respectively. The fair value of the Private Placement Warrants increased by $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 and decreased by $2.5 million and $7.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Note 10. Stockholders’ Equity
Prior to the Business Combination, OppFi-LLC had two classes of partnership interests, preferred units and profit unit interests, which were recapitalized as OppFi Units in connection with the adoption by the Members of the OppFi A&R LLCA immediately prior to the Closing. The preferred units are reflected as OppFi-LLC’s historical members’ equity in the consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity/members’ equity.
Preferred stock: OppFi is authorized to issue 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. OppFi’s Board of Directors has the authority to issue shares of preferred stock with such designations, voting and other rights and preferences as may be determined from time to time.
Class A Common Stock: OppFi is authorized to issue 379,000,000 shares of Class A Common Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of Class A Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share. Additionally, Class A Common Stock is defined as “Economic Common Stock,” and holders are entitled to receive dividends and other distributions (payable in cash, property, or capital stock of the Company) when, as and if declared thereon by OppFi’s Board of Directors from time to time out of any assets or funds of the Company legally available therefor and share equally on a per share basis in such dividends and distributions.
Class B Common Stock: OppFi is authorized to issue 6,000,000 shares of Class B Common Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Holders of Class B Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share. Class B Common Stock is defined as Economic Common Stock and holders are entitled to receive the same dividends and other distributions as Class A Common Stock. All shares of Class B Common Stock were converted into Class A Common Stock at the Closing.
Class V Voting Stock: OppFi is authorized to issue 115,000,000 shares of Class V Voting Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Class V Voting Stock represents voting, non-economic interests in OppFi. Holders of Class V Voting Stock are entitled to one vote for each share.
Share repurchase: On January 6, 2022, OppFi announced that its Board of Directors (“Board”) had authorized a program to repurchase (“Repurchase Program”) up to $20.0 million in the aggregate of shares of Class A Common Stock. Repurchases under the Repurchase Program may be made from time to time, on the open market, in privately negotiated transactions, or by other methods, at the discretion of the management of the Company and in accordance with the limitations set forth in Rule 10b-18 promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and other applicable legal requirements. The timing and amount of the repurchases will depend on market conditions and other requirements. The Repurchase Program does not obligate the Company to repurchase any dollar amount or number of shares and the Repurchase Program may be extended, modified, suspended, or discontinued at any time. For each share of Class A Common Stock that the Company repurchases under the Repurchase Program, OppFi-LLC will redeem one Class A common unit of OppFi-LLC held by OppFi, decreasing the percentage ownership of OppFi-LLC by OppFi and relatively increasing the ownership by the Members. The Repurchase Program expired on December 31, 2023.
There were no repurchase activities during the year ended December 31, 2023. During the year ended December 31, 2022, OppFi repurchased 703,914 shares of Class A Common Stock at an average purchase price of $3.47 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $2.5 million. These shares are held as treasury stock as of December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2022, $17.5 million of the repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program remained available.
Earnout Units: In connection with the Closing, 25,500,000 Retained OppFi Units (“Earnout Units”) held by the Members, and an equal number of shares of Class V Voting Stock distributed to OFS in connection with the Business Combination, are subject to certain restrictions and potential forfeiture pending the achievement (if any) of certain earnout targets pursuant to the terms of the Business Combination Agreement. But for restrictions related to a lock-up (transfer restrictions) and forfeiture (earnout criteria), as such restrictions are more specifically set forth in the Investor Rights Agreement entered into at the Closing, by and among the Company, certain founder holders of FGNA, the Members, the Members’ Representative and certain other parties thereto and/or the OppFi A&R LLCA, as applicable, the Earnout Units have all other economic and voting rights of the other units of OppFi-LLC. With respect to transfers, the Earnout Units are subject to a lock-up until the later of the end of the lock-up period applicable to other OppFi Units or until such Earnout Units are earned in accordance with the Business Combination Agreement. With respect to distributions (other than tax distributions, which in respect of such Earnout Units are treated the same as any other OppFi Unit in accordance with the OppFi A&R LLCA) in relation to the Earnout Units, such distributions (other than tax distributions) are held back until the Earnout Units are earned. If an Earnout Unit is not earned, and therefore forfeited, related distributions are distributed to the other holders of units at such time. Earnout Units are earned as follows:
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1) if, on or any time prior to the third (3rd) anniversary of the Closing Date, the volume weighted average price (“VWAP”) equals or exceeds twelve dollars ($12.00) per share for twenty (20) trading days of any thirty (30) consecutive trading day period following the Closing, thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event;
2) if, on or any time prior to the third (3rd) year anniversary of the Closing Date, the VWAP equals or exceeds thirteen dollars ($13.00) per share for twenty (20) trading days of any thirty (30) consecutive trading day period following the Closing, thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event;
3) if, on or any time prior to the third (3rd) anniversary of the Closing Date, the VWAP equals or exceeds fourteen dollars ($14.00) per share for twenty (20) trading days of any thirty (30) consecutive trading day period following the Closing, thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event; and
4) if a definitive agreement with respect to a change of control as defined in the Business Combination Agreement (“Change of Control”) is entered into on or prior to the third (3rd) anniversary of the Closing Date, then, effective as of immediately prior to closing of such Change of Control, (A) thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event if the price per share payable to the holders of Class A common stock in connection with such Change of Control is equal to or exceeds twelve dollars ($12.00), (B) an additional thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event if the price per share payable to the holders of Class A common stock in connection with such Change of Control is equal to or exceeds thirteen dollars ($13.00), and (C) an additional thirty-three and one third percent (33.3%) of each of the earnout voting shares and the Earnout Units shall be earned and no longer subject to each such event if the price per share payable to the holders of Class A common stock in connection with such Change of Control is equal to or exceeds fourteen dollars ($14.00).
Earnout Units are classified as equity transactions at initial issuance and at settlement when earned. Until the shares are issued and earned, the Earnout Units are not included in shares outstanding. The Earnout Units are not considered stock-based compensation.
