Financial Section
Exhibit 13.1
THE BANK OF NEW YORK MELLON CORPORATION
2016 Annual Report
Table of Contents
Page | |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations: | |
Results of Operations: | |
Acronyms | |
Page | ||
Financial Statements: | ||
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements: | ||
Corporate Information | Inside back cover | |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Financial Summary |
(dollar amounts in millions, except per common share amounts and unless otherwise noted) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Year ended Dec. 31 | |||||||||||||||
Fee and other revenue | $ | 12,073 | $ | 12,082 | $ | 12,649 | $ | 11,856 | $ | 11,448 | |||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds | 26 | 86 | 163 | 183 | 189 | ||||||||||
Net interest revenue | 3,138 | 3,026 | 2,880 | 3,009 | 2,973 | ||||||||||
Total revenue | 15,237 | 15,194 | 15,692 | 15,048 | 14,610 | ||||||||||
Provision for credit losses | (11 | ) | 160 | (48 | ) | (35 | ) | (80 | ) | ||||||
Noninterest expense | 10,523 | 10,799 | 12,177 | 11,306 | 11,333 | ||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 4,725 | 4,235 | 3,563 | 3,777 | 3,357 | ||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 1,177 | 1,013 | 912 | 1,592 | 842 | ||||||||||
Net income | 3,548 | 3,222 | 2,651 | 2,185 | 2,515 | ||||||||||
Net (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests (a) | (1 | ) | (64 | ) | (84 | ) | (81 | ) | (78 | ) | |||||
Net income applicable to shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | 3,547 | 3,158 | 2,567 | 2,104 | 2,437 | ||||||||||
Preferred stock dividends | (122 | ) | (105 | ) | (73 | ) | (64 | ) | (18 | ) | |||||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2,494 | $ | 2,040 | $ | 2,419 | |||||
Earnings per share applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 3.16 | $ | 2.73 | $ | 2.17 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 2.03 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 3.15 | $ | 2.71 | $ | 2.15 | $ | 1.73 | $ | 2.03 | |||||
Average common shares and equivalents outstanding (in thousands): | |||||||||||||||
Basic | 1,066,286 | 1,104,719 | 1,129,897 | 1,150,689 | 1,176,485 | ||||||||||
Diluted | 1,072,013 | 1,112,511 | 1,137,480 | 1,154,441 | 1,178,430 | ||||||||||
At Dec. 31 | |||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets | $ | 280,332 | $ | 338,955 | $ | 317,646 | $ | 305,169 | $ | 292,887 | |||||
Assets of operations | 332,238 | 392,379 | 376,021 | 363,244 | 347,745 | ||||||||||
Total assets | 333,469 | 393,780 | 385,303 | 374,516 | 359,226 | ||||||||||
Deposits | 221,490 | 279,610 | 265,869 | 261,129 | 246,095 | ||||||||||
Long-term debt | 24,463 | 21,547 | 20,264 | 19,864 | 18,530 | ||||||||||
Preferred stock | 3,542 | 2,552 | 1,562 | 1,562 | 1,068 | ||||||||||
Total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common shareholders’ equity | 35,269 | 35,485 | 35,879 | 35,935 | 35,346 | ||||||||||
At Dec. 31 | |||||||||||||||
Assets under management (in billions) (b) | $ | 1,648 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | $ | 1,557 | $ | 1,349 | |||||
Assets under custody and/or administration (in trillions) (c) | 29.9 | 28.9 | 28.5 | 27.6 | 26.3 | ||||||||||
Market value of securities on loan (in billions) (d) | 296 | 277 | 289 | 235 | 237 | ||||||||||
Return on common equity (e) | 9.6 | % | 8.6 | % | 6.8 | % | 5.9 | % | 7.0 | % | |||||
Adjusted return on common equity – Non-GAAP (e)(f) | 10.2 | 9.5 | 8.1 | 8.3 | 8.8 | ||||||||||
Return on tangible common equity – Non-GAAP (e)(f)(g) | 21.2 | 19.7 | 16.0 | 15.3 | 19.3 | ||||||||||
Adjusted return on tangible common equity – Non-GAAP (e)(f)(g) | 21.4 | 20.7 | 17.6 | 19.7 | 21.8 | ||||||||||
Return on average assets | 0.96 | 0.82 | 0.67 | 0.60 | 0.77 | ||||||||||
Pre-tax operating margin (f) | 31 | 28 | 23 | 25 | 23 | ||||||||||
Adjusted pre-tax operating margin – Non-GAAP (e)(f) | 33 | 31 | 28 | 28 | 29 | ||||||||||
Fee revenue as a percentage of total revenue | 79 | 79 | 80 | 78 | 77 | ||||||||||
Percentage of non-U.S. total revenue | 34 | 36 | 38 | 37 | 36 | ||||||||||
Net interest margin (on a fully taxable equivalent basis) | 1.05 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 1.13 | 1.21 | ||||||||||
(a) | Primarily attributable to noncontrolling interests related to consolidated investment management funds. |
(b) | Excludes securities lending cash management assets and assets managed in the Investment Services business and the Other segment. |
(c) | Includes the assets under custody and/or administration of CIBC Mellon Global Securities Services Company (“CIBC Mellon”), a joint venture with the Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce, of $1.2 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016, $1.0 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015, $1.1 trillion at Dec. 31, 2014, $1.2 trillion at Dec. 31, 2013 and $1.1 trillion at Dec. 31, 2012. |
(d) | Represents the total amount of securities on loan managed by the Investment Services business. Excludes securities for which BNY Mellon acts as an agent, beginning in 2013, on behalf of CIBC Mellon clients, which totaled $63 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, $55 billion at Dec. 31, 2015, $65 billion at Dec. 31, 2014 and $62 billion at Dec. 31, 2013. |
(e) | See “Supplemental information – Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for the reconciliation of Non-GAAP measures. |
(f) | Non-GAAP information for all periods presented excludes net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds, amortization of intangible assets and merger and integration (“M&I”), litigation and restructuring charges. Non-GAAP information for 2016 also excludes a recovery of the previously impaired loan to Sentinel Management Group, Inc. (“Sentinel”). Non-GAAP information for 2015 also excludes the impairment charge related to a court decision regarding Sentinel. Non-GAAP information for 2014 also excludes the gains on the sales of our investment in Wing Hang Bank Limited (“Wing Hang”) and our One Wall Street building, the benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim, and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. Non-GAAP information for 2013 also excludes the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives and the net charge related to the disallowance of certain foreign tax credits. |
(g) | Tangible common equity excludes goodwill and intangible assets and related deferred tax liabilities for all periods presented. |
2 BNY Mellon
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Financial Summary (continued) |
(dollar amounts in millions, except per common share amounts and unless otherwise noted) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||
Cash dividends per common share | $ | 0.72 | $ | 0.68 | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 0.52 | |||||||||
Common dividend payout ratio | 23 | % | 25 | % | 31 | % | (a) | 34 | % | (a) | 26 | % | |||||||
Common dividend yield | 1.5 | % | 1.6 | % | 1.6 | % | 1.7 | % | 2.0 | % | |||||||||
Closing stock price per common share | $ | 47.38 | $ | 41.22 | $ | 40.57 | $ | 34.94 | $ | 25.70 | |||||||||
Market capitalization (in billions) | $ | 49.6 | $ | 44.7 | $ | 45.4 | $ | 39.9 | $ | 29.9 | |||||||||
Book value per common share – GAAP (b) | $ | 33.67 | $ | 32.69 | $ | 32.09 | $ | 31.46 | $ | 30.38 | |||||||||
Tangible book value per common share – Non-GAAP (b)(c)(d) | $ | 16.19 | $ | 15.27 | $ | 14.70 | $ | 13.95 | $ | 12.81 | |||||||||
Full-time employees | 52,000 | 51,200 | 50,300 | 51,100 | 49,500 | ||||||||||||||
Year-end common shares outstanding (in thousands) | 1,047,488 | 1,085,343 | 1,118,228 | 1,142,250 | 1,163,490 | ||||||||||||||
Average total equity to average total assets | 10.7 | % | 10.2 | % | 10.2 | % | 10.6 | % | 11.0 | % | |||||||||
Capital ratios at Dec. 31 | |||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated regulatory capital ratios: (e)(f) | |||||||||||||||||||
Standardized: | |||||||||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 12.3 | % | 11.5 | % | 15.0 | % | 14.5 | % | 13.5 | % | |||||||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 14.5 | 13.1 | 16.3 | 16.2 | 15.0 | ||||||||||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 15.2 | 13.5 | 16.9 | 17.0 | 16.3 | ||||||||||||||
Advanced: | |||||||||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 10.6 | 10.8 | 11.2 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 12.6 | 12.3 | 12.2 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 13.0 | 12.5 | 12.5 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
Leverage capital ratio (f) | 6.6 | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.4 | 5.3 | ||||||||||||||
Supplementary leverage ratio (f) | 6.0 | 5.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP (b) | 11.6 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 10.0 | 10.1 | ||||||||||||||
BNY Mellon common shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP (b) | 10.6 | 9.0 | 9.3 | 9.6 | 9.8 | ||||||||||||||
BNY Mellon tangible common shareholders’ equity to tangible assets of operations ratio – Non-GAAP (b)(d) | 6.7 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.8 | 6.3 | ||||||||||||||
Selected regulatory capital ratios - fully phased-in – Non-GAAP (g): | |||||||||||||||||||
Estimated CET1 ratio (e): | |||||||||||||||||||
Standardized Approach | 11.3 | 10.2 | 10.6 | 10.6 | N/A | ||||||||||||||
Advanced Approach | 9.7 | 9.5 | 9.8 | 11.3 | 9.8 | ||||||||||||||
Estimated SLR | 5.6 | 4.9 | 4.4 | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||
(a) | The common dividend payout ratio was 25% for 2014 after adjusting for increased litigation expense, and 26% for 2013 after adjusting for the net impact of the U.S. Tax Court’s decisions regarding certain foreign tax credits. |
(b) | See “Supplemental information – Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for the reconciliation of Non-GAAP measures. |
(c) | Non-GAAP information for all periods presented excludes net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds, amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges. Non-GAAP information for 2016 also excludes a recovery of the previously impaired loan to Sentinel. Non-GAAP information for 2015 also excludes the impairment charge related to a court decision regarding Sentinel. Non-GAAP information for 2014 also excludes the gains on the sales of our investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building, the benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim, and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. Non-GAAP information for 2013 also excludes the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives, and the net charge related to the disallowance of certain foreign tax credits. |
(d) | Tangible book value and tangible common shareholders’ equity exclude goodwill and intangible assets and related deferred tax liabilities for all periods presented. Tangible assets of operations exclude goodwill, intangible assets, assets of consolidated investment management funds and cash deposited with the Federal Reserve and other central banks for all periods presented. |
(e) | Risk-based capital ratios at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015 reflect the adoption of new accounting guidance related to Consolidations (ASU 2015-02). At Dec. 31, 2014, risk-based capital ratios include the net impact of the total consolidated assets of certain consolidated investment management funds in risk-weighted assets. These assets were not included in prior periods’ risk-based ratios. The leverage capital ratio was not impacted. |
(f) | At Dec. 31, 2016, Dec. 31. 2015 and Dec. 31, 2014, the Common Equity Tier 1 (“CET1”), Tier 1 and Total risk-based consolidated regulatory capital ratios are based on Basel III components of capital, as phased-in, and credit risk asset risk-weightings using the U.S. capital rules’ advanced approaches framework (the “Advanced Approach”). The leverage capital ratio is based on Basel III’s definition of Tier 1 capital, as phased-in, and quarterly average assets. The supplementary leverage ratio (“SLR”) is based on Tier 1 capital, as phased-in, and quarterly average assets and certain off-balance sheet exposures. The capital ratios prior to Dec. 31, 2014 are based on Basel I rules (including Basel I Tier 1 common in the case of the CET1 ratio). For additional information on these ratios, see “Capital” beginning on page 53. |
(g) | The estimated fully phased-in CET1 and SLR ratios (Non-GAAP) are based on our interpretation of the U.S. capital rules, which are being gradually phased-in over a multi-year period. For additional information on these Non-GAAP ratios, see “Capital” beginning on page 53. |
BNY Mellon 3
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
Results of Operations |
General
In this Annual Report, references to “our,” “we,” “us,” “BNY Mellon,” the “Company” and similar terms refer to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term “Parent” refers to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation but not its subsidiaries.
BNY Mellon’s actual results of future operations may differ from those estimated or anticipated in certain forward-looking statements contained herein for reasons which are discussed below and under the heading “Forward-looking Statements.” When used in this Annual Report, words such as “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “anticipate,” “likely,” “target,” “expect,” “intend,” “continue,” “seek,” “believe,” “plan,” “goal,” “could,” “should,” “would,” “may,” “will,” “strategy,” “synergies,” “opportunities,” “trends” and words of similar meaning may signify forward-looking statements.
Certain business terms and commonly used acronyms used in this Annual Report are defined in the Glossary and Acronyms sections.
The following should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this report. Investors should also read the section titled “Forward-looking Statements.”
How we reported results
Throughout this Annual Report, certain measures, which are noted as “Non-GAAP financial measures,” exclude certain items or otherwise include components that differ from U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). BNY Mellon believes that these measures are useful to investors because they permit a focus on period-to-period comparisons using measures that relate to our ability to enhance revenues and limit expenses in circumstances where such matters are within our control or because they provide additional information about our ability to meet fully phased-in capital requirements. See “Supplemental information - Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for a reconciliation of financial measures presented in accordance with GAAP to adjusted Non-GAAP financial measures.
See “Capital” beginning on page 53 for information on our fully phased-in capital requirements.
We also present net interest revenue and net interest margin on a fully taxable equivalent (“FTE”) basis. We believe that this presentation allows for comparisons of amounts arising from both taxable and tax-exempt sources and is consistent with industry practice. The adjustment to an FTE basis has no impact on net income.
Overview
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation was the first company listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE symbol: BK). With a rich history of maintaining our financial strength and stability through all business cycles, BNY Mellon is a global investments company dedicated to improving lives through investing.
We manage and service assets for financial institutions, corporations and individual investors in 35 countries and more than 100 markets. As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon had $29.9 trillion in assets under custody and/or administration (“AUC/A”), and $1.6 trillion in assets under management (“AUM”).
BNY Mellon is focused on enhancing our clients’ experience by leveraging our scale and expertise to deliver innovative and strategic solutions for our clients, building trusted relationships that drive value. We hold a unique position in the global financial services industry. We service both the buy-side and sell-side, providing us with distinctive marketplace insights that enable us to support our clients’ success.
BNY Mellon’s businesses benefit from global growth in financial assets, the globalization of the investment process, changes in demographics and the continued evolution of the regulatory landscape—each providing us with opportunities to advise and service clients.
Strategy and priorities
Our strategy is designed to differentiate our services to create competitive advantages that will deliver value to our clients and shareholders, thereby creating economic value.
4 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
In late 2014, we shared our three-year strategic plan, including financial goals, at our Investor Day—a plan designed to set us on a path of continuous improvement as we transform our organization to drive growth across the enterprise and power investment success for our clients.
Even with geopolitical instability, emerging market weakness, higher regulatory compliance requirements and low interest rates during 2016, we again demonstrated that our strategic plan has positioned us to perform well, delivering 16% growth, or 11% growth on an adjusted basis (Non-GAAP), in diluted earnings per share year-over-year.
With technological change accelerating, regulatory complexities continuing and investor appetites shifting, our plan is poised to continue to deliver increasing and compelling value to our clients.
With NEXEN®, our next generation digital technology ecosystem, we are leading the digital transformation of BNY Mellon and the services we provide to our clients. NEXEN® should provide us with many competitive advantages. It is creating internal efficiencies while reducing costs and increasing speed of delivery, enhancing our clients’ experience and driving revenue opportunities as we continue to onboard clients to our new digital platform. We are collaborating with clients and leading financial technology startups, or fintechs, to develop and integrate new solutions and services, and attracting top information technology talent through our Innovation Centers worldwide.
Importantly, NEXEN® is making it easier for clients to do business with us by providing a gateway that will enable access to all of BNY Mellon’s services on desktops and mobile devices, anywhere, anytime.
Our top priorities, as outlined in our strategic plan, include:
• | driving profitable revenue growth and enhancing the client experience. We are leveraging our expertise and scale, making it easier to do business with us across our digital enterprise, and offering broad-based, innovative solutions to our clients; |
• | executing our business improvement processes to increase productivity and effectiveness while |
controlling expenses, enhancing our efficiency and continuing to rationalize our portfolio of businesses and services;
• | being a strong, trusted counterparty by maintaining our safety and soundness, low-risk business model and strong liquidity and capital positions; |
• | generating excess capital and deploying it effectively; and |
• | attracting, developing and retaining top talent. |
In 2016, we continued to execute against these priorities and deliver on our three-year plan.
Our key growth initiatives include driving profitable revenue growth by expanding middle-office outsourcing, growing our alternatives servicing business and developing our collateral management services, as well as lowering costs and reducing risks. These efforts will extend into the foreseeable future as we continue to leverage our strengths and unique capabilities while we transform our company to remain a global leader in investment services and investment management.
Increasing Safety and Soundness
As we execute our strategy, we are continuing to drive efficient regulatory compliance for us and for our clients globally. Excellence in risk management is essential, and we continue to invest in systems and capabilities to comply with evolving global regulations.
Maintaining our strong capital position is a priority as we seek to maintain our balance sheet strength and deploy our capital efficiently to fuel future growth and to return value to shareholders. In 2016, we returned $3.2 billion to our shareholders consisting of $778 million in common stock dividends and $2.4 billion in share repurchases.
With respect to our capital ratios, we expect the CET1 ratio to remain at least 100 basis points above the regulatory minimum requirement plus the applicable buffers. As a U.S. G-SIB, we are also subject to the SLR. We currently expect to maintain an SLR ratio of at least 50 basis points above the regulatory minimum requirement plus the applicable buffer.
BNY Mellon 5
Results of Operations (continued) |
Key 2016 events
Resolution plan
In April 2016, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”) and the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve”) jointly announced determinations and provided firm-specific feedback on the 2015 resolution plans of eight systemically important domestic banking institutions, including BNY Mellon. The agencies determined that the Company’s 2015 resolution plan was not credible or would not facilitate an orderly resolution under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, the statutory standard established in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 (the “Dodd-Frank Act”), and issued a joint notice of deficiencies and shortcomings regarding the Company’s plan and the actions that must be taken to address them, which we responded to in an Oct. 1, 2016 submission. In December 2016, the agencies jointly determined that our Oct. 1, 2016 submission adequately remedied the identified deficiencies. We have devoted significant resources to continue to strengthen our resolvability and our resolution plan, and will deploy additional resources to further that objective in consultation with our regulators. We estimate that our resolution planning may require us to issue incremental unsecured long-term debt above our typical funding requirements to satisfy resource needs in a time of distress. This estimate is subject to change as we further refine our strategy and related assumptions. Currently additional debt is not expected to have a material impact to our financial statements.
Capital plan, share repurchase program, preferred stock issuance and increase in cash dividend on common stock
In June 2016, BNY Mellon received confirmation that the Federal Reserve did not object to its 2016 capital plan submitted to the Federal Reserve in connection with its Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (“CCAR”). The board of directors subsequently approved the total repurchase of $2.7 billion worth of common stock over a four-quarter period beginning in the third quarter of 2016 and continuing through the second quarter of 2017. In connection with our capital plan, in August 2016, BNY Mellon issued $1 billion of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock. This new share repurchase plan replaces all previously authorized share repurchase plans.
We repurchased 30.0 million common shares for $1.3 billion during the second half of 2016 under the current program, including employee benefit plan repurchases. We expect to continue to repurchase shares in the first half of 2017 under the 2016 capital plan.
Also included in the 2016 capital plan was a 12% increase in the quarterly cash dividend on common stock, from $0.17 to $0.19 per share. The first payment of the increased quarterly cash dividend was Aug. 12, 2016.
Acquisition of Atherton Lane Advisers, LLC
In April 2016, BNY Mellon completed the acquisition of the assets of Menlo Park, CA-based Atherton Lane Advisers, LLC, an investment manager with approximately $2.45 billion in AUM and servicer for approximately 700 high net worth clients.
Summary of financial highlights
We reported net income applicable to common shareholders of $3.4 billion, or $3.15 per diluted common share, in 2016, or $3.5 billion, or $3.17 per diluted common share, adjusted for M&I, litigation and restructuring charges and the recovery related to Sentinel (Non-GAAP). In 2015, net income applicable to common shareholders was $3.1 billion, or $2.71 per diluted common share, or $3.2 billion, or $2.85 per diluted common share, adjusted for the impairment charge related to Sentinel, litigation and restructuring charges (Non-GAAP). See “Supplemental information - Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for the reconciliation of Non-GAAP measures.
Highlights of 2016 results
• | AUC/A totaled $29.9 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $28.9 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase of 3% primarily reflects higher market values, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar. (See “Investment Services business” beginning on page 22.) |
• | AUM totaled $1.65 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $1.63 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase of 1% primarily resulted from higher market values offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally |
6 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
versus the British pound). AUM excludes securities lending cash management assets and assets managed in the Investment Services business. (See “Investment Management business” beginning on page 18.)
• | Investment services fees totaled $7.2 billion in 2016, an increase of 2% compared with $7.1 billion in 2015 primarily reflecting higher money market fees and securities lending revenue, partially offset by the impact to clearing services of lost business, the impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and downsizing the UK retail transfer agency business. (See “Investment Services business” beginning on page 22.) |
• | Investment management and performance fees totaled $3.35 billion in 2016 compared with $3.44 billion in 2015, a decrease of 3%, due to the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound), net outflows of AUM and lower performance fees, partially offset by higher market values and money market fees. (See “Investment Management business” beginning on page 18.) |
• | Foreign exchange and other trading revenue totaled $701 million in 2016 compared with $768 million in 2015. Foreign exchange revenue totaled $687 million in 2016, a decrease of 8% compared with $743 million in 2015. The decrease in foreign exchange revenue primarily reflects the continued trend of clients migrating to lower margin products and lower volumes. (See “Fee and other revenue” beginning on page 9.) |
• | Financing-related fees totaled $219 million in 2016 compared with $220 million in 2015. (See “Fee and other revenue” beginning on page 9.) |
• | Net interest revenue totaled $3.1 billion in 2016 compared with $3.0 billion in 2015. The increase was primarily driven by an increase in interest rates, partially offset by lower interest-earning assets. Net interest margin (FTE) was 1.05% in 2016 compared with 0.98% in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher yields on interest-earning assets, partially offset by higher rates paid on interest-bearing liabilities. (See “Net interest revenue” beginning on page 12.) |
• | The provision for credit losses was a credit of $11 million in 2016 and a provision of $160 million in 2015. The provision in 2015 was primarily driven by an impairment charge related to a court decision regarding Sentinel. (See “Asset quality |
and allowance for credit losses” beginning on page 43.)
• | Noninterest expense totaled $10.5 billion in 2016 compared with $10.8 billion in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower expenses in nearly all categories, except distribution and servicing and software expenses, primarily driven by the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, lower staff, litigation and legal expenses and the continued benefit of the business improvement process. (See “Noninterest expense” beginning on page 15.) |
• | The provision for income taxes was $1.2 billion (24.9% effective tax rate) in 2016. (See “Income taxes” on page 16.) |
• | The net unrealized pre-tax loss on the investment securities portfolio was $221 million at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with a pre-tax gain of $357 million at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease was primarily driven by higher market interest rates. (See “Investment securities” beginning on page 37.) |
• | Our CET1 ratio determined under the Advanced Approach was 10.6% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 10.8% at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease reflects lower regulatory capital primarily due to common stock repurchases, foreign currency translation, defined benefit plan adjustments and unrealized losses on securities, partially offset by earnings retention. (See “Capital” beginning on page 53.) |
• | Our estimated CET1 ratio (Non-GAAP) calculated under the Advanced Approach on a fully phased-in basis was 9.7% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 9.5% at Dec. 31, 2015. Our estimated CET1 ratio (Non-GAAP) calculated under the Standardized Approach on a fully phased-in basis was 11.3% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 10.2% at Dec. 31, 2015. (See “Capital” beginning on page 53.) |
Results for 2015
In 2015, we reported net income applicable to common shareholders of BNY Mellon of $3.1 billion, or $2.71 per diluted common share. These results were primarily driven by:
• | Investment services fees totaled $7.1 billion in 2015, an increase of 2% compared with $6.9 billion in 2014. Higher asset servicing fees, reflecting growth in collateral, broker-dealer and other asset services, and higher clearing services |
BNY Mellon 7
Results of Operations (continued) |
fees, primarily driven by higher mutual fund fees, were partially offset by lower treasury services fees.
• | Investment management and performance fees totaled $3.4 billion in 2015, a 2% decrease compared with $3.5 billion in 2014. The decrease primarily reflects the impact of the July 2015 sale of Meriten Investment Management GmbH (“Meriten”) and lower performance fees, partially offset by the impact of the January 2015 acquisition of Cutwater Asset Management (“Cutwater”) and strategic initiatives and higher money market fees and equity market values. |
• | Foreign exchange and other trading revenue totaled $768 million in 2015, compared with $570 million in 2014. The increase primarily reflects lower volumes in standing instruction programs, which were more than offset by higher volumes in the other trading programs, higher volatility and the impact of hedging activity for foreign currency placements. |
• | The provision for credit losses was $160 million in 2015 compared with a credit of $48 million in 2014. The provision in 2015 was primarily driven by an impairment charge related to a court decision regarding Sentinel. |
• | Noninterest expense totaled $10.8 billion in 2015 compared with $12.2 billion in 2014. The decrease primarily reflects lower expenses in nearly all categories, except distribution and servicing and software expenses. The lower expenses were primarily driven by the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, lower staff, litigation and legal expenses and the continued benefit of the business improvement process which focuses on reducing structural costs. |
• | The provision for income taxes was $1.0 billion (23.9% effective tax rate) in 2015. |
Results for 2014
In 2014, we reported net income applicable to common shareholders of BNY Mellon of $2.5 billion, or $2.15 per diluted common share. These results were primarily driven by:
• | Investment services fees totaled $6.9 billion primarily reflecting higher asset servicing fees, driven by organic growth, higher market values, higher collateral management fees and net new business, as well as higher clearing services fees, primarily driven by higher mutual fund and asset-based fees, partially offset by lower Corporate Trust fees and lower corporate actions and dividend fees in Depositary Receipts. |
• | Investment management and performance fees totaled $3.5 billion primarily driven by higher equity market values, net new business and the favorable impact of a weaker U.S. dollar, partially offset by higher money market fee waivers and lower performance fees. |
• | Foreign exchange and other trading revenue totaled $570 million primarily reflecting lower volatility, partially offset by higher volumes. |
• | Investment and other income totaled $1.2 billion primarily reflecting the gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and the One Wall Street building, partially offset by lower equity investment revenue. |
• | Noninterest expense totaled $12.2 billion primarily reflecting higher litigation expense and restructuring charges, partially offset by lower staff expense. |
• | The provision for income taxes was $912 million (25.6% effective tax rate) including a net benefit primarily related to litigation expense and the approval of a tax carryback claim, offset by the sales of our investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building. |
8 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Fee and other revenue
Fee and other revenue | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
vs. | vs. | ||||||||||||
(dollars in millions, unless otherwise noted) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Investment services fees: | |||||||||||||
Asset servicing (a) | $ | 4,244 | $ | 4,187 | $ | 4,075 | 1 | % | 3 | % | |||
Clearing services | 1,404 | 1,375 | 1,335 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||
Issuer services | 1,026 | 978 | 968 | 5 | 1 | ||||||||
Treasury services | 547 | 555 | 564 | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Total investment services fees | 7,221 | 7,095 | 6,942 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
Investment management and performance fees | 3,350 | 3,438 | 3,492 | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue | 701 | 768 | 570 | (9 | ) | 35 | |||||||
Financing-related fees | 219 | 220 | 169 | — | 30 | ||||||||
Distribution and servicing | 166 | 162 | 173 | 2 | (6 | ) | |||||||
Investment and other income | 341 | 316 | 1,212 | 8 | N/M | ||||||||
Total fee revenue | 11,998 | 11,999 | 12,558 | — | (4 | ) | |||||||
Net securities gains | 75 | 83 | 91 | (10 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
Total fee and other revenue | $ | 12,073 | $ | 12,082 | $ | 12,649 | — | % | (4 | )% | |||
Fee revenue as a percentage of total revenue | 79 | % | 79 | % | 80 | % | |||||||
AUM at period end (in billions) (b) | $ | 1,648 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | 1 | % | (4 | )% | |||
AUC/A at period end (in trillions) (c) | $ | 29.9 | $ | 28.9 | $ | 28.5 | 3 | % | 1 | % | |||
(a) | Asset servicing fees include securities lending revenue of $207 million in 2016, $176 million in 2015 and $158 million in 2014. |
(b) | Excludes securities lending cash management assets and assets managed in the Investment Services business and the Other segment. |
(c) | Includes the AUC/A of CIBC Mellon of $1.2 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016, $1.0 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015 and $1.1 trillion at Dec. 31, 2014. |
Fee and other revenue totaled $12.07 billion in 2016, a slight decrease compared with $12.08 billion in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower investment management and performance fees and foreign exchange and other trading revenue, partially offset by higher investment services fees and investment and other income.
Investment services fees
Investment services fees were impacted by the following compared with 2015:
• | Asset servicing fees increased 1%, primarily reflecting higher money market fees and securities lending revenue, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and downsizing of the UK retail transfer agency business. |
• | Clearing services fees increased 2%, primarily driven by higher money market fees, partially offset by the impact of lost business and client business exits related to the broker-dealer industry consolidations. |
• | Issuer services fees increased 5%, primarily reflecting higher money market fees in Corporate Trust and higher fees in Depositary Receipts. |
• | Treasury services fees decreased 1%, primarily reflecting higher compensating balance credits provided to clients, which reduced fee revenue and increased net interest revenue, partially offset by higher payments and banking transaction services volumes. |
See the “Investment Services business” in “Review of businesses” for additional details.
Investment management and performance fees
Investment management and performance fees totaled $3.4 billion in 2016, a decrease of 3% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound), net outflows of AUM and lower performance fees, partially offset by higher market values and money market fees. Performance fees were $60 million in 2016 and $97 million in 2015.
BNY Mellon 9
Results of Operations (continued) |
Total AUM for the Investment Management business was $1.65 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016, an increase of 1% compared with $1.63 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher market values offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound). Net long-term outflows of $14 billion in 2016 were a combination of $17 billion of inflows into actively managed strategies and $31 billion of outflows from index strategies. Net short-term outflows totaled $9 billion in 2016.
See the “Investment Management business” in “Review of businesses” for additional details regarding the drivers of investment management and performance fees.
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Foreign exchange | $ | 687 | $ | 743 | $ | 578 | |||
Other trading revenue (loss) | 14 | 25 | (8 | ) | |||||
Total foreign exchange and other trading revenue | $ | 701 | $ | 768 | $ | 570 | |||
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue totaled $701 million in 2016, a decrease of 9%, compared with $768 million in 2015.
Foreign exchange revenue is primarily driven by the volume of client transactions and the spread realized on these transactions, both of which are impacted by market volatility, and the impact of foreign currency hedging activities. In 2016, foreign exchange revenue totaled $687 million, a decrease of 8% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the continued trend of clients migrating to lower margin products and lower volumes. Foreign exchange revenue is primarily reported in the Investment Services business and, to a lesser extent, the Investment Management and the Other segment.
Our custody clients may enter into foreign exchange transactions in a number of ways, including through our standing instruction programs. A shift by custody
clients from our standing instruction programs to other trading options combined with competitive market pressures on the foreign exchange business is negatively impacting our foreign exchange revenue. For the year ended Dec. 31, 2016, our total revenue for all types of foreign exchange trading transactions was $687 million, or 5% of our total revenue, and approximately 30% of our foreign exchange revenue was generated by transactions in our standing instruction programs, compared with 33% in 2015 and 35% in 2014.
Total other trading revenue was $14 million in 2016, compared with $25 million in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower results from equity and credit derivatives trading, partially offset by higher fixed income trading. Other trading revenue is reported in all three business segments.
Financing-related fees
Financing-related fees, which are primarily reported in the Investment Services business and the Other segment, include capital markets fees, loan commitment fees and credit-related fees. Financing-related fees totaled $219 million in 2016, compared with $220 million in 2015, as lower fees on standby letters of credit were essentially offset by higher fees related to secured intraday credit provided to dealers in connection with their tri-party repo activity.
Distribution and servicing fees
Distribution and servicing fees earned from mutual funds are primarily based on average assets in the funds and the sales of funds that we manage or administer and are primarily reported in the Investment Management business. These fees, which include 12b-1 fees, fluctuate with the overall level of net sales, the relative mix of sales between share classes, the funds’ market values and money market fee waivers.
Distribution and servicing fees were $166 million in 2016 compared with $162 million in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher money market fees, partially offset by fees paid to introducing brokers.
10 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Investment and other income
Investment and other income | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Corporate/bank-owned life insurance | $ | 149 | $ | 139 | $ | 131 | |||
Expense reimbursements from joint venture | 67 | 63 | 55 | ||||||
Seed capital gains (a) | 44 | 35 | 20 | ||||||
Lease-related gains | 38 | 45 | 49 | ||||||
Asset-related gains | 10 | — | 872 | ||||||
Equity investment (losses) income | (10 | ) | (19 | ) | 1 | ||||
Other income | 43 | 53 | 84 | ||||||
Total investment and other income | $ | 341 | $ | 316 | $ | 1,212 | |||
(a) | Does not include the gain on seed capital investments in consolidated investment management funds which are reflected in operations of consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests. The gain on seed capital investments in consolidated investment management funds was $16 million in 2016, $18 million in 2015 and $79 million in 2014. |
Investment and other income includes corporate and bank-owned life insurance contracts, expense reimbursements from our CIBC Mellon joint venture, and gains or losses from seed capital, leases, equity investments and other assets, as well as other income. Expense reimbursements from our CIBC Mellon joint venture relate to expenses incurred by BNY Mellon on behalf of the CIBC Mellon joint venture. Asset-related gains include real estate, loan and other asset dispositions. Other income primarily includes foreign currency remeasurement gain (loss), other investments and various miscellaneous revenues. Investment and other income was $341 million in 2016 compared with $316 million in 2015. The increase primarily reflects foreign currency remeasurement gains, higher income from corporate/bank-owned life insurance, asset-related gains, seed capital gains and lower losses on equity investments, partially offset by lower other income driven by lower dividends on Federal Reserve Bank stock, termination fees in our clearing business recorded in 2015 and the impact of increased investments in renewable energy. Investments in renewable energy generate losses in other income that are more than offset by benefits recorded to the provision for income taxes. As a result of increased investments in renewable energy in 2016, we expect investment and other income to be negatively impacted in future periods.
Net securities gains
Net securities gains totaled $75 million in 2016 and $83 million in 2015.
2015 compared with 2014
Fee and other revenue totaled $12.1 billion in 2015 compared with $12.6 billion in 2014. The decrease primarily reflects the gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building, both recorded in 2014, and lower investment management and performance fees, partially offset by higher foreign exchange and other trading revenue, investment services fees and financing-related fees.
The increase in investment services fees primarily reflects higher asset servicing fees driven by growth in global collateral services, broker-dealer services and asset servicing, and higher clearing services fees driven by higher mutual fund and asset-based fees, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lost business.
The decrease in investment management and performance fees primarily reflects the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound), the impact of the July 2015 sale of Meriten and lower performance fees, partially offset by the impact of the January 2015 acquisition of Cutwater, strategic initiatives and higher money market fees and equity market values.
The increase in foreign exchange and other trading revenue primarily reflects lower volumes in standing instruction programs, which were more than offset by higher volumes in the other trading programs, higher volatility, the impact of hedging activity for foreign currency placements and higher fixed income trading and losses on hedging activities within a boutique recorded in 2014.
The increase in financing-related fees primarily reflects fees related to secured intraday credit provided to dealers in connection with their tri-party repo activity and higher underwriting fees.
BNY Mellon 11
Results of Operations (continued) |
Net interest revenue
Net interest revenue | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
vs. | vs. | ||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Net interest revenue (non-FTE) | $ | 3,138 | $ | 3,026 | $ | 2,880 | 4% | 5% | |||||
Tax equivalent adjustment | 51 | 58 | 62 | (12 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Net interest revenue (FTE) | $ | 3,189 | $ | 3,084 | $ | 2,942 | 3% | 5% | |||||
Average interest-earning assets | $ | 303,379 | $ | 313,763 | $ | 303,991 | (3)% | 3% | |||||
Net interest margin (FTE) | 1.05 | % | 0.98 | % | 0.97 | % | 7 | bps | 1 | bps | |||
Net interest revenue totaled $3.1 billion in 2016, an increase of $112 million, compared with 2015. The increase was primarily driven by an increase in interest rates, partially offset by lower interest-earning assets.
The net interest margin (FTE) was 1.05% in 2016, compared with 0.98% in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher yields on interest-earning assets, partially offset by higher rates paid on interest-bearing liabilities.
Effective Oct. 1, 2016, we changed our accounting method for the amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts on mortgage-backed securities from the prepayment method (also referred to as the retrospective method) to the contractual method. The impact of this change was not considered material to prior periods and, as a result, the cumulative effect of the change of approximately $15 million was reflected as a positive adjustment to net interest revenue in the fourth quarter of 2016. For additional information on the change in accounting methodology, see Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Average interest-earning assets were $303 billion in 2016 compared with $314 billion in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower average interest-bearing deposits with banks, Federal Reserve and other central banks. The lower asset levels reflect a decrease in customer deposits, primarily interest bearing deposits in non-U.S. offices.
Average non-U.S. dollar deposits comprised approximately 20% of our average total deposits in 2016, compared with approximately 25% in 2015. Approximately 40% of the average non-U.S. dollar deposits in 2016, compared with approximately half of the average non-U.S. dollar deposits in 2015, were euro-denominated.
