ALTAGAS LTD.
Annual Information Form
For the year ended December 31, 2021
Dated: March 3, 2022
TABLE OF CONTENTS
EMPLOYEES | |||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
Unless otherwise noted, the information contained in this AIF is stated as at December 31, 2021 and all dollar amounts in this AIF are in Canadian dollars. Financial information is presented in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles. For an explanation of certain terms and abbreviations used in this AIF, see the "Glossary" of this AIF.
FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION AND STATEMENTS
This AIF contains forward-looking information (forward-looking statements). Words such as "may", "can", "would", "could", "should", "will", "intend", "plan", "anticipate", "believe", "aim", "seek", "propose", "contemplate", "estimate", "focus", "strive", "forecast", "expect", "project", "target", "potential", "objective", "continue", "outlook", "vision", "opportunity", and similar expressions suggesting future events or future performance, as they relate to the Corporation or any affiliate of the Corporation, are intended to identify forward-looking statements. In particular, this AIF contains forward-looking statements with respect to, among other things, business objectives, expected growth, results of operations, performance, business projects and opportunities and financial results.
Specifically, such forward-looking statements included in this document include, but are not limited to, statements with respect to the following: the Corporation’s strategy, priorities and focus with regard to its Utilities and Midstream segments; the Corporation’s 2022 strategic priorities; the Corporation's redemption of shares; timing of material regulatory filings, proceedings and decisions in the Utilities business; duration of orders by Utilities regulators addressing the COVID-19 public health emergency; expected capital expenditures, expected future growth and expansion opportunities, expected timing of costs related to merger commitments; Washington Gas' NGQSS levels; Washington Gas’ potential remediation obligations related to real property; expected in-service and completion dates for current projects and transactions in the Midstream business; and expected effective dates of material environmental legislation.
These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause actual results, events, and achievements to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such statements. Such statements reflect AltaGas' current expectations, estimates, and projections based on certain material factors and assumptions at the time the statement was made. Material assumptions include: the expected duration and impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic; expected commodity supply, demand and pricing; volumes and rates; exchange rates; inflation; interest rates; credit ratings; regulatory approvals and policies; future operating and capital costs; project completion dates; capacity expectations; and the outcomes of significant commercial contract negotiation.
AltaGas’ forward-looking statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties which could cause results or events to differ from current expectations, including, without limitation: risk related to COVID-19; health and safety risks; operating risks; natural gas supply risks; volume throughput; infrastructure; service interruptions; cyber security, information, and control systems; climate-related risks, including carbon pricing; regulatory risks; litigation; changes in law; political uncertainty and civil unrest; decommissioning, abandonment and reclamation costs; reputation risk; weather data; Indigenous and treaty rights; capital market and liquidity risks; general economic conditions; internal credit risk; foreign exchange risk; integration of Petrogas; debt financing, refinancing, and debt service risk; interest rates; counterparty and supplier risk; technical systems and processes incidents; dependence on certain partners; growth strategy risk; construction and development; transportation of petroleum products; underinsured and uninsured losses; impact of competition in AltaGas' businesses; counterparty credit risk; market risk; composition risk; collateral; rep agreements; market value of common shares and other securities; variability of dividends; potential sales of additional shares; labor relations; key personnel; risk management costs and limitations; commitments associated with regulatory approvals for the acquisition of WGL; cost of providing retirement plan benefits; failure of service providers; and the other factors discussed under the heading "Risk Factors" in this AIF.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 2
Many factors could cause AltaGas' or any particular business segment's actual results, performance, or achievements to vary from those described in this AIF, including, without limitation, those listed above and the assumptions upon which they are based proving incorrect. These factors should not be construed as exhaustive. Should one or more of these risks or uncertainties materialize, or should assumptions underlying forward-looking statements prove incorrect, actual results may vary materially from those described in this AIF as intended, planned, anticipated, believed, sought, proposed, estimated, forecasted, expected, projected, or targeted and such forward-looking statements included in this AIF should not be unduly relied upon. The impact of any one assumption, risk, uncertainty, or other factor on a particular forward-looking statement cannot be determined with certainty because they are interdependent and AltaGas’ future decisions and actions will depend on management’s assessment of all information at the relevant time. Such statements speak only as of the date of this AIF. AltaGas does not intend, and does not assume any obligation, to update these forward-looking statements except as required by law. The forward-looking statements contained in this AIF are expressly qualified by these cautionary statements.
Financial outlook information contained in this AIF about prospective results of operations, financial position, or cash flow is based on assumptions about future events, including economic conditions and proposed courses of action, based on management's assessment of the relevant information currently available. Readers are cautioned that such financial outlook information contained in this AIF should not be used for purposes other than for which it is disclosed herein.
CORPORATE STRUCTURE
Incorporation
AltaGas is a Canadian corporation amalgamated pursuant to the CBCA on January 1, 2020. AltaGas and/or its predecessors began operations in Calgary, Alberta on April 1, 1994 and AltaGas continues to maintain its head, principal, and registered office in Calgary, Alberta currently located at 1700, 355 – 4th Avenue SW, Calgary, Alberta T2P 0J1. AltaGas is a public company, the Common Shares of which trade on the TSX under the symbol "ALA".
Amended Articles
On July 1, 2010, AltaGas filed articles of arrangement under the CBCA to effect a corporate arrangement and the amalgamation of AltaGas Ltd., AltaGas Conversion Inc., and AltaGas Conversion #2 Inc. to form AltaGas. Subsequent to the filing of the articles of arrangement, AltaGas filed articles of amendment on the following dates in connection with the creation of each series of Preferred Shares: (i) August 13, 2010 to create the first series of Preferred Shares, Series A Shares and the second series of Preferred Shares, Series B Shares; (ii) June 1, 2012 to create the third series of Preferred Shares, Series C Shares and the fourth series of Preferred Shares, Series D Shares; (iii) December 9, 2013 to create the fifth series of Preferred Shares, Series E Shares and the sixth series of Preferred Shares, Series F Shares; (iv) June 27, 2014 to create the seventh series of Preferred Shares, Series G Shares and the eighth series of Preferred Shares, Series H Shares; (v) November 17, 2015 to create the ninth series of Preferred Shares, Series I Shares and the tenth series of Preferred Shares, Series J Shares; and (vi) February 15, 2017 to create the eleventh series of Preferred Shares, Series K Shares and the twelfth series of Preferred Shares, Series L Shares. On January 1, 2020, AltaGas filed articles of amalgamation to effect the amalgamation of AltaGas with its non-operating subsidiaries AltaGas Investment Ltd., 11801376 Canada Ltd., and Northwest Triumph Contracting Ltd. On January 7, 2022, AltaGas filed articles of amendment to create the thirteenth series of Preferred Shares, Series 2022-A.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 3
Subsidiary Entities
The businesses of AltaGas are operated by the Company and a number of its subsidiaries including, without limitation, AltaGas Services (U.S.) Inc., AltaGas Utility Holdings (U.S.) Inc., WGL Holdings, Inc. (WGL), Wrangler 1 LLC, Wrangler SPE LLC, Washington Gas Resources Corporation, WGL Energy Services, Inc. (WGL Energy Services), and SEMCO Holding Corporation; in regard to the Utilities business, Washington Gas Light Company (Washington Gas), Hampshire Gas Company, and SEMCO Energy, Inc. (SEMCO); and in regard to the Midstream business, AltaGas Extraction and Transmission Limited Partnership, AltaGas Pipeline Partnership, AltaGas Processing Partnership, AltaGas Northwest Processing Limited Partnership, Harmattan Gas Processing Limited Partnership, Ridley Island LPG Export Limited Partnership, AltaGas Pacific Partnership, AltaGas LPG Limited Partnership, Petrogas Energy Corporation (Petrogas), Petrogas Holdings Partnership, and Petrogas, Inc. In the Corporate/Other segment, subsidiaries include AltaGas Power Holdings (U.S.) Inc., WGL Energy Systems, Inc. (WGL Energy Systems), and Blythe Energy Inc. (Blythe). SEMCO conducts its Michigan natural gas distribution business under the name SEMCO Energy Gas Company (SEMCO Gas), its Alaska natural gas distribution business under the name ENSTAR Natural Gas Company (ENSTAR) and its 65 percent interest in an Alaska regulated gas storage utility under the name Cook Inlet Natural Gas Storage Alaska LLC (CINGSA).
Intercorporate Relationships
The following organization diagram presents the name and the jurisdiction of incorporation of certain of AltaGas' subsidiaries as at the date of this Annual Information Form. The diagram does not include all of the subsidiaries of AltaGas. The assets and revenues of those subsidiaries omitted from the diagram individually did not exceed 10 percent, and in the aggregate did not exceed 20 percent, of the total consolidated assets or total consolidated revenues of AltaGas as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 4

(1) Updated as of the date of this Annual Information Form.
(2) Unless otherwise stated, ownership is 100%.
OVERVIEW OF THE BUSINESS
AltaGas is a leading energy infrastructure company that connects natural gas and NGLs to domestic and global markets. The Company operates a diversified, lower-risk, high-growth energy infrastructure business that is focused on delivering resilient and durable value for its stakeholders.
AltaGas' operating segments include the following:
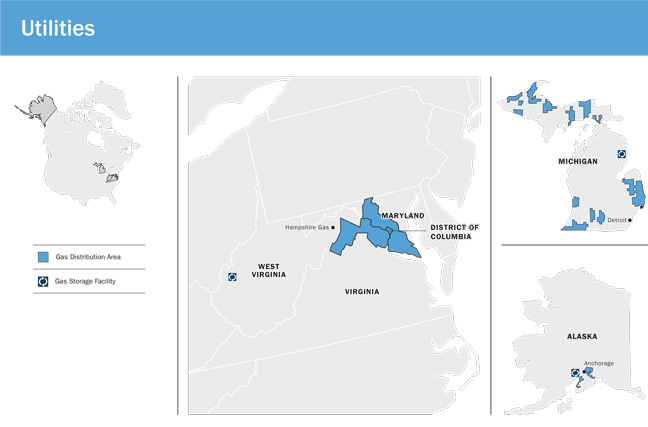
▪Utilities, which owns and operates franchised, cost-of-service, rate regulated natural gas distribution and storage utilities that provide safe, reliable, affordable energy to approximately 1.7 million residential and commercial customers. This includes operating four utilities that operate across five major U.S. jurisdictions with an average 2021 rate base of approximately US$4.7 billion. The Utilities business also includes storage facilities and contracts for interstate natural gas transportation and storage services, as well as the affiliated retail energy marketing business, which sells natural gas and electricity directly to approximately 0.5 million residential, commercial, and industrial customers located in Maryland, Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and the District of Columbia; and
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 5
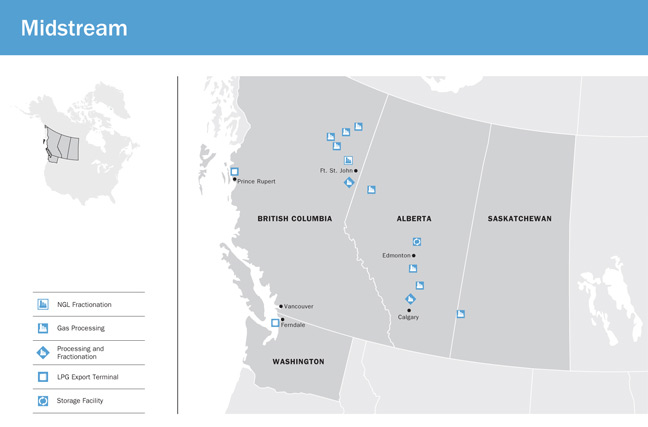
▪Midstream, which is a leading North American platform that connects customers and markets from wellhead to tidewater and beyond. The three pillars of the Midstream business include: 1) global exports, which includes AltaGas' two LPG export terminals; 2) natural gas gathering and extraction; and 3) fractionation and liquids handling. AltaGas' Midstream segment also includes its natural gas and NGL marketing business, domestic logistics, trucking and rail terminals, and liquid storage capability. The addition of Petrogas resulted in revenue of approximately $4.7 billion for the year ended December 31, 2021.
The Corporate/Other segment consists of AltaGas' corporate activities and a small portfolio of gas-fired power generation and distribution assets capable of generating 578 MW of power in California and Colorado.
ALTAGAS’ GEOGRAPHIC FOOTPRINT
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 6
GENERAL DEVELOPMENT OF ALTAGAS' BUSINESS
Below is a summary of key developments, acquisitions and dispositions, construction projects and other commercial arrangements not already discussed above, broken down by business segment, which have influenced the development of the business segments of the Corporation over the last three completed financial years.
Utilities
▪On October 15, 2019, the PSC of MD issued a Final Order approving Washington Gas' settlement agreement in their recent rate case, reflecting a US$27 million base rate increase effective October 15, 2019.
▪On December 6, 2019, the MPSC issued a Final Order approving SEMCO Gas' settlement agreement in its recent rate case, reflecting a base rate increase of approximately US$20 million effective January 1, 2020. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - SEMCO Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On March 16, 2020, the Council of the District of Columbia passed legislation prohibiting the disconnection of electric and gas services for non-payment of fees during the coronavirus public health emergency. The moratorium expired in October 2021, however Washington Gas continues to suspend disconnection activities until authorized by the PSC of DC. On April 19, 2021, Washington Gas filed an AMP proposal designed to help customers lower COVID-19 related arrearages, bring accounts current, improve payment behavior, and avoid disconnections. The PSC of DC approved the AMP on August 9, 2021 and began implementing the AMP on
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 7
November 1, 2021. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On March 16, 2020, the Governor of Maryland issued an Executive Order which ordered regulated utilities to cease disconnections and billing of late fees for residential customers. Although the moratorium ended in November 2021, Washington Gas continues to suspend dunning and disconnection activities until certain customer service thresholds have been met for three consecutive months. On February 15, 2021, the Maryland General Assembly passed the RELIEF Act to help Maryland residential customers who are in arrears. On June 15, 2021, the PSC of MD issued an order allocating US$5.7 million to Washington Gas to be reflected on customer bills. Those funds have all been applied to customer accounts. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On March 16, 2020, the SCC of VA issued an order which prohibited disconnections of electricity, gas, water, and sewer utility services during the coronavirus public health emergency. The moratoriums ended on June 30, 2021. On December 8, 2020, Washington Gas was awarded US$7.7 million under the Virginia CARES Relief Funding Award, to use for customer arrearages. In August 2021, the Virginia General Assembly appropriated US$120 million of ARPA Funds as direct financial assistance to residential utility customers with arrearages over 60 days as of August 31, 2021. On December 6, 2021, Washington Gas received US$6.9 million ARPA Funds that will be applied to customer arrearages. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On March 31, 2020, the Public Sector Pension Investment Board and the Alberta Teachers' Retirement Fund Board acquired all the issued and outstanding common shares of ACI for $33.50 per share. AltaGas owned 11,025,000 (approximately 37 percent) of ACI's common shares and received cash proceeds of approximately $369 million upon close.
▪On April 10, 2020, the Governor of Alaska signed Senate Bill 241, which allows certificated utilities to record a regulatory asset for extraordinary costs and uncollectible residential utility bills that result from the COVID-19 public health disaster emergency declared by the governor on March 11, 2020. In 2021, ENSTAR received approximately US$1.2 million of CARES Act funding from the Cities of Anchorage, Palmer, Wasilla and Mat-Su Borough. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - ENSTAR - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On April 15, 2020, the MPSC issued an order for all utilities which allows for regulatory asset accounting to capture bad debts in excess of what is in approved rates. On February 18, 2021, the MPSC issued an order that requires the MPSC staff to establish an Energy Accessibility and Affordability Collaborative to coordinate efforts and find efficiencies between the EWR Low-Income workgroup and the Monthly Energy Assistance Program workgroup. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - SEMCO Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 8
▪On February 24, 2021, the PSC of DC approved Washington Gas' settlement agreement in its recent rate case, reflecting a base rate increase of approximately US$20 million effective April 1, 2021. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On April 9, 2021, the PSC of MD issued a Final Order affirming the PULJ in Washington Gas' recent rate case, reflecting a base rate increase of approximately US$13 million effective on March 26, 2021. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On July 1, 2021, CINGSA filed a rate case with the RCA seeking approval for approximately US$1.9 million revenue increase based on US$105.5 million rate base, 11.9 percent ROE and 59.99 percent equity thickness. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - ENSTAR & CINGSA - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On July 1, 2021, SEMCO submitted its 2022-2023 EWR Plan, a form of energy efficiency program for its customers, for approval by the MPSC. SEMCO proposes to spend approximately US$30 million on energy waste reduction over 2022 and 2023 to achieve a combined first year energy savings goal of approximately 10.1 million therms. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - SEMCO Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On September 15, 2021, the PSC of DC issued an Order directing Washington Gas to submit a corrective action plan to bring Washington Gas into compliance with the NGQSS regarding call response time standards. Washington Gas was in compliance with the call answering and call abandonment NGQSS service metrics in January 2022, and expects to maintain NGQSS levels for these metrics going forward. Pursuant to a further Order issued by the PSC of DC on February 10, 2022, Washington Gas will not resume disconnections until authorized by the PSC of DC. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On September 30, 2021, the MD OPC filed a motion to establish a corrective action plan and impose civil penalties or, alternatively, to order Washington Gas to show cause why the Commission should not impose civil penalties in regards to violation of Condition 11 of the PSC of MD Order in the Washington Gas Merger proceeding with AltaGas. On October 15, 2021, the PSC of MD issued a show cause order directing Washington Gas to respond to the MD OPC motion. Washington Gas filed its reply to the MD OPC motion on October 22, 2021. On December 23, 2021, the PSC of MD accepted Washington Gas' proposed corrective action plan with modifications. A decision is pending from the Commission regarding the potential assessment of civil penalties. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
▪On December 1, 2021, Washington Gas filed its proposed amendment for the 2023 to 2027 SAVE Plan, proposing to invest approximately US$889 million from 2023 to 2027 to replace higher risk pipeline and facilities in Virginia. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 9
▪On December 17, 2021, Washington Gas filed a proposed amendment for its natural gas conservation and ratemaking efficiency plan (CARE Plan) for the period from May 2022 to April 2025, proposing to continue and expand its portfolio of energy efficiency programs to Virginia customers with a total three-year budget of approximately US$12 million. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals".
Midstream
▪On May 23, 2019, the first shipment of propane to Asia departed from RIPET, the first propane marine export facility on Canada's west coast. On August 21, 2020, the Canada Energy Regulator granted AltaGas an additional 25-year license to export an additional 46,000 Bbls/d of propane. For the year ended December 31, 2021, RIPET's export volumes averaged approximately 50,695 Bbls/d. For further details on RIPET see below under the heading "Business of the Corporation – Midstream Business – Global Exports".
▪On May 31, 2019, AltaGas completed the disposition of WGL Midstream's entire interest in the Stonewall System to a wholly-owned subsidiary of DTE Energy for total gross proceeds of approximately $379 million (US$280 million).
▪On September 30, 2019, AltaGas announced that it had entered into a definitive agreement for the sale of its indirect, non-operating interest in Central Penn held by its subsidiary WGL Midstream, Inc. to Meade Pipeline Investment, LLC, a subsidiary of NextEra Energy Partners, LP. Total cash proceeds for WGL Midstream's interest were approximately $812 million (US$611 million) and the transaction closed on November 13, 2019. Upon close of the sale, various escrow accounts were established to provide the purchaser a form of recourse for the settlement of indemnification obligations. In the third quarter of 2021, AltaGas received approximately $3 million (US$2 million) cash proceeds from the indemnity escrow account.
▪On January 2, 2020, AltaGas announced that AIJVLP had received the Put Notice from SAM pursuant to which SAM exercised the Put Option with respect to SAM's approximate one-third interest in Petrogas effective December 31, 2019. On October 16, 2020, AltaGas announced that AIJVLP and SAM had entered into a definitive agreement whereby AltaGas would acquire SAM's 37 percent of Petrogas' equity for total consideration of $715 million. On December 15, 2020, AltaGas completed the acquisition, increasing its indirectly held ownership interest in Petrogas to approximately 74 percent with Idemitsu owning the remaining interest of approximately 26 percent.
▪In February 2020, following evaluations of the diminished underlying economics for the proposed Constitution pipeline project, the partners of Constitution elected not to proceed with the project. AltaGas held a 10 percent equity interest in Constitution.
▪In the first half of 2020, the Company expanded its integrated northeast B.C. strategy with the completion of the North Pine and Townsend 2B expansions. The 10,000 Bbls/d North Pine expansion was completed and placed into service in the first quarter with additional capacity for the rail terminal to handle the additional volume. The
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 10
Townsend 2B expansion was commissioned in the second quarter and began flowing gas in early May. In March 2020, Townsend Complex licensed capacity was increased to 550 Mmcf/d.
▪On April 23, 2021, AltaGas completed the sale of the majority of WGL Midstream's commodity business for cash proceeds of approximately $341 million (US$275 million).
▪In January 2022, AltaGas agreed to sell one of its customers an interest in certain Midstream processing facilities for total consideration of approximately $234 million. The transaction is expected to close in the second quarter of 2022.
Corporate/Other
▪On January 31, 2019, AltaGas completed the sale of its remaining interest of approximately 55 percent in the Northwest Hydro facilities for net cash proceeds of approximately $1.3 billion, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $688 million. AltaGas remained operator of the facilities until the expiration of an operating and maintenance agreement on January 31, 2021.
▪On August 13, 2019, AltaGas completed the sale of its equity ownership interests in Craven County Wood Energy LP and Grayling Generation Station LP for net proceeds of approximately $25 million (US$19 million).
▪On September 26, 2019, AltaGas closed the sale of its portfolio of U.S. distributed generation assets held by its subsidiaries WGL Energy Systems, Inc. and WGSW, Inc., to TerraForm Power, Inc., an affiliate of Brookfield Asset Management. Total cash proceeds received were approximately $975 million (US$735 million) and a pre-tax gain on disposition of $168 million was recorded in 2019. Following the transfer of ownership of the final remaining distributed generation project that was previously classified as held for sale, AltaGas recognized a pre-tax loss on disposition related to this project of approximately $1 million, for the year ended December 31, 2021.
▪In October 2019, AltaGas announced the successful recontracting of the Blythe facility to SCE. Under the tolling agreement, SCE has exclusive rights to all capacity, energy, ancillary services, and resource adequacy benefits from August 1, 2020 to December 31, 2023. California Public Utilities Commission approval was received on January 16, 2020.
▪In the third quarter of 2020, AltaGas closed the dispositions of AltaGas Pomona Energy Storage Inc. and land related to a gas fired power generation facility in the U.S., as well as AltaGas Ripon Energy Inc. Aggregate gross proceeds for these dispositions, before working capital and other adjustments, were approximately $67 million, resulting in a pre-tax gain of $8 million.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 11
BUSINESS OF THE CORPORATION
AltaGas’ revenue for the year ended December 31, 2021 was approximately $10.6 billion compared to $5.6 billion for the year ended December 31, 2020. The primary reason for the increase relates to the full year impact of the consolidation of Petrogas in 2021. In 2021, 62 percent of revenue from AltaGas' operating segments (excluding Corporate/Other and intercompany eliminations) was from the Midstream segment and 38 percent was from the Utilities segment, compared to 30 percent and 70 percent, respectively, in 2020.
UTILITIES BUSINESS
The Utilities business contributed revenue of $3.9 billion for the year ended December 31, 2021 (2020 - $3.8 billion), representing approximately 38 percent (2020 – 70 percent) of AltaGas’ total revenue before Corporate/Other segment and intersegment eliminations.
Utilities Business
The Utilities segment owns utility assets that deliver natural gas to end-users in the United States, as well as operates a retail energy marketing business. The Utilities business is comprised of Washington Gas (in the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia); Hampshire Gas, a regulated natural gas storage utility in West Virginia; SEMCO Gas in Michigan; ENSTAR in Alaska; a 65 percent interest in CINGSA, a regulated natural gas storage utility in Alaska; and WGL Energy Services, which sells natural gas and electricity to retail customers on an unregulated basis.
Regulatory Process
The Utilities business predominantly operates in regulated marketplaces where, as franchise or certificate holders, regulated utilities are allowed by the regulator to charge regulated rates that provide the utilities the opportunity to recover costs and earn a return on capital. The return on capital is to reflect a fair rate of return on approved utility investments (i.e. rate base) based on a regulatory deemed or targeted capital structure. The ability of a regulated utility to recover prudently incurred costs of providing service and earn the regulator-approved rate of return on equity depends on the utility achieving the cost levels established in the rate-setting processes.
SEMCO Gas and Washington Gas have accelerated pipe and infrastructure replacement programs in place in Michigan and in the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia, respectively. These are long-term programs subject to both changing conditions and regulatory review and approval in multi-year increments. These programs enable SEMCO Gas and Washington Gas to accelerate pipe and infrastructure replacement to further enhance the safety and reliability of the natural gas delivery system. SEMCO Gas and Washington Gas are allowed to begin recovering the cost, including a return, for these investments immediately through approved surcharges for each accelerated pipe or infrastructure replacement program outside of a normal rate case process, mitigating regulatory lag. Once new base rates are put into effect in a given jurisdiction following approval of an application to increase rates, expenditures previously being recovered through the surcharge will be collected through the new base rates.
The Utilities business is subject to regulation over, among other things, rates, accounting procedures, and standards of service. The MPSC has jurisdiction over the regulatory matters related, directly or indirectly, to the services that SEMCO Gas provides to its Michigan customers. The RCA has jurisdiction over the regulatory matters related, directly or indirectly, to ENSTAR’s and CINGSA’s services provided to its Alaska customers. Washington Gas is regulated by the PSC of DC, the PSC of MD, and the SCC of VA, which approve its terms of service and the billing rates that it charges to its customers, regulate interactions with affiliates, and regulate retail competition for natural gas supply service. In all jurisdictions, the regulators approve distribution rates based on a cost-of-service regulatory model. In Alaska, the District of Columbia, and Maryland, rates are set using the results from a historical test year plus known and measurable
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 12
changes. In Michigan and Virginia, rates are set using a projected test year. In all jurisdictions, the rates charged to utility customers are designed to provide the distribution utility with an opportunity to recover all prudently incurred operating, depreciation, income tax, and financing costs and to earn a reasonable return on its investment in the net assets used in its firm gas sales and delivery service.
Utilities Business Key Utility Metrics
The following table summarizes the average rate base for the Utilities business for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
(US$ millions) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
Rate base (1) (2) | 4,655 | 4,291 | ||||||
(1)Rate base is indicative of the earning potential of each utility over time. Approved revenue requirement for each utility is typically based on the rate base as approved by the regulator for the respective rate application, but may differ from the rate base indicated above.
(2)Includes SEMCO Energy’s 65 percent interest in CINGSA.
The following table summarizes the capital expenditures for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
(US$ millions) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
New business | $ | 101 | $ | 109 | ||||
System betterment and gas supply | 200 | 191 | ||||||
General plant | 25 | 29 | ||||||
Accelerated Replacement Programs | 235 | 227 | ||||||
Total | $ | 561 | $ | 556 | ||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 13
The following table summarizes the nature of regulation applicable to each utility:
Regulated Utility | Regulated Authority | % of AltaGas' Consolidated Rate Base as at December 31, 2021 | Allowed Common Equity (%) | Allowed ROE (%) 2020 | Allowed ROE (%) 2021 | Significant Features/ Material Regulatory Developments | ||||||||||||||
Washington Gas | PSC of MD SCC of VA PSC of DC | 76% | 52.1 - 53.5 | 9.2 - 9.7 | 9.2 - 9.7 | n Distribution rates approved under cost of service model. n Rate case filed in 2018 with the SCC of VA for an increase in rates. The Final Order was received in December 2019. In January 2020, a petition for reconsideration was filed and denied, and the rate case is now final. n Rate case filed in January 2020 with the PSC of DC for an increase in rates. Settlement agreement filed December 2020 and was approved in February 2021. n Rate case filed in August 2020 with the PSC of MD for an increase in rates. Evidentiary hearing took place January 2021 and the final order was issued in April 2021. | ||||||||||||||
SEMCO Gas | MPSC | 17% | 45.86 | 9.87 | 9.87 | n Distribution rates approved under cost of service model. n Use of projected test year for rate cases with 10-month limit to issue a rate order. n Rate rider provides recovery relating to the Main Replacement Program which allows SEMCO Gas to accelerate the replacement of older portions of its system. New IRIP was approved in the 2019 rate case for the years 2020 - 2025. Customers were billed a surcharge beginning in 2021 for the IRIP. | ||||||||||||||
ENSTAR | RCA | 6% | 51.81 | 11.875 | 11.875 | n Distribution rates approved under cost of service model using historical test year and allows for known and measurable changes. n In December 2020, RCA approved ENSTAR motion to extend the filing of the next rate case to June 2022 based on 2021 historical test year. | ||||||||||||||
CINGSA | RCA | 1% | 53.04 | 10.25 | 10.25 | n Distribution rates approved under cost of service model using historical test year and allows for known and measurable changes. n Rate case hearing April 2019 with a decision received in August 2019. The decision included an ROE of 10.25 percent (compared to 11.875 percent requested) and 100 percent of Interruptible Storage Service revenues payable to customers (versus 50 percent requested). CINGSA filed a petition for partial reconsideration on September 3, 2019. The Commission denied the petition and on November 4, 2019 CINGSA filed an appeal with the Superior Court challenging one decision from the order. This appeal was also denied on May 6, 2021. n Rate case filed with the RCA in July 2021 seeking approval for approximately US$1.9 million revenue increase based on US$105.5 million rate base, 11.9 percent ROE and 59.99 percent equity thickness. A decision is expected in the third quarter of 2022. | ||||||||||||||
Hampshire Gas | FERC | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n Pass through cost of service tariff approved by FERC. | ||||||||||||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 14
Washington Gas
Washington Gas has been engaged in the natural gas distribution business since 1848 and provides regulated gas distribution services to end users in the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia. The utility has approximately 1.2 million customers across these three jurisdictions: District of Columbia (~166,000; 13 percent), Maryland (~505,000; 42 percent), and Virginia (~546,000; 45 percent). Washington Gas operations are such that the loss of any one customer or group of customers would not have a significant adverse effect on its business.
The average number of customers at Washington Gas has increased by approximately 1 percent annually during the past two years (with an increase of 1 percent in 2021).
Operations
Washington Gas obtains natural gas supplies that originate from multiple regions throughout the U.S. At December 31, 2021, it had service agreements with four pipeline companies that provided firm transportation and storage services, with contract expiration dates ranging from 2022 to 2044. Washington Gas has also contracted with various interstate pipeline and storage companies to add to its storage and transportation capacity.
The following table sets out, by customer category, Washington Gas’ deliveries:
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Deliveries: (MDth) | ||||||||
Residential | 65,779 | 62,672 | ||||||
Commercial | 20,099 | 18,845 | ||||||
Transport | 80,062 | 79,424 | ||||||
Total deliveries | 165,940 | 160,941 | ||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Customers at Year End: | ||||||||
Residential | 988,296 | 978,635 | ||||||
Commercial | 49,369 | 48,464 | ||||||
Transport | 179,514 | 178,430 | ||||||
Total customers | 1,217,179 | 1,205,529 | ||||||
Seasonality
The natural gas distribution business in the District of Columbia, Maryland, and Virginia is seasonal, as the majority of natural gas demand occurs during the winter heating season that extends from November to March. Accordingly, annualized individual quarterly revenues and earnings are not indicative of annual results.
Forecasted volumes in the District of Columbia are set based on the 30-year average Degree Days expected for the period. In Maryland and Virginia, there are billing mechanisms in place which are designed to eliminate the effects of variance in customer usage caused by weather and other factors such as conservation. In the District of Columbia, there is no weather normalization billing mechanism, nor does Washington Gas hedge to offset the effects of weather. As a result, colder or warmer weather will result in variances to financial results. See "Business of the Corporation - Utilities Business - Washington Gas - Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals - District of Columbia Jurisdiction".
