
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
(Mark One)
|
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended
OR
|
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO
Commission File Number

(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its Charter)
|
|
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer |
|
|
|
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of each class |
|
Trading Symbol(s) |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
|
☒ |
|
Accelerated Filer |
☐ |
|
|
Non-Accelerated Filer |
☐ |
|
Smaller Reporting Company |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Emerging Growth Company |
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes
As of June 30, 2019, the aggregate market value of the Registrant’s Class A common stock (based upon the closing stock price) held by non-affiliates was approximately $
As of February 20, 2020, there were
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement relating to its 2020 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
|
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART I. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 1. |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 1A. |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 1B. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 2. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 3. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 4. |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART II. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 5. |
|
|
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 6. |
|
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 7. |
|
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 7A. |
|
|
41 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 8. |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 9. |
|
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
|
88 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 9A. |
|
|
88 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 9B. |
|
|
90 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART III. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 10. |
|
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 11. |
|
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 12. |
|
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 13. |
|
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 14. |
|
|
91 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PART IV. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 15. |
|
|
92 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 16. |
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
96 |
|||
1
PJT Partners Inc. was formed in connection with certain merger and spin-off transactions whereby the financial and strategic advisory services, restructuring and reorganization advisory services and Park Hill Group businesses of The Blackstone Group Inc. (“Blackstone” or our “former Parent”) were combined with PJT Capital LP, a financial advisory firm founded by Paul J. Taubman in 2013 (together with its then affiliates, “PJT Capital”), and the combined business was distributed to Blackstone’s unitholders to create PJT Partners Inc., a stand-alone, independent publicly traded company. Throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we refer to this transaction as the “spin-off.” In October 2018, we acquired CamberView Partners Holdings, LLC (“CamberView” or “PJT Camberview”).
PJT Partners Inc. is a holding company and its only material asset is its controlling equity interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP, a holding partnership that holds the company’s operating subsidiaries, and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time as described herein in “Part II. Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Dividend Policy.” As the sole general partner of PJT Partners Holdings LP, PJT Partners Inc. operates and controls all of the business and affairs of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries.
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, unless the context requires otherwise, the words “PJT Partners Inc.” refers to PJT Partners Inc., and “PJT Partners,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to PJT Partners Inc., together with its consolidated subsidiaries, including PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries.
Forward-Looking Statements
Certain material presented herein contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Forward-looking statements include certain information concerning future results of operations, business strategies, acquisitions, financing plans, competitive position, potential growth opportunities, potential operating performance improvements, the effects of competition and the effects of future legislation or regulations. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as the words “believe,” “expect,” “opportunity,” “plan,” “intend,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential,” “continue,” “may,” “might,” “should,” “could” or the negative of these terms or similar expressions.
Forward-looking statements involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Actual results may differ materially from those expressed in such forward-looking statements. You should not put undue reliance on any forward-looking statements contained herein. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or review any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise.
The risk factors discussed in the “Risk Factors” section of this report, as such factors may be updated from time to time in our periodic filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), accessible on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov, could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed in forward-looking statements. There may be other risks and uncertainties that we are unable to predict at this time or that are not currently expected to have a material adverse effect on our business. Any such risks could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed in forward-looking statements.
Website Disclosure
We use our website (www.pjtpartners.com) as a channel of distribution of company information. The information we post may be deemed material. Accordingly, investors should monitor the website, in addition to following our press releases, SEC filings and public conference calls and webcasts. In addition, you may automatically receive e-mail alerts and other information about PJT Partners when you enroll your e-mail address by visiting the “Investor Relations” page of our website at ir.pjtpartners.com/investor-relations. Although we refer to our website in this report, the contents of our website are not included or incorporated by reference into this report. All references to our website in this report are intended to be inactive textual references only.
2
PART I.
|
ITEM 1. |
BUSINESS |
Overview
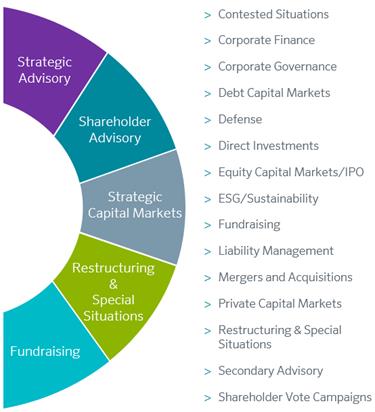
PJT Partners is a premier global advisory-focused investment bank. Our team of senior professionals delivers a wide array of strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and fundraising services to corporations, financial sponsors, institutional investors and governments around the world. We offer a unique portfolio of advisory services designed to help our clients achieve their strategic objectives. We also provide, through PJT Park Hill, private fund advisory and fundraising services for alternative investment managers, including private equity funds, real estate funds and hedge funds. PJT Partners began trading on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “PJT” on October 1, 2015.
We have world-class franchises in each of the areas in which we compete:
Strategic Advisory
Our team of leading professionals delivers innovative solutions to highly complex challenges across mergers and acquisitions (“M&A”), strategic advisory and capital markets advisory. Our strategic advisory business offers a broad range of financial advisory and transaction execution capability, including M&A, joint ventures, minority investments, asset swaps, divestitures, takeover defenses, corporate finance advisory, private placements and distressed sales. Through PJT Camberview, our industry leading shareholder advisory business, we provide investor-led advice to public company boards and management teams around the globe on shareholder engagement, strategic investor relations, activism and contested situations, sustainability and complex corporate governance matters.
Restructuring and Special Situations
Our Restructuring and Special Situations business is one of the world’s leading advisors in restructurings and recapitalizations, both in and out of court, around the globe. With expertise in highly complex capital structure challenges, we advise companies, creditors and financial sponsors on liability management and related capital raise
3
transactions including exchanges, recapitalizations, reorganizations, debt repurchases and distressed mergers and acquisitions.
PJT Park Hill
PJT Park Hill, our leading global alternative asset advisory and fundraising business, provides private fund advisory and fundraising services for a diverse range of investment strategies. Moreover, PJT Park Hill is the only group among its peers with top-tier dedicated private equity, hedge fund, real estate and secondary advisory groups. PJT Park Hill’s Secondary Advisory business is a leading advisor to global alternative asset managers and provides clients with a breadth of expertise in the secondary markets, including GP liquidity solutions, GP tender offers, GP recapitalizations, LP portfolio solutions, asset strip sales, single asset SPVs and other structured solutions.
Our Key Competitive Strengths
We intend to execute on our strategy by capitalizing on the following strengths of our organization:
|
|
• |
Young, Entrepreneurial Firm. PJT Partners combines three decades of experience and excellence with the energy and enthusiasm of a new firm. Our teams act as trusted advisors to a diverse group of clients around the world, providing clients with creative solutions addressing a range of complex strategic matters. The creativity and depth of our advice, and the integrity and judgment with which we deliver it, provide a strong foundation for our growing business. The quality of our advice is core to what we do. |
|
|
• |
Broad Based Advisory Capabilities. In addition to our leading strategic advisory, restructuring and special situations and asset advisory and fundraising businesses, we deliver a broad suite of advisory services across a growing number of industry verticals, products and geographies. We have recently partnered with Nasdaq Private Market to combine the capabilities of PJT Park Hill’s leading Secondary Advisory business with Nasdaq’s best-in-class technology platform to offer clients superior transaction execution. With the addition of PJT Camberview, our industry leading shareholder advisory business, we have further enhanced our ability to advise boards and management teams globally on shareholder engagement, strategic investor relations, activism and contested situations, sustainability and complex corporate governance matters. |
|
|
• |
One Dedicated Firm with Highly Complementary Businesses. Our firm benefits from having a number of leading and complementary businesses. Our differentiated and diverse portfolio of industry, product and geographical expertise enables us to serve our clients in a unique way. Our premier advisory practices allow us to provide best-in-class advice to clients whether they are looking for growth through strategic alternatives, advice in shareholder engagement or in a restructuring or reorganization, or access to capital. Our deep networks across businesses allow us to connect clients and help them meet their strategic objectives. |
|
|
• |
Defined by Deep Relationships. Our partners have decades of experience and long-standing relationships with a vast network of corporate executives, board members, financial sponsors, fund managers and governments. Their expertise across multiple product areas, industry verticals and geographies are sought by clients in complex, cross-border situations around the globe. Our PJT Park Hill business has long-standing relationships across Europe, the Middle East and Asia that give them unique access to global capital and drives incremental value for our clients. |
|
|
• |
Global Market Leadership. Our Restructuring and Special Situations Group is a global market leader. Our PJT Park Hill business has a leading market position across all four of its businesses: private equity, hedge funds, real estate and secondary advisory. Our rapidly growing premier Strategic Advisory business is comprised of industry leading practitioners and has been the named advisor on some of the most high-profile and complex transactions. Our leading PJT Camberview business is well-known in the marketplace, having advised more than fifty Fortune 100 companies since its founding in 2012. |
|
|
• |
Defined by Collaboration, Clients and Content. We have a cohesive partnership centered around our core values of character, collaboration, commercial impact/client relationships and content. Our culture provides the ideal environment for idea sharing, collaboration and innovation. Our bankers are encouraged to make frequent client connections and leverage the experience and insights of fellow partners to deliver clients optimal service and outcomes. Our culture also fosters retention of top talent and provides a superior platform from which to recruit top bankers at all levels. |
4
|
|
• |
Clients’ Results Are Our Reputation. Our success is built around the trust our clients have placed in us. We work every day to ensure that we are providing cutting edge advice on the critical matters facing our clients. We work to navigate our clients through complex challenges and bold opportunities to meet their strategic objectives. Delivering optimal outcomes is what we strive for – our clients’ results are our reputation. |
Our Growth Strategy
Our strategy to achieve our growth objectives has the following components:
|
|
• |
Expand Our Market Leadership in Restructuring and Special Situations and PJT Park Hill. Our firm is strengthened by the deep client relationships and strong brand reputations we have in our leading Restructuring and Special Situations and PJT Park Hill businesses. These businesses are benefiting from closer collaboration across all our businesses, increased dialogues with financial sponsors as well as the increased footprint and product expertise and capabilities of our rapidly growing Strategic Advisory business. |
|
|
• |
Expand Our Addressable Market. We are focused on expanding into new geographies, sectors and capabilities. |
|
|
• |
Significantly Increase the Breadth and Depth of Our Advisory Franchise. We are focused on expanding our capabilities in areas where a sizable market opportunity clearly exists by hiring expert, top-tier talent to expand into new industry verticals, geographies and product capabilities, which will enable us to offer increasingly comprehensive and valuable solutions to a broader base of clients. |
|
|
• |
Enhance Collaboration Among Our Businesses to Better Serve Clients. We operate a scaled, diversified global advisory franchise comprised of highly synergistic businesses, which each share our culture of excellence, teamwork and entrepreneurship. Our partners and team members have relationships with a vast network of corporate executives, board members, financial sponsors, fund managers and governments as well as expertise in multiple product areas, industry verticals and geographies. By operating in a more integrated and cohesive manner, we are able to offer our clients a comprehensive and differentiated suite of advisory services. In addition, our deep networks across our businesses allow us to connect clients and provide incremental value in helping them meet their strategic objectives. |
|
|
• |
Remain the Premier Destination for Talent. We will continue to attract best-in-class bankers who want to deliver a broad range of world-class services to their clients around the globe. We offer a unique and compelling proposition to them through our total focus on advisory services; commitment to building a culture of collaboration, character and growth; strong client relationships; deep and exceptional base of talent; and efficient and scalable support infrastructure. |
Our Talent
As a premier global advisory-focused investment bank, we believe that we must have an approach to human capital management that ensures PJT Partners remains a destination for top talent at all levels. We have been focused on this since our firm’s inception and we want to be front-footed when it comes to attracting diverse individuals to our platform. Firm culture is critical to all aspects of how we do business and to our long-term success.
Our human capital successes thus far are evident in the number and quality of hires we have made as well as in the feedback we receive through our annual employee survey. Reinforcement of the culture we are building comes through engaging with and listening to our employees, our reward principles we apply to compensation and promotion decisions and through our various talent development initiatives, which continue to evolve as we grow.
As it pertains to the recruitment of talent, all candidates for PJT Partners are interviewed by a range of professionals, with a clear focus on quality of the candidate’s capabilities as well as character. The firm seeks candidates that buy in to a philosophy that prioritizes the long-term success of the firm and its clients, over near-term gains for the individual, as reflected in our reward principles.
As of December 31, 2019, we employed 678 individuals globally, including 81 partners.
5
Competition
The financial services industry is intensely competitive, and we expect it to remain so. Our competitors are other investment banking and financial advisory firms. These entities include brokers and dealers, investment banking firms and commercial banks. We compete on both a global and a regional basis, and on the basis of a number of factors, including the strength and depth of client relationships, industry knowledge, transaction execution skills, our range of products and services, innovation, reputation and price.
We also compete to attract and retain qualified employees. Our ability to continue to compete effectively in our business will depend upon our ability to attract new employees and retain and motivate our existing employees.
Regulation
Our business, as well as the financial services industry generally, is subject to extensive regulation in the U.S. and across the globe. As a matter of public policy, regulatory bodies in the U.S. and the rest of the world are charged with safeguarding the integrity of the securities and other financial markets and with protecting the interests of customers participating in those markets. In the U.S., the SEC is the federal agency responsible for the administration of the federal securities laws. PJT Partners LP, through which strategic advisory, shareholder advisory and restructuring and special situations services are conducted in the United States, and Park Hill Group LLC, which is an entity within the PJT Park Hill private fund advisory and fundraising services business, are registered broker-dealers. These registered broker-dealers are subject to regulation and oversight by the SEC. In addition, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”), a self-regulatory organization that is subject to oversight by the SEC, adopts and enforces rules governing the conduct, and examines the activities of, its member firms, which would include any such registered broker-dealer. State securities regulators also have regulatory or oversight authority over any such registered broker-dealer.
Broker-dealers are subject to regulations that cover all aspects of the securities business, including capital structure, recordkeeping and the conduct and qualifications of directors, officers and employees. In particular, as a registered broker-dealer and member of a self-regulatory organization, we are subject to the SEC’s uniform net capital rule, Rule 15c3-1. Rule 15c3-1 specifies the minimum level of net capital a broker-dealer must maintain and also requires that a significant part of a broker-dealer’s assets be kept in relatively liquid form. The SEC and various self-regulatory organizations impose rules that require notification when net capital falls below certain predefined criteria, limit the ratio of subordinated debt to equity in the regulatory capital composition of a broker-dealer and constrain the ability of a broker-dealer to expand its business under certain circumstances. Additionally, the SEC’s uniform net capital rule imposes certain requirements that may have the effect of prohibiting a broker-dealer from distributing or withdrawing capital and requiring prior notice to the SEC for certain withdrawals of capital.
PJT Partners LP is registered as a “municipal advisor” with the SEC and the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board (the “MSRB”). In 2013, as required under the Dodd-Frank Act, the SEC issued its final rule regarding the new category of regulated financial activity: “municipal advisors” (the “MA Rule”). The MA Rule, which became effective in 2014, imposes a fiduciary duty on municipal advisors when advising municipal entities. In addition to the SEC rule, the MSRB has developed a number of implementing rules and interpretive guidance relating to municipal advisors, and we have implemented policies and procedures reasonably designed to comply with such rules and guidance. In recent years, broker-dealer and municipal advisor interaction with municipal entities has become an area of greater rulemaking and regulatory interest; however, we do not expect a materially adverse impact on municipal advisory services.
Further, Park Hill Group LLC is a registered commodity trading advisor with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) and is a member of the National Futures Association (“NFA”), a futures industry self-regulatory organization. The CFTC and NFA regulate futures contracts, swaps and various other financial instruments in which certain of Park Hill Group LLC’s clients may invest.
In addition to the regulation we are subject to in the U.S., we are subject to regulation internationally. PJT Partners (UK) Limited is licensed with the United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority. PJT Partners (HK) Limited is licensed with the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission.
6
Certain parts of our business are subject to compliance with laws and regulations of U.S. federal and state governments, non-U.S. governments, their respective agencies and/or various self-regulatory organizations or exchanges relating to, among other things, the privacy of client information. Any failure to comply with these regulations could expose us to liability and/or reputational damage.
The U.S. and non-U.S. government agencies and self-regulatory organizations, as well as state securities commissions in the U.S., are empowered to conduct periodic examinations and initiate administrative proceedings that can result in censure, fines, the issuance of cease-and-desist orders or the suspension or expulsion of a broker-dealer or its directors, officers or employees.
Broker-dealers are also subject to regulations, including the USA PATRIOT Act of 2001, which impose obligations regarding the prevention and detection of money-laundering activities, including the establishment of customer due diligence and other compliance policies and procedures.
Failure to comply with these requirements may result in monetary, regulatory and, in certain cases, criminal penalties. In connection with its administration and enforcement of economic and trade sanctions based on U.S. foreign policy and national security goals, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (“OFAC”), publishes a list of individuals and companies owned or controlled by, or acting for or on behalf of, targeted countries. It also lists individuals, groups and entities, such as terrorists and narcotics traffickers, designated under programs that are not country-specific. Collectively, such individuals and companies are called “Specially Designated Nationals,” or SDNs. Assets of SDNs are blocked, and we are generally prohibited from dealing with them. In addition, OFAC administers a number of comprehensive sanctions and embargoes that target certain countries, governments and geographic regions. We are generally prohibited from engaging in transactions involving any country, region or government that is subject to such comprehensive sanctions.
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (the “FCPA”) and the UK 2010 Bribery Act (the “UK Bribery Act”) prohibit the payment of bribes to foreign government officials and political figures. The FCPA prohibits us from making or offering to make any payment, or giving anything of value to a foreign official for the purpose of influencing that official to assist us in obtaining or retaining an improper business advantage. The FCPA has a broad reach, covering all U.S. companies and citizens doing business abroad, among others, and defining a foreign official to include not only those holding public office but also local citizens acting in an official capacity for or on behalf of foreign government-run or -owned organizations or public international organizations. The FCPA also requires maintenance of appropriate books and records and maintenance of adequate internal controls to prevent and detect possible FCPA violations. Similarly, the UK Bribery Act prohibits us from bribing, being bribed or making other prohibited payments to government officials or other persons to obtain or retain business or gain some other business advantage.
Park Hill Group LLC is also affected by various state and local regulations or policies that restrict or prohibit the use of placement agents in connection with investments by public pension funds, including but not limited to, regulations in New York State, New York City, Illinois and California. Similar measures are being considered or have been implemented in other jurisdictions.
Organizational Structure
PJT Partners Inc. is a holding company and its only material asset is its controlling equity interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP, and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time as described herein in “Part II. Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Dividend Policy.” As the sole general partner of PJT Partners Holdings LP, PJT Partners Inc. operates and controls all of the business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries. The ownership interests of the holders (other than PJT Partners Inc.) of common units of partnership interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP (“Partnership Units”) are reflected as non-controlling interests in PJT Partners Inc.’s consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2019.
Our employees and certain current and former Blackstone executive officers and employees also hold all issued and outstanding shares of the Class B common stock of PJT Partners Inc. The shares of Class B common stock have no economic rights but entitle the holder, without regard to the number of shares of Class B common stock held, to a number of votes that is equal to the aggregate number of vested and unvested Partnership Units and LTIP Units (which is a class of partnership interests) in PJT Partners Holdings LP held by such holder on all matters presented to stockholders of PJT Partners Inc. other than director elections and removals. In connection with the spin-off, Blackstone’s senior management, including Mr. Schwarzman and all of Blackstone’s other executive
7
officers, provided an irrevocable proxy to Mr. Taubman to vote their shares of Class B common stock for so long as Mr. Taubman is the Chief Executive Officer of PJT Partners Inc. With respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc., shares of Class B common stock initially entitle holders to only one vote per share, representing significantly less than one percent of the voting power entitled to vote thereon. However, the voting power of Class B common stock with respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc. may be increased to up to the number of votes to which a holder is then entitled on all other matters presented to stockholders. The voting power on applicable matters afforded to holders of partnership interests by their shares of Class B common stock is automatically and correspondingly reduced as they exchange Partnership Units for cash or for shares of Class A common stock of PJT Partners Inc. pursuant to the exchange agreement. If at any time the ratio at which Partnership Units are exchangeable for shares of Class A common stock of PJT Partners Inc. changes from one-for-one, the number of votes to which Class B common stockholders are entitled on applicable matters will be adjusted accordingly. Holders of shares of our Class B common stock will vote together with holders of our Class A common stock as a single class on all matters on which stockholders are entitled to vote generally, except as otherwise required by law.
We and the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) also have entered into an exchange agreement under which they (or certain permitted transferees) have the right, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, on a quarterly basis, to exchange all or part of their Partnership Units for cash or, at our election, for shares of our Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis, subject to customary conversion rate adjustments for splits, unit distributions and reclassifications. Further, pursuant to the terms in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, we may also require holders of Partnership Units who are not Service Providers (as defined in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP) to exchange such Partnership Units. The price per Partnership Unit to be received in a cash-settled exchange will be equal to the fair value of a share of our Class A common stock (determined in accordance with and subject to adjustment under the exchange agreement). In the event that PJT Partners Inc. elects to fund cash-settled exchanges of Partnership Units with new issuances of Class A common stock, the fair value of a share of our Class A common stock will be deemed to be equal to the net proceeds per share of Class A common stock received by PJT Partners Inc. in the related issuance. Accordingly, in this event, the price per Partnership Unit to which an exchanging Partnership Unitholder will be entitled may be greater than or less than the then-current market value of our Class A common stock.
The Company entered into a tax matters agreement with Blackstone (the “Tax Matters Agreement”) that governs the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of the Company and Blackstone after the spin-off with respect to tax liabilities and benefits, tax attributes, tax contests and other tax sharing regarding U.S. federal, state, local and foreign income taxes, other tax matters and related tax returns.
The Company has also entered into a tax receivable agreement with the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) that provides for the payment by PJT Partners Inc. to exchanging holders of Partnership Units of 85% of the benefits, if any, that PJT Partners Inc. is deemed to realize as a result of the increases in tax basis related to such exchanges of Partnership Units and of certain other tax benefits related to entering into the tax receivable agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the tax receivable agreement.
Refer to Note 14. “Transactions with Related Parties” and Note 15. “Commitments and Contingencies—Transactions and Agreements with Blackstone” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “Part II. Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” for further information about the agreements entered into in connection with the spin-off.
Available Information
We file annual, quarterly and current reports and other information with the SEC. These filings are available to the public over the internet at the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
Our website address is www.pjtpartners.com. We make available free of charge on or through www.pjtpartners.com our annual reports on Form 10‑K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8‑K, and amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Hard copies may be obtained free of charge by contacting Investor Relations at PJT Partners Inc., 280 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10017 or by calling (212) 364-7800. Although we refer to our website in this report, the contents of our website are not included or incorporated by reference into this report. All references to our website in this report are intended to be inactive textual references only.
8
|
ITEM 1A. |
RISK FACTORS |
Risks Relating to Our Business
Our future growth will depend on, among other things, our ability to successfully identify, recruit and develop talent and will require us to commit additional resources.
Our future growth will depend on, among other things, our ability to successfully identify and recruit individuals and teams to join our firm. It typically takes time for these professionals to become profitable and effective. During that time, we may incur significant expenses and expend significant time and resources toward training, integration and business development aimed at developing this new talent. If we are unable to recruit and develop profitable professionals, we will not be able to implement our growth strategy and our financial results could be materially adversely affected.
In addition, sustaining growth will require us to commit additional management, operational and financial resources and to maintain appropriate operational and financial systems to adequately support expansion, especially in instances where we open new offices that may require additional resources. There can be no assurance that we will be able to manage our expanding operations effectively, and any failure to do so could materially adversely affect our ability to grow revenue and control our expenses.
Changing market conditions, including as a result of tariffs and global trade uncertainties, can adversely affect our business in many ways, including by reducing the volume of the transactions involving our business, which could materially reduce our revenue.