2015 compared with 2014
Net interest revenue totaled $3.0 billion in 2015, an increase of $146 million, compared with 2014 primarily resulting from the shift out of cash and into securities and loans, lower interest expense on deposits and higher average interest-earning assets driven by higher deposits, partially offset by lower accretion. The net interest margin (FTE) was 0.98% in 2015, compared with 0.97% in 2014. The increase in the net interest margin (FTE) reflects lower interest rates on deposits.
12 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Average balances and interest rates | 2016 | |||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions, presented on an FTE basis) | Average balance | Interest | Average rates | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: | ||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks (primarily foreign banks) | $ | 14,704 | $ | 104 | 0.70 | % | ||||
Interest-bearing deposits held at the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 80,593 | 198 | 0.25 | |||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 25,767 | 233 | 0.91 | |||||||
Margin loans | 18,201 | 265 | 1.46 | |||||||
Non-margin loans: | ||||||||||
Domestic offices: | ||||||||||
Consumer | 8,483 | 259 | 3.05 | |||||||
Commercial | 21,820 | 417 | 1.91 | |||||||
Foreign offices | 13,177 | 197 | 1.50 | |||||||
Total non-margin loans | 43,480 | 873 | (a) | 2.01 | ||||||
Securities: | ||||||||||
U.S. government obligations | 25,074 | 378 | 1.51 | |||||||
U.S. government agency obligations | 56,384 | 986 | 1.75 | |||||||
State and political subdivisions – tax-exempt | 3,703 | 110 | 2.96 | |||||||
Other securities: | ||||||||||
Domestic offices | 12,326 | 210 | 1.71 | |||||||
Foreign offices | 20,664 | 206 | 1.00 | |||||||
Total other securities | 32,990 | 416 | 1.26 | |||||||
Trading securities (primarily domestic) | 2,483 | 63 | 2.56 | |||||||
Total securities | 120,634 | 1,953 | 1.62 | |||||||
Total interest-earning assets | $ | 303,379 | $ | 3,626 | (b) | 1.20 | % | |||
Allowance for loan losses | (158 | ) | ||||||||
Cash and due from banks | 4,308 | |||||||||
Other assets | 49,799 | |||||||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds | 1,149 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 358,477 | ||||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||||
Interest-bearing liabilities: | ||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits: | ||||||||||
Domestic offices: | ||||||||||
Money market rate accounts | $ | 7,780 | $ | 4 | 0.06 | % | ||||
Savings | 1,191 | 4 | 0.37 | |||||||
Demand deposits | 2,520 | 7 | 0.28 | |||||||
Time deposits | 43,056 | 26 | 0.06 | |||||||
Total domestic offices | 54,547 | 41 | 0.08 | |||||||
Foreign offices: | ||||||||||
Banks | 13,130 | 12 | 0.09 | |||||||
Government and official institutions | 4,159 | — | 0.01 | |||||||
Other | 85,110 | (37 | ) | (0.04 | ) | |||||
Total foreign offices | 102,399 | (25 | ) | (0.02 | ) | |||||
Total interest-bearing deposits | 156,946 | 16 | 0.01 | |||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | 14,489 | 36 | 0.25 | |||||||
Trading liabilities | 711 | 6 | 0.89 | |||||||
Other borrowed funds: | ||||||||||
Domestic offices | 93 | 4 | 4.15 | |||||||
Foreign offices | 753 | 4 | 0.51 | |||||||
Total other borrowed funds | 846 | 8 | 0.91 | |||||||
Commercial paper | 1,337 | 5 | 0.37 | |||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | 16,925 | 12 | 0.07 | |||||||
Long-term debt | 23,334 | 354 | 1.52 | |||||||
Total interest-bearing liabilities | $ | 214,588 | $ | 437 | 0.20 | % | ||||
Total noninterest-bearing deposits | 82,712 | |||||||||
Other liabilities | 21,683 | |||||||||
Liabilities and obligations of consolidated investment management funds | 245 | |||||||||
Total liabilities | 319,228 | |||||||||
Temporary equity | ||||||||||
Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 182 | |||||||||
Permanent equity | ||||||||||
Total BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity | 38,489 | |||||||||
Noncontrolling interests | 578 | |||||||||
Total permanent equity | 39,067 | |||||||||
Total liabilities, temporary equity and permanent equity | $ | 358,477 | ||||||||
Net interest margin (FTE) | 1.05 | % | ||||||||
Percentage of assets attributable to foreign offices (c) | 29 | % | ||||||||
Percentage of liabilities attributable to foreign offices | 36 | |||||||||
Note: | Interest and average rates were calculated on a taxable equivalent basis using dollar amounts in thousands and actual number of days in the year. |
(a) | Includes fees of $10 million in 2016. Non-accrual loans are included in average loans; the associated income, which was recognized on a cash basis, is included in interest income. |
(b) | The tax equivalent adjustment was $51 million in 2016, and was based on the applicable tax rate (35%). |
(c) | Includes the Cayman Islands branch office. |
BNY Mellon 13
Results of Operations (continued) |
Average balances and interest rates (continued) | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions, presented on an FTE basis) | Average balance | Interest | Average rates | Average balance | Interest | Average rates | |||||||||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks (primarily foreign banks) | $ | 20,531 | $ | 104 | 0.51 | % | $ | 35,588 | $ | 238 | 0.67 | % | |||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits held at the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 83,029 | 170 | 0.20 | 86,594 | 207 | 0.24 | |||||||||||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 23,384 | 147 | 0.63 | 14,704 | 86 | 0.59 | |||||||||||||||
Margin loans | 19,917 | 207 | 1.04 | 17,484 | 182 | 1.04 | |||||||||||||||
Non-margin loans: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 7,145 | 217 | 3.03 | 6,461 | 199 | 3.08 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial | 19,647 | 346 | 1.76 | 16,923 | 328 | 1.93 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign offices | 13,963 | 164 | 1.18 | 13,342 | 170 | 1.28 | |||||||||||||||
Total non-margin loans | 40,755 | 727 | (a) | 1.78 | 36,726 | 697 | (a) | 1.90 | |||||||||||||
Securities: | |||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. government obligations | 25,904 | 378 | 1.46 | 20,545 | 310 | 1.51 | |||||||||||||||
U.S. government agency obligations | 55,044 | 967 | 1.76 | 45,313 | 781 | 1.72 | |||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions – tax-exempt | 4,712 | 128 | 2.73 | 6,070 | 154 | 2.56 | |||||||||||||||
Other securities: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices | 14,644 | 302 | 2.06 | 15,116 | 235 | 1.56 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign offices | 22,889 | 176 | 0.77 | 20,827 | 283 | 1.36 | |||||||||||||||
Total other securities | 37,533 | 478 | 1.27 | 35,943 | 518 | 1.44 | |||||||||||||||
Trading securities (primarily domestic) | 2,954 | 78 | 2.65 | 5,024 | 123 | 2.43 | |||||||||||||||
Total securities | 126,147 | 2,029 | 1.61 | 112,895 | 1,886 | 1.67 | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets | $ | 313,763 | $ | 3,384 | (b) | 1.08 | % | $ | 303,991 | $ | 3,296 | (b) | 1.08 | % | |||||||
Allowance for loan losses | (186 | ) | (195 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Cash and due from banks | 6,180 | 5,472 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other assets | 50,320 | 52,648 | |||||||||||||||||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds | 2,110 | 10,650 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 372,187 | $ | 372,566 | |||||||||||||||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Money market rate accounts | $ | 7,272 | $ | 6 | 0.08 | % | $ | 5,605 | $ | 7 | 0.12 | % | |||||||||
Savings | 1,312 | 4 | 0.28 | 1,186 | 3 | 0.28 | |||||||||||||||
Demand deposits | 2,792 | 6 | 0.23 | 2,810 | 4 | 0.14 | |||||||||||||||
Time deposits | 44,162 | 14 | 0.03 | 41,779 | 15 | 0.04 | |||||||||||||||
Total domestic office | 55,538 | 30 | 0.06 | 51,380 | 29 | 0.06 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign offices: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Banks | 16,626 | 10 | 0.06 | 7,303 | 31 | 0.42 | |||||||||||||||
Government and official institutions | 5,591 | — | — | 4,572 | — | 0.01 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 87,341 | (3 | ) | — | 97,543 | 23 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||
Total foreign offices | 109,558 | 7 | 0.01 | 109,418 | 54 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing deposits | 165,096 | 37 | 0.02 | 160,798 | 83 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | 16,452 | (6 | ) | (0.04 | ) | 18,631 | (13 | ) | (0.07 | ) | |||||||||||
Trading liabilities | 634 | 9 | 1.39 | 2,199 | 25 | 1.12 | |||||||||||||||
Other borrowed funds: | |||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices | 162 | 4 | 2.77 | 183 | 2 | 1.32 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign offices | 652 | 5 | 0.71 | 844 | 4 | 0.45 | |||||||||||||||
Total other borrowed funds | 814 | 9 | 1.12 | 1,027 | 6 | 0.61 | |||||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 1,549 | 2 | 0.10 | 2,546 | 2 | 0.08 | |||||||||||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | 11,649 | 7 | 0.06 | 9,502 | 9 | 0.09 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 20,832 | 242 | 1.16 | 20,601 | 242 | 1.17 | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing liabilities | $ | 217,026 | $ | 300 | 0.14 | % | $ | 215,304 | $ | 354 | 0.16 | % | |||||||||
Total noninterest-bearing deposits | 86,338 | 81,741 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other liabilities | 29,127 | 26,912 | |||||||||||||||||||
Liabilities and obligations of consolidated investment management funds | 832 | 9,315 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 333,323 | 333,272 | |||||||||||||||||||
Temporary equity | |||||||||||||||||||||
Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 240 | 242 | |||||||||||||||||||
Permanent equity | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity | 37,812 | 38,180 | |||||||||||||||||||
Noncontrolling interests | 812 | 872 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total permanent equity | 38,624 | 39,052 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities, temporary equity and permanent equity | $ | 372,187 | $ | 372,566 | |||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin (FTE) | 0.98 | % | 0.97 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Percentage of assets attributable to foreign offices (c) | 30 | % | 31 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Percentage of liabilities attributable to foreign offices | 37 | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||
Note: | Interest and average rates were calculated on a taxable equivalent basis using dollar amounts in thousands and actual number of days in the year. |
(a) | Includes fees of $21 million in 2015 and $29 million in 2014. Non-accrual loans are included in the average loans; the associated income, which was recognized on a cash basis, is included in interest income. |
(b) | The tax equivalent adjustment was $58 million in 2015 and $62 million in 2014, and was based on the applicable tax rate (35%). |
(c) | Includes the Cayman Islands branch office. |
14 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Noninterest expense
Noninterest expense | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
vs. | vs. | ||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Staff | $ | 5,733 | $ | 5,837 | $ | 5,845 | (2 | )% | — | % | |||
Professional, legal and other purchased services | 1,185 | 1,230 | 1,339 | (4 | ) | (8 | ) | ||||||
Software | 647 | 627 | 620 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||
Net occupancy | 590 | 600 | 610 | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Distribution and servicing | 405 | 381 | 428 | 6 | (11 | ) | |||||||
Furniture and equipment | 247 | 280 | 322 | (12 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||||
Sub-custodian | 245 | 270 | 286 | (9 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Business development | 245 | 267 | 268 | (8 | ) | — | |||||||
Other | 940 | 961 | 1,031 | (2 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | 298 | (9 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||
M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | 1,130 | N/M | N/M | ||||||||
Total noninterest expense – GAAP | $ | 10,523 | $ | 10,799 | $ | 12,177 | (3 | )% | (11 | )% | |||
Staff expense as a percentage of total revenue | 38 | % | 38 | % | 37 | % | |||||||
Full-time employees at period end | 52,000 | 51,200 | 50,300 | 2 | % | 2 | % | ||||||
Memo: | |||||||||||||
Adjusted total noninterest expense excluding amortization of intangible assets, M&I, litigation and restructuring charges and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 10,237 | $ | 10,453 | $ | 10,645 | (2 | )% | (2 | )% | |||
(a) | The charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives, was $104 million in 2014. |
Total noninterest expense was $10.5 billion in 2016, a decrease of 3% compared with $10.8 billion in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower expenses in nearly all categories, except distribution and servicing and software expenses, primarily driven by the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, lower staff, litigation and legal expenses and the continued benefit of the business improvement process. Excluding amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges, noninterest expense, as adjusted (Non-GAAP), decreased 2% compared with 2015.
We continue to invest in our risk management, regulatory compliance and other control functions to improve our safety and soundness and in light of increasing global regulatory requirements. We expect the run rate of the expenses relating to these functions to continue to increase.
Staff expense
Given our mix of fee-based businesses, which are staffed with high-quality professionals, staff expense comprised 54% of total noninterest expense in both 2016 and 2015.
Staff expense consists of:
• | compensation expense, which includes: |
- salary expense, primarily driven by headcount;
- the cost of temporary services and overtime; and
- severance expense;
• | incentive expense, which includes: |
- additional compensation earned under incentive plans designed to reward a combination of individual, business unit and corporate performance goals; as well as,
- stock-based compensation expense; and
• | employee benefit expense, primarily medical benefits, payroll taxes, pension and other retirement benefits. |
Staff expense was $5.7 billion, a decrease of 2% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower incentives and employee benefits expenses.
Non-staff expense
Non-staff expense includes certain expenses that vary with the levels of business activity and levels of expensed business investments, fixed infrastructure costs and expenses associated with corporate activities related to technology, compliance, legal, productivity initiatives and business development.
BNY Mellon 15
Results of Operations (continued) |
Non-staff expense totaled $4.8 billion in 2016, a decrease of 3% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower expenses in nearly all categories. The lower expenses are primarily driven by lower litigation, legal, furniture and equipment, sub-custodian and business development expenses. The decrease was partially offset by an increase in distribution and servicing and software expenses. Adjusted non-staff expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges (Non-GAAP), totaled $4.5 billion in 2016, a decrease of 2% compared with 2015.
We expect to continue to benefit from the business improvement process, including the impact from vendor renegotiations, implementation of robotics process automation to reduce manual intervention and improve straight-through processing, insourcing consultant and temporary resources, and the execution of additional real estate actions that will allow us to optimize our physical footprint and improve how our employees work.
2015 compared with 2014
Noninterest expense totaled $10.8 billion in 2015, a decrease of $1.4 billion, or 11%, compared with $12.2 billion in 2014. The lower expenses primarily reflect a decrease in litigation, the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, lower consulting and legal expenses and the benefit of the business improvement process.
Income taxes
BNY Mellon recorded an income tax provision of $1.2 billion (24.9% effective tax rate) in 2016. The income tax provision was $1.0 billion (23.9% effective tax rate) in 2015. The income tax provision was $912 million (25.6% effective tax rate) in 2014 including a net benefit primarily related to litigation expense and the approval of a tax carryback claim, offset by the sales of our investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building. For additional information, see Note 10 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
We expect the effective tax rate to be approximately 25-26% in 2017 based on current income tax rates. Any legislation affecting income tax rates could have an impact on our future effective tax rate, the significance of which would depend on the timing,
nature and scope of any such legislation, as well as the level and composition of our earnings.
Review of businesses
We have an internal information system that produces performance data along product and service lines for our two principal businesses and the Other segment.
Business accounting principles
Our business data has been determined on an internal management basis of accounting, rather than the generally accepted accounting principles used for consolidated financial reporting. These measurement principles are designed so that reported results of the businesses will track their economic performance.
For information on the accounting principles of our businesses, the primary types of revenue by business and how our businesses are presented and analyzed, see Note 22 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Business results are subject to reclassification when organizational changes are made or when improvements are made in the measurement principles. In 2016, BNY Mellon reclassified the results of our credit-related activities to the Investment Services segment from the Other segment. This reclassification reflects our strategy to provide credit services to our Investment Services clients and did not impact the consolidated results. Also, concurrent with this reclassification, the provision for credit losses associated with the respective credit portfolios is now reflected in each business segment. All prior periods have been restated.
Beginning in 2016, we revised the net interest revenue for our business to reflect adjustments to our transfer pricing methodology to better reflect the value of certain deposits. Also in 2016, we refined the expense allocation process for indirect expenses to simplify the expenses recorded in the Other segment to include only expenses not directly attributable to the Investment Management and Investment Services operations. These changes did not impact the consolidated results.
The results of our businesses may be influenced by client and other activities that vary by quarter. In the first quarter, incentive expense typically increases
16 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
reflecting the vesting of long-term stock awards for retirement eligible employees. In the third quarter, Depositary Receipts revenue is typically higher due to an increased level of client dividend payments paid in the quarter. Also in the third quarter, volume-related fees may decline due to reduced client activity. In the fourth quarter, we typically incur higher business development and marketing expenses. In our Investment Management business, performance fees are typically higher in the fourth quarter, as the fourth quarter represents the end of the measurement period for many of the performance fee-eligible relationships.
The results of our businesses may also be impacted by the translation of financial results denominated in
foreign currencies to the U.S. dollar. We are primarily impacted by activities denominated in the British pound and the euro. On a consolidated basis and in our Investment Services business, we typically have more foreign currency denominated expenses than revenues. However, our Investment Management business typically has more foreign currency denominated revenues than expenses. Overall, currency fluctuations impact the year-over-year growth rate in the Investment Management business more than the Investment Services business. However, currency fluctuations, in isolation, are not expected to significantly impact net income on a consolidated basis.
The following table presents key market metrics at period end and on an average basis.
Key market metrics | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||
2016 vs. | 2015 vs. | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Standard & Poor’s (“S&P”) 500 Index (a) | 2239 | 2044 | 2059 | 10 % | (1) % | ||||||||
S&P 500 Index – daily average | 2095 | 2061 | 1931 | 2 | 7 | ||||||||
FTSE 100 Index (a) | 7143 | 6242 | 6566 | 14 | (5 | ) | |||||||
FTSE 100 Index – daily average | 6474 | 6590 | 6681 | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
MSCI EAFE (a) | 1684 | 1716 | 1775 | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
MSCI EAFE – daily average | 1645 | 1810 | 1888 | (9 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||
Barclays Capital Global Aggregate BondSM Index (a)(b) | 451 | 442 | 457 | 2 | (3 | ) | |||||||
NYSE and NASDAQ share volume (in billions) | 797 | 776 | 754 | 3 | 3 | ||||||||
JPMorgan G7 Volatility Index – daily average (c) | 10.54 | 9.97 | 7.19 | 6 | 39 | ||||||||
Average interest on excess reserves paid by the Federal Reserve | 0.51 | % | 0.26 | % | 0.25 | % | 25 bps | 1 bps | |||||
Foreign exchange rates vs. U.S. dollar: | |||||||||||||
British pound (a) | $ | 1.23 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.56 | (17) % | (5) % | |||||
British pound – average rate | 1.35 | 1.53 | 1.65 | (12 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||
Euro (a) | 1.05 | 1.09 | 1.22 | (4 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||
Euro – average rate | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.33 | — | (17 | ) | |||||||
(a) | Period end. |
(b) | Unhedged in U.S. dollar terms. |
(c) | The JPMorgan G7 Volatility Index is based on the implied volatility in 3-month currency options. |
Fee revenue in Investment Management, and to a lesser extent in Investment Services, is impacted by the value of market indices. At Dec. 31, 2016, we estimate that a 5% change in global equity markets, spread evenly throughout the year, would impact fee revenue by less than 1% and diluted earnings per common share by $0.02 to $0.04.
Fee waivers are highly sensitive to changes in the interest on excess reserves paid by the Federal Reserve. Since 2014, the interest on excess reserves paid by the Federal Reserve increased 50 basis points.
As a result of the increases, we recovered approximately 70% of the pre-tax income related to fee waivers. With an additional 25 basis point increase in the interest on excess reserves paid by the Federal Reserve, we expect to recover nearly all of the fee waivers.
See Note 22 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for the consolidating schedules which show the contribution of our businesses to our overall profitability.
BNY Mellon 17
Results of Operations (continued) |
Investment Management business
2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | vs. | vs. | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||||||
Investment management fees: | |||||||||||||
Mutual funds | $ | 1,210 | $ | 1,208 | $ | 1,231 | — | % | (2 | )% | |||
Institutional clients | 1,380 | 1,425 | 1,466 | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
Wealth management | 642 | 630 | 624 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
Investment management fees (a) | 3,232 | 3,263 | 3,321 | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Performance fees | 60 | 97 | 111 | (38 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||||
Investment management and performance fees | 3,292 | 3,360 | 3,432 | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Distribution and servicing | 192 | 152 | 157 | 26 | (3 | ) | |||||||
Other (a) | (60 | ) | 75 | 68 | N/M | N/M | |||||||
Total fee and other revenue (a) | 3,424 | 3,587 | 3,657 | (5 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 327 | 319 | 274 | 3 | 16 | ||||||||
Total revenue | 3,751 | 3,906 | 3,931 | (4 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | 6 | (1 | ) | — | N/M | N/M | |||||||
Noninterest expense (ex. amortization of intangible assets and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives) | 2,696 | 2,762 | 2,817 | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 82 | 97 | 118 | (15 | ) | (18 | ) | ||||||
Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 104 | N/M | N/M | ||||||||
Total noninterest expense | 2,778 | 2,859 | 3,039 | (3 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 967 | $ | 1,048 | $ | 892 | (8 | )% | 17 | % | |||
Income before taxes (ex. amortization of intangible assets and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives) – Non-GAAP | $ | 1,049 | $ | 1,145 | $ | 1,114 | (8 | )% | 3 | % | |||
Pre-tax operating margin | 26 | % | 27 | % | 23 | % | |||||||
Adjusted pre-tax operating margin – Non-GAAP (b) | 32 | % | 32 | % | 32 | % | |||||||
Average balances: | |||||||||||||
Average loans | $ | 15,015 | $ | 12,545 | $ | 10,589 | 20 | % | 18 | % | |||
Average deposits | $ | 15,650 | $ | 15,160 | $ | 14,154 | 3 | % | 7 | % | |||
(a) | Total fee and other revenue includes the impact of the consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests. See page 126 for a breakdown of the revenue line items in the Investment Management business impacted by the consolidated investment management funds. Additionally, other revenue includes asset servicing, treasury services, foreign exchange and other trading revenue and investment and other income. |
(b) | Excludes amortization of intangible assets, provision for credit losses, the charge recorded in 2014 related to investment management funds, net of incentives and distribution and servicing expense. See “Supplemental information – Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for the reconciliation of this Non-GAAP measure. |
18 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
AUM trends (a) | |||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in billions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
AUM at period end, by product type: | |||||||||||||||
Equity | $ | 228 | $ | 224 | $ | 260 | $ | 272 | $ | 232 | |||||
Fixed income | 214 | 216 | 204 | 200 | 188 | ||||||||||
Index | 316 | 329 | 356 | 322 | 239 | ||||||||||
Liability-driven investments (b) | 553 | 514 | 504 | 403 | 329 | ||||||||||
Alternative investments | 69 | 63 | 65 | 61 | 59 | ||||||||||
Cash | 268 | 279 | 297 | 299 | 302 | ||||||||||
Total AUM | $ | 1,648 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | $ | 1,557 | $ | 1,349 | |||||
AUM at period end, by client type: | |||||||||||||||
Institutional | $ | 1,182 | $ | 1,127 | $ | 1,164 | $ | 1,047 | $ | 864 | |||||
Mutual funds | 381 | 420 | 438 | 426 | 410 | ||||||||||
Private client | 85 | 78 | 84 | 84 | 75 | ||||||||||
Total AUM | $ | 1,648 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | $ | 1,557 | $ | 1,349 | |||||
Changes in AUM: | |||||||||||||||
Beginning balance of AUM | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | $ | 1,557 | $ | 1,349 | $ | 1,226 | |||||
Net inflows (outflows): | |||||||||||||||
Long-term strategies: | |||||||||||||||
Equity | (12 | ) | (31 | ) | (13 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Fixed income | (3 | ) | (1 | ) | 4 | 11 | 20 | ||||||||
Liability-driven investments (b) | 26 | 35 | 46 | 65 | 25 | ||||||||||
Alternative investments | 6 | 7 | 6 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||||
Total long-term active strategies inflows | 17 | 10 | 43 | 78 | 48 | ||||||||||
Index | (31 | ) | (27 | ) | 5 | 20 | 9 | ||||||||
Total long-term strategies (outflows) inflows | (14 | ) | (17 | ) | 48 | 98 | 57 | ||||||||
Short term strategies: | |||||||||||||||
Cash | (9 | ) | (18 | ) | — | 5 | (20 | ) | |||||||
Total net (outflows) inflows | (23 | ) | (35 | ) | 48 | 103 | 37 | ||||||||
Net market impact/other | 181 | (8 | ) | 122 | 94 | 73 | |||||||||
Net currency impact | (137 | ) | (36 | ) | (41 | ) | 11 | 13 | |||||||
Acquisition | 2 | 18 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Ending balance of AUM | $ | 1,648 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 1,686 | $ | 1,557 | $ | 1,349 | |||||
(a) | Excludes securities lending cash management assets and assets managed in the Investment Services business and the Other segment. |
(b) | Includes currency overlay AUM. |
Business description
With $1.65 trillion under management, our Investment Management business comprises the seventh largest global asset manager and the eighth largest U.S. wealth manager.
Investment Management encompasses Wealth Management and 13 specialist investment boutiques that deliver a highly diversified portfolio of investment strategies independently, and through our global distribution network, to institutional and retail clients globally. Each boutique follows its own independent investment approach to innovate and develop investment solutions designed to deliver performance returns and outcomes that meet the investing goals of an increasingly sophisticated client base. Our multi-boutique model is designed to provide the best elements of investment focus and infrastructure at scale to benefit clients.
The Investment Management boutiques offer a broad range of actively managed equity, fixed income, alternative and liability-driven investments, along with passive products and cash management. In addition to the investment boutiques, Investment Management has multiple global distribution entities including BNY Mellon Investment Management EMEA Limited, BNY Mellon Investment Management Hong Kong, BNY Mellon Investment Management Korea, BNY Mellon Investment Management Australia and BNY Mellon Investment Management Singapore, which are responsible for distributing investment products manufactured by the investment boutiques. In addition, the Dreyfus Corporation and its affiliate, the MBSC Securities Corporation, are responsible for U.S. investment management and distribution of retail mutual funds, and certain offshore funds.
BNY Mellon 19
Results of Operations (continued) |
BNY Mellon Wealth Management provides investment management, custody, wealth and estate planning and private banking services, and conducts business through various operating subsidiaries of the Parent. It was ranked the eighth largest U.S. wealth manager in 2016 by Barron’s. We have more than two centuries of experience in providing services to clients who today include financially successful individuals and families, their family offices and business enterprises, planned giving programs, and endowments and foundations. Client satisfaction rates are among the highest in our industry based on BNY Mellon Wealth Management’s 2016 Client Survey and Spectrem Group’s 2016 UHNW Investor Study. In 2016, BNY Mellon Wealth Management was named by Family Wealth Report the top U.S. Private Bank and rated the Top Private Bank for Family Offices by Professional Wealth Management magazine. BNY Mellon Wealth Management has more than $200 billion in total private client assets as of Dec. 31, 2016, and an extensive network of offices in the U.S. and internationally.
The results of the Investment Management business are driven by the period end, average level and mix of assets managed and the level of activity in client accounts. The overall level of AUM for a given period is determined by:
• | the beginning level of AUM; |
• | the net flows of new assets during the period resulting from new business wins and existing client enrichments, reduced by the loss of clients and withdrawals; and |
• | the impact of market price appreciation or depreciation, acquisitions or divestitures and foreign exchange rates. |
The mix of AUM is determined principally by client asset allocation decisions among equities, fixed income, passive, cash, liability-driven investments and alternative investments.
Managed equity assets typically generate higher percentage fees than liability-driven investments and fixed-income assets. Also, actively managed assets typically generate higher management fees than indexed or passively managed assets of the same type.
Investment management fees are dependent on the overall level and mix of AUM and the management fees expressed in basis points (one-hundredth of one
percent) charged for managing those assets. Management fees are typically subject to fee schedules based on the overall level of assets managed for a single client or by individual asset class and style. This is most common for institutional assets where amounts we manage for individual clients are typically large.
A key driver of organic growth in investment management and performance fees is the amount of net new AUM flows. Overall market conditions are also key drivers, with a significant long-term economic driver being growth of global financial assets.
Performance fees are generally calculated as a percentage of a portfolio’s performance in excess of a benchmark index or a peer group’s performance.
Net interest revenue is determined by loan and deposit volumes and the interest rate spread between customer rates and internal funds transfer rates on loans and deposits. Expenses in the Investment Management business are mainly driven by staffing costs, incentives and distribution and servicing expense.
Review of financial results
AUM was $1.65 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $1.63 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015, an increase of 1%. The increase primarily reflects higher market values offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound).
Net long-term outflows of $14 billion in 2016 were a combination of $17 billion of inflows into actively managed strategies, primarily liability-driven investments, and $31 billion of outflows from index strategies. Net short-term outflows were $9 billion in 2016. Similar to other asset managers, Investment Management is experiencing a shift in client assets to lower fee products.
Total revenue was $3.8 billion, a decrease of 4% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and net outflows, partially offset by higher money market fees and higher market values.
Revenue generated in the Investment Management business included 41% from non-U.S. sources in 2016, compared with 42% in 2015.
20 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Investment management fees in the Investment Management business were $3.2 billion, a decrease of 1% compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and net outflows, partially offset by higher money market fees and higher market values.
Performance fees were $60 million in 2016 compared with $97 million in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the conservative positioning of a number of our strategies in the fourth quarter of 2016 versus the market. As of year-end 2016, our largest performance fee strategies remain at or close to their high watermarks.
Distribution and servicing fees were $192 million in 2016 compared with $152 million in 2015. The increase was primarily driven by higher money market fees, partially offset by net outflows.
Other revenue was a loss of $60 million in 2016 compared with other revenue of $75 million in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects payments to Investment Services related to higher money market fees and losses on hedging activity.
Net interest revenue was $327 million in 2016 compared with $319 million in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher average loans and higher rates on deposits, partially offset by the 2016 change in internal crediting rates. Average loans increased 20% in 2016 compared with 2015, while average deposits increased 3% in 2016 compared with 2015.
Noninterest expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets, was $2.7 billion, a decrease of $66 million, or 2%, compared with 2015. The decrease compared with 2015 was primarily driven by the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower incentive expense, partially offset by higher distribution and servicing expense as a result of lower money market fee waivers.
2015 compared with 2014
Income before taxes totaled $1.048 billion in 2015 compared with $892 million in 2014. Income before taxes, excluding amortization of intangible assets and the charge related to investment management funds recorded in 2014, net of incentives (Non-GAAP), was $1,145 million in 2015, an increase of $31 million compared with 2014. Fee and other revenue decreased $70 million in 2015, or 2%, compared with 2014, primarily resulting from lower investment management and performance fees, driven by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, partially offset by higher money market fees, the impact of the Cutwater acquisition and strategic initiatives. Net interest revenue increased $45 million in 2015, or 16%, compared with 2014, primarily due to higher average loans and deposits. Noninterest expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets and the charge recorded in 2014 related to investment management funds, net of incentives, decreased $55 million, or 2%, compared with 2014, primarily reflecting the favorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and lower incentives, partially offset by investments in strategic initiatives.
BNY Mellon 21
Results of Operations (continued) |
Investment Services business
(dollars in millions, unless otherwise noted) | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
vs. | vs. | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||||||
Investment services fees: | |||||||||||||
Asset servicing | $ | 4,141 | $ | 4,098 | $ | 3,983 | 1 | % | 3 | % | |||
Clearing services | 1,399 | 1,370 | 1,329 | 2 | 3 | ||||||||
Issuer services | 1,024 | 976 | 966 | 5 | 1 | ||||||||
Treasury services | 541 | 546 | 555 | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
Total investment services fees | 7,105 | 6,990 | 6,833 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue | 663 | 722 | 643 | (8 | ) | 12 | |||||||
Other (a) | 531 | 465 | 406 | 14 | 15 | ||||||||
Total fee and other revenue | 8,299 | 8,177 | 7,882 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
Net interest revenue | 2,797 | 2,622 | 2,468 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||
Total revenue | 11,096 | 10,799 | 10,350 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
Provision for credit losses | 8 | 28 | (21 | ) | N/M | N/M | |||||||
Noninterest expense (ex. amortization of intangible assets) | 7,187 | 7,340 | 8,066 | (2 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 155 | 162 | 175 | (4 | ) | (7 | ) | ||||||
Total noninterest expense | 7,342 | 7,502 | 8,241 | (2 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 3,746 | $ | 3,269 | $ | 2,130 | 15 | % | 53 | % | |||
Income before taxes (ex. amortization of intangible assets) – Non-GAAP | $ | 3,901 | $ | 3,431 | $ | 2,305 | 14 | % | 49 | % | |||
Pre-tax operating margin | 34 | % | 30 | % | 21 | % | |||||||
Adjusted pre-tax operating margin (ex. provision for credit losses and amortization of intangible assets) – Non-GAAP | 35 | % | 32 | % | 22 | % | |||||||
Investment services fees as a percentage of noninterest expense (ex. amortization of intangible assets) | 99 | % | 95 | % | 85 | % | |||||||
Securities lending revenue | $ | 170 | $ | 153 | $ | 135 | 11 | % | 13 | % | |||
Metrics: | |||||||||||||
Average loans | $ | 44,740 | $ | 45,743 | $ | 40,137 | (2 | )% | 14 | % | |||
Average deposits | $ | 217,882 | $ | 233,833 | $ | 225,503 | (7 | )% | 4 | % | |||
AUC/A at period end (in trillions) (b) | $ | 29.9 | $ | 28.9 | $ | 28.5 | 3 | % | 1 | % | |||
Market value of securities on loan at period end (in billions) (c) | $ | 296 | $ | 277 | $ | 289 | 7 | % | (4 | )% | |||
Asset servicing: | |||||||||||||
Estimated new business wins (AUC/A) (in billions) | $ | 498 | $ | 1,191 | $ | 554 | |||||||
Depositary Receipts: | |||||||||||||
Number of sponsored programs | 1,062 | 1,145 | 1,279 | (7 | )% | (10 | )% | ||||||
Clearing services: | |||||||||||||
Average active clearing accounts (U.S. platform) (in thousands) | 5,949 | 6,023 | 5,788 | (1 | )% | 4 | % | ||||||
Average long-term mutual fund assets (U.S. platform) | $ | 431,937 | $ | 451,924 | $ | 434,959 | (4 | )% | 4 | % | |||
Average investor margin loans (U.S. platform) | $ | 10,772 | $ | 11,627 | $ | 9,687 | (7 | )% | 20 | % | |||
Broker-Dealer: | |||||||||||||
Average tri-party repo balances (in billions) | $ | 2,183 | $ | 2,156 | $ | 2,042 | 1 | % | 6 | % | |||
(a) | Other revenue includes investment management fees, financing-related fees, distribution and servicing revenue and investment and other income. |
(b) | Includes the AUC/A of CIBC Mellon of $1.2 trillion at Dec. 31, 2016, $1.0 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015 and $1.1 trillion at Dec. 31, 2014. |
(c) | Represents the total amount of securities on loan managed by the Investment Services business. Excludes securities for which BNY Mellon acts as agent on behalf of CIBC Mellon clients, which totaled $63 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, $55 billion at Dec. 31, 2015 and $65 billion at Dec. 31, 2014. |
22 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Business description
We are one of the leading global investment services providers with $29.9 trillion of AUC/A at Dec. 31, 2016.
• | We are a leader in both global and U.S. government securities clearance, settling securities transactions in over 100 markets. |
• | We are a leader in servicing tri-party repo collateral with approximately $2.3 trillion serviced globally. |
• | We service approximately $1.5 trillion, or approximately 86%, of the $1.8 trillion tri-party repo market in the U.S. |
• | Our agency securities lending program is one of the largest lenders of U.S and non-U.S. securities, servicing a lendable asset pool of approximately $3.0 trillion in 33 separate markets. |
• | We serve as trustee and/or paying agent on more than 50,000 debt-related issues globally. |
• | As one of the largest providers of depositary receipts services in the world, we served as depositary for 1,062 sponsored American and global depositary receipt programs at Dec. 31, 2016, acting in partnership with leading companies from 63 countries—an estimated 56% market share. |
BNY Mellon Investment Services provides business and technology solutions across the investments process to financial institutions, corporations, foundations and endowments, public funds and government agencies.
With NEXEN®, our next generation digital technology ecosystem, we are leading the digital transformation of BNY Mellon and the services we provide to our clients. NEXEN® should provide us with many competitive advantages. It is creating internal efficiencies while reducing costs and increasing speed of delivery, enhancing our clients’ experience and driving revenue opportunities as we continue to onboard clients to our new digital platform. We are collaborating with clients and leading financial technology startups, or fintechs, to develop and integrate new solutions and services, and attracting top information technology talent through our Innovation Centers worldwide.
We offer asset servicing, clearing services, issuer services and treasury services to our clients.
BNY Mellon’s comprehensive suite of asset servicing solutions includes: global custody, foreign exchange, global fund services, securities finance, investment manager outsourcing, performance and risk analytics, alternative investment services, broker-dealer services, and collateral and liquidity services.
As one of the largest fund accounting providers and a trusted partner, we offer services to ensure the safekeeping of assets in capital markets globally. These services include financial reporting, tax reporting services, calculating and reporting NAVs, computing yields, maintaining brokerage account records, and providing administrative support for the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission and other compliance requirements.
Our alternative investment services and structured products business provides a full range of solutions for alternative investment managers, including prime custody, fund accounting, client and regulatory reporting services; in 2016, we extended our capabilities to real estate and private equity investment managers. We also support exchange-traded funds and unit investment trusts, providing fund administration, custody, basket creation and dissemination, authorized participant interaction and order processing, among other services.
Securities finance delivers solutions on both an agency and principal basis. The principal finance program supports a diverse group of client segments, including hedge and liquid alternative funds and other institutional clients.
