PART II
ITEM 5. |
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information and Dividend Policy
The Company’s common stock trades under the symbol PLAY and is listed on the NASDAQ Global Market (“NASDAQ”).
The number of shareholders of record of the Company’s common stock as of March 18, 2022 was 413. This does not include persons whose stock is in nominee or “street name” accounts through brokers.
On December 6, 2021, our Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program with an authorization limit of $100,000, expiring at the end of fiscal 2022. Future decisions to pay cash dividends or repurchase shares continue to be at the discretion of the Board of Directors and will be dependent on our operating performance, financial condition, capital expenditure requirements and other factors that the Board of Directors considers relevant. There were no dividends declared in fiscal 2021 or fiscal 2020.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
There were no repurchases of our common stock during fiscal 2021 or fiscal 2020.
31
Performance Graph
The following performance graph depicts the total returns to shareholders for the past five fiscal years from January 29, 2017, through January 30, 2022, relative to the performance of the NASDAQ Composite Index, Standard & Poor’s (“S&P”) SmallCap 600 Index and S&P SmallCap 600 Consumer Discretionary Index. All indices shown in the graph have been set at a base of 100 as of January 29, 2017 and assume an investment of $100 on that date and the reinvestment of dividends paid since that date. The stock price performance shown in the graph is not necessarily indicative of future price performance.
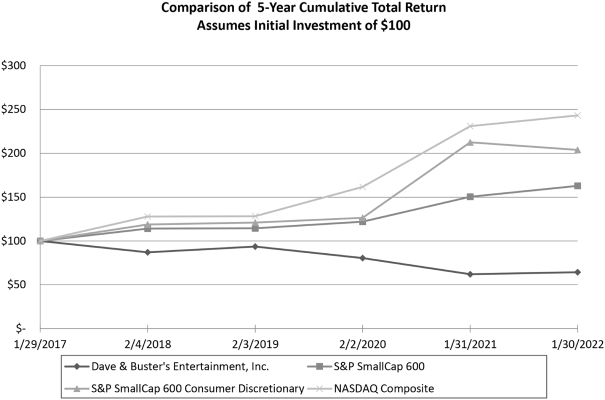
1/29/2017 |
2/4/2018 |
2/3/2019 |
2/2/2020 |
1/31/2021 |
1/30/2022 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Dave & Buster’s Entertainment, Inc. |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 87.04 | $ | 93.69 | $ | 80.58 | $ | 62.08 | $ | 64.43 | ||||||||||||
| S&P 600 Small Cap |
100.00 | 114.08 | 114.48 | 122.07 | 150.36 | 162.87 | ||||||||||||||||||
| S&P 600 Consumer Discretionary |
100.00 | 118.78 | 121.04 | 126.46 | 212.55 | 203.87 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Composite |
100.00 | 127.91 | 128.32 | 161.66 | 230.90 | 243.26 | ||||||||||||||||||
ITEM 6. |
Reserved |
ITEM 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes included herein. Unless otherwise specified, the meanings of all defined terms in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” are consistent with the meanings of such terms as defined in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. All dollar amounts are presented in thousands, unless otherwise noted, except share and per share amounts.