Note 11. Stock-Based Compensation
On July 20, 2021, the Company established the OppFi Inc. 2021 Equity Incentive Plan (“Plan”), which provides for the grant of awards in the form of options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, performance shares, performance units, cash-based awards, and other stock-based awards to employees, non-employee directors, officers, and consultants. As of December 31, 2023, the maximum aggregate number of shares of Class A Common Stock that may be issued under the Plan was 17,257,521 shares. The maximum aggregate number of shares is subject to annual increases, which began on January 1, 2022, and continues on the first day of each subsequent fiscal year through and including the tenth anniversary of the commencement of the initial annual increase, equal to the lesser of two percent of the number of shares of Class A Common Stock outstanding at the conclusion of the Company’s immediately preceding fiscal year, or an amount determined by the Company’s Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had only granted awards in the form of options, restricted stock units, and performance stock units.
Stock options: Under the terms of the Plan, incentive stock options must have an exercise price at or above the fair market value of the stock on the date of the grant. Stock options granted have service-based vesting conditions only. Stock options generally vest over four years with 25% of stock options vesting on the first anniversary of the grant and the remaining 75% vesting quarterly over the remaining 36 months. Option holders have a 10-year period to exercise the options before they expire. Stock options that are not vested and exercisable on the date of a participant’s termination generally expire on such date. Stock options that are vested and exercisable on the date of a participant’s termination are generally forfeited 90 days following the participant’s termination date. Forfeitures are recognized during the period in which they occur.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
A summary of the Company’s stock option activity for the year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | Stock Options | Weighted-Average Exercise Price | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
Outstanding as of December 31, 2022 | 1,978,972 | $ | 12.99 | | 8.7 | $ | — | |
| Granted | — | — | | — | — | |
| Exercised | (18,651) | 3.17 | | — | — | |
| Forfeited | (118,129) | 4.21 | | — | — | |
Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 1,842,192 | $ | 13.65 | | 7.6 | $ | 450 | |
Vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2023 | 1,384,570 | $ | 14.44 | | 7.6 | $ | 169 | |
Compensation expense is recorded on a straight-line basis over the vesting period, which is the requisite service period, beginning on the grant date. The compensation expense is based on the fair value of each option grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and is recognized as salaries and employee benefits expense in the consolidated statements of operations and an increase to additional paid-in capital.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Company recognized stock-based compensation of $0.6 million, $0.1 million and $0.9 million, respectively, related to stock options. As of December 31, 2023, the Company had unrecognized stock-based compensation of $0.9 million related to unvested stock options that is expected to be recognized over an estimated weighted-average period of approximately 1.8 years.
The Company did not grant stock options during the year ended December 31, 2023. The weighted-average grant date fair value of stock options granted during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was $2.33 and $2.45, respectively. The fair value of each option grant during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021 was estimated on the grant date using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The range of assumptions was as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| 2022 | 2021 |
| Volatility | 60.00% - 65.00% | 32.50 | % |
| Risk-free rate | 1.71% - 3.02% | 0.91% - 1.25% |
| Expected term | 6.1 years | 5.1 - 6.1 years |
| Dividend yield | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % |
Volatility is the measure by which the Company’s stock price is expected to fluctuate during the expected life of the stock options. Due to the lack of company-specific market data, volatility is based on an estimate of expected volatilities of a representative group of publicly traded companies.
Risk-free rate is based on U.S. Treasury Note yields.
Expected term represents the weighted-average period over which the granted stock options are expected to remain outstanding.
Dividend yield is based on the Company’s history and expectation of dividend payments.
Cash received from the exercise of stock options during the year ended December 31, 2023 was $59 thousand. The total intrinsic value of the stock option exercised during the year ended December 31, 2023 was $13 thousand. There were no stock options exercised during the years ended December 2022 and 2021.
Restricted stock units: Under the terms of the Plan, the Company may grant awards to employees, officers and directors in the form of restricted stock units (“RSUs”), which collectively represent contingent rights to receive shares of Class A Common Stock. The RSUs granted to employees and officers generally vest over four years with 25% of the RSUs vesting on the first anniversary of the grant and the remaining 75% vesting quarterly over the remaining 36 months, and the RSUs granted to directors vest on the earlier of the one-year anniversary of grant or the date of the Company’s next annual meeting of stockholders.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
A summary of the Company’s RSU activity for the year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Unvested as of December 31, 2022 | 2,174,842 | $ | 4.23 | |
| Granted | 754,642 | 2.35 | |
| Vested | (883,788) | 4.05 | |
| Forfeited | (276,885) | 3.78 | |
Unvested as of December 31, 2023 | 1,768,811 | $ | 3.45 | |
If the settlement date with respect to any Class A Common Stock shares issuable upon vesting of RSUs would otherwise occur on a day on which the sale of such shares would violate the provisions of the Company’s Trading Compliance Policy, then the settlement date shall be deferred until the next trading day on which the sale of such shares would not violate the Trading Compliance Policy. In any event, the settlement date shall be no later than the fifteenth day of the third calendar month following the year in which such RSUs vest.
The fair value of each RSU is based on the fair value of the Company’s Class A Common Stock on the date of grant. The related stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the awards, and forfeitures are recognized during the period in which they occur.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Company recognized stock-based compensation of $3.2 million, $2.8 million and $1.5 million, respectively, related to RSUs. As of December 31, 2023 total unrecognized compensation expense related to RSUs was $5.3 million which will be recognized over a weighted-average vesting period of approximately 2.3 years.
Performance stock units: Under the terms of the Plan, the Company may grant awards to employees, officers, and directors in the form of performance stock units (“PSUs”), which collectively represent the contingent rights to receive shares of Class A Common Stock based on the achievement of pre-established performance targets over the applicable performance period. PSUs generally vest over four years, provided the achievement of specified performance targets.
A summary of the Company’s PSU activity for year ended December 31, 2023 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value |
Unvested as of December 31, 2022 | 329,738 | $ | 3.46 | |
| Granted | — | — | |
| Vested | (72,877) | 3.60 | |
Performance adjustment (1) | (129,026) | 3.34 | |
| Forfeited | — | — | |
Unvested as of December 31, 2023 | 127,835 | $ | 3.42 | |
(1) This represents adjustments made to PSUs reflecting changes in estimates based upon our current performance against predefined financial targets.
