0001517302☐☐2023FYfalseP3Y0M0DP3Y0M0DP2Y0M0D00015173022023-01-012023-12-3100015173022023-06-30iso4217:USDiso4217:USDxbrli:shares0001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-02-19xbrli:shares0001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2024-02-190001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2024-02-190001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2022-12-3100015173022023-12-3100015173022022-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Member2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Member2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Member2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMember2021-01-012021-12-3100015173022022-01-012022-12-3100015173022021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ConsolidatedInvestmentProductsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ConsolidatedInvestmentProductsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ConsolidatedInvestmentProductsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2020-12-3100015173022020-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2021-12-3100015173022021-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AccumulatedOtherComprehensiveIncomeMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:NoncontrollingInterestMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:ConsolidatedEntityExcludingVieMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2023-12-31xbrli:pure0001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersLimitedPartnershipMember2023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMember2023-12-31apam:vote0001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2023-12-310001517302srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMember2023-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasuredAtNetAssetValuePerShareMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesDSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesDSeniorNotesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesESeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesESeniorNotesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesFSeniorNotesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesFSeniorNotesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SeniorNotesMemberapam:SeriesCSeniorNotesMember2022-08-160001517302apam:AdjustedTermSOFRPlusApplicableMarginMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberapam:AdjustedTermSOFRPlusApplicableMarginMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:FederalFundsEffectiveRateMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:AdjustedTermSOFRForAOneMonthInterestPeriodMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:MarginBasedOnLeverageRatioMembersrt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberapam:MarginBasedOnLeverageRatioMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:MinimumMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RevolvingCreditFacilityMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:VariableInterestEntityNotPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:MoneyMarketFundsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:EquitySecuritiesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DebtSecuritiesMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:DerivativeMemberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMemberus-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel2Member2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel3Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMemberus-gaap:VariableInterestEntityPrimaryBeneficiaryMemberus-gaap:ShortTermInvestmentsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2020-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2020-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMemberus-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2020-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMemberapam:FollowOnOfferingMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMemberapam:FollowOnOfferingMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:FollowOnOfferingMemberus-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2021-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMemberus-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2021-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMemberus-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMember2023-12-310001517302apam:LimitedPartnershipUnitsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMemberus-gaap:CapitalUnitsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMemberapam:DeferredTaxAssetsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMemberapam:DeferredTaxAssetsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:GeneralPartnershipUnitsMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-12-310001517302apam:QuarterlyCashDividendMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:QuarterlyCashDividendMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:QuarterlyCashDividendMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:SpecialAnnualDividendMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:SpecialAnnualDividendMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:SpecialAnnualDividendMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassAMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonClassBMemberus-gaap:CommonStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:CommonStockMemberus-gaap:CommonClassCMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMembersrt:ProFormaMember2023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPartnersHoldingsLPMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:AssetManagement1Memberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMemberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMemberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:InvestmentPerformanceMemberapam:SeparateAccountsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:SeparateAccountsMember2023-12-310001517302apam:SeparateAccountsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DeferredBonusMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:DeferredBonusMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:DeferredBonusMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:StockCompensationPlanMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:A2023GrantMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:PerformanceSharesMember2020-01-012020-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:OperatingExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:OperatingExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:OperatingExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:NonoperatingIncomeExpenseMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:NonoperatingIncomeExpenseMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMemberus-gaap:NonoperatingIncomeExpenseMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:LongTermCashAwardsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:CapitalUnitMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:CapitalUnitMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:PhantomEquityPlanMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:PhantomEquityPlanMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:PhantomEquityPlanMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:StockAppreciationRightsSARSMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:StockAppreciationRightsSARSMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:ComputerEquipmentMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:SoftwareAndSoftwareDevelopmentCostsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:FurnitureAndFixturesMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:LeaseholdImprovementsMember2022-12-310001517302apam:CompensationAndBenefitsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:CompensationAndBenefitsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:CompensationAndBenefitsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:OccupancyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:OccupancyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:OccupancyMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:CommunicationAndTechnologyMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:CommunicationAndTechnologyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:CommunicationAndTechnologyMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:DisposalGroupDisposedOfByMeansOtherThanSaleNotDiscontinuedOperationsAbandonmentMemberus-gaap:OccupancyMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:RelatedPartyMember2022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-10-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-10-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-10-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:MaximumMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302srt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ExpenseReimbursementMemberapam:ArtisanGlobalFundsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:MinimumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:MaximumMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ManagementFeesBeforeReimbursementRevenueMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMembersrt:SubsidiariesMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMembersrt:ConsolidationEliminationsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302apam:ArtisanPrivateFundsMemberapam:ExpenseReimbursementMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302country:US2023-01-012023-12-310001517302country:US2022-01-012022-12-310001517302country:US2021-01-012021-12-310001517302us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-01-012023-12-310001517302us-gaap:NonUsMember2022-01-012022-12-310001517302us-gaap:NonUsMember2021-01-012021-12-310001517302country:US2023-12-310001517302country:US2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:NonUsMember2023-12-310001517302us-gaap:NonUsMember2022-12-310001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberapam:LongTermIncentiveMember2024-03-010001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:RestrictedStockMember2024-03-010001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberapam:CashAwardMember2024-03-010001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2024-01-302024-01-300001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberapam:QuarterlyCashDividendMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-01-302024-01-300001517302apam:SpecialAnnualDividendMemberus-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-01-302024-01-300001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberus-gaap:CommonClassAMember2024-01-302024-01-300001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2024-01-082024-01-080001517302us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2024-02-072024-02-07
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
| | | | | |
| (Mark One) | |
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2023 |
| | | | | |
| OR |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO |
Commission file number: 001-35826
Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | |
| Delaware | 45-0969585 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| |
875 E. Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 800 Milwaukee, WI | 53202 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
(414) 390-6100
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | | | | | | | | |
| Class A Common Stock, $0.01 par value | APAM | The New York Stock Exchange |
| (Title of each class) | (Trading Symbol) | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. | | | | | | | | | | | |
Large accelerated filer þ | | | Accelerated filer o |
Non-accelerated filer o | | Smaller reporting company ☐ |
| | | Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant's executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No þ
The aggregate market value of common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant at June 30, 2023, which was the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was approximately $2.6 billion based on the closing price of $39.31 for the Class A common stock, as reported on the New York Stock Exchange on that date.
For purposes of this calculation only, it is assumed that the affiliates of the registrant include only directors and executive officers of the registrant.
The number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s Class A common stock, par value $0.01 per share, Class B common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and Class C common stock, par value $0.01 per share, as of February 19, 2024 were 68,999,125, 2,220,315 and 8,674,947, respectively.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Certain portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for its annual meeting of stockholders, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after December 31, 2023, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS | | | | | | | | |
| | Page |
| PART I | |
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 1C. | | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| | |
| PART II | |
| Item 5. | | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| Item 9C. | | |
| | |
| PART III | |
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| | |
| PART IV | |
| Item 15. | | |
| Item 16. | | |
| | |
Except where the context requires otherwise, in this report:
•“Artisan Funds” refers to each series of Artisan Partners Funds, Inc., an open-ended management investment company, registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
•“Artisan Global Funds” refers to each sub-fund of Artisan Partners Global Funds plc, an open-ended investment company registered with the Central Bank of Ireland pursuant to the European UCITS Directive.
•“Artisan Private Funds” refers to private investment funds sponsored by Artisan.
•“Client” and “clients” refer to investors who access our investment management services by investing in funds, including Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds, Artisan Private Funds, or other pooled investment vehicles (including collective investment trusts) for which we serve as investment adviser, or by engaging us to manage a separate account or provide a non-discretionary model portfolio in one or more of our investment strategies.
•“Company”, “Artisan”, “we”, “us” or “our” refer to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. (“APAM”) and its direct and indirect subsidiaries, including Artisan Partners Holdings LP (“Artisan Partners Holdings” or “Holdings”), and, for periods prior to our IPO, “Artisan,” the “company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Artisan Partners Holdings and, unless the context otherwise requires, its direct and indirect subsidiaries. On March 12, 2013, APAM closed its IPO and related IPO Reorganization. Prior to that date, APAM was a subsidiary of Artisan Partners Holdings. The IPO Reorganization and IPO are described in the notes to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II of this Form 10-K.
•“IPO” means the initial public offering of 12,712,279 shares of Class A common stock of Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. completed on March 12, 2013.
•“IPO Reorganization” means the series of transactions Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. and Artisan Partners Holdings completed on March 12, 2013, immediately prior to the IPO, in order to reorganize their capital structures in preparation for the IPO.
•“2021 Follow-On Offering” means the registered offering of 963,614 shares of Class A common stock of Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. completed on March 1, 2021.
Forward-Looking Statements
This report contains, and from time to time our management may make, forward-looking statements within the meaning of the safe harbor provisions of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Statements regarding future events and our future performance, as well as management’s current expectations, beliefs, plans, estimates or projections relating to the future, are forward-looking statements within the meaning of these laws. In some cases, you can identify these statements by forward-looking words such as “may”, “might”, “will”, “should”, “expects”, “intends”, “plans”, “anticipates”, “believes”, “estimates”, “predicts”, “potential” or “continue”, the negative of these terms and other comparable terminology. Forward-looking statements are only predictions based on current expectations of our management and information available to us at the time such statements are made. Forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, and there are important factors that could cause actual results, level of activity, performance, actions or achievements to differ materially from the results, level of activity, performance, actions or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These factors include: the loss of key investment professionals or senior management, adverse market or economic conditions, poor performance of our investment strategies, significant changes in client cash inflows or outflows or declines in market value of the assets in the accounts we manage, change in the legislative and regulatory environment in which we operate, our ability to maintain our current fee rates, operational or technical errors or other damage to our reputation and other factors disclosed in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including those factors listed under the caption entitled “Risk Factors” in Item 1A of this Form 10-K, as may be amended from time to time. We undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements in order to reflect events or circumstances that may arise after the date of this report, except as required by law.
Forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements about:
•our anticipated future results of operations;
•our potential operating performance and efficiency, including our ability to operate under different and unique circumstances;
•our expectations with respect to future business initiatives, including the development of new investment teams, strategies and vehicles;
•our expectations with respect to the performance of our investment strategies;
•our expectations with respect to future levels of assets under management, including the capacity of our strategies and client cash inflows and outflows;
•our expectations with respect to industry trends and how those trends may impact our business;
•our financing plans, cash needs and liquidity position;
•our intention to pay dividends and our expectations about the amount of those dividends;
•our expected levels of compensation of our employees, including equity- and cash-based long-term incentive compensation;
•our expectations with respect to future expenses and the level of future expenses;
•our expected tax rate, and our expectations with respect to deferred tax assets; and
•our estimates of future amounts payable pursuant to our tax receivable agreements.
Investment Performance and Assets Under Management (AUM) Information Used in this Report
We manage investments primarily through pooled investment funds and separate accounts. We serve as investment adviser to Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds. We refer to funds and other accounts that are managed by us with a broadly common investment objective and substantially in accordance with a single model account as being part of the same investment “strategy”.
We measure investment performance based upon the results of our “composites”, which represent the aggregate performance of all discretionary client accounts (including pooled investment vehicles) invested in the same strategy, except for those accounts with respect to which we believe client-imposed investment restrictions may have a material impact on portfolio construction and those accounts managed in a currency other than U.S. dollars. The results of these excluded accounts, which represented approximately 15% of our assets under management at December 31, 2023, are maintained in separate composites the results of which are not presented in this report.
The performance of accounts with client-imposed investment restrictions differs from the performance of accounts included in our principal composite for the applicable strategy because one or more securities may be omitted from the portfolio in order to comply with client restrictions and the weightings in the portfolio of other securities are typically correspondingly altered. The performance of non-U.S. dollar accounts differs from the performance of the principal composite for the applicable strategy because of the fluctuations in currency exchange rates between the currencies in which portfolio securities are traded and the currency in which the account is managed or U.S. dollars, respectively. Results for any investment strategy described herein, and for different investment vehicles within a strategy, are affected by numerous factors, including: different material market or economic conditions; different investment management fee rates, brokerage commissions and other expenses; and the reinvestment of dividends or other earnings. The returns for any strategy may be positive or negative, and past performance does not guarantee future results. In this report, we refer to the date on which we began tracking the performance of an investment strategy as the “inception date”.
Unless otherwise noted, we present the average annual returns of our composites on a “gross” basis, which represent average annual returns before payment of fees payable to us by any portfolio in the composite and net of commissions and transaction costs. An investor’s return in a portfolio would be lower than the gross results presented due to the deduction of applicable fees and expenses. We also present the average annual returns of certain market indices or “benchmarks” for the comparable period. The indices are unmanaged and have differing volatility, credit and other characteristics. You should not assume that there is any material overlap between the securities included in the portfolios of our investment strategies during these periods and those that comprise any of the strategy’s comparator index in this report. At times, this causes material differences in relative performance. It is not possible to invest directly in any of the indices. The returns of these indices, as presented in this report, have not been reduced by fees and expenses associated with investing in securities, but do include the reinvestment of dividends.
In these materials, we present Value Added, which is the difference, in basis points, between an Artisan strategy’s average annual gross return and the return of its respective benchmark. The benchmark used for purposes of presenting a strategy’s performance and calculating Value Added is generally the market index most commonly used by our clients to compare the performance of the relevant strategy or, if none, the market index used by management to evaluate the performance of the strategy. Composites / Indexes used for the comparison calculations described are: Non-U.S. Growth Strategy / International Value Strategy-MSCI EAFE Index; Global Discovery Strategy / Global Equity Strategy / Global Opportunities Strategy / Global Value Strategy-MSCI ACWI Index; Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth Strategy-MSCI ACWI ex-USA Small Mid Index; U.S. Mid-Cap Growth Strategy-Russell Midcap Growth® Index; U.S. Mid-Cap Value Strategy-Russell Midcap Value® Index; U.S. Small-Cap Growth Strategy-Russell 2000 Growth® Index; Value Equity Strategy-Russell 1000 Value® Index; Developing World Strategy / Sustainable Emerging Markets Strategy-MSCI Emerging Markets Index; High Income Strategy-ICE BofA U.S. High Yield Index; Credit Opportunities Strategy-ICE BofA US Dollar 3-Month Deposit Offered Rate Constant Maturity Index; Antero Peak Strategy / Antero Peak Hedge Strategy / Select Equity Strategy / Value Income Strategy-S&P 500® Index; China Post-Venture Strategy-MSCI China SMID Cap Index; International Explorer Strategy-MSCI All Country World Ex USA Small Cap Index; Floating Rate Strategy-Credit Suisse Leveraged Loan Total Return Index; Global Unconstrained Strategy-ICE BofA 3-month U.S. Treasury Bill Index; Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities Strategy-J.P. Morgan EMB Hard Currency / Local Currency 50-50 Index; Emerging Markets Local Opportunities Strategy-J.P. Morgan GBI-EM Global Diversified Index.
The MSCI EAFE Index, the MSCI EAFE Growth Index, the MSCI EAFE Value Index, the MSCI ACWI Index, the MSCI ACWI ex-USA SMID Index, the MSCI ACWI ex-USA Small Cap, the MSCI Emerging Markets Index and MSCI China SMID Cap Index are trademarks of MSCI Inc. MSCI Inc. is the owner of all copyrights relating to these indices and is the source of the performance statistics of these indices that are referred to in this report. MSCI makes no express or implied warranties or representations and shall have no liability whatsoever with respect to any MSCI data contained herein. The MSCI data may not be further redistributed or used to create indices or financial products. This document is not approved or produced by MSCI.
The Russell 2000® Index, the Russell 2000® Value Index, the Russell Midcap® Index, the Russell Midcap® Value Index, the Russell 1000® Index, the Russell 1000® Value Index, the Russell Midcap® Growth Index, the Russell 1000® Growth Index and the Russell 2000® Growth Index are trademarks of Russell Investment Group. Russell Investment Group is the source and owner of the Russell Index data contained or reflected in this report and all trademarks and copyrights related thereto.
The S&P 500 Index is a product of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC (S&P DJI) and/or its affiliates and has been licensed for use. Copyright© 2024 S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC, a division of S&P Global, Inc. All rights reserved. Redistribution or reproduction in whole or in part are prohibited without written permission of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC. S&P® is a registered trademark of S&P Global and Dow Jones® is a registered trademark of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC (Dow Jones). None of S&P DJI, Dow Jones, their affiliates or third party licensors makes any representation or warranty, express or implied, as to the ability of any index to accurately represent the asset class or market sector that it purports to represent and none shall have any liability for any errors, omissions, or interruptions of any index or the data included therein.
The ICE BofA U.S. High Yield Index, ICE BofA US Dollar 3-Month Deposit Offered Rate Constant Maturity Index and the ICE BofA 3-Month U.S. Treasury Bill Index are owned by ICE Data Indices, LLC, used with permission. ICE Data Indices, LLC permits use of the ICE BofA indices and related data on an "as is" basis, makes no warranties regarding same, does not guarantee the suitability, quality, accuracy, timeliness, and/or completeness of the ICE BofA indices or any data included in, related to, or derived therefrom, assumes no liability in connection with the use of the foregoing, and does not sponsor, endorse, or recommend Artisan Partners or any of its products or services.
J.P. Morgan EMB Hard Currency / Local Currency 50/50 Index and the J.P. Morgan GBI-EM Global Diversified Index are trademarks of J.P. Morgan. Information has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable but J.P. Morgan does not warrant its completeness or accuracy. Indices are used with permission and may not be copied, used, or distributed without J.P. Morgan's prior written approval. Copyright 2024, J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. All rights reserved.
In this report, we present ratings from Morningstar, Inc., for the series of Artisan Funds. The Morningstar RatingTM for funds, or “star rating” is calculated for managed products (including mutual funds, variable annuity and variable life subaccounts, exchange-traded funds, closed-end funds, and separate accounts) with at least a three-year history. Exchange-traded funds and open-ended mutual funds are considered a single population for comparative purposes. It is calculated based on a Morningstar Risk-Adjusted Return measure that accounts for variation in a managed product's monthly excess performance, placing more emphasis on downward variations and rewarding consistent performance. The top 10% of products in each product category receive 5 stars, the next 22.5% receive 4 stars, the next 35% receive 3 stars, the next 22.5% receive 2 stars, and the bottom 10% receive 1 star. The Overall Morningstar Rating for a managed product is derived from a weighted average of the performance figures associated with its three-, five-, and 10-year (if applicable) Morningstar Rating metrics. The weights are: 100% three-year rating for 36-59 months of total returns, 60% five-year rating/40% three-year rating for 60-119 months of total returns, and 50% 10-year rating/30% five-year rating/20% three-year rating for 120 or more months of total returns. While the 10-year overall star rating formula seems to give the most weight to the 10-year period, the most recent three-year period actually has the greatest impact because it is included in all three rating periods. The ratings which form the basis for the information reflected in this report, and the fund categories in which they are rated, relating to each Fund's Investor Share Class are: Artisan Developing World Fund—Diversified Emerging Markets; Artisan Focus Fund—Large Growth; Artisan Global Discovery—Global Small/Mid Stock; Artisan Global Equity Fund—Global Large-Stock Growth; Artisan Global Opportunities Fund—Global Large-Stock Growth; Artisan Global Value Fund—Global Large-Stock Value; Artisan High Income Fund—High Yield Bond; Artisan International Fund—Foreign Large Growth; Artisan International Small-Mid Fund—Foreign Small/Mid Growth; Artisan International Value Fund—Foreign Large Blend; Artisan Mid Cap Fund—Mid-Cap Growth; Artisan Mid Cap Value Fund—Mid-Cap Value; Artisan Small Cap Fund—Small Growth; Artisan Sustainable Emerging Markets Fund—Diversified Emerging Markets; Artisan Value Fund—Large Value; Artisan Select Equity Fund—Large Blend; Artisan International Explorer Fund—Foreign Small/Mid Blend; Artisan Floating Rate Fund—Bank Loan; Artisan Value Income Fund—Large Value; Artisan Global Unconstrained Fund—Nontraditional Bond; Artisan Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities Fund—Emerging Markets Bond. Morningstar ratings are initially given on a fund's three year track record and change monthly.
Throughout this report, we present historical information about our AUM, including information about changes in our AUM due to client cash flows, investment returns and transfers between investment vehicles (e.g., pooled investment vehicles and separate accounts). Client cash flows represent client fundings, terminations and client-initiated contributions and withdrawals (which could be in cash or in securities), but generally exclude Artisan Funds’ income and capital gain distributions that are not reinvested by fund shareholders. “Investment returns and other” represents realized gains and losses, the change in unrealized gains and losses, net income and certain miscellaneous items, immaterial in the aggregate, which may include payment of Artisan’s management fees or payment of custody expenses to the extent a client causes these fees to be paid from the account we manage. The effect of translating into U.S. dollars the value of portfolio securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar is also included in this value.
We use our information management systems to track our AUM, the components of investment returns, and client cash flows, and we believe the information set forth in this report regarding our AUM, investment returns, and client cash flows is accurate in all material respects. We also present information regarding the amount of our AUM and client cash flows sourced through particular investment vehicles, asset classes, and distribution channels. The allocation of AUM and client cash flows sourced through particular distribution channels involves estimates because precise information on the sourcing of assets invested in Artisan Funds or Artisan Global Funds through intermediaries is not available on a complete or timely basis and involves the exercise of judgment because the same assets, in some cases, might fairly be said to have been sourced from more than one distribution channel. We have presented the information on our AUM and client cash flows sourced by distribution channel in the way in which we prepare and use that information in the management of our business. Non-financial data, including information about our investment performance, client cash flows, and AUM sourced by distribution channel are not subject to our internal controls over financial reporting.
None of the information in this report constitutes either an offer or a solicitation to buy or sell any fund securities, nor is any such information a recommendation for any fund security or investment service.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Overview
Founded in 1994, Artisan is an investment management firm focused on providing high valued added, active investment strategies in asset classes for sophisticated clients around the world.
Since our founding, we have maintained a business model that is designed to maximize our ability to produce attractive investment results for our clients, and we believe this model has contributed to our success in doing so. We focus on attracting, retaining and developing talented investment professionals by creating an environment in which each investment team is provided ample resources and support, transparent and direct financial incentives, a high degree of investment autonomy, and a long-term time horizon. Each of our investment teams is led by one or more experienced portfolio managers and applies its own unique investment philosophy and process. We believe this autonomous investment team structure promotes independent analysis and accountability among our investment professionals, which we believe promotes superior investment results.
Each of our investment teams manages one or more investment strategies, each of which is designed to have a clearly articulated, consistent and replicable investment process that is well-understood by clients and managed to achieve long-term performance. Over our firm’s history, we have created new investment strategies that can use a broad array of securities, instruments and techniques (which we call degrees of freedom) to differentiate returns and manage risk.
We launch a new strategy when we believe it has the potential to achieve superior investment performance in an area that we believe will have sustained client demand at attractive fee rates over the long term. We strive to maintain the integrity of the investment process followed in each of our strategies by rigorous adherence to the investment parameters we have communicated to our clients. We also carefully monitor our investment capacity in each investment strategy. We believe that management of our investment capacity protects our ability to deliver strong investment returns, which protects the interests of our clients and, in the long term, protects our ability to retain client assets and maintain our profit margins. In order to better achieve our long-term goals, we are willing to close a strategy to new investors or otherwise take action to slow or restrict its growth, even though our short-term results may be impacted.
In addition to our investment teams, we have a management team with a fiduciary mindset that is focused on thoughtfully growing the business over the long term while preserving a stable environment for our talented investment professionals and associates. We believe that maintaining the firm’s talent-driven business model and investment-focused culture is critical to generating sustainable, long-term outcomes for clients, which in turn is critical to generating sustainable long-term outcomes for shareholders. To that end, our management team focuses on managing the alignment of, and resources for, the firm’s investment professionals, managing our operational infrastructure to provide a distraction-free investment environment, adhering to our transparent and predictable financial model, and promoting the sustainability of the firm.
We offer our investment management capabilities primarily to institutions and through intermediaries that operate with institutional-like decision-making processes by means of separate accounts and pooled vehicles. We access traditional institutional clients primarily through relationships with investment consultants. We access other institutional-like investors primarily through consultants, alliances with major defined contribution/401(k) platforms and relationships with financial advisors and broker-dealers.
We derive essentially all of our revenues from investment management fees, which primarily are based on a specified percentage of clients’ average assets under management. A small percentage of our clients and investors pay us performance fees or incentive allocations, in which a portion of the fee or allocation is based on the performance of clients’ accounts relative to a benchmark. These investment advisory fees are determined by the investment advisory and sub-advisory agreements between us and our clients. Investment advisory and sub-advisory agreements between us and our clients are generally terminable by our clients upon short or no notice.
Investment Teams
We offer clients a broad range of actively managed investment strategies diversified by asset class, market cap and investment style. Each strategy is managed by one of the investment teams described below. The following table sets forth total assets under management and certain performance information for our investment teams and strategies as of December 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment Team and Strategy | AUM as of December 31, 2023 | | Composite Inception Date | Value-Added Since Inception Date (1) as of December 31, 2023 | Fund Rating(2) as of December 31, 2023 |
| | (in millions) | | | | |
| Growth Team | | | | | |
| Global Opportunities | 21,232 | | February 1, 2007 | 460 | ««« |
| Global Discovery | 1,490 | | September 1, 2017 | 422 | «««« |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Growth | 12,646 | | April 1, 1997 | 476 | ««« |
| U.S. Small-Cap Growth | 3,178 | | April 1, 1995 | 286 | «« |
| | | | | |
| Global Equity Team | | | | | |
| Global Equity | 347 | | April 1, 2010 | 260 | ««« |
| Non-U.S. Growth | 13,218 | | January 1, 1996 | 438 | ««« |
| Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth | 7,151 | | January 1, 2019 | 418 | ««« |
| China Post-Venture | 160 | | April 1, 2021 | 366 | Not Applicable |
| | | | | |
| U.S. Value Team | | | | | |
| Value Equity | 4,227 | | July 1, 2005 | 176 | «««« |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Value | 2,818 | | April 1, 1999 | 270 | «« |
| Value Income | 12 | | March 1, 2022 | (468) | Not yet rated |
| | | | | |
| International Value Team | | | | | |
| International Value | 40,762 | | July 1, 2002 | 570 | ««««« |
| International Explorer | 247 | | October 1, 2020 | 773 | Not yet rated |
| | | | | |
| Global Value Team | | | | | |
| Global Value | 25,349 | | July 1, 2007 | 298 | ««« |
| Select Equity | 321 | | March 1, 2020 | (324) | «« |
| | | | | | |
| Sustainable Emerging Markets Team | | | | | |
| Sustainable Emerging Markets | 917 | | July 1, 2006 | 81 | ««« |
| | | | | | |
| Credit Team | | | | | |
| High Income | 9,407 | | April 1, 2014 | 261 | ««««« |
| Credit Opportunities | 215 | | July 1, 2017 | 1,132 | Not Applicable |
| Floating Rate | 61 | | January 1, 2022 | 102 | Not yet rated |
| | | | | |
| Developing World Team | | | | | |
| Developing World | 3,453 | | July 1, 2015 | 655 | ««« |
| | | | | |
| Antero Peak Group | | | | | |
| Antero Peak | 1,897 | | May 1, 2017 | 371 | «« |
| Antero Peak Hedge | 204 | | November 1, 2017 | (175) | Not Applicable |
| | | | | |
| EMsights Capital Group | | | | | |
| Global Unconstrained | 313 | | April 1, 2022 | 630 | Not yet rated |
| Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities | 92 | | May 1, 2022 | 770 | Not yet rated |
| Emerging Markets Local Opportunities | 450 | | August 1, 2022 | 293 | Not applicable |
| | | | | |
Total AUM as of December 31, 2023 | 150,167 | | | | |
| | | | | |
(1) Value-added is the amount, in basis points, by which the average annual gross composite return of each of our strategies has outperformed or underperformed its respective benchmark. See “Investment Performance and Assets Under Management (AUM) Information Used in this Report” for information regarding the benchmarks used. Value-added for periods less than one year is not annualized. |
(2) The Overall Morningstar RatingTM applicable to the Artisan Fund managed to each investment strategy is derived from a weighted average of the performance figures associated with its three-year, five-year, and ten-year (if applicable) Morningstar Ratings metrics. |
Growth Team
Our Growth team manages four investment strategies: Global Opportunities, Global Discovery, U.S. Mid-Cap Growth and U.S. Small-Cap Growth. James D. Hamel, Matthew H. Kamm, Craigh A. Cepukenas, Jason L. White and Jay C. Warner are the portfolio managers of all four strategies. Mr. Hamel is the lead portfolio manager of the Global Opportunities strategy; Mr. White is the lead portfolio manager of the Global Discovery strategy; Mr. Kamm is the lead portfolio manager of the U.S. Mid-Cap Growth strategy; and Mr. Cepukenas is the lead portfolio manager of the U.S. Small-Cap Growth strategy.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Global Opportunities (February 1, 2007) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 24.40 | % | | 0.32 | % | | 14.37 | % | | 11.06 | % | | 10.75 | % |
MSCI ACWI® Index | 22.20 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 11.71 | % | | 7.92 | % | | 6.15 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Global Discovery (September 1, 2017) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 22.24 | % | | (0.86) | % | | 15.77 | % | | — | % | | 12.94 | % |
MSCI ACWI® Index | 22.20 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 11.71 | % | | — | % | | 8.72 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Growth (April 1, 1997) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 25.45 | % | | (3.59) | % | | 14.88 | % | | 10.17 | % | | 14.31 | % |
Russell Midcap® Index | 17.23 | % | | 5.92 | % | | 12.67 | % | | 9.42 | % | | 10.13 | % |
Russell Midcap® Growth Index | 25.87 | % | | 1.31 | % | | 13.81 | % | | 10.56 | % | | 9.55 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Small-Cap Growth (April 1, 1995) | | | | | | | | | |
Average Annual Gross Returns | 11.38 | % | | (9.84) | % | | 11.12 | % | | 9.40 | % | | 10.40 | % |
Russell 2000® Index | 16.93 | % | | 2.22 | % | | 9.97 | % | | 7.15 | % | | 8.84 | % |
Russell 2000® Growth Index | 18.66 | % | | (3.50) | % | | 9.22 | % | | 7.16 | % | | 7.54 | % |
Global Equity Team
Our Global Equity team currently manages four investment strategies: Global Equity, Non-U.S. Growth, Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth and China Post-Venture.
Mark L. Yockey serves as portfolio manager of the Global Equity and Non-U.S. Growth strategies. Charles-Henri Hamker and Andrew J. Euretig are also portfolio managers of the Global Equity strategy and associate portfolio managers of the Non-U.S. Growth strategy. Rezo Kanovich serves as the sole portfolio manager of the Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth strategy. Tiffany Hsiao serves as portfolio manager and Yuan Yuan Ji serves as associate portfolio manager of the China Post-Venture strategy.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Global Equity (April 1, 2010) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 13.58 | % | | (0.98) | % | | 10.90 | % | | 8.84 | % | | 11.16 | % |
MSCI ACWI® Index | 22.20 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 11.71 | % | | 7.92 | % | | 8.56 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Non-U.S. Growth (January 1, 1996) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 15.53 | % | | 1.22 | % | | 8.04 | % | | 4.62 | % | | 9.29 | % |
MSCI EAFE® Index | 18.24 | % | | 4.02 | % | | 8.16 | % | | 4.28 | % | | 4.91 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth (January 1, 2019) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 12.42 | % | | (3.09) | % | | 11.25 | % | | — | % | | 11.25 | % |
| MSCI All Country World Index Ex USA Small Mid Cap (Net) | 15.79 | % | | 0.89 | % | | 7.07 | % | | — | % | | 7.07 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| China Post-Venture (April 1, 2021) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | (4.99) | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | (15.54) | % |
| MSCI China SMID Cap Index | (16.48) | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | (19.20) | % |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
U.S. Value Team
Our U.S. Value team manages three investment strategies: Value Equity, U.S. Mid-Cap Value and Value Income. Thomas A. Reynolds, Daniel L. Kane and Craig Inman are the portfolio managers for the strategies.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Value Equity (July 1, 2005) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 25.54 | % | | 12.77 | % | | 15.86 | % | | 10.30 | % | | 9.42 | % |
Russell 1000® Index | 26.53 | % | | 8.97 | % | | 15.51 | % | | 11.80 | % | | 9.95 | % |
Russell 1000® Value Index | 11.46 | % | | 8.86 | % | | 10.90 | % | | 8.39 | % | | 7.66 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Value (April 1, 1999) | | | | | | | | | |
Average Annual Gross Returns | 19.35 | % | | 10.25 | % | | 12.31 | % | | 7.51 | % | | 12.08 | % |
Russell Midcap® Index | 17.23 | % | | 5.92 | % | | 12.67 | % | | 9.42 | % | | 9.41 | % |
Russell Midcap® Value Index | 12.71 | % | | 8.36 | % | | 11.15 | % | | 8.26 | % | | 9.38 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Value Income (March 1, 2022) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 12.20 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 1.90 | % |
| S&P 500 Market Index | 26.29 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 6.58 | % |
|
International Value Team
Our International Value team, led by N. David Samra, manages two investment strategies: International Value and International Explorer. Mr. Samra serves as lead portfolio manager of the International Value strategy and managing director of the International Explorer strategy. Ian P. McGonigle serves as co-portfolio manager of the International Value strategy and Benjamin L. Herrick serves as associate portfolio manager. Beini Zhou and Anand Vasagiri serve as co-portfolio managers of the International Explorer strategy. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| International Value (July 1, 2002) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 24.19 | % | | 11.25 | % | | 13.68 | % | | 8.05 | % | | 11.71 | % |
MSCI EAFE® Index | 18.24 | % | | 4.02 | % | | 8.16 | % | | 4.28 | % | | 6.01 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| International Explorer (October 1, 2020) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 22.42 | % | | 8.63 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 15.65 | % |
| MSCI All Country World Index Ex USA Small Cap (Net) | 15.66 | % | | 1.49 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 7.92 | % |
Global Value Team
Our Global Value team, led by Daniel J. O’Keefe, manages two investment strategies. Mr. O’Keefe serves as lead portfolio manager and Michael J. McKinnon serves as portfolio manager of the team’s Global Value and Select Equity strategies. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Global Value (July 1, 2007) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 28.05 | % | | 9.34 | % | | 12.04 | % | | 8.33 | % | | 8.75 | % |
MSCI ACWI® Index | 22.20 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 11.71 | % | | 7.92 | % | | 5.77 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Select Equity (March 1, 2020) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 27.82 | % | | 7.89 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 11.90 | % |
S&P 500 Index | 26.29 | % | | 10.00 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 15.14 | % |
Sustainable Emerging Markets Team
Our Sustainable Emerging Markets team manages one investment strategy. Maria Negrete-Gruson is the portfolio manager of the Sustainable Emerging Markets strategy.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Sustainable Emerging Markets (July 1, 2006) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 18.30 | % | | (4.95) | % | | 5.22 | % | | 4.69 | % | | 5.08 | % |
MSCI Emerging Markets Index | 9.83 | % | | (5.08) | % | | 3.68 | % | | 2.66 | % | | 4.27 | % |
Credit Team
Our Credit team manages three investment strategies: High Income, Credit Opportunities and Floating Rate. Bryan C. Krug serves as portfolio manager of the High Income and Credit Opportunities strategies and lead portfolio manager of the Floating Rate strategy. Seth B. Yeager also serves as portfolio manager of the Floating Rate strategy. During the fourth quarter of 2023, the Credit team closed on $130 million in commitments for its first closed-end fund designed to capture opportunities in dislocated credit markets. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| High Income (April 1, 2014) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 16.95 | % | | 4.42 | % | | 7.78 | % | | — | % | | 6.92 | % |
| ICE BofA U.S. High Yield Index | 13.46 | % | | 2.00 | % | | 5.21 | % | | — | % | | 4.31 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Credit Opportunities (July 1, 2017) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 27.22 | % | | 13.24 | % | | 15.52 | % | | — | % | | 13.29 | % |
| ICE BofA U.S. Dollar 3-Month Deposit Offered Rate Constant Maturity Index | 5.12 | % | | 2.15 | % | | 2.02 | % | | — | % | | 1.97 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Floating Rate (January 1, 2022) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 14.94 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 6.78 | % |
| Credit Suisse Leveraged Loan Total Return Index | 13.04 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 5.76 | % |
Developing World Team
Our Developing World team manages one investment strategy. Lewis S. Kaufman is the portfolio manager of the Developing World strategy. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Developing World (July 1, 2015) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 30.96 | % | | (10.76) | % | | 13.32 | % | | — | % | | 9.60 | % |
| MSCI Emerging Markets Index | 9.83 | % | | (5.08) | % | | 3.68 | % | | — | % | | 3.05 | % |
Antero Peak Group
Antero Peak Group manages two investment strategies: Antero Peak and Antero Peak Hedge. Christopher P. Smith is the portfolio manager of both strategies. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Antero Peak (May 1, 2017) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 17.08 | % | | 3.25 | % | | 14.05 | % | | — | % | | 16.65 | % |
| S&P 500 Index | 26.29 | % | | 10.00 | % | | 15.68 | % | | — | % | | 12.94 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Antero Peak Hedge (November 1, 2017) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 13.06 | % | | 1.36 | % | | 9.59 | % | | — | % | | 10.72 | % |
| S&P 500 Index | 26.29 | % | | 10.00 | % | | 15.68 | % | | — | % | | 12.47 | % |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
EMsights Capital Group
EMsights Capital Group manages three investment strategies: Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities, Global Unconstrained and Emerging Markets Local Opportunities. Michael A. Cirami and Sarah C. Orvin serve as the portfolio managers of each strategy.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2023 |
| Investment Strategy (Composite Inception Date) | 1 Year | | 3 Years | | 5 Years | | 10 Years | | Inception |
| Global Unconstrained (April 4, 2022) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 8.94 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 9.97 | % |
| ICE BofA 3-month Treasury Bill Index | 5.01 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 3.67 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities (May 1, 2022) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 14.52 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 13.78 | % |
| J.P. Morgan EMB Hard Currency/Local Currency 50-50 | 11.43 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 6.08 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Emerging Markets Local Opportunities (August 1, 2022) | | | | | | | | | |
| Average Annual Gross Returns | 16.16 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 14.05 | % |
| J.P. Morgan GBI-EM Global Diversified | 12.70 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 11.12 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
Distribution, Investment Products and Client Relationships
The goal of our marketing, distribution and client service efforts is to grow and maintain a client base that is diversified by investment strategy, client type, distribution channel and geographic region. We focus our distribution and marketing efforts on sophisticated investors and asset allocators, including institutions and intermediaries that operate with institutional-like, centralized decision-making processes and longer-term investment horizons. We have designed our distribution strategies and structured our distribution teams to use knowledgeable, seasoned sales and client service professionals in a way intended to limit the time our investment professionals spend on marketing and client service activities. We believe that minimizing other demands allows our portfolio managers and other investment professionals to focus their energies and attention on the investment decision-making process, which we believe enhances the opportunity to achieve superior investment returns.
Institutional Channel
Our institutional distribution channel includes institutional clients, such as U.S.-registered mutual funds, non-U.S. funds and collective investment trusts we advise; state and local governments; employee benefit plans including Taft-Hartley plans; foundations; and endowments. Our institutional channel also includes AUM sourced from defined contribution plans. We offer our investment products to institutional clients directly and by marketing our services to the investment consultants and advisors that advise them. As of December 31, 2023, approximately 35% of our AUM were attributed to clients represented by investment consultants.
As of December 31, 2023, 63% of our AUM were sourced through our institutional channel.
Intermediary Channel
We maintain relationships with a number of major brokerage firms and larger private banks and trust companies at which the process for identifying which funds to offer has been centralized to a relatively limited number of key decision-makers that exhibit institutional-like decision-making behavior. We also maintain relationships with a number of financial advisory firms and broker-dealer advisors that offer our investment products to their clients. These advisors range from relatively small firms to large organizations.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 33% of our AUM were sourced through our intermediary channel.