In liquidity services, our market leading portal enables cash investments for institutional clients via money market funds, deposit products, and direct investments in money market securities, and includes fund research and analytics.
Our broker-dealer services business clears and settles equity and fixed-income transactions globally and manages more than $2 trillion in collateral, including tri-party repo collateral, worldwide. As a leader in the U.S. tri-party repo market, BNY Mellon led the way in reducing systemic risk through operational and technology enhancements.
BNY Mellon 23
Results of Operations (continued) |
Clearing services, primarily Pershing and its affiliates, provides business and technology solutions to financial organizations globally, delivering dependable operational support, robust trading services, flexible technology, an expansive array of investment and retirement solutions, practice management support and service excellence.
Our collateral services include collateral management, administration and segregation. We offer innovative solutions, like new collateral types and transaction structures, automation and efficiency, access to global markets, and industry expertise, to help financial institutions and institutional investors mine opportunities from liquidity, financing, risk and balance sheet challenges.
We are a leading provider to the debt capital markets, providing customized and market-driven solutions to investors, bondholders and lenders. Our corporate trust business delivers a full range of issuer and related investor services, including trustee, paying agency, fiduciary, escrow, and other financial services.
Our treasury services include customizable solutions and innovative technology that deliver high-quality cash management, payment and trade support for corporate and institutional global treasury needs.
We also provide credit facilities and solutions to support our clients globally.
Role of BNY Mellon, as a trustee, for mortgage-backed securitizations
BNY Mellon acts as trustee and document custodian for certain mortgage-backed security (“MBS”) securitization trusts. The role of trustee for MBS securitizations is limited; our primary role as trustee is to calculate and distribute monthly bond payments to bondholders. As a document custodian, we hold the mortgage, note, and related documents provided to us by the loan originator or seller and provide periodic reporting to these parties. BNY Mellon, either as document custodian or trustee, does not receive mortgage underwriting files (the files that contain information related to the creditworthiness of the borrower). As trustee or custodian, we have no responsibility or liability for the quality of the portfolio; we are liable only for performance of our limited duties as described above and in the trust documents. BNY Mellon is indemnified by the
servicers or directly from trust assets under the governing agreements. BNY Mellon may appear as the named plaintiff in legal actions brought by servicers in foreclosure and other related proceedings because the trustee is the nominee owner of the mortgage loans within the trusts.
BNY Mellon also has been named as a defendant in legal actions brought by MBS investors alleging that the trustee has expansive duties under the governing agreements, including to investigate and pursue claims against other parties to the MBS transaction. For additional information on our legal proceedings related to this matter, see Note 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Review of financial results
AUC/A totaled $29.9 trillion, an increase from $28.9 trillion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase was primarily driven by higher market values, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar. AUC/A consisted of 34% equity securities and 66% fixed income securities at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with 36% equity securities and 64% fixed income securities at Dec. 31, 2015.
Investment services fees were $7.1 billion, an increase of 2%, compared with 2015, reflecting the following factors:
• | Asset servicing fees (global custody, accounting, broker-dealer services, securities lending, collateral and liquidity services) were $4.141 billion compared with $4.098 billion in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher money market fees and securities lending revenue, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar and downsizing of the UK retail transfer agency business. |
• | Clearing services fees were $1.399 billion compared with $1.370 billion in 2015. The increase was primarily driven by higher money market fees, partially offset by the impact of lost business and client business exits related to the broker-dealer industry consolidations. |
• | Issuer services fees (Corporate Trust and Depositary Receipts) were $1.024 billion compared with $976 million in 2015. The increase was driven by higher money market fees in Corporate Trust and higher fees in Depositary Receipts. |
24 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
• | Treasury services fees (global payments, trade finance and cash management) were $541 million compared with $546 million in 2015. The decrease reflects higher compensating balance credits provided to clients, which reduced fee revenue and increased net interest revenue, partially offset by higher payments and banking transaction services volumes. |
Market and regulatory trends are driving investable assets toward investments in lower fee asset management products at reduced margins for our clients. These dynamics are also negatively impacting our investment services fees. However, at the same time, these trends are also providing additional outsourcing opportunities as clients and other market participants seek to comply with new regulations and reduce their operating costs.
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue totaled $663 million compared with $722 million in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects the continued trend of clients migrating to lower margin products and lower volumes.
Other revenue was $531 million compared with $465 million in 2015. The increase primarily reflects higher payments from Investment Management related to higher money market fees and higher fees
related to secured intraday credit, partially offset by certain fees paid to introducing brokers.
Net interest revenue was $2.8 billion compared with $2.6 billion in 2015. The increase primarily reflects
the impact of changes in the internal crediting rates for deposits, partially offset by a decrease in average deposit balances.
Noninterest expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets, was $7.2 billion compared with $7.3 billion in 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower litigation, temporary services, sub-custodian, legal and other purchased services expenses, partially offset by higher bank assessment charges.
2015 compared with 2014
Income before taxes totaled $3.3 billion in 2015 compared with $2.1 billion in 2014. Income before taxes, excluding amortization of intangible assets (Non-GAAP), increased $1.1 billion, or 49%. Fee and other revenue increased $295 million, or 4%, compared with 2014, primarily reflecting higher asset servicing fees, foreign exchange and other trading revenue and other revenue. The $154 million, or 6%, increase in net interest revenue primarily reflects higher average deposits and loans, as well as higher internal crediting rates on deposits. Noninterest expense, excluding intangible amortization, decreased $726 million, or 9%, compared with 2014, primarily due to lower litigation, consulting and occupancy expenses, partially offset by higher staff expense.
Other segment
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||
Fee and other revenue | $ | 366 | $ | 336 | $ | 1,189 | |||
Net interest revenue | 14 | 85 | 138 | ||||||
Total revenue | 380 | 421 | 1,327 | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | (25 | ) | 133 | (27 | ) | ||||
Noninterest expense (ex. amortization of intangible assets and M&I and restructuring charges (recoveries)) | 390 | 434 | 715 | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | — | 2 | 5 | ||||||
M&I and restructuring charges (recoveries) | 4 | (2 | ) | 177 | |||||
Total noninterest expense | 394 | 434 | 897 | ||||||
Income (loss) before taxes | $ | 11 | $ | (146 | ) | $ | 457 | ||
Income (loss) before taxes (ex. amortization of intangible assets and M&I and restructuring charges (recoveries)) – Non-GAAP | $ | 15 | $ | (146 | ) | $ | 639 | ||
Average loans and leases | $ | 1,926 | $ | 2,384 | $ | 3,484 | |||
BNY Mellon 25
Results of Operations (continued) |
Business description
The Other segment primarily includes:
• | the leasing portfolio; |
• | corporate treasury activities, including our investment securities portfolio; |
• | derivatives and other trading activity; |
• | corporate and bank-owned life insurance and renewable energy investments; and |
• | business exits. |
Revenue primarily reflects:
• | net interest revenue and lease-related gains (losses) from leasing operations; |
• | net interest revenue from corporate treasury activity; |
• | fee and other revenue from corporate and bank- owned life insurance and business exits; and |
• | gains (losses) associated with the valuation of investment securities and other assets. |
Expenses include:
• | M&I expenses; |
• | restructuring charges recorded relate to corporate-level initiatives and were therefore recorded in the Other segment; |
• | direct expenses supporting leasing, investing, and funding activities; and |
• | expenses not directly attributable to the Investment Management and Investment Services operations. |
Review of financial results
The Other segment had income before taxes of $11 million in 2016 compared with a loss of $146 million in 2015.
Total fee and other revenue increased $30 million compared with 2015. The increase primarily reflects the positive impact of foreign currency hedging activity, partially offset by lower other income driven by the impact of increased investments in renewable energy.
Net interest revenue decreased $71 million compared with 2015. The decrease was primarily driven by the results of the leasing portfolio inclusive of changes to internal transfer pricing in the first quarter of 2016.
The provision for credit losses was a credit of $25 million in 2016 primarily reflecting a net recovery of $13 million recorded in the financial institutions portfolio. The recovery reflects the receipt of trust assets from the bankruptcy proceedings of Sentinel in excess of the carrying value.
Noninterest expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets and M&I and restructuring charges (recoveries), decreased $44 million compared with 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower equipment expense and professional, legal and other purchased services, partially offset by higher software expense.
2015 compared with 2014
There was a loss before taxes in the Other segment of $146 million in 2015 compared with income of $457 million in 2014. Total revenue decreased $906 million primarily reflecting the gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building, both recorded in 2014, and the impact of the July 2015 sale of Meriten, partially offset by the impact of hedging activity for foreign currency placements. The provision for credit losses was $133 million in 2015 reflecting the impairment charge related to Sentinel. Noninterest expense, excluding amortization of intangible assets and M&I and restructuring charges (recoveries), decreased $281 million primarily reflecting lower litigation expense, the impact of curtailing the U.S. pension plan and the impact of the July 2015 sale of Meriten.
International operations
Our primary international activities consist of asset servicing and global payment services in our Investment Services business, and asset management in our Investment Management business.
Our clients include central banks and sovereigns, financial institutions, asset managers, insurance companies, corporations, local authorities and high net worth individuals and family offices. Through our global network of offices, we have developed a deep understanding of local requirements and cultural needs, and we pride ourselves on providing dedicated service through our multilingual sales, marketing and client service teams.
At Dec. 31, 2016, we had approximately 8,800 employees in Europe, the Middle East and Africa
26 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
(“EMEA”), approximately 14,700 employees in the Asia-Pacific region (“APAC”) and approximately 700 employees in other global locations, primarily Brazil.
We are the seventh largest global asset manager. At Dec. 31, 2016, our international operations managed 49% of BNY Mellon’s AUM, compared with 46% at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase in international AUM primarily resulted from higher market values and net inflows, partially offset by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar (principally versus the British pound).
In Europe, we maintain a significant presence in the Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities Directives (“UCITS”) servicing field. In Ireland, BNY Mellon is one of the largest administrators (by total net assets) for fund administration services across domiciled and non-domiciled funds. We offer a full range of tailored solutions for investment companies, financial institutions and institutional investors in Germany.
We are a leader in both global and U.S. government securities clearance, settling securities transactions in over 100 markets.
As one of the largest providers of depositary receipts services in the world, we served as depositary for 1,062 sponsored American and global depositary receipt programs at Dec. 31, 2016, acting in partnership with leading companies from 63 countries—an estimated 56% market share.
We have over 50 years of experience providing trade and cash services to financial institutions and central banks outside of the U.S. In addition, we offer a broad range of servicing and fiduciary products to financial institutions, corporations and central banks depending on the state of market development. In emerging markets, we lead with global payments and issuer services, introducing other products as the markets mature. For more established markets, our focus is on global investment services.
We are also a full-service global provider of foreign exchange services, actively trading in over 100 of the world’s currencies. We serve clients from trading desks located in Europe, Asia and North America.
Our financial results, as well as our level of AUM and AUC/A, are impacted by the translation of financial results denominated in foreign currencies to the U.S.
dollar. We are primarily impacted by activities denominated in the British pound sterling and the euro. If the U.S. dollar depreciates against these currencies, the translation impact is a higher level of fee revenue, net interest revenue, noninterest expense and AUM and AUC/A. Conversely, if the U.S. dollar appreciates, the translated levels of fee revenue, net interest revenue, noninterest expense and AUM and AUC/A will be lower.
Foreign exchange rates vs. U.S. dollar | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Spot rate (at Dec. 31): | |||||||||
British pound | $ | 1.2323 | $ | 1.4799 | $ | 1.5609 | |||
Euro | 1.0538 | 1.0883 | 1.2155 | ||||||
Yearly average rate: | |||||||||
British pound | $ | 1.3548 | $ | 1.5282 | $ | 1.6475 | |||
Euro | 1.1065 | 1.1100 | 1.3257 | ||||||
International clients accounted for 34% of revenues in 2016, compared with 36% in 2015 and 38% in 2014. Net income from international operations was $1.6 billion in 2016, compared with $1.7 billion in 2015 and $1.8 billion in 2014.
In 2016, revenues from EMEA were $3.7 billion, compared with $3.9 billion in both 2015 and 2014. Revenues from EMEA decreased 5% in 2016 compared with 2015, primarily reflecting lower revenue in the Investment Management business driven by the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, losses on hedging activity and lower performance fees, as well as lower revenue in the Investment Services business driven by lower asset servicing fees due to the unfavorable impact of a stronger U.S. dollar, the downsizing of the UK retail transfer agency business and lower fees in Corporate Trust. Our Investment Services businesses generated 68% and our Investment Management business generated 32% of EMEA revenues. Net income from EMEA was $1.0 billion in 2016, compared with $1.2 billion in 2015 and $775 million in 2014.
Revenues from APAC were $922 million in 2016 compared with $904 million in 2015 and $1.4 billion in 2014. Revenues from APAC increased 2% in 2016 compared with 2015, primarily reflecting higher revenue in the Investment Services business driven by broker-dealer services and the Depositary Receipts business. This increase was partially offset by lower revenue in the asset servicing and treasury services businesses, and lower revenue in the Investment Management business due to net outflows, lower
BNY Mellon 27
Results of Operations (continued) |
market values and lower performance fees. Our Investment Services businesses generated 80% and our Investment Management businesses generated 20% of APAC revenues. Net income from APAC was $389 million in 2016, compared with $365 million in 2015 and $719 million in 2014.
For additional information regarding our International operations, including certain key subjective assumptions used in determining the results, see Note 23 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Country risk exposure
We have exposure to certain countries and territories that have had a heightened focus in recent years. Exposure described below reflects the country of operations and risk of the immediate counterparty. We continue to monitor our exposure to these and other countries as part of our Risk Management process. See “Risk management” for additional information on how our exposures are managed.
BNY Mellon has a limited economic interest in the performance of assets of consolidated investment management funds, and therefore they are excluded from this disclosure.
Italy, Spain, Portugal and Greece
Over the past several years, there have been concerns about European sovereign debt and its impact on the European banking system, as a number of European countries, including Italy, Spain, Portugal and Greece, experienced credit deterioration. We had net exposure of $1.2 billion to Italy and $2.0 billion to Spain at Dec. 31, 2016. We had net exposure of $1.6 billion to Italy and $2.0 billion to Spain at Dec. 31, 2015. At both Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, exposure to Italy and Spain primarily consisted of investment grade sovereign debt. Investment securities exposure totaled $1.1 billion in Italy and $1.8 billion in Spain at Dec. 31, 2016 and $1.4 billion in Italy and $2.0 billion in Spain at Dec. 31, 2015. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we had exposure to Portugal of $2 million and less than $1 million, respectively. At both Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon had exposure of less than $1 million to Greece.
Brazil
Current conditions in Brazil have resulted in increased focus on its economic and political stability. We have operations in Brazil providing investment services and investment management services. In addition, at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we had total net exposure to Brazil of $1.3 billion and $2.2 billion, respectively. This included $1.3 billion and $2.1 billion, respectively, in loans, which are primarily short-term trade finance loans extended to large financial institutions. At Dec. 31, 2016, we held $73 million of noninvestment grade sovereign debt and at Dec. 31, 2015, we held $95 million of investment grade sovereign debt.
Other countries and territories
Events in recent years have resulted in increased focus on exposures to Turkey, Russia and Puerto Rico. Related to Turkey, we mainly provide treasury and issuer services, as well as foreign exchange products primarily to the top-10 largest financial institutions in the country. As of Dec. 31, 2016, our exposure totaled $713 million, consisting primarily of syndicated credit facilities and trade finance loans. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, our exposure to Russia was $79 million and $63 million, respectively. Related to Puerto Rico, BNY Mellon had margin loan exposure that was collateralized with a concentration of Puerto Rican securities. The margin loan exposure was approximately $45 million and $50 million, at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively.
Cross-border risk
Cross-border outstandings are based on the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council’s (“FFIEC”) regulatory guidelines for reporting cross-border risk. Cross-border outstandings in the table below include loans, acceptances, interest-bearing deposits with other banks, other interest-bearing investments, and other monetary assets which are denominated in U.S. dollars or other non-local currencies. Also included are local currency outstandings not hedged or funded by local borrowings. Under the FFIEC guidelines, cross-border outstandings are reported based on the domicile of the counterparty, issuer of collateral or guarantor.
Foreign assets are subject to the general risks attendant on the conduct of business in each foreign
28 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
country, including economic uncertainties and each foreign government’s regulations. In addition, our foreign assets may be affected by changes in demand or pricing resulting from fluctuations in currency exchange rates or other factors.
The table below shows our cross-border outstandings at Dec. 31 of each of the last three years where cross-border exposure exceeds 1.00% of total assets (denoted with “*”) or exceeds 0.75% but less than or equal to 1.00% of total assets (denoted with “**”).
Cross-border outstandings | Banks and other financial institutions (a) | Public sector | Commercial, industrial and other | Total cross-border outstandings (b) | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||
2016: | ||||||||||||||||||
France* | $ | 1,662 | $ | 2,559 | $ | 109 | $ | 4,330 | ||||||||||
Germany* | 2,398 | 1,408 | 357 | 4,163 | ||||||||||||||
Canada* | 2,199 | 1 | 1,211 | 3,411 | ||||||||||||||
United Kingdom** | 1,325 | 1,584 | 405 | 3,314 | ||||||||||||||
2015: | ||||||||||||||||||
United Kingdom* | $ | 1,732 | $ | 569 | $ | 2,265 | $ | 4,566 | ||||||||||
France* | 968 | 2,855 | 120 | 3,943 | ||||||||||||||
Germany** | 1,882 | 1,666 | 363 | 3,911 | ||||||||||||||
2014: | ||||||||||||||||||
France* | $ | 410 | $ | 3,770 | $ | 183 | $ | 4,363 | ||||||||||
United Kingdom** | 2,583 | 544 | 655 | 3,782 | ||||||||||||||
China** | 3,459 | — | 30 | 3,489 | ||||||||||||||
Germany** | 1,207 | 1,505 | 569 | 3,281 | ||||||||||||||
Netherlands** | 526 | 1,737 | 664 | (c) | 2,927 | |||||||||||||
(a) | Primarily short-term interest-bearing deposits with banks. Also includes global trade finance loans. |
(b) | Excludes assets of consolidated investment management funds. |
(c) | Primarily European floating rate notes. |
Emerging markets exposure
We determine our emerging markets exposures using the MSCI Emerging Markets (EM) IMI Index. Our emerging markets exposures totaled $11 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $13 billion at Dec. 31, 2015, primarily reflecting lower short-term trade finance loans extended to large financial institutions in Brazil and China, as well as lower interest-bearing deposits with banks in China.
Critical accounting estimates
Our significant accounting policies are described in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements under “Summary of significant accounting and reporting policies”. Our critical accounting estimates are those related to the allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments, fair value of financial instruments and derivatives, other-than-temporary impairment, goodwill and other intangibles, and pension accounting. Further information on policies related to the allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments can be found under “Summary of significant accounting and reporting policies” in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated
Financial Statements. Additionally, further information can be found in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements related to the following: the valuation of derivatives and securities where quoted market prices are not available can be found under “Fair value measurement” in Note 18; information on other-than-temporary impairment can be found in “Securities” in Note 3; policies related to goodwill and intangible assets can be found in “Goodwill and intangible assets” in Note 5; and information on pensions can be found in “Employee benefit plans” in Note 16.
Allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments
The allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments represent management’s estimate of losses inherent in our credit portfolio. This evaluation process is subject to numerous estimates and judgments.
We utilize a quantitative methodology and qualitative framework for determining the allowance for loan losses and the allowance for lending-related commitments. Within this qualitative framework,
BNY Mellon 29
Results of Operations (continued) |
management applies judgment when assessing internal risk factors and environmental factors to compute an additional allowance for each component of the loan portfolio.
The three elements of the allowance for loan losses and the allowance for lending-related commitments include the qualitative allowance framework. The three elements are:
• | an allowance for impaired credits of $1 million or greater; |
• | an allowance for higher risk-rated credits and pass-rated credits; and |
• | an allowance for residential mortgage loans. |
Our lending is primarily to institutional customers. As a result, our loans are generally larger than $1 million. Therefore, the first element, impaired credits, is based on individual analysis of all impaired loans of $1 million or greater. The allowance is measured by the difference between the recorded value of impaired loans and their impaired value. Impaired value is either the present value of the expected future cash flows from the borrower, the market value of the loan, or the fair value of the collateral, if the loan is collateral dependent.
The second element, higher risk-rated credits and pass-rated credits, is based on our incurred loss model. Individual credit analyses are performed on such loans before being assigned a credit rating. All borrowers are collectively evaluated based on their credit rating. The loss inherent in each loan incorporates the borrower’s credit rating, facility rating and maturity. The loss given default, derived from the facility rating, incorporates a recovery expectation and an estimate of the use of the facility at default (usage given default). The borrower’s probability of default is derived from the associated credit rating. Borrower ratings are reviewed at least annually and are periodically mapped to third-party databases, including rating agency and default and recovery databases, to ensure ongoing consistency and validity. Higher risk-rated credits are reviewed quarterly.
The third element, the allowance for residential mortgage loans, is determined by segregating six mortgage pools into delinquency periods, ranging from current through foreclosure. Each of these delinquency periods is assigned a probability of default. A specific loss given default is assigned for
each mortgage pool. BNY Mellon assigns all residential mortgage pools, except home equity lines of credit, a probability of default and loss given default based on default and loss data derived from internal historical data related to our residential mortgage portfolio. The resulting incurred loss factor (the probability of default multiplied by the loss given default) is applied against the loan balance to determine the allowance held for each pool. For home equity lines of credit, probability of default and loss given default are based on external data from third-party databases due to the small size of the portfolio and insufficient internal data.
The qualitative framework is used to determine an additional allowance for each portfolio based on the factors below:
Internal risk factors:
• | Nonperforming loans to total non-margin loans; |
• | Criticized assets to total loans and lending-related commitments; |
• | Borrower concentration; and |
• | Significant concentrations in high-risk industries and countries. |
Environmental risk factors:
• U.S. non-investment grade default rate;
• Unemployment rate; and
• Change in real gross domestic product.
The objective of the qualitative framework is to capture incurred losses that may not have been fully captured in the quantitative reserve, which is based primarily on historical data. Management determines the qualitative allowance each period based on judgment informed by consideration of internal and external risk factors and other considerations that may be deemed relevant during the period. Once determined in the aggregate, our qualitative allowance is then allocated to each of our loan classes based on the respective classes’ quantitative allowance balances with the allocations adjusted, when necessary, for class specific risk factors.
For each risk factor, we calculate the minimum and maximum values, and percentiles in-between, to evaluate the distribution of our historical experience. The distribution of historical experience is compared to the risk factor’s current quarter observed experience to assess the current risk inherent in the
30 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
portfolio and overall direction/trend of a risk factor relative to our historical experience.
Based on this analysis, we assign a risk level–no impact, low, moderate, high and elevated–to each risk factor for the current quarter. Management assesses the impact of each risk factor to determine an aggregate risk level. We do not quantify the impact of any particular risk factor. Management’s assessment of the risk factors, as well as the trend in the quantitative allowance, supports management’s judgment for the overall required qualitative allowance. A smaller qualitative allowance may be required when our quantitative allowance has reflected incurred losses associated with the aggregate risk level. A greater qualitative allowance may be required if our quantitative allowance does not yet reflect the incurred losses associated with the aggregate risk level.
To the extent actual results differ from forecasts or management’s judgment, the allowance for credit losses may be greater or less than future charge-offs.
The credit rating assigned to each credit is a significant variable in determining the allowance. If each credit were rated one grade better, the allowance would have decreased by $67 million, while if each credit were rated one grade worse, the allowance would have increased by $119 million. Similarly, if the loss given default were one rating worse, the allowance would have increased by $43 million, while if the loss given default were one rating better, the allowance would have decreased by $30 million. For impaired credits, if the net carrying value of the loans was 10% higher or lower, the allowance would have decreased or increased by less than $1 million, respectively.
Fair value of financial instruments and derivatives
The guidance included in Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820, Fair Value Measurement, defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value, and expands disclosures about assets and liabilities measured at fair value. The standard also established a three-level hierarchy for fair value measurements based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date.
Fair value - Securities
Level 1 - Securities: Recent quoted prices from exchange transactions are used for debt and equity securities that are actively traded on exchanges and for U.S. Treasury securities and U.S. government securities that are actively traded in highly liquid over-the-counter markets.
Level 2 - Securities: For securities where quotes from recent transactions are not available for identical securities, we determine fair value primarily based on pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency. The pricing sources employ financial models or obtain comparisons to similar instruments to arrive at “consensus” prices.
Specifically, the pricing sources obtain recent transactions for similar types of securities (e.g., vintage or position in the securitization structure) and ascertain variables such as discount rate and speed of prepayment for the type of transaction and apply such variables to similar types of bonds. We view these as observable transactions in the current market place and classify such securities as Level 2.
In addition, we have significant investments in more actively traded agency RMBS and other types of securities such as sovereign debt. The pricing sources derive the prices for these securities largely from quotes they obtain from three major inter-dealer brokers. The pricing sources receive their daily observed trade price and other information feeds from the inter-dealer brokers.
We obtain prices for our Level 1 and Level 2 securities from multiple pricing sources. We have designed controls to develop an understanding of the pricing sources’ securities pricing methodology and have implemented specific internal controls over the valuation of securities.
As appropriate, we review the quality control procedures and pricing methodologies used by the pricing sources, including the process for obtaining prices provided by the pricing sources, their valuation methodology and controls for each class of security.
Prices received from pricing sources are subject to validation checks that help determine the completeness and accuracy of the prices. These validation checks are reviewed by management and, based on the results, may be subject to additional
BNY Mellon 31
Results of Operations (continued) |
review and investigation. We also review securities with no price changes (stale prices) and securities with zero values.
We have a surveillance process in place to monitor the accuracy of prices provided by the pricing sources. We utilize a hierarchy that compares security prices obtained from multiple pricing sources against established thresholds. Discrepancies that fall outside of these thresholds are challenged with the pricing services and adjusted if necessary.
If further research is required, we review and validate these prices with the pricing sources. We also validate prices from pricing sources by comparing prices received to actual observed prices from actions such as purchases and sales, when possible.
At Dec. 31, 2016, more than 99% of our securities were valued by pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency.
Level 3 - Securities: Where we have used our own cash flow models, which included a significant input into the model that was deemed unobservable, to estimate the value of securities, we classify them in Level 3 of the ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, hierarchy. At both Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we have no instruments included in Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
See Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for details of our securities by ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, hierarchy level.
Fair value - Derivative financial instruments
Level 1 - Derivative financial instruments: Includes derivative financial instruments that are actively traded on exchanges, principally listed equity options.
Level 2 - Derivative financial instruments: Includes the vast majority of our over-the-counter derivative financial instruments. Derivatives classified as Level 2 are valued utilizing discounted cash flow analysis and financial models for which the valuation inputs are observable or can be corroborated, directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the instrument. Valuation inputs include interest rate yield curves, foreign exchange rates, equity prices, credit curves, option volatilities and other factors.
Where appropriate, valuation adjustments are made to account for various factors such as credit worthiness of the counterparty, credit worthiness of the Company and model and liquidity risks. Level 2 over-the-counter derivatives generally include interest rate swaps and options, foreign exchanges forwards, foreign exchange swaps and options, forward rate agreements, equity swaps and options, and credit default swaps.
Level 3 - Derivative financial instruments: Level 3 derivatives include derivatives for which valuations are based on inputs that are unobservable and significant to the overall fair value measurement, and may include certain long-dated or highly structured contracts. At both Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we have no derivatives included in Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
For details of our derivative financial instruments by level of the valuation hierarchy, see Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Fair value option
ASC 825, Financial Instruments, provides the option to elect fair value as an alternative measurement basis for selected financial assets, financial liabilities, unrecognized firm commitments and written loan commitments which are not subject to fair value under other accounting standards. Under ASC 825, Financial Instruments, fair value is used for both the initial and subsequent measurement of the designated assets, liabilities and commitments, with the changes in fair value recognized in income. See Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional disclosure regarding the fair value option.
Fair value - Judgments
In times of illiquid markets and financial stress, actual prices and valuations may significantly diverge from results predicted by models. In addition, other factors can affect our estimate of fair value, including market dislocations, incorrect model assumptions, and unexpected correlations. These valuation methods could expose us to materially different results should the models used or underlying assumptions be inaccurate. See “Summary of significant accounting and reporting policies” in Note 1 to the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
32 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Other-than-temporary impairment
The guidance included in ASC 320, Investments - Debt and Equity Securities, defines the OTTI model for investments in debt securities. Under this guidance, a debt security is considered impaired if its fair value is less than its amortized cost basis. An OTTI is triggered if (1) the intent is to sell the security; (2) the security will more likely than not have to be sold before the impairment is recovered, or (3) the amortized cost basis is not expected to be recovered. When an entity does not intend to sell the security before recovery of its cost basis, it will recognize the credit component of an OTTI of a debt security in earnings and the remaining portion in accumulated other comprehensive income.
The determination of whether a credit loss exists is based on best estimates of the present value of cash flows to be collected from the debt security. Generally, cash flows are discounted at the effective interest rate implicit in the debt security at the time of acquisition. For debt securities that are beneficial interests in securitized financial assets and are not high credit quality, ASC 325, Investment - Other, provides that cash flows be discounted at the current yield used to accrete the beneficial interest.
For each security in the investment securities portfolio (including, but not limited to, those whose fair value is less than their amortized cost basis), an extensive, quarterly review is conducted to determine if an OTTI has occurred. For example, to determine if an unrealized loss on non-agency RMBS is other-than-temporary, we project total estimated defaults of the underlying assets (mortgages) and multiply that calculated amount by an estimate of realizable value upon sale of these assets in the marketplace (severity) in order to determine the projected collateral loss. We also evaluate the current credit enhancement underlying the bond to determine the impact on cash flows. If we determine that a given non-agency RMBS will be subject to a write-down or loss, we record the expected credit loss as a charge to earnings.
In recent years, improving home prices helped to stabilize the credit performance of non-agency RMBS transactions. This in turn enabled us to maintain generally stable assumptions for these transactions with regard to estimated defaults and the amount we expect to receive to cover the value of the loans underlying the securities. See Note 3 of the Notes to
Consolidated Financial Statements for projected weighted-average default rates and loss severities at Dec. 31, 2016 and 2015 for the 2007, 2006 and late-2005 non-agency RMBS and the securities previously held in the Grantor Trust we established in connection with the restructuring of our investment securities portfolio in 2009. If actual delinquencies, default rates and loss severity assumptions worsen, we would expect additional impairment losses to be recorded in future periods.
Net securities gains in 2016 were $75 million compared with $83 million in 2015.
At Dec. 31, 2016, if we were to increase each of our projected loss severity and default rates by 100 basis points on each of the positions in our Alt-A, subprime and prime RMBS portfolios, including the securities previously held by the Grantor Trust, credit-related impairment charges on these securities would have increased by less than $1 million (pre-tax). If we were to decrease each of our projected loss severity and default rates by 100 basis points on each of the positions, credit-related impairment charges on these securities would have decreased by less than $1 million (pre-tax).
Goodwill and other intangibles
We initially record all assets and liabilities acquired in purchase acquisitions, including goodwill, indefinite-lived intangibles and other intangibles, in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations. Goodwill, indefinite-lived intangibles and other intangibles are subsequently accounted for in accordance with ASC 350, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other. The initial measurement of goodwill and intangibles requires judgment concerning estimates of the fair value of the acquired assets and liabilities. Goodwill ($17.3 billion at Dec. 31, 2016) and indefinite-lived intangible assets ($2.6 billion at Dec. 31, 2016) are not amortized but subject to tests for impairment annually or more often if events or circumstances indicate it is more likely than not they may be impaired. Other intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives and are subject to impairment if events or circumstances indicate a possible inability to realize the carrying amount.
BNY Mellon’s three business segments include eight reporting units for which annual goodwill impairment testing is performed in accordance with ASC 350,
BNY Mellon 33
Results of Operations (continued) |
Intangibles - Goodwill and Other. The Investment Management segment is comprised of two reporting units; the Investment Services segment is comprised of five reporting units and one reporting unit is included in the Other segment.
The goodwill impairment test is performed in two steps. The first step compares the estimated fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the estimated fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, goodwill of the reporting unit is considered not impaired. However, if the carrying amount of the reporting unit were to exceed its estimated fair value, a second step would be performed that would compare the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. An impairment loss would be recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair value. A substantial goodwill impairment charge would not have a significant impact on our financial condition, but could have an adverse impact on our results of operations. In addition, due to regulatory restrictions, the Company’s subsidiary banks could be restricted from distributing available cash to the Parent, resulting in the Parent needing to issue additional long-term debt.
In the second quarter of 2016, we performed our annual goodwill test on all eight reporting units using an income approach to estimate the fair values of each reporting unit. Estimated cash flows used in the income approach were based on management’s projections as of April 1, 2016. The discount rate applied to these cash flows ranged from 10.0% to 11.0% and incorporated a 7.0% market equity risk premium. Estimated cash flows extend far into the future, and, by their nature, are difficult to estimate over such an extended time frame.
As of the date of the annual test, the fair values of seven of the Company’s reporting units were substantially in excess of the respective reporting units’ carrying value. The fair value of the Asset Management reporting unit, which is one of the two reporting units in the Investment Management segment, exceeded its carrying value by 11%. The Asset Management reporting unit had $7.5 billion of allocated goodwill. For the Asset Management reporting unit, in the future, small changes in the assumptions could produce a non-cash goodwill impairment, which would have no effect on our regulatory capital ratios. In addition, certain money
market fee waiver practices and changes in the level of AUM could have an effect on Asset Management broadly, as well as the fair value of this reporting unit.
Key judgments in accounting for intangibles include useful life and classification between goodwill and indefinite-lived intangibles or other intangibles requiring amortization.
Indefinite-lived intangible assets are evaluated for impairment at least annually by comparing their fair values, estimated using discounted cash flow analyses, to their carrying values. Other amortizing intangible assets ($1.0 billion at Dec. 31, 2016) are evaluated for impairment if events and circumstances indicate a possible impairment. Such evaluation of other intangible assets is initially based on undiscounted cash flow projections.
See Notes 1 and 5 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding goodwill, intangible assets and the annual and interim impairment testing.
Pension accounting
BNY Mellon has defined benefit pension plans covering approximately 13,900 U.S. employees and approximately 14,500 non-U.S. employees.
BNY Mellon has two qualified and several non-qualified defined benefit pension plans in the U.S. and several pension plans overseas. As of Dec. 31, 2016, the U.S. plans accounted for 77% of the projected benefit obligation. The pension credit for BNY Mellon plans was $44 million in 2016 compared with a pension credit of $10 million in 2015 and pension expense of $68 million in 2014.
Effective June 30, 2015, the benefit accruals under the U.S. qualified and nonqualified defined benefit plans were frozen. This change resulted in no additional benefits being earned by participants in those plans based on service or pay after June 30, 2015. These plans were previously closed to new participants effective Dec. 31, 2010, at which time a non-elective contribution was added to the Company’s defined contribution plan for employees not eligible to join the pension plan. Employees previously participating in the pension plan received this non-elective contribution starting July 1, 2015.
34 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
A total net pension credit of $30 million is expected to be recorded by BNY Mellon in 2017, assuming currency exchange rates at Dec. 31, 2016. The expected decrease in the net pension credit in 2017 compared to 2016 is primarily driven by an increase in pension costs due to lower discount rates and reductions in the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets for U.S. and certain foreign plans.
A number of key assumptions and measurement date values determine pension expense. The key elements include the long-term rate of return on plan assets, the discount rate, the market-related value of plan assets and the price used to value stock in the Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”). Since 2014, these key elements have varied as follows:
(dollars in millions, except per share amounts) | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||
Domestic plans: | ||||||||||||
Long-term rate of return on plan assets | 6.625 | % | 7.00 | % | 7.25 | % | 7.25 | % | ||||
Discount rate (a) | 4.35 | % | 4.48 | % | 4.13 | % | 4.99 | % | ||||
Market-related value of plan assets (b) | $ | 5,026 | $ | 4,830 | $ | 4,696 | $ | 4,430 | ||||
ESOP stock price (b) | $ | 44.19 | $ | 41.66 | $ | 39.18 | $ | 32.81 | ||||
Net U.S. pension credit/(expense) | N/A | $ | 77 | $ | 52 | $ | (34 | ) | ||||
All other net pension credit/(expense) | N/A | (33 | ) | (42 | ) | (34 | ) | |||||
Total net pension credit/(expense) | N/A | $ | 44 | $ | 10 | $ | (68 | ) | ||||
(a) | As a result of the amendment to the U.S. pension plans, liabilities for 2015 were re-measured as of Jan. 29, 2015 at a discount rate of 3.73%. |
(b) | Market-related value of plan assets and ESOP stock price are for the beginning of the plan year. See “Summary of significant accounting and reporting policies” in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The market-related value of plan assets was $4,713 million as of the Jan. 29, 2015 re-measurement. |
The discount rate for U.S. pension plans was determined after reviewing equivalent rates obtained by discounting the pension plans’ expected cash flows using various high-quality, long-term corporate bond yield curves. We also reviewed the results of several models that matched bonds to our pension cash flows. After reviewing the various indices and models, we selected a discount rate of 4.35% as of Dec. 31, 2016.
The discount rates for foreign pension plans are based on high-quality corporate bond rates in countries that have an active corporate bond market. In those countries with no active corporate bond market,
discount rates are based on local government bond rates plus a credit spread.
Our expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is based on anticipated returns for each applicable asset class. Anticipated returns are weighted for the expected allocation for each asset class and are based on forecasts for prospective returns in the equity and fixed income markets, which should track the long-term historical returns for these markets. We also consider the growth outlook for U.S. and global economies, as well as current and prospective interest rates.
The market-related value of plan assets also influences the level of pension expense. Differences between expected and actual returns are recognized over five years to compute an actuarially derived market-related value of plan assets.
