UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015
OR
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001-37625
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
|
Delaware |
|
46-3003182 |
|
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) |
|
(IRS Employer Identification No.) |
|
75 Sidney Street, |
|
02139 |
|
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
(857) 259-5340
(Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
|
Accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-accelerated filer |
☒ |
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
|
Smaller reporting company |
☐ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
Registrant was not a public company as of the last business day of its most recently completed second fiscal quarter and, therefore, cannot calculate the aggregate market value of its voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates as of such date.
As of March 14, 2016, there were 26,749,240 shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to its 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K where indicated. Such Proxy Statement will be filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year to which this report relates.
2
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including statements regarding our strategy, future operations, future financial position, future revenue, projected costs, prospects, plans, objectives of management and expected market growth, are forward-looking statements. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements.
The words “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “target,” “potential,” “will,” “would,” “could,” “should,” “continue,” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. These forward-looking statements include, among other things, statements about:
• our ability to continue to advance VY-AADC01 through the current Phase 1b clinical trial as a treatment for advanced Parkinson’s disease and establish human proof-of-concept in the fourth quarter of 2016;
• the accuracy of our estimates regarding expenses, future revenues and capital requirements;
• our ability to continue to develop our product engine;
• our ability to develop a manufacturing capability compliant with current good manufacturing practices for our product candidates;
• our ability to advance our other programs through preclinical development and into clinical trials, including filing of an IND for one of these programs in 2017, and successfully complete such clinical trials;
• regulatory developments in the United States and the European Union;
• our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our proprietary assets;
• the size of the potential markets for our product candidates and our ability to serve those markets;
• the rate and degree of market acceptance of our product candidates for any indication once approved;
• our ability to obtain additional financing when needed; and
• the success of competing products that are or become available for the indications that we are pursuing.
These forward-looking statements are only predictions and we may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements, so you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in the forward-looking statements we make. We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and trends that we believe may affect our business, financial condition and operating results. We have included important factors in the cautionary statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, particularly in Part I, Item 1A. Risk Factors that could cause actual future results or events to differ materially from the forward-looking statements that we make. Our forward-looking statements do not reflect the potential impact of any future acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures or investments we may make.
You should read this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the documents that we have filed as exhibits to the Annual Report on Form 10-K with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from what we expect. We do not assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by applicable law.
3
We are a clinical-stage gene therapy company focused on developing life-changing treatments for patients suffering from severe diseases of the central nervous system, or CNS. We focus on CNS diseases where we believe that an adeno-associated virus, or AAV, gene therapy approach that either increases or decreases the production of a specific protein can slow or reduce the symptoms experienced by patients, and therefore have a clinically meaningful impact. We have created a product engine that enables us to engineer, optimize, manufacture and deliver our AAV-based therapies that have the potential to provide durable efficacy following a single administration directly to the CNS. Our product engine has rapidly generated programs for five CNS indications, including advanced Parkinson's disease; a monogenic form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or a form of the disease caused by a single gene mutation; Friedreich's ataxia; Huntington's disease; and spinal muscular atrophy. Our most advanced clinical candidate, VY-AADC01, is being evaluated for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease in an open-label, Phase 1b clinical trial with the goal of generating human proof-of-concept data in the fourth quarter of 2016. Our founders and members of our management team have extensive experience in drug discovery and development and have pioneered significant advances within the fields of AAV gene therapy and neuroscience.
We believe that AAV gene therapy is a particularly attractive treatment approach for CNS diseases that are caused by well-defined genetic mutations. CNS diseases are a leading driver of global disease burden and represent the single largest biopharmaceutical market with estimated worldwide annual sales of over $125 billion in 2014, with the five CNS indications that we are currently targeting representing only a portion of this market. Due to the limited treatment options available for many CNS diseases, there remains a significant unmet medical need and an opportunity for AAV gene therapy to transform the lives of many patients with severe CNS diseases. Based upon clinical data generated to date, we believe that durable gene expression is achievable following a single administration of AAV gene therapy. Recent advances in delivery techniques allow for targeted delivery of AAV vectors, which are modified, non-replicating versions of AAV, to discrete regions of the CNS. In addition, AAV is believed to be safe, as no vector-related serious adverse events, or SAEs, have been reported in the more than 1,300 patients that we estimate have been treated with AAV gene therapy to date, including 200 patients treated for CNS indications.
We have built a product engine that we believe positions us to be the leading company at the intersection of AAV gene therapy and severe CNS diseases. Our team of experts in the fields of AAV gene therapy and neuroscience first identifies and selects severe CNS diseases that are well-suited for treatment using AAV gene therapy. We then engineer and optimize AAV vectors for delivery to the targeted tissue or cells. Our manufacturing process employs an established system to enable production of high quality AAV vectors at commercial-scale. Finally, we leverage established routes of administration and advances in dosing techniques to optimize delivery of our AAV gene therapies directly to discrete regions of the brain or more broadly to the spinal cord region.
Our most advanced clinical candidate, VY-AADC01, is being evaluated for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease. The overall goal of treatment with VY-AADC01 is to restore advanced Parkinson's disease patients' responsiveness to levodopa, or L-Dopa, the longtime standard of care for controlling patients' symptoms at early stages of the disease. Human proof-of-concept data is being generated for VY-AADC01 in an open-label, Phase 1b clinical trial being conducted at two sites in the United States, the University of California, San Francisco, or UCSF, the initial trial site, and University of Pittsburgh, or UPMC. The main goals of this dose-escalation trial are to optimize vector delivery and dose, as well as to obtain further information on the safety profile of the treatment. Enrollment in the Phase 1b clinical trial is ongoing with the goal of generating human proof-of-concept data in the fourth quarter of 2016.
Our four preclinical programs target severe CNS indications where loss or abnormal expression of a specific gene has been identified as the cause of the disease. Furthermore, based on preclinical data, we believe that we can successfully deliver the target gene to the appropriate tissue and cells in the CNS in order to increase or decrease expression of the target protein, as required for therapeutic efficacy. Several of our product candidates may be eligible for orphan drug designation or breakthrough therapy designation.
4
In February 2015, we entered into a strategic collaboration with Sanofi Genzyme, or Genzyme, to leverage our combined expertise and assets to develop AAV gene therapies for severe CNS diseases. Under the agreement, we received $65.0 million in upfront cash, a $30.0 million upfront equity investment and an in-kind commitment of $5.0 million, totaling $100 million. Additionally, we are eligible to receive up to $745 million in option and milestone payments while retaining U.S. commercial rights to most programs.
Our pipeline of AAV gene therapy programs is summarized in the table below:

Mission and Strategy
Our mission is to become the world leader in AAV gene therapy for treating severe CNS diseases by developing transformative therapies. Our strategy to achieve this mission is to:
|
· |
Continually invest in our AAV product engine. We intend to further develop and enhance our product engine by focusing on (i) vector engineering and optimization; (ii) manufacturing; and (iii) dosing and delivery techniques. We plan to continue generating novel AAV vectors by engineering and optimizing vectors best suited to a targeted disease. We are building an onsite, state-of-the-art process research and development facility to enable the manufacturing of high quality AAV gene therapies. We expect to utilize established and novel techniques for dosing and delivery of our AAV gene therapies to the CNS. We plan to continually invest in our product engine to maintain our leadership in AAV gene therapy for CNS diseases. |
|
· |
Establish a leadership position in commercial-scale, high quality AAV manufacturing. We believe that manufacturing capacity and expertise are critical to successfully treating patients using gene therapy, and we are committed to building a system with commercial capacity. Through our collaboration with MassBiologics, a U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, licensed manufacturer affiliated with the University of |
5
Massachusetts Medical School, we are establishing a commercial-scale current good manufacturing practice, or cGMP, compliant manufacturing capability. We initiated cGMP production activities at MassBiologics earlier this year. We are using the baculovirus AAV production system, a technology for producing AAV vectors at scale in insect-derived cells, originally invented and developed by several members of our current production team while at the National Institutes of Health, or NIH, which we continue to improve upon. We believe that having oversight over our own commercial manufacturing process is critical to ensuring quality product with commercial yields. |
|
· |
Optimize and advance VY-AADC01 for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease. Human proof-of-concept data is being generated for VY-AADC01 in an open-label, Phase 1b dose-escalation trial being conducted at two sites in the United States, UCSF, the initial trial site, and UPMC. Enrollment in the Phase 1b clinical trial is ongoing. As of October 2015, we disclosed eight patients had been treated, including five patients in the first cohort and three patients in the second cohort. In the second cohort, we increased the infusion volume to improve the coverage level achieved. The main goals of this trial are to optimize vector delivery and dosing, as well as to obtain further information on the safety profile of the treatment. More specifically, we are seeking to identify the infusion volume required to achieve effective coverage of the putamen, particularly the posterior putamen, the targeted region within the brain. Once we optimize for coverage, we expect to escalate the dose of VY-AADC01 to optimize for clinical benefit. |
|
· |
Continue to build a pipeline of gene therapy programs focused on severe CNS diseases. Beyond our clinical-stage program for advanced Parkinson's disease, we have a deep and promising pipeline of AAV gene therapy programs in various stages of preclinical development. Our goal is to add at least one new pipeline program in the second quarter of 2016 and submit an Investigational New Drug Application, or IND, for one of our existing preclinical programs in 2017. We believe that our leadership position in AAV gene therapy for CNS diseases and our product engine provide us with the necessary capabilities to evaluate and capitalize on external opportunities. As such, we plan to opportunistically expand our pipeline through acquisition, in-licensing or other strategic transactions. |
|
· |
Maintain and maximize the value of our commercialization rights. Under our collaboration with Genzyme, we have retained significant commercialization rights. As we advance clinical development of our product candidates and programs, we expect to continue to explore value-maximizing avenues, including building our own sales and marketing infrastructure or partnering with third parties, for commercialization. |
|
· |
Continue to expand our intellectual property portfolio. We seek to have an industry leading intellectual property portfolio. To that end, we seek patent rights for various aspects of our programs, including vector engineering and construct design, our production process, and all features of our clinical products including compositions and methods of delivery. We expect to continue to expand our intellectual property portfolio by aggressively seeking patent rights for promising aspects of our product engine and product candidates. |
AAV Gene Therapy for CNS Diseases
Gene therapy is an approach whereby gene expression is directly altered in patients to address the underlying cause or predominant manifestations of disease. We believe that the targeted nature of gene therapy may enable powerful treatment options, and provide these patients with meaningful and durable benefits.
While AAV gene therapy can potentially be harnessed for multiple treatment methods, we are currently focused on gene replacement and gene knockdown approaches. Gene replacement is intended to restore the expression of a protein that is not expressed, expressed at abnormally low levels or functionally mutated with loss of function. Gene knockdown is intended to reduce the expression of a pathologically mutated protein that has detrimental effects.
6
Overview of AAV-Based Therapeutic Methods Currently Being Pursued by Voyager

Our gene therapy approach uses AAV vectors which we believe are ideal vectors for gene therapy for several reasons:
Broad Applicability. AAV is able to transduce, or transfer a therapeutic gene, into numerous cell types including target cells in the CNS.
Safety. AAV is believed to be safe and is not known to cause any disease in humans. No vector-related SAEs have been reported in the more than 1,300 patients, including over 200 patients for CNS indications, treated with AAV gene therapy to date.
Does Not Readily Integrate. AAV does not readily integrate into the genome of the target cell, reducing the potential for oncogenesis, or the induction of cancer.
There are several important reasons why we believe that CNS diseases are well-suited for treatment with AAV gene therapy, including the following:
Validated Targets. Many CNS diseases are caused by well-defined mutations in genes and these genes represent genetically validated drug targets for AAV gene therapy.
Targeted Delivery. Advances in delivery techniques allow for direct delivery of AAV vectors to discrete regions in the brain or broader delivery throughout the spinal cord via the cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF.
Durable Expression. Long-term gene expression may be achievable in the CNS following one-time dosing and transfer of the therapeutic gene with an AAV vector. Cells in the CNS are terminally differentiated, or no longer divide, eliminating the potential for cell division to dilute expression of the therapeutic gene. Repeated or continual dosing with direct injection of drugs into the CNS is complex, therefore a one-time AAV gene therapy has significant advantages.
Immune Privileged Site. There is a reduced risk of harmful immune response due to localized delivery in a self-contained system.
7
While we are currently focused on gene replacement and gene knockdown approaches, we are also actively exploring additional potential treatment methods that can utilize an AAV vector, including the direct delivery of monoclonal antibodies to the CNS, as well as gene editing to correct or delete a gene in the cell genome.
The Voyager Product Engine
We have built a product engine that we believe positions us to be the leading company at the intersection of AAV gene therapy and severe CNS diseases. Our team of experts in the fields of AAV gene therapy and neuroscience first identifies and selects severe CNS diseases that are well-suited for treatment using AAV gene therapy. We then apply our expertise in AAV vector engineering and optimization, process research and development, manufacturing, dosing and direct CNS delivery to generate a specific AAV gene therapy for a target disease. We believe that optimizing each of these parameters is a key factor for overall program success. We expect that our current and future pipeline programs will make use of technological advances generated with our product engine.
Disease Selection
We assess potential product programs based upon the following criteria:
Unmet Need. There is a significant unmet medical need for the indication and substantial commercial potential.
Target Validation. There is strong evidence that expression of a specific gene, or lack thereof, is causing, or critical to, the disease state.
Delivery Using AAV. There is strong evidence supporting the ability to target the relevant tissue and cells using an AAV vector to achieve sufficient target gene expression.
Clinical Readouts. The clinical impact of an AAV gene therapy can be clearly measured, including through well-accepted clinical endpoints and the use of both existing and novel biomarkers.
Scalability of Manufacturing. Sufficient AAV vector to supply late-stage clinical development and commercialization can be manufactured.
In addition to the criteria above, we also look for groups of diseases where our knowledge can be transferred. For instance, we believe that some of the delivery parameters and imaging techniques that are employed in our VY-AADC01 program can be applied to AAV gene therapy delivery for Huntington's disease or other diseases where direct, targeted delivery to the brain is warranted. Likewise, we anticipate that our programs for a monogenic form of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, Friedreich's ataxia and spinal muscular atrophy, or SMA, will all utilize injection into the CSF within the spinal column to achieve broad transgene expression in and around the spinal cord.
Vector Engineering and Optimization
We are engineering and optimizing AAV vectors that we believe are best suited for each of our programs. The key components of an AAV vector include: (i) the capsid, or the outer viral protein shell that encloses the target DNA, which includes the promoter and the therapeutic gene; (ii) the therapeutic gene, or transgene; and (iii) the promoter, or the DNA sequence that drives the expression of the transgene.
Members of our team have co-discovered many of the known naturally occurring AAV capsids and have also created promising genetically engineered AAV capsids. Genetically engineered capsids have yielded vectors with desirable properties, such as higher biological potency and enhanced tissue specificity. We believe that there is an opportunity to further optimize AAV capsids to confer desired characteristics relating to properties such as tissue specificity and immunogenicity. We have a significant effort dedicated to designing and screening for novel AAV
8
capsids using a number of different scientific approaches. We believe that the information generated by this work will enhance our ability to rationally design AAV capsids with specific properties for particular therapeutic applications.
We completed a non-human primate study that directly compared transgene expression and distribution in the spinal cord across seven different AAV capsids. The capsids were delivered via injection into the CSF within the spinal column and the specific transgene delivered by all the capsids was FXN. Levels of FXN expression were measured at multiple regions of the spinal cord, including the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions. As shown in the figure below, meaningful differences in the level and distribution of FXN expression were seen across the AAV capsids that were compared. In this study, the levels of FXN expression were highest with AAV2, AAV5 and AAVDJ, and lowest with AAV9. Additionally, FXN expression was normalized as a fold increase relative to FXN expression in a human brain reference sample. Fold increase is a measure describing how much a quantity increases from a baseline value to a final value. For example, a baseline value of 30 and a final value of 60 corresponds to a fold change of two, or a two-fold increase. Fold increase is used as a reporting measure to emphasize the increase itself as opposed to the absolute values.
Capsid Comparison Study Showed Substantial Differences in Transgene Expression
of the Spinal Cord of Non-Human Primates

With respect to the target DNA delivered through AAV gene therapy, we are selecting promoters that we believe have the appropriate activity and tissue selectively for our specific gene therapy programs. We are also designing transgenes to provide optimal expression once delivered to the targeted cells.
Manufacturing at Commercial Quality and Scale
The ability to produce high quality AAV vectors at commercial-scale is a critical success factor in AAV gene therapy. While at the NIH, members of our current production team invented and developed a baculovirus AAV
9
production system, which we use and have continued to improve. This system has a number of attributes that enable high quality commercial-scale manufacturing, including:
High Yield. A single manufacturing run at 500-liter scale can yield many thousands of doses of an AAV gene therapy.
High Purity. A relatively high percentage of AAV vectors contain the therapeutic DNA, reducing the number of empty capsids compared to alternative manufacturing approaches. In addition, the baculovirus system eliminates the risk of introducing mammalian cell derived impurities.
Scalability. This process is reproducible at volumes ranging from 0.02 liters to 500 liters.
Promising Regulatory Framework. Although to date no gene therapy product has been approved in the United States, products manufactured with the baculovirus system include the AAV gene therapy, Glybera, which is approved in Europe, and the marketed vaccines Flublok and Cervarix.
We are building a state-of-the-art process research and development production facility for manufacturing research-grade AAV vectors onsite at our Cambridge, Massachusetts headquarters and a cGMP, commercial-scale AAV manufacturing capability through our collaboration with MassBiologics, in Fall River, Massachusetts, both of which will employ our baculovirus production system.
Optimized Delivery and Route of Administration
Identifying the optimal route of administration and delivery parameters for AAV gene therapy, such as infusion volume, flow rate, vector concentration and dose and formulation for a specific disease, are critical to achieving safe and effective levels of transgene expression in the targeted location in the CNS. We aim to develop clinically feasible protocols that yield reproducible results across patients. For our current pipeline programs, we are either pursuing direct injection into the brain, called intraparenchymal injection (advanced Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease) or injection into the CSF within the cerebrospinal space, called intrathecal injection (Friedreich's ataxia, SMA and a monogenic form of ALS).
Intraparenchymal Injection to the Brain. In the development of VY-AADC01 for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease, we are using the ClearPoint System to provide real-time, intra-operative, magnetic resonance imaging, or MRI, as well as state-of-the-art infusion technologies. The ClearPoint System assists the physician in visualizing the delivery of VY-AADC01 to the putamen and to avoid specific blood vessels during the surgical procedure, with the goal of reducing the risk of hemorrhages. The surgical approach that we are using is similar to the approach used for deep brain stimulation, or DBS, a marketed device-based treatment for advanced Parkinson's disease. In multiple clinical trials to date, a similar delivery technique was used to successfully deliver AAV gene therapy to the brains of patients with Parkinson's disease. We believe that the delivery knowledge gained from our VY-AADC01 program can be applied to AAV gene therapy delivery for Huntington's disease.
10
Overview of Intraparenchymal Delivery

Courtesy of: Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology.
Intrathecal Injection to the Spinal Cord. For spinal cord disorders, including monogenic ALS, Friedreich's ataxia and SMA, we believe that intrathecal injection is the optimal route of administration to achieve broad transgene expression throughout the relevant cells in the spinal cord and sensory pathways. Preclinical studies completed by us and others have demonstrated that intrathecal delivery of AAV vectors can effectively transfer the therapeutic genes to relevant cells in all regions of the spinal cord, as well as in the sensory pathways. Currently, intrathecal injection is commonly used for the delivery of various types of medications, including those to treat pain and infections.
Overview of Intrathecal Delivery
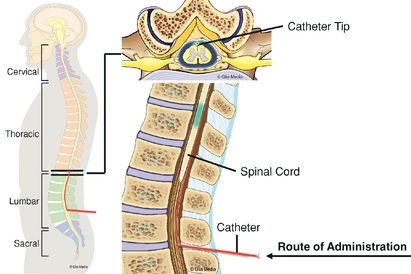
11
Overview of Our Pipeline
We have leveraged our product engine to assemble a pipeline of novel AAV gene therapies for the treatment of severe CNS diseases with high unmet medical need. Depending on the disease, our current AAV gene therapies will use either a gene replacement or gene knockdown approach. Our goal is to address the underlying cause or the predominant manifestations of a specific disease by significantly increasing or decreasing expression of the relevant proteins at targeted sites within the CNS. Several of our product candidates may be eligible for orphan drug designation or breakthrough therapy designation.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Program |
|
Indication |
|
Target |
|
Method |
|
Route of Administration |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VY-AADC01 |
|
|
Advanced Parkinson's Disease |
|
|
AADC |
|
|
Gene replacement |
|
Intraparenchymal injection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VY-SOD101 |
|
|
Monogenic ALS |
|
|
SOD1 |
|
|
Gene knockdown |
|
Intrathecal injection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VY-FXN01 |
|
|
Friedreich's Ataxia |
|
|
FXN |
|
|
Gene replacement |
|
Intrathecal injection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VY-HTT01 |
|
|
Huntington's Disease |
|
|
HTT |
|
|
Gene knockdown |
|
Intraparenchymal injection (with or without intrathecal injection) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
VY-SMN101 |
|
|
SMA |
|
|
SMN1 |
|
|
Gene replacement |
|
Intrathecal injection |
Advanced Parkinson's Disease Program: VY-AADC01
Disease Overview
Parkinson's disease is a progressive and debilitating adult-onset neurodegenerative disorder. Individuals who develop the disease are on average over 60 years of age. The cardinal clinical features of Parkinson's disease include bradykinesia, or slow movements, rigidity, rest tremor and loss of balance. While the underlying cause of Parkinson's disease is unknown, the depletion of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the region of the brain called the putamen leads to the debilitating motor symptoms associated with the disease. The prevalence of Parkinson's disease is estimated to be 700,000 patients in the United States and 7 to 10 million patients worldwide according to a 2010 article from Neuroepidemiology and the Parkinson's Disease Foundation, respectively. Due to the aging of the population in the developed world, we believe that the prevalence of Parkinson's disease will increase. It is estimated that up to 15% of the prevalent population with Parkinson's disease, or approximately 100,000 patients in the United States, have motor fluctuations that are refractory, or not well-controlled, with L-Dopa, the current mainstay of therapy, and thus may be candidates for gene therapy. These are typically patients who have progressed to an advanced stage of the disease.
The progressive motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease are due to the death of neurons in the substantia nigra region of the brain. Neurons in the substantia nigra express the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, or AADC, which is responsible for the conversion of L-Dopa into dopamine, and are also responsible for the release of dopamine into the putamen, particularly the posterior putamen, which is a region of the brain that plays a significant role in motor function and control. While Parkinson's disease causes neurons in the substantia nigra to die, the neurons in the putamen remain intact, but do not normally express AADC. We believe that an AAV gene therapy approach that allows for the
12
delivery of AADC directly to the neurons in the putamen, enabling the targeted neurons to convert L-Dopa into dopamine, is an attractive therapeutic strategy for advanced Parkinson's disease.
While symptomatic treatments exist, there are currently no therapies that effectively slow or reverse the progression of Parkinson's disease. The beneficial effects of L-Dopa on the symptoms of Parkinson's disease were discovered over 50 years ago and treatment with L-Dopa remains the standard of care for patients today. In the first several years after patients' diagnosis, sometimes referred to as the honeymoon period, patients' motor symptoms are generally well-controlled with L-Dopa treatment. However, as the disease progresses, patients become less responsive to L-Dopa. Despite increases in the amount and frequency of dosing of L-Dopa, patients with advanced forms of the disease experience longer periods of reduced mobility, termed off-time, when their medication is ineffective, increased episodes of dyskinesias, or involuntary muscle movements, due to too much drug and shorter periods of on-time when their medication is effective. These motor fluctuations and increased periods of off-time are associated with disability and a dramatically reduced quality of life. As shown in the figure below, on-time decreases, while off-time and dyskinesias increase as patients progress from the honeymoon period into later stages of Parkinson's disease.
Overview of Progression of Parkinson's Disease (PD)

While L-Dopa and other pharmacological approaches to augmenting dopamine provide symptomatic benefit during early stages of Parkinson's disease, there are relatively limited treatment options for patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. There are two FDA approved therapies used to specifically treat advanced Parkinson's disease patients with medically refractive motor fluctuations. The first, DBS, requires the implantation of an electrical stimulation device in the body, which is connected to electrodes that are placed into the brain. The second, marketed as DUODOPA in Europe and DUOPA in the United States, requires the surgical placement of a tube into the intestine so that medication is delivered by a pump that resides outside the body, which patients must carry with them.
Only a relatively small portion of eligible Parkinson's disease patients receive DBS or DUODOPA/DUOPA. In 2014, we estimated that only approximately 6,000 patients worldwide received DBS and approximately 3,500 patients in Europe received DUODOPA/DUOPA. DUOPA received FDA approval in early 2015. We believe that the need for indwelling hardware and the maintenance associated with each of these approaches are significant deterrents for many
13
potential patients. Given the size of the addressable patient population with advanced Parkinson's disease and the limitations of the currently available treatment options for these patients, we believe that a significant unmet medical need exists for new treatment options.
Our Treatment Approach: Turn Back the Clock
We are developing VY-AADC01, an AAV gene therapy product candidate, for the treatment of advanced Parkinson's disease. VY-AADC01 is comprised of the AAV2 capsid, which has been used in multiple AAV gene therapy clinical trials for a number of different diseases, and the cytomegalovirus promoter that drives expression of the AADC transgene. VY-AADC01 is intended to deliver the AADC gene directly into the putamen. Our approach bypasses the dying neurons of the substantia nigra, allowing for the conversion of L-Dopa into dopamine within the putamen. We believe that our approach has the potential to provide patients with clinically meaningful improvements in motor symptoms following a single administration.
Our goal is to restore patients' responsiveness to L-Dopa following treatment with VY-AADC01 to "turn back the clock" on their disease such that the patients' motor symptoms are returned to a well-controlled state, consistent with the level of symptomatic benefit achieved from L-Dopa during the honeymoon period. Following treatment with VY-AADC01, patients with advanced Parkinson's disease will continue to take L-Dopa, but we believe that the required dose will be reduced. The continued administration of L-Dopa will provide a means to titrate dopamine production to further optimize symptomatic control. We believe our approach will increase the conversion of dopamine from L-Dopa in the putamen, resulting in a clinically meaningful improvement in motor symptoms following a single administration.
Based upon VY-AADC01's proposed mechanism of action, we believe that if and when it is well-established as a safe and effective therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson's disease, there is the possibility that it could be evaluated as a treatment for patients with less advanced forms of the disease.
Preclinical Studies
Preclinical studies conducted by Krystof Bankiewicz, M.D., Ph.D., one of our co-founders, and his colleagues at UCSF evaluated the safety, efficacy and pharmacological activity of AAV2-AADC gene therapy, a gene therapy substantially similar to VY-AADC01, delivered directly to the putamen in a non-human primate model of Parkinson's disease. Overall, the procedure and vector were well-tolerated with no serious toxicity issues.
Positron emission tomography, or PET, imaging with tracers specific for AADC activity demonstrated a significant and sustained increase of activity in the brain region where the vector had been delivered. Increased responsiveness to L-Dopa was also evidenced by significant behavioral improvements observed pre- and post-treatment with the gene therapy. In five animals, the mean improvement in behavior was determined at various doses of L-Dopa both one month before treatment, as a baseline measure for comparison purposes, and then again six months after treatment. A strong PET signal was observed in all five animals following treatment, confirming delivery of AADC into the putamen. Animals were significantly more sensitive to L-Dopa six months following treatment with the gene therapy when compared to baseline, as shown below.
14
Behavioral Response to Various Doses of L-Dopa Pre- and Post-Treatment with AAV2-AADC in Non-Human Primates(1)

(1)Adapted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd; Forsayeth et al, Molecular Therapy (2006), 14 (4); 571-577, copyright 2006. Blue line represents base line measurements and yellow line represents six months post-treatment measurements.
*A result is considered to be statistically significant when the probability of the result occurring by random chance, rather than from the efficacy of the treatment, is sufficiently low. The conventional method for measuring the statistical significance of a result is known as the "p-value," which represents the probability that chance caused the result (e.g., a p-value = 0.001 means that there is a 0.1% or less probability that the difference between the control group and the treatment group is purely due to random chance).
We believe that these results provide evidence that AADC is active and being expressed at levels sufficient to measure a clinical benefit.
Two animals from this cohort were followed for up to eight years following a single administration of the gene therapy and sustained PET imaging signals for AADC and behavioral signs of efficacy were observed in these animals.
The results of these preclinical studies provided support for the initiation of clinical trials.
Phase 1 Clinical Trials
In a completed open-label Phase 1 clinical trial conducted at UCSF, VY-AADC01 was delivered directly to the putamen of Parkinson's disease patients. The primary endpoints of this trial were safety and tolerability of VY-AADC01. These endpoints were met as VY-AADC01 was well-tolerated and no treatment related SAEs were reported. Furthermore, pharmacologic activity of VY-AADC01 was observed. This trial was completed prior to our involvement in the program, but used a version of VY-AADC01 that is also currently being used in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial. We are currently evaluating whether to use the same version of VY-AADC01 used in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial in future clinical trials, or to use a slightly modified version of VY-AADC01, which we believe will be found to be substantially similar to the version of VY-AADC01 being used in the ongoing Phase 1b trial. Based on our discussions with the FDA, we believe that we have a good understanding of what preclinical studies we will need to demonstrate comparability between the current version and the modified version of VY-AADC01.
The Phase 1 clinical trial was conducted in a total of 10 patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. Two doses of VY-AADC01 were tested, 9 × 1010 vector genomes, or vg, and 3 × 1011 vg, with five patients per dose cohort. The
15
infusion volume was 100µl per putamen, or 200µl per patient. Patients in both cohorts treated with VY-AADC01 showed modest improvements in motor fluctuations. At six months following treatment, off-time was observed to be reduced by an average of approximately three hours and a corresponding increase in on-time without dyskinesias was also observed. In addition, at six months following treatment, an approximately 30% improvement in on- and off-time measures using the Total Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale, or UPDRS, a widely used rating scale that evaluates cognitive, functional, and motor deficits, as well as medication-related complications, was observed, as shown in the table below.
Summary of UPDRS Results from Phase 1 Trial(1)

|
(1) |
Christine et al, Neurology (2009), 73: 1662-1669. The row titled "Low-dose cohort" represents data from the five patients treated with 9 X 1010 vg of VY-AADC01. The row titled "High-dose cohort" represents data from the five patients treated with 3 X 1011 vg of VY-AADC01. The row titled "Combined cohorts" represents data from all ten patients treated with VY-AADC01. The data in the columns under the header "Off medications" represents periods during which patients' medications were not working as measured by a patient's total UPDRS score at baseline, before treatment with VY-AADC01, and at six months following treatment with VY-AADC01, along with percent change from baseline to six months and the corresponding p-value. The data in the columns under the header "On medications" represents periods during which patients' medications were working as measured by a patient's total UPDRS score at baseline, before treatment with VY-AADC01 and at six months following treatment with VY-AADC01, along with percent change from baseline to six months and the corresponding p-value. A result is considered to be statistically significant when the probability of the result occurring by random chance, rather than from the efficacy of the treatment, is sufficiently low. The conventional method for measuring the statistical significance of a result is known as the "p-value," which represents the probability that chance caused the result (e.g., a p-value = 0.001 means that there is a 0.1% or less probability that the difference between the control group and the treatment group is purely due to random chance). Because of the small size of this trial, the p-values may not be reliable or repeatable, and may not be duplicated in future trials. |
While no gene therapy related SAEs were reported, three patients experienced minor hemorrhages related to the surgical procedure. Two of the hemorrhages were asymptomatic, noticed only on imaging, and one was symptomatic with the patient making an almost complete recovery. Nevertheless, the stereotactic injection protocol used in the surgical procedure was modified to avoid specific blood vessels and no further hemorrhages were reported. The implementation of real-time, intra-operative MRI guidance in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial is a significant advancement in vector delivery.
The 10 patients were assessed clinically for up to four years after treatment and a durable, dose-dependent expression of AADC was observed. Patients treated with the low dose gene therapy were observed to have an increased PET signal, or uptake of the 18 fluoro-meta-tyrosine tracer, or 18 FMT, indicative of AADC expression and activity that persisted for up to four years. Patients treated with the high dose gene therapy were observed to have an increased PET signal that was greater on average when compared to the low dose cohort, which also persisted for up to four years.
16
Long-Term AADC Expression as Measured by PET Imaging in Patients Treated with High and Low Doses of AAV Gene Therapy in a Phase 1 Clinical Trial(1)

|
(1) |
Mittermeyer et al, Human Gene Therapy (2012), 23: 377-381. The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. Blue lines represent patients treated with the low dose and yellow lines represent patients treated with the high dose. |
A similar Phase 1 clinical trial was conducted at Jichi Medical University, or JMU, in Japan using the same vector that was used in the UCSF trial. The primary endpoints of this trial were safety and tolerability of the treatment. These endpoints were met as the treatment was well-tolerated and no treatment related SAEs were reported. Six patients were treated in this trial and an enhanced PET signal was observed in a subset of patients monitored 96 weeks following treatment. An open-label Phase 1/2 trial is currently being conducted at JMU. The primary endpoints of this trial are safety and tolerability of the treatment. This trial is using lower infusion volumes and doses compared to the ongoing Phase 1b trial. Importantly, the JMU trial is not using real-time, intra-operative MRI guidance.
While the prior UCSF and JMU clinical results were encouraging and provided evidence of long-term AADC expression, the magnitude of the clinical benefits observed did not exceed placebo effects observed in previous surgical therapy trials in Parkinson's disease patients, and the UCSF and JMU trials were not blinded. Further, based on post-operative imaging and our current work using real-time, intra-operative MRI monitoring, we estimate that less than 10% of the putamen volume was covered by the infusion in these trials, which reflects suboptimal distribution of VY-AADC01 in the putamen. We believe that there is an opportunity to further optimize the delivery, dose and infusion volume of VY-AADC01 to substantially increase the coverage of the putamen in order to achieve a more substantial clinical benefit.
Our Program Status
In 2014, UCSF initiated an open-label Phase 1b clinical trial to optimize the development of VY-AADC01. The IND for the Phase 1b trial was filed by UCSF in July 2013 and was transferred to us in October 2015. We initiated the second trial site at UPMC in December 2015. The primary endpoints of this trial are safety and tolerability of the treatment. This trial incorporates three key design features:
17
|
1) |
Use of the Clearpoint System to provide real-time, intra-operative MRI during surgery to assist the physician in visualizing the delivery of VY-AADC01 to the putamen and to avoid specific blood vessels during the surgical procedure, with the goal of reducing the risk of hemorrhages. |
|
2) |
Larger infusion volumes designed to increase coverage of the putamen with VY-AADC01. |
|
3) |
Higher doses of VY-AADC01 compared to the previously completed UCSF Phase 1 trial. |
Secondary endpoints of this trial, which will be used to assess the potential pharmacologic activity of VY-AADC01, include UPDRS, AADC PET imaging and a behavioral test using intravenous L-Dopa treatment to measure changes in a patients' sensitivity to L-Dopa.
In this Phase 1b trial, up to 20 patients with advanced Parkinson's disease are expected be treated with VY-AADC01. A total of five patients in the first dose cohort, or Cohort 1, were treated with a VY-AADC01 concentration of 0.83 × 1012 vg per milliliter or 7.5 × 1011 vg dose using a 450µl infusion volume per putamen, or 900µl per patient, and no SAEs have been observed to date in Cohort 1 patients. As shown below, the average coverage of the overall putamen achieved in the first cohort was approximately 21% and the average coverage of the posterior putamen, which is reduced in dopamine content early on in Parkinson's disease, was approximately 20%. In the portion of the putamen covered by VY-AADC01, as determined by MRI, there was approximately a 30% average increase in the PET signal at six months after surgery compared to the baseline PET signal measured prior to surgery. An increased PET signal is indicative of increased AADC expression and activity. Importantly, the PET results from Cohort 1 confirmed the overlap of the MRI and PET signals seen in previous non-human primate studies. This data supports our hypothesis that AADC is expressed post-treatment in the same region of the brain where VY-AADC01 was visualized through the use of MRI during surgery. While the coverage in Cohort 1 improved relative to the below 10% coverage of the putamen that we estimated was achieved in the prior UCSF Phase 1 trial, we believe that the coverage needs to be further increased. No meaningful signals of efficacy have been observed in these patients to date. We are continuing to monitor the patients from Cohort 1.
Prior to the initiation of the second cohort, or Cohort 2, a protocol amendment was submitted and approved by the FDA, which included an increase in the infusion volume to up to 900µl per putamen, or 1,800µl per patient, and allowed for the use of catheters with different step lengths, with the overall goal of further increasing coverage of the putamen, particularly the posterior putamen. Patients in Cohort 2 are being treated with a VY-AADC01 concentration of 0.83 × 1012 vg per milliliter or 1.5 × 1012 vg. The first patient, or Patient #6 overall, in Cohort 2 was treated in June 2015 and the coverage achieved in this patient was meaningfully improved relative to Cohort 1. The average coverage of the overall putamen achieved in Patient #6 was approximately 36% and the average coverage of the posterior putamen was approximately 46%. No SAEs were observed in Patient #6. The second patient in Cohort 2, Patient #7, was treated in July 2015. The coverage achieved in this patient was suboptimal due, we believe, to an exceptionally complex vasculature and resulting perivascular leakage, or leakage into the tissue surrounding the blood vessels. The average coverage of the overall putamen achieved in Patient #7 was approximately 25% and the average coverage of the posterior putamen was approximately 22%. Prolonged immobilization during surgery resulted in Patient #7 experiencing two SAEs, a pulmonary embolism, or blood clot in the lungs, and related heart arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat. It was determined that these SAEs were related to the surgical procedure, not VY-AADC01. The patient's symptoms associated with the SAEs have completely resolved, subject to continued monitoring and treatment with an anti-coagulant, which is anticipated to be discontinued. Patient #8 was treated in October 2015 and was the third patient treated in Cohort 2. The average coverage of the overall putamen achieved in Patient #8 was approximately 38% and the average coverage of the posterior putamen was approximately 32%. Enrollment in the Phase 1b trial is ongoing and procedures are in place to address the risk mitigation of future pulmonary emboli by using a lower limb sequential compression device on all patients, in order to prevent deep vein thrombosis, which can lead to pulmonary emboli. Patient #8 was the first to be treated with a lower limb sequential compression device during the surgical procedure.
18
Summary of Coverage of Putamen

Note: Average coverage percentages for Phase 1b include average coverage achieved in left and right putamen per patient.
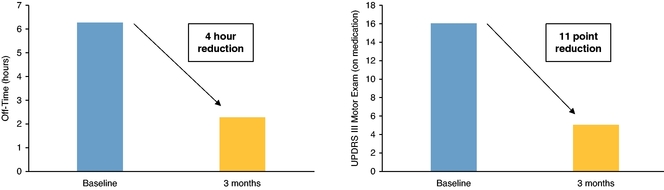
As anticipated given the increased volume administered, the coverage of the putamen achieved in Patient #6 was meaningfully better when compared to the coverage achieved in the five patients treated as part of Cohort 1 in the ongoing Phase 1b trial. A scheduled interim evaluation of Patient #6 was completed three months after treatment by a Parkinson's disease specialist. During this interim evaluation, a subset of efficacy measures were evaluated via patient diary and clinical exam, and were compared to the relevant baseline measures taken prior to treatment. As shown in the figure below, at three months following treatment, Patient #6 demonstrated an approximately four hour reduction in off-time with corresponding increases in on-time and sleep, as well as an approximately 11 point reduction, or 69% improvement, in UPDRS III score, the clinician-scored motor evaluation portion of UPDRS, while the patient was on L-Dopa. This compares to an average off-time reduction of two hours and an approximately 11% average improvement in UPDRS III score seen in Cohort 1 patients at three months after treatment. Furthermore, there was a nine point reduction, or an approximately 30% improvement, in UPDRS III score while Patient #6 was off L-Dopa. These improvements coincided with an approximately 40% reduction in Patient #6's daily L-Dopa dose. While these interim results are clinically meaningful, they should be interpreted cautiously given that they are taken from a single patient at a relatively early time point from a non-placebo-controlled, open-label trial, and may not be consistent with the results obtained for all of Cohort 2 or the trial more generally.
19
Clinical Efficacy Measures for Patient #6 Pre-Treatment and Three Months Post-Treatment
Once we are able to optimize for vector delivery and coverage, we then intend to increase and optimize the dose and concentration of VY-AADC01 used in this trial.
ALS Program: VY-SOD101
Disease Overview
ALS is a fatal neurodegenerative disease that leads to muscle weakness and loss of mobility as well as impaired speech, swallowing and breathing, with many patients requiring ventilator support as the disease progresses. The age of onset of ALS is typically around 50 years. However, most ALS patients only live an average of three years after initial symptoms appear, and it is estimated that as many as 30,000 patients in the United States are living with the disease according to the ALS Association. Familial, or inherited, ALS accounts for approximately 10% of ALS cases according to a 2006 article published in Neuron, and an estimated 20% of familial ALS is caused by mutations in the superoxide dismutase 1, or SOD1, gene according to a study published in the European Neurological Journal. Therefore, there are an estimated 600 patients in the United States with ALS caused by mutations in the SOD1 gene.
The normal function of the SOD1 protein is to break down toxic molecules. Mutations in SOD1 have been shown to lead to the formation of toxic aggregates of the mutated protein, resulting in the death of motor neurons. Patients with familial ALS caused by certain mutations in the SOD1 gene progress more rapidly than patients with other forms of ALS, although the reason for this more rapid progression is unknown.
There is currently only one FDA-approved treatment for ALS, riluzole, which has been shown to have only modest efficacy, prolonging life by just a few months.
Our Treatment Approach
We believe that AAV gene therapy is an attractive approach to treat monogenic ALS. Since the SOD1 gene mutations that cause ALS are toxic gain-of-function mutations that result in the overexpression of toxic versions of the protein, we believe that we can employ an AAV gene therapy approach that targets the knockdown of SOD1. In addition, the target cells, motor neurons and astrocytes, or cells supporting the neurons, reside within and surrounding the spinal cord and brain stem, which we believe can be effectively targeted with AAV gene therapy through intrathecal injection. The goal of VY-SOD101 is to knock down expression of SOD1, thereby reducing the level of mutated protein in the target cells in the spinal cord and brain stem to preserve motor neurons, slow the progression of the disease and prolong ventilator-independent survival.
We believe that there is also the potential to leverage our approach for the treatment of other genetically defined forms of ALS.
20
Preclinical Studies Targeting SOD1 for Monogenic ALS
Results from preclinical studies conducted at The Ohio State University support targeting mutant SOD1 for the treatment of monogenic ALS. In a non-human primate model, significant knockdown of SOD1 expression was observed following intrathecal injection of an AAV vector carrying target DNA designed to inhibit SOD1 expression. As shown in the figure below, SOD1 protein levels were successfully knocked down by greater than 80%, on average, in three non-human primates. SOD1 protein levels were normalized in this study to ß-actin as a control. In addition, SOD1 expression in motor neurons was observed to be knocked down by 95%, on average, in this cohort compared to a control group. No side effects from the treatment were reported.
Knockdown of SOD1 Using AAV-Mediated Delivery in Non-Human Primates(1)

|
(1) |
Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Foust et al, Molecular Therapy (2013), 21 (12); 2148-2159, copyright (2013). |
The knockdown of SOD1 has also been observed to provide a significant survival benefit in an animal model. As shown below, mice with a SOD1 mutation treated with an AAV vector to knock down expression of the SOD1 gene achieved median survival of 87 days longer compared to mice treated with a control vector.
Improved Survival Post Knockdown of SOD1(1)

|
(1) |
Reprinted by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd: Foust et al, Molecular Therapy (2013), 21 (12); 2148-2159, copyright (2013). Purple line represents mice treated with AAV gene therapy, while gray line represents control mice. |
21
We believe the viability of our proposed delivery approach for VY-SOD101 is supported by our proof-of-principle work demonstrating successful AAV gene therapy delivery to the spinal cord of non-human primates through intrathecal injection.
Our Program Status
VY-SOD101 is in preclinical development. We are optimizing the transgene, the promoter, the capsid and the dosing paradigm for this program.
Through our product engine efforts, we are constructing and optimizing the transgene, including the microRNA, or miRNA, cassette that will be inserted into an AAV vector to achieve targeted knockdown of SOD1 expression with RNA interference, or RNAi, a biological process in which RNA molecules inhibit gene expression. The miRNA cassette is being optimized with respect to a number of characteristics that affect specificity for the SOD1 target gene and knockdown potency. Beyond the miRNA cassette sequence, we are optimizing other design aspects of the transgene to improve the overall effectiveness of our approach. We have screened more than 100 RNAi sequences, each represented by a bar in the graph below, and have successfully identified multiple, highly-potent RNAi sequences targeting SOD1, as highlighted by the yellow bars in the figure below:
Overview of miRNA Target Sequences for Knockdown of SOD1