As a participant in the financial services industry, we are materially affected by conditions in the global financial markets and economic conditions throughout the world, including many factors beyond our control, such as tariffs and global trade uncertainties. For example, a substantial portion of our revenue is directly related to the volume and value of the transactions in which we are involved. During periods of unfavorable market or economic conditions, the volume and value of M&A transactions may decrease, thereby reducing the demand for our M&A advisory services and increasing price competition among financial services companies seeking such engagements. In addition, during periods of strong market and economic conditions, the volume and value of restructuring and reorganization transactions may decrease, thereby reducing the demand for our restructuring and special situations services and increasing price competition among financial services companies seeking such engagements. Our results of operations would be adversely affected by any such reduction in the volume or value of such advisory transactions. Further, in the period following an economic downturn, the volume and value of M&A transactions typically takes time to recover and lags a recovery in market and economic conditions.
Our profitability may also be adversely affected by our fixed costs and the possibility that we would be unable to scale back other costs within a time frame sufficient to match any decreases in revenue relating to changes in market and economic conditions.
Our private fund advisory and fundraising business is dependent on the availability of private capital for deployment in illiquid asset classes such as private equity, real estate and hedge funds for clients we serve.
PJT Park Hill provides private fund advisory and fundraising services for alternative investment managers, including private equity funds, real estate funds and hedge funds. Our ability to find suitable engagements and earn fees in this business depends on the availability of private and public capital for investments in illiquid assets such as private equity, real estate and hedge funds. Our ability to assist fund managers and sponsors raise capital from investors depends on a number of factors, including many that are outside our control, such as the general economic environment, changes in the weight investors give to alternative asset investments as part of their overall investment portfolio among asset classes, and market liquidity and volatility. Additionally, certain investors, such as public pension plans, may have policies prohibiting the use of placement agents by fund sponsors or managers in connection with a limited partner’s investment. To the extent private and public capital focused on illiquid investment opportunities for our clients is limited, the results of PJT Park Hill may be adversely affected.
Our revenue in any given period is dependent in part on the number of fee-paying clients in such period, and a significant reduction in the number of fee-paying clients in any given period could reduce our revenue and adversely affect our operating results in such period.
A substantial portion of our revenue in any given period is dependent in part on the number of fee-paying clients in such period. We had 142 clients and 141 clients that generated fees equal to or greater than $1 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. We may lose clients as a result of the sale or merger of a
9
client, a change in a client’s senior management, competition from other financial advisors and financial institutions and other causes. A significant reduction in the number of fee-paying clients in any given period could reduce our revenue and adversely affect our operating results in such period.
The composition of the group comprising our largest clients varies significantly from year to year, and a relatively small number of clients may account for a significant portion of our consolidated revenues in any given period. As a result, our operating results, financial condition and liquidity may be significantly affected by the loss of a relatively small number of mandates or the failure of a relatively small number of assignments to be completed. However, no client accounted for more than 10% of our total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019 or 2018.
We have recorded net losses in the past and we may experience net losses in the future.
We have recorded consolidated or combined net losses in two of the five years ended December 31, 2019. A primary component of these net losses in each period was significant non-cash charges, consisting primarily of transaction-related compensation charges associated with Blackstone’s initial public offering (“IPO”), our spin-off from Blackstone, the acquisition of CamberView, and the amortization of intangible assets that were recorded in connection with Blackstone’s IPO, the acquisition of PJT Capital LP and the acquisition of CamberView. We expect such non-cash charges to continue to be significant for the next few years and, as a result, we may record net losses during such periods.
If the number of debt defaults, bankruptcies or other factors affecting demand for our restructuring and special situations services declines, our restructuring and special situations business could suffer.
We provide various financial restructuring and reorganization and related advice to companies in financial distress or to their creditors or other stakeholders. A number of factors affect demand for these advisory services, including general economic conditions, the availability and cost of debt and equity financing, governmental policy and changes to laws, rules and regulations, including those that protect creditors. In addition, providing restructuring and special situations advisory services entails the risk that the transaction will be unsuccessful, takes considerable time and can be subject to a bankruptcy court’s discretionary power to disallow or discount our fees. If the number of debt defaults, bankruptcies or other factors affecting demand for our restructuring and special situations advisory services declines, our Restructuring and Special Situations business would be adversely affected.
We depend on the efforts and reputations of Mr. Taubman and other key personnel.
We depend on the efforts and reputations of Mr. Taubman and our other senior bankers. Our senior banking team’s reputations and relationships with clients and potential clients are critical elements in the success of our business. Mr. Taubman and our other senior executives and bankers are important to our success because they are instrumental in setting our strategic direction, operating our business, identifying, recruiting and training key personnel, maintaining relationships with our clients, and identifying business opportunities. The loss of one or more of these executives or other key individuals could impair our business and development until qualified replacements are found. We may not be able to replace these individuals quickly or with persons of equal experience and capabilities. Although we have employment agreements with certain of these individuals, we cannot prevent them from terminating their employment with us. In addition, our non-competition agreements with such individuals may not be enforced by the courts. The loss of the services of any of them, in particular Mr. Taubman, could have a material adverse effect on our business, including our ability to attract clients.
Our ability to retain and motivate our partners and other key personnel is critical to the success of our business.
Our future success and growth depends to a substantial degree on our ability to retain and motivate our partners and other key personnel. Our professionals possess substantial experience and expertise and have strong relationships with our clients. As a result, the loss of these professionals could jeopardize our relationships with clients and result in the loss of client engagements. We may not be successful in our efforts to retain and motivate the required personnel as the market for qualified advisory and fund advisory services professionals is extremely competitive.
The near-term vesting of equity awarded to key personnel may diminish our ability to retain and motivate our professionals. There is no guarantee that our non-competition and current compensation arrangements with our professionals, in which we mandatorily defer a substantial portion of their annual incentive bonus in the form of cash and equity awards with multi-year vesting periods, will provide sufficient protections or incentives to prevent
10
our partners and other key personnel from resigning to join our competitors. The departure of a number of partners or groups of professionals could have a material adverse effect on our business and profitability.
Our revenue and profits are highly volatile on a quarterly basis and may cause the price of our Class A common stock to fluctuate and decline.
Our revenue and profits are highly volatile. We earn advisory fees, generally from a limited number of engagements that generate significant fees at key transaction milestones, such as closing, the timing of which is outside of our control. We expect that we will continue to rely on advisory fees for a substantial portion of our revenue for the foreseeable future. Accordingly, a decline in our advisory engagements or the market for advisory services would adversely affect our business. In addition, our financial results will likely fluctuate from quarter to quarter based on the timing of when fees are recognized, and high levels of revenue in one quarter will not necessarily be predictive of continued high levels of revenue in future periods. Because advisory revenue is volatile and represents a significant portion of our total revenue, we may experience greater variations in our revenue and profits than other larger, more diversified competitors in the financial services industry. Fluctuations in our quarterly financial results could, in turn, lead to large adverse movements in the price of our Class A common stock or increased volatility in our stock price generally.
Because in many cases we are not paid until the successful consummation of the underlying transaction, our revenue is highly dependent on market conditions and the decisions and actions of our clients, interested third parties and governmental authorities. For example, we may be engaged by a client in connection with a sale or divestiture, but the transaction may not occur or be consummated because, among other things, anticipated bidders may not materialize, no bidder is prepared to pay our client’s price or because our client’s business experiences unexpected operating or financial problems. We may be engaged by a client in connection with an acquisition, but the transaction may not occur or be consummated for a number of reasons, including because our client may not be the winning bidder, failure to agree upon final terms with the counterparty, failure to obtain necessary regulatory consents or board or stockholder approvals, failure to secure necessary financing, adverse market conditions or because the target’s business experiences unexpected operating or financial problems. In these circumstances, we often do not receive significant advisory fees, despite the fact that we have devoted considerable resources to these transactions.
In addition, with respect to PJT Park Hill, our private fund advisory and fundraising business, we face the risk that we may not be able to collect all or a portion of the fees that we recognize. The placement fees earned by PJT Park Hill are generally recognized by us for accounting purposes upon the successful subscription by an investor in a client’s fund and/or the closing of that fund. However, those fees are typically paid by a PJT Park Hill client over a period of time with interest (for example, three to four years) following such successful subscription by an investor in a client’s fund and/or the closing of that fund. There is a risk that during that period of time, PJT Park Hill may not be able to collect all or a portion of the fees PJT Park Hill is due for the fund advisory services it has already provided to such client. For instance, a PJT Park Hill client’s fund may be liquidated prior to the time that all or a portion of the fees due to PJT Park Hill are due to be paid. Moreover, to the extent fewer assets are raised for funds or interest by investors in alternative asset funds declines, the placement fees earned by PJT Park Hill would be adversely affected.
In addition, we face the risk that certain clients may not have the financial resources to pay our agreed-upon advisory fees. Certain clients may also be unwilling to pay our advisory fees in whole or in part, in which case we may have to incur significant costs to bring legal action to enforce our engagement agreements to obtain our advisory fees.
Future joint ventures, strategic investments and acquisitions may result in additional risks and uncertainties in our business.
In addition to recruiting and internal expansion, we may grow our core business through joint ventures, strategic investments or acquisitions. In the event we make strategic investments or acquisitions, we would face numerous risks and would be presented with financial, managerial and operational challenges, including the difficulty of integrating personnel, retaining clients of the acquired entity, financial, accounting, technology and other systems and management controls.
11
Our failure to deal appropriately with actual, potential or perceived conflicts of interest could damage our reputation and materially adversely affect our business.
We confront actual, potential or perceived conflicts of interest in our business. We have adopted various policies, controls and procedures to address or limit actual or perceived conflicts of interest. However, these policies, controls and procedures may not timely identify or appropriately manage such conflicts of interest as identifying and managing actual or perceived conflicts of interest is complex and difficult. It is possible that actual, potential or perceived conflicts could give rise to client dissatisfaction, litigation or regulatory enforcement actions. Our reputation could be damaged if we fail, or appear to fail, to deal appropriately with one or more potential or actual conflicts of interest. Regulatory scrutiny of, or litigation in connection with, conflicts of interest could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, which could materially adversely affect our business in a number of ways, including a reluctance of some potential clients and counterparties to do business with us.
Policies, controls and procedures that we may be required to implement to address additional regulatory requirements, including as a result of additional foreign jurisdictions in which we operate, or to mitigate actual or potential conflicts of interest, may result in increased costs, including for additional personnel and infrastructure and information technology improvements, as well as limit our activities and reduce the positive synergies that we seek to cultivate across our businesses.
Employee or contractor misconduct, which is difficult to detect and deter, could harm us by impairing our ability to attract and retain clients and talent and by subjecting us to legal liability and reputational harm.
There is a risk that our employees or contractors could engage in misconduct that would adversely affect our business. For example, our business often requires that we deal with confidential matters of great significance to our clients. If our employees or contractors were to improperly use or disclose confidential information provided by our clients, we could be subject to regulatory sanctions and we could suffer serious harm to our reputation, financial position, current client relationships and ability to attract future clients. In addition, our financial professionals and other employees are responsible for following proper measures to maintain the confidentiality of information we hold. If an employee’s failure to do so results in the improper release of confidential information, we could be subject to reputational harm and legal liability, which could impair our ability to attract and retain clients and in turn materially adversely affect our business. Despite our implementation of policies, our emphasis on a culture that supports diversity and inclusion, and training to prevent and detect misconduct, we cannot completely safeguard ourselves against the risk of work place misconduct, such as sexual harassment or discrimination. In addition to impairing our ability to attract and retain clients, such misconduct may also impair our ability to attract and retain talent resulting in a materially adverse effect on our business. It is not always possible to deter such misconduct, and there can be no assurance that the precautions we take to prevent and detect misconduct will be effective in all cases. If our employees or contractors engage in misconduct, our business could be materially adversely affected.
The U.S. Department of Justice and the SEC continue to devote significant resources to the enforcement of the FCPA. In addition, the United Kingdom and other jurisdictions have significantly expanded the reach of their anti-bribery laws. While we have developed and implemented policies and procedures designed to ensure strict compliance by us and our personnel with the FCPA, such policies and procedures may not be effective in all instances to prevent violations. Any determination that we have violated the FCPA or other applicable anti-corruption laws could subject us to, among other things, civil and criminal penalties, material fines, profit disgorgement, injunctions on future conduct, securities litigation and a general loss of investor confidence, any one of which could adversely affect our business prospects, financial position or the market value of our common shares.
We may face damage to our professional reputation or negative publicity if our services are not regarded as satisfactory or for other reasons.
As an advisory service firm, we depend to a large extent on our relationships with our clients and reputation for integrity and high-caliber professional services to attract and retain clients. As a result, if a client is not satisfied with our services or we experience negative publicity related to our business and our people, regardless of whether the allegations are valid, it may be more damaging in our business than in other businesses.
12
We face strong competition from other financial advisory firms, many of which have greater resources and broader product and services offerings than we do.
The financial services industry is intensely competitive, highly fragmented and subject to rapid change, and we expect it to remain so. Our competitors are other investment banking and financial advisory firms. We compete on both a global and a regional basis, and on the basis of a number of factors, including the strength and depth of client relationships, industry knowledge, transaction execution skills, our range of products and services, innovation, reputation and price. In addition, in our business there are usually no long-term contracted sources of revenue. Each revenue-generating engagement typically is separately solicited, awarded and negotiated.
We have experienced significant competition when obtaining advisory mandates, and we may experience pricing pressures in our business in the future as some of our competitors may seek to obtain increased market share by reducing fees.
Our primary competitors are large financial institutions, many of which have far greater financial and other resources and have the ability to offer a wider range of products and services. In addition, we may be at a competitive disadvantage with regard to certain of our competitors who are able to and often do, provide financing or market making services that are often a crucial component of the types of transactions on which we advise. In addition to our larger competitors, over the last several years the number of independent investment banks that offer independent advisory services has increased. As these independent firms or new entrants into the market seek to gain market share, we could experience pricing and competitive pressures, which would adversely affect our revenues and earnings.
In addition, PJT Park Hill operates in a highly competitive environment and the barriers to entry into the private fund advisory and fundraising services business are low.
As a member of the financial services industry, we face substantial litigation and regulatory risks.
Our role as advisor to our clients on important transactions involves complex analysis and the exercise of professional judgment, including rendering “fairness opinions” in connection with mergers and other transactions. Our activities may subject us to the risk of significant legal liabilities to our clients and affected third parties, including shareholders of our clients who could bring securities class actions against us. In recent years, the volume of claims and amount of damages claimed in litigation and regulatory proceedings against financial services companies have increased. These risks are difficult to assess or quantify and their existence and magnitude often remain unknown for substantial periods of time. Our engagements typically, but not always, include broad indemnities from our clients and provisions to limit our exposure to legal claims relating to our services, but these provisions may not protect us in all cases, including when a client does not have the financial capacity to pay under the indemnity. As a result, we may incur significant legal expenses in defending against or settling litigation. In addition, we may have to spend a significant amount to adequately insure against these potential claims. Substantial legal liability or significant regulatory action against us could have material adverse financial effects or cause significant reputational harm to us, which could seriously harm our business prospects.
Extensive and evolving regulation of our business and the business of our clients exposes us to the potential for significant penalties and fines due to compliance failures, increases our costs and may result in limitations on the manner in which our business is conducted.
As a participant in the financial services industry, we are subject to extensive regulation in the U.S. and internationally. We are subject to regulation by governmental and self-regulatory organizations in the jurisdictions in which we operate. As a result of market volatility and disruption in recent years, the U.S. and other governments took unprecedented steps to try to stabilize the financial system, including providing assistance to financial institutions and taking certain regulatory actions. The long-term effects of these actions and of legislative and regulatory initiatives (including the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act) effected in connection with, and as a result of, such extraordinary disruption and volatility is uncertain, both as to the financial markets and participants in general, and as to us in particular.
We face the risk of significant intervention by regulatory authorities, including extended investigation and surveillance activity, adoption of costly or restrictive new regulations and judicial or administrative proceedings that may result in substantial penalties. Among other things, we could be fined or be prohibited from engaging in some of our business activities. In addition, the regulatory environment in which we operate is subject to modification and further regulation. Such changes may increase the expenses we incur without necessarily leading to commensurate
13
increases in revenues. Certain laws and regulations within the U.S. and internationally include extraterritorial application that may lead to overlapping or conflicting legal and regulatory burdens with additional risks and implementation expenses. New laws or regulations applicable to us and our clients also may adversely affect our business, and our ability to function in this environment will depend on our ability to constantly monitor and react to these changes.
Our ability to conduct business and our operating results, including compliance costs, may be adversely affected as a result of any new requirements imposed by the SEC, FINRA or other U.S. or foreign governmental regulatory authorities or self-regulatory organizations that regulate financial services firms or supervise financial markets. We may be adversely affected by changes in the interpretation or enforcement of existing laws and rules by these governmental authorities and self-regulatory organizations. In addition, some of our clients or prospective clients may adopt policies that exceed regulatory requirements and impose additional restrictions affecting their dealings with us. Accordingly, we may incur significant costs to comply with U.S. and international regulation. In addition, new laws or regulations or changes in enforcement of existing laws or regulations applicable to our clients may adversely affect our business. For example, changes in antitrust laws or the enforcement of antitrust laws could affect the level of M&A activity and changes in applicable regulations could restrict the activities of our clients and their need for the types of advisory services that we provide to them. Further, changes to existing tax laws and regulations in the U.S. and in other jurisdictions in which we and our clients operate may reduce the level of M&A activity, including cross-border M&A activity.
The trade agreements under which U.S. companies currently exchange products and services around the world are subject to change. It is not known what specific measures might be proposed or how they would be implemented and enforced. There can be no assurance that pending or future legislation or execution in the U.S. that could significantly increase costs with respect to our foreign operations and, consequently, adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations, will not be enacted.
In addition, several states and municipalities in the United States, including, but not limited to, California, Illinois, New York State and New York City have adopted “pay-to-play” and placement agent rules, which, in addition to imposing registration and reporting requirements, limit our ability to charge fees in connection with certain engagements of Park Hill Group LLC or restrict or prohibit the use of placement agents in connection with investments by public pension funds. These types of measures could materially and adversely impact our PJT Park Hill business.
Our failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations could result in adverse publicity and reputational harm as well as fines, suspensions of personnel or other sanctions, including revocation of our registration or any of our subsidiaries as a financial advisor and could impair retention or recruitment of personnel. In addition, any changes in the regulatory framework could impose additional expenses or capital requirements on us, result in limitations on the manner in which our business is conducted, have an adverse impact upon our financial condition and business and require substantial attention by senior management. Moreover, our business is subject to periodic examination by various regulatory authorities, and we cannot predict the outcome of any such examinations.
Our business is subject to various cybersecurity and other operational risks.
We face various cybersecurity and other operational risks related to our business on a day-to-day basis. We rely heavily on financial, accounting, communication and other information technology systems, and the people who operate them. These systems, including the systems of third parties on whom we rely, may fail to operate properly or become disabled as a result of tampering or a breach of our network security systems or otherwise, including for reasons beyond our control.
Our clients typically provide us with sensitive and confidential information. We are dependent on information technology networks and systems to securely process, transmit and store such information and to communicate among our locations around the world and with our clients and other third parties. We may be subject to attempted security breaches and cyber-attacks and, while we are not aware of any such occurrence to date, a successful breach of our systems, or the systems used by our clients and other third parties, could lead to shutdowns or disruptions of our systems or third-party systems on which we rely and potential unauthorized disclosure of sensitive or confidential information. Breaches of our or third-party network security systems on which we rely could involve attacks that are intended to obtain unauthorized access to our proprietary information, destroy data or disable, degrade or sabotage our systems, often through the introduction of computer viruses, cyber-attacks and other means and could originate from a wide variety of sources, including foreign governments or other unknown third parties. Although we take various measures to ensure the integrity of our and third-party systems on which we rely, there
14
can be no assurance that these measures will provide adequate protection, especially because the cyber-attack techniques used change frequently or are not recognized until launched. As cyber threats continue to multiply, become more sophisticated and threaten additional aspects of our businesses, we may also be required to expend additional resources on information security and compliance costs in order to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any information security vulnerabilities or other exposures. If our or third-party systems on which we rely are compromised, do not operate properly or are disabled, we could suffer a disruption of our business, financial losses, liability to clients, regulatory sanctions and damage to our reputation. Phishing attacks and email spoofing attacks are often used to obtain information to impersonate employees or clients in order to, among other things, direct fraudulent bank transfers or obtain valuable information. Fraudulent transfers resulting from phishing attacks or email spoofing of our employees could result in a material loss of assets, reputational harm or legal liability and in turn materially adversely affect our business.
We operate a business that is highly dependent on information systems and technology. Any failure to keep accurate books and records can render us liable to disciplinary action by governmental and self-regulatory authorities, as well as to claims by our clients. We rely on third-party service providers for certain aspects of our business. Any interruption or deterioration in the performance of these third parties or failures of their information systems and technology could impair our operations, affect our reputation and adversely affect our business.
In addition, a disaster or other business continuity problem, such as a pandemic, other man-made or natural disaster or disruption involving electronic communications or other services used by us or third parties with whom we conduct business, could lead us to experience operational challenges, and if we are unable to timely and successfully recover that could materially disrupt our business and cause material financial loss, regulatory actions, reputational harm or legal liability.
We are exposed to risks related to our insurance coverage.
Our operations and financial results are subject to risks and uncertainties related to our use of insurance for a variety of risks, including cybersecurity risk. While we endeavor to purchase insurance coverage appropriate for our risk assessment, we are unable to predict with certainty the frequency, nature or magnitude of claims for direct or consequential damages. Our business may be negatively affected if our insurance coverage proves to be inadequate or unavailable. Insurance claims may divert management resources away from operating our business.
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash in the future to service any current or future indebtedness or other contractual obligations, or a significant deterioration in the credit markets or the failure of one or more commercial banking institutions, could adversely affect our liquidity.
Our ability to make scheduled payments on or to refinance any current or future debt obligations or other contractual obligations depends on our financial condition and operating performance. We cannot provide assurance that we will maintain a level of cash flows from operating activities sufficient to permit us to pay the principal of, and interest on, any current or future indebtedness. If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to fund any current or future debt obligations, we may be forced to reduce or delay investments and capital expenditures, or to sell assets, seek additional capital or restructure or refinance such indebtedness or other contractual obligations.
As of December 31, 2019, we had cash, cash equivalents and investments of $217.5 million, of which $23.8 million was invested in Treasury securities. We monitor developments relating to the liquidity of these instruments on a regular basis. In the event of a significant deterioration of the credit markets or the failure of one or more commercial banking institutions, there can be no assurance that we will be able to liquidate these assets or access our cash. Our inability to access our cash or other assets could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and result in our inability to meet our obligations timely, which could have a material adverse effect on the value of our stock.
15
Our international operations are subject to certain risks, which may affect our revenue.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, we earned 9.1% of our total revenues from our international operations. We intend to continue to grow our non-U.S. business, and this growth is important to our overall success. In addition, many of our clients are non-U.S. entities seeking to enter into transactions involving U.S. businesses. Our international operations carry special financial, business, regulatory and reputational risks, which could include the following:
|
|
• |
greater difficulties in managing and staffing foreign operations; |
|
|
• |
language and cultural differences; |
|
|
• |
fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates that could adversely affect our results; |
|
|
• |
unexpected and costly changes in trading policies, regulatory requirements, tariffs and other barriers; |
|
|
• |
restrictions on travel; |
|
|
• |
longer transaction cycles; |
|
|
• |
higher operating costs; |
|
|
• |
local labor conditions and regulations; |
|
|
• |
adverse consequences or restrictions on the repatriation of earnings; |
|
|
• |
potentially adverse tax consequences, such as trapped foreign losses; |
|
|
• |
less stable political and economic environments; |
|
|
• |
civil disturbances or other catastrophic events that reduce business activity; |
|
|
• |
disasters or other business continuity problems, such as pandemics, other man-made or natural disaster or disruption involving electronic communications or other services; and |
|
|
• |
uncertainty regarding the ongoing relationship between the United Kingdom (“U.K.”) and European Union (“E.U.”). |
If our international business increases relative to our total business, these factors could have a more pronounced effect on our operating results.