Unrecognized actuarial gains and losses are amortized over the future service period of active employees if they exceed a threshold amount. As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon had $1.5 billion of unrecognized losses which are being amortized. As a result of the amendment to the U.S. pension plans described above, future unrecognized actuarial gains and losses for the U.S. plans that exceed a threshold amount will be amortized over the average future life expectancy of plan participants with a maximum of 15 years.
The annual impacts of hypothetical changes in the key assumptions on pension costs are shown in the table below.
Pension expense | ||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions, except per share amounts) | Increase in pension expense | (Decrease) in pension expense | ||||||||||||||
Long-term rate of return on plan assets | (100 | ) | bps | (50 | ) | bps | 50 | bps | 100 | bps | ||||||
Change in pension expense | $ | 60 | $ | 30 | $ | (30 | ) | $ | (60 | ) | ||||||
Discount rate | (50 | ) | bps | (25 | ) | bps | 25 | bps | 50 | bps | ||||||
Change in pension expense | $ | 29 | $ | 14 | $ | (14 | ) | $ | (27 | ) | ||||||
Market-related value of plan assets | (20 | ) | % | (10 | ) | % | 10 | % | 20 | % | ||||||
Change in pension expense | $ | 170 | $ | 85 | $ | (84 | ) | $ | (159 | ) | ||||||
ESOP stock price | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | $ | 5 | $ | 10 | ||||||
Change in pension expense | $ | 6 | $ | 3 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | ||||||
BNY Mellon 35
Results of Operations (continued) |
In addition to its pension plans, BNY Mellon has an ESOP. Benefits payable under The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation Pension Plan are offset by the equivalent value of benefits earned under the ESOP for employees who participated in the legacy Retirement Plan of The Bank of New York Company, Inc.
Consolidated balance sheet review
One of our key risk management objectives is to maintain a balance sheet that remains strong throughout market cycles to meet the expectations of our major stakeholders, including our shareholders, clients, creditors and regulators.
We also seek to ensure that the overall liquidity risk, including intra-day liquidity risk, that we undertake stays within our risk appetite. In managing the balance sheet, appropriate consideration is given to balancing the competing needs to maintain sufficient levels of liquidity and complying with applicable regulations and supervisory expectations while optimizing profitability. The objective of our balance sheet management strategy is to maintain a balance sheet that is characterized by strong liquidity and asset quality, ready access to external funding sources at competitive rates and a strong capital structure that supports our risk-taking activities and that is adequate to absorb potential losses.
In 2016, we undertook a balance sheet strategy to meet competing objectives, including maintaining sufficient liquidity and complying with applicable regulations and supervisory expectations while optimizing profitability. Specifically, we increased the SLR to 5.6% at Dec. 31, 2016 from 4.9% at Dec. 31, 2015. This is above the regulatory minimum of 5.0%, which becomes effective Jan. 1, 2018. We also took actions to increase the Liquidity coverage ratio (“LCR”) over the minimum requirement in anticipation of the regulatory minimum increasing from 90% to 100% at Jan. 1, 2017. Finally, we opportunistically reduced lower-yielding non-HQLA to more effectively position the balance sheet to support our liquidity needs while also meeting our net interest income objectives.
At Dec. 31, 2016, total assets were $333 billion compared with $394 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The
decrease in total assets was primarily driven by lower interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks, and to a lesser degree, lower securities. The lower asset levels reflect a decrease in customer deposits, primarily interest-bearing deposits in non-U.S. offices. Deposits totaled $221 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $280 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. At Dec. 31, 2016, total interest-bearing deposits were 51% of total interest-earning assets, compared with 54% at Dec. 31, 2015.
At Dec. 31, 2016, we had $41 billion of liquid funds (which include interest-bearing deposits with banks and federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements) and $63 billion of cash (including $58 billion of overnight deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks) for a total of $104 billion of available funds. This compares with available funds of $159 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Total available funds as a percentage of total assets were 31% at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with 40% at Dec. 31, 2015. For additional information on our liquid funds and available funds, see “Liquidity and dividends.”
Investment securities were $114.7 billion, or 34% of total assets, at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $119.2 billion, or 30% of total assets, at Dec. 31, 2015. For additional information on our investment securities portfolio, see “Investment securities” and Note 3 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Loans were $64.5 billion, or 19% of total assets, at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $63.7 billion, or 16% of total assets, at Dec. 31, 2015. For additional information on our loan portfolio, see “Loans” and Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Long-term debt totaled $24.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $21.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. For additional information on long-term debt, see “Liquidity and dividends” and Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation total shareholders’ equity increased to $38.8 billion from $38.0 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. For additional information on our capital, see “Capital” and Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
36 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Investment securities
In the discussion of our investment securities portfolio, we have included certain credit ratings information because the information can indicate the degree of credit risk to which we are exposed.
Significant changes in ratings classifications for our investment securities portfolio could indicate increased credit risk for us and could be accompanied by a reduction in the fair value of our investment securities portfolio.
The following table shows the distribution of our total investment securities portfolio.
Investment securities portfolio (dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2015 | 2016 change in unrealized gain (loss) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Fair value as a % of amortized cost (a) | Unrealized gain (loss) | Ratings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
BB+ and lower | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value | Amortized cost | Fair value | AAA/ AA- | A+/ A- | BBB+/ BBB- | Not rated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Agency RMBS | $ | 49,464 | $ | (314 | ) | $ | 48,150 | $ | 47,715 | 99 | % | $ | (435 | ) | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 23,920 | (147 | ) | 25,490 | 25,244 | 99 | (246 | ) | 100 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed (b) | 16,708 | 80 | 14,159 | 14,373 | 102 | 214 | 75 | 5 | 20 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (c) | 1,789 | (77 | ) | 1,080 | 1,357 | 80 | 277 | — | 1 | 2 | 87 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 914 | 6 | 698 | 718 | 94 | 20 | 8 | 4 | 15 | 72 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
European floating rate notes (d) | 1,345 | 13 | 717 | 706 | 98 | (11 | ) | 68 | 24 | 8 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Commercial MBS | 5,826 | (27 | ) | 8,106 | 8,037 | 99 | (69 | ) | 98 | 2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 4,065 | (92 | ) | 3,411 | 3,396 | 100 | (15 | ) | 80 | 17 | — | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||
Foreign covered bonds (e) | 2,242 | (25 | ) | 2,200 | 2,216 | 101 | 16 | 100 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 1,752 | (7 | ) | 1,391 | 1,396 | 100 | 5 | 18 | 67 | 15 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
CLOs | 2,351 | 17 | 2,593 | 2,598 | 100 | 5 | 100 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
U.S. government agencies | 1,810 | 16 | 1,955 | 1,964 | 101 | 9 | 100 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Consumer ABS | 2,893 | 14 | 1,729 | 1,727 | 100 | (2 | ) | 90 | 4 | 5 | 1 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Other (f) | 3,700 | (35 | ) | 2,822 | 2,833 | 100 | 11 | 83 | — | 14 | — | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total investment securities | $ | 118,779 | (g) | $ | (578 | ) | $ | 114,501 | $ | 114,280 | (g) | 99 | % | $ | (221 | ) | (g)(h) | 93 | % | 2 | % | 3 | % | 2 | % | — | % | |||
(a) | Amortized cost before impairments. |
(b) | Primarily consists of exposure to UK, France, Germany, Spain and the Netherlands. |
(c) | These RMBS were included in the former Grantor Trust and were marked-to-market in 2009. We believe these RMBS would receive higher credit ratings if these ratings incorporated, as additional credit enhancements, the difference between the written-down amortized cost and the current face amount of each of these securities. |
(d) | Includes RMBS and commercial MBS. Primarily consists of exposure to UK and the Netherlands. |
(e) | Primarily consists of exposure to Canada, UK, the Netherlands and Sweden. |
(f) | Includes commercial paper with a fair value of $1,900 million and $401 million and money market funds with a fair value of $886 million and $842 million at Dec. 31, 2015 and Dec. 31, 2016, respectively. |
(g) | Includes net unrealized losses on derivatives hedging securities available-for-sale of $292 million at Dec. 31, 2015 and $211 million at Dec. 31, 2016. |
(h) | Unrealized gains of $15 million at Dec. 31, 2016 related to available-for-sale securities, net of hedges. |
The fair value of our total investment securities portfolio was $114.3 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $118.8 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The lower level of securities primarily reflects decreases in a majority of security types, partially offset by increases in commercial MBS and U.S. Treasury securities.
At Dec. 31, 2016, the total investment securities portfolio had a net unrealized pre-tax loss of $221 million compared with a net unrealized pre-tax gain of $357 million at Dec. 31, 2015, including the impact of related hedges. The decrease in the net unrealized pre-tax gain was primarily driven by an increase in market interest rates.
The unrealized gain net of tax on our available-for-sale investment securities portfolio included in accumulated other comprehensive income was $45 million at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $329 million at Dec. 31, 2015.
At Dec. 31, 2016, 93% of the securities in our portfolio were rated AAA/AA- compared with 90% at Dec. 31, 2015.
We routinely test our investment securities for OTTI. See “Critical accounting estimates” for additional information regarding OTTI.
BNY Mellon 37
Results of Operations (continued) |
The following table presents the amortizable purchase premium (net of discount) related to the investment securities portfolio and accretable discount related to the 2009 restructuring of the investment securities portfolio.
Net premium amortization and discount accretion of investment securities (a) | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Amortizable purchase premium (net of discount) relating to investment securities: | |||||||||
Balance at period end | $ | 2,188 | $ | 2,319 | $ | 2,432 | |||
Estimated average life remaining at period end (in years) | 4.9 | 4.7 | 4.8 | ||||||
Amortization | $ | 641 | $ | 693 | $ | 626 | |||
Accretable discount related to the prior restructuring of the investment securities portfolio: | |||||||||
Balance at period end | $ | 315 | $ | 355 | $ | 413 | |||
Estimated average life remaining at period end (in years) | 6.2 | 6.1 | 5.9 | ||||||
Accretion | $ | 102 | $ | 126 | $ | 163 | |||
(a) | Amortization of purchase premium decreases net interest revenue while accretion of discount increases net interest revenue. Both were recorded on a level yield basis. |
The following table presents pre-tax net securities gains by type.
Net securities gains | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Agency RMBS | $ | 22 | $ | 10 | $ | 13 | |||
Foreign covered bonds | 10 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 8 | 7 | 17 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 4 | 45 | 25 | ||||||
Other | 31 | 19 | 33 | ||||||
Total net securities gains | $ | 75 | $ | 83 | $ | 91 | |||
The following table shows the fair value of the European floating rate notes by geographical location at Dec. 31, 2016. The unrealized loss on these securities was $11 million at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $24 million at Dec. 31, 2015.
European floating rate notes at Dec. 31, 2016 (a) | |||||||||
(in millions) | RMBS | Other | Total fair value | ||||||
United Kingdom | $ | 347 | $ | 55 | $ | 402 | |||
The Netherlands | 247 | — | 247 | ||||||
Ireland | 57 | — | 57 | ||||||
Total fair value | $ | 651 | $ | 55 | $ | 706 | |||
(a) | Sixty-eight percent of these securities are in the AAA to AA- ratings category. |
See Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for details of securities by level in the fair value hierarchy.
Equity investments
Our equity in a joint venture and other investments are primarily categorized as other assets. The following table presents the carrying values at Dec. 31, 2016 and 2015.
Equity in joint venture and other investments | Dec. 31, | |||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Renewable energy investments | $ | 1,282 | $ | 640 | ||
Equity in a joint venture and other investments: | ||||||
CIBC Mellon | 509 | 473 | ||||
Siguler Guff | 256 | 262 | ||||
ConvergEx | 76 | 86 | ||||
Other equity investments | 222 | 218 | ||||
Total equity in a joint venture and other investments | 1,063 | 1,039 | ||||
Tax-advantaged low-income housing investments | 914 | 918 | ||||
Federal Reserve Bank stock | 466 | 453 | ||||
Seed capital | 395 | 245 | ||||
Private equity investments (a) | 43 | 34 | ||||
Total equity in a joint venture and other investments | $ | 4,163 | $ | 3,329 | ||
(a) | Represents investments in small business investment companies (“SBICs”), which are compliant with the Volcker Rule. |
Renewable energy investments
We invest in renewable energy projects to receive an expected after-tax return, which consists of allocated renewable energy tax credits, tax deductions and cash distributions based on the operations of the project. The pre-tax losses on these investments are recorded in investment and other income on the Income Statement. The corresponding tax benefits and credits are recorded as a reduction to the provision for
38 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
income taxes on the Income Statement. As a result of increased investments in renewable energy in 2016, we expect investment and other income to be negatively impacted in future periods.
For additional information on the fair value of certain seed capital investments and our private equity investments, see Note 6 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Loans
Total exposure – consolidated | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
(in billions) | Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | |||||||||||||
Non-margin loans: | |||||||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | $ | 14.7 | $ | 33.7 | $ | 48.4 | $ | 15.9 | $ | 36.0 | $ | 51.9 | |||||||
Commercial | 2.6 | 17.5 | 20.1 | 2.3 | 18.2 | 20.5 | |||||||||||||
Subtotal institutional | 17.3 | 51.2 | 68.5 | 18.2 | 54.2 | 72.4 | |||||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 15.6 | 1.3 | 16.9 | 13.3 | 1.6 | 14.9 | |||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 4.7 | 3.2 | 7.9 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 7.2 | |||||||||||||
Lease financings | 1.7 | — | 1.7 | 1.9 | — | 1.9 | |||||||||||||
Other residential mortgages | 0.9 | — | 0.9 | 1.1 | — | 1.1 | |||||||||||||
Overdrafts | 5.5 | — | 5.5 | 4.5 | — | 4.5 | |||||||||||||
Other | 1.2 | — | 1.2 | 1.2 | — | 1.2 | |||||||||||||
Subtotal non-margin loans | 46.9 | 55.7 | 102.6 | 44.1 | 59.1 | 103.2 | |||||||||||||
Margin loans | 17.6 | 0.1 | 17.7 | 19.6 | 0.6 | 20.2 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 64.5 | $ | 55.8 | $ | 120.3 | $ | 63.7 | $ | 59.7 | $ | 123.4 | |||||||
At Dec. 31, 2016, total exposures were $120.3 billion, a decrease of 3% compared with Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease in total exposure primarily reflects lower exposure to financial institutions and lower margin loans, partially offset by higher wealth management loans and mortgages and overdrafts.
Our financial institutions and commercial portfolios comprise our largest concentrated risk. These portfolios comprised 57% of our total exposure at Dec. 31, 2016 and 59% at Dec. 31, 2015. Additionally, a substantial portion of our overdrafts relate to financial institutions.
Financial institutions
The financial institutions portfolio is shown below.
Financial institutions portfolio exposure (dollar amounts in billions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | % Inv. grade | % due <1 yr. | Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | ||||||||||||||||
Securities industry | $ | 3.8 | $ | 19.2 | $ | 23.0 | 99 | % | 99 | % | $ | 3.1 | $ | 20.6 | $ | 23.7 | |||||||
Banks | 7.9 | 2.0 | 9.9 | 69 | 95 | 9.4 | 2.1 | 11.5 | |||||||||||||||
Asset managers | 1.5 | 6.2 | 7.7 | 97 | 82 | 2.0 | 5.6 | 7.6 | |||||||||||||||
Insurance | 0.1 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 99 | 25 | 0.2 | 4.5 | 4.7 | |||||||||||||||
Government | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 91 | 40 | 0.1 | 1.9 | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.9 | 99 | 32 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 2.4 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 14.7 | $ | 33.7 | $ | 48.4 | 92 | % | 84 | % | $ | 15.9 | $ | 36.0 | $ | 51.9 | |||||||
The financial institutions portfolio exposure was $48.4 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $51.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower exposure in the banks, government and insurance portfolios.
Financial institution exposures are high-quality, with 92% of the exposures meeting the investment grade equivalent criteria of our internal credit rating
classification at Dec. 31, 2016. Each customer is assigned an internal credit rating, which is mapped to an equivalent external rating agency grade based upon a number of dimensions which are continually evaluated and may change over time. The exposure to financial institutions is generally short-term. Of these exposures, 84% expire within one year and 21% expire within 90 days. In addition, 80% of the financial institutions exposure is secured. For
BNY Mellon 39
Results of Operations (continued) |
example, securities industry clients and asset managers often borrow against marketable securities held in custody.
For ratings of non-U.S. counterparties, our internal credit rating is generally capped at a rating equivalent to the sovereign rating of the country where the counterparty resides, regardless of the internal credit rating assigned to the counterparty or the underlying collateral.
At Dec. 31, 2016, the secured intraday credit provided to dealers in connection with their tri-party repo activity totaled $18.7 billion and was primarily included in the securities industry portfolio. Dealers secure the outstanding intraday credit with high-quality liquid collateral having a market value in excess of the amount of the outstanding credit.
Our bank exposure primarily relates to our global trade finance. These exposures are short-term in nature, with 95% due in less than one year. The investment grade percentage of our bank exposure was 69% at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with 86% at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease in the investment grade percentage reflects the impact of the downgrade in the sovereign rating of Brazil to noninvestment grade. Our exposure in Brazil includes $1.3 billion in loans, which are primarily short-term trade finance loans extended to large financial institutions.
The asset manager portfolio exposures are high-quality with 97% of the exposures meeting our investment grade equivalent ratings criteria as of Dec. 31, 2016. These exposures are generally short-term liquidity facilities, with the vast majority to regulated mutual funds.
Commercial
The commercial portfolio is presented below.
Commercial portfolio exposure | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in billions) | Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | % Inv. grade | % due <1 yr. | Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | |||||||||||||||
Manufacturing | $ | 1.1 | $ | 6.7 | $ | 7.8 | 94 | % | 11 | % | $ | 0.6 | $ | 6.3 | $ | 6.9 | |||||||
Energy and utilities | 0.6 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 95 | 8 | 0.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | |||||||||||||||
Services and other | 0.6 | 4.3 | 4.9 | 94 | 24 | 0.8 | 5.5 | 6.3 | |||||||||||||||
Media and telecom | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.1 | 96 | 2 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2.6 | $ | 17.5 | $ | 20.1 | 94 | % | 12 | % | $ | 2.3 | $ | 18.2 | $ | 20.5 | |||||||
The commercial portfolio exposure decreased to $20.1 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, from $20.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2015, primarily reflecting a decrease in total exposure in the services and other portfolio, partially offset by an increase in exposure to the manufacturing portfolio.
Utilities-related exposure represents approximately three-quarters of the energy and utilities portfolio. The remaining exposure in the energy and utilities portfolio, which includes exposure to refining, integrated companies, exploration and production companies and pipelines, was 76% investment grade at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with 94% at Dec. 31, 2015.
The following table summarizes the percentage of the financial institutions and commercial portfolio exposures that are investment grade.
Percentage of the portfolios that are investment grade | Dec. 31, | |||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
Financial institutions | 92 | % | 96 | % | 93 | % |
Commercial | 94 | % | 94 | % | 94 | % |
Our credit strategy is to focus on investment grade clients that are active users of our non-credit services. The execution of our strategy has resulted in 92% of our financial institutions portfolio and 94% of our commercial portfolio rated as investment grade at Dec. 31, 2016.
Wealth management loans and mortgages
Our wealth management exposure was $16.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $14.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Wealth management loans and mortgages primarily consist of loans to high net worth individuals, which are secured by marketable securities and/or residential property. Wealth
40 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
management mortgages are primarily interest-only, adjustable-rate mortgages with a weighted-average loan-to-value ratio of 61% at origination. In the wealth management portfolio, less than 1% of the mortgages were past due at Dec. 31, 2016.
At Dec. 31, 2016, the wealth management mortgage portfolio consisted of the following geographic concentrations: California - 24%; New York - 19%; Massachusetts - 12%; Florida - 7%; and other - 38%.
Commercial real estate
Our income-producing commercial real estate facilities are focused on experienced owners and are structured with moderate leverage based on existing cash flows. Our commercial real estate lending activities also include construction and renovation facilities. Our client base consists of experienced developers and long-term holders of real estate assets. Loans are approved on the basis of existing or projected cash flows, and supported by appraisals and knowledge of local market conditions. Development loans are structured with moderate leverage, and in many instances, involve some level of recourse to the developer. Our commercial real estate exposure totaled $7.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $7.2 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
At Dec. 31, 2016, 60% of our commercial real estate portfolio was secured. The secured portfolio is diverse by project type, with 46% secured by residential buildings, 36% secured by office buildings, 12% secured by retail properties and 6% secured by other categories. Approximately 97% of the unsecured portfolio consists of real estate investment trusts (“REITs”) and real estate operating companies, which are both predominantly investment grade.
At Dec. 31, 2016, our commercial real estate portfolio consists of the following concentrations: New York metro - 42%; REITs and real estate operating companies - 39%; and other - 19%.
Lease financings
The leasing portfolio exposure totaled $1.7 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $1.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. At Dec. 31, 2016, approximately 93% of the leasing portfolio exposure was investment grade, or investment grade equivalent.
At Dec. 31, 2016, the lease financing portfolio consisted of exposures backed by well-diversified assets, primarily large-ticket transportation equipment. The largest component is rail, consisting of both passenger and freight train cars. Assets are both domestic and foreign-based, with primary concentrations in the United States and Germany. Approximately 45% of this portfolio is additionally secured by highly rated securities and/or secured by letters of credit from investment grade issuers. Counterparty rating equivalents at Dec. 31, 2016 were as follows:
• | 42% of the counterparties were A, or equivalent; |
• | 51% were BBB; and |
• | 7% were non-investment grade. |
Other residential mortgages
The other residential mortgages portfolio primarily consists of 1-4 family residential mortgage loans and totaled $0.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $1.1 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Included in this portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016 are $221 million of mortgage loans purchased in 2005, 2006 and the first quarter of 2007 that are predominantly prime mortgage loans, with a small portion of Alt-A loans. As of Dec. 31, 2016, the purchased loans in this portfolio had a weighted-average loan-to-value ratio of 76% at origination and 14% of the serviced loan balance was at least 60 days delinquent. The properties securing the prime and Alt-A mortgage loans were located (in order of concentration) in California, Florida, Virginia, the tri-state area (New York, New Jersey and Connecticut) and Maryland.
To determine the projected loss on the prime and Alt-A mortgage portfolios, we calculate the total estimated defaults of these mortgages and multiply that amount by an estimate of realizable value upon sale in the marketplace (severity).
Overdrafts
Overdrafts primarily relate to custody and securities clearance clients. Overdrafts occur on a daily basis in the custody and securities clearance business and are generally repaid within two business days.
Other loans
Other loans primarily include loans to consumers that are fully collateralized with equities, mutual funds and fixed income securities.
BNY Mellon 41
Results of Operations (continued) |
Margin loans
Margin loans are collateralized with marketable securities, and borrowers are required to maintain a daily collateral margin in excess of 100% of the value
of the loan. Margin loans include $6.3 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $7.8 billion at Dec. 31, 2015 related to a term loan program that offers fully collateralized loans to broker-dealers.
Loans by category
The following table shows loans outstanding at year-end over the last five years.
Loans by category – at year-end | Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Domestic: | |||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | $ | 6,342 | $ | 6,640 | $ | 5,603 | $ | 4,511 | $ | 5,455 | |||||
Commercial | 2,286 | 2,115 | 1,390 | 1,534 | 1,306 | ||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 15,555 | 13,247 | 11,095 | 9,743 | 8,796 | ||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 4,639 | 3,899 | 2,524 | 2,001 | 1,677 | ||||||||||
Lease financings | 989 | 1,007 | 1,282 | 1,322 | 1,329 | ||||||||||
Other residential mortgages | 854 | 1,055 | 1,222 | 1,385 | 1,632 | ||||||||||
Overdrafts | 1,055 | 911 | 1,348 | 1,314 | 2,228 | ||||||||||
Other | 1,202 | 1,137 | 1,113 | 768 | 639 | ||||||||||
Margin loans | 17,503 | 19,340 | 20,034 | 15,652 | 13,397 | ||||||||||
Total domestic | 50,425 | 49,351 | 45,611 | 38,230 | 36,459 | ||||||||||
Foreign: | |||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | 8,347 | 9,259 | 7,716 | 9,848 | 5,833 | ||||||||||
Commercial | 331 | 227 | 252 | 113 | 111 | ||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 99 | 100 | 89 | 75 | 68 | ||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 15 | 46 | 6 | 9 | 63 | ||||||||||
Lease financings | 736 | 850 | 889 | 945 | 1,025 | ||||||||||
Other (primarily overdrafts) | 4,418 | 3,637 | 4,569 | 2,437 | 3,070 | ||||||||||
Margin loans | 87 | 233 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Total foreign | 14,033 | 14,352 | 13,521 | 13,427 | 10,170 | ||||||||||
Total loans (a) | $ | 64,458 | $ | 63,703 | $ | 59,132 | $ | 51,657 | $ | 46,629 | |||||
(a) | Net of unearned income of $527 million at Dec. 31, 2016, $674 million at Dec. 31, 2015, $866 million at Dec. 31, 2014, $1,020 million at Dec. 31, 2013 and $1,135 million at Dec. 31, 2012, primarily on domestic and foreign lease financings. |
Foreign loans
We have credit relationships in foreign markets, particularly in areas associated with our securities servicing and trade finance activities. Excluding lease financings, these activities resulted in outstanding foreign loans of $13.3 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $13.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease primarily resulted from lower loans to financial institutions and margin loans, partially offset by higher other loans.
Maturity of loan portfolio
The following table shows the maturity structure of our loan portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016.
Maturity of loan portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016 (a) | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Within 1 year | Between 1 and 5 years | After 5 years | Total | ||||||||||
Domestic: | ||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | $ | 5,120 | $ | 837 | $ | 385 | $ | 6,342 | ||||||
Commercial | 314 | 1,972 | — | 2,286 | ||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 680 | 2,508 | 1,451 | 4,639 | ||||||||||
Overdrafts | 1,055 | — | — | 1,055 | ||||||||||
Other | 1,202 | — | — | 1,202 | ||||||||||
Margin loans | 17,253 | 250 | — | 17,503 | ||||||||||
Subtotal | 25,624 | 5,567 | 1,836 | 33,027 | ||||||||||
Foreign | 12,266 | 877 | 55 | 13,198 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 37,890 | $ | 6,444 | (b) | $ | 1,891 | (b) | $ | 46,225 | ||||
(a) | Excludes loans collateralized by residential properties, lease financings and wealth management loans and mortgages. |
(b) | Variable rate loans due after one year totaled $8.3 billion and fixed rate loans totaled $69 million. |
42 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Asset quality and allowance for credit losses
Over the past several years, we have improved our risk profile through greater focus on clients who are active users of our non-credit services. Our primary exposure to the credit risk of a customer consists of funded loans, unfunded formal contractual commitments to lend, standby letters of credit and overdrafts associated with our custody and securities clearance businesses.
The role of credit has shifted to one that complements our other services instead of as a lead product. We believe credit solidifies customer relationships and, through a disciplined allocation of capital, we can earn acceptable rates of return as part of an overall relationship.
The following table details changes in our allowance for credit losses.
Allowance for credit losses activity (dollar amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Margin loans | $ | 17,590 | $ | 19,573 | $ | 20,034 | $ | 15,652 | $ | 13,397 | |||||
Non-margin loans | 46,868 | 43,708 | 39,077 | 36,005 | 33,232 | ||||||||||
Total loans | $ | 64,458 | $ | 63,281 | $ | 59,111 | $ | 51,657 | $ | 46,629 | |||||
Average loans outstanding | $ | 61,681 | $ | 60,672 | $ | 54,210 | $ | 48,316 | $ | 43,060 | |||||
Balance, Jan. 1 | |||||||||||||||
Domestic | $ | 240 | $ | 236 | $ | 288 | $ | 339 | $ | 439 | |||||
Foreign | 35 | 44 | 56 | 48 | 58 | ||||||||||
Total allowance at Jan. 1 | 275 | 280 | 344 | 387 | 497 | ||||||||||
Charge-offs: | |||||||||||||||
Commercial | — | — | (12 | ) | (4 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||
Commercial real estate | — | — | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | — | ||||||||
Financial institutions | — | (170 | ) | — | — | (13 | ) | ||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | — | — | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||
Other residential mortgages | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | (8 | ) | (22 | ) | |||||
Foreign | — | — | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | — | ||||||||
Total charge-offs | (2 | ) | (172 | ) | (20 | ) | (17 | ) | (38 | ) | |||||
Recoveries: | |||||||||||||||
Commercial | — | — | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||
Financial institutions | 13 | 1 | 1 | 4 | — | ||||||||||
Other residential mortgages | 5 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 6 | ||||||||||
Foreign | 1 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Total recoveries | 19 | 7 | 4 | 9 | 8 | ||||||||||
Net recoveries (charge-offs) | 17 | (165 | ) | (16 | ) | (8 | ) | (30 | ) | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | (11 | ) | 160 | (48 | ) | (35 | ) | (80 | ) | ||||||
Balance, Dec. 31, | |||||||||||||||
Domestic | 245 | 240 | 236 | 288 | 339 | ||||||||||
Foreign | 36 | 35 | 44 | 56 | 48 | ||||||||||
Total allowance, Dec. 31, | $ | 281 | $ | 275 | $ | 280 | $ | 344 | $ | 387 | |||||
Allowance for loan losses | $ | 169 | $ | 157 | $ | 191 | $ | 210 | $ | 266 | |||||
Allowance for lending-related commitments | 112 | 118 | 89 | 134 | 121 | ||||||||||
Net (recoveries) charge-offs to average loans outstanding | (0.03 | )% | 0.27 | % | 0.03 | % | 0.02 | % | 0.07 | % | |||||
Net (recoveries) charge-offs to total allowance for credit losses | (6.05 | ) | 60.00 | 5.71 | 2.33 | 7.75 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses as a percentage of total loans | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 0.57 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses as a percentage of non-margin loans | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.80 | ||||||||||
Total allowance for credit losses as a percentage of total loans | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.83 | ||||||||||
Total allowance for credit losses as a percentage of non-margin loans | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.96 | 1.16 | ||||||||||
Net recoveries of $17 million in 2016 were primarily reflected in the financial institutions portfolio. Recoveries primarily reflect the receipt of trust assets from the bankruptcy proceedings of Sentinel in excess of the carrying value of $171 million. Net charge-offs of $165 million in 2015 were primarily reflected in the financial institutions portfolio and included a portion of the unsecured loan to Sentinel
that was reestablished in December 2015. Net charge-offs of $16 million in 2014 were primarily reflected in the commercial loan and foreign loan portfolios.
The provision for credit losses was a credit of $11 million in 2016, a provision of $160 million in 2015 and a credit of $48 million in 2014. The provision in
BNY Mellon 43
Results of Operations (continued) |
2015 was primarily driven by an impairment charge related to a court decision regarding Sentinel.
The total allowance for credit losses was $281 million at Dec. 31, 2016, $275 million at Dec. 31, 2015 and $280 million at Dec. 31, 2014. The ratio of the total allowance for credit losses to non-margin loans was 0.60% at Dec. 31, 2016, 0.63% at Dec. 31, 2015 and 0.72% at Dec. 31, 2014. The ratio of the allowance for loan losses to non-margin loans was 0.36% at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with 0.36% at Dec. 31, 2015 and 0.49% at Dec. 31, 2014. The lower ratios at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with Dec. 31, 2015 primarily reflect an improvement in the credit quality in the loan portfolio.
We had $17.6 billion of secured margin loans on our balance sheet at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $19.6 billion at Dec. 31, 2015 and $20.0 billion at Dec. 31, 2014. We have rarely suffered a loss on these types of loans and do not allocate any of our allowance for credit losses to them. As a result, we believe that the ratio of total allowance for credit losses as a percentage of non-margin loans is a more appropriate metric to measure the adequacy of the reserve.
The allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments represent
management’s estimate of losses inherent in our credit portfolio. This evaluation process is subject to numerous estimates and judgments.
Based on an evaluation of the allowance for credit losses as discussed in “Critical accounting estimates” and Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, we have allocated our allowance for credit losses as follows.
Allocation of allowance | Dec. 31, | |||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||
Commercial | 29 | % | 30 | % | 21 | % | 24 | % | 27 | % |
Commercial real estate | 26 | 22 | 18 | 12 | 8 | |||||
Foreign | 13 | 13 | 16 | 16 | 12 | |||||
Other residential mortgages | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 23 | |||||
Financial institutions | 9 | 11 | 11 | 14 | 9 | |||||
Wealth management (a) | 8 | 7 | 8 | 7 | 8 | |||||
Lease financing | 5 | 5 | 12 | 11 | 13 | |||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % |
(a) | Includes the allowance for wealth management mortgages. |
The allocation of the allowance for credit losses is inherently judgmental, and the entire allowance for credit losses is available to absorb credit losses regardless of the nature of the loss.
Nonperforming assets
The following table shows the distribution of nonperforming assets.
Nonperforming assets | Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Nonperforming loans: | |||||||||||||||
Other residential mortgages | $ | 91 | $ | 102 | $ | 112 | $ | 117 | $ | 158 | |||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 8 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 30 | ||||||||||
Lease financings | 4 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Financial institutions | — | 171 | — | — | 3 | ||||||||||
Commercial real estate | — | 2 | 1 | 4 | 18 | ||||||||||
Commercial | — | — | — | 15 | 27 | ||||||||||
Foreign | — | — | — | 6 | 9 | ||||||||||
Total nonperforming loans | 103 | 286 | 125 | 153 | 245 | ||||||||||
Other assets owned | 4 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||
Total nonperforming assets (a) | $ | 107 | $ | 292 | $ | 128 | $ | 156 | $ | 249 | |||||
Nonperforming assets ratio | 0.17 | % | 0.46 | % | 0.22 | % | 0.30 | % | 0.53 | % | |||||
Nonperforming assets ratio, excluding margin loans | 0.23 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.43 | 0.75 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses/nonperforming loans | 164.1 | 54.9 | 152.8 | 137.3 | 108.6 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses/nonperforming assets | 157.9 | 53.8 | 149.2 | 134.6 | 106.8 | ||||||||||
Total allowance for credit losses/nonperforming loans | 272.8 | 96.2 | 224.0 | 224.8 | 158.0 | ||||||||||
Total allowance for credit losses/nonperforming assets | 262.6 | 94.2 | 218.8 | 220.5 | 155.4 | ||||||||||
(a) | Loans of consolidated investment management funds are not part of BNY Mellon’s loan portfolio. Included in the loans of consolidated investment management funds are nonperforming loans of $53 million at Dec. 31, 2014, $16 million at Dec. 31, 2013 and $174 million at Dec. 31, 2012. These loans are recorded at fair value and therefore do not impact the provision for credit losses and allowance for loan losses, and accordingly are excluded from the nonperforming assets table above. In the second quarter of 2015, BNY Mellon adopted the accounting guidance included in ASU 2015-02, Consolidations. As a result, we deconsolidated substantially all of the loans of consolidated investment management funds retrospectively to Jan. 1, 2015. |
44 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Nonperforming assets activity | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||
(in millions) | ||||||
Balance at beginning of period | $ | 292 | $ | 128 | ||
Additions | 20 | 360 | ||||
Return to accrual status | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | ||
Charge-offs | (1 | ) | (172 | ) | ||
Paydowns/sales | (202 | ) | (21 | ) | ||
Balance at end of period | $ | 107 | $ | 292 | ||
Nonperforming assets were $107 million at Dec. 31, 2016, a decrease of $185 million compared with $292 million at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease in nonperforming assets primarily reflects the receipt of trust assets from the bankruptcy proceedings of Sentinel.
The nonperforming assets ratio was 0.17% at Dec. 31, 2016, 0.46% at Dec. 31, 2015 and 0.22% at Dec. 31, 2014. The ratio of the allowance for loan losses to nonperforming loans was 164.1% at Dec. 31, 2016, 54.9% at Dec. 31, 2015 and 152.8% at Dec. 31, 2014. The ratio of the total allowance for credit losses to nonperforming loans was 272.8% at Dec. 31, 2016, 96.2% at Dec. 31, 2015 and 224.0% at Dec. 31, 2014. The changes in these ratios at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with the prior year reflect the decrease in nonperforming assets as a result of the recovery related to Sentinel.
The following table shows loans past due 90 days or more and still accruing interest.
Past due loans ≥ 90 days still accruing interest at year-end | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Domestic: | |||||||||||||||
Consumer | $ | 7 | $ | 5 | $ | 6 | $ | 7 | $ | 6 | |||||
Commercial | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Total domestic | 7 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | ||||||||||
Foreign | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Total past due loans | $ | 7 | $ | 5 | $ | 6 | $ | 7 | $ | 6 | |||||
Loans past due 90 days or more at Dec. 31, 2016 primarily consisted of other residential mortgage loans. See Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on our past due loans. See “Nonperforming assets” in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for our policy for placing loans on nonaccrual status.
Deposits
We receive client deposits through a variety of Investment Management and Investment Services businesses and we rely on those deposits as a low-cost and stable source of funding.
Total deposits were $221 billion, a decrease of 21% compared with $280 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease in deposits primarily reflects lower interest-bearing deposits in non-U.S. offices primarily driven by lower client deposits in our Investment Services business.
Noninterest-bearing deposits were $78 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $96 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Interest-bearing deposits were $143 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $183 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
The aggregate amount of deposits by foreign customers in domestic offices was $36 billion and $43 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively. The Dec. 31, 2015 amount was adjusted to reflect enhanced information.
Deposits in foreign offices totaled $99 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $139 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The majority of these deposits were in amounts in excess of $100,000 and were primarily overnight foreign deposits.
The following table shows the maturity breakdown of domestic time deposits of $100,000 or more at Dec. 31, 2016.