32
COVID-19
Pandemic In March 2020, a novel strain of coronavirus
(“COVID-19”)
outbreak was declared a global pandemic and a National Public Health Emergency. Shortly after the national emergency declaration, state and local officials began placing restrictions on businesses, some of which allowed To-Go
or curbside service only while others limited capacity in the dining room or Midway. By March 20, 2020, all our 137 operating stores were temporarily closed. On April 30, 2020, our first store re-opened
to the public, and, by the end of fiscal 2020, 107 of our 140 stores were open and operating in limited capacity. The Company re-opened
the remaining 33 stores that had been temporarily closed by August 1, 2021, the end of the second quarter of fiscal 2021. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2021, our two Canadian stores temporarily closed due to the resurgence, and shortly after the end of our fiscal year, these two stores re-opened
with limited operations. By the end of March 2022, the Company expects all types of COVID-19
related restrictions to be lifted in all but three of our stores. These developments have had a material adverse impact on the Company’s revenues, results of operations and cash flows for fiscal 2020, and during fiscal 2021, continued to have a significant impact on our business and results of operations. The ongoing effects of
COVID-19
and its variants, including, but not limited to, consumer behavior, capacity restrictions, mask and vaccination mandates, wage inflation, our ability to continue to staff our stores and disruptions in the supply chain, will determine the impact to our operating results and financial position. The impact to our operations has been most notable during the periods of greatest accelerating COVID-19
case counts. We have incurred and will continue to incur additional costs to address government regulations and the safety of our team members and customers. Financial Highlights
| • | Revenues totaled $1,304,056 compared with $1,354,691 in fiscal 2019. Revenues were unfavorably impacted in the first half of fiscal 2021 by fewer operating weeks, and primarily in the fourth quarter, by consumer behavior after masking and vaccination requirements were implemented in a number of jurisdictions in which we operate as well as by the resurgence of the Omicron variant of COVID-19. Revenues totaled $436,512 in fiscal 2020, which ended with 107 of our 140 stores open and operating in limited capacity. |
| • | Overall comparable store sales decreased 10.6% compared with the same period in 2019. Comparable store sales increased 199.1% compared with the same period in 2020, which ended with 83 of our 113 comparable stores open and operating in limited capacity. |
| • | Net income totaled $108,640, or $2.21 per diluted share, compared with net income of $100,263, or $2.94 per diluted share in the same period of 2019. Diluted shares increased from approximately 34.1 million at the end of fiscal 2019 to 49.3 million at the end of fiscal 2021, largely due to the sale of common stock during fiscal 2020 to obtain additional liquidity. In the same period of 2020, we recorded a net loss of $206,974. |
| • | Adjusted EBITDA totaled $351,725, or 27.0% of revenues, compared with Adjusted EBITDA of $308,222 or 22.8% of revenues in fiscal 2019. The increase in Adjusted EBITDA over fiscal 2019 is largely driven by the higher mix of amusements, reductions in hourly labor costs, and reduced discretionary marketing spend. We recorded an Adjusted EBITDA loss of $81,273 in fiscal 2020. |
| • | The Company ended the fiscal year with $25,910 in cash and $492,495 of liquidity available under our revolving credit facility. |
General
We are a leading owner and operator of high-volume venues in North America that combine dining and entertainment for both adults and families under the name “Dave & Buster’s”. Founded in 1982, the core of our concept is to offer our customers the opportunity to “Eat Drink Play and Watch” all in one location. Eat and Drink are offered through a full menu of entrées and appetizers and a full selection of
non-alcoholic
and 33
alcoholic beverages. Our Play and Watch offerings provide an extensive assortment of entertainment attractions centered around playing games and watching live sports and other televised events. Our brand appeals to a relatively balanced mix of male and female adults, as well as families and teenagers. We believe we appeal to a diverse customer base by providing a highly customizable experience in a dynamic and fun setting.
Our stores average 40,000 square feet and range in size between 16,000 and 70,000 square feet. During the
COVID-19
pandemic recovery period, to comply with various federal, state, and local guidelines and in response to changing customer levels, our stores operated with reduced hours of operation. Generally, our stores have returned to pre-pandemic operating hours and are open seven days a week, with normal hours of operation typically from 11:00 a.m. to midnight, with some stores open for extended hours on weekends. Strategy
Our strategy is built on four key components, including offering the latest entertainment to enjoy together, novel food & drink to bring people together, creating an aligned team and integrated experience, and driving customer engagement. For further information about our strategy, refer to “Item 1. Strategy”.
Key Measures of Our Performance
We monitor and analyze several key performance measures to manage our business and evaluate financial and operating performance. These measures include:
Comparable store sales.
COVID-19
pandemic, the comparable store base for fiscal 2021 is defined as stores open for a full 18 months before the beginning of fiscal 2020 and excludes two stores that the Company elected not to reopen after they were closed in March 2020 due to local operating limitations and one store in Cary, North Carolina that was closed and relocated during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2021. Our comparable store base consisted of 113, 114, and 99 stores as of the end of fiscal 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. New store openings.