As part of our day-to-day operations outside of the United States, we are required to create compensation programs, employment policies, compliance policies and procedures and other administrative programs that comply with the laws of multiple countries. We also must communicate and monitor standards and directives across our global operations. Our failure to successfully manage and grow our geographically diverse operations could impair our ability to react quickly to changing business and market conditions and to enforce compliance with non-U.S. standards and procedures.
We may enter into new lines of business, which may result in additional risks and uncertainties in our business.
We currently generate substantially all of our revenue from our strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and fundraising services businesses. However, we may grow our business by entering into new lines of business. To the extent we enter into new lines of business, we will face numerous risks and uncertainties, including risks associated with actual or perceived conflicts of interest because we would no longer be limited to the advisory business, the possibility that we have insufficient expertise to engage in such activities profitably or without incurring inappropriate amounts of risk, the required investment of capital and other resources and the loss of clients due to the perception that we are no longer focusing on our core business.
Entry into certain lines of business may subject us to new laws and regulations with which we are not familiar, or from which we are currently exempt, and may lead to increased litigation and regulatory risk. In addition, certain aspects of our cost structure, such as costs for compensation, occupancy and equipment rentals, communication and information technology services, and depreciation and amortization will be largely fixed, and we may not be able to timely adjust these costs to match fluctuations in revenue related to our entering into new lines of business. If a new business generates insufficient revenues or if we are unable to efficiently manage our expanded operations, our results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
16
Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates could adversely affect our results.
Because our financial statements are denominated in U.S. dollars and we receive a portion of our revenue in other currencies, we are exposed to fluctuations in foreign currencies. In addition, we pay certain of our expenses in such currencies. We have not entered into any transactions to hedge our exposure to these foreign exchange fluctuations through the use of derivative instruments or otherwise. An appreciation or depreciation of any of these currencies relative to the U.S. dollar would result in an adverse or beneficial impact, respectively, to our financial results.
A change in relevant income tax laws, regulations or treaties or an adverse interpretation of these items by tax authorities could result in an audit adjustment or revaluation of our deferred tax assets that may cause our effective tax rate and tax liability to be higher than what is currently presented in the consolidated financial statements.
As part of the process of preparing our consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. Significant management judgment is required in determining our provision for income taxes, our deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance recorded against our deferred tax assets. This process requires us to estimate our actual current tax liability and to assess temporary differences resulting from differing book versus tax treatment. Our effective tax rate and tax liability is based on the application of current income tax laws, regulations and treaties. These laws, regulations and treaties are complex, and the manner in which they apply to our facts and circumstances is sometimes open to interpretation. Management believes its application of current laws, regulations and treaties to be correct and sustainable upon examination by the tax authorities. However, the tax authorities could challenge our interpretation resulting in additional tax liability or adjustment to our income tax provision that could increase our effective tax rate. In addition, tax laws, regulations or treaties newly enacted or enacted in the future may cause us to remeasure our deferred tax assets and have a material change to our effective tax rate.
The range of potential outcomes relating to arrangements between the European Union and the United Kingdom may adversely affect our business.
We conduct our business in European Union countries through our U.K. subsidiary, PJT Partners (UK) Limited, which is authorized and regulated in the U.K. by the Financial Conduct Authority. On June 23, 2016, the U.K. voted to leave the E.U. and on March 29, 2017, the U.K. began the process to withdraw from the E.U. The U.K. formally left the E.U. on January 31, 2020 and has immediately entered into a transition period, which is expected to continue until December 31, 2020.
The full commercial, regulatory and legal impact of the U.K.’s departure from the E.U. is yet to be determined. Our U.K. entity, PJT Partners (UK) Limited, primarily services U.K. and European-domiciled clients. The U.K.’s exit from the E.U. will cause PJT Partners (UK) Limited to lose its E.U. financial services passporting rights, which allows it to operate, on a cross-border and off-shore basis, in all E.U. countries. We have developed contingency plans with respect to the regulation of our European operations. However, there is no certainty that our European operations will not be disrupted at the end of the current transition period. In addition, the ongoing uncertainty around the U.K.’s exit from the E.U. has impacted the geopolitical and macroeconomic environment. If these conditions continue or if current conditions worsen, our business could potentially be adversely affected, which may materially impact our financial position and results of operations.
The cost of compliance with international broker-dealer, employment, labor, benefits, privacy and tax laws and regulations may adversely affect our business and hamper our ability to expand internationally.
Since we operate our business both in the U.S. and internationally, we are subject to many distinct broker-dealer, employment, labor, benefits, privacy and tax laws in each jurisdiction in which we operate, including regulations affecting our employment practices and our relations with our employees and service providers. If we are required to comply with other new regulations or new interpretations of existing regulations, or if we are unable to comply with these regulations or interpretations, our business could be adversely affected or the cost of compliance may make it difficult to expand into new international markets. Additionally, our competitiveness in international markets may be adversely affected by regulations requiring, among other things, the awarding of contracts to local contractors, the employment of local citizens and/or the purchase of services from local businesses or favoring or requiring local ownership.
17
In May 2018, the E.U.’s General Data Protection Regulations (“GDPR”) came into effect, and changed how businesses can collect, use and process the personal data of E.U. residents. As we engage in significant business in the E.U., we are subject to the GDPR’s requirements. The GDPR has extraterritorial effect and imposes a mandatory duty on businesses to self-report personal data breaches to authorities, and, under certain circumstances, to affected individuals. The GDPR also grants individuals the right to erasure (commonly referred to as the right to be forgotten), which may put a burden on us to erase records upon request. Compliance with the GDPR’s requirements may increase our legal, compliance and operational costs. Non-compliance with the GDPR’s requirements can result in significant penalties, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, expose us to legal and regulatory costs and impair our reputation.
Other jurisdictions, including certain U.S. states and non-U.S. jurisdictions where we conduct business, have also enacted or are considering data privacy legislation. For example, in June 2018, California’s legislature passed the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018, which went into effect in 2020. Increasingly numerous, fast-changing and complex legislation related to data privacy may result in greater compliance costs, heightened regulatory scrutiny and significant penalties. New and changing regulations may increase compliance costs such that they hamper our ability to expand into new territories.
Restrictions in the credit agreement governing our term loan and revolving credit facility may impair our ability to finance our future operations or capital needs or engage in other business activities that may be in our interests.
We have obtained a revolving credit facility in an aggregate principal amount of $40 million with the option for a temporary increase of up to $60 million total. We also borrowed $30 million under a term loan under the credit agreement, which was repaid in full in January 2020.
The credit agreement governing such revolving credit facility and term loan contains a number of significant covenants that, among other things, would require us to maintain certain minimum tangible net worth and liquidity and maximum leverage levels and the covenants may restrict our ability to:
|
|
• |
sell assets; |
|
|
• |
incur more indebtedness; |
|
|
• |
repay certain indebtedness; |
|
|
• |
make certain investments or business acquisitions; |
|
|
• |
make certain capital expenditures; |
|
|
• |
engage in business mergers or consolidations; and |
|
|
• |
engage in certain transactions with subsidiaries and affiliates. |
These restrictions could impair our ability to finance our future operations or capital needs or engage in other business activities that may be in our interests. In addition, such credit agreement could also require us to maintain compliance with certain financial ratios, including those relating to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization and consolidated indebtedness. Our ability to comply with these ratios and covenants may be affected by events beyond our control. A breach of the provisions of our credit agreement or our inability to comply with the required financial ratios or covenants included therein could result in a default thereunder. In the event of any such default, the lenders under the credit agreement could elect to:
|
|
• |
declare all outstanding debt, accrued interest and fees to be due and immediately payable; and |
|
|
• |
require us to apply all of our available cash to repay our outstanding senior debt. |
Failure to maintain effective internal controls in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act could have a material adverse effect on our business and share price.
We have documented and tested our internal control procedures in order to satisfy the requirements of Section 404(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which requires annual management assessments of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Our independent registered public accounting firm may not be able or willing to issue an unqualified report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. Matters impacting our internal controls may cause us to be unable to report our financial information on a timely basis and thereby subject us to adverse regulatory consequences, including sanctions by the SEC, or
18
violations of applicable stock exchange listing rules. There could also be a negative reaction in the financial markets due to a loss of investor confidence in us and the reliability of our financial statements. Confidence in the reliability of our financial statements is also likely to suffer if we identify a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. This could materially adversely affect us and lead to a decline in the market price of our shares.
Risks Relating to Our Organizational Structure
PJT Partners Inc.’s only material asset is its interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time, and it is accordingly dependent upon distributions from PJT Partners Holdings LP to pay taxes, make payments under the tax receivable agreement or pay dividends.
PJT Partners Inc. is a holding company and has no material assets other than its ownership of Partnership Units, and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time as described herein in “Part II. Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Dividend Policy.” PJT Partners Inc. has no independent means of generating revenue. PJT Partners Holdings LP makes distributions to holders of its Partnership Units in an amount sufficient to cover all applicable taxes at assumed tax rates, payments under the tax receivable agreement and dividends, if any, declared by it. Deterioration in the financial condition, earnings or cash flow of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its subsidiaries for any reason could limit or impair their ability to pay such distributions. Additionally, to the extent that PJT Partners Inc. needs funds, and PJT Partners Holdings LP is restricted from making such distributions under applicable law or regulation or under the terms of our financing arrangements, or is otherwise unable to provide such funds, it could materially adversely affect our liquidity and financial condition.
Payments of dividends, if any, will be at the discretion of our board of directors after taking into account various factors, including our financial condition, earnings, cash flows, capital requirements, cash settlement of Partnership Unit exchanges, previous and anticipated amounts of dividend payments and share repurchases, level of indebtedness, statutory and contractual restrictions applicable to the payment of dividends, general economic, market and industry conditions and other considerations that our board of directors deem relevant from time to time. The credit agreement governing our revolving credit facility contains, and any financing arrangement that we enter into in the future may include, restrictive covenants that limit our ability to pay dividends. In addition, PJT Partners Holdings LP is generally prohibited under Delaware law from making a distribution to a partner to the extent that, at the time of the distribution, after giving effect to the distribution, liabilities of PJT Partners Holdings LP (with certain exceptions) exceed the fair value of its assets. Subsidiaries of PJT Partners Holdings LP are generally subject to similar legal limitations on their ability to make distributions to PJT Partners Holdings LP. See “—While we currently intend to pay a quarterly cash dividend to our stockholders, there can be no assurance that we will continue to declare cash dividends.”
A significant portion of the voting power in PJT Partners Inc. is controlled by holders of our Class B common stock, whose interests may differ from those of our public stockholders that hold Class A common stock.
The shares of Class B common stock have no economic rights but entitle the holder, without regard to the number of shares of Class B common stock held, to a number of votes that is equal to the aggregate number of vested and unvested Partnership Units and LTIP Units in PJT Partners Holdings LP held by such holder on all matters presented to stockholders of PJT Partners Inc. other than director elections and removals. With respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc., shares of Class B common stock initially entitle holders to only one vote per share, representing significantly less than one percent of the voting power entitled to vote thereon. However, the voting power of Class B common stock with respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc. may be increased to up to the number of votes to which a holder is then entitled on all other matters presented to stockholders. At December 31, 2019, our executive officers and directors held and/or controlled (including by way of the proxy granted to Mr. Taubman by certain executive officers of Blackstone in connection with the spin-off) 2.9% of the voting power of PJT Partners Inc. with regard to the election and removal of directors, and 32.3% of the combined voting power of PJT Partners Inc. with regard to all other matters presented to stockholders of PJT Partners Inc. At December 31, 2019, our Class B common stockholders held significantly less than one percent of the voting power of PJT Partners Inc. with regard to the election and removal of directors, and 45.5% of the combined voting power of PJT Partners Inc., with regard to all other matters presented to stockholders of PJT Partners Inc. As a result, our Class B common stockholders, including Mr. Taubman, have the ability to exercise influence over the outcome of all matters requiring stockholder approval, other than director elections and removals, including those related to equity compensation plans, certain related party transactions, and certain significant issuances of Class A common stock and other significant transactions, such as those involving a change of control or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. This concentration of ownership could deprive our Class A
19
stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their common stock as part of a sale of our company and might ultimately affect the market price of our Class A common stock. Moreover, our Class B common stockholders, including Mr. Taubman, may gain the ability in the future to exercise significant influence over the outcome of director elections and removals as well.
Additionally, as of December 31, 2019, our Class B common stockholders own 40.5% of the Partnership Units. Because they hold all or a portion of their economic ownership interest in our business directly in PJT Partners Holdings LP, rather than through PJT Partners Inc., our Class B common stockholders may have conflicting interests with holders of shares of our Class A common stock. For example, if PJT Partners Holdings LP makes distributions to PJT Partners Inc., the limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP will also be entitled to receive such distributions pro rata in accordance with the percentages of their respective partnership interests in PJT Partners Holdings LP and their preferences as to the timing and amount of any such distributions may differ from those of our public stockholders. Our Class B common stockholders may also have different tax positions from us that could influence their decisions regarding whether and when to dispose of assets, especially in light of the existence of the tax receivable agreement that we entered into in connection with the spin-off, whether and when to incur new indebtedness, and whether and when PJT Partners Inc. should terminate the tax receivable agreement and accelerate its obligations thereunder. In addition, the structuring of future transactions may take into consideration these Partnership Unitholders’ tax or other considerations even where no similar benefit would accrue to us.
PJT Partners Inc. may be required to make payments under a tax receivable agreement for most of the benefits relating to certain tax depreciation or amortization deductions that we may claim as a result of certain increases in tax basis.
Holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) have the right, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, on a quarterly basis (subject to the terms of the exchange agreement), to exchange all or part of their Partnership Units for cash or, at our election, for shares of our Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis, subject to customary conversion rate adjustments for splits, unit distributions and reclassifications. Stock-settled exchanges and certain of these cash-settled exchanges are expected to result in increases in the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of PJT Partners Holdings LP. These increases in tax basis may increase (for tax purposes) depreciation and amortization deductions and therefore reduce the amount of tax that PJT Partners Inc. would otherwise be required to pay in the future, although the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) may challenge all or part of that tax basis increase, and a court could sustain such a challenge.
We entered into a tax receivable agreement with the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) that provides for the payment by PJT Partners Inc. to exchanging holders of Partnership Units of 85% of the benefits, if any, that PJT Partners Inc. is deemed to realize as a result of these increases in tax basis and of certain other tax benefits related to entering into the tax receivable agreement, including tax benefits attributable to payments under the tax receivable agreement.
This payment obligation is an obligation of PJT Partners Inc. and not of PJT Partners Holdings LP. While the actual increase in tax basis, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under the tax receivable agreement, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of exchanges, the price of shares of our Class A common stock at the time of the exchange, the extent to which such exchanges are taxable and the amount and timing of our income, we expect that as a result of the size of the transfers and increases in the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of PJT Partners Holdings LP, the payments that PJT Partners Inc. may make under the tax receivable agreement will be substantial. The payments under the tax receivable agreement are not conditioned upon continued ownership of us by the holders of Partnership Units.
In certain cases, such as upon a change in control, payments under the tax receivable agreement may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits PJT Partners Inc. realizes in respect of the tax attributes subject to the tax receivable agreement.
The tax receivable agreement provides that upon certain changes of control, or if, at any time, PJT Partners Inc. elects an early termination of the tax receivable agreement, PJT Partners Inc.’s obligations under the tax receivable agreement (with respect to all Partnership Units whether or not previously exchanged) would be calculated by reference to the value of all future payments that holders of Partnership Units would have been entitled to receive under the tax receivable agreement using certain valuation assumptions, including that PJT Partners Inc. will have sufficient taxable income to fully utilize the deductions arising from the increased tax deductions and tax basis and other benefits related to entering into the tax receivable agreement and, in the case of an early termination election, that any Partnership Units that have not been exchanged are deemed exchanged for the market value of the
20
shares of Class A common stock at the time of termination. In addition, if PJT Partners Inc. elects an early termination of the tax receivable agreement, holders of Partnership Units will generally not reimburse us for any payments previously made under the tax receivable agreement if such tax basis increase is successfully challenged by the IRS. PJT Partners Inc.’s ability to achieve benefits from any tax basis increase, and the payments to be made under the tax receivable agreement, will depend upon a number of factors, including the timing and amount of our future income. As a result, even in the absence of a change of control or an election to terminate the tax receivable agreement, payments under the tax receivable agreement could be in excess of PJT Partners Inc.’s actual cash tax savings.
There may be a material negative effect on our liquidity if the payments under the tax receivable agreement exceed the actual cash tax savings that PJT Partners Inc. realizes in respect of the tax attributes subject to the tax receivable agreement and/or if distributions to PJT Partners Inc. by PJT Partners Holdings LP are not sufficient to permit PJT Partners Inc. to make payments under the tax receivable agreement after it has paid taxes and other expenses. Based on the market value of a share of Class A common stock of $45.13 and the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) of 2.00% at December 29, 2019, we estimate that if PJT Partners Inc. exercised its termination on December 31, 2019, the aggregate amount of these termination payments would be $140.0 million. The foregoing number is merely an estimate and the actual payments could differ materially. We may need to incur additional indebtedness to finance payments under the tax receivable agreement to the extent our cash resources are insufficient to meet our obligations under the tax receivable agreement as a result of timing discrepancies or otherwise.
We may be responsible for U.S. federal income tax liabilities that relate to the distribution.
The spin-off was conditioned on the receipt of an opinion of tax counsel to the effect that certain transactions in Blackstone’s internal reorganization should qualify as tax-free distributions under Section 355 of the Internal Revenue Code (the “Code”), and a certain transaction in the internal reorganization should qualify as a tax-free reorganization under Section 368 of the Code. Blackstone’s receipt of the opinion of tax counsel satisfied a condition to completion of the spin-off. An opinion of tax counsel is not binding on the IRS. Accordingly, the IRS may reach conclusions with respect to the spin-off that are different from the conclusions reached in the opinion. The opinion is based on certain factual statements and representations, which, if incomplete or untrue in any material respect, could cause the tax consequences of the transactions to be different than those set forth in the opinion.
At the time of the spin-off, Blackstone represented to us that it was not aware of any facts or circumstances that would cause any such factual statements or representations in the opinion of tax counsel to be incomplete or untrue or cause the facts on which the opinion will be based to be materially different from the facts at the time of the spin-off. If, notwithstanding the receipt of the opinion of tax counsel, the IRS were to successfully assert that certain transactions in the internal reorganization were not tax-free distributions under Section 355 of the Code or that a certain transaction in the internal reorganization did not qualify as a tax-free reorganization under Section 368 of the Code, one or both of the Blackstone subsidiaries that distributed their interest in our business (the “Distributing Corporations”) or we would recognize a substantial tax liability.
Even if such transactions in the internal reorganization otherwise qualify as tax-free distributions for U.S. federal income tax purposes, such transactions will be taxable to one or both of the Distributing Corporations (but not to Blackstone common unitholders) pursuant to Section 355(e) of the Code if there are one or more acquisitions (including by reason of issuances) of our stock in excess of specified thresholds, measured by vote or value, or acquisitions of the stock of one or both of the Distributing Corporations representing 50% or more, measured by vote or value, of the then-outstanding stock of us or such Distributing Corporation and the acquisition or acquisitions are deemed to be part of a plan or series of related transactions that include the transactions in the internal reorganization. Any acquisition of any class of our common stock or stock of a Distributing Corporation within two years before or after the distribution (with exceptions, including public trading by less-than-5% shareholders and certain compensatory stock issuances) generally will be presumed to be part of such a plan unless that presumption is rebutted. The resulting tax liability may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We have agreed not to enter into certain transactions that could cause any portion of the spin-off to be taxable to the Distributing Corporations, including under Section 355(e) of the Code. Pursuant to the Tax Matters Agreement, we agreed to indemnify Blackstone for any tax to a Distributing Corporation resulting from certain acquisitions of our stock, whether or not Blackstone consented to such actions or we were otherwise permitted to take such action under the Tax Matters Agreement. In addition, if certain transactions in the internal reorganization
21
were taxable or became taxable, then under U.S. Department of the Treasury regulations we would be severally liable for the resulting U.S. federal income tax liability of one of the Distributing Corporations. These obligations may discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of PJT Partners Inc.
Anti-takeover provisions in our organizational documents and Delaware law might discourage or delay acquisition attempts for us that you might consider favorable.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws contain provisions that may make the merger or acquisition of our company more difficult without the approval of our board of directors. Among other things, these provisions:
|
|
• |
authorize the issuance of undesignated preferred stock, the terms of which may be established and the shares of which may be issued without stockholder approval, and which may include super voting, special approval, dividend or other rights or preferences superior to the rights of the holders of Class A common stock; |
|
|
• |
provide that our board of directors will be divided into three classes, with terms of the directors of only one class expiring in any given year; |
|
|
• |
prohibit Class A common stockholders from acting by written consent unless such action is recommended by all directors then in office, but permit Class B common stockholders to act by written consent without requiring any such recommendation; |
|
|
• |
provide that our board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal our bylaws and that our stockholders may only amend our bylaws with the approval of 80% or more of the voting power of all of the outstanding shares of our capital stock entitled to vote; |
|
|
• |
provide that certain provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, including those providing for a classified board of directors, may be amended, altered, repealed or rescinded, in whole or in part, or any provision inconsistent therewith may be adopted, only with the approval of 80% or more of the voting power of all of the outstanding shares of our capital stock entitled to vote; and |
|
|
• |
establish advance notice procedures and minimum stock ownership requirements for stockholder nominations for elections to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings, as well as provide for director qualification requirements. |
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation requires, to the fullest extent permitted by law, that (i) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf; (ii) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers or stockholders to us or our stockholders; (iii) any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”) or as to which the DGCL confers jurisdiction in the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware; or (iv) any action asserting a claim governed by the internal affairs doctrine will have to be brought only in the Court of Chancery in the State of Delaware, unless we agree otherwise. Although we believe this provision benefits us by providing increased consistency in the application of Delaware law in the types of lawsuits to which it applies, the provision may have the effect of discouraging lawsuits against our directors, officers and stockholders.
Certain provisions of the limited partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP may also prevent, delay or make more difficult, a transaction or a change in control that might involve a premium price for holders of our Class A common stock or otherwise be in their best interests. These provisions include, among others:
|
|
• |
rights of limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP, subject to certain exceptions and qualifications, to approve certain change of control transactions involving us; and |
|
|
• |
following the occurrence of a “Board Change of Control,” rights of limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP to consent to certain corporate actions and transactions. |
Further, as a Delaware corporation, we are also subject to provisions of Delaware law, which may impair a takeover attempt that our stockholders may find beneficial. These anti-takeover provisions and other provisions under Delaware law could discourage, delay or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our company, including actions that our stockholders may deem advantageous, or negatively affect the trading price of our Class A common stock. These provisions could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for you and other stockholders to elect directors of your choosing and to cause us to take other corporate actions you desire.
22
See “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions—PJT Partners Holdings LP Amended and Restated Limited Partnership Agreement” in our definitive proxy statement filed in connection with our 2019 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (our “2019 Proxy Statement”).
Risks Relating to Our Class A Common Stock
You may be diluted by the future issuance of additional Class A common stock by PJT Partners Inc. and the future issuance of additional partnership units by PJT Partners Holdings LP, in each case in connection with our incentive plans, acquisitions or otherwise.