Domestic time deposits ≥ $100,000 at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||||
(in millions) | Certificates of deposit | Other time deposits | Total | ||||||
3 months or less | $ | 32 | $ | 36,728 | $ | 36,760 | |||
Between 3 and 6 months | 36 | — | 36 | ||||||
Between 6 and 12 months | 9 | — | 9 | ||||||
Over 12 months | 2 | — | 2 | ||||||
Total | $ | 79 | $ | 36,728 | $ | 36,807 | |||
BNY Mellon 45
Results of Operations (continued) |
Short-term borrowings
We fund ourselves primarily through deposits and, to a lesser extent, other short-term borrowings and long-term debt. Short-term borrowings consist of federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements, payables to customers and broker-dealers, commercial paper and other borrowed funds. Certain other borrowings, for example, securities sold under repurchase agreements, require the delivery of securities as collateral.
See “Liquidity and dividends” for a discussion of long-term debt and liquidity metrics that we monitor.
Information related to federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements is presented below.
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the year | $ | 25,995 | $ | 30,160 | $ | 24,422 | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 14,489 | $ | 16,452 | $ | 18,631 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the year | 0.25 | % | (0.04 | )% | (0.07 | )% | |||
Ending balance at Dec. 31 | $ | 9,989 | $ | 15,002 | $ | 11,469 | |||
Weighted-average rate at Dec. 31 | 0.38 | % | 0.10 | % | (0.02 | )% | |||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | |||||||||
Quarter ended | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the quarter | $ | 12,418 | $ | 11,184 | $ | 30,160 | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 11,567 | $ | 9,585 | $ | 20,349 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the quarter | 0.30 | % | 0.24 | % | (0.03 | )% | |||
Ending balance | $ | 9,989 | $ | 8,052 | $ | 15,002 | |||
Weighted-average rate at period end | 0.38 | % | 0.25 | % | 0.10 | % | |||
Fluctuations of federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements between periods resulted from changes in overnight borrowing opportunities. The increase in the weighted-average rates, compared to prior periods, primarily reflects increases in the Fed Funds effective rate.
Information related to payables to customers and broker-dealers is presented below.
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the year | $ | 22,327 | $ | 23,027 | $ | 21,181 | |||
Average daily balance (a) | $ | 21,149 | $ | 22,062 | $ | 17,950 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the year (a) | 0.07 | % | 0.06 | % | 0.09 | % | |||
Ending balance at Dec. 31 | $ | 20,987 | $ | 21,900 | $ | 21,181 | |||
Weighted-average rate at Dec. 31 | 0.09 | % | 0.07 | % | 0.09 | % | |||
(a) | The weighted-average rate is calculated based on, and is applied to, the average interest-bearing payables to customers and broker-dealers, which were $16,925 million in 2016, $11,649 million in 2015 and $9,502 million in 2014. |
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | |||||||||
Quarter ended | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the quarter | $ | 21,082 | $ | 21,162 | $ | 23,027 | |||
Average daily balance (a) | $ | 20,978 | $ | 20,616 | $ | 22,654 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the quarter (a) | 0.07 | % | 0.07 | % | 0.06 | % | |||
Ending balance | $ | 20,987 | $ | 21,162 | $ | 21,900 | |||
Weighted-average rate at period end | 0.09 | % | 0.07 | % | 0.07 | % | |||
(a) | The weighted-average rate is calculated based on, and is applied to, the average interest-bearing payables to customers and broker-dealers, which were $17,091 million in the fourth quarter of 2016, $16,873 million in the third quarter of 2016 and $12,904 million in the fourth quarter of 2015. |
Payables to customers and broker-dealers represent funds awaiting re-investment and short sale proceeds payable on demand. Payables to customers and broker-dealers are driven by customer trading activity levels and market volatility.
Information related to commercial paper is presented below.
Commercial paper | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the year | $ | 4,950 | $ | 4,849 | $ | 5,003 | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 1,337 | $ | 1,549 | $ | 2,546 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the year | 0.37 | % | 0.10 | % | 0.08 | % | |||
Ending balance at Dec. 31 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||
Weighted-average rate at Dec. 31 | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||
46 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Commercial paper | Quarter ended | ||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the quarter | $ | 1,239 | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 383 | $ | 1,173 | $ | — | |||
Weighted-average rate during the quarter | 0.34 | % | 0.35 | % | — | % | |||
Ending balance | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||
Weighted-average rate at period end | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||
The Parent’s commercial paper program was discontinued in August 2015. In the first quarter of 2016, The Bank of New York Mellon, our largest bank subsidiary, began issuing commercial paper that matures within 364 days from the date of issue and is not redeemable prior to maturity or subject to voluntary prepayment.
Information related to other borrowed funds is presented below.
Other borrowed funds | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the year | $ | 1,280 | $ | 1,151 | $ | 1,723 | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 846 | $ | 814 | $ | 1,027 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the year | 0.91 | % | 1.12 | % | 0.61 | % | |||
Ending balance at Dec. 31 | $ | 754 | $ | 523 | $ | 786 | |||
Weighted-average rate at Dec. 31 | 0.89 | % | 0.97 | % | 1.15 | % | |||
Other borrowed funds | Quarter ended | ||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||
Maximum month-end balance during the quarter | $ | 1,280 | $ | 993 | $ | 846 | |||
Average daily balance | $ | 903 | $ | 874 | $ | 733 | |||
Weighted-average rate during the quarter | 0.95 | % | 0.76 | % | 1.13 | % | |||
Ending balance | $ | 754 | $ | 993 | $ | 523 | |||
Weighted-average rate at period end | 0.89 | % | 0.75 | % | 0.97 | % | |||
Other borrowed funds primarily include overdrafts of sub-custodian account balances in our Investment Services businesses and borrowings under lines of credit by our Pershing subsidiaries. Overdrafts typically relate to timing differences for settlements. Fluctuations in other borrowed funds balances primarily reflect changes in overdrafts of sub-custodian account balances in our Investment Services businesses.
Liquidity and dividends
BNY Mellon defines liquidity as the ability of the Parent and its subsidiaries to access funding or convert assets to cash quickly and efficiently, or to rollover or issue new debt, especially during periods of market stress and in order to meet its short-term (up to one year) obligations. Liquidity risk is the risk that BNY Mellon cannot meet its cash and collateral obligations at a reasonable cost for both expected and unexpected cash flows without adversely affecting daily operations or our financial condition. Liquidity risk can arise from cash flow mismatches, market constraints from the inability to convert assets to cash, the inability to raise cash in the markets, deposit run-off or contingent liquidity events. We also manage liquidity risks on an intra-day basis, in a manner designed to ensure that we can access required funds during the business day to make payments or settle immediate obligations, often in real time. Changes in economic conditions or exposure to credit, market, operational, legal and reputational risks also can affect BNY Mellon’s liquidity risk profile and are considered in our liquidity risk framework.
For additional information on our liquidity policy, see “Risk Management - Liquidity risk.”
Our overall approach to liquidity management is to ensure that sources of liquidity are sufficient in amount and diversity such that changes in funding requirements at the Parent and at our significant bank and broker-dealer subsidiaries can be accommodated routinely without material adverse impact on earnings, daily operations or our financial condition.
BNY Mellon seeks to maintain an adequate liquidity cushion in both normal and stressed environments and seeks to diversify funding sources by line of business, customer and market segment. In addition, we monitor and control liquidity exposures and funding needs within and across significant legal entities, branches, currencies and business lines, taking into account, among other factors, any applicable restrictions on the transfer of liquidity among entities.
Additionally, we seek to maintain liquidity ratios within approved limits and liquidity risk tolerance, maintain a liquid asset buffer that can be liquidated, financed and/or pledged as necessary, and control the levels and sources of wholesale funds. Moreover,
BNY Mellon 47
Results of Operations (continued) |
BNY Mellon also manages potential intraday liquidity risks, which are the risks that the firm cannot fund or settle obligations during the business day. Sources of intraday liquidity risks include timing mismatches of inflows and outflows, the inability to hold or raise intraday cash, and unexpected market or idiosyncratic events. We monitor and manage intraday liquidity against existing and expected intraday liquid resources (such as cash balances, remaining intraday credit capacity, intraday contingency funding and available collateral) to enable BNY Mellon to meet its obligations under normal and reasonably severe stressed conditions.
When monitoring liquidity, we evaluate multiple metrics in order to have sufficient liquidity for expected and unexpected events. Metrics include cash flow mismatches, asset maturities, debt spreads, peer ratios, liquid assets, unencumbered collateral, funding sources and balance sheet liquidity ratios. We also maintain various internal liquidity limits as part of our standard analysis to monitor depositor and market funding concentration, liability maturity
profile and potential liquidity draws due to off-balance sheet exposures.
The Parent’s liquidity policy is to have sufficient unencumbered cash and cash equivalents on hand at each quarter-end to cover forecasted debt redemptions, net interest payments and net tax payments for the following 18-month period, and to provide sufficient collateral to satisfy transactions subject to Section 23A of the Federal Reserve Act. As of Dec. 31, 2016, the Parent was in compliance with this policy.
We define available funds for internal liquidity management purposes as liquid funds (which include interest-bearing deposits with banks and federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements), cash and due from banks, and interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks. The following table presents our total available funds including liquid funds at period end and on an average basis.
Available and liquid funds | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Average | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||
Available funds: | |||||||||||||||
Liquid funds: | |||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | $ | 15,086 | $ | 15,146 | $ | 14,704 | $ | 20,531 | $ | 35,588 | |||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 25,801 | 24,373 | 25,767 | 23,384 | 14,704 | ||||||||||
Total liquid funds | 40,887 | 39,519 | 40,471 | 43,915 | 50,292 | ||||||||||
Cash and due from banks | 4,822 | 6,537 | 4,308 | 6,180 | 5,472 | ||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 58,041 | 113,203 | 80,593 | 83,029 | 86,594 | ||||||||||
Total available funds | $ | 103,750 | $ | 159,259 | $ | 125,372 | $ | 133,124 | $ | 142,358 | |||||
Total available funds as a percentage of total assets | 31 | % | 40 | % | 35 | % | 36 | % | 38 | % | |||||
At Dec. 31, 2016, we had $41 billion of liquid funds, compared with $40 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Of the $41 billion in liquid funds held at Dec. 31, 2016, $15 billion was placed in interest-bearing deposits with large, highly-rated global financial institutions with a weighted-average life to maturity of approximately 31 days. Of the $15 billion, $4 billion was placed with banks in the Eurozone.
Total available funds totaled $104 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $159 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease was primarily due to a decrease in overnight deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks, which reflects a decrease of customer deposits, primarily interest bearing deposits in non-U.S. offices.
On an average basis for 2016 and 2015, non-core sources of funds, such as money market rate accounts, federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements, trading liabilities, commercial paper and other borrowings, were $25.2 billion and $26.7 billion, respectively. The decrease primarily reflects a decrease in securities sold under repurchase agreements, partially offset by an increase in money market rate accounts. Average foreign deposits, primarily from our European-based Investment Services business, were $102.4 billion for 2016 compared with $109.6 billion for 2015. Domestic savings, interest-bearing demand and time deposits averaged $46.8 billion for 2016 and $48.3 billion for 2015. The decrease primarily reflects lower time deposits. Average payables to customers and broker-dealers were $16.9 billion for 2016 and
48 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
$11.6 billion for 2015. Payables to customers and broker-dealers are driven by customer trading activity and market volatility. Long-term debt averaged $23.3 billion for 2016 and $20.8 billion for 2015. Average noninterest-bearing deposits decreased to $82.7 billion for 2016 from $86.3 billion for 2015, reflecting a decrease in client deposits.
A significant reduction in our Investment Services business would reduce our access to deposits. See “Asset/liability management” for additional factors that could impact our deposit balances.
Sources of liquidity
The Parent’s three major sources of liquidity are cash on hand, access to the debt and equity markets and dividends from its subsidiaries.
The Parent had cash of $8.7 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, compared with $9.1 billion at Dec. 31, 2015, a decrease of $337 million primarily reflecting long-term debt maturities, common stock repurchases, dividends paid and a net decrease in loans from subsidiaries, partially offset by the issuance of long-term debt and preferred stock.
Our ability to access the capital markets on favorable terms, or at all, is partially dependent on our credit ratings, which are as follows:
Credit ratings at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||
Moody’s | S&P | Fitch | DBRS | ||||
Parent: | |||||||
Long-term senior debt | A1 | A | AA- | AA (low) | |||
Subordinated debt | A2 | A- | A+ | A (high) | |||
Preferred stock | Baa1 | BBB | BBB | A (low) | |||
Trust preferred securities | A3 | BBB | BBB+ | A (high) | |||
Outlook - Parent: | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | |||
The Bank of New York Mellon: | |||||||
Long-term senior debt | Aa2 | AA- | AA | AA | |||
Subordinated debt | Aa3 | A | A+ | NR | |||
Long-term deposits | Aa1 | AA- | AA+ | AA | |||
Short-term deposits | P1 | A-1+ | F1+ | R-1 (high) | |||
Commercial paper | P1 | A-1+ | F1+ | R-1 (high) | |||
BNY Mellon, N.A.: | |||||||
Long-term senior debt | Aa2 | AA- | AA | (a) | AA | ||
Long-term deposits | Aa1 | AA- | AA+ | AA | |||
Short-term deposits | P1 | A-1+ | F1+ | R-1 (high) | |||
Outlook - Banks: | Stable | Stable | Stable | Stable | |||
(a) | Represents senior debt issuer default rating. |
NR - Not rated.
In October 2016, S&P stated that in light of the resubmissions by the eight U.S. global systemically important banks (“G-SIBs”) of their resolution plans, S&P will include the ramifications of structural changes resulting from those resolution plans in its evaluations of the U.S. G-SIBs’ credit profiles. If S&P determines that such structural changes increase risks to our debtholders, our ratings could be negatively impacted.
In October 2016, Moody’s noted that while the U.S. G-SIB resolution plans are likely to have moderately negative implications for creditors, Moody’s did not
believe that the specific disclosed features of the resolution plans would impact these issuers’ ratings.
Long-term debt totaled $24.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $21.5 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase reflects issuances of $6.25 billion, partially offset by maturities of $2.45 billion and a call of $500 million of long-term debt and a decrease in the fair value of hedged long term debt. Additionally, the Parent has $750 million of long-term debt that will mature in 2017.
The following table presents the long-term debt issued by the Parent in 2016.
BNY Mellon 49
Results of Operations (continued) |
Debt issuances | |||
(in millions) | 2016 | ||
Senior notes: | |||
2.50% senior notes due 2021 | $ | 1,000 | |
2.05% senior notes due 2021 | 1,250 | ||
2.20% senior notes due 2023 | 1,250 | ||
3-month LIBOR + 105 bps senior notes due 2023 | 750 | ||
2.45% senior notes due 2026 | 750 | ||
2.80% senior notes due 2026 | 750 | ||
Senior subordinated notes: | |||
3.00% senior subordinated notes due 2028 | 500 | ||
Total debt issuances | $ | 6,250 | |
In January 2017, we announced that all outstanding trust preferred securities issued by Mellon Capital III will be redeemed on March 20, 2017. The redemption price for the trust-preferred securities will be equal to the par value plus interest accrued up to and excluding the redemption date. For additional information on our trust-preferred securities, see Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
In February 2017, we issued $1.25 billion of senior notes maturing in 2022 at an annual interest rate of 2.6%, and $1.0 billion of fixed rate to floating rate callable senior notes maturing in 2028 at an annual interest rate of 3.442% for the first 10 years and at 3-month LIBOR plus 106.9 basis points in the remaining year.
In conjunction with our 2016 capital plan, on Aug. 1, 2016, we completed a $1 billion offering of preferred stock, which satisfied the contingency for the repurchase of up to $560 million of common stock. We issued 10,000 shares of Series F preferred stock, which have a liquidation preference of $100,000 per share. Dividends on the Series F noncumulative perpetual preferred stock will be paid, if declared by our board of directors, at an annual rate equal to 4.625% on each March 20 and September 20, commencing March 20, 2017, through and including Sept. 20, 2026; and a floating rate equal to three-month LIBOR plus 3.131% on each March 20, June 20, September 20 and December 20, commencing Dec. 20, 2026. For additional information on our preferred stock, see Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Bank of New York Mellon, our largest bank subsidiary, began issuing commercial paper in 2016. The commercial paper matures within 364 days from date of issue and is not redeemable prior to maturity or subject to voluntary prepayment. The Parent’s commercial paper program was discontinued in
August 2015. The average commercial paper borrowings were $1.3 billion (The Bank of New York Mellon) in 2016 and $1.5 billion (Parent) in 2015. There was no commercial paper outstanding at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Subsequent to Dec. 31, 2016, our U.S. bank subsidiaries could declare dividends to the Parent of approximately $5.4 billion, without the need for a regulatory waiver. Currently, The Bank of New York Mellon, our primary subsidiary, is no longer paying regular dividends to the Parent in order to increase its Tier 1 capital in advance of the SLR becoming effective. In addition, at Dec. 31, 2016, non-bank subsidiaries of the Parent had liquid assets of approximately $1.3 billion. Restrictions on our ability to obtain funds from our subsidiaries are discussed in more detail in “Supervision and Regulation - Capital Planning and Stress Testing - Payment of Dividends, Stock Repurchases and Other Capital Distributions” and in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Pershing LLC, an indirect subsidiary of BNY Mellon, has uncommitted lines of credit in place for liquidity purposes which are guaranteed by the Parent. Pershing LLC has eight separate uncommitted lines of credit amounting to $1.5 billion in aggregate. Average daily borrowing under these lines was $5 million, in aggregate, in 2016. Pershing Limited, an indirect UK-based subsidiary of BNY Mellon, has two separate uncommitted lines of credit amounting to $250 million in aggregate in place for liquidity purposes, which are guaranteed by the Parent. Average borrowings under these lines were $87 million, in aggregate, in 2016.
The double leverage ratio is the ratio of our equity investment in subsidiaries divided by our consolidated parent company equity, which includes our noncumulative perpetual preferred stock plus qualifying trust preferred securities. In short, the double leverage ratio measures the extent to which equity in subsidiaries is financed by Parent company debt. As the double leverage ratio increases, this can reflect greater demands on a company’s cash flows in order to service interest payments and debt maturities. BNY Mellon’s double leverage ratio is managed in a range considering the high level of unencumbered available liquid assets held in its principal subsidiaries (such as central bank deposits and government securities), the Company’s cash generating fee-based business model, with fees representing approximately 80% of revenue, and the
50 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
dividend capacity of our banking subsidiaries. Our double leverage ratio was 119.1% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 115.7% at Dec. 31, 2015, and within the range targeted by management.
Uses of funds
The Parent’s major uses of funds are payment of dividends, repurchases of common stock, principal and interest payments on its borrowings, acquisitions and additional investments in, and loans to, its subsidiaries.
Included in the 2016 capital plan was a 12% increase in the quarterly cash dividend on common stock to $0.19 per share. This increased quarterly cash dividend was paid beginning in the third quarter of 2016. Our common stock dividend payout ratio was 23% for 2016. The Federal Reserve’s instructions for the 2016 CCAR provided that, for large bank holding companies like us, dividend payout ratios exceeding 30% of after-tax net income would receive particularly close scrutiny.
In 2016, we repurchased 58.6 million common shares at an average price of $40.91 per common share for a total cost of $2.4 billion.
Liquidity coverage ratio
U.S. regulators have established an LCR that requires certain banking organizations, including BNY Mellon, to maintain a minimum amount of unencumbered high quality liquid assets (“HQLA”) sufficient to withstand the net cash outflow under a hypothetical standardized acute liquidity stress scenario for a 30-day time horizon.
The following table presents the Company’s consolidated HQLA and LCR as of Dec. 31, 2016.
Consolidated HQLA and LCR | Dec. 31, 2016 | ||
(in billions) | |||
Securities (a) | $ | 104 | |
Cash (b) | 52 | ||
Total consolidated HQLA (c) | $ | 156 | |
Liquidity coverage ratio | 114 | % | |
(a) | Primarily includes U.S. Treasury, U.S. agency, sovereign securities, securities of U.S. government-sponsored enterprises, investment-grade corporate debt and publicly traded common equity. |
(b) | Primarily includes cash on deposit with central banks. |
(c) | Consolidated HQLA presented before adjustments. After haircuts and the impact of trapped liquidity, consolidated HQLA totaled $127 billion. |
The U.S. LCR rules became effective on Jan. 1, 2015, and require BNY Mellon and our affected domestic bank subsidiaries to meet an LCR of 100% since becoming fully phased-in on Jan. 1, 2017. The LCR for BNY Mellon and our domestic bank subsidiaries was compliant with the fully phased-in requirements of the U.S. LCR as of Dec. 31, 2016.
For additional information on the LCR, see “Supervision and Regulation - Liquidity Standards - Basel III and U.S. Rules and Proposals.”
We also perform liquidity stress tests to ensure the Company maintains sufficient liquidity resources under multiple stress scenarios. Stress tests are based on scenarios that measure liquidity risks under unlikely but plausible events. We perform these tests under various time horizons ranging from one day to one year in a base case, as well as supplemental tests to determine whether the Company’s liquidity is sufficient for severe market events and firm-specific events. Under our scenario testing program, the results of the tests indicate that the Company has sufficient liquidity.
Beginning on Jan. 1, 2015, Bank Holding Companies (“BHCs”) with total consolidated assets of $50 billion or more were subject to the Federal Reserve’s Enhanced Prudential Standards, which include liquidity standards, described under “Supervision and Regulation - Enhanced Prudential Standards and Large Exposures.” BNY Mellon has taken actions to comply with these standards, including the adoption of various liquidity risk management standards and maintenance of a liquidity buffer of unencumbered highly liquid assets based on the results of internal liquidity stress testing.
Statement of cash flows
The following summarizes the activity reflected on the statement of cash flows. While this information may be helpful to highlight certain macro trends and business strategies, the cash flow analysis may not be as relevant when analyzing changes in our net earnings and net assets. We believe that in addition to the traditional cash flow analysis, the discussion related to liquidity and dividends and asset/liability management herein may provide more useful context in evaluating our liquidity position and related activity.
BNY Mellon 51
Results of Operations (continued) |
Cash provided by operating activities was $6.2 billion in 2016, compared with $4.1 billion in 2015 and $4.5 billion in 2014. In all three periods cash flows from operations were principally the result of earnings. In 2016 and 2014, cash flows from operations were also the result of changes in trading activities, partially offset by changes in accruals and other balances. In 2015, cash flows from operations were partially offset by both changes in trading activities and changes in accruals and other balances.
Cash provided by investing activities was $51.2 billion in 2016, compared with cash used for investing activities of $19.8 billion in 2015 and $11.7 billion in 2014. In 2016, the decrease in interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks and sales, paydowns and maturities of securities were significant sources of funds, partially offset by purchases of securities. In 2015, purchases of securities, an increase in interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks, changes in loans and changes in federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements were significant uses of funds, partially offset by sales, paydowns and maturities of securities and a decrease in interest bearing deposits with banks. In 2014, purchases of securities, changes in federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements and an increase in loans were significant uses of funds, partially offset by sales, paydowns and maturities of securities and decreases in deposits with banks and with the Federal Reserve and other central banks.
Cash used for financing activities was $59.1 billion in 2016, compared with cash provided by financing of
$15.2 billion in 2015 and $7.8 billion in 2014. In 2016, a decrease in deposits, changes in federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements, repayments of long-term debt and treasury stock repurchases were significant uses of funds, partially offset by proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt. In 2015, an increase in deposits, proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt and changes in federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements were significant sources of funds, partially offset by the repayment of long-term debt and treasury stock repurchases. In 2014, increases in payables to broker-dealers and the proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt were significant sources of funds, partially offset by the repayment of long-term debt and treasury stock repurchases.
Commitments and obligations
We have contractual obligations to make fixed and determinable payments to third parties as indicated in the table below. The table excludes certain obligations such as trade payables and trading liabilities, where the obligation is short-term or subject to valuation based on market factors. In addition to the amounts shown in the table below, at Dec. 31, 2016, $146 million of unrecognized tax benefits have been recorded as liabilities in accordance with ASC 740, Income Taxes. Related to these unrecognized tax benefits, we have also recorded a liability for potential interest of $18 million. At this point, it is not possible to determine when these amounts will be settled or resolved.
Contractual obligations at Dec. 31, 2016 | Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | Over 5 years | ||||||||||
Deposits without a stated maturity | $ | 103,328 | $ | 103,328 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Term deposits | 39,820 | 39,816 | 3 | 1 | — | ||||||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | 9,989 | 9,989 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | 20,987 | 20,987 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Other borrowed funds | 754 | 754 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Long-term debt (a) | 27,875 | 1,385 | 9,002 | 8,960 | 8,528 | ||||||||||
Unfunded pension and post-retirement benefits | 302 | 35 | 76 | 58 | 133 | ||||||||||
Capital leases | 36 | 22 | 14 | — | — | ||||||||||
Investment commitments (b) | 369 | 152 | 200 | 3 | 14 | ||||||||||
Total contractual obligations | $ | 203,460 | $ | 176,468 | $ | 9,295 | $ | 9,022 | $ | 8,675 | |||||
(a) | Includes interest. |
(b) | Includes Community Reinvestment Act commitments. |
52 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
We have entered into fixed and determinable commitments as indicated in the table below:
Other commitments at Dec. 31, 2016 | Amount of commitment expiration per period | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | Over 5 years | ||||||||||
Securities lending indemnifications (a) | $ | 317,690 | $ | 317,690 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Lending commitments | 51,270 | 28,855 | 8,760 | 13,378 | 277 | ||||||||||
Standby letters of credit | 4,185 | 2,679 | 1,227 | 277 | 2 | ||||||||||
Operating leases | 2,129 | 334 | 506 | 419 | 870 | ||||||||||
Purchase obligations (b) | 1,033 | 557 | 359 | 80 | 37 | ||||||||||
Commercial letters of credit | 339 | 335 | — | — | 4 | ||||||||||
Private equity commitments (c) | 46 | 2 | 24 | 20 | — | ||||||||||
Total commitments | $ | 376,692 | $ | 350,452 | $ | 10,876 | $ | 14,174 | $ | 1,190 | |||||
(a) | Excludes the indemnifications for securities booked at BNY Mellon beginning in late 2013 resulting from the CIBC Mellon joint venture which totaled $61 billion at Dec. 31, 2016. |
(b) | Purchase obligations are defined as agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable and legally binding and specify all significant terms. |
(c) | Related to SBIC investments, which are compliant with the Volcker Rule. |
See “Liquidity and dividends” and Note 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of the source of funds for our commitments and obligations and known material trends in our capital resources.
Off-balance sheet arrangements
Off-balance sheet arrangements discussed in this section are limited to guarantees, retained or contingent interests and obligations arising out of
unconsolidated variable interest entities (“VIEs”). For BNY Mellon, these items include certain credit guarantees and securitizations. Guarantees include lending-related guarantees issued as part of our corporate banking business and securities lending indemnifications issued as part of our Investment Services business. See Note 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of our off-balance sheet arrangements.
Capital
Capital data (dollar amounts in millions except per share amounts; common shares in thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
At period end: | ||||||
BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP (a) | 11.6 | % | 9.7 | % | ||
BNY Mellon common shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP (a) | 10.6 | % | 9.0 | % | ||
BNY Mellon tangible common shareholders’ equity to tangible assets of operations ratio – Non-GAAP (a) | 6.7 | % | 6.5 | % | ||
Total BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity – GAAP | $ | 38,811 | $ | 38,037 | ||
Total BNY Mellon common shareholders’ equity – GAAP | $ | 35,269 | $ | 35,485 | ||
BNY Mellon tangible common shareholders’ equity – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 16,957 | $ | 16,574 | ||
Book value per common share – GAAP (a) | $ | 33.67 | $ | 32.69 | ||
Tangible book value per common share – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 16.19 | $ | 15.27 | ||
Closing stock price per common share | $ | 47.38 | $ | 41.22 | ||
Market capitalization | $ | 49,630 | $ | 44,738 | ||
Common shares outstanding | 1,047,488 | 1,085,343 | ||||
Full-year: | ||||||
Average common equity to average assets | 9.9 | % | 9.6 | % | ||
Cash dividends per common share | $ | 0.72 | $ | 0.68 | ||
Common dividend payout ratio | 23 | % | 25 | % | ||
Common dividend yield | 1.5 | % | 1.6 | % | ||
(a) | See “Supplemental information – Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures” beginning on page 121 for a reconciliation of GAAP to Non-GAAP. |
BNY Mellon 53
Results of Operations (continued) |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation total shareholders’ equity increased to $38.8 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 from $38.0 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. The increase primarily reflects earnings retention, issuance of preferred stock and approximately $724 million resulting from stock awards, the exercise of stock options and stock issued for employee benefit plans. The increase was partially offset by share repurchases, foreign currency translation adjustments and a decrease in the unrealized gain on our investment securities portfolio.
The unrealized gain net of tax on our investment securities portfolio recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income was $45 million at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $329 million at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease in the unrealized gain, net of tax, was primarily driven by an increase in market interest rates.
BNY Mellon’s tangible common shareholders’ equity to tangible assets of operations ratio (Non-GAAP) was 6.7% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 6.5% at Dec. 31, 2015.
In conjunction with our 2016 capital plan, in August 2016, BNY Mellon issued $1 billion of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock which satisfied the contingency for the repurchase of up to $560 million of common stock.
We repurchased 30.0 million common shares for $1.3 billion in 2016 under the current program, which began in the third quarter of 2016 and continues through the second quarter of 2017, including employee benefit plan repurchases. We expect to continue to repurchase shares in the first half of 2017 under the 2016 capital plan.
Also included in the 2016 capital plan was a 12% increase in the quarterly cash dividend on common stock, from $0.17 to $0.19 per share. The first payment of the increased quarterly cash dividend was Aug. 12, 2016.
Capital adequacy
Regulators establish certain levels of capital for bank holding companies and banks, including BNY Mellon and our bank subsidiaries, in accordance with established quantitative measurements. For the Parent to maintain its status as a financial holding company, our bank subsidiaries and BNY Mellon
must, among other things, qualify as “well capitalized.”
As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries were “well capitalized.” As of Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries, with the exception of BNY Mellon, N.A., were “well capitalized.” As of Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon, N.A. was not “well capitalized” because its Total capital ratio was 9.89%, which was below the 10% “well capitalized” threshold. With the filing of its March 31, 2016 Call Report, BNY Mellon, N.A.’s Total capital ratio was 10.94%, which is above the 10% “well capitalized” threshold.
Failure to satisfy regulatory standards, including “well capitalized” status or capital adequacy rules more generally, could result in limitations on our activities and adversely affect our financial condition. See the discussion of these matters in “Supervision and Regulation - Regulated Entities of BNY Mellon and Ancillary Regulatory Requirements” and “Risk Factors - Operational Risk - Failure to satisfy regulatory standards, including “well capitalized” and “well managed” status or capital adequacy and liquidity rules more generally, could result in limitations on our activities and adversely affect our business and financial condition.”
The “well capitalized” and other capital categories (where applicable), as established by applicable regulations for bank holding companies and depository institutions, have been established by those regulations solely for purposes of implementing their respective requirements (for example, eligibility for financial holding company status in the case of bank holding companies and prompt corrective action measures in the case of depository institutions). A bank holding company’s or depository institution’s qualification for a capital category may not constitute an accurate representation of the entity’s overall financial condition or prospects.
The U.S. banking agencies’ capital rules have been based on the framework adopted by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, as amended from time to time. For additional information on these capital requirements, see “Supervision and Regulation.” BNY Mellon is subject to the U.S. capital rules, which are being gradually phased-in over a multi-year period through 2018.
54 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Our estimated CET1 and SLR ratios on a fully phased-in basis are based on our current interpretation of the U.S. capital rules. Our risk-based capital adequacy is determined using the higher of risk-weighted assets (“RWAs”) determined using the Advanced Approach and Standardized Approach.
The transitional capital ratios for Dec. 31, 2016 included in the table below were negatively impacted by the additional phase-in requirements that became effective on Jan. 1, 2016.
Consolidated and largest bank subsidiary regulatory capital ratios | Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
Well capitalized | Minimum required | Capital ratios | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||
(a) | |||||||||||
Consolidated regulatory capital ratios: (b) | |||||||||||
Standardized: | |||||||||||
CET1 ratio | N/A | (c) | 5.5 | % | 12.3 | % | 11.5 | % | |||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 6 | % | 7 | 14.5 | 13.1 | ||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 10 | 9 | 15.2 | 13.5 | |||||||
Advanced: | |||||||||||
CET1 ratio | N/A | (c) | 5.5 | % | 10.6 | % | 10.8 | % | |||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 6 | % | 7 | 12.6 | 12.3 | ||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 10 | 9 | 13.0 | 12.5 | |||||||
Leverage capital ratio (b) | N/A | (c) | 4 | 6.6 | 6.0 | ||||||
SLR (d) | 5 | (c)(e) | 3 | 6.0 | 5.4 | ||||||
Selected regulatory capital ratios – fully phased-in – Non-GAAP: (c) | |||||||||||
Estimated CET1 ratio: | |||||||||||
Standardized Approach | 8.5 | % | (e) | 5.5 | % | 11.3 | % | 10.2 | % | ||
Advanced Approach | 8.5 | (e) | 5.5 | 9.7 | 9.5 | ||||||
Estimated SLR (d) | 5 | (e) | 3 | 5.6 | 4.9 | ||||||
The Bank of New York Mellon regulatory capital ratios: (b) | |||||||||||
Advanced: | |||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 6.5 | % | 5.125 | % | 13.6 | % | 11.8 | % | |||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 8 | 6.625 | 13.9 | 12.3 | |||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 10 | 8.625 | 14.2 | 12.5 | |||||||
Leverage capital ratio | 5 | 4 | 7.2 | 5.9 | |||||||
SLR (d) | 6 | 3 | 6.5 | 5.3 | |||||||
Selected regulatory capital ratios – fully phased-in – Non-GAAP: | |||||||||||
Estimated SLR (d) | 6 | % | 3 | % | 6.1 | % | 4.8 | % | |||
(a) | Minimum requirements for Dec. 31, 2016 include Basel III minimum thresholds plus then applicable buffers. See page 57 for the minimum ratios with buffers phased-in to 2017 levels. |
(b) | For our CET1, Tier 1 capital and Total capital ratios, our effective capital ratios under U.S. capital rules are the lower of the ratios as calculated under the Standardized and Advanced Approaches. The leverage capital ratio is based on Tier 1 capital, as phased-in and quarterly average total assets. |
(c) | The Federal Reserve’s regulations do not establish well capitalized thresholds for these measures for bank holding companies. |
(d) | The SLR does not become a binding measure until the first quarter of 2018. The SLR is based on Tier 1 capital, as phased-in, and average quarterly assets and certain off-balance sheet exposures. |
(e) | Fully phased-in Basel III minimum with expected buffers. See page 57 for the capital ratios with the phase-in of the capital conservation buffer and the U.S. G-SIB surcharge, as well as the introduction of the SLR buffer. |
Our CET1 ratio determined under the Advanced Approach was 10.6% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 10.8% at Dec. 31, 2015. The decrease reflects lower regulatory capital primarily due to common stock repurchases, foreign currency translation, defined benefit plan adjustments and unrealized losses on securities, partially offset by earnings retention.
Our estimated CET1 ratio (Non-GAAP) calculated under the Advanced Approach on a fully phased-in basis was 9.7% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 9.5% at Dec. 31, 2015. Our estimated CET1 ratio (Non-GAAP) calculated under the Standardized Approach on a fully phased-in basis was 11.3% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 10.2% at Dec. 31, 2015.
BNY Mellon 55
Results of Operations (continued) |
The estimated fully phased-in SLR (Non-GAAP) of 5.6% at Dec. 31, 2016 and 4.9% at Dec. 31, 2015 was based on our interpretation of the U.S. capital rules, as supplemented by the Federal Reserve’s final rules on the SLR. BNY Mellon will be subjected to an enhanced SLR, which will require a buffer in excess of 2% over the minimum SLR of 3%. The insured depository institution subsidiaries of the U.S. G-SIBs, including those of BNY Mellon, must maintain a 6% SLR to be considered “well capitalized.”
For additional information on the U.S. capital rules, see “Supervision and Regulation - Capital Requirements - Generally.”
The Basel III Advanced Approach capital ratios are significantly impacted by RWAs for operational risk. Our operational loss risk model is informed by external losses, including fines and penalties levied against institutions in the financial services industry, particularly those that relate to businesses in which we operate, and as a result external losses have impacted and could in the future impact the amount of capital that we are required to hold.
Management views the estimated fully phased-in CET1 and other risk-based capital ratios and SLR as key measures in monitoring BNY Mellon’s capital position and progress against future regulatory capital standards. Additionally, the presentation of the estimated fully phased-in CET1 and other risk-based capital ratios and SLR are intended to allow investors to compare these ratios with estimates presented by other companies.
Our capital ratios are necessarily subject to, among other things, anticipated compliance with all necessary enhancements to model calibration, approval by regulators of certain models used as part of RWA calculations, further implementation guidance from regulators, market practices and standards and any changes BNY Mellon may make to its businesses. As a consequence of these factors, our capital ratios may materially change, and may be volatile over time and from period to period.
Minimum capital ratios and capital buffers
The U.S. capital rules include a series of buffers and surcharges over required minimums that apply to bank holding companies, including BNY Mellon, which are being phased-in over time. Banking
organizations with a risk-based ratio or SLR above the minimum required level, but with a risk-based ratio or SLR below the minimum level with buffers will face constraints on dividends, equity repurchases and discretionary executive compensation based on the amount of the shortfall. Different regulatory capital minimums, buffers and surcharges apply to our banking subsidiaries.
The U.S. capital rules introduced a capital conservation buffer and countercyclical capital buffer that add to the minimum regulatory capital ratios. The capital conservation buffer–0.625% for 2016, 1.25% for 2017 and 2.5% when fully phased-in on Jan. 1, 2019–is designed to absorb losses during periods of economic stress and applies to all banking organizations. During periods of excessive growth, the capital conservation buffer may be expanded through the imposition of a countercyclical capital buffer that may be as high as an additional 2.5%. The countercyclical capital buffer, when applicable, applies only to Advanced Approach banking organizations. The countercyclical capital buffer is currently set to zero with respect to U.S. exposures, but it could increase if the banking agencies determine that systemic vulnerabilities are meaningfully above normal.