Retail Channel
We primarily access retail investors indirectly through mutual fund supermarkets through which investors have the ability to purchase and redeem fund shares. U.S. investors can also invest directly in Artisan Funds. Our subsidiary, Artisan Partners Distributors LLC, a registered broker-dealer, distributes shares of Artisan Funds. Publicity and ratings and rankings from Morningstar, Lipper and others are essential to building the Artisan Partners brand, which is important for attracting retail investors. As a result, we publicize the ratings and rankings received by Artisan Funds and work to ensure that potential retail investors have appropriate information to evaluate a potential investment in Artisan Funds. We do not generally use direct marketing campaigns as we believe that their cost outweighs their potential benefits.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 4% of our AUM were sourced from investors we categorize as retail investors.
Access Through a Range of Investment Vehicles
Our clients access our investment strategies through a range of investment vehicles, including separate accounts and pooled vehicles. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds accounted for approximately 48% of our total AUM, and approximately 52% of our AUM were managed in separate accounts and other pooled vehicles.
Separate Accounts and Other
We manage traditional separate accounts within most of our investment strategies. As of December 31, 2023, we managed 212 traditional separate accounts spanning 128 client relationships with our largest separate account relationship representing approximately 11% of our AUM. These separate account clients include both institutional and intermediary channel relationships, such as pension and profit sharing plans, corporations, trusts, endowments, foundations, charitable organizations, high net worth individuals, governmental entities, insurance companies, commingled investment vehicles, investment advisers and other financial institutions, trustees of collective investment trusts and investment companies and similar pooled investment vehicles. The fees we charge on separate accounts vary by client, investment strategy and the size of the account. Fees are accrued monthly, but generally are paid quarterly in arrears.
A number of our investment strategies are accessible to certain types of employee benefit plans through Artisan-branded collective investment trusts, or CITs. We act as investment adviser to the CITs and earn a management fee for providing this service. As of December 31, 2023, CITs represented approximately 5% of our AUM.
Certain of our investment strategies are primarily offered through Artisan-sponsored unregistered pooled investment vehicles, referred to as Artisan Private Funds. For serving as investment adviser to Artisan Private Funds, we earn a management fee and, for certain funds, are entitled to receive either an allocation of profits or a performance-based fee. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Private Funds comprised approximately 1% of our AUM.
In our reporting materials, unless otherwise stated, our ‘separate accounts and other’ AUM includes assets we manage in traditional separate accounts, Artisan-branded CITs and Artisan Private Funds. In addition, assets under advisement related to clients for whom we provide investment models but do not have discretionary investment authority are also included within the ‘separate accounts and other’ category. As of December 31, 2023, these assets under advisement represented less than 1% of our AUM.
Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds
U.S. investors that do not meet our minimum account size for a separate account, or who otherwise prefer to invest through a mutual fund, can invest in our strategies through Artisan Funds. We serve as the investment adviser to each series of Artisan Funds, SEC-registered mutual funds that offer no-load, no 12b-1 share classes designed to meet the needs of a range of investors. Each series of Artisan Funds corresponds to an investment strategy we offer to clients. We earn management fees, which are based on the average daily net assets of each Artisan Fund and are paid monthly, for serving as investment adviser to these funds. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Funds represented approximately 44% of our AUM.
We also serve as investment manager of Artisan Global Funds, a family of Ireland-based UCITS funds. Artisan Global Funds provides non-U.S. investors with access to a number of our investment strategies in a pooled vehicle structure. We earn investment management fees, which are based on the average daily net assets of each sub-fund and are generally paid monthly, for serving as investment adviser to these funds. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Global Funds represented approximately 4% of our AUM.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
Our business is subject to extensive regulation in the United States at the federal level and, to a lesser extent, the state level, as well as by self-regulatory organizations and regulators located outside the United States. Under these laws and regulations, agencies that regulate investment advisers, investment funds and other related entities have broad administrative powers, including the power to limit, restrict or prohibit the regulated entity from conducting business in the event that it fails to comply with such laws and regulations. Breaches of these laws and regulations could result in regulatory enforcement actions, civil liability, criminal liability and/or the imposition of sanctions, including monetary damages, injunctions, disgorgements, fines, censures, and the revocation, cancellation, suspension or restriction of licenses, registration status or approvals held by us or our employees in a jurisdiction or market. In addition, a regulatory proceeding, regardless of whether it results in a sanction, can require substantial expenditures and can have an adverse effect on our reputation or business.
The domestic, international and extra-territorial laws and regulations that apply to our business relate to a broad range of subjects, including securities, compliance, corporate governance, financial reporting and disclosure, tax, privacy and data protection, sustainability, information security, anti-bribery and anti-corruption, anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing. These laws and regulations are complex and continue to change and evolve over time. As a result, there is a level of uncertainty associated with the regulatory environments in which we operate. Accordingly, the discussion below is general in nature, does not purport to be complete and is current only as of the date of this report.
U.S. Regulation
As a publicly traded company, we are subject to U.S. federal securities laws, state securities and corporate laws, and the rules and regulations of U.S. regulatory and self-regulatory organizations. In particular, we are subject to the Securities Act of 1933, the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”), the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and, because we are listed on the New York Stock Exchange, the NYSE listing rules.
Artisan Partners Limited Partnership and Artisan Partners UK LLP are registered with the SEC as investment advisers under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 (the “Advisers Act”), and Artisan Funds and several of the investment companies we sub-advise are registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the “1940 Act”). The Advisers Act and the 1940 Act, together with other applicable securities laws and the SEC’s regulations and interpretations thereunder, impose substantive and material restrictions and requirements on the operations of investment advisers and mutual funds. The SEC is authorized to institute proceedings and impose sanctions for violations, ranging from fines and censures to, in the case of investment advisers, the termination of an adviser’s registration.
Artisan Partners Limited Partnership is registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) as a commodity pool operator, and is a member of the National Futures Association (“NFA”), with respect to its management of certain investment vehicles. The CFTC and NFA each administer a comparable regulatory system covering futures, swaps and other derivative instruments. As the commodity pool operator of these investment vehicles, Artisan Partners claims relief under the Commodity Exchange Act from certain reporting and recordkeeping requirements.
Artisan Partners Limited Partnership is a fiduciary under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, (“ERISA”) with respect to assets that we manage for certain benefit plan clients. ERISA imposes duties on persons who are ERISA fiduciaries, and prohibits certain transactions between related parties to a retirement plan. The U.S. Department of Labor administers ERISA and regulates plan fiduciaries, including investment advisers who service retirement plan clients.
Artisan Partners Distributors LLC, our SEC-registered limited purpose broker-dealer subsidiary, is subject to the Exchange Act, the SEC’s rules promulgated thereunder and the rules and regulations of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”), which generally relate to sales practices, registration of personnel, compliance and supervision, and compensation and disclosure. FINRA has the authority to conduct periodic examinations of member broker-dealers, and may initiate administrative proceedings. Artisan Partners Distributors LLC is also subject to the SEC’s Uniform Net Capital Rule and the National Securities Clearing Corporation’s excess net capital requirement, which require that at least a minimum amount of a registered broker-dealer’s assets be kept in relatively liquid form.
The legislative and regulatory environment in the U.S. is subject to continual change. Political and electoral changes and developments have in the past introduced, and may in the future introduce, additional uncertainty. New legal or regulatory requirements often add further complexity to our business and operations, and addressing such new requirements may require substantial expenditures of time and capital. Certain regulatory reforms in the U.S. that have impacted, or may in the future impact, our business include the following items:
•The SEC has recently proposed and/or adopted a number of new rules impacting registered investment advisers (e.g. private fund adviser rules, ESG disclosure rules, cybersecurity risk management and disclosure rules, beneficial ownership rules, service provider oversight requirements, rules on safeguarding client assets and predictive data analytics, and amendments to Form PF) and registered investment companies (e.g. ESG disclosure rules, amendments to the names rule, liquidity risk management and reporting modernization). In addition, the SEC has proposed and/or adopted a number of rules impacting public companies (e.g. new disclosure requirements on topics such as climate change, human capital management and cybersecurity risk governance). These rules impact us and the funds we manage to varying degrees.
•There continues to be an increased focus on the protection of customer and personal privacy and data, and the need to secure sensitive information. We are subject to the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), which took effect in January 2020, and provides for enhanced consumer protections for California residents. Since then, California amended the CCPA by adopting the California Privacy Rights Act, and several additional states have proposed and/or adopted data privacy laws with which we are or may be required to comply.
Non-U.S. Regulation
In addition to the extensive regulation we are subject to in the United States, a number of our subsidiaries and certain of our non-U.S. operations are subject to regulation in non-U.S. jurisdictions. Some laws in non-U.S. jurisdictions are also extra-territorial and may apply to our business.
Artisan Partners UK LLP is authorized and regulated by the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority, which is responsible for the conduct of business and supervision of financial firms in the United Kingdom. The FCA imposes a comprehensive system of regulation that is primarily principles-based (compared to the primarily rules-based U.S. regulatory system). The FCA’s rules under this system govern, among other things, capital resources requirements, senior management arrangements, business conduct, interaction with clients, and systems and controls.
Artisan Partners Europe is authorized and regulated by the Central Bank of Ireland, which regulates our Irish business activities, including our management of Artisan Global Funds, a family of Ireland-domiciled UCITS funds. Artisan Global Funds are registered for sale in many countries around the world, both in the EU and beyond, and thus are also subject to the laws of, and supervision by, the governmental authorities of those countries.
Artisan Partners Hong Kong Limited, our Hong Kong subsidiary, is licensed and regulated by the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (the “SFC”). Artisan Partners Hong Kong Limited and its employees conducting regulated activities under the Securities and Futures Ordinance are subject to the rules, codes and guidelines issued by the SFC from time to time.
We have historically operated in Australia on the basis of a “sufficient equivalence relief” exemption from local licensing with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission. This relief is set to expire for foreign financial service providers like us and, as a result, Artisan Partners Limited Partnership or one of its affiliates may need to apply for and obtain a securities license or a new exemption by April 2025.
Certain Artisan Private Funds are regulated as mutual funds under the Mutual Funds Law (as amended) of the Cayman Islands, and the Cayman Islands Monetary Authority has supervisory and enforcement powers to ensure the funds’ compliance with the Mutual Funds Law.
Our business is also subject to the rules and regulations of the countries in which we conduct distribution or investment management activities. We have relationships with clients located outside of the U.S., which are subject to the laws and regulations of the jurisdictions in which the client is domiciled. In addition, 46% of our AUM were invested in securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar as of December 31, 2023. Our investments in these non-U.S. securities subject us to certain laws and regulations of the jurisdictions in which the issuer resides or is traded. We may also be subject to U.S. laws and regulations with respect to our distribution or investment management activities in non-U.S. markets, including in jurisdictions that may be considered higher risk.
Regulatory reforms in jurisdictions in which we currently operate or invest and expansion of our business into new international jurisdictions, further complicate our compliance efforts. Addressing these legal and regulatory matters may require substantial time and expense. Certain non-U.S. regulatory reforms or guidance regarding such regulations that have impacted, or may in the future impact, our business include the following items:
•Under the Sustainability-Related Finance Disclosure Regulation (“SFDR”) and the EU Taxonomy Regulation, financial services companies operating in the European Union are required to disclose information on the impact of environmental, social and governance (ESG) effects on their portfolios. Asset managers are required to categorize their products and show their own processes of ESG integration and the extent to which ESG risks are expected to affect the returns on products sold. In addition, asset managers are required to annually report certain detailed information depending on the categorization of the product.
•The EU’s Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II regulates the use of soft dollars to pay for research and other soft dollar services. MiFID II’s soft dollar rules do not directly apply to our business because we currently conduct our investment management activities in the U.S. However, in response to MiFID II and the industry-wide changes prompted by it, we have in the past experienced requests from clients to bear research expenses that are currently paid for using soft dollars. In response to such requests or as a result of changes in our operations, we may eventually bear more of the costs of research that are currently paid for using soft dollars, which would increase our operating expenses materially.
We may become subject to additional regulatory demands in the future to the extent we expand our business in existing and new jurisdictions. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Legal or Regulatory Factors and Taxation—We are subject to extensive, complex and sometimes overlapping laws, rules and regulations.” and “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Legal or Regulatory Factors and Taxation—The regulatory environment in which we operate is subject to continual change, and regulatory developments may adversely affect our business.”
Industry Trends and Competition
The investment management industry continues to evolve as market trends and other forces, including the current regulatory environment, create headwinds for traditional asset management firms.
•Passive and alternative investment options continue to grow organically while traditional actively managed strategies have had net organic outflows over the past five years.
•A number of shifts in the distribution landscape are putting pressure on traditional distribution models. These shifts include:
◦distribution partners becoming more selective and maintaining fewer relationships with investment managers
◦intermediaries capturing a greater share of inflows via proprietary investment solutions
◦client demand for new investment vehicles that may be lower fee or more tax efficient
In response to these and other headwinds, we have continued to build out our alternatives capabilities and increased degrees of investment freedom within our existing investment strategies. We also regularly evaluate potential new investment teams and talent to enhance and expand our investment platform. In addition, we have evolved our distribution structure, incorporating additional associates, re-aligning incentives and providing a robust set of resources, as well as making continued investments to deepen our digital distribution capabilities.
The industry in which we operate is highly competitive. In order to be successful and grow our business, we must be able to compete effectively for AUM. We compete to attract clients and investors principally on the basis of:
•the performance of our investment strategies
•the continuity of our investment and distribution professionals
•the quality of the service we provide to our clients
•the range of investment strategies and vehicles we offer
•our brand recognition and reputation within the investing community
•the fees we charge for the investment management services we provide
We compete in all aspects of our business with a large number of investment management firms, commercial banks, broker-dealers, insurance companies and other financial institutions. For additional information concerning the competitive risks that we face, see “Risk Factors—Competition and Distribution Risks—The investment management industry is intensely competitive.”
Human Capital Resources
Since Artisan Partners was founded in 1994, our success as an investment management firm has been predicated on having talented associates throughout the organization in every role, at every level. We understand that attracting, developing and retaining talented professionals is an essential component of our business strategy. As a result, we are committed to providing an environment that is attractive to our current and prospective associates and that allows our talented associates to thrive throughout the course of their careers at Artisan.
As of December 31, 2023, we employed 573 associates. Approximately 31% of our associates work within our investment teams, 25% within our distribution teams and 45% within our business management and operations teams. Approximately 93% of our associates operate from our U.S. offices and 7% operate from our offices outside of the U.S. As of December 31, 2023, 41% of our U.S. associates were female and 22% of our U.S. associates self-identified as ethnically diverse.
We invest significant energy in the recruitment of our associates as they are critical to ensuring the long-term success of our firm. We strive to recruit and hire outstanding associates who thrive in broad roles and want the freedom to grow their talents and careers. We are committed to seeking professionals from different backgrounds, experiences and locations to foster creative thinking and differentiated perspectives that remain a pillar of the firm’s culture. We have built relationships with a variety of recruitment partners and community organizations to broaden our candidate pools and increase our access to diverse talent.
We actively support associate engagement and development, both formally and informally, and encourage advancement from within the firm. Our tuition reimbursement program is available to associates who are pursuing applicable undergraduate and graduate degrees or certifications or licenses relevant to the business. Our diversity, equity and inclusion committee champions our DEI initiatives by bringing together a group of individuals with broad representation across the firm, as well as diverse social, regional and cultural identities. We also actively support a number of associate-led groups including the Pride Alliance, Multicultural Exchange, diffAbilities and the Women’s Networking Initiative. These groups create supportive and collaborative networks, encourage engagement and a sense of belonging, and enhance professional and personal growth. Our support of these and other associate-led programs are part of our ongoing commitment to providing an environment that allows our talented associates to thrive.
We believe in order to attract and retain talent, it is critical that we continue to foster an engaging environment and provide attractive compensation and benefits programs. We regularly review compensation paid to associates to ensure it is competitive, equitable and fair for the role, experience, location and individual contribution. We provide equity or equity-linked incentives to all of our associates in order to align their economic interests with those of our clients and stockholders. We encourage our associates to save for retirement. In the U.S., we match 100% of associate 401(k) contributions dollar for dollar (fully vested), up to the IRS limit. We also maintain competitive retirement programs or benefits for all non-U.S. associates. In addition, we offer a comprehensive benefits program that is available to all associates regardless of title, role, or responsibility.
Sustainability
Artisan Partners' purpose is to generate and compound wealth over the long-term for our clients. The wealth we generate improves retirement outcomes, pays for education, funds charitable purposes and in general improves people's lives. In addition to generating successful investment outcomes for our clients, we strive to promote success across a diverse group of associates and generate sustainable financial outcomes for our shareholders.
To achieve our purpose, we must continue to thoughtfully grow our business over the long term while preserving a consistent environment in which our talented investment professionals and associates can thrive. Maintaining our talent-driven business model and investment-focused culture is critical to providing a stable environment for our associates, generating sustainable, long-term investment outcomes for clients, and creating long-term successful financial outcomes for shareholders.
To us, sustainability means the following:
•Building relationships with the right clients, on the right terms and with the right long-term investment horizons. We foster client relationships by prioritizing investment returns. Prioritizing clients’ investment returns may, at times, require us to limit client cash flows and overall assets managed in a strategy—a practice we refer to as capacity management.
•Using a deliberate process to bring on new investment talent, launch new strategies and build sustainable franchises. We are patient in developing our talent, teams and strategies. We are comfortable with evolving—and sometimes even disrupting—our firm to increase the probability of long-term successful investment outcomes through market cycles.
•Compelling work in a tailored environment, with long-term opportunities for associates across our firm. Our culture promotes associates’ success—ideally over their entire careers—with economic alignment in the form of variable compensation and long-duration incentive awards.
•Growing our business value while maintaining financial discipline and continuing to generate and distribute significant cash to our shareholders. By taking care of our people and fulfilling our fiduciary duty to our clients, we create a waterfall effect that helps generate sustainable financial outcomes for our shareholders over the long term.
Our Structure
Holding Company Structure
We are a holding company and our assets principally consist of our ownership of partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings, deferred tax assets and cash. As the sole general partner of Artisan Partners Holdings, we operate and control all of its business and affairs, subject to certain voting rights of its limited partners. We conduct all of our business activities through operating subsidiaries of Artisan Partners Holdings. Net profits and net losses are allocated based on the ownership of partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings. As of December 31, 2023, we owned approximately 86% of Artisan Partners Holdings, and the other 14% was owned by the limited partners of Artisan Partners Holdings.
Our holding company structure is predominantly a result of our IPO, which we completed in March 2013. In connection with the IPO, we and Artisan Partners Holdings completed a series of reorganization transactions, which we refer to as the IPO Reorganization, in order to reorganize our capital structures in preparation for the IPO. The IPO Reorganization included, among other changes, the following:
•Our appointment as the sole general partner of Artisan Partners Holdings.
•The modification of our capital structure into three classes of common stock and a series of convertible preferred stock. We issued shares of our Class B common stock and Class C common stock and convertible preferred stock to pre-IPO partners of Artisan Partners Holdings. Each share of Class B common stock corresponds to a Class B common unit of Artisan Partners Holdings. Each share of Class C common stock corresponds to either a Class A, Class D or Class E common unit of Artisan Partners Holdings. Subject to certain restrictions, each common unit of Artisan Partners Holdings (together with the corresponding share of Class B or Class C common stock) is exchangeable for a share of our Class A common stock.
•A corporation (“H&F Corp”) merged with and into Artisan Partners Asset Management, which we refer to in this document as the H&F Corp Merger.
•We entered into two tax receivable agreements (“TRAs”), one with a private equity fund (the “Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder”) and the other with each limited partner of Artisan Partners Holdings. Pursuant to the first TRA, APAM pays to the assignees of the Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder a portion of certain tax benefits APAM realizes as a result of the H&F Corp Merger. Pursuant to the second TRA, APAM pays to current or former limited partners of Artisan Partners Holdings (or their assignees) a portion of certain tax benefits APAM realizes as a result of the purchase or exchange of their limited partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings.
The diagram below depicts our organizational structure as of December 31, 2023:

| | | | | |
(1) | Our employees to whom we have granted equity have entered into a stockholders agreement with respect to all shares of our common stock they have acquired from us and any shares they may acquire from us in the future, pursuant to which they granted an irrevocable voting proxy to a stockholders committee currently consisting of Eric R. Colson (Chief Executive Officer), Charles J. Daley, Jr. (Chief Financial Officer) and Gregory K. Ramirez (Executive Vice President). The stockholders committee, by vote of a majority of its members, will determine the vote of all of the shares subject to the stockholders agreement. In addition to owning all of the shares of our Class B common stock, our employee-partners, together with our other employees, owned unvested restricted shares of our Class A common stock representing approximately 8% of our outstanding Class A common stock as of December 31, 2023. |
(2) | Each class of common units generally entitles its holders to the same economic and voting rights in Artisan Partners Holdings as each other class of common units, except that the Class E common units have no voting rights except as required by law. |
Available Information
Our website address is www.artisanpartners.com. We make available free of charge through our website all of the materials we file with or furnish to the SEC as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Information contained on our website is not part of, nor is it incorporated by reference into, this Form 10-K. The company was incorporated in Wisconsin on March 21, 2011 and converted to a Delaware corporation on October 29, 2012.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Human Capital Risks
The loss of key investment professionals or senior members of our distribution and management teams could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our success depends on our ability to attract, retain and motivate, including through competitive compensation packages, the portfolio managers who manage our investment strategies and have been primarily responsible for the historically strong investment performance we have achieved. The departure of a portfolio manager has in the past contributed to clients’ decisions to withdraw funds from an investment strategy and could in the future cause clients to withdraw funds or terminate their relationship with us entirely. Such client cash outflows reduce our AUM, and therefore reduce our investment advisory fees and our net income. The departure of a portfolio manager has in the past and could in the future also cause consultants and intermediaries to stop recommending a strategy for a period of time, and clients to refrain from allocating additional funds to a strategy or delay such additional funds until a sufficient new track record has been established. Although we have not been materially impacted by the departure of a portfolio manager to date, we cannot guarantee that any future impacts from departures would not be material, particularly if the departing portfolio manager is responsible for managing a significant percentage of our AUM that account for a high proportion of our revenues. For example, the International Value team, led by N. David Samra, was responsible for managing $41.0 billion, or 27%, of our AUM as of December 31, 2023. The team generated $302 million, or 31% of our total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2023, representing the largest proportion of our AUM and revenue, managed by a single investment team.
In addition to our key investment professionals, we also depend on the contributions of our senior management team led by Eric R. Colson and Jason A. Gottlieb, and our senior marketing and client service personnel who have direct contact with our institutional clients, consultants, intermediaries and other key individuals within each of our distribution channels. The loss of any of these key professionals could limit our ability to successfully execute our business strategy or adversely affect our ability to retain existing and attract new client assets and related revenues.
Competition for highly-skilled and motivated portfolio managers and other key professionals in the investment management industry is intense, and the market for qualified professionals in our industry is characterized by the frequent movement of portfolio managers and other key professionals among different firms. Any of our key professionals may resign at any time, retire, join our competitors or form a competing company. Although many of our portfolio managers and each of our named executive officers are subject to one-year post-employment non-compete obligations, these non-competition provisions are not enforceable in certain jurisdictions or may not be enforceable to their full extent. In addition, we have in the past and may again in the future agree to waive non-competition provisions or other restrictive covenants applicable to former key professionals in light of the circumstances surrounding their relationship with us. We do not carry “key person” insurance that would provide us with proceeds in the event of the death or disability of any of our key professionals.
Changes to our investment environment or compensation structures could cause instability within our investment teams and/or have an adverse effect on the performance of our investment strategies, our financial results and our ability to grow.
Attracting, developing and retaining talented investment professionals is an essential component of our business strategy. To do so, it is critical that we continue to foster an environment and provide opportunities, compensation and benefits that are attractive for existing and prospective investment professionals. If we are unsuccessful in maintaining such an environment or compensation levels or structures, our existing investment professionals may leave our firm or fail to produce their best work on a consistent, long-term basis and/or we may be unsuccessful in attracting talented new investment professionals, any of which could negatively impact the performance of our investment strategies, our financial results and our ability to grow.
Over our firm’s history we have sought to successfully design and implement compensation structures that align our investment professionals’ economic interests with those of our clients and stockholders. We believe such alignment is important to our long-term growth and that objective, predictable, and transparent compensation structures work best to incentivize investment professionals to perform over the long-term.
With respect to asset-based revenues, we use a single revenue share arrangement across all of our investment teams, pursuant to which each team shares a bonus pool consisting of 25% of the asset-based revenues earned by the strategies managed by the respective team. The revenue share directly links the majority of the investment teams’ cash compensation to long-term growth in revenues, which, over the long-term, we believe is primarily linked to investment performance. The asset-based revenue share is objective, predictable, transparent, and the same for all teams. Each team is also entitled to a share of the performance-based revenues earned by the strategies it manages. In addition to the revenue share arrangement, we also provide supplemental incentive payments to investment professionals in support of new or subscale teams or strategies.
The equity we award to our investment professionals consists of a mix of standard restricted shares which vest pro rata over the five years following the year of grant, and career or franchise shares that generally vest on, or 18 months after, a “qualified retirement” as defined in the applicable award agreement. Franchise shares are further subject to the franchise protection clause, which applies to current or former portfolio managers and founding investment team members. Pursuant to this clause, the number of shares ultimately vesting may be reduced to the extent that cumulative net client cash outflows from the award recipient’s investment team during a period beginning on the date of the recipient’s retirement notice exceeds a set threshold.
We also grant franchise capital awards to investment professionals to enhance the alignment between our investment professionals and clients, and to provide investment professionals with greater control over their long-term economic outcome. Franchise capital awards are cash awards that are subject to the same long-term vesting and forfeiture provisions as the restricted share-based awards described above. Prior to vesting, though, the franchise capital awards will generally be invested in one or more of the investment strategies managed by the award recipient’s investment team.
We regularly assess the effectiveness of our compensation arrangements and long-term incentive structures in aligning the long-term interests of our investment professionals with those of our clients and stockholders and whether different, or modified, arrangements or structures would enhance incentives for long-term growth and succession planning.
The implementation of new or modified compensation arrangements or long-term incentive programs has in the past led to friction within our investment teams. Future modifications to compensation arrangements or long-term incentive programs could cause instability within our investment teams if those modifications were perceived to negatively impact portfolio managers’ economic outcomes or treated teams differently from one another. In addition, any new arrangements or structures could materially impact our financial performance and results (or expectations about our future financial performance and results), reduce the amount of cash available for dividends and distributions to our stockholders and partners, or result in dilution to other stockholders.
Market and Investment Performance Risks
Poor investment performance over the long-term leads to a loss of assets under management which reduces our revenues and negatively impacts our financial condition.
The performance of our investment strategies is critical in retaining existing client assets and in attracting new client assets. Poor performance causes financial intermediaries, advisors and consultants to remove our investment products from recommended lists and can result in lower Morningstar and Lipper ratings and rankings. During periods of long-term poor performance, our clients have in the past withdrawn funds from our investment strategies and, in some cases, have decided to end their relationship with us entirely. In addition, our ability to attract new client assets is adversely affected by prolonged periods of poor performance. A decrease in the value of our AUM as a result of poor performance has in the past, and would in the future, have an adverse impact on our revenues, as nearly all of the investment management fees we earn are based on a specified percentage of clients’ average AUM. Poor performance also adversely affects the portion of our revenues attributed to performance-based fees.
Our investment strategies can perform poorly for a number of reasons, including general market conditions; investor sentiment about market and economic conditions; investment styles and philosophies; investment decisions; the performance of the companies in which our investment strategies invest and the currencies in which those investments are made; the liquidity of securities or instruments in which our investment strategies invest; our inability to identify sufficient appropriate investment opportunities for existing and new client assets on a timely basis; and our inability to retain key investment professionals and other personnel. In addition, while we seek to deliver long-term value to our clients, volatility may lead to underperformance in the near term, which could adversely affect our results of operations.
Moreover, when our strategies experience strong results relative to the market, clients’ allocations to our strategies typically increase relative to their other investments and we sometimes experience withdrawals as our clients rebalance their investments to fit their asset allocation preferences despite our strong results.
While clients do not have legal recourse against us solely on the basis of poor investment results, if our investment strategies perform poorly, we are more likely to become subject to litigation brought by dissatisfied clients. In addition, to the extent clients are successful in claiming that their losses resulted from fraud, negligence, willful misconduct, breach of contract or similar misconduct, these clients may have remedies against us, the mutual funds and other funds we advise and/or our investment professionals under various U.S. and non-U.S. laws.
Difficult market conditions typically adversely affect our business in many ways, including by reducing our assets under management and causing clients to withdraw funds, each of which reduces our revenues and impacts our financial condition.
Financial markets have experienced, and may continue to experience, volatility and disruption amid continued concerns about elevated inflation, interest rate increases, effects of geopolitical tensions, conflicts, and wars, and other global economic conditions. This continued volatility and uncertainty in global financial markets has impacted the value of our AUM. Because the revenue we earn is based on the value of our AUM, fluctuations in our AUM result in corresponding fluctuations in our revenues and earnings. Difficult market conditions have in the past and may in the future cause investors in the mutual funds we advise to redeem their investments in those funds which they can do at any time and without prior notice. Our separate account clients have in the past and may in the future reduce the aggregate amount of AUM with us with minimal or no notice for any reason, including due to declining financial market conditions. In addition, the prices of the securities held in the portfolios we manage have in the past and may in the future decline for any number of reasons beyond our control, including, among others, a declining market, general economic downturn or recession, political uncertainty, inflation rates, natural disasters, war, acts of terrorism, or other unpredictable events.
In connection with the severe market dislocations of 2008 and 2009, for example, the value of our AUM declined substantially. In the period from June 30, 2008 through March 31, 2009, our AUM decreased by approximately 43%, primarily as a result of
general market conditions. During the first quarter of 2020, AUM levels decreased by approximately 24% from February 19, 2020 to March 31, 2020, as a result of sharp global equity market declines related to the COVID-19 pandemic. More recently, over the course of 2022, our assets declined by approximately 27%, as persistent inflation and efforts by central banks to combat that inflation through increasing interest rates, and the Russian invasion of Ukraine caused widespread turmoil in global financial markets.
The fees we earn under our investment management agreements are typically based on the market value of our AUM, and to a much lesser extent based directly on investment performance. Difficult market conditions have in the past led, and may again lead, to a decline in our AUM, thereby resulting in a decline in our investment advisory fees. If our revenues decline without a commensurate reduction in our expenses, our net income will be reduced.
Several of our investment strategies invest principally in the securities of non-U.S. companies, which involve foreign currency exchange, tax, political, social and economic uncertainties and risks.
As of December 31, 2023, approximately 57% of our AUM were invested in strategies that primarily invest in securities of non-U.S. companies. Some of our other strategies also invest on a more limited basis in securities of non-U.S. companies. Approximately 46% of our AUM were invested in securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar at December 31, 2023. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates could negatively affect the returns of our clients who are invested in these strategies. In addition, an increase in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to non-U.S. currencies is likely to result in a decrease in the U.S. dollar value of our AUM, which, in turn, would likely result in lower revenue and profits. See “Qualitative and Quantitative Disclosures Regarding Market Risk-Exchange Rate Risk” in Item 7A of this report for more information about exchange rate risk.
Investments in non-U.S. issuers are affected by tax positions taken in countries or regions in which we are invested as well as political, social and economic uncertainty. Declining tax revenues have in the past and could in the future cause governments to assert their ability to tax the local gains and/or income of foreign investors, which has in the past and could in the future adversely affect clients’ interests in investing outside their home markets. Many financial markets are not as developed, or as efficient, as the U.S. financial markets and, as a result, those markets typically have limited liquidity and higher price volatility, and in some cases lack established regulations.
Liquidity may also be adversely affected by political or economic events, government policies, and social or civil unrest within a particular country. For example, in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the U.S. and other countries imposed broad-ranging economic sanctions on Russia and certain Russian individuals, banking entities and corporations, which has impacted liquidity of Russian holdings. Our ability to dispose of an investment may be adversely affected if we increase the size of our holdings in smaller non-U.S. issuers. Non-U.S. legal and regulatory environments, including financial accounting standards and practices, may also be different, and there may be less publicly available information about such companies. These risks could adversely affect the performance of our strategies that are invested in securities of non-U.S. issuers and may be particularly acute in the emerging or less developed markets in which we invest. In addition to our Sustainable Emerging Markets and Developing World strategies, and the strategies managed by the EMsights Capital Group, which invest primarily in emerging markets, several of our other investment strategies are permitted to invest, and do invest, in emerging or less developed markets to a more limited extent.
Competition and Distribution Risks
We may not be able to maintain our current fee rates as a result of poor investment performance, competitive pressures, changes in global markets and asset classes, changes in our business mix or for other reasons, which could have a material adverse effect on our profit margins and results of operations.
We may not be able to maintain our current fee rates for any number of reasons, including as a result of poor investment performance, competitive pressures, changes in global markets and asset classes, or as a result of changes in our business mix. Although our investment management fees vary by client, investment strategy and investment vehicle, we historically have been successful in maintaining an attractive overall rate of fee and profit margin due to the strength of our investment performance and our focus on high value-added investment strategies. In recent years, however, there has been a general trend toward lower fees in the investment management industry as a result of competition and regulatory and legal pressures. In order to maintain our fee structure in a competitive environment, we must retain the ability to decline additional assets to manage from potential clients who demand lower fees even though our revenues may be adversely affected in the short term. In addition, we must be able to continue to provide clients with investment returns and service that our clients believe justify our fees.
From time to time we offer lower fees in order to retain current, and attract additional, assets to manage. We also make fee concessions in certain circumstances, for example in order to attract early investors in a new strategy or increase marketing momentum in a strategy. Downward pressure on fees may also result from the growth and evolution of the universe of potential investments in a market or asset class or by transformative pressures impacting the investment management industry, including the continued growth of allocations to passive and alternative investment options. Changes in how clients choose to access asset management services may also exert downward pressure on fees. Some investment consultants, for example, have implemented programs in which the consultant provides a range of services, including selection, in a fiduciary capacity, of asset managers to serve as sub-adviser at lower fee rates than the manager’s otherwise applicable rates, with the expectation of a larger amount of AUM through that consultant. The expansion of those and similar programs could, over time, make it more difficult for us to maintain our fee rates. In addition, from time to time, plan sponsors of 401(k) and other defined contribution assets that we
manage choose to invest plan assets in vehicles with lower cost structures than mutual funds (such as a collective investment trust) or may choose to access our services through a separate account. We provide fewer services to collective investment trusts and separate accounts than we provide to Artisan Funds and we receive fees at lower rates.
The investment management agreements pursuant to which we advise mutual funds are subject to an annual process of review and renewal by the funds’ boards. As part of that process, the fund board considers, among other things, the level of compensation that the fund has been paying us for our services. That process may result in the renegotiation of our fee structure or an increase in the cost of the performance of our obligations. Any fee reductions on existing or future new business would have an adverse effect on our profit margins and results of operations.
We depend on third parties to market our investment strategies.
Our ability to attract additional assets to manage is highly dependent on our access to third-party intermediaries. We gain access to investors primarily through consultants, 401(k) platforms, mutual fund platforms, broker-dealers and financial advisors through which shares of the funds are sold. We have relationships with some third-party intermediaries through which we access clients in multiple distribution channels. Our two largest intermediary relationships across multiple distribution channels represented approximately 9% and 8% of our total AUM as of December 31, 2023.
Intermediaries through which we distribute our mutual funds may also sell their own funds and technology-enabled investment solutions. Investment products offered by intermediaries may have lower fees and be provided in more tax efficient wrappers, which could limit the distribution of our investment strategies that are offered through more traditional vehicles. Certain intermediaries have reduced the number of investment options they make available to their clients and/or are seeking to reduce the number of investment management firms with whom they work. Any failure to maintain strong business relationships with these intermediaries due to any of the above-described factors would impair our ability to sell our products, which in turn could have a negative effect on our AUM, revenues and net income.
We compensate most of the intermediaries through which we gain access to investors in Artisan Funds by paying fees, most of which are a percentage of assets invested in Artisan Funds through that intermediary and with respect to which that intermediary provides shareholder and administrative services. The allocation of such fees between us and Artisan Funds is determined by the Artisan Funds’ board, based on information and a recommendation from us, with the goal of allocating to us, at a minimum, all costs attributable to marketing and distribution of shares of Artisan Funds. In the future, our expenses in connection with those intermediary relationships could increase if the portion of those fees determined to be in connection with marketing and distribution, or otherwise allocated to us or payable by us, increased.
We access institutional clients primarily through consultants upon whose referrals our institutional business is highly dependent. These consultants review and evaluate our products and our firm from time to time. As of December 31, 2023, the investment consultant advising the largest portion of our AUM represented approximately 5% of our total AUM. Poor reviews or evaluations of us or a particular strategy may result in client withdrawals or may impair our ability to attract new assets through these consultants.
The investment management industry is intensely competitive.
Competition within the investment management industry is based on a variety of factors, including investment performance, management fee rates, continuity of investment professionals and client relationships, the quality of client service, corporate positioning and business reputation, continuity of distribution arrangements with intermediaries and product mix and offerings. A number of factors, including the following, serve to increase our competitive risks:
•Unlike some of our competitors, we do not currently engage in impact investing, offer passive investment strategies, exchange-traded funds or “solutions” products like target-date funds.
•A number of our competitors have greater financial, technical, marketing and other resources, more comprehensive name recognition and more personnel than we do.
•Potential competitors have a relatively low cost of entering the investment management industry.
•Some investors may prefer to invest with an investment manager that is not publicly traded based on the perception that a publicly-traded asset manager may focus on the manager’s own growth to the detriment of investment performance.
•Other industry participants may seek to recruit our investment professionals.
•Many competitors charge lower fees for their investment management services than we do.
For example, the trend in favor of low-fee passive products such as index and certain exchange-traded funds favors those of our competitors who provide passive investment strategies. That trend has presented, and likely will continue to present, a headwind to our business. If we are unable to compete effectively, our earnings would be reduced and our business could be materially adversely affected.
Risks Related to our Business
Our efforts to establish and develop new teams, strategies and vehicles may face challenges or ultimately be unsuccessful, which could impact our results of operations, reputation and culture.
We seek to recruit new investment teams that manage high value-added investment strategies and would allow us to grow strategically. We also look to develop new, differentiated strategies managed by our existing teams. We expect the costs associated with establishing a new investment team, strategy or vehicle to initially exceed the revenues generated, which will negatively impact our results of operations. New strategies or vehicles, whether managed by a new team or by an existing team, may make investments or present operational, legal, regulatory, or distribution-related issues and risks that we have not yet encountered or with which we have less experience. The incorporation of new teams, strategies, vehicles and types of investments could strain our resources and increase the likelihood of an error or failure, a risk which is exacerbated by the increasingly specialized nature of newer investment teams and strategies. The establishment of new teams or strategies (in particular, alternative investment teams or strategies) may also cause us to depart from our traditional compensation and economic model, which could reduce our profitability and harm our firm’s culture.
Historical returns of our existing investment strategies will not be indicative of the investment performance of any new strategy and new strategies may have higher performance expectations that are more difficult to meet. Poor performance of any new strategy could negatively impact our reputation and the reputation of our other investment strategies.
We generally support the development of new strategies by making one or more seed investments using capital that would otherwise be available for our general corporate purposes. Making such seed investments exposes us to capital losses and reduces the amount of capital available for other purposes. In addition, the development of new investment teams and strategies requires the support of well-qualified investment, distribution and operational talent, the market for which has been and may continue to be tight. The inability to recruit or retain such personnel may negatively impact our ability to develop investment teams and strategies and may ultimately hinder our growth.
We derive substantially all of our revenues from contracts and relationships that may be terminated upon short or no notice.
We derive substantially all of our revenues from investment advisory and sub-advisory agreements, all of which are terminable by clients upon short or no notice. Our investment management agreements with mutual funds, as required by law, are generally terminable by the funds’ boards or a vote of a majority of the funds’ outstanding voting securities on not more than 60 days’ written notice. After an initial term, each fund’s investment management agreement must be renewed annually by that fund’s board, including by its independent members. In addition, all of our separate accounts and some of the mutual funds that we sub-advise have the ability to re-allocate all or any portion of the assets that we manage away from us at any time with little or no notice. The decrease in revenues that could result from the termination of a material client relationship or the re-allocation of assets away from us could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Investors in many of the funds we advise can redeem their investments at any time without prior notice or with fairly limited notice, which would reduce our assets under management and could adversely affect our earnings.