As of December 31, 2019, we have 2,974,378,549 shares of Class A common stock authorized but unissued, including 15,757,507 shares of Class A common stock that may be issued upon exchange of Partnership Units. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes us to issue these shares of Class A common stock and options, rights, warrants and appreciation rights relating to Class A common stock for the consideration and on the terms and conditions established by our board of directors in its sole discretion, whether in connection with acquisitions or otherwise. Similarly, the limited partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP permits PJT Partners Holdings LP to issue an unlimited number of additional partnership interests of PJT Partners Holdings LP with designations, preferences, rights, powers and duties that are different from, and may be senior to, those applicable to the Partnership Units, and which may be exchangeable for shares of our Class A common stock. We have reserved 17,000,000 shares for issuance of new awards under our Amended and Restated 2015 Omnibus Incentive Plan. In addition, as described under “Report of the Compensation Committee—Narrative Disclosure Relating to the Summary Compensation Table, Grants of Plan-Based Awards Table, Outstanding Equity Awards at 2018 Fiscal Year-End Table, and 2018 Option Exercises and Stock Vested Table—Partner Agreements—Merger and Spin-off Transaction Equity Grants—Founder Earn-Out Units” in our 2019 Proxy Statement, Mr. Taubman and the other partners and employees of the Company received Earn-Out Units in PJT Partners Holdings LP that are subject to both service and market conditions. Any Class A common stock that we issue, including under our Amended and Restated 2015 Omnibus Incentive Plan or other equity incentive plans that we may adopt in the future, would dilute your percentage ownership of PJT Partners Inc.
The market price of our Class A common stock may decline due to the large number of shares of Class A common stock eligible for exchange and future sale.
The market price of shares of our Class A common stock could decline as a result of sales of a large number of shares of Class A common stock in the market or the perception that such sales could occur. These sales, or the possibility that these sales may occur, also might make it more difficult for us to sell shares of Class A common stock in the future at a time and at a price that we deem appropriate.
In addition, we and the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) have entered into an exchange agreement under which they (or certain permitted transferees) have the right, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, on a quarterly basis, to exchange all or part of their Partnership Units for cash or, at our election, for shares of our Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis, subject to customary conversion rate adjustments for splits, unit distributions and reclassifications. Further, pursuant to the terms of the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, we may also require holders of Partnership Units who are not Service Providers (as defined in the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP) to exchange such Partnership Units.
Depending on our liquidity and capital resources, market conditions, the timing and concentration of exchange requests and other considerations, we may choose to fund cash-settled exchanges of Partnership Units with available cash, borrowings or new issuances of Class A common stock or to settle exchanges by issuing Class A common stock to the exchanging Partnership Unitholder. Issuing significant numbers of shares of our Class A common stock upon exchange of Partnership Units could adversely affect the tax consequences to Blackstone of the distribution. Accordingly, while we retain the right under the Exchange Agreement to elect to settle exchanges in cash or in shares of our Class A common stock in our sole discretion, we currently intend to limit such issuances of Class A common stock in settlement of exchanges of Partnership Units to the extent necessary to preserve the intended tax-free nature of the spin-off and to comply with our obligations under the Tax Matters Agreement. The market price of shares of our Class A common stock could decline as a result of sales of our Class A common stock to fund cash-settled exchanges of Partnership Units, or sales by exchanging holders of Partnership Units of Class A common stock received in stock-settled exchanges or, in each case, the perception that such sales could occur. These sales, or the possibility that these sales may occur, also might make it more difficult for holders of our Class A common stock to sell such stock in the future at a time and at a price that they deem appropriate. See “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions—Exchange Agreement” in our 2019 Proxy Statement.
23
Our decision to return cash to our shareholders through repurchases of our Class A common stock may not prove to be the best use of our capital or result in the effects we anticipated, including a positive return of capital to stockholders.
We have authority from our board of directors to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock in an amount up to $100 million. As of December 31, 2019, the available amount remaining for repurchases under this program was $85.1 million, which we may implement through open market purchases, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise, after taking into account our results of operations, financial position and capital requirements, general business conditions, legal, tax and regulatory constraints or restrictions, any contractual restrictions (including any restrictions contained in the credit agreement) and other factors we deem relevant. There can be no assurances of the price at which we may be able to repurchase our shares or that we will repurchase the full amount authorized. Furthermore, there can be no assurance that any past or future repurchases will have a positive impact on our stock price or that the share repurchase plan provides the best use of our capital because the value of our common stock may decline significantly below the levels at which we repurchased shares of common stock.
If we were to cease or were unable to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock, or choose to allocate available capital to the repayment of borrowings, payment of dividends or other corporate purposes, the number of shares outstanding may increase over time, diluting the ownership of our existing stockholders.
Our decision to repurchase shares of our Class A common stock will reduce our public float, which could cause our share price to decline.
The share repurchase plan will reduce our “public float,” (the number of shares of our Class A common stock that are owned by non-affiliated stockholders and available for trading in the securities markets), which may reduce the volume of trading in our shares and result in reduced liquidity and cause fluctuations in the trading price of our common stock unrelated to our performance. Furthermore, certain institutional holders of shares of our Class A common stock (including index funds) may require a minimum market capitalization of each of their holdings in excess of our market capitalization and therefore be required to dispose of shares of our Class A common stock, which may cause the value of our Class A common stock to decline. There can be no assurance that this reduction in our public float will not result in a lower share price or reduced liquidity in the trading market for shares of our Class A common stock during and upon completion of our share repurchase plan.
While we currently intend to pay a quarterly cash dividend to our stockholders, there can be no assurance that we will continue to declare cash dividends.
Although we currently intend to pay a quarterly cash dividend to our stockholders, we have no obligation to do so, and our dividend policy may change at any time. Whether we continue and the amount and timing of any dividends are subject to capital availability and periodic determinations by our board of directors that cash dividends are in the best interest of our stockholders and are in compliance with all respective laws and agreements of the Company applicable to the declaration and payment of cash dividends. The reduction in or elimination of our dividend payments could have a negative effect on our stock price.
The market price of our Class A common stock may be volatile, which could cause the value of our Class A common stock to decline.
Securities markets worldwide experience significant price and volume fluctuations. This market volatility, as well as general economic, market or political conditions, could reduce the market price of our Class A common stock in spite of our operating performance. In addition, our operating results could be below the expectations of public market analysts and investors, and in response, the market price of our Class A common stock could decrease significantly.
If securities analysts do not publish research or reports about our business or if they downgrade our Company or our sector, the price of our Class A common stock could decline.
The trading market for our Class A common stock depends in part on the research and reports that industry or financial analysts publish about us or our business. We do not control the research decisions made by these analysts. Furthermore, if one or more of the analysts who do cover us downgrades our Company or our industry, or the stock of any of our competitors, the price of our Class A common stock could decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases coverage of our Company, we could lose visibility in the market, which in turn could cause the price of our Class A common stock to decline.
24
|
ITEM 1B. |
UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
|
ITEM 2. |
PROPERTIES |
Our principal executive offices are located in leased office space at 280 Park Avenue, New York, New York 10017. We currently lease the space for our offices in Boston, Chicago, Hong Kong, London, Madrid and San Francisco. We do not own any real property.
|
ITEM 3. |
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
From time to time, the Company and its affiliates may be subject to legal proceedings and claims in the ordinary course of business. In addition, government agencies and self-regulatory organizations in countries in which we conduct business conduct periodic examinations and may initiate administrative proceedings regarding the Company’s and its affiliates’ business, including, among other matters, accounting and operational matters, that can result in censure, fine, the issuance of cease-and-desist orders or the suspension or expulsion of a broker-dealer, or its directors, officers or employees. It is our policy to cooperate fully with such governmental requests, examinations and administrative proceedings. In view of the inherent difficulty of determining whether any loss in connection with any such matters is probable and whether the amount of such loss can be reasonably estimated, particularly in cases where claimants seek substantial or indeterminate damages or where investigations and proceedings are in the early stages, we cannot estimate the amount of such loss or range of loss, if any, related to such matters, how or if such matters will be resolved, when they will ultimately be resolved, or what the eventual settlement, fine, penalty or other relief, if any, might be. Subject to the foregoing, we believe, based on current knowledge and after consultation with counsel, that we are not currently party to any material pending proceedings, individually or in the aggregate, the resolution of which would have a material effect on the Company.
In June 2017, an action was filed in New York state court against defendants PJT Partners Inc., Park Hill Group LLC and Andrew W.W. Caspersen, arising out of the fraudulent conduct of Caspersen. PJT Partners Inc. and Park Hill Group LLC moved to dismiss the complaint on August 24, 2017. On August 13, 2018, the court dismissed all of the claims asserted against PJT Partners Inc. and Park Hill Group LLC, except for the fraud-based apparent authority claim. Plaintiffs and PJT Partners Inc. and Park Hill Group LLC appealed the court’s August 2018 decision. On December 3, 2019, the appellate court dismissed the complaint in its entirety as against PJT Partners Inc. and Park Hill Group LLC. On January 2, 2020, plaintiffs filed a motion with the appellate court seeking reargument or, alternatively, leave to appeal, which we believe is without merit. We will continue to vigorously defend this action.
On June 16, 2009, Plaintiffs Frank Foy and Suzanne Foy, purportedly as qui tam plaintiffs on behalf of the State of New Mexico, filed a case in New Mexico state court against Park Hill Group LLC and one of its officers, as well as The Blackstone Group L.P. (together, “Park Hill Defendants”), in addition to dozens of other named and unnamed defendants, alleging violations of New Mexico’s Fraud Against Taxpayers Act (“FATA”) in an action styled Foy v. Austin Capital Management, Ltd., et al., Case No. D-101-CV-2009-01189 (N.M. Dist. Ct.). The complaint alleged, among other things, that the New Mexico Educational Retirement Board and the New Mexico State Investment Council made investments that were influenced by kickbacks and other inducements. In the complaint, the Park Hill Defendants were grouped together with other defendants who were all alleged generically to have conspired to defraud the State of New Mexico. On November 30, 2015, after several years of motion practice, including an earlier decision by the New Mexico Supreme Court to consolidate this case with another case by the same plaintiffs (in which the Park Hill Defendants were not parties), the New Mexico Attorney General filed a motion on behalf of the State of New Mexico seeking wholesale dismissal of these proceedings. On June 6, 2017, the court granted the motion to dismiss brought on behalf of the State of New Mexico, the effect of which dismissed the action against the Park Hill Defendants. Plaintiffs have filed an appeal of the court’s decision.
|
ITEM 4. |
MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
None.
25
PART II.
|
ITEM 5. |
MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our Class A common stock is traded on the NYSE under the symbol “PJT.” There is no publicly traded market for our Class B common stock, which is held by the limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP.
As of February 20, 2020, there were 128 holders of record of our Class A common stock. This does not include the number of holders that hold Class A common stock in “street name” through banks or broker-dealers.
Dividend Policy
The Company currently plans to regularly pay quarterly dividends. The declaration and payment of any future dividends will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors. Our board of directors will take into account general economic and business conditions; our financial condition and operating results; our available cash and current anticipated cash needs; capital requirements; contractual, legal, tax and regulatory restrictions and implications on the payment of dividends by us to our stockholders; and such other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant.
PJT Partners Inc. is a holding company and has no material assets other than its controlling equity interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP, and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time as described below. In accordance with the partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, we intend to cause PJT Partners Holdings LP to make pro rata cash distributions, to the extent of available cash, to the holders of the partnership interests in PJT Partners Holdings LP, including PJT Partners Inc., in amounts equal to 50% of the taxable income allocated to such holders for purposes of funding their tax obligations in respect of the income of PJT Partners Holdings LP that is allocated to them, which we refer to as “tax distributions.” In certain periods, we expect that PJT Partners Inc. will receive tax distributions in excess of the amount required to cover cash dividends, if any, declared by us, and taxes and payments under the tax receivable agreement payable by PJT Partners Inc. To the extent the amount of accumulated cash at PJT Partners Inc. becomes material in future periods, we anticipate that our board of directors will consider appropriate actions, which may include special cash dividends to holders of our Class A common stock. Holders of Partnership Units will not be precluded from effecting exchanges under our exchange agreement prior to any such actions being taken. Because PJT Partners Inc. must pay taxes and make payments under the tax receivable agreement, amounts ultimately distributed as dividends to holders of our Class A common stock are expected to be less than the amounts distributed by PJT Partners Holdings LP to its limited partners on a per unit basis.
Our revolving credit facility and term loan include, and financing arrangements that we may enter into in the future may include, restrictive covenants that limit our ability to pay dividends or repurchase our capital stock. In addition, PJT Partners Holdings LP is generally prohibited under Delaware law from making a distribution to a partner to the extent that, at the time of the distribution, after giving effect to the distribution, liabilities of PJT Partners Holdings LP (with certain exceptions) exceed the fair value of its assets. Subsidiaries of PJT Partners Holdings LP are generally subject to similar legal limitations on their ability to make distributions to PJT Partners Holdings LP.
26
Stock Performance
The following performance graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act except to the extent we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing. Our stock price performance shown in the graph below is not indicative of future stock price performance.
The stock performance graph below compares the performance of an investment in our Class A common stock from October 1, 2015 (the first day our common stock began “regular-way” trading on the NYSE) through December 31, 2019, with that of the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Financials Index. Prior to October 1, 2015, there was no public market for our Class A common stock. Our Class A common stock traded on a “when-issued” basis prior to October 1, 2015. The graph assumes $100 was invested in our Class A common stock on October 1, 2015, and in the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Financials Index on September 30, 2015. It also assumes that the dividends were reinvested on the date of payment without payment of commissions. The performance shown in the graph represents past performance and should not be considered an indication of future performance.
27
Share Repurchases in the Fourth Quarter of 2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Number of |
|
|
|
Approximate Dollar |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of Shares |
|
|
|
Value of Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchased as |
|
|
|
that May Yet Be |
|
|
|
|
Total Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part of Publicly |
|
|
|
Purchased Under |
||
|
|
|
of Shares |
|
|
Average Price |
|
|
Announced Plans |
|
|
|
the Plans or |
|||
|
|
|
Repurchased |
|
|
Paid Per Share |
|
|
or Programs (a) |
|
|
|
Programs (a) |
|||
|
October 1 to October 31 |
|
|
111,023 |
|
|
$ |
39.10 |
|
|
|
111,023 |
|
|
$ |
85.1 million |
|
November 1 to November 30 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
85.1 million |
|
December 1 to December 31 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
85.1 million |
|
Total |
|
|
111,023 |
|
|
$ |
39.10 |
|
|
|
111,023 |
|
|
$ |
85.1 million |
|
(a) |
On April 24, 2019, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock in an amount up to $100 million. As of December 31, 2019, the Company’s remaining repurchase authorization was $85.1 million. Under the repurchase program, shares of the Company’s Class A common stock may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The timing and the actual number of shares repurchased depend on a variety of factors, including legal requirements, price and economic and market conditions. The repurchase program may be suspended or discontinued at any time and does not have a specified expiration date. |
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
In connection with the issuance during the fourth quarter of 2019 of LTIP Units in PJT Partners Holdings LP to certain personnel and the transfer of Partnership Units in PJT Partners Holdings LP, PJT Partners Inc. issued three corresponding shares of its Class B common stock, par value $0.01 per share, to these limited partners. Shares of Class B common stock have no economic rights but entitle the holder, without regard to the number of shares of Class B common stock held, to a number of votes that is equal to the aggregate number of vested and unvested Partnership Units and LTIP Units in PJT Partners Holdings LP held by such holder on all matters presented to stockholders of PJT Partners Inc. other than director elections and removals. With respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc., shares of Class B common stock will initially entitle holders to only one vote per share. However, the voting power of Class B common stock with respect to the election and removal of directors of PJT Partners Inc. may be increased to up to the number of votes to which a holder is then entitled on all other matters presented to stockholders. The issuance of shares of Class B common stock was not registered under the Securities Act of 1933 because such shares were not issued in a transaction involving the offer or sale of securities.
|
ITEM 6. |
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2015 reflect the combined results of Blackstone’s operations for the period from January 1, 2015 to October 1, 2015 and the consolidated results of PJT Partners Inc., as reorganized and separated from Blackstone, through December 31, 2015. The results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, 2017 and 2016 reflect the results as a stand-alone, independent publicly traded company.
The statement of operations data for each of the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 and the statement of financial condition data as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 set forth below are derived from the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 and the statement of financial condition data as of December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 are derived from the Company’s audited financial statements that are not included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Company’s financial data are not indicative of our future performance and, for the years ended prior to December 31, 2016, do not necessarily reflect what our financial condition and results of operations would have been had we been operating as an independent, publicly traded company, including changes that occurred in our operations and capitalization as a result of the spin-off from Blackstone.
28
The selected consolidated and combined financial data should be read in conjunction with “—Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(Dollars in Thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Statement of Operations Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advisory Fees |
|
$ |
571,771 |
|
|
$ |
451,553 |
|
|
$ |
386,263 |
|
|
$ |
377,610 |
|
|
$ |
286,014 |
|
|
Placement Fees |
|
|
133,180 |
|
|
|
111,035 |
|
|
|
102,785 |
|
|
|
114,968 |
|
|
|
114,058 |
|
|
Interest Income and Other |
|
|
12,688 |
|
|
|
17,660 |
|
|
|
10,234 |
|
|
|
6,852 |
|
|
|
5,866 |
|
|
Total Revenues |
|
|
717,639 |
|
|
|
580,248 |
|
|
|
499,282 |
|
|
|
499,430 |
|
|
|
405,938 |
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
502,165 |
|
|
|
424,459 |
|
|
|
391,514 |
|
|
|
381,000 |
|
|
|
315,195 |
|
|
Non-Compensation Expenses |
|
|
133,284 |
|
|
|
114,276 |
|
|
|
97,714 |
|
|
|
103,930 |
|
|
|
96,679 |
|
|
Total Expenses |
|
|
635,449 |
|
|
|
538,735 |
|
|
|
489,228 |
|
|
|
484,930 |
|
|
|
411,874 |
|
|
Income (Loss) Before Provision(Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
82,190 |
|
|
|
41,513 |
|
|
|
10,054 |
|
|
|
14,500 |
|
|
|
(5,936 |
) |
|
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
18,403 |
|
|
|
(1,045 |
) |
|
|
38,380 |
|
|
|
9,392 |
|
|
|
239 |
|
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
|
63,787 |
|
|
|
42,558 |
|
|
|
(28,326 |
) |
|
|
5,108 |
|
|
|
(6,175 |
) |
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
34,225 |
|
|
|
15,388 |
|
|
|
4,228 |
|
|
|
8,142 |
|
|
|
(13,751 |
) |
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
29,562 |
|
|
$ |
27,170 |
|
|
$ |
(32,554 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,034 |
) |
|
$ |
7,576 |
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
1.23 |
|
|
$ |
1.23 |
|
|
$ |
(1.73 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.17 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
1.21 |
|
|
$ |
1.16 |
|
|
$ |
(1.73 |
) |
|
$ |
(0.17 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Shares of Class A Common Stock Outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
24,007,138 |
|
|
|
21,879,574 |
|
|
|
18,858,010 |
|
|
|
18,292,717 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
25,014,569 |
|
|
|
24,254,061 |
|
|
|
18,858,010 |
|
|
|
18,292,717 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends Declared Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
$ |
0.20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
October 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
Net Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(24,935 |
) |
|
Net Loss Attributable to Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(13,751 |
) |
|
Net Loss Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(11,184 |
) |
|
Net Loss Per Share of Class A Common Stock — Basic and Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
(0.61 |
) |
|
Weighted-Average Shares of Class A Common Stock Outstanding — Basic and Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
18,258,174 |
|
29
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
|
2015 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(Dollars in Thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Statement of Financial Condition Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Assets (a) |
|
$ |
952,777 |
|
|
$ |
671,817 |
|
|
$ |
558,965 |
|
|
$ |
590,476 |
|
|
$ |
467,252 |
|
|
Total Liabilities (b) |
|
$ |
378,260 |
|
|
$ |
184,068 |
|
|
$ |
136,511 |
|
|
$ |
177,060 |
|
|
$ |
125,317 |
|
|
Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests (c) |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
421,976 |
|
|
$ |
309,855 |
|
|
Non-Controlling Interests (c) |
|
$ |
543,127 |
|
|
$ |
514,205 |
|
|
$ |
586,515 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Total Equity (Deficit) (c) |
|
$ |
574,517 |
|
|
$ |
487,749 |
|
|
$ |
422,454 |
|
|
$ |
(8,560 |
) |
|
$ |
32,080 |
|
|
(a) |
Total Assets increased at December 31, 2019 primarily due to operating lease right-of-use assets recorded as a result of new lease accounting guidance adopted as of January 1, 2019. Total Assets increased at December 31, 2018 primarily due to goodwill recorded related to the acquisition of CamberView. Total Assets decreased at December 31, 2017 primarily due to decreases in Accounts Receivable, Net and Deferred Tax Asset, Net being partially offset by an increase in investments in Treasury securities. The decrease in Deferred Tax Asset, Net was primarily related to the remeasurement of deferred tax assets due to the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. Total Assets increased at December 31, 2016 primarily due to increases in Cash and Cash Equivalents generated from operating activities during the year. |
|
(b) |
Total Liabilities increased at December 31, 2019 primarily due to operating lease liabilities recorded as a result of new lease accounting guidance adopted as of January 1, 2019. Total Liabilities increased at December 31, 2018 primarily due to a term loan entered into in connection with the acquisition of CamberView. Total Liabilities decreased at December 31, 2017 primarily related to a decrease in Accrued Compensation and Benefits. Total Liabilities increased at December 31, 2016 primarily related to an increase in Accrued Compensation and Benefits, partially offset by a decrease in Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities. |
|
(c) |
These amounts reflected the allocation of Net Income (Loss) and the adjustment to measure the Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests at their current redemption value at each reporting date. The value of these interests was reclassified to Non-Controlling Interests at their redemption value as of October 1, 2017. |
On January 1, 2019, the Company adopted new guidance from the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) regarding leases using the transition method that allows such guidance to be applied initially at the adoption date without restating comparative periods. The guidance requires lessees to recognize, on the balance sheet, assets and liabilities for the rights and obligations created by leases. For additional detail, see Note 2. “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On January 1, 2018, the Company adopted amended guidance from the FASB with respect to revenue from contracts with customers using a modified retrospective approach. The Company recognized the cumulative effect of initially applying the new revenue guidance as an adjustment to the opening balance of Accumulated Deficit. The comparative information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods. On an ongoing basis, the effect of the change in timing of revenue and expense recognition could be material to any given reporting period.
30
|
ITEM 7. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with PJT Partners Inc.’s Consolidated Financial Statements and the related notes included in this Annual Report on Form 10‑K.
Our Business
PJT Partners is a premier global advisory-focused investment bank. Our team of senior professionals delivers a wide array of strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and placement services to corporations, financial sponsors, institutional investors and governments around the world. We offer a unique portfolio of advisory services designed to help our clients achieve their strategic objectives. We also provide, through PJT Park Hill, private fund advisory and fundraising services for alternative investment managers, including private equity funds, real estate funds and hedge funds.
We have world-class franchises in each of the areas in which we compete.
|
|
• |
Our Strategic Advisory business offers a broad range of financial advisory and transaction execution capability, including mergers and acquisitions (“M&A”), joint ventures, minority investments, asset swaps, divestitures, takeover defenses, corporate finance advisory, private placements and distressed sales. Through PJT Camberview, our industry leading shareholder advisory business, we provide investor-led advice to public company boards and management teams around the globe on shareholder engagement, strategic investor relations, activism and contested situations, sustainability and complex corporate governance matters. |
|
|
• |
Our Restructuring and Special Situations business is one of the world’s leading advisors in restructurings and recapitalizations, both in and out of court, around the globe. With expertise in highly complex capital structure challenges, we advise companies, creditors and financial sponsors on liability management and related capital raise transactions including exchanges, recapitalizations, reorganizations, debt repurchases and distressed mergers and acquisitions. |
|
|
• |
PJT Park Hill, our leading global alternative asset advisory and fundraising business, provides private fund advisory and fundraising services for a diverse range of investment strategies. Moreover, PJT Park Hill is the only group among its peers with top-tier dedicated private equity, hedge fund, real estate and secondary advisory groups. |
Business Environment
Economic and global financial conditions can materially affect our operational and financial performance.