We have identified a number of potential lead candidates for the VY-SOD101 program and are in the process of completing the necessary experiments to evaluate these potential lead candidates based upon multiple criteria, including safety, overall level of transgene expression achieved, distribution of transgene expression and specific cell types transduced.
In addition, we are evaluating intrathecal dosing paradigms for the best distribution and delivery to the relevant regions of the spinal cord and brain stem. We are studying parameters such as site of intrathecal administration, volume of administration and rate of infusion to identify the dosing paradigm that we believe will translate into an effective therapy in patients.
We expect to use relevant animal models to select our lead candidate for this program. Once a lead candidate and intrathecal dosing paradigm are identified, we plan to complete a number of preclinical studies to evaluate the safety and pharmacology of our lead candidate, including studies in animal models and IND-enabling studies. We expect that the first clinical trial of VY-SOD101 will enroll ALS patients with relevant mutations in the SOD1 gene, bypassing the more traditional approach of enrolling healthy volunteers.
Friedreich's Ataxia Program: VY-FXN01
Disease Overview
22
Friedreich's ataxia is a debilitating neurodegenerative disease resulting in poor coordination of legs and arms, progressive loss of the ability to walk, generalized weakness, loss of sensation, scoliosis, diabetes and cardiomyopathy as well as impaired vision, hearing and speech. The typical age of onset is 10 to 12 years, and life expectancy is severely reduced with patients generally dying of neurological and cardiac complications between the ages of 35 and 45. According to the Friedreich's Ataxia Research Alliance, there are approximately 6,400 patients living with the disease in the United States and there are currently no FDA-approved treatments for the disease.
Friedreich's ataxia patients have mutations of the FXN gene that reduce production of the frataxin protein, resulting in the degeneration of sensory pathways and a variety of debilitating symptoms. Friedreich's ataxia is an autosomal recessive disorder, meaning that a person must obtain a defective copy of the FXN gene from both parents in order to develop the condition. One healthy copy of the FXN gene, or 50% of normal frataxin protein levels, is sufficient to prevent the disease phenotype. We believe that this will provide the approximate level of gene replacement necessary for successful treatment with an AAV gene therapy.
Our Treatment Approach
We believe that an AAV gene therapy approach that delivers a functional version of the FXN gene to the sensory pathways through intrathecal injection has the potential to improve the balance, ability to walk, sensory capability, coordination, strength and functional capacity of Friedreich's ataxia patients. Unlike in many genetic disorders, most Friedreich's ataxia patients normally produce very low levels of the frataxin protein, which although insufficient to prevent the disease, exposes the patient's immune system to frataxin. This reduces the likelihood that the FXN gene delivered with AAV gene therapy will trigger harmful immune response.
Preclinical Studies
We conducted preclinical studies in non-human primates and achieved high FXN expression levels within the target sensory ganglia, or clusters of neurons, along the entire length of the spinal region following intrathecal injection. As depicted in the figure below, FXN expression was normalized as a fold increase relative to FXN expression in a human brain reference sample. The levels of FXN expression observed using an AAVrh10 vector were, on average, greater than FXN levels present in normal human brain tissue. The increased levels of FXN were achieved across the entire length of the spinal region including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral levels. Relatively low, but measurable, levels of FXN expression were also observed in the cerebellar dentate nucleus, another area of the CNS that is often affected in Friedreich's ataxia, and that is often considered difficult to target therapeutically.
FXN Expression in Sensory Ganglia Following Intrathecal Delivery in Non-Human Primates

23
Our Program Status
VY-FXN01 is currently in preclinical development. We are in the process of completing a number of AAV capsid screening experiments to identify the capsid that we believe is optimal for the VY-FXN01 program. We are comparing capsids in non-human primates following intrathecal injection, and we are evaluating these capsids based upon multiple criteria including safety, overall level of transgene expression achieved, distribution of transgene expression and the specific cell types transduced. In addition, we are optimizing the promoter and specific characteristics of the FXN transgene that we expect to use for VY-FXN01. We also have a significant effort focused on better understanding the clinical course of Friedreich's ataxia and identifying potential clinical endpoints for future clinical trials.
Once we identify a lead candidate for this program, we plan to complete a number of preclinical studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of our lead candidate, including studies in relevant animal models of Friedreich's ataxia and IND-enabling studies. We expect that the first clinical trial of VY-FXN01 will enroll Friedreich's ataxia patients, bypassing the more traditional approach of enrolling healthy volunteers.
Huntington's Disease Program: VY-HTT01
Disease Overview
Huntington's disease is a fatal, inherited neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive decline of motor and cognitive functions and a range of behavioral and psychiatric disturbances, including depression. The average age of onset is 40, with patients typically dying approximately 17 to 20 years following diagnosis. According to Huntington's Disease Society of America, Huntington's disease affects approximately 30,000 patients in the United States. Huntington's disease is caused by mutations in the huntingtin, or HTT, gene. Huntington's disease is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that an individual is at risk of inheriting the disease if only one parent is affected. While the exact function of the HTT gene in healthy individuals is unknown, it is essential for normal development before birth and mutations in the HTT gene ultimately lead to the production of abnormal intracellular huntingtin protein aggregates that cause neuronal cell death. Currently, there are no approved treatments targeting the underlying cause of the disease and only one drug, tetrabenazine, has been approved for the treatment of the specific motor symptoms of Huntington's disease.
Our Treatment Approach
We believe that AAV gene therapy is an attractive approach to treat Huntington's disease. Since HTT mutations that cause Huntington's disease are toxic gain-of-function mutations, we believe that we can employ an AAV gene therapy approach designed to knock down expression of the HTT gene. In addition, the targeted cells for treatment primarily reside in discrete regions of the brain, the striatum and the cortex, that can be targeted with AAV gene therapy delivered directly to these site-specific regions. The goal of VY-HTT01 is to knock down expression of the HTT gene, thereby reducing the level of mutated HTT protein in these brain regions and slowing the progression of the cognitive and motor symptoms associated with Huntington's disease. We believe that we can use the same surgical approach for this program that has been used for VY-AADC01 delivery to the brain, allowing us to leverage prior clinical experience.
Preclinical Studies
Our collaborators at Genzyme have completed significant preclinical work focused on AAV gene therapy for Huntington's disease. Genzyme's preclinical studies in a mouse model of Huntington's disease demonstrated the safety and efficacy of AAV gene therapy targeting the knockdown of the HTT gene in the CNS.
As shown in the figure below, using an AAV vector delivered directly to the CNS, HTT gene expression was observed to be reduced by over 50%, on average, in the treatment group as compared to the control group. HTT protein levels were normalized in this study to -Tubulin as a control. No signs of toxicity were reported.
24
Knockdown of HTT Following AAV Delivery(1)

(1)Stanek et al, Human Gene Therapy (2014); 25; 461-474. The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers.
*p<0.05
In addition, a significant functional benefit was observed in the treatment group, as measured by the Porsolt Swim Test, which is commonly used to measure depressive behavior in mice. In the figure below, both normal, or wild type mice, and mice with the mutation, or YAC128, were evaluated following treatment with either an AAV vector targeting the knockdown of the HTT gene, labeled as AAV2/1-miRNA-Htt below, or a negative control vector, labeled as AAV2/1-Null below. As expected, knocking down HTT in the control mice was observed to have no functional impact.
Motor Deficit Reduction in an Animal Model of Huntington's Disease(2)

(2)Stanek et al, Human Gene Therapy (2014); 25; 461-474. The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers.
*p<0.05
25
Our Program Status
VY-HTT01 is currently in preclinical development. Genzyme's Huntington's disease gene therapy program was combined with our efforts in connection with entering into our collaboration agreement in February 2015. We are optimizing the transgene, the capsid and the dosing paradigm for this program.
Through our product engine efforts, we are constructing and optimizing the transgene, including the miRNA cassette that will be inserted into an AAV vector to achieve targeted knockdown of HTT expression with RNAi. We are optimizing the miRNA cassette with respect to a number of characteristics that affect specificity for the HTT target gene and knockdown potency. Beyond the miRNA cassette sequence, we are optimizing other design aspects of the transgene to improve the overall effectiveness of our approach. This work leverages the learnings from the VY-SOD101 program, as the miRNA cassettes designed are anticipated to be applicable to the VY-HTT01 program. We are also optimizing the promoter that we expect to use for VY-HTT01.
In addition, we are in the process of confirming in non-human primate studies that the current lead capsid is optimal for the VY-HTT01 program. Capsids are being compared in non-human primates following direct injection into the striatum or intrathecal injection, and are being evaluated based upon multiple criteria, including safety, overall level of transgene expression achieved, distribution of transgene expression and the specific cell types transduced.
We are evaluating direct injection into the striatum and intrathecal dosing paradigms for the best distribution and delivery to the relevant regions of the brain, the striatum and cortex. Parameters such as site of administration, volume of administration and rate of infusion are being studied to identify the dosing paradigm that we believe will translate into an effective therapy in patients.
Once we identify a lead candidate and dosing paradigm for this program, we plan to complete a number of preclinical studies to evaluate the safety, pharmacology and efficacy of our lead candidate, including studies in relevant animal models and IND-enabling studies. We expect that the first clinical trial of VY-HTT01 will enroll Huntington's disease patients, bypassing the more traditional approach of enrolling healthy volunteers.
SMA Program: VY-SMN101
Disease Overview
SMA is an inherited neuromuscular disease that results in progressive muscle weakness and paralysis. It is estimated that SMA affects approximately 10,000 patients in the United States according to the SMA Foundation. Patients with SMA may have difficulty sitting, standing, walking, eating and breathing, depending upon the severity of the disease. There are four primary types of SMA, with SMA type I being the most severe. SMA type I is the leading genetic cause of death in infancy and early childhood in the United States and accounts for approximately 50% of all SMA cases. Infants affected by SMA type I never sit or stand and usually die of respiratory failure before two years of age. SMA type II is of intermediate severity, with onset at approximately seven to 18 months of age and a slower progression compared to type I. Children with SMA type II will generally sit, but never stand. SMA type III is less severe, presenting at 18 months of age or later, and SMA type IV is a mild adult subtype generally presenting in patients between 20 and 30 years of age. There are currently no approved treatments for any type of SMA.
SMA is caused primarily by mutations of the SMN1 gene, which eliminate full-length protein expression of the SMN1 gene. Clinical severity is related to the number of copies of the SMN2 gene, which is able to produce small amounts of functional protein. The precise role of the SMN protein in the pathogenesis of SMA is unknown. SMA is an autosomal recessive disorder. One healthy copy of the SMN1 gene, or 50% of normal SMN1 protein levels, is sufficient to prevent the disease phenotype. We believe this will provide the approximate level of gene replacement necessary for successful treatment with an AAV gene therapy.
Our Treatment Approach
26
We believe that an AAV gene therapy that delivers a functional version of the SMN1 gene to the spinal cord and brainstem through intrathecal injection has the potential to prolong survival, increase the amount of time of independent respiration and improve clinical and electrophysiological measures of motor function in severe SMA patients. Unlike many genetic disorders, most SMA patients normally produce very low levels of the SMN1 protein, which although insufficient to prevent the disease, exposes the patient's immune system to the SMN1 protein. This reduces the likelihood that the SMN1 gene delivered with AAV gene therapy will trigger a harmful immune response.
Preclinical Studies
Our collaborators at Genzyme have completed significant preclinical work focused on AAV gene therapy for SMA. Preclinical animal model studies demonstrated the safety and efficacy of SMN1 gene replacement delivered directly into the CNS.
Studies completed in a transgenic mouse model of SMA demonstrated that the SMN1 gene could be successfully delivered to the spinal cord in a vector dose-dependent fashion, as shown in the figure below. At the highest AAV dose tested, 5 × 1010 vg, or 5e10 vg, the average SMN1 expression observed in the lumbar region of the spinal cords of the treatment group was approximately 150% of the control group.
Replacement of SMN1 Using AAV Gene Therapy(1)

|
(1) |
Passini et al, Human Gene Therapy (2014); 25; 619-630. The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. SMN levels in control SMA mice vs. SMA mice treated with escalating doses of AAV9-hSMN1. |
**p<0.01 ***p<0.001
In the same transgenic mouse model, replacement of the SMN1 gene using AAV gene therapy was delivered directly to the CNS demonstrated an improvement in survival in the treatment groups compared to the control group, as shown in the figure below. The median survival benefit at the highest dose tested, represented by the square line below, was 136 days longer than the median survival benefit for the control group, represented by the circle line below.
27
Survival Post Replacement of SMN1 Using AAV Gene Therapy(1)