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 15
Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals
District of Columbia Jurisdiction
Washington Gas has an Accelerated Pipe Replacement Plan (PROJECTpipes) for the replacement of higher-risk pipe associated with an aging infrastructure in its distribution system in the District of Columbia. The first phase of this plan expired in September 2019. In 2018, Washington Gas filed a request with the PSC of DC for the approval of the second phase of this plan (PROJECTpipes 2). Given the length of the proceeding, the PSC of DC approved additional extensions of the plan for the period from October 2019 to December 2020. On December 11, 2020, the PSC of DC approved a 3-year, US$150 million plan covering the period from January 1, 2021 to December 31, 2023.
On January 13, 2020, Washington Gas filed an application with the PSC of DC to increase its base rates by approximately US$35 million, including approximately US$9 million pertaining to a PROJECTpipes surcharge that customers are currently paying in the form of a rate rider. The filing requested a return on equity of 10.4 percent on allowed common equity of 52.2 percent, which is based on a US$532 million rate base value. Additionally, Washington Gas requested approval for a Revenue Normalization Adjustment mechanism to reduce customer bill fluctuations due to weather-related and conservation-related usage variations, similar to existing mechanisms in both Maryland and Virginia. On December 8, 2020, Washington Gas filed, for PSC of DC approval, a settlement agreement to resolve all issues in the case. The settling parties agreed to a US$20 million increase in base rates including PROJECTpipes surcharges previously collected as a rider and return on equity of 9.25 percent. The settling parties agree that this settlement is limited to resolving PROJECTpipes costs that are completed and in service, as of the date of Washington Gas' filed rebuttal testimony (i.e., September 14, 2020). Washington Gas' rebuttal testimony included an amount of up to approximately US$100 million of PROJECTpipes plant in service being transferred to base rates. This settlement does not set any precedent with respect to any future requests for PROJECTpipes cost recovery. Washington Gas agreed it would not file for a distribution rate increase or request any new rate or tariff mechanisms that have a related customer rate increase in the District of Columbia before August 31, 2021. On February 24, 2021, the PSC of DC approved the US$20 million base rate case recommended in the settlement agreement. The new rates became effective on April 1, 2021.
On March 16, 2020, the Council of the District of Columbia (DC Council) passed legislation prohibiting the disconnection of electric and gas services for non-payment of fees during the coronavirus public health emergency. The moratorium expired in October 2021, however as a result of customer service issues, Washington Gas continues to suspend certain collection activities, including disconnections, until authorized by the PSC of DC. On April 15, 2020, the PSC of DC issued an order authorizing Washington Gas to establish a regulatory asset to capture and track the incremental costs related to COVID-19 that were prudently incurred beginning March 11, 2020. On April 19, 2021, Washington Gas filed an AMP proposal designed to help customers: 1) lower or eliminate existing COVID-19 related arrearages, 2) bring accounts current, 3) improve payment behavior on customers’ new bills, and 4) avoid disconnection and allow customers to remain current in their payment obligations. Under the proposed AMP plan, each participating customer would be enrolled in the plan for approximately 12 months. After an eligible customer enrolls in the program and pays each new monthly amount due on a timely basis, Washington Gas will grant a pro-rated monthly arrearage reduction amount toward the goal of full arrearage elimination at the end of the 12 month period. On August 9, 2021, the PSC of DC approved Washington Gas' AMP. On October 8, 2021, Washington Gas filed new tariff provisions regarding the AMP and implemented the AMP starting November 1, 2021.
On September 15, 2021, the PSC of DC issued an Order directing Washington Gas to submit a corrective action plan to bring Washington Gas into compliance with the NGQSS regarding call response time standards. The Order also stated that Washington Gas shall not disconnect gas customers for non-payment until Washington Gas complies with NGQSS or such time as the PSC of DC otherwise determines. The PSC of DC also found that costs incurred by complying with this Order are not to be included in Washington Gas' COVID-19 regulatory asset. Finally, the Order stated that the PSC of DC found that although it cannot stop Washington Gas from seeking a rate increase, any petition for a rate increase may be held in abeyance either at the request of a party or by the PSC of DC until this performance issue is satisfactorily addressed. Washington Gas filed a corrective action plan with the PSC of DC on September 27, 2021. Washington Gas
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 16
was in compliance with the call answering and call abandonment NGQSS service metrics in January 2022, and expects to maintain NGQSS levels for these metrics going forward. Pursuant to an Order issued by the PSC of DC on February 10, 2022, Washington Gas will not resume disconnection activities until authorized by the Commission.
Maryland Jurisdiction
On December 18, 2020, the PSC of MD found that Washington Gas failed to file annual reports informing the PSC of MD of the status of Washington Gas' 2003 mercury regulator replacement program and imposed a US$750,000 penalty on Washington Gas for reporting violations. The penalty was paid in January 2021 and Washington Gas believes that there is no additional liability as a result of the ruling from the PSC of MD. In its December 18, 2020 order, the PSC of MD also found that Washington Gas’ proposed implementation plan to replace all remaining mercury regulators within five years of completing a mercury regulator survey adequately addresses the need to replace all remaining mercury regulators in Maryland, and is in the public interest. The costs of the proposed implementation program are not yet known, and the recovery of these costs must be deferred until a future rate case. Washington Gas continues to file required annual and other periodic reports on the status and costs of the program with the PSC of MD.
On March 16, 2020, the Governor of Maryland issued an Executive Order which ordered regulated utilities to cease disconnections and billing of late fees for residential customers through May 1, 2020, which was subsequently amended to extend the order through August 31, 2020. On April 9, 2020, the PSC of MD issued an order and authorized each utility company to establish a regulatory asset to record the effects of incremental collection and other costs related to COVID-19 prudently incurred beginning on March 16, 2020. On September 22, 2020, the PSC of MD took action that had the effect of extending the moratorium on service disconnections through November 15, 2020. Due to the winter moratorium on disconnections (November 1 to March 31), this had the effect of delaying residential terminations until April 1, 2021. On August 31, 2020, the PSC of MD issued an order directing, among other things, that Utilities may not engage in service terminations and/or charge late fees until October 1, 2020 and only after meeting termination notification requirements. The PSC of MD also added conditions for implementing customer payment plans. As requested by the PSC of MD, investor-owned utilities in Maryland filed a joint proposed AMP plan on October 7, 2020, which was followed by a legislative style hearing in November 2020. On December 21, 2020, the PSC of MD rejected the proposed AMP plan. The PSC of MD will continue to monitor the customer arrearage data provided by utilities, and may revisit this issue in the future. On February 15, 2021, the Maryland General Assembly passed the RELIEF Act. The RELIEF Act includes approximately US$83 million in funds to help Maryland residential customers who are in arrears. On June 15, 2021, the PSC of MD issued an order allocating US$5.7 million to Washington Gas to be reflected on customer bills. The funds were received in July and Washington Gas has applied the amounts in full to customer accounts.
On August 28, 2020, Washington Gas filed an application with the PSC of MD to increase its base rates by approximately US$28 million, including approximately US$6 million currently collected through the STRIDE surcharges for system upgrades. The proposed rates reflect a 10.45 percent return on equity and a 7.73 percent return on an average rate base. On December 8, 2020, Washington Gas filed rebuttal testimony with a revised revenue requirement of approximately US$27 million. On February 12, 2021, the PULJ issued a Proposed Order in the Case and an ERRATA filing correcting of the Proposed Order on February 19, 2021. The Proposed Order, as corrected, authorizes Washington Gas to increase its Maryland natural gas distribution rates by approximately US$13 million (including US$5 million for the STRIDE surcharge), reflecting a return of equity of 9.70 percent. On April 9, 2021, after considering the appeals, the PSC of MD issued an order which authorized Washington Gas to increase its Maryland natural gas distribution rates by approximately US$13 million (including US$5 million currently collected through the STRIDE surcharge), reflecting a return on equity of 9.70 percent. The revenue increase became effective on March 26, 2021. On May 14, 2021, the MD OPC filed a petition for re-hearing and on June 2, 2021, Washington Gas filed an opposition to the re-hearing. On July 29, 2021, the PSC of MD denied the petition for rehearing. On August 31, 2021, the MD OPC filed an appeal of the PSC of MD's denial of their petition for a re-hearing with the Circuit Court of Baltimore. Washington Gas has filed a notice of intervention. The MD OPC's Initial Memorandum was filed on December 15, 2021, and the PSC of MD and Washington Gas filed their Answering Memoranda on January 14, 2022. The MD OPC's following Reply Memorandum was filed on January 31,
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 17
2022, and the Circuit Court trial was held on February 16, 2022. On February 25, 2022, the Circuit Court of Baltimore City reversed the July 29, 2021 order from the PSC of MD and remanded two issues back to the PSC of MD.
On September 30, 2021, the MD OPC filed a motion to establish a corrective action plan and impose civil penalties or, alternatively, to order Washington Gas to show cause why the Commission should not impose civil penalties. The MD OPC's request asserts that Washington Gas has violated Condition 11 of the PSC of MD Order in the Washington Gas Merger proceeding with AltaGas because it has not devoted the resources necessary to ensure continued compliance with all Commission regulations. In particular, the MD OPC asserts that Washington Gas’ failure to devote enough resources to customer service has made it impossible for customers to successfully and promptly communicate complaints and disputes. Finally, MD OPC asserts that because Washington Gas cannot receive complaints and disputes, it is unable to satisfactorily resolve them or report them pursuant to its obligations under the Code of Maryland regulations. On October 15, 2021, the PSC of MD issued a show cause order directing Washington Gas to respond to the MD OPC motion and to show cause why the PSC of MD should not impose civil penalties. Additionally, the PSC of MD ordered Washington Gas to include a proposed corrective plan, which addresses the decline in customer service post-merger. On October 22, 2021, Washington Gas filed its reply to the MD OPC's motion. On November 12, 2021, the MD OPC, Montgomery County and Staff filed responses to Washington Gas' reply. On December 23, 2021, the PSC of MD found that, among other things: (1) Washington Gas violated the Maryland Code of Regulations from 2016 through June 22, 2021; (2) Washington Gas violated Conditions 11 and 11F of the AltaGas Merger Order from June 2018 through June 22, 2021; (3) the Commission will schedule a hearing to address whether and to what extent civil penalties are appropriate; and (4) Washington Gas’ proposed Corrective Action Plan was accepted with modifications. On January 24, 2022, Washington Gas filed for rehearing of two issues from the Order, including the imposition of certain call center performance metrics and the creation of a regulatory liability to account for past costs. Washington Gas has accrued US$350,000 in anticipation of civil penalties related to reporting violations. On February 2, 2022, the Staff of the Maryland Public Service Commission (the MD Staff) filed comments regarding the penalty for Washington Gas' violations of the Code of Maryland Regulations (COMAR) and merger conditions. The MD Staff recommended that the Commission assess a civil penalty against Washington Gas in the range of US$750,000 to US$1.5 million. The Commission held a hearing on February 9, 2022 to address civil penalties and to consider Washington Gas' rehearing request. A decision is pending. The PSC of MD's decision may also address its current directive that Washington Gas shall continue the suspension of dunning letters, disconnections, and late fees until Washington Gas meets required customer service standards for three consecutive months.
Virginia Jurisdiction
On July 31, 2018, Washington Gas filed an application with the SCC of VA to increase its base rates for natural gas service by US$38 million, which included US$15 million related to the SAVE surcharge. Additionally, the requested revenue increase incorporated the effects of the TCJA. Interim rates became effective, subject to refund, for usage in the January 2019 billing cycle. On April 12, 2019, Washington Gas filed rebuttal testimony and revised its original return on equity down from 10.6 percent to 10.3 percent and its overall rate of return down from 7.94 percent to 7.81 percent. On December 20, 2019, the Commission issued a Final Order that approved: (i) an increase in base rates of US$13 million to reflect the transfer of US$102 million of SAVE investment from the SAVE rider to rate base; (ii) an ROE range of 8.7 percent to 9.7 percent with a mid-point of 9.2 percent; (iii) the amortization of unprotected excess deferred income tax over eight years; and (iv) the refund of a US$26 million TCJA liability over a 12-month period as a sur-credit.
On March 16, 2020, SCC of VA issued an order which prohibited disconnections of electricity, gas, water, and sewer utility services during the coronavirus public health emergency, and established certain consumer protection measures. While the SCC of VA order was extended, the disconnection order, but not the consumer protections expired on October 5, 2020. However, following the expiration of the disconnection order, on October 16, 2020, the Virginia General assembly approved legislation that would extend the disconnection prohibition for residential customers for nonpayment of bills or fees until the Governor determines the prohibition does not need to remain in place or until at least 60 days after the state of emergency declared on March 12, 2020 ends, whichever is sooner. The legislation also codified the consumer protection plans, requiring utilities to offer customers in arrears fee-free repayment plans without deposit or eligibility
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 18
requirements. The legislation became effective in November 2020. On April 29, 2020, the SCC of VA issued an order approving a request from Washington Gas and other Virginia utilities to create a regulatory asset to record incremental prudently incurred costs and suspended late payment fees attributable to the COVID-19 pandemic. The October 16, 2020 legislation approved by the general assembly established certain reporting requirements for utilities to report bad debt information and provides utilities with certain exemptions from such requirements based on a utilities' particular facts and circumstances. On December 8, 2020, Washington Gas was awarded US$7.7 million under the Virginia CARES Relief Funding Award, to use for customer arrearages. Virginia customers must meet the criteria established by the program to receive the funds. The funds have been fully applied.
In August 2021, the Virginia General Assembly appropriated US$120 million of ARPA Funds as direct financial assistance to residential utility customers with arrearages over 60 days as of August 31, 2021. On December 6, 2021, Washington Gas received US$6.9 million of ARPA Funds to be applied to residential customers arrearages.
On December 1, 2021, Washington Gas filed its proposed amendment for the 2023 to 2027 SAVE Plan, proposing to invest approximately US$889 million from 2023 to 2027 to replace higher risk pipeline and facilities in Virginia. Interested parties may file comments with the SCC of VA on or before April 8, 2022. Staff of the SCC of VA shall file its report with the Commission on or before April 22, 2022 containing its findings and recommendations, and Washington Gas may file its response to the Staff report on or before May 8, 2022. A decision from the SCC of VA is expected around May 30, 2022.
On December 17, 2021, Washington Gas filed a proposed amendment for its natural gas conservation and ratemaking efficiency plan (CARE Plan) for the period from May 2022 to April 2025, proposing to continue and expand its portfolio of energy efficiency programs to Virginia customers with a total three-year budget of approximately US$12 million. The Staff Report on findings and recommendation is due March 18, 2022, and Washington Gas comment on the Report is due April 1, 2022. A decision from the SCC of VA is expected in the second quarter of 2022.
In connection with the WGL Acquisition, AltaGas and WGL have made commitments related to the terms of the PSC of DC settlement agreement and the conditions of approval from the PSC of MD and the SCC of VA. Among other things, these commitments include rate credits distributable to both residential and non-residential customers to partially offset rate increases resulting from gas expansion, extension of natural gas service over a 10-year period and other programs, various public interest commitments, and safety programs. As at December 31, 2021, approximately US$7 million of these merger commitments have been charged to expense but not paid. Additionally, there are a number of operational commitments, including the funding of leak mitigation and reducing leak backlogs, the funding of damage prevention efforts, developing projects to extend natural gas service, maintaining pre-merger quality of service standards including odor call response times, increasing supplier diversity, achieving synergy savings benefits, as well as reporting and tracking related to all the commitments, and developing 15 megawatts of either electric grid energy storage or Tier 1 renewable resources within five years after the merger closed.
Hampshire Gas
Hampshire owns underground natural gas storage facilities, including pipeline delivery facilities located in and around Hampshire County, West Virginia, and operates these facilities to serve Washington Gas. Hampshire is regulated by the FERC. Washington Gas purchases all of the storage services of Hampshire, and includes the cost of the services in the commodity cost of its regulated energy bills to customers. Hampshire operates under a “pass-through” cost-of-service based tariff approved by FERC.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 19
SEMCO Energy
SEMCO Energy’s head office is located in Port Huron, Michigan. SEMCO Energy’s primary business is a gas utility business. It operates regulated natural gas transmission and distribution divisions in Michigan, doing business as SEMCO Gas, and in Alaska, doing business as ENSTAR. SEMCO Energy’s gas utility business also includes a 65 percent ownership interest in CINGSA, a regulated natural gas storage utility in Alaska. The gas utility business accounts for approximately 99 percent of SEMCO Energy’s 2021 consolidated revenues. The gas utility business purchases, transports, distributes, stores and sells natural gas and related gas distribution services to residential and C&I customers and is SEMCO Energy's largest business segment.
SEMCO Gas
In Michigan, SEMCO Gas distributes natural gas to approximately 317,000 regulated customers located in both southern Michigan and Michigan’s Upper Peninsula, approximately 92 percent of which are residential. The remaining customers include power plants, food production facilities, furniture manufacturers, and other industrial customers.
The average number of customers at SEMCO Gas has increased by an average of approximately 1 percent annually during the past three years (with an increase of approximately 1 percent in 2021). While there may occasionally be variations in this pattern, average per customer annual gas consumption in Michigan over the longer-term has been gradually decreasing because of, among other things, the availability of and incentive to invest in more energy efficient homes and appliances.
SEMCO Gas pursues opportunities to develop service areas that are not currently served with natural gas. Expansion opportunities that currently exist represent relatively minor asset growth, but SEMCO Gas remains committed to its strategy of pursuing expansion projects that meet management’s target return on investment.
Operations
The SEMCO Gas natural gas transmission and delivery system in Michigan includes approximately 197 miles of gas transmission pipelines and 6,460 miles of gas distribution mains. The pipelines and mains are located throughout the southern half of Michigan’s Lower Peninsula (including in and around the cities of Albion, Battle Creek, Holland, Niles, Port Huron, and Three Rivers) and also in the central, eastern, and western areas of Michigan’s Upper Peninsula.
SEMCO Gas has access to natural gas supplies throughout the U.S. and Canada via interstate and intrastate pipelines in and near Michigan. To provide gas to SEMCO Gas sales customers, SEMCO Gas has negotiated standard terms and conditions for the purchase of natural gas under the NAESB form of agreement with a variety of suppliers.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 20
The following table sets out, by customer category, SEMCO Gas’ deliveries:
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Deliveries: (MDth) | ||||||||
Residential | 24,245 | 24,973 | ||||||
Commercial | 14,027 | 14,072 | ||||||
Transport | 20,920 | 21,422 | ||||||
Gas Customer Choice (1) | 3,049 | 3,219 | ||||||
Total deliveries | 62,241 | 63,686 | ||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Customers at Year End (2): | ||||||||
Residential | 270,312 | 265,168 | ||||||
Commercial | 24,500 | 24,113 | ||||||
Transport | 268 | 255 | ||||||
Gas Customer Choice (1) | 21,490 | 22,988 | ||||||
Total customers | 316,570 | 312,524 | ||||||
(1)In Michigan, the MPSC has a program known as the Gas Customer Choice Program, under which gas sales customers may choose to purchase natural gas from third-party suppliers, while SEMCO Gas continues to charge these customers applicable distribution charges and customer fees, plus a balancing fee.
(2)Excludes customers from SEMCO Gas’ non-regulated business.
Seasonality
The natural gas distribution business in Michigan is seasonal, as the majority of natural gas demand occurs during the winter heating season that extends from November to March. Accordingly, annualized individual quarterly revenues and earnings are not indicative of annual results.
Forecasted volumes for SEMCO Gas are set based on the 15-year rolling average Degree Days expected for the period. Temperature fluctuations impact the operating results of SEMCO Gas.
Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals
As required by an order issued by the MPSC in September 2012, SEMCO Gas filed a depreciation study with the MPSC in September 2017, using 2016 data. On April 9, 2018, the MPSC issued an order approving the settlement agreement and new depreciation rates. The new rates reflect an approximately US$2 million upward adjustment to depreciation expense when compared to the current rates and were effective on January 1, 2019. SEMCO Gas is required to file a new depreciation case and updated depreciation study with the MPSC no later than September 30, 2022, using 2021 data.
On May 31, 2019, SEMCO Gas filed a request with the MPSC seeking authority to increase SEMCO Gas' base rates by approximately US$38 million on an annual basis established with a forecasted test year of 2020. The increase in rates requested captured the inflation of operations and maintenance costs from the last rate case in 2010 as well as the investment in the Marquette Connector Pipeline. With the upcoming sunset of the MRP in 2020, this case included the addition of a new MRP and the introduction of an IRIP to recover the capital costs associated with the replacement of certain mains, services, and other infrastructure through surcharges similar to the currently-enacted MRP program. In November 2019, a settlement agreement was filed for a rate increase of approximately US$20 million and an allowed return on equity of 9.87 percent. The MPSC approved the settlement in December 2019 and the new rates were effective January 1, 2020. Pursuant to the approval of the IRIP, SEMCO Gas will complete certain projects totaling US$55 million to improve the reliability of infrastructure and customers will be billed a surcharge beginning in 2021. SEMCO Gas cannot seek an increase in its general rates to take effect prior to January 1, 2023.
On April 15, 2020, the MPSC issued an order for all utilities which allows for regulatory asset accounting to capture bad debts in excess of what is in approved rates. Incremental cost recovery was not addressed in the order; however, utilities
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 21
filed comments and reply on April 30, 2020 and May 13, 2020, respectively, on what extraordinary costs, costs savings, and incremental revenues related to COVID-19 should be considered by the MPSC and how those costs should be tracked. In addition, the order included a list of additional customer protection requirements. On July 23, 2020, the MPSC issued an order asking that any rate-regulated utility seeking recovery of COVID-19 related expenses beyond uncollectible expenses make an informational filing with the MPSC no later than November 2, 2020. SEMCO Gas did not establish a regulatory asset for bad debts since the bad debt expense is not expected to exceed the level approved in the last rate case proceeding. Furthermore, SEMCO Gas determined that the benefit would be de minimis to proceed with filing for the recovery for the incremental COVID-19 costs considering the legal fees associated with completing such a regulatory filing.
The MPSC issued an order on February 18, 2021, following a MPSC staff report on energy accessibility and affordability. The order requires the MPSC Staff to establish an Energy Accessibility and Affordability Collaborative to coordinate efforts and find efficiencies between the EWR Low-Income workgroup and the Monthly Energy Assistance Program workgroup. The Collaborative’s first meeting occurred on April 8, 2021. MPSC Staff filed an interim report on progress and recommendations on December 17, 2021, which recommended continuation of collaboration between energy waste reduction services and energy assistance to promote energy affordability and accessibility.
On July 1, 2021, SEMCO submitted its 2022-2023 EWR Plan, a form of energy efficiency program for its customers, for MPSC approval. SEMCO proposes to spend approximately US$30 million on energy waste reduction over 2022 and 2023 to achieve a combined first year energy savings goal of approximately 10.1 million therms. SEMCO filed its Brief and Reply Brief on December 3, and December 22, 2021, respectively. A Commission order is expected around the second quarter of 2022.
ENSTAR
In Alaska, ENSTAR distributes natural gas to approximately 150,000 customers in the metropolitan Anchorage area and surrounding Cook Inlet area, approximately 91 percent of which are residential. The remaining gas sales customers include hospitals, universities, and government buildings. ENSTAR also provides gas transportation service to power plants and an LNG plant. ENSTAR’s service area encompasses over 60 percent of the population of Alaska.
The average number of customers at ENSTAR has increased by an average of approximately 1 percent annually during the past three years (with an increase of 1 percent in 2021). While there may occasionally be variations in this pattern, average per customer annual gas consumption in Alaska over the longer term has been gradually decreasing due to the availability of and incentive to invest in more energy efficient homes and appliances.
Operations
ENSTAR’s natural gas delivery system (including SEMCO Energy’s Alaska Pipeline Company) includes approximately 444 miles of gas transmission pipelines and 3,199 miles of gas distribution mains. ENSTAR’s pipelines and mains are located in Anchorage and the Cook Inlet area of Alaska.
Historically, ENSTAR has had access to significant natural gas supplies in Cook Inlet, which are within or adjacent to its service territory. ENSTAR’s distribution system, including the Alaska Pipeline Company transmission-level pipeline system, is not linked to major interstate or intrastate pipelines and thus does not have access to natural gas supplies elsewhere in Alaska, Canada, or the lower 48 states. As a result, ENSTAR must procure its natural gas supplies under gas supply agreements from producers in and near the Cook Inlet area. Natural gas production in Cook Inlet has decreased significantly in recent years as has the amount of deliverability available from Cook Inlet producers. The majority of ENSTAR’s gas supply and deliverability needs are provided by long-term contracts with Cook Inlet producers into 2033.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 22
In order to better address the seasonal deliverability demands of ENSTAR’s customers, SEMCO Energy developed the CINGSA Storage facility.
The following table sets out, by customer category, ENSTAR’s deliveries:
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Deliveries: (MDth) | ||||||||
Residential | 21,230 | 20,738 | ||||||
Commercial | 14,203 | 13,887 | ||||||
Transport | 22,385 | 22,046 | ||||||
Total deliveries | 57,818 | 56,671 | ||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | |||||||
Customers at Year End: | ||||||||
Residential | 137,229 | 135,782 | ||||||
Commercial | 13,114 | 13,096 | ||||||
Transport | 13 | 13 | ||||||
Total customers | 150,356 | 148,891 | ||||||
Seasonality
The natural gas distribution business in Alaska is seasonal, as the majority of natural gas demand occurs during the winter heating season that extends from November to March. Accordingly, annualized individual quarterly revenues and earnings are not indicative of annual results.
Forecasted volumes for ENSTAR are set based on the 10-year rolling average Degree Days expected for the period. Temperature fluctuations impact the operating results of ENSTAR.
Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals
On March 23, 2018, the RCA sent a letter to several investor-owned utilities in Alaska, asking for the utilities’ proposed response to the TCJA. On April 26, 2018, ENSTAR filed its proposed reduction in rates with the RCA, reflecting a US$5 million decrease from the annual revenue requirement that was determined in October 2017. On May 29, 2018, the RCA approved ENSTAR’s proposed rate decrease and the reduced rates went into effect on June 1, 2018. ENSTAR anticipates addressing excess deferred income taxes in its next rate case. On November 4, 2020, ENSTAR filed a motion requesting relief from the obligation to file a rate case on June 1, 2021 based on a 2020 test year, requesting that filing deadline be moved to June 1, 2022 based on a 2021 test year. Three ENSTAR customers filed joinders in the motion and the Attorney General filed a non-opposition. The RCA issued an order on December 15, 2020 extending the filing deadline of the next ENSTAR rate case to June 1, 2022 based on a 2021 test year.
On November 30, 2018, Southcentral Alaska experienced a magnitude 7.1 earthquake with an epicenter close to Anchorage, Alaska. ENSTAR experienced a large number of above and below ground gas leaks in its service territory. On December 2, 2019, ENSTAR filed a request to establish a regulatory deferred asset with the RCA to recover uninsured losses associated with the earthquake in its next rate case. On October 20, 2020, the RCA approved creation of a regulatory asset in the amount of approximately US$1 million, to be amortized and recovered through rates over a period of time to be determined at ENSTAR's next rate case.
On April 10, 2020, the Governor of Alaska signed Senate Bill 241, which allows certificated utilities to record a regulatory asset for extraordinary costs and uncollectible residential utility bills that result from the COVID-19 public health disaster emergency declared by the governor on March 11, 2020. The determination as to whether an extraordinary expense resulted from the COVID-19 emergency is subject to approval by the RCA before recovery occurs through future rates. In response to Senate Bill 241, on April 15, 2020, the RCA opened an information docket to gather information including how utilities are dealing with COVID-19 and its effects. It will also discuss specific sections of Senate Bill 241 regarding deadlines for Commission actions and regulatory assets in a later public meeting. ENSTAR received approximately
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 23
US$1.2 million of CARES Act funding from the Cities of Anchorage, Palmer, Wasilla and Mat-Su Borough, all of which has been applied toward ENSTAR customer accounts.
CINGSA
SEMCO Energy, through a subsidiary, holds a 65 percent interest in CINGSA. CINGSA was formed to construct, own, and operate the CINGSA Storage facility. Natural gas is injected into the CINGSA Storage facility during each summer and withdrawn as needed for use each winter.
CINGSA provides firm gas storage service to ENSTAR and to two Cook Inlet area electric utilities and provides interruptible gas storage service to ENSTAR and four other customers. ENSTAR has subscribed for approximately 80 percent of CINGSA’s initial capacity and approximately 69 percent of the associated initial gas injection and withdrawal capability, with the remainder of the capacity and injection and withdrawal capability split among the other customers.
Material Regulatory Developments and Approvals
On March 2, 2020, CINGSA filed a FRM proposal as required by the RCA in the August 2019 CINGSA rate case decision. CINGSA submitted its direct testimonies in August 2020 and other parties filed their responsive testimonies in November 2020. CINGSA filed its reply testimony on January 15, 2021. On February 22, 2021, CINGSA filed a stipulation with the RCA. The RCA issued an order on May 21, 2021 accepting the stipulation.
On July 1, 2021, CINGSA filed a rate case with the RCA seeking approval for approximately US$1.9 million revenue increase based on US$105.5 million rate base, 11.9 percent ROE and 59.99 percent equity thickness. The filing proposed an across-the-board 2 percent interim rate increase to be effective August 1, 2021, which the RCA approved on July 29, 2021. Discovery on CINGSA's direct testimony closed on December 30, 2021, CINGSA filed supplemental testimony on January 31, 2022, and interveners' testimony was due February 11, 2022. Evidentiary hearing is scheduled for June 2022, and a decision is expected around the end of the third quarter of 2022.
Retail Energy Marketing
AltaGas' retail energy marketing business consists of the operations of WGL Energy Services, which sells natural gas and electricity directly to residential, commercial, and industrial customers located in Maryland, Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and the District of Columbia.
WGL Energy Services has a secured supply arrangement with Shell Energy North America (US), L.P. Under this arrangement, WGL Energy Services has the ability to purchase the majority of its power, natural gas, and related products from Shell Energy in a structure that reduces WGL Energy Services’ cash flow risk from collateral posting requirements. While Shell Energy is intended to be the majority provider of natural gas and electricity, WGL Energy Services retains the right to purchase supply from other providers. The supply arrangement with Shell Energy expires in March 2024.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 24
Natural Gas
As of December 31, 2021, WGL Energy Services served approximately 89,500 residential, commercial and industrial natural gas customers located in Maryland, Virginia, Delaware, Pennsylvania, and the District of Columbia. WGL Energy Services is subject to regulation by the public service regulatory commission of the jurisdictions in which it is authorized as a competitive service provider. WGL Energy Services contracts for storage and pipeline capacity to meet its customers’ needs primarily through transportation releases and storage services allocated from the utility companies in the various service territories through several interstate natural gas pipelines. To supplement WGL Energy Services’ natural gas supplies during periods of high customer demand, WGL Energy Services maintains gas storage inventory in storage facilities that are assigned by natural gas utilities such as Washington Gas. This storage inventory enables WGL Energy Services to meet daily and monthly fluctuations in demand and to minimize the effect of market price volatility.
Electricity
As of December 31, 2021, WGL Energy Services served approximately 88,100 residential, commercial, and industrial electricity customer accounts located in Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and the District of Columbia. WGL Energy Services does not own or operate any other electric generation, transmission, or distribution assets.
Competition
WGL Energy Services competes with wholesale energy suppliers, regulated electric utilities, and other third-party marketers to sell natural gas and electricity to customers. Marketers of natural gas and electric supply compete largely on price; therefore, gross margins are relatively small.
Operations can be positively or negatively affected by significant volatility in the wholesale price of natural gas. Accordingly, risk management policies and procedures are designed to minimize the risk that purchase commitments and the related sale commitments do not closely match. In general, profit opportunities for trading activities are increased with increased volatility in natural gas prices. These opportunities are primarily in short-term transportation and storage spreads, seasonal storage spreads, and long-term supply or basis transactions.
To provide competitive pricing to its retail customers and in adherence to its risk management policies and procedures, WGL Energy Services manages its contract portfolios by attempting to closely match the commitments for deliveries from suppliers with requirements to serve sales customers. WGL Energy Services’ residential and small commercial electric customer growth opportunities are significantly affected by the price for SOS offered by electric utilities. These rates are periodically reset for each customer class based on the regulatory requirements in each jurisdiction. Customer growth opportunities either expand or contract due to the relationship of these SOS rates to current market prices.