M&A is a cyclical business that is impacted by macroeconomic conditions. According to Refinitiv, worldwide M&A announced volumes during 2019 were down 3% compared with 2018, but still the fourth strongest year since records began in 1980.1 We remain in a very constructive environment for M&A by historical standards. We expect corporate boards and management teams to continue to use M&A as a key strategic tool.
Global restructuring activity for 2019 was strong despite continued low default rates in a benign credit environment. Notwithstanding, a balanced mix of in-court and out-of-court transactions for companies, creditors and financial sponsors has driven increased demand for restructuring and liability management services across a broad range of industries including technology, media and telecommunications; oil and gas; pharmaceuticals; and consumer products. PJT Partners maintained strong market share and was ranked #1 in global completed restructurings.2
As investors seek to enhance returns, diversification and portfolio yield, alternative assets continue to be in demand by institutional investors on a global basis. Within certain asset classes, we are seeing increased interest in narrow and niche strategies as well as customized solutions such as joint ventures, separate accounts and direct investment opportunities.
|
|
1 |
Source: Refinitiv. Global Mergers & Acquisitions Review for Full Year 2019 as of December 31, 2019. |
|
2 |
Source: Refinitiv. League Table ranking extracted from SDC Platinum as of February 11, 2020. |
31
On June 23, 2016, the United Kingdom (“U.K.”) voted to leave the European Union (“E.U.”), commonly referred to as “Brexit,” and on March 29, 2017, the U.K. began the process to withdraw from the E.U. The U.K. formally left the E.U. on January 31, 2020 and has immediately entered into a transition period, which is expected to continue until December 31, 2020. The full impact of Brexit remains uncertain and the political climate in Europe continues to take shape. During this period, the future terms of the U.K.’s relationship with the E.U. will be determined. We expect that circumstances relating to Brexit will impact the Company’s organization and/or operations and we are taking preparatory steps accordingly.
Key Financial Measures
Revenues
Substantially all of our revenues are derived from Advisory Fees and Placement Fees. This revenue is primarily a function of the number of active engagements we have, the size of each of those engagements and the fees we charge for our services.
Advisory Fees – Our strategic advisory services include a broad range of financial advisory and transaction execution services relating to acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, minority investments, asset swaps, divestitures, takeover defenses, corporate finance advisory, shareholder advisory and distressed sales. Our restructuring and special situations services include providing advice to corporations and creditors in recapitalizations and restructurings around the world, with particular expertise in large, complex and high-profile deals. In conjunction with providing such restructuring advice, we may also assist with raising various forms of financing, including debt and equity. Our secondary advisory services provided by PJT Park Hill include providing solutions to investing clients seeking portfolio liquidity, unfunded commitment relief and investments in secondary markets. Advisory Fees typically consist of retainer and transaction-based fee arrangements. The amount and timing of the fees paid vary by the type of engagement. The majority of our Advisory Fees recognized are dependent on the successful completion of a transaction.
A transaction can fail to be completed for many reasons, including failure of parties to agree upon final terms, to secure necessary board or shareholder approvals, to secure necessary financing or to achieve necessary regulatory approvals. In the case of bankruptcy engagements, fees are subject to approval of the court.
Placement Fees – Our fundraising services are provided within PJT Park Hill and primarily serve private equity, real estate and hedge funds. Our team advises on all aspects of the fundraising process including competitive positioning and market assessment, marketing materials and related documentation and partnership terms and conditions most prevalent in the current environment. We also provide private placement fundraising services to our corporate clients and earn placement fees based on successful completion of the transaction.
Fund placement fees earned for services provided to alternative asset managers are typically recognized upon acceptance by a fund of capital or capital commitments (referred to as a “closing”), in accordance with terms set forth in individual agreements. For commitment based fees, revenue is recognized over time as commitments are accepted. Fees for such closed-end fund arrangements are generally paid in installments over three or four years and interest is charged to the outstanding balance at an agreed upon rate (typically the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) plus a market-based margin). For funds with multiple closings, the constraint on variable consideration is lifted upon each closing. For open-end fund structures, placement fees are typically calculated as a percentage of a placed investor’s month-end net asset value. Typically, we earn fees for such open-end fund structures over a 48 month period. For these arrangements, revenue is recognized over time as the constraint over variable consideration is lifted.
We may receive non-refundable up-front fees in our contracts with customers, which are recorded as revenues in the period over which services are estimated to be provided.
Interest Income and Other – Interest Income and Other represents interest typically earned on Cash and Cash Equivalents, investments in Treasury securities and outstanding placement fees receivable; miscellaneous income; foreign exchange gains and losses arising on transactions denominated in currencies other than U.S. dollars; sublease income; and the amount of expense reimbursement invoiced to clients related to out-of-pocket expenses. Interest on placement fees receivable is earned from the time revenue is recognized and is calculated based upon LIBOR plus an additional percentage as mutually agreed upon with the receivable counterparty. Interest receivable is included in Accounts Receivable, Net in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
32
Expenses
Compensation and Benefits – Compensation and Benefits expense includes salaries, cash bonuses, benefits, employer taxes and equity-based compensation associated with the grants of equity-based awards to partners and employees. Changes in this expense are driven by fluctuations in the number of employees, business performance, compensation adjustments in relation to market movements, changes in rates for employer taxes and other cost increases affecting benefit plans. In addition, this expense is affected by the composition of our work force. The expense associated with our bonus and equity plans can also have a significant impact on this expense category and may vary from year to year.
We maintain compensation programs, including salaries, annual incentive compensation (that may include components of cash, restricted cash and/or equity-based awards) and benefits programs. We manage compensation to estimates of competitive levels based on market conditions and performance. Our level of compensation reflects our plan to maintain competitive compensation levels to retain key personnel and it reflects the impact of newly-hired senior professionals, including related grants of equity awards that are generally valued at their grant date fair value.
Increasing the number of high-caliber, experienced senior level employees is critical to our growth efforts. In our advisory businesses, these hires generally do not begin to generate significant revenue in the year they are hired.
Our remaining expenses are the other costs typical to operating our business, which generally consist of:
|
|
• |
Occupancy and Related – consisting primarily of costs related to leased property, including rent, maintenance, real estate taxes, utilities and other related costs. Our company headquarters are located in New York, New York, and we maintain additional offices in the U.S. and throughout the world; |
|
|
• |
Travel and Related – consisting of costs for our partners and employees to render services where our clients are located; |
|
|
• |
Professional Fees – consisting primarily of consulting, audit and tax, recruiting and legal and other professional services; |
|
|
• |
Communications and Information Services – consisting primarily of costs for our technology infrastructure and telecommunications costs; |
|
|
• |
Depreciation and Amortization – consisting of depreciation and amortization on our furniture, equipment, leasehold improvements and intangible assets; and |
|
|
• |
Other Expenses – consisting primarily of bad debt, regulatory fees, insurance, fees paid for access to external market data, advertising, other general operating expenses and transaction-related payable to The Blackstone Group Inc. (“Blackstone”). |
Income Taxes – PJT Partners Inc. is a corporation subject to U.S. federal, state and local income taxes in jurisdictions where it does business. The Company’s businesses generally operate as partnerships for U.S. federal and state purposes and as corporate entities in non-U.S. jurisdictions. In the U.S. federal and state jurisdictions, taxes related to income earned by these entities generally represent obligations of the individual members and partners.
The operating entities have generally been subject to New York City Unincorporated Business Tax and to entity-level income taxes imposed by non-U.S. jurisdictions, as applicable. These taxes have been reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
PJT Partners Inc. is subject to U.S. corporate federal, state and local income tax on its allocable share of results of operations from the operating partnership (PJT Partners Holdings LP).
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act was signed into law on December 22, 2017, which lowered the U.S. corporate income tax rate to 21% as of January 1, 2018.
Non-Controlling Interests
PJT Partners Inc. is a holding company and its only material asset is its controlling equity interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP, and certain cash and cash equivalents it may hold from time to time. As the sole general partner of PJT Partners Holdings LP, PJT Partners Inc. operates and controls all of the business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries.
33
Prior to October 1, 2017, the ownership interests of holders of common units of partnership interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP (“Partnership Units”) (other than PJT Partners Inc.) were considered redeemable non-controlling interests. On October 1, 2017, certain of the restrictive covenants entered into in connection with the spin-off expired. Previously, the ability to settle exchanges of Partnership Units in shares of the Company’s Class A common stock was not entirely within the Company’s control. Consequently, the value of these interests was reclassified from Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests to Non-Controlling Interests at their redemption value as of October 1, 2017. The portion of net income (loss) attributable to the non-controlling interests is presented separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Consolidated Results of Operations
The following table sets forth our consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
2019 vs. 2018 |
|
|
2018 vs. 2017 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|
$ |
|
|
% |
|
|
$ |
|
|
% |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(Dollars in Thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advisory Fees |
|
$ |
571,771 |
|
|
$ |
451,553 |
|
|
$ |
386,263 |
|
|
$ |
120,218 |
|
|
|
27 |
% |
|
$ |
65,290 |
|
|
|
17 |
% |
|
Placement Fees |
|
|
133,180 |
|
|
|
111,035 |
|
|
|
102,785 |
|
|
|
22,145 |
|
|
|
20 |
% |
|
|
8,250 |
|
|
|
8 |
% |
|
Interest Income and Other |
|
|
12,688 |
|
|
|
17,660 |
|
|
|
10,234 |
|
|
|
(4,972 |
) |
|
|
(28 |
%) |
|
|
7,426 |
|
|
|
73 |
% |
|
Total Revenues |
|
|
717,639 |
|
|
|
580,248 |
|
|
|
499,282 |
|
|
|
137,391 |
|
|
|
24 |
% |
|
|
80,966 |
|
|
|
16 |
% |
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
502,165 |
|
|
|
424,459 |
|
|
|
391,514 |
|
|
|
77,706 |
|
|
|
18 |
% |
|
|
32,945 |
|
|
|
8 |
% |
|
Occupancy and Related |
|
|
31,547 |
|
|
|
27,125 |
|
|
|
26,889 |
|
|
|
4,422 |
|
|
|
16 |
% |
|
|
236 |
|
|
|
1 |
% |
|
Travel and Related |
|
|
25,700 |
|
|
|
23,374 |
|
|
|
13,617 |
|
|
|
2,326 |
|
|
|
10 |
% |
|
|
9,757 |
|
|
|
72 |
% |
|
Professional Fees |
|
|
21,779 |
|
|
|
20,631 |
|
|
|
19,276 |
|
|
|
1,148 |
|
|
|
6 |
% |
|
|
1,355 |
|
|
|
7 |
% |
|
Communications and Information Services |
|
|
13,380 |
|
|
|
12,539 |
|
|
|
10,770 |
|
|
|
841 |
|
|
|
7 |
% |
|
|
1,769 |
|
|
|
16 |
% |
|
Depreciation and Amortization |
|
|
14,496 |
|
|
|
9,973 |
|
|
|
8,143 |
|
|
|
4,523 |
|
|
|
45 |
% |
|
|
1,830 |
|
|
|
22 |
% |
|
Other Expenses |
|
|
26,382 |
|
|
|
20,634 |
|
|
|
19,019 |
|
|
|
5,748 |
|
|
|
28 |
% |
|
|
1,615 |
|
|
|
8 |
% |
|
Total Expenses |
|
|
635,449 |
|
|
|
538,735 |
|
|
|
489,228 |
|
|
|
96,714 |
|
|
|
18 |
% |
|
|
49,507 |
|
|
|
10 |
% |
|
Income Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
82,190 |
|
|
|
41,513 |
|
|
|
10,054 |
|
|
|
40,677 |
|
|
|
98 |
% |
|
|
31,459 |
|
|
|
313 |
% |
|
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
18,403 |
|
|
|
(1,045 |
) |
|
|
38,380 |
|
|
|
19,448 |
|
|
N/M |
|
|
|
(39,425 |
) |
|
N/M |
|
||
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
|
63,787 |
|
|
|
42,558 |
|
|
|
(28,326 |
) |
|
|
21,229 |
|
|
|
50 |
% |
|
|
70,884 |
|
|
N/M |
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
34,225 |
|
|
|
15,388 |
|
|
|
4,228 |
|
|
|
18,837 |
|
|
|
122 |
% |
|
|
11,160 |
|
|
|
264 |
% |
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
29,562 |
|
|
$ |
27,170 |
|
|
$ |
(32,554 |
) |
|
$ |
2,392 |
|
|
|
9 |
% |
|
$ |
59,724 |
|
|
N/M |
|
|
|
N/M |
Not meaningful. |
Year Ended December 31, 2019 versus Year Ended December 31, 2018
Revenues
Total Revenues were $717.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared with $580.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, an increase of 24%. The change in Total Revenues was primarily driven by increases of $120.2 million in Advisory Fees and $22.1 million in Placement Fees, and partially offset by a decrease of $5.0 million in Interest Income and Other. The increase in Advisory Fees was primarily driven by significant
34
growth in our strategic advisory business. The increase in Placement Fees was driven by growth in corporate private placement activity and increased fundraising activity for alternative asset managers. The decrease in Interest Income and Other was primarily driven by realized and unrealized foreign currency losses.
The following table provides revenue statistics for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Advisory Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Clients |
|
|
287 |
|
|
|
274 |
|
|
|
153 |
|
|
Number of Fee-Paying Clients with $1 Million or More |
|
|
104 |
|
|
|
107 |
|
|
|
88 |
|
|
Number of Fee-Paying Clients Representing Greater than 10% of Advisory Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Percentage of Such Clients’ Fees of Total Advisory Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Placement Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Clients |
|
|
78 |
|
|
|
81 |
|
|
|
79 |
|
|
Number of Fee-Paying Clients with $1 Million or More |
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
36 |
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
Number of Fee-Paying Clients Representing Greater than 10% of Placement Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Percentage of Such Clients’ Fees of Total Placement Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Expenses
Expenses were $635.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, an increase of $96.7 million compared with $538.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in expenses was primarily attributable to increases in Compensation and Benefits of $77.7 million, Other Expenses of $5.7 million, Depreciation and Amortization of $4.5 million and Occupancy and Related of $4.4 million. The increase in Compensation and Benefits reflected higher revenues during the year ended December 31, 2019 as well as increased headcount. The increase in Other Expenses was due to interest expense associated with the acquisition of CamberView and additional market data and other expenses associated with increased headcount and business activity. The increase in Depreciation and Amortization was due to additional amortization expense related to intangible assets recorded in the acquisition of CamberView during the fourth quarter of 2018. The increase in Occupancy and Related was due to expansion in footprint in our existing locations as well as the assumption of leases in connection with the CamberView acquisition. The increase in Travel and Related was driven by increased headcount and business activity.
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes
The Company’s Provision for Taxes for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $18.4 million and Benefit for Taxes for the year ended December 31, 2018 was $1.0 million. This resulted in an effective tax rate of 22.4% and ‑2.5%, respectively, based on our Income Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes of $82.2 million and $41.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. While the Company benefited in 2019 from the tax impact relating to the delivery of vested shares at a value in excess of their amortized cost, this benefit was less for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared with the year ended December 31, 2018.
Non-Controlling Interests
Net Income Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests is derived from the Income Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes and the percentage allocation of the income (loss) between the holders of Partnership Units and holders of Class A common stock of PJT Partners Inc. after considering any contractual arrangements that govern the allocation of income (loss).
35
Year Ended December 31, 2018 versus Year Ended December 31, 2017
We have omitted the discussion of the earliest of the three years covered in the 2019 Annual Report on Form 10-K. Such discussion is included in “Part II. Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in the 2018 Annual Report on Form 10-K, as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 28, 2019, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
General
We regularly monitor our liquidity position, including cash and cash equivalents, investments, working capital assets and liabilities, any commitments and other liquidity requirements.
Our assets have historically been comprised of cash and cash equivalents, investments, receivables arising from strategic advisory and placement engagements and operating lease right-of-use assets. Our liabilities primarily include accrued compensation and benefits, accounts payable and accrued expenses, taxes payable and operating lease liabilities. We expect to pay a significant amount of incentive compensation late each year or during the beginning of the next calendar year with respect to the prior year’s results. A portion of annual compensation may be awarded with equity-based compensation and thus requires less cash. We expect levels of cash to decline at year-end or during the first quarter of each year after incentive compensation is paid to our employees. We then expect cash to gradually increase over the remainder of the year.
On October 1, 2018, PJT Partners Holdings LP, as borrower (the “Borrower”), entered into an Amended and Restated Loan Agreement (the “Amended and Restated Loan Agreement”) and related documents with First Republic Bank, as lender (the “Lender”). The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement provides for a revolving credit facility with aggregate commitments in an amount equal to $40 million, which aggregate commitments may be increased, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, to up to $60 million during the period beginning December 1 each year through March 1 of the following year. The revolving credit facility will mature and the commitments thereunder will terminate on October 1, 2020, subject to extension by agreement of the Borrower and Lender. On February 4, 2020, the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement was further amended to extend the maturity date to October 1, 2021.
The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement also provides for a term loan with an aggregate commitment of $30 million (the “Term Loan”). The Term Loan matures on January 2, 2021. In addition to the payment of interest described below, Borrower shall pay to the Lender installment payments of principal in the amount of (a) $4.25 million on July 1, 2019 and quarterly thereafter to January 2, 2021, and (b) $4.5 million on January 2, 2021. The Term Loan was repaid in full in January 2020.
The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement requires the Borrower to maintain certain minimum financial covenants and limits or restricts the ability of the Borrower (subject to certain qualifications and exceptions) to incur additional indebtedness in excess of $20 million. Outstanding borrowings under the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement are secured by the accounts receivable of Park Hill Group LLC and PJT Partners LP.
Outstanding borrowings under the revolving credit facility bear interest equal to the greater of a per annum rate of (a) 3%, or (b) the prime rate minus 1.0%. Outstanding borrowings under the Term Loan bear interest equal to the greater of a per annum rate of (a) 3.25%, or (b) the prime rate minus 0.75%. During an event of default, overdue principal under both the revolving credit facility and Term Loan bear interest at a rate 2.0% in excess of the otherwise applicable rate of interest. In connection with the closing of the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, the Borrower paid the Lender certain closing costs and fees. In addition, on and after the closing date, the Borrower will also pay a commitment fee on the undrawn portion of the revolving credit facility of 0.125% per annum, payable quarterly in arrears.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we were in compliance with the debt covenants under the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement.
We evaluate our cash needs on a regular basis in light of current market conditions. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, we had cash, cash equivalents and investments of $217.5 million and $108.3 million, respectively.
Our liquidity is highly dependent upon cash receipts from clients, which are generally dependent upon the successful completion of transactions as well as the timing of receivable collections. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, total accounts receivable were $227.5 million and $217.8 million, respectively. There was no allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2019 and $0.7 million at December 31, 2018. Included in Accounts Receivable
36
are long-term receivables of $77.6 million and $77.9 million as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, related to placement fees that are generally paid in installments over a period of three to four years.
Sources and Uses of Liquidity
Our primary cash needs are for working capital, paying operating expenses, including cash compensation to our employees, funding the cash redemption of Partnership Units, repurchasing shares of the Company’s Class A common stock, paying income taxes, making distributions to our shareholders in accordance with our dividend policy, capital expenditures, commitments and strategic investments. We expect to fund these liquidity requirements through cash flows from operations and borrowings under our revolving credit facility. Our ability to fund these needs through cash flows from operations will depend, in part, on our ability to generate or raise cash in the future. This depends on our future financial results, which are subject to general economic, financial, competitive, legislative and regulatory factors. Furthermore, our ability to forecast future cash flows is more limited because we do not have a long-established operating history as a stand-alone company. If our cash flows from operations are less than we expect, we may need to incur debt, issue additional equity or borrow from our revolving credit facility. Although we believe that the arrangements we have in place will permit us to finance our operations on acceptable terms and conditions, our access to, and the availability of, financing on acceptable terms and conditions in the future will be impacted by many factors, including: (a) our credit ratings or absence of a credit rating, (b) the liquidity of the overall capital markets, and (c) the current state of the economy. We cannot provide any assurance that such financing will be available to us on acceptable terms or that such financing will be available at all. We believe that our future cash from operations and availability under our revolving credit facility, together with our access to funds on hand, will provide adequate resources to fund our short-term and long-term liquidity and capital needs.
Subject to the terms and conditions of the exchange agreement between us and certain of the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.), Partnership Units are exchangeable at the option of the holder for cash or, at our election, for shares of our Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis. Depending on our liquidity and capital resources, market conditions, the timing and concentration of exchange requests and other considerations, we may choose to fund cash-settled exchanges of Partnership Units with available cash, borrowings or new issuances of Class A common stock or to settle exchanges by issuing Class A common stock to the exchanging Partnership Unitholder. Issuing significant numbers of shares of our Class A common stock upon exchange of Partnership Units could adversely affect the tax consequences to Blackstone of the distribution. Accordingly, while we will retain the right under the Exchange Agreement to elect to settle exchanges in cash or Class A common stock in our sole discretion, we intend to limit such issuances of Class A common stock in settlement of exchanges of Partnership Units to the extent necessary to preserve the intended tax-free nature of the spin-off and to comply with our obligations under the Tax Matters Agreement.
Estimating the amount of payments that may be made under the tax receivable agreement entered into with the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) is by its nature imprecise, insofar as the calculation of amounts payable depends on a variety of factors. While the actual increase in tax basis, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under the tax receivable agreement, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of exchanges, the price of shares of our Class A common stock at the time of the exchange, the extent to which such exchanges are taxable and the amount and timing of our income, we expect that as a result of the size of the transfers and increases in the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of PJT Partners Holdings LP, the payments that PJT Partners Inc. may make under the tax receivable agreement will be substantial. There may be a material negative effect on our liquidity if, as a result of timing discrepancies or otherwise, the payments under the tax receivable agreement exceed the actual cash tax savings that PJT Partners Inc. realizes in respect of the tax attributes subject to the tax receivable agreement and/or distributions to PJT Partners Inc. by PJT Partners Holdings LP are not sufficient to permit PJT Partners Inc. to make payments under the tax receivable agreement after it has paid taxes. Late payments under the tax receivable agreement generally will accrue interest at an uncapped rate equal to LIBOR plus 500 basis points. The payments under the tax receivable agreement are not conditioned upon continued ownership of us by holders of Partnership Units.
Regulatory Capital
We actively monitor our regulatory capital base. We are subject to regulatory requirements in the U.S. and certain international jurisdictions to ensure general financial soundness and liquidity. This requires, among other things, that we comply with certain minimum capital requirements, recordkeeping, reporting procedures, experience and training requirements for employees and certain other requirements and procedures. These regulatory requirements may restrict the flow of funds to and from affiliates. See Note 17. “Regulated Entities” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing for
37
further information. The licenses under which we operate are meant to be appropriate to conduct our strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and placement services businesses. We believe that we provide each of these entities with sufficient capital and liquidity, consistent with their business and regulatory requirements.
Our activities may also be subject to regulation, including regulatory capital requirements, by various other foreign jurisdictions and self-regulatory organizations.
We do not anticipate that compliance with any and all such requirements will materially adversely impact the availability of funds for domestic and parent-level purposes.
Share Repurchase Program
On April 24, 2019, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock in an amount up to $100 million, which is in addition to the previous October 26, 2017 authorization. Under the repurchase program, shares of the Company’s Class A common stock may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The timing and the actual number of shares repurchased depend on a variety of factors, including legal requirements, price and economic and market conditions. The repurchase program may be suspended or discontinued at any time and does not have a specified expiration date.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we repurchased 1.2 million shares of Class A common stock at an average price per share of $40.11, or $47.8 million in aggregate, pursuant to this share repurchase program. As of December 31, 2019, the available amount remaining for repurchases under this program was $85.1 million.
During the year ended December 31, 2018, we repurchased 1.3 million shares of Class A common stock at an average price of $50.14, or $64.9 million in aggregate, pursuant to this share repurchase program.