|
(1) |
Passini et al, Human Gene Therapy (2014); 25; 619-630. The publisher for this copyrighted material is Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. Overall survival post treatment with: saline (circle); or escalating doses of AAV9-hSMN1 (triangle, diamond, square). |
We believe the viability of our proposed delivery approach for VY-SMN101 is supported by our proof-of-principle work demonstrating successful AAV gene therapy delivery to the spinal cord of non-human primates through intrathecal injection.
Our Program Status
VY-SMN101 is currently in preclinical development. Genzyme's SMA gene therapy program was contributed to us in connection with entering into our collaboration agreement in February 2015.
We are in the process of completing a number of AAV capsid screening experiments to identify the capsid that we believe is optimal for the VY-SMN101 program. We are screening capsids in non-human primates following intrathecal injection, and are evaluating based upon multiple criteria, including safety, overall level of transgene expression achieved, distribution of transgene expression and the specific cell types transduced. Genzyme has already optimized the promoter and transgene for VY-SMN101.
Once we identify a lead candidate and dosing paradigm for this program, we plan to complete a number of preclinical studies to evaluate the safety, pharmacology and efficacy of our lead candidate, including studies in relevant animal models and IND-enabling studies. We expect that the first clinical trial of VY-SMN101 will enroll SMA patients, bypassing the more traditional approach of enrolling healthy volunteers.
Future Programs
We are evaluating additional severe CNS diseases that could be treated using AAV gene therapy through application of either a gene replacement or a gene knockdown approach. Beyond these approaches, we are also actively exploring additional potential treatment methods that can utilize an AAV vector, including the direct delivery of monoclonal antibodies to the CNS, as well as gene editing to correct or delete a gene in the cell genome. We believe that AAV-based delivery of antibodies to the CNS could be used to treat diseases such as frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease and that gene editing could be applied to a number of different genetic diseases.
28
For information regarding amounts spent during each of the last three fiscal years on company-sponsored research and development activities, see Part II “Item 6 – Selected Financial Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Collaborations and License Agreements
Genzyme Collaboration
In February 2015, we entered into a strategic collaboration with Genzyme to leverage our combined expertise and assets to develop AAV gene therapies for CNS diseases. Under the agreement, we retained U.S. rights to VY-AADC01 and VY-FXN01, as well as at least co-commercialization rights to VY-HTT01 in the United States. VY-SOD101 is not included as part of the Genzyme collaboration and we retain unencumbered worldwide rights to this program. We have granted Genzyme an exclusive option to license, develop and commercialize (i) ex-U.S. rights to the following programs, which we refer to as the Split Territory Programs, VY-AADC01, VY-FXN01, a future program to be designated by Genzyme, or Future Program, and VY-HTT01 with an incremental option to co-commercialize VY-HTT01 in the United States, and (ii) worldwide rights to VY-SMN101. Genzyme's option for the Split Territory Programs and VY-SMN101 is triggered following the completion of the first proof-of-principle human clinical study, or POP Study, on a program-by-program basis.
Prior to any option exercise by Genzyme, we will collaborate with Genzyme in the development of products under each Split Territory Program and VY-SMN101 pursuant to a written development plan and under the guidance of an alliance joint steering committee, comprised of an equal number of our employees and Genzyme employees.
We are required to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop products under each Split Territory Program and VY-SMN101 through completion of the applicable POP Study. During the development of our joint programs, our and Genzyme's activities are guided by a Development Advisory Committee, which we refer to as the DAC. The DAC may elect to utilize certain Genzyme technology relating to the VY-AADC01 program, the VY-HTT01 Program, or generally with the manufacture of Split Territory Program products.
We will be solely responsible for all costs incurred in connection with the development of Split Territory Programs and VY-SMN101 products prior to option exercise, subject to the following: (i) Genzyme may agree to provide additional funds in return for agreed-upon payback or other agreed economic terms; (ii) we may request, and upon mutual agreement, Genzyme will provide in-kind services valued at up to $5.0 million; and (iii) expenses of certain activities under the VY-HTT01 development plan may be funded to the extent such activities are reimbursed through financial support that Genzyme may receive from a disease foundation group.
Other than the VY-AADC01 program (for which a POP Study has already been commenced), if we do not initiate a POP Study for a given Split Territory Program by December 31, 2026 (or for the Future Program by the tenth anniversary of the date the Future Program is nominated by Genzyme), and Genzyme has not terminated this agreement with respect to such Collaboration program, then Genzyme shall be entitled, at its sole and exclusive remedy, to a credit of $10.0 million for each such program against other amounts payable by Genzyme under the Collaboration. However, if we do not initiate a POP Study by such date as a result of a regulatory delay or a force majeure event, such time period shall be extended for so long as such regulatory delay or force majeure event continues and we shall not be deemed to have failed to initiate a POP Study.
Post-Option Exercise
Upon Genzyme's exercise of its option to license a given product in a Split Territory Program, which we refer to as a Split Territory Licensed Product, we will have sole responsibility for the development of such Split Territory Licensed Product in the United States and Genzyme shall have sole responsibility for development of such Split Territory Licensed Product in the rest of the world. We and Genzyme will have shared responsibility for execution of ongoing development of such Split Territory Licensed Product that is not specific to either of our territories, including costs associated therewith.
29
A steering committee for each Program will review and approve a written plan and budget for each relevant program. In addition, all development activities to be undertaken with respect to each Split Territory Licensed Product by or on behalf of either party will be set forth in a written development plan.
Genzyme shall have the sole right to develop VY-SMN101 worldwide. Genzyme shall be responsible for all of the development costs that occur after the option exercise date for VY-SMN101.
Commercialization
We shall be solely responsible, at our expense, for all commercialization activities relating to Split Territory Licensed Products in the United States. Genzyme shall be solely responsible, at its expense, for all commercialization activities relating to Split Territory Licensed Products in the rest of the world. If Genzyme has exercised the co-commercialization option, Genzyme will be the lead party responsible for all commercialization activities relating to the Huntington's disease product in the United States. If Genzyme has exercised its option to co-commercialize VY-HTT01 in the United States, commercialization activities that are undertaken for VY-HTT01 in the United States will be set forth in reasonable detail in a written commercialization plan.
Genzyme shall be solely responsible, at its expense, for all commercialization activities relating to VY-SMN101 worldwide. Genzyme shall use commercially reasonable efforts to commercialize VY-SMN101 in each major market specified in the agreement where Genzyme has obtained required governmental approvals
Financial Terms
We received $65.0 million in upfront cash, a $30.0 million upfront equity investment and an in-kind commitment of $5.0 million, totalling $100 million. If Genzyme exercises its option for a collaboration program, with the exception of VY-AADC01, Genzyme is required to make an option exercise payment of $20.0 million or $30.0 million for each program. In addition, Genzyme shall pay us up to $645 million across product programs upon the achievement of specified regulatory and commercial milestones.
In addition, to the extent any Split Territory Licensed Product or the VY-SMN101 Product is commercialized, we are entitled to receive tiered royalty payments ranging from the mid-single digits to mid-teens based on a percentage of net sales. Genzyme is entitled to receive royalty payments from us related to sales of the Split Territory Licensed Products ranging from the low-single digits to mid-single digits, depending on whether we use Genzyme technology in a Split Territory Licensed Product or the VY-SMN101 Product. If Genzyme exercises its option to co-commercialize VY-HTT01 in the United States, we will share any profits or losses from VY-HTT01 product sales.
Term And Termination; Remedies
Our collaboration agreement with Genzyme will continue in effect until the later of (i) the expiration of the last to expire of the option rights and (ii) the expiration of all payment obligations unless sooner terminated by us or Genzyme.
We and Genzyme have customary termination rights including the right to terminate for an uncured material breach of the agreement committed by the other party and Genzyme has the right to terminate for convenience.
License Agreement with University of Massachusetts
On January 30, 2014, we entered into a license agreement with the University of Massachusetts, or UMass, pursuant to which UMass granted us an exclusive, worldwide, royalty-bearing license to certain of its licensed patents to make, have made, use, offer for sale, sell, have sold and import certain licensed products in the field of human diseases that use gene therapy applications. Our license is subject to any rights that may be required to be granted to the
30
government of the United States, and UMass reserves the right to use the licensed patents for education and research and, with our consent, for non-commercial patient care, without the payment of any compensation to us.
In consideration for rights granted to us under the agreement, we made an upfront payment of $200,000 to UMass. We are obligated to pay UMass (i) low-single digit royalty payments based on net sales of the licensed products, (ii) annual maintenance payments of $30,000, which are creditable against royalties payable in such period, (iii) minimum aggregate annual royalty payments that are creditable against royalties payable in such period, with the minimum aggregate amount payable being in the low-six digits for each of the first four years of this agreement and a minimum aggregate amount payable being in the mid-six digits for each year, thereafter, (iv) milestone payments of up to $1.8 million, per licensed product for the first five licensed products, based on the achievement of development and regulatory milestones and (v) a percentage of sublicensing income that decreases over time from low double digit percentages to a mid-single digit percentage. We also agreed to reimburse UMass approximately $678,000 for patent related expenses incurred by UMass as of the effective date of the agreement over a two year period.
Under the agreement, we agreed to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop licensed products and to introduce such licensed products into the commercial market, and further agreed to certain development milestones.
The agreement will terminate on the date that is the later of (i) seven years after the first commercial sale of the last licensed product under the agreement or (ii) such time as there are no valid claims covering a licensed product. We have the right to terminate the agreement for any reason upon 90 days prior written notice, and we and UMass have the right to terminate the agreement if the other party fails to cure a written breach within 60 days of receiving written notice of such breach.
MassBiologics and UMass Collaboration Agreement
On October 20, 2014, we entered into a Collaboration Agreement with UMass and MassBiologics, pursuant to which we shall (i) fund certain projects that will be conducted by UMass or MassBiologics, (ii) fund certain educational programs of UMass, including post-doctoral research at our laboratories beginning in 2015 and an annual lecture series beginning in 2015 and (iii) collaborate with MassBiologics to establish scalable processes for manufacturing recombinant AAV vector products using cGMP.
In November 2014, we agreed to the first project under this agreement whereby we will fund approximately $2.9 million over a 16-month period for certain research and development services performed by MassBiologics. The project commenced in January 2015. If the agreement is terminated for any reason, we are obligated to fund the remaining balance of the total price of all work completed and any other out of pocket costs incurred by MassBiologics. We and UMass and/or MassBiologics may agree to conduct other projects in the future, the terms of which will be agreed upon at such time.
This agreement will remain in effect for a period of five years and automatically renews for additional one year periods. Either party has the right to terminate this agreement, once in each renewal period, for any reason upon providing the other party with 90 days written notice or in the event of a material breach of the agreement by the other party that is not cured within 60 days of written notice.
We will own all intellectual property rights generated under this agreement, either by our employees, UMass and/or MassBiologics employees, or jointly by our employees and UMass and/or MassBiologics employees, that cover AAV materials. We and UMass and/or MassBiologics, as applicable, will jointly own any intellectual property rights generated under this agreement jointly by our employees and the employees of UMass and/or MassBiologics, as applicable, that do not cover AAV materials.
License Agreement with REGENX
31
In May 2014, we entered into a license agreement with REGENXBIO Inc., formerly known as ReGenX Biosciences, LLC, or REGENX, for the development and commercialization of gene therapies to treat ALS, Friedreich's ataxia and Huntington's disease. Under this license agreement, REGENX granted us a non-exclusive worldwide license to make, have made and use its technology solely for internal research and preclinical development for the identification of specific vectors that could be commercialized. Following identification, we have an option to obtain a non-exclusive worldwide license under the licensed intellectual property to a single specified AAV vector to make, have made, use, import, sell and offer for sale licensed products using the selected vector, which can be exercised for each of ALS, Friedreich's ataxia, or Huntington's disease.
Under the terms of this license agreement, we paid REGENX an upfront fee of $500,000, an extension fee of $100,000 and are required to make an annual maintenance fee in the five digits. If we exercise any or all of the commercial options by a specified date, we will be required to make upfront payments to REGENX of up to $1.5 million and to pay to REGENX an annual maintenance fee payment ranging from five digits to six digits depending on the number of disease indication options exercised. In addition, we will be required to pay to RENGENX up to $5.0 million in milestone fees per disease indication, mid- to high-single digit royalty percentages on net sales of licensed products, and low- to mid-single digit percentages of any sublicense fees that we receive from sublicensees for the licensed intellectual property rights.
Our license agreement with REGENX will expire upon the expiration, lapse, abandonment, or invalidation of the last claim of the licensed intellectual property to expire, lapse, or become abandoned or unenforceable in all the countries of the world. The license agreement will automatically terminate if we do not exercise any commercial options within a specified time period after entering into the license agreement, which may be extended. We may terminate the license agreement upon a specified number of days prior written notice. REGENX may terminate the license agreement if we, our affiliates, or sublicensees experience insolvency, if we are more than a specified number of days late in paying money due under the license agreement, or, effective immediately, if we or our affiliates commence any action against REGENX or its licensors to declare or render any claim of the licensed patent rights invalid or unenforceable. Either party may terminate the license agreement for material breach that is not cured within a specified number of days.
Competition
The biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by intense and dynamic competition to develop new technologies and proprietary therapies. Any product candidates that we successfully develop into products and commercialize may compete with existing therapies and new therapies that may become available in the future. While we believe that our product engine, product programs, product candidates and scientific expertise in the fields of gene therapy and neuroscience provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from various sources, including larger and better-funded pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, as well as from academic institutions, governmental agencies and public and private research institutions.
We are aware of several companies focused on developing gene therapies in various indications, including bluebird bio, Inc., Agilis Biotherapeutics, LLC, Applied Genetic Technologies Corporation, Asklepios BioPharmaceutical, Inc., Audentes Therapeutics, Inc., Avalanche Biotechnologies, Inc., Bamboo Therapeutics, Dimension Therapeutics, Inc., GenSight Biologies SA, NightstaRx Ltd, REGENX, uniQure NV, or uniQure, and Spark Therapeutics, Inc. as well as several companies addressing other methods for modifying genes and regulating gene expression. Any advances in gene therapy technology made by a competitor may be used to develop therapies that could compete against any of our product candidates.
We expect that VY-AADC01 will compete with a variety of therapies currently marketed and in development for advanced Parkinson's disease, including DBS marketed by Medtronic plc, St. Jude Medical, Inc. and other medical device companies, DUOPA/Duodopa marketed by AbbVie Inc., as well as potentially AMT-090 or AAV-GDNF in development at uniQure NV, or uniQure, OXB-102/Prosavin in development at Oxford Biomedica plc, and ND0612H in development at NeuroDerm Ltd.
We expect that our preclinical programs will compete with a variety of therapies in development, including:
32
|
· |
VY-SOD101 for a monogenic form of ALS will potentially compete with IONIS-SOD1Rx being developed by Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., or Ionis, in collaboration with Biogen and Tirasemtiv being developed by Cytokinetics, Inc., or Cytokinetics; |
|
· |
VY-FXN01 for Friedreich's ataxia will potentially compete with RG2833 being developed by BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., AAV-FXN being developed by Annapurna Therapeutics, AAV-FXN being developed by Bamboo Therapeutics, and frataxin targeted gene therapy being developed by Agilis Biotherapeutics, LLC in collaboration with Intrexon Corporation and BB-FA being developed by BioBlast Pharma Ltd., or BioBlast; |
|
· |
VY-HTT01 for Huntington's disease will potentially compete with IONIS-HTTRx being developed by Ionis in collaboration with F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd., or Roche, gene editing approach being developed by Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. in collaboration with Shire plc, and another gene therapy being developed by uniQure; and |
|
· |
VY-SMN101 for spinal muscular atrophy will potentially compete with AVXS-101 being developed by AveXis Inc., IONIS-SMNRX being developed by Ionis and Biogen, LMI-070 being developed by Novartis AC, RO6885247 being developed by PTC Therapeutics, Inc. and Roche, BBrm02 being developed by BioBlast and CK-2127107 being developed by Cytokinetics in collaboration with Astellas Pharma US, Inc. |
In addition, companies that are currently engaged in gene therapy for non-CNS diseases could at any time decide to develop gene therapies for CNS diseases.
Many of our competitors, either alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do and significantly greater experience in the discovery and development of product candidates, obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals of product candidates and commercializing those product candidates. Accordingly, our competitors may be more successful than us in obtaining approval for product candidates and achieving widespread market acceptance. Our competitors' product candidates may be more effective, or more effectively marketed and sold, than any product candidate we may commercialize and may render our treatments obsolete or non-competitive before we can recover the expenses of developing and commercializing any of our product candidates.
Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. These competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel and establishing clinical trial sites and subject registration for clinical trials, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies.
We anticipate that we will face intense and increasing competition as new product candidates enter the market and advanced technologies become available. We expect any product candidates that we develop and commercialize to compete on the basis of, among other things, efficacy, safety, convenience of administration and delivery, price, and the availability of reimbursement from government and other third-party payers.
Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any products that we may develop. Our competitors also may obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their product candidates more rapidly than we may obtain approval for ours, which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market.
33
Intellectual Property
Overview
We strive to protect the proprietary technology, inventions, and to enhance improvements that are commercially important to the development of our business, including seeking, maintaining, and defending patent rights, whether developed internally or licensed from third parties. We also rely on trade secrets and know-how relating to our proprietary technology platform, on continuing technological innovation and on in-licensing opportunities to develop, strengthen and maintain the strength of our position in the field of gene therapy that may be important for the development of our business. We additionally may rely on regulatory protection afforded through data exclusivity, market exclusivity and patent term extensions where available.
Our commercial success may depend in part on our ability to: obtain and maintain patent and other protections for commercially important technology, inventions and know-how related to our business; defend and enforce our patents; preserve the confidentiality of our trade secrets; and operate without infringing the valid enforceable patents and intellectual property rights of third parties. Our ability to stop third parties from making, having made, using, selling, offering to sell or importing our products may depend on the extent to which we have rights under valid and enforceable licenses, patents or trade secrets that cover these activities. In some cases, these rights may need to be enforced by third party licensors. With respect to both licensed and company-owned intellectual property, we cannot be sure that patents will be granted with respect to any of our pending patent applications or with respect to any patent applications filed by us in the future, nor can we be sure that any of our existing patents or any patents that may be granted to us in the future will be commercially useful in protecting our commercial products and methods of manufacturing the same.
We have 28 patent applications pending in the United States and foreign jurisdictions. At least 20 patent applications have been filed and are pending in the United States and foreign jurisdictions by or on behalf of universities which have granted us exclusive license rights to the technology. To date, 25 patents have issued to our licensors which have granted us exclusive license rights to the technology. To date, 28 patents have issued to our licensors which have granted us non-exclusive license rights to the technology with 10 applications pending. Our policy is to file patent applications to protect technology, inventions and improvements to inventions that are commercially important to the development of our business. We seek United States and international patent protection for a variety of technologies, including: research tools and methods, methods for transferring genetic material into cells, AAV-based biological products, methods of designing novel AAV constructs, methods for treating diseases of interest and methods for manufacturing our AAV-based products. We also intend to seek patent protection or rely upon trade secret rights to protect other technologies that may be used to discover and validate targets and that may be used to identify and develop novel biological products. We seek protection, in part, through confidentiality and proprietary information agreements. We are a party to various other license agreements that give us rights to use specific technologies in our research and development.
Company-Owned Intellectual Property
We own a patent application directed to capsid engineering and domain swapping. This application is pending in the United States, and was filed internationally on June 9, 2015 in combination with our application directed to AAV production. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own a patent application directed to AAV production. This application is pending in the United States, and was filed internationally on June 9, 2015 in combination with our application directed to capsid engineering and domain swapping. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own two patent families with a total of six patent applications directed to AAV constructs encoding the gene AADC for therapeutic uses. These applications are pending in the United States, and one family was filed
34
internationally on November 5, 2015, and the second family is due to convert at the earliest of July 31, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own three patent applications directed to targeting SOD1 for the treatment of ALS. These applications are pending in the United States, and were filed internationally on November 13, 2015. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own two patent applications directed to delivery of AAV gene therapies to the CNS. These applications are pending in the United States, and was filed internationally on January 15, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2036, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own a patent application directed to the production of scAAV particles. This application is pending in the United States, and was filed internationally on December 11, 2015. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own three patent applications directed to the design of AAV drug delivery cassettes. This application is pending in the United States, and was filed internationally on November 13, 2015. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own two patent applications directed to regulatable expression control of AAV transgenes. These applications are pending in the United States, and are due to convert at the earliest on February 23, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2036, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own three patent applications directed to AAVs encoding frataxin constructs for the treatment of Friedreich's Ataxia. These applications are pending in the United States, and were filed internationally on January 15, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2036, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own one patent application directed to the design of Inverted Terminal Repeats. This application is pending in the United States, and is due to convert August 11, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2036, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We have filed a patent application directed to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the treatment of ALS to protect our intellectual property arising from a funded grant from The Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Association. This application is pending in the United States, and is due to convert April 30, 2016. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2036, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We own three patent applications directed to the delivery of AAV gene therapies to the CNS. These applications are pending in the United States and are due to convert October 29, 2016. Patents that grant from this family are generally expected to expire in 2036.
We own one patent application directed to regulatable expression control of AAV transgenes. This application is pending in the United States, and is due to convert October 28, 2016. Patents that grant from this family are generally expected to expire in 2036.
Licensed Intellectual Property
We have obtained exclusive licenses and non-exclusive licenses to patents directed to both compositions of matter and methods of use.
35
We have licensed six families of patents and patent applications, in the exclusive field of gene therapy for human diseases, directed to RNAi constructs as vector payloads, their design and use in the treatment of CNS disorders from the University of Massachusetts. This family of patents and applications is pending and/or granted in the United States and other territories and comprises 38 granted patents and 16 applications. Patents have been granted in the United States, Canada, Europe, Israel, Japan, Korea and Australia. Nationalization for some members has taken place in Germany, Spain, France, Great Britain Italy, and Sweden. Patents that grant from these patent families are generally expected to expire between 2022 and 2025, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We have exclusively licensed three families of patents and patent applications directed to novel AAV capsids from the University of Massachusetts. These families of patents and applications, pending and/or granted in the United States, comprise of 2 granted patents and 10 applications. The two patents were granted in the United States. Patents that grant from these patent families are generally expected to expire between 2030 and 2035, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We have non-exclusively licensed a patent family directed to production methods for AAV in insect cells from the NIH, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. This family of patents is granted in the United States, Canada, Australia and Europe and further nationalized in Germany, France and Great Britain and comprises eight granted patents. Patents that grant from this patent family are generally expected to expire in 2022, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We have licensed two families of patents and patent applications directed to novel AAV capsids from the Board of Trustees of the Leland Stanford Junior University. These families of patents and applications, pending and/or granted in the United States, comprise five granted patents and four applications. Patents that grant from these patent families are generally expected to expire between 2027 and 2032, subject to possible patent term extensions.
Trademark Protection
We have filed and obtained trademark protection for the VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS character mark for pharmaceutical research and development in the field of gene therapy. The mark is listed on the Principal Register, Registration No. 4545283.
We have filed and obtained trademark protection for the VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS service mark logo for pharmaceutical research and development in the field of gene therapy. The mark is listed on the Principal Register, Registration No. 4621083.
We plan to register trademarks in connection with our biological products.
In addition to the above, we have established expertise and development capabilities focused in the areas of preclinical research and development, manufacturing and manufacturing process scale-up, quality control, quality assurance, regulatory affairs and clinical trial design and implementation. We believe that our focus and expertise will help us develop products based on our proprietary intellectual property.
Trade Secret Protection
Finally, we may rely, in some circumstances, on trade secrets to protect our technology. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our consultants, contractors
36
or collaborators use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resulting know-how and inventions.
To the extent that the valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3. A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Government Regulation
Biological products, including gene therapy products, are subject to regulation under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or FD&C Act, and the Public Health Service Act, or PHS Act, and other federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations. Both the FD&C Act and the PHS Act and their corresponding regulations govern, among other things, the testing, manufacturing, safety, purity, potency, efficacy, labeling, packaging, storage, record keeping, distribution, import, export, reporting, advertising and other promotional practices involving biological products. FDA approval must be obtained before clinical testing of biological products, and each clinical study protocol for a gene therapy product is reviewed by the FDA and, in some instances, the NIH, through its RAC. FDA approval also must be obtained before marketing of biological products. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources and we may not be able to obtain the required regulatory approvals.
Within the FDA, the Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, or CBER, regulates gene therapy products. CBER works closely with the NIH and its RAC, which makes recommendations to the NIH on gene therapy issues and engages in a public discussion of scientific, safety, ethical and societal issues related to proposed and ongoing gene therapy protocols. The FDA and the NIH have published guidance documents with respect to the development and submission of gene therapy protocols. The FDA also has published guidance documents related to, among other things, gene therapy products in general, their preclinical assessment, observing subjects involved in gene therapy studies for delayed adverse events, viral shedding, environmental assessments, potency testing, and chemistry, manufacturing and control information in gene therapy INDs. FDA guidance documents provide the agency's current thinking about a particular subject, but are not legally binding.
U.S. Biological Products Development Process
The process required by the FDA before a biological product may be marketed in the United States generally involves the following:
|
· |
completion of nonclinical laboratory tests and animal studies according to good laboratory practice, or GLPs, and applicable requirements for the humane use of laboratory animals or other applicable regulations; |
|
· |
submission to the FDA of an application for an IND, which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin; |
|
· |
performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials according to the FDA's regulations commonly referred to as good clinical practice, or GCPs, and any additional requirements for the protection of human research subjects and their health information, to establish the safety and efficacy of the proposed biological product for its intended use; |
|
· |
submission to the FDA of a Biologics License Application, or BLA, for marketing approval that includes substantive evidence of safety, purity, and potency from results of nonclinical testing and clinical trials; |
|
· |
satisfactory completion of an FDA inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities where the biological product is produced to assess compliance with cGMP, to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to preserve the biological product's identity, strength, quality and purity; |
37
|
· |
potential FDA audit of the nonclinical and clinical study sites that generated the data in support of the BLA; and |
|
· |
FDA review and approval, or licensure, of the BLA. |
Before testing any biological product candidate, including a gene therapy product, in humans, the product candidate enters the preclinical testing stage. Preclinical tests, also referred to as nonclinical trials, include laboratory evaluations of product chemistry, toxicity and formulation, as well as animal studies to assess the potential safety and activity of the product candidate. The conduct of the preclinical tests must comply with federal regulations and requirements including GLPs.
Where a gene therapy study is conducted at, or sponsored by, institutions receiving NIH funding for recombinant DNA research, prior to the submission of an IND to the FDA, a protocol and related documentation is submitted to and the study is registered with the NIH Office of Biotechnology Activities, or OBA, pursuant to the NIH Guidelines for Research Involving Recombinant DNA Molecules, or NIH Guidelines. Compliance with the NIH Guidelines is mandatory for investigators at institutions receiving NIH funds for research involving recombinant DNA, however many companies and other institutions not otherwise subject to the NIH Guidelines voluntarily follow them. The NIH is responsible for convening the RAC, a federal advisory committee, that discusses protocols that raise novel or particularly important scientific, safety or ethical considerations at one of its quarterly public meetings. The OBA will notify the FDA of the RAC's decision regarding the necessity for full public review of a gene therapy protocol. RAC proceedings and reports are posted to the OBA website and may be accessed by the public.
The clinical study sponsor must submit the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical data or literature and a proposed clinical protocol, to the FDA as part of the IND. Some preclinical testing typically continues after the IND is submitted. The IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless the FDA places the clinical study on a clinical hold within that 30-day time period. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical study can begin. With gene therapy protocols, if the FDA allows the IND to proceed, but the RAC decides that full public review of the protocol is warranted, the FDA will request at the completion of its IND review that sponsors delay initiation of the protocol until after completion of the RAC review process. The FDA may also impose clinical holds on a biological product candidate at any time before or during clinical trials due to safety concerns or non-compliance. If the FDA imposes a clinical hold, studies may not recommence without FDA authorization and then only under terms authorized by the FDA. Accordingly, we cannot be sure that submission of an IND will result in the FDA allowing clinical trials to begin, or that, once begun, issues will not arise that suspend or terminate such studies.
Clinical trials involve the administration of the biological product candidate to healthy volunteers or patients under the supervision of qualified investigators, generally physicians not employed by or under the study sponsor's control. Clinical trials are conducted under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the clinical study, dosing procedures, subject selection and exclusion criteria, and the parameters to be used to monitor subject safety, including stopping rules that assure a clinical study will be stopped if certain adverse events should occur. Each protocol and any amendments to the protocol must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. Clinical trials must be conducted and monitored in accordance with the FDA's regulations comprising the GCP requirements, including the requirement that all research subjects provide informed consent. Further, each clinical study must be reviewed and approved by an independent institutional review board, or IRB, at or servicing each institution at which the clinical study will be conducted. An IRB is charged with protecting the welfare and rights of study participants and considers such items as whether the risks to individuals participating in the clinical trials are minimized and are reasonable in relation to anticipated benefits. The IRB also approves the form and content of the informed consent that must be signed by each clinical study subject or his or her legal representative and must monitor the clinical study until completed. Clinical trials involving recombinant or synthetic (or both) nucleic acid molecules performed at or sponsored by an institution that receives any NIH funding for such research also must be reviewed by an institutional biosafety committee, or IBC, a local institutional committee that reviews and oversees basic and clinical research conducted at that institution. The IBC assesses the safety of the research and identifies any potential risk to public health or the environment.
38
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases that may overlap or be combined:
|
· |
Phase 1. The biological product is initially introduced into healthy human subjects and tested for safety. In the case of some products for severe or life-threatening diseases, especially when the product may be too inherently toxic to ethically administer to healthy volunteers, the initial human testing is often conducted in patients. |
|
· |
Phase 2. The biological product is evaluated in a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the product for specific targeted diseases and to determine dosage tolerance, optimal dosage and dosing schedule. |
|
· |
Phase 3. Clinical trials are undertaken to further evaluate dosage, clinical efficacy, potency and safety in an expanded patient population at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites. These clinical trials are intended to establish the overall risk/benefit ratio of the product and provide an adequate basis for product labeling. |
Post-approval clinical trials, sometimes referred to as Phase 4 clinical trials, may be conducted after initial marketing approval. These clinical trials are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of patients in the intended therapeutic indication, particularly for long-term safety follow-up. The FDA recommends that sponsors observe subjects for potential gene therapy-related delayed adverse events for a 15-year period, including a minimum of five years of annual examinations followed by ten years of annual queries, either in person or by questionnaire, of trial subjects.
During all phases of clinical development, regulatory agencies require extensive monitoring and auditing of all clinical activities, clinical data, and clinical trial investigators. Annual progress reports detailing the results of the clinical trials must be submitted to the FDA. Written IND safety reports must be promptly submitted to the FDA, the NIH and the investigators for serious and unexpected adverse events, any findings from other studies, tests in laboratory animals or in vitro testing that suggest a significant risk for human subjects, or any clinically important increase in the rate of a serious suspected adverse reaction over that listed in the protocol or investigator brochure. The sponsor must submit an IND safety report within 15 calendar days after the sponsor determines that the information qualifies for reporting. The sponsor also must notify the FDA of any unexpected fatal or life-threatening suspected adverse reaction within seven calendar days after the sponsor's initial receipt of the information. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, if at all. The FDA or the sponsor or its data safety monitoring board may suspend a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB's requirements or if the biological product has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
Human gene therapy products are a new category of therapeutics. Because this is a relatively new and expanding area of novel therapeutic interventions, there can be no assurance as to the length of the study period, the number of patients the FDA will require to be enrolled in the studies in order to establish the safety, efficacy, purity and potency of human gene therapy products, or that the data generated in these studies will be acceptable to the FDA to support marketing approval. The NIH and the FDA have a publicly accessible database, the Genetic Modification Clinical Research Information System which includes information on gene transfer studies and serves as an electronic tool to facilitate the reporting and analysis of adverse events on these studies.
Concurrent with clinical trials, companies usually complete additional animal studies and must also develop additional information about the physical characteristics of the biological product as well as finalize a process for manufacturing the product in commercial quantities in accordance with cGMP requirements. To help reduce the risk of the introduction of adventitious agents with use of biological products, the Public Health Service Act, or PHS Act, emphasizes the importance of manufacturing control for products whose attributes cannot be precisely defined. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of the product candidate and, among other things, the sponsor must develop methods for testing the identity, strength, quality, potency and purity of the final biological product. Additionally, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested and stability studies must be
39
conducted to demonstrate that the biological product candidate does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
U.S. Review and Approval Processes
After the completion of clinical trials of a biological product, FDA approval of a BLA, must be obtained before commercial marketing of the biological product. The BLA must include results of product development, laboratory and animal studies, human studies, information on the manufacture and composition of the product, proposed labeling and other relevant information. In addition, under the Pediatric Research Equity Act, or PREA, a BLA or supplement to a BLA must contain data to assess the safety and effectiveness of the biological product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. The FDA may grant deferrals for submission of data or full or partial waivers. Unless otherwise required by regulation, PREA does not apply to any biological product for an indication for which orphan designation has been granted. The testing and approval processes require substantial time and effort and there can be no assurance that the FDA will accept the BLA for filing and, even if filed, that any approval will be granted on a timely basis, if at all.
Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act, or PDUFA, as amended, each BLA must be accompanied by a user fee. The FDA adjusts the PDUFA user fees on an annual basis. PDUFA also imposes an annual product fee for biologics and an annual establishment fee on facilities used to manufacture prescription biologics. Fee waivers or reductions are available in certain circumstances, including a waiver of the application fee for the first application filed by a small business. Additionally, no user fees are assessed on BLAs for products designated as orphan drugs, unless the product also includes a non-orphan indication.
Within 60 days following submission of the application, the FDA reviews a BLA submitted to determine if it is substantially complete before the agency accepts it for filing. The FDA may refuse to file any BLA that it deems incomplete or not properly reviewable at the time of submission and may request additional information. In this event, the BLA must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application also is subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review of the BLA. The FDA reviews the BLA to determine, among other things, whether the proposed product is safe and potent, or effective, for its intended use, and has an acceptable purity profile, and whether the product is being manufactured in accordance with cGMP to assure and preserve the product's identity, safety, strength, quality, potency and purity. The FDA may refer applications for novel biological products or biological products that present difficult questions of safety or efficacy to an advisory committee, typically a panel that includes clinicians and other experts, for review, evaluation and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions. During the biological product approval process, the FDA also will determine whether a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, or REMS, is necessary to assure the safe use of the biological product. If the FDA concludes a REMS is needed, the sponsor of the BLA must submit a proposed REMS; the FDA will not approve the BLA without a REMS, if required.
Before approving a BLA, the FDA will inspect the facilities at which the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the product unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving a BLA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical trial sites to assure that the clinical trials were conducted in compliance with IND study requirements and GCP requirements. To assure cGMP and GCP compliance, an applicant must incur significant expenditure of time, money and effort in the areas of training, record keeping, production, and quality control.
Notwithstanding the submission of relevant data and information, the FDA may ultimately decide that the BLA does not satisfy its regulatory criteria for approval and deny approval. Data obtained from clinical trials are not always conclusive and the FDA may interpret data differently than we interpret the same data. If the agency decides not to approve the BLA in its present form, the FDA will issue a complete response letter that usually describes all of the
40
specific deficiencies in the BLA identified by the FDA. The deficiencies identified may be minor, for example, requiring labeling changes, or major, for example, requiring additional clinical trials. Additionally, the complete response letter may include recommended actions that the applicant might take to place the application in a condition for approval. If a complete response letter is issued, the applicant may either resubmit the BLA, addressing all of the deficiencies identified in the letter, or withdraw the application.
If a product receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific diseases and dosages or the indications for use may otherwise be limited, which could restrict the commercial value of the product. Further, the FDA may require that certain contraindications, warnings or precautions be included in the product labeling. The FDA may impose restrictions and conditions on product distribution, prescribing, or dispensing in the form of a risk management plan, or otherwise limit the scope of any approval. In addition, the FDA may require post marketing clinical trials, sometimes referred to as Phase 4 clinical trials, designed to further assess a biological product's safety and effectiveness, and testing and surveillance programs to monitor the safety of approved products that have been commercialized.
One of the performance goals agreed to by the FDA under the PDUFA is to review standard BLAs in 10 months from filing and priority BLAs in six months from filing, whereupon a review decision is to be made. The FDA does not always meet its PDUFA goal dates for standard and priority BLAs and its review goals are subject to change from time to time. The review process and the PDUFA goal date may be extended by three months if the FDA requests or the BLA sponsor otherwise provides additional information or clarification regarding information already provided in the submission within the last three months before the PDUFA goal date.
Post-Approval Requirements
Maintaining substantial compliance with applicable federal, state, and local statutes and regulations requires the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources. Rigorous and extensive FDA regulation of biological products continues after approval, particularly with respect to cGMP. We will rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties for the production of clinical and commercial quantities of any products that we may commercialize. Manufacturers of our products are required to comply with applicable requirements in the cGMP regulations, including quality control and quality assurance and maintenance of records and documentation. Other post-approval requirements applicable to biological products, include reporting of cGMP deviations that may affect the identity, potency, purity and overall safety of a distributed product, record-keeping requirements, reporting of adverse effects, reporting updated safety and efficacy information, and complying with electronic record and signature requirements. After a BLA is approved, the product also may be subject to official lot release. As part of the manufacturing process, the manufacturer is required to perform certain tests on each lot of the product before it is released for distribution. If the product is subject to official release by the FDA, the manufacturer submits samples of each lot of product to the FDA together with a release protocol showing a summary of the history of manufacture of the lot and the results of all of the manufacturer's tests performed on the lot. The FDA also may perform certain confirmatory tests on lots of some products, such as viral vaccines, before releasing the lots for distribution by the manufacturer. In addition, the FDA conducts laboratory research related to the regulatory standards on the safety, purity, potency, and effectiveness of biological products.
We also must comply with the FDA's advertising and promotion requirements, such as those related to direct-to-consumer advertising, the prohibition on promoting products for uses or in patient populations that are not described in the product's approved labeling (known as "off-label use"), industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities, and promotional activities involving the internet. Discovery of previously unknown problems or the failure to comply with the applicable regulatory requirements may result in restrictions on the marketing of a product or withdrawal of the product from the market as well as possible civil or criminal sanctions. Failure to comply with the applicable U.S. requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process or after approval, may subject an applicant or manufacturer to administrative or judicial civil or criminal sanctions and adverse publicity. FDA sanctions could include refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, clinical hold, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, mandated corrective advertising or communications with doctors, debarment,
41
restitution, disgorgement of profits, or civil or criminal penalties. Any agency or judicial enforcement action could have a material adverse effect on us.
Biological product manufacturers and other entities involved in the manufacture and distribution of approved biological products are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and certain state agencies for compliance with cGMPs and other laws. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain cGMP compliance. Discovery of problems with a product after approval may result in restrictions on a product, manufacturer, or holder of an approved BLA, including withdrawal of the product from the market. In addition, changes to the manufacturing process or facility generally require prior FDA approval before being implemented and other types of changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications and additional labeling claims, are also subject to further FDA review and approval.
Orphan Drug Designation
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan designation to a drug or biological product intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more than 200,000 individuals in the United States and for which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making a drug or biological product available in the United States for this type of disease or condition will be recovered from sales of the product. Orphan product designation must be requested before submitting a BLA. After the FDA grants orphan product designation, the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan product designation does not convey any advantage in or shorten the duration of the regulatory review and approval process.
If a product that has orphan designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan product exclusivity, which means that the FDA may not approve any other applications to market the same biological product for the same indication for seven years, except in limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority to the product with orphan exclusivity. Competitors, however, may receive approval of different products for the indication for which the orphan product has exclusivity or obtain approval for the same product but for a different indication for which the orphan product has exclusivity. Orphan product exclusivity also could block the approval of one of our products for seven years if a competitor obtains approval of the same biological product as defined by the FDA or if our product candidate is determined to be contained within the competitor's product for the same indication or disease. If a biological product designated as an orphan product receives marketing approval for an indication broader than what is designated, it may not be entitled to orphan product exclusivity.
Special FDA Expedited Review and Approval Programs
The FDA has various programs, including fast track designation, accelerated approval, priority review and breakthrough therapy designation, that are intended to expedite or simplify the process for the development and FDA review of biological products that are intended for the treatment of serious or life threatening diseases or conditions and demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs. The purpose of these programs is to provide important new biological products to patients earlier than under standard FDA review procedures. To be eligible for a fast track designation, the FDA must determine, based on the request of a sponsor, that a biological product is intended to treat a serious or life threatening disease or condition and demonstrates the potential to address an unmet medical need. The FDA will determine that a product will fill an unmet medical need if it will provide a therapy where none exists or provide a therapy that may be potentially superior to existing therapy based on efficacy or safety factors.
The FDA may give a priority review designation to biological products that offer major advances in treatment, or provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists. A priority review means that the goal for the FDA to review an application is six months, rather than the standard review of ten months under current PDUFA guidelines. Most products that are eligible for fast track designation are also likely to be considered appropriate to receive a priority review.
42
In addition, biological products studied for their safety and effectiveness in treating serious or life-threatening illnesses and that provide meaningful therapeutic benefit over existing treatments may receive accelerated approval and may be approved on the basis of adequate and well-controlled clinical trials establishing that the biological product has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. As a condition of approval, the FDA may require a sponsor of a biological product receiving accelerated approval to perform post-marketing studies to verify and describe the predicted effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical endpoint, and the biological product may be subject to accelerated withdrawal procedures.
Moreover, under the provisions of the new Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act, or FDASIA, enacted in 2012, a sponsor can request designation of a product candidate as a "breakthrough therapy." A breakthrough therapy is defined as a biological product that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the biological product may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. Biological products designated as breakthrough therapies are also eligible for accelerated approval. The FDA must take certain actions, such as holding timely meetings and providing advice, intended to expedite the development and review of an application for approval of a breakthrough therapy.
Even if a product qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or decide that the time period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened. Furthermore, fast track designation, priority review, accelerated approval and breakthrough therapy designation, do not change the standards for approval and may not ultimately expedite the development or approval process.