Non-GAAP
Financial Measures In addition to the results provided in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), we provide
non-GAAP
measures which present operating results on an adjusted basis. These are supplemental measures of performance that are not required by or presented in accordance with GAAP and include Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted EBITDA Margin, Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization and Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization Margin (defined below). These non-GAAP
measures do not represent and should not be considered as an alternative to net income or cash flows from operations, as determined in accordance with GAAP, and our calculations thereof may not be comparable to similarly entitled measures reported by other companies and should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for measures of performance prepared in accordance with GAAP. Although we use these non-GAAP
measures to assess the operating performance of our business, they have significant limitations as an analytical tool because they exclude certain material costs. For example, Adjusted EBITDA does not take into account a number of significant items, including our interest expense and depreciation and amortization expense. In addition, Adjusted EBITDA excludes pre-opening
and other costs which may be important in analyzing our GAAP results. Because Adjusted EBITDA does not account for these expenses, its utility as a measure of our operating performance has material limitations. Our calculations of Adjusted EBITDA adjust for these amounts because they vary from period to period and do not directly relate to the ongoing operations of the currently underlying business of our 34
stores and therefore complicate comparison of the underlying business between periods. Nevertheless, because of the limitations described above, management does not view Adjusted EBITDA or Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization in isolation and also uses other measures, such as revenues, gross margin, operating income and net income to measure operating performance.
Adjusted EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA Margin
pre-opening
costs, currency transaction (gains) losses and other costs. “Adjusted EBITDA Margin” is defined as Adjusted EBITDA divided by total revenues. Adjusted EBITDA is presented because we believe that it provides useful information to investors and analysts regarding our operating performance. By reporting Adjusted EBITDA, we provide a basis for comparison of our business operations between current, past and future periods by excluding items that we do not believe are indicative of our core operating performance.
Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization and Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization Margin.
pre-opening
costs. “Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization Margin” is defined as Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization divided by total revenues. Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization Margin allows us to evaluate operating performance of each store across stores of varying size and volume. We believe that Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization is another useful measure in evaluating our operating performance because it removes the impact of general and administrative expenses, which are not incurred at the store level, and the costs of opening new stores, which are
non-recurring
at the store level, and thereby enables the comparability of the operating performance of our stores for the periods presented. We also believe that Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization is a useful measure in evaluating our operating performance within the entertainment and dining industry because it permits the evaluation of store-level productivity, efficiency, and performance, and we use Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization as a means of evaluating store financial performance compared with our competitors. However, because this measure excludes significant items such as general and administrative expenses and pre-opening
costs, as well as our interest expense, net and depreciation and amortization expense, which are important in evaluating our consolidated financial performance from period to period, the value of this measure is limited as a measure of our consolidated financial performance. Presentation of Operating Results
The Company’s fiscal year consists of 52 or 53 weeks ending on the Sunday after the Saturday closest to January 31. Each quarterly period has 13 weeks, except in a
53-week
year when the fourth quarter has 14 weeks. Fiscal 2021, 2020 and 2019, which ended on January 30, 2022, January 31, 2021, and February 2, 2020, respectively, each contained 52 weeks. All dollar amounts are presented in thousands, unless otherwise noted, except share and per share amounts. Store-Level Variability, Quarterly Fluctuations, Seasonality and Inflation
We have historically operated stores varying in size and have experienced significant variability among stores in volumes, operating results and net investment costs.
Our new stores typically open with sales volumes in excess of their expected long-term
run-rate
levels, which we refer to as a “honeymoon” effect. We traditionally expect our new store sales volumes in year two to be 10% to 20% lower than our year one targets, and to grow in line with the rest of our comparable store base 35
thereafter. As a result of the substantial revenues associated with each new store, the number and timing of new store openings will result in significant fluctuations in quarterly results.
While fiscal 2020 and fiscal 2021 were unusual years with the impact of
COVID-19,
historically in the first year of operation, new store operating margins (excluding pre-opening
expenses) typically benefit from honeymoon sales leverage on occupancy, management labor and other fixed costs. This benefit is partially offset by normal inefficiencies in hourly labor and other costs associated with establishing a new store. In year two, operating margins may decline due to the loss of honeymoon sales leverage on fixed costs which is partially offset by improvements in store operating efficiency. Furthermore, rents in our new stores are typically higher than our comparable store base. Our operating results historically have fluctuated due to seasonal factors. Typically, we have higher revenues associated with the spring and fall season, has historically had lower revenues as compared to other quarters. During fiscal 2020 and fiscal 2021, results also fluctuated due to the timing and frequency of temporary closures and operating restrictions due to state and local guidelines imposed due to the
year-end
holidays, which will continue to be susceptible to the impact of severe or unseasonably mild weather on customer traffic and sales during that period. Our third quarter, which encompasses the back-to-school
COVID-19
pandemic. We expect that economic and environmental conditions and changes in regulatory legislation will continue to exert pressure on both supplier pricing and consumer spending related to entertainment and dining alternatives. Although there is no assurance that our cost of products will remain stable or that federal, state, or local minimum wage rates will not increase beyond amounts currently legislated, the effects of any supplier price increase or wage rate increases might be partially offset by selected menu price increases if competitively appropriate. In addition, how quickly and to what extent, normal economic and operating conditions can resume cannot be predicted, and the resumption of normal business operations may be delayed or constrained by lingering effects of the
COVID-19
pandemic on us or our suppliers, third-party service providers, and/or customers. 36
Fiscal 2021 Compared to Fiscal 2020
Results of operations.