Investors in the mutual funds, UCITS funds, and some other pooled investment vehicles that we advise may redeem their investments in those funds at any time without prior notice. Investors in certain other pooled vehicles may redeem their investments with fairly limited prior notice. These investors may redeem for any number of reasons, including general financial market conditions, the absolute or relative investment performance we have achieved, or their own financial condition and requirements. In a declining stock market, the pace of redemptions could accelerate. These redemptions would reduce our AUM and adversely affect our revenues.
The majority of our assets under management are managed in primarily long-only, equity investment strategies, which exposes us to greater risk than certain of our competitors who may manage more assets in diverse strategies.
19 of our 25 investment strategies, which accounted for over 90% of our AUM as of December 31, 2023, invest primarily in publicly-traded equity securities. Under market conditions in which there is a general decline in the value of equity securities, the AUM in each of these strategies is likely to decline. Although certain strategies have the ability to take short positions in equity securities, such investments have not typically been made in practice. In addition, there is no guarantee that such short positions would meaningfully offset the poor performance of our long-only equity strategies under such market conditions. Even if our investment performance remains strong during such market conditions relative to other long-only, equity strategies, investors may choose to withdraw assets from our management or allocate a larger portion of their assets to non-long-only or non-equity strategies. In addition, the prices of equity securities may fluctuate more widely than the prices of other types of securities, making the level of our AUM and related revenues more volatile.
Our newest investment strategies and strategies we may establish in the future present certain investment, operational, distribution and other risks that are different in kind and/or degree from those presented by our earlier investment strategies and dealing with those risks could place additional demands on our existing operational infrastructure and employees.
Our newest investment strategies have the ability to make investments that present different risks and/or degrees of risk than our other strategies, which invest primarily in publicly traded equity securities. For example, several of our newest strategies invest in securities that are not publicly traded. We may be prohibited from selling these investments for a period of time and generally will be unable to sell these securities publicly unless their sale is registered under applicable securities law or unless an
exemption from such registration is available. Illiquid securities are more difficult to value and dispose of when desired and, under certain circumstances, may make it more difficult to manage investors’ redemption requests. Our newer strategies, and strategies we may offer in the future, may also invest in certain instruments (such as derivative securities) and engage in activities (such as shorting and use of leverage) the complexity of which may place additional demands on our existing operational infrastructure and our existing employees, and increase the risk of operational errors. Any such errors could damage our reputation or result in regulatory scrutiny or legal liability. And any real or perceived problems could cause a disproportionate negative impact on our business and reputation.
Several of our newest investment strategies are primarily offered through private funds, which present operational, regulatory and distribution-related risks that are different than those associated with the mutual funds and traditional separate accounts through which we offer our earlier investment strategies. In the future, we expect to offer new investment strategies in new asset classes through different types of investment vehicles and fund structures which could present different types of operational, regulatory and distribution-related risks with which we have little to no experience. For example, our reputation as a long-only manager of traditional investment products has been an impediment to penetrating new channels and selling our newer alternative investment strategies. Although we continue to build out a team of distribution professionals with deep alternatives experience and strong fundraising networks, we cannot be sure that these changes will have a meaningful impact on selling our alternatives strategies. In general, the complexity of these newer strategies and vehicles could strain our resources and increase the likelihood of real or perceived problems, which could damage our reputation or result in regulatory scrutiny or legal liability.
Several of our newer investment strategies and vehicles, and strategies and vehicles that we may establish in the future, have more limited capacity than our earlier large capacity investment strategies. Despite the limited capacity, these newer strategies with broader degrees of freedom may require increased access to specialized technology, market data with advanced data analytic capabilities, and operational resources, including bespoke operational solutions and third-party service providers as well as operational, distribution and other personnel with specialized talent to align with the increasing complexity of the investment strategies. In addition to the risk that our newer investment teams, strategies or vehicles may not experience the requisite growth to compensate for these increased operational support costs, requests for resources that are disproportionate to the size of the investment team may put pressure on our resource allocation model and cause friction and instability among the teams. Friction among investment teams may also occur if these newer strategies with broader degrees of freedom take action or make investments that ultimately impact the ability of our other investment teams to invest in a manner consistent with their philosophy and process. Friction and distraction within our investment teams may cause our existing investment professionals to leave our firm or fail to produce their best work on a consistent, long-term basis and/or we may be unsuccessful in attracting talented new investment professionals, any of which could negatively impact the performance of our investment strategies, our financial results and our ability to grow.
If our techniques for managing risk are ineffective, we may be exposed to material unanticipated losses.
In order to manage the significant risks inherent in our business, we must maintain effective policies, procedures and systems that enable us to identify, monitor and mitigate our exposure to operational, legal and reputational risks. Our risk management methods may prove to be ineffective due to their design or implementation, or as a result of a lack of adequate, accurate or timely information or otherwise. If our risk management efforts are ineffective, we could suffer losses that could have a material adverse effect on our operating results or financial condition. Additionally, we could be subject to litigation, particularly from our clients or investors, and sanctions or fines from regulators.
We may, from time to time, strategically manage our exposure to market, interest or exchange rate risks on our own behalf or on behalf of our clients. However, because our clients invest in our investment strategies in order to gain exposure to the portfolio securities of the respective strategies, we have not adopted corporate-level risk management policies to manage market, interest rate, or exchange rate risks that would affect the value of our overall AUM.
We provide a range of services to Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds, Artisan Private Funds and sub-advised funds which may expose us to liability.
We provide a broad range of administrative services to Artisan Funds, including providing personnel to serve as directors and officers of Artisan Funds and to serve on the valuation and liquidity committee of Artisan Funds. We prepare or supervise the preparation of Artisan Funds’ regulatory filings and financial statements, and manage compliance and regulatory matters. We provide shareholder services, accounting services including the supervision of the activities of Artisan Funds’ accounting services provider in the calculation of the funds’ net asset values, and tax services including calculation of dividend and distribution amounts. We also coordinate the audits of financial statements and supervise tax return preparation. Although less extensive than the range of services we provide to Artisan Funds, we provide a range of similar services to Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds. In addition, from time to time we provide information to other funds we advise (or to an entity providing services to such a fund) which may be used by those funds in their efforts to comply with various regulatory requirements.
The services we provide to Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds, Artisan Private Funds, and other funds we advise may expose us to liability. For example, if we make a mistake in the provision of such services, a fund could incur costs for which we might be liable. If it were determined that a fund failed to comply with applicable regulatory requirements as a result of our action or our employees’ failure to act, we could be responsible for losses suffered or penalties imposed. In addition, we could have penalties imposed on us, be required to pay fines or be subject to private litigation, any of which could decrease our future income or negatively affect our current business or our future growth prospects.
Risks Related to Legal or Regulatory Factors and Taxation
Failure to properly address conflicts of interest could harm our reputation or cause clients to withdraw funds, each of which could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The SEC and other regulators have continued to focus on potential conflicts of interest and our fiduciary duties as an adviser. We have implemented procedures and controls that we believe are reasonably designed to address these issues. However, appropriately dealing with conflicts of interest is complex and if we fail, or appear to fail, to deal appropriately with conflicts of interest, we could face reputational damage, litigation or regulatory proceedings or penalties, any of which may adversely affect our results of operations.
As we expand the scope of our business and our client base, we must continue to monitor and address any conflicts between the interests of our stockholders and those of our clients. Our clients may withdraw funds if they perceive conflicts of interest between the investment decisions we make for strategies in which they have invested and our obligations to our stockholders. For example, we may limit the growth of assets in or close strategies when we believe it is in the best interests of our clients even though our AUM and investment advisory fees may be negatively impacted in the short term. Similarly, we may establish new investment teams or strategies or expand operations into other geographic areas if we believe such actions are in the best interests of our clients, even though our profitability may be adversely affected in the short term. Although we believe such actions enable us to retain client assets and maintain our profitability, which benefits both our clients and stockholders, if clients perceive a change in our investment or operations decisions in favor of a strategy to maximize short term results, they may withdraw funds, which could reduce our revenue and impact our financial condition.
Offering private funds also poses risks associated with side by side management and the potential for real or perceived conflicts of interest, which, if not managed correctly, could cause reputational harm, regulatory scrutiny or litigation. Although we have established policies and procedures to manage potential conflicts of interest, we are unable to completely eliminate these risks.
Our failure to comply with clients’ investment guidelines and applicable legal limitations could result in damage awards against us and a loss of assets under management, either of which could adversely affect our financial condition.
When clients retain us to manage assets on their behalf, they generally specify certain investment guidelines that we are required to follow in managing their portfolios. In addition, some of our clients are subject to laws that impose restrictions and limitations on the investment of their assets. For example, U.S. mutual fund assets that we manage must be invested in accordance with limitations under the 1940 Act and applicable provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. Our failure to comply with any of these guidelines and other limitations could result in losses to clients or fund investors which, depending on the circumstances, could result in our obligation to reimburse clients or fund investors for such losses. If we believed that the circumstances did not justify a reimbursement, or clients and investors believed the reimbursement we offered was insufficient, they could seek to recover damages from us or could withdraw assets from our management or terminate their investment management agreement with us. Any of these events could harm our reputation and adversely affect our business.
Employee misconduct, or perceived misconduct, could expose us to significant legal liability and/or reputational harm.
We are vulnerable to reputational harm because we operate in an industry in which integrity and the confidence of our clients are of critical importance. Our employees, or third parties with whom we are affiliated, could engage in misconduct, or perceived misconduct, that adversely affects our business. It is not always possible to deter employee misconduct and the precautions we take to prevent and detect this activity may not always be effective. Misconduct or perceived misconduct by our employees, or even unsubstantiated allegations of such conduct, could cause serious damage to our reputation, resulting in the loss of clients and an adverse effect on our revenues. Employee misconduct could also subject us to regulatory scrutiny and legal liability.
The expansion of our business inside and outside of the United States raises tax and regulatory risks, may adversely affect our profit margins and places additional demands on our resources and employees.
We continue to expand our distribution efforts into non-U.S. markets. The number of client relationships outside the U.S. has grown from 54 as of December 31, 2013 to 216 as of December 31, 2023. Costs related to our distribution efforts in non-U.S. markets have often been more expensive than comparable costs in the U.S. and our non-U.S. clients may be accustomed to certain practices that differ from and may conflict with practices that are customary in the U.S. For example, the use of soft dollars for research products and services are generally accepted in the U.S. However, other jurisdictions (for example, the European Union) have requirements that limit or prohibit the use of soft dollars for research products and services. Such conflicting practices add complexity, costs and risk to our non-U.S. client relationships.
While a majority of our operations take place in the U.S., we do maintain offices in a number of other countries including the U.K., Ireland, Singapore, Australia and Hong Kong. Operating our business in non-U.S. markets is generally more expensive than in the U.S. Among other expenses, the effective tax rates applicable to our income allocated to some non-U.S. markets may be higher than the effective rates applicable to our income allocated to the U.S. To the extent that our revenues do not increase to the same degree our expenses increase in connection with our continuing expansion outside the U.S., our profitability could be adversely affected. Expanding our business into new markets may also place significant demands on our existing operational infrastructure and on our existing employees.
Regulators in non-U.S. jurisdictions in which we currently operate could change their laws or regulations, or change the way they interpret existing laws and regulations, in a manner that might restrict or otherwise impede our ability to operate in their respective markets. Any such changes could increase the costs we incur in a specific jurisdiction without any corresponding increase in revenues and income from operating in the jurisdiction. For example, in response to Brexit, we established an Irish subsidiary regulated by the Central Bank of Ireland to carry out distribution efforts in the EU. Brexit added complexity to our global operations, imposed additional risks and resulted in additional legal and compliance costs, without an increase in revenues to offset those costs. Despite those increased costs, Brexit did not have a material impact on our business.
Our employees routinely travel inside and outside the U.S. as a part of our investment research process, to market our services and to supervise and manage our business. Their activities in the jurisdictions they travel to on our behalf may raise both tax and regulatory issues. If and to the extent we are incorrect in our analysis of the applicability or impact of these tax or regulatory requirements, we could incur costs, penalties or be the subject of an enforcement or other action.
Changes in tax laws or exposure to additional tax liabilities could have a material impact on our financial condition, results of operations and liquidity.
We are subject to income taxes, as well as non-income based taxes, in both the U.S. and various foreign jurisdictions at the federal, state and local levels of government. We cannot predict future changes in the tax laws, regulations, administrative guidance or judicial decisions to which we are subject or that could apply to our business. Any such changes could have a material impact on our tax liability, materially impact our effective tax rate, result in additional tax reporting obligations, or result in increased costs associated with our tax compliance efforts.
From time to time, we are subject to income and non-income based tax audits in the jurisdictions in which we operate. The calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax rules and regulations in a number of jurisdictions. From time to time, tax authorities have disagreed with certain positions we have taken which has resulted in additional taxes and, in certain cases interest payments. In the future, such instances may result in additional taxes, interest, fines and penalties becoming due. We evaluate whether to record tax liabilities for possible tax audit issues based on our estimate of whether, and the extent to which, additional income taxes will be due. We adjust these liabilities in light of changing facts and circumstances as well as consult with our outside tax advisors. However, due to the complexity of some of these uncertainties, the ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from our estimates.
We are subject to extensive, complex and sometimes overlapping laws, rules and regulations.
The industry in which we operate is subject to extensive and complex laws, rules and regulations. We are subject to extensive regulation in the United States, primarily at the federal level, including regulation by the SEC, the U.S. Department of Labor, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Our business is also subject to the laws and regulations of the various countries in which we conduct distribution or investment management activities. For a more extensive discussion of certain laws and regulations to which we are subject, see “Item 1—Business—Regulatory Environment and Compliance” in Part I of this report.
As a result of the extensive and complex regulatory environment in which we operate, we face risk of regulatory actions and litigation, which could consume substantial expenditures of time and capital. Our regulatory and compliance obligations impose significant operational and cost burdens on us and cover a broad range of topics including, investment advisory matters, securities and other financial instruments, financial reporting and other disclosure matters, sustainability, accounting, tax, data protection, and privacy. As our business expands into new geographic regions and introduces new investment products with expanded degrees of freedom, the regulatory requirements to which we are subject will increase in number. While we have focused significant attention and resources on the development and maintenance of compliance policies, procedures and practices, any inadvertent non-compliance with applicable laws, rules or regulations, either in the U.S. or abroad, could result in various legal proceedings, including civil litigation and regulatory investigations and enforcement actions that could result in fines, suspensions of individual employees, or limitations on particular business activities, any of which could have an adverse impact on our reputation and business.
We carry insurance in amounts and under terms that we believe are appropriate. Our insurance does not cover all liabilities and losses to which we may be exposed. Certain insurance coverage may not be available or may be prohibitively expensive in future periods. As our insurance policies come up for renewal, we may need to assume higher deductibles or pay higher premiums, which could have an adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
The regulatory environment in which we operate is subject to continual change, and regulatory developments may adversely affect our business.
We operate in a legislative and regulatory environment that is subject to continual change, the nature of which we cannot predict. The laws and regulations applicable to our business generally involve restrictions and requirements in connection with a variety of technical, specialized, and expanding matters and concerns. We may be adversely affected as a result of new or revised legislation or regulations imposed by the SEC, other U.S. or non-U.S. regulatory authorities or self-regulatory organizations that supervise the financial markets. We also may be adversely affected by changes in the interpretation or enforcement of existing laws and rules by these governmental authorities and self-regulatory organizations, as well as by courts. It is impossible to determine the extent of the impact of any new laws, regulations or initiatives that may be proposed, or whether any such proposals will become law. Further, new laws, regulations or interpretations of existing laws may result in enhanced disclosure
and other obligations, including with respect to climate change or other environmental, social and governance (ESG) matters and cybersecurity. Compliance with any new laws or regulations, or changes in the interpretation or enforcement of existing laws or regulations, could be difficult and expensive and affect the manner in which we conduct business. Non-compliance with applicable new laws, rules or regulations could result in litigation, governmental investigations and enforcement actions that could result in fines, penalties, suspensions of individual employees, or limitations on particular business activities, any of which could have an adverse impact on our reputation and business.
The investment management industry faces substantial litigation risks which could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations or cause significant reputational harm to us.
We depend to a large extent on our network of relationships and on our reputation in order to attract and retain client assets. We make investment decisions on behalf of our clients that could result in substantial losses to them. If our clients suffer significant losses, or are otherwise dissatisfied with our services, we could be subject to legal liability or actions alleging negligence, breach of fiduciary duty, breach of contract, unjust enrichment and/or fraud. These risks are often difficult to assess or quantify and their existence and magnitude often remain unknown for substantial periods of time, even after an action has been commenced.
We may incur significant legal expenses in defending against litigation whether or not we engaged in conduct as a result of which we might be subject to legal liability. Substantial legal liability or significant regulatory action against us could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations or cause significant reputational harm to us.
A change of control could result in termination of our investment advisory agreements with mutual funds and could trigger consent requirements in our other investment advisory agreements.
Under the 1940 Act, each of the investment advisory agreements between SEC-registered mutual funds and our subsidiary, Artisan Partners Limited Partnership, will terminate automatically in the event of its assignment. Upon the occurrence of such an assignment, our subsidiary could continue to act as adviser to any such fund only if that fund’s board and shareholders approved a new investment advisory agreement, except in the case of certain funds that we sub-advise for which only board approval would be necessary. In addition, as required by the Advisers Act, each of the investment advisory agreements for the separate accounts we manage provides that it may not be assigned, as defined in the Advisers Act, without the consent of the client. An assignment occurs under the 1940 Act and the Advisers Act if, among other things, Artisan Partners Limited Partnership undergoes a change of control as recognized under the 1940 Act and the Advisers Act. If such an assignment were to occur, we cannot be certain that we would be able to obtain the necessary approvals from the boards and shareholders of the mutual funds we advise or the necessary consents from our separate account clients.
Operational and Cybersecurity Risks
Operational risks may disrupt our business, result in losses, damage our reputation or limit our growth.
We are heavily dependent on the capacity and reliability of the communications and information technology systems supporting our operations, whether developed, owned and operated by us or by third parties. We also rely on manual workflows and a variety of manual user controls. As our clients, physical locations and investment teams and strategies increase in number and grow in complexity, and as our employees become increasingly mobile, developing and maintaining the systems supporting our operations becomes increasingly challenging. Moreover, the introduction of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence, presents new challenges and introduces operational and legal risks. Any changes or upgrades to our systems to support increased volumes or complexity of transactions or to otherwise support growth of the business may require significant expenditures and may increase the probability that we will experience operational errors. Operational risks or errors or interruption or failure of our financial, trading, compliance and other data processing systems, whether caused by human error, power or telecommunications failure, cyber-attack, ransomware or viruses, severe weather events, natural disaster, fire, act of terrorism or war, pandemics or other unpredictable events, could result in a disruption of our business, liability to clients, regulatory intervention or reputational damage, and thus adversely affect our business. In addition, since implementing broad remote-work measures during the pandemic, we have an increased dependency on remote equipment and connectivity infrastructure to access critical business systems that may be subject to failure, disruption, or unavailability that could negatively impact our business operations. The potential for some types of operational risks, including trading errors, may increase in periods of increased volatility, which can magnify the cost of an error. We have back-up systems and a business continuity plan in place, however, these arrangements may not be adequate in the event of a significant interruption or failure of the systems or operations that are critical to our business, however caused. Although we have not suffered material operational errors, including material trading errors, in the past, we may experience such errors in the future, the losses related to which we would absorb. Insurance and other safeguards might not be available or might only partially reimburse us for our losses.
We rely on a number of key vendors for trading, middle- and back-office functions, various fund administration, accounting, custody and transfer agent roles and other operational needs. These key vendors may themselves rely on third party service providers to support their own operations. The failure of any key vendor, or of any service provider to a key vendor, to fulfill its obligations could cause operational issues that could lead to legal liability, regulatory issues, reputational harm and financial losses. Some of the key service providers and vendors upon which we rely operate in a remote or hybrid environment, which subjects both us and third-party service providers and key vendors to risk of operational issues and interruptions as well as to a heightened risk of cyberattacks or other privacy or data security incidents. We and our service providers are also subject to the risk that employees or contractors, or other third parties, may deliberately seek to circumvent established controls to commit
fraud or act in ways that are inconsistent with our or their controls, policies, and procedures, and which may be harder to monitor in remote working environments. The financial and reputational impact of control failures can be significant. Moreover, as we grow our operations in new geographic regions, the potential for particular types of political, economic or infrastructure instabilities, information, technology or security limitations or breaches, or other country- or region-specific business continuity risks increases.
Any significant limitation, failure or breach of the information security infrastructure, software applications, or other systems that are critical to our operations could disrupt our business, damage our reputation, and result in regulatory penalties or other additional costs to us.
We are heavily reliant upon internal and third party technology systems, networks and applications to view, process, transmit and store information, including sensitive client and proprietary information, and to conduct many of our business activities and transactions with our clients, vendors and other third parties. In addition, in recent years we have increased our use of and reliance on mobile, remote work and cloud technologies. Maintaining the integrity of these systems, networks and technologies is critical to the success of our business operations. We rely on our (and our vendors’) information security and cybersecurity infrastructure, policies, procedures and capabilities to protect these systems, networks and applications and the data that reside on or are transmitted through them.
To date, we have not experienced any known material breaches of or interference with our systems, networks or applications, nor to our knowledge have we been materially impacted by a breach of our vendors’ systems, networks or applications. However, we routinely encounter and address such threats, and the number and frequency of potential threats or security incidents experienced by us or our vendors has increased in recent years due to, among other factors, an increase in the number of security vulnerabilities, more sophisticated and automated attacks, proliferation of cloud-based solutions, increased operations in China and Hong Kong and the increase in remote work. Our experiences with and preparation for cybersecurity and other technology threats have included phishing scams, introductions of malware, attempts at electronic break-ins, brand infringements or impersonations, ransomware and unauthorized payment requests.
Despite the measures we have taken and may in the future take to address and mitigate cybersecurity and other technology risks, we cannot guarantee that our systems, networks and applications, and those of third parties on whom we rely, will not be subject to disruptions, system failures or outages, unauthorized access, ransomware, breaches or other interference. In addition, our third-party service providers and other intermediaries with which we conduct business and transmit data have in the past been, and may in the future be, subject to successful cyberattacks or other data security events, and, despite our service provider oversight processes and practices, we cannot ensure that such third parties have appropriate controls in place to protect the confidentiality of data in the custody of those third parties or to allow them to continue their business operations, including their services to us, in a timely manner.
Cybersecurity and information security events may result in operational disruptions as well as unauthorized access to or the disclosure, corruption or loss of our proprietary information or our clients’ or employees’ information. Any such events may result in legal claims, regulatory scrutiny and liability, reputational damage, the incurrence of costs to eliminate or mitigate further exposure, the loss of clients or other damage to our business. Ultimately, such an event may have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations. In addition, required public notification of such incidents could exacerbate the harm to our business, financial condition or results of operations. Even if our and our service providers’ technology infrastructure and the confidentiality of sensitive data are successfully protected, we may incur significant expense in connection with our response to any such attacks and the adoption and maintenance of additional security measures. We cannot be certain that future advances in criminal capabilities, the discovery of new vulnerabilities or other developments will not compromise or breach the security measures protecting the networks, systems and applications we use.
Indebtedness Risks
Our indebtedness may expose us to material risks.
We have indebtedness outstanding in the amount of $200 million in unsecured notes, which exposes us to risks associated with the use of leverage. In addition, we maintain a $100 million revolving credit agreement, though no amounts are outstanding as of the date of this filing. Our indebtedness may make it more difficult for us to withstand or respond to adverse or changing business, regulatory and economic conditions or to take advantage of new business opportunities or make necessary capital expenditures. To the extent we service our debt from our cash flow, such cash will not be available for our operations or other purposes. Because our debt service obligations are fixed, the portion of our cash flow used to service those obligations could become substantial if our revenues decline significantly, whether because of market declines or other reasons.
Our Series D, Series E and Series F notes bear interest at a rate equal to 4.29%, 4.53%, and 3.10% per annum, respectively. The interest rate on each of the notes is subject to a 100 basis point increase in the event Holdings receives a below-investment grade rating. Each series requires a balloon payment at maturity. Any substantial decrease in net operating cash flows or substantial increase in expenses could make it difficult for us to meet our debt service requirements or force us to modify our operations. Our ability to repay the principal amount of our notes or any outstanding loans under our revolving credit agreement, to refinance our debt or to obtain additional financing through debt or the sale of additional equity securities will depend on our performance, as well as financial, business and other general economic factors affecting the credit and equity markets generally or our business in particular, many of which are beyond our control. Any such alternatives may not be available to us on satisfactory terms or at all.
Our note purchase agreements and revolving credit agreement contain, and our future indebtedness may contain, various covenants that may limit our business activities.
Our note purchase agreements and revolving credit agreement contain financial and operating covenants that limit our business activities, including restrictions on our ability to incur additional indebtedness and pay dividends to our stockholders. The agreements also restrict Holdings from making distributions to its partners (including us), other than tax distributions or distributions to fund our ordinary expenses, if a default (as defined in the respective agreements) has occurred and is continuing or would result from such a distribution. In addition, if our average AUM for a fiscal quarter falls below $45 billion, Holdings will generally be required to offer to pre-pay the unsecured notes. Failure to comply with any of these restrictions could result in an event of default, giving our lenders the ability to accelerate repayment of our obligations. As of December 31, 2023, we believe we are in compliance with all of the covenants set forth in the agreements.
Risks Related to Our Structure
Control by our stockholders committee of approximately 11% of the combined voting power of our capital stock and the rights of holders of limited partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings may give rise to conflicts of interest.
As of February 19, 2024, our employees to whom we have granted equity (including our employee-partners) held approximately 11% of the combined voting power of our capital stock. These employees have entered into a stockholders agreement pursuant to which they granted an irrevocable voting proxy with respect to all shares of our common stock they have acquired from us and any shares they may acquire from us in the future to a stockholders committee. Any additional shares of our common stock that we issue to our employees will be subject to the stockholders agreement so long as the agreement has not been terminated. Shares held by an employee cease to be subject to the stockholders agreement upon termination of employment.
The stockholders committee currently consists of Eric R. Colson (Chief Executive Officer), Charles J. Daley, Jr. (Chief Financial Officer) and Gregory K. Ramirez (Executive Vice President). All shares subject to the stockholders agreement are voted in accordance with the majority decision of those three members providing the committee with approximately 11% of the aggregate voting power.
The consent of the holders of our Class A common units, voting as a single and separate class, is required for Holdings to engage in certain material corporate transactions, including a merger, consolidation, dissolution or sale of greater than 25% of the fair market value of Holdings’ assets. These voting and class approval rights may enable the holders of Class A common units to prevent the consummation of transactions that may be in the best interests of the holders of our Class A common stock.
In addition, because the majority of our pre-IPO owners (including certain members of our board of directors) hold or held a portion of their ownership interests in our business through Holdings, rather than through Artisan Partners Asset Management, these pre-IPO owners may have conflicting interests with holders of our Class A common stock. For example, our pre-IPO owners may have different tax positions from us which could influence their decisions regarding whether and when we should dispose of assets, whether and when we should incur new or refinance existing indebtedness, especially in light of the existence of the tax receivable agreements, and whether and when Artisan Partners Asset Management should terminate the tax receivable agreements and accelerate its obligations thereunder. In addition, the structuring of future transactions may take into consideration these pre-IPO owners’ tax or other considerations even where no similar benefit would accrue to us.
Our ability to pay regular dividends to our stockholders is subject to the discretion of our board of directors and may be limited by our structure and applicable provisions of Delaware law.
We intend to pay dividends to holders of our Class A common stock as described in “Dividend Policy”. Our board of directors may, in its sole discretion, change the amount or frequency of dividends or discontinue the payment of dividends entirely. In addition, as a holding company, we are dependent upon the ability of our subsidiaries to generate earnings and cash flows and distribute them to us so that we may pay dividends to our stockholders. We expect to cause Holdings, a Delaware limited partnership, to make distributions to its partners, including us, in an amount sufficient for us to pay dividends. However, its ability to make such distributions will be subject to its and its subsidiaries’ operating results, cash requirements and financial condition, the applicable provisions of Delaware law, its compliance with covenants related to existing or future indebtedness, its other agreements with third parties, as well as its obligation to make tax distributions under its partnership agreement (which distributions would reduce the cash available for distributions by Holdings to us). As a result of these limitations and restrictions, we may not be able to pay, or may have to reduce, the dividends on our Class A common stock. Any change in the level of our dividends or the suspension of the payment thereof could adversely affect the market price of our Class A common stock.
Our ability to pay taxes and expenses, including payments under the tax receivable agreements (“TRAs”), may be limited by our holding company structure.
As a holding company, our assets principally consist of our ownership of partnership units of Holdings, deferred tax assets and cash and we have no independent means of generating revenue. Holdings is a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes and, as such, is not subject to U.S. federal income tax. Instead, Holdings’ taxable income is allocated to holders of its partnership units, including us. Accordingly, we incur income taxes on our proportionate share of Holdings’ taxable income and also may incur expenses related to our operations. Under the terms of its amended and restated limited partnership agreement, Holdings is obligated to make tax distributions to holders of its partnership units, including us. In addition to tax expenses, we are also required to make payments under the TRAs, which will be significant, and we incur other expenses related to the TRAs and our
operations. We intend to fund the payment of amounts due under the TRAs out of the reduced tax payments that APAM realizes in respect of the tax attributes to which the TRAs relate. We also intend to cause Holdings to make distributions in an amount sufficient to allow us to pay our taxes and pay any additional operating expenses. However, its ability to make such distributions will be subject to various limitations and restrictions as set forth in the preceding risk factor. If, as a consequence of these various limitations and restrictions, we do not have sufficient funds to pay tax or other liabilities or to fund our operations, we may have to borrow funds and thus our liquidity and financial condition could be materially adversely affected. To the extent that we are unable to make payments when due under the TRAs, such payments will be deferred and will accrue interest from the due date (without extension) until such payments are made.
We will be required to pay the TRA beneficiaries for certain tax benefits we claim, and we expect that the payments we will be required to make will be substantial.
We are party to two TRAs. The first TRA generally provides for the payment by APAM to the assignees of the Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder of 85% of the applicable cash savings, if any, of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes that APAM actually realizes (or is deemed to realize in certain circumstances) as a result of (i) the tax attributes of the preferred units APAM acquired in the merger of a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder into APAM in March 2013 and (ii) tax benefits related to imputed interest.
The second TRA generally provides for the payment by APAM to current or former limited partners of Holdings or their assignees of 85% of the applicable cash savings, if any, of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes that APAM actually realizes (or is deemed to realize in certain circumstances) as a result of (i) certain tax attributes of their partnership units sold to us or exchanged (for shares of Class A common stock, convertible preferred stock or other consideration) and that are created as a result of such sales or exchanges and payments under the TRAs and (ii) tax benefits related to imputed interest.
The payment obligation under the TRAs is an obligation of APAM, not Holdings, and we expect that the payments we will be required to make under the TRAs will be substantial. Assuming no material changes in the relevant tax law and that APAM earns sufficient taxable income to realize all tax benefits that are subject to the TRAs, we expect that the reduction in tax payments for us associated with (i) the merger described above; (ii) the purchase or exchange of partnership units from March 2013 through December 31, 2023; and (iii) projected future purchases or exchanges of partnership units would aggregate to approximately $553 million over generally a minimum of 15 years, assuming the future purchases or exchanges described in clause (iii) occurred at a price of $44.18 per share of our Class A common stock, the closing price of our Class A common stock on December 31, 2023. Under such scenario we would be required to pay the other parties to the TRAs 85% of such amount, or approximately $507 million, over generally a minimum of 15 years. The actual amounts may materially differ from these hypothetical amounts, as potential future reductions in tax payments for us and TRA payments by us will be calculated using the market value of our Class A common stock at the time of purchase or exchange and the prevailing tax rates applicable to us over the life of the TRAs and will be dependent on us generating sufficient future taxable income to realize the benefit. As of December 31, 2023, we recorded a $364 million liability, representing amounts payable under the TRAs equal to 85% of the tax benefit we expected to realize from the H&F Corp merger described above, our purchase of partnership units from limited partners of Holdings and the exchange of partnership units from March 2013 through December 31, 2023, assuming no material changes in the related tax law and that APAM earns sufficient taxable income to realize all tax benefits subject to the TRAs.
The liability will increase upon future purchases or exchanges of limited partnership units with the increase representing amounts payable under the TRAs equal to 85% of the estimated future tax benefits, if any, resulting from such purchases or exchanges. Payments under the TRAs are not conditioned on the counterparties’ continued ownership of us. The actual increase in tax basis, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under these agreements, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units, the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, whether such sales or exchanges are taxable, the amount and timing of the taxable income APAM generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable and the portion of APAM’s payments under the TRAs constituting imputed interest or depreciable basis or amortizable basis. Payments under the TRAs are expected to give rise to certain additional tax benefits attributable to either further increases in basis or in the form of deductions for imputed interest, depending on the TRA and the circumstances. Any such benefits are covered by the TRAs and will increase the amounts due thereunder. In addition, the TRAs provide for interest accrued from the due date (without extensions) of the corresponding APAM tax return to the actual payment date, provided that the actual payment date is on or before the payment due date, as specified in the TRAs. In addition, to the extent that we are unable to make payments when due under the TRAs, such payments will be deferred and will accrue interest at a rate specified under the TRAs.
Payments under the TRAs will be based on the tax reporting positions that we determine. Although we are not aware of any issue that would cause the IRS or other taxing authority to challenge a tax basis increase or other tax attributes subject to the TRAs, we will not be reimbursed for any payments previously made under the TRAs if such basis increases or other benefits are subsequently disallowed (however, any such additional payments may be netted against future payments (if any) that are made under the TRAs). As a result, in certain circumstances, payments could be made under the TRAs in excess of the benefits that we actually realize in respect of the attributes to which the TRAs relate.
In certain cases, payments under the TRAs may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the TRAs.
The TRAs provide that (i) upon certain mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes of control, (ii) in the event that we materially breach any of our material obligations under the agreements, or (iii) if, at any time, we elect an early termination of the agreements, our (or our successor’s) obligations under the agreements (with respect to all units, whether or not units have been exchanged or acquired before or after such transaction) would be based on certain assumptions. In the case of a material breach or if we elect early termination, those assumptions include that we would have sufficient taxable income to fully utilize the deductions arising from the increased tax deductions and tax basis and other benefits related to entering into the TRAs. In the case of a change of control, the assumptions include that in each taxable year ending on or after the closing date of the change of control, our taxable income (prior to the application of the tax deductions and tax basis and other benefits related to entering into the TRAs) will equal the greater of (i) the actual taxable income (prior to the application of the tax deductions and tax basis and other benefits related to entering into the TRAs) for the taxable year and (ii) the highest taxable income (calculated without taking into account extraordinary items of income or deduction and prior to the application of the tax deductions and tax basis and other benefits related to entering into the TRAs) in any of the four fiscal quarters ended prior to the closing date of the change of control, annualized and increased by 10% for each taxable year beginning with the second taxable year following the closing date of the change of control. In the event we elect to terminate the agreements early or we materially breach a material obligation, our obligations under the agreements will accelerate. As a result, (i) we could be required to make payments under the TRAs that are greater than or less than the specified percentage of the actual benefits we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the agreements and (ii) if we materially breach a material obligation under the agreements or if we elect to terminate the agreements early, we would be required to make an immediate payment equal to the present value of the anticipated future tax benefits, which payment may be made significantly in advance of the actual realization of such future benefits. In these situations, our obligations under the TRAs could have a substantial negative impact on our liquidity and could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing certain mergers, asset sales, other forms of business combinations or other changes of control. There can be no assurance that we will be able to finance our obligations under the TRAs. If we were to elect to terminate the TRAs associated with (i) the merger described above; (ii) the purchase or exchange of partnership units from March 2013 through December 31, 2023; and (iii) projected future purchases or exchanges of partnership units, as of December 31, 2023, based on a share price of $44.18 per share of Class A common stock and certain other assumptions, we estimate that we would be required to pay approximately $349 million in the aggregate under the TRAs.
If we were deemed an investment company under the 1940 Act as a result of our ownership of Artisan Partners Holdings, applicable restrictions could make it impractical for us to continue our business as contemplated and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We do not believe that we are an “investment company”, as such term is defined in Sections 3(a)(1)(A) and (C) of the 1940 Act. As its sole general partner, we control and operate Holdings. However, if we were to cease participation in the management of Holdings, our interest in Holdings could be deemed an “investment security” and we ultimately could be deemed an “investment company.”
We and Holdings intend to continue to conduct our operations so that we will not be deemed an investment company. However, if we were to be deemed an investment company, restrictions imposed by the 1940 Act, including limitations on our capital structure and our ability to transact with affiliates, could make it impractical for us to continue our business as contemplated and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Risks Related to Our Class A Common Stock
Equity markets and the price of our Class A common stock have been, and will continue to be, volatile, which could result in rapid and substantial losses for our stockholders.
The market price of our Class A common stock is significantly impacted by fluctuations in the broader equity markets and, as a result, has experienced and may continue to experience volatility in price and volume. In addition, a relatively concentrated number of institutional stockholders own our Class A common stock. If our larger stockholders decide to reduce or liquidate their positions, the trading volume of our Class A common stock may fluctuate and cause significant price variations to occur. If the market price of our Class A common stock declines significantly, investors may be unable to sell shares of Class A common stock at or above their purchase price, if at all. The market price of our Class A common stock may fluctuate or decline significantly in the future.
Future sales of our Class A common stock in the public market could lower our stock price, and any future sale of equity or convertible securities may dilute existing stockholders’ ownership in us.
The market price of our Class A common stock could decline as a result of future sales of a large number of shares of our Class A common stock, or the perception that such sales could occur. These sales, or the possibility that such sales may occur, may make it more difficult for us to raise capital by selling equity securities in the future, at a time and price that we deem appropriate.
We are party to a resale and registration rights agreement pursuant to which the shares of our Class A common stock issued upon exchange of limited partnership units, on a one-for-one basis, are eligible for resale. Such shares of Class A common stock may be transferred in accordance with the terms and conditions of the resale and registration rights agreement, which our board of directors may waive or modify at any time.
There is no limit on the number of shares of our Class A common stock that our Class A limited partners or AIC are permitted to sell. As of February 19, 2024, our Class A limited partners owned approximately 4.4 million Class A common units and AIC owned approximately 3.5 million Class D common units.
Our board of directors has modified the limitations on the number of shares of our Class A common stock that our employee-partners are permitted to sell. As of February 19, 2024, our employee-partners owned 2.2 million Class B common units, all of which are now eligible for sale. In addition, approximately 0.8 million Class E common units are eligible for exchange and sale by former employee-partners in 2024.
We may also purchase limited partnerships units of Holdings at any time and may issue and sell additional shares of our Class A common stock to fund such purchases. We cannot predict the size of future issuances of our Class A common stock or the effect, if any, that such future issuances and sales may have on the market price of our Class A common stock. Sales or distributions of substantial amounts of our Class A common stock (including shares issued in connection with an acquisition), or the perception that such sales could occur, may cause the market price of our Class A common stock to decline.
As of February 19, 2024, there were 5,052,404 outstanding unvested restricted share-based awards granted pursuant to the 2013 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan, as amended and 250,876 outstanding restricted stock units granted pursuant to the 2013 Non-Employee Director Plan. In addition, in January 2024 our board of directors approved 531,814 restricted share-based awards pursuant to the 2023 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan and the 2023 Non-Employee Director Plan. Awards granted under these plans, which consist of a mix of restricted stock units, performance share units and restricted shares of Class A common stock, remain in effect until they have vested or been forfeited in accordance with the terms of the applicable plan and award agreement. Once shares issued pursuant to these plans have vested, they will be able to be sold in the public market.
Provisions in our organizational documents, equity award agreements and Delaware law could discourage a change of control that stockholders may favor, which could negatively affect the market price of our Class A common stock.
Provisions in our restated certificate of incorporation, amended and restated bylaws and in the Delaware General Corporation Law, as well as the terms of our equity awards, may make it more difficult and expensive for a third party to acquire control of us even if a change of control would be beneficial to the interests of our stockholders. Those provisions include:
•The right of the certain classes of our capital stock to vote, as separate classes, on certain amendments to our restated certificate of incorporation and certain fundamental transactions.