Environmental Considerations Impacting the Utilities Business
Washington Gas
Washington Gas is subject to federal, state, and local laws and regulations related to environmental matters. These laws and regulations may require sustained expenditures over time to control environmental effects. The cost of compliance associated with environmental laws and regulation can be significant and is subject to change. Almost all environmental liabilities associated with Washington Gas operations are costs expected to be incurred to remediate sites where Washington Gas or a predecessor affiliate operated MGPs or gas holder sites. Estimates of liabilities for environmental response costs are difficult to determine with precision because of the various and variable factors that can affect eventual remediation costs for a given site. These factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
•the complexity of the site;
•changes in environmental laws and regulations at the federal, state, and local levels;
•the number of regulatory agencies or other parties involved;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 25
•new technology that renders previous technology obsolete or experience with existing technology that proves ineffective;
•the level of remediation required; and
•variations between the estimated and actual time required to remediate an environmentally contaminated site.
Washington Gas has identified up to ten sites where it or its predecessors may have operated MGPs. Washington Gas last used any such plant in 1984. In connection with these operations, Washington Gas is aware that coal tar and certain other by-products of the gas manufacturing process are present at or near some former sites and may be present at others.
Washington Gas is currently remediating its East Station property located in Washington, D.C., which is adjacent to the Anacostia River, under a 2012 Consent Decree with the District of Columbia and federal government. Remedial measures include ground water pump and treat, tar recovery, soil encapsulation, and other treatment. In addition, at another adjoining property located to the east of the property owned by the District of Columbia, Washington Gas agreed to perform a site investigation and report the findings pursuant to oversight by the Department of Energy and Environment (DOEE). Additional remediation may be required at this property.
At another adjoining property known as the "Eastern Power Boat Club Property", located to the east of the property owned by the District of Columbia, Washington Gas agreed to perform a site investigation and report the findings pursuant to oversight by the DOEE. The property was subject to a July 12, 2019 Administrative Order from the DOEE. That Administrative Order was withdrawn, and Washington Gas entered into a negotiated Administrative Order on Consent with the DOEE that was effective on March 11, 2020. Under the terms of the Administrative Order on Consent, Washington Gas submitted a Remedial Investigative Report on February 26, 2021. On March 11, 2021, Washington Gas received an Administrative Order related to the alleged presence of sheens in the Anacostia River. Washington Gas filed an appeal of the Administrative Order with the District of Columbia Office of Administrative Hearings on March 26, 2021. The appeal is pending.
Washington Gas may be responsible for environmental cleanup and government costs associated with the Anacostia River Sediment Project (ARSP). In February 2016, Washington Gas received a letter from the DOEE and National Park Service (NPS) regarding the ARSP, indicating that the District of Columbia is conducting a separate remedial investigation and feasibility study of the river to determine if and what cleanup measures may be required and to prepare a natural resource damage assessment. Subsequently, the DOEE issued an Interim Record of Decision (ROD) for remediation of “Early Action Areas” in the Anacostia River. Although the Interim ROD identifies East Station as one of fifteen potential environmental cleanup sites, the DOEE is proposing to continue the remediation of East Station under Washington Gas’ existing Consent Decree rather than as part of the ARSP. On June 14, 2021, Washington Gas received letters from the DOEE and NPS notifying the Company that it may be responsible for environmental cleanup and government costs associated with the ARSP. On November 12, 2021, Washington Gas was notified by DOEE, the U.S. Department of Interior, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration that those agencies, as Trustees, will perform a Natural Resource Damage Assessment of the Anacostia River and that Washington Gas was identified as a potentially responsible party. Washington Gas is not able to estimate the total amount of potential damages or timing associated with the District of Columbia's environmental investigation on the Anacostia River at this time. While an allocation method has not been established, Washington Gas has accrued an amount based on a potential range of estimates for its share of the feasibility study costs.
On May 27, 2021, Washington Gas submitted an application to the Maryland Department of Environment’s Voluntary Cleanup Program (VCP) for a former gas holder site located in Chillum, Maryland. Based upon the VCP application, Washington Gas has accrued an amount for the Chillum site based on the potential costs of a range of remedial options. Regulatory orders issued by the PSC of MD allow Washington Gas to recover the costs associated with the sites applicable to Maryland over the period ending in 2035. Rate orders issued by the PSC of DC allow Washington Gas a three-year recovery of prudently incurred environmental response costs and allow Washington Gas to defer additional
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 26
costs incurred between rate cases. Regulatory orders from the SCC of VA have generally allowed the recovery of prudent environmental remediation costs to the extent they were included in the underlying financial data supporting an application for rate change.
If revisions to applicable environmental laws or regulations require further investigation and remediation to be performed at the sites in the future, Washington Gas could incur a material liability. This liability would be offset by a corresponding regulatory asset. To the extent that any costs are not fully recoverable from customers through regulatory proceedings or from insurance or other potentially responsible persons in any of Washington Gas' jurisdictions, these costs would reduce its earnings and results of operations.
SEMCO Gas
SEMCO Gas had completed its investigation and remediation at the two MGP sites it was responsible for and has received NFA letters from the Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy for both sites. SEMCO Gas will continue to monitor these sites in the future as required by the NFA letters.
In accordance with an MPSC accounting order, SEMCO Gas’ environmental investigation and remediation costs associated with these MGP sites are deferred and amortized over ten years. Rate recognition of the related amortization expense does not begin until the costs are subject to review by the MPSC in a base rate case. To the extent that any costs are not fully recoverable from customers through regulatory proceedings or from insurance or other potentially responsible persons, these costs would reduce SEMCO Gas’ earnings and results of operations.
As a result of the NFA letters received to date, SEMCO Gas believes that the likelihood of any further liability at either of these sites is remote. However, if applicable environmental laws change that require further investigation and remediation to be performed at the sites in the future, SEMCO Gas could incur a material liability. This liability would be offset by a corresponding regulatory asset.
Environmental, health, and safety regulations may also require SEMCO Gas to install pollution control equipment, modify its operations, or perform other corrective actions at its facilities.
U.S. Federal Air and GHG Regulations
Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (U.S. GHGRP)
The U.S. GHGRP requires reporting of GHG data and other relevant information from large GHG emission sources, fuel, and industrial gas suppliers, and CO2 injection sites in the United States. A total of 41 categories of reporters are covered by the U.S. GHGRP. Facilities determine whether they are required to report based on the types of industrial operations located at the facility, their emission levels, or other factors. Facilities are generally required to submit annual reports under Part 98 if:
▪GHG emissions from covered sources exceed 25,000 metric tons CO2e per year;
▪Supply of certain products would result in over 25,000 metric tons CO2e of GHG emissions if those products were released, combusted, or oxidized; or
▪The facility receives 25,000 metric tons or more of CO2 for underground injection.
All of AltaGas’ operating facilities and certain of its utilities located in the U.S. operate under and comply with requirements set forth by the U.S. GHGRP.
For further discussion of the U.S. federal and state air emission regulations, please see "Business of the Corporation – Corporate/Other Segment – Environmental Considerations Impacting the Corporate/Other Segment".
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 27
MIDSTREAM BUSINESS
AltaGas’ Midstream business contributed revenue of $6.5 billion for the year ended December 31, 2021 (2020 - $1.6 billion), representing approximately 62 percent (2020 – 30 percent) of AltaGas’ total revenue before the Corporate/Other segment and intersegment eliminations. The primary driver of this increase relates to the full year impact of the consolidation of Petrogas in 2021.
Midstream Business
AltaGas’ Midstream segment is a leading North American platform that connects customers and markets. From wellhead to tidewater and beyond, the Company is focused on providing its customers with safe and reliable service and connectivity that facilitates the best outcomes for their businesses. This includes global market access for North American LPGs, which provides North American producers and aggregators with attractive netbacks for propane and butane while delivering diversity of supply and supporting stronger energy security in Asia.
AltaGas’ Midstream platform is heavily focused on the Montney resource play in Northeastern B.C. and centers around global exports, which is where the Company believes the market is headed for resource development over the long-term. AltaGas also operates a broader set of midstream infrastructure assets across the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin (WCSB) and select regions in the U.S., which are all focused on connecting customers and markets in the most efficient manner possible.
There are three core pillars to AltaGas’ Midstream platform that are integral to each other and facilitate the Company’s wellhead to tidewater and beyond value chain. These include:
▪Global Exports, which includes AltaGas’ two LPG export terminals where the Company has capacity to export up to 150,000 Bbl/d of propane and butane to key markets in Asia;
▪Natural Gas Gathering and Extraction, which includes 1.2 Bcf/d of extraction processing capacity and approximately 1.2 Bcf/d of raw field gas processing capacity, which is heavily focused on the Montney; and
▪Fractionation and Liquids Handling platform, which includes 65 MBbl/d of fractionation capacity and a sizable liquids handling footprint that operates under the AltaGas and Petrogas banners.
The Midstream segment also consists of natural gas and NGL marketing business, domestic logistics, trucking and rail terminals, and approximately 3.2 million barrels of liquid storage capability though a network of underground salt caverns through the Company’s Strathcona Storage JV with ATCO Energy Solutions Ltd, as well as AltaGas’ 10 percent interest in the Mountain Valley Pipeline.
Global Exports
AltaGas' global export assets are focused on providing North American producers global market access and incremental value for NGLs. Global export assets extend AltaGas' integrated value chain and attract additional volumes to the AltaGas system, supporting future growth of the overall Midstream infrastructure platform with current export capacity of up to 150,000 Bbls/d to Asian markets.
On October 15, 2021, AltaGas filed an application with the Canada Energy Regulator for a 25-year butane export license for 40,000 Bbls/d. The application positions AltaGas and its partners to continue to connect growing LPG production volumes from Western Canada to global markets.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 28
RIPET
On October 16, 2015, AltaGas entered into a project agreement with RTI for RIPET, with construction commencing in April 2017. In May 2017, AltaGas entered into a joint venture agreement with Vopak pursuant to which Vopak acquired a 30 percent interest in RIPET. The commercial operations of RIPET commenced in May 2019, with the first propane shipment departing from the terminal to Asia.
Based on production at AltaGas' Midstream facilities and commercial contracts executed or under negotiation, RIPET ended the year with physical throughput of approximately 54,000 Bbls/d in December of 2021, with the ability to increase throughput to upwards of 80,000 Bbls/d.
The terminal leverages CN’s existing railway network and the deepest harbor in North America to offer Canada’s natural gas producers direct access to international markets and a 15-day shipping advantage versus the U.S. Gulf Coast. With RIPET being the closest North American LPG terminal to Asia, it allows Canadian natural gas and propane producers and aggregators to diversify their market access to Asia, a premium market for propane. RIPET is capable of storing 600,000 Bbls of propane. AltaGas expects to increase throughput from RIPET as it builds on the operational capabilities and global counterparty networks for RIPET. On August 21, 2020, the Canada Energy Regulator granted AltaGas an additional 25 year license to export up to 46,000 Bbls/d of propane to North American and global markets from RIPET, bringing the aggregate propane export capacity under 25 year export licenses to 92,000 Bbls/d. In December 2020, the Minister of Natural Resources approved the additional license.
Ferndale LPG Export Facility
Located approximately 100 miles north of Seattle, the Ferndale LPG export terminal represents a strategic outlet point for North American LPG volumes. Like RIPET, it is competitively situated to serve the high-demand Far East market with shorter average shipping times and has a competitive arbitrage as RIPET vs. the U.S. Gulf Coast.
Terminal demand is supported through various long-term purchase agreements with Canadian and U.S. suppliers, primarily from key producing regions, processing facilities and refineries in parts of Western Canada and the Northern U.S., including the Bakken in North Dakota. Petrogas also maintains service agreements with numerous Tier 1 rail providers in order to leverage existing railway networks to take advantage of competitively priced product across North America. The terminal is also pipeline connected to two regional refineries, providing additional supply, sales and fee-for-service opportunities for the terminal. The terminal is capable of handling upwards of 75,000 Bbls/d of throughput capacity, with 800,000 Bbls of on-site storage capacity and rail siding capacity for up to 40 railcars.
Gas Processing and Extraction
Midstream processing activities are comprised of gathering systems that move natural gas on behalf of producers from the wellhead to AltaGas plants where impurities and certain hydrocarbon components are removed, and the gas is compressed to meet the operating specifications of downstream pipeline systems. AltaGas’ Midstream processing facilities serve customers primarily in the WCSB that deliver natural gas into downstream pipeline systems and can connect producers to the global export markets for LPG. AltaGas has a total net licensed processing capacity of approximately 2.4 Bcf/d, of which approximately 15 percent is capable of processing sour gas. All AltaGas' processing facilities are capable of extracting NGLs. The main drivers of AltaGas' processing activities are throughput, inlet composition, gathering and processing fees, and operating costs, with several facilities having the benefit of take-or-pay contracts. Throughput is impacted by new well tie‑ins, re-activations, re-completions, well optimizations performed by producers, natural production declines in areas served by AltaGas’ processing facilities, and gas available on the main lines.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 29
AltaGas' significant processing facilities are as follows:
2021 Licensed Capacity (Net) | ||||||||||||||
| Facility | Location | Interest (%) | Operated / Non-Operated | Licensed Capacity Gas Processing - Net (Mmcf/d) | ||||||||||
| Townsend | North of Fort St. John, BC | 100 | % | Operated | 550 | |||||||||
| Gordondale | Bonanza, AB | 100 | % | Operated | 150 | |||||||||
| Blair Creek | North of Fort St. John, BC | 100 | % | Operated | 120 | |||||||||
Aitken Creek (1) (2) | Aitken, BC | 50 | % | Non-Operated | 145 | |||||||||
| JEEP | Joffre, AB | 100 | % | Operated | 250 | |||||||||
| EEEP | Edmonton, AB | 100 | % | Operated | 390 | |||||||||
| Empress Pembina (PEEP) | Empress, AB | 11 | % | Non-Operated | 135 | |||||||||
| Harmattan | Sundre, AB | 100 | % | Operated | 490 | |||||||||
| Younger | Taylor, BC | 28 | % | Non-Operated | 213 | |||||||||
Total | 2,443 | |||||||||||||
(1)As total actual throughput is included, future capacity associated with projects not yet in-service is excluded.
(2)Includes Aitken Creek North and Nig Creek.
Townsend Complex
The Townsend facility, which is wholly owned by AltaGas, is a 550 Mmcf/d gas processing facility located approximately 100 km north of Fort St. John and 20 km southeast of AltaGas’ Blair Creek facility. The majority of the processing capacity is contracted with Montney producers in the area under long-term take-or-pay agreements. In addition, the Townsend facility is able to provide NGL handling, treatment, and storage services to producers. Refer to the "Fractionation and Logistics" section below.
A 25 km gas gathering line connects the Blair Creek field gathering area to the Townsend facility.
In August 2018, AltaGas entered into definitive agreements with Kelt to provide an energy infrastructure solution for the liquids-rich Inga Montney development located in British Columbia. In the second quarter of 2020, Townsend 2B and a gas gathering pipeline that connects upstream fields to AltaGas facilities were commissioned, which added 198 Mmcf/d C3+ deep cut gas processing capacity at the Townsend Complex. The expanded facility provided Kelt with firm processing of 75 Mmcf/d of raw gas under an initial 10 year take-or-pay agreement. In the third quarter of 2020, ConocoPhillips acquired oil and gas assets in the Inga/Fireweed/Stoddart division in the Montney area from Kelt. All operating agreements of AltaGas remain in effect with ConocoPhillips since the acquisition.
Gordondale
AltaGas owns 100 percent of the Gordondale facility which has licensed capacity of 150 Mmcf/d for processing sour natural gas. AltaGas operates the facility which is located in the Gordondale area of the Montney reserve area approximately 100 km northwest of Grande Prairie, Alberta. The Gordondale facility processes gas gathered from Birchcliff's Gordondale Montney development under a long-term take-or-pay contract. The plant is equipped with liquids extraction facilities to capture the NGL value for the producer. The plant also has peaking power plant generators which serve as emergency back-up generation for the plant as well as power supply to the grid when demand is high or supply is low.
Blair Creek
AltaGas owns 100 percent of the Blair Creek facility which has licensed capacity of 120 Mmcf/d of natural gas. AltaGas operates the facility which is located approximately 140 km northwest of Fort St. John, British Columbia. The facility
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 30
processes gas gathered from Montney producers in the area. The plant is equipped with liquids extraction facilities to capture the NGL value for the producer.
Aitken Creek
In October 2018, AltaGas acquired a 50 percent ownership in the Aitken Creek processing facilities, including Aitken Creek North and Nig Creek from Black Swan Energy Ltd. Aitken Creek North is a shallow gas plant with current capacity of 110 Mmcf/d (55 Mmcf/d net). Nig Creek is a deep cut gas plant with capacity of 180 Mmcf/d (90 Mmcf/d net) and came on-stream in the third quarter of 2019. Phase 1 of Nig Creek GP2B increased inlet capacity by 55 Mmcf/d (28 Mmcf/d net) by adding inlet compression, sales compression, and other plant equipment. Phase 1 of Nig Creek GP2B was completed early in the third quarter of 2021 and is now on stream. The second phase increased capacity by an additional 25 Mmcf/d gross (12.5 Mmcf/d net) and includes a deep cut plant for additional liquids recoveries. Phase 2 was completed at the end of the fourth quarter of 2021. The Aitken processing facilities are located in the liquids-rich Montney resource play in NEBC and are operated by Tourmaline. AltaGas and Tourmaline have long-term processing, transportation, and marketing agreements that include AltaGas liquids handling infrastructure in NEBC.
JEEP
AltaGas owns 100 percent of JEEP which has processing capacity of 250 Mmcf/d of natural gas and is capable of producing up to 10,400 Bbls/d of ethane and other NGLs.
The plant is adjacent to Nova Chemicals’ Joffre petrochemical complex and recovers ethane and other NGLs from the fuel gas used at the complex. All ethane production from JEEP is sold under a long-term, cost-of-service type contract with Nova Chemicals. AltaGas delivers its NGL production to the Harmattan fractionation plant for further processing. The resulting spec products are sold into markets throughout North America to maximize plant gate netbacks.
EEEP
AltaGas owns 100 percent of EEEP. EEEP is directly connected to the Alberta Ethane Gathering System and to Plains Midstream Canada’s Co-Ed NGL pipeline. The plant has a licensed gross inlet capacity of 390 Mmcf/d of natural gas and gross production capacity of 30,500 Bbls/d of ethane and other NGLs.
The processed gas from the facility supplies end-use markets in the city of Edmonton, Alberta. Almost all of EEEP ethane production capacity is currently sold to ethane buyers under long-term fee-for-service contracts. The NGL production is delivered to a Fort Saskatchewan fractionator for further processing. AltaGas takes the resulting spec products in-kind and sells to North American and global markets, through RIPET, to maximize plant gate netbacks.
Gas is supplied to EEEP under a gas supply agreement with NGTL which includes the right for AltaGas to extract liquids from all gas processed at EEEP.
Harmattan
AltaGas owns a 100 percent interest in Harmattan located 100 km north of Calgary, Alberta. Harmattan has natural gas processing capacity of 490 Mmcf/d consisting of sour gas treating, co-stream processing, and NGL extraction. In addition, Harmattan has fractionation and terminalling facilities (see the "Fractionation and Logistics" section below). Harmattan’s raw natural gas supply is based on producer activity in the west‑central region of Alberta. Harmattan is well-positioned as the high-volume, low-cost processing facility in its service area.
At Harmattan, natural gas processing services are provided to approximately 70 producers under contracts with a variety of commercial arrangements and terms. Approximately 17 percent of the natural gas volume processed at Harmattan is done under the terms of the Rep Agreements which have life-of-reserves dedications. The balance of the raw natural gas
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 31
processed at Harmattan is processed under contracts with terms varying from one month to life-of-reserves. The majority of the contracts provide for fee escalation based on CPI.
The Co-stream processing allows the extraction of NGLs from gas in the west leg of the NGTL system using unused capacity in the NGL recovery units at Harmattan. The Co‑stream processing has resulted in increased utilization at the plant, with the added benefit that the equipment installed for the Co-stream process increases reliability and efficiency for both gas processing and Co-streaming customers. AltaGas entered into a 250 Mmcf/d cost-of-service Co-stream processing agreement with Nova Chemicals related to ethane and other NGL extraction at Harmattan in 2012 for an initial term of 20 years. AltaGas will deliver all NGLs or Co-stream gas products on a full cost-of-service basis to Nova Chemicals.
AltaGas has 45 MW of cogeneration capacity in Alberta through three co-generation facilities, each of which can generate 15 MW of power. The co-generation facilities are located at AltaGas' Midstream Harmattan facility and have a heat recovery steam generator that is capable of producing all of the steam required to process gas at Harmattan from the waste heat in the exhaust gases from the turbine. Excess electricity from the co-generation units are delivered to the Alberta power market.
Management had identified environmental issues associated with the prior activities of Harmattan. An environmental allocation agreement is in place with the former operator that allocates the liability. This agreement significantly reduces soil and groundwater contamination liability to AltaGas. See "Risk Factors - Decommissioning, Abandonment, and Reclamation Costs" in this AIF.
Younger
Effective April 1, 2018, AltaGas’ ownership was reduced to a 28.33 percent interest in Younger processing and extraction assets and a 50 percent interest in Younger's fractionation and terminalling assets (see the "Fractionation and Logistics" section below). Younger has licensed capacity to process up to 750 Mmcf/d of natural gas and AltaGas’ share of such capacity is 213 Mmcf/d. The remaining interest is held by Pembina and Pembina has assumed plant operatorship. Younger processes natural gas transported on the West Coast transmission system and other regional transmission systems to recover NGLs. Natural gas supply to Younger is dependent on the amount of raw gas processed at the McMahon gas plant, which is based on the robust natural gas producing region of northeastern British Columbia.
Fractionation and Logistics
Fractionation production is a function of NGL mix volumes processed, liquids composition, recovery efficiency of the plants, and plant on-line time. Due to the integration and inter-connectivity of AltaGas' Midstream assets, the fractionation and logistics activities provide integral services to the other Midstream segments and customers by providing access to NGL products with access to North American and global markets through rail networks, pipelines, RIPET, and the Ferndale terminal.
AltaGas' logistics infrastructure consists of NGL pipelines, treating, storage, truck and rail terminal infrastructure centered around AltaGas’ key Midstream operating assets at RIPET, Ferndale, Harmattan, and in NEBC, Townsend and North Pine.
In the NEBC area, a network of NGL pipelines connects upstream gas plant producers to the AltaGas North Pine facility. The NEBC NGL pipelines consist of three liquids egress lines, with the third line commissioned in the third quarter of 2020, connecting the Townsend facility to the Townsend truck terminal on the Alaska Highway (30 km) and AltaGas' North Pine facility (70 km). In addition, NGL and spec propane lines that connect the Townsend complex in the North, to the Aitken Creek facilities through a 60 km NGL pipeline (Aitken Connector), Canadian Natural Resources Limited's Nig plant through a lateral, and to the Tourmaline Gundy facility in the West, through a 15 km spec propane line were all commissioned in the first half of 2020. AltaGas' logistics infrastructure also consists of a 15,000 Bbls/d NGL treatment facility at the Townsend complex designed to process mercaptan rich NGL volumes delivered from the Townsend deep-cut plant and Aitken Connector.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 32
AltaGas' significant fractionation facilities are as follows:
| 2021 Licensed Capacity (Net) | ||||||||||||||
| Facility | Location | Interest (%) | Operated / Non-Operated | Licensed Capacity NGL Fractionation - Net (Bbls/d) | ||||||||||
| Harmattan | Sundre, AB | 100 | % | Operated | 35,000 | |||||||||
| Younger | Taylor, BC | 50 | % | Non-Operated | 9,750 | |||||||||
| North Pine | Fort St. John, BC | 100 | % | Operated | 20,000 | |||||||||
Total | 64,750 | |||||||||||||
Harmattan
Harmattan has NGL fractionation capacity of 35,000 Bbls/d, a 450 Bbls/d capacity frac oil processing facility, and a 200 tonnes/d capacity industrial grade CO2 facility. Harmattan is the only deep‑cut and full fractionation plant in its operating area. Fractionation services at Harmattan are provided under contracts with a variety of commercial arrangements and terms, typically fee-for-service revenues. Harmattan fractionation services include a truck terminal for NGL mix delivered from adjacent plants in the area, as well as a rail terminal at Didsbury with a loading capacity of approximately 10,000 Bbls/d.
Younger
Effective April 1, 2018, AltaGas’ ownership was reduced to a 50 percent interest in Younger's fractionation, storage, loading, treating and terminalling of NGL, with the remaining interest held by Pembina, which has assumed plant operatorship. While Younger is the only straddle plant in its operating area, the Alliance pipeline competes for local natural gas supply. Pembina is responsible for sourcing AltaGas’ gas supply and AltaGas markets its share of NGLs produced.
North Pine Facility
The North Pine facility is the only custom fractionation plant in B.C., providing area producers with a lower cost, higher netback alternative for their NGLs than transporting and fractionating in Edmonton. Commissioning of the first train of the North Pine facility was completed in 2017. The first train of the North Pine facility is capable of processing up to 10,000 Bbls/d of NGL mix. The second train, commissioned in the first quarter of 2020, provides an additional 10,000 Bbls/d of NGL mix.
The North Pine facility is connected via the North Pine pipelines to the Townsend truck terminal which has a capacity of 10,000 Bbls/d and is contracted through long-term supply agreements with the producers at the Townsend and Aitken Creek facilities. The North Pine facility is also connected to the Tourmaline Gundy facility, and has access to the CN rail network, allowing for the transportation of propane, butane, and condensate to North American markets and propane to global markets via RIPET.
Aitken
AltaGas and Tourmaline have entered into long-term processing, transportation and marketing agreements including the AltaGas liquids handling infrastructure at the Townsend complex and North Pine facility. In March 2020, the Aitken liquids pipeline was placed in service, and connected to the Townsend North Liquids pipelines to transport NGL volumes from the Aitken Creek and Nig Creek facilities to the Townsend Complex.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 33
Terminals and Storage Business
AltaGas' Midstream business also includes Petrogas' terminals business, which provides support to its marketing and distribution business by providing the ability to source, transport, process, store, and deliver products through strategically located fixed assets throughout North America. In addition, the terminals business provides various terminalling services to third party customers through take-or-pay or fee-for-service agreements which provide earnings stability through volatile commodity price environments.
The terminals business consists of strategically located crude oil and NGL assets which provide storage, blending, rail and truck logistical support and waterborne LPG export capabilities.
AltaGas' significant terminals are as follows:
2021 Licensed Capacity | |||||||||||||||||
| Facility | Location | Interest (%) | Operated / Non-Operated | Operational Capacity LPG/NGL/Crude - Gross (Bbls/d) | Storage Capacity - Gross (Bbls) | ||||||||||||
Griffith LPG Terminal (1) | Griffith, IN | 74 | % | Operated | 12,000 | 700,000 | |||||||||||
Fort Sask. NGL Terminal (1) | Fort Saskatchewan, AB | 74 | % | Operated | 25,000 | 180,000 | |||||||||||
Strathcona Storage JV (1) | Fort Saskatchewan, AB | 30 | % | Non-Operated | — | 2,516,000 | |||||||||||
Petrogas Blending Terminals (1) | Various | 74 | % | Operated | 12,900 | 20,000 | |||||||||||
Total | 49,900 | 3,416,000 | |||||||||||||||
(1)Acquired as part of the Petrogas Acquisition on December 15, 2020.
2021 Licensed Capacity | ||||||||||||||
| Facility | Location | Interest (%) | Operated / Non-Operated | Storage Capacity - Gross (Bcf) | ||||||||||
| Sarnia Gas Storage | Sarnia, ON | 50 | % | Non-Operated | 6.4 | |||||||||
Griffith LPG Terminal
100 percent owned and operated by Petrogas, the Griffith LPG terminal directly supports domestic propane and butane marketing efforts. Equipped with inbound and outbound truck and rail infrastructure, the terminal is capable of handling approximately 12,000 Bbls/d, and can be easily expandable to 30,000 Bbls/d. Underground caverns provide 700,000 barrels of storage and rail siding capacity exists for up to 220 railcars. Storage services are provided on a fee for service basis including to pipeline connected refiners.
Fort Saskatchewan NGL Terminal
100 percent owned and operated by Petrogas, this greenfield facility was built by Petrogas and provides multiproduct storage and handling support to the marketing business while also generating fee-for-service revenues through third party agreements.
Pipeline connected to a regional fractionation facility and to the Strathcona Storage Caverns through a 10 km Petrogas constructed and owned pipeline, the Fort Saskatchewan facility is equipped with truck and rail loading and offloading infrastructure, providing 25,000 Bbls/d of throughput capacity. The terminal has rail siding capacity for up to 265 railcars and on-site tank storage for 180,000 Bbls. The terminal is an important staging area for RIPET and Ferndale destined product, providing key export exposure optionality to regional producers.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 34
Sarnia Storage and Crude Oil Terminal JV Agreement
The Sarnia storage and crude oil terminal is a joint venture agreement with Nova Chemicals, providing Petrogas with crude oil storage and crude-to-rail infrastructure accessibility. Situated in southern Ontario, this terminal provides the ability to service crude oil demand needs to eastern refiners and end users through regional rail networks and Enbridge pipeline infrastructure. The joint venture partner supplies and manages the terminal assets, while Petrogas manages the marketing and commercial agreements for the terminal. The right to access the terminal assets under the joint venture arrangement have been recorded as a lease by Petrogas. This terminal provides up to 2.1 million Bbls of crude oil and refined product storage capacity with outbound throughput supported by 10,000 Bbls/d of rail loading capacity. The terminal generates revenue through storage contracts and storage tank leases, rail loading, and term commitments for crude oil supply. The joint venture agreement expires in 2028 and can be renewed at the discretion of the parties.
Strathcona Storage JV
The Strathcona Storage facility is a joint venture with ATCO Energy Solutions Ltd. which is located near Fort Saskatchewan. Petrogas holds a 40 percent working interest in the facility, resulting in AltaGas' 30 percent net ownership interest. The facility is strategically positioned to help satisfy storage needs from increased liquids rich production from the Duvernay and Montney shale basins, while also supporting petrochemical requirements in the Edmonton area. The facility consists of four underground storage salt caverns in service, which have a combined storage capacity of 2,516,000 Bbls. A fifth cavern is under development and is expected to be placed in service in the first half of 2022.
Crude Blending Terminals
100 percent owned and operated by Petrogas, the crude blending terminals consist of five blending terminals located throughout Alberta and Southern Saskatchewan. These terminals blend heavier grade crude oil to meet pipeline specification requirements and are designed to operate at an average capacity of 15,300 Bbls/d. Feedstock is sourced through trucking infrastructure and pipeline connected batteries, with offloading capability through connections to regional pipelines.
Other
Petrogas maintains an assortment of ancillary owned and leased storage assets across North America to support marketing and distribution and terminal efforts. Locations include the Yahk BC propane truck terminal, Scranton propane terminal, Guernsey and Edmonton leased crude tanks and various other strategic leased NGL storage at key hubs.
In addition, AltaGas' natural gas storage assets include a 50 percent ownership of the 6.4 Bcf Sarnia natural gas storage facility connected to the Dawn Hub in Eastern Canada.
Trucking and Wellsite Fluids
Trucking Business
AltaGas' Midstream business includes Petrogas' three primary trucking entities, which provide transportation related services within the WCSB and the United States Pacific Northwest by hauling frac fluid, produced water, crude oil and NGLs between producers, terminals, customers and end users. Trucking operations are instrumental in connecting suppliers and customers to either the Petrogas infrastructure assets, third party terminals, or long-haul transportation to domestic wholesale markets.