Fiscal Year Ended |
Fiscal Year Ended |
|||||||||||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
|||||||||||||||
| Food and beverage revenues |
$ | 436,637 | 33.5 | % | $ | 159,501 | 36.5 | % | ||||||||
| Amusement and other revenues |
867,419 | 66.5 | 277,011 | 63.5 | ||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total revenues |
1,304,056 | 100.0 | 436,512 | 100.0 | ||||||||||||
| Cost of food and beverage (as a percent of food and beverage revenues) |
119,123 | 27.3 | 45,207 | 28.3 | ||||||||||||
| Cost of amusement and other (as a percent of amusement and other revenues) |
85,848 | 9.9 | 29,698 | 10.7 | ||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total cost of products |
204,971 | 15.7 | 74,905 | 17.2 | ||||||||||||
| Operating payroll and benefits |
287,263 | 22.0 | 117,475 | 26.9 | ||||||||||||
| Other store operating expenses |
402,661 | 30.9 | 299,464 | 68.6 | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
75,501 | 5.8 | 47,215 | 10.8 | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
138,329 | 10.6 | 138,789 | 31.8 | ||||||||||||
| Pre-opening costs |
8,150 | 0.6 | 11,276 | 2.6 | ||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total operating costs |
1,116,875 | 85.6 | 689,124 | 157.9 | ||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
187,181 | 14.4 | (252,612 | ) | (57.9 | ) | ||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
53,910 | 4.2 | 36,890 | 8.4 | ||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment / refinancing |
5,617 | 0.4 | 904 | 0.2 | ||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Income (loss) before provision (benefit) for income taxes |
127,654 | 9.8 | (290,406 | ) | (66.5 | ) | ||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes |
19,014 | 1.5 | (83,432 | ) | (19.1 | ) | ||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 108,640 | 8.3 | % | $(206,974) | (47.4 | )% | |||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Change in comparable store sales |
199.1 | % | (70.2 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Company-owned stores at end of period (1) |
144 | 140 | ||||||||||||||
| Comparable stores at end of period (1) |
113 | 114 | ||||||||||||||
(1) |
As of the end of fiscal 2021, all 144 of our stores were open except for our two comparable stores in Canada. Our total and comparable store counts as of the end of fiscal 2021 exclude a store in Cary, North Carolina, which was closed on January 2, 2022, and relocated prior to the end of our fiscal year. As of the end of fiscal 2020, 107 of our 140 stores were open and 84 of our 114 comparable stores were open. Our total and comparable store counts as of the end of fiscal 2020 exclude a store in Chicago, Illinois and a store in Houston, Texas which were at or near the end of their respective lease terms which the Company decided not to re-open. We opened five new stores during fiscal 2021, including our relocated Cary, North Carolina store, and we opened six new stores during fiscal 2020. |
37
Reconciliations of
Non-GAAP
Financial Measures Adjusted EBITDA
The following table reconciles Net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA for the periods indicated:
Fiscal Year Ended |
Fiscal Year Ended |
|||||||||||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
|||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 108,640 | 8.3 | % | $ | (206,974 | ) | -47.4 | % | |||||||
| Interest expense, net |
53,910 | 36,890 | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment / refinancing |
5,617 | 904 | ||||||||||||||
| Provision (benefit) for income tax |
19,014 | (83,432 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
138,329 | 138,789 | ||||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| EBITDA |
325,510 | 25.0 | % | (113,823 | ) | -26.1 | % | |||||||||
| Loss on asset disposal |
1,392 | 577 | ||||||||||||||
| Impairment of long-lived assets and lease termination costs |
912 | 13,727 | ||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
12,472 | 6,985 | ||||||||||||||
| Pre-opening costs |
8,150 | 11,276 | ||||||||||||||
| Other costs (1) |
3,289 | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 351,725 | 27.0 | % | $ | (81,273 | ) | -18.6 | % | |||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
(1) |
Primarily represents costs related to currency transaction (gains) or losses. The third quarter of fiscal 2021 includes a $3,230 severance obligation to the Company’s former Chief Executive Officer, who terminated his service in this position effective September 30, 2021. |
Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization
The following table reconciles Operating income (loss) to Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization for the periods indicated:
Fiscal Year Ended |
Fiscal Year Ended |
|||||||||||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
|||||||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
$ | 187,181 | 14.4 | % | $ | (252,612 | ) | -57.9 | % | |||||||
| General and administrative expenses |
75,501 | 47,215 | ||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
138,329 | 138,789 | ||||||||||||||
| Pre-opening costs |
8,150 | 11,276 | ||||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Store Operating Income Before Depreciation and Amortization |
$ | 409,161 | 31.4 | % | $ | (55,332 | ) | -12.7 | % | |||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Capital Additions
The following table reflects accrual-based capital additions. Capital additions do not include any reductions for accrual-based tenant improvement allowances or proceeds from sale-leaseback transactions (collectively, “Payments from landlords”).