The fair value of each PSU is based on the fair value of the Company’s Class A Common Stock on the date of grant. The related stock-based compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the awards based on management’s determination of the probable achievement of the pre-established performance targets. If necessary, the Company adjusts the expense recognized to reflect the actual vested shares following the final determination of the achievement of the pre-established performance targets. PSU forfeitures are recognized during the period in which they occur.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, the Company recognized stock-based compensation of $0.2 million, $0.4 million and $0.1 million, respectively, related to PSUs. As of December 31, 2023 total unrecognized compensation expense related to PSUs was $0.2 million which will be recognized over a weighted-average vesting period of approximately 2.3 years.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan: On July 20, 2021, the Company established the OppFi Inc. 2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”). The ESPP permits eligible employees to contribute up to 10% of their compensation, not to exceed the IRS allowable limit, to purchase shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock during six month offerings. Eligible employees will purchase the shares at a price per share equal to the lesser of 85% of the fair market value of the Company’s Class A Common Stock on the first trading day of the offering period or the last trading day of the offering period. The offering periods
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
begin each January 1 and July 1, with the initial offering period beginning on January 1, 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the maximum aggregate number of shares of Class A Common Stock that may be issued under the ESPP was 1,483,919 and may consist of authorized but unissued or reacquired shares of Class A Common Stock. The maximum aggregate number of shares of Class A Common Stock that may be issued under the ESPP shall be cumulatively increased on January 1, 2022 and on each subsequent January 1, through and including January 1, 2030, by a number of shares equal to the smallest of (a) one percent of the number of shares of Class A Common Stock issued and outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, (b) 2,400,000 shares, or (c) an amount determined by the Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2023, there were 234,249 shares of Class A Common Stock purchased under the ESPP. As of December 31, 2022, 44,627 shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock had been purchased under the ESPP.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, ESPP employee payroll contributions accrued of $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively, are included within accrued expenses on the consolidated balance sheets. Payroll contributions accrued as of December 31, 2023 will be used to purchase shares at the end of the ESPP offering period ending on December 31, 2023. Payroll contributions ultimately used to purchase shares are reclassified to stockholders’ equity on the purchase date.
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company recognized ESPP compensation expense of $0.1 million and $0.1 million, respectively.
Profit unit interests: Prior to the Business Combination, OppFi-LLC issued profit unit interests, which were recapitalized as OppFi Units in connection with the adoption by the Members of the OppFi A&R LLCA immediately prior to the Closing.
Total profit interest compensation expense for the year ended December 31, 2021 was $0.5 million.
The compensation expense accounted for all vested units based on the following assumptions:
| | | | | | | | |
| Expected term | | 3 years |
| Volatility | | 68.0 | % |
| Discount for lack of marketability | | 45.0 | % |
| Risk free rate | | 0.2 | % |
The following table summarizes the Company’s profit unit interests activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Units | | Average
Fair Value
at Grant Date |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2020 | | 12,202,135 | | | $ | 0.08 | |
| Granted | | — | | | — | |
| Forfeited | | (591,078) | | | 0.10 | |
| Exchanged in reverse recapitalization | | (11,611,057) | | | 0.08 | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | — | | | $ | — | |
The following table summarizes the Company’s non-vested units activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Units | | Average
Fair Value
at Grant Date |
| Non-vested units at December 31, 2020 | | 4,738,333 | | $ | 0.12 | |
| Granted | | — | | — | |
| Vested | | (2,933,300) | | 0.08 | |
| Forfeited | | (591,078) | | 0.10 | |
| Exchanged in reverse recapitalization | | (1,213,955) | | 0.22 | |
| Non-vested units at December 31, 2021 | | — | | $ | — | |
Subsequent to the Business Combination, there was no unrecognized compensation expense related to profit unit interests.
Note 12. Income Taxes
The Company is the sole managing member of OppFi-LLC and, as a result, consolidates the financial results of OppFi-LLC. OppFi-LLC is treated as a partnership for U.S. federal and most applicable state and local income tax purposes. As a
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
partnership, OppFi-LLC is not subject to U.S. federal and certain state and local income taxes. Any taxable income or loss generated by OppFi-LLC is passed through to and included in the taxable income or loss of its members, including OppFi, on a pro rata basis. OppFi is subject to U.S. federal income taxes, in addition to state and local income taxes with respect to its allocable share of any taxable income or loss of OppFi-LLC, as well as any stand-alone income or loss generated by OppFi.
For the year ended December 31, 2023, OppFi recorded an income tax expense of $2.3 million and reported consolidated income before taxes of $41.8 million, resulting in a 5.6% effective income tax rate. For the year ended December 31, 2022, OppFi recorded an income tax benefit of $0.3 million and reported consolidated income before taxes of 3.1 million, resulting in a negative 9.0% effective income tax rate. For the year ended December 31, 2021, OppFi recorded an income tax expense of $0.3 million and reported consolidated income before taxes of 90.1 million, resulting in a 0.3% effective income tax rate. Prior to the Closing Date, OppFi-LLC was classified as a partnership for income tax purposes, and was therefore not subject to federal income tax and did not record an expense for income taxes.