In addition to first party volumes, the trucking business maintains various agreements with regional oil and gas production companies for hauling services from remote drilling locations. Agreements could include master service agreements, evergreen term contracts or spot loadings. Third party hauling rates are determined by receipt location, delivery point and length of haul.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 35
Wellsite Fluids and Fuels
Enerchem International Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Petrogas, is a Canadian corporation which focuses on the production of drilling and wellsite fluids, and consumer fuels. Through the fractionation of crude oil feedstock, Enerchem produces and distributes proprietary hydrocarbon fluids for drilling oil and gas wells to improve productivity and to resolve oilfield production challenges for downstream producers.
Enerchem operates two primary facilities located in Sundre and Slave Lake Alberta, which are capable of processing over 1.5 million Bbls of finished products per year. These plants are supported by various ancillary storage and distribution facilities located across the WCSB providing over 150,000 Bbls of storage capacity, strategically placed within the vicinity of active drilling regions.
Other Liquids Handling Services
To support LPG and NGL handling, AltaGas manages a rail logistics network consisting of approximately 4,600 rail cars. AltaGas is active in identifying opportunities to buy and resell NGLs for producers and exchange, reallocate, or resell pipeline capacity and storage to earn a profit. Net revenues from these activities are derived from low risk opportunities based on transportation cost differentials between pipeline systems and differences in commodity prices from one period to another. Margins are earned by locking in buy and sell transactions in compliance with AltaGas’ credit and commodity risk policies. AltaGas also provides energy procurement services for utility gas users and manages the third-party pipeline transportation requirements for many of its gas marketing customers.
Petrogas' marketing business is focused on the purchase, sale, exchange, and distribution of NGLs and crude oil, primarily in proximity to its strategically owned and leased asset base. By leveraging Petrogas' fully integrated infrastructure base and extensive logistical capabilities, the marketing team is able to source competitively priced supply at the key hubs and across various hydrocarbon basins in order to capture arbitrage opportunities derived through regional pricing differentials. Marketing efforts are driven by two primary focuses: 1) domestic NGL and crude oil wholesale, and 2) LPG waterborne exports. Additionally, this business provides operational support to the Ferndale export terminal by providing product supply and export sales agreement negotiation services. Petrogas supports its distribution efforts by maintaining an extensive leased rail fleet. Leases are established on a staggered maturity schedule with multiple lessors, to ensure railcar integrity and up-to-date DOT classification and all leases are on a full-service basis.
On April 23, 2021, AltaGas completed the sale of the majority of WGL Midstream's commodity business for cash proceeds of approximately $341 million (US$275 million).
Mountain Valley
AltaGas owns a 10 percent equity interest in Mountain Valley. The proposed FERC regulated interstate natural gas pipeline, which is being developed, constructed, and owned by Mountain Valley (a venture of EQT and other entities), is planned to transport approximately 2.0 Bcf/d of natural gas and to extend 300 miles from Equitrans LP’s system in Wetzel County, West Virginia to Transco’s Station 165 in Pittsylvania County, Virginia.
On January 25, 2022, the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals vacated U.S. Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management permits that allow the pipeline to pass through 3.5 miles of the Jefferson National Forest. On February 2, 2022, the Fourth Circuit Court also issued a decision vacating MVP’s U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Endangered Species Act Biological Opinion (Biological Opinion), remanding it on specific issues. Until the pipeline has a valid Biological Opinion, the Army Corps has stated they will not approve the necessary permits. MVP continues to review these decisions and evaluate the possible paths forward, which include working with the relevant federal agencies and the considerations of potential legal appeals. As of December 31, 2021, approximately 94 percent of the project is complete, which includes construction of all original interconnects and compressor stations. AltaGas' exposure is contractually capped to the original estimated contributions of approximately US$352 million, which was met as of December 31, 2021. In the fourth quarter of 2021,
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 36
AltaGas impaired its equity investment in MVP to a carrying value of US$352 million as a result of these ongoing legal and regulatory challenges. See Note 14 of the 2021 Annual Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details.
In April 2018, AltaGas entered into a separate agreement with EQM to acquire a 5 percent equity interest in a lateral project to build an interstate natural gas pipeline (MVP Southgate project). The proposed pipeline would receive gas from the Mountain Valley mainline in Pittsylvania County, Virginia and extend approximately 73 miles south to new delivery points in Rockingham and Alamance counties, North Carolina. Due to the evolving regulatory and legal environment for pipeline construction and ongoing challenges related to MVP and the MVP Southgate project, MVP is evaluating the MVP Southgate project, including engaging in discussions with the shipper regarding options for the project, including potential changes to the project design and timing in lieu of pursuing the project as originally contemplated. As originally designed, AltaGas' total capital contributions were expected to be approximately US$20 million for the project. In the fourth quarter of 2021, AltaGas' impaired its investment in the MVP Southgate project to a carrying value of $nil as a result of these ongoing legal and regulatory challenges. See Note 14 of the 2021 Annual Consolidated Financial Statements for additional details.
Competition
As a leading provider of LPG services connecting producers to domestic and global markets, AltaGas has refined its strategy and realigned its assets to increase the utilization of its existing assets and attract future growth while facilitating the delivery of affordable, reliable and cleaner sources of energy for today and tomorrow. AltaGas’ unique integrated value chain from wellhead to tidewater and beyond offers customers egress solutions and higher netbacks as a result of access to higher value global energy markets, including Asia.
Through its integrated infrastructure value chain, AltaGas is able to connect North American producers from the wellhead to the global LPG markets via RIPET and Ferndale. With the recent addition of two VLGCs to its value chain that are currently under construction, AltaGas' integrated value proposition is a unique offering that is challenging to replicate. Regardless, ensuring consistent cost competitiveness and the highest netbacks is critical as AltaGas is competing for LPG supply from the WCSB. Currently, RIPET and Ferndale, at upwards of 150,000 Bbls/d of throughput capacity, account for approximately one third of the LPG demand in the WCSB. The expectation of continued North American natural gas development and the resulting LPG supply/demand imbalance in North America, combined with strong Asian demand, is expected to maintain a robust pricing differential between North America and Asia. AltaGas' structural and locational advantage through RIPET and Ferndale will enhance producers' netbacks and be highly competitive with other North American LPG exports for LPG supply as AltaGas' global export operations continue to be optimized. To protect and enhance our competitive advantage, logistics optimization is AltaGas' top priority.
On the upstream side of the value chain, AltaGas competes with large, sophisticated integrated upstream natural gas exploration and production entities, as well as other midstream entities operating in the WCSB for natural gas processing services. AltaGas' core gas processing facilities are strategically located in liquids rich basins and offer additional services such as LPG fractionation, liquids handling and rail loading. These facilities provide AltaGas' producers and other customers with access to lower cost and higher netback alternatives for their NGL, the opportunity to market their LPGs regionally and most importantly, attracts supply to AltaGas' export terminals. In 2021, AltaGas processed an average of 1.5 Bcf/d, which is approximately 14 percent of volumes produced in the WCSB. The majority of WCSB processing capacity generally continues to be provided by the upstream natural gas exploration and production companies. With the ability to provide Western Canadian producers a fully integrated value chain, supported by liquids processing and handling and global export capabilities, AltaGas is well positioned to compete for incremental throughput for its existing processing facilities and attract future growth.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 37
Midstream Utilization
AltaGas strives for continued improvement, operational excellence, and maximum utilization of all facilities over which it has operational control and to consistently exceed WCSB average utilization rates. Volume additions at plants, which come from new well tie-ins and from re-activations, re-completions, and well optimizations performed by producers, are offset by natural production declines. Global export volumes are driven by production at AltaGas' Midstream facilities, LPG supply from the WCSB, and various long-term purchase agreements with Canadian and American suppliers.
Global Exports
Average global exports utilization at RIPET was 63 percent in 2021 and 2020, however, with the additional license granted to RIPET in 2020, throughput volumes increased to 50,695 Bbls/d during the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to 39,285 Bbls/d in 2020. The increase in throughput volumes was mainly due to improved logistics and supply volumes. There were 32 shipments to Asia during the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to 27 shipments in the same period of 2020. Propane and butane export volumes at Ferndale averaged 38,636 Bbls/d, with 28 shipments to Asia during the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to 33,979 Bbls/d, with 2 shipments for the 2020 period subsequent to close of the Petrogas Acquisition.
Gas Processing
Average processing facility utilization of core assets increased to 62 percent in 2021 from 57 percent in 2020 primarily due to increased throughput volumes at the extraction facilities and a ramp up in volumes at the Townsend complex.
Fractionation
Average fractionation utilization of 47 percent in 2021 is higher than 38 percent utilization in 2020 due to the North Pine expansion project being placed in-service in the first quarter of 2020 and additional liquids volumes from the NEBC facilities including the Townsend deep cut facility, higher volumes at Younger due to a scheduled turnaround in 2020, and higher trucked-in volumes at Harmattan.
Significant Operating Areas and Customers
Global Exports
As two of the only three LPG terminals operating on the west coast of North America and the only two able to ship with VLGCs and Large Gas Carriers, RIPET and the Ferndale terminal offer significantly reduced shipping times to the Asian LPG markets compared to the other North American LPG terminals that are not located on the west coast. Both terminals are connected to the key North American hubs with rail networks.
Processing and Fractionation
Approximately 47 percent of AltaGas’ processing volumes are processed through the Townsend complex, Blair Creek facility, Gordondale facility, Aitken Creek facilities, and the Younger facility located in the liquids-rich Montney resource play in NEBC.
AltaGas has also fractionation capacity in the NEBC area through the North Pine and Younger facilities. The North Pine facility is interconnected to the Townsend complex, and is the only custom fractionation plant in British Columbia, providing area producers with a lower cost, higher netback alternative for their NGLs than fractionating in Edmonton.
The JEEP and EEEP facilities are strategically located and take advantage of the gas consumption by the petrochemical industry and the City of Edmonton. Harmattan is a significant service provider with a large capture area in west central
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 38
Alberta. Many other facilities in the Harmattan area are currently underutilized, providing AltaGas with opportunities to consolidate and increase asset utilization and profitability.
Midstream Contractual Arrangements
Global Exports
RIPET and Ferndale annual capacity is currently managed through a combination of merchant supply agreements and tolling arrangements for both propane and butane. AltaGas' plans are to have an increasing amount of RIPET and Ferndale's capacity underpinned by tolling arrangements with focus on creating an integrated value chain for AltaGas' customers and suppliers in the WCSB from the wellhead to the global export markets.
In 2022, AltaGas has in place agreements for the purchase of approximately 75 percent of the propane expected to be shipped from RIPET. Approximately 67 percent of RIPET propane volumes are exported under term and semi-term contracts, while 33 percent are under current year strip or spot contracts.
In 2022, AltaGas also has in place agreements for propane and butane offtake volumes, for the purchase of approximately 76 percent of the product expected to be shipped from Ferndale. Approximately 76 percent of Ferndale propane and butane volumes are exported under term and semi-term contracts, while 24 percent are under current year strip or spot contracts.
Processing and Fractionation
AltaGas gathers, processes, and fractionates natural gas and NGL under contracts with natural gas producers. There are approximately 208 active processing contracts with approximately 60 counterparties. These contracts, in general:
▪Establish fees for the gathering and processing services offered by AltaGas;
▪Establish operating costs flow through to the producers for a significant portion of the contracts;
▪Define the producers’ access rights to gathering and processing services;
▪Establish minimum throughput commitments with producers and use appropriate fee structures to recover invested capital early in the life of the contract where capital investment is required by AltaGas;
▪Define the terms and conditions under which future production is processed at an AltaGas facility; and
▪Establish processing fees at several facilities on a take-or-pay basis.
The majority of contracts in place at December 31, 2021 were subject to annual price escalation related to changes in CPI.
Where natural gas reserves have been dedicated under a contract, the contract normally extends beyond one year and up to the life of the reserves, depending on the amount of capital AltaGas has invested in the facility. Where reserves have not been dedicated under a contract or AltaGas has not made a significant capital investment, the contracts are normally subject to termination by either party upon one to three months' notice. Producing wells typically remain connected to a processing system for their entire productive lives.
Natural gas processing facility owners have the right to extract liquids from the natural gas stream, either directly as the owner of the natural gas, or through NGL extraction agreements. The typical commercial arrangement involves the ethane and NGL extraction plant owner contracting with the gas shipper on a natural gas transmission system for the right to extract NGL from the transporter’s natural gas. Ethane and NGL are extracted from the energy content of the shipper’s natural gas.
The value of ethane and NGL extraction is a function of the difference between the value of the ethane, propane, butane and condensate as separate marketable commodities and their heating value as constituents of the natural gas stream. If
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 39
the components are not extracted and sold at prices that reflect the value for each of the individual commodities, they are sold as part of natural gas and generate revenue for their heating value at the prevailing natural gas price.
Fractionation facilities charge a fee to separate NGL mix into specification propane, butane, and condensate.
Environmental Considerations Impacting the Midstream Business
The Midstream business is subject to the following environmental regulations:
Canadian Federal Air and GHG Regulations
Multi-Sector Air Pollutants Regulations
The Multi-Sector Air Pollutants Regulation promulgated under the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (the Canadian EPA), was passed on June 17, 2016. The regulation requires owners and operators of specific industrial facilities and equipment types to meet consistent performance standards across the country. The objectives of the regulations are to limit the amount of NOx emitted from modern (new) and pre-existing (existing), gaseous-fuel-fired non-utility boilers and heaters used in many industrial facilities.
Certain provisions of the Multi-Sector Air Pollutants Regulations came into effect on July 1, 2017, requiring registration and compliance reporting for modern engines. Compliance obligations for pre-existing engines were introduced in 2019 that will include NOx limits, NOx testing and O2 measurements, specified maintenance/operational requirements, and annual reporting and record keeping. Regulated entities will be subject to enforcement and compliance requirements and penalties as specified under the Canadian EPA.
AltaGas is currently focused on evaluating and implementing emissions reductions opportunities to reduce NOx emission associated with its engine, heater, and boiler fleet. Through a combination of engine modifications, implementation of technology, and/or changes in operating parameters, AltaGas expects to achieve a limit of 4g/kWh for 50 percent of the total rated brake power of AltaGas' regulated engines, with the goal of achieving a NOx limit of 4g/kWh for all pre-existing engines by 2026.
Federal Carbon Pricing
On December 9, 2016, the Government of Canada formally announced the "Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change". As a result, on June 21, 2018, the federal government enacted the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act to implement a carbon pollution pricing system that took effect beginning in 2019, to be applied in provinces and territories that do not have a carbon pricing system that aligns with the federal benchmark.
In December 2020, the government released its strengthened climate plan, "A Healthy Environment and a Healthy Economy", which proposed to implement annual carbon price increases of $15/tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) GHG emissions from 2023 to 2030 and to consider changes to strengthen the federal benchmark criteria. In August 2021, the Government of Canada updated the federal benchmark for carbon pricing post-2022. This update includes confirming the national minimum price on carbon pollution to 2030 and strengthening the criteria that all provincial pricing systems across Canada must meet.
The federal carbon pollution pricing scheme is composed of two elements, both of which may impact AltaGas’ business:
▪A carbon levy applied to combusted fossil fuels, priced at $50 per tonne in 2022, and then increasing by $15 per year starting in 2023, reaching $170 per tonne of carbon emitted in 2030; and,
▪An output-based pricing system for industrial facilities that emit 50,000 tonnes of CO2e per year or more, with an opt-in capability for smaller facilities with emissions below the threshold.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 40
The output-based pricing system will apply to emissions from fuel combustion as well as emissions of synthetically produced GHG’s from industrial processes and products. As of December 31, 2021, AltaGas has three processing facilities that would exceed the 50,000 tonnes of CO2e per year threshold, including two facilities in Alberta and one facility in British Columbia. These facilities will continue to be regulated by the carbon pricing and reporting systems within those provinces. The carbon pricing schemes in both Alberta and British Columbia have been granted equivalency by the federal government until 2022.
Beginning in 2023, provincial and territorial carbon pollution pricing systems will be required to meet the strengthened 2023 to 2030 benchmark criteria to be a federally recognized carbon pollution pricing system. The minimum requirements include:
▪Carbon pollution pricing systems must have a minimum carbon pollution price of at least $65 per tonne of GHG emissions calculated in CO2e in 2023, rising by $15 per year to $170 per tonne of CO2e in 2030; and,
▪The carbon pollution price must apply to an equivalent percentage of GHG emissions from combustion sources as would be covered by the federal backstop system in the jurisdiction.
The federal government will seek confirmation from provinces and territories on whether they intend to maintain or implement a carbon pollution pricing system for the 2023 to 2030 period. The federal government will assess provincial and territorial submissions against the updated federal benchmark criteria in 2022. This will inform the application of the federal backstop carbon pollution pricing system as of 2023, pursuant to the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act.
Federal Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program (GHGRP)
Environment and Climate Change Canada reduced the reporting threshold for the GHGRP reports for the 2017 operating year. Under this rule, the GHGRP will apply to a wider range of GHG emitting operations in Canada. The reporting threshold for industrial facilities was reduced from 50,000 tonnes CO2e to 10,000 tonnes CO2e.
As of June 1, 2021, nine facilities within the Midstream segment reported to the GHGRP as a result of the lower reporting threshold.
Alberta
TIER
TIER automatically applies to facilities that produce 100,000 tonnes or more of emissions per year. Facilities under this threshold have the option to voluntarily become a regulated facility under TIER by becoming an aggregate facility. Emission reduction obligations under TIER are determined according to a facility specific benchmark approach and high-performance benchmark approach. Under the facility specific benchmark methodology, a facility is required to reduce emissions intensity by 10 percent relative to the facility's historical production weighted average emissions intensity. The stringency of the facility specific benchmark will increase by 1 percent annually beginning in 2021. High performance benchmarks are set to the average emission intensity of the most efficient facilities producing each benchmarked product over selected reference years.
TIER provides regulated facilities with the same compliance options available to them, as they did under the CCIR. Emission performance credits and emissions offsets combined may not be used to satisfy more than 60 percent of the facility's total compliance obligation for a single compliance year. TIER will also maintain the credit expiry timeline for emission performance credits and offsets, where credits will expire eight years after creation. Both AltaGas' Harmattan and Gordondale facilities produce 100,000 tonnes or more of emissions per year and are regulated under the TIER program.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 41
The Government of Canada applied the federal fuel charge in Alberta beginning January 1, 2020 under the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act (GGPPA). The charge applies to all fossil fuels used in Alberta, including those in the oil and gas sector, that previously had been given a carbon tax exemption until 2023 under the previous provincial administration, while the province focused on methane reduction. The GGPPA includes provisions to exempt facilities subject to provincial policies that meet the federal benchmark criteria. The TIER program was designed to meet federal requirements and protect regulated facilities from the full costs of complying with the GGPPA, while achieving emission reductions using an approach that is cost efficient and tailored to Alberta's industry. AltaGas facilities under 100,000 tonnes of emissions in Alberta have voluntarily opted in to the TIER program as an aggregate facility. Each opted in facility will be required to meet the compliance requirements under the TIER program, but will be exempt from paying the federal fuel charge under the GGPPA.
Methane Reduction Regulation
The Government of Alberta has committed to reduce methane emissions from oil and gas operations by 45 percent relative to 2014 levels by 2025. Execution of the new oil and gas methane standards will be led by the Alberta Energy Regulator, in collaboration with Alberta Energy and the Alberta Climate Change Office. Details with respect to the Alberta Government’s methane reduction program were released on December 13, 2018, and effective January 1, 2020. The AER Directive 060 sets out requirements for flaring, incinerating, and venting in Alberta at all upstream petroleum industry wells and facilities, with specific operational requirements to address fugitive emissions and venting, which are the primary sources of methane emissions from the oil and gas industry. These operational requirements could result in significant equipment retrofit, equipment replacement, advanced planning, and investment to ensure compliance. In addition, companies are also required to have in place a fugitive emissions management program that must be designed to reduce fugitive emissions over time to achieve the 45 percent reduction target relative to 2014 levels. Companies will also be required to conduct leak detection surveys at their facilities at a prescribed frequency (annually or tri-annually) based on equipment or facility type. The AER Directive 017 also sets out measurement requirements associated with the requirements under AER Directive 060.
British Columbia (B.C.)
Greenhouse Gas Industrial Reporting and Control Act
On January 1, 2016, the Greenhouse Gas Industrial Reporting and Control Act came into force to, among other things, ensure LNG facilities in B.C. have an emissions cap. The legislation replaced the previous Greenhouse Gas Reduction (Cap and Trade) Act.
The Blair Creek facility, Townsend complex, North Pine facility, RIPET, and other assets in B.C. are subject to the reporting obligations and as at December 31, 2021, are in compliance with the Greenhouse Gas Emission Reporting Regulation.
Methane Reduction
The amended Oil and Gas Commission Drilling and Production Regulation in B.C took effect on January 1, 2020. Amendments to the regulation included Leak Detection and Repair. A facility permit holder in B.C. will be required to conduct leak detection surveys at their facilities at a prescribed frequency (annually or tri-annually) based on equipment or facility type.
Detected leaks at a facility identified during a survey must be repaired within 30 days or, if the repair requires the facility to be shut down, then the repair must be completed at the next turnaround. Records of the surveys at a facility must be maintained and include date of survey and method used, leak rate for any leak detected, and leak repair information.
In addition to the above requirements, the amended regulations contain various natural gas vent gas limits or restrictions on the following types of equipment: tanks, compressors, gas conservation equipment, pneumatic devices, pneumatic
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 42
pumps and compressor starters and glycol dehydrators. These equipment specific natural gas vent limits may result in equipment retrofit or replacement.
Carbon Tax Act
AltaGas’ operating facilities in B.C. operate under and comply with requirements set forth by the Carbon Tax Act of B.C. B.C.’s carbon tax is currently set at $45 per tonne of CO2e and will increase to $50 per tonne on April 1, 2022.
CleanBC
In October 2021, the Government of British Columbia announced an updated clean energy plan, "CleanBC Roadmap to 2030", which seeks to ensure that B.C. achieves its GHG emissions reduction target by 2030 and sets the course to fulfill their net-zero commitment by 2050. The B.C. plan includes several strategies targeting the industrial, transportation, construction, and waste sectors of the B.C. economy. Key initiatives include:
•A stronger price on carbon pollution, aligned with or exceeding federal requirements from 2023 to 2030, with built-in supports for people and businesses;
•Increased clean fuel requirements and doubling the target for renewable fuels produced in B.C. to 1.3 billion litres by 2030;
•Stronger methane policies that will reduce methane emissions from the oil and gas sector by 75 percent by 2030 and nearly eliminate all industrial methane emissions by 2035;
•Requirements for new large industrial facilities to work with government to demonstrate how they align with B.C.’s legislated targets and submit plans to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050;
•Enhancing the CleanBC Program for Industry to reduce emissions while supporting a strong economy;
•Implement programs and policies so that oil and gas emissions are reduced in line with sectoral targets;
•A cap on emissions for natural gas utilities with a variety of pathways to achieve it;
•Support for innovation in areas like low to no carbon solutions such as hydrogen, the forest-based bioeconomy and negative emissions technologies.
Washington State
Department of Ecology Reporting of Emissions of Greenhouse Gases
The Department of Ecology has established Greenhouse Gas Reporting requirements for any facility that exceeds the threshold of 10,000 metrics tonnes of CO2e or more per calendar year in total GHG emissions from applicable source categories. If the reporting threshold is exceeded, an annual GHG report must be filed with Department of Ecology.
As of December 31, 2021, the Ferndale LPG export facility was in material compliance with its GHG emissions reporting requirements.
U.S. Federal Air and GHG Regulations
The U.S. GHGRP requires reporting of GHG data and other relevant information from large GHG emission sources, fuel, and industrial gas suppliers, and CO2 injection sites in the United States. A total of 41 categories of reporters are covered by the U.S. GHGRP. Facilities determine whether they are required to report based on the types of industrial operations located at the facility, their emission levels, or other factors. Facilities are generally required to submit annual reports under Part 98 if:
▪GHG emissions from covered sources exceed 25,000 metric tons CO2e per year;
▪Supply of certain products would result in over 25,000 metric tons CO2e of GHG emissions if those products were released, combusted, or oxidized; or
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 43
▪The facility receives 25,000 metric tons or more of CO2 for underground injection.
All of AltaGas’ operating facilities located in the U.S. operate under and comply with requirements set forth by the U.S. GHGRP.
CORPORATE/OTHER SEGMENT
The Corporate/Other business consists of power assets and AltaGas' corporate activities, including general corporate investments and other revenue and expense items, such as general corporate overhead and interest expense, which are not directly attributable to AltaGas’ operating business segments. For the year ended December 31, 2021, the revenue for the Corporate/Other business was $108 million excluding intersegment eliminations and risk management and trading activities (2020 – $135 million).
Power Assets
AltaGas' power assets are engaged in the generation and sale of capacity, electricity, ancillary services, and related products in California and Colorado. After the sale of Pomona and Ripon in the third quarter of 2020, AltaGas has 578 MW of installed power capacity from a combination of gas-fired and remaining distributed generation assets, as more particularly set forth in the below table:
Facility | Interest (%) | Capacity (MW) | Type | Geographic Region | Contracted Expiry Date | ||||||||||||
Blythe | 100 | % | 507 | Gas-fired | California, U.S. | 2023 | |||||||||||
Brush II (1) | 100 | % | 70 | Gas-fired | Colorado, U.S. | 2022 | |||||||||||
Distributed Generation | 100 | % | 1 | Various | Various regions in the U.S. | Various | |||||||||||
Total | 578 | ||||||||||||||||
(1)In February 2022, AltaGas entered into agreement to sell the Brush II plant. The transaction is expected to close in the second quarter of 2022.
Gas-Fired Generation
In southern California, the 507 MW Blythe Energy Center utilizes gas-fired generation to produce power and serves the transmission grid operated by the CAISO to cover periods of high demand primarily driven by the Los Angeles area. Due to the structure of the long-term PPA with SCE, the majority of the revenue from the facility is derived from being available to produce and not from actual production, therefore providing stable cash flow. The facility is directly connected to an El Paso Gas Company natural gas pipeline for its primary supply and a Southern California Gas Company pipeline as a secondary supply source, and interconnects to SCE and CAISO via a 67‑mile transmission line also owned by Blythe and part of the Blythe Energy Center. In 2019, AltaGas announced the successful recontracting of the Blythe facility to SCE. Under the tolling agreement, SCE has exclusive rights to all capacity, energy, ancillary services, and resource adequacy benefits. The agreement became effective on August 1, 2020 and runs through December 31, 2023.
Competition
The Blythe Energy Center is contracted under a PPA until December 31, 2023. Under the tolling agreement(s), SCE has exclusive rights to all capacity, energy, ancillary services, and resource adequacy benefits during the PPA term.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 44
Environmental Considerations Impacting the Corporate/Other Segment
AltaGas' power assets included in the Corporate/Other segment are subject to the following environmental regulations:
U.S. Federal Air and GHG Regulations
Clean Air Act
Under the Clean Air Act, the USEPA has the authority to set federal ambient air quality standards for certain air pollutants which apply throughout the U.S. The Clean Air Act could increase regulatory burdens for AltaGas’ natural gas-fired power plants, which emit volatile organic compounds and nitrogen oxides, by leading to additional control requirements, obligations to obtain emission offsets, or permitting delays.
Individual states must ensure that, at a minimum, their air quality meets the ambient federal standards set by the USEPA. In general, states may choose to impose stricter performance requirements than does the USEPA.
In addition, the Clean Air Act requires certain facilities to obtain construction and operating permits for their air emissions.
As of December 31, 2021, AltaGas’ operating natural gas-fired power generation facility in California was in compliance with its air permit requirements, which are issued in accordance with federal and state emissions standards.
California GHG Regulations
Cap-and-Trade Program
The California ARB originally designed the California cap-and-trade regulations to meet the requirements of Assembly Bill No. 32 (AB 32). The California cap-and-trade program is a mandatory market-based system designed to reduce GHG emissions over time from multiple sources by setting a declining cap on GHG emissions. The program began in 2013 and has been extended to 2030. The emissions cap declines at approximately 3 percent per annum with the objective of reaching at least a 40 percent reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. Large GHG emitters must submit compliance instruments to the ARB in proportion to their annual emissions. Compliance instruments include emission allowances purchased at auction or in private sales, emission allowances distributed to certain industry participants, and limited proportions of offset credits.
As of December 31, 2021, AltaGas’ Blythe facility in California was in compliance with cap and trade requirements. Costs associated with meeting AB 32 and California’s cap-and-trade program have been passed through to the utilities pursuant to the applicable PPA.
California Groundwater Regulation
In California, water supply availability can be volatile, particularly as implementation moves forward on the SGMA. SGMA will require adoption of new mandatory requirements with the aim of managing groundwater "sustainably" over the long term. SGMA gives primary responsibility for regulating groundwater to local agencies referred to as GSAs. GSAs must develop plans that allow the maximum quantity of groundwater to be withdrawn without causing the lowering of groundwater levels, reduction of storage, seawater intrusion, degraded water quality, land subsidence, or depletion of interconnected surface water. Although SGMA focuses on groundwater supplies, reduced availability of groundwater might increase surface water demands, whether originating from local or imported surface water supply sources. It is uncertain whether or how SGMA may impact water supplies for Blythe. Blythe was designed to operate with wastewater capture and other water recycling techniques. Water is reused at Blythe in steam generation, reducing the amount of water used by the facility.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 45
CAPITAL STRUCTURE
Description of Capital Structure
The authorized share capital of AltaGas consists of an unlimited number of Common Shares and such number of Preferred Shares issuable in series at any time as have aggregate voting rights either directly or on conversion or exchange that in the aggregate represent less than 50 percent of the voting rights attaching to the then issued and outstanding Common Shares. At December 31, 2021, AltaGas had 280,269,038 outstanding Common Shares, 6,746,679 outstanding Series A Shares, 1,253,321 outstanding Series B Shares, 8,000,000 outstanding Series C Shares, 8,000,000 outstanding Series E Shares, 6,885,823 outstanding Series G Shares, 1,114,177 Series H Shares, and 12,000,000 outstanding Series K Shares.
On December 31, 2020, AltaGas redeemed all its 8,000,000 issued and outstanding Series I Shares for a redemption price equal to $25.00 per Series I Share, in accordance with the terms of the Cumulative Redeemable 5-Year Minimum Rate Reset Preferred Shares, Series I.
The summary below of the rights, privileges, restrictions and conditions attaching to the Common Shares and the Preferred Shares is subject to, and qualified by reference to, AltaGas’ articles and by-laws.
Common Shares
Holders of Common Shares are entitled to one vote per share at meetings of Shareholders of AltaGas, to receive dividends if, as and when declared by the Board of Directors and to receive the remaining property and assets of AltaGas upon its dissolution or winding-up, subject to the rights of shares having priority over the Common Shares.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 46
Preferred Shares (1)
The following table summarizes AltaGas' preferred shares outstanding as at December 31, 2021:
Current Yield | Annual dividend per share (2) | Redemption price per share (7) | Redemption and conversion option date (3) (7) | Right to convert into (4) | |||||||||||||
Series A Shares (5) | 3.060 | % | $0.76500 | $25 | September 30, 2025 | Series B | |||||||||||
Series B Shares (6) (7) | Floating | Floating | $25 | September 30, 2025 | Series A | ||||||||||||
Series C Shares (8) | 5.290 | % | US$1.32250 | US$25 | September 30, 2022 | Series D | |||||||||||
Series E Shares (5) | 5.393 | % | $1.34825 | $25 | December 31, 2023 | Series F | |||||||||||
Series G Shares (5) | 4.240 | % | $1.06050 | $25 | September 30, 2024 | Series H | |||||||||||
Series H Shares (6) (7) | Floating | Floating | $25 | September 30, 2024 | Series G | ||||||||||||
Series K Shares | 5.000 | % | $1.25000 | $25 | March 31, 2022 | n/a (3) | |||||||||||
(1)This table only includes those series of preferred shares that are currently issued and outstanding. The Corporation is authorized to issue up to 8,000,000 of each of Series D Shares, Series F Shares, subject to certain conditions, upon conversion by the holders of the applicable currently issued and outstanding series of preferred shares noted opposite such series in the table on the applicable conversion option date. If issued upon the conversion of the applicable series of preferred shares, Series F Shares are also redeemable for $25.50 and Series D Shares are redeemable for US$25.50 on any date after the applicable conversion option date, plus all accrued but unpaid dividends to, but excluding, the date fixed for redemption.