Fiscal Year Ended |
Fiscal Year Ended |
|||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
|||||||
| New store and operating initiatives |
$ | 58,879 | $ | 51,572 | ||||
| Games |
14,523 | 8,795 | ||||||
| Maintenance capital |
30,602 | 3,266 | ||||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||
| Total capital additions |
$ | 104,004 | $ | 63,633 | ||||
| |
|
|
|
|||||
| Payments from landlords |
$ | 16,073 | $ | 12,923 | ||||
38
Results of Operations
Revenues
In response to the
COVID-19
outbreak, which was declared a global pandemic and a National Public Health Emergency in the United States in March 2020, the Company temporarily closed all our stores. On April 30, 2020, our first store re-opened
to the public, and by the end of fiscal 2020, 107 of our 140 stores were open and operating in limited capacity. Of these 107 open stores, 83 were comparable stores. By the end of our second quarter of fiscal 2021, all the Company’s stores were open and operating, the majority of which having no operating restrictions. However, several of the local jurisdictions in which we operate instituted masking and vaccination restrictions. During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2021, our two Canadian stores temporarily closed due to the resurgence, and shortly after the end of our fiscal year, re-opened
in limited capacity. Selected revenue and store data for the periods indicated are as follows:
Fiscal Year Ended |
||||||||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
Change |
||||||||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 1,304,056 | $ | 436,512 | $ | 867,544 | ||||||
| Total store operating weeks |
7,161 | 3,922 | 3,239 | |||||||||
| Comparable store revenues |
$ | 1,066,085 | $ | 356,473 | $ | 709,612 | ||||||
| Comparable store operating weeks |
5,666 | 3,134 | 2,532 | |||||||||
| Noncomparable store revenues |
$ | 250,297 | $ | 83,194 | $ | 167,103 | ||||||
| Noncomparable store operating weeks |
1,495 | 788 | 707 | |||||||||
| Other revenues and deferrals |
$ | (12,326) | $ | (3,155) | $ | (9,171) | ||||||
Total revenues increased $867,544, or 198.7%, to $1,304,056 in fiscal 2021 compared to total revenues of $436,512 in fiscal 2020. The increase in revenue is attributable primarily to more store operating weeks in fiscal 2021 compared to the prior year due to temporary store closures during fiscal 2020, as a result of the
COVID-19
pandemic. The table below represents our revenue mix for the fiscal years indicated. The shift in mix from food and beverage sales to amusement sales of 300 basis points is due, in part, to reduced special events and less discounting of amusements, offset somewhat by food price increases effective midway through the third quarter of fiscal 2021. Fiscal Year Ended |
Fiscal Year Ended |
|||||||
January 30, 2022 |
January 31, 2021 |
|||||||
| Food sales |
22.7 | % | 24.1 | % | ||||
| Beverage sales |
10.8 | % | 12.4 | % | ||||
| Amusement sales |
66.1 | % | 63.1 | % | ||||
| Other |
0.4 | % | 0.4 | % | ||||
Comparable store revenue increased $709,612 or 199.1%, in fiscal 2021 compared to fiscal 2020, due primarily to an 80.8% increase in comparable store operating weeks. Comparable store sales in fiscal 2021 were approximately 88.8% of the levels achieved
pre-pandemic
during fiscal 2019. Our individual comparable stores generally experienced gradual increases in weekly sales performance as operating weeks increased. Individual store performance after re-opening
was also impacted by changes in local operating restrictions and consumer reactions to changes in local COVID-19
infection rates. Food sales at comparable stores increased by $155,171, or 180.5%, to $241,127 in fiscal 2021 from $85,956 in fiscal 2020. Beverage sales at comparable stores increased by $72,108, or 160.6%, to $117,006 in fiscal 2021 from $44,898 in fiscal 2020. Comparable store amusement and other revenues in fiscal 2021 increased by $482,333, or 213.8%, to $707,952 from $225,619 in fiscal 2020.
