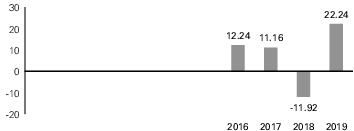
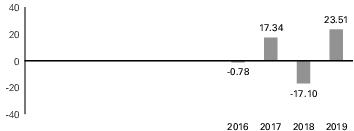Index Description. The MSCI ACWI ex USA US Dollar Hedged Index is designed to provide exposure to equity securities in developed and emerging stock markets (excluding the United States), while at the same time mitigating exposure to fluctuations between the value of the US dollar and selected non-US currencies. As of July 31, 2020, the Underlying Index consisted of issuers from the following 48 developed and emerging market countries: Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Canada, Chile, China, Colombia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Egypt, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Poland, Portugal, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates and the United Kingdom.
Main Risks
As with any investment, you could lose all or part of your investment in the fund, and the fund’s performance could trail that of other investments. The fund is subject to the main risks noted below, any of which may adversely affect the fund’s net asset value (“NAV”), trading price, yield, total return and ability to meet its investment objective.
Stock market risk. When stock prices fall, you should expect the value of your investment to fall as well. Stock prices can be hurt by poor management on the part of the stock’s issuer, shrinking product demand and other business risks. These may affect single companies as well as groups of companies. The market as a whole may not favor the types of investments the fund makes, which could adversely affect a stock’s price, regardless of how well the company performs, or the fund’s ability to sell a stock at an attractive price. There is a chance that stock prices overall will decline because stock markets tend to move in cycles, with periods of rising and falling prices. Events in the US and global financial markets, including actions taken by the US Federal Reserve or foreign central banks to stimulate or stabilize economic growth, may at times result in unusually high market volatility which could negatively affect performance. To the extent that the fund invests in a particular geographic region, capitalization or sector, the fund’s performance may be affected by the general performance of that region, capitalization or sector.
Market disruption risk. Geopolitical and other events, including war, terrorism, economic uncertainty, trade disputes, public health crises and related geopolitical events have led, and in the future may lead, to disruptions in the US and world economies and markets, which may increase financial market volatility and have significant adverse direct or indirect effects on the fund and its investments. Market disruptions could cause the fund to lose money, experience significant redemptions, and encounter
operational difficulties. Although multiple asset classes may be affected by a market disruption, the duration and effects may not be the same for all types of assets.
Recent market disruption events include the pandemic spread of the novel coronavirus known as COVID-19, and the significant uncertainty, market volatility, decreased economic and other activity and increased government activity that it has caused. Specifically, COVID-19 has led to significant death and morbidity, and concerns about its further spread have resulted in the closing of schools and non-essential businesses, cancellations, shelter-in-place orders, lower consumer spending in certain sectors, social distancing, bans on large social gatherings and travel, quarantines, government economic stimulus measures, reduced productivity, rapid increases in unemployment, increased demand for and strain on government and medical resources, border closings and global trade and supply chain interruptions, among others. The full effects, duration and costs of the COVID-19 pandemic are impossible to predict, and the circumstances surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic will continue to evolve. The pandemic may affect certain countries, industries, economic sectors, companies and investment products more than others, may exacerbate existing economic, political, or social tensions and may increase the probability of an economic recession or depression. The fund and its investments may be adversely affected by the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, and a prolonged pandemic may result in the fund and its service providers experiencing operational difficulties in coordinating a remote workforce and implementing their business continuity plans, among others.
Foreign investment risk. The fund faces the risks inherent in foreign investing. Adverse political, economic or social developments could undermine the value of the fund’s investments or prevent the fund from realizing the full value of its investments. Financial reporting standards for companies based in foreign markets differ from those in the US. Additionally, foreign securities markets generally are smaller and less liquid than US markets. To the extent that the fund invests in non-US dollar denominated foreign securities, changes in currency exchange rates may affect the US dollar value of foreign securities or the income or gain received on these securities.
Foreign governments may restrict investment by foreigners, limit withdrawal of trading profit or currency from the country, restrict currency exchange or seize foreign investments. The investments of the fund may also be subject to foreign withholding taxes. Foreign brokerage commissions and other fees are generally higher than those for US investments, and the transactions and custody of foreign assets may involve delays in payment, delivery or recovery of money or investments.
Foreign markets can have liquidity risks beyond those typical of US markets. Because foreign exchanges generally are smaller and less liquid than US exchanges, buying