BNY Mellon is subject to an additional G-SIB surcharge, which is implemented as an extension of the capital conservation buffer and must be satisfied with CET1 capital. For 2016, the G-SIB surcharge applicable to BNY Mellon was 0.375%, and for 2017 it is 0.75%, and, when fully phased-in on Jan. 1, 2019 as calculated, applying metrics as currently applicable to BNY Mellon, would be 1.5%.
The following table presents the principal minimum capital ratio requirements with buffers and surcharges, as phased-in, applicable to the Parent and The Bank of New York Mellon. This table does not include the imposition of a countercyclical capital buffer. The U.S. capital rules also provide for transitional arrangements for qualifying instruments, deductions, and adjustments, which are not reflected in this table. Buffers and surcharges are not applicable to the leverage capital ratio. These buffers, other than the SLR buffer, and surcharge began to phase-in on Jan. 1, 2016 and will be fully implemented on Jan. 1, 2019.
56 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Consolidated capital ratio requirements | Well capitalized | Minimum ratios | Minimum ratios with buffers, as phased-in (a) | |||||||||||||||
2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Capital conservation buffer (CET1) | 0.625 | % | 1.25 | % | 1.875 | % | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||
U.S. G-SIB surcharge (CET1) (b)(c) | 0.375 | % | 0.75 | % | 1.125 | % | 1.5 | % | ||||||||||
Consolidated: | ||||||||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | N/A | 4.5 | % | 5.5 | % | 6.5 | % | 7.5 | % | 8.5 | % | |||||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 6.0 | % | 6.0 | % | 7.0 | % | 8.0 | % | 9.0 | % | 10.0 | % | ||||||
Total capital ratio | 10.0 | % | 8.0 | % | 9.0 | % | 10.0 | % | 11.0 | % | 12.0 | % | ||||||
Enhanced SLR buffer (Tier 1 capital) | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2.0 | % | 2.0 | % | |||||||||||
SLR | N/A | 3.0 | % | N/A | N/A | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | |||||||||
Bank subsidiaries: (c) | ||||||||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 6.5 | % | 4.5 | % | 5.125 | % | 5.75 | % | 6.375 | % | 7.0 | % | ||||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 8.0 | % | 6.0 | % | 6.625 | % | 7.25 | % | 7.875 | % | 8.5 | % | ||||||
Total capital ratio | 10.0 | % | 8.0 | % | 8.625 | % | 9.25 | % | 9.875 | % | 10.5 | % | ||||||
SLR | 6.0 | % | 3.0 | % | N/A | N/A | 6.0 | % | (d) | 6.0 | % | (d) | ||||||
(a) | Countercyclical capital buffer currently set to 0%. |
(b) | The fully phased-in U.S. G-SIB surcharge of 1.5% applicable to BNY Mellon is subject to change. |
(c) | The U.S. G-SIB surcharge is not applicable to the regulatory capital ratios of the bank subsidiaries. |
(d) | Well capitalized threshold. |
The table below presents the factors that impacted the transitional and fully phased-in CET1 (Non-GAAP).
Estimated CET1 generation presented on a transitional and fully phased-in basis – Non-GAAP | Year ended Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||
(in millions) | Transitional basis (b) | Fully phased-in Non-GAAP (c) | ||||
CET1 – Beginning of period | $ | 18,417 | $ | 16,082 | ||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – GAAP | 3,425 | 3,425 | ||||
Goodwill and intangible assets, net of related deferred tax liabilities | (19 | ) | 599 | |||
Gross CET1 generated | 3,406 | 4,024 | ||||
Capital deployed: | ||||||
Common stock dividends | (778 | ) | (778 | ) | ||
Common stock repurchased | (2,398 | ) | (2,398 | ) | ||
Total capital deployed | (3,176 | ) | (3,176 | ) | ||
Other comprehensive income: | ||||||
Foreign currency translation | (819 | ) | (819 | ) | ||
Unrealized loss on assets available-for-sale | (109 | ) | (291 | ) | ||
Defined benefit plans | (289 | ) | (51 | ) | ||
Unrealized gain on cash flow hedges | (5 | ) | (4 | ) | ||
Total other comprehensive income | (1,222 | ) | (1,165 | ) | ||
Additional paid-in capital (a) | 700 | 700 | ||||
Other additions (deductions): | ||||||
Net pension fund assets | (8 | ) | 26 | |||
Deferred tax assets | (11 | ) | (12 | ) | ||
Embedded goodwill | (17 | ) | 3 | |||
Other | 4 | 8 | ||||
Total other additions | (32 | ) | 25 | |||
Net CET1 generated | (324 | ) | 408 | |||
CET1 – End of period | $ | 18,093 | $ | 16,490 | ||
(a) | Primarily related to stock awards, the exercise of stock options and stock issued for employee benefit plans. |
(b) | Reflects transitional adjustments to CET1 required under the U.S. capital rules. |
(c) | Estimated. |
BNY Mellon 57
Results of Operations (continued) |
The following table presents the components of our transitional and fully phased-in CET1, Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital, the RWAs determined under both the Standardized and Advanced Approaches, the average assets used for leverage capital purposes and the total leverage exposure for estimated SLR purposes.
Capital components and ratios | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Transitional Approach (a) | Fully phased-in - Non-GAAP (b) | Transitional Approach (a) | Fully phased-in - Non-GAAP (b) | |||||||||
CET1: | |||||||||||||
Common shareholders’ equity | $ | 35,794 | $ | 35,269 | $ | 36,067 | $ | 35,485 | |||||
Goodwill and intangible assets | (17,314 | ) | (18,312 | ) | (17,295 | ) | (18,911 | ) | |||||
Net pension fund assets | (55 | ) | (90 | ) | (46 | ) | (116 | ) | |||||
Equity method investments | (313 | ) | (344 | ) | (296 | ) | (347 | ) | |||||
Deferred tax assets | (19 | ) | (32 | ) | (8 | ) | (20 | ) | |||||
Other | — | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
Total CET1 | 18,093 | 16,490 | 18,417 | 16,082 | |||||||||
Other Tier 1 capital: | |||||||||||||
Preferred stock | 3,542 | 3,542 | 2,552 | 2,552 | |||||||||
Trust preferred securities | — | — | 74 | — | |||||||||
Deferred tax assets | (13 | ) | — | (12 | ) | — | |||||||
Net pension fund assets | (36 | ) | — | (70 | ) | — | |||||||
Other | (121 | ) | (121 | ) | (25 | ) | (22 | ) | |||||
Total Tier 1 capital | $ | 21,465 | $ | 19,911 | $ | 20,936 | $ | 18,612 | |||||
Tier 2 capital: | |||||||||||||
Trust preferred securities | $ | 148 | $ | — | $ | 222 | $ | — | |||||
Subordinated debt | 550 | 550 | 149 | 149 | |||||||||
Allowance for credit losses | 281 | 281 | 275 | 275 | |||||||||
Other | (12 | ) | (11 | ) | (12 | ) | (12 | ) | |||||
Total Tier 2 capital - Standardized Approach | 967 | 820 | 634 | 412 | |||||||||
Excess of expected credit losses | 50 | 50 | 37 | 37 | |||||||||
Less: Allowance for credit losses | 281 | 281 | 275 | 275 | |||||||||
Total Tier 2 capital - Advanced Approach | $ | 736 | $ | 589 | $ | 396 | $ | 174 | |||||
Total capital: | |||||||||||||
Standardized Approach | $ | 22,432 | $ | 20,731 | $ | 21,570 | $ | 19,024 | |||||
Advanced Approach | $ | 22,201 | $ | 20,500 | $ | 21,332 | $ | 18,786 | |||||
Risk-weighted assets: | |||||||||||||
Standardized Approach | $ | 147,671 | $ | 146,475 | $ | 159,893 | $ | 158,015 | |||||
Advanced Approach: | |||||||||||||
Credit Risk | $ | 97,659 | $ | 96,391 | $ | 106,974 | $ | 105,099 | |||||
Market Risk | 2,836 | 2,836 | 2,148 | 2,148 | |||||||||
Operational Risk | 70,000 | 70,000 | 61,262 | 61,262 | |||||||||
Total Advanced Approach | $ | 170,495 | $ | 169,227 | $ | 170,384 | $ | 168,509 | |||||
Standardized Approach: | |||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 12.3 | % | 11.3 | % | 11.5 | % | 10.2 | % | |||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 14.5 | 13.6 | 13.1 | 11.8 | |||||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 15.2 | 14.2 | 13.5 | 12.0 | |||||||||
Advanced Approach: | |||||||||||||
CET1 ratio | 10.6 | % | 9.7 | % | 10.8 | % | 9.5 | % | |||||
Tier 1 capital ratio | 12.6 | 11.8 | 12.3 | 11.0 | |||||||||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 13.0 | 12.1 | 12.5 | 11.1 | |||||||||
Average assets for leverage capital purposes | $ | 326,809 | $ | 351,435 | |||||||||
Total leverage exposure for SLR purposes | $ | 355,083 | $ | 382,810 | |||||||||
(a) | Reflects transitional adjustments to CET1, Tier 1 capital and Tier 2 capital required in 2016 and 2015 under the U.S. capital rules. |
(b) | Estimated. |
58 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
The following table presents the amount of capital by which BNY Mellon and our largest bank subsidiary, The Bank of New York Mellon, exceeded the capital thresholds determined under the transitional rules at Dec. 31, 2016.
Capital above thresholds at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||
(in millions) | Consolidated | The Bank of New York Mellon (b) | |||||
CET1 | $ | 8,716 | (a) | $ | 9,644 | ||
Tier 1 capital | 9,530 | (a) | 8,091 | ||||
Total capital | 5,152 | (b) | 5,747 | ||||
Leverage capital | 8,393 | (a) | 5,824 | ||||
(a) | Based on minimum required standards, with applicable buffers. |
(b) | Based on well capitalized standards. |
The following table shows the impact on the consolidated capital ratios at Dec. 31, 2016 of a $100 million increase or decrease in common equity, or a $1 billion increase or decrease in RWA, quarterly average assets or total leverage exposure.
Sensitivity of consolidated capital ratios at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||
Increase or decrease of | ||||
(in basis points) | $100 million in common equity | $1 billion in RWA, quarterly average assets or total leverage exposure | ||
CET1: | ||||
Standardized Approach | 7 | bps | 8 | bps |
Advanced Approach | 6 | 6 | ||
Tier 1 capital: | ||||
Standardized Approach | 7 | 10 | ||
Advanced Approach | 6 | 7 | ||
Total capital: | ||||
Standardized Approach | 7 | 10 | ||
Advanced Approach | 6 | 8 | ||
Leverage capital | 3 | 2 | ||
SLR | 3 | 2 | ||
Estimated CET1 ratio, fully phased-in – Non-GAAP: | ||||
Standardized Approach | 7 | 8 | ||
Advanced Approach | 6 | 6 | ||
Estimated SLR, fully phased-in – Non-GAAP | 3 | 2 | ||
At Dec. 31, 2016, we had $247 million of outstanding trust preferred securities, a portion of which is eligible for inclusion in Tier 2 capital. In January 2017, we announced that these trust preferred securities will be redeemed on March 20, 2017.
Capital ratios vary depending on the size of the balance sheet at quarter-end and the levels and types of investments in assets. The balance sheet size fluctuates from quarter to quarter based on levels of customer and market activity. In general, when servicing clients are more actively trading securities, deposit balances and the balance sheet as a whole are higher. In addition, when markets experience significant volatility or stress, our balance sheet size may increase considerably as client deposit levels increase.
Supplementary Leverage Ratio
BNY Mellon has presented its consolidated and largest bank subsidiary’s estimated fully phased-in SLRs based on its interpretation of the U.S. capital rules, which are being gradually phased-in over a multi-year period and on the application of such rules to BNY Mellon’s businesses as currently conducted.
BNY Mellon 59
Results of Operations (continued) |
The following table presents the components of our SLR on both the transitional and fully phased-in basis.
SLR | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Transitional basis | Fully phased-in Non-GAAP (a) | Transitional basis | Fully phased-in Non-GAAP (a) | |||||||||
Consolidated: | |||||||||||||
Total Tier 1 capital | $ | 21,465 | $ | 19,911 | $ | 20,936 | $ | 18,612 | |||||
Total leverage exposure: | |||||||||||||
Quarterly average total assets | $ | 344,142 | $ | 344,142 | $ | 368,590 | $ | 368,590 | |||||
Less: Amounts deducted from Tier 1 capital | 17,333 | 18,887 | 17,650 | 19,403 | |||||||||
Total on-balance sheet assets, as adjusted | 326,809 | 325,255 | 350,940 | 349,187 | |||||||||
Off-balance sheet exposures: | |||||||||||||
Potential future exposure for derivatives contracts (plus certain other items) | 6,021 | 6,021 | 7,158 | 7,158 | |||||||||
Repo-style transaction exposures | 533 | 533 | 440 | 440 | |||||||||
Credit-equivalent amount of other off-balance sheet exposures (less SLR exclusions) | 23,274 | 23,274 | 26,025 | 26,025 | |||||||||
Total off-balance sheet exposures | 29,828 | 29,828 | 33,623 | 33,623 | |||||||||
Total leverage exposure | $ | 356,637 | $ | 355,083 | $ | 384,563 | $ | 382,810 | |||||
SLR - Consolidated | 6.0 | % | 5.6 | % | 5.4 | % | 4.9 | % | |||||
The Bank of New York Mellon, our largest bank subsidiary: | |||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital | $ | 19,011 | $ | 17,708 | $ | 16,814 | $ | 15,142 | |||||
Total leverage exposure | $ | 291,022 | $ | 290,230 | $ | 316,812 | $ | 316,270 | |||||
SLR - The Bank of New York Mellon | 6.5 | % | 6.1 | % | 5.3 | % | 4.8 | % | |||||
(a) | Estimated. |
Issuer purchases of equity securities
Share repurchases - fourth quarter of 2016 | ||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions, except per share information; common shares in thousands) | Total shares repurchased | Average price per share | Total shares repurchased as part of a publicly announced plan or program | Maximum approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the publicly announced plans or programs at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
October 2016 | 12,433 | $ | 46.02 | 12,433 | $ | 1,669 | ||||||||
November 2016 | 2,078 | 46.70 | 2,078 | 1,572 | ||||||||||
December 2016 | 3,876 | 46.03 | 3,876 | 1,393 | ||||||||||
Fourth quarter of 2016 (a) | 18,387 | $ | 46.10 | 18,387 | $ | 1,393 | (b) | |||||||
(a) | Includes 17 thousand shares repurchased at a purchase price of $1 million from employees, primarily in connection with the employees’ payment of taxes upon the vesting of restricted stock. The average price per share of open market purchases was $46.10. |
(b) | Represents the maximum value of the shares authorized to be repurchased through the second quarter of 2017, including employee benefit plan repurchases, in connection with the Federal Reserve’s non-objection to our 2016 capital plan. |
On June 29, 2016, in connection with the Federal Reserve’s non-objection to our 2016 capital plan, BNY Mellon announced a stock purchase program providing for the total repurchase of up to $2.7 billion of common stock. The 2016 capital plan began in the third quarter of 2016 and continues through the second quarter of 2017. Also, in connection with the 2016 capital plan, in August 2016, BNY Mellon
issued $1 billion of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock.
Share repurchases may be executed through repurchase plans designed to comply with Rule 10b5-1 and through derivative, accelerated share repurchase and other structured transactions.
60 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Trading activities and risk management
Our trading activities are focused on acting as a market-maker for our customers and facilitating customer trades in compliance with the Volcker Rule. The risk from market-making activities for customers is managed by our traders and limited in total exposure through a system of position limits, value-at-risk (“VaR”) methodology based on a Monte Carlo simulation and other market sensitivity measures. The calculation of our VaR used by management and presented below assumes a one-day holding period, utilizes a 99% confidence level, and incorporates the non-linear characteristics of options. See Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on the VaR methodology.
The following tables indicate the calculated VaR amounts for the trading portfolio for the designated periods.
VaR (a) | 2016 | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Average | Minimum | Maximum | Dec. 31, | ||||||||
Interest rate | $ | 6.3 | $ | 4.3 | $ | 8.9 | $ | 5.5 | ||||
Foreign exchange | 2.9 | 1.2 | 11.1 | 2.8 | ||||||||
Equity | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.4 | ||||||||
Credit | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||||||||
Diversification | (4.2 | ) | N/M | N/M | (3.7 | ) | ||||||
Overall portfolio | 5.9 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 5.3 | ||||||||
VaR (a) | 2015 | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Average | Minimum | Maximum | Dec. 31, | ||||||||
Interest rate | $ | 5.1 | $ | 3.6 | $ | 8.0 | $ | 5.2 | ||||
Foreign exchange | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 1.2 | ||||||||
Equity | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.9 | 0.6 | ||||||||
Credit | — | — | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||||||||
Diversification | (1.9 | ) | N/M | N/M | (2.2 | ) | ||||||
Overall portfolio | 5.2 | 3.9 | 8.5 | 5.1 | ||||||||
(a) | VaR figures do not reflect the impact of the credit valuation adjustment (“CVA”) guidance in ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement. This is consistent with the regulatory treatment. VaR exposure does not include the impact of the Company’s consolidated investment management funds and seed capital investments. |
N/M - Because the minimum and maximum may occur on different days for different risk components, it is not meaningful to compute a minimum and maximum portfolio diversification effect.
The interest rate component of VaR represents instruments whose values predominantly vary with the level or volatility of interest rates. These
instruments include, but are not limited to: debt securities, mortgage-backed securities, swaps, swaptions, forward rate agreements, exchange-traded futures and options, and other interest rate derivative products.
The foreign exchange component of VaR represents instruments whose values predominantly vary with the level or volatility of currency exchange rates or interest rates. These instruments include, but are not limited to: currency balances, spot and forward transactions, currency options, exchange-traded futures and options, and other currency derivative products.
The equity component of VaR consists of instruments that represent an ownership interest in the form of domestic and foreign common stock or other equity-linked instruments. These instruments include, but are not limited to: common stock, exchange-traded funds, Depositary Receipts, listed equity options (puts and calls), over-the-counter (“OTC”) equity options, equity total return swaps, equity index futures and other equity derivative products.
The credit component of VaR represents instruments whose values predominantly vary with the credit worthiness of counterparties. These instruments include, but are not limited to, credit derivatives (credit default swaps and exchange-traded credit index instruments). Credit derivatives are used to hedge various credit exposures.
The diversification component of VaR is the risk reduction benefit that occurs when combining portfolios and offsetting positions, and from the correlated behavior of risk factor movements.
During 2016, interest rate risk generated 63% of average gross VaR, foreign exchange risk generated 29% of average gross VaR, equity risk accounted for 5% of average gross VaR and credit risk generated 3% of average gross VaR. During 2016, our daily trading loss exceeded our calculated VaR amount of the overall portfolio on three occasions.
The following table of total daily trading revenue or loss illustrates the number of trading days in which our trading revenue or loss fell within particular ranges during the past five quarters.
BNY Mellon 61
Results of Operations (continued) |
Distribution of trading revenue (loss) (a) | Quarter ended | |||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | June 30, 2016 | March 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||
Revenue range: | Number of days | |||||||||
Less than $(2.5) | — | — | 1 | — | — | |||||
$(2.5) – $0 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |||||
$0 – $2.5 | 28 | 22 | 20 | 29 | 23 | |||||
$2.5 – $5.0 | 23 | 25 | 38 | 21 | 29 | |||||
More than $5.0 | 7 | 11 | 3 | 9 | 6 | |||||
(a) | Trading revenue (loss) includes realized and unrealized gains and losses primarily related to spot and forward foreign exchange transactions, derivatives, and securities trades for our customers and excludes any associated commissions, underwriting fees and net interest revenue. |
Trading assets include debt and equity instruments and derivative assets, primarily interest rate and foreign exchange contracts, not designated as hedging instruments. Trading assets were $6 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $7 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
Trading liabilities include debt and equity instruments and derivative liabilities, primarily interest rate and foreign exchange contracts, not designated as hedging instruments. Trading liabilities were $4 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $5 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
Under our fair value methodology for derivative contracts, an initial “risk-neutral” valuation is performed on each position assuming time-discounting based on a AA credit curve. In addition, we consider credit risk in arriving at the fair value of our derivatives.
We reflect external credit ratings as well as observable credit default swap spreads for both ourselves and our counterparties when measuring the fair value of our derivative positions. Accordingly, the valuation of our derivative positions is sensitive to the current changes in our own credit spreads, as well as those of our counterparties.
At Dec. 31, 2016, our OTC derivative assets of $4.3 billion included a CVA deduction of $38 million. Our OTC derivative liabilities of $4.4 billion included a
debit valuation adjustment (“DVA”) of $3 million related to our own credit spread. Net of hedges, the CVA decreased by $16 million and the DVA decreased by $4 million in 2016. The net impact of these adjustments increased foreign exchange and other trading revenue by $12 million in 2016. During 2016, no realized loss was charged off against CVA reserves.
At Dec. 31, 2015, our OTC derivative assets of $4.7 billion included a CVA deduction of $46 million. Our OTC derivative liabilities of $4.3 billion included a DVA of $6 million related to our own credit spread. Net of hedges, the CVA increased by $2 million and the DVA increased $1 million in 2015. The net impact of these adjustments decreased foreign exchange and other trading revenue by $1 million in 2015. During 2015, a $2 million realized loss was charged off against CVA reserves.
The table below summarizes the risk ratings for our foreign exchange and interest rate derivative counterparty credit exposure during the past five quarters. This information indicates the degree of risk to which we are exposed. Significant changes in ratings classifications for our foreign exchange and other trading activity could result in increased risk for us.
Foreign exchange and other trading counterparty risk rating profile (a) | Quarter ended | |||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | June 30, 2016 | March 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||
Rating: | ||||||||||
AAA to AA- | 35 | % | 45 | % | 38 | % | 44 | % | 43 | % |
A+ to A- | 39 | 32 | 40 | 37 | 42 | |||||
BBB+ to BBB- | 22 | 19 | 18 | 14 | 13 | |||||
Non-investment grade (BB+ and lower) | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 2 | |||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % |
(a) | Represents credit rating agency equivalent of internal credit ratings. |
62 BNY Mellon
Results of Operations (continued) |
Asset/liability management
Our diversified business activities include processing securities, accepting deposits, investing in securities, lending, raising money as needed to fund assets, and other transactions. The market risks from these activities are interest rate risk and foreign exchange risk. Our primary market risk is exposure to movements in U.S. dollar interest rates and certain foreign currency interest rates. We actively manage interest rate sensitivity and use earnings simulation and discounted cash flow models to identify interest rate exposures.
An earnings simulation model is the primary tool used to assess changes in pre-tax net interest revenue. The model incorporates management’s assumptions regarding interest rates, balance changes on core deposits, market spreads, changes in the prepayment behavior of loans and securities and the impact of derivative financial instruments used for interest rate risk management purposes. These assumptions have been developed through a combination of historical analysis and future expected pricing behavior and are inherently uncertain. As a result, the earnings simulation model cannot precisely estimate net
interest revenue or the impact of higher or lower interest rates on net interest revenue. Actual results may differ from projected results due to timing, magnitude and frequency of interest rate changes, and changes in market conditions and management’s strategies, among other factors.
The table below relies on certain critical assumptions regarding the balance sheet and depositors’ behavior related to interest rate fluctuations and the prepayment and extension risk in certain of our assets. Generally, there has been an inverse relationship between interest rates and client deposit levels. To the extent that actual behavior is different from that assumed in the models, there could be a change in interest rate sensitivity.
We evaluate the effect on earnings by running various interest rate ramp scenarios from a baseline scenario. The interest rate ramp scenarios are reviewed to examine the impact of large interest rate movements. In each scenario, all currencies interest rates are shifted higher or lower. Interest rate sensitivity is quantified by calculating the change in pre-tax net interest revenue between the scenarios over a 12-month measurement period.
The following table shows net interest revenue sensitivity for BNY Mellon.
Estimated changes in net interest revenue (dollars in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Sept. 30, 2016 | June 30, 2016 | March 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
up 200 bps parallel rate ramp vs. baseline (a) | $ | 6 | $ | 62 | $ | 91 | $ | 103 | $ | 179 | |||||
up 100 bps parallel rate ramp vs. baseline (a) | 145 | 147 | 158 | 189 | 191 | ||||||||||
Long-term up 50 bps, short-term unchanged (b) | 81 | 116 | 130 | 104 | 33 | ||||||||||
Long-term down 50 bps, short-term unchanged (b) | (88 | ) | (128 | ) | (96 | ) | (93 | ) | (91 | ) | |||||
(a) | In the parallel rate ramp, both short-term and long-term rates move in four equal quarterly increments. |
(b) | Long-term is equal to or greater than one year. |
The baseline scenario used for the calculations in the estimated changes in net interest revenue table above as of Dec. 31, 2016 is based on our quarter-end balance sheet and the spot yield curve. The baseline scenarios used for periods prior to Dec. 31, 2016 were based on implied forward yield curves. We revised the methodology as of Dec. 31, 2016 as we believe using the spot yield curve for the baseline scenario provides a more accurate reflection of net interest revenue sensitivity given the recent increase in short-term interest rates and the implied forward rates. Because interest rates and the implied forward yield curves were lower in prior periods, the impact of using a flat yield curve versus an implied forward yield curve was not as significant. The 100 basis
point ramp scenario assumes rates increase 25 basis points above the yield curve in each of the next four quarters and the 200 basis point ramp scenario assumes a 50 basis point per quarter increase.
Our net interest revenue sensitivity table above incorporates assumptions about the impact of changes in interest rates on depositor behavior based on historical experience. Given the current historically low interest rate environment and the potential change to implementation of monetary policy, the impact of depositor behavior is highly uncertain. The lower sensitivity in the ramp up 200 basis point scenario compared with the 100 basis point scenario
BNY Mellon 63
Results of Operations (continued) |
is driven by the assumption of increased deposit runoff and forecasted changes in the deposit pricing.
Growth or contraction of deposits could also be affected by the following factors:
• | Monetary policy; |
• | Global economic uncertainty; |
• | Our ratings relative to other financial institutions’ ratings; and |
• | Regulatory reform. |
Any of these events could change our assumptions about depositor behavior and have a significant impact on our balance sheet and net interest revenue.
We also project future cash flows from our assets and liabilities over a long-term horizon and then discount these cash flows using instantaneous parallel shocks to prevailing interest rates. This measure reflects the structural balance sheet interest rate sensitivity by discounting all future cash flows. The aggregation of these discounted cash flows is the economic value of equity (“EVE”). The following table shows how the EVE would change in response to changes in interest rates.
Estimated changes in EVE | Dec. 31, 2016 | |
Rate change: | ||
up 200 bps vs. baseline | (2.0 | )% |
up 100 bps vs. baseline | (0.7 | )% |
The asymmetrical accounting treatment of the impact of a change in interest rates on our balance sheet may create a situation in which an increase in interest rates can adversely affect reported equity and regulatory capital, even though economically there may be no impact on our economic capital position. For example, an increase in rates will result in a decline in the value of our available-for-sale securities portfolio, which will be reflected through a reduction
in accumulated other comprehensive income in our shareholders’ equity thereby affecting our tangible common equity (“TCE”) ratios. Under current accounting rules, to the extent the fair value option provided in ASC 825, Financial Instruments, is not applied, there is no corresponding change on our fixed liabilities, even though economically these liabilities are more valuable as rates rise.
We project the impact of this change using the same interest rate shock assumptions described earlier and compare the projected mark-to-market on the investment securities portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016, under the higher rate environments versus a stable rate scenario. The table below shows the impact of a change in interest rates on the TCE ratio.
Estimated changes in TCE ratio (in basis points) | Dec. 31, 2016 | |
up 200 bps vs. baseline | (73 | ) |
up 100 bps vs. baseline | (36 | ) |
These results do not reflect strategies that management could employ to limit the impact as interest rate expectations change.
To manage foreign exchange risk, we fund foreign currency-denominated assets with liability instruments denominated in the same currency. We utilize various foreign exchange contracts if a liability denominated in the same currency is not available or desired, and to minimize the earnings impact of translation gains or losses created by investments in foreign markets. The foreign exchange risk related to the interest rate spread on foreign currency-denominated asset/liability positions is managed as part of our trading activities. We use forward foreign exchange contracts to protect the value of our net investment in foreign operations. At Dec. 31, 2016, net investments in foreign operations totaled $12 billion and were spread across 13 foreign currencies.
64 BNY Mellon
Risk Management |
Risk management overview
Governance
Risk management and oversight begin with the board of directors and two key board committees: the Risk Committee and the Audit Committee.
The Risk Committee is comprised entirely of independent directors and meets on a regular basis to review and assess the control processes with respect to the Company’s inherent risks. It also reviews and assesses the risk management activities of the Company and the Company’s fiduciary risk policies and activities. Policy formulation and day-to-day oversight of the Risk Management Framework is delegated to the Chief Risk Officer, who, together with the Chief Auditor and Chief Compliance Officer, helps ensure an effective risk management governance structure. The roles and responsibilities of the Risk Committee are described in more detail in its charter, a copy of which is available on our website, www.bnymellon.com.
The Audit Committee is also comprised entirely of independent directors, all of whom are financially literate within the meaning of the NYSE listing standards. Two members of the Audit Committee have been determined to be audit committee financial experts as set out in the rules and regulations under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), with accounting or related financial management expertise within the meaning of the NYSE listing standards, and to have banking and financial management expertise within the meaning of the FDIC rules. The Audit Committee meets on a regular basis to perform an oversight review of the integrity of the financial statements and financial reporting process, compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, our independent registered public accountant’s qualifications and independence, and the performance of our registered public accountant and internal audit function. The Audit Committee also reviews management’s assessment of the adequacy of internal controls. The functions of the Audit Committee are described in more detail in its charter, a copy of which is available on our website, www.bnymellon.com.
The Senior Risk Management Committee (“SRMC”) is the most senior management body responsible for ensuring that emerging risks are weighed against the corporate risk appetite and that any material amendments to the risk appetite statement are properly vetted and recommended to the Executive Committee and the Board for approval. The SRMC also reviews any material breaches to our risk appetite and approves action plans required to remediate the issue. SRMC provides oversight for the risk management, compliance and ethics framework. The Chief Executive Officer, Chief Risk Officer and Chief Financial Officer are among SRMC’s members.
Primary risk types
The understanding, identification and management of risk are essential elements for the successful management of BNY Mellon. Our primary risk categories are:
Type of risk | Description |
Operational | The risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, human factors and systems, breaches of technology and information systems, or from external events. Also includes fiduciary risk, reputational risk, and litigation risk. |
Market | The risk of loss due to adverse changes in the financial markets. Our market risks are primarily interest rate, foreign exchange, and equity risk. Market risk particularly impacts our exposures that are marked-to-market such as the securities portfolio, trading book, and equity investments. |
Credit | The risk of loss if any of our borrowers or other counterparties were to default on their obligations to us. Credit risk is resident in the majority of our assets, but primarily concentrated in the loan and securities books, as well as off-balance sheet exposures such as lending commitments, letters of credit, and securities lending indemnifications. |
Liquidity | The risk that BNY Mellon cannot meet its cash and collateral obligations at a reasonable cost for both expected and unexpected cash flows, without adversely affecting daily operations or financial conditions. Liquidity risk can arise from cash flow mismatches, market constraints from the inability to convert assets to cash, the inability to raise cash in the markets, deposit run-off, or contingent liquidity events. |
Strategic | The risk that BNY Mellon doesn’t effectively manage and protect the firm’s market positioning and stability. This includes risks associated with the inability to maintain a strong understanding of clients’ needs, provide suitable product offerings that are financially viable and fit within the firm’s operating model and adapt to transformational change in the industry. |
BNY Mellon 65
Risk Management (continued) |
The following table presents the primary types of risk typically embedded in on- and off-balance sheet instruments.
Risks of our on- and off-balance sheet instruments | |
Assets: | |
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | credit |
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | market, credit |
Securities | market, credit, liquidity |
Trading assets | market, credit, liquidity |
Loans | credit, liquidity |
Goodwill | operational, market |
Intangible assets | operational, market |
Liabilities: | |
Deposits | liquidity |
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | market, liquidity |
Trading liabilities | market, liquidity |
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | liquidity |
Off-balance sheet instruments: | |
Lending commitments | credit, liquidity |
Standby letters of credit | credit, liquidity |
Commercial letters of credit | credit, liquidity |
Securities lending indemnifications | market, credit |
The following chart provides the economic capital allocated to our businesses. Liquidity and strategic risks are managed on a stand-alone basis at the consolidated and bank levels. Management of liquidity risk is the responsibility of Corporate Treasury, which is reported in the Other segment. The percentages below are based on the allocation of economic capital at Dec. 31, 2016 to protect against unexpected economic losses over a one-year period at a level consistent with the solvency of a target debt rating.
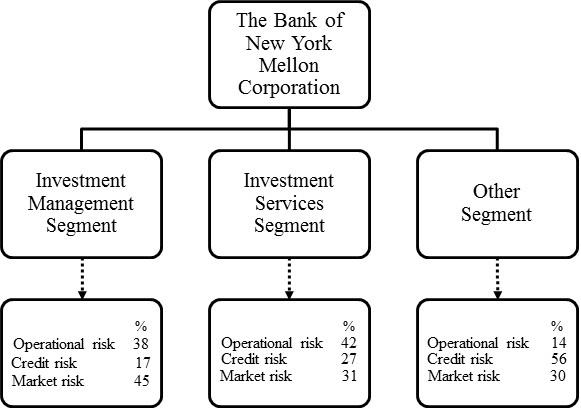
Operational risk
In providing a comprehensive array of products and services, we may be exposed to operational risk. Operational risk may result from, but is not limited to, errors related to transaction processing, breaches of internal control systems and compliance requirements, fraud by employees or persons outside BNY Mellon or business interruption due to system failures or other events. Operational risk may also include breaches of our technology and information systems resulting from unauthorized access to confidential information or from internal or external threats, such as cyberattacks. Operational risk also includes potential legal or regulatory actions that could arise as a result of noncompliance with applicable laws and/or regulatory requirements. In the case of an operational event, we could suffer a financial loss as well as reputational damage.
To address these risks, we maintain comprehensive policies and procedures and an internal control framework designed to provide a sound operational environment. These controls have been designed to manage operational risk at appropriate levels given our financial strength, the business environment and markets in which we operate, and the nature of our businesses, and considering factors such as competition and regulation. Our internal auditors and internal control group monitor and test the overall effectiveness of our internal controls and financial reporting systems on an ongoing basis.
We have also established procedures that are designed to ensure compliance with generally accepted conduct, ethics and business practices which are defined in our corporate policies. These include training programs, such as for our “Code of Conduct” and “Know Your Customer” programs, and compliance training programs, such as those regarding information protection, suspicious activity reporting and operational risk.
We have established operational risk management as an independent risk discipline. The organizational framework for operational risk is based upon a strong risk culture that incorporates both governance and risk management activities comprising:
• | Board Oversight and Governance – The Risk Committee of the Board approves and oversees our operational risk management strategy in addition to credit and market risk. The Risk |
66 BNY Mellon
Risk Management (continued) |
Committee meets regularly to review operational risk management initiatives, discuss key risk issues and review the effectiveness of the risk management systems.
• | Accountability of Businesses – Business managers are responsible for maintaining an effective system of internal controls commensurate with their risk profiles and in accordance with BNY Mellon policies and procedures. |
• | Corporate Operational Risk Management is responsible for developing risk management policies and tools for assessing, measuring, monitoring and managing operational risk for BNY Mellon. The primary objectives of Corporate Operational Risk Management are to promote effective risk management, identify emerging risks, create incentives for generating continuous improvement in controls and to optimize capital. |
• | The Information Risk Management Group is responsible for developing policies, methods and tools for identifying, assessing, measuring, monitoring and governing information and technology risk for BNY Mellon. The Information Risk Management Group partners with the businesses to help maintain and protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the firm’s information and technology assets from internal and external threats such as cyberattacks. |
Market risk
Outside of the exposure that our businesses have to capital markets generally, our business activity tends to minimize outright or direct exposure to market risk, with such risk primarily limited to market volatility from trading activity in support of clients. More significant direct market risk is assumed in the form of interest rate and credit spread risk within the investment portfolio both as a means for forward asset/liability management and net interest revenue generation.
In addition to the Risk Committee and SRMC, oversight of market risk is performed by certain committees and through executive review meetings. Detailed reviews of derivative trading positions and stress tests results are conducted during the Markets Weekly Risk Review. Senior managers from Risk
Management, Finance and Sales and Trading attend the review.
Regarding the Corporate Treasury function, oversight is provided by the Treasury Risk Committee, bi-weekly Portfolio Management Group risk meetings, Business Risk Committee and numerous portfolio reviews.
The Collateral Margin Review Committee reviews and approves the standards for collateral received or paid in respect of collateralized derivative agreements and securities financing transactions.
The Business Risk Committee for the Markets business also provides a forum for market risk oversight. The goal of the Business Risk Committee meeting, which is held at least quarterly, is to review key risk and control issues and related initiatives facing all lines of business, including Markets. The following activities are also addressed during Business Risk Committee meetings:
• | Reporting of all new Monitoring Limits and changes to existing limits; and |
• | Monitoring of trading exposures, VaR, market sensitivities and stress testing results. |
Finally, the Risk Quantification Review Group reviews backtesting results for the Company’s VaR model.
Credit risk
The extension of credit is not considered a discrete product and is not, typically, attributable to a specific business, but instead is used as a means of supporting our clients and our business activity more holistically. Specifically, we extend direct credit in order to foster client relationships and as a method by which to generate interest income from the deposits that result from business activity. We extend and incur intraday credit exposure in order to facilitate our various processing activities.
To balance the value of our activities with the credit risk incurred in pursuing them, we set and monitor internal credit limits for activities that entail credit risk, most often on the size of the exposure and the quality of the counterparty. For credit exposures driven by changing market rates and prices, exposure measures include an add-on for such potential changes.