Non-comparable
store revenue increased $167,103 in fiscal 2021 compared to fiscal 2020, for the same reasons noted above, including 707 more store operating weeks. 39
Cost of products
The total cost of products was $204,971 for fiscal 2021 and $74,905 for fiscal 2020. The total cost of products as a percentage of total revenues decreased 150 basis points to 15.7% for fiscal 2021 compared to 17.2% for fiscal 2020.
Cost of food and beverage products increased to $119,123 compared to $45,207 for fiscal 2020. Cost of food and beverage products, as a percentage of food and beverage revenues, decreased 100 basis points to 27.3% for fiscal 2021 from 28.3% for fiscal 2020. The impact of year-over-year cost increases in food products, primarily poultry, were offset by lower closure-related spoilage costs and food price increases effective midway through the third quarter of fiscal 2021.
Cost of amusement and other increased to $85,848 in fiscal 2021 compared to $29,698 in fiscal 2020. The costs of amusement and other, as a percentage of amusement and other revenues, decreased 80 basis points to 9.9% for fiscal 2021 from 10.7% in fiscal 2020. This decrease was driven primarily by lower ticket redemption activity as a percent of tickets issued during the first half of fiscal 2021, partially offset by higher freight costs.
Operating payroll and benefits
Total operating payroll and benefits increased by $169,788, or 144.5%, to $287,263 in fiscal 2021 compared to $117,475 in fiscal 2020. Nearly all our store workforce, except a small team of essential personnel, were furloughed in
mid-March
2020. Hourly team members began to return as stores re-opened
at reduced staffing levels. The total cost of operating payroll and benefits as a percentage of total revenues was 22.0% in fiscal 2021 compared to 26.9% in 2020. This decrease is primarily due to favorable leveraging on management labor and benefits and lower labor hours due to labor efficiency initiatives and hourly labor staffing shortages, partially offset by increases in the hourly labor costs and higher incentive compensation, including referral and retention incentives implemented during the second quarter of fiscal 2021. Other store operating expenses
Other store operating expenses increased by $103,197, or 34.5%, to $402,661 in fiscal 2021 compared to $299,464 in fiscal 2020. The increase is primarily due to the impact of increased store weeks during fiscal 2021 on costs such as utilities, supplies, maintenance, and other services and an approximate $11,000 increase in marketing spend. These increases were offset somewhat by a $13,727 charge for impairment of long-lived assets and lease termination costs incurred during fiscal 2020. Other store operating expense as a percentage of total revenues decreased to 30.9% in fiscal 2021 compared to 68.6% in fiscal 2020. This decrease was due primarily to favorable sales leveraging on occupancy costs and utilities and the absence of any impairment charges in fiscal 2021.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $28,286, or 59.9%, to $75,501in fiscal 2021 compared to $47,215 in fiscal 2020. The increase in general and administrative expenses was driven primarily by higher incentive compensation, salaries and benefits, professional fees, board fees, hiring cost, travel, and share-based compensation. Fiscal 2021 also includes a $3,230 severance obligation to the Company’s former Chief Executive Officer, who terminated his service in this position effective September 30, 2021, and a $912 impairment charge related to the relocation of our store support center and abandonment of our former corporate office lease. Effective near the end of March 2020, due to the impacts of the
COVID-19
pandemic, most of our corporate team members were furloughed, with reduced pay and benefits for the remaining team members for a twelve-week period, and board fees were temporarily suspended. Share-based compensation was also lower during that same time due to changes in performance stock unit expense. 40