
CORPORATE PRESENTATION May 2022 Exhibit 99.2

FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS This presentation contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the federal securities laws, which statements are subject to substantial risks and uncertainties and are based on estimates and assumptions. All statements, other than statements of historical facts included in this presentation, including statements concerning our plans, objectives, goals, strategies, future events, plans or intentions relating to product candidates, estimates of market size, the anticipated timing, design and conduct of our planned clinical trials, the anticipated timing for clinical data, the development of our product candidates, the potential clinical benefits of our product candidates, including efficacy and safety benefits, the potential benefits of strategic partnerships and licensing arrangements and our intent to enter into any strategic partnerships or licensing arrangements, the timing and likelihood of success, plans and objectives of management for future operations and future results of anticipated product development efforts, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “objective,” “intend,” “should,” “could,” “can,” “would,” “expect,” “believe,” “design,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential,” “plan” or the negative of these terms, and similar expressions intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements expressed or implied in this presentation, including those described in “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, and elsewhere in such filing and in other subsequent disclosure documents, including our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. We cannot assure you that we will realize the results, benefits or developments that we expect or anticipate or, even if substantially realized, that they will result in the consequences or affect us or our business in the way expected. Forward-looking statements are not historical facts and reflect our current views with respect to future events. Given the significant uncertainties, you should evaluate all forward-looking statements made in this presentation in the context of these risks and uncertainties and not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. All forward-looking statements in this presentation apply only as of the date made and are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements included in this presentation. We disclaim any intent to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances, except as required by law. Industry and Market Data: We obtained the industry, market, and competitive position data used throughout this presentation from our own internal estimates and research, as well as from industry and general publications, and research, surveys, and studies conducted by third parties. Internal estimates are derived from publicly available information released by industry analysts and third-party sources, our internal research and our industry experience, and are based on assumptions made by us based on such data and our knowledge of the industry and market, which we believe to be reasonable. In addition, while we believe the industry, market, and competitive position data included in this prospectus is reliable and based on reasonable assumptions, we have not independently verified any third-party information, and all such data involve risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors. These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in the estimates made by the independent parties and by us.

WHAT WE DO Developing innovative oral biotherapeutics for gastrointestinal health and beyond TARGETED THERAPEUTICS SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS PGN-001 Adalimumab variant + DDS OBDS Systemic Oral Biotherapeutics Delivery System DDS Targeted Drug Delivery System PGN-600 Tofacitinib + DDS Capsule technology designed for systemic delivery of biotherapeutics, replacing injection with needle-free, oral delivery technology. Targeted delivery of therapeutics to the site of disease in the gastrointestinal tract could improve outcomes for patients with IBD. PGN-OB1 Adalimumab variant + OBDS PGN-OB2 GLP-1 agonist + OBDS Ionis Pharma Antisense therapy + OBDS Large Pharma 1 Undisclosed drug + OBDS Large Pharma 2 Undisclosed drug + OBDS

THERAPEUTICS PIPELINE PROGRAM PROGRAM INDICATION DESIGN/FEASIBILITY PRECLINICAL CLINICAL TARGETED THERAPEUTICS DDS IBD PGN-600 Ulcerative Colitis PGN-001 Ulcerative Colitis SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS OBDS – PGN-OB1 Autoimmune PGN-OB2 Diabetes – Undisclosed – Undisclosed – Undisclosed GLP-1 agonist + Device Adalimumab variant + Device Tofacitinib + Device Undisclosed Drug + Device Targeted Therapeutics Device Adalimumab variant + Device Systemic Therapeutics Device Undisclosed Drug + Device Antisense Therapy + Device in partnership with LARGE PHARMA 1 in partnership with LARGE PHARMA 2 in partnership with