The following table summarizes income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Federal income taxes: | | | | | |
| Current | $ | 27 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (4) | |
| Deferred | 1,058 | | | (350) | | | (225) | |
| State income taxes: | | | | | |
| Current | 480 | | | 312 | | | 582 | |
| Deferred | 766 | | | (239) | | | (42) | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | $ | 2,331 | | | $ | (277) | | | $ | 311 | |
The following table summarizes the differences between the effective income tax rate and the federal statutory income tax rate of 21% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively (dollars in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Amount | Percentage | | Amount | Percentage | | Amount | Percentage |
| Federal income taxes at statutory rate | $ | 8,780 | | 21.0 | % | | $ | 643 | | 21.0 | % | | $ | 18,922 | | 21.0 | % |
| State tax expense, net of federal income tax benefit | 1,239 | | 3.0 | % | | 73 | | 2.4 | % | | 549 | | 0.6 | % |
| Fair market value adjustment of warrants | 1,045 | | 2.5 | % | | (1,964) | | (64.1) | % | | (5,545) | | (6.2) | % |
| Effect of flow-through entity | (8,831) | | (21.1) | % | | 981 | | 32.0 | % | | (13,615) | | (15.1) | % |
| Other | 98 | | 0.2 | % | | (10) | | (0.3) | % | | — | | — | % |
| Total | $ | 2,331 | | 5.6 | % | | $ | (277) | | (9.0) | % | | $ | 311 | | 0.3 | % |
OppFi’s effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 differs from the federal statutory income tax rate of 21% primarily due to the noncontrolling interest in the Up-C partnership structure, warrant fair market value fluctuations, and state income taxes.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between financial statement and tax bases using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The components of deferred taxes were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Investment in partnership | $ | 15,921 | | | $ | 16,239 | |
| Tax receivable agreement liability | 5,891 | | | 6,195 | |
| Net operating loss | 3,275 | | | 3,603 | |
| Intangibles | 523 | | | 580 | |
| Stock compensation | 105 | | | 82 | |
| Other | 62 | | | 60 | |
| Deferred tax asset | $ | 25,777 | | | $ | 26,758 | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2023, OppFi had approximately $13.7 million of federal net operating loss carryovers and $8.2 million of state net operating loss carryovers. As of December 31, 2022, OppFi had approximately $14.9 million of federal net operating loss carryovers and $9.1 million of state net operating loss carryovers. The entirety of the federal net operating loss carryover has no expiration date and the state net operating loss carryovers will expire in varying amounts beginning in 2027.
At the time of the Business Combination, OppFi recorded a deferred tax asset of $18.9 million with an offset to additional paid-in capital for the difference between the book value and the tax basis of OppFi’s investment in OppFi-LLC. As of December 31, 2023, the related deferred tax asset was $15.9 million. The decrease was due to additional differences between the book and taxable income in 2023. Based on the Company’s cumulative earnings history and forecasted future sources of taxable income, the Company believes that it will be able to realize the deferred tax assets in the future. As the Company reassesses this position in the future, changes in cumulative earnings history, excluding non-recurring charges, or changes to forecasted taxable income may alter this expectation and may result in an increase in the valuation allowance and an increase in the effective tax rate.
In connection with the Business Combination, the Company entered into the TRA, which provides for payment to the Members of 90% of the U.S. federal, state and local income tax savings realized by the Company as a result of the increases in tax basis and certain other tax benefits related to the transactions contemplated under the Business Combination Agreement and the exchange of Retained OppFi Units for Class A Common Stock or cash. The Company has in effect an election under Section 754 of the Internal Revenue Code and will have such an election effective for each taxable year in which a redemption or exchange (including deemed exchange) of OppFi-LLC interests for shares of Class A Common Stock or cash occurs. The Company will retain the benefit of the remaining 10% of these cash savings. For the period from the Closing Date through December 31, 2023, the TRA liability decreased by $0.6 million related to exchanges that occurred during that period. The lower expected benefit of the TRA payments resulted in a decrease of the deferred tax asset of $0.3 million, with a net offsetting entry to additional paid-in capital.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, OppFi had unrecognized tax benefit of $38 thousand and $20 thousand, respectively, related to research and development credits allocated from OppFi-LLC. ASC 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. For those benefits to be recognized, a tax position must be more-likely-than-not to be sustained upon examination by taxing authorities. The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as income tax expense. No amounts were accrued for the payment of interest and penalties as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. The Company is currently not aware of any issues under review that could result in significant payments, accruals or material deviation from its position. The Company is subject to income tax examinations by major taxing authorities since inception.
The following table summarizes the change in unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of the year | | $ | 20 | | | $ | — | |
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | | 19 | | | 20 | |
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | | — | | | — | |
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | | (1) | | | — | |
| Settlements with taxing authorities | | — | | | — | |
| Other, net | | — | | | — | |
| Net change in unrecognized tax benefits | | 18 | | | 20 | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits at end of the year | | $ | 38 | | | $ | 20 | |
Note 13. Fair Value Measurements
Fair value on a nonrecurring basis: As of December 31, 2023, the Company has no assets or liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis; that is, the instruments are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis but are subject to fair value adjustments in certain circumstances. As of December 31, 2022, the Company’s financial assets that are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis included assets held for sale. Assets held for sale were measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis using Level 3 inputs.
Fair value measurement on a recurring basis: Effective January 1, 2021, the Company elected the fair value option to account for its installment finance receivables and measures the installment finance receivables at fair value on a recurring basis. Prior to the Business Combination, OppFi-LLC only had warrant units that were measured at fair market value on a
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
recurring basis. Subsequent to the Business Combination, the Company measures the Public Warrants and Private Placement Warrants at fair value on a recurring basis.
The Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Fair Value Measurements |
| | December 31, 2023 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Financial assets: | | | | | | | | |
Finance receivables at fair value, excluding accrued interest and fees receivable (1) | | $ | 445,255 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 445,255 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Warrant liability - Public Warrants (2) | | 4,636 | | | 4,636 | | | — | | | — | |
Warrant liability - Private Placement Warrants (3) | | 2,228 | | | — | | | — | | | 2,228 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | Fair Value Measurements |
| | December 31, 2022 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Financial assets: | | | | | | | | |
Finance receivables at fair value, excluding accrued interest and fees receivable (1) | | $ | 441,496 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 441,496 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Financial liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Warrant liability - Public Warrants (2) | | 1,189 | | | 1,189 | | | — | | | — | |
Warrant liability - Private Placement Warrants (3) | | 699 | | | — | | | — | | | 699 | |
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no transfers of assets or liabilities in or out of Level 3 fair value measurements. |
| | | | | | | | |
(1) The Company primarily estimates the fair value of its installment finance receivables portfolio using discounted cash flow models that have been internally developed. The models use inputs that are unobservable but reflect the Company’s best estimates of the assumptions a market participant would use to calculate fair value. |
The following table presents quantitative information about the significant unobservable inputs used for the Company’s installment finance receivables fair value measurements as of December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Interest rate on finance receivables | | 156.15 | % | | 152.39 | % |
| Discount rate | | 26.34 | % | | 25.89 | % |
| Servicing cost* | | 2.96 | % | | 5.01 | % |
| Remaining life | | 0.60 years | | 0.59 years |
| Default rate* | | 25.63 | % | | 20.27 | % |
| Accrued interest* | | 4.34 | % | | 3.93 | % |
| Prepayment rate* | | 20.90 | % | | 21.33 | % |
| | | | |
| *Stated as a percentage of finance receivables | | |
(2) The fair value measurement for the Public Warrants is categorized as Level 1 due to the use of an observable market quote in an active market under the ticker OPFI WS.