•The ability of our board of directors to determine to issue shares of preferred stock.
•Advance notice procedures that stockholders must comply with in order to nominate candidates to our board of directors or to propose matters to be acted upon at a stockholders’ meeting.
•A limitation that, generally, stockholder action may only be taken at an annual or special meeting or by unanimous written consent.
•A requirement that a special meeting of stockholders may be called only by our board of directors, the Chair of the board or the Chief Executive Officer.
•The ability of our board of directors to adopt, amend and repeal our amended and restated bylaws by majority vote, while such action by stockholders would require a super majority vote.
•Except with respect to awards held by our named executive officers which are double trigger, single trigger vesting upon a change in control for unvested employee equity awards. Prior to February 2019, our awards generally included double trigger vesting upon a change in control.
The market price of our Class A common stock could be adversely affected to the extent that the above factors discourage or delay potential takeover attempts that our stockholders may favor.
Our restated certificate of incorporation contains a forum selection clause, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents.
Our restated certificate of incorporation provides that, unless we consent in writing to an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders. Any person acquiring any interest in any shares of our capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and to have consented to this provision of our restated certificate of incorporation. This choice of forum provision may limit our stockholders’ ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers, employees or agents, which may discourage lawsuits against such parties. Alternatively, if a court were to find the forum selection clause inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Our indemnification obligations may pose substantial risks to our financial condition.
Pursuant to our restated certificate of incorporation, we will indemnify our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law against all liability and expense incurred by them in their capacities as directors or officers of us, and we are obligated to pay their expenses in connection with the defense of claims. Our bylaws provide for similar indemnification of, and advancement of expenses to, our directors, officers, employees and agents and members of our stockholders committee. We have
also entered into indemnification agreements with our directors and executive officers and each member of our stockholders committee, pursuant to which we will indemnify them to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law in connection with their service in such capacities. Holdings will also indemnify and advance expenses to AIC (its former general partner), former members of its pre-IPO advisory committee, members of our stockholders committee, our directors and officers, and its officers and employees against any liability and expenses incurred by them as a result of the capacities in which they serve or served Holdings.
We have obtained liability insurance insuring our directors, officers, members of our stockholders committee and our associates against liability for acts or omissions in their capacities as such, subject to certain exclusions. These obligations may pose substantial risks to our financial condition, if we are not able to maintain our insurance or, even if we are able to maintain our insurance, claims in excess of our coverage could be material. In addition, indemnification obligations and other provisions of our restated certificate of incorporation and the amended and restated partnership agreement of Holdings, may have the effect of reducing the likelihood of derivative litigation against indemnified persons, and may discourage or deter stockholders or management from bringing a lawsuit against such persons, even though such an action, if successful, might otherwise have benefited us and our stockholders.
Our restated certificate of incorporation provides that certain of our investors do not have an obligation to offer us business opportunities.
Our restated certificate of incorporation provides that, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, certain of our investors and their respective affiliates (including affiliates who serve on our board of directors) have no obligation to offer us an opportunity to participate in the business opportunities presented to them, even if the opportunity is one that we might reasonably have pursued. Therefore, they may be free to compete with us in the same or a similar business. Furthermore, we renounce and waive and agree not to assert any claim for breach of any duty relating to any such opportunity against those investors and their affiliates by reason of any such activities unless, in the case of any person who is our director or officer, such opportunity is expressly offered to such person in writing solely in his or her capacity as an officer or director of us. This may create actual and potential conflicts of interest between us and certain of our investors and their affiliates (including certain of our directors).
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Risk Management and Strategy
Information Security Program
Our processes for assessing, identifying and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats, as defined in Item 106(a) of Regulation S-K, are integrated into our overall risk management strategy. We regularly assess the risks inherent in operating our business as well as the effectiveness of our risk management activities. The Artisan Risk and Integrity Committee, which includes members of the Company’s senior leadership team including senior representation from the firm’s operations, distribution, finance, internal audit, investment strategy and legal functions, facilitates our annual enterprise risk assessment process, which uses a top-down approach to identify and prioritize key risks to achieving our purpose and maintaining our business model. We also conduct a bottom-up information and cybersecurity risk assessment on an annual basis, which focuses on the evolving threat landscape, changes in the firm’s operations, changes in regulatory requirements and security incidents. This risk assessment informs the Company’s information security awareness training and testing and assessment program.
We manage risk, including cybersecurity risk, via three distinct lines of defense. As the first line of defense, business managers, including IT managers, are responsible for maintaining effective internal controls and executing risk and control procedures on a day-to-day basis. As the second line of defense, the legal, compliance and information security governance functions provide guidance and training, as well as perform monitoring, testing and surveillance activities relating to compliance with the firm’s policies and procedures, applicable laws and regulations, contractual requirements, ethical standards and industry best practices. As the third line of defense, our internal audit team provides periodic and independent assurance that the firm’s internal controls are implemented and operating effectively.
With respect to cybersecurity risk, we have a dedicated security engineering and operations team, supplemented with security consultants and two managed security service providers, that performs first line responsibilities by identifying security risks, deciding if and how to implement security tools and controls, and implementing and maintaining those tools and controls. This team is led by our Director of Technical Services, who has 32 years of information technology experience, and reports to our Chief Information Officer (CIO), who has 40 years of information technology experience. We also have an information security governance team that is responsible for performing second line responsibilities, including training associates, providing advice to our associates in carrying out their responsibilities consistent with the goals of the security program, assessing whether the program is reasonably designed and operating effectively, and responding to and reporting to stakeholders on the reasonableness and effectiveness of the security program. The information security governance team is led by our Chief Information Security Officer (CISO), who is a Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) and has 37 years of experience in the field of cybersecurity. Our CISO reports directly to our Chief Legal Officer and General Counsel. Together, these teams maintain a robust information
security program that utilizes a multi-layered defense-in-depth strategy and is designed to prevent, detect, mitigate and remediate cybersecurity incidents.
Our information security program is subject to periodic internal audits and independent third-party reviews. We use third party security firms for security consulting, including configuration reviews and assessments, as well as performing periodic (no less frequently than annual) penetration tests to evaluate the integrity of our systems. We also conduct monitoring and testing activities, such as phishing simulations.
Our associates receive annual, mandatory information security training, which includes information regarding specific policies and procedures and education on risks such as phishing attacks, social engineering, password management and privacy. New associates receive cybersecurity training as part of their orientation process.
To date, we have not experienced any known material cybersecurity breach or threat that resulted in or is reasonably likely to result in any material loss, or any material impact on our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition.
Oversight of Third-Party Service Providers
We engage many service providers in connection with our business operations. Some of these service providers play a minor role, while others perform services that are critical to our operations. We have a service provider oversight committee that oversees and facilitates the management of third-party relationships that are integral to our investment management activities. The committee maintains a written policy and other guidance that set forth our approach to managing and providing oversight of those third-party service providers in a manner consistent with the level of risk and complexity of the services provided. Our approach to oversight, which includes considerations regarding selection, initial and ongoing due diligence, contracting, ongoing monitoring and oversight and compliance with applicable regulatory and service level expectations, is tailored to each such service provider based on the scope of the services provided. Security assessments of those service providers may include questionnaires, meetings and onsite visits. We also consider contingency plans in the event a key service provider is not able to provide its respective services.
In addition, our internal audit team periodically tests the firm’s management and oversight of certain key third-party service providers, including those overseen by the service provider oversight committee, as well as third parties that support financial reporting.
Governance
Role of Management
Management is responsible for the assessment and management of risk, including cybersecurity risk. The Artisan Risk and Integrity Committee facilitates the annual enterprise risk assessment that identifies and prioritizes the Company’s key risks, including cybersecurity risk. The information security governance team also reports to members of senior management the results of its annual cybersecurity risk assessment.
Cybersecurity risks are managed by and through our information security program, which consists of the activities of teams managed by our CIO (first line of defense) and CISO (second line of defense). In the normal course of business, executive management is informed about the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation of cybersecurity risks through these established reporting lines and through its oversight of the information security program.
Outside of the normal course of business, in the event a cybersecurity incident occurs, our incident response plan provides guidance in assessing and responding to the incident. The incident response plan establishes mechanisms by which we determine the scope of and potential damage caused by the incident and determine and execute the appropriate response. The plan outlines roles and responsibilities and sets forth escalation points to ensure that appropriate individuals and groups are notified and provided relevant information depending on the type and severity of the incident. Cybersecurity incidents are reported to each of the Company’s Chief Legal Officer, Chief Administrative Officer, and the Chair of the Artisan Risk and Integrity Committee, who oversee the investigation and remain apprised of information regarding the remediation of the incident. This group, based on its assessment of the incident’s potential impact to the Company and its stakeholders, will also make determinations regarding further escalation of the incident to the full senior leadership team. The senior leadership team is kept informed of the investigation and is responsible for making certain decisions throughout the course of the investigation, including whether it is appropriate to report the incident to the Board prior to its next meeting.
Role of the Board of Directors
Our Board is responsible for overseeing management in the execution of its risk management responsibilities, including with respect to cybersecurity risk management. In addition, an overall review of risk is inherent in the Board’s ongoing oversight of our business, long-term strategies and other matters presented to our Board. Our Board exercises its risk oversight responsibilities periodically as part of actions taken and matters reviewed during its meetings and also through the activities of its standing committees. The Board has delegated responsibility for cybersecurity risk oversight to the Audit Committee.
The Audit Committee oversees cybersecurity risk management through the periodic reports it receives from management. On a quarterly basis, management reports on any significant cybersecurity events and trends impacting the Company. Annually, our CIO and CISO report to the Audit Committee on our information security program, including with respect to team updates, key areas of risk and the effectiveness of the program. The Audit Committee also reviews the Company’s cybersecurity insurance
program on an annual basis in connection with the program’s renewal and receives periodic reports from our Director of Internal Audit regarding internal audits of our information security program.
Item 2. Properties
We lease all of our office space, including our largest office in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, where a majority of our employees are based. We believe our existing and contracted-for facilities are adequate to meet our requirements.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In the normal course of business, we may be subject to various legal and administrative proceedings. Currently, there are no legal or administrative proceedings that management believes may have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable
Information about our Executive Officers
Information regarding our executive officers is as follows:
Eric R. Colson, age 54, has been chief executive officer and a director of Artisan Partners Asset Management since March 2011. Mr. Colson also served as the president of Artisan Partners Asset Management from March 2011 to January 2021 and as chairman of the Company’s board of directors from August 2015 to August 2021. Mr. Colson has served as the chief executive officer of Artisan Partners since January 2010. Prior to January 2010, Mr. Colson served as chief operating officer of investment operations from March 2007 through January 2010. Mr. Colson has been a managing director of Artisan Partners since he joined the firm in January 2005.
Charles J. Daley, Jr., age 61, has been executive vice president, chief financial officer and treasurer of Artisan Partners Asset Management since March 2011. He has served as the chief financial officer of Artisan Partners since August 2010 and has been a managing director since July 2010 when he joined the firm.
Jason A. Gottlieb, age 54, has been president of Artisan Partners Asset Management since January 2021. From February 2017 to January 2021, he served as executive vice president of Artisan Partners Asset Management. Mr. Gottlieb joined Artisan Partners in October 2016 as a managing director and the chief operating officer of investments.
Christopher J. Krein, age 52, has been executive vice president of Artisan Partners Asset Management and Artisan Partners’ head of Global Distribution since January 2020. Prior to becoming head of Global Distribution, Mr. Krein was responsible for institutional marketing and client service for the Artisan Developing World team. Mr. Krein has been a managing director of Artisan Partners since he joined the firm in September 2015.
Eileen L. Kwei, age 45, has been executive vice president and chief administrative officer of Artisan Partners Asset Management since January 2021. From February 2018 to January 2021, Ms. Kwei was responsible for institutional marketing and client service for the Artisan Credit team. Prior to February 2018, Ms. Kwei was a relationship manager for the Artisan Global Equity team. Ms. Kwei joined Artisan Partners in June 2013 and has been a managing director of Artisan Partners since 2018.
Gregory K. Ramirez, age 53, has been executive vice president of Artisan Partners Asset Management since February 2016. From October 2013 to February 2016, he served as senior vice president and from April 2013 to October 2013 as assistant treasurer. Mr. Ramirez is currently head of Vehicle and Investor Operations for Artisan Partners and serves as chair of the Artisan Risk and Integrity Committee. Mr. Ramirez was named a managing director of Artisan Partners in April 2003.
Samuel B. Sellers, age 41, has been executive vice president and chief operating officer of Artisan Partners Asset Management since January 2023. Prior to his current role, Mr. Sellers was head of Investment Operations from January 2021. Previously, he served as deputy general counsel from January 2015 and associate counsel from April 2013.
Laura E. Simpson, age 48, has been executive vice president, chief legal officer and secretary of Artisan Partners Asset Management since October 2023. From January 2023 to October 2023 she served as assistant secretary of Artisan Partners Asset Management. She has served as general counsel of Artisan Partners since October 2022. Prior to then she served as deputy general counsel from January 2015 and associate counsel from April 2011.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Shares of our Class A common stock have been listed and traded on the NYSE under the symbol “APAM” since March 7, 2013. As of February 19, 2024, there were approximately 123 stockholders of record of our Class A common stock, 22 stockholders of record of our Class B common stock, and 25 stockholders of record of our Class C common stock. These figures do not reflect beneficial ownership or shares held in nominee name, nor do they include holders of any restricted stock units or performance share units. There is no trading market for shares of our Class B common stock or Class C common stock.
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the year-end cumulative total stockholder return of our Class A common stock during the five-year period ended December 31, 2023, with the year-end cumulative total return of the S&P 500® and the Dow Jones U.S. Asset Managers Index. The graph assumes the investment of $100 in our common stock and in the market indices and the reinvestment of all dividends.
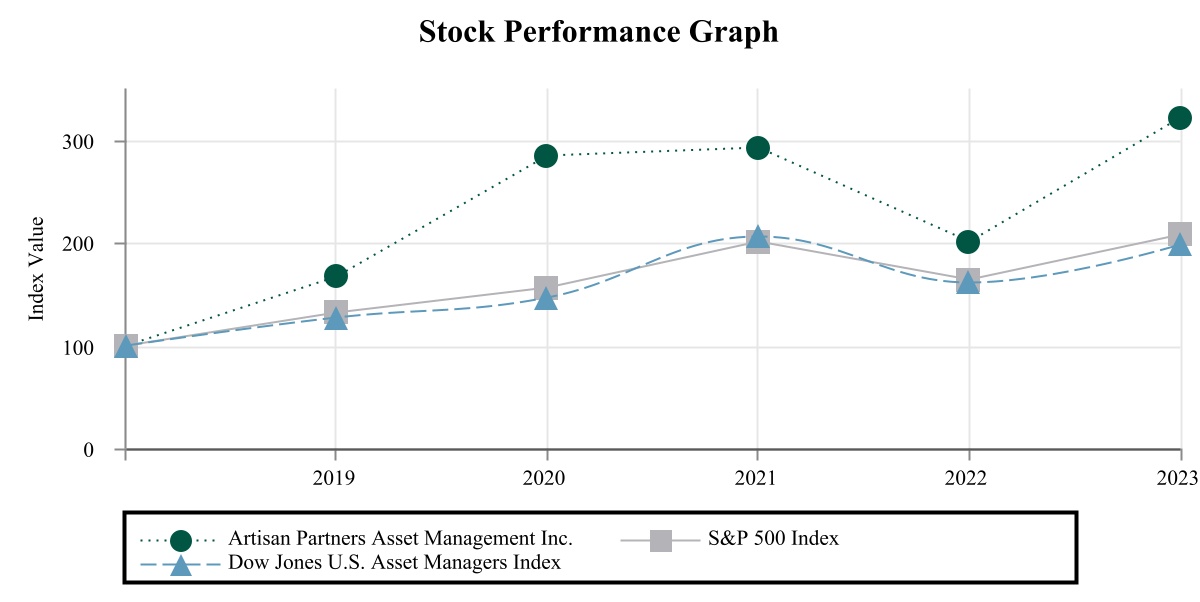
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
| Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. | $ | 166.53 | | $ | 284.70 | | $ | 292.39 | | $ | 200.90 | | $ | 321.79 | |
| S&P 500 Index | $ | 131.49 | | $ | 155.68 | | $ | 200.37 | | $ | 164.08 | | $ | 207.21 | |
| Dow Jones U.S. Asset Managers Index | $ | 126.72 | | $ | 145.92 | | $ | 205.19 | | $ | 160.83 | | $ | 197.56 | |
The above table is provided pursuant to SEC regulations and the outcomes are impacted significantly by beginning- and end-point stock price, as well as the price at which dividends are reinvested. A stockholder who invested in APAM at its IPO on March 7, 2013, at the IPO price of $30 per share would have experienced a 9% annual total return as of December 31, 2023 if all dividends were retained, compared to a 13% annual total return if all dividends were reinvested.
Dividend Policy
During the first quarter of 2024, our board of directors declared a variable quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share with respect to the fourth quarter of 2023 and a special annual dividend of $0.34 per share. The variable quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share represents approximately 80% of the cash generated in the fourth quarter of 2023. Subject to Board approval each quarter, we currently expect to pay a quarterly dividend of approximately 80% of the cash the Company generates each quarter. We expect quarterly cash generation to approximate adjusted net income plus long-term incentive compensation award expense, less cash reserved for future franchise capital awards (which we expect will generally approximate 4% of investment management revenues each quarter), with additional adjustments made for certain other sources and uses of cash, including capital expenditures. After the end of the year, our Board will consider paying a special dividend after determining the amount of cash needed for general corporate purposes and investments in growth and strategic initiatives. Although we expect to pay dividends according to our dividend policy, we may not pay dividends according to our policy or at all.
We intend to fund dividends from our portion of distributions made by Holdings from its available cash generated from operations. The holders of our Class B common stock and Class C common stock are not entitled to any cash dividends in their capacity as stockholders but, in their capacity as holders of limited partnership units of Holdings, they generally participate on a pro rata basis in distributions by Holdings.
The declaration and payment of all future dividends, if any, will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors. In determining the amount of any future dividends, our board of directors will take into account: (i) our financial results, (ii) our available cash, as well as anticipated cash requirements (including debt servicing, seed capital for new investment strategies and vehicles, and cash required to support growth and strategic initiatives), (iii) our capital requirements and the capital requirements of our subsidiaries (including Holdings), (iv) contractual, legal, tax and regulatory restrictions on, and implications of, the payment of dividends by us to our stockholders or by our subsidiaries (including Holdings) to us, including the obligation of Holdings to make tax distributions to the holders of partnership units (including us), (v) general economic and business conditions and (vi) any other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant.
As a holding company, our assets principally consist of our ownership of partnership units of Holdings, deferred tax assets and cash. Accordingly, we depend on distributions from Holdings to fund any dividends we may pay. We intend to cause Holdings to distribute cash to its partners, including us, in an amount sufficient to cover dividends, if any, declared by us. If we do cause Holdings to make such distributions, holders of Holdings limited partnership units will be entitled to receive equivalent distributions on a pro rata basis.
Our dividend policy has certain risks and limitations, particularly with respect to liquidity. Although we expect to pay dividends according to our dividend policy, we may not pay dividends according to our policy, or at all, if, among other things, Holdings is unable to make distributions to us as a result of its operating results, cash requirements and financial condition, the applicable laws of the State of Delaware (which may limit the amount of funds available for distribution), its compliance with covenants and financial ratios related to indebtedness (including the notes and the revolving credit agreement) and its other agreements with third parties. Our note purchase and revolving credit agreements contain covenants limiting Holdings’ ability to make distributions if a default has occurred and is continuing or would result from such a distribution. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity, Capital Resources, and Contractual Obligations”.
Under the Delaware General Corporation Law, we may only pay dividends from legally available surplus or, if there is no such surplus, out of our net profits for the fiscal year in which the dividend is declared and/or the preceding fiscal year. Surplus is defined as the excess of the fair value of our total assets over the sum of the fair value of our total liabilities plus the par value of our outstanding capital stock. Capital stock is defined as the aggregate of the par value of all issued capital stock. To the extent we do not have sufficient cash to pay dividends, we may decide not to pay dividends.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
As described in Note 8, “Stockholders’ Equity”, to the consolidated financial statements included in Item 8 of this report, upon termination of employment with Artisan, an employee-partner’s Class B common units are exchanged for Class E common units and the corresponding shares of Class B common stock are canceled. APAM issues the former employee-partner a number of shares of Class C common stock equal to the former employee-partner’s number of Class E common units. Class E common units are exchangeable for Class A common stock subject to the same restrictions and limitations on exchange applicable to the other common units of Holdings. There were no such issuances during the three months ended December 31, 2023.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis of the results of operations and financial condition of the Company should be read in conjunction with the “Forward-Looking Statements” disclosure preceding Part I and the “Risk Factors” set forth in Item 1A of Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10‑K, each of which describe our risks, uncertainties and other important factors in more detail.
Overview and Recent Highlights
We are an investment management firm focused on providing high-value added, active investment strategies in asset classes for sophisticated clients around the world. As of December 31, 2023, our ten autonomous investment teams managed a total of 25 investment strategies across multiple asset classes and investment styles.
We focus on attracting, retaining and developing talented investment professionals and creating an environment in which each investment team is provided ample resources and support, transparent and direct financial incentives, a high degree of investment autonomy, and a long-term time horizon. We create new investment strategies when we identify opportunities to add value for clients, oftentimes through the use of a broad array of securities, instruments, and techniques (which we call degrees of freedom) to differentiate returns and manage risk.
We offer our investment management capabilities primarily to sophisticated investors that operate with institutional decision-making processes and longer-term investment horizons. We employ knowledgeable and investment focused relationship managers who are directly aligned with our investment teams, and we pair them with regional and distribution channel experts. We provide access to our investment strategies through multiple investment vehicles, including separate accounts and different types of pooled vehicles. As of December 31, 2023, approximately 76% of our assets under management were managed for clients and investors domiciled in the U.S. and 24% of our assets under management were managed for clients and investors domiciled outside of the U.S.
As a high-value added investment manager we expect that long-term investment performance will be the primary driver of our long-term business and financial results. If we maintain and evolve existing investment strategies and launch new investment strategies that meet the needs of and generate attractive outcomes for sophisticated asset allocators, we believe that we will continue to generate strong business and financial results.
Over shorter time periods, changes in our business and financial results are largely driven by market conditions and fluctuations in our assets under management that may not necessarily be the result of our long-term investment performance or the long-term demand for our strategies. For this reason, we expect that our business and financial results will be lumpy over time.
We strive to maintain a financial model that is transparent and predictable. Currently, we derive nearly all of our revenues from investment management fees, most of which are based on a specified percentage of clients’ average assets under management. A majority of our expenses, including most of our compensation expense, vary directly with changes in our revenues.
We invest thoughtfully to support our investment teams and future growth, while also paying out to stockholders and partners a majority of the cash that we generate from operations through dividends and distributions. We expect to continue to invest in the growth of the business, with a focus on adding new investment capabilities and more degrees of freedom in areas where both opportunity and client demand exist, and in which we can differentiate our active management and add value for clients.
Business highlights for 2023 included the following:
•We closed on $130 million in commitments for our first closed-end drawdown fund managed by the Credit team.
•We launched two new accounts for the EMsights Capital Group’s investment strategies.
•During 2023, our fixed income strategies, consisting of the strategies managed by the Credit team and EMsights Capital Group, surpassed $10 billion in assets under management, 10 years after the Credit team was established.
•We continued to evolve our distribution structure, resources, and operations to better align our dedicated distribution teams and centralized sales functions across servicing and sales.
Financial highlights for 2023 included the following:
•During the year ended December 31, 2023, our assets under management increased to $150.2 billion, an increase of $22.3 billion, or 17%, compared to $127.9 billion at December 31, 2022, as a result of $27.1 billion of market appreciation, partially offset by $4.1 billion of net client cash outflows, and $0.7 billion of Artisan Funds’ distributions that were not reinvested by fund shareholders.
•Average assets under management for the year ended December 31, 2023 was $139.3 billion, a decrease of 1.6% from the average of $141.5 billion for the year ended December 31, 2022.
•We earned $975.1 million in revenue for the year ended December 31, 2023, a 2% decrease from revenues of $993.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
•Our GAAP operating margin was 31.1% in 2023, compared to 34.6% in 2022. Adjusted operating margin was 31.6% in 2023, compared to 34.3% in 2022.
•We generated $3.19 of earnings per basic and diluted share and $2.89 of adjusted EPS.
•We declared and distributed dividends of $2.66 per share of Class A common stock during 2023.
•We declared, effective January 30, 2024, a quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share of Class A common stock with respect to the December 2023 quarter and a special annual dividend of $0.34 per share, for a total of $2.78 of dividends per share with respect to 2023.
Organizational Structure
Organizational Structure
Our operations are conducted through Artisan Partners Holdings LP (“Holdings”) and its subsidiaries. On March 12, 2013, Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. (“APAM”) and Holdings completed a series of transactions (the “IPO Reorganization”) to reorganize their capital structures in connection with the initial public offering (“IPO”) of APAM’s Class A common stock. The IPO Reorganization and IPO were completed on March 12, 2013.
Limited partners of Holdings, some of whom are employees, held approximately 14% of the equity interests in Holdings as of December 31, 2023. Our results reflect that significant noncontrolling interest.
We operate our business in a single segment.
Holdings Unit Exchanges
During the year ended December 31, 2023, certain limited partners of Holdings exchanged 163,345 common units (along with a corresponding number of shares of Class B or Class C common stock of APAM, as applicable) for 163,345 shares of Class A common stock. In connection with the exchanges, APAM received 163,345 GP units of Holdings.
APAM’s equity ownership interest in Holdings increased from 85% at December 31, 2022 to 86% at December 31, 2023, as a result of these transactions and other equity transactions during the period.
Financial Overview
Economic Environment
Global market conditions materially affect our financial performance. During the year ended December 31, 2023, global markets experienced meaningful gains, despite significant hurdles, including elevated inflation, high interest rates and the effects of geopolitical tensions, conflicts and wars.
The following table presents the total returns of relevant market indices for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| S&P 500 total returns | 26.3 | % | | (18.1) | % | | 28.7 | % |
| MSCI All Country World total returns | 22.2 | % | | (18.4) | % | | 18.5 | % |
| MSCI EAFE total returns | 18.2 | % | | (14.5) | % | | 11.3 | % |
| Russell Midcap® total returns | 17.2 | % | | (17.3) | % | | 22.6 | % |
| MSCI Emerging Markets Index | 9.8 | % | | (20.1) | % | | (2.5) | % |
| ICE BofA US High Yield Index | 13.5 | % | | (11.2) | % | | 5.4 | % |
Key Performance Indicators
When we review our business and financial performance we consider, among other things, the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (unaudited; dollars in millions) |
| Assets under management at period end | $ | 150,167 | | | $ | 127,892 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
Average assets under management (1) | $ | 139,321 | | | $ | 141,516 | | | $ | 171,767 | |
Net client cash flows (2) | $ | (4,076) | | | $ | (9,813) | | | $ | 1,678 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 975 | | | $ | 993 | | | $ | 1,227 | |
Weighted average management fee (3) | 69.8 bps | | 70.2 bps | | 70.7 bps |
| Operating margin | 31.1 | % | | 34.6 | % | | 44.0 | % |
Adjusted operating margin (4) | 31.6 | % | | 34.3 | % | | 44.1 | % |
(1) We compute average assets under management by averaging day-end assets under management for the applicable period. |
(2) Net client cash flows excludes Artisan Funds’ income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested by fund shareholders. |
(3) We compute our weighted average management fee by dividing annualized investment management fees (which excludes performance fees) by average assets under management for the applicable period. Assets under management within our consolidated investment products, and any investment advisory fees earned thereon, are excluded from our weighted average fee calculations since any such revenues are eliminated upon consolidation. |
(4) Adjusted measures are non-GAAP measures and are explained and reconciled to the comparable GAAP measures in “Supplemental Non-GAAP Financial Information” below. |
Assets Under Management and Investment Performance
Changes to our operating results from one period to another are primarily caused by changes in the amount of our assets under management. Changes in the relative composition of our assets under management among our investment strategies and vehicles and the effective fee rates on our investment products also impact our operating results.
The amount and composition of our assets under management are, and will continue to be, influenced by a variety of factors including, among others:
•investment performance, including fluctuations in both the financial markets and foreign currency exchange rates and the quality of our investment decisions;
•flows of client assets into and out of our various strategies and investment vehicles;
•our decision to close strategies or limit the growth of assets in a strategy or a vehicle when we believe it is in the best interest of our clients, as well as our decision to re-open strategies, in part or entirely;
•our ability to attract and retain qualified investment, management, and marketing and client service professionals;
•industry trends towards products, strategies, vehicles or services that we do not offer;
•competitive conditions in the investment management and broader financial services sectors; and
•investor sentiment and confidence.
The table below sets forth changes in our total assets under management: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (unaudited; dollars in millions) |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 127,892 | | | $ | 174,754 | | | $ | 157,776 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 21,395 | | | 27,227 | | | 33,725 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (25,471) | | | (37,040) | | | (32,047) | |
| Net client cash flows | (4,076) | | | (9,813) | | | 1,678 | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (1) | (684) | | | (497) | | | (2,295) | |
Investment returns and other (2) | 27,035 | | | (36,552) | | | 17,595 | |
| | | | | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 150,167 | | | $ | 127,892 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 139,321 | | | $ | 141,516 | | | $ | 171,767 | |
(1) Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested represents the amount of income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested in the Artisan Funds. |
(2) Includes the impact of translating the value of assets under management denominated in non-USD currencies into U.S. dollars. The impact was immaterial for the periods presented. |
During 2023 our assets under management increased by $22.3 billion due to $27.1 billion of market appreciation, partially offset by $4.1 billion of net client cash outflows and $0.7 billion of Artisan Funds’ distributions that were not reinvested by fund shareholders. For the year, 10 of our 25 investment strategies had net inflows totaling $6.2 billion, which were offset by $10.3 billion of net outflows from the remaining strategies.
Over the long-term, we expect to generate the majority of our AUM growth through investment returns, which has been our historical experience.
We monitor the availability of attractive investment opportunities relative to the amount of assets we manage in each of our investment strategies and the velocity at which the strategies are experiencing inflows. When appropriate, we will close a strategy to new investors or otherwise take action to slow or restrict its growth, even though our aggregate assets under management may be negatively impacted in the short term. We may also re-open a strategy, widely or selectively, to fill available capacity or manage the diversification of our client base in that strategy. We believe that management of our investment capacity protects our ability to manage assets successfully, which protects the interests of our clients and, in the long term, protects our ability to retain client assets and maintain our profit margins.
As of the date of this filing, the Artisan High Income Fund, Artisan International Value Fund and Artisan International Small-Mid Fund are closed to most new investors and their respective strategies have limited availability to most new client relationships. In addition, we are actively managing the capacity of our U.S. Small-Cap Growth strategy with respect to new client relationships.
When we close or otherwise restrict the growth of a strategy, we typically continue to allow additional investments in the strategy by existing clients and certain related entities. We may also permit new investments by other eligible investors in our discretion. As a result, during a given period we may have net client cash inflows in a closed strategy. However, when a strategy is closed or its growth is restricted we expect there to be periods of net client cash outflows.
The unaudited table on the following page sets forth the average annual total returns for each composite and its respective benchmark (and style benchmark, if applicable) over a multi-horizon time period as of December 31, 2023. Returns for periods less than one year are not annualized.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Composite Inception | | Strategy AUM | | Average Annual Total Returns (Gross of Fees) | | Average Annual Value-Added (1) Since Inception (bps) |
| Investment Team and Strategy | Date | | (in $MM) (2) | | 1 YR | 3 YR | 5 YR | 10 YR | Inception | |
| Growth Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Opportunities Strategy | 2/1/2007 | | $ | 21,232 | | | 24.40% | 0.32% | 14.37% | 11.06% | 10.75% | | 460 |
| MSCI All Country World Index | | | | | 22.20% | 5.75% | 11.71% | 7.92% | 6.15% | | |
| Global Discovery Strategy | 9/1/2017 | | 1,490 | | | 22.24% | (0.86)% | 15.77% | --- | 12.94% | | 422 |
| MSCI All Country World Index | | | | | 22.20% | 5.75% | 11.71% | --- | 8.72% | | |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Growth Strategy | 4/1/1997 | | 12,646 | | | 25.45% | (3.59)% | 14.88% | 10.17% | 14.31% | | 476 |
Russell® Midcap Index | | | | | 17.23% | 5.92% | 12.67% | 9.42% | 10.13% | | |
Russell® Midcap Growth Index | | | | | 25.87% | 1.31% | 13.81% | 10.56% | 9.55% | | |
| U.S. Small-Cap Growth Strategy | 4/1/1995 | | 3,178 | | | 11.38% | (9.84)% | 11.12% | 9.40% | 10.40% | | 286 |
Russell® 2000 Index | | | | | 16.93% | 2.22% | 9.97% | 7.15% | 8.84% | | |
Russell® 2000 Growth Index | | | | | 18.66% | (3.50)% | 9.22% | 7.16% | 7.54% | | |
| Global Equity Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Equity Strategy | 4/1/2010 | | 347 | | | 13.58% | (0.98)% | 10.90% | 8.84% | 11.16% | | 260 |
| MSCI All Country World Index | | | | | 22.20% | 5.75% | 11.71% | 7.92% | 8.56% | | |
| Non-U.S. Growth Strategy | 1/1/1996 | | 13,218 | | | 15.53% | 1.22% | 8.04% | 4.62% | 9.29% | | 438 |
| MSCI EAFE Index | | | | | 18.24% | 4.02% | 8.16% | 4.28% | 4.91% | | |
| Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth Strategy | 1/1/2019 | | 7,151 | | | 12.42% | (3.09)% | 11.25% | --- | 11.25% | | 418 |
| MSCI All Country World Index Ex USA Small Mid Cap | | | | | 15.79% | 0.89% | 7.07% | --- | 7.07% | | |
| China Post-Venture Strategy | 4/1/2021 | | 160 | | | (4.99)% | --- | --- | --- | (15.54)% | | 366 |
| MSCI China SMID Cap Index | | | | | (16.48)% | --- | --- | --- | (19.20)% | | |
| U.S. Value Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Value Equity Strategy | 7/1/2005 | | 4,227 | | | 25.54% | 12.77% | 15.86% | 10.30% | 9.42% | | 176 |
| Russell® 1000 Index | | | | | 26.53% | 8.97% | 15.51% | 11.80% | 9.95% | | |
| Russell® 1000 Value Index | | | | | 11.46% | 8.86% | 10.90% | 8.39% | 7.66% | | |
| U.S. Mid-Cap Value Strategy | 4/1/1999 | | 2,818 | | | 19.35% | 10.25% | 12.31% | 7.51% | 12.08% | | 270 |
| Russell® Midcap Index | | | | | 17.23% | 5.92% | 12.67% | 9.42% | 9.41% | | |
| Russell® Midcap Value Index | | | | | 12.71% | 8.36% | 11.15% | 8.26% | 9.38% | | |
| Value Income Strategy | 3/1/2022 | | 12 | | | 12.20% | --- | --- | --- | 1.90% | | (468) |
| S&P 500 Market Index | | | | | 26.29% | --- | --- | --- | 6.58% | | |
| International Value Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| International Value Strategy | 7/1/2002 | | 40,762 | | | 24.19% | 11.25% | 13.68% | 8.05% | 11.71% | | 570 |
| MSCI EAFE Index | | | | | 18.24% | 4.02% | 8.16% | 4.28% | 6.01% | | |
| International Explorer Strategy | 10/1/2020 | | 247 | | | 22.42% | 8.63% | --- | --- | 15.65% | | 773 |
| MSCI All Country World Index Ex USA Small Cap (Net) | | | | | 15.66% | 1.49% | --- | --- | 7.92% | | |
| Global Value Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Value Strategy | 7/1/2007 | | 25,349 | | | 28.05% | 9.34% | 12.04% | 8.33% | 8.75% | | 298 |
| MSCI All Country World Index | | | | | 22.20% | 5.75% | 11.71% | 7.92% | 5.77% | | |
| Select Equity Strategy | 3/1/2020 | | 321 | | | 27.82% | 7.89% | --- | --- | 11.90% | | (324) |
| S&P 500 Market Index | | | | | 26.29% | 10.00% | --- | --- | 15.14% | | |
| Sustainable Emerging Markets Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sustainable Emerging Markets Strategy | 7/1/2006 | | 917 | | | 18.30% | (4.95)% | 5.22% | 4.69% | 5.08% | | 81 |
| MSCI Emerging Markets Index | | | | | 9.83% | (5.08)% | 3.68% | 2.66% | 4.27% | | |
| Credit Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| High Income Strategy | 4/1/2014 | | 9,407 | | | 16.95% | 4.42% | 7.78% | --- | 6.92% | | 261 |
| ICE BofA U.S. High Yield Index | | | | | 13.46% | 2.00% | 5.21% | --- | 4.31% | | |
| Credit Opportunities Strategy | 7/1/2017 | | 215 | | | 27.22% | 13.24% | 15.52% | --- | 13.29% | | 1,132 |
| ICE BofA U.S. Dollar 3-Month Deposit Offered Rate Constant Maturity Index | | | | | 5.12% | 2.15% | 2.02% | --- | 1.97% | | |
| Floating Rate Strategy | 1/1/2022 | | 61 | | | 14.94% | --- | --- | --- | 6.78% | | 102 |
| Credit Suisse Leveraged Loan Total Return Index | | | | | 13.04% | --- | --- | --- | 5.76% | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Developing World Team | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Developing World Strategy | 7/1/2015 | | 3,453 | | | 30.96% | (10.76)% | 13.32% | --- | 9.60% | | 655 |
| MSCI Emerging Markets Index | | | | | 9.83% | (5.08)% | 3.68% | --- | 3.05% | | |
| Antero Peak Group | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Antero Peak Strategy | 5/1/2017 | | 1,897 | | | 17.08% | 3.25% | 14.05% | --- | 16.65% | | 371 |
| S&P 500 Market Index | | | | | 26.29% | 10.00% | 15.68% | --- | 12.94% | | |
| Antero Peak Hedge Strategy | 11/1/2017 | | 204 | | | 13.06% | 1.36% | 9.59% | --- | 10.72% | | (175) |
| S&P 500 Market Index | | | | | 26.29% | 10.00% | 15.68% | --- | 12.47% | | |
| EMsights Capital Group | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Global Unconstrained Strategy | 4/1/2022 | | 313 | | | 8.94% | --- | --- | --- | 9.97% | | 630 |
| ICE BofA 3-month Treasury Bill Index | | | | | 5.01% | --- | --- | --- | 3.67% | | |
| Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities Strategy | 5/1/2022 | | 92 | | | 14.52% | --- | --- | --- | 13.78% | | 770 |
| J.P. Morgan EMB Hard Currency/Local Currency 50-50 Index | | | | | 11.43% | --- | --- | --- | 6.08% | | |
| Emerging Markets Local Opportunities Strategy | 8/1/2022 | | 450 | | | 16.16% | --- | --- | --- | 14.05% | | 293 |
| J.P. Morgan GBI-EM Global Diversified Index | | | | | 12.70% | --- | --- | --- | 11.12% | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Assets Under Management | | | $ | 150,167 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
(1) Value-added is the amount, in basis points, by which the average annual gross composite return of each of our strategies has outperformed or underperformed its respective benchmark. See “Investment Performance and Assets Under Management (AUM) Information Used in this Report” for additional information regarding the benchmarks used. |
(2) AUM for certain strategies include the following amounts for which Artisan Partners provides investment models to managed account sponsors (reported on a one-month lag): Artisan Sustainable Emerging Markets $78 million. |
The tables below set forth changes in our assets under management by investment team: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| By Investment Team |
| Year Ended | Growth | Global Equity | U.S. Value | International Value | Global Value | Sustainable Emerging Markets | Credit | Developing World | Antero Peak Group | EMsights Capital Group | Total |
| December 31, 2023 | (unaudited; in millions) |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 33,977 | | $ | 20,623 | | $ | 6,088 | | $ | 30,210 | | $ | 21,767 | | $ | 873 | | $ | 7,140 | | $ | 3,466 | | $ | 3,676 | | $ | 72 | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 3,730 | | 1,486 | | 452 | | 8,190 | | 2,092 | | 138 | | 3,623 | | 585 | | 342 | | 757 | | 21,395 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (6,570) | | (3,822) | | (762) | | (4,415) | | (3,755) | | (236) | | (2,063) | | (1,513) | | (2,331) | | (4) | | (25,471) | |
| Net client cash flows | (2,840) | | (2,336) | | (310) | | 3,775 | | (1,663) | | (98) | | 1,560 | | (928) | | (1,989) | | 753 | | (4,076) | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (1) | (11) | | (27) | | (36) | | (325) | | (15) | | — | | (270) | | — | | — | | — | | (684) | |
Investment returns and other (2) | 7,420 | | 2,616 | | 1,315 | | 7,349 | | 5,581 | | 142 | | 1,253 | | 915 | | 414 | | 30 | | 27,035 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 38,546 | | $ | 20,876 | | $ | 7,057 | | $ | 41,009 | | $ | 25,670 | | $ | 917 | | $ | 9,683 | | $ | 3,453 | | $ | 2,101 | | $ | 855 | | $ | 150,167 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 36,541 | | $ | 20,798 | | $ | 6,514 | | $ | 35,990 | | $ | 23,332 | | $ | 874 | | $ | 8,328 | | $ | 3,512 | | $ | 3,041 | | $ | 391 | | $ | 139,321 | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 52,434 | | $ | 32,998 | | $ | 8,053 | | $ | 31,816 | | $ | 26,744 | | $ | 1,173 | | $ | 8,157 | | $ | 8,102 | | $ | 5,277 | | $ | — | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 7,069 | | 3,252 | | 544 | | 7,560 | | 2,759 | | 293 | | 3,021 | | 1,599 | | 1,064 | | 66 | | 27,227 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (8,579) | | (8,681) | | (1,617) | | (6,617) | | (4,003) | | (226) | | (3,033) | | (2,998) | | (1,286) | | — | | (37,040) | |
| Net client cash flows | (1,510) | | (5,429) | | (1,073) | | 943 | | (1,244) | | 67 | | (12) | | (1,399) | | (222) | | 66 | | (9,813) | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (1) | (5) | | (35) | | (47) | | (173) | | (16) | | — | | (209) | | (7) | | (5) | | — | | (497) | |
Investment returns and other (2) | (16,942) | | (6,911) | | (845) | | (2,376) | | (3,717) | | (367) | | (796) | | (3,230) | | (1,374) | | 6 | | (36,552) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 33,977 | | $ | 20,623 | | $ | 6,088 | | $ | 30,210 | | $ | 21,767 | | $ | 873 | | $ | 7,140 | | $ | 3,466 | | $ | 3,676 | | $ | 72 | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 38,565 | | $ | 24,019 | | $ | 7,146 | | $ | 30,406 | | $ | 23,574 | | $ | 996 | | $ | 7,548 | | $ | 4,872 | | $ | 4,350 | | $ | 53 | | $ | 141,516 | |
| December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 52,685 | | $ | 32,056 | | $ | 7,149 | | $ | 24,123 | | $ | 22,417 | | $ | 679 | | $ | 6,338 | | $ | 8,853 | | $ | 3,476 | | $ | — | | $ | 157,776 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 7,418 | | 4,384 | | 407 | | 8,121 | | 4,723 | | 499 | | 3,158 | | 3,499 | | 1,516 | | — | | 33,725 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (12,528) | | (5,313) | | (1,189) | | (4,057) | | (3,809) | | (54) | | (1,582) | | (3,035) | | (480) | | — | | (32,047) | |
| Net client cash flows | (5,110) | | (929) | | (782) | | 4,064 | | 914 | | 445 | | 1,576 | | 464 | | 1,036 | | — | | 1,678 | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (1) | (302) | | (545) | | (47) | | (701) | | (46) | | — | | (217) | | (286) | | (151) | | — | | (2,295) | |
Investment returns and other (2) | 5,161 | | 2,416 | | 1,733 | | 4,330 | | 3,459 | | 49 | | 460 | | (929) | | 916 | | — | | 17,595 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 52,434 | | $ | 32,998 | | $ | 8,053 | | $ | 31,816 | | $ | 26,744 | | $ | 1,173 | | $ | 8,157 | | $ | 8,102 | | $ | 5,277 | | $ | — | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 53,375 | | $ | 33,679 | | $ | 7,835 | | $ | 28,998 | | $ | 25,463 | | $ | 924 | | $ | 7,576 | | $ | 9,541 | | $ | 4,376 | | $ | — | | $ | 171,767 | |
|
(1) Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested represents the amount of income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested in the Artisan Funds. |
(2) Includes the impact of translating the value of assets under management denominated in non-USD currencies into U.S. dollars. The impact was immaterial for the periods presented. |
The goal of our marketing, distribution and client services efforts is to establish and maintain a client base that is diversified by investment strategy, client type and distribution channel. As distribution channels have evolved to have more institutional-like decision making processes and longer-term investment horizons, we have expanded our distribution efforts into those areas. The table below sets forth our assets under management by distribution channel: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 | | As of December 31, 2022 | | As of December 31, 2021 |
| $ in millions | | % of total | | $ in millions | | % of total | | $ in millions | | % of total |
| (unaudited) | | | | (unaudited) | | | | (unaudited) | | |
| Institutional | $ | 94,652 | | | 63.0 | % | | $ | 82,456 | | | 64.5 | % | | $ | 111,705 | | | 63.9 | % |
| Intermediary | 49,871 | | | 33.2 | % | | 39,851 | | | 31.1 | % | | 55,198 | | | 31.6 | % |
| Retail | 5,644 | | | 3.8 | % | | 5,585 | | | 4.4 | % | | 7,851 | | | 4.5 | % |
Ending Assets Under Management (1) | $ | 150,167 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 127,892 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 174,754 | | | 100.0 | % |
(1) The allocation of assets under management by distribution channel involves the use of estimates and the exercise of judgment. |
Our institutional channel includes assets under management sourced from defined contribution plan clients, which made up approximately 9% of our total assets under management as of December 31, 2023.