TARGETED THERAPEUTICS

ULCERATIVE COLITIS: THE TREATMENT GAP Despite advanced therapeutics targeting different pathways, few patients achieve long-term remission Alsoud D, Verstockt B, Fiocchi C, Vermeire S. Breaking the therapeutic ceiling in drug development in ulcerative colitis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(7):589-595. Hirten RP, Sands BE. New Therapeutics for Ulcerative Colitis. Annu Rev Med. 2021;72:199-213. Shivashankar R, Tremaine WJ, Harmsen WS, Loftus EV Jr. Incidence and Prevalence of Crohn's Disease and Ulcerative Colitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota From 1970 Through 2010. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(6):857-863. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) UC causes inflammation and damage to the large intestine About 1 million people in the U.S. are affected with UC, and ~40,000 cases are diagnosed each year3 ABOUT ULCERATIVE COLITIS The goal is deep remission: a combination of symptom remission and endoscopic healing TREATMENT OBJECTIVE Treatment begins with induction: 2-3 months of drug therapy to reach therapeutic levels Only 15% of patients achieve remission of symptoms following induction with any drug therapy1,2 UC TREATMENT CYCLE Patient undergoes induction (2-3 months) with a different drug. Efficacy rate decreases with successive rounds of therapy1 60% of patients who achieve short-term remission relapse within 12 months2 INDUCTION TRIAL INDUCTION TRIAL RELAPSE NO RESPONSE MAINTENANCE Patients who achieve remission continue drug therapy to prevent relapse