BNY Mellon 67
Risk Management (continued) |
We manage credit risk at both the individual exposure level as well as the portfolio level. Credit risk at the individual exposure level is managed through our credit approval system and involves four approval levels up to and including the Chief Risk Officer of the Company. The requisite approvals are based upon the size and relative risk of the aggregate exposure under consideration. The Credit Risk Group is responsible for approving the size, terms and maturity of all credit exposures as well as the ongoing monitoring of the creditworthiness of the counterparty. In addition, they are responsible for assigning and maintaining the internal risk ratings on each exposure.
Credit risk management at the portfolio level is supported by the Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group, within the Risk Management and Compliance Sector. The Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group is responsible for calculating two fundamental credit measures. First, we project a statistically probable credit loss, used to help determine the appropriate loan loss reserve and to measure customer profitability. Credit loss considers three basic components: the estimated size of the exposure whenever default might occur, the probability of default before maturity and the severity of the loss we would incur, commonly called “loss given default.” For institutional lending, where most of our credit risk is created, unfunded commitments are assigned a usage given default percentage. Borrowers/Counterparties are assigned ratings by Credit Portfolio Managers on an 18-grade scale, which translate to a scaled probability of default. Additionally, transactions are assigned loss-given-default ratings (on a 7-grade scale) that reflect the transactions’ structures including the effects of guarantees, collateral and relative seniority of position.
The second fundamental measurement of credit risk calculated by the Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group is called economic capital. Our economic capital model estimates the capital required to support the overall credit risk portfolio. Using a Monte Carlo simulation engine and measures of correlation among borrower defaults, the economic capital model examines extreme and highly unlikely scenarios of portfolio credit loss in order to estimate credit-related capital, and then allocates that capital to individual borrowers and exposures. The credit-related capital calculation supports a second tier of policy standards and limits by serving as an input to both profitability
analysis and concentration limits of capital at risk with any one borrower, industry or country.
The Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group is responsible for the calculation methodologies and the estimates of the inputs used in those methodologies for the determination of expected loss and economic capital. These methodologies and input estimates are regularly evaluated to ensure their appropriateness and accuracy. As new techniques and data become available, the Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group attempts to incorporate, where appropriate, those techniques or data.
Credit risk is intrinsic to much of the banking business. However, BNY Mellon seeks to limit both on- and off-balance sheet credit risk through prudent underwriting and the use of capital only where risk-adjusted returns warrant. We seek to manage risk and improve our portfolio diversification through syndications, asset sales, credit enhancements, credit derivatives, and active collateralization and netting agreements. In addition, we have a separate Credit Risk Review Group, which is part of Internal Audit, made up of experienced loan review officers who perform timely reviews of the loan files and credit ratings assigned to the loans.
Liquidity risk
Access to global capital markets and financial market utilities are fundamental to both our operating model and overall strategy. Without such access, it would be difficult if not impossible to process payments as well as settle and clear transactions on behalf of clients. Deterioration in our liquidity position, whether actual or perceived, can impact our market access by affecting participants’ willingness to transact with us. Changes to our liquidity can be caused by various factors, such as funding mismatches, market constraints limiting the ability to liquidate assets, inability to issue debt, run-off of core deposits and contingent liquidity events, such as additional collateral posting. Changes in economic conditions or exposure to credit, market, operational, legal and reputational risks can also affect our liquidity. Our liquidity risk management practices are designed to maintain a strong liquidity profile, by actively managing both the quality of the investment portfolio and intraday liquidity positions, and by having sufficient deposits and other funding to meet timely payment and settlement obligations under both normal and stressed conditions.
68 BNY Mellon
Risk Management (continued) |
Our overall approach to liquidity management is to ensure that sources of liquidity are sufficient in amount and diversity such that changes in funding requirements at the Parent and at the various bank subsidiaries can be accommodated routinely without material adverse impact on earnings, daily operations or our financial condition.
The board of directors has the responsibility for oversight of liquidity risk management for the Company and approves the liquidity risk tolerances. The Asset Liability Committee (“ALCO”) is the senior management committee responsible for the oversight of liquidity management. ALCO is responsible to ensure that board approved strategies, policies and procedures for managing liquidity are appropriately executed. Senior management is also responsible for regularly reporting the liquidity position of the Company to the board of directors. The Treasury Risk Committee is responsible for reviewing liquidity stress tests and various liquidity metrics, including contractual cash flow gaps for liquidity, liquidity stress metrics and ratios, Liquidity Coverage Ratio, Net Stable Funding Ratio and client deposit concentration. The Treasury Risk Committee approves and validates stress test methodologies and assumptions.
BNY Mellon seeks to maintain an adequate liquidity cushion in both normal and stressed environments and seeks to diversify funding sources by line of business, customer and market segment. Additionally, we seek to maintain liquidity ratios within approved limits and liquidity risk tolerance, maintain a liquid asset buffer that can be liquidated, financed and/or pledged as necessary, and control the levels and sources of wholesale funds.
Potential uses of liquidity include withdrawals of customer deposits and client drawdowns on unfunded credit or liquidity facilities. We actively monitor unfunded lending-related commitments, thereby reducing unanticipated funding requirements.
When monitoring liquidity, we evaluate multiple metrics to ensure ample liquidity for expected and unexpected events. Metrics include cash flow mismatches, asset maturities, debt spreads, peer ratios, liquid assets, unencumbered collateral, funding sources and balance sheet liquidity ratios. We monitor the LCR, as well as various internal liquidity limits as part of our standard analysis to monitor
depositor and market funding concentration, liability maturity profile and potential liquidity draws due to off-balance sheet exposure.
We also perform liquidity stress tests to ensure the Company maintains sufficient liquidity resources under multiple stress scenarios, including stress tests required by rules adopted by the Federal Reserve under the Dodd-Frank Act. Stress tests are based on scenarios that measure liquidity risks under unlikely but plausible events. The Company performs these tests under various time horizons ranging from one day to one year in a base case, as well as supplemental tests to determine whether the Company’s liquidity is sufficient for severe market events and firm-specific events. Under our scenario testing program, the results of the tests indicate that the Company has sufficient liquidity.
Strategic Risk
Our strategy includes expanding our client base, increasing product offerings and better aligning certain business activities with market demand. Successful realization of our strategy requires that we provide expertise and insight through market-leading solutions that drive economies of scale while developing highly talented people and protecting our financial strength and stability. We understand and meet market and client expectations with suitable products and offerings that are financially viable and leverageable and that integrate into our business model.
Markets, and the manner in which our clients interact and transact within markets, can evolve quickly, such as when new or disruptive technologies are introduced. Failure to either anticipate or participate in transformational change within a given market could result in poor strategic positioning and potential negative financial impact.
Stress Testing
It is the policy of the Company to perform Enterprise-wide Stress Testing at regular intervals as part of its Internal Capital Adequacy Assessment Process (“ICAAP”). Additionally, the Company performs an analysis of capital adequacy in a stressed environment in its Enterprise-Wide Stress Test Framework, as required by the enhanced prudential standards issued pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act.
BNY Mellon 69
Risk Management (continued) |
Enterprise-Wide Stress Testing performs analyses across the Company’s lines of business, products, geographic areas, and risk types incorporating the results from the different underlying models and projections given a certain stress-test scenario. It is an important component of assessing the adequacy of capital as well as identifying any high risk touch points in business activities. Furthermore, by integrating enterprise-wide stress testing into the Company’s capital planning process, the results provide a forward-looking evaluation of the ability to complete planned capital actions in a more-adverse-than-anticipated economic environment.
Economic capital required
BNY Mellon has implemented a methodology to quantify economic capital. We define economic capital as the capital required to protect against unexpected economic losses over a one-year period at a level consistent with the solvency of a target debt rating. We quantify economic capital requirements for the risks inherent in our business activities using statistical modeling techniques and then aggregate them at the consolidated level. A capital reduction, or diversification benefit, is applied to reflect the unlikely event of experiencing an extremely large loss in each type of risk at the same time. Economic capital requirements are directly related to our risk profile. As such, they have become a part of our ICAAP and, along with regulatory capital, are a key component to ensuring that the actual level of capital is commensurate with our risk profile and sufficient to provide the financial flexibility to undertake future strategic business initiatives.
The framework and methodologies to quantify each of our risk types have been developed by the Enterprise Capital Adequacy Group and are designed to be consistent with our risk management principles. The framework has been approved by senior management and has been reviewed by the Risk Committee of the board of directors. Due to the evolving nature of quantification techniques, we expect to continue to refine the methodologies used to estimate our economic capital requirements.
The following table presents our economic capital required at Dec. 31, 2016, on a consolidated basis.
Economic capital required at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||
(in millions) | |||
Credit | $ | 4,680 | |
Market | 3,388 | ||
Operational | 5,545 | ||
Other (a) | 853 | ||
Economic capital required - consolidated | $ | 14,466 | |
CET1 | $ | 18,093 | |
Capital cushion | $ | 3,627 | |
(a) | Includes interest rate risk, reputational risk and diversification benefit. |
Global compliance
Our global compliance function provides leadership, guidance and oversight to help our businesses identify applicable laws and regulations and implement effective measures to meet the specific requirements. Compliance takes a proactive approach by anticipating evolving regulatory standards and remaining aware of industry best practices, legislative initiatives, competitive issues, and public expectations and perceptions. The function uses its global reach to disseminate information about compliance-related matters throughout BNY Mellon. The Chief Compliance and Ethics Officer reports to the Chief Risk Officer, is a member of key committees of BNY Mellon and provides regular updates to the Risk Committee of the board of directors.
Internal audit
Internal Audit is an independent, objective assurance function that reports directly to the Audit Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors. It assists the Company in accomplishing its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined, risk-based approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of the Company’s risk management, control and governance processes. The scope of Internal Audit’s work includes the review and evaluation of the adequacy, effectiveness and sustainability of risk management procedures, internal control systems, information systems and governance processes.
70 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation |
Evolving Regulatory Environment
BNY Mellon engages in banking, investment advisory and other financial activities in the U.S. and 34 other countries, and is subject to extensive regulation in the jurisdictions in which it operates. Global supervisory authorities generally are charged with ensuring the safety and soundness of financial institutions, protecting the interests of customers, including depositors in banking entities and investors in mutual funds and other pooled vehicles, safeguarding the integrity of securities and other financial markets and promoting systemic resiliency and financial stability in the relevant country. They are not, however, generally charged with protecting the interests of our shareholders or non-deposit creditors. This discussion outlines the material elements of selected laws and regulations applicable to us. Changes in these standards, or in their application, cannot be predicted, but may have a material effect on our businesses and results of operations.
The financial services industry has been the subject of enhanced regulatory scrutiny in recent years globally, and this trend may continue in the future. Our businesses have been subject to a significant number of global reform measures. In particular, the Dodd-Frank Act and its implementing regulations have significantly restructured the financial regulatory regime in the United States and enhanced supervision and prudential standards for large BHCs like BNY Mellon. The implications of the Dodd-Frank Act for our businesses depend to a large extent on the manner in which its implementing regulations continue to be established and interpreted by the primary U.S. financial regulatory agencies - the Federal Reserve, the FDIC, the OCC, the SEC and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”). The implications are also dependent on continuing changes in market practices and structures in response to the requirements of the Dodd-Frank Act and financial reforms in other jurisdictions. Certain aspects of the Dodd-Frank Act remain subject to further rulemaking, take effect over various transition periods, or contain other elements that make it difficult to precisely anticipate their full impact. In addition, other national and global reform measures adopted by various policy makers or are being considered may materially impact us. Recent political developments, including the change in presidential administrations in the U.S. and the UK referendum vote to leave the European Union, have
resulted in greater uncertainty as to the implementation, scope and timing of regulatory reforms.
Enhanced Prudential Standards and Large Exposures
Sections 165 and 166 of the Dodd-Frank Act direct the Federal Reserve to enact heightened prudential standards and early remediation requirements applicable to BHCs with total consolidated assets of $50 billion or more, such as BNY Mellon, and certain designated nonbank financial companies (generally referred to as “SIFIs”). The Dodd-Frank Act mandates that the requirements applicable to SIFIs be more stringent than those applicable to other financial companies.
The Federal Reserve has adopted rules (“Final SIFI Rules”) to implement the following aspects of Section 165:
• | liquidity requirements; |
• | stress testing of capital; and |
• | overall risk management requirements. |
BNY Mellon must comply with enhanced liquidity and overall risk management standards, which include maintenance of a buffer of highly liquid assets based on projected funding needs for 30 days. The liquidity buffer is in addition to the U.S. banking agencies’ rules regarding the LCR, discussed below, and is described by the Federal Reserve as being “complementary” to those liquidity standards.
The Final SIFI Rules do not address single-counterparty credit limits or early remediation provisions. On March 4, 2016, the Federal Reserve issued its re-proposal to limit credit exposures to single counterparties. With respect to BNY Mellon, which is a “major covered company” as defined in the re-proposal, the re-proposal prohibits having aggregate net credit exposure in excess of 15% of its Tier 1 capital to a “major counterparty,” and 25% of its Tier 1 capital to any other counterparty. A “major counterparty” is any counterparty that is (i) a U.S. G-SIB; (ii) a foreign banking organization (“FBO”), that has the characteristics of a G-SIB under the BCBS G-SIB methodology; (iii) an FBO with respect to which the Federal Reserve determines that the FBO would be a G-SIB or that the U.S. IHC of the FBO would be a G-SIB; or (iv) is a nonbank financial company supervised by the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve’s re-proposal requires securities finance
BNY Mellon 71
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
transaction (SFT) exposures to be calculated using the “collateral haircut approach” in the Standardized Approach, described below.
The Basel Committee has also developed a framework for large exposures, which is scheduled to become effective on Jan. 1, 2019. It will become binding on U.S. banking organizations only to the extent that the U.S. banking agencies implement the framework, including through the Federal Reserve’s adoption of final single counterparty credit limits.
Capital Planning and Stress Testing
Payment of Dividends, Stock Repurchases and Other Capital Distributions
The Parent is a legal entity separate and distinct from its banks and other subsidiaries. Dividends and interest from its subsidiaries are the Parent’s principal sources of funds to make capital contributions or loans to its subsidiaries, to service its own debt, to honor its guarantees of debt issued by its subsidiaries or to make its own capital distributions. Various federal and state laws and regulations limit the amount of dividends that may be paid to the Parent by our bank subsidiaries without regulatory consent. If, in the opinion of the applicable federal regulatory agency, a depository institution under its jurisdiction is engaged in or is about to engage in an unsafe or unsound practice (which, depending on the financial condition of the bank, could include the payment of dividends), the regulator may require, after notice and hearing, that the bank cease and desist from such practice. The OCC, the Federal Reserve and the FDIC have indicated that the payment of dividends would constitute an unsafe and unsound practice if the payment would reduce a depository institution’s capital to an inadequate level. Moreover, under the Federal Deposit Insurance Act, as amended (the “FDI Act”), an insured depository institution may not pay any dividends if the institution is undercapitalized or if the payment of the dividend would cause the institution to become undercapitalized. In addition, the federal bank regulatory agencies have issued policy statements which provide that FDIC-insured depository institutions and their holding companies should generally pay dividends only out of their current operating earnings.
In general, the amount of dividends that may be paid by our U.S. banking subsidiaries, including to the Parent, is limited to the lesser of the amounts
calculated under a “recent earnings” test and an “undivided profits” test. Under the recent earnings test, a dividend may not be paid if the total of all dividends declared and paid by the entity in any calendar year exceeds the current year’s net income combined with the retained net income of the two preceding years, unless the entity obtains prior regulatory approval. Under the undivided profits test, a dividend may not be paid in excess of the entity’s “undivided profits” (generally, accumulated net profits that have not been paid out as dividends or transferred to surplus). The ability of our bank subsidiaries to pay dividends to the Parent may also be affected by various minimum capital requirements for banking organizations.
BNY Mellon’s capital distributions are subject to Federal Reserve oversight. The major component of that oversight is the Federal Reserve’s CCAR, implementing its capital plan rule. That rule requires BHCs having $50 billion or more in total consolidated assets (including BNY Mellon) to submit annual capital plans to their respective Federal Reserve Bank. We are also required to collect and report certain related data on a quarterly basis to allow the Federal Reserve to monitor progress against the annual capital plans. Generally, BNY Mellon and other affected BHCs may pay dividends, repurchase stock and make other capital distributions only in accordance with a capital plan that has been reviewed by the Federal Reserve and as to which the Federal Reserve has not objected. The Federal Reserve may object to a capital plan, submitted by a large covered BHC, such as BNY Mellon, for quantitative or qualitative reasons, including if the plan does not show that the covered BHC will meet, for each quarter throughout the nine-quarter planning horizon covered by the capital plan, all minimum regulatory capital ratios under applicable capital rules as in effect for that quarter on a pro forma basis under the base case and stressed scenarios (including a severely adverse scenario provided by the Federal Reserve). The capital plan rule also stipulates that a covered BHC may not make a capital distribution unless after giving effect to the distribution it will meet all minimum regulatory capital ratios.
The purpose of CCAR is to ensure that these BHCs have robust, forward-looking capital planning processes that account for their unique risks and that permit continued operations during times of economic and financial stress. The 2017 CCAR instructions, consistent with prior Federal Reserve
72 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
guidance, provide that capital plans contemplating dividend payout ratios exceeding 30% of projected after-tax net income will receive particularly close scrutiny. BNY Mellon’s common stock dividend payout ratio was 23% for 2016. See “Capital” for information about our 2016 capital plan.
In December 2015, the Federal Reserve issued guidance that consolidates capital planning expectations, including expectations for CCAR. The guidance makes explicit that the Federal Reserve maintains heightened expectations regarding capital planning by large BHCs such as BNY Mellon. In particular, the Federal Reserve expects firms such as BNY Mellon to exceed the minimum expectations set forth in the Federal Reserve’s guidance and maintain highly sophisticated, comprehensive and robust capital planning practices.
On Jan. 30, 2017, the Federal Reserve released a rule that introduces several changes to the 2017 CCAR cycle, including: (i) reducing the de minimis exception for additional capital distributions from 1.00% of a BHC’s Tier 1 capital to 0.25%; (ii) introducing “blackout periods” for notices regarding or requests for approval to make additional capital distributions; and (iii) extending the range of dates from which the Federal Reserve may select the “as of” date for the global market shock component of the supervisory stress test macroeconomic scenarios applicable to certain BHCs.
Regulatory Stress-Testing Requirements
In addition to the CCAR stress testing requirements, Federal Reserve regulations also include complementary Dodd-Frank Act Stress Tests (“DFAST”). The CCAR and DFAST requirements substantially overlap, and the Federal Reserve implements them at the BHC level on a coordinated basis. Under these DFAST regulations, we are required to undergo regulatory stress tests conducted by the Federal Reserve annually, and to conduct our own internal stress tests pursuant to regulatory requirements twice annually. In addition, The Bank of New York Mellon is required to conduct its own annual internal stress test (although this bank is permitted to combine certain reporting and disclosure of its stress test results with the results of BNY Mellon). These requirements involve testing of capital under various scenarios, including baseline, adverse and severely adverse scenarios provided by the appropriate banking regulator. Results from our
annual company-run stress tests are reported to the appropriate regulators and published. The Federal Reserve published the results of its most recent annual 2016 DFAST stress-test on June 23, 2016. We published the results of our most recent company-run annual stress test on June 24, 2016, and the results of our company-run mid-year stress test on Oct. 14, 2016.
Capital Requirements - Generally
As a BHC, we are subject to U.S. capital rules, administered by the Federal Reserve. Our bank subsidiaries are subject to similar capital requirements administered by the Federal Reserve in the case of The Bank of New York Mellon and by the OCC in the case of our national bank subsidiaries, BNY Mellon, N.A. and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, National Association. These requirements are intended to ensure that banking organizations have adequate capital given the risk levels of their assets and off-balance sheet exposures.
The U.S. capital rules are largely based on the Basel Committee’s December 2010 final capital framework for strengthening international capital standards, now officially identified by the Basel Committee as “Basel III”, and the “Standardized Approach” to calculating RWAs discussed below. Notwithstanding the detailed U.S. capital rules, the federal banking agencies retain significant discretion to set higher capital requirements for categories of BHCs or banks or for an individual BHC or bank as situations warrant.
The U.S. capital rules allow a graduated implementation schedule and will be substantially phased-in by 2019. BNY Mellon began using the new Standardized Approach risk-weightings on Jan. 1, 2015. In addition, BNY Mellon began meeting the minimum ratios for the capital conservation buffer and countercyclical capital buffer, including the G-SIB surcharge, during the transition period beginning on Jan. 1, 2016 and must begin compliance with the SLR on Jan. 1, 2018.
U.S. Capital Rules - Minimum Risk-Based Capital Ratios and Capital Buffers
Consistent with the terms of the Basel III framework and the Dodd-Frank Act, the U.S. capital rules require Advanced Approaches banking organizations, such as BNY Mellon, to satisfy minimum risk-based capital ratios using both the Standardized Approach
BNY Mellon 73
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
risk-weightings and the Advanced Approaches. These requirements are detailed above under “Results of Operations - Capital.” In addition, these minimum ratios will be supplemented by a capital conservation buffer required threshold that began being phased in on Jan. 1, 2016, in increments of 0.625% per year until it reaches 2.5% on Jan. 1, 2019. The capital conservation buffer required threshold can only be satisfied with CET1 capital.
When systemic vulnerabilities are meaningfully above normal, the capital conservation buffer may be expanded up to an additional 2.5% through the imposition of a countercyclical capital buffer. For internationally active banks such as BNY Mellon, the countercyclical capital buffer required threshold is a weighted average of the countercyclical capital buffers deployed in each of the jurisdictions in which the bank has private sector credit exposures. The Federal Reserve, in consultation with the OCC and FDIC, has affirmed the current countercyclical capital buffer level for U.S. exposures of 0% and noted that any future modifications to the buffer would generally be subject to a 12-month phase-in period. Any countercyclical capital buffer required threshold arising from exposures outside the United States will also generally be subject to a 12-month phase-in period.
The U.S. capital rules’ buffers are also supplemented by a risk-based capital surcharge on G-SIB (the “Final U.S. G-SIB Rule”). The final rule requires G-SIBs to calculate their surcharges under two methods (referred to as “method 1” and “method 2”) and use the higher of the two surcharges. The first method is based on the Basel Committee’s framework and considers a G-SIB’s size, interconnectedness, cross-jurisdictional activity, substitutability and complexity. The second method uses similar inputs, but is calibrated to result in significantly higher surcharges and replaces substitutability with a measure of reliance on short-term wholesale funding. The Final U.S. G-SIB Rule does not add the G-SIB surcharge to post-stress minimum risk-based capital ratios for purposes of DFAST or CCAR. Consistent with the phase-in of the capital conservation buffer, the G-SIB capital surcharge began to be phased-in beginning on Jan. 1, 2016 and will become fully effective on Jan. 1, 2019. For 2017, the G-SIB surcharge applicable to BNY Mellon will be 1.5%, subject to applicable phase-ins.
At Dec. 31, 2016, calculated on a transitionally phased-in basis and under the Advanced Approach, BNY Mellon’s CET1 ratio was 10.6%, the Tier 1 capital ratio was 12.6%, the Total capital ratio was 13.0% and its leverage ratio was 6.6%.
At Dec. 31, 2016, our estimated fully phased-in CET1 ratio was 9.7% under the Advanced Approach and 11.3% under the Standardized Approach, based on our current interpretations of the U.S. capital rules.
U.S. Capital Rules - Deductions from and Adjustments to Capital Elements
The U.S. capital rules, like Basel III, provide for a number of deductions from and adjustments to CET1 capital. These include, for example, providing that unrealized gains and losses on all available-for-sale debt securities may not be filtered out for regulatory capital purposes, and the requirement that mortgage servicing rights, deferred tax assets dependent upon future taxable income and significant investments in non-consolidated financial entities be deducted from CET1 to the extent that any one such category exceeds 10% of CET1 or all such categories in the aggregate exceed 15% of CET1.
U.S. Capital Rules - Advanced Approach Risk-Based Capital Rules
The U.S. capital rules’ Advanced Approach asset risk-weighting framework (the “Advanced Approach”) is based on Basel II’s Advanced Approach. Under the U.S. capital rule’s Advanced Approaches framework, credit risk risk-weightings are generally based on risk-sensitive approaches that largely rely on the use of internal credit models and parameters, whereas under the Standardized Approach credit risk risk-weightings are generally based on supervisory risk-weightings which vary primarily by counterparty type and asset class. BNY Mellon is required to comply with Advanced Approach reporting and public disclosures. Under the U.S. capital rules, this means, among other things, for purposes of determining whether we meet minimum risk-based capital requirements, our CET1 ratio, Tier 1 capital ratio, and total capital ratio is the lower of that calculated under the generally applicable risk-based capital standard and under the Advanced Approach rule.
74 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
U.S. Capital Rules - Generally Applicable Risk-Based Capital Rules: Standardized Approach
The agencies’ generally applicable risk-based capital rules calculate risk-weighted assets in the denominator of capital ratios using a broad array of risk weighting categories that are intended to be risk sensitive (the “Standardized Approach”). The risk-weights for the Standardized Approach generally range from 0% to 1,250%. Higher risk-weights under the Standardized Approach apply to a variety of exposures, including certain securitization exposures, equity exposures, claims on securities firms and exposures to counterparties on over-the-counter derivatives.
Concerning securities finance transactions, including transactions in which we serve as agent and provide securities replacement indemnification to a securities lender, the U.S. capital rules do not permit a banking organization to use a simple VaR approach to calculate exposure amounts for repo-style transactions or to use internal models to calculate the exposure amount for the counterparty credit exposure for repo-style transactions under the Standardized Approach (although these methodologies are included in the Advanced Approach). Under the Standardized Approach, a banking organization may use a collateral haircut approach to recognize the credit risk mitigation benefits of financial collateral that secures a repo-style transaction, including an agented securities lending transaction, among other transactions. To apply the collateral haircut approach, a banking organization must determine the exposure amount and the relevant risk weight for the counterparty or guarantor. Banking organizations may calculate market price volatility and foreign exchange volatility using their own internal estimates with prior written approval of their primary Federal supervisor.
In December 2015, the Basel Committee issued a consultative document proposing revisions to the Standardized Approach. Among other things, the proposal maintains external credit ratings as the primary basis for determining risk weights for financial institution and corporate exposures, but requires additional due diligence by firms to confirm the credit risk exposure. The new proposal offers alternative approaches for jurisdictions that do not allow the use of credit ratings, such as the United States. The new proposal also includes a revised framework for credit risk mitigation, including for
securities financing transactions and higher credit conversion factors for commitments. The U.S. banking agencies, including the Federal Reserve, have issued a joint statement stating that they intend to consider the new Basel Committee proposal with the goal of developing a stronger and more transparent risk-based capital framework for the largest financial institutions.
Leverage Ratios
The U.S. capital rules require a minimum 4% leverage ratio for all banking organizations. At Dec. 31, 2016, the Tier 1 leverage ratio for the Parent was 6.6% and the Tier 1 leverage ratio for our primary banking subsidiary, The Bank of New York Mellon, was 7.2%.
The U.S. capital rules also implement a new 3% Basel III-based SLR for Advanced Approach banking organizations, including BNY Mellon, to become effective Jan. 1, 2018. Unlike the Tier 1 leverage ratio, the SLR includes certain off-balance sheet exposures in the denominator, including the potential future credit exposure of derivative contracts and 10% of the notional amount of unconditionally cancelable commitments.
The U.S. G-SIBs (including BNY Mellon) and their insured depository institution subsidiaries are subject to an enhanced SLR, which requires BNY Mellon and other U.S. G-SIBs to maintain an SLR of greater than 5% (composed of the current minimum requirement of 3% plus a greater than 2% buffer) and requires bank subsidiaries of those bank holding companies to maintain at least a 6% SLR in order to qualify as “well capitalized” under the prompt corrective action regulations discussed below. The final enhanced SLR rule for U.S. G-SIBs, like the SLR more generally applicable to all Advanced Approach banking organizations, will become effective on Jan. 1, 2018.
Interest Rate Risk in the Banking Book
On April 1, 2016 the Basel Committee issued final standards for risk management and supervision of interest rate risk in the banking book (“IRRBB”), which updates its 2004 Principles for the management and supervision of interest rate risk. These standards adopt a supervisory approach that includes quantitative calculation and disclosure and not a measure that imposes minimum quantitative
BNY Mellon 75
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
capital requirements. Historically, IRRBB has been regulated under a supervisory approach.
Fundamental Review of the Trading Book
The Basel Committee released revised minimum capital requirements for market risk in January 2016. The purpose of the revised market risk framework is to ensure that the standardized and internal model approaches to market risk deliver credible capital outcomes and promote consistent implementation of the standards across jurisdictions. BNY Mellon is assessing the final framework but does not expect material business issues or compliance matters should the framework be implemented in the U.S.
Total Loss-Absorbing Capacity
On Dec. 15, 2016, the Federal Reserve issued a final rule (the “TLAC Rule”) establishing external total loss-absorbing capacity (“TLAC”) and related requirements for U.S. G-SIBs, including BNY Mellon, at the top-tier holding company level. The TLAC Rule will be effective on Jan. 1, 2019. Under the TLAC Rule, U.S. G-SIBs will be required to maintain a minimum external TLAC of the greater of 18% of risk-weighted assets and 7.5% of the denominator of the SLR. The external TLAC requirement will be met using a combination of Tier 1 capital and eligible external long-term debt securities. The TLAC Rule applies an additional buffer to the risk-weighted assets prong of the external TLAC requirement consisting of the sum of 2.5% of risk-weighted assets, the G-SIB surcharge calculated under method 1, and any applicable countercyclical buffer to be met using CET1. The TLAC Rule also applies a buffer equal to 2% of total leverage exposure to the SLR prong of the external TLAC requirements, consistent with the enhanced SLR, consisting solely of Tier 1 capital. Separately, eligible external long-term debt (“LTD”) will be required to be maintained in an amount equal to the greater of 6% of risk-weighted assets plus the G-SIB surcharge (calculated using the greater of method 1 and method 2), and 4.5% of the denominator of the SLR. In order to be deemed eligible external long-term debt securities and count toward the LTD and TLAC requirements, debt instruments must, among other requirements, be unsecured, not be structured notes, and have a maturity of more than one year from the date of issuance. In addition, the TLAC Rule requires that LTD issued on or after Dec. 31, 2016 (i) not have acceleration rights, other than in the
event of non-payment or the bankruptcy or insolvency of the issuer and (ii) be governed by U.S. law. However, debt issued by a U.S. G-SIB prior to Dec. 31, 2016 can qualify as TLAC and LTD, even if the debt contains other acceleration provisions or is governed by U.S. law. Amounts payable under eligible external long-term debt securities due to be paid within less than two years but within more than one year are subject to a 50% haircut for purposes of the LTD requirement but not the TLAC requirement. Further, the top-tier holding companies of U.S. G-SIBs are not permitted to issue certain guarantees of subsidiary liabilities, incur certain liabilities guaranteed by subsidiaries, issue short-term debt to third parties, or enter into derivatives and certain other financial contracts with external counterparties. Finally, certain liabilities of the top-tier holding companies of U.S. G-SIBs, such as those that are junior to or pari passu with eligible external long-term debt securities are capped at 5% of the value of the U.S. G-SIB’s eligible external TLAC instruments.
The Financial Stability Board (“FSB”) also issued a final TLAC standard on Nov. 9, 2015. There are several important differences between the final FSB TLAC standard and the TLAC Rules. Importantly, the final FSB standard sets an “internal” TLAC requirement requiring material sub-groups of G-SIBs that are not themselves resolution entities to maintain 75-90% of the external TLAC minimum. Under the TLAC Rules, the Federal Reserve is considering requiring internal TLAC at domestic subsidiaries of U.S. G-SIBs, but has not yet proposed rules implementing such internal TLAC requirements.
Prompt Corrective Action
The FDI Act, as amended by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Improvement Act of 1991 (“FDICIA”), requires the federal banking agencies to take “prompt corrective action” in respect of depository institutions that do not meet specified capital requirements. FDICIA establishes five capital categories for FDIC-insured banks: “well capitalized,” “adequately capitalized,” “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized,” and “critically undercapitalized.” The FDI Act imposes progressively more restrictive constraints on operations, management and capital distributions the less capital the institution holds.
The U.S. capital rules maintain “well capitalized” thresholds for insured depository institutions under
76 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
the federal banking agencies’ prompt corrective action framework. Under the U.S. capital rules, an insured depository institution is deemed to be “well capitalized” if it has capital ratios as detailed above under “Results of Operations - Capital.”
Effective Jan. 1, 2018, the U.S. capital rules also require an Advanced Approach banking organization to maintain a SLR of at least 3% to qualify for the “adequately capitalized” status.
In addition, as noted above, the U.S. federal banking agencies’ revisions to the enhanced SLR establish a SLR “well capitalized” threshold of 6% for covered insured depository institutions, including The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon N.A.
FDICIA’s prompt corrective action provisions only apply to depository institutions and not to BHCs. The Federal Reserve’s regulations applicable to BHCs separately define “well capitalized” for BHCs to require maintaining a total risk-based capital ratio of at least 10.0% and a Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio of at least 6.0% (but not a leverage measure). A financial holding company (“FHC”) that is not well capitalized and well managed (or whose bank subsidiaries are not well capitalized and well managed under applicable prompt corrective action standards) may be restricted in certain of its activities and ultimately may lose FHC status.
As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries were “well capitalized” based on the ratios and rules applicable to them noted above. A bank’s capital category, however, is determined solely for the purpose of applying the prompt corrective action rules and may not be an accurate representation of the bank’s overall financial condition or prospects.
BCBS Consultative Document on Operational Risk and Federal Reserve Comment
On March 4, 2016, the BCBS released a consultative document proposing revisions to its approach for calculating operational risk capital. The document proposes to replace the Advanced Measurement Approach in its regulatory framework with the Standardized Measurement Approach, a single non-model-based method. The Federal Reserve released guidance relating to the above consultative document which states that staff will contact affected banking
organizations to discuss individual supervisory plans for calculating operational risk capital.
Liquidity Standards - Basel III and U.S. Rules and Proposals
BNY Mellon is subject to the Final LCR Rule which is designed to ensure that BNY Mellon and its domestic bank subsidiaries maintain an adequate level of unencumbered high-quality liquid assets equal to their expected net cash outflow for a 30-day time horizon under an acute liquidity stress scenario.
The required minimum LCR level has been increased annually by 10% increments until Jan. 1, 2017, at which time covered companies were required to meet an LCR of 100%. As of Dec. 31, 2016, both the Parent and its domestic bank subsidiaries were in compliance with applicable LCR requirements on a fully phased-in basis.
The Basel III framework contemplates an additional liquidity measure, referred to as the net stable funding ratio (“NSFR”), which is designed to promote more medium- and long-term funding of the assets and activities of banking entities over a one-year time horizon. The Basel Committee issued the final NSFR document in October 2014.
In April 2016 and May 2016, the FDIC and the Federal Reserve, respectively, proposed an NSFR rule that would implement a quantitative long-term liquidity requirement applicable to large and internationally active banking organizations, including BNY Mellon. The proposed NSFR rule would implement the Basel III framework’s similar test for medium- and long-term funding of the assets and activities of banking entities over a one-year time horizon. Under the proposed rule, BNY Mellon’s NSFR would be expressed as a ratio of its available stable funding to its required stable funding amount, and BNY Mellon would be required to maintain an NSFR of 1.0. BNY Mellon continues to evaluate the potential effects of this proposal on its operations. The proposed NSFR rule would be effective Jan. 1, 2018.
Separately, as noted above, the Final SIFI Rules address liquidity requirements for BHCs with $50 billion or more in total assets, including BNY Mellon. These enhanced liquidity requirements include an independent review of liquidity risk management; establishment of cash flow projections; a contingency
BNY Mellon 77
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
funding plan, and liquidity risk limits; liquidity stress testing under multiple stress scenarios and time horizons tailored to the specific products and profile of the company; and maintenance of a liquidity buffer of unencumbered highly liquid assets sufficient to meet projected net cash outflows over 30 days under a range of stress scenarios. In the release accompanying those rules, the Federal Reserve states that these enhanced liquidity requirements are designed to complement the LCR. The LCR provides a standardized measure to allow comparison across BHCs, while the Final SIFI Rules’ internal stress test requirements provide a view of the BHC under various scenarios and time horizons which is tailored to the profile of the company. On Dec. 19, 2016, the Federal Reserve issued a final rule requiring that large banking organizations, including BNY Mellon, publicly disclose certain quantitative liquidity metrics, including their consolidated LCR each quarter and consolidated HQLA amounts, broken down by HQLA category. BNY Mellon will commence this disclosure for the second quarter of 2017.
Volcker Rule
The Dodd-Frank Act imposed broad prohibitions and restrictions on proprietary trading and investments in or sponsorship of hedge funds and private equity funds by banking organizations and their affiliates, commonly referred to as the “Volcker Rule.”
The Volcker Rule, subject to certain exceptions, prohibits “banking entities,” including BNY Mellon, from engaging in proprietary trading and limits our sponsorship of, and investments in, private equity and hedge funds (“covered funds”), including our ability to own or provide seed capital to covered funds and the ability for a covered fund to share the same or similar name with a BNY Mellon affiliate. In addition, the Volcker Rule restricts us from engaging in certain transactions with covered funds (including, without limitation, certain U.S. funds for which BNY Mellon acts as both sponsor/manager and custodian).
The restrictions concerning proprietary trading do not contain a broad exemption for asset-liability management functions, but contain more limited exceptions for, among other things, bona fide liquidity risk management and risk-mitigating hedging activities, as well as certain classes of exempted instruments, including government securities. Ownership interests in covered funds that
banking organizations organize and offer are generally limited to 3% of the total number or value of the outstanding ownership interests of any individual fund at any time more than one year after the date of its establishment, and with respect to the aggregate value of all such ownership interests in covered funds (when combined with ownership interests in covered funds held under the Volcker Rule’s ABS issuer exemption and underwriting and market-making exemption), 3% of the banking organization’s Tier 1 capital. Moreover, a banking entity relying on the final Volcker Rule’s exemption for sponsoring covered funds must deduct from its Tier 1 capital, the value of related ownership interests, calculated in accordance with the final rule.