(3) The fair value of the Private Placement Warrants is measured using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model; accordingly, the fair value measurement for the Private Placement Warrants is categorized as Level 3.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| The following table presents the significant assumptions used in the simulation at December 31, 2023 and 2022: |
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | $11.50 Exercise
Price Warrants | | $15 Exercise
Price Warrants | | $11.50 Exercise
Price Warrants | | $15 Exercise
Price Warrants |
| Risk-free interest rate | | 4.07 | % | | 3.84 | % | | 4.11 | % | | 3.88 | % |
| Expected term (years) | | 2.6 years | | 7.6 years | | 3.5 years | | 8.5 years |
| Expected volatility | | 44.10 | % | | 44.10 | % | | 53.90 | % | | 53.90 | % |
| Exercise price | | $ | 11.50 | | | $ | 15.00 | | | $ | 11.50 | | | $ | 15.00 | |
| Fair value of warrants | | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | 1.30 | | | $ | 0.11 | | | $ | 0.46 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| The following table presents the changes in the fair value of the warrant liability - Private Placement Warrants (in thousands): |
| | | | | | |
| | $11.50 Exercise
Price Warrants | | $15 Exercise
Price Warrants | | Total |
| Fair value as of December 31, 2021 | | $ | 1,879 | | | $ | 1,278 | | | $ | 3,157 | |
| Change in fair value | | (1,600) | | | (858) | | | (2,458) | |
| Fair value as of December 31, 2022 | | 279 | | | 420 | | | 699 | |
| Change in fair value | | 762 | | | 767 | | | 1,529 | |
| Fair value as of December 31, 2023 | | $ | 1,041 | | | $ | 1,187 | | | $ | 2,228 | |
Financial assets and liabilities not measured at fair value: The following table presents the carrying value and estimated fair values of financial assets and liabilities disclosed but not carried at fair value and the level within the fair value hierarchy as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Fair Value Measurements |
| | December 31, 2023 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | | $ | 31,791 | | | $ | 31,791 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Restricted cash | | 42,152 | | | 42,152 | | | — | | | — | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | 18,065 | | | 18,065 | | | — | | | — | |
| Finance receivables at amortized cost, net | | 110 | | | — | | | — | | | 110 | |
| Settlement receivable | | 1,904 | | | 1,904 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Senior debt, net | | 332,667 | | | — | | | — | | | 332,667 | |
| Notes payable | | 1,449 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,449 | |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Fair Value Measurements |
| | December 31, 2022 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Cash | | $ | 16,239 | | | $ | 16,239 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Restricted cash | | 33,431 | | | 33,431 | | | — | | | — | |
| Accrued interest and fees receivable | | 15,800 | | | 15,800 | | | — | | | — | |
| Finance receivables at amortized cost, net | | 643 | | | — | | | — | | | 643 | |
| Settlement receivable | | 2,000 | | | 2,000 | | | — | | | — | |
| Assets held for sale | | 550 | | | — | | | — | | | 550 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
| Secured borrowing payable | | 756 | | | — | | | — | | | 756 | |
| Senior debt, net | | 344,688 | | | — | | | — | | | 344,688 | |
| Notes payable | | 1,616 | | | — | | | — | | | 1,616 | |
Note 14. Commitments, Contingencies and Related Party Transactions
Legal contingencies: Due to the nature of its business activities, the Company is subject to extensive regulations and legal actions and is currently involved in certain legal proceedings, including class action allegations, and regulatory matters, which arise in the normal course of business. In accordance with applicable accounting guidance, the Company establishes an accrued liability for legal proceedings and regulatory matters when those matters present loss contingencies which are both probable and reasonably estimable.
The Company has received inquiries from certain agencies and states on its lending compliance, the validity of the bank partnership model, and its ability to facilitate the servicing of bank originated loans. Management is confident that its lending practices and the bank partnership structure, in addition to the Company’s technologies, services, and overall relationship with its bank partners, complies with state and federal laws. However, the inquiries are still in process and the outcome is unknown at this time.
The Company is vigorously defending all legal proceedings and regulatory matters. Except as described below, management does not believe that the resolution of any currently pending legal proceedings and regulatory matters will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
On November 18, 2021, the Company entered into a Consent Judgement and Order (“Settlement”) with the Attorney General of the District of Columbia (“District”) to resolve all matters in a dispute related to the action previously filed against the Company by the District (“Action”). The Company denies the allegations in the Action and denies that it has violated any law or engaged in any deceptive or unfair practices. The Action was resolved to avoid the expense of protracted litigation. As part of the Settlement, the Company agreed to, among other things, refrain from certain business activities in the District of Columbia, pay $0.3 million to the District of Columbia and provide refunds totaling $1.5 million to certain District of Columbia consumers. As of December 31, 2021, unpaid refunds due to certain District of Columbia consumers totaled $1.5 million. During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company distributed refunds totaling $1.5 million to the District of Columbia consumers and there were no unpaid refunds due as of December 31, 2022. The Company has fulfilled all terms of the Settlement as of December 31, 2022.