Contractual Obligations
The following table sets forth information relating to our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2019:
|
Contractual Obligations |
|
2020 |
|
|
2021–2022 |
|
|
2023–2024 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(Dollars in Thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
Operating Leases (a) |
|
$ |
24,173 |
|
|
$ |
56,093 |
|
|
$ |
54,473 |
|
|
$ |
92,375 |
|
|
$ |
227,114 |
|
|
Finance Leases (including interest) |
|
|
136 |
|
|
|
45 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
199 |
|
|
Loan Payable (b) |
|
|
17,000 |
|
|
|
4,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
21,500 |
|
|
Tax Benefit Liability (c) |
|
|
1,301 |
|
|
|
538 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,839 |
|
|
Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement (d) |
|
|
964 |
|
|
|
1,259 |
|
|
|
1,259 |
|
|
|
5,807 |
|
|
|
9,289 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
43,574 |
|
|
$ |
62,435 |
|
|
$ |
55,750 |
|
|
$ |
98,182 |
|
|
$ |
259,941 |
|
|
(a) |
We lease our office space under agreements that expire at various dates through 2036. Further disclosure regarding our leases is provided in Note 13. “Leases” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing. In connection with these lease agreements, we are responsible for escalation payments. The contractual obligation table above includes fixed payments for such leases and does not project potential escalation or other lease-related payments. These leases are classified as operating leases and have been recorded as Operating Lease Liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition upon adoption of new lease guidance on January 1, 2019. |
|
(b) |
Pursuant to the employee matters agreement entered into with Blackstone (the “Employee Matters Agreement”), we have agreed to pay Blackstone the net realized cash benefit resulting from certain compensation-related tax deductions. Amounts are payable annually (for periods in which a cash benefit is realized) within nine months of the end of the relevant tax period. Further disclosure regarding this liability is provided in Note 15. “Commitments and Contingencies—Transactions and Agreements with Blackstone, Employee Matters Agreement” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing. |
38
|
(c) |
Represents the principal payments due on the term loan as set forth in the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement. As of December 31, 2019, we had an outstanding principal balance of $21.5 million. The term loan bears interest at a variable rate, and is further described in Note 15. “Commitments and Contingencies—Commitments, Term Loan” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing. The term loan was subsequently repaid in full in January 2020. |
|
(d) |
As of December 31, 2019, we had an amount due of $9.3 million pursuant to the tax receivable agreement, which represents management’s best estimate of the amounts currently expected to be owed under the tax receivable agreement. Actual payments may differ significantly from estimated payments. Further disclosure regarding the tax receivable agreement is presented in Note 2. “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement” and Note 14. “Transactions with Related Parties—Tax Receivable Agreement” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing. |
Commitments and Contingencies
Litigation
As previously disclosed, with respect to actual and potential additional claims related to funds fraudulently obtained by Andrew Caspersen, we believe that the total potential amount of any such claims to be less than $30 million, any such claims are without merit and we will vigorously defend any such actions.
With respect to our other litigation matters, including the litigation discussed under the caption “Legal Proceedings” elsewhere in this report, we are not currently able to estimate the possible loss or range of loss until developments in such matters have provided sufficient information to support such an assessment, including quantification of a damage demand from plaintiffs, discovery from other parties and investigation of factual allegations, rulings by courts on motions or appeals, analysis by experts or the status of any settlement negotiations. However, the disposition of these contingencies could be material to our financial results in the period in which it occurs.
Guarantee
The Company provides a guarantee to a lending institution for certain loans held by employees for investment in funds of its former Parent, which are secured by the underlying investments in those funds. The amount guaranteed was $8.0 million and $8.9 million as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. In connection with this guarantee, the Company currently expects any associated risk of loss to be insignificant.
Indemnifications
We have entered and may continue to enter into contracts, including contracts with Blackstone relating to the spin-off, which contain a variety of indemnification obligations. Our maximum exposure under these arrangements is not known; however, we currently expect any associated risk of loss to be insignificant. In connection with these matters, we have incurred and may continue to incur legal expenses, which are expensed as incurred.
Other
See Notes 9, 11, 13, 15 and 16 in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing for further information in connection with income taxes, equity-based and other deferred compensation plans, leasing arrangements, commitments and employee benefit plans, respectively.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
The Company is not involved with any off-balance sheet arrangements that are not elsewhere reflected in our consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Policies
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In applying many of these accounting principles, we need to make estimates and
39
assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. These assumptions, estimates and/or judgments; however, are often subjective. Actual results may be affected negatively based on changing circumstances. If actual amounts are ultimately different from our estimates, the revisions are included in our results of operations for the period in which the actual amounts become known. We believe the following critical accounting policies could potentially produce materially different results if we were to change underlying assumptions, estimates and/or judgments. (See Note 2. “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing.)
Revenue from Contracts with Customers
The services provided under contracts with customers include advisory and placement services, which are recorded as Advisory Fees and Placement Fees, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Additionally, we are typically reimbursed for certain professional fees and other expenses incurred that are necessary in order to provide services to the customer. These expenses are recorded in the relevant expense caption in the Consolidated Statements of Operations when incurred and recognized as revenue and recorded in accounts receivable when these amounts are invoiced to the customer. Such revenue amounts are recorded in Interest Income and Other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
At contract inception, we assess the services promised in our contracts with customers and identify a performance obligation for each promise to transfer to the customer a service (or a bundle of services) that is distinct. To identify the performance obligations, we consider all of the services promised in the contract regardless of whether they are explicitly stated or are implied by customary business practices. Additionally, we allocate the transaction price to the respective performance obligation(s) by estimating the amount of consideration in which we expect to be entitled in exchange for transferring the promised services to the customer.
For performance obligations that are satisfied over time, determining a measure of progress requires management to make judgments that affect the timing of revenue recognized.
For performance obligations that are satisfied at a point in time, we have determined that the customer is able to direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the benefits from, the output of the service at the time it is provided to the client. Additionally, we consider control to have transferred at that point because we have a present right to payment, we have transferred the output of the service and the customer has significant risks and rewards of ownership.
Expenses
Compensation and Benefits – Compensation and Benefits includes salaries, cash bonuses, benefits, employer taxes and equity-based compensation associated with the grants of equity-based awards to partners and employees. Compensation cost relating to the issuance of equity-based awards with a requisite service period to partners and employees is measured at fair value at the grant date, taking into consideration expected forfeitures, and expensed over the vesting period on a straight-line basis. Equity-based awards that do not require future service are expensed immediately. Cash settled equity-based awards are classified as liabilities and are remeasured at the end of each reporting period.
In certain instances, we may grant equity-based awards containing both a service and a market condition. The effect of the market condition is reflected in the grant date fair value of the award. Compensation cost is recognized for an award with a market condition over the requisite service period, provided that the requisite service period is completed, irrespective of whether the market condition is satisfied. If a recipient terminates employment before completion of the requisite service period, any compensation cost previously recognized is reversed unless the market condition has been satisfied prior to termination. If the market condition has been satisfied during the vesting period, the remaining unrecognized compensation cost is accelerated.
At our discretion, we may provide compensation to certain employees with repayment obligations and/or service provisions. Such payments are recorded in Compensation and Benefits in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. We assess the potential risk of forfeiture and likelihood of recouping amounts paid, and if deemed necessary, record a provision for forfeitures in the financial statements.
40
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill recorded arose from the contribution and reorganization of Blackstone’s predecessor entities in 2007 immediately prior to Blackstone’s initial public offering (“IPO”), the acquisition of PJT Capital LP that occurred on October 1, 2015 and the acquisition of CamberView that occurred on October 1, 2018. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment at least annually utilizing a qualitative or quantitative approach and more frequently if circumstances indicate impairment may have occurred. Goodwill is tested for impairment at the reporting unit level. A reporting unit is a component of an operating segment for which discrete financial information is available that is regularly reviewed by management. The impairment testing for goodwill under the qualitative approach is based first on a qualitative assessment to determine if it is more likely than not that the fair value of the Company’s reporting unit is less than its respective carrying value. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that the reporting unit’s fair value is less than its carrying value or when the quantitative approach is used, a quantitative assessment is performed to (a) calculate the fair value of the reporting unit and compare it to its carrying value, and (b) if the carrying value exceeds its fair value, to measure an impairment loss.
Our intangible assets are derived from (a) customer relationships that were established as part of Blackstone’s IPO and acquired as part of CamberView, and (b) the value of the trade name as part of the acquisitions of PJT Capital LP and CamberView. Identifiable finite-lived intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives of four to fifteen years, reflecting the average time over which such intangible assets are expected to contribute to cash flows. Amortization expense is included in Depreciation and Amortization in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. We do not hold any indefinite-lived intangible assets. Intangible assets are reviewed for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for deferred tax assets and liabilities. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, using the enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period when the change is enacted. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when we believe that it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The realization of deferred tax assets arising from timing differences and net operating losses requires taxable income in future years in order to deduct the reversing timing differences and absorb the net operating losses. We assess positive and negative evidence in determining whether to record a valuation allowance with respect to deferred tax assets. This assessment is performed separately for each taxing jurisdiction.
Recent Accounting Developments
Information regarding recent accounting developments and their impact on PJT Partners can be found in Note 2. “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Recent Accounting Developments” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” in “—Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this filing.
|
ITEM 7A. |
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Market Risk and Credit Risk
Our business is not capital-intensive and we do not invest in derivative instruments or, generally, borrow through issuing debt. As a result, we are not subject to significant market risk (including interest rate risk, foreign currency exchange rate risk and commodity price risk) or credit risk.
Risks Related to Cash, Cash Equivalents and Investments
Our cash and cash equivalents include all short-term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and have original maturities of three months or less from the date of purchase. Cash and cash equivalents are primarily maintained at three major U.S. financial institutions. In addition to cash and cash equivalents, we hold investments in Treasury securities, certain of which are classified as Investments in our Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. We believe our cash, cash equivalents and investments are not subject to any material interest rate risk, equity price risk, credit risk or other market risk.
41
Credit Risk
We regularly review our accounts receivable and allowance for doubtful accounts by considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, age of the accounts receivable and recoverable expense balances and the current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay such amounts owed to us. We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts that, in our opinion, provides for an adequate reserve to cover losses that may be incurred. As of December 31, 2019, we had no allowance for doubtful accounts and as of December 31, 2018, our allowance for doubtful accounts was $0.7 million, which represented 0.3% of the gross accounts receivable at that date.
Exchange Rate Risk
We are exposed to the risk that the exchange rate of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies may have an adverse effect on the reported value of our non-U.S. dollar denominated or based assets and liabilities. In addition, the reported amounts of our advisory revenues may be affected by movements in the rate of exchange between the currency in which an invoice is issued and paid and the U.S. dollar, the currency in which our financial statements are denominated. The principal non-U.S. dollar currencies include the pound sterling, the euro, the Japanese yen and the Hong Kong dollar. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, the impact of the fluctuation of foreign currencies in Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Tax – Currency Translation Adjustment in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) were a gain of $1.5 million, loss of $1.6 million and gain of $0.2 million, respectively, and in Interest Income and Other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, a loss of $2.7 million, loss of $0.1 million and gain of $0.2 million, respectively. We have not entered into any transaction to hedge our exposure to these foreign currency fluctuations through the use of derivative instruments or other methods as we do not consider there to be significant foreign exchange risk at this time.
42
|
ITEM 8. |
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
43
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of PJT Partners Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition of PJT Partners Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 27, 2020, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, effective January 1, 2019, the company adopted FASB ASC Topic 842, Leases, using the modified retrospective method.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Revenue from Contracts with Customers – Refer to Notes 2 & 4 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company’s services provided under contracts with customers include advisory and placement services, which are recorded as advisory and placement fees, respectively. With respect to contracts for which advisory fees are recognized, the Company’s primary performance obligation is to stand ready to perform a broad range of services the client may need over the course of the engagement. For such engagements, the customer obtains a
44
benefit from the assurance that the Company is available to it, when-and-if needed or desired. Fees related to these stand-ready performance obligations are recognized over time using a time-based measure of progress. With respect to contracts for which placement fees are recognized, the Company has determined that the provision of overall capital advisory services in contemplation of a potential fund placement or capital raise is satisfied over time. Fees related to this performance obligation are recognized over time using a time-based method as the customer simultaneously receives and consumes the benefits of the capital advisory services as they are provided. With respect to the transaction price for advisory and placement services, the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled is predominantly variable as the consideration is susceptible to factors outside of the Company’s influence and/or contains a large number and broad range of possible consideration amounts. As such, these amounts are excluded from the transaction price until the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved, which is expected to occur upon achievement of the specified event.
In certain circumstances, management may be required to apply judgment in determining the timing of when there is no longer uncertainty associated with the variable consideration and when it is probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur (e.g. when publicly available information regarding the close of a transaction is not available). We identified advisory and placement fee revenue recognition as a critical audit matter because of the judgment involved in determining the timing of when there is no longer uncertainty associated with the variable consideration and whether it is probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. This required a high degree of auditor judgment and increased extent of effort to audit and evaluate the client’s determination.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the timing of recording of revenue from contracts with customers included the following, among others:
|
• |
We tested the effectiveness of controls over revenue, including those over the timing of recording revenue. |
|
• |
We selected a sample of contracts for which revenue was recognized in 2019 and January 2020 and performed the following: |
|
|
– |
Evaluated whether the Company appropriately recognized revenue in the correct period by obtaining and evaluating evidence, including, but not limited to, inquiry with management, transaction close documents, press releases, confirmations, court approvals, executed agreements and communications, regarding the extent of uncertainty associated with variable consideration. |
|
|
– |
Obtained evidence, including, but not limited to, inquiry with management, examination of transaction close documents, press releases, confirmations, court approvals, executed agreements and communications and evaluated when it was probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized would not occur. |
|
• |
We selected a sample of contracts for which revenue was recognized in 2019 and evaluated the accuracy of management’s calculation by recalculating the revenue amounts and comparing our expectation to the amount recorded by management. |
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
New York, New York
February 27, 2020
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2015.
45
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data)
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and Cash Equivalents |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Receivable (net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $ $ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangible Assets, Net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Tax Asset, Net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Liabilities and Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued Compensation and Benefits |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Lease Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred Rent Liability |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes Payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loan Payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and Contingencies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A Common Stock, par value $ shares authorized; December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively; respectively) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class B Common Stock, par value $ authorized; |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Paid-In Capital |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated Deficit |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Treasury Stock at Cost ( December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total PJT Partners Inc. Equity (Deficit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Liabilities and Equity |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
46
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Advisory Fees |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Placement Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Income and Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Occupancy and Related |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Travel and Related |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Professional Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Communications and Information Services |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and Amortization |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Income Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Weighted-Average Shares of Class A Common Stock Outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
47
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Tax — Currency Translation Adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Less: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive Income Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
48
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (Deficit)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Share Data)
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Redeemable |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non- |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Paid-In |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Controlling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Controlling |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Income |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Interests |
|
|
Total |
|
|
Interests |
|
||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Other Comprehensive Income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends Declared ($ of Class A Common Stock) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Tax Distributions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Equity-Based Compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeiture Liability for Equity Awards |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net Share Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Deliveries of Vested Shares of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Change in Ownership Interest |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Treasury Stock Purchases |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Adjustment of Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests to Redemption Value |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Reclassification of Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests to Non- Controlling Interests |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
(continued)
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
49
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (Deficit)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Share Data)
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non- |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Paid-In |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Controlling |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Interests |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Adoption of Accounting Standard |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Comprehensive Loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Dividends Declared ($ of Class A Common Stock) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Tax Distributions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Equity-Based Compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeiture Liability for Equity Awards |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Share Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Deliveries of Vested Shares of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Acquisition-Related Equity Issuance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in Ownership Interest |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Treasury Stock Purchases |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
(continued)
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
50
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (Deficit)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Share Data)
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A |
|
|
Class B |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non- |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Common |
|
|
Paid-In |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Comprehensive |
|
|
Treasury |
|
|
Controlling |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Capital |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Income (Loss) |
|
|
Stock |
|
|
Interests |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Comprehensive Income |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends Declared ($ of Class A Common Stock) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Tax Distributions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Equity-Based Compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeiture Liability for Equity Awards |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Share Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Deliveries of Vested Shares of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Acquisition-Related Equity Issuance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in Ownership Interest |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Treasury Stock Purchases |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Balance at December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
51
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income (Loss) to Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity-Based Compensation Expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and Amortization Expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Gain on Reversal of Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Cash Flows Due to Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Receivable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Other Assets |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accrued Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Operating Lease Liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deferred Rent Liability |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes Payable |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Investing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash Paid for Acquisition, Net of Cash Received |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Purchases of Investments |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Proceeds from Sales and Maturities of Investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchases of Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Settlement of Acquisition-Related Escrow |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
(continued)
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
52
PJT Partners Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Financing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Proceeds from Revolving Credit Facility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Payments on Revolving Credit Facility |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Proceeds from Term Loan |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Principal Payments on Term Loan |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Tax Distributions |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Employee Taxes Paid for Shares Withheld |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Cash-Settled Exchanges of Partnership Units |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Treasury Stock Purchases |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Payments Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Principal Payments on Finance Leases |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Cash Used in Financing Activities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Effect of Exchange Rate Changes on Cash and Cash Equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Cash and Cash Equivalents, Beginning of Period |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and Cash Equivalents, End of Period |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flows Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments for Income Taxes, Net of Refunds Received |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Payments for Interest |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Non-Cash Receipt of Shares |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Supplemental Disclosure of Significant Non-Cash Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of CamberView Partners Holdings, LLC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets Acquired |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Liabilities Assumed |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Equity Purchase Price Consideration |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
53
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
1. |
ORGANIZATION |
PJT Partners Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries (the “Company” or “PJT Partners”) deliver a wide array of strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and fundraising services to corporations, financial sponsors, institutional investors and governments around the world. The Company offers a unique portfolio of advisory services designed to help clients achieve their strategic objectives. Also, through PJT Park Hill, the Company provides private fund advisory and fundraising services for alternative investment managers, including private equity funds, real estate funds and hedge funds.
On October 1, 2015, The Blackstone Group Inc. (“Blackstone” or the “former Parent”) distributed on a pro rata basis to its common unitholders all of the issued and outstanding shares of Class A common stock of PJT Partners Inc. held by it. This pro rata distribution is referred to as the “Distribution.” The separation of the PJT Partners business from Blackstone and related transactions, including the Distribution, the internal reorganization that preceded the Distribution and the acquisition by PJT Partners of PJT Capital LP (together with its general partner and their respective subsidiaries, “PJT Capital”) that occurred substantially concurrently with the Distribution, is referred to as the “spin-off.”
As the sole general partner of PJT Partners Holdings LP, PJT Partners Inc. operates and controls all of the business and affairs and consolidates the financial results of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries. The Company operates through the following subsidiaries: PJT Partners LP, Park Hill Group LLC, PJT Partners (UK) Limited and PJT Partners (HK) Limited.
|
2. |
SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Basis of Presentation
The Company prepared the accompanying consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Intercompany transactions have been eliminated for all periods presented. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
During the second quarter of 2019, an adjustment was identified relating to the presentation of changes in the Company’s ownership interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP, which resulted in a reclassification between Additional Paid-In Capital and Non-Controlling Interests. This immaterial correction had no impact on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations and Statements of Cash Flows. The adjustment increased Additional Paid-In Capital by $
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. Estimates and assumptions are reviewed periodically, and the effects of revisions are reflected in the period in which they are determined to be necessary. In preparing the consolidated financial statements, management makes estimates regarding the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts, evaluation of goodwill and intangible assets, realization of deferred taxes, measurement of equity-based compensation and other matters that affect the reported amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements.
54
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Business Combinations
The purchase price allocations for acquisitions are based on estimates of the fair value of tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The Company engages independent valuation specialists, when necessary, to assist with purchase price allocations and uses recognized valuation techniques, including the income and market approaches, to determine fair value. Management makes estimates and assumptions in determining purchase price allocations and valuation analyses, which may involve significant unobservable inputs. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the underlying assets acquired and liabilities assumed is allocated to goodwill. In certain circumstances, the allocations of the purchase price are based upon preliminary estimates and assumptions. Accordingly, the allocations may be subject to revision when the Company receives final information, including appraisals and other analyses.
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in business combinations are recorded in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of the respective acquisition dates based upon their estimated fair values at such dates. The results of operations of businesses acquired by the Company are included in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Operations from their respective dates of acquisition.
Revenue Recognition
The services provided under contracts with customers include advisory and placement services, which are recorded as Advisory Fees and Placement Fees, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Additionally, the Company is typically reimbursed for certain professional fees and other expenses incurred that are necessary in order to provide services to the customer. These expenses are recorded in the relevant expense caption in the Consolidated Statements of Operations when incurred and recognized as revenue and recorded in accounts receivable when these amounts are invoiced to the customer. Such revenue amounts are recorded in Interest Income and Other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
At contract inception, the Company assesses the services promised in its contracts with customers and identifies a performance obligation for each promise to transfer to the customer a service (or a bundle of services) that is distinct. To identify the performance obligations, the Company considers all of the services promised in the contract regardless of whether they are explicitly stated or are implied by customary business practices. Additionally, the Company allocates the transaction price to the respective performance obligation(s) by estimating the amount of consideration in which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for transferring the promised services to the customer.
Advisory Fees
Strategic advisory services include a broad range of financial advisory and restructuring services, which includes providing financial advice regarding acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, minority investments, asset swaps, divestitures, takeover defenses, corporate finance advisory, shareholder advisory, distressed sales, recapitalizations and restructurings, including raising various forms of financing, and portfolio liquidity solutions related to unfunded commitment relief and investments in secondary markets.
With respect to contracts for which Advisory Fees are recognized, the Company’s primary performance obligation is to stand ready to perform a broad range of services the client may need over the course of the engagement. For such engagements, the customer obtains a benefit from the assurance that the Company is available to it, when-and-if needed or desired. Fees related to these stand-ready performance obligations are recognized over time using a time-based measure of progress.
The Company may also be engaged to provide a fairness opinion to the client or the client may request that the Company arrange interim financing. The Company has determined that the delivery of either of these services represents a separate performance obligation that is satisfied at a point in time when the opinion or interim financing is delivered to the client as the customer is able to direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the benefits from, the service at that point.
55
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
With respect to the transaction price for advisory services, the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled is predominantly variable as the consideration is susceptible to factors outside of the Company’s influence and/or contain a large number and broad range of possible consideration amounts. As such, these amounts are excluded from the transaction price until the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved and the Company has determined it is probable that there is not a significant risk of a revenue reversal in the future. The types of fees may vary in each engagement, but payments for Advisory Fees are generally due promptly upon completion of a specified event or, for retainer fees, periodically over the course of the engagement.
Placement Fees
The Company’s fund placement services are provided within PJT Park Hill and primarily serve private equity, real estate and hedge funds. PJT Park Hill advises on all aspects of the fundraising process including competitive positioning and market assessment, marketing materials and related documentation and partnership terms and conditions most prevalent in the current environment. The Company also provides private placement fundraising services to corporate clients and earns placement fees based on successful completion of the transaction.
With respect to contracts for which Placement Fees are recognized, the Company has determined that the provision of overall capital advisory services in contemplation of a potential fund placement or capital raise is satisfied over time. Fees related to this performance obligation are recognized over time using a time-based method as the customer simultaneously receives and consumes the benefits of the capital advisory services as they are provided.
With respect to the transaction price for placement services, the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled is predominantly variable as the consideration is susceptible to factors outside of the Company’s influence and/or contain a large number and broad range of possible consideration amounts. As such, these amounts are excluded from the transaction price until the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved and the Company has determined it is probable that there is not a significant risk of a revenue reversal in the future. Placement Fees are typically payable upon completion of a fund closing or may be paid in installments over
Determining the Timing of Satisfaction of Performance Obligations
For performance obligations that are satisfied over time, determining a measure of progress requires management to make judgments that affect the timing of revenue recognized. The Company has determined that the methods described above provide a faithful depiction of the transfer of services to the customer.
For performance obligations that are satisfied at a point in time, the Company has determined that the customer is able to direct the use of, and obtain substantially all of the benefits from, the output of the service at the time it is provided to the client. Additionally, the Company considers control to have transferred at that point because the Company has a present right to payment, the Company has transferred the output of the service and the customer has significant risks and rewards of ownership.