(2)The holders of Series A Shares, Series C Shares, Series E Shares, Series G Shares, and Series K Shares are entitled to receive a cumulative quarterly fixed dividend as and when declared by the Board of Directors. The holders of Series B Shares and Series H Shares are entitled to receive a quarterly floating dividend as and when declared by the Board of Directors. If issued upon the conversion of the applicable series of Preferred Shares, the holders of Series D Shares and Series F Shares will be entitled to receive a quarterly floating dividend as and when declared by the Board of Directors.
(3)AltaGas may, at its option, redeem all or a portion of the outstanding shares for the redemption price per share, plus all accrued and unpaid dividends on the applicable redemption option date and on every fifth anniversary thereafter. On February 16, 2022, Series K holders received formal notice that all outstanding Series K preferred shares will be redeemed on March 31, 2022.
(4)The holder will have the right, subject to certain conditions, to convert their preferred shares of a specified series into Preferred Shares of that other specified series as noted in this column of the table on the applicable conversion option date and every fifth anniversary thereafter.
(5)Holders of Series A Shares, Series E Shares, and Series G Shares will be entitled to receive cumulative quarterly fixed dividends, which will reset on the redemption and conversion option date and every fifth year thereafter, at a rate equal to the sum of the then five-year Government of Canada bond yield plus 2.66 percent (Series A Shares), 3.17 percent (Series E Shares), and 3.06 percent (Series G Shares).
(6)Holders of Series B Shares and Series H Shares will be entitled to receive cumulative quarterly floating dividends, which will reset each quarter thereafter at a rate equal to the sum of the then 90-day Government of Canada Treasury Bill rate plus 2.66 percent (Series B Shares) and 3.06 percent (Series H Shares). Each quarterly dividend is calculated as the annualized amount multiplied by the number of days in the quarter, divided by the number of days in the year. Commencing December 31, 2021, the floating quarterly dividend rate is $0.17192 per share for Series B Shares and $0.196582 per share for Series H Shares for the period starting December 31, 2021 to, but excluding, March 31, 2022.
(7)Series B Shares can be redeemed for $25.50 per share on any date after September 30, 2015 that is not a Series B conversion date, plus all accrued and unpaid dividends to, but excluding, the date fixed for redemption. Series H Shares can be redeemed for $25.50 per share on any date after September 30, 2019 that is not a Series H conversion date, plus all accrued and unpaid dividends to, but excluding, the date fixed for redemption.
(8)Holders of Series C Shares will be entitled to receive cumulative quarterly fixed dividends, which will reset on the redeemable and conversion option date and every fifth year thereafter, at a rate equal to the sum of the five-year U.S. Government bond yield plus 3.58 percent.
Preferred Shares may be used by AltaGas for any appropriate corporate purposes, including, without limitation, public or private financing transactions or issuance as a means of obtaining additional capital for use in AltaGas’ business and operations or in connection with acquisitions of other businesses and properties. AltaGas does not intend to use Preferred Shares as a defensive tactic to block take-over bids.
The Board of Directors may divide any unissued Preferred Shares into series and fix the number of shares in each series and the designation, rights, privileges, restrictions, and conditions thereof. The Preferred Shares of each series will rank on parity with Preferred Shares of every other series with respect to accumulated dividends and return of capital and the holders of Preferred Shares will rank prior to the holders of Common Shares and any other shares of AltaGas ranking junior to the Preferred Shares with respect to the payment of dividends and the distribution of assets in the event of liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of AltaGas, whether voluntary or involuntary.
The rights, privileges, restrictions and conditions attaching to the Preferred Shares as a class may be repealed, altered, modified, amended or amplified or otherwise varied only with the sanction of the holders of the Preferred Shares given in such manner as may then be required by law, subject to a minimum requirement that such approval be given by resolution in writing executed by all holders of Preferred Shares entitled to vote on that resolution or passed by the affirmative vote of at least 66⅔ percent of the votes cast at a meeting of holders of Preferred Shares duly called for such purpose.
For the specific rights, privileges, restrictions, and conditions attaching to the currently issued and, as applicable, outstanding: (i) Series A Shares and the Series B Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 47
AltaGas dated August 11, 2010; (ii) Series C Shares and the Series D Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of AltaGas dated May 30, 2012; (iii) Series E Shares and Series F Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of AltaGas dated December 6, 2013; (iv) Series G Shares and Series H Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of AltaGas dated June 25, 2014; (v) Series I Shares and Series J Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of AltaGas dated November 16, 2015; and (vi) Series K Shares and Series L Shares, reference should be made to the prospectus supplement of AltaGas dated February 15, 2017. The articles of the corporation and each of the prospectus supplements described herein have been filed with, and may be retrieved from, SEDAR at www.sedar.com.
Medium Term Notes
AltaGas has issued senior unsecured notes in the form of MTNs. Details with respect to the issued and outstanding MTNs can be found in Note 16 to AltaGas’ audited Consolidated Financial Statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021 filed on SEDAR at www.sedar.com. The MTNs are not listed or quoted on any exchange.
WGL and Washington Gas Notes
WGL and Washington Gas issue long-term notes with individual terms regarding interest rates, maturities and call or put options. These notes can have maturity dates of one or more years from the date of issuance. For a complete list of such notes currently outstanding please refer to Note 16 of AltaGas’ audited Consolidated Financial Statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Fixed-to-Fixed Rate Subordinated Notes, Series 1
On January 11, 2022, AltaGas closed its offering of $300 million of 5.25 percent Fixed-to-Fixed Rate Subordinated Notes, Series 1, due January 11, 2082. Details with respect to the issuance can be found in Note 33 of AltaGas' audited Consolidated Financial Statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021.
GENERAL
Employees
At December 31, 2021, there were 2,926 individuals employed by AltaGas.
| December 31, 2021 | |||||
Utilities | 2,141 | ||||
Midstream | 566 | ||||
Corporate/Other | 219 | ||||
Total | 2,926 | ||||
Directors and Officers
As at February 25, 2022, the directors and executive officers of AltaGas Ltd., as a group, owned beneficially, directly or indirectly, or exercised control or direction over 1,909,570 of the outstanding Common Shares, or approximately 0.68 percent of the 280,443,077 Common Shares issued and outstanding.
Directors
The number of directors of AltaGas is to be determined from time to time by resolution of the Board of Directors. The number of directors is currently 11, of which 10 are independent directors.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 48
The term of office of any director continues until the annual meeting of Shareholders of AltaGas next following the director’s election or appointment, unless the term ends earlier in the event of death, resignation, or removal, disqualification or other reason in accordance with the constating documents of AltaGas. The Shareholders are annually entitled to elect the Board of Directors. Mr. McCallister has advised that he will retire at the 2022 meeting of shareholders.
The following table sets forth the names of the directors of AltaGas on February 25, 2022, their municipalities of residence, and their principal occupations within the last five years.
Name of Director, Municipality of Residence, and Position | Principal Occupation During the Past Five Years | Director Since | ||||||
Victoria A. Calvert (1) Calgary, Alberta, Canada Director | Ms. Calvert is a Corporate Director and Professor Emerita of Business at Mount Royal University in Calgary, where she taught from 1988 to 2018. She was also a Director of the Canadian Alliance of Community Service Learning from 2009 to 2017. Prior to this, she held corporate positions at Hudson's Bay Oil and Gas and the Bank of Nova Scotia. | November 1, 2015 | ||||||
David W. Cornhill (1) (2) Calgary, Alberta, Canada Director | Mr. Cornhill is a founding shareholder of AltaGas and its predecessors. Mr. Cornhill was Chief Executive Officer from 1994 to 2016 and served as interim Co-CEO from July to December 2018. He was Chairman of the Board from 1994 to April 2019. Prior to forming AltaGas, Mr. Cornhill served in various capacities with Alberta and Southern Gas Co. Ltd., including Vice President, Finance and Administration, Treasurer and President and Chief Executive Officer. | Director of AltaGas (and its predecessors) since April 1, 1994 | ||||||
Randall L. Crawford (3) Naples, Florida, USA Director | Mr. Crawford has been the Chief Executive Officer since December 2018. Refer to the disclosure under "Executive Officers" for further information. | December 10, 2018 | ||||||
Jon-Al Duplantier (1) (4) Houston, Texas, USA Director | Mr. Duplantier retired from Parker Drilling Company in July 2020, where he held a number of executive roles since joining in 2009, most recently as President, Rental Tools and Well Services from April 2018. Prior thereto, he served as Senior Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer and General Counsel from April 2014 to March 2018. | February 2, 2021 | ||||||
Robert B. Hodgins (1) (5) Calgary, Alberta, Canada Director | Mr. Hodgins is a CA, CPA and has been an independent businessman since November 2004. Mr. Hodgins has been serving as a non-executive part-time Senior Advisor, Investment Banking for Canaccord Genuity Corp. since September 2018. Mr. Hodgins also held the positions of Chief Financial Officer of Pengrowth Energy Trust, Vice President and Treasurer of Canadian Pacific Limited and Chief Financial Officer of TransCanada PipeLines Limited. | Director of AltaGas (and its predecessors) since March 2, 2005 | ||||||
Cynthia Johnston (1) Victoria, B.C., Canada Director | Ms. Johnston is a Corporate Director. She was Executive Vice President, Gas, Renewables and Operations Services at TransAlta Corporation from 2015 to 2017. From 2011 to 2015, she held various positions, including Executive Vice President, Enterprise Risk and Corporate Services and Executive Vice President Corporate Services. Prior thereto, Ms. Johnston held various executive leadership positions with TransAlta and FortisAlberta Inc. | July 25, 2018 | ||||||
Pentti O. Karkkainen (1) West Vancouver, B.C., Canada Chair of the Board | Mr. Karkkainen is the Chair of the Board. He was a co-founder and General Partner of KERN Partners from 2000 to 2014, and was the firm’s Senior Strategy Advisor from 2014 until his retirement in 2015. Prior thereto, Mr. Karkkainen was the Managing Director and Head of Oil and Gas Equity Research at RBC Capital Markets. | July 25, 2018 | ||||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 49
Name of Director, Municipality of Residence, and Position | Principal Occupation During the Past Five Years | Director Since | ||||||
Phillip R. Knoll (1) (2) Kelowna, B.C., Canada Director | Mr. Knoll is a Professional Engineer and has been the President of Knoll Energy Inc., a private consulting company, since 2006. Mr. Knoll served as interim Co-CEO of AltaGas from July to December 2018. He was CEO of Corridor Resources Inc. from October 2010 to September 2014. Prior thereto, Mr. Knoll held senior roles with a number of companies, including Duke Energy Gas Transmission, Maritimes & Northeast Pipeline, Westcoast Energy Inc., TransCanada Pipelines Limited and Alberta Natural Gas Company Ltd. | November 1, 2015 | ||||||
Terry D. McCallister (1)(2) Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA Director | Mr. McCallister is an independent businessman. He was the Chair and Chief Executive Officer of WGL and Washington Gas from October 2009 until his retirement in July 2018. Prior to this, he served as President and Chief Operating Officer of WGL and Washington Gas, joining Washington Gas in 2000 as Vice President of Operations. He has also held various leadership positions with Southern Natural Gas and Atlantic Richfield Company. | July 25, 2018 | ||||||
Linda G. Sullivan (1) Moneta, Virginia, USA Director | Ms. Sullivan is a Corporate Director. She was Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at American Water Works Company, Inc. from 2016 until her retirement in August 2019, and prior thereto was Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from 2014. Prior to joining American Water Works, she held various roles with the Edison International companies during her 22 years there, including Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at Southern California Edison Company. | January 9, 2020 | ||||||
Nancy G. Tower (1) Calgary, Alberta, Canada Director | Ms. Tower served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Tampa Electric Company, a regulated electric utility and a subsidiary of Emera Incorporated, from December 2017 until 2021. As part of her planned retirement she transitioned from the role of President in February 2021 and retired in June 2021. From 2014 to 2017, she was the Chief Corporate Development Officer of Emera. Since joining Emera in 1997, Ms. Tower has held several senior positions in corporate finance and in operations at Emera and with its subsidiaries, including Controller and Vice President, Customer Operations of Nova Scotia Power Inc., Chief Financial Officer of Emera, and Chief Executive Officer of Emera Newfoundland and Labrador. | January 9, 2020 | ||||||
(1)Independent director.
(2)The Board has determined that Mr. Cornhill and Mr. McCallister are independent under National Instrument 52-110. Mr. Cornhill retired as CEO of AltaGas in April 2016 and Mr. McCallister retired as CEO of Washington Gas in July 2018. In each case, over three years has elapsed from their respective dates of retirement and they are no longer deemed to be in a material relationship with AltaGas. Mr. Cornhill and Mr. Knoll acted as interim Co-CEOs from July 24, 2018 to December 9, 2018 until the appointment of Mr. Crawford as CEO, however the interim role did not impact their independence.
(3)Mr. Crawford, as current CEO of the Corporation, is not considered independent.
(4)Mr. Duplantier was an officer of Parker Drilling Company (Parker) from 2009 until July 2020. Parker and certain of its U.S. subsidiaries (collectively, the Debtors) commenced voluntary Chapter 11 proceedings and filed a prearranged Joint Chapter 11 Plan of Reorganization under Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code in the United States Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of Texas, Houston Division. The Plan was subsequently amended and was confirmed by the Bankruptcy Court on March 7, 2019. The Plan became effective on March 26, 2019 and the Debtors emerged from the Chapter 11 Cases.
(5)Mr. Hodgins was a director of Skope Energy Inc. (Skope) from December 15, 2010 to February 19, 2013. On November 27, 2012, Skope was granted protection from its creditors by the Court of Queen’s Bench of Alberta pursuant to the CCAA to implement a restructuring which was approved by the required majority of Skope’s creditors. The restructuring was sanctioned by the Court of Queen’s Bench of Alberta in February of 2013.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 50
AltaGas has four standing committees of the Board of Directors: (1) Audit, (2) Governance, (3) Human Resources and Compensation (HRC), and (4) Environment, Health and Safety (EH&S). The members of each of these committees as of February 25, 2022 are identified below:
Director | Audit Committee | Governance Committee | HRC Committee | EH&S Committee | ||||||||||
Victoria A. Calvert | n | n | ||||||||||||
David W. Cornhill | ||||||||||||||
| Jon-Al Duplantier | n | n | ||||||||||||
Cynthia Johnston | n | Chair | ||||||||||||
Pentti O. Karkkainen | ||||||||||||||
Robert B. Hodgins | Chair (1) | n | ||||||||||||
Phillip R. Knoll | Chair | n | ||||||||||||
Terry D. McCallister | n | |||||||||||||
Linda G. Sullivan | n | n | ||||||||||||
Nancy G. Tower | n | Chair | ||||||||||||
(1) Ms. Sullivan will assume the role of Chair of the Audit Committee on March 5, 2022.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 51
Executive Officers
The names, municipality of residence and position of each of the current executive officers of AltaGas are as follows:
Name of Officer, Municipality of Residence, and Position with AltaGas Ltd. | Principal Occupation During the Past Five Years | ||||
Randall L. Crawford Naples, Florida, USA President and Chief Executive Officer Director | President and Chief Executive Officer of AltaGas since December 2018. Prior to joining AltaGas, Mr. Crawford was with EQT Midstream Partners, LP from 2012 to 2017, most recently as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer, and with EQT Corporation as Senior Vice President and President Midstream, Commercial and Distribution from 2007 to 2017. | ||||
D. James Harbilas Calgary, Alberta, Canada Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of AltaGas from June 2019. Prior to joining AltaGas, Mr. Harbilas was the Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Enerflex Ltd. from 2007. | ||||
Corine R.K. Bushfield Airdrie, Alberta, Canada Executive Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer | Executive Vice President, Chief Administrative Officer of AltaGas from December 2016. Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Long Run Exploration Ltd. from March 2013 to September 2016. Vice President and Assistant Controller of Encana Corporation from 2010 to March 2013. | ||||
Donald M. Jenkins Oxon Hill, Maryland, USA Executive Vice President and President Utilities, President of Washington Gas Light Company | Executive Vice President and President, Utilities of AltaGas from December 2019. President of WGL and Washington Gas from December 2019. Prior thereto, Mr. Jenkins was with EQT Corporation from 2012, most recently as Chief Commercial Officer. | ||||
Randy W. Toone Calgary, Alberta, Canada Executive Vice President and President, Midstream | Executive Vice President and President, Midstream from January 2019. Executive Vice President and Acting President from July to December 2018. Executive Vice President Gas from June 2017. Executive Vice President, Commercial and Business Development from December 2016 to June 2017. Chief Operating Officer of CSV Midstream Solutions from July 2014 to November 2016. Country Manager of TAG Oil Ltd. from May 2013 to June 2014. Other roles with AltaGas prior to 2014 include President Utilities, President Gas, and Co-President Gas. | ||||
Bradley B. Grant Calgary, Alberta, Canada Executive Vice President and Chief Legal Officer | Executive Vice President and Chief Legal Officer of AltaGas since July 2018. Prior thereto, Vice President and General Counsel of AltaGas from May 2015. Partner with the law firm of Stikeman Elliott LLP from January 2004 to May 2015. | ||||
Shaheen Amirali Calgary, Alberta, Canada Executive Vice President, Chief External Affairs and Sustainability Officer | Executive Vice President, Chief External Affairs and Sustainability Officer from October 2020. Also served as Corporate Secretary until May 2021. Prior thereto, Senior Vice President and Corporate Secretary from May 2019, Vice President and Corporate Secretary from October 2017, Associate General Counsel from January 2017 and Senior Corporate Counsel from 2007 to 2016. | ||||
Audit Committee
Composition of the Audit Committee
The Committee is currently comprised of four members, Robert Hodgins, Cynthia Johnston, Linda Sullivan and Nancy Tower. Mr. Hodgins is the chair of the Committee. Ms. Sullivan will assume the role of chair on March 5, 2022. All of the members of the Committee are independent and financially literate as defined under Canadian securities law.
Relevant Education and Experience
Mr. Hodgins was the Chief Financial Officer at Pengrowth Energy Trust from 2002 to 2004. Mr. Hodgins was Vice President and Treasurer at Canadian Pacific Limited from 1998 to 2002 and Chief Financial Officer of TransCanada PipeLines Limited from 1993 to 1998. Mr. Hodgins has an Honours Degree in Business from the Richard Ivey School of Business at the University of Western Ontario, and is a CA, CPA in Ontario and Alberta. He has served on a number of
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 52
public company audit committees, and is currently chair of the audit and risk management committee of Enerplus Corporation and serves on the audit committees of Gran Tierra Energy Inc. and MEG Energy Corp.
Ms. Sullivan was Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at American Water Works Company, Inc. from 2016 until 2019, and prior thereto was Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from 2014. Prior to joining American Water Works, she held various roles with the Edison International companies, last serving as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at Southern California Edison Company from 2009 to 2014. Ms. Sullivan began her career in public accounting as an auditor with Arthur Andersen. Ms. Sullivan has over 30 years of utility finance and regulatory experience. She received her Certified Public Accountant designation (inactive) and Certified Management Accountant designation in 1991 and 1996, respectively. Ms. Sullivan holds a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration and Accounting from Portland State University. Ms. Sullivan is the chair of the audit committee at NorthWestern Energy, a U.S. public company.
Ms. Johnston was Executive Vice President, Gas, Renewables and Operations Services at TransAlta Corporation from 2015 to 2017. From 2011 to 2015, she held a number of other executive positions with TransAlta, including Chief Operating Officer of TransAlta Renewables Inc., President, TAMA Transmission, and Executive Vice President, Enterprise Risk and Corporate Services. Prior thereto, Ms. Johnston held various executive leadership positions with TransAlta and FortisAlberta. In these roles, she had financial oversight responsibilities and actively supervised financial officers and public accountants. She also had executive accountability for the enterprise risk management function of a large publicly traded company. She is on the audit committee of Russel Metals Inc., a public company, and has served on the audit committees of other private entities, including as chair. She holds a Bachelor of Arts in Economics from the University of Calgary and a Masters in Applied Economics from the University of Victoria.
Ms. Tower served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Tampa Electric Company, a regulated electric utility and a subsidiary of Emera Incorporated in Tampa, Florida from 2017 until her retirement in 2021. Prior thereto, she was the Chief Corporate Development Officer of Emera from 2014 to 2017. From 1997 until 2014, Ms. Tower held several senior positions in corporate finance and in operations at Emera and with its subsidiaries, including Controller and Vice President, Customer Operations of Nova Scotia Power Inc., Chief Financial Officer of Emera, and Chief Executive Officer of Emera Newfoundland and Labrador. Ms. Tower holds a Bachelor of Commerce from Dalhousie University and received her Fellow Chartered Accountant designation in 1985.
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
As set forth in the Committee’s charter, the Committee must pre-approve services provided by the external auditor and has direct responsibility for overseeing the work of the external auditor.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 53
External Auditor Service Fees by Category
The fees billed by Ernst & Young LLP (E&Y), AltaGas’ external auditor, during 2021 and 2020 were as follows:
Category of External Auditor Service Fee (1) ($ millions) | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||
Audit fees | $ | 4.2 | $ | 4.9 | ||||
Audit-related fees (2) | 0.3 | 1.2 | ||||||
Tax compliance fees (3) | 0.3 | 0.1 | ||||||
All other fees (4) | 0.4 | 0.7 | ||||||
Total | $ | 5.2 | $ | 6.9 | ||||
(1)Due to the timing of invoices received, $1.7 million of fees relating to 2019 were paid in 2020.
(2)Represent the aggregate fees billed by E&Y for assurance and related services that were reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of AltaGas’ financial statements and were not reported under "Audit fees". During 2021 and 2020, the nature of the services provided included: review of prospectuses and security filings; research of accounting and audit-related issues; review of pro forma consolidated financial statements; specified audit procedures; review of the change in accounting principle related to pensions; internal controls assessment; cost allocation manual audits; environmental, social, and governance services; and registration costs for the Canadian Public Accountability Board.
(3)During 2021 and 2020, the nature of the services provided was for tax consultations, tax compliance, and transfer pricing.
(4)Represents the aggregate fees billed by E&Y for products and services, other than those reported with respect to the other categories of service fees, as well as any out-of-pocket costs incurred. During 2021 and 2020, the nature of the services provided was for translation services and an assessment of AltaGas' IT risk management and cyber security.
RISK FACTORS
Set forth below is a summary of certain risk factors relating to AltaGas and the business of AltaGas. The risks described below are not an exhaustive list of all risks, nor should they be taken as a complete summary of all the risks associated with the applicable business being conducted. Security holders and prospective security holders of AltaGas should carefully review and consider the risk factors set out below as well as all other information contained and incorporated by reference in this AIF before making a decision on investment and should consult their own experts where necessary. Information regarding AltaGas’ risk management activities can be found in AltaGas’ management information circular dated March 11, 2021 and will also be included in AltaGas’ management information circular for its 2022 annual meeting of Shareholders.
Pandemics, epidemics or disease outbreaks, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, may adversely affect local and global economies and our business, operations or financial results
Disruptions caused by pandemics, epidemics or disease outbreaks could materially adversely affect AltaGas' business, operations, financial results and forward-looking expectations. As seen in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, emergency measures enacted by governments to combat the spread of the virus and its variants include restrictions on business activity and travel, mandates related to vaccination, and public health directives such as requirements to isolate or quarantine. These actions have interrupted business activities and supply chains; disrupted travel; contributed to significant volatility in the financial and commodity markets; impacted social conditions; impacted national and international economic conditions, and disrupted the labor market. Additionally, such actions have put inflationary pressures on operating costs such as labour, materials and equipment, which have decreased price predictability. There can be no assurance that AltaGas' strategies to address potential disruptions will mitigate these risks or the adverse impacts to its business, operations and financial results. Future adverse impacts to AltaGas' business, operations and financial results may materialize that are not yet known.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, AltaGas, with its subsidiaries, activated its pandemic response team early in 2020 to monitor developments related to COVID-19 and to ensure the Corporation was responding swiftly and appropriately. Continuity plans and preparedness measures have been implemented at each of AltaGas’ businesses, with safeguarding the well-being of its personnel as the primary concern. To date, AltaGas has been able to respond to the COVID-19 related challenges without materially disrupting its operations and business. As the COVID-19 pandemic
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 54
persists, AltaGas continues to take proactive steps to effectively prepare for and address the evolving risks and regulatory mandates in the jurisdictions in which it operates, including changing international travel restrictions, potential for higher incidents of colds and influenza in the winter season, vaccination rates and mandates, vaccine effectiveness, and the evolution of COVID-19 variants. While the Company is moving toward reintegration of its workplaces, AltaGas' approach has been, and will continue to be, risk-based and guided by its core values. The health and safety of AltaGas' employees, customers, contractors, and the communities in which it operates is the top priority and is integrated into each aspect of AltaGas' response efforts.
Given the ongoing and dynamic nature of the circumstances surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic, it is difficult to predict the ultimate duration or magnitude of the impact on North American or global economies or our business. The extent of such impact will depend on future developments and factors which are highly uncertain and rapidly evolving. To the extent these risks materialize, the Corporation’s ability to carry out its business plans for 2022 may be adversely impacted.
Health and Safety
The ownership and operation of AltaGas’ business is subject to hazards of gathering, processing, transporting, fractionating, storing, and marketing hydrocarbon products, including, without limitation, blowouts, fires, explosions, gaseous leaks, releases and migration of harmful substances, hydrocarbon spills, corrosion, and acts of vandalism and terrorism. Any of these hazards can interrupt operations, impact AltaGas’ reputation, cause loss of life or personal injury, result in loss of or damage to equipment, property, information technology systems, related data and control systems, and cause environmental damage that may include polluting water, land or air.
Further, such ownership and operations carry the potential for liability related to worker health and safety, including, without limitation, the risk of any or all of government imposed orders to remedy unsafe conditions, potential penalties for contravention of health and safety laws, licenses, permits and other approvals, and potential civil liability. Compliance with health and safety laws (and any future changes) and the requirements of licenses, permits and other approvals are expected to remain material to AltaGas’ business.
Safety has been and continues to be a core value of AltaGas and is integral to how AltaGas operates. AltaGas actively works with industry groups and communities within which it operates to improve safety. Also, AltaGas has policies, procedures, and emergency response plans in place, which AltaGas regularly monitors and evaluates to identify opportunities for improvement in its safety programs. In addition, in the Utilities business, with support from each of certain regulatory commissions, AltaGas is accelerating the replacement of aging pipeline infrastructure prioritized on a risk-based approach and has implemented preventive and remedial measures to address increased leak rates in its distribution system caused by an increase in the volume of natural gas containing low concentration of light hydrocarbons received from its suppliers.
However, no assurances can be given that the occurrence of any of the above listed events or the additional workers’ health and safety issues relating thereto will not require unanticipated expenditures, or result in fines, penalties or other consequences (including, without limitation, changes to operations) material to AltaGas’ business and operations.
Operating Risk
AltaGas’ businesses are subject to the risks normally associated with the operation and development, and storage and transportation of natural gas, NGL, LNG, LPG, and power systems and facilities, including, without limitation, mechanical failure, transportation problems, physical degradation, operator error, manufacturer defects, constraints on natural resource development, delay of or restrictions for projects due to climate change policies and initiatives, protests, activist activity, sabotage, terrorism, failure of supply, weather, wind or water resource deviation, catastrophic events and natural disasters, fires, floods, explosions, earthquakes, and other similar events. These types of events could result in injuries to personnel, damage to property and the environment, as well as unplanned outages or prolonged downtime for
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 55
maintenance and repair. Among other things, these events typically increase operation and maintenance expenses and reduce revenues. The occurrence or continuation of any of these events could increase AltaGas’ costs and reduce its ability to process, store, transport, deliver, or distribute natural gas, NGLs, LNG, and LPG, and result in significant losses for which insurance may not be sufficient or available. Environmental damage could also result in increased costs to operate and insure AltaGas’ assets and have a negative impact on AltaGas’ reputation and its ability to work collaboratively with stakeholders.
As AltaGas continues to grow and diversify its energy infrastructure businesses, the risk profile of AltaGas may change. Operating entities may enter into or expand business segments where there is greater economic exposure and more "at-risk" capital.
Natural Gas Supply Risk
Adequate supplies of natural gas and pipeline and storage capacity may not be available to satisfy committed obligations as a result of economic events, natural occurrences, and/or failure of a counterparty to perform under gas purchase, capacity, or storage contracts and, accordingly, could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial conditions and cash flow.
In addition, Washington Gas, SEMCO Gas, and ENSTAR must acquire additional interstate pipeline transportation or storage capacity and construct transmission and distribution pipe to deliver additional capacity into growth areas on its system. The specific timing of any larger customer additions to its market may not be forecasted with sufficiently long lead time and the availability of these supply options to serve any of its customer additions may be limited by market supply and demand, the timing of Washington Gas’ participation in new interstate pipeline construction projects, local permitting requirements, and the ability to acquire necessary rights of way. These limitations could result in an interruption in Washington Gas’ ability to satisfy the needs of some of its customers.
ENSTAR’s gas distribution system, including, without limitation, the Alaska Pipeline Company pipeline system, is not linked to major interstate and intrastate pipelines or natural gas supplies in the lower 48 states of the United States or in Canada. As a result, ENSTAR procures natural gas supplies under long-term RCA-approved contracts from producers in and near the Cook Inlet area. Declining production from the Cook Inlet gas fields may result in potential deliverability problems in ENSTAR’s service area. There is ongoing exploration for natural gas in the Cook Inlet area, including, without limitation, producers that have supply contracts with ENSTAR. Activity also continues with respect to the possible construction of a natural gas pipeline that would extend from Alaska’s North Slope, through interior Alaska to a liquefaction facility located in south central Alaska. There are no assurances, however, with respect to these gas supply-related matters, including when such pipelines might be constructed and put in service or whether natural gas supplies transported by such pipelines would be available to ENSTAR’s customers and secured by ENSTAR on terms and conditions that would be acceptable to the RCA.
Volume Throughput
AltaGas’ businesses process, transport, and store natural gas, ethane, NGLs, and other commodities. Throughput within the business is dependent on a number of factors, including the level of exploration and development activity within the WCSB, the long-term supply and demand dynamics for the applicable commodities, and the regulatory and stakeholder environment for market participants. Notably, as a result of the development of non-conventional shale gas supplies in North America, the price of natural gas in North America has declined and there has been a shift towards richer, wet gas with higher NGL content. Areas with dryer gas have seen depressed activity. These factors and industry trends may result in AltaGas being unable to maintain throughput in certain areas. Consequently, AltaGas may be exposed to declining cash flow and profitability arising from reduced natural gas, ethane, and NGL throughput and from rising operating costs.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 56
Infrastructure
As utilities infrastructure matures, several of AltaGas’ utilities have implemented replacement programs to replace aging infrastructure and taken other preventative and remedial measures. If certain pipelines and related infrastructure were to become unexpectedly unavailable for delivery of current or future volumes of natural gas because of repairs, damage, spills or leaks, or any other reason, it could have a material adverse impact on financial conditions and results of operation of the utilities business. Although the costs of infrastructure replacement programs are typically recovered in rates, on-going capital is required to fund such programs. In addition, operating issues resulting from maturing infrastructure such as leaks, equipment problems and incidents, including, without limitation, explosions and fire, could result in legal liability, repair and remediation costs, increased operating costs, increased capital expenditures, regulatory fines and penalties, and other costs and a loss of customer confidence. Any liabilities resulting from the occurrence of these events may not be fully covered by insurance or rates.
Service Interruptions
Service interruption incidents that may arise through unexpected major power disruptions to facilities or pipeline systems, third-party negligence or unavailability of critical replacement parts could cause AltaGas to be unable to safely and effectively operate its assets. This could adversely affect AltaGas’ business operations and financial results.