U.S. Patent Term Restoration and Marketing Exclusivity
Depending upon the timing, duration and specifics of the FDA approval of the use of our product candidates, some of our U.S. patents may be eligible for limited patent term extension under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, commonly referred to as the Hatch-Waxman Amendments. The Hatch-Waxman Amendments permit a patent restoration term of up to five years as compensation for patent term lost during product development and the FDA regulatory review process. However, patent term restoration cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the product's approval date. The patent term restoration period is generally one-half the time between the effective date of an IND and the submission date of a BLA plus the time between the submission date of a BLA and the approval of that application. Only one patent applicable to an approved biological product is eligible for the extension and the application for the extension must be submitted prior to the expiration of the patent. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, in consultation with the FDA, reviews and approves the application for any patent term extension or restoration. In the future, we may intend to apply for restoration of patent term for one of our currently owned or licensed patents to add patent life beyond its current expiration date, depending on the expected length of the clinical trials and other factors involved in the filing of the relevant BLA.
A biological product can obtain pediatric market exclusivity in the United States. Pediatric exclusivity, if granted, adds six months to existing exclusivity periods and patent terms. This six-month exclusivity, which runs from the end of other exclusivity protection or patent term, may be granted based on the voluntary completion of a pediatric study in accordance with an FDA-issued "Written Request" for such a study.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, or Affordable Care Act, signed into law on March 23, 2010, includes a subtitle called the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 which created an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products shown to be similar to, or interchangeable with, an FDA-licensed reference biological product. This amendment to the PHS Act attempts to minimize duplicative testing. Biosimilarity, which
43
requires that there be no clinically meaningful differences between the biological product and the reference product in terms of safety, purity, and potency, can be shown through analytical studies, animal studies, and a clinical trial or trials, including clinical pharmacology trials and assessment of immunogenicity. Interchangeability requires that a product is biosimilar to the reference product and the product must demonstrate that it can be expected to produce the same clinical results as the reference product and, for products administered multiple times, the biologic and the reference biologic may be switched after one has been previously administered without increasing safety risks or risks of diminished efficacy relative to exclusive use of the reference biologic. However, complexities associated with the larger, and often more complex, structure of biological products, as well as the process by which such products are manufactured, pose significant hurdles to implementation that are still being worked out by the FDA.
A reference biologic is granted twelve years of exclusivity from the time of first licensure of the reference product. On February 4, 2015, President Obama released his proposed budget for fiscal year 2016 and proposed to cut this twelve-year period of exclusivity down to seven years. He also proposed to prohibit additional periods of exclusivity for brand biologics due to minor changes in product formulations, a practice often referred to as "evergreening." The first biologic product submitted under the abbreviated approval pathway that is determined to be interchangeable with the reference product has exclusivity against other biologics submitting under the abbreviated approval pathway for the lesser of (i) one year after the first commercial marketing, (ii) 18 months after approval if there is no legal challenge, (iii) 18 months after the resolution in the applicant's favor of a lawsuit challenging the biologics' patents if an application has been submitted or (iv) 42 months after the application has been approved if a lawsuit is ongoing within the 42-month period.
Other Healthcare Laws
Although we currently do not have any products on the market, we may be subject to additional healthcare regulation and enforcement by the federal government and by authorities in the states in which we conduct our business. Such laws include, without limitation, state and federal anti-kickback, fraud and abuse, false claims, privacy and security and physician sunshine laws and regulations, many of which may become more applicable to us if our product candidates are approved and we begin commercialization. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of such laws or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including, without limitation, administrative, civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, exclusion from participation in federal and state healthcare programs and imprisonment, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results.
In addition, the Affordable Care Act intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add transparency requirements for the healthcare and health insurance industries, impose taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms. With regard to biopharmaceutical products, in addition to the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 included in the Affordable Care Act, among other things, the Affordable Care Act expanded and increased industry rebates for drugs covered under Medicaid programs and made changes to the coverage requirements under the Medicare prescription drug benefit. We continue to evaluate the effect that the Affordable Care Act has on our business. In the coming years, additional legislative and regulatory changes could be made to governmental health programs that could significantly impact the biopharmaceutical industry and the success of our product candidates. The Affordable Care Act, as well as other federal, state and foreign healthcare reform measures that have been and may be adopted in the future, could harm our future revenues.
Additional Regulation
In addition to the foregoing, state and federal laws regarding environmental protection and hazardous substances, including the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Resource Conservancy and Recovery Act and the Toxic Substances Control Act, affect our business. These and other laws govern our use, handling and disposal of various biological, chemical and radioactive substances used in, and wastes generated by, our operations. If our operations result in contamination of the environment or expose individuals to hazardous substances, we could be liable
44
for damages and governmental fines. We believe that we are in material compliance with applicable environmental laws and that continued compliance therewith will not have a material adverse effect on our business. We cannot predict, however, how changes in these laws may affect our future operations.
U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, to which we are subject, prohibits corporations and individuals from engaging in certain activities to obtain or retain business or to influence a person working in an official capacity. It is illegal to pay, offer to pay or authorize the payment of anything of value to any foreign government official, government staff member, political party or political candidate in an attempt to obtain or retain business or to otherwise influence a person working in an official capacity.
Government Regulation Outside of the United States
In addition to regulations in the United States, we will be subject to a variety of regulations in other jurisdictions governing, among other things, clinical trials and any commercial sales and distribution of our products. Because biologically sourced raw materials are subject to unique contamination risks, their use may be restricted in some countries.
Whether or not we obtain FDA approval for a product, we must obtain the requisite approvals from regulatory authorities in foreign countries prior to the commencement of clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries. Certain countries outside of the United States have a similar process that requires the submission of a clinical trial application much like the IND prior to the commencement of human clinical trials.
If we fail to comply with applicable foreign regulatory requirements, we may be subject to, among other things, fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals, product recalls, seizure of products, operating restrictions and criminal prosecution.
Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement for Biopharmaceutical Products
Sales of our products, when and if approved for marketing, will depend, in part, on the extent to which our products will be covered by third-party payors, such as federal, state, and foreign government health care programs, commercial insurance and managed healthcare organizations. These third-party payors are increasingly reducing reimbursements for medical products, drugs and services. In addition, the U.S. government, state legislatures and foreign governments have continued implementing cost containment programs, including price controls, restrictions on coverage and reimbursement and requirements for substitution of generic products. Adoption of price controls and cost containment measures, and adoption of more restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could further limit our net revenue and results. Decreases in third-party reimbursement for our product candidates or a decision by a third-party payor not to cover our product candidates could reduce physician usage of our products once approved and have a material adverse effect on our sales, results of operations and financial condition.
Employees
As of December 31, 2015, we employed 52 full-time employees in the United States, including 42 in research and development and 10 in general and administrative. We have one part-time employee. Twenty-three of our employees have either an M.D. or a Ph.D. We have never had a work stoppage, and none of our employees is represented by a labor organization or under any collective-bargaining arrangements. We consider our employee relations to be good.
Facilities
45
We lease our office and laboratory space, which consists of approximately 19,000 square feet located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Our lease expires in 2019. In January 2016, we signed an agreement to lease an additional facility in Cambridge, Massachusetts to support our continued growth. The additional facility will include laboratory and office space, and is projected to be ready for occupancy in early 2017. We believe our current office and laboratory space, combined with the new lease, is sufficient to meet our needs until the expiration of our leases.
Legal Proceedings
As of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we were not party to any legal matters or claims. In the future, we may become party to legal matters and claims arising in the ordinary course of business, the resolution of which we do not anticipate would have a material adverse impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
An investment in shares of our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the following information about these risks, together with the other information appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our financial statements and related notes hereto, before deciding to invest in our common stock. The occurrence of any of the following risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects. In these circumstances, the market price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Capital
We have incurred net losses since inception and anticipate that we will continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future and may never achieve or maintain profitability.
We are a clinical‑stage biotechnology company with a limited operating history, and have not yet generated revenues from the sales of our product candidates. Investment in biotechnology companies is highly speculative because it entails substantial upfront capital expenditures and significant risk that the product candidate will fail to obtain regulatory approval or become commercially viable. We have not yet demonstrated the ability to complete any clinical trials of our product candidates, obtain marketing approvals, manufacture a commercial‑scale product or conduct sales and marketing activities necessary for successful commercialization. We continue to incur significant expenses related to research and development, and other operations in order to commercialize our product candidates. As a result, we are not and have never been profitable and have incurred losses since our inception. Our net loss was $29.7 million, $16.3 million, and $3.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and the period ended December 31, 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, we had an accumulated deficit of $49.8 million.
We historically have financed our operations primarily through private placements of our redeemable convertible preferred stock and our recent collaboration agreement with Genzyme. On November 16, 2015 we closed our Initial Public Offering, or IPO, whereby we sold 5,750,000 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $14.00 per share, including 750,000 shares of common stock issued upon the full exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase additional shares, resulting in net proceeds to us of $72.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us. To date, we have devoted substantially all of our financial resources to building our product engine, selecting product programs, conducting research and development, including preclinical development of our product candidates, building our intellectual property portfolio, building our team and establishing our collaboration with Genzyme. We expect that it could be several years, if ever, before we have a commercialized product candidate. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for the foreseeable future. The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter. We anticipate that our expenses will increase substantially if, and as, we:
|
· |
continue investing in our product engine to optimize vector engineering, manufacturing and dosing and delivery techniques; |
46
|
· |
continue development of our clinical candidate, VY‑AADC01; |
|
· |
initiate additional preclinical studies and clinical trials for our other programs; |
|
· |
continue our process research and development activities, as well as establish our research‑grade and commercial manufacturing capabilities; |
|
· |
identify additional CNS diseases for treatment with our AAV gene therapies; |
|
· |
seek marketing approvals for VY‑AADC01 or other product candidates that arise from our programs that successfully complete clinical trials; |
|
· |
develop a sales, marketing and distribution infrastructure to commercialize any product candidates for which we may obtain marketing approval; |
|
· |
maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio; and |
|
· |
identify, acquire or in‑license other product candidates and technologies. |
To become and remain profitable, we must develop and eventually commercialize product candidates with significant market potential, which will require us to be successful in a range of challenging activities. These activities can include completing preclinical studies and clinical trials of our product candidates, obtaining marketing approval for these product candidates, manufacturing, marketing and selling those products that are approved and satisfying any post‑marketing requirements. We may never succeed in any or all of these activities and, even if we do, we may never generate revenues that are significant or large enough to achieve profitability. If we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis. Our failure to become and remain profitable would decrease the value of our company and could impair our ability to raise capital, maintain our research and development efforts, expand our business or continue our operations. A decline in the value of our company also could cause you to lose all or part of your investment.
We may not be able to generate sufficient revenue from the commercialization of our product candidates and may never be profitable.
Our ability to generate revenue and achieve profitability depends on our ability, alone or with our collaborative partners, to successfully complete the development of, and obtain the regulatory approvals necessary to commercialize, our current and future product candidates. Our lead product candidate VY‑AADC01 is being evaluated in a Phase 1b clinical trial, and we do not anticipate generating revenues from product sales for the next several years, and we may never succeed in doing so. Our ability to generate future revenues from product sales depends heavily on our and our collaborators’ success in:
|
· |
completing preclinical and clinical development of our product candidates and identifying new product candidates; |
|
· |
seeking and obtaining regulatory and marketing approvals for product candidates for which we complete clinical trials; |
|
· |
launching and commercializing product candidates for which we obtain regulatory and marketing approval by establishing a sales force, marketing and distribution infrastructure or, alternatively, collaborating with a commercialization partner; |
|
· |
qualifying for adequate coverage and reimbursement by government and third‑party payors for our product candidates if and when approved; |
47
|
· |
maintaining and enhancing a sustainable, scalable, reproducible and transferable manufacturing process for our vectors and product candidates; |
|
· |
establishing and maintaining supply and manufacturing relationships with third parties that can provide adequate, in both amount and quality, products and services to support clinical development and the market demand for our product candidates, if approved; |
|
· |
obtaining market acceptance of our product candidates as a viable treatment option; |
|
· |
addressing any competing technological and market developments; |
|
· |
implementing additional internal systems and infrastructure, as needed; |
|
· |
negotiating favorable terms in any collaboration, licensing or other arrangements into which we may enter and performing our obligations in such collaborations; |
|
· |
maintaining, protecting and expanding our portfolio of intellectual property rights, including patents, trade secrets and know‑how; |
|
· |
avoiding and defending against third‑party interference or infringement claims; and |
|
· |
attracting, hiring and retaining qualified personnel. |
Even if one or more of the product candidates that we develop is approved for commercial sale, we anticipate incurring significant costs associated with commercializing any approved product candidate. Our expenses could increase beyond expectations if we are required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or the FDA, European Medicines Agency, or EMA, or other regulatory authorities to perform preclinical studies and clinical trials in addition to those that we currently anticipate. Even if we are able to generate revenues from the sale of any approved products, we may not become profitable and may need to obtain additional funding to continue operations.
We will need to raise additional funding, which may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all. Failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed may force us to delay, limit or terminate certain of our product development efforts or other operations.
We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we continue the research and development of, initiate further clinical trials of and seek marketing approval for, our product candidates. In addition, if we obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates, we expect to incur significant expenses related to product sales, medical affairs, marketing, manufacturing and distribution. Given the completion of our IPO on November 16, 2015, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on acceptable terms, we would be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate certain of our research and development programs.
Our operations have consumed significant amounts of cash since inception. As of December 31, 2015, our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities were $224.3 million. Based upon our current operating plan, we expect that our existing cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements into 2019.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
|
· |
the scope, progress, results and costs of product discovery, preclinical studies and clinical trials for our product candidates; |
48
|
· |
the scope, prioritization and number of our research and development programs; |
|
· |
the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates; |
|
· |
our ability to establish and maintain collaborations on favorable terms, if at all; |
|
· |
the achievement of milestones or occurrence of other developments that trigger payments under the Genzyme Collaboration and any other collaboration agreements we obtain; |
|
· |
the ability of our collaboration partners to exercise options to extend research and development programs |
|
· |
the extent to which we are obligated to reimburse, or entitled to reimbursement of, clinical trial costs under collaboration agreements, if any; |
|
· |
the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending intellectual property‑related claims; |
|
· |
the extent to which we acquire or in‑license other product candidates and technologies; |
|
· |
the costs of securing manufacturing arrangements for commercial production; and |
|
· |
the costs of establishing or contracting for sales and marketing capabilities if we obtain regulatory approvals to market our product candidates. |
Identifying potential product candidates and conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials is a time‑consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete, and we may never generate the necessary data or results required to obtain marketing approval and achieve product sales. In addition, our product candidates, if approved, may not achieve commercial success. Our product revenues, if any, and any commercial milestones or royalty payments under our collaboration agreements, will be derived from or based on sales of products that may not be commercially available for many years, if at all. Accordingly, we will need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve our business objectives. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the sale of equity or equity‑linked securities, the issuance of those securities could result in substantial dilution for our current stockholders and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our current stockholders. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the issuance of debt, the agreement governing such debt may contain restrictive covenants related to our capital raising and other financial and operational matters, which may make it more difficult for us to obtain additional capital and to pursue business operations, including potential acquisitions. Furthermore, the issuance of additional securities, whether equity or debt, by us, or the possibility of such issuance, may cause the market price of our common stock to decline and our existing stockholders may not agree with the terms of such financings. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Risks Related to the Development and Regulatory Approval of Our Product Candidates
Our AAV gene therapy product candidates are based on a relatively novel technology, which makes it difficult to predict the time and cost of development and of subsequently obtaining regulatory approval, if at all. No gene therapy product has been approved in the United States and only one such product has been approved in the European Union.
We have concentrated our research and development efforts to date on our product engine, identifying our initial targeted disease indications, and our initial product candidates, and our future success depends on our successful development of viable AAV gene therapy product candidates. Currently, only one of our product candidates, VY‑AADC01, is in clinical development, and the remainder of our product candidates are in preclinical development. There can be no assurance that we will not experience problems or delays in developing our product candidates and that
49
such problems or delays will not cause unanticipated costs, or that any such development problems can be solved. We also may experience unanticipated problems or delays in expanding our manufacturing capacity.
The clinical trial requirements of the FDA, the EMA and other regulatory authorities and the criteria these regulators use to determine the safety and efficacy of a product candidate vary substantially according to the type, complexity, novelty and intended use and market of the product candidate. The regulatory approval process for novel product candidates such as gene therapies can be more expensive and take longer than for other, better known or more extensively studied product candidates. Only one gene therapy product, uniQure N.V.’s, or uniQure, Glybera, has received marketing authorization from the European Commission and no gene therapy products have received marketing authorization in the United States. It is difficult to determine how long it will take or how much it will cost to obtain regulatory approvals for our product candidates in either the United States or the European Union or how long it will take to commercialize our product candidates. Approvals by the European Commission may not be indicative of what the FDA may require for approval and different or additional pre‑clinical studies or clinical trials may be required to support regulatory approval in each respective jurisdiction. Delay or failure to obtain, or unexpected costs in obtaining, the regulatory approval necessary to bring a potential product candidate to market could decrease our ability to generate sufficient product revenue, and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be harmed.
Regulatory requirements governing gene and cell therapy products have changed frequently and may continue to change in the future.
The FDA has established the Office of Cellular, Tissue and Gene Therapies within CBER, to consolidate the review of gene therapy and related products, and has established the Cellular, Tissue and Gene Therapies Advisory Committee to advise CBER in its review. Gene therapy clinical trials conducted at institutions that receive funding for recombinant DNA research from the National Institute of Health, or NIH, are also potentially subject to review by the NIH Office of Biotechnology Activities’ Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee, or the RAC. The ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 is being conducted at UCSF and UPMC and therefore is subject to oversight by these authorities. Even though the FDA decides whether individual gene therapy protocols may proceed, the RAC public review process, if undertaken, can delay the initiation of a clinical trial, even if the FDA has reviewed the trial design and details and permitted its initiation. Conversely, the FDA may place an IND on a clinical hold even if the RAC has provided a favorable review or an exemption from in‑depth, public review. In addition, NIH‑funded institutions need to have their institutional biosafety committee as well as their institutional review board, or IRB, review proposed clinical trials to assess the safety of the trial. The ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 has been reviewed by the Institutional Review Boards, or IRBs, of UCSF and UPMC, and such trials will need to be re‑reviewed by both institutional IRBs if the protocol for the trial is further amended. In addition, adverse developments in clinical trials of gene therapy products conducted by us or others may cause the FDA or other oversight bodies to change the requirements for approval of any of our product candidates. Similarly, EMA may issue new guidelines concerning the development and marketing authorization for gene therapy medicinal products and require that we comply with these new guidelines. The EMA and agencies at both the federal and state level in the United States have expressed an interest in further regulating new biotechnologies, including gene therapy.
These regulatory review committees and advisory groups and the new guidelines they promulgate may lengthen the regulatory review process, require us to perform additional studies, increase our development costs, lead to changes in regulatory positions and interpretations, delay or prevent approval and commercialization of these product candidates or lead to significant post‑approval limitations or restrictions. As we advance our product candidates, we will be required to consult with these regulatory and advisory groups, and comply with applicable guidelines. If we fail to do so, we may be required to delay or discontinue development of certain of our product candidates. These additional processes may result in a review and approval process that is longer than we otherwise would have expected. Delays as a result of increased or lengthier regulatory approval process and further restrictions on development of our product candidates can be costly and could negatively impact our or our collaborators’ ability to complete clinical trials and commercialize our current and future product candidates in a timely manner, if at all.
Positive results from preclinical studies and early‑stage clinical trials may not be indicative of efficacy in late‑stage clinical trials.
50
All of our product candidates are in early stages of development. Study designs and results from previous clinical trials are not necessarily predictive of our future clinical trial designs or results, and initial results may not be confirmed upon full analysis of the complete trial or study data. Our product candidates may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy in later stages of clinical development despite having successfully advanced through preclinical studies and initial clinical trials.
A number of companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have suffered significant setbacks in late‑stage clinical trials even after achieving promising results in early‑stage clinical trials. If a larger population of patients does not experience positive results, if these results are not reproducible, or if our products show diminishing activity over time, our products may not receive approval from the EMA or the FDA. Data obtained from preclinical and clinical activities are subject to varying interpretations, which may delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. In addition, we may encounter regulatory delays or rejections as a result of many factors, including changes in regulatory policy during the period of product development. Failure to confirm favorable results from earlier trials by demonstrating the safety and effectiveness of our products in late‑stage clinical trials with larger patient populations could harm our business and we may never succeed in commercialization or generating product revenue.
The dosing and delivery techniques being employed in the ongoing VY‑AADC01 Phase 1b clinical trial are different from those used in prior trials, and dosing and delivery must be further optimized in this trial or we may not generate the human proof‑of‑concept data we seek.
The clinical trial results of some of our collaborators have been negatively affected by factors that had not been fully anticipated prior to examination of the trial results. For example, the magnitude of the clinical responses seen in the Phase 1 clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 conducted by UCSF were similar to placebo effects observed in previous surgical therapies for Parkinson’s disease. As a result, we are unable to rely on the results of this Phase 1 trial for an indication of the efficacy of treatment with VY‑AADC01. We believe that there is a need to optimize the delivery, dose and volume of infusion of VY‑AADC01 to substantially increase the coverage of the putamen, the region of the brain targeted by VY‑AADC01, to achieve a clinical benefit. However, we can provide no assurances that we will be able to optimize these parameters and thereby achieve sufficient coverage of the putamen to achieve a clinical benefit.
The ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 incorporates several design features that are different from those used in UCSF’s previously completed Phase 1 clinical trial, in an attempt to increase the area of the putamen, particularly the posterior putamen, which receives VY‑AADC01 treatment. Larger infusion volumes of VY‑AADC01 are being employed along with higher doses of VY‑AADC01. In addition, the Clearpoint System, which is manufactured by MRI Interventions, Inc., is being used during the surgical procedure to provide accurate placement of the cannula, or small tube used in the procedure, in the putamen to allow for real‑time, intra‑operative MRI to assist the physician in visualizing the delivery of VY‑AADC01 to the putamen and to avoid specific blood vessels during the surgical procedure, with the goal of reducing the risk of hemorrhages. In the prior Phase 1 clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 conducted by UCSF, physicians surgically administered VY‑AADC01 without the use of the Clearpoint System, and therefore did not have real‑time visualization of treatment delivery.
Due to the nature of the techniques being used in the Phase 1b clinical trial and the numerous variables that can be changed, it is possible that the data generated from this trial may not provide evidence of clinical benefit. For example, physicians may use needles of differing lengths in the infusion procedure, or may use differing infusion speeds or infusion angles. These differences could affect the dose of VY‑AADC01 that ultimately reaches the putamen, leading to highly variable results.
Furthermore, we plan to use a slightly modified version of VY‑AADC01 in future clinical trials compared to the version of VY‑AADC01 used in the prior Phase 1 clinical trial and in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial. In order to use the modified version of VY‑AADC01 in our future clinical trials, we will need to complete preclinical studies that demonstrate comparability between the current version and the modified version of VY‑AADC01. Although we believe the current version of VY‑AADC01 to be substantially similar to the modified version, we can provide no assurances that we will be able to successfully complete such preclinical studies and demonstrate comparability.
51
We may encounter substantial delays in commencement, enrollment or completion of our clinical trials or we may fail to demonstrate safety and efficacy to the satisfaction of applicable regulatory authorities, which could prevent us from commercializing our current and future product candidates on a timely basis, if at all.
Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of our current and future product candidates, we must conduct extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the product candidates. Clinical trials are expensive, time‑consuming and outcomes are uncertain.
We have very limited experience with clinical trials. To date, we have neither commenced nor completed any clinical trials. The ongoing Phase 1b clinical trials of VY‑AADC01 are being conducted at UCSF and UPMC. We cannot guarantee that any clinical trials will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, if at all. A clinical trial failure can occur at any stage of testing.
Identifying and qualifying patients to participate in clinical trials of our product candidates is critical to our success. We may not be able to identify, recruit and enroll a sufficient number of patients, or those with required or desired characteristics, to complete our clinical trials in a timely manner. Patient enrollment and trial completion is affected by factors including:
|
· |
perceived risks and benefits of AAV gene therapy‑based approaches for the treatment of CNS diseases; |
|
· |
size of the patient population and process for identifying patients; |
|
· |
design of the trial protocol; |
|
· |
eligibility and exclusion criteria; |
|
· |
patients with preexisting antibodies to the vector that preclude their participation in the trial; |
|
· |
perceived risks and benefits of the product candidate under study; |
|
· |
availability of competing therapies and clinical trials; |
|
· |
severity of the disease under investigation; |
|
· |
availability of genetic testing for potential patients; |
|
· |
proximity and availability of clinical trial sites for prospective patients; |
|
· |
ability to obtain and maintain patient consent; |
|
· |
risk that enrolled patients will drop out before completion of the trial; |
|
· |
our inability to locate appropriately trained physicians to conduct such clinical trials, which may be particularly difficult for the VY‑AADC01 clinical trial, in which we are using the ClearPoint System, which is only available at a small number of academic medical centers in the United States; |
|
· |
patient referral practices of physicians; and |
|
· |
ability to monitor patients adequately during and after treatment. |
52
Further, we plan to seek marketing approvals in the United States, the European Union and other jurisdictions, which may require that we conduct clinical trials in foreign countries. Our ability to successfully initiate, enroll and complete a clinical trial in any foreign country is subject to numerous risks unique to conducting business in foreign countries, including:
|
· |
difficulty in establishing or managing relationships with clinical research organizations, or CROs, and physicians; |
|
· |
different standards for the conduct of clinical trials; |
|
· |
absence in some countries of established groups with sufficient regulatory expertise for review of AAV gene therapy protocols; |
|
· |
our inability to locate qualified local partners or collaborators for such clinical trials; and |
|
· |
the potential burden of complying with a variety of foreign laws, medical standards and regulatory requirements, including the regulation of pharmaceutical and biotechnology products and treatment. |
If we have difficulty enrolling a sufficient number of patients to conduct our clinical trials as planned, we may need to delay, limit or terminate ongoing or planned clinical trials, any of which would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Other events that may prevent successful or timely completion of clinical development include:
|
· |
delays in reaching a consensus with regulatory authorities on trial design; |
|
· |
delays in reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective CROs, and clinical trial sites; |
|
· |
delays in opening clinical trial sites or obtaining required IRB or independent ethics committee approval at each clinical trial site; |
|
· |
imposition of a clinical hold by regulatory authorities as a result of a serious adverse event or after an inspection of our clinical trial operations or trial sites; |
|
· |
failure by us, any CROs we engage or any other third parties to adhere to clinical trial requirements; |
|
· |
failure to perform in accordance with the FDA’s good clinical practices, or GCP, or applicable regulatory guidelines in the European Union; |
|
· |
failure by physicians to adhere to delivery protocols leading to variable results; |
|
· |
delays in the testing, validation, manufacturing and delivery of our product candidates to the clinical sites, including delays by third parties with whom we have contracted to perform certain of those functions; |
|
· |
delays in having patients complete participation in a trial or return for post‑treatment follow‑up; |
|
· |
clinical trial sites or patients dropping out of a trial; |
|
· |
selection of clinical endpoints that require prolonged periods of clinical observation or analysis of the resulting data; |
53
|
· |
occurrence of serious adverse events associated with the product candidate that are viewed to outweigh its potential benefits; |
|
· |
occurrence of serious adverse events in trials of the same class of agents conducted by other sponsors; or |
|
· |
changes in regulatory requirements and guidance that require amending or submitting new clinical protocols. |
Any inability to successfully complete preclinical studies and clinical trials could result in additional costs to us or impair our ability to generate revenues from product sales, regulatory and commercialization milestones and royalties. In addition, if we make manufacturing or formulation changes to our product candidates, we may need to conduct additional studies to bridge our modified product candidates to earlier versions. Clinical trial delays also could shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our product candidates or allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do, which could impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and may harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Additionally, if the results of our clinical trials are inconclusive or if there are safety concerns or serious adverse events associated with our product candidates, we may:
|
· |
be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our product candidates, if at all; |
|
· |
obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired; |
|
· |
obtain approval with labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or safety warnings; |
|
· |
be subject to changes in the way the product is administered; |
|
· |
be required to perform additional clinical trials to support approval or be subject to additional post‑marketing testing requirements; |
|
· |
have regulatory authorities withdraw, or suspend, their approval of the product or impose restrictions on its distribution in the form of a REMS; |
|
· |
be subject to the addition of labeling statements, such as warnings or contraindications; |
|
· |
be sued; or |
|
· |
experience damage to our reputation. |
Our product candidates or the process for administering our product candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval, limit their commercial potential or result in significant negative consequences following any potential marketing approval.
In past clinical trials that were conducted by others with non‑AAV vectors, several significant side effects were caused by gene therapy treatments, including reported cases of leukemia and death. Other potential side effects could include an immunologic reaction and insertional oncogenesis, which is the process whereby the insertion of a functional gene near a gene that is important in cell growth or division results in uncontrolled cell division, which could potentially enhance the risk of malignant transformation. If our vectors demonstrate a similar adverse effect, or other adverse events, we may be required to halt or delay further clinical development of our product candidates. For example, in a recently published review of patients with hepatocellular carcinomas, it was shown that a small subset contained an integrated genome sequence of wild-type AAV2 and it was suggested that AAV2 may be associated with insertional oncogenesis.
54
In addition to side effects caused by the product candidate, the administration process or related procedures also can cause side effects. VY‑AADC01 and VY‑HTT01 will be administered directly to the targeted cells in the brain, requiring the patient to undergo brain surgery. In a previous Phase 1 clinical trial conducted by UCSF, three patients experienced hemorrhages caused by the surgical procedure for administering VY‑AADC01. We are using the ClearPoint System, which has only been used in limited gene therapy neurosurgeries to date, in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 to provide accurate placement of the cannula in the putamen, to allow for real‑time, intra‑operative MRI to assist the physician in visualizing the delivery of VY‑AADC01 to the putamen and to avoid specific blood vessels during the duration of the surgical procedure, with the goal of reducing the risk of hemorrhages. One patient in the ongoing Phase 1b trial at UCSF experienced two SAEs, a pulmonary embolism, or blood clot in the lungs, and related heart arrhythmia, or irregular heartbeat, which were determined to be related to the surgical procedure and prolonged immobility, not VY‑AADC01. If other side effects were to occur in connection with the surgical procedure, our clinical trials could be suspended or terminated.
If in the future we are unable to demonstrate that such side effects were caused by the administration process or related procedures, the FDA, the European Commission, the EMA or other regulatory authorities could order us to cease further development of, or deny approval of, our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. Even if we are able to demonstrate that any future SAEs are not product‑related, and regulatory authorities do not order us to cease further development of our product candidates, such occurrences could affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled patients to complete the trial. Moreover, if we elect, or are required, to delay, suspend or terminate any clinical trial of any of our product candidates, the commercial prospects of such product candidates may be harmed and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these product candidates may be delayed or eliminated. Any of these occurrences may harm our ability to develop other product candidates, and may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly.
Additionally, if any of our product candidates receives marketing approval, the FDA could require us to adopt a REMS to ensure that the benefits outweigh its risks, which may include, among other things, a medication guide outlining the risks of the product for distribution to patients and a communication plan to health care practitioners. Furthermore, if we or others later identify undesirable side effects caused by our product candidate, several potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
|
· |
regulatory authorities may suspend or withdraw approvals of such product candidate; |
|
· |
regulatory authorities may require additional warnings on the label; |
|
· |
we may be required to change the way a product candidate is administered or conduct additional clinical trials; |
|
· |
we could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients; and |
|
· |
our reputation may suffer. |
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of our product candidates and could significantly harm our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
We may be unable to obtain orphan drug designation or exclusivity. If our competitors are able to obtain orphan drug exclusivity for products that constitute the same drug and treat the same indications as our product candidates, we may not be able to have competing products approved by the applicable regulatory authority for a significant period of time.
Regulatory authorities in some jurisdictions, including the United States and the European Union, may designate drugs for relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Under the Orphan Drug Act of 1983, the FDA may designate a product candidate as an orphan drug or biological product if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally defined as having a patient population of fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United
55
States, or a patient population greater than 200,000 in the United States where there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing the drug or biological product will be recovered from sales in the United States. In the European Union, EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products grants orphan drug designation to promote the development of products that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a life‑threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting not more than five in 10,000 persons in the European Union. Additionally, orphan designation is granted for products intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a life‑threatening, seriously debilitating or serious and chronic condition and when, without incentives, it is unlikely that sales of the drug in the European Union would be sufficient to justify the necessary investment in developing the drug or biologic product.
Generally, if a product candidate with an orphan drug designation receives the first marketing approval for the indication for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to a period of marketing exclusivity, which precludes the FDA or the European Commission from approving another marketing application for a product that constitutes the same drug treating the same indication for that marketing exclusivity period, except in limited circumstances. If another sponsor receives such approval before we do (regardless of our orphan drug designation), we will be precluded from receiving marketing approval for our product for the applicable exclusivity period. The applicable period is seven years in the United States and 10 years in the European Union. The exclusivity period in the United States can be extended by nine months if the BLA, sponsor submits pediatric data that fairly respond to a written request from the FDA for such data. The exclusivity period in the European Union can be reduced to six years if a product no longer meets the criteria for orphan drug designation or if the product is sufficiently profitable so that market exclusivity is no longer justified. Orphan drug exclusivity may be revoked if any regulatory agency determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if the manufacturer is unable to assure sufficient quantity of the product to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition.
We believe that all of our current programs may qualify for orphan drug designation. Even if we obtain orphan drug exclusivity for a product candidate, that exclusivity may not effectively protect the product candidate from competition because different drugs or biological products can be approved for the same condition. In the United States, even after an orphan drug is approved, the FDA may subsequently approve another drug or biological product for the same condition if the FDA concludes that the latter drug or biological product is not the same drug or biological product or is clinically superior in that it is shown to be safer, more effective or makes a major contribution to patient care. In the European Union, marketing authorization may be granted to a similar medicinal product for the same orphan indication if:
|
· |
the second applicant can establish in its application that its medicinal product, although similar to the orphan medicinal product already authorized, is safer, more effective or otherwise clinically superior; |
|
· |
the holder of the marketing authorization for the original orphan medicinal product consents to a second orphan medicinal product application; or |
|
· |
the holder of the marketing authorization for the original orphan medicinal product cannot supply sufficient quantities of orphan medicinal product. |
A potential breakthrough therapy designation by the FDA for our product candidates may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process, and it does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
We may seek a breakthrough therapy designation for some of our product candidates. A breakthrough therapy is defined as a drug or biological product that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life‑threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug or biological product may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. For drugs or biological products that have been designated as breakthrough therapies, interaction and communication between the FDA and the sponsor of the trial can help to identify the most efficient path for clinical development while minimizing the number of patients
56
placed in ineffective control regimens. Drugs designated as breakthrough therapies by the FDA are also eligible for accelerated approval.
Designation as a breakthrough therapy is within the discretion of the FDA. Accordingly, even if we believe one of our product candidates meets the criteria for designation as a breakthrough therapy, the FDA may disagree and instead determine not to make such designation. In any event, the receipt of a breakthrough therapy designation for a product candidate may not result in a faster development process, review or approval compared to drugs considered for approval under conventional FDA procedures and does not assure ultimate approval by the FDA. In addition, even if one or more of our product candidates qualify as breakthrough therapies, the FDA may later decide that the drugs or biological products no longer meet the conditions for qualification.
Even if we successfully complete the necessary clinical trials, we cannot predict when, or if, we will obtain regulatory approval to commercialize a product candidate and the approval may be for a more narrow indication than we seek.
We cannot commercialize a product candidate until the appropriate regulatory authorities have reviewed and approved the product candidate. Even if our product candidates meet their safety and efficacy endpoints in clinical trials, the regulatory authorities may not complete their review processes in a timely manner, or we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval. Additional delays may result if an FDA Advisory Committee or other regulatory authority recommends non‑approval or restrictions on approval. In addition, we may experience delays or rejections based upon additional government regulation from future legislation or administrative action, or changes in regulatory authority policy during the period of product development, clinical trials and the review process.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval for a product candidate, our products will remain subject to regulatory oversight.
Even if we obtain any regulatory approval for our product candidates, they will be subject to ongoing regulatory requirements for manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, advertising, promotion, sampling, record‑keeping and submission of safety and other post‑market information. Any regulatory approvals that we receive for our product candidates also may be subject to a REMS, limitations on the approved indicated uses for which the product may be marketed or to the conditions of approval, or contain requirements for potentially costly post‑marketing testing, including Phase 4 clinical trials, and surveillance to monitor the quality, safety and efficacy of the product. For example, the holder of an approved BLA, is obligated to monitor and report adverse events and any failure of a product to meet the specifications in the BLA. FDA guidance advises that patients treated with some types of gene therapy undergo follow‑up observations for potential adverse events for as long as 15 years. The holder of an approved BLA also must submit new or supplemental applications and obtain FDA approval for certain changes to the approved product, product labeling or manufacturing process. Advertising and promotional materials must comply with FDA rules and are subject to FDA review, in addition to other potentially applicable federal and state laws.
In addition, product manufacturers and their facilities are subject to payment of user fees and continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with current good manufacturing practices, or cGMP, requirements and adherence to commitments made in the BLA or foreign marketing application. If we, or a regulatory authority, discover previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the facility where the product is manufactured or disagrees with the promotion, marketing or labeling of that product, a regulatory authority may impose restrictions relative to that product, the manufacturing facility or us, including requiring recall or withdrawal of the product from the market or suspension of manufacturing.
If we fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements following approval of any of our product candidates, a regulatory authority may:
|
· |
issue a warning letter asserting that we are in violation of the law; |
|
· |
seek an injunction or impose administrative, civil or criminal penalties or monetary fines; |
57
|
· |
suspend or withdraw regulatory approval; |
|
· |
suspend any ongoing clinical trials; |
|
· |
refuse to approve a pending BLA or comparable foreign marketing application, or any supplements thereto, submitted by us or our strategic partners; |
|
· |
restrict the marketing or manufacturing of the product; |
|
· |
seize or detain the product or otherwise require the withdrawal of the product from the market; |
|
· |
refuse to permit the import or export of products; or |
|
· |
refuse to allow us to enter into supply contracts, including government contracts. |
Any government investigation of alleged violations of law could require us to expend significant time and resources in response and could generate negative publicity. The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our product candidates and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
In addition, FDA policies, and those of equivalent foreign regulatory agencies, may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we may have obtained and we may not achieve or sustain profitability, which would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We face significant competition in an environment of rapid technological change and the possibility that our competitors may achieve regulatory approval before us or develop therapies that are more advanced or effective than ours, which may harm our business and financial condition, and our ability to successfully market or commercialize our product candidates.
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, including the gene therapy field, are characterized by rapidly changing technologies, significant competition and a strong emphasis on intellectual property. We face substantial competition from many different sources, including large and specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic research institutions, government agencies and public and private research institutions.
We are aware of several companies focused on developing gene therapies in various indications, including bluebird bio, Inc., Applied Genetic Technologies Corporation, Asklepios BioPharmaceutical, Inc., Audentes Therapeutics, Inc., Avalanche Biotechnologies, Inc., Bamboo Therapeutics, Dimension Therapeutics, Inc., GenSight Biologies SA, NightstaRx Ltd, REGENXBIO Inc., uniQure and Spark Therapeutics, Inc. as well as several companies addressing other methods for modifying genes and regulating gene expression. Any advances in gene therapy technology made by a competitor may be used to develop therapies that could compete against any of our product candidates.
The main competitors for our specific programs include:
|
· |
VY‑AADC01 will compete with a variety of therapies currently marketed and in development for advanced Parkinson’s disease, including deep brain simulation marked by Medtronic plc, St. Jude Medical Inc. and other medical device companies, DUOPA/Duodopa marketed by AbbVie Inc., as well as AMT‑090 or AAV‑GDNF in development at uniQure, OXB‑102/Prosavin in development at Oxford Biomedica plc and ND0612H in development at NeuroDerm Ltd.; |
58
|
· |
VY‑SOD101 for a monogenic form of ALS will potentially compete with IONIS-SODIRx being developed by Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., or Ionis, in collaboration with Biogen and Tirasemtiv being developed by Cytokinetics, Inc., or Cytokinetics; |
|
· |
VY‑FXN01 for Friedreich’s ataxia will potentially compete with RG2833 being developed by BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., AAV‑FXN being developed by Annapurna Therapeutics, AAV-FXN being developed by Bamboo Therapeutics, and frataxin targeted gene therapy being developed by Agilis Biotherapeutics, LLC in collaboration with Intrexon Corporation and BB‑FA being developed by BioBlast Pharma Ltd., or BioBlast; |
|
· |
VY‑HTT01 for Huntington’s disease will potentially compete with IONIS‑HTTRx being developed by Ionis in collaboration with F. Hoffman‑La Roche Ltd., or Roche, gene editing approach being developed by Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. in collaboration with Shire plc, and another gene therapy being developed by uniQure; and |
|
· |
VY‑SMN101 for spinal muscular atrophy will potentially compete with AVXS-101 being developed by AveXis Inc., IONIS‑SMNRX being developed by Ionis and Biogen, LMI‑070 being developed by Novartis AC, RO6885247 being developed by PTC Therapeutics, Inc. and Roche, BBrm1 being developed by BioBlast and CK‑2127107 being developed by Cytokinetics in collaboration with Astellas Pharma US, Inc. |