On March 7, 2022, the Company filed a complaint for declaratory and injunctive relief (“Complaint”) against the Commissioner (in her official capacity) of the Department of Financial Protection and Innovation of the State of California (“Defendant”) in the Superior Court of the State of California, County of Los Angeles, Central Division (“Court”). The Complaint seeks a declaration that the interest rate caps set forth in the California Financing Law, as amended by the Fair Access to Credit Act, a/k/a AB 539 (“CFL”), do not apply to loans that are originated by the Company’s federally-insured state-chartered bank partners and serviced through the Company’s technology and service platform pursuant to a contractual arrangement with each such bank (“Program”). The Complaint further seeks injunctive relief against the Defendant, preventing the Defendant from enforcing interest rate caps under the CFL against the Company based on activities related to the Program. On April 8, 2022, the Defendant filed a cross-complaint against the Company attempting to enforce the CFL against the Company and, among other things, void loans that are originated by the Company’s federally-insured state-chartered bank partners through the Program in California and seek financial penalties against the Company. On October 17, 2022, the Company filed a cross-complaint against the Defendant seeking declaratory relief for issuing an underground regulation to
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
determine the “true lender” under the CFL without complying with California’s Administrative Procedures Act. On January 30, 2023, the Commissioner filed a motion for a preliminary injunction seeking to enjoin the Company from providing services to FinWise in connection with loans made to California consumers to the extent that such loans are in excess of California’s interest rate caps. On September 26, 2023, the Court sustained the Commissioner’s demurrer to the Company’s cross-complaint with leave to amend. On October 26, 2023, the Company filed its amended cross-complaint. On October 30, 2023, the Commissioner’s motion for preliminary injunction was denied. On November 27, 2023, the Commissioner filed their answer to the Company’s cross-complaint. The Company intends to continue to aggressively prosecute the claims set forth in the Complaint and vigorously defend itself and its position as the matter proceeds through the court process. The Company believes that the Defendant’s position is without merit as explained in the Company’s initial Complaint.
On July 20, 2023, a stockholder filed a putative class action complaint in the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware (Case No. 2023-0737) on behalf of a purported class of Company stockholders naming certain of FGNA’s former directors and officers and its controlling stockholder, FG New America Investors, LLC (the “Sponsor”), as defendants. The lawsuit alleges that the defendants breached their fiduciary duties to the stockholders of FGNA stemming from FGNA’s merger with OppFi-LLC and that the defendants were unjustly enriched. The lawsuit seeks, among other relief, unspecified damages, redemption rights, and attorneys’ fees. Neither the Company nor any of the Company’s current officers or directors are parties to the lawsuit. The Company is obligated to indemnify certain of the defendants in the action. The Company has tendered defense of this action under its directors’ and officers' insurance policy. Due to the early stage of this case, neither the likelihood that a loss, if any, will be realized, nor an estimate of the possible loss or range of loss, if any, can be determined.
Related party transactions: OppFi-LLC previously had an unsecured line of credit agreement with SCG with a maximum available amount of $4.0 million, which was paid in full on March 30, 2021. There were no interest expense related to this related transaction for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. Interest expense related to this related party transaction was $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2021.
In August 2020, OppFi-LLC entered into a Management Fee Agreement (“Management Fee Agreement”) with SCG. Pursuant to the terms of the Management Fee Agreement, SCG provided board and advisory services. Effective upon the Closing, OppFi-LLC terminated the Management Fee Agreement and incurred $3.0 million in transaction costs, which has been offset against additional paid-in capital in the consolidated balance sheets. There were no management fees under the Management Fee Agreement for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. For the year ended December 31, 2021, management fees under the Management Fee Agreement totaled $0.4 million.
In connection with the Business Combination, OppFi entered into the Tax Receivable Agreement with the Members and the Members’ Representative (the “Tax Receivable Agreement”). The Tax Receivable Agreement provides for payment to the Members of 90% of the U.S. federal, state and local income tax savings realized by the Company as a result of the increases in tax basis and certain other tax benefits related to the transactions contemplated under the Business Combination Agreement and the exchange of Retained OppFi Units for Class A Common Stock or cash.
Christopher McKay is one of our executive officers. Mr. McKay’s daughter is an employee whose employment with the Company predates Mr. McKay’s designation as an executive officer in 2021. For the year ended December 31, 2023, Ms. McKay’s total compensation was approximately $133 thousand. For the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, Ms. McKay’s total compensation did not exceed $120 thousand. These compensation arrangements are consistent with those made available to other employees of the Company with similar years of experience and positions. Ms. McKay also participated in the Company’s benefit plans available to all other employees in similar positions.
Note 15. Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to significant concentration of credit risk consist primarily of finance receivables. As of December 31, 2023, consumers living primarily in Texas, Florida and Virginia made up approximately 16%, 12% and 11%, respectively, of the gross amount of the Company’s portfolio of finance receivables. As of December 31, 2023, there were no other states that made up more than 10% or more of the gross amount of the Company’s portfolio of finance receivables. As of December 31, 2022, consumers living primarily in Texas, Florida and Virginia made up approximately 14%, 13%, and 11%, respectively, of the gross amount of the Company’s portfolio of finance receivables. Furthermore, such consumers’ ability to honor their installment contracts may be affected by economic conditions in these areas. The Company is also exposed to a concentration of credit risk inherent in providing alternate financing programs to borrowers who cannot obtain traditional bank financing.