Cyber Security, Information, and Control Systems
AltaGas’ business processes are increasingly reliant upon information systems and automation provided by infrastructure, technologies, and data. A failure of these information systems could lead to the impairment of business processes, and there is a risk of cascading failure of information systems leading to the impairment of multiple business processes. The risk of cyber-attacks is increasing, with strong evidence of the energy industry being specifically targeted. In addition, AltaGas collects and stores sensitive information in the ordinary course of business, including personal information in respect of its employees and proprietary information in respect of its stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, and investors.
Increased volume and sophistication of targeted cyber-attacks have been seen since the declaration of the global COVID-19 pandemic. Pandemic-adjusted operations, such as work from home arrangements and remote access to the Corporation's systems, may pose heightened risk of cyber security and privacy breaches and may put additional stress on the Corporation's IT infrastructure. A failure of such infrastructure could severely limit AltaGas' ability to conduct ordinary operations. To date, AltaGas’ systems have functioned capably, and it has not experienced a material impact to its operations as a result of an IT infrastructure issue.
Security breaches of AltaGas’ information technology or operational technology infrastructure, including, without limitation, cyber-attacks and cyber-terrorism, or other failures of AltaGas’ information technology and operational technology infrastructure could result in disruptions of natural gas distribution operations and other operational outages, ability to operate safely, delays, damage to assets, the environment or to AltaGas’ reputation, diminished customer confidence, lost profits, lost data including, without limitation, the unauthorized release of customer, employee, financial, or company data that is crucial to AltaGas’ operational security or could adversely affect the ability to deliver and collect on customer bills, increased regulation and other adverse outcomes, including, without limitation, material legal claims and liability or fines or penalties under applicable laws and adversely affect its business operations and financial results. If any of AltaGas' systems are damaged, fail to function properly, or otherwise become unavailable, AltaGas may incur substantial costs to repair or replace them.
AltaGas’ cybersecurity strategy focuses on identifying, detecting, and protecting information technology assets, and responding and recovering when an incident occurs, which includes, without limitation, continuous security event and incident management monitoring, ongoing cybersecurity training and awareness, conducting third-party vulnerability and penetration testing, and cyber incident response planning and testing. However, there is no assurance that AltaGas will
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 57
not suffer a cyber-attack or an information technology failure notwithstanding the implementation of this strategy and the measures taken pursuant to that strategy, including, without limitation, as set forth above and the occurrence of any of these cyber events could adversely affect AltaGas’ financial condition and results of operations.
AltaGas relies on third parties and managed service providers for various services. If these third parties undergo cyber-attacks, the services they provide AltaGas could be disrupted. The disruption could interfere with AltaGas’ ability to conduct its business, which it turn could negatively affect AltaGas’ financial condition and reputation. Additionally, the theft, damage, or improper disclosure of sensitive data held by these third parties may subject AltaGas to adverse consequences.
Climate-Related Risks including Carbon Pricing
AltaGas may be subject to both transition and physical risks related to climate change. See sections "Environmental Regulation", "Business of the Corporation – Utilities Business – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Utilities Business", "Business of the Corporation – Midstream Business – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Midstream Business", "Business of the Corporation – Corporate/Other Segment - Environmental Regulations Impacting the Corporate/Other Segment", "Environmental, Social and, Governance - Climate Change" of this AIF. AltaGas' climate strategy is influenced by the climate-related risks and opportunities to its businesses over the short term (less than three years), medium term (three-10) and long term (+10 years) horizon. AltaGas has incorporated the management of climate-related risks into all areas of its business through its ERM processes. By integrating these considerations throughout our decision-making process, we ensure AltaGas is well-positioned to capitalize on the swiftly changing landscape. Climate-related risks AltaGas considers include:
▪Current and Emerging Legislation and Regulations: AltaGas' facilities and operations are, and may become subject to, provincial, state, or federal climate change regulations and other standards designed to manage or limit GHG emissions or enhance reporting requirements. The direct or indirect costs of compliance with these regulations, including carbon pricing, may have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. Most of these costs flow through to AltaGas' producing customers, which impact their profits and their future capital investment decisions. AltaGas’ business could also be indirectly impacted by laws and regulations that affect its customers or suppliers to the extent such changes result in reductions in the use of natural gas by its customers or limit the operations of or increase the costs of goods and services acquired from AltaGas producers and other suppliers. AltaGas mitigates these risks by working to reduce its energy consumption, improving operating efficiency, and pursuing carbon reduction strategies. Some of AltaGas' carbon reduction strategies include investments in technology to meet or exceed compliance requirements to minimize the cost of these impacts. AltaGas actively monitors legislative developments and participates in public engagement opportunities to ensure industry perspectives are considered.
▪Markets: AltaGas is subject to market risks resulting from fluctuations in commodity prices as well as changes in demand, supply and consumption patterns that could impact our business. AltaGas' diversification across business lines, commodities, markets and risk management, hedging and contracting policies assists with mitigating and managing these risks. AltaGas' growth plans and investments use market fundamental data and forecasts to estimate the supply and demand of its products, including customer growth, changes in preferences, consumption patterns and the impacts to commodity prices.
▪Technology: Technology advancements and improvements can impact the pace of decarbonization that can affect AltaGas and its customers. Changes in energy consumption by consumers as a result of the availability of and incentive to invest in energy efficient technology have the potential to reduce customer demand and impact our business. Emerging technologies are considered as part of AltaGas' strategic planning processes and risk assessment. They are pursued as part of decarbonization strategies such as the use of co-generation facilities, acid gas injection, carbon capture and storage, advanced leak detection and methane capture technologies such as Washington Gas’ patented miniature drawdown compressors used to capture methane in small spaces.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 58
▪Reputational Risks: AltaGas places great importance on establishing and maintaining positive relationships with all stakeholders, including regulators, customers, and local Indigenous Peoples within its communities of operation. With increased public scrutiny relating to natural resource activities, opposition in the sector can impact our business and reputation. AltaGas engages proactively with its key stakeholders and the relationships the Company builds are core to the ability to execute on its strategy.
▪Physical: Climate-related physical risks such as wildfires, floods, and storms or from progressive shifts in climate patterns such as increasing temperatures, sea level rise and changes in precipitation are monitored as such events may impact our assets, capital investments, operations or supply chain. Such risks are factored into capital investment, project design, logistics planning of AltaGas' supply chains, such as shipping distances and routes, and emergency response planning. These risks are also mitigated though optimizing the ways in which AltaGas handles and moves products and through appropriate insurance coverage.
Regulatory
AltaGas’ businesses are subject to extensive and complex laws and regulations in the jurisdictions in which they carry on business. Regulations and laws are subject to ongoing policy initiatives, and AltaGas cannot definitively predict the future course of regulations. Changes in the regulatory environment may be beyond AltaGas’ control and may significantly affect AltaGas' businesses, results of operations, and financial conditions. Pipelines and facilities can be subject to common carrier and common processor applications and to rate setting by the regulatory authorities in the event an agreement on fees or tariffs cannot be reached with producers. The export and import of energy is also subject to regulatory approvals. Power facilities are subject to regulatory approvals and regulatory changes in tariffs, market structure, and penalties. Washington Gas, SEMCO Gas, ENSTAR, and CINGSA operate in regulated marketplaces where regulatory approval is required to afford the utilities the opportunity to earn their regulated returns that provide for recovery of costs and a return on capital and may limit the ability to make and implement independent management decisions, including, without limitation, setting rates charged to customers, determining methods of cost recovery, and issuing debt. Earnings of AltaGas’ regulated utilities may be impacted by a number of factors, including, without limitation, (i) changes in the regulator-approved allowed return on equity and common equity component of capital structure; (ii) changes in rate base; (iii) changes in gas delivery volumes; (iv) changes in the number and composition of customers; (v) variances between actual expenses incurred and forecast expenses used to determine revenue requirements and set customer rates; and (vi) recovery of unplanned costs through rate cases. Changes to regulatory and environmental laws could increase AltaGas’ operating costs and require enhanced disclosures. Increased expenditures could include capital expenditures, operating expenditures, and decommissioning, abandonment, and reclamation costs, which may not be recoverable in the marketplace or through rate cases. These changes could adversely affect AltaGas, resulting in current operations and projects becoming less profitable or uneconomic and could require significant investment to develop new technologies.
Litigation
In the course of its business, AltaGas is subject to lawsuits and other claims. Defense and settlement costs associated with such lawsuits and claims can be substantial, even with respect to lawsuits and claims that have no merit. Due to the inherent uncertainty of the litigation process, the resolution of any particular legal proceeding could have a material adverse effect on the financial position or operating results of AltaGas.
Changes in Laws
Applicable laws, including, without limitation, international trade laws and tariffs, environmental laws, policies, or government incentive programs may be changed in a manner that adversely affects AltaGas through the imposition of restrictions on its business activities or by the introduction of regulations that increase AltaGas’ operating costs. There can be no assurance that applicable laws, policies, or government incentive programs relating to energy infrastructure will not be changed in a manner which adversely affects AltaGas.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 59
Regulatory and environmental laws affecting AltaGas have changed, and will continue to change, over time. Concerns over climate change, including GHG emissions, fossil fuels, and land use, could lead to the introduction of additional or more stringent laws and regulation that would impact AltaGas, increasing AltaGas' exposure to legal risk.
Income tax laws relating to AltaGas may be changed in a manner that adversely affects its shareholders. This includes, without limitation, taxation and tax policy changes, tax rate changes, new tax laws, and revised tax law interpretations that may individually or collectively cause an increase in AltaGas’ effective tax rate.
AltaGas may face regulatory and financial risks related to pipeline safety legislation seeking to require increased oversight over pipeline operations and increased investment in and inspections of pipeline. Additional operating expenses and capital expenditures may be necessary to remain in compliance with the increased federal oversight resulting from such proposals. While AltaGas cannot predict with certainty the extent of these expenses and expenditures or when they will become effective, the adoption of such proposals could result in significant additional costs to AltaGas' businesses. AltaGas' utilities may be unable to recover from customers through the regulatory process all or some of these costs which could impact the ability to earn its authorized rate of return on these costs.
Political Uncertainty, Civil Unrest, Terrorist Attacks and Threats, Escalation of Military Activity in Response to these Attacks or Acts of War, and other Civil Unrest or Activism
Uncertainty exists with regard to the political climate in the jurisdictions where AltaGas operates. Changes in social, political, regulatory, or economic conditions, or in laws and policies governing environment, development, tax, foreign trade, investment or energy could materially adversely affect AltaGas' business and operations.
Recently there have been significant incidents of civil unrest in areas where AltaGas operates. To the extent that civil unrest is accompanied by disruption to transportation routes, damage to infrastructure, violence or destruction, AltaGas' personnel, physical facilities, and operations may be placed at risk and financial and operational results may be adversely impacted.
Terrorist attacks and threats, escalation of military activity or acts of war, or other civil unrest or activism may have significant effects on general economic conditions and may cause fluctuations in consumer confidence and spending and market liquidity, each of which could adversely affect AltaGas' business. Future terrorist attacks, rumors or threats of war, actual conflicts involving the US or Canada, or military or trade disruptions may significantly affect AltaGas' operations and those of its customers. Strategic targets, such as energy related assets, may be at greater risk of future attacks than other targets in the US and Canada. In addition, increased environmental activism against pipeline construction and operation could potentially result in work delays, reduced demand for AltaGas' products and services, increased legislation or denial or delay of permits and rights-of-way. Finally, the disruption or a significant increase in energy prices could result in government-imposed price controls. It is possible that any of these occurrences, or a combination of them, could adversely affect AltaGas' business, operations or financial results.
Decommissioning, Abandonment, and Reclamation Costs
AltaGas is responsible for compliance with all applicable laws and regulations regarding the decommissioning, abandonment and reclamation of its facilities at the end of their economic life, the costs of which may be substantial. It is not possible to predict these costs with certainty since they are a function of regulatory requirements at the time of decommissioning, abandonment and reclamation and the actual costs may exceed current estimates which are the basis of the asset retirement obligation shown in AltaGas’ financial statements. In particular, management has identified environmental issues associated with the prior activities of Harmattan and the Utilities. There are indications of significant groundwater and soil contamination resulting from Harmattan’s prior activities. There is a risk that the costs of addressing these environmental issues could be significant.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 60
As well, Washington Gas has recorded environmental liabilities for costs expected to be incurred to remediate sites where Washington Gas or a predecessor affiliate operated manufactured gas plants (MGPs). Estimates of liabilities for environmental response costs are difficult to determine with precision because of the various factors, including the likely effects of inflation, that can affect their ultimate level. See the section "Environmental Regulation", "Business of the Corporation – Utilities Business – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Utilities Business".
Reputation
AltaGas places great importance on establishing and maintaining positive relationships with its stakeholders, including, without limitation, within the communities in which AltaGas operates, regulators, and local Indigenous peoples. There is an increasing level of public concern and scrutiny relating to the perceived effect of natural resources activities, including, without limitation: exploration, development, production, processing, and transportation; on certain environmental and social aspects such as overall environmental performance, emissions, air and water quality, noise, dust, land, and ecological disturbance; and employment and economic development opportunities. Opposition to natural resources activities by communities, special interest groups (including non-governmental organizations), or Indigenous peoples may ultimately impact AltaGas, including its ability to obtain or maintain permits, the anticipated timing and costs associated with capital projects, its operations, shareholder confidence, and its reputation. Recent and proposed regulatory changes could increase the ability of special interest groups to object to and/or delay certain capital projects. See "Changes in Laws" above. Publicity adverse to AltaGas’ operations, AltaGas’ partners, or others operating in the energy industry generally, could have an adverse effect on AltaGas and its operations. While AltaGas is committed to operating in a socially responsible manner, there can be no assurance that its efforts in this respect will mitigate this potential risk.
Weather Data
The utilities and natural gas distribution business is highly seasonal, with the majority of natural gas demand occurring during the winter heating season, the length of which varies in each jurisdiction in which AltaGas’ utilities operate. Natural gas distribution revenue during the winter typically accounts for the largest share of annual revenue in the Utilities business. There can be no assurance that the long-term historical weather patterns will remain unchanged. Annual and seasonal deviations from the long-term average can be significant. In Maryland and Virginia, Washington Gas has in place regulatory mechanisms and rate designs intended to stabilize the level of net revenues that it collects from customers by eliminating the effect of deviations in customer usage caused by variations in weather from normal levels and other factors such as conservation. If Washington Gas’ rates and tariffs are modified to eliminate these provisions, then Washington Gas would be exposed to significant risk associated with weather.
The operations of AltaGas’ retail energy-marketing business, are weather sensitive and seasonal, with a significant portion of revenues derived from the sale of natural gas to retail customers for space heating during the winter months, and from the sale of electricity to retail customers for cooling during the summer months. Weather conditions directly influence the volume of natural gas and electricity delivered to customers. Weather conditions can also affect the short-term pricing of energy supplies that the retail energy-marketing business may need to procure to meet the needs of its customers. Similarly, the business of AltaGas’ Midstream business is seasonal due to the tendency of storage and transportation spreads to increase during the winter. Deviations from normal weather conditions and the seasonal nature of these businesses can create large fluctuations in short-term cash requirements and earnings for these businesses.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 61
Indigenous and Treaty Rights
Indigenous peoples assert and claim Indigenous (as defined under S.35 of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms) and Treaty rights in relation to a substantial portion of the lands in Canada and the United States. Governments in Canada and the United States have a duty to consult with and, where appropriate, accommodate Indigenous peoples where the rights of Indigenous peoples may be affected by a government action or decision. AltaGas operates in territories in which such claims have been advanced. Such claims, if advanced, could conflict with development activity and, if successful, could have a significant adverse effect on matters, including, without limitation, natural gas production, the development of natural gas and NGL extraction projects in Alberta and British Columbia, and the operations of RIPET in British Columbia and Ferndale in Washington State, which could have a materially adverse effect on AltaGas’ business and operations, including, without limitation, the volume of natural gas processed at AltaGas’ facilities, or on the operation or development of facilities for gathering and processing, energy exports, natural gas distribution, storage, power generation, or extraction and transmission.
In 2021, AltaGas enacted an Indigenous Engagement Guideline, which supports an approach of active engagement with Indigenous communities that serves to ensure the identification of issues and facilitates constructive problem-solving. Further, AltaGas has taken a proactive approach to enhance the economic participation of Indigenous peoples in its operations where feasible and reasonable. The Guideline, agreements enacted with Indigenous governments, and other measures undertaken by AltaGas strengthen relationships between the parties while respecting the ever evolving regulatory and judicial relationship between governments and Indigenous peoples. However, AltaGas cannot predict whether future Indigenous land claims and the assertion of other rights will affect its ability to conduct its business and operations as currently undertaken or as may be undertaken in the future in such regions. Furthermore, any failure to reach an agreement, or a conflict or disagreement, with an Indigenous group could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial condition, and results of operations.
In June 2021, the British Columbia Supreme Court ruled in the case of Yahey vs. British Columbia that B.C.’s regulatory mechanisms for assessing and taking into account the cumulative effects of development on rights conveyed to Indigenous peoples under Treaty 8 were lacking, and that B.C. may not continue to authorize activities that breach the promises included in the Treaty. AltaGas operates natural gas processing facilities in the Treaty 8 region of B.C., and requires continued volumes of natural gas production in this region in order to grow and sustain these developments. The Court has required B.C. to consult with Treaty 8 Nations for the purpose of establishing timely enforceable mechanisms to assess and manage the cumulative impact of industrial development on Treaty rights. These consultations, as of this writing, are proceeding. While AltaGas is optimistic that a new regulatory framework that is supportive of continued natural gas development in the Treaty 8 region will ultimately be negotiated and implemented, AltaGas cannot predict the outcomes of these negotiations and the resulting regulatory framework.
Capital Market and Liquidity Risks
AltaGas may have restricted access to capital and increased borrowing costs. As AltaGas’ future capital expenditures will be financed out of cash generated from operations, borrowings, and possible future equity sales, AltaGas’ ability to finance such expenditures is dependent on, among other factors, the overall state of capital markets and investor demand for investments in the energy industry generally and AltaGas’ securities in particular.
To the extent that external sources of capital become unavailable or available on onerous terms or otherwise limited, AltaGas’ ability to make capital investments and maintain existing assets may be impaired, and its assets, liabilities, business, financial condition, results of operations, and dividends may be materially and adversely affected as a result.
If cash flow from operations is lower than expected or capital costs for these projects exceed current estimates, or if AltaGas incurs major unanticipated expenses related to construction, development, or maintenance of its existing assets, AltaGas may be required to seek additional capital to maintain its capital expenditures at planned levels. Failure to obtain
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 62
financing necessary for AltaGas’ capital expenditure plans may result in a delay in AltaGas’ capital program or a decrease in dividends.
Washington Gas and the SPE made certain ring-fencing commitments, such that the assets of the Ring-Fenced Entities will not be available to satisfy the debt or contractual obligations of any Non-Ring-Fenced Entity.
General Economic Conditions
AltaGas’ operations are affected by the condition and overall strength of the global economy and, in particular, the economies of Canada and the U.S. During economic downturns, the demand for the products and services that AltaGas provides and the supply of or demand for power, natural gas, and NGLs may be adversely affected. The occurrence of periods of poor economic conditions or low or negative economic growth could have an adverse impact on AltaGas’ results and restrict AltaGas’ ability to make dividends to Shareholders.
Internal Credit Risk
Credit ratings affect AltaGas’ ability to obtain short-term and long-term financing and the cost of such financing. Additionally, the ability of AltaGas to engage in ordinary course derivative or hedging transactions and maintain ordinary course contracts with customers and suppliers on acceptable terms depends on AltaGas’ credit ratings.
A reduction in the current rating on AltaGas’ debt by one or more of its rating agencies below an investment grade rating would adversely affect AltaGas’ cost of financing and its access to sources of liquidity and capital.
In addition, a downgrade in AltaGas’ credit ratings may affect AltaGas’ ability to, and the associated costs to, (i) enter into ordinary course derivative or hedging transactions and may require AltaGas to post additional collateral under certain of its contracts, and (ii) enter into and maintain ordinary course contracts with customers and suppliers on acceptable terms.
Additionally, with respect to WGL, a reduction in credit rating could lead to higher borrowing costs. Merger-related commitments placed limitations on Washington Gas' ability to recover increased costs of financing from customers if caused by the ongoing affiliation of AltaGas and its affiliates. Therefore, a downgrade in AltaGas' or WGL's credit ratings could adversely affect earnings or cash flows by limiting Washington Gas’ ability to earn its allowed rate of return. Credit ratings are intended to provide investors with an independent measure of credit quality of any issuer of securities. The credit ratings assigned to AltaGas’ securities by the rating agencies are not recommendations to purchase, hold, or sell the securities in as much as such ratings do not comment as to market price or suitability for a particular investor. Any rating may not remain in effect for any given period of time or may be revised or withdrawn entirely by a rating agency in the future if in its judgment circumstances so warrant.
Foreign Exchange Risk
AltaGas' functional currency is the Canadian dollar. AltaGas is exposed to foreign exchange risk through its investments in the U.S. and is exposed to foreign exchange risk through its export business. Changes in the Canadian dollar/U.S. dollar exchange rate could impact the earnings of AltaGas, the value of the U.S. investments, and the cash generated from the U.S. businesses. AltaGas operates internationally, with an increasing amount of the Corporation’s net income earned outside of Canada. As a result, AltaGas may experience a discrepancy between the currencies in which liabilities are incurred and the currency in which revenues are generated. This could adversely affect AltaGas’ results due to the imposition of additional taxes and cost of currency exchange.
Integration of Petrogas
AltaGas acquired its controlling interest in Petrogas with the expectation that the acquisition will be accretive to certain financial metrics and result in other operational benefits, including, among other things, cost savings and operating
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 63
efficiencies. Achieving the anticipated benefits of the acquisition of Petrogas is subject to a number of uncertainties, including whether AltaGas is able to realize the anticipated growth opportunities and synergies from such integration. The overall combination of the businesses may also result in material unanticipated problems, expenses, liabilities, competitive responses and loss of customer and other business relationships. Failure to achieve the anticipated benefits or the incurrence of unanticipated expenses and liabilities could materially adversely affect AltaGas’ business, financial condition, operating results and prospects.
Debt Financing, Refinancing, and Debt Service
AltaGas relies on debt financing for some of its business activities, including capital and operating expenditures. The credit facilities and long-term senior unsecured notes have defined terms and there are no assurances that AltaGas will be able to refinance any or all of the borrowings at their maturity. In addition, there are no assurances that AltaGas will be able to comply at all times with the covenants applicable under its current borrowings, nor are there assurances that AltaGas will be able to secure new financing that may be necessary to finance its operations and capital growth program. Any failure of AltaGas to secure refinancing, to obtain new financing, or to comply with applicable covenants under its borrowings could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas' financial results, including its ability to maintain dividends to Shareholders. Further, any inability of AltaGas to obtain new financing may limit its ability to support future growth.
Borrowings or additional borrowings made by or on behalf of AltaGas will affect the leverage of the business. Interest and principal payments on such borrowings will take precedence over cash dividends and may increase the level of financial risk in the operations of AltaGas. AltaGas’ debt prohibits the payment of dividends at any time at which a default or event of default would exist under such debt, or if a default or event of default would exist as a result of paying a dividend.
If AltaGas is unable to refinance debt obligations at the time of maturity or is unable to refinance on equally favorable terms, the level of cash dividends to Shareholders may be affected. Details regarding the maturity dates of debt facilities can be found in Note 16 to AltaGas' audited Consolidated Financial Statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021.
AltaGas believes that the existing credit facilities will be sufficient for its immediate requirements and has no reason to believe that it will not be able to renew its existing credit facilities or refinance its long-term senior unsecured notes on commercially reasonable terms. However, continued uncertainty in the global economic situation means AltaGas, along with other energy companies, may have restricted access to capital and increased borrowing costs. AltaGas’ ability to raise debt is dependent upon, among other factors, the overall state of the capital markets, the quality of AltaGas’ credit ratings, and investor appetite for investments in the energy industry and AltaGas’ securities in particular. The ability to make scheduled payments on or to refinance debt obligations depends on the financial condition and operating performance of AltaGas, which is subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business, and other factors beyond its control. As a result, AltaGas may be unable to maintain a level of cash flow from operations sufficient to permit it to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on its indebtedness. These conditions could have an adverse effect on the industry in which AltaGas operates and its business, including future operating and financial results. There can be no assurance that AltaGas’ cash flow will be adequate for future financial obligations or that additional funds will be able to be obtained.
Interest Rates
AltaGas is exposed to interest rate fluctuations on variable rate debt. Interest rates are influenced by Canadian, U.S., and global economic conditions beyond AltaGas’ control and, accordingly, could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial condition and cash flow.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 64
Counterparty and supplier risk
Currently there are significant delays and disruption in global supply chains, resulting in part from mitigation strategies employed in response to COVID-19. As the global economy recovers, these supply challenges may lead to a shortage of available products and higher prices. To the extent AltaGas is unable to secure products required for its operations at acceptable pricing or at all, it may result in delays in planned operational activities and higher costs of doing business. AltaGas could also face increased exposure that contract counterparties could fail to meet their obligations to AltaGas. Such non-performance by a significant counterparty could adversely affect AltaGas' operations and financial results. To date, any cases of force majeure invoked by counterparties related to the AltaGas’ assets as a result of COVID-19 have not been material.
Technical Systems and Processes Incidents
Failure of key technical systems and processes to effectively support information requirements and business processes may lead to AltaGas’ inability to effectively and efficiently measure, record, access, analyze, and accurately report key data. This could result in increased costs and missed business opportunities.
Dependence on Certain Partners
AltaGas co-owns certain facilities with joint venture partners. Failure by the operators of these facilities to operate at the cost or in the manner projected by AltaGas could negatively affect AltaGas’ results. In addition, for non-wholly owned subsidiaries, AltaGas relies on other investors to fulfill their commitments and obligations in respect of the project or facility. AltaGas has entered into various types of arrangements with joint venture partners for any or all of the construction, operation or ownership of certain facilities. Certain of these partners may have or develop interests or objectives which are different from or even in conflict with the objectives of AltaGas. AltaGas does not have the sole power to direct the business and operations of such facilities and AltaGas faces the risk of being impacted by partners’ decisions and by potential disagreements regarding operations and other business decisions. Any such differences could have a negative impact on the success of such facilities.
Growth Strategy Risk
It is possible that the strategy AltaGas has implemented and plans to continue implementing in 2022 and onwards will not be as successful as projected. A failure to fully realize the anticipated benefits of AltaGas' strategy could have a negative impact on AltaGas' results, including causing the failure to achieve all or any targets provided in its financial guidance.
Construction and Development
The construction and development of AltaGas’ projects and their future operations are subject to changes in the policies and laws of both Canadian and U.S. federal, provincial, state, and local governments, including, without limitation, regulatory approvals and regulations relating to the environment, land use, health, culture, conflicts of interest with other parties, and other matters beyond the direct control of AltaGas.
The construction of AltaGas’ pipeline assets have experienced and may continue to experience legislative and regulatory obstacles, and the construction and operation of these assets are subject to hazards, equipment failures, supply chain disruptions, personnel issues, and related risks, which could result in decreased values of these investments, including impairments, and/or delays to their in-service dates, which would negatively affect results of operations. For instance, AltaGas is required to test certain assets for impairment on either an annual basis or when events or circumstances occur which indicate that the carrying value of such assets might be impaired. That testing might result in the impairment of assets, including goodwill, property, plant and equipment, intangible assets, or certain investments.
Because these assets are interconnected with facilities of third parties, the operation of these facilities could also be adversely affected by unexpected or uncontrollable events occurring on the systems of such third parties. These events
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 65
could further delay the in-service date of AltaGas' projects or disrupt operations on these projects, which could have an adverse effect on AltaGas’ financial results.
Transportation of Petroleum Products
AltaGas' operations include transportation by truck and rail of petroleum products, including NGLs, crude oil, and other refined products. Natural Gas Liquids are transported from natural gas producers to RIPET and Ferndale by rail and truck and are delivered to customers by marine transport. Shipments may be impacted by protests, activist activities, strikes, service delays, inclement weather, rail car availability, rail car derailment, or other transport incidents and could adversely impact volumes or the price received for product or impact its reputation or result in legal liability, loss of life or personal injury, loss of equipment or property, or environmental damage. Costs for environmental damage, damage to property, and/or personal injury in the event of a transportation incident involving petroleum products have the potential to be significant. Major Canadian railways have adopted standard contract provisions designed to shift liability for third-party claims to shippers. In the event that AltaGas is ultimately held liable for any damages resulting from its activities relating to rail or marine transport of petroleum products, and for which insurance is not available, or increased costs or obligations are imposed on AltaGas as a result of new regulations, AltaGas’ business, operations, and financial condition may be adversely impacted. In addition, in instances where transport is not available, AltaGas may not be able to procure substitute transportation and, as a result, may experience an adverse impact on its operations at RIPET, Ferndale or other assets.
Underinsured and Uninsured Losses
There can be no assurance that AltaGas will be able to obtain or maintain adequate insurance coverage at all or at rates it considers reasonable. Further, there can be no assurance that available insurance will cover all losses or liabilities that might arise in the conduct of AltaGas’ business. The occurrence of a significant uninsured claim, a claim in excess of the insurance coverage limits maintained by AltaGas, or a claim that falls within a significant self-insured retention could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business or its results. Further, significant insured claims could lead to an increased cost of operating and insuring AltaGas’ assets in the future.
Impact of Competition in AltaGas’ Businesses
AltaGas faces strong competition in its Retail Energy Marketing business. It competes with other non-regulated retail suppliers of natural gas and electricity, as well as with the commodity rate offerings of electric and gas utilities. Increases in competition, including utility commodity rate offers that are below prevailing market rates, may result in a loss of sales volumes or a reduction in growth opportunities. AltaGas’ Midstream business competes with other midstream infrastructure and energy services companies, wholesale energy suppliers, and other non-utility affiliates of regulated utilities to acquire natural gas storage and transportation assets. AltaGas’ Corporate/Other segment faces many competitors in the commercial energy systems business, including, for government customers, companies that contract with customers under Energy Savings Performance Contracting (ESPC) and other utilities providing services under UESC and, in the renewable energy market, other developers, tax equity investors, distributed generation asset owner firms and lending institutions. These competitors may have diversified energy platforms with multiple marketing approaches; broader geographic coverage, greater access to credit and other financial resources, or lower cost structures, and may make strategic acquisitions or establish alliances among themselves. There can be no assurances that AltaGas can compete successfully, and its failure to do so could have an adverse impact on AltaGas’ results of operations and cash flow.
Counterparty Credit Risk
AltaGas is exposed to credit-related losses in the event that counterparties to contracts fail to fulfill their present or future obligations to AltaGas. AltaGas has credit risk relating to, among others, counterparties to the sale, purchase, and delivery of commodity, transportation capacity, energy system design and construction, investment terms, as well as long-term
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 66
contracts including PPAs, EPAs, and take-or-pay agreements. While the majority of AltaGas’ counterparties are of investment grade quality, AltaGas can provide no assurance as to whether the credit quality of its counterparties will remain at current levels or decline. In addition, for non-wholly owned subsidiaries, AltaGas relies on other investors to fulfill their commitments and obligations in respect of the project or facility. In the event such entities fail to meet their contractual obligations to AltaGas, such failures may have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects. AltaGas mitigates these increased risks through diversification and a review process of the creditworthiness of their counterparties.
Market Risk
AltaGas is exposed to market risks resulting from fluctuations in commodity prices and interest rates, in both North American markets and, with respect to the export business, offshore markets. In these markets, commodity supply and demand is affected by a number of factors including, without limitation: the significant cost of inflation, the amount of the commodity available to specific market areas either from the wellhead or from storage facilities; prevailing weather patterns; the U.S., Canadian and Asian economies; the occurrence of natural disasters; and pipeline restrictions. In addition, the retail energy marketing business is exposed to pricing of certain ancillary services provided by the power pool in which it operates. The fluctuations in commodity prices are beyond AltaGas’ control and, accordingly, could have a material adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, financial condition, and cash flow.