Many of our potential competitors, alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and other resources, such as larger research and development, clinical, marketing and manufacturing organizations. Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of competitors. Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any products that we may develop. Competitors also may obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their products more rapidly or earlier than us, which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market. Additionally, technologies developed by our competitors may render our potential product candidates uneconomical or obsolete, and we may not be successful in marketing our product candidates against competitors.
In addition, as a result of the expiration or successful challenge of our patent rights, we could face more litigation with respect to the validity and scope of patents relating to our competitors’ products. The availability of our competitors’ products could limit the demand, and the price we are able to charge, for any products that we may develop and commercialize. If we are not able to compete effectively against potential competitors, our business will not grow and our financial condition and operations will be harmed.
Even if we obtain and maintain approval for our product candidates from the FDA, we may never obtain approval for our product candidates outside of the United States, which would limit our market opportunities and adversely affect our business.
Approval of a product candidate in the United States by the FDA does not ensure approval of such product candidate by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions, and approval by one foreign regulatory authority does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other foreign countries or by the FDA. Sales of our product candidates outside of the United States will be subject to foreign regulatory requirements governing clinical trials and marketing approval. Even if the FDA grants marketing approval for a product candidate, comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries also must approve the manufacturing and marketing of the product candidates in those countries. Approval procedures vary among jurisdictions and can involve requirements and administrative review periods different from, and more onerous than, those in the United States, including additional preclinical studies or clinical trials. In many countries outside the United States, a product candidate must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that country. In some cases, the price that we intend to charge for our products, if approved, is also subject to approval. We intend to submit a marketing authorization application to EMA for approval of our product candidates in the European Union, but obtaining such approval from the European Commission following the opinion of EMA is a lengthy and expensive process. Even if a product candidate is approved, the FDA or the
59
European Commission, as the case may be, may limit the indications for which the product may be marketed, require extensive warnings on the product labeling or require expensive and time‑consuming additional clinical trials or reporting as conditions of approval. Regulatory authorities in countries outside of the United States and the European Union also have requirements for approval of product candidates with which we must comply prior to marketing in those countries. Obtaining foreign regulatory approvals and compliance with foreign regulatory requirements could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and could delay or prevent the introduction of our product candidates in certain countries.
Further, clinical trials conducted in one country may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries. Also, regulatory approval for any of our product candidates may be withdrawn. If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our product candidates will be harmed and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects will be harmed.
Risks Related to Third Parties
To date, all of our revenue has been derived from our collaboration with Genzyme, and if this collaboration agreement were to be terminated, our business financial condition, results of operations and prospects would be harmed.
In February 2015, we entered into a collaboration agreement with Genzyme to leverage our combined expertise and assets in gene therapy for CNS diseases. Under the agreement, we received an upfront commitment of approximately $100 million. Pursuant to the agreement, we granted Genzyme an exclusive option to license, develop and commercialize (i) ex‑U.S. rights to our advanced Parkinson’s disease, Friedreich’s ataxia and Huntington’s disease programs and a future program, or the Split Territory Programs, with an incremental option to co‑commercialize the product candidate from our Huntington’s disease program in the United States and (ii) worldwide rights to our SMA program. If Genzyme exercises an option for a Split Territory Program, except for our advanced Parkinson’s disease program, it is required to make an option exercise payment to us. Furthermore, Genzyme shall pay up to $645 million in the aggregate upon the achievement of specified regulatory and commercial milestones, and will pay us tiered royalty payments based on a percentage of net sales of product candidates from the programs for which it is exercised its option, or the Optioned Programs.
Following Genzyme’s exercise of an option for a program, Genzyme will have sole responsibility for the development and commercialization of the product candidates from such program in the applicable territory. Genzyme will have the sole discretion to determine and direct its efforts and resources, including the ability to discontinue all efforts and resources, it applies to the development and, if approval is obtained, commercialization and marketing of the product candidates covered by the Optioned Programs in the applicable territories. Genzyme may not be effective in obtaining approvals for the product candidates developed from the Optioned Programs or in marketing, or arranging for necessary supply, manufacturing or distribution relationships for, any approved products. Furthermore, Genzyme may change its strategic focus or pursue alternative technologies in a manner that results in reduced, delayed or no revenue to us. Genzyme has a variety of marketed products and product candidates under collaboration with other companies, including some of our competitors, and its own corporate objectives may not be consistent with our best interests. If Genzyme fails to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or ultimately commercialize any product candidate from the Optioned Programs in the applicable territories, or if Genzyme terminates our collaboration, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects would be harmed. In addition, any dispute or litigation proceedings we may have with Genzyme in the future could delay development programs, create uncertainty as to ownership of or access to intellectual property rights, distract management from other business activities and generate substantial expense.
We expect to rely on the ClearPoint System for the foreseeable future for the delivery of our product candidates that are injected directly into targeted regions of the brain. If there are any issues with the ClearPoint System or the manufacturer of the ClearPoint System, our business could be adversely affected.
The ClearPoint System is being used in the ongoing Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 as a treatment for advanced Parkinson’s disease, and we may continue to use the ClearPoint System in future clinical trials of VY‑AADC01 and any other of our product candidates that are injected directly into the brain. Therefore, any issues with the ClearPoint System, such as a finding that use of the ClearPoint System causes adverse events or a product recall, or
60
the manufacturer of the ClearPoint System, such as bankruptcy or a decision to stop production of the system due to lack of profitability, could delay the development or commercialization of certain of our product candidates, which would have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
We may enter into collaborations in the future with other third parties. If these collaborations are not successful, our business could be adversely affected.
We may enter into additional collaborations in the future. Our ability to generate revenues from our collaborations will depend on our and our collaborators’ abilities to successfully perform the functions assigned to each of us in these arrangements. In addition, our collaborators have the ability to abandon research or development projects and terminate applicable agreements. Moreover, an unsuccessful outcome in any clinical trial for which our collaborator is responsible could be harmful to the public perception and prospects of our gene therapy platform.
Our relationship with any future collaborations may pose several risks, including the following:
|
· |
collaborators have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these collaborations; |
|
· |
collaborators may not perform their obligations as expected; |
|
· |
the clinical trials conducted as part of these collaborations may not be successful; |
|
· |
collaborators may not pursue development and commercialization of any product candidates that achieve regulatory approval or may elect not to continue or renew development or commercialization programs based on clinical trial results, changes in the collaborators’ strategic focus or available funding or external factors, such as an acquisition, that divert resources or create competing priorities; |
|
· |
collaborators may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for clinical trials, stop a clinical trial or abandon a product candidate, repeat or conduct new clinical trials or require a new formulation of a product candidate for clinical trials; |
|
· |
we may not have access to, or may be restricted from disclosing, certain information regarding product candidates being developed or commercialized under a collaboration and, consequently, may have limited ability to inform our stockholders about the status of such product candidates; |
|
· |
collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that compete directly or indirectly with our product candidates if the collaborators believe that competitive products are more likely to be successfully developed or can be commercialized under terms that are more economically attractive than ours; |
|
· |
product candidates developed in collaboration with us may be viewed by our collaborators as competitive with their own product candidates or products, which may cause collaborators to cease to devote resources to the commercialization of our product candidates; |
|
· |
a collaborator with marketing and distribution rights to one or more of our product candidates that achieve regulatory approval may not commit sufficient resources to the marketing and distribution of any such product candidate; |
|
· |
disagreements with collaborators, including disagreements over proprietary rights, contract interpretation or the preferred course of development of any product candidates, may cause delays or termination of the research, development or commercialization of such product candidates, may lead to additional |
61
responsibilities for us with respect to such product candidates or may result in litigation or arbitration, any of which would be time‑consuming and expensive; |
|
· |
collaborators may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual property rights or may use our proprietary information in such a way as to invite litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential litigation; |
|
· |
disputes may arise with respect to the ownership or inventorship of intellectual property developed pursuant to our collaborations; |
|
· |
collaborators may infringe the intellectual property rights of third parties, which may expose us to litigation and potential liability; |
|
· |
the terms of our collaboration agreement may restrict us from entering into certain relationships with other third parties, thereby limiting our options; and |
|
· |
collaborations may be terminated for the convenience of the collaborator and, if terminated, we could be required to raise additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable product candidates. |
If our collaborations do not result in the successful development and commercialization of products, or if one of our collaborators terminates its agreement with us, we may not receive any future research funding or milestone or royalty payments under the collaboration. If we do not receive the funding we expect under these agreements, our development of product candidates could be delayed and we may need additional resources to develop our product candidates. In addition, if one of our collaborators terminates its agreement with us, we may find it more difficult to attract new collaborators and the perception of us in the business and financial communities could be adversely affected. All of the risks relating to product development, regulatory approval and commercialization described in this Annual Report apply to the activities of our collaborators.
If we decide to enter into future collaborations, we could face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators and the negotiation process is time‑consuming and complex. Our ability to reach a definitive collaboration agreement with any future collaborators will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator’s evaluation of several factors. If we license rights to product candidates, we may not be able to realize the benefit of such transactions if we are unable to successfully integrate them with our existing operations and company culture.
We expect to rely on third parties to conduct, supervise and monitor our clinical trials, and if these third parties perform in an unsatisfactory manner, our business could be harmed.
We expect to rely on CROs and clinical trial sites to ensure our clinical trials are conducted properly and on time. While we will have agreements governing their activities, we will have limited influence over their actual performance. We will control only certain aspects of our CROs’ activities. Nevertheless, we will be responsible for ensuring that each of our clinical studies is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol, legal, regulatory and scientific standards, and our reliance on the CROs does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. For example, the only clinical trial of any of our product candidates or programs is being conducted by UCSF and UPMC. If UCSF or UPMC terminated the clinical trial of VY‑AADC01, we would be required to find another party to conduct any new trials. We may be unable to find a new party to conduct new trials of our product candidates or obtain clinical supply of our product candidates or AAV vectors for such trials.
We and our CROs are required to comply with the FDA’s GCPs for conducting, recording and reporting the results of IND‑enabling studies and clinical studies to assure that the data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of clinical trial participants are protected. The FDA enforces these GCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and clinical trial sites. If we or our CROs fail to comply with applicable GCPs, the clinical data generated in our future clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving any marketing applications. Upon inspection, the FDA may determine that our clinical trials did not comply with GCPs. In addition, our future clinical trials will
62
require a sufficient number of patients to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of our product candidates. Accordingly, if our CROs fail to comply with these regulations or fail to recruit a sufficient number of patients, we may be required to repeat such clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process.
Our CROs are not our employees, and we are therefore unable to directly monitor whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our clinical and nonclinical programs. These CROs may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including our competitors, for whom they may also be conducting clinical trials or other drug development activities that could harm our competitive position. If our CROs do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations, fail to meet expected deadlines, or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols or regulatory requirements, or for any other reasons, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for, or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, our financial results and the commercial prospects for our product candidates would be harmed, our costs could increase, and our ability to generate revenues could be delayed.
Risks Related to Manufacturing
Gene therapies are novel, complex and difficult to manufacture. We could experience manufacturing problems that result in delays in the development or commercialization of our product candidates or otherwise harm our business.
The manufacturing process used to produce our product candidates is complex, novel and has not been validated for commercial use. Several factors could cause production interruptions, including equipment malfunctions, facility contamination, raw material shortages or contamination, natural disasters, disruption in utility services, human error or disruptions in the operations of our suppliers and collaborators.
Our product candidates require processing steps that are more complex than those required for most chemical pharmaceuticals. Moreover, unlike chemical pharmaceuticals, the physical and chemical properties of a biologic such as ours generally cannot be fully characterized. As a result, assays of the finished product may not be sufficient to ensure that the product will perform in the intended manner. Accordingly, we and our collaborators employ multiple steps to control the manufacturing process to assure that the process works and the product candidate is made strictly and consistently in compliance with the process. Problems with the manufacturing process, even minor deviations from the normal process, could result in product defects or manufacturing failures that result in lot failures, product recalls, product liability claims or insufficient inventory. We or our collaborators may encounter problems achieving adequate quantities and quality of clinical‑grade materials that meet the FDA, EMA or other applicable standards or specifications with consistent and acceptable production yields and costs.
In addition, the FDA, EMA and other foreign regulatory authorities may require us to submit samples of any lot of any approved product together with the protocols showing the results of applicable tests at any time. Under some circumstances, the FDA, EMA or other foreign regulatory authorities may require that we not distribute a lot until the agency authorizes its release. Slight deviations in the manufacturing process, including those affecting quality attributes and stability, may result in unacceptable changes in the product that could result in lot failures or product recalls. Lot failures or product recalls could cause us to delay product launches or clinical trials, which could be costly to us and otherwise harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We or our collaborators also may encounter problems hiring and retaining the experienced scientific, quality‑control and manufacturing personnel needed to operate our manufacturing processes, which could result in delays in production or difficulties in maintaining compliance with applicable regulatory requirements.
Any problems in our or our collaborators’ manufacturing process or facilities could make us a less attractive collaborator for potential partners, including larger pharmaceutical companies and academic research institutions, which could limit our access to additional attractive development programs. Problems in our or our collaborators’ manufacturing process could restrict our ability to meet market demand for our products.
63
Delays in obtaining regulatory approval of our or our collaborators’ manufacturing process and facility or disruptions in our manufacturing process may delay or disrupt our commercialization efforts. To date, no cGMP gene therapy manufacturing facility in the United States has received approval from the FDA for the manufacture of an approved gene therapy product.
Before we can begin to commercially manufacture our product candidates in our own facility, or the facility of a collaborator, we must obtain regulatory approval from the FDA for our manufacturing process and our collaborator’s facility. A manufacturing authorization must also be obtained from the appropriate European Union regulatory authorities. To date, no cGMP gene therapy manufacturing facility in the United States has received approval from the FDA for the manufacture of an approved gene therapy product and, therefore, the timeframe required for us to obtain such approval is uncertain. In addition, we must pass a pre‑approval inspection of our or our collaborator’s manufacturing facility by the FDA before any of our product candidates can obtain marketing approval. In order to obtain approval, we will need to ensure that all of our processes, methods and equipment are compliant with cGMP, and perform extensive audits of vendors, contract laboratories and suppliers. If any of our vendors, contract laboratories or suppliers is found to be out of compliance with cGMP, we may experience delays or disruptions in manufacturing while we work with these third parties to remedy the violation or while we work to identify suitable replacement vendors. The cGMP requirements govern quality control of the manufacturing process and documentation policies and procedures. In complying with cGMP, we will be obligated to expend time, money and effort in production, record keeping and quality control to assure that the product meets applicable specifications and other requirements. If we fail to comply with these requirements, we would be subject to possible regulatory action and may not be permitted to sell any products that we may develop.
Failure to comply with ongoing regulatory requirements could cause us to suspend production or put in place costly or time‑consuming remedial measures.
The regulatory authorities may, at any time following approval of a product for sale, audit the manufacturing facilities for such product. If any such inspection or audit identifies a failure to comply with applicable regulations, or if a violation of product specifications or applicable regulations occurs independent of such an inspection or audit, the relevant regulatory authority may require remedial measures that may be costly or time‑consuming to implement and that may include the temporary or permanent suspension of a clinical trial or commercial sales or the temporary or permanent closure of a manufacturing facility. Any such remedial measures imposed upon our third‑party manufacturers or us could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If our third‑party manufacturers or we fail to comply with applicable cGMP regulations, FDA and foreign regulatory authorities can impose regulatory sanctions including, among other things, refusal to approve a pending application for a new product candidate or suspension or revocation of a pre‑existing approval. Such an occurrence may cause our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be harmed.
Additionally, if supply from any third‑party manufacturers is delayed or interrupted, there could be a significant disruption in the supply of our clinical or commercial material. We have an agreement in place with MassBiologics pursuant to which we are collaborating on cGMP manufacturing of VY-AADC01 and processes for the manufacture of other AAV product candidates. Therefore, if we are unable to enter into an agreement with MassBiologics or another manufacturer to manufacture clinical or commercial material for our product programs beyond VY-AADC01, or if our agreement with MassBiologics were terminated, we would have to find suitable alternative manufacturers. This could delay our or our collaborators’ ability to conduct clinical trials or commercialize our current and future product candidates. The regulatory authorities also may require additional trials if a new manufacturer is relied upon for commercial production. Switching manufacturers may involve substantial costs and could result in a delay in our desired clinical and commercial timelines.
Any contamination in the manufacturing process for our products, shortages of raw materials or failure of any of our key suppliers to deliver necessary components could result in delays in our clinical development or marketing schedules.
Given the nature of biologics manufacturing, there is a risk of contamination. Any contamination could adversely affect our ability to produce product candidates on schedule and could, therefore, harm our results of operations and cause reputational damage.
64
Some of the raw materials required in our manufacturing process are derived from biologic sources. Such raw materials are difficult to procure and may be subject to contamination or recall. A material shortage, contamination, recall or restriction on the use of biologically derived substances in the manufacture of our product candidates could adversely impact or disrupt the commercial manufacturing or the production of clinical material, which could adversely affect our development timelines and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Interruptions in the supply of product candidates or inventory loss may harm our operating results and financial condition.
Our product candidates are manufactured using technically complex processes requiring specialized facilities, highly specific raw materials and other production constraints. The complexity of these processes, as well as strict government standards for the manufacture and storage of our product candidates, subjects us to manufacturing risks. While product candidate batches released for use in clinical trials or for commercialization undergo sample testing, some defects may only be identified following product release. In addition, process deviations or unanticipated effects of approved process changes may result in these intermediate products not complying with stability requirements or specifications. Our product candidates must be stored and transported at temperatures within a certain range. If these environmental conditions deviate, our product candidates’ remaining shelf‑lives could be impaired or their efficacy and safety could be negatively impacted, making them no longer suitable for use.
The occurrence, or suspected occurrence, of manufacturing and distribution difficulties can lead to lost inventories and, in some cases, product recalls, with consequential reputational damage and the risk of product liability. The investigation and remediation of any identified problems can cause production delays, substantial expense, lost sales and delays of new product launches. Any interruption in the supply of finished products or the loss thereof could hinder our ability to timely distribute our products and satisfy customer demand. Any unforeseen failure in the storage of the product or loss in supply could delay our clinical trials and, if our product candidates are approved, result in a loss of our market share and negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
We may not be successful in our efforts to identify or discover additional product candidates and may fail to capitalize on programs or product candidates that may be a greater commercial opportunity, or for which there is a greater likelihood of success.
The success of our business depends upon our ability to identify, develop and commercialize product candidates generated through our product engine. Research programs to identify new product candidates require substantial technical, financial and human resources. Although VY‑AADC01 is currently in clinical development and our other product candidates are in preclinical development, we may fail to identify other potential product candidates for clinical development for several reasons. For example, our research may be unsuccessful in identifying potential product candidates or our potential product candidates may be shown to have harmful side effects, may be commercially impracticable to manufacture or may have other characteristics that may make the products unmarketable or unlikely to receive marketing approval.
Additionally, because we have limited resources, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with certain programs or product candidates or for indications that later prove to have greater commercial potential. Our spending on current and future research and development programs may not yield any commercially viable products. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential for a particular product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to that product candidate through strategic collaboration, licensing or other arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such product candidate. Alternatively, we may allocate internal resources to a product candidate in a therapeutic area in which it would have been more advantageous to enter into a partnering arrangement.
If any of these events occur, we may be forced to abandon our development efforts with respect to a particular product candidate or fail to develop a potentially successful product candidate, which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
65
Our future success depends on our ability to retain key members of our management team, and to attract, retain and motivate qualified personnel.
We are highly dependent on Steven M. Paul, M.D., our President and Chief Executive Officer as well as other members of our management team, the loss of whose services may adversely impact the achievement of our objectives. While we have entered into employment agreements or offer letters with each of our executive officers, any of them could leave our employment at any time, as all of our employees are “at will” employees. We currently do not have “key person” insurance on any of our employees. The loss of the services of one or more of our current employees might impede the achievement of our research, development and commercialization objectives.
Recruiting and retaining other qualified employees, consultants and advisors for our business, including scientific and technical personnel, also will be critical to our success. There currently is a shortage of skilled individuals with substantial gene therapy experience, which is likely to continue. As a result, competition for skilled personnel, including in gene therapy research and vector manufacturing, is intense and the turnover rate can be high. We may not be able to attract and retain personnel on acceptable terms given the competition among numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and academic institutions for individuals with similar skill sets. In addition, failure to succeed in preclinical or clinical trials or applications for marketing approval may make it more challenging to recruit and retain qualified personnel. The inability to recruit, or loss of services of certain executives, key employees, consultants or advisors, may impede the progress of our research, development and commercialization objectives and could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If we are unable to manage expected growth in the scale and complexity of our operations, our performance may suffer.
If we are successful in executing our business strategy, we will need to expand our managerial, operational, financial and other systems and resources to manage our operations, continue our research and development activities and, in the longer term, build a commercial infrastructure to support commercialization of any of our product candidates that are approved for sale. We can provide no assurances that we will have sufficient resources in the future to manage all of our planned programs. Future growth would impose significant added responsibilities on members of management. It is likely that our management, finance, development personnel, systems and facilities currently in place may not be adequate to support this future growth. Our need to effectively manage our operations, growth and product candidates requires that we continue to develop more robust business processes and improve our systems and procedures in each of these areas and to attract and retain sufficient numbers of talented employees. We may be unable to successfully implement these tasks on a larger scale and, accordingly, may not achieve our research, development and growth goals.
Our employees, principal investigators, consultants and commercial partners may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non‑compliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading.
We are exposed to the risk of fraud or other misconduct by our employees, principal investigators, consultants and commercial partners. Misconduct by these parties could include intentional failures to comply with FDA regulations or the regulations applicable in the European Union and other jurisdictions, provide accurate information to the FDA, the European Commission and other regulatory authorities, comply with healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations in the United States and abroad, report financial information or data accurately or disclose unauthorized activities to us. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, misconduct, kickbacks, self‑dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Such misconduct also could involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials or interactions with the FDA or other regulatory authorities, which could result in regulatory sanctions and cause serious harm to our reputation. We have adopted a code of conduct applicable to all of our employees, but it is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from government investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to comply with these laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in
66
defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, including the imposition of significant fines or other sanctions.
Healthcare legislative reform measures may harm our business and results of operations.
In the United States, there have been, and continue to be, several legislative initiatives to contain healthcare costs. For example, in March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, or the Affordable Care Act, was passed, which substantially changes the way health care is financed by both the government and private insurers, and significantly impacts the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. The Affordable Care Act, among other things: (i) imposes a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected; (ii) increases the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program; (iii) extends manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability to covered drugs dispensed to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations; (iv) establishes an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain branded prescription drugs and biologic agents; (v) expands the availability of lower pricing under the 340B drug pricing program by expanding the types of entities eligible to participate in the program; and (vi) establishes a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point‑of‑sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; (vii) expands entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health Services pharmaceutical pricing program; and (viii) initiates a new Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research. Additionally, in the United States, the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 created an abbreviated approval pathway for biologic products that are demonstrated to be “highly similar” or “biosimilar or interchangeable” with an FDA‑approved biologic product. This new pathway could allow competitors to reference data from biologic products already approved after 12 years from the time of approval. This could expose us to potential competition by lower‑cost biosimilars even if we commercialize a product candidate faster than our competitors.
Additional changes that may affect our business include those governing enrollment in federal healthcare programs, reimbursement changes, rules regarding prescription drug benefits under the health insurance exchanges and fraud and abuse and enforcement. Continued implementation of the Affordable Care Act and the passage of additional laws and regulations may result in the expansion of new programs such as Medicare payment for performance initiatives, and may impact existing government healthcare programs, such as by improving the physician quality reporting system and feedback program. Other legislative changes have been adopted since the Affordable Care Act was enacted, including aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year effective April 1, 2013. These reductions will stay in effect through 2024 unless additional congressional action is taken. Additionally, in January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several providers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding, which could have a material adverse effect on customers for our drugs, if approved, and, accordingly, our financial operations. Further, as part of the proposed 2016 budget, President Obama has sought to reduce the current 12‑year exclusivity period that a reference biologic is granted to a seven‑year exclusivity period.
For each state that does not choose to expand its Medicaid program, there may be fewer insured patients overall, which could impact the sales, business and financial condition of manufacturers of branded prescription drugs. Where patients receive insurance coverage under any of the new options made available through the Affordable Care Act, the possibility exists that manufacturers may be required to pay Medicaid rebates on that resulting drug utilization, a decision that could impact manufacturer revenues. The U.S. federal government also has announced delays in the implementation of key provisions of the Affordable Care Act. The implications of these delays for our and our partners’ business and financial condition, if any, are not yet clear.
We expect that additional state and federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in reduced demand for our product candidates or additional pricing pressures. We cannot predict what
67
healthcare reform initiatives may be adopted in the future. Further federal, state and foreign legislative and regulatory developments are likely, and we expect ongoing initiatives to increase pressure on drug pricing. Such reforms could have an adverse effect on anticipated revenues from product candidates that we may successfully develop and for which we may obtain regulatory approval and may affect our overall financial condition and ability to develop product candidates.
We may be subject, directly or indirectly, to federal, state, and foreign healthcare laws and regulations, including fraud and abuse laws, false claims laws and health information privacy and security laws. If we are unable to comply, or have not fully complied, with such laws, we could face substantial penalties.
If we obtain FDA approval for any of our product candidates and begin commercializing those products in the United States, our operations will be directly, or indirectly through our prescribers, customers and purchasers, subject to various federal and state laws and regulations, including, without limitation, the federal Anti‑Kickback Statute, the federal civil and criminal False Claims Act, and the Physician Payments Sunshine Act and regulations. These laws will impact, among other things, our proposed sales, marketing and educational programs. In addition, we may be subject to data privacy laws by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. Such laws that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we conduct our operations include, but are not limited to:
|
· |
the federal Anti‑Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons and entities from knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying any remuneration (including any kickback, bribe or rebate), directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce or in return for either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, recommendation, leasing or furnishing of, an item or service reimbursable under a federal healthcare program, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs. This statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand, and prescribers, purchasers and formulary managers on the other. Further, the Affordable Care Act amends the intent requirement of the federal Anti‑Kickback Statute. A person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of this statute or specific intent to violate it; |
|
· |
the federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, including the civil False Claims Act, which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment or approval from Medicare, Medicaid or other government payors that are false or fraudulent, or making a false statement to avoid, decrease, or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government. The Affordable Care Act provides and recent government cases against pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers support the view that federal Anti‑Kickback Statute violations and certain marketing practices, including off‑label promotion, may implicate the civil False Claims Act; |
|
· |
the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, which created additional federal criminal statutes that prohibit a person from knowingly and willfully executing or attempting to execute a scheme or from making false or fraudulent statements to defraud any healthcare benefit program, regardless of the payor (e.g., public or private); |
|
· |
HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, or HITECH, and its implementing regulations, and as amended again by the final HIPAA omnibus rule, Modifications to the HIPAA Privacy, Security, Enforcement, and Breach Notification Rules Under HITECH and the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act; Other Modifications to HIPAA, published in January 2013, which imposes certain requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information without appropriate authorization by entities subject to the rule, such as health plans, health care clearinghouses and health care providers; |
|
· |
federal transparency laws, including the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act, that requires certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid, or the Children’s Health Insurance Program, with specific exceptions, to report annually to CMS information related to payments and other transfers of value provided to physicians and teaching hospitals, and ownership and investment interests held by physicians and other healthcare |
68
providers and their immediate family members and applicable group purchasing organizations, by the 90th day of each subsequent calendar year, and disclosure of such information is made by CMS on a publicly available website; and |
|
· |
state and/or foreign law equivalents of each of the above federal laws, such as state anti‑kickback and false claims laws that may apply to arrangements and claims involving health care items or services reimbursed by non‑governmental third party payors; state laws that require drug manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures; state laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government; and state and foreign laws governing the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and may not have the same effect, thus complicating compliance efforts in certain circumstances, such as specific disease states. |
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and safe harbors available, it is possible that some of our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other government regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, exclusion from participation in government health care programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, disgorgement, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, imprisonment and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
The provision of benefits or advantages to physicians to induce or encourage the prescription, recommendation, endorsement, purchase, supply, order or use of medicinal products is prohibited in the European Union. The provision of benefits or advantages to physicians is also governed by the national anti‑bribery laws of European Union Member States, such as the UK Bribery Act 2010. Infringement of these laws could result in substantial fines and imprisonment.
Payments made to physicians in certain European Union Member States must be publically disclosed. Moreover, agreements with physicians often must be the subject of prior notification and approval by the physician’s employer, his or her competent professional organization and/or the regulatory authorities of the individual European Union Member States. These requirements are provided in the national laws, industry codes or professional codes of conduct, applicable in the European Union Member States. Failure to comply with these requirements could result in reputational risk, public reprimands, administrative penalties, fines or imprisonment.
The collection and use of personal health data in the European Union is governed by the provisions of the Data Protection Directive. This directive imposes several requirements relating to the consent of the individuals to whom the personal data relates, the information provided to the individuals, notification of data processing obligations to the competent national data protection authorities and the security and confidentiality of the personal data. The Data Protection Directive also imposes strict rules on the transfer of personal data out of the European Union to the United States. Failure to comply with the requirements of the Data Protection Directive and the related national data protection laws of the European Union Member States may result in fines and other administrative penalties. The draft Data Protection Regulation currently going through the adoption process is expected to introduce new data protection requirements in the European Union and substantial fines for breaches of the data protection rules. If the draft Data Protection Regulation is adopted in its current form it may increase our responsibility and liability in relation to personal data that we process and we may be required to put in place additional mechanisms ensuring compliance with the new data protection rules. This may be onerous and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Product liability lawsuits against us could cause us to incur substantial liabilities and could limit commercialization of any product candidates that we may develop.
We will face an inherent risk of product liability exposure related to the testing of our product candidates in clinical trials and may face an even greater risk if we commercialize any products that we may develop. If we cannot
69
successfully defend ourselves against claims that our product candidates caused injuries, we could incur substantial liabilities. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
|
· |
decreased demand for any product candidates that we may develop; |
|
· |
loss of revenue; |
|
· |
substantial monetary awards to trial participants or patients; |
|
· |
significant time and costs to defend the related litigation; |
|
· |
withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
|
· |
the inability to commercialize any product candidates that we may develop; and |
|
· |
injury to our reputation and significant negative media attention. |
Although we maintain product liability insurance coverage in the amount of $5.0 million per occurrence and $5.0 million in the aggregate, this insurance may not be adequate to cover all liabilities that we may incur. We anticipate that we will need to increase our insurance coverage each time we commence a clinical trial and if we successfully commercialize any product candidate. Insurance coverage is increasingly expensive. We may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could harm our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the generation, handling, use, storage, treatment, manufacture, transportation and disposal of, and exposure to, hazardous materials and wastes, as well as laws and regulations relating to occupational health and safety. Our operations involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biologic and radioactive materials. Our operations also produce hazardous waste products. We generally contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties.
Although we maintain workers’ compensation insurance for certain costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials or other work related injuries, this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us in connection with our storage or disposal of biologic, hazardous or radioactive materials.
In addition, we may incur substantial costs in order to comply with current or future environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, which have tended to become more stringent over time. These current or future laws and regulations may impair our research, development or production efforts. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations also may result in substantial fines, penalties or other sanctions or liabilities, which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Unfavorable global economic conditions could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by general conditions in the global economy and in the global financial markets. The most recent global financial crisis caused extreme volatility and disruptions in the capital and credit markets. A severe or prolonged economic downturn, such as the most recent global financial crisis, could
70
result in a variety of risks to our business, including weakened demand for our product candidates and our ability to raise additional capital when needed on acceptable terms, if at all. This is particularly true in the European Union, which is undergoing a continued severe economic crisis. A weak or declining economy could strain our suppliers, possibly resulting in supply disruption, or cause delays in payments for our services by third‑party payors or our collaborators. Any of the foregoing could harm our business and we cannot anticipate all of the ways in which the current economic climate and financial market conditions could adversely impact our business.
Our internal computer systems, or those of our collaborators or other contractors or consultants, may fail or suffer security breaches, which could result in a material disruption of our product development programs.
Our internal computer systems and those of our current and any future collaborators and other contractors or consultants are vulnerable to damage from computer viruses, unauthorized access, natural disasters, terrorism, war and telecommunication and electrical failures. While we have not experienced any such material system failure, accident or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, it could result in a disruption of our development programs and our business operations, whether due to a loss of our trade secrets or other proprietary information or other similar disruptions. For example, the loss of clinical trial data from completed or future clinical trials could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability, our competitive position could be harmed and the further development and commercialization of our product candidates could be delayed.
Risks Related to the Commercialization of Our Product Candidates
The affected populations for our product candidates may be smaller than we or third parties currently project, which may affect the addressable markets for our product candidates.
Our projections of the number of people who have the diseases we are seeking to treat, as well as the subset of people with these diseases who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our product candidates, are estimates based on our knowledge and understanding of these diseases. The total addressable market opportunity for our product candidates will ultimately depend upon a number of factors including the diagnosis and treatment criteria included in the final label, if approved for sale in specified indications, acceptance by the medical community, patient access and product pricing and reimbursement. Prevalence estimates are frequently based on information and assumptions that are not exact and may not be appropriate, and the methodology is forward‑looking and speculative. The process we have used in developing an estimated prevalence range for the indications we are targeting has involved collating limited data from multiple sources. Accordingly, the prevalence estimates included in this Annual Report should be viewed with caution. Further, the data and statistical information used in this Annual Report, including estimates derived from them, may differ from information and estimates made by our competitors or from current or future studies conducted by independent sources.
The use of such data involves risks and uncertainties and is subject to change based on various factors. Our estimates may prove to be incorrect and new studies may change the estimated incidence or prevalence of the diseases we seek to address. The number of patients with the diseases we are targeting in the United States, the European Union and elsewhere may turn out to be lower than expected or may not be otherwise amenable to treatment with our products, or new patients may become increasingly difficult to identify or access, all of which would harm our results of operations and our business.
If we are unable to establish sales, medical affairs and marketing capabilities or enter into agreements with third parties to market and sell our product candidates, we may be unable to generate any product revenue.
We currently have no sales and marketing organization. To successfully commercialize any products that may result from our clinical development programs, we will need to develop these capabilities, either on our own or with others. The establishment and development of our own commercial team or the establishment of a contract sales force to market any products we may develop will be expensive and time‑consuming and could delay any product launch.
71
Moreover, we cannot be certain that we will be able to successfully develop this capability. Under our collaboration agreement with Genzyme, we have granted Genzyme an exclusive option to license, develop and commercialize ex‑U.S. rights to our advanced Parkinson’s disease program, our Friedreich’s ataxia program, a future program to be designated by Genzyme and our Huntington’s disease program. Additionally, we have granted Genzyme an incremental option to co‑commercialize our Huntington’s disease program in the United States and to worldwide rights to our spinal muscular atrophy program. If Genzyme exercises any of these options, except for our advanced Parkinson’s disease program, we would be eligible to receive specified option fees. In addition we would be eligible to receive specified milestone payments and royalties for any product developed in such programs. In the future, we may enter into collaborations regarding other of our product candidates with other entities to utilize their established marketing and distribution capabilities, but we may be unable to enter into such agreements on favorable terms, if at all. If any current or future collaborators do not commit sufficient resources to commercialize our products, or we are unable to develop the necessary capabilities on our own, we will be unable to generate sufficient product revenue to sustain our business. We compete with many companies that currently have extensive, experienced and well‑funded medical affairs, marketing and sales operations to recruit, hire, train and retain marketing and sales personnel. We also face competition in our search for third parties to assist us with the sales and marketing efforts of our product candidates. Without an internal team or the support of a third‑party to perform marketing and sales functions, we may be unable to compete successfully against these more established companies.
Our efforts to educate the medical community and third‑party payors on the benefits of our product candidates may require significant resources and may never be successful. Such efforts may require more resources than are typically required due to the complexity and uniqueness of our potential products. If any of our product candidates is approved but fails to achieve market acceptance among physicians, patients or third‑party payors, we will not be able to generate significant revenues from such product, which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The insurance coverage and reimbursement status of newly‑approved products is uncertain. Failure to obtain or maintain adequate coverage and reimbursement for our product candidates, if approved, could limit our ability to market those products and decrease our ability to generate product revenue.
We expect the cost of a single administration of gene therapy products, such as those we are developing, to be substantial, when and if they achieve regulatory approval. We expect that coverage and reimbursement by government and private payors will be essential for most patients to be able to afford these treatments. Accordingly, sales of our product candidates will depend substantially, both domestically and abroad, on the extent to which the costs of our product candidates will be paid by health maintenance, managed care, pharmacy benefit and similar healthcare management organizations, or will be reimbursed by government authorities, private health coverage insurers and other third‑party payors. Coverage and reimbursement by a third‑party payor may depend upon several factors, including the third‑party payor’s determination that use of a product is:
|
· |
a covered benefit under its health plan; |
|
· |
safe, effective and medically necessary; |
|
· |
appropriate for the specific patient; |
|
· |
cost‑effective; and |
|
· |
neither experimental nor investigational. |
No uniform policy requirement for coverage and reimbursement for drug products exists among third‑party payors. Therefore, coverage and reimbursement for drug products can differ significantly from payor to payor. As a result, obtaining coverage and reimbursement for a product from third‑party payors is a time‑consuming and costly process that could require us to provide to each different payor supporting scientific, clinical and cost‑effectiveness data. We may not be able to provide data sufficient to gain acceptance with respect to coverage and reimbursement. If coverage and reimbursement are not available, or are available only at limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our product candidates. Even if coverage is provided, the approved reimbursement amount may not be
72
adequate to realize a sufficient return on our investment. Assuming we obtain coverage for a given product by a third‑party payor, the resulting reimbursement payment rates may not be adequate or may require co‑payments that patients find unacceptably high. Patients who are prescribed medications for the treatment of their conditions, and their prescribing physicians, generally rely on third‑party payors to reimburse all or part of the costs associated with their prescription drugs. Patients are unlikely to use our products unless coverage is provided and reimbursement is adequate to cover all or a significant portion of the cost of our products. Therefore, coverage and adequate reimbursement is critical to new product acceptance. Additionally, there may be significant delays in obtaining coverage and reimbursement for newly approved drugs and biologics, and coverage may be more limited than the purposes for which the drug is approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities.
There is significant uncertainty related to third‑party coverage and reimbursement of newly approved products. In the United States, third‑party payors, including government payors such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs, play an important role in determining the extent to which new drugs and biologics will be covered and reimbursed. The Medicare and Medicaid programs increasingly are used as models for how private payors and government payors develop their coverage and reimbursement policies. Currently, no gene therapy product has been approved for coverage and reimbursement by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, the agency responsible for administering the Medicare program. It is difficult to predict what CMS will decide with respect to coverage and reimbursement for fundamentally novel products such as ours, as there is no body of established practices and precedents for these types of products. Moreover, reimbursement agencies in the European Union may be more conservative than CMS. For example, several cancer drugs have been approved for reimbursement in the United States and have not been approved for reimbursement in certain European Union Member States. It is difficult to predict what third‑party payors will decide with respect to the coverage and reimbursement for our product candidates, especially given that the cost of our product candidates is likely to be very high and pricing of such products is highly uncertain.