The following tables set forth the changes in our assets under management by vehicle type: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended | Artisan Funds & Artisan Global Funds | | Separate Accounts and Other (1) | | Total |
| December 31, 2023 | (unaudited; in millions) |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 60,811 | | | $ | 67,081 | | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 15,138 | | | 6,257 | | | 21,395 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (15,079) | | | (10,392) | | | (25,471) | |
| Net client cash flows | 59 | | | (4,135) | | | (4,076) | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (2) | (684) | | | — | | | (684) | |
Investment returns and other (3) | 12,592 | | | 14,443 | | | 27,035 | |
Net transfers (4) | (15) | | | 15 | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 72,763 | | | $ | 77,404 | | | $ | 150,167 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 67,412 | | | $ | 71,909 | | | $ | 139,321 | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 84,363 | | | $ | 90,391 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 18,632 | | | 8,595 | | | 27,227 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (24,552) | | | (12,488) | | | (37,040) | |
| Net client cash flows | (5,920) | | | (3,893) | | | (9,813) | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (2) | (497) | | | — | | | (497) | |
Investment returns and other (3) | (16,834) | | | (19,718) | | | (36,552) | |
Net transfers (4) | (301) | | | 301 | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 60,811 | | | $ | 67,081 | | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 68,080 | | | $ | 73,436 | | | $ | 141,516 | |
| December 31, 2021 | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 74,746 | | | $ | 83,030 | | | $ | 157,776 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 23,957 | | | 9,768 | | | 33,725 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (18,628) | | | (13,419) | | | (32,047) | |
| Net client cash flows | 5,329 | | | (3,651) | | | 1,678 | |
Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested (2) | (2,295) | | | — | | | (2,295) | |
Investment returns and other (3) | 6,984 | | | 10,611 | | | 17,595 | |
Net transfers (4) | (401) | | | 401 | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 84,363 | | | $ | 90,391 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 83,533 | | | $ | 88,234 | | | $ | 171,767 | |
(1) Separate accounts and other consists of AUM we manage in or through vehicles other than Artisan Funds or Artisan Global Funds. This AUM includes assets we manage in traditional separate accounts, as well as assets we manage in Artisan-branded collective investment trusts and in Artisan Private Funds. As of December 31, 2023, AUM for certain strategies include the following amounts for which Artisan Partners provides investment models to managed account sponsors (reported on a one-month lag): Artisan Sustainable Emerging Markets $78 million. |
(2) Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested represents the amount of income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested in the Artisan Funds. |
(3) Includes the impact of translating the value of assets under management denominated in non-USD currencies into U.S. dollars. The impact was immaterial for the periods presented. |
(4) Net transfers represent certain amounts that we have identified as having been transferred out of one investment strategy, investment vehicle or account and into another strategy, vehicle or account. |
The following table sets forth our assets under management by asset class:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended | Equity (1) | | Fixed Income (1) | | Alternative (1) | | Total |
| December 31, 2023 | (unaudited; in millions) |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 116,832 | | | $ | 7,059 | | | $ | 4,001 | | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 16,671 | | | 4,046 | | | 678 | | | 21,395 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (21,072) | | | (2,059) | | | (2,340) | | | (25,471) | |
Net client cash flows (2) | (4,401) | | | 1,987 | | | (1,662) | | | (4,076) | |
Artisan Funds' distributions not reinvested (3) | (414) | | | (270) | | | — | | | (684) | |
| Investment returns and other | 25,351 | | | 1,233 | | | 451 | | | 27,035 | |
Net transfers (4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 137,368 | | | $ | 10,009 | | | $ | 2,790 | | | $ | 150,167 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 127,390 | | | $ | 8,440 | | | $ | 3,491 | | | $ | 139,321 | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 161,083 | | | $ | 8,037 | | | $ | 5,634 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 23,064 | | | 3,038 | | | 1,125 | | | 27,227 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (32,714) | | | (3,020) | | | (1,306) | | | (37,040) | |
Net client cash flows (2) | (9,650) | | | 18 | | | (181) | | | (9,813) | |
Artisan Funds' distributions not reinvested (3) | (283) | | | (209) | | | (5) | | | (497) | |
| Investment returns and other | (34,318) | | | (787) | | | (1,447) | | | (36,552) | |
Net transfers (4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 116,832 | | | $ | 7,059 | | | $ | 4,001 | | | $ | 127,892 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 129,387 | | | $ | 7,443 | | | $ | 4,686 | | | $ | 141,516 | |
| December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | |
| Beginning assets under management | $ | 147,962 | | | $ | 6,241 | | | $ | 3,573 | | | $ | 157,776 | |
| Gross client cash inflows | 28,789 | | | 3,146 | | | 1,790 | | | 33,725 | |
| Gross client cash outflows | (29,986) | | | (1,576) | | | (485) | | | (32,047) | |
Net client cash flows (2) | (1,197) | | | 1,570 | | | 1,305 | | | 1,678 | |
Artisan Funds' distributions not reinvested (3) | (1,927) | | | (217) | | | (151) | | | (2,295) | |
| Investment returns and other | 16,245 | | | 443 | | | 907 | | | 17,595 | |
Net transfers (4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Ending assets under management | $ | 161,083 | | | $ | 8,037 | | | $ | 5,634 | | | $ | 174,754 | |
| Average assets under management | $ | 159,698 | | | $ | 7,463 | | | $ | 4,606 | | | $ | 171,767 | |
| | | | | | | |
(1) Equity includes the following investment strategies: Mid-Cap Growth, Small-Cap Growth, Mid-Cap Value, Non-U.S. Growth, International Value, Global Opportunities, Global Equity, Value Equity, Global Value, Sustainable Emerging Markets, Global Discovery, Developing World, Non-U.S. Small-Mid Growth, International Explorer, Select Equity, and Value Income. Fixed Income includes the following investment strategies: High Income, Floating Rate, Emerging Markets Debt Opportunities, and Emerging Markets Local Opportunities. Alternative includes the following investment strategies: Antero Peak, Antero Peak Hedge, China Post-Venture, Credit Opportunities, and Global Unconstrained. |
(2) Net client cash flows excludes Artisan Funds’ income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested. |
(3) Artisan Funds’ distributions not reinvested represents the amount of income and capital gain distributions that were not reinvested in the Artisan Funds. |
(4) Net transfers represent certain amounts that we have identified as having been transferred out of one investment strategy, investment vehicle or account and into another strategy, vehicle or account. |
Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds
As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Funds comprised $66.5 billion, or 44%, of our assets under management. For the year ended December 31, 2023, fees from Artisan Funds represented $562.8 million, or 58%, of our revenues. Our contractual tiered fee rates for the series of Artisan Funds range from 0.60% to 1.05% of fund assets, depending on the investment strategy, the amount invested and other factors.
As of December 31, 2023, Artisan Global Funds comprised $6.3 billion, or 4%, of our assets under management. For the year ended December 31, 2023, fees from Artisan Global Funds represented $43.5 million, or 4%, of our revenues. Our contractual fee rates for Artisan Global Funds range from 0.50% to 1.85% of assets under management.
The weighted average management fee rate paid by our Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds clients in the aggregate was 0.901%, 0.907%, and 0.912%, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Separate Accounts and Other
Assets under management within the “separate accounts and other” category consists of assets we manage in or through vehicles other than Artisan Funds or Artisan Global Funds, including traditional separate accounts, Artisan-branded collective investment trusts and Artisan Private Funds, as well as assets under advisement related to clients for whom we provide investment models but do not have discretionary investment authority. Assets within the “separate accounts and other” category comprised $77.4 billion, or 52%, of our assets under management as of December 31, 2023. For the year ended December 31, 2023, fees from these clients represented $368.8 million, or 38%, of our revenues.
Traditional separate account clients are generally subject to standard fee schedules that vary by investment strategy and, through the application of standard breakpoints, reflect the size of the account and client relationship. The weighted average management fee rate paid by our traditional separate account clients was 0.489%, 0.484%, and 0.484% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. There are a number of exceptions to our standard fee schedules, including exceptions based on the nature of a client relationship and the aggregate value of a client’s assets under our management. In general, our effective rate of fee for a particular client relationship declines as the assets we manage for that client increase, which we believe is typical for the asset management industry.
A number of our investment strategies are accessible to certain types of employee benefit plans through Artisan-branded collective investment trusts. We act as investment adviser to the collective investment trusts and earn a management fee for providing this service. The weighted average management fee rate paid by our Artisan-branded collective investment trust clients was 0.665%, 0.714%, and 0.729% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Artisan serves as the investment manager and acts as the general partner for certain Artisan Private Funds. Under the terms of these agreements, Artisan earns a management fee, and for certain funds is entitled to receive either an allocation of profits or a performance-based fee. The weighted average management fee rate paid by our Artisan Private Funds clients was 0.654%, 0.809%, and 0.786% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
The weighted average management fee rate paid by clients within the “separate accounts and other” category in the aggregate was 0.508%, 0.512% and 0.513% for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Because, as is typical in the asset management industry, our rates of fee decline as the assets under our management in a relationship increase, and because of differences in our fees by investment strategy or investment vehicle, a change in the composition of our assets under management, in particular a shift of assets to strategies or vehicles with lower effective rates of fees, could have a material impact on our overall weighted average rate of fee. See “—Qualitative and Quantitative Disclosures Regarding Market Risk—Market Risk” for a sensitivity analysis that demonstrates the impact that certain changes in the composition of our assets under management could have on our revenues.
Investment Advisory Revenues
Essentially all of our revenues consist of fees earned from managing clients’ assets. Investment advisory fees, which are comprised of management fees and performance fees, fluctuate based on a number of factors, including the total value of our assets under management, the composition of assets under management among investment vehicles and our investment strategies, changes in the investment management fee rates on our products, the extent to which we enter into fee arrangements that differ from our standard fee schedules, which can be affected by custom and the competitive landscape in the relevant market, and, for the accounts on which we earn performance fees, the investment performance of those accounts.
The different fee structures associated with Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds and separate accounts and other pooled vehicles, and the different fee schedules applicable to each of our investment strategies, make the composition of our assets under management an important determinant of the investment management fees we earn. Historically, we have received higher effective rates of investment management fees from Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds than from traditional separate accounts, reflecting, among other things, the different and broader array of services we provide to Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds. Investment management fees for non-U.S. funds may also be higher because they include fees to offset higher distribution costs. Our investment management fees also differ by investment strategy, with higher-capacity strategies having lower standard fee rates than strategies with more limited capacity.
Certain separate account clients pay us fees based on the performance of their accounts relative to agreed-upon benchmarks, which typically results in a lower base fee, but allows us to earn higher fees if the performance we achieve for that client is superior to the performance of the agreed-upon benchmark. We may also receive performance fees or incentive allocations from Artisan Private Funds. Approximately 3% of our $150.2 billion of assets under management as of December 31, 2023 have performance fee billing arrangements. Performance fees of $4.3 million, $0.6 million, and $13.3 million were recognized in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
The following table sets forth revenues we earned by vehicle type for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Revenues | (in millions) |
| Management fees | | | | | |
| Artisan Funds & Artisan Global Funds | $ | 606.3 | | | $ | 617.0 | | | $ | 761.4 | |
| Separate accounts and other | 364.5 | | | 375.7 | | | 452.5 | |
| Performance fees | 4.3 | | | 0.6 | | | 13.3 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 975.1 | | | $ | 993.3 | | | $ | 1,227.2 | |
| Average assets under management for period | $ | 139,321 | | | $ | 141,516 | | | $ | 171,767 | |
Management fees, performance fees and incentive allocations earned from consolidated investment products are eliminated from revenue upon consolidation. For each of the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, approximately 82%, 82%, and 83%, respectively, of our investment advisory fees were earned from clients located in the United States.
Operating Expenses
Our operating expenses consist primarily of compensation and benefits, distribution, servicing and marketing, occupancy, communication and technology, and general and administrative expenses.
Our expenses fluctuate due to a number of factors, including the following:
•variations in the amount of total compensation expense due to, among other things, changes in the amount of incentive compensation earned and equity awards made, variations in our employee count (including the addition of new investment teams) and changes in our product mix and other competitive factors; and
•expenses, such as distribution fees, rent, professional service fees, technology and data-related costs, incurred, as necessary, to operate and grow our business.
A significant portion of our operating expenses are variable and fluctuate in direct relation to our assets under management and revenues. Even if we experience declining revenues, we expect to continue to make the expenditures necessary for us to manage and grow our business. As a result, our profits may decline.
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits includes (i) salaries, incentive compensation and benefits costs and (ii) long-term incentive compensation expense related to equity and cash awards granted to employees.
Incentive compensation comprises a significant portion of our senior employees’ total compensation. The amount of incentive compensation paid to members of our investment teams and distribution team is based in large part on formulas that are tied directly to revenues. For each of our investment teams, incentive compensation generally represents 25% of the asset-based management fees and a share of performance-based fees generated by assets under management in the team’s strategy or strategies. Incentive compensation paid to most other employees is discretionary and determined based on individual performance and our overall results during the applicable year.
The Company is primarily self-insured for health benefits up to certain annual stop-loss limits. Expense is recognized based on claims filed and an estimate of claims incurred but not yet reported, as determined by an independent third party.
Fixed compensation costs are comprised primarily of salaries, benefits, and long-term incentive compensation expense. Fixed compensation costs, exclusive of long-term incentive compensation, are expected to rise 4% to 8% in 2024 reflecting merit increases, the absorption of a full year of expense for full time employees hired in 2023, and an expected increase of approximately 5% in full time employees in 2024. The additional full time employees in 2024 will primarily relate to investment and distribution roles to capitalize on our growth strategy.
Certain compensation and benefits expenses are generally higher in the beginning of the year, including employer funded retirement and health care contributions and payroll taxes. We expect these expenses will add approximately $6 million to our expenses in the first quarter of 2024, compared to the fourth quarter of 2023.
We have granted equity awards to our employees that consist of standard restricted awards that generally vest on a pro rata basis over 5 years and career awards that vest when both of the following conditions are met (1) pro-rata time vesting over 5 years and (2) qualifying retirement (as defined in the award agreements). The 2024 grant also includes a new traditional retirement provision that eliminates the 5-year vesting requirement when career award recipients have a qualified retirement after having met an age plus years of service threshold of 70. Career vesting awards granted to investment team members are generally further subject to the Franchise Protection Clause, which applies to current or future portfolio managers and founding investment team members. The Franchise Protection Clause provides that the total number of awards ultimately vesting will be reduced to the extent that cumulative net client cash outflows from the award recipient’s investment team during a specified measurement period exceeds a set threshold. Performance share units (“PSUs”) were granted to certain executive officers of the Company in 2020, 2021 and 2022. The number of PSUs that will vest is dependent upon the Company’s adjusted operating margin and total stockholder return relative to a peer group over a three year measurement period. Once determined the extent to which the performance conditions have been met, 50% of the PSUs eligible for vesting will vest, and 50% of the PSUs eligible for vesting will vest upon a qualified retirement. No performance share units were granted in 2023 or 2024.
The estimated grant date fair value of equity awards is recognized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the award. The initial requisite service period is generally three years for PSUs and five years for all other equity awards that have been granted to date. Compensation expense for PSUs is only recognized if it is probable that the performance conditions will be achieved. For all awards, if a service or performance condition is not achieved, the corresponding awards are forfeited and any previously recognized compensation expense is reversed.
We grant cash-based long-term incentive awards, referred to as franchise capital awards, to certain investment team members in lieu of additional equity awards. Franchise capital awards are subject to the same vesting and forfeiture provisions as the equity awards. Prior to vesting, franchise capital awards are generally allocated to one or more of Artisan’s investment strategies. The underlying investment holdings and franchise capital award liability are marked to market value each quarter. The change in value of the award liability is included in compensation expense. The change in value of the underlying investment holdings is included in non-operating income/(expense).
We expect to reserve approximately 4% of our management fee revenues each quarter for future franchise capital awards, which we expect to make after the conclusion of each year. Over the long-term, we believe the economic impact of the reduced cash available for dividends will be offset by a corresponding reduction in dilution, as we expect to grant fewer equity awards as a result of the franchise capital awards.
During the first quarter of 2024, the board of directors of APAM approved the grant of long-term incentive awards with a grant date fair value of $59.2 million consisting of $20.8 million of restricted share-based awards and $38.4 million of franchise capital awards, to certain employees pursuant to the Company’s 2023 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan. The grant will be effective March 1, 2024.
Since the IPO and including the grant in the first quarter of 2024, our board of directors has approved equity grants of 12,363,069 restricted share-based awards. Total unrecognized non-cash compensation expense for these awards is $85.2 million. As of the date of this filing, unvested equity awards consist of the following number of shares by vesting condition: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Service Only | | Service & Performance Conditions | | Service & Market Conditions | | Total |
| Standard Pro Rata Time Vesting | | 1,563,630 | | | 43,581 | | | 43,581 | | | 1,650,792 | |
| Qualified Retirement | | 2,962,855 | | | 1,479,652 | | | 57,002 | | | 4,499,509 | |
| Total Unvested | | 4,526,485 | | | 1,523,233 | | | 100,583 | | | 6,150,301 | |
Including the long-term incentive award approved in the first quarter of 2024, total unrecognized long-term incentive compensation expense (including both equity grants and franchise capital awards) is $205.7 million. The 2024 grant includes a traditional retirement acceleration feature. The new provision eliminates the 5-year vesting requirement when career award recipients have a qualified retirement after having met an age plus years of service threshold of 70. All other vesting conditions, including notice periods and clawbacks, remain in effect. Long-term incentive compensation expense in 2024 is expected to increase by $8 to $9 million due to the provision, resulting in approximately $69.0 million of expense for 2024, excluding the impact of investment returns on the franchise capital awards’ underlying investments. Total compensation expense recorded over the vesting term of the awards is not impacted by the retirement acceleration provision.
We expect to continue to make long-term incentive awards each year, though the form and structure of the awards may change as we seek to maximize alignment between our associates and our clients and stockholders. The actual amount of the expense over time will depend primarily on the size of awards made. The size of long-term incentive awards will vary from year to year and will be influenced by our results and other factors. From time to time, we may also make individual long-term incentive grants to people we hire.
Distribution, Servicing and Marketing
Distribution, servicing and marketing expenses primarily represent payments we make to broker-dealers, financial advisors, defined contribution plan providers, mutual fund supermarkets and other intermediaries for selling, servicing and administering accounts invested in shares of Artisan Funds. Artisan Funds authorizes intermediaries to accept purchase, exchange and redemption orders for shares of Artisan Funds on behalf of Artisan Funds. Many intermediaries charge a fee for those services. Artisan Funds pays a portion of some of those fees, which portion is intended to compensate the intermediary for its provision of services of the type that would be provided by Artisan Funds’ transfer agent or other service providers if the shares were registered directly on the books of Artisan Funds’ transfer agent. Like the investment management fees we earn as adviser to Artisan Funds, distribution, servicing and marketing fees typically vary with the value of the assets invested in shares of Artisan Funds. The allocation of such fees between us and Artisan Funds is determined by the board of Artisan Funds, based on information and a recommendation from us, with the goal of allocating to us, at a minimum, all costs attributable to the marketing and distribution of shares of Artisan Funds. A significant portion of Artisan Funds’ shares are held by investors through intermediaries to which we pay distribution, servicing and marketing expenses.
Total distribution, servicing and marketing fees will increase as we increase our assets under management sourced through intermediaries that charge these fees or similar fees. The amount we pay to intermediaries for distribution and administrative services varies by share class. As assets have transferred from the Investor share class to the Advisor and Institutional share classes, the amount we have paid for distribution, servicing and marketing relative to average AUM in the Artisan Funds has decreased. Consistent with the experience of other investment managers, as the foregoing expenses have decreased, we have seen increased requests from intermediaries for alternative forms of compensation. To date, such alternative forms of compensation have not been material, but they could be over time.
Occupancy
Occupancy expenses include operating leases for facilities, furniture and office equipment, miscellaneous facility related costs and depreciation expense associated with furniture purchases and leasehold improvements. We expect 2024 occupancy expenses to be relatively consistent with 2023.
Communication and technology
Communication and technology expenses include information and data subscriptions, telephone costs, information systems consulting fees, equipment and software maintenance expenses, operating leases for information technology equipment and depreciation and amortization expenses associated with computer hardware and software. Information and data subscriptions represent the costs we pay to obtain investment research and other data we need to operate our business. A portion of these expenses generally increase or decrease in relative proportion to the number of our employees and the overall size and scale of our business operations. We expect to continue our measured investments in technology to support our investment teams, distribution efforts, and scalable operations. We expect 2024 communication and technology expenses to be relatively consistent with 2023.
On behalf of our clients, we make decisions to buy and sell securities for each portfolio, select broker-dealers to execute trades and negotiate brokerage commission rates. In connection with these transactions, we receive research products and services from broker-dealers in exchange for the business we conduct with such firms. Some of those research products and services could be acquired for cash and our receipt of those products and services through the use of client commissions, or soft dollars, reduces cash expenses we would otherwise incur. In response to the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II and industry changes prompted by it, we have in the past experienced requests from clients to bear research expenses that are currently paid for using soft dollars. In response to such requests or as a result of changes in our operations, we may eventually bear a significant portion of the costs of research that are currently paid for using soft dollars, which would increase our operating expenses materially.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses include professional fees, travel and entertainment, certain state and local taxes, directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, director fees, and other miscellaneous expenses we incur in operating our business. We expect travel costs to increase in 2024 as we execute on our investment and distribution growth strategy.
Non-Operating Income (Expense)
Interest Expense
Interest expense primarily relates to the interest we pay on our debt. For a description of the terms of our debt, see “—Liquidity, Capital Resources, and Contractual Obligations”. Interest expense also includes interest on TRA payments, which is incurred between the due date (without extension) for our federal income tax return and the date on which we make TRA payments.
Interest Income on Cash and Cash Equivalents and Other
Interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other includes income earned from investing excess operating cash in various money market funds.
Net Gain (Loss) on the Tax Receivable Agreements
Non-operating income (expense) also includes gains or losses related to the changes in our estimate of the payment obligation under the TRAs, including the impact of tax rate changes. The effect of changes in our estimate of amounts payable under the TRAs, including the effect of changes in enacted tax rates and in applicable tax laws, is included in net income.
Net Investment Gain (Loss) of Consolidated Investment Products
Net investment gain (loss) of consolidated investment products represents the realized and unrealized investment gains (losses) related to investment products that are included in our consolidated financial statements because Artisan holds a controlling financial interest in the respective investment entities. Significant portions of net investment gain (loss) of consolidated investment products are offset by noncontrolling interests in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Net Investment Gain (Loss) of Nonconsolidated Investment Products
Net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products includes realized and unrealized investment gains (losses) related to nonconsolidated investment products and dividends earned on nonconsolidated equity securities.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests - Holdings
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests - Holdings represents the portion of earnings or loss attributable to the ownership interests in Artisan Partners Holdings held by the limited partners of Artisan Partners Holdings.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests - Consolidated Investment Products
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products represents the portion of earnings or loss attributable to third-party investors’ ownership interests in consolidated investment products.
Provision for Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes primarily represents APAM’s U.S. federal, state and local income taxes on its allocable portion of Holdings’ income, as well as foreign income taxes payable by Holdings’ subsidiaries. Our effective income tax rate is dependent on many factors, including a rate benefit attributable to the fact that a portion of Holdings’ taxable earnings are not subject to corporate level taxes. Thus, income before income taxes includes amounts that are attributable to noncontrolling interests and not taxable to APAM and its subsidiaries, which reduces the effective tax rate. The effective tax rate is also lower than the statutory rate due to dividends paid on unvested share-based awards. These favorable impacts are partially offset by the impact of permanent items, including certain executive compensation expenses, that are not deductible for tax purposes.
As APAM’s equity ownership in Holdings increases, the effective tax rate will likewise increase as more income will be subject to corporate-level taxes.
Results of Operations
Year Ended December 31, 2023, Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, | | Period-to-Period |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| Statements of operations data: | (in millions, except share and per-share data) |
| Revenues | $ | 975.1 | | | $ | 993.3 | | | $ | (18.2) | | | (2) | % |
| Operating Expenses | | | | | | | |
| Total compensation and benefits | 529.4 | | | 510.4 | | | 19.0 | | | 4 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Other operating expenses | 142.1 | | | 138.8 | | | 3.3 | | | 2 | % |
| Total operating expenses | 671.5 | | | 649.2 | | | 22.3 | | | 3 | % |
| Total operating income | 303.6 | | | 344.1 | | | (40.5) | | | (12) | % |
| Non-operating income (expense) | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | (8.6) | | | (9.9) | | | 1.3 | | | 13 | % |
| Other non-operating income (expense) | 88.7 | | | (22.4) | | | 111.1 | | | 496 | % |
| Total non-operating income (expense) | 80.1 | | | (32.3) | | | 112.4 | | | 348 | % |
| Income before income taxes | 383.7 | | | 311.8 | | | 71.9 | | | 23 | % |
| Provision for income taxes | 71.9 | | | 63.4 | | | 8.5 | | | 13 | % |
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | 311.8 | | | 248.4 | | | 63.4 | | | 26 | % |
| Less: Noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 49.5 | | | 49.1 | | | 0.4 | | | 1 | % |
| Less: Noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products | 40.0 | | | (7.5) | | | 47.5 | | | 633 | % |
| Net income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. | $ | 222.3 | | | $ | 206.8 | | | $ | 15.5 | | | 7 | % |
| Share Data | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | | | |
| Diluted earnings per share | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 63,451,932 | | | 62,475,960 | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 63,486,479 | | | 62,498,509 | | | | | |
Revenues
The decrease in revenues of $18.2 million, or 2%, for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, was driven primarily by a $2.2 billion, or 2%, decrease in our average assets under management, partially offset by a $3.7 million increase in performance fee revenue. The weighted average investment management fee, which excludes performance fees, was 69.8 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to 70.2 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2022. The weighted average investment management fee decreased primarily due to a decrease in average management fee rate paid by the Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds vehicles from 90.7 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2022 to 90.1 basis points for the year ended December 31, 2023 as a result of a change in mix of AUM amongst our strategies.
The following table sets forth investment advisory fees and the weighted average management fee by investment vehicle. The weighted average management fee for Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds reflects the additional services we provide to these pooled vehicles.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Separate Accounts and Other (2) | | Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds |
| For the Years Ended December 31, | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Investment advisory fees | $ | 368.8 | | | $ | 376.3 | | | $ | 606.3 | | | $ | 617.0 | |
Weighted average management fee (1) | 50.8 bps | | 51.2 bps | | 90.1 bps | | 90.7 bps |
| Percentage of ending AUM | 52 | % | | 52 | % | | 48 | % | | 48 | % |
(1) We compute our weighted average management fee by dividing annualized management fees (which excludes performance fees) by average assets under management for the applicable period. Assets under management within our consolidated investment products, and any investment advisory fees earned thereon, are excluded from our weighted average fee calculations since any such revenues are eliminated upon consolidation. |
(2) Separate accounts and other consists of assets we manage in or through vehicles other than Artisan Funds or Artisan Global Funds, including assets we manage in traditional separate accounts, Artisan-branded collective investment trusts and Artisan Private Funds, as well as assets under advisement related to clients for whom we provide investment models but do not have discretionary investment authority. |
Operating Expenses
The increase in total operating expenses of $22.3 million, or 3%, for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, is due to higher fixed compensation and benefits costs, reflecting an increase in the number of full time associates and annual merit increases as well as increases in long-term incentive compensation costs resulting from the market valuation impact on compensation plans, and higher travel expenses.
Compensation and Benefits | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, | | Period-to-Period |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| (in millions) | | |
Salaries, incentive compensation and benefits (1) | $ | 469.9 | | | $ | 458.6 | | | $ | 11.3 | | | 2 | % |
| Long-term incentive compensation awards | 59.5 | | | 51.8 | | | 7.7 | | | 15 | % |
Total compensation and benefits | $ | 529.4 | | | $ | 510.4 | | | $ | 19.0 | | | 4 | % |
(1) Excluding long-term incentive compensation awards | | | | | | | |
The increase in salaries, incentive compensation and benefits was driven primarily by a 4% increase in the number of full-time employees.
Long-term incentive compensation award expense increased $7.7 million predominantly as a result of the increase driven by the impact of market valuation changes on franchise capital awards.
Total compensation and benefits was 54% and 51% of our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Other operating expenses
Other operating expenses increased $3.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to increased travel expenses.
Non-Operating Income (Expense)
Non-operating income (expense) consisted of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, | | Period-to-Period |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | $ | | % |
| (in millions) | | |
| Interest expense | $ | (8.6) | | | $ | (9.9) | | | $ | 1.3 | | | 13 | % |
| Interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other | 6.3 | | | 0.3 | | | 6.0 | | | 2,000 | % |
| Net investment gain (loss) of consolidated investment products | 62.7 | | | (7.0) | | | 69.7 | | | 996 | % |
| Net gain (loss) on the tax receivable agreements | 0.5 | | | 1.0 | | | (0.5) | | | (50) | % |
| Net investment gain (loss) on nonconsolidated seed investments | 2.7 | | | (3.5) | | | 6.2 | | | 177 | % |
| Net investment gain (loss) on nonconsolidated franchise capital investments | 16.5 | | | (13.2) | | | 29.7 | | | 225 | % |
Total non-operating income (expense) | $ | 80.1 | | | $ | (32.3) | | | $ | 112.4 | | | 348 | % |
Net investment gain (loss) of consolidated investment products, net investment gain (loss) on nonconsolidated seed investments, and net investment gain (loss) on franchise capital investments increased $105.6 million in the aggregate for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, predominantly due to market conditions. In addition, the increase in interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other increased $6.0 million due to higher yields. Interest expense decreased $1.3 million as a result of the lower interest rate on the Series F senior note, which replaced the higher interest rate Series C senior note that matured in August 2022.
Provision for Income Taxes
APAM’s effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 was 18.7% and 20.3%, respectively. The decrease in effective tax rate was primarily due to an increase in the non-controlling interest attributable to consolidated investment product gains.
Several factors contribute to the effective tax rate, including a rate benefit attributable to the fact that approximately 16% and 17% of Holdings’ full year projected taxable earnings were not subject to corporate-level taxes for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Thus, income before income taxes includes amounts that are attributable to noncontrolling interests and not taxable to APAM and its subsidiaries, which reduces the effective tax rate. As APAM’s equity ownership in Holdings increases, the effective tax rate will likewise increase as more income will be subject to corporate-level taxes. The effective tax rate was favorably impacted in both periods due to tax deductible dividends paid on unvested restricted share-based awards.
Earnings Per Share
Weighted average basic and diluted shares of Class A common stock outstanding were higher for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, as a result of unit exchanges and equity award grants. See Note 12, “Earnings Per Share” in the Notes to the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this report for further discussion of earnings per share.
Year Ended December 31, 2022, Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2021 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, | | For the Period-to-Period |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | $ | | % |
| Statements of operations data: | (in millions, except share and per-share data) |
| Revenues | $ | 993.3 | | | $ | 1,227.2 | | | $ | (233.9) | | | (19) | % |
| Operating Expenses | | | | | | | |
| Total compensation and benefits | 510.4 | | | 563.0 | | | (52.6) | | | (9) | % |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Other operating expenses | 138.8 | | | 123.7 | | | 15.1 | | | 12 | % |
| Total operating expenses | 649.2 | | | 686.7 | | | (37.5) | | | (5) | % |
| Total operating income | 344.1 | | | 540.5 | | | (196.4) | | | (36) | % |
| Non-operating income (expense) | | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | (9.9) | | | (10.8) | | | 0.9 | | | 8 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Other non-operating income | (22.4) | | | 21.9 | | | (44.3) | | | (202) | % |
| Total non-operating income (expense) | (32.3) | | | 11.1 | | | (43.4) | | | (391) | % |
| Income before income taxes | 311.8 | | | 551.6 | | | (239.8) | | | (43) | % |
| Provision for income taxes | 63.4 | | | 107.1 | | | (43.7) | | | (41) | % |
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | 248.4 | | | 444.5 | | | (196.1) | | | (44) | % |
| Less: Noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 49.1 | | | 96.9 | | | (47.8) | | | (49) | % |
| Less: Noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products | (7.5) | | | 11.1 | | | (18.6) | | | (168) | % |
| Net income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. | $ | 206.8 | | | $ | 336.5 | | | $ | (129.7) | | | (39) | % |
| Share Data | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.10 | | | | | |
| Diluted earnings per share | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.09 | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 62,475,960 | | | 59,866,790 | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 62,498,509 | | | 59,881,039 | | | | | |
A detailed discussion of the year-over-year results for the year ended December 31, 2022, compared to the year ended December 31, 2021, can be found in “Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2022, filed with the SEC on February 27, 2023.
Supplemental Non-GAAP Financial Information
Our management uses non-GAAP measures (referred to as “adjusted” measures) of net income to evaluate the profitability and efficiency of the underlying operations of our business and as a factor when considering net income available for distributions and dividends. These adjusted measures remove the impact of (1) net gain (loss) on the tax receivable agreements (if any), (2) compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans, and (3) net investment gain (loss) of investment products. These adjustments also remove the non-operational complexities of our structure by adding back noncontrolling interests and assuming all income of Artisan Partners Holdings is allocated to APAM. Management believes these non-GAAP measures provide meaningful information to analyze our profitability and efficiency between periods and over time. We have included these non-GAAP measures to provide investors with the same financial metrics used by management to manage the Company.
Non-GAAP measures should be considered in addition to, and not as a substitute for, financial measures prepared in accordance with GAAP. Our non-GAAP measures may differ from similar measures used by other companies, even if similar terms are used to identify such measures. Our non-GAAP measures are as follows:
•Adjusted net income represents net income excluding the impact of (1) net gain (loss) on the tax receivable agreements (if any), (2) compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans, and (3) net investment gain (loss) of investment products. Adjusted net income also reflects income taxes assuming the vesting of all unvested Class A share-based awards and as if all outstanding limited partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings had been exchanged for Class A common stock of APAM on a one-for-one basis. Assuming full vesting and exchange, all income of Artisan Partners Holdings is treated as if it were allocated to APAM, and the adjusted provision for income taxes represents an estimate of income tax expense at an effective rate reflecting APAM's current federal, state, and local income statutory tax rates. The adjusted tax rate was 24.7% for all periods presented.