Composition Risk
The extraction business is influenced by the composition of natural gas produced in the WCSB and processed at AltaGas’ facilities. The composition of the gas stream has the potential to vary over time due to factors such as the level of processing done at plants upstream of AltaGas’ facilities and the composition of the natural gas produced from reservoirs upstream of AltaGas’ facilities.
Collateral
AltaGas is able to obtain unsecured credit limits from its counterparties in order to procure natural gas and NGL supply and services for its energy services business. If counterparties’ credit exposure to AltaGas exceeds the unsecured credit limits granted, AltaGas may have to provide collateral such as letters of credit.
Rep Agreements
If AltaGas becomes insolvent or is in material default under the terms of the Rep Agreements for an extended period, effective ownership of the natural gas processing plant within Harmattan can be claimed by the original Harmattan owners for a nominal fee. Accordingly, under these circumstances, AltaGas could lose its investment in the natural gas processing plant, excluding the facilities that are owned 100 percent by AltaGas.
Market Value of Common Shares and Other Securities
AltaGas cannot predict at what price the Common Shares, Preferred Shares, or other securities issued by AltaGas will trade in the future. Common Shares, Preferred Shares, and other securities of AltaGas will not necessarily trade at values determined solely by reference to the underlying value of the Corporation’s assets. One of the factors that may influence the market price of such securities is the annual yield on such securities. An increase in market interest rates may lead purchasers of securities of AltaGas to demand a higher annual yield and this could adversely affect the market price of such securities. In addition, the market price for securities of AltaGas may be affected by announcements of new developments, changes in AltaGas’ operating results, differences between results and analysts’ expectations, changes in credit ratings, changes in general market conditions, fluctuations in the market for securities, and numerous other factors beyond the control of AltaGas.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 67
Variability of Dividends
The declaration and payment of dividends on Common Shares by AltaGas are at the discretion of the Board of Directors. The cash available for dividends to Shareholders is a function of numerous factors, including, without limitation, AltaGas’ financial performance, the impact of interest rates, electricity prices, natural gas, NGL, LNG and LPG prices, debt covenants and obligations, working capital requirements, liquidity, and future capital requirements. Dividends may be reduced or suspended entirely depending on the operations of AltaGas and the performance of its assets. The market value of AltaGas’ shares may deteriorate if AltaGas is unable to meet or otherwise chooses to modify its dividend targets, and that deterioration may be material.
Potential Sales of Additional Shares
AltaGas may issue additional shares in the future to directly or indirectly fund, among other things, capital expenditure requirements of entities now or hereafter owned directly or indirectly by AltaGas, including financing acquisitions by those entities. Such additional shares may be issued without the approval of Shareholders. Shareholders will have no pre-emptive rights in connection with such additional issuances. The Board of Directors has discretion in connection with the price and the other terms of the issue of such additional shares. Any issuance of Common Shares or securities convertible into Common Shares may have a dilutive effect on existing Shareholders.
Labor Relations
The operations and maintenance staff at the Blythe Energy Center and Younger, as well as some employees of Washington Gas and SEMCO Energy, are members of a labor union. Aspects of RIPET’s operations are also performed by employees that are members of a labor union. Labor disruptions could restrict the ability of the Blythe Energy Center to generate power, the ability of Younger to process natural gas and produce NGLs, operations at RIPET, or could affect Washington Gas and SEMCO Energy’s operations and therefore could affect AltaGas’ cash flow and net income.
Key Personnel
AltaGas’ success has been largely dependent on the skills and expertise of its key personnel. The continued success of AltaGas will be dependent on its ability to retain such personnel and to attract additional talented personnel to the organization. Access to a sustained labor market from which to attract the required expertise, knowledge, and experience is a critical factor to AltaGas’ success. Costs associated with attracting and retaining key personnel could adversely affect AltaGas’ business operations and financial results.
Risk Management Costs and Limitations
AltaGas uses derivative financial instruments to hedge risks associated with exchange rates, interest rates, and commodity price fluctuations. AltaGas does not enter into derivatives transactions for speculative purposes. AltaGas' derivative transactions cannot mitigate all risk associated with AltaGas’ business nor the risk of unauthorized activities notwithstanding appropriate oversight through AltaGas’ risk management function. Any such unauthorized activities could materially adversely affect AltaGas' business, operations, and financial condition.
Commitments Associated with Regulatory Approvals for the Acquisition of WGL
As a result of the process to obtain any consents required of each of the PSC of DC, the PSC of MD, the SCC of VA, and FERC, as well as to obtain CFIUS approval for the acquisition of WGL, AltaGas is committed to various programs, contributions, and investments in several agreements and regulatory approval orders. It is possible that AltaGas may encounter delays, unexpected difficulties, or additional costs in meeting these commitments in compliance with the terms of the relevant agreements and orders. Failure to fulfill the commitments in accordance with their terms could result in increased costs or result in penalties or fines that could materially adversely affect AltaGas’ business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 68
Cost of Providing Retirement Plan Benefits
The cost of providing retirement plan benefits to eligible current and former employees is subject to changes in the market value of AltaGas’ retirement plan assets, changing bond yields, changing demographics and changing assumptions. Any sustained declines in equity markets, reductions in bond yields, increases in health care cost trends, or increases in life expectancy of beneficiaries may have an adverse effect on AltaGas’ retirement plan liabilities, assets and benefit costs. Additionally, AltaGas may be required to increase its contributions in future periods in order to preserve the current level of benefits under the plans and/or due to U.S. federal funding requirements.
Failure of Service Providers
Certain of AltaGas’ information technology, customer service, supply chain, pipeline and infrastructure installation and maintenance, engineering, payroll, and human resources functions that AltaGas relies on are provided by third party vendors. Some of these services may be provided by vendors from centers located outside of Canada or the U.S. Services provided pursuant to these agreements could be disrupted due to events and circumstances beyond AltaGas’ control. AltaGas’ reliance on these service providers could have an adverse effect on AltaGas’ business, results of operations and financial condition.
ENVIRONMENTAL, SOCIAL AND GOVERNANCE
Values
AltaGas' core values form the foundation from which AltaGas does business with its customers, partners, and other stakeholders, and serve as a blueprint to fulfill the Company's vision and strategy. AltaGas' core values are:
▪Work Safely, Think Responsibly;
▪Act with Integrity;
▪Make Informed Decisions;
▪Achieve Results; and
▪Invest in People and Foster Diversity.
The initiatives that AltaGas is focused on to advance each ESG priority are:
•Safety and Reliability;
•Energy Affordability
•Energy Evolution
•Cybersecurity
•Diversity and Inclusion
•Culture
•Community Partnerships
AltaGas' commitment to ESG means upholding its core values and operating with purpose towards a shared mission; providing safe and reliable service; protecting the environment and minimizing its impact including actively reducing GHG emissions; investing in its people and culture; being the energy service partner of choice for its customers; investing in its communities; building long-term relationships with Indigenous Peoples, local communities, governments and regulatory bodies; ensuring sound leadership and oversight with clear roles, responsibilities and accountabilities; adhering to robust risk management practices; and being disciplined in capital deployment.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 69
In December 2021, AltaGas released its 2021 ESG Report, highlighting its 2020 performance against material ESG performance indicators and outlining a number of sustainability goals within the core areas of climate, diversity and inclusion, and safety. This report covers AltaGas’ consolidated enterprise-wide ESG performance (with the exception of Petrogas, due to the timing of the acquisition close in mid-December 2020) and presents a consolidated look at several key areas relevant to the long-term sustainability of AltaGas’ business. The ESG Report can be accessed at www.altagas.ca.
Governance
AltaGas' governance, policies, and procedures are the framework and foundation that support sound decision making. The Board oversees social and environmental strategies, initiatives, goals, and risk management, and each standing committee of the Board assists in defining ESG strategies and managing related risks within their mandates and functional areas of responsibility. For more details on the role of each standing committee, see page 16 of the ESG Report. The Board also evaluates and measures progress made towards strategy execution, including ESG initiatives, and short, medium and long-term risks to meet strategic objectives.
Policies
AltaGas has a number of policies in place with respect to environmental stewardship, health and safety, and social responsibility. Notably, AltaGas’ Code of Business Ethics (COBE) ensures it upholds its core values and conducts business in a safe, respectful, and ethical manner. The COBE and its related policies are approved by the Board. Directors, officers and employees of AltaGas, and its contractors, consultants and other representatives, are required to certify that they have read, understand and will comply with the COBE and its key policies when joining AltaGas and on an annual basis thereafter. The Board monitors compliance with the COBE and its key policies and related procedures and oversees training initiatives implemented to support compliance. Training includes specific initiatives throughout the year, based on new or updated policies or procedures or to mitigate emerging risks. With continued remote working and the evolving cybersecurity landscape, there was an increased focus on cybersecurity training in 2021, including a series of mandatory sessions for all employees. In addition, virtual training modules on a variety of topics are part of the annual COBE certification process. Modules that are introduced are informed by external and internal factors and designed to provide practical examples and guidance to ensure a deeper understanding of the COBE. AltaGas' COBE related policies include:
•Anti-Bribery and Anti-Corruption;
•Alcohol and Drug;
•Conflicts of Interest;
•Disclosure;
•Environment, Health and Safety;
•Human Rights;
•Information Security;
•Privacy;
•Respectful Workplace;
•Securities Trading and Reporting;
•Social Media and Acceptable Use; and
•Whistleblower.
Environment
Environment, Health and Safety
AltaGas' focus is on operational excellence to minimize environmental impacts throughout the lifecycle of its operations while meeting the energy needs of its customers. The Board of Directors has established the Environment, Health and
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 70
Safety Committee to review, monitor, and make recommendations to the Board of Directors regarding Environment, Health and Safety strategy, policy, compliance, and risk (including climate related risks and opportunities).
AltaGas' EHS policy guides its commitment to managing and minimizing its environmental impacts and enabling a strong, environmentally conscious culture. This includes implementing programs to safeguard the environment by proactively identifying and managing risks, using innovative technology, and applying lessons learned and best practices to improve its performance. AltaGas’ EHS Management System provides a traceable and transparent framework that can be consistently applied across its operations to drive accountability, operational excellence, and manage risk. Each business division is responsible for its internal policies and adhering to jurisdictional requirements specific to areas of operation.
To ensure AltaGas is prepared and its teams are equipped to quickly and safely respond to emergency situations, it maintains comprehensive emergency response plans for each of its facilities, and for all lines of business. It conducts regular emergency response tabletops, drills and exercises coordinated with its Incident Command System (ICS) involving first responders. These exercises offer a better understanding of each party's roles and responsibilities in the event of an emergency, resulting in a more effective response.
Environmental Regulation
AltaGas faces uncertainties related to future environmental laws and regulations affecting its business and operations. Existing environmental laws and regulations may be revised or interpreted more strictly, and new laws or regulations may be adopted or become applicable to AltaGas, which may result in increased compliance costs or additional operating restrictions, each of which could reduce AltaGas’ earnings and adversely affect AltaGas’ business.
The Midstream and Utilities segments are subject to environmental regulation pursuant to local, provincial, state, territorial, and federal legislation. Environmental legislation places restrictions and prohibitions on various substances discharged to the air, land, and water in association with certain Utilities and Midstream operations, as well as restrictions on land and water use in association with certain operations. AltaGas’ operations are required to obtain and comply with a variety of environmental licenses, permits, approvals, and registrations. In addition to the license and permit requirements, provincial, state, territorial, and federal legislation may require that end of life assets be abandoned, remediated, and reclaimed to the satisfaction of provincial, state, or territorial authorities. Failure to comply with applicable environmental legislation can result in civil or criminal penalties, environmental contamination clean-up requirements, and government orders affecting future operations. It is possible that increasingly strict environmental laws, regulations, and enforcement policies, and potential claims for damages and injuries to property, employees, other persons, and the environment resulting from current or discontinued operations, could result in substantial costs and liabilities in the future. Environmental risks from AltaGas’ operations can typically include, but are not limited to: air emissions, such as sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter and greenhouse gases; potential impacts on land; the use, storage, or release of chemicals or hydrocarbons; the generation, handling, and disposal of wastes and hazardous wastes; and water impacts. AltaGas assesses its environmental risk on an ongoing basis and strategically manages its liabilities to meet jurisdictional requirements while reducing risk exposure. AltaGas may also be subject to opposition from special interest groups resulting in regulatory process delays, which can impact schedules and increase cost.
Please also refer to the "Risk Factors – Reputation", "Risk Factors – Regulatory", "Risk Factors – Climate-Related Risks including Carbon Pricing", "Risk Factors - Changes in Laws" and "Risk Factors – Decommissioning, Abandonment, and Reclamation Costs" sections of this AIF.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 71
Climate Change
Changes in laws and regulations relating to GHG emissions could require AltaGas, in addition to complying with monitoring and reporting requirements applicable to its operations, to do one or more of the following: (i) comply with stricter emissions standards for internal combustion engines; (ii) take additional steps to control transmission and distribution system leaks; (iii) retrofit existing equipment with pollution controls or replace such equipment; or (iv) reduce AltaGas' GHG emissions or, depending on the requirements enacted, acquire emissions offsets, credits, or allowances or pay taxes on the emissions emitted in connection with its operations. AltaGas’ business could also be indirectly impacted by laws and regulations that affect its customers or suppliers to the extent such changes result in reductions in the use of natural gas by its customers or limit the operations of or increase the costs of goods and services acquired from AltaGas suppliers.
Certain climate change regulations specific to AltaGas’ business segments are discussed under the sections "Business of the Corporation – Utilities Business – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Utilities Business", "Business of the Corporation – Midstream Business – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Midstream Business", and "Business of the Corporation – Corporate/Other – Environmental Regulations Impacting the Corporate/Other Business" of this AIF.
Social
Indigenous Groups
AltaGas recognizes the value of building enduring, trusting, and mutually beneficial relationships with Indigenous Peoples. In 2021, AltaGas enacted an Indigenous Engagement Guideline to ensure in applying a consistent approach to engagement practices, areas of focus for economic and social benefit, and record keeping. As part of AltaGas' engagement, the Company may enter into agreements with Indigenous Peoples. These agreements range from short-term arrangements enabling Indigenous Peoples to learn more about AltaGas' proposed developments and participate in regulatory processes, to agreements that define how AltaGas and Indigenous communities can collaborate over the long-term. AltaGas' longer-term initiatives include training, employment, contracting, supplier procurement, environmental protection, and community investment.
Communities
AltaGas operates in many diverse jurisdictions and recognizes that each community has unique needs. To meet each community's individual needs, AltaGas strives to build long-term collaborative relationships that are based on trust and a willingness to listen, learn and adapt. AltaGas' commitment to communities is visible through several programs including:
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 72
| Program | Description | ||||
| Community Investment | •AltaGas’ corporate giving is focused on three pillars: healthy and safe communities, bright futures, and environmental champions. •AltaGas contributed through direct financial contributions, volunteer time and in-kind donations to charitable organizations across operating regions. •The focus in 2021 was to help communities with food security. Meeting the basic needs of food security is a common concern across all our jurisdictions with demand rising through the pandemic. | ||||
Energy affordability and assistance programs for customers | •Utilities provide energy assistance and affordability programs through direct programming and gifts of warmth. | ||||
| Workforce training development and employment opportunities | •AltaGas is committed to training and hiring locally, leading to a workforce that reflects the diversity of the communities where it operates. •AltaGas has developed and funded workforce training programs to provide opportunities for local participants to gain skills in the energy sector. | ||||
Public awareness and safety programs | •AltaGas conducts regular emergency response tabletops, drills and exercises that involve first responders so that the Company and communities can collectively respond more effectively. •Customer outreach, education and public information campaigns relating to pipeline safety and damage prevention. | ||||
Building economic value within local communities through business development and contracting opportunities | •AltaGas incorporates diverse supplier practices to enhance opportunities for local diverse communities to participate through the supply of goods and services. •To expand the reach of programs, AltaGas partners with Indigenous communities, external supplier diversity organizations, chambers and community based advisory boards. AltaGas leverages these groups to identify and source new diverse suppliers, enhance the visibility of new developments in the supply base, and maintain a strong network with influential leaders in the sector. | ||||
Employee engagement through volunteerism and giving | •AltaGas Cares is the tool which empowers employees to support the causes they are passionate about in their communities through donations and volunteering. •As part of AltaGas Cares, a $250 match is provided to each employee through the "Dollars for Dollars" and "Dollars for Doers" programs. | ||||
Workforce
AltaGas' people are the heart of the Company and are key to delivering operational excellence. Spanning North America, AltaGas' diverse workforce of approximately 3,000 employees is guided by one set of Core Values and a common mission. This connection to a common set of principles provides the basis for how AltaGas does business and executes its strategic priorities. AltaGas' model for a high-performance culture is based on attracting, developing, and retaining great people. AltaGas invests in its people through talent development, diversity and inclusion initiatives and engagement strategies.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 73
DIVIDENDS
Dividends are declared at the discretion of the Board of Directors and dividend levels are reviewed periodically by the Board of Directors, giving consideration to the ongoing sustainable cash flow as impacted by the consolidated net income, maintenance and growth capital and debt repayment requirements of AltaGas. The Corporation targets to pay a portion of its ongoing cash flow through regular monthly dividends made to Shareholders.
During 2021, AltaGas paid cash dividends on the Common Shares monthly. On December 3, 2021, AltaGas announced that effective March 31, 2022, common share dividends will be declared and paid on a quarterly basis, instead of monthly. Dividends on the Series A Shares, Series B Shares, Series C Shares, Series E Shares, Series G Shares, Series H, and Series K Shares are paid quarterly.
AltaGas’ payment of dividends may be limited by covenants under its credit agreements, including, without limitation, in circumstances when a default or event of default exists or would be reasonably expected to exist upon or as a result of making such dividend payment. In the event of liquidation, dissolution, or winding-up of AltaGas, the preferred shareholders have priority in the payment of dividends over the common shareholders.
The table below shows the cash dividends paid by AltaGas on Common Shares and Preferred Shares for the three most recently completed financial years and the cash dividends paid by Washington Gas on Washington Gas Preferred Shares for the period from the close of the WGL Acquisition until redemption on December 20, 2019.
$ per share | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||
Common Shares | 1.082900 | 0.963300 | 0.960000 | ||||||||
Series A Shares | 0.765000 | 0.825000 | 0.845000 | ||||||||
Series B Shares | 0.694360 | 0.894890 | 1.084641 | ||||||||
Series C Shares (1) | 1.322500 | 1.322500 | 1.322500 | ||||||||
Series E Shares | 1.348252 | 1.348252 | 1.348252 | ||||||||
Series G Shares | 1.060500 | 1.060500 | 1.155750 | ||||||||
Series H Shares | 0.794372 | 0.994890 | 0.296040 | ||||||||
Series I Shares (2) | — | 1.312500 | 1.312500 | ||||||||
Series K Shares | 1.250000 | 1.250000 | 1.250000 | ||||||||
Washington Gas $4.25 Series (1) | — | — | 2.125000 | ||||||||
Washington Gas $4.80 Series (1) | — | — | 2.400000 | ||||||||
Washington Gas $5.00 Series (1) | — | — | 2.500000 | ||||||||
(1)Amounts disclosed are in U.S. dollars. Washington Gas preferred shares were redeemed on December 20, 2019.
(2)Series I shares were redeemed on December 31, 2020.
▪On December 3, 2021, AltaGas announced that its Board of Directors approved a 6 percent increase to its annual common share dividends. Concurrently, AltaGas is moving from a monthly to quarterly payment schedule with dividends expected to be paid in March, June, September and December of the 2022 calendar year at the rate of $0.265 per common share ($1.06 per common share annually). This change will be effective for the March dividend that will be paid on March 31, 2022.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 74
MARKET FOR SECURITIES
The following chart provides the reported high and low trading prices and volume of Common Shares, traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA, traded by month from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 20.21 | 18.75 | 13,650,533 | ||||||||
February | 20.06 | 19.21 | 16,480,155 | ||||||||
March | 21.39 | 19.26 | 19,782,128 | ||||||||
April | 22.97 | 20.92 | 16,131,623 | ||||||||
May | 24.24 | 23.19 | 20,325,718 | ||||||||
June | 26.33 | 24.07 | 16,320,422 | ||||||||
July | 26.54 | 25.83 | 11,265,334 | ||||||||
August | 26.63 | 24.89 | 11,146,512 | ||||||||
September | 26.20 | 24.98 | 13,990,276 | ||||||||
October | 26.78 | 24.94 | 14,147,393 | ||||||||
November | 25.75 | 24.30 | 15,464,598 | ||||||||
December | 27.31 | 24.26 | 26,939,551 | ||||||||
Series A Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.A. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series A Shares from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 16.32 | 14.07 | 812,674 | ||||||||
February | 17.50 | 16.18 | 257,495 | ||||||||
March | 17.64 | 17.16 | 228,058 | ||||||||
April | 18.57 | 17.19 | 340,098 | ||||||||
May | 19.20 | 18.40 | 91,456 | ||||||||
June | 19.75 | 19.00 | 86,243 | ||||||||
July | 19.40 | 18.69 | 84,435 | ||||||||
August | 20.14 | 19.25 | 144,707 | ||||||||
September | 20.20 | 19.60 | 89,117 | ||||||||
October | 20.95 | 20.00 | 104,063 | ||||||||
November | 21.35 | 20.69 | 84,332 | ||||||||
December | 20.70 | 19.48 | 41,596 | ||||||||
Series B Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.B. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series B Shares for the period from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 15.60 | 13.50 | 42,900 | ||||||||
February | 16.70 | 15.36 | 83,945 | ||||||||
March | 16.77 | 16.26 | 145,313 | ||||||||
April | 17.65 | 16.51 | 20,858 | ||||||||
May | 18.44 | 17.43 | 8,165 | ||||||||
June | 19.27 | 17.53 | 59,106 | ||||||||
July | 19.11 | 18.23 | 45,918 | ||||||||
August | 18.64 | 18.15 | 24,600 | ||||||||
September | 18.85 | 18.33 | 22,018 | ||||||||
October | 19.95 | 18.90 | 18,823 | ||||||||
November | 20.64 | 19.99 | 15,443 | ||||||||
December | 20.05 | 19.00 | 43,100 | ||||||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 75
Series C Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.U. The following table sets forth the monthly price range (in US dollars) and volume traded for Series C Shares from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 20.61 | 18.75 | 89,584 | ||||||||
February | 21.00 | 19.81 | 129,271 | ||||||||
March | 21.82 | 20.70 | 189,650 | ||||||||
April | 22.89 | 21.40 | 150,808 | ||||||||
May | 23.60 | 22.98 | 156,468 | ||||||||
June | 24.00 | 23.30 | 147,659 | ||||||||
July | 24.38 | 23.62 | 132,878 | ||||||||
August | 24.80 | 24.28 | 437,737 | ||||||||
September | 24.99 | 23.92 | 145,743 | ||||||||
October | 25.05 | 24.40 | 242,336 | ||||||||
November | 25.00 | 24.55 | 110,499 | ||||||||
December | 24.75 | 24.35 | 130,040 | ||||||||
Series E Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.E. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series E Shares from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 20.92 | 19.23 | 317,504 | ||||||||
February | 21.73 | 20.69 | 360,466 | ||||||||
March | 22.81 | 21.40 | 228,290 | ||||||||
April | 23.35 | 21.88 | 98,889 | ||||||||
May | 24.39 | 23.10 | 273,479 | ||||||||
June | 24.90 | 24.27 | 212,775 | ||||||||
July | 25.11 | 24.44 | 404,455 | ||||||||
August | 25.19 | 24.78 | 383,701 | ||||||||
September | 25.87 | 24.96 | 452,721 | ||||||||
October | 26.68 | 25.27 | 217,345 | ||||||||
November | 26.60 | 25.33 | 158,858 | ||||||||
December | 25.91 | 24.60 | 109,896 | ||||||||
Series G Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.G. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series G Shares from January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 19.74 | 18.09 | 502,673 | ||||||||
February | 20.25 | 19.27 | 100,306 | ||||||||
March | 20.45 | 19.95 | 169,111 | ||||||||
April | 21.60 | 20.30 | 60,244 | ||||||||
May | 22.96 | 21.60 | 140,540 | ||||||||
June | 23.58 | 22.53 | 79,533 | ||||||||
July | 23.39 | 22.62 | 93,055 | ||||||||
August | 24.03 | 23.36 | 93,864 | ||||||||
September | 24.30 | 23.90 | 93,476 | ||||||||
October | 25.26 | 24.31 | 68,237 | ||||||||
November | 25.12 | 24.40 | 310,550 | ||||||||
December | 24.60 | 23.59 | 67,131 | ||||||||
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 76
Series H Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.H. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series H Shares for the period of January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 16.88 | 14.83 | 8,194 | ||||||||
February | 17.75 | 16.88 | 37,772 | ||||||||
March | 17.75 | 17.50 | 12,661 | ||||||||
April | 19.00 | 17.55 | 28,007 | ||||||||
May | 20.45 | 19.70 | 44,192 | ||||||||
June | 22.06 | 20.45 | 15,802 | ||||||||
July | 22.06 | 20.00 | 12,547 | ||||||||
August | 21.80 | 20.00 | 60,400 | ||||||||
September | 22.14 | 21.80 | 86,900 | ||||||||
October | 23.96 | 22.90 | 20,133 | ||||||||
November | 24.00 | 23.00 | 30,200 | ||||||||
December | 23.00 | 23.00 | 23,000 | ||||||||
Series K Shares are traded on the TSX under the symbol ALA.PR.K. The following table sets forth the monthly price range and volume traded for Series K Shares for the period of January to December 2021 as reported by the TSX:
Month | High | Low | Volume Traded | ||||||||
January | 24.60 | 24.60 | 244,184 | ||||||||
February | 24.95 | 24.95 | 150,021 | ||||||||
March | 24.96 | 24.96 | 196,969 | ||||||||
April | 25.13 | 25.13 | 105,050 | ||||||||
May | 25.30 | 25.30 | 257,979 | ||||||||
June | 25.23 | 25.23 | 172,404 | ||||||||
July | 25.25 | 25.25 | 143,552 | ||||||||
August | 25.25 | 25.25 | 192,318 | ||||||||
September | 25.09 | 25.09 | 153,637 | ||||||||
October | 25.33 | 25.33 | 160,163 | ||||||||
November | 25.00 | 25.00 | 76,115 | ||||||||
December | 25.33 | 25.00 | 89,944 | ||||||||
On December 31, 2020, AltaGas redeemed all of its outstanding Series I preferred shares. On February 16, 2022, AltaGas announced that it intends to redeem all of its outstanding Series K Preferred Shares on March 31, 2022 for a redemption price equal to $25.00 per Series K share.
CREDIT RATINGS
Credit ratings are intended to provide investors with an independent measure of credit quality of an issue of securities and are indicators of the likelihood of payment and of the capacity and willingness of a company to meet its financial commitment on an obligation in accordance with the terms of an obligation. This information concerning AltaGas’ credit ratings relates to AltaGas’ financing costs, liquidity, and operations. The availability of AltaGas’ funding options may be affected by certain factors, including the global capital markets environment and outlook as well as AltaGas’ financial performance. AltaGas’ access to capital markets at competitive rates is influenced by credit ratings and rating outlook, as determined by credit rating agencies such as S&P, Fitch, and Moody's, and if AltaGas’ ratings were downgraded, AltaGas’ financing costs and future debt issuances could be unfavorably impacted.
S&P, Fitch, and Moody's are rating agencies that provide credit ratings. Ratings for debt instruments from S&P, and Fitch range from a high of AAA to a low of D. Moody's ratings for debt instruments range from a high of AAA to a low of C. S&P,
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 77
and Fitch also provide credit ratings for preferred shares. S&P ratings for preferred shares range from a high of P-1 to a low of D. Fitch ratings for preferred shares range from a high of AAA to a low of D.
The below table summarizes the most recent credit ratings for AltaGas and subsidiaries:
| Entity | Rating Agency | Debt Rated | Most Recent Rating | Comments | ||||||||||
| AltaGas | Standard & Poor's (S&P) | Issuer rating | BBB- | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||
| Senior unsecured | BBB- | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||||
| Preferred shares and Junior Subordinated | P-3 / BB | Last reviewed December 20, 2021, Junior Subordinated added on January 5, 2022. | ||||||||||||
| Fitch Ratings (Fitch) | Issuer | BBB | Affirmed on March 31, 2021. | |||||||||||
| Preferred shares and Junior Subordinated | BB+ | Affirmed on March 31, 2021, Junior Subordinated added on January 5, 2022. | ||||||||||||
| Washington Gas | S&P | Issuer and unsecured debt | A- | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||
| Commercial paper | A-2 | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||||
| Fitch | Issuer | A- | Affirmed on April 3, 2020. | |||||||||||
| WGL | S&P | Issuer | BBB- | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||
| Senior unsecured | BB+ | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||||
| Commercial paper | A-3 | Last reviewed December 20, 2021. | ||||||||||||
| Fitch | Issuer | BBB | Affirmed on April 3, 2020. | |||||||||||
| SEMCO | Moody's | Long-term issuer | A3 | Raised from Baa1 to A3 on January 22, 2021 with stable outlook. | ||||||||||
| Senior secured notes | A1 | Raised from A2 to A1 on January 22, 2021 with stable outlook. | ||||||||||||
| S&P | Long-term issuer | BBB | Last reviewed May 21, 2021. | |||||||||||
| Senior secured notes | A- | Last reviewed May 21, 2021. | ||||||||||||
According to the S&P rating system, an obligor rated BBB has adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitments. The ratings from AA to CCC may be modified by the addition of a plus (+) or minus (-) sign to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
According to the Fitch rating system, ‘BBB’ ratings indicate that expectations of default risk are currently low. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate, but adverse business or economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity.
According to the Moody’s rating system, A3 ratings indicate low credit risk. Obligations rated A3 are considered upper-medium grade.
A P-3 rating by S&P is the third highest of eight categories granted by S&P under its Canadian preferred share rating scale and a P-3 rating directly corresponds with a BB rating under its global preferred rating scale. The Canadian preferred share rating scale is fully determined by the global preferred rating scale and there are no additional analytical criteria associated with the determination of ratings on the Canadian preferred share rating scale. According to the S&P rating system, while securities rated P-3 are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, they are less vulnerable to non-payment than other speculative issues. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions which could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation. The ratings from P-1 to P-5 may be modified by "high" and "low" grades which indicate relative standing within the major rating categories.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 78
A ‘BB’ rating by Fitch indicates an elevated vulnerability to default risk, particularly in the event of adverse changes in business or economic conditions over time; however, business or financial flexibility exists that support the servicing of financial commitments.
A P-2 rating by Moody's is the second highest of four categories granted by Moody's under its global short-term rating scale. According to the Moody's rating definitions, issuers rated P-2 have a strong ability to repay short-term debt obligations. P-2 ratings generally correspond with A2 to Baa2 under the long-term rating scale.
The credit ratings accorded to the securities by the rating agencies are not recommendations to purchase, hold, or sell the securities in as much as such ratings do not comment as to market price or suitability for a particular investor. There is no assurance that any rating will remain in effect for any given period of time or that any rating will not be revised or withdrawn entirely by a rating agency in the future if, in its judgment, circumstances so warrant.
Except as set forth above, none of S&P, Fitch, nor Moody's has announced that it is reviewing or intends to revise or withdraw the ratings on AltaGas.
AltaGas provides an annual fee to S&P, Fitch, and Moody's for credit rating services. AltaGas has paid each of S&P, Fitch, and Moody's its respective fees in connection with the provision of the above ratings. Over the past two years, in addition to the aforementioned fees, AltaGas has made payments in respect of certain other services provided to the Corporation by S&P, Fitch, and Moody's.