Outside the United States, international operations generally are subject to extensive government price controls and other market regulations, and increasing emphasis on cost‑containment initiatives in the European Union, Canada and other countries may put pricing pressure on us. For example, one gene therapy product was approved in the European Union in 2012 but is yet to be widely available commercially. In many countries, the prices of medical products are subject to varying price control mechanisms as part of national health systems. In general, the prices of medicines under such systems are substantially lower than in the United States. Other countries allow companies to fix their own prices for medical products, but monitor and control company profits. Additional foreign price controls or other changes in pricing regulation could restrict the amount that we are able to charge for our product candidates. Accordingly, in markets outside the United States, the reimbursement for our products may be reduced compared with the United States and may be insufficient to generate commercially reasonable product revenues.
Moreover, increasing efforts by government and third‑party payors in the United States and abroad to cap or reduce healthcare costs may cause such organizations to limit both coverage and the level of reimbursement for new products approved and, as a result, they may not cover or provide adequate payment for our product candidates. Payors increasingly are considering new metrics as the basis for reimbursement rates, such as average sales price, or ASP, average manufacturer price, or AMP, and Actual Acquisition Cost. The existing data for reimbursement based on some of these metrics is relatively limited, although certain states have begun to survey acquisition cost data for the purpose of setting Medicaid reimbursement rates, and CMS has begun making pharmacy National Average Drug Acquisition Cost and National Average Retail Price data publicly available on at least a monthly basis. Therefore, it may be difficult to project the impact of these evolving reimbursement metrics on the willingness of payors to cover candidate products that we or our partners are able to commercialize. We expect to experience pricing pressures in connection with the sale of any of our product candidates due to the trend toward managed healthcare, the increasing influence of health maintenance organizations and additional legislative changes. The downward pressure on healthcare costs in general, particularly prescription drugs and surgical procedures and other treatments, has become intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products such as ours.
The commercial success of any of our product candidates will depend upon its degree of market acceptance by physicians, patients, third‑party payors and others in the medical community.
73
Ethical, social and legal concerns about gene therapy could result in additional regulations restricting or prohibiting our products. Even with the requisite approvals from the FDA in the United States, EMA in the European Union and other regulatory authorities internationally, the commercial success of our product candidates will depend, in part, on the acceptance of physicians, patients and health care payors of gene therapy products in general, and our product candidates in particular, as medically necessary, cost‑effective and safe. Any product that we commercialize may not gain acceptance by physicians, patients, health care payors and others in the medical community. If these products do not achieve an adequate level of acceptance, we may not generate significant product revenue and may not become profitable. The degree of market acceptance of gene therapy products and, in particular, our product candidates, if approved for commercial sale, will depend on several factors, including:
|
· |
the efficacy and safety of such product candidates as demonstrated in clinical trials; |
|
· |
the potential and perceived advantages of product candidates over alternative treatments; |
|
· |
the cost of treatment relative to alternative treatments; |
|
· |
the clinical indications for which the product candidate is approved by the FDA or the European Commission; |
|
· |
patient awareness of, and willingness to seek, genotyping; |
|
· |
the willingness of physicians to prescribe new therapies; |
|
· |
the willingness of physicians to undergo specialized training with respect to administration of our product candidates; |
|
· |
the willingness of the target patient population to try new therapies; |
|
· |
the prevalence and severity of any side effects; |
|
· |
product labeling or product insert requirements of the FDA, EMA or other regulatory authorities, including any limitations or warnings contained in a product’s approved labeling; |
|
· |
relative convenience and ease of administration; |
|
· |
the strength of marketing and distribution support; |
|
· |
the timing of market introduction of competitive products; |
|
· |
publicity concerning our products or competing products and treatments; and |
|
· |
sufficient third‑party payor coverage and reimbursement. |
Even if a potential product displays a favorable efficacy and safety profile in preclinical studies and clinical trials, market acceptance of the product will not be fully known until after it is launched.
Our gene therapy approach utilizes vectors derived from viruses, which may be perceived as unsafe or may result in unforeseen adverse events. Negative public opinion and increased regulatory scrutiny of gene therapy may damage public perception of the safety of our product candidates and adversely affect our ability to conduct our business or obtain regulatory approvals for our product candidates.
74
Gene therapy remains a novel technology, with no gene therapy product approved to date in the United States and only one gene therapy product approved to date in the European Union. Public perception may be influenced by claims that gene therapy is unsafe, and gene therapy may not gain the acceptance of the public or the medical community. In particular, our success will depend upon physicians who specialize in the treatment of genetic diseases targeted by our product candidates, prescribing treatments that involve the use of our product candidates in lieu of, or in addition to, existing treatments with which they are familiar and for which greater clinical data may be available. More restrictive government regulations or negative public opinion would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects and may delay or impair the development and commercialization of our product candidates or demand for any products we may develop. For example, earlier gene therapy trials led to several well‑publicized adverse events, including cases of leukemia and death seen in other trials using non-AAV vectors. Serious adverse events in our clinical trials, or other clinical trials involving gene therapy products or our competitors’ products, even if not ultimately attributable to the relevant product candidates, and the resulting publicity, could result in increased government regulation, unfavorable public perception, potential regulatory delays in the testing or approval of our product candidates, stricter labeling requirements for those product candidates that are approved and a decrease in demand for any such product candidates.
If we obtain approval to commercialize our product candidates outside of the United States, in particular in the European Union, a variety of risks associated with international operations could harm our business.
We expect that we will be subject to additional risks in commercializing our product candidates outside the United States, including:
|
· |
different regulatory requirements for approval of drugs and biologics in foreign countries; |
|
· |
reduced protection for intellectual property rights; |
|
· |
unexpected changes in tariffs, trade barriers and regulatory requirements; |
|
· |
economic weakness, including inflation, or political instability in particular foreign economies and markets; |
|
· |
compliance with tax, employment, immigration and labor laws for employees living or traveling abroad; |
|
· |
foreign currency fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and reduced revenues, and other obligations incident to doing business in another country; |
|
· |
workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the United States; |
|
· |
shortages resulting from any events affecting raw material supply or manufacturing capabilities abroad; |
|
· |
business interruptions resulting from geopolitical actions, including war and terrorism or natural disasters including earthquakes, typhoons, floods and fires, or from economic or political instability; and |
|
· |
greater difficulty with enforcing our contracts in jurisdictions outside of the United States. |
Further, in many foreign countries it is common for others to engage in business practices that are prohibited by U.S. laws and regulations applicable to us, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act. Although we expect to implement policies and procedures designed to comply with these laws and policies, there can be no assurance that our employees, contractors and agents will comply with these laws and policies. If we are unable to successfully manage the challenges of international expansion and operations, our business and operating results could be harmed.
75
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
Our rights to develop and commercialize our product candidates are subject to, in part, the terms and conditions of licenses granted to us by others.
We are reliant upon licenses to certain patent rights and proprietary technology from third parties that are important or necessary to the development of our technology and products, including technology related to our manufacturing process and our product candidates. These and other licenses may not provide exclusive rights to use such intellectual property and technology in all relevant fields of use and in all territories in which we may wish to develop or commercialize our technology and products in the future. As a result, we may not be able to prevent competitors from developing and commercializing competitive products in territories included in all of our licenses.
In some circumstances, particularly in licenses with academic institutions, we may not have the right to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of patent applications, or to maintain the patents, covering technology that we license from third parties. Therefore, we cannot be certain that these patents and applications will be prosecuted, maintained and enforced in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. If our licensors fail to maintain such patents, or lose rights to those patents or patent applications, the rights we have licensed may be reduced or eliminated and our right to develop and commercialize any of our products that are the subject of such licensed rights could be adversely affected. In addition to the foregoing, the risks associated with patent rights that we license from third parties will also apply to patent rights we may own in the future.
Further, in many of our license agreements we are responsible for bringing any actions against any third party for infringing on the patents we have licensed. Certain of our license agreements also require us to meet development thresholds to maintain the license, including establishing a set timeline for developing and commercializing products and minimum yearly diligence obligations in developing and commercializing the product. Disputes may arise regarding intellectual property subject to a licensing agreement, including:
|
· |
the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation‑related issues; |
|
· |
the extent to which our technology and processes infringe on intellectual property of the licensor that is not subject to the licensing agreement; |
|
· |
the sublicensing of patent and other rights under our collaborative development relationships; |
|
· |
our diligence obligations under the license agreement and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; |
|
· |
the inventorship or ownership of inventions and know‑how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property by our licensors and us and our partners; and |
|
· |
the priority of invention of patented technology. |
If disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on acceptable terms, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected product candidates.
If we fail to comply with our obligations under these license agreements, or we are subject to a bankruptcy, the licensor may have the right to terminate the license, in which event we would not be able to market products covered by the license.
Furthermore, the research resulting in certain of our licensed patent rights and technology was funded by the U.S. government. As a result, the government may have certain rights, or march‑in rights, to such patent rights and technology. When new technologies are developed with government funding, the government generally obtains certain
76
rights in any resulting patents, including a non‑exclusive license authorizing the government to use the invention for non‑commercial purposes. These rights may permit the government to disclose our confidential information to third parties and to exercise march‑in rights to use or allow third parties to use our licensed technology. The government can exercise its march‑in rights if it determines that action is necessary because we fail to achieve practical application of the government‑funded technology, because action is necessary to alleviate health or safety needs, to meet requirements of federal regulations or to give preference to U.S. industry. In addition, our rights in such inventions may be subject to certain requirements to manufacture products embodying such inventions in the United States. Any exercise by the government of such rights could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for our products and technology, or if the scope of the patent protection obtained is not sufficiently broad, our competitors could develop and commercialize products and technology similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our products and technology may be adversely affected.
Our success depends, in large part, on our ability to obtain and maintain patent protection in the United States and other countries with respect to our proprietary product candidates and manufacturing technology. Our licensors have sought and we intend to seek to protect our proprietary position by filing patent applications in the United States and abroad related to many of our novel technologies and product candidates that are important to our business.
The patent prosecution process is expensive, time‑consuming and complex, and we may not be able to file, prosecute, maintain, enforce or license all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. For example, in some cases, the work of certain academic researchers in the gene therapy field has entered the public domain, which may compromise our ability to obtain patent protection for certain inventions related to or building upon such prior work. Consequently, we will not be able to obtain any such patents to prevent others from using our technology for, and developing and marketing competing products to treat, these indications. It is also possible that we will fail to identify patentable aspects of our research and development output before it is too late to obtain patent protection.
The patent position of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain, involves complex legal and factual questions and has, in recent years, been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our patent rights are highly uncertain. Our pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued which protect our technology or product candidates or which effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and product candidates. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the United States and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection.
We may not be aware of all third‑party intellectual property rights potentially relating to our product candidates. Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing or, in some cases, not at all. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make the inventions claimed in any owned or any licensed patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
Even if the patent applications we license or may own in the future do issue as patents, they may not issue in a form that will provide us with any meaningful protection, prevent competitors or other third parties from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Our competitors or other third parties may be able to circumvent our patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or products in a non‑infringing manner.
The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. Such challenges may result in loss of exclusivity or in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, which could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our technology and product candidates. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or
77
shortly after such candidates are commercialized. As a result, our intellectual property may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours.
Our intellectual property licenses with third parties may be subject to disagreements over contract interpretation, which could narrow the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology or increase our financial or other obligations to our licensors.
The agreements under which we currently license intellectual property or technology from third parties are complex, and certain provisions in such agreements may be susceptible to multiple interpretations. The resolution of any contract interpretation disagreement that may arise could narrow what we believe to be the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or increase what we believe to be our financial or other obligations under the relevant agreement, either of which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may not be successful in obtaining necessary rights to our product candidates through acquisitions and in‑licenses.
We currently have rights to certain intellectual property, through licenses from third parties, to develop our product candidates. Because our programs may require the use of proprietary rights held by third parties, the growth of our business likely will depend, in part, on our ability to acquire, in‑license or use these proprietary rights. We may be unable to acquire or in‑license any compositions, methods of use, processes or other intellectual property rights from third parties that we identify as necessary for our product candidates. The licensing or acquisition of third‑party intellectual property rights is a competitive area, and several more established companies may pursue strategies to license or acquire third‑party intellectual property rights that we may consider attractive. These established companies may have a competitive advantage over us due to their size, capital resources and greater clinical development and commercialization capabilities. In addition, companies that perceive us to be a competitor may be unwilling to assign or license rights to us. We also may be unable to license or acquire third‑party intellectual property rights on terms that would allow us to make an appropriate return on our investment.
We sometimes collaborate with non‑profit and academic institutions to accelerate our preclinical research or development under written agreements with these institutions. Typically, these institutions provide us with an option to negotiate a license to any of the institution’s rights in technology resulting from the collaboration. Regardless of such option, we may be unable to negotiate a license within the specified timeframe or under terms that are acceptable to us. If we are unable to do so, the institution may offer the intellectual property rights to other parties, potentially blocking our ability to pursue our program.
If we are unable to successfully obtain rights to required third‑party intellectual property rights or maintain the existing intellectual property rights we have, we may be required to expend significant time and resources to redesign our product candidates or the methods for manufacturing them or to develop or license replacement technology, all of which may not be feasible on a technical or commercial basis. If we are unable to do so, we may be unable to develop or commercialize the affected product candidates, which could harm our business significantly.
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by government patent agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for non‑compliance with these requirements.
Periodic maintenance fees, renewal fees, annuity fees and various other government fees on patents and/or applications will be due to be paid to the United States Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO, and various government patent agencies outside of the United States over the lifetime of our licensed patents and/or applications and any patent rights we may own in the future. We rely on our outside counsel or our licensing partners to pay these fees due to non‑U.S. patent agencies. The USPTO and various non‑U.S. government patent agencies require compliance with several procedural, documentary, fee payment and other similar provisions during the patent application process. We employ reputable law firms and other professionals to help us comply and we are also dependent on our licensors to take the necessary action to comply with these requirements with respect to our licensed intellectual property. In many cases, an inadvertent lapse can be cured by payment of a late fee or by other means in accordance with the applicable rules.
78
There are situations, however, in which non‑compliance can result in abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. In such an event, potential competitors might be able to enter the market and this circumstance could harm our business.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting and defending patents on product candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the United States could be less extensive than those in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the United States. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in all countries outside the United States, or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop their own products and, further, may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as that in the United States. These products may compete with our products and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents, trade secrets and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to biotechnology products, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights generally. For example, an April 2014 report from the Office of the United States Trade Representative identified a number of countries, including India and China, where challenges to the procurement and enforcement of patent rights have been reported. Several countries, including India and China, have been listed in the report every year since 1989. Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license.
Issued patents covering our product candidates could be found invalid or unenforceable if challenged in court. We may not be able to protect our trade secrets in court.
If one of our licensing partners or we initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering one of our product candidates, the defendant could counterclaim that the patent covering our product candidate is invalid or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity or unenforceability are commonplace. Grounds for a validity challenge could be an alleged failure to meet any of several statutory requirements, including lack of novelty, obviousness, lack of written description or non‑enablement. Grounds for an unenforceability assertion could be an allegation that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld information material to patentability from the USPTO, or made a misleading statement, during prosecution. Third parties also may raise similar claims before administrative bodies in the United States or abroad, even outside the context of litigation. Such mechanisms include re‑examination, post grant review, inter partes review and equivalent proceedings in foreign jurisdictions. Such proceedings could result in the revocation or cancellation of or amendment to our patents in such a way that they no longer cover our product candidates. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability is unpredictable. With respect to the validity question, for example, we cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art, of which the patent examiner and we or our licensing partners were unaware during prosecution. If a defendant were to prevail on a legal assertion of invalidity or unenforceability, we could lose at least part, and perhaps all, of the patent protection on one or more of our product candidates. Such a loss of patent protection could harm our business.
In addition to the protection afforded by patents, we rely on trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect proprietary know‑how that is not patentable or that we elect not to patent, processes for which
79
patents are difficult to enforce and any other elements of our product candidate discovery and development processes that involve proprietary know‑how, information or technology that is not covered by patents. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect and some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We cannot guarantee that we have entered into such agreements with each party that may have or have had access to our trade secrets or proprietary technology and processes. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors.
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could harm our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability and the ability of our collaborators to develop, manufacture, market and sell our product candidates and use our proprietary technologies without infringing the proprietary rights and intellectual property of third parties. The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are characterized by extensive and complex litigation regarding patents and other intellectual property rights. We may in the future become party to, or be threatened with, adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our product candidates and technology, including interference proceedings, post grant review and inter partes review before the USPTO. Third parties may assert infringement claims against us based on existing patents or patents that may be granted in the future, regardless of their merit. There is a risk that third parties may choose to engage in litigation with us to enforce or to otherwise assert their patent rights against us. Even if we believe such claims are without merit, a court of competent jurisdiction could hold that these third‑party patents are valid, enforceable and infringed, which could adversely affect our ability to commercialize our product candidates or any other of our product candidates or technologies covered by the asserted third‑party patents. In order to successfully challenge the validity of any such U.S. patent in federal court, we would need to overcome a presumption of validity. As this burden is a high one requiring us to present clear and convincing evidence as to the invalidity of any such U.S. patent claim, there is no assurance that a court of competent jurisdiction would invalidate the claims of any such U.S. patent. If we are found to infringe a third party’s valid and enforceable intellectual property rights, we could be required to obtain a license from such third party to continue developing, manufacturing and marketing our product candidates and technology. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be non‑exclusive, thereby giving our competitors and other third parties access to the same technologies licensed to us, and it could require us to make substantial licensing and royalty payments. We could be forced, including by court order, to cease developing, manufacturing and commercializing the infringing technology or product candidates. In addition, we could be found liable for monetary damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees, if we are found to have willfully infringed a patent or other intellectual property right. A finding of infringement could prevent us from manufacturing and commercializing our product candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could harm our business. Claims that we have misappropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Intellectual property litigation could cause us to spend substantial resources and distract our personnel from their normal responsibilities.
Competitors may infringe our patents or the patents of our licensing partners, or we may be required to defend against claims of infringement. To counter infringement or unauthorized use claims or to defend against claims of infringement can be expensive and time consuming. Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses, and could distract our technical and management personnel from their normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock. Such litigation or proceedings could substantially increase our operating losses and reduce the resources available for development activities or any future sales, marketing or distribution activities. We may not have sufficient financial or other resources
80
to adequately conduct such litigation or proceedings. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources and more mature and developed intellectual property portfolios. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could adversely affect our ability to compete in the marketplace.
We may be subject to claims asserting that our employees, consultants or advisors have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets of their current or former employers or claims asserting ownership of what we regard as our own intellectual property.
Many of our employees, consultants or advisors are currently, or were previously, employed at universities or other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Although we try to ensure that our employees, consultants and advisors do not use the proprietary information or know‑how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that these individuals or we have used or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such individual’s current or former employer. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management.
In addition, while it is our policy to require our employees and contractors who may be involved in the conception or development of intellectual property to execute agreements assigning such intellectual property to us, we may be unsuccessful in executing such an agreement with each party who, in fact, conceives or develops intellectual property that we regard as our own. The assignment of intellectual property rights may not be self‑executing or the assignment agreements may be breached, and we may be forced to bring claims against third parties, or defend claims that they may bring against us, to determine the ownership of what we regard as our intellectual property.
Changes in U.S. patent law could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
Recent patent reform legislation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of patent applications and the enforcement or defense of issued patents. On September 16, 2011, the Leahy‑Smith America Invents Act, or the Leahy‑Smith Act, was signed into law. The Leahy‑Smith Act includes several significant changes to U.S. patent law. These include provisions that affect the way patent applications are prosecuted and also may affect patent litigation. These also include provisions that switched the United States from a “first‑to‑invent” system to a “first‑to‑file” system, allow third‑party submission of prior art to the USPTO during patent prosecution and set forth additional procedures to attack the validity of a patent by the USPTO administered post grant proceedings. Under a first‑to‑file system, assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application generally will be entitled to the patent on an invention regardless of whether another inventor had made the invention earlier. The USPTO recently developed new regulations and procedures to govern administration of the Leahy‑Smith Act, and many of the substantive changes to patent law associated with the Leahy‑Smith Act, and in particular, the first to file provisions, only became effective on March 16, 2013. Accordingly, it is not clear what, if any, impact the Leahy‑Smith Act will have on the operation of our business. However, the Leahy‑Smith Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents, all of which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
The patent positions of companies engaged in the development and commercialization of biologics and pharmaceuticals are particularly uncertain. Two cases involving diagnostic method claims and “gene patents” have recently been decided by the Supreme Court of the United States, or Supreme Court. On March 20, 2012, the Supreme Court issued a decision in Mayo Collaborative Services v. Prometheus Laboratories, Inc., or Prometheus, a case involving patent claims directed to a process of measuring a metabolic product in a patient to optimize a drug dosage for the patient. According to the Supreme Court, the addition of well‑understood, routine or conventional activity such as “administering” or “determining” steps was not enough to transform an otherwise patent‑ineligible natural phenomenon into patent‑eligible subject matter. On July 3, 2012, the USPTO issued a guidance memo to patent examiners indicating that process claims directed to a law of nature, a natural phenomenon or a naturally occurring relation or correlation that
81
do not include additional elements or steps that integrate the natural principle into the claimed invention such that the natural principle is practically applied and the claim amounts to significantly more than the natural principle itself should be rejected as directed to not patent‑eligible subject matter. On June 13, 2013, the Supreme Court issued its decision in Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc., or Myriad, a case involving patent claims held by Myriad Genetics, Inc. relating to the breast cancer susceptibility genes BRCA1 and BRCA2. Myriad held that an isolated segment of naturally occurring DNA, such as the DNA constituting the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, is not patent eligible subject matter, but that complementary DNA, which is an artificial construct that may be created from RNA transcripts of genes, may be patent eligible.
On March 4, 2014, the USPTO issued a guidance memorandum to patent examiners titled 2014 Procedure For Subject Matter Eligibility Analysis Of Claims Reciting Or Involving Laws Of Nature/Natural Principles, Natural Phenomena, and/or Natural Products. These guidelines instruct USPTO examiners on the ramifications of the Prometheus and Myriad rulings and apply the Myriad ruling to natural products and principles including all naturally occurring nucleic acids. Patents for certain of our product candidates contain claims related to specific DNA sequences that are naturally occurring and, therefore, could be the subject of future challenges made by third parties. In addition, the recent USPTO guidance could make it impossible for us to pursue similar patent claims in patent applications we may prosecute in the future.
We cannot assure you that our efforts to seek patent protection for our technology and products will not be negatively impacted by the decisions described above, rulings in other cases or changes in guidance or procedures issued by the USPTO. We cannot fully predict what impact the Supreme Court’s decisions in Prometheus and Myriad may have on the ability of life science companies to obtain or enforce patents relating to their products and technologies in the future. These decisions, the guidance issued by the USPTO and rulings in other cases or changes in USPTO guidance or procedures could have an adverse effect on our existing patent portfolio and our ability to protect and enforce our intellectual property in the future.
Moreover, although the Supreme Court has held in Myriad that isolated segments of naturally occurring DNA are not patent‑eligible subject matter, certain third parties could allege that activities that we may undertake infringe other gene‑related patent claims, and we may deem it necessary to defend ourselves against these claims by asserting non‑infringement and/or invalidity positions, or paying to obtain a license to these claims. In any of the foregoing or in other situations involving third‑party intellectual property rights, if we are unsuccessful in defending against claims of patent infringement, we could be forced to pay damages or be subjected to an injunction that would prevent us from utilizing the patented subject matter. Such outcomes could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects.
Outside the United States, other courts have also begun to address the patenting of genetic material. In August 2015, the Australian High Court ruled that isolated genes cannot be patented in Australia. The decision did not address methods of using genetic material. Any ruling of a similar scope in other countries could affect the scope of our intellectual property rights.
If we do not obtain patent term extension and data exclusivity for our product candidates, our business may be harmed.
Depending upon the timing, duration and specifics of any FDA marketing approval of our product candidates, one or more of our U.S. patents may be eligible for limited patent term extension under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, or Hatch‑Waxman Amendments. The Hatch‑Waxman Amendments permit a patent extension term of up to five years as compensation for patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. A patent term extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval, only one patent may be extended and only those claims covering the approved drug, a method for using it or a method for manufacturing it may be extended. However, we may not be granted an extension because of, for example, failing to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, failing to apply within applicable deadlines, failing to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents or otherwise failing to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the applicable time period or the scope of patent protection afforded could be less than we request. If we are
82
unable to obtain patent term extension or the term of any such extension is less than we request, our competitors may obtain approval of competing products following our patent expiration, and our revenue could be reduced.
If our trademarks and trade names are not adequately protected, then we may not be able to build name recognition in our markets of interest and our business may be adversely affected.
We have registered trademarks with the USPTO for the mark “Voyager Therapeutics” and the Voyager logo. Our trademarks or trade names may be challenged, infringed, circumvented or declared generic or determined to be infringing on other marks. We may not be able to protect our rights to these trademarks and trade names, which we need to build name recognition among potential partners or customers in our markets of interest. At times, competitors may adopt trade names or trademarks similar to ours, thereby impeding our ability to build brand identity and possibly leading to market confusion. In addition, there could be potential trade name or trademark infringement claims brought by owners of other registered trademarks or trademarks that incorporate variations of our registered or unregistered trademarks or trade names. Over the long term, if we are unable to establish name recognition based on our trademarks and trade names, then we may not be able to compete effectively and our business may be adversely affected. Our efforts to enforce or protect our proprietary rights related to trademarks, trade secrets, domain names, copyrights or other intellectual property may be ineffective and could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources and could adversely impact our financial condition or results of operations.
Intellectual property rights do not necessarily address all potential threats.
The degree of future protection afforded by our intellectual property rights is uncertain because intellectual property rights have limitations, and may not adequately protect our business or permit us to maintain our competitive advantage. For example:
|
· |
others may be able to make gene therapy products that are similar to our product candidates but that are not covered by the claims of the patents that we license or may own in the future; |
|
· |
we, or our license partners or current or future collaborators, might not have been the first to make the inventions covered by the issued patent or pending patent application that we license or may own in the future; |
|
· |
we, or our license partners or current or future collaborators, might not have been the first to file patent applications covering certain of our or their inventions; |
|
· |
others may independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of our technologies without infringing our owned or licensed intellectual property rights; |
|
· |
it is possible that our pending patent applications or those that we may own in the future will not lead to issued patents; |
|
· |
issued patents that we hold rights to may be held invalid or unenforceable, including as a result of legal challenges by our competitors; |
|
· |
our competitors might conduct research and development activities in countries where we do not have patent rights and then use the information learned from such activities to develop competitive products for sale in our major commercial markets; |
|
· |
we may not develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; |
|
· |
the patents of others may have an adverse effect on our business; and |
|
· |
we may choose not to file a patent for certain trade secrets or know‑how, and a third party may subsequently file a patent covering such intellectual property. |
83
Should any of these events occur, they could significantly harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our reliance on third parties requires us to share our trade secrets, which increases the possibility that a competitor will discover them or that our trade secrets will be misappropriated or disclosed.
Because we currently rely on certain third parties to manufacture all or part of our product candidates and to perform quality testing, and because we collaborate with various organizations and academic institutions for the advancement of our product engine and pipeline, we must, at times, share our proprietary technology and confidential information, including trade secrets, with them. We seek to protect our proprietary technology, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements and, if applicable, material transfer agreements, collaborative research agreements, consulting agreements or other similar agreements with our collaborators, advisors, employees and consultants prior to beginning research or disclosing proprietary information. These agreements typically limit the rights of the third parties to use or disclose our confidential information. Despite the contractual provisions employed when working with third parties, the need to share trade secrets and other confidential information increases the risk that such trade secrets become known by our competitors, are inadvertently incorporated into the technology of others or are disclosed or used in violation of these agreements. Given that our proprietary position is based, in part, on our know‑how and trade secrets, a competitor’s discovery of our proprietary technology and confidential information or other unauthorized use or disclosure would impair our competitive position and may harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Despite our efforts to protect our trade secrets, our competitors may discover our trade secrets, either through breach of these agreements, independent development or publication of information including our trade secrets by third parties. A competitor’s discovery of our trade secrets would impair our competitive position and have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Common Stock
Our executive officers, directors, principal stockholders and their affiliates exercise significant influence over our company.
The holdings of our executive officers, directors, principal stockholders and their affiliates, including investment funds affiliated with Third Rock Ventures and Funds affiliated with Fidelity Management Research Company, or Fidelity, represent beneficial ownership, in the aggregate, of approximately 62% of our outstanding common stock as of December 31, 2015. As a result, these stockholders, if they act together, will be able to influence our management and affairs and the outcome of matters submitted to our stockholders for approval, including the election of directors and any sale, merger, consolidation, or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. In addition, this concentration of ownership might adversely affect the market price of our common stock by:
|
· |
delaying, deferring or preventing a change of control of us; |
|
· |
impeding a merger, consolidation, takeover or other business combination involving us; or |
|
· |
discouraging a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us. |
If securities analysts do not publish research or reports about our business or if they publish negative evaluations of our stock, the price of our stock could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will rely in part on the research and reports that industry or financial analysts publish about us or our business. If no or few analysts maintain coverage of us, the trading price of our stock would likely decrease. If one or more of the analysts covering our business downgrade their evaluations of our stock, the price of our stock could decline. If one or more of these analysts cease to cover our stock, we could lose visibility in the market for our stock, which in turn could cause our stock price to decline.
Future sales of our common stock may cause our stock price to decline.
84
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market or the perception that these sales might occur could significantly reduce the market price of our common stock and impair our ability to raise adequate capital through the sale of additional equity securities.
The price of our common stock is volatile and fluctuates substantially, which could result in substantial losses for purchasers of our common stock.
The price of our common stock is likely to be volatile and fluctuates substantially. Since our stock began trading on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on November 11, 2015, through December 31, 2015, the closing price of our common stock ranged from a high of $30.20 to a low of $17.50. The stock market in general, and the market for biopharmaceutical companies in particular, has experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The market price for our common stock may be influenced by many factors, including:
|
· |
regulatory action and results of clinical trials of our product candidates or those of our competitors; |
|
· |
the success of competitive products or technologies; |
|
· |
commencement or termination of collaborations; |
|
· |
regulatory or legal developments in the United States and other countries; |
|
· |
developments or disputes concerning patent applications, issued patents or other proprietary rights; |
|
· |
the recruitment or departure of key personnel; |
|
· |
the level of expenses related to any of our product candidates or clinical development programs; |
|
· |
the results of our efforts to discover, develop, acquire or in‑license additional product candidates; |
|
· |
actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results, development timelines or recommendations by securities analysts; |
|
· |
variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us; |
|
· |
changes in the structure of healthcare payment systems; |
|
· |
market conditions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors; |
|
· |
general economic, industry and market conditions; and |
|
· |
the other factors described in the section titled “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report. |
If our quarterly operating results fall below the expectations of investors or securities analysts, the price of our common stock could decline substantially. Furthermore, any quarterly fluctuations in our operating results may, in turn, cause the price of our stock to fluctuate substantially. We believe that quarterly comparisons of our financial results are not necessarily meaningful and should not be relied upon as an indication of our future performance.
In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class‑action litigation often has been instituted against that company. Such litigation, if instituted against us, could cause us to incur substantial costs to defend such claims and divert management’s attention and resources, which could seriously harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We have broad discretion in how we use the proceeds from our IPO and may not use these proceeds effectively, which could affect our results of operations and cause our stock price to decline.
85
We will have considerable discretion in the application of the net proceeds from our recently completed IPO. As a result, investors will be relying upon management’s judgment with only limited information about our specific intentions for the use of the balance of the net proceeds from our IPO. We may use the net proceeds for purposes that do not yield a significant return or any return at all for our stockholders. In addition, pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from this the IPO in a manner that does not produce income or that loses value.
We are an “emerging growth company,” and the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies may make our common stock less attractive to investors.
For so long as we remain an “emerging growth company,” or EGC, as defined in the JOBS Act, we are permitted and intend to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not EGCs. These exemptions include:
|
· |
not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002; |
|
· |
not being required to comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements; |
|
· |
reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation; and |
|
· |
exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. |
We may take advantages of these exemptions until we are no longer an EGC. We would cease to be an EGC upon the earlier of: (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenue of $1.0 billion or more; (ii) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of our IPO; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission or SEC, which means the first day of the year following the first year in which the market value of our common stock that is held by non‑affiliates exceeds $700 million as of June 30th.
We may choose to take advantage of some, but not all, of the available exemptions. In particular, we have not included all of the executive compensation information that would be required if we were not an EGC. We cannot predict whether investors will find our common stock less attractive if we rely on certain or all of these exemptions.
In addition, the JOBS Act provides that an EGC may take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards. This allows an EGC to delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, we will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile and may decline.
We will incur increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives.
As a public company, and particularly after we are no longer an EGC, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. In addition, the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002 and rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and The NASDAQ Stock Market have imposed various requirements on public companies, including establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to these compliance initiatives. Moreover, these rules and regulations will increase our legal and financial compliance costs
86
and will make some activities more time‑consuming and costly. For example, we expect that these rules and regulations may make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified people to serve on our board of directors, our board committees or as executive officers.
Pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002, or Section 404, we will be required to furnish a report by our management on our internal control over financial reporting. However, while we remain an EGC, we will not be required to include an attestation report on internal control over financial reporting issued by our independent registered public accounting firm. To achieve compliance with Section 404 within the prescribed period, we will be engaged in a process to document and evaluate our internal control over financial reporting, which is both costly and challenging. In this regard, we will need to continue to dedicate internal resources, potentially engage outside consultants and adopt a detailed work plan to assess and document the adequacy of internal control over financial reporting, continue steps to improve control processes as appropriate, validate through testing that controls are functioning as documented and implement a continuous reporting and improvement process for internal control over financial reporting. Despite our efforts, there is a risk that neither we nor our independent registered public accounting firm will be able to conclude within the prescribed timeframe that our internal control over financial reporting is effective as required by Section 404. This could result in an adverse reaction in the financial markets due to a loss of confidence in the reliability of our financial statements.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws and Delaware law could make an acquisition of us, which may be beneficial to our stockholders, more difficult and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws may discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other change in control of us that stockholders may consider favorable, including transactions in which you might otherwise receive a premium for your shares. These provisions also could limit the price that investors might be willing to pay in the future for shares of our common stock, thereby depressing the market price of our common stock. In addition, because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors. Among other things, these provisions:
|
· |
establish a classified board of directors such that not all members of the board are elected at one time; |
|
· |
allow the authorized number of our directors to be changed only by resolution of our board of directors; |
|
· |
limit the manner in which stockholders can remove directors from the board; |
|
· |
establish advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals that can be acted on at stockholder meetings and nominations to our board of directors; |
|
· |
require that stockholder actions must be effected at a duly called stockholder meeting and prohibit actions by our stockholders by written consent; |
|
· |
limit who may call stockholder meetings; |
|
· |
authorize our board of directors to issue preferred stock without stockholder approval, which could be used to institute a stockholder rights plan, or so‑called “poison pill,” that would work to dilute the stock ownership of a potential hostile acquirer, effectively preventing acquisitions that have not been approved by our board of directors; and |
87
|
· |
require the approval of the holders of at least 75% of the votes that all our stockholders would be entitled to cast to amend or repeal certain provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or bylaws. |
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits a person who owns in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a prescribed manner.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, provides that, unless we consent in writing to an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers and employees to us or our stockholders, (iii) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our certificate of incorporation or our bylaws or (iv) any action asserting a claim that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine, in each case subject to the Court of Chancery having personal jurisdiction over the indispensable parties named as defendants therein. Any person purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in any shares of our capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and to have consented to this provision of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation. This choice of forum provision may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and employees even though an action, if successful, might benefit our stockholders. Stockholders who do bring a claim in the Court of Chancery could face additional litigation costs in pursuing any such claim, particularly if they do not reside in or near the State of Delaware. The Court of Chancery may also reach different judgments or results than would other courts, including courts where a stockholder considering an action may be located or would otherwise choose to bring the action, and such judgments or results may be more favorable to us than to our stockholders. Alternatively, if a court were to find this provision of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Because we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future, capital appreciation, if any, will be your sole source of gain.
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all of our future earnings, if any, to finance the growth and development of our business. In addition, the terms of any future debt agreements may preclude us from paying dividends. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be your sole source of gain for the foreseeable future.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not applicable.
Our corporate headquarters are located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Our current leased facility encompasses approximately 19,000 square feet of office and laboratory space, located at 75 Sidney Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts. In January 2016, we signed an amendment to extend the current lease through December 31, 2024. In January 2016, we also signed a non-cancelable lease for an additional approximately 26,000 square feet in Cambridge, Massachusetts that will support our continued growth. The additional facility will include laboratory and office space, and is projected to be ready for occupancy in early 2017.
88
In the ordinary course of business, we are from time to time involved in lawsuits, claims, investigations, proceedings, and threats of litigation relating to intellectual property, commercial arrangements and other matters. While the outcome of these proceedings and claims cannot be predicted with certainty, as of December 31, 2015, we were not party to any legal or arbitration proceedings that may have, or have had in the recent past, significant effects on our financial position or profitability. No governmental proceedings are pending or, to our knowledge, contemplated against us. We are not a party to any material proceedings in which any director, member of senior management or affiliate of ours is either a party adverse to us or our subsidiaries or has a material interest adverse to us or our subsidiaries.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Our common stock has been traded on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol “VYGR” since November 11, 2015. Prior to this time, there was no public market for our common stock. The following table shows the high and low sale prices per share of our common stock as reported on the Nasdaq Global Select Market for the periods indicated:
|
Year ended December 31, 2015 |
|
High |
|
Low |
|
||
|
Fourth Quarter (from November 11, 2015) |
|
$ |
30.20 |
|
$ |
17.50 |
|
On March 16, 2016, the last reported sale price for our common stock on the Nasdaq Global Select Market was $10.33 per share.
Stock Performance Graph
The graph set forth below compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock between November 11, 2015 and December 31, 2015, with the cumulative total return of (a) the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index and (b) the Nasdaq Composite Index, over the same period. This graph assumes the investment of $100 on November 11, 2015 in our common stock, the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index and the Nasdaq Composite Index and assumes the reinvestment of dividends, if any. The graph assumes our closing sales price on November 11, 2015 of $17.75 per share as the initial value of our common stock and not the initial offering price to the public of $14.00 per share.
The comparisons shown in the graph below are based upon historical data. We caution that the stock price performance shown in the graph below is not necessarily indicative of, nor is it intended to forecast, the potential future performance of our common stock. Information used in the graph was obtained from the Nasdaq Stock Market LLC, a financial data provider and a source believed to be reliable. The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC is not responsible for any errors or omissions in such information.
89