•Adjusted net income per adjusted share is calculated by dividing adjusted net income by adjusted shares. The number of adjusted shares is derived by assuming the vesting of all unvested Class A share-based awards and the exchange of all outstanding limited partnership units of Artisan Partners Holdings for Class A common stock of APAM on a one-for-one basis.
•Adjusted operating income represents the operating income of the consolidated company excluding compensation expense related to market valuation changes in compensation plans.
•Adjusted operating margin is calculated by dividing adjusted operating income by total revenues.
•Adjusted EBITDA represents adjusted net income before interest expense, income taxes, depreciation and amortization expense.
Net gain (loss) on the tax receivable agreements represents the income (expense) associated with the change in estimate of amounts payable under the tax receivable agreements entered into in connection with APAM’s initial public offering and related reorganization.
Compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans represents the expense (income) associated with the change in the long term incentive award liability resulting from investment returns of the underlying investment products. Because the compensation expense impact of the investment market exposure is economically hedged, management believes it is useful to reflect the expected net income offset in the calculation of adjusted operating income, adjusted net income, and adjusted EBITDA. The related investment gain (loss) on the underlying investments is included in the adjustment for net investment gain (loss) of investment products.
Net investment gain (loss) of investment products represents the non-operating income (expense) related to the Company’s investments, in both consolidated sponsored investment products and nonconsolidated sponsored investment products, including investments in sponsored investment products held to economically hedge compensation plans. Excluding these non-operating market gains or losses on investments provides greater transparency to evaluate the profitability and efficiency of the underlying operations of the business. Interest income generated on cash and cash equivalents is considered part of normal operations, and therefore, is not excluded from adjusted net income.
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, a reconciliation from GAAP financial measures to non-GAAP measures: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, |
| | | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | | | (unaudited; in millions, except per share data) |
| Reconciliation of non-GAAP financial measures: | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. (GAAP) | | | | | $ | 222.3 | | | $ | 206.8 | | | $ | 336.5 | |
Add back: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | | | | | 49.5 | | | 49.1 | | | 96.9 | |
| Add back: Provision for income taxes | | | | | 71.9 | | | 63.4 | | | 107.1 | |
| Add back: Compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans | | | | | 4.8 | | | (3.8) | | | 0.3 | |
| Add back: Net (gain) loss on the tax receivable agreements | | | | | (0.5) | | | (1.0) | | | (0.4) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Add back: Net investment (gain) loss of investment products attributable to APAM | | | | | (38.4) | | | 16.9 | | | (9.3) | |
| Less: Adjusted provision for income taxes | | | | | 76.5 | | | 81.8 | | | 131.2 | |
| Adjusted net income (Non-GAAP) | | | | | $ | 233.1 | | | $ | 249.6 | | | $ | 399.9 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Average shares outstanding | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A common shares | | | | | 63.4 | | | 62.5 | | | 59.9 | |
| Assumed vesting or exchange of: | | | | | | | | | |
| Unvested Class A restricted share-based awards | | | | | 5.7 | | | 5.7 | | | 5.4 | |
| Artisan Partners Holdings units outstanding (noncontrolling interests) | | | | | 11.5 | | | 12.0 | | | 14.2 | |
| Adjusted shares | | | | | 80.6 | | | 80.2 | | | 79.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share (GAAP) | | | | | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.10 | |
| Diluted earnings per share (GAAP) | | | | | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.09 | |
| Adjusted net income per adjusted share (Non-GAAP) | | | | | $ | 2.89 | | | $ | 3.11 | | | $ | 5.03 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income (GAAP) | | | | | $ | 303.6 | | | $ | 344.1 | | | $ | 540.5 | |
| Add back: Compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans | | | | | 4.8 | | | (3.8) | | | 0.3 | |
| Adjusted operating income (Non-GAAP) | | | | | $ | 308.4 | | | $ | 340.3 | | | $ | 540.8 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Operating margin (GAAP) | | | | | 31.1 | % | | 34.6 | % | | 44.0 | % |
| Adjusted operating margin (Non-GAAP) | | | | | 31.6 | % | | 34.3 | % | | 44.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. (GAAP) | | | | | $ | 222.3 | | | $ | 206.8 | | | $ | 336.5 | |
Add back: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | | | | | 49.5 | | | 49.1 | | | 96.9 | |
| Add back: Compensation expense (reversal) related to market valuation changes in compensation plans | | | | | 4.8 | | | (3.8) | | | 0.3 | |
| Add back: Net (gain) loss on the tax receivable agreements | | | | | (0.5) | | | (1.0) | | | (0.4) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Add back: Net investment (gain) loss of investment products attributable to APAM | | | | | (38.4) | | | 16.9 | | | (9.3) | |
| Add back: Interest expense | | | | | 8.6 | | | 9.9 | | | 10.8 | |
| Add back: Provision for income taxes | | | | | 71.9 | | | 63.4 | | | 107.1 | |
| Add back: Depreciation and amortization | | | | | 9.3 | | | 7.9 | | | 7.0 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA (Non-GAAP) | | | | | $ | 327.5 | | | $ | 349.2 | | | $ | 548.9 | |
Liquidity, Capital Resources, and Contractual Obligations
Our working capital needs, including accrued incentive compensation payments, have been and are expected to be met primarily through cash generated by our operations. The assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products attributable to third-party investors do not impact our liquidity and capital resources. We have no right to the benefits from, nor do we bear the risks associated with, the assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products, beyond our direct equity investment and any investment advisory fees earned. Accordingly, assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products attributable to third-party investors are excluded from the amounts and discussions below. The following table shows our liquidity position as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| | | |
| (in millions) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 141.0 | | | $ | 114.8 | |
| Accounts receivable | $ | 101.2 | | | $ | 98.6 | |
Seed investments (1) | $ | 150.1 | | | $ | 124.8 | |
| Undrawn commitment on revolving credit facility | $ | 100.0 | | | $ | 100.0 | |
(1) Seed investments include Artisan's direct equity investments in consolidated and nonconsolidated Artisan-sponsored investment products. The balance excludes $115.3 million and $67.3 million of investments made related to funded long-term incentive compensation plans as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively. |
We manage our cash balances in order to fund our day-to-day operations. The Company did not have any deposits with financial institutions directly impacted by the regional bank failures that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2023. We continue to mitigate concentration risk through the diversification of financial institutions holding daily operating cash balances and by investing excess operating cash in various money market funds. $118.8 million of our cash and cash equivalents balance was invested in money market funds as of December 31, 2023.
Accounts receivable primarily represent investment advisory fees that have been earned, but not yet received from our clients. We perform a review of our receivables on a monthly basis to assess collectability. As of December 31, 2023, none of our receivables were considered uncollectible.
We utilize cash to make seed investments in Artisan-sponsored investment products to support the development of new investment strategies and vehicles. As of December 31, 2023, the balance of all seed investments, including investments in consolidated investment products, was $150.1 million. Subject to certain restrictions on the timing of redemptions, the seed investments are generally redeemable at our discretion. We monitor for opportunities to redeem existing seed investments as sufficient scale in those strategies and vehicles is achieved.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, we also made investments of $39.0 million related to our economic hedge of franchise capital awards. As of December 31, 2023, the value of investments held to economically hedge our franchise capital awards was $115.3 million. In the first quarter of 2024, we intend to invest an additional $38.4 million related to our economic hedge of franchise capital awards in connection with the grant that was approved by our Board on January 25, 2024.
We expect our investment portfolio to continue to grow as we grant additional annual franchise capital awards and make additional seed capital investments in new strategies and vehicles to support our growth. In October 2023, we committed $16.0 million of capital as a seed investment in the Artisan Dislocation Opportunities Fund LP, a private fund that will call capital contributions and begin investment activity upon the occurrence of a market-based trigger. As of December 31, 2023, the trigger had not occurred and the capital had not yet been called, therefore the committed capital is not recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. The capital commitment terminates if the market trigger does not occur within three years of the October 30, 2023 initial closing date.
On August 16, 2022, Artisan Partners Holdings issued $90.0 million of 3.10% Series F notes pursuant to an agreement executed in December 2021 and used the proceeds to repay the $90.0 million of Series C senior notes that matured on August 16, 2022. In addition, Holdings amended and extended its $100.0 million revolving credit facility for an additional five-year period.
As of December 31, 2023, we have $200 million in unsecured notes outstanding and a $100 million revolving credit facility with a five-year term ending in August 2027. The notes are comprised of three series, Series D, Series E, and Series F, each with a balloon payment at maturity. The $100 million revolving credit facility was unused as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023.
The fixed interest rate on each series of unsecured notes is subject to a 100 basis point increase in the event Holdings receives a below-investment grade rating and any such increase will continue to apply until an investment grade rating is received. Holdings maintained an investment grade rating for the year ended December 31, 2023.
These borrowings contain certain customary covenants including limitations on Artisan Partners Holdings’ ability to: (i) incur additional indebtedness or liens, (ii) engage in mergers or other fundamental changes, (iii) sell or otherwise dispose of assets
including equity interests, and (iv) make dividend payments or other distributions to Artisan Partners Holdings’ partners (other than, among others, tax distributions paid to partners for the purpose of funding tax liabilities attributable to their interests) when a default occurred and is continuing or would result from such a distribution. In addition, in the event of a Change of Control (as defined in the Note Purchase Agreement) or if Artisan’s average assets under management for a fiscal quarter is below $45 billion, Holdings is generally required to offer to pre-pay the notes. Artisan Partners Limited Partnership, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Holdings, has guaranteed Holdings’ obligations under the terms of the Note Purchase Agreement.
In addition, covenants in the note purchase and revolving credit agreements require Artisan Partners Holdings to maintain the following financial ratios:
•leverage ratio (calculated as the ratio of consolidated total indebtedness on any date to consolidated EBITDA for the period of four consecutive fiscal quarters ended on or prior to such date) cannot exceed 3.00 to 1.00 (Artisan Partners Holdings’ leverage ratio for the year ended December 31, 2023 was 0.6 to 1.00); and
•interest coverage ratio (calculated as the ratio of consolidated EBITDA for any period of four consecutive fiscal quarters to consolidated interest expense for such period) cannot be less than 4.00 to 1.00 for such period (Artisan Partners Holdings’ interest coverage ratio for the year ended December 31, 2023 was 46.0 to 1.00).
Our failure to comply with any of the covenants or restrictions described above could result in an event of default under the agreements, giving our lenders the ability to accelerate repayment of our obligations. We were in compliance with all debt covenants as of December 31, 2023.
See Note 5, “Borrowings”, for further information on our outstanding notes and revolving credit facility.
As of December 31, 2023, we had approximately $133.5 million of future minimum rent commitments under non-cancellable leasing arrangements.
Distributions and Dividends
Artisan Partners Holdings’ distributions, including distributions to APAM, for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Holdings Partnership Distributions to Limited Partners | $ | 44.7 | | | $ | 57.2 | |
| Holdings Partnership Distributions to APAM | 248.3 | | | 299.0 | |
| Total Holdings Partnership Distributions | $ | 293.0 | | | $ | 356.2 | |
APAM, acting as the general partner of Artisan Partners Holdings, declared, effective January 30, 2024, a distribution of $30.2 million payable by Artisan Partners Holdings on February 21, 2024 to holders of its partnership units, including APAM.
APAM declared and paid the following dividends per share during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Type of Dividend | | Class of Stock | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Quarterly | | Common Class A | | $ | 2.31 | | | $ | 2.95 | |
| Special Annual | | Common Class A | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.72 | |
| | | | | | |
|
Our board of directors declared, effective January 30, 2024, a variable quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share of Class A common stock with respect to the December quarter of 2023 and a special annual dividend of $0.34. The combined amount, $1.02 per share of Class A common stock, will be paid on February 29, 2024 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on February 15, 2024. The variable quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share represents approximately 80% of the cash generated (as described below) in the December quarter of 2023 and a pro-rata portion of 2023 tax savings related to our tax receivable agreements. The special dividend represents the remainder of undistributed cash generated during the year ended December 31, 2023, less cash reserved for future growth initiatives including seed investments in new investment strategies and vehicles.
Subject to Board approval each quarter, we currently expect to pay a quarterly dividend of approximately 80% of the cash the Company generates each quarter. We expect our quarterly cash generation to approximate adjusted net income plus long-term incentive compensation award expense, less cash reserved for future franchise capital awards (which we generally expect will approximate 4% of investment management revenues each quarter) with additional adjustments made for certain other sources and uses of cash, including capital expenditures. After the end of the year, our Board will consider paying a special dividend after determining the amount of cash needed for general corporate purposes and investments in growth and strategic initiatives.
Although we expect to pay dividends according to our dividend policy, we may not pay dividends according to our policy or at all.
Tax Receivable Agreements (“TRAs”)
In addition to funding our normal operations, we will be required to fund amounts payable under the TRAs that we entered into in connection with the IPO, which resulted in the recognition of a $364.0 million liability as of December 31, 2023. The liability generally represents 85% of the tax benefits APAM expects to realize as a result of the merger of an entity into APAM as part of the IPO Reorganization, our purchase of partnership units from limited partners of Holdings and the exchange of partnership units (for shares of Class A common stock or other consideration).
The estimated liability assumes no material changes in the relevant tax law and that APAM earns sufficient taxable income to realize all tax benefits subject to the TRAs. An increase or decrease in future tax rates will increase or decrease, respectively, the expected tax benefits APAM would realize and the amounts payable under the TRAs. Changes in the estimate of expected tax benefits APAM would realize and the amounts payable under the TRAs as a result of change in tax rates have been and will be recorded in net income.
The liability will increase upon future purchases or exchanges of limited partnership units with the increase representing amounts payable under the TRAs equal to 85% of the estimated future tax benefits, if any, resulting from such purchases or exchanges. We intend to fund the payment of amounts due under the TRAs out of the reduced tax payments that APAM realizes in respect of the tax attributes to which the TRAs relate.
The actual increase in tax basis, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under these agreements, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units, the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, whether such sales or exchanges are taxable, the amount and timing of the taxable income APAM generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable and the portion of APAM’s payments under the TRAs constituting imputed interest or depreciable basis or amortizable basis.
In certain cases, payments under the TRAs may be accelerated and/or significantly exceed the actual benefits we realize in respect of the tax attributes subject to the TRAs. In such cases, we intend to fund those payments with cash on hand, although we may have to borrow funds depending on the amount and timing of the payments. During the year ended December 31, 2023, we made payments totaling $36.0 million, related to the TRAs, including interest. In 2024, we expect to make payments of approximately $37.2 million related to the TRAs.
Cash Flows | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (in millions) |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash as of January 1, | $ | 143.3 | | | $ | 200.8 | | | $ | 199.5 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 253.1 | | | 312.6 | | | 398.5 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (38.2) | | | (63.7) | | | (27.0) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (175.0) | | | (306.4) | | | (335.4) | |
| Net impact of deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | (4.7) | | | — | | | (34.8) | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash as of December 31, | $ | 178.5 | | | $ | 143.3 | | | $ | 200.8 | |
Year Ended December 31, 2023, Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2022
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased $59.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to a decrease in operating income and changes in working capital. Operating income, excluding share based compensation expense, decreased $48.3 million due to lower average AUM and revenues.
Investing activities consist primarily of the purchase and sale of investment securities, the acquisition of property and equipment and leasehold improvements. Net cash used in investing activities decreased $25.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily due to a $14.6 million decrease in net purchases of investment securities, including a $9.6 million decrease in the purchase of investment securities related to the economic hedge of our franchise capital awards. Further, acquisitions of property and equipment and leasehold improvements decreased $10.9 million, primarily related to the completion of build outs of leased space in the year ended December 31, 2022.
Financing activities consist primarily of partnership distributions to non-controlling interests, dividend payments to holders of our Class A common stock, proceeds from the issuance of Class A common stock in follow-on offerings, payments to purchase Holdings partnership units, and payments of amounts owed under the tax receivable agreements. Net cash used in financing activities decreased $131.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily due to a $65.3 million decrease in dividends paid and a $12.5 million decrease in distributions paid to limited partners, each primarily related to the decrease in operating income for the year ended December 31, 2023, driven by the decrease in AUM. Further contributing to the overall decrease in net cash used in financing activities was a $54.7 million net increase in contributions from noncontrolling interests in our consolidated investment products.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company determined that it no longer had a controlling financial interest in an investment product that was previously consolidated. The deconsolidation of the investment product resulted in a $4.7 million increase in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The accompanying consolidated financial statements were prepared in accordance with GAAP, and related rules and regulations of the SEC. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates or assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the periods presented. Actual results could differ from these estimates or assumptions and may have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements.
Accounting policies are an integral part of our financial statements. A thorough understanding of these accounting policies is essential when reviewing our reported results of operations and our financial condition. Management believes that the critical accounting policies and estimates discussed below involve additional management judgment due to the sensitivity of the methods and assumptions used.
Consolidation
We consolidate all subsidiaries or other entities in which we have a controlling financial interest. We assess each legal entity in which we hold a variable interest on a quarterly basis to determine whether consolidation is appropriate. We determine whether we have a controlling financial interest in the entity by evaluating whether the entity is a voting interest entity (“VOE”) or a variable interest entity (“VIE”) under GAAP. Assessing whether an entity is a VIE or VOE and if it requires consolidation involves judgment and analysis. Factors considered in this assessment include the legal organization of the entity, our equity ownership and contractual involvement with the entity and any related party or de facto agent implications of our involvement with the entity.
Voting Interest Entities - A VOE is an entity in which (i) the total equity investment at risk is sufficient to enable the entity to finance its activities independently and (ii) the equity holders at risk have the obligation to absorb losses, the right to receive residual returns and the right to direct the activities of the entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance, whereby the equity investment has all the characteristics of a controlling financial interest. As a result, voting rights are a key driver of determining which party, if any, should consolidate the entity. Under the VOE model, controlling financial interest is generally defined as a majority ownership of voting interests.
Variable Interest Entities - A VIE is an entity that lacks one or more of the characteristics of a VOE. In accordance with GAAP, an enterprise must consolidate all VIEs of which it is the primary beneficiary. We determine if a legal entity meets the definition of a VIE by considering whether the fund’s equity investment at risk is sufficient to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support and whether the fund’s at-risk equity holders absorb any losses, have the right to receive residual returns and have the right to direct the activities of the entity most responsible for the entity’s economic performance.
Under the VIE model, controlling financial interest is defined as (i) the power to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the entity and (ii) the right to receive potentially significant benefits or the obligation to absorb potentially significant losses. We will generally consolidate VIEs in which we meet the power criteria and hold an equity ownership interest of greater than 10%.
We serve as the investment adviser for Artisan Funds, a family of mutual funds registered with the SEC under the Investment Company Act of 1940, and investment manager of Artisan Global Funds, a family of Ireland-based UCITS funds. Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds are corporate entities the business and affairs of which are managed by their respective boards of directors. The shareholders of the funds retain voting rights, including the right to elect and reelect members of their respective boards of directors. Each series of Artisan Funds is a VOE and is separately evaluated for consolidation under the VOE model. The shareholders of Artisan Global Funds lack simple majority liquidation rights, and as a result, Artisan Global Funds is evaluated for consolidation under the VIE model. Artisan Private Funds are also evaluated for consolidation under the VIE model because third-party equity holders of the funds lack the ability to remove Artisan as the general partner, or otherwise divest Artisan of its control of the funds.
Seed Investments - We generally make seed investments in sponsored investment portfolios at the portfolio’s formation. If the seed investment results in a controlling financial interest, we will consolidate the investment, and the underlying individual securities will be accounted for based on their classification at the underlying fund. If the seed investment results in significant influence, but not control, the investment will be accounted for as an equity method investment. Significant influence is generally considered to exist with equity ownership levels between 20% and 50%, although other factors are considered. Seed investments in which we do not have a controlling financial interest or significant influence are accounted for as investment securities. These investments are measured at fair value in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. Realized and unrealized gains (losses) on investment securities are recorded in net investment income in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Dividend income from these investments is recognized when earned and is included in net investment income in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Revenue Recognition
Investment management fees are generally computed as a percentage of assets under management and are recognized as revenue at the end of each distinct service period. Fees for providing investment management services are computed and billed in accordance with the underlying investment management agreements, which is generally on a monthly or quarterly basis. Investment management fees are presented net of cash rebates to certain Artisan Global Fund investors and expense reimbursements pursuant to contractual expense limitations of pooled investment vehicles.
A number of investment management agreements provide for performance-based fees or incentive allocations, collectively “performance fees”. Performance fees, if earned, are recognized upon completion of the contractually determined measurement period, which is generally quarterly or annually. Performance fees generally are not subject to claw back as a result of performance declines subsequent to the most recent measurement date.
Artisan accounts for asset management services as a single performance obligation that is satisfied over time, using a time-based measure of progress to recognize revenue. Customer consideration is variable due to the uncertainty of the value of assets under management during each distinct service period. At the end of each quarter, Artisan records revenue for the actual amount of investment management fees for that quarter because the uncertainty has been resolved.
Performance fees are subject to the uncertainty of market volatility, and as a result, the entire amount of the variable consideration related to performance fees is constrained until the end of each measurement period. At the end of the quarterly or annual measurement period, revenue is recorded for the actual amount of performance fees earned during that period because the uncertainty has been resolved.
The portfolios of Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds, as well as the portfolios we manage for our other clients, are invested principally in securities for which market values are readily available, with a portion of each portfolio held in cash or cash-like instruments. With the exception of the assets managed by our Credit team and EMsights Capital Group (which together represented approximately 7.0% of our assets under management at December 31, 2023), the portfolios are invested principally in publicly-traded equity securities.
The investment management fees that we receive are calculated based on the values of the securities held in the accounts that we manage for our clients. For our U.S.-registered mutual fund and UCITS fund clients, including Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds, and for Artisan Private Funds, our fees are based on the values of the funds’ assets as determined for purposes of calculating their net asset values. Securities held by Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds, and Artisan Private Funds are generally valued at closing market prices, or if closing market prices are not readily available or are not considered reliable, at a fair value determined under procedures established by the fund’s board (fair value pricing). Values of securities determined using fair value pricing are likely to be different than they would be if only closing market prices were used.
For separate account clients, our fees may be based, at the client’s option, on the values of the securities in the portfolios we manage as determined by the client (or its custodian or other service provider) or by us in accordance with valuation procedures we have adopted. The valuation procedures we have adopted generally use closing market prices in the markets in which the securities trade, without adjustment for subsequent events except in unusual circumstances. We believe that our fees based on valuations determined under our procedures are not materially different from the fees we receive that are based on valuations determined by clients, their custodians or other service providers.
Income Taxes
We operate in numerous states and countries and must allocate our income, expenses, and earnings under the various laws and regulations of each of these taxing jurisdictions. Accordingly, our provision for income taxes represents our total estimate of the liability for income taxes that we have incurred in doing business each year in all of our locations. Annually, we file tax returns that represent our filing positions with each jurisdiction and settle our tax return liabilities. Each jurisdiction has the right to audit those tax returns and may take different positions with respect to income and expense allocations and taxable earnings determinations. Because the determination of our annual income tax provision is subject to judgments and estimates, actual results may vary from those recorded in our financial statements. We recognize additions to and reductions in income tax expense during a reporting period that pertains to prior period provisions as our estimated liabilities are revised and our actual tax returns and tax audits are completed.
Our management is required to exercise judgment in developing our provision for income taxes, including the determination of deferred tax assets and liabilities and any valuation allowance that might be required against deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2023, we have not recorded a valuation allowance on any deferred tax assets. In the event that sufficient taxable income of the same character does not result in future years, among other things, a valuation allowance for certain of our deferred tax assets may be required.
Payments pursuant to the Tax Receivable Agreements (“TRAs”)
We have recorded a liability of $364.0 million as of December 31, 2023, representing 85% of the estimated future tax benefits subject to the TRAs. The actual amount and timing of any payments under these agreements will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units, the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, whether such sales or exchanges are taxable, the amount and timing of the taxable income APAM generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable and the portion of APAM’s payments under the TRAs constituting imputed interest or depreciable basis or amortizable basis.
New or Revised Accounting Standards
See Note 2, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies — Recent accounting pronouncements” to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Qualitative and Quantitative Disclosures Regarding Market Risk
Market Risk
Our exposure to market risk is directly related to the role of our operating company as an investment adviser for the pooled vehicles and separate accounts it manages. Essentially all of our revenues are derived from investment management agreements with these vehicles and accounts. Under these agreements, the investment advisory fees we receive are generally based on the value of our assets under management, our fee rates and, for the accounts on which we earn performance based fees, the investment performance of those accounts. Accordingly, if our assets under management decline as a result of market depreciation, our revenues and net income will also decline. In addition, such a decline could cause our clients to withdraw their funds in favor of investments believed to offer higher returns or lower risk, which would cause our revenues to decline further.
The value of our assets under management was $150.2 billion as of December 31, 2023. A 10% increase or decrease in the value of our assets under management, if proportionately distributed over all our investment strategies, products and client relationships, would cause an annualized increase or decrease in our revenues of approximately $104.9 million at our current weighted average fee rate of 70 basis points. Because of our declining rates of fee for larger relationships and differences in our rates of fee across investment strategies, a change in the composition of our assets under management, in particular an increase in the proportion of our total assets under management attributable to strategies, clients or relationships with lower effective rates of fees, could have a material negative impact on our overall weighted average rate of fee. The same 10% increase or decrease in the value of our total assets under management, if attributed entirely to a proportionate increase or decrease in the assets of each of the Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds, to which we provide a range of services in addition to those provided to separate accounts and therefore charge a higher rate of fee, would cause an annualized increase or decrease in our revenues of approximately $135.2 million at the Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds aggregate weighted average fee of 90 basis points. If the same 10% increase or decrease in the value of our total assets under management was attributable entirely to a proportionate increase or decrease in the assets of each separate account we manage, it would cause an annualized increase or decrease in our revenues of approximately $76.3 million at the current weighted average fee rate across all of our separate accounts of 51 basis points.
As is customary in the asset management industry, clients invest in particular strategies to gain exposure to certain asset classes, which exposes their investment to the benefits and risks of those asset classes. Because we believe that our clients invest in each of our strategies in order to gain exposure to the portfolio securities of the respective strategies and may implement their own risk management program or procedures, we have not adopted a corporate-level risk management policy regarding client assets, nor have we attempted to hedge at the corporate level or within individual strategies the market risks that would affect the value of our overall assets under management and related revenues. Some of these risks (e.g., sector risks and currency risks) are inherent in certain strategies, and clients may invest in particular strategies to gain exposure to particular risks. While negative returns in our investment strategies and net client cash outflows do not directly reduce the assets on our balance sheet (because the assets we manage are owned by our clients, not us), any reduction in the value of our assets under management would result in a reduction in our revenues.
We are subject to market risk from a decline in the prices of marketable securities that we own. The total value of marketable securities we owned, including our direct equity investments in consolidated investment products, was $265.4 million as of December 31, 2023. We invested in certain Artisan Private Funds, Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds in amounts sufficient to cover certain organizational expenses and to ensure that the funds had sufficient assets at the commencement of their operations to build a viable investment portfolio. In addition, we invested in Artisan investment strategies to hedge our economic exposure to the change in value of our franchise capital awards due to market movements. Assuming a 10% increase or decrease in the values of our total marketable securities, the fair value would increase or decrease by $26.5 million at December 31, 2023. Management regularly monitors the value of these investments; however, given their nature and relative size, we have not adopted a specific risk management policy to manage the associated market risk.
Exchange Rate Risk
A substantial portion of the accounts that we advise, or sub-advise, hold investments that are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Movements in the rate of exchange between the U.S. dollar and the underlying foreign currency affect the values of assets held in accounts we manage, thereby affecting the amount of revenues we earn. The value of the assets we manage was $150.2 billion as of December 31, 2023. As of December 31, 2023, approximately 57% of our assets under management were invested in strategies that primarily invest in securities of non-U.S. companies and approximately 46% of our assets under management were invested in securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. To the extent our assets under management are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar, the value of those assets under management will decrease with an increase in the value of the U.S. dollar, or increase with a decrease in the value of the U.S. dollar. Each investment team monitors its own exposure to exchange rate risk and makes decisions on how to manage that risk in the portfolios managed by that team.
We have not adopted a corporate-level risk management policy to manage exchange rate risk in the assets we manage. Assuming that 46% of our assets under management is invested in securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar and excluding the impact of any hedging arrangements, a 10% increase or decrease in the value of the U.S. dollar would decrease or increase the fair value of our assets under management by $6.9 billion, which would cause an annualized increase or decrease in revenues of approximately $48.2 million at our current weighted average fee rate of 70 basis points.
We operate in several foreign countries of which the United Kingdom is the most prominent. We incur operating expenses and have foreign currency-denominated assets and liabilities associated with these operations. In addition, we have revenue arrangements that are denominated in non-U.S. currencies. We do not believe these revenue arrangements denominated in foreign currencies or our operations in foreign countries create foreign currency fluctuations that materially affect our results of operations.
Interest Rate Risk
We generally invest our available cash balances in money market mutual funds that invest primarily in U.S. Treasury or agency-backed money market instruments. These funds attempt to maintain a stable net asset value but interest rate changes or other market risks may affect the fair value of those funds’ investments and, if significant, could result in a loss of investment principal. Interest rate changes affect the income we earn from our excess cash balances. As of December 31, 2023, $118.8 million of our available cash was invested in money market funds that invested solely in U.S. Treasuries. Interest rate changes would not have a material impact on the income we earn from these investments. The remaining portion of our cash was held in demand deposit accounts.
Interest rate changes may affect the amount of our interest payments in connection with our revolving credit agreement, and thereby affect future earnings and cash flows. As of December 31, 2023, there were no borrowings outstanding under the revolving credit agreement.
The credit strategies managed by our Credit and EMsights Capital Group teams, which had $10.5 billion of assets under management as of December 31, 2023, invest in fixed income securities. The values of debt instruments held by these strategies may fall in response to increases in interest rates, which would reduce our revenues. We have considered the potential impact of a 100 basis point movement in market interest rates on the portfolios of the strategies managed by these teams. Based on our analysis, we do not expect that such a change would have a material impact on our revenues or results of operations in the next twelve months.
Item 8. Financial Information and Supplementary Data
| | | | | |
| Index to Financial Statements: | Page |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc.:
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial condition of Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the related consolidated statements of operations, of comprehensive income, of changes in stockholders’ equity and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A “Controls and Procedures”. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB and in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Income Taxes – Deferred Tax Assets and Amounts Payable Under Tax Receivable Agreements
As described in Notes 2 and 11 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has recorded a deferred tax assets (“DTA”) balance of $436.5 million at December 31, 2023 while the amount payable under the tax receivable agreements (“TRA”) was $364 million. DTAs are determined by management based upon the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and tax bases of assets. The TRAs generally provide for payment of 85% of the applicable cash savings, if any, of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes that the Company actually realizes (or is deemed to realize in certain circumstances) as a result of certain tax attributes or benefits. The cash savings are calculated by comparing the Company’s actual income tax liability to the amount it would have been required to pay had it not been able to utilize any of the tax benefits subject to the TRAs. The increase in tax basis, which results in a DTA, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under these agreements, will vary depending on a number of factors, which include the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units, the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, whether such sales or exchanges are taxable, the amount and timing of the taxable income the Company generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable, and the portion of the Company’s payments under the TRAs constituting imputed interest or depreciable basis or amortizable basis.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to deferred tax assets and amounts payable under tax receivable agreements is a critical audit matter are (1) the significant audit effort necessary in performing procedures related to the aforementioned factors utilized in the estimate and the assessment of the application of the tax laws, and (2) the use of professionals with specialized skill and knowledge to assist in evaluating the audit evidence obtained from these procedures.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to income taxes, including controls over the deferred tax assets and tax receivable agreements. These procedures also included, among others, testing management’s process for estimating the deferred tax assets and amounts payable under tax receivable agreements, including (1) testing the factors to the Company’s estimates, related to the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units and the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, (2) assessing the reasonableness of the factors used in the Company’s estimates, related to the likelihood of the Company having sufficient future taxable income to utilize the deferred tax asset as well as the portion of the Company’s payments under the TRA constituting depreciable basis or amortizable basis, and (3) testing the impact of sales or exchanges of limited partnership units on the deferred tax asset and amounts payable under tax receivable agreements. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in testing the estimates and assessing the appropriateness of the application of the tax laws related to evaluating whether the sales or exchanges of partnership units are taxable.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 22, 2024
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1995.
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition
(U.S. dollars in thousands, except per share amounts) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| ASSETS |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 141,008 | | | $ | 114,832 | |
| Accounts receivable | 101,169 | | | 98,634 | |
| Investment securities | 150,522 | | | 85,415 | |
| Prepaid expenses | 14,791 | | | 15,723 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 46,638 | | | 48,104 | |
| Operating lease assets | 94,747 | | | 101,410 | |
| Deferred tax assets | 436,529 | | | 477,024 | |
| Other | 5,557 | | | 4,330 | |
| Assets of consolidated investment products | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | 37,459 | | | 28,416 | |
Accounts receivable and other | 13,343 | | | 4,977 | |
Investment assets, at fair value | 364,095 | | | 255,743 | |
| Total assets | $ | 1,405,858 | | | $ | 1,234,608 | |
| LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS, AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other | $ | 25,509 | | | $ | 24,414 | |
| Accrued incentive compensation | 52,226 | | | 29,762 | |
| | | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 113,391 | | | 120,847 | |
| Borrowings | 199,267 | | | 199,050 | |
| | | |
| Amounts payable under tax receivable agreements | 364,048 | | | 398,789 | |
| Liabilities of consolidated investment products | | | |
Accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other | 38,080 | | | 26,358 | |
Investment liabilities, at fair value | 9,580 | | | 20,751 | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 802,101 | | | $ | 819,971 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | |
| Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 252,406 | | | 135,280 | |
| Common stock | | | |
Class A common stock ($0.01 par value per share, 500,000,000 shares authorized, 68,554,078 and 67,982,025 shares outstanding at December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively) | 685 | | | 680 | |
Class B common stock ($0.01 par value per share, 200,000,000 shares authorized, 2,435,739 and 2,583,884 shares outstanding at December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively) | 24 | | | 26 | |
Class C common stock ($0.01 par value per share, 400,000,000 shares authorized, 9,024,947 and 9,040,147 shares outstanding at December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, respectively) | 90 | | | 90 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 193,722 | | | 171,416 | |
| Retained earnings | 132,126 | | | 93,088 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (2,496) | | | (3,079) | |
| Total Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. stockholders’ equity | 324,151 | | | 262,221 | |
| Noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 27,200 | | | 17,136 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $ | 351,351 | | | $ | 279,357 | |
| Total liabilities, redeemable noncontrolling interests, and stockholders’ equity | $ | 1,405,858 | | | $ | 1,234,608 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
66
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(U.S. dollars in thousands, except per share amounts) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Revenues | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Management fees | $ | 970,812 | | | $ | 992,728 | | | $ | 1,213,924 | |
| Performance fees | 4,319 | | | 557 | | | 13,312 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 975,131 | | | $ | 993,285 | | | $ | 1,227,236 | |
| Operating Expenses | | | | | |
| Compensation and benefits | 529,395 | | | 510,382 | | | 563,054 | |
| Distribution, servicing and marketing | 23,621 | | | 24,612 | | | 31,719 | |
| Occupancy | 28,931 | | | 28,833 | | | 21,942 | |
| Communication and technology | 51,742 | | | 50,257 | | | 43,899 | |
| General and administrative | 37,850 | | | 35,104 | | | 26,131 | |
| Total operating expenses | 671,539 | | | 649,188 | | | 686,745 | |
| Total operating income | 303,592 | | | 344,097 | | | 540,491 | |
| Non-operating income (expense) | | | | | |
| Interest expense | (8,571) | | | (9,912) | | | (10,803) | |
| Interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other | 6,301 | | | 333 | | | 559 | |
| Net gain on the tax receivable agreements | 505 | | | 913 | | | 358 | |
| Net investment gain (loss) of consolidated investment products | 62,702 | | | (6,990) | | | 19,748 | |
| Net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products | 19,163 | | | (16,606) | | | 1,197 | |
| Total non-operating income (expense) | 80,100 | | | (32,262) | | | 11,059 | |
| Income before income taxes | 383,692 | | | 311,835 | | | 551,550 | |
| Provision for income taxes | 71,888 | | | 63,450 | | | 107,026 | |
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | 311,804 | | | 248,385 | | | 444,524 | |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 49,522 | | | 49,123 | | | 96,879 | |
| Less: Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products | 39,993 | | | (7,493) | | | 11,129 | |
| Net income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. | $ | 222,289 | | | $ | 206,755 | | | $ | 336,516 | |
| | | | | |
| Basic earnings per share | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.10 | |
| Diluted earnings per share | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.09 | |
| Basic weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 63,451,932 | | | 62,475,960 | | | 59,866,790 | |
| Diluted weighted average number of common shares outstanding | 63,486,479 | | | 62,498,509 | | | 59,881,039 | |
| Dividends declared per Class A common share | $ | 2.66 | | | $ | 3.67 | | | $ | 4.23 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
67
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
(U.S. dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | $ | 311,804 | | | $ | 248,385 | | | $ | 444,524 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation gain (loss) | 957 | | | (2,053) | | | (319) | |
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 957 | | | (2,053) | | | (319) | |
| Comprehensive income | 312,761 | | | 246,332 | | | 444,205 | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 49,873 | | | 48,839 | | | 96,879 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products | 39,993 | | | (7,493) | | | 11,129 | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. | $ | 222,895 | | | $ | 204,986 | | | $ | 336,197 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
68
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity
(U.S. dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A Common Stock | Class B Common Stock | Class C Common Stock | | Additional Paid-in Capital | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Noncontrolling Interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | Total Stockholders’ Equity | Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests |
Balance at January 1, 2021 | $ | 631 | | $ | 45 | | $ | 110 | | | $ | 107,738 | | $ | 72,944 | | $ | (991) | | $ | 10,565 | | $ | 191,042 | | $ | 93,753 | |
| Net income | — | | — | | — | | | — | | 336,516 | | — | | 96,879 | | 433,395 | | 11,129 | |
| Other comprehensive income - foreign currency translation | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | (271) | | (48) | | (319) | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative impact of changes in ownership of Artisan Partners Holdings LP, net of tax | — | | — | | — | | | (563) | | — | | (48) | | 611 | | — | | — | |
| Amortization of equity-based compensation | — | | — | | — | | | 32,750 | | — | | — | | 6,899 | | 39,649 | | — | |
| Deferred tax assets, net of amounts payable under tax receivable agreements | — | | — | | — | | | 9,656 | | — | | — | | — | | 9,656 | | — | |
| Issuance of Class A common stock, net of issuance costs | 10 | | — | | — | | | 46,630 | | — | | — | | — | | 46,640 | | — | |
| Forfeitures and employee/partner terminations | (1) | | — | | — | | | 1 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Issuance of restricted stock awards | 7 | | — | | — | | | (7) | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Employee net share settlement | (2) | | — | | — | | | (7,452) | | — | | — | | (1,791) | | (9,245) | | — | |
| Exchange of subsidiary equity | 22 | | (6) | | (16) | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Purchase of equity and subsidiary equity | — | | (7) | | (3) | | | (46,918) | | — | | — | | — | | (46,928) | | — | |
| Capital contributions, net | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 73,236 | |
| Impact of deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (67,083) | |
| Distributions | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | (93,189) | | (93,189) | | — | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | — | | | — | | (274,571) | | — | | (169) | | (274,740) | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2021 | $ | 667 | | $ | 32 | | $ | 91 | | | $ | 141,835 | | $ | 134,889 | | $ | (1,310) | | $ | 19,757 | | $ | 295,961 | | $ | 111,035 | |
| Net income | — | | — | | — | | | — | | 206,755 | | — | | 49,123 | | 255,878 | | (7,493) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) - foreign currency translation | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | (1,736) | | (317) | | (2,053) | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative impact of changes in ownership of Artisan Partners Holdings LP | — | | — | | — | | | (1,087) | | — | | (33) | | 1,120 | | — | | — | |
| Amortization of equity-based compensation | — | | — | | — | | | 35,494 | | — | | — | | 6,038 | | 41,532 | | — | |
| Deferred tax assets, net of amounts payable under tax receivable agreements | — | | — | | — | | | 1,894 | | — | | — | | — | | 1,894 | | — | |
| Issuance of Class A common stock, net of issuance costs | — | | — | | — | | | (94) | | — | | — | | — | | (94) | | — | |
| Forfeitures and employee/partner terminations | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Issuance of restricted stock awards | 8 | | — | | — | | | (8) | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Employee net share settlement | (2) | | — | | — | | | (6,618) | | (25) | | — | | (1,221) | | (7,866) | | — | |
| Exchange of subsidiary equity | 7 | | (6) | | (1) | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital contributions, net | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 41,011 | |
| Impact of deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (9,273) | |
| Distributions | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | (57,199) | | (57,199) | | — | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | — | | | — | | (248,531) | | — | | (165) | | (248,696) | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 680 | | $ | 26 | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 171,416 | | $ | 93,088 | | $ | (3,079) | | $ | 17,136 | | $ | 279,357 | | $ | 135,280 | |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
69
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity, continued
(U.S. dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Class A Common Stock | Class B Common Stock | Class C Common Stock | | Additional Paid-in Capital | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Noncontrolling Interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | Total Stockholders’ Equity | Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests |
Balance at January 1, 2023 | $ | 680 | | $ | 26 | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 171,416 | | $ | 93,088 | | $ | (3,079) | | $ | 17,136 | | $ | 279,357 | | $ | 135,280 | |
| Net income | — | | — | | — | | | — | | 222,289 | | — | | 49,522 | | 271,811 | | 39,993 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) - foreign currency translation | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | 606 | | 351 | | 957 | | — | |
| Cumulative impact of changes in ownership of Artisan Partners Holdings LP | — | | — | | — | | | (1,385) | | — | | (23) | | 1,408 | | — | | — | |
| Amortization of equity-based compensation | — | | — | | — | | | 29,074 | | — | | — | | 4,623 | | 33,697 | | — | |
| Deferred tax assets, net of amounts payable under tax receivable agreements | — | | — | | — | | | 481 | | — | | — | | — | | 481 | | — | |
| Issuance of Class A common stock, net of issuance costs | — | | — | | — | | | (84) | | — | | — | | — | | (84) | | — | |
| Forfeitures and employee/partner terminations | (1) | | — | | — | | | 1 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Issuance of restricted stock awards | 6 | | — | | — | | | (6) | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Employee net share settlement | (2) | | — | | — | | | (5,775) | | — | | — | | (981) | | (6,758) | | — | |
| Exchange of subsidiary equity | 2 | | (2) | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital contributions, net | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 95,662 | |
| Impact of deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (18,529) | |
| Distributions | — | | — | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | (44,732) | | (44,732) | | — | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | — | | | — | | (183,251) | | — | | (127) | | (183,378) | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 685 | | $ | 24 | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 193,722 | | $ | 132,126 | | $ | (2,496) | | $ | 27,200 | | $ | 351,351 | | $ | 252,406 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
70
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(U.S. dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Cash flows from operating activities | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Net income before noncontrolling interests | $ | 311,804 | | | $ | 248,385 | | | $ | 444,524 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 9,348 | | | 7,797 | | | 6,933 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 42,496 | | | 30,156 | | | 38,382 | |
| Asset impairment | — | | | 1,413 | | | — | |
| Noncash lease expense | (242) | | | 1,865 | | | (1,931) | |
| Net investment (gain) loss on nonconsolidated investment securities | (19,163) | | | 16,606 | | | (2,315) | |
| Net (gain) loss on the tax receivable agreements | (505) | | | (913) | | | (358) | |
| Loss on disposal of property and equipment | 4 | | | 51 | | | 4 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 442 | | | 440 | | | 421 | |
| Share-based compensation | 33,697 | | | 41,532 | | | 39,649 | |
| | | | | |
| Net investment (gain) loss of consolidated investment products | (62,702) | | | 6,990 | | | (19,748) | |
| Purchase of investments by consolidated investment products | (406,318) | | | (335,647) | | | (252,399) | |
| Proceeds from sale of investments by consolidated investment products | 281,640 | | | 211,537 | | | 196,620 | |
| Net change in operating assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products including net investment income | 35,094 | | | 45,970 | | | (30,804) | |
| Change in assets and liabilities resulting in an increase (decrease) in cash: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | 125 | | | 16,622 | | | (15,962) | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (85) | | | 3,348 | | | (3,164) | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 27,393 | | | 16,458 | | | (1,301) | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 253,028 | | | 312,610 | | | 398,551 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | |
| Acquisition of property and equipment | (2,257) | | | (6,637) | | | (2,435) | |
| Leasehold improvements | (6,374) | | | (12,921) | | | (3,532) | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from sale of investment securities | 5,947 | | | 5,164 | | | 12,813 | |
| Purchase of investment securities | (35,483) | | | (49,337) | | | (33,820) | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (38,167) | | | (63,731) | | | (26,974) | |
|
| | | | | |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
71
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows (continued)
(U.S. dollars in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Cash flows from financing activities | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Partnership distributions | (44,732) | | | (57,199) | | | (93,189) | |
| Dividends paid | (183,378) | | | (248,696) | | | (274,740) | |
| Payment of debt issuance costs | — | | | (543) | | | — | |
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable | — | | | 90,000 | | | — | |
| Principal payments on notes payable | — | | | (90,000) | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Payments under the tax receivable agreements | (35,757) | | | (33,109) | | | (31,250) | |
| Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | — | | | — | | | 46,928 | |
| Payment of costs directly associated with the issuance of Class A common stock | — | | | — | | | (244) | |
| Purchase of equity and subsidiary equity | — | | | — | | | (46,928) | |
| | | | | |
| Taxes paid related to employee net share settlement | (6,758) | | | (7,866) | | | (9,246) | |
| Capital contributions to consolidated investment products, net | 95,662 | | | 41,011 | | | 73,236 | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (174,963) | | | (306,402) | | | (335,433) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | 39,898 | | | (57,523) | | | 36,144 | |
| Net cash impact of deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | (4,679) | | | — | | | (34,823) | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 143,248 | | | 200,771 | | | 199,450 | |
| End of period | $ | 178,467 | | | $ | 143,248 | | | $ | 200,771 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash as of the end of the period | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 141,008 | | | $ | 114,832 | | | $ | 189,226 | |
| Restricted cash | — | | | — | | | 629 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents of consolidated investment products | 37,459 | | | 28,416 | | | 10,916 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 178,467 | | | $ | 143,248 | | | $ | 200,771 | |
| | | | | |
| Supplementary information | | | | | |
| Noncash activity: | | | | | |
| Establishment of deferred tax assets | $ | 3,462 | | | $ | 9,054 | | | $ | 54,214 | |
| Establishment of amounts payable under tax receivable agreements | 1,016 | | | 6,471 | | | 44,209 | |
| Increase in investment securities due to deconsolidation of consolidated investment products | 19,612 | | | 9,970 | | | 20,900 | |
| Operating lease assets obtained in exchange for operating leases | 6,644 | | | 32,055 | | | 20,830 | |
| Settlement of franchise capital liability via transfer of investment securities | 3,204 | | | — | | | — | |
| Cash paid for: | | | | | |
| Interest on borrowings | $ | 7,679 | | | $ | 10,299 | | | $ | 10,210 | |
| Income tax | 30,724 | | | 31,571 | | | 70,337 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
72
ARTISAN PARTNERS ASSET MANAGEMENT INC.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(U.S. currencies in thousands, except share and per share amounts and as otherwise indicated)
Note 1. Nature of Business and Organization
Nature of Business
Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. (“APAM”), through its subsidiaries, is an investment management firm focused on providing high-value added, active investment strategies to sophisticated clients globally. APAM and its subsidiaries are hereafter referred to collectively as “Artisan” or the “Company”.