Note 16. Retirement Plan
The Company sponsors a 401(k) retirement plan (“401(k) Plan”) for its employees. Full time employees (except certain non-resident aliens) and others, as defined in the plan document, who are age 21 and older are eligible to participate in the 401(k) Plan. The 401(k) Plan participants may elect to contribute a portion of their eligible compensation to the 401(k) Plan. The
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Company has elected a matching contribution up to 4% on eligible employee compensation. The Company’s contribution, which is included in salaries and employee benefits in the consolidated statements of operations, totaled $1.5 million, $1.5 million, and $1.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 17. (Loss) Earnings Per Share
Prior to the reverse recapitalization in connection with the Closing, all net income was attributable to the noncontrolling interest. For the periods prior to July 20, 2021, earnings per share was not calculated because net income prior to the Business Combination was attributable entirely to OppFi-LLC.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted (loss) earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Numerator: | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to OppFi Inc. | $ | (1,005) | | | $ | 7,098 | | | $ | 25,554 | |
| Net (loss) income available to Class A common stockholders - Basic | (1,005) | | | 7,098 | | | 25,554 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — | | | (3,758) | | | 19,271 | |
| Income tax benefit (expense) | — | | | 908 | | | (4,626) | |
| Net (loss) income available to Class A common stockholders - Diluted | $ | (1,005) | | | $ | 4,248 | | | $ | 40,199 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
| Weighted average Class A common stock outstanding - Basic | 16,391,199 | | 13,913,626 | | 13,218,119 |
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | |
| Stock options | — | | — | | — |
| Restricted stock units | — | | 105,928 | | 8,930 |
| Performance stock units | — | | 9,492 | | — |
| Warrants | — | | — | | — |
| Employee stock purchase plan | — | | 2,551 | | — |
| Retained OppFi Units, excluding Earnout Units | — | | 70,224,487 | | 71,246,990 |
| Dilutive potential common shares | — | | 70,342,458 | | 71,255,920 |
| Weighted average units outstanding - diluted | 16,391,199 | | 84,256,084 | | 84,474,039 |
| (Loss) earnings per share: | | | | | |
| Basic EPS | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.51 | | | $ | 1.93 | |
| Diluted EPS | $ | (0.06) | | | $ | 0.05 | | | $ | 0.48 | |
| | | | | |
The following table presents securities that have been excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share as their effect would have been anti-dilutive for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Public Warrants | 11,887,500 | | 11,887,500 | | 11,887,500 |
| Private Unit Warrants | 231,250 | | 231,250 | | 231,250 |
| $11.50 Exercise Price Warrants | 2,248,750 | | 2,248,750 | | 2,248,750 |
| $15 Exercise Price Warrants | 912,500 | | 912,500 | | 912,500 |
| Underwriter Warrants | 59,437 | | 59,437 | | 59,437 |
| Stock Options | 1,922,473 | | 2,128,503 | | 3,375,000 |
| Restricted stock units | 2,006,596 | | 1,847,291 | | 1,766,714 |
| Performance stock units | 183,526 | | 247,565 | | 78,907 |
| Noncontrolling interest - Earnout Units | 25,500,000 | | 25,500,000 | | 25,500,000 |
| Noncontrolling interest - OppFi Units | 68,357,926 | | — | | — |
| Potential common stock | 113,309,958 | | 45,062,796 | | 46,060,058 |
OppFi Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 18. Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated the impact of events that have occurred through the date these financial statements were issued and identified the following event that require disclosure.
Borrowings:
The Company was in breach of a collateral performance trigger in its revolving credit agreement with UMB Bank, N.A. as of the reporting dates occurring in December 2023 and January 2024. The Company obtained waivers from the lenders waiving any default or event of default resulting from the breaches. On March 19, 2024, the Company entered into an amendment (the “First Amendment”) to the revolving credit agreement with UMB Bank, N.A. The First Amendment, among other things, removed the specific collateral performance trigger that the Company had previously been out of compliance with.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENT WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, management has evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2023 (“Evaluation Date”). Based upon that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of the Evaluation Date, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were not effective due to the material weakness in its internal control over financial reporting described below.
Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Notwithstanding the material weakness in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting described below, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that the consolidated financial statements of the Company as included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K present fairly, in all material respects, the Company's financial condition, results of operations and cash flows as of and for the periods presented in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States.
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act and based upon the criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the “COSO framework”). The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the Company’s financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Because of its inherent limitations, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect all misstatements. Effective internal controls can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements.
Under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, management has conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on the COSO framework. Based on evaluation under these criteria, management determined that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2023 due to the existence of the previously reported material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to information technology general controls (“ITGCs”) associated with the Company’s financially relevant information systems. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. As previously disclosed in Part II, Item 9A of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022, management determined that the Company’s user access controls designed to ensure appropriate segregation of duties, adequate restriction of users and privileged access to the Company’s financially relevant information systems were not operating effectively. As previously disclosed in Part I, Item 4 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2023, management also determined that the Company’s user access control designed to ensure appropriate segregation of duties was not designed effectively. Management believes that compensating controls are in place and operating effectively to mitigate the risks associated with the identified material weakness as it is being remediated (as described below).
Remediation Plan for Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is committed to remediating the material weakness described above as promptly as possible. Management believes that certain of the controls in question are designed effectively and that these controls, when operating effectively, will provide appropriate remediation of part of the material weakness. In particular, as part of its remediation plan, the Company is implementing comprehensive access control protocols in order to implement restrictions on user and privileged access to the Company’s financially relevant information systems and will be providing internal control training for personnel involved in remediating this material weakness. In addition, management continues to design and implement new controls to ensure appropriate segregation of duties. Management intends to test the ongoing operating effectiveness of the controls in future periods. The material weakness cannot be considered completely remediated until the applicable controls have operated for a sufficient period of time and management has concluded, through testing, that these controls are designed and operating
effectively. The Company can provide no assurance that its remediation efforts described herein will be successful and that the Company will not have material weaknesses in the future.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Other than the changes to the Company’s internal control over financial reporting described in “Remediation Plan for Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” above, there were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act) during the year ended December 31, 2023 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
On November 16, 2023, Ms. Jocelyn Moore, a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, adopted a trading arrangement for the sale of the Company’s Class A Common Stock (a “Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plan”) that is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense conditions of Securities Exchange Act Rule 10b5-1(c). The Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plan provides for the sale of up to 32,488 shares of Class A Common Stock pursuant to the terms of the Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plan beginning in June 2024 and ending in October 2024.
With the exception of Ms. Moore, during the quarter ended December 31, 2023, no other director or Section 16 officer adopted or terminated any Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangements or non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangements, as defined in Item 408 of Regulation S-K.
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
Not applicable.
Part III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Information regarding directors, executive officers, code of business conduct and ethics, delinquent Section 16(a) Reports (if applicable) and corporate governance of the Company will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement for the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (“Definitive Proxy Statement”) and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Information regarding executive compensation will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Information regarding security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR
INDEPENDENCE
Information regarding certain relationships and related transactions, and director independence will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
Information regarding principal accounting fees and services will be set forth in the Definitive Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The Definitive Proxy Statement will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after December 31, 2023.
Part IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBIT AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) The following is a list of documents filed as part of this report:
Financial Statements:
The following financial statements are included under Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K:
(b) The required exhibits are filed as part of this Form 10-K or are incorporated by reference herein.