Stockholders
As of March 14, 2016, there were approximately 59 holders of record of our common stock. The actual number of stockholders is greater than this number of record holders, and includes stockholders who are beneficial owners, but whose shares are held in street name by brokers and other nominees. This number of holders of record also does not include stockholders whose shares may be held in trust by other entities.
Dividends
We have not paid any cash dividends on our common stock since inception and do not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
Securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans
Information about our equity compensation plans is incorporated herein by reference to Item 12 of Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
On February 6, 2015, we issued 20,000,000 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock to one investor for $20,000,000.
On February 11, 2015, we issued 10,000,000 shares of our Series B convertible preferred stock to one investor for $30,000,000. On April 9, 2015, we issued an aggregate of 20,000,001 shares of our Series B convertible preferred stock to nine investors for aggregate consideration of $60,000,003.
All sales of securities described above were made in reliance upon the exemption from registration provided by Section 4(2) of the Securities Act (and/or Regulation D promulgated thereunder) for transactions by an issuer not involving a public offering. All of the foregoing securities are deemed restricted securities for the purposes of the Securities Act.
Prior to our IPO, we granted stock options to purchase an aggregate of 1,011,152 shares of our common stock, with exercise prices ranging from $7.27 to $9.48 per share, to our employees, directors and consultants pursuant to our 2014 Stock Incentive Plan.
We deemed the grants of stock options described above as exempt pursuant to Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act or to be exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance on Rule 701 of the Securities Act as offers and
90
sales of securities under compensatory benefit plans and contracts relating to compensation in compliance with Rule 701. Each of the recipients of securities in any transaction exempt from registration had either received or had adequate access, through employment, business or other relationships, to information about us.
No underwriters were used in the foregoing transactions.
Use of Proceeds from Initial Public Offering of Common Stock
On November 16, 2015 we closed our IPO whereby we sold 5,750,000 shares of common stock, at a public offering price of $14.00 per share, including 750,000 shares of common stock issued upon the full exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase additional shares, resulting in net proceeds to the Company of $72.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company. The underwriters were Cowen and Company, LLC, Piper Jaffray & Co., Wedbush Securities Inc. and Nomura Securities International, Inc. The offer and sale of the shares in the IPO was registered under the Securities Act pursuant to registration statements on Form S-1 (File No. 333-207367), which was filed with the SEC on October 9, 2015 and amended subsequently and declared effective on November 10, 2015.
We raised approximately $72.9 million in net proceeds after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us. None of these expenses consisted of direct or indirect payments made by us to directors, officers or persons owning 10% or more of our common stock or to their associates, or to our affiliates. There has been no material change in the planned use of proceeds from our initial public offering as described in our final prospectus filed with the SEC on November 12, 2015 pursuant to Rule 424(b)(4). We invested the funds received in cash equivalents and other short-term investments in accordance with our investment policy
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer or Affiliated Purchasers
There were no repurchases of shares of common stock made during the year ended December 31, 2015.
91
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following financial data should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”, the financial statements and related notes, and other financial information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We have derived the statements of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013, and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have derived the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013 from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in future periods.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Inception) to |
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except for per share data) |
|||||||
|
Consolidated statements of operations data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Collaboration revenue |
|
$ |
17,334 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
27,679 |
|
|
8,898 |
|
|
2,316 |
|
General and administrative |
|
|
9,909 |
|
|
5,469 |
|
|
1,450 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
37,588 |
|
|
14,367 |
|
|
3,766 |
|
Loss from operations |
|
|
(20,254) |
|
|
(14,367) |
|
|
(3,766) |
|
Interest income (expense), net |
|
|
332 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(67) |
|
Other income (expense), net |
|
|
(9,750) |
|
|
(1,949) |
|
|
— |
|
Net loss |
|
|
(29,672) |
|
|
(16,317) |
|
|
(3,833) |
|
Net unrealized gain on available-for-sale-securities, net |
(251) |
— |
— |
||||||
|
Comprehensive loss |
|
|
(29,923) |
|
|
(16,317) |
|
|
(3,833) |
|
Accretion of preferred stock to redemption value |
|
|
(7,373) |
|
|
(1,366) |
|
|
— |
|
Accrued dividends on series A preferred stock |
|
|
(1,245) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ |
(38,290) |
$ |
(17,683) |
$ |
(3,833) | |||
|
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted(1) |
$ |
(9.14) |
$ |
(27.83) |
$ |
(1,629.68) | |||
|
Weighted average number of common shares used in net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted(1) |
4,191,210 | 635,448 | 2,352 | ||||||
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
|
Consolidated balance sheet data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities |
|
$ |
224,345 |
|
$ |
7,035 |
|
$ |
135 |
|
|
Working capital(2) |
|
|
171,963 |
|
|
5,884 |
|
|
(3,847) |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
229,457 |
|
|
11,497 |
|
|
149 |
|
|
Redeemable convertible preferred stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
21,979 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Common stock and additional paid-in capital |
|
|
219,147 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
|
|
169,074 |
|
|
(20,830) |
|
|
(3,833) |
|
92
(1) See Statements of Operations Data and Note 2 to our financial statements for further details on the calculation of net loss per share, basic and diluted, attributable to common stockholders and the weighted-average number of shares used in the computation of the per share amounts.
(2) We define working capital as current assets less current liabilities. See our financial statements for further details regarding our current assets and current liabilities.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition to historical information, this discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of certain factors. We discuss factors that we believe could cause or contribute to these differences below and elsewhere in this report, including those set forth under Item 1A. “Risk Factors” and under “Forward-Looking Statements” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We are a clinical‑stage gene therapy company focused on developing life‑changing treatments for patients suffering from severe diseases of the central nervous system, or CNS. We focus on CNS diseases where we believe an adeno‑associated virus, or AAV, gene therapy approach that either increases or decreases the production of a specific protein can slow or reduce the symptoms experienced by patients, and therefore have a clinically meaningful impact. We have created a product engine, which enables us to engineer, optimize, manufacture and deliver our AAV‑based gene therapies that have the potential to provide durable efficacy following a single administration directly to the CNS. Our product engine has rapidly generated programs for five CNS indications, including advanced Parkinson’s disease; a monogenic form of ALS; Friedreich’s ataxia; Huntington’s disease; and spinal muscular atrophy. Our most advanced clinical candidate, VY‑AADC01, is being evaluated for the treatment of advanced Parkinson’s disease in an open‑label, Phase 1b clinical trial with the goal of generating human proof‑of‑concept data in the fourth quarter of 2016. Our goal is to submit our next IND for one of our current preclinical programs in 2017.
Since our inception on June 19, 2013, our operations have focused on organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, establishing our intellectual property portfolio, determining which CNS indications to pursue and conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials. We do not have any product candidates approved for sale and have not generated any revenue from product sales. We have funded our operations primarily through private placements of redeemable convertible preferred stock and common stock and our collaboration with Genzyme, or the Genzyme Collaboration, which commenced in February 2015.
On October 29, 2015, in preparation for the IPO, our Board of Directors and stockholders approved a 1-for-4.25 reverse split of our common stock, which became effective on October 29, 2015. All share and per share amounts in our consolidated financial statements and notes have been retroactively adjusted for all periods presented to give effect to this reverse split, including reclassifying an amount equal to the reduction in par value of common stock to additional paid-in capital.
On November 16, 2015 we completed the sale of 5,750,000 shares of common stock in our initial public offering, or IPO, at a price to the public of $14.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds of $72.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us.
Upon the closing of the IPO, all of the outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock automatically converted into shares of common stock as of November 16, 2015, resulting in our issuance of an additional 17,647,054 shares of common stock.
Since inception, we have incurred significant operating losses. Our net losses were $29.7 million, $16.3 million, and $3.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, we had an accumulated deficit of $49.8 million. We expect
93
to continue to incur significant expenses and operating losses for the foreseeable future. We anticipate that our expenses will increase significantly in connection with our ongoing activities, as we:
|
· |
continue investing in our product engine to optimize vector engineering, manufacturing and dosing and delivery techniques; |
|
· |
continue development of our clinical candidate, VY‑AADC01; |
|
· |
initiate additional preclinical studies and clinical trials for our other programs; |
|
· |
continue our process research and development activities, as well as establish our research‑grade and commercial manufacturing capabilities; |
|
· |
identify additional CNS diseases for treatment with our AAV gene therapies; |
|
· |
seek marketing approvals for VY‑AADC01 or other product candidates that arise from our programs that successfully complete clinical trials; |
|
· |
develop a sales, marketing and distribution infrastructure to commercialize any product candidates for which we may obtain marketing approval; |
|
· |
maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio; and |
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
To date, we have not generated any revenue from product sales and do not expect to generate any revenue from product sales for the forseeable future. For the year ended December 31, 2015, we recognized $17.3 million of collaboration revenue from the Genzyme Collaboration. For additional information about our revenue recognition policy related to the Genzyme Collaboration, see the section titled “—Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates—Revenue.”
For the foreseeable future, we expect substantially all of our revenue will be generated from the Genzyme Collaboration, and any other strategic relationships we may enter into. If our development efforts are successful, we may also generate revenue from product sales.
Expenses
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for our research activities, including our program discovery efforts, and the development of our programs and product engine, which include:
|
· |
employee‑related expenses including salaries, benefits and stock‑based compensation expense; |
|
· |
costs of funding research performed by third parties that conduct research and development, preclinical activities, manufacturing and production design on our behalf; |
|
· |
the cost of purchasing lab supplies and non‑capital equipment used in designing, developing and manufacturing preclinical study materials; |
94
|
· |
consultant fees; |
|
· |
facility costs including rent, depreciation and maintenance expenses; and |
|
· |
fees for maintaining licenses under our third‑party licensing agreements. |
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Costs for certain activities, such as manufacturing and preclinical studies and clinical trials, are generally recognized based on an evaluation of the progress to completion of specific tasks using information and data provided to us by our vendors and collaborators.
At this time, we cannot reasonably estimate or know the nature, timing and estimated costs of the efforts that will be necessary to complete the development of our product candidates. We are also unable to predict when, if ever, material net cash inflows will commence from sales of our product candidates. This is due to the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with developing such product candidates, including the uncertainty of:
|
· |
successful enrollment in and completion of clinical trials; |
|
· |
establishing an appropriate safety profile; |
|
· |
establishing commercial manufacturing capabilities or making arrangements with third‑party manufacturers; |
|
· |
receipt of marketing approvals from applicable regulatory authorities; |
|
· |
commercializing the product candidates, if and when approved, whether alone or in collaboration with others; |
|
· |
obtaining and maintaining patent and trade secret protection and regulatory exclusivity for our product candidates; |
|
· |
continued acceptable safety profiles of the products following approval; and |
|
· |
retention of key research and development personnel. |
A change in the outcome of any of these variables with respect to the development of any of our product candidates would significantly change the costs, timing and viability associated with the development of that product candidate.
Research and development activities are central to our business model. We expect research and development costs to increase significantly for the foreseeable future as our development programs progress, including as we continue to support the Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 as a treatment for advanced Parkinson’s disease, and move such product candidates into additional clinical trials. There are numerous factors associated with the successful commercialization of any of our product candidates, including future trial design and various regulatory requirements, many of which cannot be determined with accuracy at this time based on our stage of development. Additionally, future commercial and regulatory factors beyond our control will impact our clinical development programs and plans.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related costs, including stock‑based compensation, for personnel in executive, finance, accounting, business development, legal and human resource functions. Other significant costs include corporate facility costs not otherwise included in research and development expenses, legal fees related to patent and corporate matters and fees for accounting and consulting services.
95
We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase in the future to support continued research and development activities, including the continuation of the Phase 1b clinical trial of VY‑AADC01 and the initiation of our clinical trials for our other product candidates. These increases will likely include increased costs related to the hiring of additional personnel and fees to outside consultants. We also anticipate increased expenses associated with being a public company, including costs for audit, legal, regulatory and tax‑related services, director and officer insurance premiums and investor relations costs.
Other Expense
Other expense consists primarily of the re‑measurement losses associated with the change in the fair value of the Series A Preferred Stock tranche rights for the Series A Preferred Stock. $9.8 million of expense was recorded during the year ended December 31, 2015 related to the change in fair value of these rights. In February 2015, upon the issuance of the final tranche of Series A Preferred Stock, the tranche right liability was reclassified to Series A Preferred Stock and no further re‑measurement gains or losses will be recognized related to these tranche rights.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our management's discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make judgments and estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. We base our estimates on historical experience, known trends and events, and various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our judgments and estimates in light of changes in circumstances, facts and experience. The effects of material revisions in estimates, if any, will be reflected in the financial statements prospectively from the date of change in estimates.
While our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in the notes to our financial statements appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we believe the following accounting policies used in the preparation of our financial statements require the most significant judgments and estimates.
Revenue Recognition
As of December 31, 2015, all of our revenue was generated exclusively from the Genzyme Collaboration. We recognize revenue in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC, Topic 605 Revenue Recognition, or ASC 605. Accordingly, revenue is recognized for each unit of accounting when all of the following criteria are met:
|
· |
persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; |
|
· |
delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; |
|
· |
the seller's price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and |
|
· |
collectability is reasonably assured. |
Amounts received prior to satisfying the revenue recognition criteria are recorded as deferred revenue in our balance sheets. Amounts expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, current portion. Amounts not expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, net of current portion.
Multiple Elements Arrangements
96
Determination of Accounting Units
We analyze multiple element arrangements based on the guidance in FASB ASC Topic 605-25, Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements, or ASC 605-25. Pursuant to the guidance in ASC 605-25, we evaluate multiple element arrangements to determine (1) the deliverables included in the arrangement and (2) whether the individual deliverables represent separate units of accounting or whether they must be accounted for as a combined unit of accounting. This evaluation involves subjective determinations and requires management to make judgments about the individual deliverables and whether such deliverables are separate from other aspects of the contractual relationship. Deliverables are considered separate units of accounting provided that: (i) the delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a standalone basis and (ii) if the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item(s), delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially within our control. In assessing whether an item has standalone value, we consider factors such as the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the collaboration partner and the availability of the associated expertise in the general marketplace. We also consider whether our collaboration partner can use the other deliverable(s) for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining element(s), whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered item(s) and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered element(s). The Genzyme Collaboration does not provide for a general right of return relative to any delivered items.
Options are considered substantive if, at the inception of the arrangement, we are at risk as to whether the collaboration partner will choose to exercise the option. Factors that we consider in evaluating whether an option is substantive include the cost to exercise the option, the overall objective of the arrangement, the benefit the collaborator might obtain from the arrangement without exercising the option and the likelihood the option will be exercised. When an option is considered substantive, we do not consider the option or item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and the associated option fees are not included in allocable consideration, assuming the option is not priced at a significant and incremental discount. Conversely, when an option is not considered substantive, we would consider the option, including other deliverables contingent upon the exercise of the option, to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and a corresponding amount would be included in allocable arrangement consideration. In addition, if the price of the option includes a significant incremental discount, the option would be included as a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement.
Allocation of Arrangement Consideration
Arrangement consideration that is fixed or determinable is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling price method. The applicable revenue recognition criteria in ASC 605 are applied to each of the separate units of accounting in determining the appropriate period and pattern of recognition. We determine the selling price of a unit of accounting following the hierarchy of evidence prescribed by ASC 605-25. Accordingly, we determine the estimated selling price for units of accounting within each arrangement using vendor specific objective evidence, or VSOE, of selling price, if available, third party evidence, or TPE, of selling price if VSOE is not available, or best estimate of selling price, or BESP, if neither VSOE or TPE is available. We have only used BESP to estimate the selling price, since we have not had VSOE or TPE of selling price for any units of accounting to date. Determining BESP for a unit of accounting requires significant judgment. In developing the BESP for a unit of accounting, we consider applicable market conditions and relevant entity specific factors, including factors that were contemplated in negotiating the agreement with the customer and estimated costs. We validate BESP for units of accounting by evaluating whether changes in the key assumptions used by us to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple units of accounting.
Pattern of Recognition
We recognize the arrangement's consideration allocated to each unit of accounting when all of the revenue recognition criteria in ASC 605 are satisfied for that particular unit of accounting. We will recognize revenue associated with license options upon exercise of the option, if the underlying license has standalone value from the other deliverables to be provided after delivering that license. If the license does not have standalone value, the amounts
97
allocated to the license option will be combined with the related undelivered items as a single unit of accounting. The amounts allocated to the license option in the Genzyme Collaboration will be deferred until the option is exercised. The revenue recognition upon option exercise will be determined based on whether the license has standalone value from the remaining deliverables under the arrangement at the time of exercise.
We recognize the amounts associated with research and development services, alliance joint steering committees and development advisory committees ratably over the associated period of performance. If there is no discernible pattern of performance or objectively measurable performance measures do not exist, then we recognize revenue under the arrangement on a straight-line basis over the period that we are expected to complete our performance obligations. Conversely, if the pattern of performance in which the service is provided to the customer can be determined and objectively measureable performance exists, then we recognize revenue under the arrangement using the proportional performance method. Revenue recognized is limited to the lesser of the cumulative amount of payments received or the cumulative revenue earned determined using the straight line method or proportional performance, as applicable, as of the period end date.
Recognition of Milestones and Royalties
At the inception of an arrangement that includes milestone payments, we evaluate whether each milestone is substantive and at risk to both parties on the basis of the contingent nature of the milestone. This evaluation includes an assessment of whether: (i) the consideration is commensurate with either our performance to achieve the milestone or the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting from our performance to achieve the milestone, (ii) the consideration relates solely to past performance and (iii) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. We evaluate factors such as clinical, regulatory, commercial and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone and the level of effort and investment required to achieve the respective milestone in making this assessment. There is considerable judgment involved in determining whether a milestone satisfies all of the criteria required to conclude that a milestone is substantive. In accordance with FASB ASC Topic 605-28, Revenue Recognition—Milestone Method, or ASC 605-28, clinical and regulatory milestones that are considered substantive, will be recognized as revenue in its entirety upon successful accomplishment of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Milestones that are not considered substantive would be recognized as revenue over the remaining period of performance, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Revenue from commercial milestone payments will be accounted for as royalties and recorded as revenue upon achievement of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
We will recognize royalty revenue in the period of sale of the related product(s), based on the underlying contract terms, provided that the reported sales are reliably measurable, we have no remaining performance obligations, and assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
Classifications of Payments to Customers
We also consider the impact of potential future payments we make in our role as a vendor to our customers or collaboration partners and evaluate if these potential future payments could be reductions of revenue from that customer. If the potential future payments to the customer are (i) a separately identifiable benefit and (ii) the fair value of the identifiable benefit can be reasonably estimated, then the payments are accounted for separately from the revenue received from the customer. If however, both of these criteria are not satisfied, then the payments are treated as a reduction of revenue.
Accrued Research and Development Expenses
As part of the process of preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date. This process involves reviewing open contracts and purchase orders, communicating with our personnel to identify services that have been performed on our behalf and estimating the level of service performed and the associated cost incurred for the service when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of the actual cost. The majority of our service providers invoice us monthly in arrears for services performed or when contractual
98
milestones are met. We make estimates of our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. We periodically confirm the accuracy of our estimates with the service providers and make adjustments if necessary. The significant estimates in our accrued research and development expenses include the costs incurred for services performed by our vendors in connection with research and development activities for which we have not yet been invoiced.
We record our expenses related to research and development activities on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to quotes and contracts with vendors that conduct research and development on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the research and development expense. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period. If the actual timing of the performance of services or the level of effort varies from our estimate, we adjust the accrual or prepaid accordingly. Non-refundable advance payments for goods and services that will be used in future research and development activities are expensed when the activity has been performed or when the goods have been received rather than when the payment is made.
Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, if our estimates of the status and timing of services performed differ from the actual status and timing of services performed, it could result in us reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period. To date, there have been no material differences between our estimates of such expenses and the amounts actually incurred.
Fair Value Measurements—Tranche Rights
The January 2014 Series A Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement provides the investors the right, and upon achievement of certain milestones, obligates the investors to participate in subsequent offerings of Series A Preferred Stock, or Tranche Rights. The Tranche Rights meet the definition of a freestanding financial instrument, as the Tranche Rights are legally detachable and separately exercisable from the Series A Preferred Stock. Since the Series A Preferred Stock is redeemable at the holder's option, the Tranche Rights are classified as an asset or liability and are initially recorded at fair value and marked to market at each subsequent reporting period, through the settlement of the Tranche Rights.
We determine fair value utilizing the concept of "Fair Value" from FASB ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement, or ASC 820, that states that any fair value measurement requires that the reporting entity to determine the valuation technique(s) appropriate for the measurement, considering the availability of data with which to develop inputs that represent the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability and the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the inputs are categorized.
The estimated fair value of the Tranche Rights was determined using a probability-weighted present value model that considers the probability of closing a tranche, the estimated future value of Series A Preferred Stock at each closing, and the amount of the investment required at each closing. Future values are converted to present value using a discount rate appropriate for probability-adjusted cash flows. Upon the settlement of each tranche, the fair value of the Tranche Rights associated with that tranche was reclassified to Series A Preferred Stock at its then fair value and is no longer re-measured.
Stock-based Compensation
We account for our stock-based compensation awards in accordance with ASC Topic 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation, or ASC 718. ASC 718 requires all stock-based payments to employees and directors, including grants of restricted stock and stock options, to be recognized as expense in the statements of operations based on their grant date fair values. Grants of restricted stock and stock options to other service providers, referred to as non-employees, are required to be recognized as expense in the statements of operations based on their vesting date fair
99
values. We estimate the fair value of options granted using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. We use the value of our common stock to determine the fair value of restricted stock awards.
The Black-Scholes option pricing model requires inputs based on certain subjective assumptions, including (a) the expected stock price volatility, (b) the calculation of expected term of the award, (c) the risk-free interest rate and (d) expected dividends. Due to the lack of a public market for the trading of our common stock prior to the completion of our IPO and a lack of company-specific historical and implied volatility data, we have based the estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. The historical volatility is calculated based on a period of time commensurate with the expected term assumption. The computation of expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of a representative group of companies with similar characteristics to us, including stage of product development and life science industry focus. We use the simplified method as prescribed by the SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107, Share-Based Payment, to calculate the expected term for options granted to employees and directors as we do not have sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate the expected term. For options granted to non-employees, we utilize the contractual term of the arrangement as the basis for the expected term assumption. The risk-free interest rate is based on a treasury instrument whose term is consistent with the expected term of the stock options. The expected dividend yield is assumed to be zero as we have never paid dividends and do not have current plans to pay any dividends on common stock.
The weighted average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options granted to employees and directors were as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
% |
|
Expected term (in years) |
|
6.0 |
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
78.6 |
% |
The weighted average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options granted to non-employees were as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
% |
|
Expected term (in years) |
|
10.0 |
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
84.0 |
% |
We expense the fair value of our stock-based compensation awards to employees and directors on a straight-line basis over the associated service period, which is generally the period in which the related services are received. Stock-based compensation awards to non-employees are adjusted through stock-based compensation expense at each reporting period end to reflect the current fair value of such awards and are expensed on a straight-line basis.
We record the expense for stock-based compensation awards subject to performance-based milestone vesting over the remaining service period when management determines that achievement of the milestone is probable. Management evaluates when the achievement of a performance-based milestone is probable based on the expected satisfaction of the performance conditions as of the reporting date. We have not recognized any expense related to performance-based awards to date as achievement of the performance milestones has not been determined to be probable.
100
Stock-based compensation totaled approximately $4,027,000 and $425,000 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We did not have stock-based compensation for the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2015, we had $32,047,000 and $4,753,000 of unrecognized compensation expense related to restricted stock awards and stock option awards, respectively, which are expected to be recognized over weighted-average remaining vesting periods of approximately 2.35 and 3.36 years, respectively. We expect the impact of our stock-based compensation expense for restricted stock and stock options granted to employees, directors and other service providers to grow in future periods due to the potential increases in the value of our common stock and headcount.
Prior to our IPO, the estimated fair value of our common stock was determined contemporaneously by our board of directors based on valuation estimates provided by management and prepared in accordance with the framework of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Technical Practice Aid, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation, or AICPA Practice Aid, as well as independent third-party valuations. Our contemporaneous valuations of our common stock were based on a number of objective and subjective factors, including external market conditions affecting the biotechnology industry sector and the prices at which we sold shares of preferred stock, the superior rights and preferences of securities senior to our common stock at the time of each grant and the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event such as an IPO. After the completion of the IPO the fair value of the shares of common stock underlying the stock options is the closing price on the option grant date.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, together with the changes in those items in dollars:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|||||
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
Change |
|||
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
|
Collaboration revenue |
$ |
17,334 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
17,334 |
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
27,679 |
|
|
8,898 |
|
|
18,781 |
|
General and administrative |
|
9,909 |
|
|
5,469 |
|
|
4,440 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
37,588 |
|
|
14,367 |
|
|
23,221 |
|
Other expense, net: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense), net |
|
332 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
333 |
|
Other expense |
|
(9,750) |
|
|
(1,949) |
|
|
(7,801) |
|
Total other expense, net |
|
(9,418) |
|
|
(1,950) |
|
|
(7,468) |
|
Net loss |
$ |
(29,672) |
|
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(13,355) |
Collaboration Revenue
Collaboration revenue was $17.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, all of which related to the Genzyme Collaboration. We did not earn any revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014. In the year ended December 31, 2015 we recorded $17.3 million in recognition of amounts allocated to research and development services for various programs under the Genzyme Collaboration, which was entered into in February 2015. Generally, the amounts allocated to these programs are expected to be recognized on a straight line basis over the period the services are provided for each program.
101
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expense increased by $18.8 million from $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $27.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The following table summarizes our research and development expenses, for years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|||||
|
|
December 31, |
|
|
|||||
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
Change |
|||
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
|
Employee and contractor related expenses |
$ |
11,351 |
|
$ |
4,319 |
|
$ |
7,032 |
|
Process and platform development expenses |
|
14,128 |
|
|
2,842 |
|
|
11,286 |
|
License fees |
|
294 |
|
|
872 |
|
|
(578) |
|
Facility expenses |
|
1,373 |
|
|
554 |
|
|
819 |
|
Other expenses |
|
533 |
|
|
311 |
|
|
222 |
|
Total research and development expenses |
$ |
27,679 |
|
$ |
8,898 |
|
$ |
18,781 |
The change in research and development expense for the year ended December 31, 2015 was primarily attributable to the following:
|
· |
approximately $9.0 million for increased costs of funding research performed by third parties that conduct research and development, preclinical and clinical activities and manufacturing and production design on our behalf and increased purchases of lab supplies and non‑capital equipment used in designing, developing and manufacturing preclinical study materials, and an additional expense of approximately $2.3 million attributable to in‑kind research and development services incurred by Genzyme and provided to us under the Genzyme Collaboration; |
|
· |
approximately $7.0 million for increased research and development employee compensation costs; |
|
· |
approximately $0.8 million for increased facility costs including rent, depreciation, and maintenance expenses; and |
|
· |
a decrease of approximately $0.6 million related to lower licensing costs. |
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense increased by $4.4 million from $5.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $9.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The change in general and administrative expense was primarily attributable to the following:
|
· |
approximately $2.0 million related to the increase in administrative function headcount; |
|
· |
approximately $1.2 million for increased consulting and professional services; |
|
· |
approximately $0.4 million for increased in legal fees; and |
|
· |
approximately $0.9 million for increased facility costs including rent, depreciation, maintenance and administrative expenses. |
Other Expense, Net
Other expense increased by $7.4 million from $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 to $9.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in expense primarily related to the mark to market
102
adjustments recorded on our Series A Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability during the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in value of the Series A Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability was a result of the increase in the fair value of our Series A Preferred Stock and the increase in the probability of closing the tranche during the year ended December 31, 2015. The Series A Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability was settled in February 2015 upon the issuance of the final tranche of Series A Preferred Stock.
Comparison of year ended December 31, 2014 and the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013:
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the year and period ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, together with the changes in those items in dollars:
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|
|
|
||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
|
||
|
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
Change |
|||
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
|
Collaboration revenue |
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
8,898 |
|
|
2,316 |
|
|
6,582 |
|
General and administrative |
|
5,469 |
|
|
1,450 |
|
|
4,019 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
14,367 |
|
|
3,766 |
|
|
10,601 |
|
Other expense, net: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense), net |
|
(1) |
|
|
(67) |
|
|
66 |
|
Other expense |
|
(1,949) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(1,949) |
|
Total other expense, net |
|
(1,950) |
|
|
(67) |
|
|
(1,883) |
|
Net loss |
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
$ |
(12,484) |
Revenue
During the year and period ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, we did not earn any revenue from product sales or from collaboration agreements.
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expense increased by $6.6 million from $2.3 million for the period ended December 31, 2013 to $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The following table summarizes our research and development expenses, for the year and period ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively:
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
||
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|
|
|||
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|
|||
|
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
Change |
|||
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
|
Employee and contractor related expenses |
$ |
4,319 |
|
$ |
2,152 |
|
$ |
2,167 |
|
Process and platform development expenses |
|
2,842 |
|
|
32 |
|
|
2,810 |
|
License fees |
|
872 |
|
|
— |
|
|
872 |
|
Facility expenses |
|
554 |
|
|
— |
|
|
554 |
|
Other expenses |
|
311 |
|
|
132 |
|
|
179 |
|
Total research and development expenses |
$ |
8,898 |
|
$ |
2,316 |
|
$ |
6,582 |
103
The increase in research and development expense was primarily attributable to research and development, and included the following:
|
· |
approximately $2.8 million for increased purchases of lab supplies and non-capital equipment, funding preclinical and research development efforts and process development and design costs; |
|
· |
approximately $2.2 million for increased compensation expenses, of which $2.6 million related to increased employee compensation costs, including hiring of personnel during 2014, which were partially offset by a $0.4 million decrease in contractor and consulting fees; |
|
· |
approximately $0.9 million related to acquiring patents and licensing rights; and |
|
· |
approximately $0.6 million for increases in facility costs including rent, depreciation, and maintenance expenses; |
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense increased by $4.0 million from $1.5 million for the period ended December 31, 2013 to $5.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in general and administrative expense was primarily attributable to 12 months of operations being included in 2014 versus the six months of operations during 2013 and included the following:
|
· |
approximately $1.5 million for patent-related and other corporate legal fees incurred; |
|
· |
approximately $1.0 million for increased employee compensation costs, including hiring of personnel; |
|
· |
approximately $0.6 million for renting and operating our corporate facilities; and |
|
· |
approximately $0.4 million for administrative consulting and professional services. |
Other Expense, Net
Other expense increased by $1.9 million from $0.1 million for the period ended December 31, 2013 to $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in expense primarily related to the mark to market adjustments recorded on our Series A Preferred Stock Tranche Right liability during 2014. Additionally, interest expense decreased by $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 from $0.1 million for the period ended December 31, 2013. The decrease related to the exchange of the convertible promissory notes payable, which were issued during the period ended December 31, 2013, into Series A Preferred Stock in January 2014.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources of Liquidity
Prior to our IPO, we had funded our operations primarily through proceeds from private placements of our redeemable convertible preferred stock and convertible promissory notes.
On November 16, 2015 we closed our IPO whereby we sold 5,750,000 shares of common stock, at a public offering price of $14.00 per share, including 750,000 shares of common stock issued upon the full exercise by the
104
underwriters of their option to purchase additional shares, resulting in net proceeds to us of $72.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us.
As of December 31, 2015, we had cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities of $224.3 million.
Cash Flows
The following table provides information regarding our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and the period ended December 31, 2013:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
|
Net cash provided by (used in): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating activities |
|
$ |
41,299 |
|
$ |
(11,918) |
|
$ |
(2,725) |
|
Investing activities |
|
|
(194,769) |
|
|
(3,302) |
|
|
— |
|
Financing activities |
|
|
177,744 |
|
|
22,120 |
|
|
2,860 |
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
24,274 |
|
$ |
6,900 |
|
$ |
135 |
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $41.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in cash provided by operating activities was primarily due to the receipt of the $65.0 million upfront payment from Genzyme under the Genzyme Collaboration offset by an increase in net loss of $13.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014.
Net cash used in operating activities was $11.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in cash used in operating activities was due to an increase in net loss of $12.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to the period ended December 31, 2013.
Net cash used in operating activities was $2.7 million during the period ended December 31, 2013.
Cash Flows from Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $194.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2015 The cash used for investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2015 was primarily due to purchases of marketable securities partially offset by proceeds from maturities of marketable securities.
Net cash used in investing activities was $3.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in cash used in investing activities was due to purchases of property and equipment of $1.7 million, the build-out of our leased facilities under the tenant improvements allowance of $1.3 million, and setting aside $0.3 million in restricted cash as required by our lease agreement and credit card agreements.
No cash was used in investing activities during the period ended December 31, 2013.
Cash Flows from Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $177.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2015. The cash provided by financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 was primarily due to the receipt of IPO proceeds (net of underwriting discounts and commissions, but prior to deducting other transaction expenses) of $72.9 million, the issuance of $20.0 million of Series A Preferred Stock and $90.0 million of Series B Preferred Stock of which
105
$5.0 million in proceeds were in excess of the Series B Preferred Stock’s fair value and were allocated to deferred revenue. Cash payments of IPO related expenses totaled $1.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2015.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $22.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase in cash provided by financing activities was primarily due to the closing of the first four Series A Preferred Stock financing rounds for aggregate gross proceeds of $22.0 million during 2014.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $2.9 million during the period ended December 31, 2013. The increase in cash provided by financing activities was primarily due to the issuance of convertible promissory notes during 2013.
Funding Requirements
We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we continue the research and development of, continue or initiate clinical trials of, and seek marketing approval for, our product candidates. In addition, if we obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates, we expect to incur significant commercialization expenses related to program sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution to the extent that such sales, marketing and distribution are not the responsibility of potential collaborators. Furthermore, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, we would be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our research and development programs or future commercialization efforts.
Based upon our current operating plan, we expect our existing cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements into 2019. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
|
· |
the scope, progress, results and costs of product discovery, preclinical studies and clinical trials for our product candidates; |
|
· |
the scope, prioritization and number of our research and development programs; |
|
· |
the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates; |
|
· |
our ability to establish and maintain collaborations on favorable terms, if at all; |
|
· |
the achievement of milestones or occurrence of other developments that trigger payments under the Genzyme Collaboration and any other collaboration agreements we obtain; |
|
· |
the ability of our collaboration partners to exercise options to extend research and development programs |
|
· |
the extent to which we are obligated to reimburse, or entitled to reimbursement of, clinical trial costs under collaboration agreements, if any; |
|
· |
the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending intellectual property‑related claims; |
|
· |
the extent to which we acquire or in‑license other product candidates and technologies; |
|
· |
the costs of securing manufacturing arrangements for commercial production; and |
106
|
· |
the costs of establishing or contracting for sales and marketing capabilities if we obtain regulatory approvals to market our product candidates. |
Identifying potential product candidates and conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials is a time‑consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes many years to complete, and we may never generate the necessary data or results required to obtain marketing approval and achieve product sales. In addition, our product candidates, if approved, may not achieve commercial success. Our commercial revenues, if any, will be derived from sales of gene therapies that we do not expect to be commercially available for many years, if at all. Accordingly, we will need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve our business objectives. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenues, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or redeemable convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a common stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If we raise funds through additional collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or to grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our significant contractual obligations as of payment due date by period at December 31, 2015 (in thousands):
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less Than |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
More than |
|
||
|
|
|
Total |
|
1 Year |
|
1 to 3 Years |
|
3 to 5 Years |
|
5 Years |
|
|||||
|
Operating lease commitments(1) |
|
$ |
4,760 |
|
$ |
1,170 |
|
$ |
2,406 |
|
$ |
1,184 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
(1) |
We lease office space at 75 Sidney Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts under a non‑cancelable operating lease that expires in December 2019. This table excludes payments related to a new lease and a lease amendment executed in January 2016. |
In January 2016, we executed an amendment to extend the lease for 75 Sidney Street in Cambridge, Massachusetts to December 2024 and an agreement to lease an additional facility for approximately 26,000 square feet in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The additional facility will include laboratory and office space, and is projected to be ready for occupancy in early 2017. The table above excludes estimated payments of approximately $25.0 million, related to the amendment extending the 75 Sidney Street lease to December 2024 and the new lease for approximately 26,000 square feet in Cambridge, Massachusetts to December 2024.
We enter into agreements in the normal course of business with CROs and institutions to license intellectual property. We have not included these future payments in the table of contractual obligations above since the contracts are cancelable at any time by us, generally upon 30 to 90 days prior written notice.
Our agreements to license intellectual property include potential milestone payments that are dependent upon the development of products using the intellectual property licensed under the agreements and contingent upon the achievement of clinical trial or regulatory approval milestones. The maximum aggregate potential milestone payments payable by us total approximately $12.0 million. Additionally, under the terms of one agreement, we have options to license intellectual property to be used in the development of therapies for four disease indications. If we exercise all of the options under the agreement, we would be obligated to pay aggregate up‑front fees of up to approximately
107
$1.5 million and milestone payments that are contingent upon clinical trial results and regulatory approval of $5.0 million per disease indication, or up to $20.0 million in total. We may also be required to pay annual maintenance fees or minimum amounts payable ranging from low‑four digits to low five‑digits depending upon the terms of the applicable agreement.
Off‑Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have, during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off‑balance sheet arrangements, as defined under applicable Securities and Exchange Commission rules.
JOBS Act
In April 2012, the JOBS Act, was enacted. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company, or EGC, can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Thus, an EGC can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this extended transition period and, as a result, we will adopt new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for other public companies.
We are in the process of evaluating the benefits of relying on other exemptions and reduced reporting requirements under the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions, as an EGC, we intend to rely on certain of these exemptions, including without limitation, (i) providing an auditor’s attestation report on our system of internal controls over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act and (ii) complying with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board, or PCAOB, regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements, known as the auditor discussion and analysis. We will remain an EGC until the earlier of (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1.0 billion or more; (ii) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the completion of our IPO; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest rate sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates, particularly because our investments, including cash equivalents, are in the form of money market fund and marketable securities and are invested in U.S. Treasury and U.S. government agency obligations.
We are not currently exposed to market risk related to changes in foreign currency exchange rates; however, we may contract with vendors that are located in Asia and Europe in the future and may be subject to fluctuations in foreign currency rates at that time.
Inflation generally affects us by increasing our cost of labor and clinical trial costs. We do not believe that inflation had a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations during the year ended December 31, 2015.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The financial statements required to be filed pursuant to this Item 8 are appended to this report. An index of those financial statements is found in Item 15.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
108
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934 is (1) recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and (2) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer, who is our principal executive officer and Chief Financial Officer, who is also our principal financial and accounting officer, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As of December 31, 2015, our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial and accounting officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934). Our management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives, and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Our principal executive officer and principal financial and accounting officer have concluded based upon the evaluation described above that, as of December 31, 2015, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
This Annual Report on Form 10-K does not include a report of management’s assessment regarding internal control over financial reporting or an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm due to a transition period established by rules of the SEC for newly public companies.
Not applicable.
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Incorporated by reference from the information in our Proxy Statement for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which we will file with the SEC within 120 days of the end of the fiscal year to which this Annual Report on Form 10-K relates.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Incorporated by reference from the information in our Proxy Statement for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which we will file with the SEC within 120 days of the end of the fiscal year to which this Annual Report on Form 10-K relates.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Incorporated by reference from the information in our Proxy Statement for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which we will file with the SEC within 120 days of the end of the fiscal year to which this Annual Report on Form 10-K relates.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
109
Incorporated by reference from the information in our Proxy Statement for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which we will file with the SEC within 120 days of the end of the fiscal year to which this Annual Report on Form 10-K relates.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
Incorporated by reference from the information in our Proxy Statement for our 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, which we will file with the SEC within 120 days of the end of the fiscal year to which this Annual Report on Form 10-K relates.
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)(1) Financial Statements.
|
|
|
Pages |
|
|
F-1 |
|
|
|
F-2 |
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss |
|
F-3 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|
F-4 |
|
F-5 |
||
|
|
F-6 |
|
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules.
All schedules have been omitted because they are not required or because the required information is given in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes thereto set forth under Item 8 above.
(a)(3) Exhibits.
See the Exhibit Index immediately following the signature page of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The exhibits listed in the Exhibit Index below are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
110
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Voyager Therapeutics, Inc. as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Voyager Therapeutics, Inc. at December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 17, 2016
F-1
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
(amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
31,309 |
|
$ |
7,035 |
|
|
Marketable investments, current |
|
|
163,028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
1,557 |
|
|
1,323 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
195,894 |
|
|
8,358 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
3,234 |
|
|
2,804 |
|
|
Deposits and other non-current assets |
|
|
321 |
|
|
335 |
|
|
Marketable investments, non-current |
|
|
30,008 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
229,457 |
|
$ |
11,497 |
|
|
Liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
612 |
|
$ |
1,554 |
|
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
3,430 |
|
|
642 |
|
|
Deferred rent, current portion |
|
|
300 |
|
|
278 |
|
|
Deferred revenue, current portion |
|
|
19,589 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
23,931 |
|
|
2,474 |
|
|
Deferred rent, net of current portion |
|
|
1,015 |
|
|
1,314 |
|
|
Deferred revenue, net of current portion |
|
|
35,393 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Other non-current liabilities |
|
|
44 |
|
|
255 |
|
|
Preferred stock tranche liability |
|
|
— |
|
|
6,305 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
60,383 |
|
|
10,348 |
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (see note 7) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.001 par value: 0 and 45,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively; 0 and 25,000,000 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively; aggregate liquidation preference of $26,086 at December 31, 2014 |
|
|
— |
|
|
21,979 |
|
|
Stockholders’ equity (deficit): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock $0.001 par value: 5,000,000 and 0 shares authorized at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively; 0 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015 and 2014 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value: 120,000,000 and 65,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively; 24,930,979 and 814,834 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively |
|
|
25 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
219,122 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(251) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(49,822) |
|
|
(20,831) |
|
|
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
|
|
169,074 |
|
|
(20,830) |
|
|
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
|
$ |
229,457 |
|
$ |
11,497 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-2
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(amounts in thousands, except per share and share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
Collaboration revenue |
|
$ |
17,334 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Operating expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
27,679 |
|
|
8,898 |
|
|
2,316 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
9,909 |
|
|
5,469 |
|
|
1,450 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
37,588 |
|
|
14,367 |
|
|
3,766 |
|
|
Operating loss |
|
|
(20,254) |
|
|
(14,367) |
|
|
(3,766) |
|
|
Other expense, net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest income (expense), net |
|
|
332 |
|
|
(1) |
|
|
(67) |
|
|
Other expense |
|
|
(9,750) |
|
|
(1,949) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total other expense, net |
|
|
(9,418) |
|
|
(1,950) |
|
|
(67) |
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(29,672) |
|
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net unrealized loss on available-for-sale-securities |
|
|
(251) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(251) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Comprehensive loss |
|
$ |
(29,923) |
|
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Reconciliation of net loss to net loss attributable to common stockholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(29,672) |
|
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value |
|
|
(7,373) |
|
|
(1,366) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Accrued dividends on series A preferred stock |
|
|
(1,245) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
|
$ |
(38,290) |
|
$ |
(17,683) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted |
|
$ |
(9.14) |
|
$ |
(27.83) |
|
$ |
(1,629.68) |
|
|
Weighted-average common shares outstanding, basic and diluted |
|
|
4,191,210 |
|
|
635,448 |
|
|
2,352 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
Statements of Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders' Equity (Deficit)
(amounts in thousands except share data)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Series A |
|
Series B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Redeemable |
|
Redeemable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Convertible |
|
Convertible |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional |
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Preferred Stock |
|
Preferred Stock |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
Paid-In |
|
Comprehensive |
|
Accumulated |
|
Stockholders’ |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
Capital |
|
Loss |
|
Deficit |
|
Equity (Deficit) |
|
|||||||
|
Balance at June 19, 2013 (inception) |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Issuance of common stock |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
2,352 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(3,833) |
|
|
(3,833) |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
2,352 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Issuance of common stock for services |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
494,118 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
251 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
252 |
|
|
Initial issuance of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock, including exchange of convertible notes payable of $2,929 and net of tranche rights of $2,600 and issuance costs of $22 |
|
6,500,000 |
|
|
3,878 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Subsequent issuance of preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $9 |
|
18,500,000 |
|
|
18,491 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Reclassification of tranche rights upon issuance of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
|
— |
|
|
(1,756) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Vesting of restricted common stock |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
318,364 |
|
|
— |
|
|
9 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
9 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
425 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
425 |
|
|
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value |
|
— |
|
|
1,366 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(685) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(681) |
|
|
(1,366) |
|
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(16,317) |
|
|
(16,317) |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
25,000,000 |
|
$ |
21,979 |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
814,834 |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
(20,831) |
|
$ |
(20,830) |
|
|
Issuance of Series A preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $1 |
|
20,000,000 |
|
|
19,999 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Reclassification of tranche rights upon issuance of preferred stock |
|
— |
|
|
16,055 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Issuance of Series B preferred stock, net of discount of $5,000 and issuance costs of $220 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
30,000,001 |
|
|
84,780 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Vesting of restricted stock |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
717,747 |
|
|
— |
|
|
22 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
22 |
|
|
Exercises of vested stock options |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,344 |
|
|
— |
|
|
10 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
10 |
|
|
Issuance of common stock from initial public offering (net of underwriters, discounts, and issuance costs) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
5,750,000 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
72,948 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,954 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,027 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
4,027 |
|
|
Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities, net of tax |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(251) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(251) |
|
|
Accretion of preferred stock to redemption value |
|
— |
|
|
2,149 |
|
— |
|
|
5,225 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(2,560) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(4,813) |
|
|
(7,373) |
|
|
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to common stock |
|
(45,000,000) |
|
|
(60,182) |
|
(30,000,001) |
|
|
(90,005) |
|
|
17,647,054 |
|
|
18 |
|
|
144,675 |
|
|
— |
|
|
5,494 |
|
|
150,187 |
|
|
Net loss |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(29,672) |
|
|
(29,672) |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
24,930,979 |
|
$ |
25 |
|
$ |
219,122 |
|
$ |
(251) |
|
$ |
(49,822) |
|
$ |
169,074 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
F-4
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
Condensed Statements of Cash Flows
(amounts in thousands)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
Cash flow from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(29,672) |
|
$ |
(16,317) |
|
$ |
(3,833) |
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
|
4,027 |
|
|
425 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
600 |
|
|
184 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Amortization of premiums and discounts on marketable securities |
|
|
452 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Change in fair value of preferred stock tranche liability |
|
|
9,750 |
|
|
1,949 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Non-cash interest on convertible promissory notes payable |
|
|
— |
|
|
2 |
|
|
67 |
|
|
Expense related to shares issued in connection with services performed |
|
|
— |
|
|
250 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
|
(277) |
|
|
342 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(234) |
|
|
(1,185) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Other non-current assets |
|
|
14 |
|
|
(7) |
|
|
(14) |
|
|
Deferred revenue |
|
|
54,982 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
(942) |
|
|
604 |
|
|
950 |
|
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
2,788 |
|
|
537 |
|
|
105 |
|
|
Other non-current liabilities |
|
|
(189) |
|
|
186 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Lease incentive benefit |
|
|
— |
|
|
1,112 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
|
|
41,299 |
|
|
(11,918) |
|
|
(2,725) |
|
|
Cash flow from investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(1,030) |
|
|
(2,988) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Change in restricted cash |
|
|
— |
|
|
(314) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Purchases of marketable securities |
|
|
(220,399) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from maturities or sales of marketable securities |
|
|
26,660 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(194,769) |
|
|
(3,302) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Cash flow from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of series A preferred stock |
|
|
19,999 |
|
|
22,040 |
|
|
2,860 |
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of series B preferred stock |
|
|
84,780 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options |
|
|
10 |
|
|
80 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from the issuance of common stock and restricted stock |
|
|
72,955 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
177,744 |
|
|
22,120 |
|
|
2,860 |
|
|
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
24,274 |
|
|
6,900 |
|
|
135 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
|
7,035 |
|
|
135 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
|
$ |
31,309 |
|
$ |
7,035 |
|
$ |
135 |
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash and non-cash activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value |
|
$ |
7,373 |
|
$ |
1,366 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Exchange of promissory notes payable and accrued interest into Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock and tranche rights |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
2,929 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to common stock |
|
$ |
150,187 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Nature of business
Voyager Therapeutics, Inc. (“the Company”) is a clinical‑stage gene therapy company focused on developing life‑changing treatments for patients suffering from severe diseases of the central nervous system (the “CNS”). The Company focuses on CNS diseases where it believes that an adeno‑associated virus (“AAV”) gene therapy approach can have a clinically meaningful impact by either increasing or decreasing the production of a specific protein. The Company has created a product engine that enables it to engineer, optimize, manufacture and deliver its AAV‑based gene therapies that have the potential to provide durable efficacy following a single administration directly to the CNS. The Company’s product engine has rapidly generated programs for five CNS indications, including advanced Parkinson’s disease, a form of monogenic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Friedreich’s ataxia, Huntington’s disease and spinal muscular atrophy. The Company’s most advanced clinical candidate, VY‑AADC01, is being evaluated for the treatment of advanced Parkinson’s disease in an open‑label, Phase 1b clinical trial with the goal of generating human proof‑of‑concept data in the fourth quarter of 2016.
The Company is devoting substantially all of its efforts to product research and development, market development, and raising capital. The Company is subject to risks common to companies in the biotechnology and gene therapy industry, including but not limited to, risks of failure of pre‑clinical studies, and clinical trials, the need to obtain marketing approval for its drug product candidates, the need to successfully commercialize and gain market acceptance of its drug product candidates, dependence on key personnel, protection of proprietary technology, compliance with government regulations, development by competitors of technological innovations and ability to transition from pilot‑scale manufacturing to large‑scale production of products.
The Company has incurred annual net operating losses in every year since its inception. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had incurred losses since inception of $49.8 million. The Company has not generated any product revenues and has financed its operations primarily through public offerings and private placements of its equity securities, and funding from its collaboration with Genzyme. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain additional debt or equity financing or generate product revenue or revenues from collaborative partners, on terms acceptable to the Company, on a timely basis or at all. The failure of the Company to obtain sufficient funds on acceptable terms when needed could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations, and financial condition.
2. Summary of significant accounting policies
The following is a summary of significant accounting policies followed in the preparation of these financial statements.
Basis of presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include those of the Company and its subsidiary, Voyager Securities Corporation, after elimination of all intercompany accounts and transactions. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Initial public offering
On November 16, 2015 the Company completed the sale of 5,750,000 shares of its common stock in its initial public offering (the “IPO”), at a price to the public of $14.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds to the Company of $72.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company.
On October 29, 2015, in preparation for the Company’s IPO, the Company’s Board of Directors and stockholders approved a 1-for-4.25 reverse split of the Company’s common stock, which became effective on October 29, 2015. All share and per share amounts in the financial statements and notes thereto have been retroactively adjusted
F-6
for all periods presented to give effect to this reverse split, including reclassifying an amount equal to the reduction in par value of common stock to additional paid-in capital.
Upon the closing of the IPO, all of the Company’s outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock automatically converted into shares of common stock as of November 16, 2015, resulting in the issuance by the Company of an additional 17,647,054 shares of common stock. The significant increase in shares outstanding in November 2015 is expected to impact the year-over-year comparability of the Company’s net loss per share calculations.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. On an ongoing basis, the Company’s management evaluates its estimates, which include, but are not limited to, estimates related to revenue recognition, accrued expenses, valuation of the tranche rights, stock‑based compensation expense, income taxes and the fair value of common stock. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and other market specific or other relevant assumptions that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from those estimates or assumptions.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurement (“ASC 820”), establishes a fair value hierarchy for instruments measured at fair value that distinguishes between assumptions based on market data (observable inputs) and the Company’s own assumptions (unobservable inputs). Observable inputs are inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability based on market data obtained from sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect the Company’s assumptions about the inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, and are developed based on the best information available in the circumstances.
ASC 820 identifies fair value as the exchange price, or exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As a basis for considering market participant assumptions in fair value measurements, ASC 820 establishes a three‑tier fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between the following:
|
· |
Level 1—Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
|
· |
Level 2—Inputs other than Level 1 inputs that are either directly or indirectly observable, such as quoted market prices, interest rates, and yield curves. |
|
· |
Level 3—Unobservable inputs developed using estimates of assumptions developed by the Company, which reflect those that a market participant would use. |
To the extent that the valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3. A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The carrying amounts reflected in the balance sheets for cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expenses and other current assets, accounts payable and accrued expenses approximate their fair values, due to their short‑term nature.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of 90 days or less at acquisition to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include cash held in banks and amounts held in money market funds.
F-7
Marketable Securities
The Company classifies marketable securities with a remaining maturity when purchased of greater than three months as available‑for‑sale. Marketable securities with a remaining maturity date greater than one year are classified as non‑current where the Company has the intent and ability to hold these securities for at least the next twelve months. Available‑for‑sale securities are maintained by an investment manager and may consist of U.S. Treasury securities and U.S. government agency securities. Available‑for‑sale securities are carried at fair value with the unrealized gains and losses included in other comprehensive income as a component of stockholders’ deficit until realized. Any premium or discount arising at purchase is amortized and/or accreted to interest income and/or expense. Realized gains and losses are determined using the specific identification method and are included in other income (expense). If any adjustment to fair value reflects a decline in value of the investment, the Company considers all available evidence to evaluate the extent to which the decline is “other‑than‑temporary” and, if so, recognizes the unrealized loss through a charge to the Company’s statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
There were no marketable securities held as of December 31, 2014.
Marketable securities as of December 31, 2015 consist of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross |
|
Gross |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Amortized |
|
Unrealized |
|
Unrealized |
|
Fair |
|
||||
|
|
|
Cost |
|
Gains |
|
Losses |
|
Value |
|
||||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||||||||
|
As of December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Money market funds included in cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
|
Total money market funds included in cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
|
Marketable securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. Treasury notes |
|
|
158,166 |
|
|
— |
|
|
185 |
|
|
157,981 |
|
|
U.S. Government agency bonds |
|
|
35,121 |
|
|
— |
|
|
66 |
|
|
35,055 |
|
|
Total marketable securities |
|
$ |
193,287 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
251 |
|
$ |
193,036 |
|
|
Total money market funds and marketable securities |
|
$ |
222,888 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
251 |
|
$ |
222,637 |
|
The estimated fair value of the Company’s marketable securities balance at December 31, 2015, by contractual maturity, is as follows:
|
Due in one year or less |
|
$ |
163,028 |
|
|
Due after one year through two years |
|
|
30,008 |
|
|
Total marketable securities |
|
$ |
193,036 |
|
Restricted Cash
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company maintained restricted cash totaling approximately $314,000 held in the form of money market accounts as collateral for the Company’s facility lease obligation and credit cards. The balance is included within deposits and other non‑current assets in the accompanying balance sheets.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consists of laboratory equipment, furniture and office equipment and leasehold improvements and is stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Maintenance and repairs that do not improve or extend the lives of the respective assets are expensed to operations as incurred; while costs of major additions and betterments are capitalized. Depreciation is calculated over the estimated useful lives of the assets using the straight‑line method.
Impairment of Long‑Lived Assets