TARGETED THERAPEUTICS: A POTENTIAL SOLUTION FOR UNMET NEED IN UC Verstockt B, Alsoud D, van Oostrom J, et al. Tofacitinib tissue exposure correlates with endoscopic outcome. Oral presentation at the 34th edition of the Belgian Week of Gastroenterology, February 9, 2022. Alsoud D, Verstockt B, Fiocchi C, Vermeire S. Breaking the therapeutic ceiling in drug development in ulcerative colitis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6(7):589-595. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00065-0 Van Oostrom J, Hanzel J, Verstockt B, et al. Pharmacokinetic stratification of cytokine profiles during anti-TNF induction treatment in moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis. Poster presented at the 17th Congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO); February 18, 2022. CURRENT THERAPEUTIC CHALLENGES FOR UC TARGETED THERAPEUTIC DELIVERY: POTENTIAL SOLUTIONS UC drugs have systemic toxicity issues that may limit daily dosage Reduced systemic uptake should reduce toxicity and adverse events 1 Achieving sufficient drug levels at the site of disease is difficult with systemic delivery. 2 Increased drug levels in tissue are correlated with improved endoscopic outcomes1 Only 1 in 4 UC patient achieves short-term response2 3 Targeted delivery could enable rapid induction, which should improve patient response UC has multiple pathways,3 but current protocols target single pathways due to toxicity concerns 4 Targeted delivery could enable combination therapy to target multiple inflammatory pathways simultaneously3
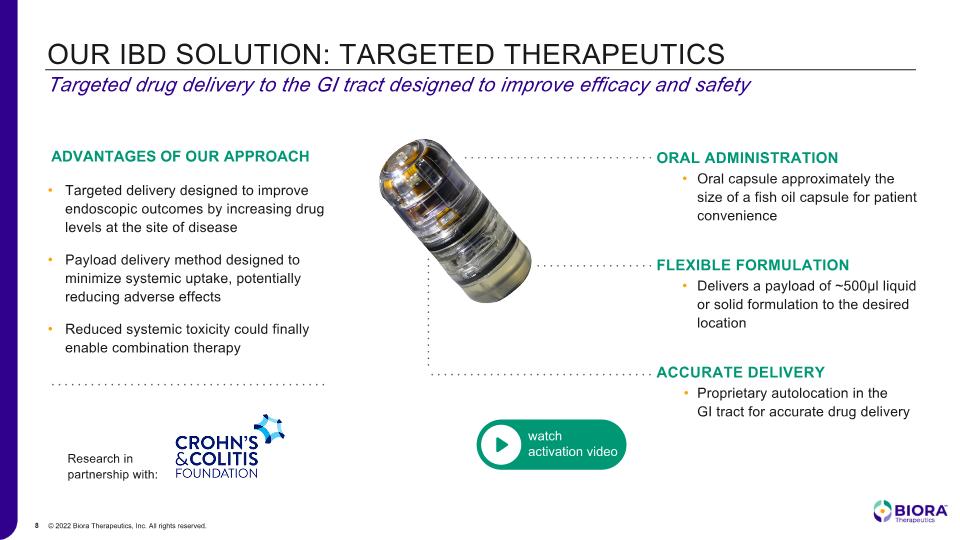
OUR IBD SOLUTION: TARGETED THERAPEUTICS Targeted drug delivery to the GI tract designed to improve efficacy and safety Targeted delivery designed to improve endoscopic outcomes by increasing drug levels at the site of disease Payload delivery method designed to minimize systemic uptake, potentially reducing adverse effects Reduced systemic toxicity could finally enable combination therapy Research in partnership with: ADVANTAGES OF OUR APPROACH ORAL ADMINISTRATION Oral capsule approximately the size of a fish oil capsule for patient convenience FLEXIBLE FORMULATION Delivers a payload of ~500µl liquid or solid formulation to the desired location ACCURATE DELIVERY Proprietary autolocation in the GI tract for accurate drug delivery watch activation video
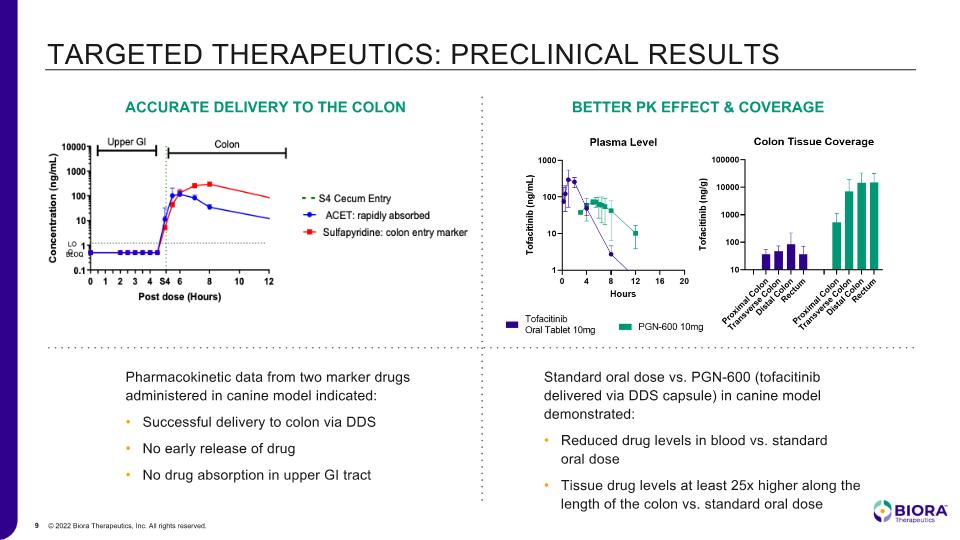
TARGETED THERAPEUTICS: PRECLINICAL RESULTS Pharmacokinetic data from two marker drugs administered in canine model indicated: Successful delivery to colon via DDS No early release of drug No drug absorption in upper GI tract Standard oral dose vs. PGN-600 (tofacitinib delivered via DDS capsule) in canine model demonstrated: Reduced drug levels in blood vs. standard oral dose Tissue drug levels at least 25x higher along the length of the colon vs. standard oral dose ACCURATE DELIVERY TO THE COLON BETTER PK EFFECT & COVERAGE