Artisan’s autonomous investment teams manage a broad range of U.S., non-U.S. and global investment strategies that are diversified by asset class, market cap and investment style. Strategies are offered through multiple investment vehicles to accommodate a broad range of client mandates. Artisan offers its investment management services primarily to institutions and through intermediaries that operate with institutional-like decision-making processes and have long-term investment horizons.
Organization
On March 12, 2013, APAM completed its initial public offering (the “IPO”). APAM was formed for the purpose of becoming the general partner of Artisan Partners Holdings LP (“Artisan Partners Holdings” or “Holdings”) in connection with the IPO. Holdings is a holding company for the investment management business conducted under the name “Artisan Partners”. The reorganization (“IPO Reorganization”) established the necessary corporate structure to complete the IPO while at the same time preserving the ability of the firm to conduct operations through Holdings and its subsidiaries.
As its sole general partner, APAM controls the business and affairs of Holdings. As a result, APAM consolidates Holdings’ financial statements and records a noncontrolling interest for the equity interests in Holdings held by the limited partners of Holdings. At December 31, 2023, APAM held approximately 86% of the equity ownership interest in Holdings.
Holdings, together with its wholly owned subsidiary, Artisan Investments GP LLC, controls a 100% interest in Artisan Partners Limited Partnership (“APLP”), a multi-product investment management firm that is the principal operating subsidiary of Artisan Partners Holdings. APLP is registered as an investment adviser with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940. APLP provides investment advisory services to traditional separate accounts and pooled investment vehicles, including Artisan Partners Funds, Inc. (“Artisan Funds”), Artisan Partners Global Funds plc (“Artisan Global Funds”), and Artisan sponsored private funds (“Artisan Private Funds”). Artisan Funds are a series of open-end, mutual funds registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended. Artisan Global Funds is a family of Ireland-domiciled UCITS funds. Artisan Private Funds consist of a number of Artisan-sponsored unregistered pooled investment vehicles.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements were prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”) and related rules and regulations of the SEC. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates or assumptions that affect the reported amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Actual results could differ from these estimates or assumptions.
Principles of consolidation
Artisan’s policy is to consolidate all subsidiaries or other entities in which it has a controlling financial interest. The consolidation guidance requires an analysis to determine if an entity should be evaluated for consolidation using the voting interest entity (“VOE”) model or the variable interest entity (“VIE”) model. Under the VOE model, controlling financial interest is generally defined as a majority ownership of voting interests. Under the VIE model, controlling financial interest is defined as (i) the power to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the entity and (ii) the right to receive potentially significant benefits or the obligation to absorb potentially significant losses. Artisan generally consolidates VIEs in which it meets the power criteria and holds an equity ownership interest of greater than 10%. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of APAM and all subsidiaries or other entities in which APAM has a direct or indirect controlling financial interest. All material intercompany balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Artisan serves as the investment adviser to Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds. Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds are corporate entities the business and affairs of which are managed by their respective boards of directors. The shareholders of the funds retain voting rights, including rights to elect and reelect members of their respective boards of directors. Each series of Artisan Funds is a VOE and is separately evaluated for consolidation under the VOE model. The shareholders of Artisan Global Funds lack simple majority liquidation rights, and as a result, each sub-fund of Artisan Global Funds is evaluated for consolidation under the VIE model. Artisan Private Funds are also evaluated for consolidation under the VIE model because third-party equity holders of the funds generally lack the ability to divest Artisan of its control of the funds.
From time to time, the Company makes investments in Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds. If the investment results in a controlling financial interest, APAM consolidates the fund, and the underlying activity of the entire fund is included in Artisan’s Consolidated Financial Statements. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan had a controlling financial interest in one series of Artisan Funds, five sub-funds of Artisan Global Funds and two Artisan Private Funds and, as a result, these funds are included in Artisan’s Consolidated Financial Statements. Because these consolidated investment products meet the definition of investment companies under U.S. GAAP, Artisan has retained the specialized industry accounting principles for investment companies in the consolidated financial statements. See Note 6, “Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products” for additional details.
Reclassification
In the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company changed the presentation of “Other net investment gain (loss)” within the Consolidated Statements of Operations to expand its disaggregation of the components comprising this balance. “Other net investment gain (loss)” has been replaced by “Interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other” and “Net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products” within the Non-operating income (expense) section of the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Amounts for the comparative prior fiscal year periods have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. These reclassifications had no impact on previously reported operating income, non-operating income, net income, or financial position. Management believes the revised presentation is more useful to readers of its financial statements.
Operating segments
Artisan operates in one segment, the investment management industry. Artisan provides investment management services to separate accounts and pooled investment vehicles. Management assesses the financial performance of these vehicles on a combined basis.
Cash and cash equivalents
Artisan defines cash and cash equivalents as money market funds and other highly liquid investments with original maturities of 90 days or less. Cash and cash equivalents are stated at cost, which approximates fair value due to the short-term nature and liquidity of these financial instruments. For disclosure purposes, cash equivalents are categorized as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy. Cash and cash equivalents are subject to credit risk and were primarily maintained in demand deposit accounts with financial institutions or treasury money market funds. Interest and dividends related to cash and cash equivalents is recorded in interest income on cash and cash equivalents and other in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Foreign currency translation
Assets and liabilities of foreign operations whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar are translated at prevailing year-end exchange rates. Revenue and expenses of such foreign operations are translated at average exchange rates during the year. The net effect of the translation adjustment for foreign operations is included in other comprehensive income (loss) in the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income. The cumulative effect of translation adjustments is included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition, based on period-end ownership levels.
Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable are carried at invoiced amounts and consist primarily of investment advisory fees that have been earned, but not yet received from clients. Due to the short-term nature of the receivables, the carrying values of these assets approximate fair value. The accounts receivable balance does not include any allowance for doubtful accounts as Artisan believes all accounts receivable balances are fully collectible. There has not been any bad debt expense recorded for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
Investment securities
Investment securities consist of nonconsolidated investments in shares of Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds, and Artisan Private Funds. Investments provide exposure to various risks, including price risk (the risk of a potential future decline in value of the investment) and foreign currency risk. Investments are carried at fair value based on net asset values as of the valuation date.
Realized and unrealized gains (losses) on nonconsolidated investment securities are recorded in net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Dividend income from these investments is recognized when earned and is also included in net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products.
Property and equipment
Property and equipment are carried at cost, less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets or the remaining lease term, whichever is shorter.
The estimated useful lives of property and equipment as of December 31, 2023 are as follows: | | | | | | | | |
| Property and Equipment Type | | Useful Life |
| Computers and equipment | | Three to Five years |
| Computer software | | Three to Five years |
| Furniture and fixtures | | Seven years |
| Leasehold improvements | | Two to 14 years |
Implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software, including hosting arrangements, are capitalized and expensed on a straight-line basis over either the estimated useful life of the respective software or the term of the hosting arrangement.
Property and equipment is tested for impairment when there is an indication that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. When an asset is determined to not be recoverable, the impairment loss is measured based on the excess, if any, of the carrying value of the asset over its fair value.
Leases
Artisan has lease commitments for office space, parking structures, and equipment, which are all accounted for as operating leases. Artisan records expense for operating leases on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Any lease incentives received by Artisan are also amortized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Artisan assesses its contractual arrangements for the existence of a lease at inception. Operating leases with an initial term greater than 12 months are recorded as operating lease assets and operating lease liabilities in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. Lease components (e.g. fixed rental payments) and non-lease components (e.g. fixed common-area maintenance costs) are generally accounted for as a single component.
Operating lease liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. Operating lease assets are recognized at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term, adjusted for prepaid rent and the remaining balance of lease incentives received. Artisan's lease agreements generally do not provide an implicit interest rate, and therefore the present value calculation uses Artisan's estimated incremental borrowing rate. A market-based approach is used to estimate the incremental borrowing rate for each individual lease using observable market interest rates and Artisan specific inputs. The lease terms include periods covered by options to extend or exclude periods covered by options to terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that Artisan will exercise that option.
Restricted cash
Restricted cash represents cash that was restricted as collateral on a standby letter of credit related to a lease obligation.
Cash and cash equivalents of consolidated investment products
Cash and cash equivalents of consolidated investment products consist of highly liquid investments, including money market funds. See Note 6, “Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products” for additional details.
Investment assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products
Investment assets and liabilities of consolidated investment products primarily consist of equity securities, fixed income securities, short-term investments, and derivatives. The carrying value of the investment assets and liabilities is also their fair value. Changes in the fair value of the investments are recognized as gains and losses in earnings. Equity securities are generally valued based upon closing market prices of the security on the principal exchange on which the security is traded. Fixed income securities include corporate bonds, convertible bonds and bank loans. Fixed income securities are generally valued based on prices provided by independent pricing vendors. Short-term investments are comprised of repurchase agreements and U.S Treasury obligations. Repurchase agreements are valued at cost plus accrued interest and U.S. treasury obligations are valued using the same principles as fixed income securities. Derivative assets and liabilities are generally comprised of put and call swaps on securities or indices and open forward foreign currency contracts. Put and call swaps are valued at the mid price (average of the bid price and ask price) as provided by the pricing vendor at the close of trading on the contract’s principal exchange. Open forward foreign currency contracts are valued using the market spot rate. See Note 6, “Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products” for additional details.
Redeemable noncontrolling interests
Redeemable noncontrolling interests represent third-party investors’ ownership interest in consolidated investment products. Third-party investors in consolidated investment products generally have the right to withdraw their capital, subject to certain conditions. Noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment products that are currently redeemable or convertible for cash or other assets at the option of the holder are classified as temporary equity.
Revenue recognition
Artisan’s investment advisory revenue is derived from contracts with customers in the form of investment management fees and performance fees.
Investment Management Fees
Investment management fees are generally computed as a percentage of assets under management and are recognized as revenue at the end of each distinct service period. Management fees for providing investment advisory services are computed and billed in accordance with the underlying investment management agreements, which is generally on a monthly or quarterly basis. Investment management fees are presented net of cash rebates and expense reimbursements pursuant to contractual expense limitations of certain funds.
Performance Fees
A number of investment management agreements provide for performance-based fees or incentive allocations, collectively “performance fees”. Performance fees, if earned, are recognized upon completion of each contractually determined measurement period, which is generally quarterly or annually. Performance fees generally are not subject to claw back as a result of performance declines subsequent to the most recent measurement date.
Revenue Recognition
Artisan accounts for asset management services as a single performance obligation that is satisfied over time, using a time-based measure of progress to recognize revenue. Customer consideration is variable due to the uncertainty of the value of assets under management during each distinct service period. At the end of each period, Artisan records revenue for the actual amount of investment management fees earned for that period because the uncertainty has been resolved.
Performance fees are subject to the uncertainty of market volatility, and as a result, the entire amount of the variable consideration related to performance fees is constrained until the end of each measurement period. At the end of the measurement period, revenue is recorded for the actual amount of performance fees earned during that period because the uncertainty has been resolved. For performance fees with annual measurement periods, revenue recognized in the current period could relate to performance obligations that were partially satisfied in prior periods.
Customer Rebates and Expense Reimbursements
Artisan has contractually agreed to reimburse for expenses incurred to the extent necessary to limit annualized ordinary operating expenses incurred by certain funds to not more than a fixed percentage of the funds’ average daily net assets. Artisan may also contractually agree to pay fee rebates to certain investors in Artisan Global Funds. Artisan accounts for all reimbursements and rebates as a reduction of the transaction price (and, hence, of revenue) because the billing adjustments and payments represent consideration payable to customers and Artisan does not receive any distinct goods or services from the customers in exchange.
Share-based compensation
Share-based compensation expense is recognized based on the estimated grant date fair value on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the award. The initial requisite service period is generally five years for restricted share-based awards. The Company’s accounting policy is to record the impact of forfeitures when they occur.
Distribution, servicing and marketing
Artisan Funds has authorized certain financial services companies, broker-dealers, banks or other intermediaries, and in some cases other organizations designated by an authorized intermediary, to accept purchase, exchange, and redemption orders for shares of Artisan Funds on the funds’ behalf. Many intermediaries charge a fee for accounting and shareholder services provided to fund shareholders on the funds’ behalf. Those services typically include recordkeeping, transaction processing for shareholders’ accounts, and other services.
Fees are either based on the number of accounts to which the intermediary provides such services or a percentage of the average daily value of fund shares held in such accounts. The funds pay a portion of such fees directly to the intermediaries, which are intended to compensate the intermediary for its provision of services of the type that would be provided by the funds’ transfer agent or other service providers if the shares were registered directly on the books of the funds’ transfer agent. Artisan pays the balance of those fees which includes compensation to the intermediary for its distribution, servicing and marketing of Artisan Funds shares.
Artisan Global Funds also have arrangements pursuant to which Artisan is required to pay a portion of its investment management fee for distribution, servicing and marketing of Artisan Global Funds shares.
Distribution, servicing and marketing fees paid by Artisan are presented as an operating expense because Artisan is the principal in its role as the primary obligor related to these services. Expenses incurred were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Expenses incurred with respect to Artisan Funds | $ | 19,746 | | | $ | 20,708 | | | $ | 28,640 | |
| Expenses incurred with respect to Artisan Global Funds | 935 | | | 903 | | | 899 | |
| Other marketing expenses | 2,940 | | | 3,001 | | | 2,180 | |
| Total distribution, servicing and marketing | $ | 23,621 | | | $ | 24,612 | | | $ | 31,719 | |
Accrued fees to intermediaries were $2.6 million and $3.8 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and are included in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
Loss contingencies
Artisan considers the assessment of loss contingencies as a significant accounting policy because of the significant uncertainty relating to the outcome of any potential legal actions and other claims and the difficulty of predicting the likelihood and range of the potential liability involved, coupled with the material impact on Artisan’s results of operations that could result from legal actions or other claims and assessments. Artisan recognizes estimated costs to defend as incurred. Potential loss contingencies are reviewed at least quarterly and are adjusted to reflect the impact and status of settlements, rulings, advice of counsel and other information pertinent to a particular matter. Significant differences could exist between the actual cost required to investigate, litigate and/or settle a claim or the ultimate outcome of a suit and management’s estimate. These differences could have a material impact on Artisan’s results of operations, financial position, or cash flows. Recoveries of losses are recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Operations when receipt is deemed probable. No loss contingencies were recorded at December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021. Currently, there are no legal or administrative proceedings that management believes may have a material effect on Artisan’s consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations.
Commitments
In October 2023, Artisan launched Artisan Dislocation Opportunities Fund LP, a private fund that calls committed capital from investors and begins investment activities upon achievement of a market-based triggering event. Capital commitments from investors are released after three years if the market-based trigger is not achieved, which it had not been as of December 31, 2023. The Company has committed $16.0 million of capital in conjunction with the launch, predominantly as a seed investment in the fund.
Income taxes
Artisan accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be realized or settled. Artisan recognizes a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Artisan accounts for uncertain income tax positions by recognizing the impact of a tax position in its consolidated financial statements when Artisan believes it is more likely than not that the tax position would not be sustained upon examination by the appropriate tax authorities based on the technical merits of the position.
Comprehensive income (loss)
Total comprehensive income (loss) includes net income and other comprehensive income. Other comprehensive income (loss) consists of foreign currency translation.
Partnership distributions
Artisan makes distributions to its partners for purposes of paying income taxes as required under the terms of Artisan Partners Holdings’ partnership agreement. Tax distributions are calculated utilizing the highest combined individual federal, state and local income tax rate among the various locations in which the partners, as a result of owning their interests in the partnership, are subject to tax, assuming maximum applicability of the phase-out of itemized deductions contained in the Internal Revenue Code that apply to any specific tax year. Artisan also makes additional distributions under the terms of the partnership agreement. Distributions are recorded in the financial statements on the declaration date.
Earnings per share
Basic earnings per share is computed under the two-class method by dividing income available to Class A common stockholders by the weighted average number of Class A common shares outstanding during the period. Unvested restricted share-based awards are excluded from the number of Class A common shares outstanding for the basic earnings per share calculation because the shares have not yet been earned by employees. Income available to Class A common stockholders is computed by reducing
net income attributable to APAM by earnings (both distributed and undistributed) allocated to participating securities, according to their respective rights to participate in those earnings. Except for certain performance share units, unvested share-based awards are participating securities because the awards include non-forfeitable dividend rights during the vesting period. Class B and Class C common shares do not share in profits of APAM and therefore are not reflected in the calculations.
Diluted earnings per share is computed under the more dilutive of the treasury stock method or the two-class method. The weighted average number of Class A common shares outstanding during the period is increased by the assumed conversion of nonparticipating unvested share-based awards into Class A common stock using the treasury stock method.
Recent accounting pronouncements
In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, “Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures”, which improves reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through requirements for more detailed information about significant segment expenses. The Company is required to adopt the guidance for the year ending December 31, 2024. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU on its Consolidated Financial Statements.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, “Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures”, which requires disaggregated income tax disclosures on the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid. The Company is required to adopt the guidance for the year ending December 31, 2025. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU on its Consolidated Financial Statements.
Note 3. Investment Securities
The disclosures below include details of Artisan’s investments, excluding money market funds and consolidated investment products. Investments held by consolidated investment products are described in Note 6, “Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products”. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 | | As of December 31, 2022 |
| Investments in equity securities | $ | 139,240 | | | $ | 76,156 | |
| Investments in equity securities accounted for under the equity method | 11,282 | | | 9,259 | |
| Total investment securities | $ | 150,522 | | | $ | 85,415 | |
Artisan’s investments in equity securities consist of investments in Artisan Funds, Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds. As of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022, $107.0 million and $63.3 million, respectively, of Artisan’s investment securities were related to funded long-term incentive compensation plans (excluding investments in consolidated investment products).
Unrealized gain (loss) related to investment securities held on the dates indicated below were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 | | As of December 31, 2022 | | As of December 31, 2021 |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on investment securities held at the end of the period | $ | 15,664 | | | $ | (14,799) | | | $ | 1,602 | |
Note 4. Fair Value Measurements
The table below presents information about Artisan’s assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value and the valuation techniques Artisan utilized to determine such fair value. The financial instruments held by consolidated investment products are excluded from the table below and are presented in Note 6, “Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products”.
In accordance with ASC 820, fair value is defined as the price that Artisan would receive upon selling an investment in an orderly transaction to an independent buyer in the principal or most advantageous market for the investment. The following three-tier fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value:
•Level 1 – Observable inputs such as quoted (unadjusted) market prices in active markets for identical securities.
•Level 2 – Other significant observable inputs (including but not limited to quoted prices for similar instruments, interest rates, prepayment speeds, credit risk, etc.).
•Level 3 – Significant unobservable inputs (including Artisan’s own assumptions in determining fair value).
The following provides the hierarchy of inputs used to derive fair value of Artisan’s assets and liabilities that are financial instruments as of December 31, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets and Liabilities at Fair Value |
| Total | | NAV Practical Expedient (No Fair Value Level) | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | |
Money market funds (1) | $ | 118,768 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 118,768 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities | 150,522 | | | 10,744 | | | 139,778 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | |
Money market funds (1) | $ | 3,297 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,297 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities | 85,415 | | | 8,835 | | | 76,580 | | | — | | | — | |
(1) Money market funds are included within cash and cash equivalents on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition. |
Fair values determined based on Level 1 inputs utilize quoted market prices for identical assets. Level 1 assets generally consist of money market funds, open-end mutual funds and UCITS funds. Equity securities without a fair value level consist of the Company’s investments in Artisan Private Funds, which are measured at the underlying fund’s net asset value (“NAV”), using the ASC 820 practical expedient. The NAV is provided by the fund and is derived from the fair values of the underlying investments as of the reporting date. Cash maintained in demand deposit accounts is excluded from the table above.
Note 5. Borrowings
Artisan’s borrowings consist of the following as of December 31, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Maturity(1) | | Outstanding Balance at December 31, 2023 | | Outstanding Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | | Interest Rate Per Annum |
| Revolving credit agreement | August 2027 | | — | | | — | | | | | NA |
| Senior notes | | | | | | | | | |
| Series D | August 2025 | | 60,000 | | | 60,000 | | | | | 4.29 | % |
| Series E | August 2027 | | 50,000 | | | 50,000 | | | | | 4.53 | % |
| Series F | August 2032 | | 90,000 | | | 90,000 | | | | | 3.10 | % |
| Total gross borrowings | | | $ | 200,000 | | | $ | 200,000 | | | | | |
| Unamortized debt issuance costs | | | $ | (733) | | | $ | (950) | | | | | |
| Total borrowings | | | $ | 199,267 | | | $ | 199,050 | | | | | |
(1) The Company is not required to make principal payments on any of the outstanding obligations prior to contractual maturity. |
The fair value of borrowings was approximately $184.4 million as of December 31, 2023. Fair value was determined based on future cash flows, discounted to present value using current market interest rates. The inputs are categorized as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy, as defined in Note 4, “Fair Value Measurements”.
On August 16, 2022, Artisan Partners Holdings issued $90.0 million of 3.10% Series F notes pursuant to an agreement executed in December 2021 and used the proceeds to repay the $90.0 million of Series C senior notes that matured on August 16, 2022. The Company incurred debt issuance costs related to the notes of $0.6 million, which are amortized as interest expense over the life of the instrument.
The fixed interest rate on each series of unsecured notes is subject to a one percentage point increase in the event Holdings receives a below-investment grade rating and any such increase will continue to apply until an investment grade rating is received.
Revolving credit agreement - On August 16, 2022, Artisan Partners Holdings amended and extended its $100.0 million revolving credit facility for an additional five-year period. The Company incurred debt issuance costs related to the revolving credit facility of $1.1 million, which are amortized as interest expense over the life of the instrument. Any loans outstanding under the revolving credit agreement bear interest at a rate per annum equal to, at the Company’s election, (i) adjusted Term SOFR plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.25% to 2.25%, depending on Holdings’ leverage ratio (as defined in the revolving credit agreement) or (ii) an alternate base rate equal to the highest of (a) Citibank, N.A.’s prime rate, (b) the federal funds effective rate plus 0.50%, and (c) the adjusted Term SOFR for a one-month interest period plus 1.00%, plus, in each case, an applicable margin ranging from 0.25% to 1.25%, depending on Holdings’ leverage ratio. Unused commitments will bear interest at a rate that ranges from 0.15% to 0.45%, depending on Holdings’ leverage ratio.
As of and for the year-ended December 31, 2023, there were no borrowings outstanding under the revolving credit agreement and the interest rate on the unused commitment was 0.15%.
The unsecured notes and the revolving credit agreement contain certain restrictive financial covenants including a limitation on the leverage ratio of Holdings and a minimum interest coverage ratio. The Company was in compliance with all debt covenants as of December 31, 2023.
Interest expense incurred on the unsecured notes and revolving credit agreement was $7.8 million, $9.3 million, and $10.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Note 6. Variable Interest Entities and Consolidated Investment Products
Artisan serves as the investment adviser for various types of investment products, consisting of both VIEs and VOEs. Artisan consolidates an investment product if it has a controlling financial interest in the entity. See Note 2, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”. Any such entities are collectively referred to herein as consolidated investment products or CIPs.
As of December 31, 2023, Artisan is considered to have a controlling financial interest in one series of Artisan Funds, five sub-funds of Artisan Global Funds and two Artisan Private Funds, with an aggregate direct equity investment in the consolidated investment products of $114.8 million.
Artisan’s maximum exposure to loss in connection with the assets and liabilities of CIPs is limited to its direct equity investment, while the potential benefit is limited to the management and performance fees received and the return on its direct equity investment. With the exception of Artisan’s direct equity investment, the assets of CIPs are not available to Artisan’s creditors, nor are they available to Artisan for general corporate purposes. In addition, third-party investors in the CIPs have no recourse to the general credit of the Company.
Management and performance fees earned from CIPs are eliminated from revenue upon consolidation. See Note 17, “Related Party Transactions” for additional information on management and performance fees earned from CIPs.
Third-party investors’ ownership interest in CIPs is presented as redeemable noncontrolling interests in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as third-party investors have the right to withdraw their capital, subject to certain conditions. Net income attributable to third-party investors is reported as net income attributable to noncontrolling interests - consolidated investment products in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company determined that it no longer had a controlling financial interest in one series of Artisan Funds as a result of third party capital contributions. Upon loss of control, the fund was deconsolidated and the related assets, liabilities and equity of the fund were derecognized from the Company’s consolidated statements of financial condition. There was no net impact to the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023. Artisan generally does not recognize a gain or loss upon deconsolidation of investment products as the assets and liabilities of CIPs are carried at fair value. Artisan’s 19.6 million direct equity investment was reclassified from investment assets of consolidated investment products to investment securities.
As of December 31, 2023, Artisan held direct equity investments of $11.3 million in VIEs for which the Company does not hold a controlling financial interest. These direct equity investments consisted of seed investments in sub-funds of Artisan Global Funds and Artisan Private Funds, both of which are accounted for under the equity method of accounting because Artisan has significant influence over the funds.
Fair Value Measurements - Consolidated Investment Products
Investments held by CIPs are reflected at fair value. Short and long positions on equity securities are valued based upon closing prices of the security on the exchange or market designated by the accounting agent or pricing vendor as the principal exchange. The closing price may represent last sale price, official closing price, a closing auction or other information depending on market convention. Short and long positions on fixed income instruments are valued at market value. Market values are generally evaluations based on prices provided by independent pricing vendors, which may consider, among other factors, the prices at which securities actually trade, broker-dealer quotations, pricing formulas, estimates of market values obtained from yield data relating to investments or securities with similar characteristics and/or discounted cash flow models that might be applicable.
Short-term investments are comprised of repurchase agreements and U.S. Treasury obligations. Repurchase agreements are valued at cost plus accrued interest and U.S. treasury obligations are valued using the same principles as fixed income securities. Derivative assets and liabilities are generally comprised of put and call options on securities and indices and forward foreign currency contracts. Put and call options are valued at the mid price (average of bid price and ask price) as provided by the pricing vendor at the close of trading on the contract’s principal exchange. Open forward foreign currency contracts are valued using the market spot rate.
The following tables present the fair value hierarchy levels of assets and liabilities held by CIPs measured at fair value as of December 31, 2023 and 2022: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets and Liabilities at Fair Value |
| Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | |
| Assets | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 18,156 | | $ | 18,156 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities - long position | 42,693 | | 40,838 | | 1,855 | | — | |
| Fixed income instruments - long position | 315,183 | | — | | 309,110 | | 6,073 | |
| Derivative assets | 1,004 | | — | | 1,004 | | — | |
| Short-term investments | 5,215 | | — | | 5,215 | | — | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | |
| | | | |
| Fixed income instruments - short position | 7,392 | | — | | 7,392 | | — | |
| Derivative liabilities | 2,188 | | 843 | | 1,345 | | — | |
| | | | |
| December 31, 2022 | | | | |
| Assets | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 25,140 | | $ | 25,140 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Equity securities - long position | 32,388 | | 30,179 | | 2,209 | | — | |
| Fixed income instruments - long position | 216,638 | | — | | 212,368 | | 4,270 | |
| Derivative assets | 951 | | 74 | | 877 | | — | |
| Short-term investments | 5,766 | | — | | 5,766 | | — | |
| | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | |
| Equity securities - short position | $ | 256 | | $ | 256 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Fixed income instruments - short position | 17,273 | | — | | 17,273 | | — | |
| Derivative liabilities | 3,222 | | 2,462 | | 760 | | — | |
CIP balances included in the Company's consolidated statements of financial condition were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 | | As of December 31, 2022 |
| Net CIP assets included in the table above | $ | 372,671 | | | $ | 260,132 | |
| Net CIP assets (liabilities) not included in the table above | (5,434) | | | (18,105) | |
| Total Net CIP assets | 367,237 | | | 242,027 | |
| Less: redeemable noncontrolling interests | 252,406 | | | 135,280 | |
| Artisan’s direct equity investment in CIPs | $ | 114,831 | | | $ | 106,747 | |
Note 7. Noncontrolling Interests - Holdings
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings in the Consolidated Statements of Operations represents the portion of earnings or loss attributable to the equity ownership interests in Holdings held by the limited partners of Holdings. As of December 31, 2023, APAM held approximately 86% of the equity ownership interests in Holdings.
Limited partners of Artisan Partners Holdings are entitled to exchange partnership units (along with a corresponding number of shares of Class B or C common stock of APAM, as applicable) for shares of Class A common stock from time to time (the "Holdings Common Unit Exchanges"). The Holdings Common Unit Exchanges increase APAM's equity ownership interest in Holdings and result in an increase to deferred tax assets and amounts payable under the tax receivable agreements. See Note 11, “Income Taxes and Related Payments”.
In order to maintain the one-to-one correspondence of the number of Holdings partnership units and APAM common shares, Holdings will issue one general partner (“GP”) unit to APAM for each share of Class A common stock issued by APAM.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, APAM’s equity ownership interest in Holdings has increased as a result of the following transactions: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Holdings GP Units | Limited Partnership Units | Total | APAM Ownership % |
Balance at January 1, 2021 | 63,131,007 | | 15,441,103 | | 78,572,110 | | 80 | % |
Issuance of APAM Restricted Shares, Net (1) | 562,289 | | — | | 562,289 | | 1 | % |
Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs (1) | 1,074 | | — | | 1,074 | | — | % |
2021 Follow-On Offering | 963,614 | | (963,614) | | — | | 1 | % |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | 2,142,292 | | (2,142,292) | | — | | 2 | % |
Forfeitures from Employee Terminations (1) | (100,404) | | — | | (100,404) | | — | % |
Balance at December 31, 2021 | 66,699,872 | | 12,335,197 | | 79,035,069 | | 84 | % |
Issuance of APAM Restricted Shares, Net (1) | 588,598 | | — | | 588,598 | | — | % |
Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs (1) | 1,060 | | — | | 1,060 | | — | % |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | 711,166 | | (711,166) | | — | | 1 | % |
Forfeitures from Employee Terminations (1) | (18,671) | | — | | (18,671) | | — | % |
Balance at December 31, 2022 | 67,982,025 | | 11,624,031 | | 79,606,056 | | 85 | % |
Issuance of APAM Restricted Shares, Net (1) | 328,415 | | — | | 328,415 | | 1 | % |
Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs (1) | 100,043 | | — | | 100,043 | | — | % |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | 163,345 | | (163,345) | | — | | — | % |
Forfeitures from Employee Terminations (1) | (19,750) | | — | | (19,750) | | — | % |
Balance at December 31, 2023 | 68,554,078 | | 11,460,686 | | 80,014,764 | | 86 | % |
(1) The impact of the transaction on APAM’s ownership percentage was less than 1%. |
Changes in ownership of Holdings are accounted for as equity transactions because APAM continues to have a controlling interest in Holdings. Additional paid-in capital and noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings in the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition are adjusted to reallocate Holdings’ historical equity to reflect the change in APAM’s ownership of Holdings.