The Company evaluates long‑lived assets for potential impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by comparing the book values of the assets to the expected future net undiscounted cash flows that the assets are expected to generate. If such
F-8
assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the book values of the assets exceed their fair value. The Company has not recognized any impairment losses from inception through December 31, 2015.
Revenue Recognition
As of December 31, 2015, all of the Company’s revenue is generated exclusively from its collaboration agreement with Genzyme Corporation, a Sanofi company (“Genzyme”).
The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with ASC Topic 605, Revenue Recognition (“ASC 605”). Accordingly, revenue is recognized for each unit of accounting when all of the following criteria are met:
|
· |
Persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; |
|
· |
Delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; |
|
· |
The seller’s price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and |
|
· |
Collectability is reasonably assured. |
Amounts received prior to satisfying the revenue recognition criteria are recorded as deferred revenue in the Company’s balance sheet. Amounts expected to be recognized as revenue within 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, current portion. Amounts not expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, net of current portion.
The Company analyzes the multiple element arrangements based on the guidance in ASC Topic 605‑25, Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements (“ASC 605‑25”). Pursuant to the guidance in ASC 605‑25, the Company evaluates multiple element arrangements to determine (1) the deliverables included in the arrangement and (2) whether the individual deliverables represent separate units of accounting or whether they must be accounted for as a combined unit of accounting. This evaluation involves subjective determinations and requires management to make judgements about the individual deliverables and whether such deliverables are separate from other aspects of the contractual relationship. Deliverables are considered separate units of accounting provided that: (i) the delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a standalone basis and (ii) if the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item(s), delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially within control of the Company. In assessing whether an item has standalone value, the Company considers factors such as the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the collaboration partner and the availability of the associated expertise in the general marketplace. In addition, the Company considers whether the collaboration partner can use the other deliverable(s) for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining element(s), whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered item(s) and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered element(s). The Company’s collaboration agreement does not contain a general right of return relative to any delivered items.
Arrangement consideration that is fixed or determinable is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling price method. Then the applicable revenue recognition criteria in ASC 605 are applied to each of the separate units of accounting in determining the appropriate period and pattern of recognition. The Company determines the selling price of a unit of accounting following the hierarchy of evidence prescribed by ASC 605‑25. Accordingly, the Company determines the estimated selling price for units of accounting within each arrangement using vendor specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) of selling price, if available, third party evidence (“TPE”) of selling price if VSOE is not available, or best estimate of selling price (“BESP”) if neither VSOE or TPE is available. The Company has only used BESP to estimate the selling price, since it has not had VSOE or TPE of selling price of any units of accounting to date. Determining BESP for a unit of accounting requires significant judgement. In developing the BESP for a unit of accounting, the Company considers applicable market conditions and relevant entity specific factors, including factors that were contemplated in negotiating the agreement with the customer and estimated costs. The Company validates BESP for units of accounting by evaluating whether changes in the key assumptions used to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple units of accounting.
F-9
Options are considered substantive if, at the inception of the arrangement, the Company is at risk as to whether the collaboration partner will choose to exercise the option. Factors that the Company considers in evaluating whether an option is substantive include the cost to exercise the option, the overall objective of the arrangement, the benefit the collaborator might obtain from the arrangement without exercising the option and the likelihood the option will be exercised. When an option is considered substantive, the Company does not consider the option or item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and the associated option fees are not included in allocable consideration, assuming the option is not priced at a significant and incremental discount. Conversely, when an option is not considered substantive, the Company would consider the option, including other deliverables contingent upon the exercise of the option, to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and a corresponding amount would be included in allocable arrangement consideration. In addition, if the price of the option includes a significant incremental discount, the option would be included as a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement.
The Company recognizes arrangement consideration allocated to each unit of accounting when all of the revenue recognition criteria in ASC 605 are satisfied for that particular unit of accounting. The Company will recognize revenue associated with license options upon exercise of the option, if the underlying license has standalone value from the other deliverables to be provided subsequent to delivery of the license. If the license does not have standalone value, the amounts allocated to the license option will be combined with the related undelivered items as a single unit of accounting. The amounts allocated to the license option in the Genzyme agreement will be deferred until the option is exercised. The revenue recognition upon option exercise will be determined based on whether the license has standalone value from the remaining deliverables under the arrangement at the time of exercise.
The Company recognizes the amounts associated with research and development services, alliance joint steering committees and development advisory committees ratably over the associated period of performance. If there is no discernible pattern of performance and/or objectively measurable performance measures do not exist, then the Company recognizes revenue under the arrangement on a straight‑line basis over the period the Company is expected to complete its performance obligations. Conversely, if the pattern of performance in which the service is provided to the customer can be determined and objectively measureable performance exist, then the Company recognizes revenue under the arrangement using the proportional performance method. Revenue recognized is limited to the lesser of the cumulative amount of payments received of the cumulative revenue earned determined using the straight line method or proportional performance, as applicable, as of the period end date.
At the inception of an arrangement that includes milestone payments, the Company evaluates whether each milestone is substantive and at risk to both parties on the basis of the contingent nature of the milestone. This evaluation includes an assessment of whether: (i) the consideration is commensurate with either the Company’s performance to achieve the milestone or the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting from the Company’s performance to achieve the milestone, (ii) the consideration relates solely to past performance and (iii) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. The Company evaluates factors such as clinical, regulatory, commercial and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone and the level of effort and investment required to achieve the respective milestone in making this assessment. There is considerable judgement involved in determining whether a milestone satisfies all of the criteria required to conclude that a milestone is substantive. In accordance with ASC Topic 605‑28, Revenue Recognition—Milestone Method (“ASC 605‑28”) clinical and regulatory milestones that are considered substantive, will be recognized as revenue in its entirety upon successful accomplishment of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Milestones that are not considered substantive would be recognized as revenue over the remaining period of performance, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Revenue from commercial milestone payments will be accounted for as royalties and recorded as revenue upon achievement of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
The Company will recognize royalty revenue in the period of sale of the related product(s), based on the underlying contract terms, provided that the reported sales are reliably measurable and the Company has no remaining performance obligations, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
The Company also considers the impact of potential future payments it makes in its role as a vendor to its customers or collaboration partners and evaluates if these potential future payments could be reductions of revenue from that customer. If the potential future payments to the customer are (i) a separately identifiable benefit and (ii) the fair value of the identifiable benefit can be reasonably estimated, then the payments are accounted for separately from the revenue received from the customer. If however, both of these criteria are not satisfied, then the payments are treated as a reduction of revenue.
F-10
Research and Development
Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred in performing research and development activities. The costs include employee compensation costs, external research, consultant costs, sponsored research, in‑kind services provided under the Genzyme agreement, license fees, process development and facilities costs. Facilities costs primarily include the allocation of rent, utilities and depreciation.
Research Contract Costs and Accruals
The Company has entered into various research and development contracts with research institutions and other companies. These agreements are generally cancelable. The Company records accruals for estimated ongoing research costs. When evaluating the adequacy of the accrued liabilities, the Company analyzes progress of the studies, including the phase or completion of events, invoices received and contracted costs. Significant judgments and estimates may be made in determining the accrued balances at the end of any reporting period. Actual results could differ from the Company’s estimates. The Company’s historical accrual estimates have not been materially different from the actual costs.
Patent Costs
The Company expenses patent application and related legal costs as incurred and classifies such costs as general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statements of operations.
Stock‑Based Compensation Expense
The Company accounts for its stock‑based compensation awards in accordance with ASC Topic 718 Compensation—Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”). ASC 718 requires all stock‑based payments to employees and directors, including grants of restricted stock and stock options, to be recognized as expense in the statements of operations based on their grant date fair values. Grants of restricted stock and stock options to other service providers, referred to as non‑employees, are required to be recognized as expense in the statements of operations based on their vesting date fair values. The Company estimates the fair value of options granted using the Black‑Scholes option pricing model. The Company uses the value of its common stock to determine the fair value of restricted stock awards.
The Black‑Scholes option pricing model requires inputs based on certain subjective assumptions, including (a) the expected stock price volatility, (b) the calculation of expected term of the award, (c) the risk‑free interest rate and (d) expected dividends. Due to a lack of company‑specific historical and implied volatility data of the Company’s common stock, the Company has based its estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. The historical volatility is calculated based on a period of time commensurate with the expected term assumption. The computation of expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of a representative group of companies with similar characteristics to the Company, including stage of product development and life science industry focus. The Company uses the simplified method as prescribed by the SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107, Share‑Based Payment, to calculate the expected term for stock options granted to employees as it does not have sufficient historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate the expected term. For stock options granted to non‑employees, the Company utilizes the contractual term of the arrangement as the basis for the expected term assumption. The risk‑free interest rate is based on a treasury instrument whose term is consistent with the expected term of the stock options. The expected dividend yield is assumed to be zero as the Company has never paid dividends and has no current plans to pay any dividends on its common stock.
The Company expenses the fair value of its stock‑based compensation awards to employees on a straight‑line basis over the associated service period, which is generally the period in which the related services are received. Stock‑based compensation awards to non‑employees are adjusted through stock‑based compensation expense at each reporting period end to reflect the current fair value of such awards and are expensed on a straight‑line basis.
The Company records the expense for stock‑based compensation awards subject to performance conditions over the remaining service period when management determines that achievement of the performance condition is probable. Management evaluates when the achievement of a performance condition is probable based on the expected satisfaction of the performance conditions as of the reporting date.
F-11
Income Taxes
Income taxes are recorded in accordance with ASC Topic 740, Income Taxes (“ASC 740”), which provides for deferred taxes using an asset and liability approach. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the financial reporting and the tax reporting basis of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that are expected to be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. The Company provides a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets unless, based upon the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized.
The Company accounts for uncertain tax positions in accordance with the provisions of ASC 740. When uncertain tax positions exist, the Company recognizes the tax benefit of tax positions to the extent that the benefit will more likely than not be realized. The determination as to whether the tax benefit will more likely than not be realized is based upon the technical merits of the tax position as well as consideration of the available facts and circumstances. As of December 31, 2015, the Company does not have any significant uncertain tax positions.
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss is comprised of net loss and other comprehensive income or loss. Other comprehensive loss consists of unrealized losses on marketable securities.
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
Basic net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is calculated by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted‑average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, without consideration for potentially dilutive securities. Diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is computed by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted‑average number of shares of common stock and potentially dilutive securities outstanding for the period determined using the treasury‑stock and if‑converted methods.
For purposes of the diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders calculation, redeemable convertible preferred stock, unvested restricted common stock, and outstanding stock options are considered to be potentially dilutive securities, but are excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders because their effect would be anti‑dilutive and therefore, basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders were the same for all periods presented.
The following table sets forth the outstanding potentially dilutive securities that have been excluded in the calculation of diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders because to do so would be anti‑dilutive (in common stock equivalent shares):
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
Redeemable convertible preferred stock |
|
— |
|
5,882,352 |
|
— |
|
Unvested restricted common stock |
|
1,818,261 |
|
2,578,817 |
|
— |
|
Outstanding stock options |
|
2,905,458 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
Total |
|
4,723,719 |
|
8,461,169 |
|
— |
All of the Company’s outstanding convertible preferred stock automatically converted into shares of common stock as of November 16, 2015, resulting in the issuance by the Company of an additional 17,647,054 shares of common stock.
Concentrations of Credit Risk and Off‑Balance Sheet Risk
The Company has no financial instruments with off‑balance sheet risk such as foreign exchange contracts, option contracts or other foreign hedging arrangements. Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a concentration of credit risk are cash and cash equivalents. The Company’s cash is held in accounts at a financial
F-12
institution that may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced any credit losses in such accounts and does not believe it is exposed to any significant credit risk on these funds.
Concentration of Suppliers
The Company is dependent on a third‑party manufacturer to supply certain products for research and development activities in its programs. In particular, the Company relies and expects to continue to rely on a sole manufacturer to supply it with specific vectors related to the Company’s research and development programs.
Segment Information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources and assess performance. The Company and the Company’s chief operating decision maker, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, views the Company’s operations and manages its business as a single operating segment, which is the business of developing and commercializing gene therapies.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014‑09, Revenue From Contracts With Customers. ASU 2014‑09 amends Accounting Standards Codification ASC 605, Revenue Recognition, by outlining a single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers. ASU 2014‑09 will be effective for the Company for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company is evaluating the impact that this ASU may have on its financial statements, if any.
In August 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014‑15, which requires management to assess an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern every reporting period, and provide certain disclosures if management has substantial doubt about the entity’s ability to operate as a going concern, or an express statement if not, by incorporating and expanding upon certain principles that are currently in U.S. auditing standards. This guidance is effective for the annual period ending after December 15, 2016, and for annual periods and interim periods thereafter. The adoption of this accounting standard may affect our financial statement disclosures in future periods.
In November 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes, which simplifies the classification of deferred tax assets and liabilities. The new standard requires that all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any related valuation allowance, be classified as noncurrent on the balance sheet. The standard is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016 and allows for early adoption using a full retrospective method or a prospective method. The Company adopted ASU 2015-17 as of December 31, 2015, which resulted in the netting of deferred tax assets and liabilities as non-current assets on the consolidated balance sheet. The adoption of the standard did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements as the Company maintained a full valuation allowance at December 31, 2015.
3. Fair Value Measurements
All Convertible Preferred Stock converted at the time of the IPO, therefore there were no liabilities outstanding as of December 31, 2015. Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2014 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quoted Prices |
|
Significant |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
in Active |
|
Other |
|
Significant |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Markets for |
|
Observable |
|
Unobservable |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identical Assets |
|
Inputs |
|
Inputs |
|
|||
|
Liabilities |
|
Total |
|
(Level 1) |
|
(Level 2) |
|
(Level 3) |
|
||||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||||||||
|
Convertible PS tranche liability |
|
$ |
6,305 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
6,305 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
6,305 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
6,305 |
|
F-13
The Company estimates the fair value of its Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Series A Preferred Stock”) tranche liability at the time of issuance and subsequently remeasures it using a probability‑weighted present value model that considers the probability of closing a tranche (67%), the estimated future value of Series A Preferred Stock at closing ($1.51), and the investment required ($20.0 million) at closing. Future values are converted to present value using a discount rate (16.2%) appropriate for probability‑adjusted cash flows. These estimates are based, in part, on subjective assumptions. Changes to these assumptions as well as the Company’s stock value on the reporting date can have a significant impact on the fair value of the Series A Preferred Stock tranche liability.
The following table provides a reconciliation of all assets and liabilities measured at fair value using Level 3 significant unobservable inputs (in thousands):
|
|
|
Preferred Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
Tranche Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
6,305 |
|
|
Changes in fair value |
|
|
9,750 |
|
|
Reclassification to Series A Preferred Stock |
|
|
(16,055) |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
— |
|
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2015 are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quoted Prices |
|
Significant |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
in Active |
|
Other |
|
Significant |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Markets for |
|
Observable |
|
Unobservable |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Identical Assets |
|
Inputs |
|
Inputs |
|
|||
|
Assets |
|
Total |
|
(Level 1) |
|
(Level 2) |
|
(Level 3) |
|
||||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||||||||
|
Money market funds included in cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
$ |
29,601 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Marketable securities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U.S. Treasury notes |
|
|
157,981 |
|
|
157,981 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
U.S. Government agency securities |
|
|
35,055 |
|
|
— |
|
|
35,055 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
222,637 |
|
$ |
187,582 |
|
$ |
35,055 |
|
$ |
— |
|
The Company measures the fair value of money market funds and U.S. Treasuries based on quoted prices in active markets for identical securities. The Level 2 marketable securities include U.S. government agency securities that are valued either based on recent trades of securities in inactive markets or based on quoted market prices of similar instruments and other significant inputs derived from or corroborated by observable market data. The Company did not hold any marketable securities at December 31, 2014.
F-14
4. Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expense and other current assets consist of the following:
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Prepaid insurance |
|
$ |
424 |
|
$ |
18 |
|
|
Prepaid research and development contracts |
|
|
340 |
|
|
899 |
|
|
Accrued interest receivable |
|
|
411 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
|
382 |
|
|
406 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,557 |
|
$ |
1,323 |
|
5. Property and Equipment, net
Property and equipment, net consists of the following:
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Laboratory equipment |
|
$ |
2,183 |
|
$ |
1,223 |
|
|
Furniture and office equipment |
|
|
499 |
|
|
441 |
|
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
|
1,336 |
|
|
1,324 |
|
|
|
|
|
4,018 |
|
|
2,988 |
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(784) |
|
|
(184) |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
$ |
3,234 |
|
$ |
2,804 |
|
The Company recorded $600,000 and $184,000 in depreciation expense during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company did not have depreciation expense for the period from June 19, 2013 (Inception) to December 31, 2013.
6. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Patent costs |
|
$ |
235 |
|
$ |
274 |
|
|
Research and development costs |
|
|
1,329 |
|
|
125 |
|
|
Professional services |
|
|
350 |
|
|
81 |
|
|
Employee compensation costs |
|
|
1,338 |
|
|
85 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
178 |
|
|
77 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
3,430 |
|
$ |
642 |
|
7. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases
During March 2014, the Company entered into an agreement to lease its facility under a non‑cancelable operating lease that expires December 15, 2019. The lease includes two renewal options, each for five year terms and at fair market value upon exercise. The lease contains escalating rent clauses which require higher rent payments in future years. The Company expenses rent on a straight‑line basis over the term of the lease, including any rent‑free periods.
The Company received a leasehold improvement incentive from the landlord totaling $1,250,000. The Company recorded these incentives as a component of deferred rent and will amortize these incentives as a reduction of rent expense over the life of the lease. These leasehold improvements have been recorded as fixed assets.
F-15
Rent expense of approximately $ 910,000, $686,000, and $48,000 was incurred during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and the period ended December 31, 2013, respectively.
Future annual minimum lease payments at December 31, 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Total Minimum |
|
|
|
|
|
Lease Payments |
|
|
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
1,170 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
1,192 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
1,214 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
1,184 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
4,760 |
|
In January 2016, the Company executed an amendment to extend the lease to December 2024 and an agreement to lease an additional facility for approximately 26,000 square feet in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The additional facility will include laboratory and office space, and is projected to be ready for occupancy in early 2017. The table above excludes estimated payments of approximately $25.0 million, related to the amendment extending the 75 Sidney Street lease to December 2024 and the new lease for approximately 26,000 square feet in Cambridge, Massachusetts to December 2024.
Significant Agreements
Genzyme Collaboration Agreement
Summary of Agreement
In February 2015, the Company entered into an agreement with Genzyme (“Collaboration Agreement”), which included a non‑refundable upfront payment of $65.0 million. In addition, contemporaneous with entering into the Collaboration Agreement, Genzyme entered into a Series B Stock Purchase Agreement, under which Genzyme purchased 10,000,000 shares of Series B Preferred Stock for $30.0 million. The fair value of the Series B Preferred Stock at the time of issuance was approximately $25.0 million. The $5.0 million premium over the fair value is accounted for as additional consideration under the Collaboration Agreement.
Under the Collaboration Agreement, the Company granted Genzyme an exclusive option to license, develop and commercialize (i) ex‑U.S. rights to the following programs, which are referred to as Split Territory Programs; VY‑AADC01 (“Parkinson’s Program”), VY‑FXN01 (“Friedreich’s Ataxia Program”), a future program to be designated by Genzyme (“Future Program”) and VY‑HTT01 (“Huntington’s Program”) with an incremental option to co‑commercialize VY‑HTT01 in the United States and (ii) worldwide rights to VY‑SMN101 (“Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program”). Genzyme’s option for the Split Territory Programs and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program is triggered following the completion of the first proof‑of‑principle human clinical study (“POP Study”), on a program by program basis.
Prior to any option exercise by Genzyme, the Company will collaborate with Genzyme in the development of products under each Split Territory Program and VY‑SMN101 pursuant to a written development plan and under the guidance of an Alliance Joint Steering Committee (“AJSC”), comprised of an equal number of employees from the Company and Genzyme.
The Company is required to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop products under each Split Territory Program and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program through the completion of the applicable POP Study. During the development of these joint programs, the activities are guided by a Development Advisory Committee (“DAC”). The DAC may elect to utilize certain Genzyme technology relating to the VY‑AADC01 Program, the VY‑HTT01 Program or generally with the manufacture of Split Territory Program products.
The Company is solely responsible for all costs incurred in connection with the development of the Split Territory Programs and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program products prior to the exercise of an option by Genzyme
F-16
with the exception of the following: (i) at the Company’s request and upon mutual agreement, Genzyme will provide “in‑kind” services valued at up to $5.0 million and (ii) Genzyme shall be responsible for the costs and expenses of activities under the Huntington’s Program development plan to the extent such activities are covered by financial support Genzyme is entitled to receive from a patient advocacy group, collectively Genzyme “in‑kind” and other funding.
Other than the Parkinson’s Program (for which a POP Study has already been commenced), if the Company does not initiate a POP Study for a given Split Territory Program by December 31, 2026 (or for the Future Program by the tenth anniversary of the date the Future Program is nominated by Genzyme), and Genzyme has not terminated the Collaboration Agreement with respect to the collaboration program, then Genzyme shall be entitled, as its sole and exclusive remedy, to a credit of $10.0 million for each such program against other milestone or royalty payments payable by Genzyme under the Collaboration Agreement. However, if the POP Study is not initiated due to a regulatory delay or a force majeure event, such time period shall be extended for so long as such delay continues.
With the exception of the Parkinson’s Program, Genzyme is required to pay an option exercise payment of $20.0 million or $30.0 million for each Split Territory Program, as well as the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program.
Upon Genzyme’s exercise of its option to license a given product in a Split Territory Program (“Split Territory Licensed Product”), the Company will have sole responsibility for the development of such Split Territory Licensed Product in the United States and Genzyme shall have sole responsibility for development of such Split Territory Licensed Product in the rest of the world. The Company and Genzyme will have shared responsibility for execution of ongoing development of such Split Territory Licensed Product that is not specific to either territory, including costs associated therewith. The Company is responsible for all commercialization activities relating to Split Territory Licensed Products in the United States, including all of the associated costs. Genzyme is responsible for all commercialization activities relating to the Split Territory Licensed Products in the rest of the world, including all of the associated costs. If Genzyme exercised its co‑commercialization rights, Genzyme will be the lead party responsible for all commercialization activities related to Huntington’s Licensed Product in the United States.
Upon exercise of the option, Genzyme shall have the sole right to develop the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Product worldwide. Genzyme shall be responsible for all of the development costs that occur after the option exercise date for the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program. Genzyme is also responsible for commercialization activities relating to the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Product worldwide.
Genzyme is required to pay the Company for specified regulatory and commercial milestones, if achieved, up to $645 million across all programs. The regulatory approval milestones are payable upon either regulatory approval in the United States or regulatory and reimbursement approval in the European Union and range from $40.0 million to $50.0 million per milestone, with an aggregate total of $265 million. The commercial milestones are payable upon achievement of specified annual net sales in each program and range from $50.0 million to $100 million per milestone, with an aggregate total of $380 million.
In addition, to the extent any Split Territory Licensed Products or the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Licensed Product are commercialized, the Company is entitled to tiered royalty payments ranging from the mid‑single digits to mid‑teens based on a percentage of net sales by Genzyme. Genzyme is entitled to receive tiered royalty payments related to sales of Split Territory Licensed Product ranging from the low‑single digits to mid‑single digits based on a percentage of net sales by the Company depending on whether the Company uses Genzyme technology in the Split Territory Licensed Product. If Genzyme elects to co‑commercialize VY‑HTT01 in the United States, the Company and Genzyme will share in any profits or losses from VY‑HTT01 product sales.
The Collaboration Agreement will continue in effect until the later of (i) the expiration of the last to expire of the option rights and (ii) the expiration of all payment obligations unless sooner terminated by the Company or Genzyme. The Company and Genzyme have customary termination rights including the right to terminate for an uncured material breach of the agreement committed by the other party and Genzyme has the right to terminate for convenience.
Accounting Analysis
The Collaboration Agreement includes the following deliverables: (i) research and development services for each of the Split Territory License Programs and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program, (ii) participation in the AJSC, (iii) participation in the DAC and (iv) the option to obtain a development and commercial license in the Parkinson’s
F-17
Program and related deliverables. The Company has determined that the option to obtain a development and commercial license in the Parkinson’s program is not a substantive option for accounting purposes, primarily because there is no additional option exercise payment payable by Genzyme at the time the option is exercised. Therefore, the option to obtain a license and other obligations of the Company that are contingent upon exercise of the option are considered deliverables at the inception of the arrangement. The options in the other Split Territory Programs and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program are considered substantive as there is substantial option exercise payments payable by Genzyme upon exercise. In addition, as a result of the uncertainties related to the discovery, research, development and commercialization activities, the Company is at risk with regard to whether Genzyme will exercise the options. Moreover, the substantive options are not priced at a significant incremental discount. Accordingly, the substantive options are not considered deliverables at the inception of the arrangement and the associated option exercise payments are not included in allocable arrangement consideration. The Company has also determined that any obligations which are contingent upon the exercise of a substantive option are not considered deliverables at the outset of the arrangement, as these deliverables are contingent upon the exercise of the options. In addition, any option exercise payments associated with the substantive options are not included in the allocable arrangement consideration.
The Company has concluded that each of the deliverables identified at the inception of the arrangement has standalone value from the other undelivered elements. Additionally, the Collaboration Agreement does not include return rights related to the initial collaboration term. Accordingly, each deliverable qualifies as a separate unit of accounting.
The Company has identified $79.3 million of allocable arrangement consideration consisting of the $65 million upfront fee, the $5.0 million premium paid in excess of fair value of the Series B Preferred Stock and $9.3 million of Genzyme “in‑kind” and other funding.
The Company has allocated the allocable arrangement consideration based on the relative selling price of each unit of accounting. For all units of accounting, the Company determined the selling price using the best estimate of selling price (“BESP”). The Company determined the BESP for the service related deliverable for the research and development activities based on internal estimates of the costs to perform the services, including expected internal expenses and expenses with third parties for services and supplies, marked up to include a reasonable profit margin and adjusted for the scope of the potential license. Significant inputs used to determine the total expense of the research and development activities include, the length of time required and the number and costs of various studies that will be performed to complete the POP Study. The BESP for the AJSC and DAC have been estimated based on the costs incurred to participate in the committees, marked up to include a reasonable profit margin. The BESP for the license option was determined based on the estimated value of the license and related deliverables adjusted for the estimated probability that the option would be exercised by Genzyme.
F-18
Based on the relative selling price allocation, the allocable arrangement consideration was allocated as follows:
|
Unit of Accounting |
|
Amount |
|
|
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
Research and Development Services for: |
|
|
|
|
|
Huntington’s Program |
|
$ |
15,662 |
|
|
Parkinson’s Program |
|
|
6,648 |
|
|
Friedreich’s Ataxia Program |
|
|
16,315 |
|
|
Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program |
|
|
32,050 |
|
|
Future Program |
|
|
2,464 |
|
|
Committee Obligations: |
|
|
|
|
|
AJSC |
|
|
147 |
|
|
DAC |
|
|
227 |
|
|
License Option and related deliverables |
|
|
5,743 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
79,256 |
|
The Company recognizes the amounts associated with research and development services on a straight line basis over the period of service as there is no discernable pattern or objective measure of performance for the services. Similarly, the Company recognizes the amount associated with the committee obligations on a straight line basis over the period of service consistent with the expected pattern of performance. The amounts allocated to the license option will be deferred until the option is exercised. The revenue recognition upon option exercise will be determined based on whether the license has standalone value from the remaining deliverables at the time of exercise.
The Company has evaluated all of the milestones that may be received in connection with the Split Territory Licensed Product and the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Program Licensed Product. In evaluating if a milestone is substantive, the Company assesses whether: (i) the consideration is commensurate with either the Company’s performance to achieve the milestone or the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting from the Company performance to achieve the milestone, (ii) the consideration relates solely to past performance and (iii) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. All regulatory milestones are considered substantive on the basis of the contingent nature of the milestone, specifically reviewing factors such as the scientific, clinical, regulatory, and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the milestone as well as the level of effort and investment required. Accordingly, such amounts will be recognized as revenue in full in the period in which the associated milestone is achieved, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met. All commercial milestones will be accounted for in the same manner as royalties and recorded as revenue upon achievement of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company recognized $ 17,334,000 of revenue associated with its collaboration with Genzyme related to research and development services performed during the period. As of December 31, 2015, there is $ 54,982,000 of deferred revenue related to the Collaboration Agreement, which is classified as either current or noncurrent in the accompanying balance sheet based on the period the services are expected to be delivered.
Costs incurred relating to the programs that Genzyme has the option to license under the Collaboration Agreement consist of internal and external research and development costs, which primarily include: salaries and benefits, lab supplies and preclinical research studies. The Company does not separately track or segregate the amount of costs incurred under the Collaboration Agreement. All of these costs are included in research and development expenses in the Company’s statement of operations during the year ended December 31, 2015. The Company estimates that the majority of research and development expense during the period relate to programs for which Genzyme has an option right.
University of Massachusetts (“UMass”) and MassBiologics Collaboration
In January 2014, UMass and the Company entered into a Collaboration Agreement wherein the Company granted UMass 23,529 shares of common stock, valued at $12,000, which was recorded as research and development expense. This was the only payment made under the Collaboration Agreement until it was amended by the Collaboration Agreement entered into with UMass and MassBiologics in October 2014.
F-19
On October 20, 2014, the Company entered into a Collaboration Agreement with UMass and MassBiologics (of the UMass Medical School).
Under the agreement, the Company shall (i) fund certain projects that will be conducted by UMass or MassBiologics, (ii) fund certain educational programs of UMass, including post‑doctoral research at the Company’s laboratories beginning in 2015, and (iii) collaborate with MassBiologics to establish scalable processes for manufacturing recombinant adeno‑associated viral vector products using current good manufacturing practices.
In November 2014, the parties agreed to the first project under this agreement whereby the Company will fund approximately $2,861,000 over a sixteen month period for certain research and development services performed by MassBiologics. The project commenced in January 2015. If the agreement is terminated for any reason, the Company is obligated to fund the remaining balance of the total price of all work completed and any other out of pocket costs incurred by MassBiologics on behalf of the Company. As of December 31, 2014 and 2015, the Company had provided cumulative funding of approximately $376,000 and $1,867,000, respectively, which exceeded costs incurred by $376,000 and $0, respectively. The amount funded in excess of costs incurred is recorded in prepaid expenses as of the balance sheet at December 31, 2014 and recorded in accrued expenses for the amounts due at December 31, 2015. Research and development costs incurred by MassBiologics under the project agreement will be expensed by the Company as incurred.
Other Agreements
During 2015 and 2014, the Company entered into various agreements with contract research organizations and institutions to license intellectual property. In consideration for the licensed rights the Company generally made upfront payments, which were recorded as research and development expense as the acquired technologies were considered in‑process research and development. During the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company paid $75,000 and $830,000, respectively, in up‑front license fees. The license agreements also obligate the Company to make additional payments that are contingent upon specific clinical trial and regulatory approval milestones being achieved as well as royalties on future product sales. The agreements to license intellectual property include potential milestone payments that are dependent upon the development of products licensed under the agreements and contingent upon the achievement of clinical trial or regulatory approval milestones. The maximum aggregate potential milestone payments payable by the Company total approximately $12.0 million. Additionally, under the terms of one agreement, the Company has options to license intellectual property to be used in the development of therapies for four additional disease indications. If the Company exercises all of the options under the agreement, it would be obligated to pay aggregate up‑front fees of up to approximately $1.5 million and milestone payments that are contingent upon clinical trial results and regulatory approval of $5.0 million per disease indication, or up to $20.0 million in total. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, there have been no milestones achieved. The Company can generally terminate the license agreements upon 30‑90 days prior written notice.
Additionally, certain license agreements require the Company to reimburse the licensor for certain past and ongoing patent related expenses. During the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company incurred $295,000 and $872,000 of expense, respectively, related to these reimbursable patent costs which are recorded as general and administrative expense.
Litigation
The Company is not a party to any litigation and does not have contingency reserves established for any litigation liabilities as of December 31, 2015 or December 31, 2014.
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock
In November 2015, upon the closing of the Company’s IPO, all issued and outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock was automatically converted into 17,647,054 shares of common stock, see Note 2.
The Company has newly authorized preferred stock amounting to 5,000,000 and 0 shares as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The newly authorized preferred stock was classified under stockholders’ equity (deficit) at December 31, 2015.
F-20
The Company’s redeemable convertible preferred stock (“Preferred Stock”) has been classified as temporary equity on the accompanying balance sheets instead of in stockholders’ deficit in accordance with authoritative guidance for the classification and measurement of redeemable securities as the redeemable convertible preferred stock is redeemable at the option of the holder after the redemption date, February 2021.
Series A Preferred Stock
45,000,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock were issued during 2014 and 2015.These shares were issued at various closings in 2014 and 2015 for $1.00 per share. The shares were issued in exchange for cash proceeds of $42,039,000, net of issuance costs of $32,000, and the exchange of outstanding redeemable Convertible Notes, including accrued interest, of approximately $2,929,000.
Tranche Rights Issued with Series A Preferred Stock
Included in the terms of the January 2014 Series A Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement were certain rights (“Tranche Rights”) granted to the investors of Series A Preferred Stock purchased in January 2014, including the holders of the redeemable Convertible Notes who exchanged the redeemable Convertible Notes. The Tranche Rights obligated the investors in Series A Preferred Stock to purchase and the Company to sell an additional 18,500,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock at $1.00 per share contingent upon successful near term in‑licensing and progress on initial experiments and research and development planning (“Tranche Right I”). In addition, the investors are obligated to purchase and the Company is obligated to sell an additional 20,000,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock upon the development of project engine and achievement of certain clinical milestones (“Tranche Right II”). In addition, the Tranche Rights allowed the investors the ability to purchase the additional shares at their option at any time. The Tranche Rights were transferrable by the investors, subject to approval by the Board.
The Company has concluded the Tranche Rights meet the definition of a freestanding financial instrument, as the Tranche Rights are legally detachable and separately exercisable from the Series A Preferred Stock. Therefore, the Company has allocated the proceeds between the Tranche Rights and the Series A Preferred Stock. As the Series A Preferred Stock is redeemable at the holder’s option, the Tranche Rights are classified as an asset or liability and are initially recorded at fair value. The Tranche Rights are measured at fair value at each reporting period. Since the Tranche Rights are subject to fair value accounting, the Company allocated the proceeds to the Tranche Rights based on the fair value at the date of issuance with the remaining proceeds being allocated to the Series A Preferred Stock. The estimated fair value of the Tranche Rights was determined using a probability‑weighted present value model that considers the probability of closing a tranche, the estimated future value of Series A Preferred Stock each closing, and the investment required at each closing. Future values are converted to present value using a discount rate appropriate for probability‑adjusted cash flows.
The following table summarizes the initial value of the Tranche Rights included in the Series A Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement (in thousands):
|
|
|
Fair Value of |
|
|
|
|
|
Tranche Right |
|
|
|
|
|
Asset (Liability) |
|
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||
|
Tranche Right I |
|
$ |
1,495 |
|
|
Tranche Right II |
|
|
(4,095) |
|
|
Total value of Tranche Rights |
|
$ |
(2,600) |
|
Tranche Right I was initially recorded as an asset of $1,495,000 as the purchase price of the additional shares was greater than the estimated value of the Series A Preferred Stock at the expected settlement date. The Company issued 18,500,000 additional shares under Tranche Right I, in three separate closings during the year ended December 31, 2014 with total proceeds of $18,491,000, net of issuance costs. Prior to each closing, any change in the value of Tranche Right I was recorded as other financing expense. The fair value of the portion of the Tranche Right I settled at each closing was reclassified to Series A Preferred Stock. The Company recognized income of $261,000 related to the mark to market of Tranche Right I during the year ended December 31, 2014, which is included in other financing expense.
F-21
Tranche Right II was initially recorded as a liability of $4,095,000 as the purchase price of the additional shares was less than the estimated price of the Series A Preferred Stock at the expected settlement date. The Company recognized expense of $2,210,000 related to the mark to market of Tranche Right II during the year ended December 31, 2014, which is included in other financing expense.
In February 2015, Tranche Right II was settled when the Company closed the final issuance of Series A Preferred Stock. The Company recognized expense of $9,750,000 related to the mark to market of Tranche Right II during the period ended December 31, 2015, which is included in other financing expense. The fair value of the Tranche Right II settled at closing was reclassified to Series A Preferred Stock. The initial carrying amount of the Series A Preferred Stock issued upon the closing of Tranche Right II amounted to approximately $36,054,000 which exceeds the redemption value, therefore the carrying value is not being subsequently adjusted. However, the Company has reflected accrued dividends of approximately $1,245,000 related to this issuance in the net loss attributable to common shareholders for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Series B Preferred Stock
30,000,001 shares of Series B Preferred Stock were issued during 2015. These shares were issued for $3.00 per share. This issuance resulted in cash proceeds of $89,780,000, net of issuance costs of $220,000. Additionally, a discount of $5,000,000 was recorded against the proceeds as the amount paid by Genzyme was in excess of fair value of the Series B Preferred Stock at issuance.
Preferred Stock
The rights, preferences, and privileges of the Preferred Stock are listed below:
Conversion
Shares of Preferred Stock are convertible at any time at the option of the holder into such number of shares as is determined by dividing the original issuance price by the conversion price in effect at the time. Immediately prior to the IPO, the conversion price was $4.25 for Series A Preferred Stock and $12.75 for Series B Preferred Stock, subject to adjustments to reflect the issuance of Common Stock, options, warrants, or other rights to subscribe for or to purchase Common Stock for a consideration per share, less than the conversion price then in effect and subsequent stock dividends and stock splits. In addition any reorganization, recapitalization, reclassification, consolidation or merger in which common stock is exchanged for securities, cash or other property.
All outstanding shares of Preferred Stock are automatically converted upon the completion of either an IPO resulting in gross proceeds to the Company of at least $50.0 million or the vote or written consent of 67% of the then outstanding shares of preferred stock.
Dividends
Holders of Preferred Stock are entitled to receive, before any cash is paid out or set aside for any Common Stock, cash dividends at a rate of 8% of the original purchase price per share annually (the “Accruing Dividends”). The dividends accrue cumulatively on a daily basis and are payable only when, and if, declared by the Board of Directors or upon liquidation or redemption.
In addition, the holders of Preferred Stock are entitled to additional dividends based on dividends declared to common stockholders, thereby giving the preferred stockholders the right to participate in undistributed earnings of the Company above the stated per share dividend rate. The preferred stockholders do not have a contractual obligation to share in the losses of the Company.
Redemption
The Preferred Stock is redeemable at the option of the holder after the redemption date of February 2021. The redemption value of the Preferred Stock is equal to $3.00 per share for Series B Preferred Stock and $1.00 per share for Series A Preferred Stock plus any accrued but unpaid dividends. Accordingly, the Preferred Stock is being accreted to
F-22
redemption value through its redemption date, including accruals for cumulative dividend rights. If the initial carrying value exceeds the redemption value the carrying value is not adjusted.
Liquidation Preference
Holders of Series B Preferred Stock and Series A Preferred Stock have preference to the assets of the Company in the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding‑up of the Company, equal to $3.00 per share for Series B Preferred Stock and $1.00 per share for Series A Preferred Stock, plus any accrued but unpaid dividends, whether or not declared, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon, on a pari passu basis. After the payment of the preference amounts to the holders of Series B Preferred Stock and Series A Preferred Stock, the remaining assets of the Company are to be distributed among the holders of Series A Preferred Stock and holders of Common Stock on a pro rata basis. However, if the aggregate amount which the holders of Series A Preferred Stock would be entitled to receive exceeds $2.50 per share (subject to appropriate adjustment in the event of any stock dividend, stock split, combination, reclassification or other similar event) (the “Maximum Participant Amount”), each holder of Series A Preferred Stock will receive the greater of the Maximum Participant Amount or the amount such holder would have received if all shares of Series A Preferred Stock had been converted into Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation.
Voting Rights
Holders of Series A Preferred Stock and Series B Preferred Stock are entitled to vote as a single class with the holders of Common Stock on all matters submitted for vote to the Stockholders of the Company. The holders of Preferred Stock are entitled to one vote for each equivalent common share on an as‑converted basis. In addition, the holders of Series A Preferred Stock are entitled to elect two (2) directors. The remaining directors shall be elected by the holders of Common Stock voting together with the holders of the Series B Preferred Stock as one class on an as‑converted basis.
The holders of Series A Preferred Stock and Series B Preferred Stock have certain protective rights as defined. These protective rights require the Required Vote before action can be taken to (i) increase or decrease the number of shares of Series A Preferred Stock or Series B Preferred Stock that the Company has authority to issue, (ii) change the par value of the Series A Preferred Stock or Series B Preferred Stock, (iii) amend the Certificate of Incorporation in any way that adversely affects the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock or Series B Preferred Stock.
9. Common Stock
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had authorized 120,000,000 and 65,000,000 shares of Common Stock, respectively at $0.001 par value per share.
General
The voting, dividend and liquidation rights of the holders of the Common Stock are subject to and qualified by the rights, powers and preferences of the holders of Preferred Stock. The Common Stock has the following characteristics:
Voting
The holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share of Common Stock held at all meetings of stockholders and written actions in lieu of meetings.
Dividends
The holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to receive dividends, if and when declared by the Board of Directors. Cash dividends may not be declared or paid to holders of shares of Common Stock until all accrued unpaid dividends on Series A Preferred Stock and Series B Preferred Stock have been paid in accordance with their terms. No dividends have been declared or paid by the Company since its inception.
F-23
Liquidation
After payment to of their respective liquidation preferences to the holders of shares of Series A Preferred Stock and Series B Preferred Stock, the holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to share ratably in the Company’s remaining assets available for distribution to its stockholders in the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company or upon occurrence of a deemed liquidation event.
Shares Reserved For Future Issuance
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
|
Shares reserved for Series A Preferred Stock outstanding |
|
— |
|
5,882,352 |
|
|
Shares reserved for future issuances of Series A Preferred Stock |
|
— |
|
4,705,883 |
|
|
Shares reserved for vesting of restricted stock awards under the Founder Agreements |
|
853,680 |
|
1,068,383 |
|
|
Shares reserved for vesting of restricted stock awards under the 2014 Option and Stock Plan |
|
964,581 |
|
1,510,434 |
|
|
Shares reserved for exercise of stock options |
|
1,022,617 |
|
291,052 |
|
|
Shares reserved for issuances under the 2015 Stock Option Plan |
|
1,620,479 |
|
— |
|
|
Shares reserved for employee stock purchase plan |
|
262,362 |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
4,723,719 |
|
13,458,104 |
|
10. Stock‑Based Compensation
2015 Stock Option Plan
In October 2015, the Company’s board of directors and stockholders approved the 2015 Stock Option and Incentive Plan, or 2015 Stock Option Plan, which became effective upon the completion of the IPO. The 2015 Stock Option Plan provides the Company with the flexibility to use various equity-based incentive and other awards as compensation tools to motivate our workforce. These tools include stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, unrestricted stock, performance share awards and cash-based awards. The 2015 Stock Option Plan replaced the 2014 Plan. Any options or awards outstanding under the 2014 Stock Option Plan remained outstanding and effective. The number of shares initially reserved for issuance under the 2015 Stock Option Plan is the sum of (i) 1,311,812 shares of common stock and (ii) the number of shares under the 2014 Plan that are not needed to fulfill the Company’s obligations for awards issued under the 2014 Plan as a result of forfeiture, expiration, cancellation, termination or net issuances of awards thereunder. The number of shares of common stock that may be issued under the 2015 Stock Option Plan is also subject to increase on the first day of each fiscal year by up to 4% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock on the immediately preceding December 31.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company issued 960,275 stock options to employees and directors and 69,793 stock options to non‑employees. As of December 31, 2015, there were 1,620,479 shares available for future issuance under the 2015 Plan.
2014 Stock Option and Grant Plan
In January 2014, the Company adopted the Voyager Therapeutics, Inc. 2014 Stock Option and Grant Plan (the “2014 Plan”), under which it may grant incentive stock options, non‑qualified stock options, restricted stock awards, unrestricted stock awards, or restricted stock units to purchase up to 823,529 shares of Common Stock to employees, officers, directors and consultants of the Company.
In April 2014, the Company amended the Plan to allow for the issuance of up to 1,411,764 shares of Common Stock. In August 2014, April 2015, August 2015 and October 2015 the Company further amended the Plan to allow for the issuance of up to 2,000,000, 2,047,058, 2,669,411 and 2,998,823 shares of Common Stock, respectively. During 2014 the Company issued only restricted stock awards under the Plan and during 2015 the Company only granted stock options.
The terms of stock awards agreements, including vesting requirements, are determined by the Board of Directors and are subject to the provisions of the 2014 Plan. Restricted Stock awards granted by the Company generally vest based on each grantee’s continued service with the Company during a specified period following grant. Awards
F-24
granted to employees generally vest over four years, with 25% vesting on the one year anniversary and 75% vesting ratably, on a monthly basis, over the remaining three years. Awards granted to non‑employee consultants generally vest monthly over a period of one to four years.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company granted a total of 1,597,988 shares of restricted stock to employees and 110,960 shares of restricted stock to non‑employee consultants at an original issuance price of $0.04 per share.
Founder Awards
In January 2014, the Company issued 1,188,233 shares of restricted stock to its Founders at an original issuance price of $0.0425 per share. Of the total restricted shares awarded to the Founders, 835,292 shares generally vest over one to four years, based on each Founder’s continued service to the Company in varying capacity as a Scientific Advisory Board member, consultant, director, officer or employee, as set forth in each grantee’s individual restricted stock purchase agreement. The remaining 352,941 of the shares issued will begin vesting upon the achievement of certain performance objectives as well as continued service to the Company, as set forth in the agreements.
These performance conditions are tied to certain milestone events specific to the Company’s corporate goals, including but not limited to preclinical and clinical development milestones related to the Company’s product candidates. Stock‑based compensation expense associated with these performance‑based awards will be recognized when the achievement of the performance condition is considered probable, using management’s best estimates. As of December 31, 2014 and 2015, management has concluded that achievement of such performance‑based milestones was not probable. Accordingly, no stock‑based compensation expense was recorded as of December 31, 2014 and 2015 related to these awards.
2015 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In October 2015, the Company’s board of directors and stockholders approved the 2015 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. A total of 262,362 shares of common stock were initially authorized for issuance under this plan. The 2015 Employee Stock Purchase Plan became effective upon the completion of the IPO.
Stock‑Based Compensation Expense
Total compensation cost recognized for all stock‑based compensation awards in the statements of operations and comprehensive loss is as follows:
|
Period from |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
(Inception) to |
|
|||||
|
December 31, |
December 31, |
|||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
|
Research and development |
|
$ |
3,218 |
|
$ |
297 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
809 |
|
|
128 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total stock-compensation expense |
|
$ |
4,027 |
|
$ |
425 |
|
$ |
— |
|
F-25
Restricted Stock
A summary of the status of and changes in unvested restricted stock as of December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013 was as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fair Value |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Per Share |
|
|
|
|
Unvested restricted common stock as of December 31, 2013 |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issued |
|
2,897,181 |
|
$ |
0.77 |
|
|
|
Vested |
|
(318,364) |
|
$ |
0.68 |
|
|
|
Repurchased |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
Unvested restricted common stock as of December 31, 2014 |
|
2,578,817 |
|
$ |
0.77 |
|
|
|
Issued |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vested |
|
(717,747) |
|
$ |
0.77 |
|
|
|
Repurchased |
|
(42,809) |
|
$ |
0.68 |
|
|
|
Unvested restricted common stock as of December 31, 2015 |
|
1,818,261 |
|
$ |
0.76 |
|
|
The expense related to awards granted to employees and non‑employees was $455,000 and $2,551,000, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2015.
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had unrecognized stock‑based compensation expense related to its unvested restricted stock awards of $32,047,000, which is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 2.35 years.
Stock Options
A summary of the status of, and changes in, stock options as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 was as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
Remaining |
|
Aggregate |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
Contractual |
|
Intrinsic |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise |
|
Life |
|
Value |
||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Price |
|
(in years) |
|
(in thousands) |
||
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Granted |
|
1,030,068 |
|
$ |
8.34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised |
|
(1,344) |
|
$ |
8.39 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cancelled or forfeited |
|
(6,107) |
|
$ |
7.27 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
|
1,022,617 |
|
$ |
8.35 |
|
9.5 |
|
$ |
13,887 |
|
Exercisable at December 31, 2015 |
|
94,762 |
|
$ |
7.51 |
|
9.2 |
|
$ |
1,363 |
|
Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2015 |
|
1,022,617 |
|
$ |
8.35 |
|
9.5 |
|
$ |
13,887 |
Using the Black‑Scholes option pricing model, the weighted average fair value of options granted to employees and directors during the year ended December 31, 2015 was $5.68. The expense related to awards granted to employees and directors was $720,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. There were no stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2014 or the period ended December 31, 2013.
F-26
The fair value of each option issued to employees and directors was estimated at the date of grant using the Black‑Scholes option pricing model with the following weighted‑average assumptions:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
1.6 |
% |
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
% |
|
Expected term (in years) |
|
6.0 |
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
78.6 |
% |
Using the Black‑Scholes option pricing model, the weighted average grant date fair value of options granted to non‑employees during the year ended December 31, 2015 was $7.95. Unvested options granted to non‑employees are revalued at each measurement period until they vest. The expense related to awards granted to non‑employees was $301,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. There were no stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2014.
The fair value of each option issued to non‑employees was estimated at each vesting and reporting date using the Black‑Scholes option pricing model. The reporting date fair value was determined using the following weighted‑average assumptions:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|
Risk-free interest rate |
|
2.0 |
% |
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
% |
|
Expected term (in years) |
|
10.0 |
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
84.0 |
% |
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had unrecognized stock‑based compensation expense related to its unvested stock options of $4,753,000 which is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 3.36 years.
11. 401(k) Savings Plan
The Company has a defined‑contribution savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code (the “401(k) Plan”). The 401(k) Plan covers all employees who meet defined minimum age and service requirements, and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pretax basis. As currently established, the Company is not required to make and has not made any contributions to the 401(k) Plan to date.
12. Income Taxes
A reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Period from |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
June 19, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Inception) to |
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||
|
Income tax computed at federal statutory tax rate |
|
34.0 |
% |
|
34.0 |
% |
|
34.0 |
% |
|
State taxes, net of federal benefit |
|
4.0 |
% |
|
5.5 |
% |
|
6.3 |
% |
|
General business credit carryovers |
|
3.2 |
% |
|
2.2 |
% |
|
2.4 |
% |
|
Non-deductible expenses |
|
(15.6) |
% |
|
(5.0) |
% |
|
(0.7) |
% |
|
Change in valuation allowance |
|
(25.6) |
% |
|
(36.7) |
% |
|
(42.0) |
% |
|
|
|
— |
% |
|
— |
% |
|
— |
% |
The Company has incurred net operating losses (NOLs) since June 2013. At December 31, 2015, the Company had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $32.1 million and $30.2 million, respectively, which expire
F-27
beginning in 2033. As of December 31, 2015, the Company also had federal and state research and development tax credit carryforwards of $1.4 million and $0.9 million, respectively, which expire beginning in 2028.
Under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, certain substantial changes in the Company’s ownership may result in a limitation on the amount of NOL carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards that may be utilized annually to offset future taxable income and taxes payable. The Company has not completed a formal analysis under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code and therefore, has not determined whether a limitation has occurred. The Company will complete a full analysis of our tax attribute carryforwards prior to any utilization.
The significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
||||
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
||
|
|
(in thousands) |
|||||
|
Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net operating loss carryforwards |
$ |
12,521 |
|
$ |
6,643 |
|
|
Tax credit carryforwards |
|
1,969 |
|
|
673 |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
516 |
|
|
626 |
|
|
Non-deductible expenses |
|
577 |
|
|
79 |
|
|
Intangibles |
|
376 |
|
|
327 |
|
|
Stock compensation |
|
115 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total deferred tax assets |
|
16,074 |
|
|
8,348 |
|
|
Less valuation allowance |
|
(15,207) |
|
|
(7,599) |
|
|
Net deferred tax assets |
|
867 |
|
|
749 |
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities—depreciation and amortization |
|
(867) |
|
|
(749) |
|
|
Net deferred taxes |
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax bases of the assets and liabilities using the enacted tax rates in effect in the years in which the differences are expected to reverse. A valuation allowance against deferred tax assets is recorded if, based on the weight of the available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In November 2015, the Financial Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2015-17, Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes. ASU 2015-17 simplifies the presentation of deferred income taxes by eliminating the requirement for entities to separate deferred tax assets and liabilities into current and non-current amounts in the balance sheet. Rather, it requires that deferred tax assets and liabilities are classified as non-current in the balance sheet. The Company adopted this standard prospectively for the year ended December 31, 2015 and prior periods were not retrospectively adjusted.
Management has evaluated the positive and negative evidence bearing upon the realizability of its deferred tax assets, which are principally comprised of NOL carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards. Management has determined that it is more likely than not that the Company will not recognize the benefits of its federal and state deferred tax assets, and as a result, a valuation allowance of $15.2 million and $7.6 million has been established at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The change in valuation allowance was $7.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, principally due to additional federal and state operating losses.
The Company has not yet conducted a study of its research and development credit carryforwards. This study may result in an adjustment to the Company’s research and development credit carryforwards; however, until a study is completed and any adjustment is known, no amounts are being presented as an uncertain tax position. A full valuation allowance has been provided against the Company’s research and development credits, and if an adjustment is required, this adjustment would be offset by an adjustment to the valuation allowance. Thus, there would be no impact to the balance sheets or statements of operations if an adjustment were required.
The Company applies ASC 740 related to accounting for uncertainty in income taxes. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits. Interest and penalty charges, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits would be classified as income tax expense in the accompanying statements of operations. Since the
F-28
Company has incurred operating losses since inception, it is generally subject to examination by the U.S. federal, state, and local income tax authorities for all tax years in which a loss carryforward is available. The Company did not have any international operations as of December 31, 2015. There are currently no federal or state audits in process.
13. Related‑Party Transactions
Since inception, the Company received consulting and management services from one of its investors. In January 2014, the Company issued 470,589 shares of common stock as partial compensation for these services. The fair value of the shares was approximately $238,000.
The total amount of consulting and management services provided by this investor was approximately $122,000, $1,280,000, and $2,379,000 during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and the period ended December 31, 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, the Company included approximately $7,000 in accounts payable related to service fees charged by this investor.
During the year ended December 31, 2015 the Company recognized $17,334,000 of revenue associated with its collaboration with Genzyme related to research and development services provided during this period. The company also recognized $2,316,000 of expense during the year ended December 31, 2015 related to in‑kind services provided by Genzyme associated with the collaboration arrangement.
14. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The following table contains quarterly financial information for 2015 and 2014. The Company believes that the following information reflects all normal recurring adjustments necessary for a fair statement of the information for the periods presented. The operating results for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of results for any future period.
|
|
2015 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
First |
|
Second |
|
Third |
|
Fourth |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Total |
|||||
|
|
(in thousands, except per share data) |
|||||||||||||
|
Collaboration revenue |
$ |
2,576 |
|
$ |
4,884 |
|
$ |
4,937 |
|
$ |
4,937 |
|
$ |
17,334 |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
7,404 |
|
|
8,851 |
|
|
8,956 |
|
|
12,377 |
|
|
37,588 |
|
Loss from operations |
|
(4,828) |
|
|
(3,967) |
|
|
(4,019) |
|
|
(7,440) |
|
|
(20,254) |
|
Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
|
(15,813) |
|
|
(6,746) |
|
|
(6,914) |
|
|
(8,817) |
|
|
(38,290) |
|
Net loss per share applicable to common stockholders – basic and diluted |
$ |
(15.81) |
|
$ |
(5.80) |
|
$ |
(5.25) |
|
$ |
(0.67) |
|
$ |
(9.14) |
|
|
2014 |
|||||||||||||
|
|
First |
|
Second |
|
Third |
|
Fourth |
|
|
|
||||
|
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Total |
|||||
|
|
(in thousands, except per share data) |
|||||||||||||
|
Collaboration revenue |
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
Total operating expenses |
|
2,985 |
|
|
3,230 |
|
|
3,656 |
|
|
4,496 |
|
|
14,367 |
|
Loss from operations |
|
(2,985) |
|
|
(3,230) |
|
|
(3,656) |
|
|
(4,496) |
|
|
(14,367) |
|
Net loss attributable to common shareholders |
|
(3,211) |
|
|
(4,864) |
|
|
(4,411) |
|
|
(5,197) |
|
|
(17,683) |
|
Net loss per share applicable to common stockholders – basic and diluted |
$ |
(6.93) |
|
$ |
(8.11) |
|
$ |
(6.45) |
|
$ |
(6.58) |
|
$ |
(27.83) |
F-29
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Form 10-K to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VOYAGER THERAPEUTICS, INC. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Steven Paul, M.D. |
SIGNATURES AND POWER OF ATTORNEY
We, the undersigned directors and officers of Voyager Therapeutics, Inc. (the "Company"), hereby severally constitute and appoint Steven Paul, M.D. and J. Jeffrey Goater, and each of them singly, our true and lawful attorneys, with full power to them, and to each of them singly, to sign for us and in our names in the capacities indicated below, any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file or cause to be filed the same, with all exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as each of us might or could do in person, and hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys, and each of them, or their substitute or substitutes, shall do or cause to be done by virtue of this Power of Attorney.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Name |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Steven Paul, M.D. |
|
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Steven Paul, M.D. |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Jeff Goater |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Jeff Goater |
|
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Mark Levin |
|
Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Mark Levin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Jim Geraghty |
|
Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Jim Geraghty |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Michael Higgins |
|
Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Michael Higgins |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Perry A. Karsen |
|
Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Perry A. Karsen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Steven Hyman, M.D. |
|
Director |
|
March 17, 2016 |
|
Steven Hyman, M.D. |
|
|
|
|
F-30
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference to: |
|||||||
|
Exhibit |
|
Description |
|
Form or |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing |
|
SEC File |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant. |
|
8-K |
|
3.1 |
|
11/16/2015 |
|
001-37625 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Amended and Restated By-Laws of the Registrant. |
|
8-K |
|
3.2 |
|
11/16/2015 |
|
001-37625 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
Specimen Common Stock Certificate of the Registrant. |
|
S-1 |
|
4.1 |
|
10/28/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
2014 Stock Option and Grant Plan and forms of award agreements thereunder |
|
S-1/A |
|
10.1 |
|
10/28/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
2015 Stock Option and Incentive Plan and forms of award agreements thereunder |
|
S-1/A |
|
10.2 |
|
10/28/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
Collaboration Agreement by and between the Registrant and Genzyme Corporation, dated February 11, 2015. |
|
S-1/A |
|
10.3 |
|
11/06/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
Exclusive License Agreement by and between the Registrant and the University of Massachusetts, dated January 30, 2014. |
|
S-1/A |
|
10.4 |
|
11/04/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
Lease Agreement by and between the Registrant and UP 45/75 Sidney Street, LLC, dated as of April 1, 2014. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.5 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
Offer Letter by and between the Registrant and Bernard Ravina, M.D., dated January 15, 2014. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.6 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
Offer Letter by and between the Registrant and Robert Pietrusko, Pharm. D., dated May 13, 2014. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.7 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.8 |
|
Offer Letter by and between the Registrant and Steven Paul, M.D., dated July 24, 2014. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.8 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
Form of Indemnification Agreement to be entered into between the Registrant and its directors. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.9 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.10 |
|
Form of Indemnification Agreement to be entered into between the Registrant and its executive officers. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.10 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.11 |
|
License Agreement, by and between the Registrant and ReGenX Biosciences, LLC, dated May 28, 2015. |
|
S-1/A |
|
10.11 |
|
11/04/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F-31
|
10.12 |
|
2015 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. |
|
S-1 |
|
10.12 |
|
10/30/2015 |
|
333-207367 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.1 |
|
Consent of Ernst & Young, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.1 |
|
Power of Attorney (see signature page of this Annual Report on Form 10-K) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.1 |
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 or 15d-14. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.2 |
|
Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14 or 15d-14. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.1+ |
|
Certification of Chief Executive Officer and Principal Chief Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(b) or 15d-14(b) and 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS |
|
XBRL Instance Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Link Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ The certification furnished in Exhibit 32.1 hereto is deemed to be furnished with this Annual Report on Form 10-K and will not be deemed to be “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, except to the extent that the Registrant specifically incorporates it by reference.
F-32