TARGETED THERAPEUTICS: CLINICAL DEVICE PERFORMANCE Accurate localization and delivery demonstrated in humans Successful clinical device validation for localization and delivery function using scintigraphic imaging: Safety and tolerability in normal healthy volunteers; devices recovered intact 83% accuracy of localization function (10/12) No early release before colon detection DEVICE LOCALIZATION AND DELIVERY TO COLON
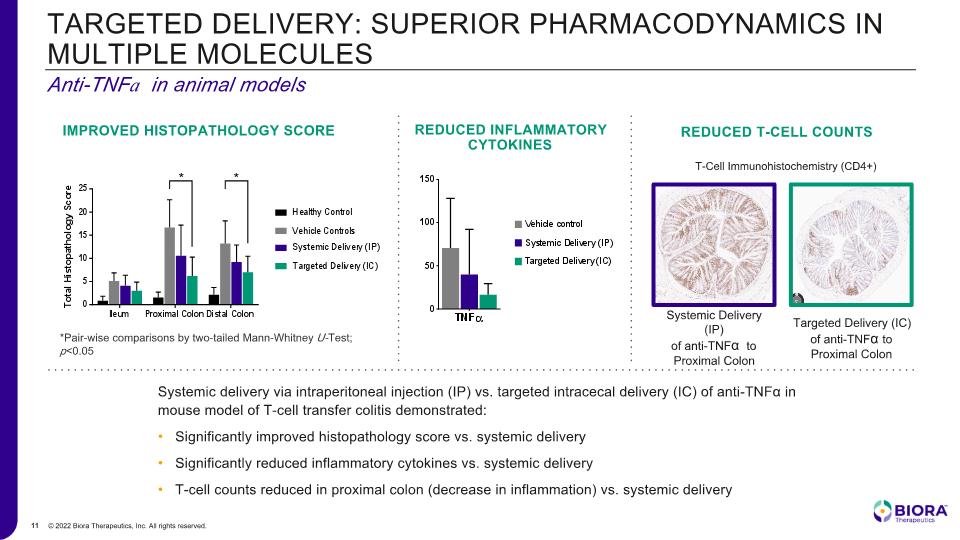
Anti-TNFa in animal models TARGETED DELIVERY: SUPERIOR PHARMACODYNAMICS IN MULTIPLE MOLECULES Systemic delivery via intraperitoneal injection (IP) vs. targeted intracecal delivery (IC) of anti-TNFα in mouse model of T-cell transfer colitis demonstrated: Significantly improved histopathology score vs. systemic delivery Significantly reduced inflammatory cytokines vs. systemic delivery T-cell counts reduced in proximal colon (decrease in inflammation) vs. systemic delivery *Pair-wise comparisons by two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-Test; p<0.05 IMPROVED HISTOPATHOLOGY SCORE REDUCED INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES Targeted Delivery (IC) of anti-TNFα to Proximal Colon Systemic Delivery (IP) of anti-TNFα to Proximal Colon T-Cell Immunohistochemistry (CD4+) REDUCED T-CELL COUNTS
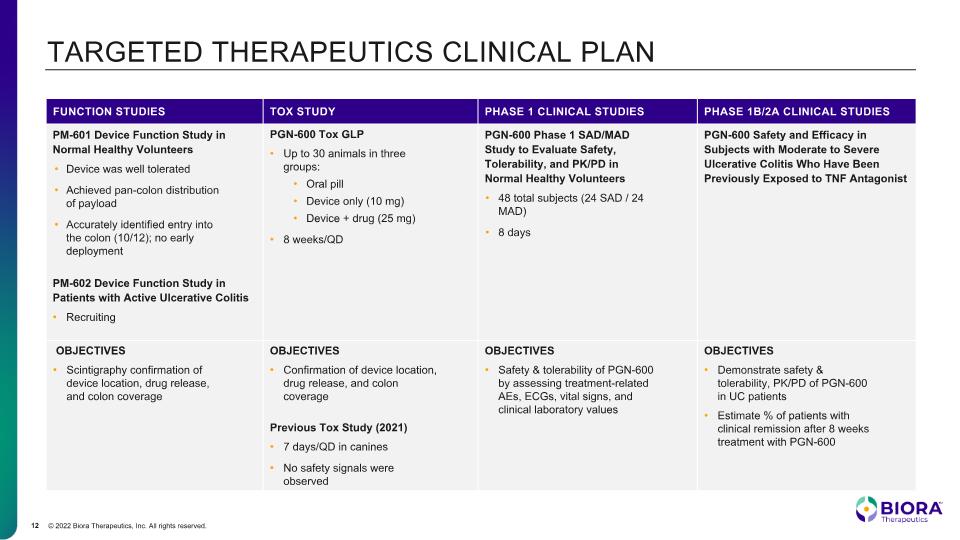
TARGETED THERAPEUTICS CLINICAL PLAN FUNCTION STUDIES TOX STUDY PHASE 1 CLINICAL STUDIES PHASE 1B/2A CLINICAL STUDIES PM-601 Device Function Study in Normal Healthy Volunteers Device was well tolerated Achieved pan-colon distribution of payload Accurately identified entry into the colon (10/12); no early deployment PM-602 Device Function Study in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis Recruiting PGN-600 Tox GLP Up to 30 animals in three groups: Oral pill Device only (10 mg) Device + drug (25 mg) 8 weeks/QD PGN-600 Phase 1 SAD/MAD Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, and PK/PD in Normal Healthy Volunteers 48 total subjects (24 SAD / 24 MAD) 8 days PGN-600 Safety and Efficacy in Subjects with Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis Who Have Been Previously Exposed to TNF Antagonist OBJECTIVES Scintigraphy confirmation of device location, drug release, and colon coverage OBJECTIVES Confirmation of device location, drug release, and colon coverage Previous Tox Study (2021) 7 days/QD in canines No safety signals were observed OBJECTIVES Safety & tolerability of PGN-600 by assessing treatment-related AEs, ECGs, vital signs, and clinical laboratory values OBJECTIVES Demonstrate safety & tolerability, PK/PD of PGN-600 in UC patients Estimate % of patients with clinical remission after 8 weeks treatment with PGN-600

SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS

Patients prefer oral delivery of medication NEEDLE AVERSION LEADS TO POOR PATIENT ADHERENCE Wright S, Yelland M, Heathcote K, Ng SK, Wright G. Fear of needles--nature and prevalence in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 2009;38(3):172-176. Spain CV, Wright JJ, Hahn RM, Wivel A, Martin AA. Self-reported Barriers to Adherence and Persistence to Treatment With Injectable Medications for Type 2 Diabetes. Clin Ther. 2016;38(7):1653-1664.e1. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.05.009 Frost & Sullivan research commissioned by Rani Therapeutics Holdings, Inc. https://ir.ranitherapeutics.com/static-files/b1f080bf-a860-4136-87cb-d6f7c49c1502 of adults avoid medical treatment due to fear of needles1 20 % among diabetes patients initiating treatment with injectable GLP-1 agonist of patients fail to maintain injectable treatment due to needle aversion3 42 % of patients prefer a daily oral capsule to bi-weekly injection3 among rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing anti-TNFa therapy 88 %

x SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS DELIVERY SYSTEM Needle-free, oral delivery to small intestine designed for optimal systemic uptake Needle-free, liquid jet administration to intestinal tissue for enhanced systemic uptake More frequent administration vs. injection may improve outcomes Versatile platform can deliver a range of large molecules, including: Monoclonal antibodies Peptides Nucleic acids RESEARCH PARTNERSHIPS ADVANTAGES OF SYSTEMIC ORAL BIOTHERAPEUTICS LIQUID FORMULATION Delivers a payload of ~400µl liquid drug with little to no reformulation PRECISE DELIVERY Enteric trigger for precise timing of drug delivery to the small intestine NEEDLE-FREE ADMINISTRATION Capsule about the size of a multivitamin for pain-free oral administration Large Pharma 1 Large Pharma 2 watch activation video

SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS: PRECISION DELIVERY Preclinical studies demonstrate precise and reliable release of payload ACCURATE DELIVERY IN SMALL INTESTINE STUDY DESIGN RESULTS Capsule loaded with a radio-opaque marker (iohexal) Two different enteric triggers evaluated Sequential imaging as the capsule transits through the GI tract in canines Reliable triggering and iohexal release Ability to optimize timing of trigger release No safety issues observed chamber empty After deployment in the small intestine T iohexol in chamber Immediately after dosing in the stomach
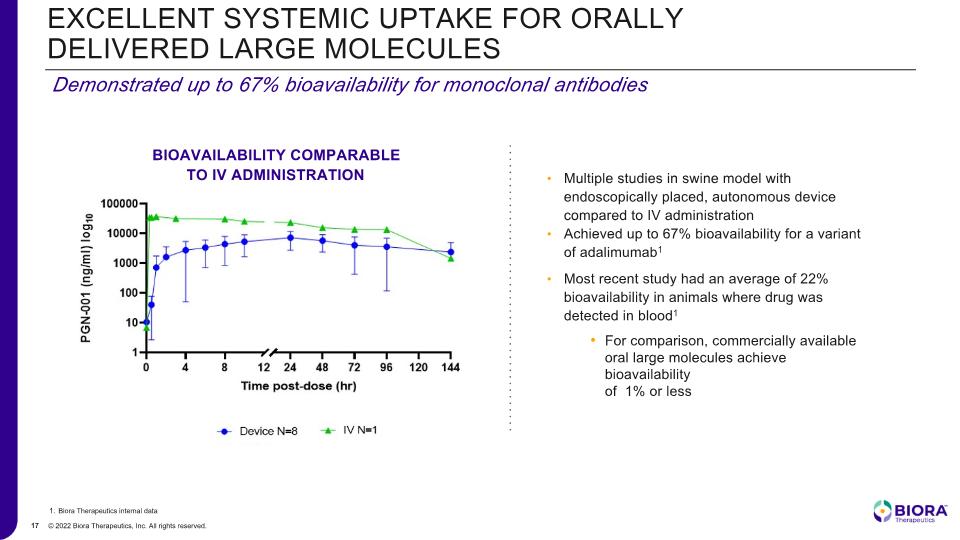
Demonstrated up to 67% bioavailability for monoclonal antibodies EXCELLENT SYSTEMIC UPTAKE FOR ORALLY DELIVERED LARGE MOLECULES Biora Therapeutics internal data Multiple studies in swine model with endoscopically placed, autonomous device compared to IV administration Achieved up to 67% bioavailability for a variant of adalimumab1 Most recent study had an average of 22% bioavailability in animals where drug was detected in blood1 For comparison, commercially available oral large molecules achieve bioavailability of 1% or less BIOAVAILABILITY COMPARABLE TO IV ADMINISTRATION

MILESTONES & CORPORATE HIGHLIGHTS

DEVELOPMENT TIMELINE PROGRAM PROGRAM Q1 2022 Q2 2022 Q3 2022 Q4 2022 H1 2023 ENABLES TARGETED THERAPEUTICS PM-611 PM-602 Establishes device performance in healthy volunteers & UC patients PRECLINICAL TOXOLOGY Preclinical toxicology to support phase 1b/2a study PHASE 1 CLINICAL TRIAL Evaluate the safety & tolerability, PK/PD of PGN-600 subject to FDA review SYSTEMIC THERAPEUTICS PRECLINICAL STUDIES Bioavailability performance of oral delivery of biologics using OBDS; enables human studies CLINICAL STUDIES Establish device performance in healthy volunteers PM-611 PM-602 Preclinical Tox Clinical Studies Phase 1 Preclinical PK Studies