Contract Balances
The timing of revenue recognition may differ from the timing of payment. The Company records a receivable when revenue is recognized prior to payment and the Company has an unconditional right to payment. The beginning and ending balances of Accounts Receivable, Net are included in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
The Company may receive non-refundable up-front fees in its contracts with customers, which are recorded as revenues in the period over which services are estimated to be provided. Additionally, the Company may receive payment of certain announcement, retainer or milestone fees before the performance obligation has been fully satisfied. Such fees give rise to a contract liability and are recorded as Deferred Revenue in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. The beginning and ending balances of Deferred Revenue are included in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
56
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The Company does not establish a provision for refunds or similar obligations. Additionally, the Company is the principal in the satisfaction of performance obligations.
To obtain a contract with a customer, the Company may incur costs such as advertising, marketing costs, bid and proposal costs and legal fees. The Company has determined that these costs would have been incurred regardless of whether the contract with the customer was obtained. Additionally, the Company does not expect to recover any of these costs from the customer; therefore, the costs of obtaining contracts with customers are expensed as incurred.
The compensation of employees assigned to provide services to customers are direct costs of fulfilling the contract. In addition, out-of-pocket expenses may be incurred as part of fulfilling the promised services under the contract. As these costs are related to performance obligations that are satisfied over time, the costs do not meet the criteria for capitalization.
Interest Income and Other – Interest Income and Other represents interest typically earned on Cash and Cash Equivalents, investments in Treasury securities and outstanding placement fees receivable; miscellaneous income; foreign exchange gains and losses arising on transactions denominated in currencies other than U.S. dollars; sublease income; and the amount of expense reimbursement invoiced to clients related to out-of-pocket expenses. Interest on placement fees receivable is earned from the time revenue is recognized and is calculated based upon the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) plus an additional percentage as mutually agreed upon with the receivable counterparty. Interest receivable is included in Accounts Receivable, Net in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying value of financial instruments approximates fair value. Financial instruments held by the Company include Cash Equivalents, Investments, Accounts Receivable and Loan Payable.
GAAP establishes a hierarchical disclosure framework that prioritizes and ranks the level of market price observability used in measuring financial instruments at fair value. Market price observability is affected by a number of factors, including the type of financial instrument, the characteristics specific to the financial instrument and the state of the marketplace, including the existence and transparency of transactions between market participants. Financial instruments with readily available quoted prices in active markets generally will have a higher degree of market price observability and a lesser degree of judgment used in measuring fair value.
Financial instruments measured and reported at fair value are classified and disclosed based on the observability of inputs used in the determination of fair values, as follows:
|
|
• |
Level I – Quoted prices are available in active markets for identical financial instruments as of the reporting date. |
|
|
• |
Level II – Pricing inputs are other than quoted prices in active markets, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date, and fair value is determined through the use of models or other valuation methodologies. |
|
|
• |
Level III – Pricing inputs are unobservable for the financial instruments and includes situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the financial instrument. The inputs into the determination of fair value require significant management judgment or estimation. |
In certain cases, the inputs used to measure fair value may fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In such cases, the determination of which category within the fair value hierarchy is appropriate for any given financial instrument is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Investments in common stock are measured based on quoted closing exchange prices and are categorized within Level I of the fair value hierarchy. To the extent these securities are actively traded, valuation adjustments are not applied.
57
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
In making an assessment of the fair value hierarchy classification of investments in Treasury securities, the Company considers the amount of trading activity, observability of pricing inputs as well as whether the securities are of the most recent issuance of that security with the same maturity (referred to as “on-the-run”, which is the most liquid version of the maturity band).
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Investments
Cash and Cash Equivalents include short-term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to known amounts of cash and have original maturities of three months or less from the date of purchase. Cash and Cash Equivalents are primarily held at three major U.S. financial institutions. Also included in Cash and Cash Equivalents are amounts held in bank accounts that are subject to advance notification to withdraw. Such amounts totaled $
Treasury securities with original maturities greater than three months when purchased are classified as Investments in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. These securities are recorded at fair value using broker quotes, reflecting inputs from auction yields.
Accounts Receivable
Accounts Receivable includes placement fees, interest and advisory fee receivables. Accounts receivable are assessed periodically for collectibility and an allowance is recognized for doubtful accounts, if required.
Included in Accounts Receivable are long-term receivables which relate to placement fees that are generally paid in installments over a period of
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The Company performs periodic reviews of outstanding accounts receivable and its clients’ financial condition. The Company generally does not require collateral and establishes an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon factors such as historical experience, credit quality, age of the accounts receivable balances and the current economic conditions that may affect a counterparty’s ability to pay such amounts owed to the Company.
After concluding that a reserved accounts receivable balance is no longer collectible, the Company will reduce both the gross receivable and the allowance for doubtful accounts. This is determined based on several factors, including the age of the accounts receivable balance and the creditworthiness of the counterparty.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill recorded arose from the contribution and reorganization of Blackstone’s predecessor entities in 2007 immediately prior to Blackstone’s initial public offering (“IPO”), the acquisition of PJT Capital LP that occurred on October 1, 2015 and the acquisition of CamberView Partners Holdings, LLC (“CamberView”) that occurred on October 1, 2018. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment at least annually utilizing a qualitative or quantitative approach and more frequently if circumstances indicate impairment may have occurred. Goodwill is tested for impairment at the reporting unit level. A reporting unit is a component of an operating segment for which discrete financial information is available that is regularly reviewed by management. The impairment testing for goodwill under the qualitative approach is based first on a qualitative assessment to determine if it is more likely than not that the fair value of the Company’s reporting unit is less than its respective carrying value. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that the reporting unit’s fair value is less than its carrying value or when the quantitative approach is used, a quantitative assessment is performed to (a) calculate the fair value of the reporting unit and compare it to its carrying value, and (b) if the carrying value exceeds its fair value, to measure an impairment loss.
58
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The Company’s intangible assets are derived from (a) customer relationships that were established as part of Blackstone’s IPO and acquired as part of CamberView, and (b) the value of the trade name as part of the acquisitions of PJT Capital LP and CamberView. Identifiable finite-lived intangible assets are amortized on a
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net consist primarily of leasehold improvements, furniture, fixtures and equipment and office equipment, and are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are calculated using the
Fixed assets held under finance leases are recorded at the present value of the future minimum lease payments, less accumulated depreciation and amortization in Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. Depreciation and amortization are calculated using the straight-line method over the life of the lease and are included in Depreciation and Amortization in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The finance lease liabilities are included in Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Leases
The Company adopted the new lease accounting guidance as of January 1, 2019. The Company determines if an arrangement is, or contains, a lease at inception.
The Company leases office space under non-cancelable lease agreements, which expire at
The Company leases certain office equipment pursuant to finance leases, which expire at
Right-of-Use Assets (“ROU assets”) represent the Company’s right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the Company’s obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. ROU assets and lease liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of the lease payments over the lease term. The Company’s lease agreements generally do not provide an implicit rate, so the Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate considering the collateral, term and the economic environment of the lease arrangement with reference to the Company’s term loan. Certain leases may include options to extend or terminate; however, the Company only reflects such renewal or termination option in the lease term when it is reasonably certain to exercise the option.
The Company records ROU assets and lease liabilities for operating leases in Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Operating Lease Liabilities, respectively, on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
The Company does not record ROU assets or lease liabilities for leases with a term of twelve months or less. Lease expense for such leases is recognized on a straight-line basis.
59
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Foreign Currency
In the normal course of business, the Company may enter into transactions not denominated in U.S. dollars. Foreign exchange gains and losses arising on such transactions are recorded in Interest Income and Other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. In addition, the Company consolidates a number of businesses that have a non-U.S. dollar functional currency. Non-U.S. dollar denominated assets and liabilities are translated to U.S. dollars at the exchange rate prevailing at the reporting date and income, expenses, gains and losses are translated at the prevailing monthly average exchange rate on the dates they were recorded. Cumulative translation adjustments arising from the translation of non-U.S. dollar denominated operations are recorded in Other Comprehensive Income (Loss).
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive Income (Loss) consists of Net Income (Loss) and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss). The Company’s Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) is comprised of foreign currency cumulative translation adjustments.
Non-Controlling Interests
Prior to October 1, 2017, the ownership interests of holders (other than PJT Partners Inc.) of the common units of partnership interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP (“Partnership Units”) were considered redeemable non-controlling interests. Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests were presented separately from Equity in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition and the portion of net income (loss) attributable to the redeemable non-controlling interests was presented separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
On October 1, 2017, certain of the restrictive covenants entered into in connection with the spin-off expired. Previously, the ability to settle exchanges of Partnership Units in shares of the Company’s Class A common stock was not entirely within the Company’s control. Consequently, the value of these interests was reclassified from Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests to Non-Controlling Interests at their redemption value as of October 1, 2017. The portion of net income (loss) attributable to the non-controlling interests is presented separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company previously elected to recognize any changes in the redemption value immediately as they occurred and adjusted the carrying amount of the redeemable non-controlling interests to its redemption value at the end of each reporting period. Reductions in the carrying amount of the redeemable non-controlling interests were only recorded if the Company had previously recorded increases in the carrying amount of the redeemable non-controlling interests. The change in redemption value was recognized in Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests with a corresponding adjustment to permanent equity in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Repurchases of Common Stock
Shares of the Company’s Class A common stock may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The Company may structure such repurchases as either a purchase of treasury stock or a retirement of shares. The Company records its purchases of treasury stock at cost as a separate component of stockholders’ equity. The Company may re-issue treasury stock, at average cost.
60
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and Benefits includes salaries, cash bonuses, benefits, employer taxes and equity-based compensation associated with the grants of equity-based awards to partners and employees. Compensation cost relating to the issuance of equity-based awards with a requisite service period to partners and employees is measured at fair value at the grant date, taking into consideration expected forfeitures, and expensed over the vesting period on a straight-line basis. Equity-based awards that do not require future service are expensed immediately. Cash settled equity-based awards are classified as liabilities and are remeasured at the end of each reporting period.
In certain instances, the Company may grant equity-based awards containing both a service and a market condition. The effect of the market condition is reflected in the grant date fair value of the award. Compensation cost is recognized for an award with a market condition over the requisite service period, provided that the requisite service period is completed, irrespective of whether the market condition is satisfied. If a recipient terminates employment before completion of the requisite service period, any compensation cost previously recognized is reversed unless the market condition has been satisfied prior to termination. If the market condition has been satisfied during the vesting period, the remaining unrecognized compensation cost is accelerated.
At the Company’s discretion, the Company may provide compensation to certain employees with repayment obligations and/or service provisions. Such payments are recorded in Compensation and Benefits in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company assesses the potential risk of forfeiture and likelihood of recouping amounts paid, and if deemed necessary, records a provision for forfeitures in the financial statements.
Income Taxes
PJT Partners Inc. is a corporation subject to U.S. federal, state and local income taxes in jurisdictions where it does business. The Company’s businesses generally operate as partnerships for U.S. federal and state purposes and as corporate entities in non-U.S. jurisdictions. In the U.S. federal and state jurisdictions, taxes related to income earned by these entities generally represent obligations of the individual members and partners.
The operating entities have generally been subject to New York City Unincorporated Business Tax and to entity-level income taxes imposed by non-U.S. jurisdictions, as applicable. These taxes have been reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
PJT Partners Inc. is subject to U.S. corporate federal, state and local income tax on its allocable share of results of operations from the operating partnership (PJT Partners Holdings LP).
Current tax liabilities are recorded in Taxes Payable in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
The Company uses the asset and liability method of accounting for deferred tax assets and liabilities. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, using the enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period when the change is enacted. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when the Company believes that it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The Company records uncertain tax positions on the basis of a two-step process: (a) a determination is made whether it is more likely than not that the tax positions will be sustained based on the technical merits of the position, and (b) those tax positions that meet the recognition threshold described in the first step are recorded based on the largest amount of tax benefit that is more likely than not to be realized upon ultimate settlement with the tax authority.
The effects of tax adjustments and settlements with taxing authorities are presented in the Company’s consolidated financial statements in the period to which they relate as if the Company were a separate tax filer in those years.
61
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in Other Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations, as applicable.
Unrecognized tax benefits are recorded in Taxes Payable in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, as applicable.
Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement
The Company has entered into a tax receivable agreement with the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) that provides for the payment by PJT Partners Inc. to exchanging holders of Partnership Units of
For purposes of the tax receivable agreement, the cash tax savings in income tax is computed by comparing the actual income tax liability of PJT Partners Inc. (calculated with certain assumptions) to the amount of such taxes that PJT Partners Inc. would have been required to pay had there been no increase to the tax basis of the assets of PJT Partners Holdings LP as a result of the exchanges and had PJT Partners Inc. not entered into the tax receivable agreement. The term of the tax receivable agreement continues until all such tax benefits have been utilized or expired, unless PJT Partners Inc. exercises its right to terminate the tax receivable agreement for an amount based on the agreed payments remaining to be made under the agreement or PJT Partners Inc. breaches any of its material obligations under the tax receivable agreement in which case all obligations generally will be accelerated and due as if PJT Partners Inc. had exercised its right to terminate the tax receivable agreement.
The Company accounts for the effects of these increases in tax basis and associated payments under the tax receivable agreement arising from exchanges as follows:
|
|
• |
the Company records an increase in deferred tax assets for the estimated income tax effects of the increases in tax basis based on enacted federal, state and local tax rates at the date of the exchange; |
|
|
• |
to the extent the Company estimates that it will not realize the full benefit represented by the deferred tax asset, based on an analysis that will consider, among other things, the Company’s expectation of future earnings, the Company reduces the deferred tax asset with a valuation allowance; and |
|
|
• |
the Company records |
The effects of changes in estimates after the date of the redemption or exchange as well as subsequent changes in the enacted tax rates are included in net income.
62
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Class A Common Stock
Basic Net Income (Loss) Per Share is computed using the weighted-average number of shares of Class A common stock outstanding; vested, undelivered restricted stock units (“RSUs”); and unvested RSUs that have met requisite service requirements.
Diluted Net Income (Loss) Per Share is computed using the number of shares of Class A common stock included in the Basic Net Income (Loss) Per Share calculation, and if dilutive, the incremental common stock that the Company would issue upon the assumed vesting of RSUs using the treasury stock method.
Contingencies and Litigation
The Company records loss contingencies if (a) information available prior to issuance of the consolidated financial statements indicates that it is probable that an asset had been impaired or a liability had been incurred at the date of the consolidated financial statements, and (b) the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. If one or both criteria for accrual are not met, but there is at least a reasonable possibility that a loss will occur, the Company does not record an accrual for a loss contingency but describes the contingency and provides detail, when possible, of the estimated potential loss or range of loss. If an estimate cannot be made, a statement to that effect is made. Costs incurred with defending matters are expensed as incurred. Accruals related to loss contingencies are recorded in Other Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Insurance Reimbursements
Receipts from insurance reimbursements up to the amount of the losses recognized are considered recoveries. These recoveries are accounted for when they are probable of receipt. Insurance recoveries are not recognized prior to the recognition of the related loss. Any receivable for insurance recoveries is recorded separately from the corresponding liability, and only if recovery is determined to be probable and reasonably estimable. Insurance reimbursements are recorded in Other Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Recent Accounting Developments
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued new guidance regarding leases. The guidance requires lessees to recognize, on the balance sheet, assets and liabilities for the rights and obligations created by leases. The lease-related assets are amortized to expense over the life of the leases and the liability, and related interest expense, are reduced as lease payments are made over the life of the lease. Entities are also required to provide enhanced disclosure about leasing arrangements. The amendments retain lease classifications, distinguishing finance leases from operating leases, using criteria that are substantially similar for distinguishing capital leases from operating leases in previous guidance.
The Company adopted the new guidance as of January 1, 2019 using the transition method that allows such guidance to be applied initially at the adoption date without restating comparative periods. The Company elected the transition package of practical expedients to alleviate certain operational complexities related to the adoption.
The impact of adoption of the lease guidance as of January 1, 2019 was as follows:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
January 1, 2019 |
|
|||
|
Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Other Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Lease Liabilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Rent Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
In June 2016, the FASB issued guidance regarding the measurement of credit losses on financial instruments. The new guidance replaces the incurred loss impairment methodology with a methodology that reflects expected credit losses and requires consideration of a broader range of reasonable and supportable information to inform
63
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
credit loss estimates, which primarily impacts the recording of the Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts on accounts receivable balances. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company adopted this guidance using the modified retrospective method to the opening balance of retained earnings as of January 1, 2020. The Company is finalizing its assessment of the opening adjustment, but does not expect the adjustment to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In February 2018, the FASB issued guidance that allows a reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income to retained earnings for stranded tax effects resulting from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2018, with an option to apply it in the period of adoption or on a retrospective basis for each period in which the effect of the change in the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate is recognized. Early adoption of the new guidance is permitted for reporting periods for which financial statements have not yet been issued. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2019 with no material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In August 2018, the FASB issued updated guidance on the accounting for implementation costs incurred in a cloud computing arrangement. The updated guidance requires the capitalization of implementation costs incurred in a cloud computing arrangement to be aligned with the requirements for capitalizing costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software. The updated guidance is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2020 for cloud computing arrangements on a prospective basis.
In August 2018, the FASB issued updated guidance that modifies the disclosure requirements for fair value measurements. The updated guidance removes and modifies various disclosures under current guidance and includes additional requirements. The updated guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2020 with no material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In December 2019, the FASB issued guidance that modifies the accounting for income taxes. The guidance provides clarification on multiple topics, including hybrid tax regimes, the tax basis step-up in goodwill that is not classified as a business combination, separate financial statements of legal entities not subject to tax, intraperiod tax allocation, ownership changes in investments, interim period accounting for enacted changes in tax law and year-to-date loss limitations in interim period tax accounting. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2020, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adoption will have on its consolidated financial statements.
|
3. |
BUSINESS COMBINATIONS |
Acquisition of CamberView
On
Pursuant to the Agreement and Plan of Merger, by and among the Company, PJT Partners Holdings LP (“Purchaser”), Blue Merger Sub LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Purchaser, CamberView and CC CVP Partners Holdings, L.L.C., solely in its capacity as securityholder representative, dated as of August 27, 2018 (the “Agreement”), the Company acquired
This transaction was accounted for as a business combination and CamberView’s operating results have been included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements from the date of the transaction. The Company incurred $
64
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The purchase price was comprised of the following:
|
Cash (a) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
Common Stock (b) |
|
|
|
|
|
Partnership Units (c) |
|
|
|
|
|
Total Purchase Price |
|
$ |
|
|
|
(a) |
Reflects cash paid to selling unitholders and employees of CamberView at closing, payoff of an existing term loan facility held by CamberView at closing and settlement of escrow balances in March 2019. |
|
(b) |
Reflects the value of |
|
(c) |
Reflects the value of |
The total purchase price includes Securityholder Representative Funds, as defined in the Agreement, of $
Under the terms of the acquisition agreement, the Company was required to replace a portion of CamberView employees’ former equity awards and, as such, was required to allocate a portion of the newly issued awards to the purchase price. The portion not included in the purchase price is recorded in compensation expense according to the vesting conditions of the respective equity award agreements.
65
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The following table summarizes the allocation of the total purchase price:
|
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
|
Measurement Period Adjustments |
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Accounts Receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Identifiable Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Tax Asset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued Compensation and Benefits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Rent Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Taxes Payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Revenue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired of $
The business combination was treated as an asset purchase for tax purposes. Similar to the purchase accounting method used for book purposes, the excess of the purchase price paid over the fair value of the net assets acquired was recorded as goodwill for tax purposes. The amount of goodwill recorded for tax purposes was determined based on the consideration paid at closing and is amortized for tax purposes ratably over a
The fair value of the intangible assets acquired, which consisted of CamberView’s customer relationships and trade name, is based, in part, on a valuation using an income approach. The Company considered, among other factors, the analyses of historical financial performance and an estimate of the future performance of the CamberView business. The risk adjusted discount rates used to compute the present value of individual intangible assets expected net cash flows were based upon PJT Partners Inc.’s estimated weighted average cost of capital. The estimated fair value ascribed to the identifiable intangible assets is amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of each of the intangible assets over periods ranging between
66
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2019 includes the results of CamberView and the Consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2018 includes the results of CamberView from the date of acquisition, October 1, 2018, through December 31, 2018.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
||
|
Total Revenues |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
The unaudited pro forma results of operations do not purport to represent what the Company’s results of operations would actually have been had the acquisition occurred on January 1, 2017 or to project the Company’s results of operations for any future period. Actual future results may vary considerably based on a variety of factors beyond the Company’s control.
|
4. |
REVENUES FROM CONTRACTS WITH CUSTOMERS |
The following table provides a disaggregation of revenues recognized from contracts with customers for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Advisory Fees |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Placement Fees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest Income from Placement Fees and Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues from Contracts with Customers |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Remaining Performance Obligations and Revenue Recognized from Past Performance
As of December 31, 2019, the aggregate amount of the transaction price allocated to performance obligations yet to be satisfied is $
The Company recognized revenue of $
Contract Balances
There were no significant impairments related to contract balances during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
For the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, $
67
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
5. |
ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE AND ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS |
Included in Accounts Receivable, Net are long-term receivables of $
The Company does not have any long-term receivables on non-accrual status. Of receivables that originated as long-term, there were $
|
6. |
GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
Changes in the carrying value of goodwill consist of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Balance, Beginning of Year |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Goodwill Acquired (a) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Measurement Period Adjustments (b) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance, End of Year |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
(a) |
|
|
(b) |
|
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company’s assessment did
Intangible Assets, Net consists of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Finite-Lived Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer Relationships |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Trade Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated Amortization |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Intangible Assets, Net |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Changes in the Company’s Intangible Assets, Net consist of the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Balance, Beginning of Year |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Additions |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Amortization Expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Measurement Period Adjustments (a) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance, End of Year |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
(a) |
|
68
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Amortization of Intangible Assets held at December 31, 2019 is expected to be $
|
7. |
FURNITURE, EQUIPMENT AND LEASEHOLD IMPROVEMENTS |
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net consists of the following:
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Office Equipment |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Leasehold Improvements |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture and Fixtures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated Depreciation |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Furniture, Equipment and Leasehold Improvements, Net |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Depreciation expense was $
|
8. |
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS |
The following tables summarize the valuation of the Company’s investments by the fair value hierarchy:
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Level I |
|
|
Level II |
|
|
Level III |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Treasury Instruments |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
Level I |
|
|
Level II |
|
|
Level III |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Treasury Instruments |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Investments |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
Investments in Treasury securities were included in both Cash and Cash Equivalents and Investments at December 31, 2019 and in Cash and Cash Equivalents at December 31, 2018 in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
During the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, there were
The carrying value of the loan payable approximates fair value based on Level II inputs.
69
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
9. |
INCOME TAXES |
The Company’s pretax income is associated with activities in domestic and international jurisdictions, as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Income (Loss) Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
International |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
The Provision (Benefit) for Income Taxes consists of the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal Income Tax |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
State and Local Income Tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign Income Tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal Income Tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
State and Local Income Tax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign Income Tax |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
The following table summarizes the Company’s tax position:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Income Before Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Provision (Benefit) for Taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
Effective Income Tax Rate |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
|
% |
70
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The following table reconciles the U.S. federal statutory tax rate to the effective income tax rate:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Expected Income Tax Expense at the Federal Statutory Rate |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
Remeasurement of Deferred Tax Assets Pursuant to Tax Legislation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
% |
|
Permanent Differences for Compensation |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
Accrual to Blackstone Related to Employee Matters Agreement |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
Partnership (Income) Loss Not Subject to U.S. Corporate Income Taxes |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
Foreign Income Taxes |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
State and Local Income Taxes, Net of Federal Benefit |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
Return to Provision |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
% |
|
Change in Amount Due Pursuant to Tax Receivable Agreement Related to Tax Legislation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
- |
% |
|
Rate Change Impact |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
— |
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
% |
|
Effective Income Tax Rate |
|
|
|
% |
|
|
- |
% |
|
|
|
% |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences that may exist between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse.