MATERIAL CONTRACTS
Except for contracts entered into in the ordinary course of business, the only material contracts entered into by AltaGas within the most recently completed financial year, or before the most recently completed financial year but which are still material and are still in effect, are the following:
▪The trust indenture between AltaGas and Computershare Trust Company of Canada dated July 1, 2010, as supplemented, related to the issuance and sale of MTNs pursuant to AltaGas’ medium term note program;
▪The trust indenture between AltaGas and Computershare Trust Company of Canada dated September 26, 2017, as supplemented, related to the issuance and sale of MTNs pursuant to AltaGas’ medium term note program;
▪The letter agreement dated October 15, 2020 among AIJVLP, SAM and Petrogas, related to AltaGas' acquisition of SAM's approximately 37 percent interest in Petrogas; and
▪The Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated May 4, 2021 among AltaGas Ltd., AltaGas Services (U.S.) Inc., Royal Bank of Canada as agent and certain financial institutions as lenders.
Copies of each of these documents have been filed on SEDAR at www.sedar.com.
INTEREST OF MANAGEMENT AND OTHERS IN MATERIAL TRANSACTIONS
AltaGas is not aware of any material interest, direct or indirect, of any director or officer of AltaGas, any director or officer of a corporation that is an insider or subsidiary of AltaGas, or any other insider of AltaGas, or any associate or affiliate of any such person, in any transaction since the commencement of AltaGas’ last three completed financial years, or in any proposed transaction, that has materially affected or would materially affect AltaGas or any of its subsidiaries.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 79
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
AltaGas is not aware of any material legal proceedings to which the Corporation or its affiliates are party or to which their property is subject during AltaGas’ most recently completed financial year and AltaGas is not aware of any such material legal proceedings being contemplated. See “Risk Factors – Litigation”.
REGULATORY ACTIONS
AltaGas is not aware of any (i) penalties or sanctions imposed against it by a court relating to securities legislation or by a securities regulatory authority during its most recently completed financial year, or (ii) other penalties or sanctions imposed by a court or regulatory body against it that would likely be considered important to a reasonable investor in making an investment decision. There were no settlement agreements entered into by AltaGas before a court relating to securities legislation or with a securities regulatory authority during AltaGas’ most recently completed financial year.
INTERESTS OF EXPERTS
The auditors of the Corporation are Ernst & Young LLP, Chartered Accountants, 2200 – 215 2nd Street SW, Calgary, Alberta T2P 1M4. Ernst & Young LLP is independent in accordance with the Rules of Professional Conduct as outlined by the Chartered Professional Accountants of Alberta.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Additional information, including, without limitation, directors’ and officers’ remuneration and indebtedness, principal holders of AltaGas’ securities, Share Options, and interests of insiders in material transactions, where applicable, is contained in AltaGas’ management information circular for AltaGas’ most recent annual meeting of Shareholders that involved the election of directors.
Additional financial information is contained in AltaGas’ audited Consolidated Financial Statements as at and for the year ended December 31, 2021 and Management’s Discussion and Analysis for the year ended December 31, 2021.
The Corporation routinely files all required documents through the SEDAR system and on its own website. Internet users may retrieve such material through the SEDAR website www.sedar.com. AltaGas’ website is located at www.altagas.ca, but AltaGas’ website is not incorporated by reference into this AIF.
TRANSFER AGENTS AND REGISTRARS
The registrar and transfer agent for the Common Shares and the Preferred Shares is Computershare Investor Services Inc., Home Oil Tower 800, 324-8th Avenue SW, Calgary, Alberta T2P 2Z2, Tel: 1-800-564-6253.
The registrar and trustee for AltaGas’ MTNs is Computershare Trust Company of Canada, Home Oil Tower 800, 324-8th Avenue SW, Calgary, Alberta T2P 2Z2, Tel: 1-800-564-6253.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 80
METRIC CONVERSION
The following table sets forth certain standard conversions between Standard Imperial Units and the International System of Units (or metric units).
To Convert From | To | Multiply by | To Convert From | To | Multiply by | |||||||||||||||
Mcf | cubic meters | 28.174 | feet | meters | 0.305 | |||||||||||||||
cubic meters | cubic feet | 35.494 | meters | feet | 3.281 | |||||||||||||||
Bbls | cubic meters | 0.159 | miles | km | 1.609 | |||||||||||||||
cubic meters | Bbls | 6.29 | km | miles | 0.621 | |||||||||||||||
tonnes | long tons | 0.98 | gigajoule | Mcf | 0.9482 | |||||||||||||||
metric tonnes | Bbls (propane) | 12.40 | metric tonnes | Bbls (butane) | 10.90 | |||||||||||||||
GLOSSARY
Unless the context otherwise requires, terms used in this AIF have the following meanings and references to agreements include any amendments, restatements, modifications, or supplements in effect as of the date hereof:
"ACI" means AltaGas Canada Inc., which has since been renamed TriSummit Utilities Inc.;
"AER" means the Alberta Energy Regulator;
"AESO" means the Alberta Electric System Operator;
"AIF" means this Annual Information Form;
"AIJVLP" means AltaGas Idemitsu Joint Venture Limited Partnership;
"AltaGas", the "Company", or the "Corporation" means AltaGas Ltd., including, where the context requires, the affiliates of AltaGas Ltd.;
"ARB" means the California Air Resources Board;
"AMP" means Arrearage Management Plan;
"ARPA Funds" means American Rescue Plan Act Funds;
"ASC" means the Alberta Securities Commission;
"B.C." or "BC" means the province of British Columbia in Canada;
"Bbls" means stock tank barrels of ethane and other NGLs, expressed in standard 42 U.S. gallon barrels or 34.972 imperial gallon barrels;
"Bbls/d" means Bbls per day;
"Bcf" means billion cubic feet or 1,000,000 Mcf of natural gas;
"Bcf/d" means Bcf per day;
"Birchcliff" means Birchcliff Energy Ltd.;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 81
"Black Swan" means Black Swan Energy Ltd.;
"Blair Creek facility" means the Blair Creek processing facility located approximately 140 km northwest of Fort St. John, British Columbia, owned by AltaGas’ indirect wholly-owned subsidiary AltaGas Northwest Processing Limited Partnership;
"Blythe" means Blythe Energy Inc.;
"Blythe Energy Center" means the 507 MW gas-fired generation facility located near Blythe, California, together with the related 67 miles transmission lines, owned by AltaGas’ indirect wholly-owned subsidiary Blythe;
"Board of Directors" means the board of directors of AltaGas, as from time to time constituted;
"Brush II" means the 70 MW gas-fired generation facility in Colorado, owned by AltaGas’ indirect wholly-owned subsidiary AltaGas Brush Energy Inc., which is pending sale;
"C&I" means commercial and industrial;
"CAISO" means the California Independent System Operator;
"CARES Act" means Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act;
"CBCA" means the Canada Business Corporations Act, R.S.C. 1985, c. C 44, as amended from time to time, including the regulations from time to time promulgated thereunder;
"CCAA" means the Companies’ Creditors Arrangement Act, R.S.C. 1985, c. C 36, as amended from time to time, including the regulations from time to time promulgated thereunder;
"CCEMA" means the Climate Change and Emissions Management Act, S.A. 2003, C-16.7, as amended from time to time, including the regulations from time to time promulgated thereunder;
"CCIR" means the Carbon Competitiveness Incentive Regulation, A.R. 255/2017 under the CCEMA, as amended from time to time;
"Central Penn" means the Central Penn pipeline, a 185-mile pipeline originating in Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania and extending to Lancaster County, Pennsylvania;
"CFIUS" means the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States;
"CINGSA" means Cook Inlet Natural Gas Storage Alaska, LLC;
"CINGSA Storage facility" means the in-field storage facility in the Cook Inlet area of Alaska owned and operated by CINGSA;
"CN" means Canadian National Railway Company;
"CO2" means carbon dioxide;
"CO2e" means carbon dioxide equivalent;
"Common Shares" means common shares of AltaGas Ltd.;
"Constitution" means Constitution Pipeline Company, LLC, an entity formed to create a pipeline to transport natural gas from the Marcellus region in northern Pennsylvania to northeastern markets;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 82
"COVID-19" means the 2019 novel coronavirus;
"CPI" means the Consumer Price Index;
"Degree Day" means the amount that the daily mean temperature deviates below 65 degrees Fahrenheit at SEMCO Gas, ENSTAR, and Washington Gas, such that a one degree difference equates to one Degree Day;
"Dekatherm (Dth)" means 10 Therms;
"DOEE" means the Department of Energy and Environment;
"EEEP" means the Edmonton ethane extraction plant and related facilities, AltaGas’ interest being owned by its indirect wholly-owned subsidiary AltaGas Extraction and Transmission Limited Partnership;
"EH&S Committee" means the Environment, Health and Safety Committee of the Board of Directors;
"EHS Management System" means AltaGas’ Environmental, Health & Safety Management System;
"Enerchem" means Enerchem International Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Petrogas;
"ENSTAR" means the natural gas distribution business conducted by SEMCO Energy in Alaska under the name ENSTAR Natural Gas Company;
"EPA" means electricity purchase agreement;
"EQM" means EQM Gathering Opco, LLC;
"EQT" means EQT Midstream Partners, LP;
"ERM" means Enterprise Risk Management;
"ESG" means Environment, Social & Governance;
"EWR" means Energy Waste Reduction;
"FERC" means the United States Federal Energy Regulatory Commission;
"Ferndale terminal" means the storage, distribution, and export facility for bulk shipments of propane, and butane located on the west coast near Ferndale, Washington, and owned by a subsidiary of Petrogas;
"Fitch" means Fitch Ratings Inc.;
"Fixed-to-Fixed Rate Subordinated Notes, Series 1" means the 5.25 percent Fixed-to-Fixed Rate Subordinated Notes, Series 1 of AltaGas;
"FRM" means formula rate methodology;
"g" means grams;
"GHG" means greenhouse gas;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 83
"Gordondale facility" means the Gordondale Gas processing facility in the Gordondale area of the Montney reserve area approximately 100 km northwest of Grande Prairie, Alberta, owned by AltaGas’ indirect wholly-owned subsidiary AltaGas Northwest Processing Limited Partnership;
"GSAs" means Groundwater Sustainability Agencies;
"Hampshire" or "Hampshire Gas" means Hampshire Gas Company, a subsidiary of WGL that provides regulated interstate natural gas storage services to Washington Gas under a FERC approved interstate storage service tariff;
"Harmattan" means the combined Harmattan gas processing facility and extraction plant and associated facilities, owned by AltaGas’ indirect wholly-owned subsidiary Harmattan Gas Processing Limited Partnership;
"HE" means Hearing Examiner;
"Idemitsu" means Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd.;
"IRIP" means the Infrastructure Reliability Improvement Program;
"JEEP" means the Joffre ethane extraction plant and related facilities;
"Kelt" means Kelt Exploration (LNG) Ltd;
"km" means kilometer;
"kWh" means kilowatt hour;
"LNG" means liquefied natural gas;
"LPG" means liquefied petroleum gas;
"Marquette Connector Pipeline" means the recently completed pipeline that is owned and operated by SEMCO Gas and connects the Great Lakes Gas Transmission pipeline to the Northern Natural Gas pipeline in Marquette, Michigan;
"Mcf" means a thousand cubic feet of natural gas at standard imperial conditions of measurement;
"Mcf/d" means Mcf per day;
"MDth" means millions of Dekatherms;
"MD OPC" means Maryland Office of People's Counsel
"Merger Agreement" means the agreement and plan of merger dated as of January 25, 2017, among AltaGas, Merger Sub and WGL;
"Merger Sub" means Wrangler Inc., a Virginia corporation and an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of AltaGas;
"MGP" means manufactured gas plant;
"Mmcf" means a million cubic feet of natural gas at standard conditions of measurement;
"Mmcf/d" means Mmcf per day;
"Moody's" means Moody's Investor Service;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 84
"Mountain Valley" or "MVP" means Mountain Valley pipeline, an equity investment of Washington Gas Resources;
"MPSC" means the Michigan Public Service Commission;
"MRP" means Main Replacement Program;
"MTN" means medium term notes issued from time to time under either the amended and restated trust indenture dated July 1, 2010 between AltaGas and Computershare Trust Company of Canada, as further amended, restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time or the trust indenture dated September 26, 2017 between AltaGas and Computershare Trust Company of Canada, as amended, restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, as the case may be;
"MW" means megawatt; one MW is 1,000,000 watts; the watt is the basic electrical unit of power;
"MWh" means megawatt-hour or 1,000,000 watt-hours; the watt-hour is equal to one watt of power flowing steadily for one hour;
"NAESB" means North American Energy Standards Board;
"NEBC" means Northeast British Columbia;
"NFA" means No Further Action;
"NGL" or "NGLs" means natural gas liquids, which includes primarily propane, butane, and condensate;
"NGTL" means NOVA Gas Transmission Ltd.;
"Non-Ring-Fenced Entities" means AltaGas and its affiliates other than Washington Gas and the SPE;
"NGQSS" means Natural Gas Quality of Service Standards
"North Pine facility" means the NGL separation facility, located approximately 40 km northwest of Fort St. John, British Columbia.
"North Pine pipelines" means two eight-inch diameter NGL supply pipelines, each approximately 40 km in length, which run from the existing Alaska Highway truck terminal to the North Pine facility;
"Northwest Hydro facilities" means the three previously owned run-of-river hydroelectric facilities in northwest British Columbia;
"Nova Chemicals" means NOVA Chemicals Corporation;
"NOx" means nitrogen oxides;
"NTSB" means the National Transportation Safety Board;
"O2" means oxygen;
"PEEP" means the Pembina Empress extraction plant and related facilities;
"Pembina" means Pembina Infrastructure and Logistics LP;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 85
"Petrogas" means Petrogas Energy Corp., a North American integrated midstream company in which AltaGas acquired a controlling interest on December 15, 2020;
"Petrogas Acquisition" means AltaGas' acquisition of a controlling interest in Petrogas on December 15, 2020;
"Plan" means the Premium DividendTM, Dividend Reinvestment, and Optional Cash Purchase Plan of the Corporation;
"Pomona" means the 44.5 MW gas-fired generation facility located in Pomona, California, which was sold during 2020;
"Pool" means the scheme operated by the AESO for (i) exchanges of electric energy, and (ii) financial settlement for the exchange of electric energy;
"PPA" means power purchase agreement;
"Preferred Shares" means the preferred shares of AltaGas Ltd. as a class, including, without limitation, the Series A Shares, Series B Shares, Series C Shares, Series E Shares, Series G Shares, Series H Shares, Series I Shares, Series K Shares, and Fixed-to-Fixed Rate Subordinated Notes, Series 1;
"PROJECTpipes" means Washington Gas' 40-year accelerated pipeline replacement program, that was launched in 2014 in the District of Columbia and is designed to enhance the safety and reliability of its system;
"PRPA" means Prince Rupert Port Authority;
"PSC of DC" means the Public Service Commission of the District of Columbia;
"PSC of MD" means the Maryland Public Service Commission;
"PULJ" means the Public Utility Law Judge;
"Put Notice" means the notice received by AIJVLP from SAM of its exercise of a put option with respect to its approximate one-third interest in Petrogas;
"Put Option" means the put option with respect to SAM's approximate one-third interest in Petrogas;
"RCA" means the Regulatory Commission of Alaska;
"Rep Agreements" mean the Representation, Management and Processing Agreements at Harmattan;
"RELIEF Act" means the Recovery for the Economy, Livelihoods, Industries, Entrepreneurs and Families Act;
"Ring-Fenced Entities" means Washington Gas and the SPE;
"RIPET" means the Ridley Island Propane Export Terminal, the propane export terminal constructed by AltaGas' subsidiary, Ridley Island LPG Export Limited Partnership, to ship up to 1.2 million tonnes of propane per annum and to be located on a portion of land leased by Ridley Terminals Inc. from the PRPA, located on Ridley Island, near Prince Rupert, British Columbia;
"Ripon" means the 49.5 MW gas-fired generation facility in Ripon, California, which was sold during 2020;
"ROE" means return on equity;
"Royal Vopak" means Koninklijke Vopak N.V., a public company incorporated under the laws of the Netherlands;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 86
"RTI" means Ridley Terminals Inc.;
"S&P" means Standard & Poor's Ratings Services and its successors;
"SAM" means Sam Holdings Ltd.;
"Sarbanes-Oxley" means the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002;
"SAVE" means Steps to Advance Virginia's Energy Plan;
"SCC of VA" means the Commonwealth of Virginia State Corporation Commission;
"SCE" means Southern California Edison Company;
"SEDAR" means System for Electronic Document Analysis and Retrieval, at www.sedar.com;
"SEMCO Energy" means SEMCO Energy, Inc.;
"SEMCO Gas" means the Michigan natural gas distribution business conducted by SEMCO Energy in Michigan under the name SEMCO Energy Gas Company;
"Series A Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series A, of AltaGas;
"Series B Shares" means the cumulative redeemable floating rate preferred shares, Series B, of AltaGas
"Series C Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series C, of AltaGas (US dollar);
"Series E Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series E, of AltaGas;
"Series G Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series G, of AltaGas;
"Series H Shares" means the cumulative redeemable floating rate preferred shares, Series H, of AltaGas;
"Series I Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year minimum fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series I, of AltaGas, which were redeemed by AltaGas on December 31, 2020;
"Series K Shares" means the cumulative redeemable 5-year minimum fixed rate reset preferred shares, Series K, of AltaGas, which are to be redeemed by AltaGas on March 31, 2022;
"SGMA" means the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act;
"Share Options" means options to acquire Common Shares granted pursuant to AltaGas' share option plan;
"Shareholders" mean the holders of Common Shares;
"Shell Energy" means Shell Energy North America (US), LP;
"SOS" means Standard offer Service;
"SPE" means Wrangler SPE LLC, a wholly-owned special purpose entity subsidiary of WGL incorporated as a bankruptcy remote entity;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 87
"Stonewall System" means the Stonewall Gas Gathering System;
"STRIDE" means Strategic Infrastructure Development Enhancement Plan;
"TCJA" means the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017;
"TIER" means Technology Innovation and Emissions Reduction;
"Tourmaline" means Tourmaline Oil Corp.;
"Townsend 2B" means the 198 Mmcf/d C3+ deep cut gas processing facility located on the existing Townsend complex;
"Townsend complex" means the 550 Mmcf/d gas processing facility, including shallow cut and deep cut processing;
"Transco" means Transcontinental Gas Pipeline Company LLC;
"TSX" means the Toronto Stock Exchange;
"UESC" means Utility Energy Savings Contracts;
"United States", "US", or "U.S." means the United States of America;
"US dollar" or "US$" means currency in the form of United States dollars;
"USEPA" means United States Environmental Protection Agency;
"VLGCs" means Very Large Gas Carriers;
"Vopak" means Vopak Development Canada Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Royal Vopak;
"Washington Gas" means Washington Gas Light Company, a subsidiary of WGL that sells and delivers natural gas primarily to retail customers in the District of Columbia, Maryland and Virginia in accordance with tariffs approved by the PSC of DC, the PSC of MD and the SCC of VA;
"Washington Gas $4.25 Shares" means the US$4.25 series cumulative preferred shares of Washington Gas that were redeemed by Washington Gas on December 20, 2019;
"Washington Gas $4.80 Shares" means the US$4.80 series cumulative preferred shares of Washington Gas that were redeemed by Washington Gas on December 20, 2019;
"Washington Gas $5.00 Shares" means the US$5.00 series cumulative preferred shares of Washington Gas that were redeemed by Washington Gas on December 20, 2019;
"Washington Gas Preferred Shares" means the preferred shares of Washington Gas as a class, including, without limitation, the Washington Gas $4.25 Shares, Washington Gas $4.80 Shares and Washington Gas $5.00 Shares;
"Washington Gas Resources" means Washington Gas Resources Corporation, a subsidiary of WGL that owns the majority of the non-utility subsidiaries;
"WCSB" means Western Canada Sedimentary Basin;
"WGL" means WGL Holdings, Inc., an indirect subsidiary of AltaGas;
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 88
"WGL Acquisition" means the acquisition by AltaGas, indirectly through Merger Sub, of WGL through a merger of Merger Sub with and into WGL pursuant to the Merger Agreement, which closed on July 6, 2018;
"WGL Energy Services" means WGL Energy Services, Inc. (formerly Washington Gas Energy Services, Inc.), a subsidiary of Washington Gas Resources that sells natural gas and electricity to retail customers on an unregulated basis;
"WGL Energy Systems" means WGL Energy Systems, Inc. (formerly Washington Gas Energy Systems, Inc.), a subsidiary of Washington Gas Resources, which provides commercial energy efficient and sustainable solutions to government and commercial clients;
"WGL Midstream" means WGL Midstream, Inc., a former subsidiary of Washington Gas Resources that, prior to the divisive merger and sale of the majority of its assets on April 23, 2021, engaged in acquiring and optimizing natural gas storage and transportation assets;
"WGSW" means WGSW, Inc., a subsidiary of Washington Gas Resources that was formed to invest in certain renewable energy projects; and
"Younger" means the Younger extraction plant and related facilities, AltaGas’ interest being owned by its indirect wholly-owned subsidiary AltaGas Extraction and Transmission Limited Partnership.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 89
SCHEDULE A: AUDIT COMMITTEE MANDATE
I. PURPOSE
The Board of Directors (the “Board”) of AltaGas Ltd. (“AltaGas” or the “Corporation”) has established an Audit Committee (the “Committee”) to serve as the Audit Committee of the Board. The Committee is responsible for performing such duties as delegated by the Board to assist the Board in fulfilling its oversight role in relation to financial reporting. This oversight role includes reviewing the quality and integrity of the Corporation’s financial statements, financial disclosure, and internal controls over financial reporting; reviewing the qualifications, independence, and performance of the external and internal auditors and assessing the Corporation’s risks associated with financial reporting and other enterprise risk.
II. MEMBERSHIP
The Board shall elect from its members not less than three (3) Directors to serve on the Committee (the “Members”) and shall appoint one such Member as Chair of the Committee.
Every Member must be:
•independent (in accordance with National Instrument 52-110 – Audit Committees of the Canadian Securities Administrators (“NI 52-110”) and, if AltaGas is at such time an SEC Issuer, the rules of the SEC); and
•financially literate (in accordance with NI 52-110).
For so long as the Corporation has a class of securities registered under section 12 of the United States Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “1934 Act”) or is required to file reports under section 15(d) of the 1934 Act (at such time, an “SEC Issuer”), at least one Member shall be an “audit committee financial expert” as such term is defined under applicable SEC rules.
No Member shall be an officer or employee of AltaGas or any subsidiary or affiliate of AltaGas.
Each Member shall hold office until the Member resigns or is replaced, whichever first occurs. Any Member may be removed or replaced at any time by the Board and shall cease to be a Member upon ceasing to be a Director of the Corporation. Where a vacancy occurs at any time in the membership of the Audit Committee, it may be filled by the Board on the recommendation of the Governance Committee, provided that the proposed Member meets the above criteria (and, if applicable in the circumstances where the vacancy was in relation to the sole “audit committee financial expert”, the proposed Member is also an “audit committee financial expert”). Provided the Committee includes three Members, including an “audit committee financial expert” if required, it may continue to act in the event of a vacancy. When appointing a Member to the Committee, the Board shall take into consideration the number of other audit committees upon which the proposed Member sits.
The Corporate Secretary of AltaGas shall be secretary to the Committee unless the Committee directs otherwise.
III. MEETINGS
The Committee shall convene no less than four times per year at such times and places designated by its Chair or whenever a meeting is requested by a Member, the Board, or an officer of the Corporation. A minimum of twenty-four (24) hours’ notice of each meeting, plus a copy of the proposed agenda, shall be given to each Member. Members may waive notice of the meeting in any manner, including through their attendance at the meeting. Members of management of the Corporation or any subsidiary or affiliate of the Corporation shall attend whenever requested to do so by a Member. The Committee shall have the right to determine who shall be present at any time during a meeting of the Committee.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 90
A meeting of the Committee shall be duly convened if a majority of Members are present. Members may participate in a meeting of the Committee by means of such telephonic, electronic or other communication facilities as permits all persons participating in the meeting to communicate adequately with each other, and a Member participating in such a meeting by any such means is deemed to be present at that meeting.
In the absence of the Chair of the Committee, the Members may choose one of the Members to be the chair of the meeting.
The external auditor will be given notice of all Committee meetings and be provided the opportunity to attend every meeting relating to financial reporting.
The Committee will hold in camera sessions without management present, including with internal and external auditors, as may be deemed appropriate by the Members.
Minutes shall be kept of all meetings of the Committee by the Corporate Secretary of the Corporation or a designate of the Corporate Secretary, as approved by the Chair.
IV. DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE CHAIR
The Chair of the Committee is responsible for:
1.providing leadership to the Committee and assisting the Committee in reviewing and monitoring its responsibilities;
2.working with management on the development of agendas;
3.ensuring, to the extent possible, the Committee has sufficient information to properly discharge its duties and responsibilities;
4.presiding over meetings and ensuring such meetings are conducted in an efficient, effective and focused manner;
5.advising the Committee of any finance, accounting or misappropriation matters brought to the Chair’s attention;
6.facilitating information sharing with other Board committees as required to address matters of mutual interest or concern; and
7.reporting to the Board on the activities, decisions and recommendations of the Committee after each meeting.
V. DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF THE COMMITTEE
The Committee is hereby delegated by the Board, as permitted and in accordance with the requirements of the Canada Business Corporations Act, the Articles and By-Laws of the Corporation and any legal or regulatory authority having jurisdiction, the authority to perform the following functions:
Financial Reporting and Public Disclosure
1.Approve and recommend to the Board for approval, the annual consolidated financial statements, including management's discussion and analysis and press release containing annual financial results.
2.Approve or recommend to the Board for approval, the interim consolidated financial statements, including management's discussion and analysis and press release containing interim financial results (provided that any declaration of dividends incorporated in the press release has been approved by the Board).
3.Review the analysis by management and the external auditor regarding financial reporting made in connection with the preparation of the consolidated financial statements.
4.Approve the financial information and financial related matters contained in public disclosure documents including information on audited or unaudited financial statements and external auditor appointment, services or fees, including such information contained in, prospectuses, annual information forms, and management information circulars.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 91
5.Satisfy itself that adequate procedures are in place for review of public disclosure of financial information and periodically assess the adequacy of such procedures.
6.Approve any significant changes to the Corporation’s accounting principles and procedures.
7.Review reports from auditors, and the audit committee or board of directors of subsidiaries that produce audited financial statements, relating to financial reporting of such subsidiaries.
External Auditors
8.On an annual basis, approve and recommend to the Board for approval, the appointment of the external auditor subject to shareholder approval.
9.Approve and recommend to the Board for approval the retention and any termination of the external auditor of the Corporation.
10.Approve the terms of the external auditor’s annual engagement letter, including the proposed audit fee for the Corporation and its subsidiaries.
11.Review and pre-approve all non-audit services to be provided to the Corporation and its’ subsidiaries by the external auditor.
12.Approve the Corporation’s policies with respect to the hiring of current and former partners and employees of the external auditors.
13.Review the experience and qualifications of the audit team and assess the performance and effectiveness of the external auditor in its provision of services.
14.Review the report pertaining to auditor independence prepared by the external auditor on an annual basis, which report shall delineate all relationships between the external auditor and the Corporation and its subsidiaries, and determine the auditor’s independence.
15.Review and pre-approve the audit plans (and any changes) of the external auditor and determine the degree of coordination with the internal audit plan.
16.Oversee the work of the external auditor in the preparation of the auditor’s report, including the resolution of any disagreements between management and the auditors regarding financial reporting.
17.Review other reports from the external auditor, as necessary.
18.Regularly meet independently with external auditor in the absence of management on matters of interest, including matters that the external auditor recommends bringing to the attention of the Committee or the Board.
Internal Auditor
19.Review the responsibilities, budget and staffing of the Corporation’s internal audit function.
20.Approve the Internal Audit Charter and the internal audit plan and any changes thereto.
21.Assess the performance and effectiveness of the internal audit function and participate in succession planning for the head of internal audit.
22.Review the reports prepared periodically by the head of internal audit regarding the activities of the internal audit function, including any significant disagreements between internal auditor and management.
23.Receive summaries of significant reports to management prepared by the internal auditors and managements’ responses (or the full report if requested).
24.Regularly meet independently with internal auditor in the absence of management on matters of interest, including matters that the internal auditor recommends bringing to the attention of the Board.
Internal Control over Financial Reporting and Disclosure Controls
25.Review the adequacy and effectiveness of the accounting and internal control policies and procedures, including internal controls over financial reporting, through inquiry and discussions with the external auditor, management and the internal auditor, including about the extent to which the scope of the internal and external audit plans can be relied upon to detect weakness in internal control policies, fraud or other illegal acts.
26.Review the effectiveness of procedures for the receipt, retention and resolution of complaints regarding accounting, internal accounting controls or auditing matters, and review any complaints raised by employees or
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 92
others regarding accounting, internal accounting controls, financial reporting, auditing matters or otherwise relating to matters within the Committee’s mandate.
27.Review management’s periodic reports on the adequacy and effectiveness of the disclosure control policies and procedures of the Corporation.
28.Review with management and the external auditor the certification and reports of management and the external auditor required in the Corporation’s periodic SEC reports concerning the Corporation’s internal controls over financial reporting and disclosure controls and procedures, the adequacy of such controls and any remedial steps being undertaken to address any material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in internal control over financial reporting.
Risk Management
29.On a quarterly basis, review the Corporation's enterprise risk management (ERM) processes, including processes relating to management’s identification of material risks and methods of risk analysis.
30.On a quarterly basis, review management’s reporting on financial risk exposures, including commodity risk, counterparty and credit risk and management’s processes and practices for risk mitigation.
31.Review management’s periodic reports on the status of material litigation, claims and contingencies.
32.Review the financial aspects of any transactions of the Corporation that involve related parties (other than wholly-owned subsidiaries).
33.On a quarterly basis, review management’s reporting on information security matters, including processes for identifying and managing data, cyber and other information technology related risk and processes for the development of data security, training and compliance programs and practices.
34.Review the Corporation's insurance programs.
Policies and Mandate
35.Approve key policies under the Code of Business Ethics relating to the Committee’s mandate.
36.On an annual basis, review the Committee mandate and recommend any changes.
Pension and Benefits
37.Oversee financial aspects of pension and benefit plans that are delegated to the management Retirement and Savings Committee (the “RSC”) to manage and administer.
38.Review, at least annually, the financial management activities of the RSC, including funding levels, investment decisions and changes to valuation assumptions performed by the RSC.
39.Review any proposed changes to pension or benefit plans that may impact financial matters relating to such plans and make recommendations to the Human Resources and Compensation Committee in relation thereto.
40.Approve the financial information that supports the calculation of financial metrics used to evaluate performance under incentive compensation plans and funding pools under compensation plans and report to the Human Resources and Compensation Committee.
Other
41.Annually review and approve the election of the end-user exemption from mandatory clearing, as defined in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, by the Corporation and its subsidiaries, and the provision of swap guarantees by the Corporation to one of its subsidiaries from time to time.
42.Review the solvency and liquidity tests used to support dividend declarations by the Corporation.
43.Review asset retirement obligations in relation to decommissioning, reclamation and remediation.
44.Receive updates on material tax policies, tax planning initiatives and tax audits or assessments.
45.Review management’s process for certification under the Extractive Sector Transparency Measures Act (Canada), if applicable.
46.Review, approve or make recommendations in respect of any other matters considered necessary or appropriate in the context of the mandate of this Committee, or otherwise delegated to it by the Board from time to time.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 93
V. OUTSIDE EXPERTS AND ADVISORS
The Committee is authorized, when deemed necessary or desirable, to engage independent counsel, outside experts and other advisors, at the Corporation’s expense, to advise the Committee on any matter.
VII. RELIANCE
Absent actual knowledge to the contrary (which shall be promptly reported to the Board), each member of the Committee shall be entitled to rely on (i) the integrity of those persons or organizations within and outside the Corporation from which it receives information, (ii) the accuracy of the financial and other information provided to the Committee by such persons or organizations, and (iii) representations made by management and the external auditor, as to any information technology, internal audit and other non-audit services provided by the external auditor to the Corporation and its subsidiaries.
VIII. COMMITTEE TIMETABLE
The major activities of the Committee will be outlined in an annual schedule.
Approved by the Board on October 27, 2021.
AltaGas Ltd. – 2021 Annual Information Form – 94