The reallocation of equity had the following impact on the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Statements of Financial Condition | For the Years Ended December 31, |
2023 | | 2022 |
| Additional paid-in capital | $ | (1,385) | | | $ | (1,087) | |
| Noncontrolling interests - Artisan Partners Holdings | 1,408 | | | 1,120 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (23) | | | (33) | |
| Net impact to financial condition | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
In addition to the reallocation of historical equity, the change in ownership resulted in an increase to deferred tax assets and additional paid-in capital of $0.2 million and $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Note 8. Stockholders’ Equity
APAM - Stockholders’ Equity
APAM had the following authorized and outstanding equity as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Outstanding | | | | |
| Common shares | Authorized | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 | | Voting Rights (1) | | Economic Rights |
Class A, par value $0.01 per share | 500,000,000 | | | 68,554,078 | | | 67,982,025 | | | 1 vote per share | | Proportionate |
Class B, par value $0.01 per share | 200,000,000 | | | 2,435,739 | | | 2,583,884 | | | 1 vote per share | | None |
Class C, par value $0.01 per share | 400,000,000 | | | 9,024,947 | | | 9,040,147 | | | 1 vote per share | | None |
(1) The Company’s employees to whom Artisan has granted equity have entered into a stockholders agreement with respect to all shares of APAM common stock they have acquired from the Company and any shares they may acquire from the Company in the future, pursuant to which they granted an irrevocable voting proxy to a Stockholders Committee. As of December 31, 2023, Artisan’s employees held 5,241,153 restricted shares of Class A common stock and all 2,435,739 outstanding shares of Class B common stock, all of which were subject to the agreement. |
APAM is dependent on cash generated by Holdings to fund any dividends. Generally, Holdings will make distributions to all of its partners, including APAM, based on the proportionate share of ownership each has in Holdings. APAM will fund dividends to its stockholders from its proportionate share of those distributions after provision for its taxes and other obligations. APAM declared and paid the following dividends per share during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Type of Dividend | | Class of Stock | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Quarterly | | Common Class A | | $ | 2.31 | | | $ | 2.95 | | | $ | 3.92 | |
| Special Annual | | Common Class A | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.72 | | | $ | 0.31 | |
The following table summarizes APAM’s stock transactions for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Stock Outstanding | Class A Common Stock(1) | Class B Common Stock | Class C Common Stock |
Balance at January 1, 2021 | 78,572,110 | | 63,131,007 | | 4,457,958 | | 10,983,145 | |
2021 Follow-On Offering | — | | 963,614 | | (638,614) | | (325,000) | |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | — | | 2,142,292 | | (612,764) | | (1,529,528) | |
| Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs | 1,074 | | 1,074 | | — | | — | |
| Restricted Share Award Grants | 740,249 | | 740,249 | | — | | — | |
| Restricted Share Net Share Settlement | (177,960) | | (177,960) | | — | | — | |
| Employee/Partner Terminations | (100,404) | | (100,404) | | — | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2021 | 79,035,069 | | 66,699,872 | | 3,206,580 | | 9,128,617 | |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | — | | 711,166 | | (622,696) | | (88,470) | |
| Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs | 1,060 | | 1,060 | | — | | — | |
| Restricted Share Award Grants | 787,372 | | 787,372 | | | — | |
| Restricted Share Net Share Settlement | (198,774) | | (198,774) | | — | | — | |
| Employee/Partner Terminations | (18,671) | | (18,671) | | — | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2022 | 79,606,056 | | 67,982,025 | | 2,583,884 | | 9,040,147 | |
| | | | |
| Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | — | | 163,345 | | (148,145) | | (15,200) | |
| Delivery of Shares Underlying RSUs | 100,043 | | 100,043 | | — | | — | |
| Restricted Share Award Grants | 515,702 | | 515,702 | | — | | — | |
| Restricted Share Net Share Settlement | (187,287) | | (187,287) | | — | | — | |
| Employee/Partner Terminations | (19,750) | | (19,750) | | — | | — | |
Balance at December 31, 2023 | 80,014,764 | | 68,554,078 | | 2,435,739 | | 9,024,947 | |
(1) There were 361,215, 367,392, and 327,713 restricted stock units outstanding at December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. In addition, there were 216,170, 231,170, and 135,230 performance share units outstanding at December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, respectively. Based on the current status of the market and performance conditions, the 216,170 unvested performance share units would ultimately result in the issuance of 264,143 shares of Class A common stock if all other vesting conditions were met. Restricted stock units and performance share units are not reflected in the table because they are not considered outstanding or issued stock. |
Each Class A, Class B, Class D and Class E common unit of Holdings (together with the corresponding share of Class B or Class C common stock) is exchangeable for one share of Class A common stock. The corresponding shares of Class B and Class C common stock are immediately canceled upon any such exchange.
Upon termination of employment with Artisan, an employee-partner’s Class B common units are exchanged for Class E common units and the corresponding shares of Class B common stock are canceled. APAM issues the former employee-partner a number of shares of Class C common stock equal to the former employee-partner’s number of Class E common units. Class E common units are exchangeable for Class A common stock subject to the same restrictions and limitations on exchange applicable to the other common units of Holdings.
Artisan Partners Holdings - Partners’ Equity
Holdings makes distributions of its net income to the holders of its partnership units for income taxes as required under the terms of the partnership agreement and also makes additional distributions under the terms of the partnership agreement as required. The distributions are recorded in the financial statements on the declaration date, or on the payment date in lieu of a declaration date. Holdings’ partnership distributions for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Holdings Partnership Distributions to Limited Partners | $ | 44,732 | | | $ | 57,199 | | | $ | 93,189 | |
| Holdings Partnership Distributions to APAM | 248,278 | | | 299,040 | | | 400,191 | |
| Total Holdings Partnership Distributions | $ | 293,010 | | | $ | 356,239 | | | $ | 493,380 | |
The distributions are recorded as a reduction to consolidated stockholders’ equity, with the exception of distributions made to APAM, which are eliminated upon consolidation.
Note 9. Revenue From Contracts with Customers
The following table presents a disaggregation of investment advisory revenue by type and vehicle for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Management fees | | | | | |
| Artisan Funds | $ | 562,803 | | | $ | 573,924 | | | $ | 712,952 | |
| Artisan Global Funds | 43,464 | | | 43,128 | | | 48,498 | |
Separate accounts and other(1) | 364,545 | | | 375,676 | | | 452,474 | |
| Performance fees | | | | | |
Separate accounts and other(1) | 4,319 | | | 557 | | | 13,312 | |
| | | | | |
Total revenues(2) | $ | 975,131 | | | $ | 993,285 | | | $ | 1,227,236 | |
(1) Separate accounts and other revenue consists of management fees and performance fees earned from vehicles other than Artisan Funds or Artisan Global Funds, and therefore includes revenue earned from traditional separate accounts, Artisan-branded collective investment trusts and Artisan Private Funds. |
(2) All management fees and performance fees from consolidated investment products were eliminated upon consolidation and therefore are omitted from this table. See Note 17, “Related Party Transactions”. |
The following table presents the balances of receivables related to contracts with customers: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Customer | December 31,
2023 | | December 31,
2022 |
| Artisan Funds | $ | 8,251 | | | $ | 5,597 | |
| Artisan Global Funds | 5,047 | | | 4,453 | |
| Separate accounts and other | 81,441 | | | 74,936 | |
| Total receivables from contracts with customers | $ | 94,739 | | | $ | 84,986 | |
| Non-customer receivables | 6,430 | | | 13,648 | |
| Accounts receivable | $ | 101,169 | | | $ | 98,634 | |
Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds are billed on the last day of each month. Artisan Funds and Artisan Global Funds make payments on the same day the invoice is received for the majority of the invoiced amount. The remainder of the invoice is generally paid in the month following receipt of the invoice. Separate accounts and other clients are generally billed on a monthly or quarterly basis, with payments due within 30 days of billing.
Artisan had no other contract assets or liabilities from contracts with customers as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Non-customer receivables includes state tax payments on behalf of certain limited partners, which are then netted from subsequent distributions or payments to the limited partners, as well as investment redemptions that have not yet been collected.
Note 10. Compensation and Benefits
Total compensation and benefits consists of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
Salaries, incentive compensation and benefits (1) | $ | 469,869 | | | $ | 458,609 | | | $ | 516,931 | |
| Franchise capital award compensation expense | 27,359 | | | 11,769 | | | 6,887 | |
| Restricted share-based award compensation expense | 32,167 | | | 40,004 | | | 39,236 | |
| Long-term incentive compensation expense | 59,526 | | | 51,773 | | | 46,123 | |
| Total compensation and benefits | $ | 529,395 | | | $ | 510,382 | | | $ | 563,054 | |
(1) Excluding long-term incentive compensation expense. |
Incentive compensation
Cash incentive compensation paid to members of Artisan’s investment teams and members of its distribution team is generally based on formulas that are tied directly to revenues. The majority of this incentive compensation is earned on a quarterly basis and paid in the quarter following the quarter in which it was earned with the exception of fourth quarter incentive compensation, which is earned and paid in the fourth quarter of the year. Cash incentive compensation paid to most other employees is determined based on individual performance and Artisan’s overall results during the applicable year and is generally paid on an annual basis.
Long-term incentive compensation awards consist of both APAM equity awards and long-term cash awards, which are referred to as franchise capital awards. These awards are described in more detail below.
Equity awards
APAM has granted a combination of restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, and performance share units (collectively referred to as “restricted share-based awards” or “awards”) of Class A common stock to employees.
Standard Restricted Shares. Standard restricted shares are generally subject to a pro rata five-year service vesting condition.
Career Shares. Career shares are generally subject to both (i) a qualifying retirement (as defined in the award agreement) condition and, (ii) a pro rata five-year service vesting condition.
Franchise Shares. Like career shares, franchise shares are generally subject to both (i) a qualifying retirement condition and (ii) a pro rata five-year service vesting condition. In addition, franchise shares, which are only granted to investment team members, are subject to a Franchise Protection Clause, which provides that the number of shares that ultimately vest depends on whether certain conditions relating to client cash flows are met. If such conditions are not met, compensation cost will be reversed for any shares that do not vest.
Performance Share Units (PSUs). PSUs are generally subject to (i) a three-year service vesting condition, (ii) certain performance conditions related to the Company's adjusted operating margin and total shareholder return compared to a peer group during a three-year performance period, and (iii) for one-half of the PSUs eligible to vest at the end of the performance period, a qualifying retirement condition. The number of shares of Class A common stock that are ultimately issued in connection with each PSU award will depend upon the outcome of the performance, market and qualified retirement conditions. For the portion of a PSU award with a "performance condition" under ASC 718, expense is recognized over the service period if it is probable that the performance condition will be achieved.
Compensation expense is recognized based on the estimated grant date fair value on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period of the award. The initial requisite service period is generally five years for restricted stock awards and restricted stock units, and three years for performance share units. The fair value of each award is equal to the market price of the Company's common stock on the grant date, except for performance share units with a "market condition" performance metric under ASC 718, which have a grant-date fair value based on a Monte Carlo valuation model.
Unvested restricted share-based awards are subject to forfeiture. Grantees are generally entitled to dividends or dividend equivalents on unvested and vested awards. 6,401,834 shares of Class A common stock were reserved and available for issuance under the Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc. 2023 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan (the “Plan”) as of December 31, 2023, which includes 3,945,902 shares registered in the year ended December 31, 2023.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, Artisan granted 515,702 restricted stock awards and 1,684 restricted stock units of Class A common stock to employees of the Company. Total compensation expense associated with the 2023 grant is expected to be approximately $18.1 million.
The following tables summarize the restricted share-based award activity for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Restricted Stock Awards and Restricted Stock Units |
Unvested at January 1, 2021 | $ | 35.09 | | | 5,293,642 | |
| Granted | 52.93 | | | 741,555 | |
| Forfeited | 29.99 | | | (101,001) | |
| Vested | 31.51 | | | (688,802) | |
Unvested at January 1, 2022 | $ | 38.18 | | | 5,245,394 | |
| Granted | 41.86 | | | 788,703 | |
| Forfeited | 40.11 | | | (18,671) | |
| Vested | 34.85 | | | (619,083) | |
Unvested at January 1, 2023 | $ | 39.09 | | | 5,396,343 | |
| Granted | 34.99 | | | 517,386 | |
| Forfeited | 42.95 | | | (19,750) | |
| Vested | 37.55 | | | (542,487) | |
Unvested at December 31, 2023 | $ | 38.84 | | | 5,351,492 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Performance Share Units |
Unvested at January 1, 2021 | $ | 52.45 | | | 60,000 | |
| Granted | 68.58 | | | 75,230 | |
| Forfeited | — | | | — | |
| Vested | — | | | — | |
Unvested at January 1, 2022 | $ | 61.42 | | | 135,230 | |
| Granted | 53.50 | | | 95,940 | |
| Forfeited | — | | | — | |
| Vested | — | | | — | |
Unvested at January 1, 2023 | $ | 58.13 | | | 231,170 | |
| Granted | — | | | — | |
| Forfeited | — | | | — | |
Vested (1) | 34.97 | | | (15,000) | |
Unvested at December 31, 2023 | $ | 54.89 | | | 216,170 | |
(1) During the year ended December 31, 2023, the 60,000 PSUs granted in 2020 met the requisite three-year performance conditions, resulting in the potential vesting of 150% of the PSUs, or 90,000 shares of Class A common stock. 45,000 shares of Class A common stock were promptly delivered at that time, while the remaining 45,000 PSUs remain subject to the qualified retirement vesting condition. |
Based on the current status of the market and performance conditions, the 216,170 unvested performance share units would ultimately result in the issuance of 264,143 shares of Class A common stock if all other vesting conditions were met.
The aggregate vesting date fair value of awards that vested during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 was approximately $21.2 million, $24.4 million, and $35.8 million, respectively. The unrecognized compensation expense for the unvested restricted stock awards and restricted stock units as of December 31, 2023 was $61.1 million with a weighted average recognition period of 3.0 years remaining. The unrecognized compensation expense for the unvested performance share units as of December 31, 2023 was $3.3 million with a weighted average recognition period of 1.9 years remaining.
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company withheld a total of 187,287 and 198,774 restricted shares, respectively, and paid $6.8 million and $7.9 million, respectively, as a result of net share settlements to satisfy employee tax withholding obligations. These net share settlements had the effect of shares repurchased and retired by the Company, as they reduced the number of shares outstanding.
Long-term cash awards (franchise capital awards)
During the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, Artisan granted $39.0 million and $48.6 million, respectively, of franchise capital awards to investment team members in lieu of certain additional restricted share-based awards. The franchise capital awards are subject to the same long-term vesting and forfeiture provisions as restricted share-based awards. Prior to vesting, franchise capital awards are generally allocated to one or more of the investment strategies managed by the award recipient's investment team. During the vesting period, the value of the awards will increase or decrease based on the investment returns of the strategies in which the awards are invested. Compensation expense, including the appreciation or depreciation related to investment returns, is recognized on a straight-line basis over the required service period, which is generally five years. Because the awards will generally be paid out in cash upon vesting, the fair value of unvested awards is recorded as a liability based on the percentage of the service requirement that has been completed.
The company hedges its economic exposure to the change in value of these awards due to market movements by investing the cash reserved for the awards in the underlying investments. The franchise capital award liability and the underlying investment holdings are marked to market each quarter. The change in value of the award liability is recognized as a compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the required service period. The change in value of the underlying investment holdings is recognized in non-operating income (expense) in the period of change. While there is a timing difference between the recognition of the compensation expense and the offsetting investment gain or loss, the compensation expense and investment income will net to zero at the end of the multi-year vesting period for all awards that ultimately vest. The change in value of the investments had the following impact on the Consolidated Statements of Operations:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Statement of Operations Section | Statement of Operations Line Item | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Operating expense (benefit) | Compensation and benefits | $ | 4,775 | | | $ | (3,391) | | | $ | 520 | |
| Non-operating income (expense) | Net investment gain (loss) of nonconsolidated investment products | 16,543 | | | (13,198) | | | 2,717 | |
The franchise capital award liability was $33.0 million and $14.5 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and is included in accrued incentive compensation in the consolidated statements of financial condition. The unrecognized compensation expense for the unvested franchise capital awards as of December 31, 2023 was $82.1 million with a weighted average recognition period of 3.6 years remaining.
Note 11. Income Taxes and Related Payments
APAM is subject to U.S. federal, state and local income taxation on APAM’s allocable portion of Holdings’ income, as well as foreign income taxes payable by Holdings’ subsidiaries. Components of the provision for income taxes consist of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Current: | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Federal | $ | 21,776 | | | $ | 25,903 | | | $ | 53,131 | |
| State and local | 6,580 | | | 6,870 | | | 14,990 | |
| Foreign | 1,036 | | | 521 | | | 523 | |
| Total | 29,392 | | | 33,294 | | | 68,644 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
| Federal | 36,128 | | | 25,670 | | | 32,655 | |
| State and local | 6,368 | | | 4,486 | | | 5,727 | |
| Total | 42,496 | | | 30,156 | | | 38,382 | |
| Income tax expense | $ | 71,888 | | | $ | 63,450 | | | $ | 107,026 | |
The provision for income taxes differs from the amount of income tax computed by applying the applicable U.S. statutory federal income tax rate to income before provision for income taxes as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| U.S. federal statutory rate | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % |
| State and local taxes, net of federal tax effect | 3.4 | | | 3.7 | | | 3.5 | |
| Excess tax benefits on share-based compensation | (0.9) | | | (1.7) | | | (1.4) | |
| Rate benefit from the flow through entity | (4.9) | | | (2.8) | | | (4.1) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits | — | | | (0.1) | | | — | |
| Other | 0.1 | | | 0.2 | | | 0.4 | |
| Effective tax rate | 18.7 | % | | 20.3 | % | | 19.4 | % |
The effective tax rate includes a rate benefit attributable to the fact that, for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, approximately 16%, 17% and 19%, respectively, of Artisan Partners Holdings’ taxable earnings were attributable to other partners and not subject to corporate-level taxes. The effective tax rate was also lower than the statutory rate due to tax deductible dividends paid on unvested restricted share-based awards.
In connection with the IPO, APAM entered into two tax receivable agreements (“TRAs”). The first TRA, generally provides for the payment by APAM to a private equity fund (the “Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder”) or its assignees of 85% of the applicable cash savings, if any, of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes that APAM actually realizes (or is deemed to realize in certain circumstances) as a result of (i) the tax attributes of the preferred units APAM acquired in the merger of a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Pre-H&F Corp Merger Shareholder into APAM in March 2013 and (ii) tax benefits related to imputed interest.
The second TRA generally provides for the payment by APAM to current or former limited partners of Holdings or their assignees of 85% of the applicable cash savings, if any, of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes that APAM actually realizes (or is deemed to realize in certain circumstances) as a result of (i) certain tax attributes of their partnership units sold to APAM or exchanged (for shares of Class A common stock, convertible preferred stock or other consideration) and that are created as a result of such sales or exchanges and payments under the TRAs and (ii) tax benefits related to imputed interest. Under both agreements, APAM generally will retain the benefit of the remaining 15% of the applicable tax savings.
For purposes of the TRAs, cash savings of income taxes are calculated by comparing APAM’s actual income tax liability to the amount it would have been required to pay had it not been able to utilize any of the tax benefits subject to the TRAs, unless certain assumptions apply. The TRAs will continue in effect until all such tax benefits have been utilized or expired, unless APAM exercises its right to terminate the agreements or payments under the agreements are accelerated in the event that APAM materially breaches any of its material obligations under the agreements.
The actual increase in tax basis, as well as the amount and timing of any payments under these agreements, will vary depending upon a number of factors, including the timing of sales or exchanges by the holders of limited partnership units, the price of the Class A common stock at the time of such sales or exchanges, whether such sales or exchanges are taxable, the amount and timing of the taxable income APAM generates in the future and the tax rate then applicable and the portion of APAM’s payments under the TRAs constituting imputed interest or depreciable basis or amortizable basis.
Payments under the TRAs, if any, will be made pro rata among all TRA counterparties entitled to payments on an annual basis to the extent APAM has sufficient taxable income to utilize the increased depreciation and amortization charges and imputed interest deductions. Artisan expects to make one or more payments under the TRAs, to the extent they are required, prior to or within 125 days after APAM’s U.S. federal income tax return is filed for each fiscal year. Interest on the TRA payments will accrue from the due date (without extension) of such tax return until such payments are made.
Amounts payable under the TRAs are estimates which may be impacted by factors, including but not limited to, expected tax rates, projected taxable income, and projected ownership levels and are subject to change. Changes in the estimates of amounts payable under tax receivable agreements are recorded as non-operating income (loss) in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The change in the Company’s deferred tax assets related to the tax benefits described above and the change in corresponding amounts payable under the TRAs for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred Tax Asset - Amortizable Basis | | Amounts Payable Under Tax Receivable Agreements |
| December 31, 2021 | $ | 459,893 | | | $ | 425,427 | |
2022 Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | 8,687 | | | 7,384 | |
| Amortization | (42,122) | | | — | |
Payments under TRAs (1) | — | | | (33,109) | |
| Change in estimate | 10 | | | (913) | |
| December 31, 2022 | $ | 426,468 | | | $ | 398,789 | |
2023 Holdings Common Unit Exchanges | 1,789 | | | 1,521 | |
| Amortization | (43,832) | | | — | |
Payments under TRAs (1) | — | | | (35,757) | |
| Change in estimate | (2) | | | (505) | |
| December 31, 2023 | $ | 384,423 | | | $ | 364,048 | |
(1) Interest payments of $0.2 million and $0.1 million were paid in addition to these TRA payments for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. |
Net deferred tax assets comprise the following: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred tax assets: | As of December 31, 2023 | | As of December 31, 2022 |
Amortizable basis (1) | $ | 384,423 | | | $ | 426,468 | |
Other (2) | 52,106 | | | 50,556 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 436,529 | | | 477,024 | |
Less: valuation allowance (3) | — | | | — | |
| Net deferred tax assets | $ | 436,529 | | | $ | 477,024 | |
(1) Represents the unamortized step-up of tax basis and other tax attributes from the merger and partnership unit sales and exchanges described above. These future tax benefits are subject to the TRA agreements. |
(2) Represents the net deferred tax assets associated with Artisan’s investment in Holdings, related primarily to incentive compensation plan deduction timing differences. These future tax benefits are not subject to the TRA agreements. |
(3) Artisan assessed whether the deferred tax assets would be realizable and determined based on its history of taxable income that the benefits would more likely than not be realized. Accordingly, no valuation allowance is required. |
Accounting standards establish a minimum threshold for recognizing, and a process for measuring, the benefits of income tax return positions in financial statements. The change in the Company’s gross unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 is summarized as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 147 | | | $ | 1,085 | | | $ | 1,085 | |
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | — | | | 117 | | | — | |
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | — | | | (476) | | | — | |
| Tax positions related to the current year | 26 | | | 30 | | | — | |
| Settlements with taxing authorities | — | | | (609) | | | — | |
| Expirations of statute of limitations | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 173 | | | $ | 147 | | | $ | 1,085 | |
If recognized, $0.2 million and $0.1 million of the benefits (expense) recorded as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, would favorably (unfavorably) impact the effective tax rate in future periods. The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits is currently not expected to significantly increase or decrease within the next twelve months.
The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as a component of the income tax provision. Accrued interest on uncertain tax positions was less than $0.1 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and is excluded from the unrecognized tax benefits total above. The gross unrecognized tax benefit is recorded within accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other in the Company's Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition.
In the normal course of business, Artisan is subject to examination by federal and certain state, local and foreign tax regulators. As of December 31, 2023, U.S. federal income tax returns filed for the years 2020 through 2022 are open and therefore subject to examination. State, local and foreign income tax returns filed are generally subject to examination from 2019 to 2022.
Note 12. Earnings Per Share
The computation of basic and diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Basic and Diluted Earnings Per Share | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Numerator: | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to APAM | $ | 222,289 | | | $ | 206,755 | | | $ | 336,516 | |
| Less: Allocation to participating securities | 19,880 | | | 22,801 | | | 31,430 | |
| Net income available to common stockholders | $ | 202,409 | | | $ | 183,954 | | | $ | 305,086 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | 63,451,932 | | | 62,475,960 | | | 59,866,790 | |
| Dilutive effect of nonparticipating equity awards | 34,547 | | | 22,549 | | | 14,249 | |
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 63,486,479 | | | 62,498,509 | | | 59,881,039 | |
| Earnings per share - Basic | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.10 | |
| Earnings per share - Diluted | $ | 3.19 | | | $ | 2.94 | | | $ | 5.09 | |
Allocation to participating securities in the table above primarily represents dividends paid to holders of unvested restricted share-based awards, which reduces net income available to common stockholders.
The Holdings limited partnership units are anti-dilutive primarily due to the impact of public company expenses. Unvested restricted share-based awards with non-forfeitable dividend rights during the vesting period are considered participating securities and are therefore anti-dilutive.
The following table summarizes the weighted-average shares outstanding that are excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because their effect would have been anti-dilutive: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Anti-Dilutive Weighted Average Shares Outstanding | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Holdings limited partnership units | 11,505,766 | | | 12,022,633 | | | 14,167,538 | |
| Unvested restricted share-based awards | 5,572,690 | | | 5,601,756 | | | 5,410,221 | |
| Total | 17,078,456 | | | 17,624,389 | | | 19,577,759 | |
Note 13. Benefit Plans
Artisan has a 401(k) plan and similar foreign arrangements for its non-U.S. employees, under which it provides a matching contribution on employees’ pre-tax contributions. Expenses related to Artisan’s benefits plans for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were $11.0 million, $9.7 million and $8.4 million, respectively, and are included in compensation and benefits in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Artisan provides an opportunity for eligible employees to participate in Artisan’s financial growth and success through phantom equity awards, pursuant to the Artisan Partners Holdings LP Phantom Equity Plan. The phantom equity awards provide participants the right to receive cash payments upon vesting based on the trading price of APAM’s Class A common stock. Awards made under the Phantom Equity Plan are liability awards and are subject to vesting on a pro-rata basis over five years. Award recipients must be employed by Artisan on the vesting date in order to receive payment.
Expense related to the Phantom Equity Plan for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $2.2 million, $0.7 million and $1.6 million, respectively, and is included in compensation and benefits in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The liability at December 31, 2023 and 2022 for the plan was $1.7 million and $0.8 million, respectively.
Note 14. Indemnifications
In the normal course of business, APAM enters into agreements that include indemnities in favor of third parties. Holdings has also agreed to indemnify APAM as its general partner, Artisan Investment Corporation (“AIC”) as its former general partner, the directors and officers of APAM, the directors and officers of AIC as its former general partner, the members of its former Advisory Committee, and its partners, directors, officers, employees and agents. Holdings’ subsidiaries may also have similar agreements to indemnify their respective general partner(s), directors, officers, directors and officers of their general partner(s), partners, members, employees, and agents. The Company’s maximum exposure under these arrangements is unknown, as this would involve future claims that may be made against the Company that have not yet occurred. APAM maintains insurance policies that may provide coverage against certain claims under these indemnities.
Note 15. Property and Equipment
The composition of property and equipment at December 31, 2023 and 2022 are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| Computers and equipment | $ | 4,301 | | | $ | 6,132 | |
| Computer software | 7,412 | | | 6,740 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 15,352 | | | 14,785 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 71,444 | | | 66,304 | |
| Total cost | $ | 98,509 | | | $ | 93,961 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (51,871) | | | (45,857) | |
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation | $ | 46,638 | | | $ | 48,104 | |
Depreciation expense totaled $9.3 million, $7.7 million and $6.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Note 16. Leases
Operating lease expense was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | For the Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| Lease Type | | Classification | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| Parking leases | | Compensation and benefits | | $ | 393 | | | $ | 398 | | | $ | 518 | | | | | |
Office leases (1) | | Occupancy | | 18,046 | | | 18,979 | | | 14,463 | | | | | |
Variable lease cost (2) | | Occupancy | | 935 | | | 351 | | | 110 | | | | | |
Short-term lease cost (2) | | Occupancy | | 469 | | | 710 | | | 455 | | | | | |
| Sublease income | | Occupancy | | — | | | (133) | | | (267) | | | | | |
| Office equipment leases | | Communication and technology | | 67 | | | 134 | | | 247 | | | | | |
| Total operating lease expense | | | | $ | 19,910 | | | $ | 20,439 | | | $ | 15,526 | | | | | |
(1) Office lease expense includes an impairment charge of $1.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022 related to the abandonment of leased office space. | | | | |
(2) Variable and short-term lease costs are excluded from the measurement of operating lease liabilities. | | | | |
During the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company recognized asset impairment loss of $1.4 million related to the abandonment of a leased office location. The loss is recorded in occupancy expense based on the present value of expected future cash flows.
The table below presents the maturity of operating lease liabilities: | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2023 |
| 2024 | $ | 18,995 | |
| 2025 | 19,342 | |
| 2026 | 18,896 | |
| 2027 | 17,468 | |
| 2028 | 16,410 | |
| Thereafter | 42,378 | |
| Total undiscounted lease payments | 133,489 | |
| Adjustment to discount to present value | (20,098) | |
| Operating lease liabilities | $ | 113,391 | |
As of December 31, 2023, none of the options to extend lease terms were reasonably certain of being exercised. Other information related to leases was as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Weighted average discount rate | 4.1 | % | | 4.1 | % | | 4.4 | % |
| Weighted average remaining lease term | 8.4 years | | 9.0 years | | 8.3 years |
| Operating cash flows for operating leases | 19,668 | | | 16,393 | | | 16,821 | |
Note 17. Related Party Transactions
Several of the current executive officers and directors of APAM, or entities associated with those individuals, are or were limited partners of Holdings. As a result, certain transactions (such as TRA payments) between Artisan and these persons are considered to be related party transactions.
Holdings makes estimated state tax payments on behalf of certain limited partners, including related parties. These payments are then netted from subsequent distributions to the limited partners. At December 31, 2023 and 2022, accounts receivables included $0.2 million and $6.5 million, respectively, of partnership tax reimbursements due from Holdings’ limited partners, including related parties.
Affiliate transactions—Artisan Funds
Artisan has an agreement to serve as the investment adviser to Artisan Funds, with which certain Artisan employees are affiliated. Under the terms of the agreement, which generally is reviewed and continued by the board of directors of Artisan Funds annually, a fee is paid to Artisan based on an annual percentage of the average daily net assets of each Artisan Fund ranging from 0.60% to 1.05%. Artisan has contractually agreed to reimburse for expenses incurred to the extent necessary to limit annualized ordinary operating expenses incurred by certain of the Artisan Funds to not more than a fixed percentage (ranging from 0.83% to 1.50%) of a fund’s average daily net assets. In addition, Artisan may voluntarily waive fees or reimburse any of the Artisan Funds for other expenses. Expense waivers and reimbursements are reflected as a reduction of management fees within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The officers and directors of Artisan Funds who are affiliated with Artisan receive no compensation from the funds.
Investment advisory fees for managing Artisan Funds and amounts reimbursed by Artisan for fees and expenses (including management fees) are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Artisan Funds | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 564,413 | | | $ | 575,286 | | | $ | 713,595 | |
Elimination of fees from consolidated investment products (1) | (338) | | | (217) | | | (8) | |
| Consolidated investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 564,075 | | | $ | 575,069 | | | $ | 713,587 | |
| | | | | |
| Expense reimbursements | $ | 1,788 | | | $ | 1,515 | | | $ | 676 | |
Elimination of expense reimbursements from consolidated investment products (1) | (516) | | | (370) | | | (41) | |
| Consolidated expense reimbursements | $ | 1,272 | | | $ | 1,145 | | | $ | 635 | |
(1) Investment advisory fees and expense reimbursements related to consolidated investment products are eliminated from revenue upon consolidation. |
Affiliate transactions—Artisan Global Funds
Artisan has an agreement to serve as the investment manager to Artisan Global Funds, with which certain Artisan employees are affiliated. Under the terms of these agreements, a fee is paid based on an annual percentage of the average daily net assets of each fund ranging from 0.50% to 1.85%. Artisan reimburses each sub-fund of Artisan Global Funds to the extent that sub-fund’s annual expenses, not including Artisan’s fee, exceed certain levels, which range from 0.10% to 0.20%. In addition, Artisan may voluntarily waive fees or reimburse any of the Artisan Global Funds for other expenses. The directors of Artisan Global Funds who are also employees of Artisan receive no compensation from the funds.
Investment advisory fees for managing Artisan Global Funds and amounts reimbursed to Artisan Global Funds by Artisan are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Artisan Global Funds | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 43,868 | | | $ | 43,326 | | | $ | 48,622 | |
Elimination of fees from consolidated investment products (1) | (402) | | | (164) | | | (75) | |
| Consolidated investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 43,466 | | | $ | 43,162 | | | $ | 48,547 | |
| | | | | |
| Expense reimbursements | $ | 477 | | | $ | 424 | | | $ | 489 | |
Elimination of expense reimbursements from consolidated investment products (1) | (475) | | | (390) | | | (440) | |
| Consolidated expense reimbursements | $ | 2 | | | $ | 34 | | | $ | 49 | |
(1) Investment advisory fees and expense reimbursements related to consolidated investment products are eliminated from revenue upon consolidation. |
Affiliate transactions—Artisan Private Funds
Pursuant to written agreements, Artisan serves as the investment manager and acts as the general partner for certain Artisan Private Funds. Under the terms of these agreements, Artisan earns a management fee and for certain funds is entitled to receive either an allocation of profits or a performance-based fee. In addition, Artisan has agreed to reimburse certain funds to the extent that expenses, excluding Artisan’s management fee, performance fee and certain transaction related costs, exceed certain levels, which range from 0.10% to 1.00% per annum of the net assets of the fund. Artisan may also voluntarily waive fees or reimburse the funds for other expenses. The directors of Artisan Private Funds and the officers of the general partners of the Artisan Private Funds who are affiliated with Artisan receive no compensation from the funds.
Artisan and certain related parties, including employees, officers and members of the board of directors of APAM have invested in one or more of the Artisan Private Funds and, for certain of those investments, do not pay a management fee, performance fee or incentive allocation.
Investment advisory fees for managing Artisan Private Funds and amounts reimbursed to Artisan Private Funds by Artisan are as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| Artisan Private Funds | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 13,863 | | | $ | 15,025 | | | $ | 14,519 | |
Elimination of fees from consolidated investment products (1) | (3,063) | | | (583) | | | (1,246) | |
| Consolidated investment advisory fees (Gross of expense reimbursements) | $ | 10,800 | | | $ | 14,442 | | | $ | 13,273 | |
| | | | | |
| Expense reimbursements | $ | 278 | | | $ | 286 | | | $ | 281 | |
Elimination of expense reimbursements from consolidated investment products (1) | (119) | | | (132) | | | (154) | |
| Consolidated expense reimbursements | $ | 159 | | | $ | 154 | | | $ | 127 | |
(1) Investment advisory fees and expense reimbursements related to consolidated investment products are eliminated from revenue upon consolidation. |
Note 18. Geographic Information
Artisan generates a portion of its revenues from clients domiciled in countries outside the United States. Revenues by geographic location based on client domicile for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| U.S. | $ | 794,847 | | | $ | 812,390 | | | $ | 1,021,595 | |
| Non-U.S. | 180,284 | | | 180,895 | | | 205,641 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 975,131 | | | $ | 993,285 | | | $ | 1,227,236 | |
The following table sets forth Artisan’s long-lived assets by geographic area, which consist of net property and equipment and operating lease assets: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| U.S. | $ | 132,810 | | | $ | 146,816 | |
| Non-U.S. | 8,575 | | | 2,698 | |
| Total long-lived assets | $ | 141,385 | | | $ | 149,514 | |
Note 19. Litigation Matters
In the normal course of business, Artisan may be subject to various legal and administrative proceedings. Currently, there are no legal or administrative proceedings that management believes may have a material effect on Artisan’s consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations.
Note 20. Subsequent Events
Long-term incentive awards
During the first quarter of 2024, the board of directors of APAM approved the grant of long-term incentive awards with a grant date fair value of $59.2 million consisting of $20.8 million of restricted share-based awards and $38.4 million of franchise capital awards, to certain employees pursuant to the Company’s 2023 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan. The grant will be effective March 1, 2024. Compensation expense associated with these awards will be recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally three or five years. Expense for the franchise capital (cash based) awards will be variable based on the investment returns of the investment strategies to which the awards are allocated.
Distributions and dividends
APAM, acting as the general partner of Artisan Partners Holdings, declared, effective January 30, 2024, a distribution by Artisan Partners Holdings of $30.2 million to holders of Artisan Partners Holdings partnership units, including APAM. The board of directors of APAM declared, effective January 30, 2024, a quarterly dividend of $0.68 per share of Class A common stock and a special annual dividend of $0.34 per share of Class A common stock. Both APAM common stock dividends, a total of $1.02 per share, are payable on February 29, 2024 to stockholders of record as of February 15, 2024.
Holdings unit exchanges
On January 8, 2024 and February 7, 2024, limited partners of Artisan Partners Holdings exchanged 350,000 common units and 215,424 common units, for 350,000 Class A common shares and 215,424 Class A common shares, respectively. The exchanges increased APAM’s equity ownership interest in Holdings and together resulted in a $7.6 million increase in deferred tax assets and a $6.4 million increase in amounts payable under the tax receivable agreements.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) at December 31, 2023. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Company management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Company management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the 2013 version of the Internal Control - Integrated Framework set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control - Integrated Framework. Based on that assessment, Company management concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2023.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing in Item 8, which expresses an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act), during the quarter ended December 31, 2023, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item 10 (other than the information set forth below) will be set forth in our proxy statement for our 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2023 (the “Proxy Statement”), under the sections titled “Proposal 1: Election of Directors” and “Board Composition and Leadership – Committees of the Board” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Executive Officers
The information required by this Item 10 with respect to our executive officers is included at the end of Part I of this Form 10-K under the heading “Information about our Executive Officers.”
Code of Ethics
Our board of directors has adopted a Code of Business Conduct applicable to all directors, officers and employees of the Company to provide a framework for the highest standards of professional conduct and foster a culture of honesty and accountability. The Code of Business Conduct satisfies applicable SEC requirements and NYSE listing standards. The Code of Business Conduct is available under the Corporate Governance link on our website at www.apam.com.
We intend to post on our website at www.apam.com, all disclosures that are required by law or NYSE listing standards concerning any amendments to, or waivers from, any provision of our Code of Business Conduct.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 will be set forth in the Proxy Statement, under the sections titled “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Board Composition and Leadership – Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Director Compensation,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
The information required by this Item 12 will be set forth in the Proxy Statement, under the section titled “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 will be set forth in the Proxy Statement, under the sections titled “Board Composition and Leadership – Director Independence” and “Relationships and Related Party Transactions,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 will be set forth in the Proxy Statement, under the section titled “Ratification of the Appointment of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP for the Fiscal Year Ending December 31, 2024,” and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(1) Financial Statements: The information required by this Item is contained in Item 8 of Part II of this report.
(2) Financial Statement Schedules: None
(3) Exhibits: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed or Furnished Herewith |
| 2.1 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 2.1 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 3.1 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 3.1 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 3.2 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 3.2 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 4.1 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 4.1 | | February 18, 2020 | | |
| 10.1 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.2 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.2 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.3 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.3 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.4 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.4 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.5 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.6 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.5 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.7 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.8 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.6 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.9 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.12 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.10 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.14 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.11 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.15 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.12 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.26 | | February 27, 2023 | | |
| 10.13 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.9 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.14 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.8 | | February 27 2023 | | |
| 10.15 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.10 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.16 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.18 | | February 25, 2016 | | |
| 10.17 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.13 | | February 20, 2019 | | |
| 10.18 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.14 | | February 20, 2019 | | |
| 10.19 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.15 | | February 20, 2019 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed or Furnished Herewith |
| 10.20 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.16 | | February 20, 2019 | | |
| 10.21 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.17 | | February 20, 2019 | | |
| 10.22 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.18 | | February 18, 2020 | | |
| 10.23 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.19 | | February 23, 2021 | | |
| 10.24 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.20 | | February 22, 2022 | | |
| 10.25 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.20 | | February 23, 2021 | | |
| 10.26 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.22 | | February 22, 2022 | | |
| 10.27 | | | | 10-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.23 | | February 22, 2022 | | |
| 10.28 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | June 1, 2023 | | |
| 10.29 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.02 | | June 1, 2023 | | |
| 10.30 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | January 30, 2024 | | |
| 10.31 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.2 | | January 30, 2024 | | |
| 10.32 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.33 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.34 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.35 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.36 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 10.37 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | August 18, 2017 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Description | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Filed or Furnished Herewith |
| 10.38 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | June 6, 2019 | | |
| 10.39 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | December 7, 2021 | | |
| 10.40 | | | | 8-K | | 001-35826 | | 10.1 | | August 17, 2022 | | |
| 21.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 23.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 31.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 31.2 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 32.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 32.2 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 97.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 101 | | The following Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) documents are collectively included herewith as Exhibit 101: (i) the Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of December 31, 2023 and 2022; (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021; (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021; (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021; (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within the Inline XBRL document contained in Exhibit 101) | | | | | | | | | | X |
(1) Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
(2) These certifications are deemed to be furnished and not filed for purposes of Sections 11 and 12 of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Artisan Partners Asset Management Inc.
Dated: February 22, 2024
| | | | | |
| By: | /s/ Eric R. Colson |
| Eric R. Colson
Chief Executive Officer
(principal executive officer) |
| |
| /s/ Charles J. Daley, Jr. |
| Charles J. Daley, Jr. Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer (principal financial and accounting officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on the 22nd day of February, 2024. | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title |
| /s/ Jennifer Barbetta | | Director |
| Jennifer A. Barbetta | | |
| /s/ Matthew R. Barger | | Director |
| Matthew R. Barger | | |
| /s/ Tench Coxe | | Director |
| Tench Coxe | | |
| /s/ Stephanie G. DiMarco | | Chair of the Board |
| Stephanie G. DiMarco | | |
| /s/ Jeffrey A. Joerres | | Director |
| Jeffrey A. Joerres | | |
| /s/ Saloni S. Multani | | Director |
| Saloni S. Multani | | |