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Deferred Tax Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Lease Liabilities |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Tax Basis Step-Up from Blackstone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Partner Exchange Basis Step-Up |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Operating Loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Rent |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Tax Assets Before Valuation Allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Valuation Allowance |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total Deferred Tax Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Deferred Tax Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Intangible Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fixed Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Deferred Tax Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred Tax Asset, Net |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
71
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“Tax Legislation”) was signed into law on December 22, 2017, which lowered the U.S. corporate income tax rate to
With respect to foreign operations, the Company has recorded a tax benefit of $
The realization of deferred tax assets arising from timing differences and net operating losses requires taxable income in future years in order to deduct the reversing timing differences and absorb the net operating losses. The Company assesses positive and negative evidence in determining whether to record a valuation allowance with respect to deferred tax assets. This assessment is performed separately for each taxing jurisdiction.
The Company considered its cumulative taxable income earned in recent periods and projections of future taxable income based on the growth trajectory of its business as positive evidence in evaluating its ability to utilize the deferred tax assets. The Company’s projections of future taxable income currently indicate that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized.
The Company does not believe that it meets the indefinite reversal criteria that would allow the Company to refrain from recognizing any deferred tax liability with respect to its foreign subsidiaries. Accordingly, the Company records a deferred tax liability with respect to an outside basis difference in its investment in a foreign subsidiary, where applicable.
The Company is subject to taxation in the United States and various state, local and foreign jurisdictions. As of December 31, 2019, the Company is not generally subject to examination by the tax authorities for years before 2016.
The Company had
The Company does not anticipate a material increase or decrease in unrecognized tax benefits during the coming year.
During the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017,
72
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
10. |
NET INCOME (LOSS) PER SHARE OF CLASS A COMMON STOCK |
Basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of Class A common stock for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 is presented below:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Less: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends on Participating Securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to Participating Securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Shares of Class A Common Stock — Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Incremental Net Income from Dilutive Securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Shares of Class A Common Stock — Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Shares of Class A Common Stock Outstanding — Basic |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Number of Incremental Shares from Unvested RSUs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Shares of Class A Common Stock Outstanding — Diluted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
(a) |
These securities were determined to be anti-dilutive and therefore were excluded from the calculation of net income (loss) per share of Class A common stock. |
Partnership Units may be exchanged for PJT Partners Inc. Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis, subject to applicable vesting and transfer restrictions. If all Partnership Units were exchanged for Class A common stock, weighted-average Class A common stock outstanding would be
The following table summarizes the anti-dilutive securities for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Weighted-Average Unvested RSUs |
|
(a) |
|
|
(a) |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Weighted-Average Participating RSUs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Partnership Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
These securities were determined to be dilutive. |
73
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
11. |
EQUITY-BASED AND OTHER DEFERRED COMPENSATION |
Overview
On October 1, 2015, the Company adopted the PJT Partners Inc. 2015 Omnibus Incentive Plan, and on April 24, 2019, the Company adopted the Amended and Restated PJT Partners Inc. Omnibus Plan (the “PJT Equity Plan”) for the purpose of providing incentive compensation measured by reference to the value of the Company’s Class A common stock or Partnership Units. The PJT Equity Plan provides for the granting of incentive stock options, nonqualified stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, partnership interests and other stock-based or cash-based awards. The Company has authorized
The following table represents equity-based compensation expense and related income tax benefit for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Equity-Based Compensation Expense |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Income Tax Benefit |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Restricted Stock Units
Pursuant to the PJT Equity Plan and in connection with the spin-off, acquisition of CamberView, annual compensation process and ongoing hiring process, the Company has issued RSUs, which generally vest over a service life of
A summary of the status of the Company’s unvested RSUs as of December 31, 2019 and for changes during the year ended December 31, 2019 is presented below:
|
|
|
Restricted Stock Units |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
PJT Partners Inc. |
|
|
PJT Partners Holdings LP |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
||
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
||||
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
(in dollars) |
|
|
Units |
|
|
(in dollars) |
|
||||
|
Balance, December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Dividends Reinvested on RSUs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
As of December 31, 2019, there was $
74
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
RSU Awards with Both Service and Market Conditions
In connection with the acquisition of CamberView and ongoing hiring process, the Company has granted RSU awards containing both service and market conditions. The service condition requirement with respect to such equity-based awards is
A summary of the status of the Company’s unvested RSU awards with both a service and market condition as of December 31, 2019 and of changes during the year ended December 31, 2019 is presented below:
|
|
|
RSU Awards with Both Service and Market Conditions |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
||
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
(in dollars) |
|
||
|
Balance, December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
As of December 31, 2019, there was $
The following table presents the assumptions used to determine the fair value of the RSU awards with both a service and market condition granted during the year ended December 31, 2019:
|
Risk-Free Interest Rate |
|
|
|
Dividend Yield |
|
|
|
Expected Volatility Factor |
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Volatility Factor |
|
|
|
Expected Life (in years) |
|
|
Restricted Share Awards
In connection with the acquisition of CamberView, certain individuals were issued restricted shares of the Company’s Class A common stock. Based on the terms of the award, compensation expense will be recognized over
Partnership Units
In connection with the spin-off, acquisition of CamberView, annual compensation process and ongoing hiring process, certain individuals were issued Partnership Units that, subject to certain terms and conditions, are exchangeable at the option of the holder for cash or, at the Company’s election, for shares of PJT Partners Inc. Class A common stock on a
75
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
A summary of the status of the Company’s unvested Partnership Units as of December 31, 2019 and of changes during the year ended December 31, 2019 is presented below:
|
|
|
Partnership Units |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Grant Date |
|
||
|
|
|
Partnership |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
||
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
(in dollars) |
|
||
|
Balance, December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
As of December 31, 2019, there was $
Partnership Unit Awards with Both Service and Market Conditions
In connection with the spin-off, the Company also granted Partnership Unit awards containing both service and market conditions. The effect of the market condition is reflected in the grant date fair value of the award. Compensation cost is recognized over the requisite service period, provided that the service period is completed, irrespective of whether the market condition is satisfied. The service condition requirement with respect to such Partnership Unit awards is generally
The market condition requirements must be met prior to the sixth anniversary of the consummation of the spin-off. No portion of these awards will become vested until both the service and market conditions have been satisfied.
A summary of the status of the Company’s unvested Partnership Unit awards with both a service and market condition as of December 31, 2019 and of changes during the year ended December 31, 2019 is presented below:
|
|
|
Partnership Unit Awards with Both Service and Market Conditions |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Grant Date |
|
||
|
|
|
Partnership |
|
|
Fair Value |
|
||
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
(in dollars) |
|
||
|
Balance, December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
As of December 31, 2019, there was $
76
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Units Expected to Vest
The following unvested units, after expected forfeitures, as of December 31, 2019, are expected to vest:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Service Period |
|
|
|
|
|
Units |
|
|
in Years |
|
||
|
Partnership Units (a) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restricted Stock Units |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Restricted Share Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Equity-Based Awards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Excludes |
Deferred Cash Compensation
The Company has periodically issued deferred cash compensation in connection with annual incentive compensation as well as other hiring or retention related awards. These awards typically vest over a period of
|
12. |
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
Class A and Class B Common Stock
Holders of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock are (a) entitled to
With respect to all matters presented to stockholders of the Company other than director elections and removals, each holder of Class B common stock is entitled, without regard to the number of shares of Class B common stock held by such holder, to
In connection with the acquisition of CamberView, the Company issued
77
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Non-Controlling Interests
PJT Partners Inc. is the sole general partner of PJT Partners Holdings LP. PJT Partners Inc. owns less than
Partnership Units are exchangeable at the option of the holder for cash or, at the Company’s election, for shares of Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis. The election to exchange Partnership Units is entirely within the control of the Partnership Unitholder, although the Company retains the sole option to determine whether to settle the exchange in either cash or shares of Class A common stock.
On October 1, 2017, certain of the restrictive covenants entered into in connection with the spin-off expired. Previously, the ability to settle exchanges of Partnership Units in shares of the Company’s Class A common stock was not entirely within the Company’s control. Consequently, the value of these interests was reclassified from Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests to Non-Controlling Interests at their redemption value as of October 1, 2017. This reclassification had the effect of reducing Redeemable Non-Controlling Interests and increasing Non-Controlling Interests each by $
PJT Partners Inc. operates and controls all of the business and affairs of PJT Partners Holdings LP and its operating subsidiaries indirectly through its equity interest in PJT Partners Holdings LP; therefore, the shares of Class A common stock outstanding represent the controlling interest.
In connection with the acquisition of CamberView, the Company issued
Treasury Stock
On April 24, 2019, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of shares of the Company’s Class A common stock in an amount up to $
During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company repurchased
78
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
13. |
LEASES |
The components of lease expense were as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
Operating Lease Cost |
|
$ |
|
|
|
Finance Lease Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of Right-of-Use Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
Interest on Lease Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
Total Finance Lease Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
Short-Term Lease Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
Variable Lease Cost |
|
|
|
|
|
Sublease Income |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total Lease Cost |
|
$ |
|
|
Supplemental information related to leases was as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
Cash Paid for Amounts Included in Measurement of Lease Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Cash Flows from Operating Leases |
|
$ |
|
|
|
Operating Cash Flows from Finance Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
Financing Cash Flows from Finance Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
Right-of-Use Assets Obtained in Exchange for Lease Liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
Finance Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Remaining Lease Term (in years) |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
Finance Leases |
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-Average Discount Rate |
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Leases |
|
|
|
% |
|
Finance Leases |
|
|
|
% |
For the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017, rent expense was $
As of December 31, 2018, the Company maintained an irrevocable standby letter of credit for certain operating leases of $
79
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
The following is a maturity analysis of the annual undiscounted cash flows of the finance and operating lease liabilities as of December 31, 2019:
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
Finance |
|
|
Operating |
|
||
|
2020 |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Lease Payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Imputed Interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
In October 2019, the Company entered into a lease agreement for office space. Such lease has not been included in Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Operating Lease Liabilities on the Consolidated Statement of Financial Condition as the Company does not yet have the right to use the premises.
As of December 31, 2018, the aggregate minimum future payments required on non-cancelable leases, under legacy accounting guidance, were as follows:
|
|
|
Minimum Lease Payments |
|
|||||
|
Year Ending December 31, |
|
Capital |
|
|
Operating |
|
||
|
2019 |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Minimum Lease Payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Amount Representing Interest |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capital Lease Obligation |
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Less: Sublease Proceeds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Minimum Lease Payments |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
14. |
TRANSACTIONS WITH RELATED PARTIES |
Exchange Agreement
The Company has entered into an exchange agreement with the limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP pursuant to which they (or certain permitted transferees) have the right, subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the limited partnership agreement of PJT Partners Holdings LP, on a quarterly basis, to exchange all or part of their Partnership Units for cash or, at the Company’s election, for shares of PJT Partners Inc. Class A common stock on a
80
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
then-current market value of PJT Partners Inc. Class A common stock. The exchange agreement also provides that a holder of Partnership Units will not have the right to exchange Partnership Units in the event that PJT Partners Inc. determines that such exchange would be prohibited by law, or would result in any breach of any debt agreement or other material contract of PJT Partners Inc. or PJT Partners Holdings LP.
Certain Partnership Unitholders exchanged
During the fourth quarter of 2019, the Company was presented with
Registration Rights Agreement
The Company has entered into a registration rights agreement with the limited partners of PJT Partners Holdings LP pursuant to which the Company granted them, their affiliates and certain of their transferees the right, under certain circumstances and subject to certain restrictions, to require the Company to register under the Securities Act of 1933 shares of Class A common stock delivered in exchange for Partnership Units. The registration rights agreement does not contain any penalties associated with failure to file or to maintain the effectiveness of a registration statement covering the shares owned by individuals covered by such agreement.
Tax Receivable Agreement
The Company has entered into a tax receivable agreement with the holders of Partnership Units (other than PJT Partners Inc.) that provides for the payment by PJT Partners Inc. to exchanging holders of Partnership Units of
Aircraft Lease
We make available to our partners, including the Company’s executive officers, personal use of a company leased business aircraft when the aircraft is not being used for business purposes, for which the executive officers pay the full incremental costs associated with such use. Such amount is not material to the consolidated financial statements.
|
15. |
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Commitments
Line of Credit
On October 1, 2018, PJT Partners Holdings LP, as borrower (“Borrower”) entered into an Amended and Restated Loan Agreement (the “Amended and Restated Loan Agreement”) and related documents with First Republic Bank, as lender (the “Lender”). The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement provides for a revolving credit facility with aggregate commitments in an amount equal to $
81
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
be increased, on the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, to up to $
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there were
Term Loan
The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement also provides for a term loan with an aggregate commitment of $
The Amended and Restated Loan Agreement requires the Borrower to maintain certain minimum financial covenants and limits or restricts the ability of the Borrower (subject to certain qualifications and exceptions) to incur additional indebtedness in excess of $
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company was in compliance with the debt covenants under the Amended and Restated Loan Agreement.
As of December 31, 2019, the Term Loan balance was $
Contingencies
Litigation
From time to time, the Company is named as a defendant in legal actions relating to transactions conducted in the ordinary course of business. Some of these matters may involve claims of substantial amounts. Although there can be no assurance of the outcome of such legal actions, in the opinion of management, after consultation with external counsel, the Company believes it is not probable and/or reasonably possible that any current legal proceedings or claims would individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on the consolidated financial statements of the Company. The Company is not currently able to estimate the possible loss or range of loss until developments in such matters have provided sufficient information to support such an assessment, including quantification of a damage demand from plaintiffs, discovery from other parties and investigation of factual allegations, rulings by courts on motions or appeals, analysis by experts or the status of any settlement negotiations.
82
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Guarantee
The Company provides a guarantee to a lending institution for certain loans held by employees for investment in funds of its former Parent, which are secured by the underlying investments in those funds. The amount guaranteed was $
Indemnifications
The Company has entered and may continue to enter into contracts, including contracts with Blackstone relating to the spin-off, which contain a variety of indemnification obligations. The Company’s maximum exposure under these arrangements is not known; however, the Company currently expects any associated risk of loss to be insignificant. In connection with these matters, the Company has incurred and may continue to incur legal expenses, which are expensed as incurred.
Transactions and Agreements with Blackstone
Employee Matters Agreement
The Company is required to reimburse Blackstone for the value of forfeited unvested equity awards granted to former Blackstone employees that transitioned to PJT Partners in connection with the spin-off. Such reimbursement is recorded in Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities with an offset to Equity in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. The Company will cash settle the liability to Blackstone quarterly as the forfeitures attributable to these employees crystallize. The accrual for these forfeitures was $
Pursuant to the Employee Matters Agreement, the Company has agreed to pay Blackstone the net realized cash benefit resulting from certain compensation-related tax deductions. The amount payable to Blackstone arising from the tax deductions has been recorded in Other Expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and is payable annually (for periods in which a cash benefit is realized) within nine months of the end of the relevant tax period. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had accrued $
Tax Matters Agreement
The Company entered into a Tax Matters Agreement with Blackstone that governs the respective rights, responsibilities and obligations of the Company and Blackstone after the spin-off with respect to tax liabilities and benefits, tax attributes, tax contests and other tax sharing regarding U.S. federal, state, local and foreign income taxes, other tax matters and related tax returns. The Company has joint and several liability with Blackstone to the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) for the consolidated U.S. federal income taxes of the Blackstone consolidated group relating to the taxable periods in which the Company was part of that group. However, the Tax Matters Agreement specifies the portion, if any, of this tax liability for which the Company bears responsibility, and Blackstone agrees to indemnify the Company against any amounts for which the Company is not responsible. The Tax Matters Agreement also provides special rules for allocating tax liabilities in the event that the spin-off is determined not to be tax-free. Though valid as between the parties, the Tax Matters Agreement is not binding on the IRS.
|
16. |
EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS |
The Company contributes to employer sponsored defined contribution plans for certain employees, subject to eligibility and statutory requirements. The Company incurred expenses with respect to these defined contribution plans in the amounts of $
83
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
17. |
REGULATED ENTITIES |
Certain subsidiaries of the Company are subject to various regulatory requirements in the United States, United Kingdom and Hong Kong, which specify, among other requirements, minimum net capital requirements for registered broker-dealers.
PJT Partners LP is a registered broker-dealer through which strategic advisory, shareholder advisory and restructuring and special situations services are conducted in the United States, and is subject to the net capital requirements of Rule 15c3-1 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). PJT Partners LP computes net capital based upon the aggregate indebtedness standard, which requires the maintenance of minimum net capital, as defined, which shall be the greater of $
Park Hill Group LLC is a registered broker-dealer through which private fund advisory and fundraising services are conducted in the United States and is subject to the net capital requirements of Rule 15c3-1 under the Exchange Act. Park Hill Group LLC elected to adopt the alternative standard, which defines minimum net capital as the greater of $
PJT Partners LP and Park Hill Group LLC do not carry customer accounts and do not otherwise hold funds or securities for, or owe money or securities to, customers and, accordingly, are both exempt from the SEC Customer Protection Rule (Rule 15c3-3).
PJT Partners (UK) Limited is licensed with the United Kingdom’s Financial Conduct Authority and is required to maintain regulatory net capital of €
|
18. |
BUSINESS INFORMATION |
The Company’s activities providing strategic advisory, shareholder advisory, restructuring and special situations and private fund advisory and fundraising services constitute a single reportable segment. An operating segment is a component of an entity that conducts business and incurs revenues and expenses for which discrete financial information is available that is reviewed by the chief operating decision maker in assessing performance and making resource allocation decisions. The Company has a operating segment and therefore a reportable segment.
The Company is organized as one operating segment in order to maximize the value of advice to clients by drawing upon the diversified expertise and broad relationships of senior professionals across the Company. The chief operating decision maker assesses performance and allocates resources based on broad considerations, including the market opportunity, available expertise across the Company and the strength and efficacy of professionals’ collaboration, and not based upon profit or loss measures for the Company’s separate product lines.
84
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
Since the financial markets are global in nature, the Company generally manages its business based on the operating results of the Company taken as a whole, not by geographic region.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
International |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
International |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
The Company is not subject to any material concentrations with respect to its revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, or credit risk with respect to its accounts receivable as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
|
19. |
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS |
The Company did not identify any other subsequent events besides those described in Note 14. “Transactions with Related Parties—Exchange Agreement” and Note 15. “Commitments and Contingencies—Commitments, Line of Credit” and Note 15. “Commitments and Contingencies—Commitments, Term Loan.”
|
20. |
QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED) |
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
March 31, 2019 |
|
|
June 30, 2019 |
|
|
September 30, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
||||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (Loss) Before Provision for Taxes |
|
$ |
( |
) |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Dividends Declared Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
85
PJT Partners Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Continued
(All Dollars Are in Thousands, Except Share and Per Share Data, Except Where Noted)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
March 31, 2018 |
|
|
June 30, 2018 |
|
|
September 30, 2018 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Before Provision for Taxes |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to Non-Controlling Interests |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Income Attributable to PJT Partners Inc. |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Net Income Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Dividends Declared Per Share of Class A Common Stock |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
86
PJT Partners Inc.
Schedule II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
|
|
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2017 |
|
|||
|
Balance, Beginning of Period |
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
Additions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bad Debt Expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deductions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge-offs of Uncollectible Balances |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Balance, End of Period |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
87
|
ITEM 9. |
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
|
ITEM 9A. |
CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based upon this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No change in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act) occurred during our most recent quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed under the supervision of its principal executive and principal financial officers to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of its financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes policies and procedures that pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect transactions and dispositions of assets; provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and the directors; and provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on its financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 based on the framework established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management has determined that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 was effective.
Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the Company’s consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and issued its report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, which is included below.
88
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of PJT Partners Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of PJT Partners Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2019, of the Company and our report dated February 27, 2020, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and included an explanatory paragraph regarding the Company’s adoption of a new accounting standard.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
New York, New York
February 27, 2020
89
|
ITEM 9B. |
OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
90
PART III.
|
ITEM 10. |
DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information regarding directors and executive officers set forth under the caption “Proposal 1—Election of Directors” and “Executive Officers” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed in connection with our 2020 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “Proxy Statement”) is incorporated herein by reference.
The information regarding our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, our audit committee and our audit committee financial expert under the caption “Corporate Governance Matters” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
We post our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics on our corporate website at www.pjtpartners.com under the “Investor Relations/Corporate Governance/Governance Documents” section. Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics applies to all directors, officers and employees, including our chairman and chief executive officer and our principal financial and accounting officer. We will post any amendments to the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and any waivers that are required to be disclosed by the rules of either the SEC or the NYSE, on our website within the required periods.
|
ITEM 11. |
EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information contained in the sections captioned “Compensation of Our Executive Officers,” “Compensation of Directors” and “Report of the Compensation Committee” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding our compensation committee and compensation committee interlocks under the caption “Corporate Governance Matters—Board Committees” and “Corporate Governance Matters—Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
|
ITEM 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information contained in the sections captioned “Compensation of Our Executive Officers—Equity Compensation Plan Information” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
|
ITEM 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information contained in the sections captioned “Certain Relationships and Related Person Transactions” and “Corporate Governance Matters—Director Independence” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
|
ITEM 14. |
PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The information regarding our independent registered public accounting firm fees and services in the section captioned “Proposal 3—Ratification of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
91
PART IV.
|
ITEM 15. |
EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
|
1. |
Financial Statements |
The consolidated financial statements required to be filed in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are included in Item 8 above.
|
2. |
Financial Statement Schedules |
See “Index to Consolidated Financial Statements” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K included in Item 8 above.
|
3. |
Exhibits: |
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.1* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
Description of Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
|
|
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
92
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.12+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.13+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.14+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.15+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.16+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.17+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
93
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.18+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.19+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.20+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.21+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.22+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.23+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.24+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.25+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.26+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.27+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.28+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.29+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.30+ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
94
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
24.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.1 |
|
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a). |
|
|
|
|
|
31.2 |
|
Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a). |
|
|
|
|
|
32.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS |
|
Inline XBRL Instance Document – the instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because iXBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
|
|
|
|
|
104 |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
|
+ |
Indicates management or compensating plan or arrangement |
|
* |
Certain schedules and exhibits to this agreement have been omitted in accordance with Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. The descriptions of the omitted schedules and exhibits are contained within the relevant agreement. A copy of any omitted schedule and/or exhibit will be furnished supplementally to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request. |
The agreements and other documents filed as exhibits to this report are not intended to provide factual information or other disclosure other than with respect to the terms of the agreements or other documents themselves, and you should not rely on them for that purpose. In particular, any representations and warranties made by us in these agreements or other documents were made solely within the specific context of the relevant agreement or document and may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at any other time.
|
ITEM 16. |
FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
None.
95
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
Date: February 27, 2020 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
PJT Partners Inc. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Paul J. Taubman |
|
|
|
Name: |
|
Paul J. Taubman |
|
|
|
Title: |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
Each of the officers and directors of PJT Partners Inc. whose signature appears below, in so signing, also makes, constitutes and appoints Paul J. Taubman and Helen T. Meates, and each of them, his true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power and substitution and resubstitution, for him in any and all capacities, to execute and cause to be filed with the SEC any and all amendments (including post-effective amendments) to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, with exhibits thereto and other documents connected therewith and to perform any acts necessary to be done in order to file such documents, and hereby ratifies and confirms all that said attorneys-in-fact or their substitute or substitutes may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant, in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Name |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Paul J. Taubman |
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Paul J. Taubman |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Helen T. Meates |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Helen T. Meates |
|
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ James Costos |
|
Director |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
James Costos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dennis S. Hersch |
|
Director |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Dennis S. Hersch |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Emily K. Rafferty |
|
Director |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Emily K. Rafferty |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Thomas M. Ryan |
|
Director |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Thomas M. Ryan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Kenneth C. Whitney |
|
Director |
|
February 27, 2020 |
|
Kenneth C. Whitney |
|
|
|
|
96