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Description |
| |
| 2.1 | | |
| | |
| 3.1 | | |
| | |
| 3.2 | | |
| | |
| 4.1 | | |
| | |
| 4.2 | | |
| | |
| 4.3 | | |
| | |
| 10.1 | | |
| | |
| 10.2 | | |
| | |
| 10.3+ | | |
| | |
| 10.4 | | |
| | |
| 10.5† | | Revolving Credit Agreement, dated December 14, 2022, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IX, LLC, the other credit parties and guarantors thereto, UMB Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, Randolph Receivables LLC, as Castlelake Representative, and the lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022). |
| | |
| 10.6* | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.7†+ | | Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated January, 31, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.8† | | Amendment No. 1 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated June 5, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.9† | | Amendment No. 2 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated June 26, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.10† | | Amendment No. 3 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated November 13, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.11† | | Amendment No. 4 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement and Amendment No. 2 to Fee Letter, dated December 16, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.12†+ | | Revolving Credit Agreement, dated April 15, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.13† | | Amendment No. 1 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated July 18, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021) |
| | |
| 10.14† | | Amendment No. 2 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated December 20, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.15† | | Amendment No. 3 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated January 31, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.16† | | Amendment No. 4 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated February 14, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.17† | | Amendment No. 5 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated June 5, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.19 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.18† | | Amendment No. 6 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated June 26, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.19† | | Amendment No. 7 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated November 13, 2020 by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021) |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.20† | | Amendment No. 8 to Revolving Credit Agreement and Amendment No. 2 to Fee Letter, dated December 16, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021) |
| | |
| 10.21†+ | | |
| | |
| 10.22 | | |
| | |
| 10.23† | | |
| | |
| 10.24 | | |
| | |
| 10.25† | | |
| | |
| 10.26† | | |
| | |
| 10.27† | | |
| | |
| 10.28 | | |
| | |
| 10.29† | | |
| | |
| 10.30†+ | | |
| | |
| 10.31† | | |
| | |
| 10.32 | | |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.33†+ | | Revolving Credit Agreement, dated April 15, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.34† | | First Amendment to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated June 20, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.35† | | Amendment No. 2 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated December 26, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.35 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.36† | | Amendment No. 3 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated February 14, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.36 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.37† | | Amendment No. 4 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated May 11, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.38† | | |
| | |
| 10.39†+ | | Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated July 19, 2023, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE V LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Midtown Madison Management LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2023). |
| | |
| 10.40†+ | | Revolving Credit Agreement, dated August 19, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.38 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.41† | | Amendment No. 1 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated December 20, 2019, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.42† | | Amendment No. 2 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated February 13, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.43† | | Amendment No. 3 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated May 5, 2020, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.41 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.44† | | Amendment No. 4 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated March 31, 2021, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.42 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 26, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.45†+ | | Amendment No. 6 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated September 30, 2021, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, SalaryTap, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, the other parties thereto and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC October 5, 2021). |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.46† | | |
| | |
| 10.47†+ | | |
| | |
| 10.48 | | |
| | |
| 10.49†+ | | |
| | |
| 10.50† | | |
| | |
| 10.51 | | |
| | |
| 10.52 | | |
| | |
| 10.53 | | |
| | |
| 10.54 | | |
| | |
| 10.55†+ | | |
| | |
| 10.56 | | |
| | |
| 10.57 | | |
| | |
| 10.58 | | |
| | |
| 10.59† | | |
| | |
| 10.60†+ | | Amendment No. 5 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated August 6, 2021, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2021). |
| | |
| 10.61† | | |
| | |
| 10.62†+ | | Amendment No. 7 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated March 31, 2022, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, SalaryTap, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, the other parties thereto and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2022) |
| | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.63† | | Amendment No. 5 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated July 11, 2022, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2022). |
| | |
| 10.64† | | Amendment No. 6 to Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement, dated August 15, 2022, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE III, LLC, OppWin, LLC, OppFi Management Holdings, LLC, Opportunity Financial Card Company, LLC, the Lenders party thereto, and Ares Agent Services, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2022). |
| | |
| 10.65† | | Amendment No. 8 to Revolving Credit Agreement, dated September 1, 2022, by and among Opportunity Financial, LLC, Opportunity Funding SPE IV, LLC, OppWin, LLC, SalaryTap, LLC, SalaryTap Funding SPE, LLC, the other parties thereto and BMO Harris Bank N.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2022). |
| | |
| 21.1* | | |
| | |
| 23.1* | | |
| | |
31.1* | | |
| |
31.2* | | |
| |
32.1** | | |
| |
32.2** | | |
| | |
| 97.1* | | |
| | |
| 101.INS | | Inline XBRL Instance Document - the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document |
| | |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| | |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| | |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| | |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| | |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
___________________________
† Certain portions of this exhibit have been omitted pursuant to Regulation S-K Item (601)(b)(10).
+ Certain of the exhibits and schedules to this exhibit have been omitted in accordance with Regulation S-K Item 601(a)(5). The Registrant agrees to furnish a copy of all omitted exhibits and schedules to the SEC upon its request.
* Filed herewith.
** Furnished herewith.
++ Management contracts or compensation plans, contracts or arrangements.
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| Date: March 27, 2024 | OppFi Inc. |
| | |
| By: | /s/ Todd G. Schwartz |
| | Todd G. Schwartz |
| | Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | |
| Name | Position | Date |
| | |
| /s/ Todd G. Schwartz | Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) and | March 27, 2024 |
| Todd G. Schwartz | Executive Chairman of the Board | |
| | |
| /s/ Pamela D. Johnson | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and | March 27, 2024 |
| Pamela D. Johnson | Accounting Officer) | |
| | |
| /s/ Jocelyn Moore | Lead Independent Director | March 27, 2024 |
| Jocelyn Moore | | |
| | |
| /s/ Christina Favilla | Director | March 27, 2024 |
| Christina Favilla | | |
| | |
| /s/ Theodore Schwartz | Director | March 27, 2024 |
| Theodore Schwartz | | |
| | |
| /s/ David Vennettilli | Director | March 27, 2024 |
| David Vennettilli | | |
| | |
| /s/ Greg Zeeman | Director | March 27, 2024 |
| Greg Zeeman | | |