Banking organizations, including BNY Mellon, and their affiliates generally were required to conform their covered activities and investments with the final Volcker Rule regulations by July 21, 2015. The Federal Reserve extended this conformance period by two years (until July 21, 2017) for investments in and relationships with covered funds and foreign funds that were in place prior to Dec. 31, 2013. We are expected to engage in good-faith efforts that will result in conformance of all of our covered activities and investments by no later than the end of this conformance period. The final Volcker Rule regulations also require us to develop and maintain an extensive compliance program, subject to CEO attestation, addressing proprietary trading and covered fund activities.
Derivatives
U.S., EU and APAC regulators are in the process of implementing comprehensive rules governing the supervision, structure, trading and regulation of cleared and over-the-counter derivatives markets and participants. The Dodd-Frank Act, the European regulation on OTC derivatives (European Market Infrastructure Regulation, or “EMIR”), central counterparties and trade repositories, and APAC regulations each require or impose, or are in the process of formulating, a large number of requirements in this area, not all of which are final. However, increasingly, these regulatory regimes, individually and collectively, tend to affect the way various BNY Mellon subsidiaries operate, including where and with whom they transact, and therefore any such changes may impact business models and profitability of certain BNY Mellon subsidiaries.
78 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
The U.S. prudential regulators have adopted joint final rules establishing minimum margin requirements for the uncleared swap transactions engaged in by those dealers subject to their jurisdiction (each, a “Covered Swap Entity”) with compliance requirements which began to apply in September 2016. From that point forward, variation margin requirements are being phased in over a six-month period while initial margin requirements are being phased in over a four-year period. In each instance, the higher a Covered Swap Entity’s derivatives exposure, the earlier in the phase-in period it will be required to comply. In addition, the new rules will require the initial margin posted to or by a Covered Swap Entity be segregated at a third-party custodian. While BNY Mellon does not expect to be impacted by the initial margin component of these new rules in 2017, we do expect to become subject to substantial, new variation margin requirements (the “VM Regulations”) effective March 1, 2017. Should the initial margin requirements be implemented as currently required, it is possible that a number of BNY Mellon OTC derivatives trading relationships may be temporarily interrupted.
Money Market Fund Reforms
The SEC has finalized rules (the “MMF Rules”) that will require institutional prime money market funds (including institutional municipal money market funds) to maintain a floating net asset value (“NAV”) based on the current market value of the securities in their portfolios rounded to the fourth decimal place.
Previously, such funds could maintain a stable NAV of $1.00. Government MMFs and retail MMFs are exempt from these requirements and may continue to maintain a stable NAV, provided each type of fund continues to satisfy certain definitional requirements under the new rule. The MMF Rules also provide new tools to MMFs’ boards of directors to address high net redemption activity during periods of market stress. In particular, the MMF Rules allow a MMF’s board of directors to impose liquidity fees or temporarily suspend redemptions if a MMF’s level of weekly liquid assets falls below certain thresholds. Government MMFs are not required to adopt the liquidity fees and redemption gates provision, but they may opt to do so.
Beyond these primary reforms, the MMF Rules also expand disclosure requirements, tighten the
diversification requirements and impose additional stress testing requirements. The MMF Rules also introduce a new Form N-CR, which requires MMFs to disclose certain events (for example, the imposition or removal of fees or gates, the primary consideration or factors taken into account by a board of directors, in its decision related to fees and gates, and portfolio security defaults).
The compliance date for the amendments related to the fundamental reforms (floating NAV and liquidity fees and redemption sales, etc.) was Oct. 14, 2016. The required changes were implemented by BNY Mellon’s U.S. money market funds in a timely manner.
The text of the European Union’s Money Market Funds Regulation (“MMFR”) was finalized in December 2016, and is expected to apply beginning in 2018. MMFR is a significant change for the money market fund sector in the EU. In particular, constant net asset value (“CNAV”) MMFs as they currently exist will need to convert into variable net asset value (“VNAV”) MMFs, low volatility net asset value (“LVNAV”) MMFs or public debt CNAV MMFs. Other significant restrictions would apply, such as the need for MMFs to apply liquidity fees and redemption gates, to diversify asset portfolios, extensive valuation and reporting requirements and prohibitions on external support.
SEC rules on mutual funds
On Oct. 13, 2016, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) adopted regulations that impose new requirements on mutual funds, exchange-traded funds, and other registered investment companies. The new rules would require mutual funds (other than money market funds) to provide portfolio-wide and position-level holdings data to the SEC on a monthly basis. This data would include the pricing of portfolio securities, information regarding repurchase and securities lending activities, and the terms of derivatives contracts. Information contained in reports for the last month of each fund’s fiscal quarter would be made available to the public within 60 days of the end of the relevant quarter.
The new rules also impose liquidity risk management requirements that are intended to reduce the risk that funds will not be able to meet shareholder redemptions and to minimize the impact of redemptions on remaining shareholders. Each fund
BNY Mellon 79
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
will be required to establish a liquidity risk management program; classify the investments in its portfolio into one of four liquidity categories; maintain a highly liquid investment minimum; and limit illiquid investments to 15% of net assets. The new rules also permit funds to use swing pricing in certain circumstances. The compliance dates for the reporting requirements depend on the applicable reporting form. Most funds will be required to comply with the liquidity risk management requirements by Dec. 1, 2018. The SEC has delayed the effective date of the swing pricing amendments. BNY Mellon is evaluating the cost of compliance and the impact of the new regulations on its activities.
Recovery and Resolution
As required by the Dodd-Frank Act, the Federal Reserve and FDIC have jointly issued a final rule requiring certain organizations, including each BHC with consolidated assets of $50 billion or more, such as BNY Mellon, to submit annually to the Federal Reserve and the FDIC a plan - referred to as the 165(d) resolution plan - for its rapid and orderly resolution in the event of material financial distress or failure. In addition, the FDIC has issued a final rule that requires insured depository institutions with $50 billion or more in total assets, such as The Bank of New York Mellon, to submit annually to the FDIC a plan for resolution in the event of the institution’s failure.
In April 2016, the FDIC and the Federal Reserve jointly determined that BNY Mellon’s 2015 165(d) resolution plan was not credible or would not facilitate an orderly resolution under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, the statutory standard established in the Dodd-Frank Act, and issued a joint notice of deficiencies and shortcomings regarding our plan and the actions that must be taken to address them, which we responded to in an Oct. 1, 2016 submission.
In December 2016, the agencies jointly determined that our October submission adequately remedied the identified deficiencies. A public portion of our resolution plans and our October 2016 submission are available on the Federal Reserve’s and FDIC’s websites.
Following the receipt of the agencies’ April 2016 feedback on our 2015 resolution plan, we have changed our preferred resolution strategy in the event of our material financial distress or failure to a single
point of entry (“SPOE”) strategy, which involves recapitalization of our material operating subsidiaries prior to the Parent’s entry into insolvency proceedings.
If the Federal Reserve and FDIC jointly determine that our future submissions are not credible and the covered BHC fails to address the deficiencies in a timely manner, the FDIC and the Federal Reserve may jointly impose more stringent capital, leverage or liquidity requirements or restrictions on our growth, activities or operations. If we continue to fail to adequately remedy any deficiencies, we could be required to divest assets or operations that the regulators determine necessary to facilitate our orderly resolution.
BNY Mellon is also subject to heightened supervisory expectations for recovery and resolution preparedness. These expectations, issued by the Federal Reserve in January 2014, apply to eight domestic bank holding companies designated by the Federal Reserve, including BNY Mellon, and relate to capabilities critical to operational resilience and contingency planning, including: effective processes for managing, identifying, and valuing collateral; a comprehensive understanding of obligations and exposures associated with payment, clearing, and settlement activities; the ability to analyze liquidity and funding sources, uses, and risks; demonstrated management information systems capabilities on a legal entity basis; and robust arrangements for the continued provision of shared and outsourced services. The Federal Reserve incorporates reviews of these key capabilities as part of its ongoing supervision of BNY Mellon.
The European Union Bank Recovery and Resolution Directive (“BRRD”) applies to various subsidiaries and branches of BNY Mellon.
BRRD provides for recovery and resolution planning and a set of harmonized powers to resolve or implement recovery of relevant institutions, including branches of non-European Economic Area (“EEA”) banks operating within the EEA. The directive includes the preparation of recovery and resolution plans, giving relevant EEA regulators powers to impose requirements on an institution before resolution actions become necessary; a set of resolution tools and powers to facilitate the resolution of failing entities, such as the power to “bail-in” the debt of an institution (including certain deposit
80 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
obligations); and the power to require a firm to change its structure to remove impediments to resolvability.
BRRD includes a minimum requirement for own funds, defined as regulatory capital, and eligible liabilities (“MREL”) to ensure that institutions maintain enough capital capable of being written down and/or bailed-in. MREL will be set on a case-by-case basis for each institution subject to BRRD. MREL is the EU equivalent of TLAC, and is generally aligned with the FSB’s TLAC proposals. In contrast with TLAC, MREL will apply to all institutions subject to BRRD (not only G-SIBs).
In addition, BRRD requires EU-domiciled credit institutions, and certain other firms, to prepare recovery plans. We submitted recovery plans in respect of the following EMEA entities during 2016: The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, The Bank of New York Mellon (Luxembourg) SA, BNY Mellon Holdings (UK) Limited (a UK group recovery plan encompassing The Bank of New York Mellon (International) Limited), and BNY Mellon Capital Markets EMEA Limited. We will submit a group recovery plan for Pershing Holdings (UK) Limited during 2017. We will submit updated recovery plans during 2017 as required under applicable timescales.
The FSB is also focused on cross-border resolution and measures to promote resolvability. In November 2015, the FSB published a consultative document on Arrangements to Support Operational Continuity in Resolution and a separate consultative document on Temporary Funding Needed to Support the Orderly Resolution of a Global Systemically Important Bank. The proposed guidance on operational continuity sets out arrangements to ensure the continuity of critical shared services that are necessary to maintain a firm’s critical functions in resolution. The proposed guidance on funding addresses the risk of G-SIBs not having sufficient liquidity to maintain critical operations during resolution, and proposes principles to ensure that temporary funding is available to allow the effective resolution of G-SIBs.
BRRD also requires each EU Member State (either individually, or collectively with other EU Member States) to establish a resolution fund, which is to be funded by the banking industry. Most EU Member States participate in the Single Resolution Fund (“SRF”), under the control of the Single Resolution Board (“SRB”). The SRB commenced operation on
Jan. 1, 2015, and has broad powers in case of bank resolution. Contributions to the SRF started in 2016, and the SRF will build up over eight years, to a target level of 1% of covered deposits. Certain BNY Mellon entities are subject to contributions to the SRF, most notably The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV. The UK is not participating in the SRB nor SRF. The Bank of England is the equivalent resolution authority in the UK, with similarly broad powers in case of bank resolution.
Proposed Rule on Contractual Stay of Qualified Financial Contracts
On May 3, 2016, the Federal Reserve issued a proposed rule that would require all U.S. G-SIBs, including BNY Mellon, and their subsidiaries that are not regulated by the OCC, as well as all U.S. operations of all non-U.S. G-SIBs, to include an agreement to obey certain resolution-related stay requirements in all of their non-cleared qualified financial contracts (“QFCs”) with any counterparty. The FDIC and OCC have since issued equivalent proposals for their regulated institutions. QFCs generally include derivatives, repurchase agreements, and securities lending arrangements, among others. All BNY Mellon entities that currently engage in QFC activities as principal have adhered to the 2015 Resolution Stay Protocol developed by the International Swaps and Derivatives Association, Inc. that applies contractual resolution stay language to QFCs among Protocol adherents, which are primarily G-SIBs and their subsidiaries. If implemented as proposed, the Federal Reserve’s rule would require BNY Mellon, other U.S. G-SIBs and the U.S. operations of non-U.S. G-SIBs to ensure that certain contractual resolution stay language is included in all of its QFCs with any counterparty globally. In addition, several other jurisdictions where BNY Mellon and its QFC counterparties operate are in various stages of considering and implementing similar rules.
Cybersecurity regulatory proposals
On Sept. 13, 2016, the New York State Department of Financial Services (“NYSDFS”) proposed a new cybersecurity regulation. An updated version of this proposal was issued on Dec. 28, 2016. The proposed rule, scheduled to become effective on March 1, 2017, would require financial institutions regulated by NYSDFS, including BNY Mellon, to establish a cybersecurity program, adopt a written cybersecurity
BNY Mellon 81
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
policy, designate a chief information security officer, and have policies and procedures in place to ensure the security of information systems and non-public information accessible to, or held by, third parties. The proposed rule also includes a variety of other requirements to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems.
Following the NYSDFS proposal, the Federal Reserve, FDIC, and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (the “OCC”) approved a joint advance notice of proposed rulemaking that would impose enhanced cyber risk management standards on banking organizations with $50 billion or more in total consolidated assets and certain of their service providers. The standards address five categories:
• | cyber risk governance; |
• | cyber risk management; |
• | internal dependency management; |
• | external dependency management; |
• | incident response, cyber resilience, and situational awareness. |
The agencies are also considering proposing more stringent “Sector Critical Standards” that would apply to systems “deemed critical to the financial sector.”
Insolvency of an Insured Depository Institution or a Bank Holding Company; Orderly Liquidation Authority
If the FDIC is appointed as conservator or receiver for an insured depository institution such as The Bank of New York Mellon or BNY Mellon, N.A., upon its insolvency or in certain other circumstances, the FDIC has the power to:
• | Transfer any of the depository institution’s assets and liabilities to a new obligor, including a newly formed “bridge” bank without the approval of the depository institution’s creditors; |
• | Enforce the terms of the depository institution’s contracts pursuant to their terms without regard to any provisions triggered by the appointment of the FDIC in that capacity; or |
• | Repudiate or disaffirm any contract or lease to which the depository institution is a party, the performance of which is determined by the FDIC to be burdensome and the disaffirmance or repudiation of which is determined by the FDIC to |
promote the orderly administration of the depository institution.
In addition, under federal law, the claims of holders of domestic deposit liabilities and certain claims for administrative expenses against an insured depository institution would be afforded a priority over other general unsecured claims against such an institution, including claims of debt holders of the institution, in the “liquidation or other resolution” of such an institution by any receiver. As a result, whether or not the FDIC ever sought to repudiate any debt obligations of The Bank of New York Mellon or BNY Mellon, N.A., the debt holders would be treated differently from, and could receive, if anything, substantially less than, the depositors of the bank.
The Dodd-Frank Act created a new resolution regime (known as the “orderly liquidation authority”) for systemically important financial companies, including BHCs and their affiliates. Under the orderly liquidation authority, the FDIC may be appointed as receiver for the systemically important institution, and its failed nonbank subsidiaries, for purposes of liquidating the entity if, among other conditions, it is determined at the time of the institution’s failure that it is in default or in danger of default and the failure poses a risk to the stability of the U.S. financial system.
If the FDIC is appointed as receiver under the orderly liquidation authority, then the powers of the receiver, and the rights and obligations of creditors and other parties who have dealt with the institution, would be determined under the Dodd-Frank Act’s orderly liquidation authority provisions, and not under the insolvency law that would otherwise apply. The powers of the receiver under the orderly liquidation authority were based on the powers of the FDIC as receiver for depository institutions under the FDI Act. However, the provisions governing the rights of creditors under the orderly liquidation authority were modified in certain respects to reduce disparities with the treatment of creditors’ claims under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code as compared to the treatment of those claims under the new authority. Nonetheless, substantial differences in the rights of creditors exist as between these two regimes, including the right of the FDIC to disregard the strict priority of creditor claims in some circumstances, the use of an administrative claims procedure to determine creditors’ claims (as opposed to the judicial procedure utilized in bankruptcy proceedings), and the right of
82 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
the FDIC to transfer assets or liabilities of the institution to a third party or a “bridge” entity.
In December 2013, the FDIC released a notice outlining the SPOE strategy and soliciting comments on how an SPOE resolution approach would be implemented in the U.S. An SPOE approach would replace a distressed BHC with a bridge holding company, which could then continue subsidiary bank operations.
Depositor Preference
Under U.S. federal law, certain deposits and certain claims for administrative expenses and employee compensation against an insured depository institution are afforded a priority over other general unsecured claims, including federal funds and letters of credit, in the “liquidation or other resolution” of such an institution by any receiver.
In September 2014, the UK PRA, as the successor to the prudential functions of the Financial Services Authority, published “Supervisory Statement SS10/14 - Supervising international banks: the PRA’s approach to branch supervision”. In SS10/14, the PRA expressed concern with non-EEA national depositor preference regimes, and stated that the PRA would consider a range of options, such as liaising with non-EEA regulatory authorities in regard to the non-EEA institution’s recovery plan and the adequacy of the recovery plan from the perspective of the UK branch, or to require certain non-EEA institutions to convert their UK branch into a UK subsidiary.
Transactions with Affiliates
Transactions between BNY Mellon’s banking subsidiaries, on the one hand, and the Parent and its nonbank subsidiaries and affiliates, on the other, are subject to certain restrictions, limitations and requirements, which include limits on the types and amounts of transactions (including extensions of credit and asset purchases by our banking subsidiaries) that may take place and generally require those transactions to be on arm’s-length terms. In general, extensions of credit by a BNY Mellon banking subsidiary to any nonbank affiliate, including the Parent, must be secured by designated amounts of specified collateral and are limited in the aggregate to 10% of the relevant bank’s capital and surplus for transactions with a single affiliate and to 20% of the relevant bank’s capital and surplus for
transactions with all affiliates. There are also limitations on affiliate credit exposures arising from derivative transactions and securities lending and borrowing transactions.
Deposit Insurance
Our U.S. banking subsidiaries, including The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon, N.A., accept deposits, and those deposits have the benefit of FDIC insurance up to the applicable limit. The current limit for FDIC insurance for deposit accounts is $250,000 for each depositor account. Under the FDI Act, insurance of deposits may be terminated by the FDIC upon a finding that the insured depository institution has engaged in unsafe and unsound practices, is in an unsafe or unsound condition to continue operations or has violated any applicable law, regulation, rule, order or condition imposed by a bank’s federal regulatory agency.
The FDIC’s Deposit Insurance Fund (the “DIF”) is funded by assessments on insured depository institutions. The FDIC assesses DIF premiums based on a bank’s average consolidated total assets, less the average tangible equity of the insured depository institution during the assessment period. For larger institutions, such as The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon, N.A., assessments are determined based on CAMELS ratings and forward-looking financial measures to calculate the assessment rate, which is subject to adjustments by the FDIC, and the assessment base.
The Dodd-Frank Act also directed the FDIC to determine whether and to what extent adjustments to the assessment base are appropriate for custody banks. Under the FDIC’s regulations, a custody bank may deduct 100% of cash and balances due from depository institutions, securities, federal funds sold, and securities purchased under agreement to resell with a Standardized Approach risk-weight of 0% and may deduct 50% of such asset types with a Standardized Approach risk-weight of greater than 0% and up to and including 20%. This assessment base deduction may not exceed the average value of deposits that are classified as transaction accounts and are identified by the bank as being directly linked to a fiduciary or custodial and safekeeping account.
On March 15, 2016, the FDIC issued a final rule that imposes on insured depository institutions with at least $10 billion in assets, which includes The Bank
BNY Mellon 83
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon, N.A., an annual surcharge of 4.5 basis points until the DIF reaches the required ratio of 1.35, which the FDIC estimates would take approximately two years. Surcharges commenced in the second half of 2016.
Source of Strength and Liability of Commonly Controlled Depository Institutions
Federal Reserve policy historically has required BHCs to act as a source of strength to their bank subsidiaries and to commit capital and financial resources to support those subsidiaries. The Dodd-Frank Act codified this policy as a statutory requirement. Such support may be required by the Federal Reserve at times when we might otherwise determine not to provide it. In addition, any loans by BNY Mellon to its bank subsidiaries would be subordinate in right of payment to depositors and to certain other indebtedness of its banks. In the event of a BHC’s bankruptcy, any commitment by the BHC to a federal bank regulator to maintain the capital of a subsidiary bank will be assumed by the bankruptcy trustee and entitled to a priority of payment. In addition, in certain circumstances, BNY Mellon’s insured depository institution subsidiaries could be held liable for losses incurred by another BNY Mellon insured depository institution subsidiary. In the event of impairment of the capital stock of one of BNY Mellon’s national bank subsidiaries or The Bank of New York Mellon, BNY Mellon, as the banks’ stockholder, could be required to pay such deficiency.
Incentive Compensation Arrangements Proposal
Section 956 of the Dodd-Frank Act requires federal regulators to prescribe regulations or guidelines regarding incentive-based compensation practices at certain financial institutions, including BNY Mellon. In April 2016, a joint proposed rule was released, replacing a previous 2011 proposal, which each of six agencies must separately approve.
The general qualitative requirements applicable to “covered institutions” with consolidated assets of at least $1 billion, including BNY Mellon, include (1) prohibiting incentive-based compensation arrangements that are determined to encourage inappropriate risks, (2) prohibiting incentive arrangements that encourage inappropriate risks that could lead to a material financial loss, (3) establishing requirements for performance measures to
appropriately balance risk and reward, (4) requiring board of director oversight of incentive arrangements and (5) mandating appropriate recordkeeping. The proposal contemplates additional requirements for covered institutions with consolidated assets of at least $250 billion, such as BNY Mellon, including that incentive arrangements will have certain deferral, downward adjustments and forfeiture requirements and clawback provisions.
Anti-Money Laundering and the USA Patriot Act
A major focus of governmental policy on financial institutions has been aimed at combating money laundering and terrorist financing. The USA PATRIOT Act of 2001 contains numerous anti-money laundering requirements for financial institutions that are applicable to BNY Mellon’s bank, broker-dealer and investment adviser subsidiaries and mutual funds and private investment companies advised or sponsored by our subsidiaries. Those regulations impose obligations on financial institutions to maintain appropriate policies, procedures and controls to detect, prevent and report money laundering and terrorist financing and to verify the identity of their customers. Certain of those regulations impose specific due diligence requirements on financial institutions that maintain correspondent or private banking relationships with non-U.S. financial institutions or persons.
New York State Department of Financial Services (“NYSDFS”) anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism regulations
In December 2015, the NYSDFS proposed regulations requiring regulated institutions, including The Bank of New York Mellon, to maintain a transaction monitoring program to monitor transactions for potential Bank Secrecy Act (“BSA”)/anti-money laundering (“AML”) violations and suspicious activity reporting, and a watch list filtering program to interdict transactions prohibited by applicable sanctions programs.
On June 30, 2016, the NYSDFS finalized its regulations. The final regulations require a regulated institution to maintain programs to monitor and filter transactions for potential BSA and AML violations and prevent transactions with sanctioned entities. The final regulation requires regulated institutions annually to submit a board resolution or senior officer compliance finding confirming steps taken to
84 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
ascertain compliance with the regulation. The final regulation is effective Jan. 1, 2017, and the annual certification requirement begins April 15, 2018.
Privacy
The privacy provisions of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act generally prohibit financial institutions, including BNY Mellon, from disclosing nonpublic personal financial information of consumer customers to third parties for certain purposes (primarily marketing) unless customers have the opportunity to “opt out” of the disclosure. The Fair Credit Reporting Act restricts information sharing among affiliates for marketing purposes.
In the EU, privacy law is currently regulated under the Data Protection Directive (“DPD”), implemented as a minimum standard into the domestic law of each EU member state. The DPD will be replaced in the EU by the General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”), which will take effect in May 2018. The GDPR contains enhanced compliance obligations and increased penalties for non-compliance compared to the DPD.
Acquisitions/Transactions
Federal and state laws impose notice and approval requirements for mergers and acquisitions involving depository institutions or BHCs. The BHC Act requires the prior approval of the Federal Reserve for the direct or indirect acquisition by a BHC of more than 5% of any class of the voting shares or all or substantially all of the assets of a commercial bank, savings and loan association or BHC. In reviewing bank acquisition and merger applications, the bank regulatory authorities will consider, among other things, the competitive effect of the transaction, financial and managerial resources including the capital position of the combined organization, convenience and needs of the community factors, including the applicant’s record under the Community Reinvestment Act of 1977 (the “CRA”), the effectiveness of the subject organizations in combating money laundering activities and the risk to the stability of the U.S. banking or financial system. In addition, prior Federal Reserve approval would be required for certain large nonbanking acquisitions and investments.
Regulated Entities of BNY Mellon and Ancillary Regulatory Requirements
BNY Mellon is registered as an FHC under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended by the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and by the Dodd-Frank Act (the “BHC Act”). We are subject to supervision by the Federal Reserve. In general, the BHC Act limits an FHC’s business activities to banking, managing or controlling banks, performing certain servicing activities for subsidiaries, engaging in activities incidental to banking, and engaging in any activity, or acquiring and retaining the shares of any company engaged in any activity, that is either financial in nature or complementary to a financial activity and does not pose a substantial risk to the safety and soundness of depository institutions or the financial system generally.
A BHC’s ability to maintain FHC status is dependent on: (i) its U.S. depository institution subsidiaries qualifying on an ongoing basis as “well capitalized” and “well managed” under the prompt corrective regulations of the appropriate regulatory agency (discussed above under “Prompt Corrective Action”); (ii) the BHC itself, qualifying on an ongoing basis as “well capitalized” and “well managed” under applicable Federal Reserve regulations; and (iii) its U.S. depository institution subsidiaries continuing to maintain at least a “satisfactory” rating under the CRA.
An FHC that does not continue to meet all the requirements for FHC status will, depending on which requirements it fails to meet, lose the ability to undertake new activities, or make acquisitions, that are not generally permissible for BHCs without FHC status or to continue such activities. As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries were “well capitalized” based on the ratios and rules applicable to them.
The Bank of New York Mellon, which is BNY Mellon’s largest banking subsidiary, is a New York state-chartered bank, and a member of the Federal Reserve System and is subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the Federal Reserve, the FDIC and the NYSDFS. BNY Mellon’s national bank subsidiaries, BNY Mellon, N.A. and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, National Association, are chartered as national banking associations subject to primary regulation, supervision and examination by the OCC.
BNY Mellon 85
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
We operate a number of broker-dealers that engage in securities underwriting and other broker-dealer activities in the United States. These companies are SEC-registered broker-dealers and members of Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. (“FINRA”), a securities industry self-regulatory organization. BNY Mellon’s nonbank subsidiaries engaged in securities-related activities are regulated by supervisory agencies in the countries in which they conduct business.
Certain of BNY Mellon’s public finance and advisory activities are regulated by the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board and are required under the SEC’s Municipal Advisors Rule to register with the SEC if they provide advice to municipal entities or certain other persons on the issuance of municipal securities, or about certain investment strategies or municipal derivatives.
Certain of BNY Mellon’s subsidiaries are registered with the CFTC as commodity pool operators and/or commodity trading advisors and, as such, are subject to CFTC regulation. The Bank of New York Mellon is provisionally registered as a Swap Dealer (as defined in the Dodd-Frank Act) with the CFTC, and is a member of the National Futures Association (“NFA”) in that same capacity. As a Swap Dealer, The Bank of New York Mellon is subject to regulation, supervision and examination by the CFTC and NFA.
Certain of our subsidiaries are registered investment advisors under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, and as such are supervised by the SEC. They are also subject to various U.S. federal and state laws and regulations and to the laws and regulations of any countries in which they conduct business. Our subsidiaries advise both public investment companies which are registered with the SEC under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the “‘40 Act”), including the Dreyfus family of mutual funds, and private investment companies which are not registered under the ‘40 Act.
Certain of our investment management, trust and custody operations provide services to employee benefit plans that are subject to the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended (“ERISA”), administered by the U.S. Department of Labor (“DOL”). ERISA imposes certain statutory duties, liabilities, disclosure obligations, and
restrictions on fiduciaries, as applicable, related to the services being performed and fees being paid.
Department of Labor Fiduciary Rule
The U.S. Department of Labor has issued a final rule that, among other things, expands the definition of who is designated a “fiduciary” of an employee benefit plan or individual retirement account (“IRA”) under ERISA and the Internal Revenue Code, respectively. The final rule was originally scheduled to be phased in beginning in April 2017 and fully phased in by Jan. 1, 2018. However, on Feb. 3, 2017, President Trump issued a memorandum directing the acting Secretary of Labor to examine the rule. In response, the Department of Labor issued a press statement indicating that they will consider legal options to delay the applicability date.
In the event the rule becomes applicable under its current terms, if an entity or individual is designated an ERISA fiduciary, the entity or individual will be subject to various duties, liabilities, disclosure obligations, and restrictions related to the services it performs for ERISA plans and IRAs, as well as the compensation or other benefits the fiduciary receives in connection with those services. Certain BNY Mellon businesses interface and transact with clients and external business partners that will need to modify their practices in order to comply with the rule, which could adversely affect the financial results of such BNY Mellon businesses. BNY Mellon believes it will be able to conform its business practices to address changes required by the rule.
Operations and Regulations Outside the United States
In Europe, branches of The Bank of New York Mellon are subject to regulation in the countries in which they are established, in addition to being subject to oversight by the U.S. regulators referred to above. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV is a public limited liability company incorporated under the laws of Belgium. The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV, has been granted a banking license by the National Bank of Belgium (“NBB”) and is authorized to carry out all banking and savings activities as a credit institution. The European Central Bank (“ECB”) has responsibility for the supervision of 120 significant banks and banking groups in the euro area, including The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV. The ECB’s supervision is carried out in conjunction
86 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
with the relevant national prudential regulator (NBB in The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV’s case). The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV conducts its activities in Belgium as well as through branch offices in the United Kingdom, Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, France and Germany.
Certain of our financial services operations in the UK are subject to regulation and supervision by the FCA and PRA. The PRA is responsible for the authorization and prudential regulation of firms that carry on PRA-regulated activities, including banks. PRA-authorized firms are also subject to regulation by the FCA for conduct purposes. In contrast, FCA-authorized firms (such as investment management firms) have the FCA as their sole regulator for both prudential and conduct purposes although subject to the residual overarching jurisdiction of the PRA, if matters of systemic significance are in issue. As a result, FCA-authorized firms must comply with FCA prudential and conduct rules and the FCA’s Principles for Businesses, while dual-regulated firms must comply with the FCA conduct rules and FCA Principles, as well as the applicable PRA prudential rules and the PRA’s Principles for Businesses.
The PRA regulates The Bank of New York Mellon (International) Limited, our UK incorporated bank, as well as the UK branch of The Bank of New York Mellon and, to a more limited extent, The Bank of New York Mellon SA/NV. Certain of BNY Mellon’s UK incorporated subsidiaries are authorized to conduct investment business in the UK. Their investment management advisory activities and their sale and marketing of retail investment products are regulated by the FCA. Certain UK investment funds, including BNY Mellon Investment Funds, are registered with the FCA and are offered for retail sale in the UK.
Since the financial crisis, the European Union and its Member States have engaged in a significant overhaul of bank regulation and supervision. To increase the resilience of banks and to reduce the impact of potential bank failures, new rules on capital requirements for banks and bank recovery and resolution have been adopted. The European Union’s Banking Union has been launched. Further measures are under way, including providing for a structural separation of the risks associated with certain banks’ trading activities from their deposit-taking function.
Aspects of the Banking Union have entered into force in most EU jurisdictions. The UK is not participating in the Banking Union. The key components of the Banking Union include a single resolution mechanism (“SRM”) and a single supervisory mechanism (“SSM”). The SRM approach endorses the bail-in rules established in the BRRD and is described in more detail above in the section addressing Recovery and Resolution.
In addition, the Capital Requirements Directive IV (“CRD IV”) and Capital Requirements Regulation (“CRR”) affect BNY Mellon’s EU subsidiaries by implementing Basel III and other changes, including the enhancement of the quality of capital, and the strengthening of capital requirements for counterparty credit risk, resulting in higher capital requirements. In the EU Member States, CRD IV/CRR also introduces substantive parts of the new European supervisory architecture, including the development of a single set of harmonized prudential rules for financial services. This set of rules would replace existing separately implemented rules within EU Member States, with a harmonized approach to implementation across the EU. Elements of CRD IV/CRR apply not only to BNY Mellon banking branches and subsidiaries but also to investment management and brokerage entities. CRD IV/CRR became effective on Jan. 1, 2014, with certain provisions to be phased in from 2014 to 2019.
Our Investment Management and Investment Services businesses are subject to significant regulation in numerous jurisdictions around the world relating to, among other things, the safeguarding, administration and management of client assets and client funds.
Various new, revised and/or proposed European Union directives and regulations have an impact on our provision of many of our products and services, including the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II and Markets in Financial Instruments Regulations (collectively, “MiFID II”), the Alternative Investment Fund Managers Directive (“AIFMD”), the Directive on Undertakings for Collective Investments in Transferable Securities (“UCITS V”), the Central Securities Depositories Regulation (“CSDR”), the regulation on OTC derivatives, central counterparties and trade repositories (commonly known as “EMIR”), the Securities Financing Transactions Regulation (“SFTR”) and the Payment Services Directive
BNY Mellon 87
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
(“PSD”). These European Union directives and regulations may impact our operations and risk profile but may also provide new opportunities for the provision of BNY Mellon products and services. Several of these European directives and regulations are still subject to finalization by the legislature and/or substantial secondary legislation. This creates uncertainty as to business impact.
The types of activities in which the foreign branches of our banking subsidiaries and our international subsidiaries may engage are subject to various restrictions imposed by the Federal Reserve. Those foreign branches and international subsidiaries are also subject to the laws and regulatory authorities of the countries in which they operate and, in the case of banking subsidiaries, may be subject to regulatory capital requirements in the jurisdictions in which they operate.
EU Banking Reform Package
In November 2016, the European Commission published the so-called EU Banking Reform Package. This legislative package would amend CRD IV, CRR, BRRD and the Single Resolution Mechanism Regulation (“SRMR”).
The proposed amendments to CRD IV include a proposal for non-EU G-SIBs (such as BNY Mellon) and certain other non-EU banking groups to have an “intermediate EU parent undertaking”. All EU credit institutions and EU investment firms in such non-EU G-SIBs/banking groups would need to fall within a corporate structure headed by the “intermediate EU parent undertaking”. If this proposal is implemented in its current form, BNY Mellon would need to undertake significant changes in its corporate structure. Furthermore the “intermediate EU parent undertaking” proposal may result in conflict with existing U.S. banking regulations. BNY Mellon is evaluating the impact of the “intermediate EU parent undertaking” proposal. The proposed amendments to CRD IV also include provisions relating to interest rate risk in the banking book.
The proposed amendments to CRR include provisions relating to the leverage ratio, NSFR, MREL (including closer alignment to the final FSB TLAC standard), fundamental review of the trading book, counterparty credit risk, exposures to CCPs, exposures to collective investment undertakings,
large exposures, and reporting/disclosure requirements.
The timeframe in which the EU Banking Reform Package may enter into force is dependent upon the EU legislative process, and is therefore unclear at this stage. BNY Mellon is closely monitoring developments.
European Central Bank SSM and Comprehensive Assessments
The Council of the European Union created an SSM to oversee banks and other credit institutions. The SSM is composed of the ECB and the supervisory authorities of the member states. It covers the prudential supervision of all major banks in the 19 euro area countries as well as any non-euro area countries that choose to participate through close cooperation agreements.
European Resolution Legislation and Structural Reform Proposals
Deposit Guarantee Scheme Directive. Under the recast Deposit Guarantee Scheme Directive, the scope of deposit protection in the EU was extended to cover most corporate entities. The extension of deposit protection to most corporate entities will require certain BNY Mellon entities to contribute to relevant deposit protection schemes. The contributions and required systems enhancements may constitute a meaningful cost for those BNY Mellon entities.
The European Commission has proposed a European Deposit Insurance Scheme (“EDIS”) for euro area member states. Under the EDIS proposal, existing euro area deposit guarantee schemes would transition over a number of years to a mutualized deposit guarantee scheme applicable in the Eurozone.
Structural Reform. In addition, European and Member State regulators (for example, the PRA in the UK) continue to develop proposals in regard to bank structural reform. The details of the European Union Bank Structural Reform proposal continue to be developed, and at this stage the final outcome of such proposal is not certain. Bank structural reform proposals, if implemented, may require BNY Mellon to review its existing corporate structure, and may impact the business activities that BNY Mellon subsidiaries and branches can undertake. It is not
88 BNY Mellon
Supervision and Regulation (continued) |
clear whether bank structural reforms in the European Union will operate on the basis of changes to corporate structure or prohibitions on certain forms of trading (including proprietary trading), or a combination of these approaches. The proposal on structural reform of European Union banks is intended to apply only to the largest and most complex European Union banks with significant trading activities.
Transactions with the Shadow Banking Sector
In December 2015, the EBA finalized its guidance on large exposure limits of credit institutions to shadow banking entities. The guidelines imposed a large exposure limit to the shadow banking sector as a whole. The EBA has used a broad definition of the shadow banking sector (for example, money market funds are in scope). EU member states implemented the guidelines into their domestic rules by January 2017.
In January 2016, the European Commission finalized measures, entitled Securities Financing Transactions Regulation, aimed at increasing the transparency of certain transactions in the “shadow banking” sector, including providing for enhanced transparency and reporting of SFTs.
European Financial Markets and Market Infrastructure
The EU continues to develop proposals and regulations in relation to financial markets and market infrastructures. The MiFID II, Markets in Financial Instruments Regulation (“MiFIR”) and European Market Infrastructure Regulation (“EMIR”) are at the detailed rule-making stage, and involve a significant volume of change to be implemented in
relatively short timeframes. MiFID II/MiFIR/EMIR may create new business opportunities in European markets, but will also require existing business activities and processes to be reviewed. The volume of change required may result in some implementation/execution risk.
A key policy objective of the 2014-19 European Commission is to develop a Capital Markets Union (“CMU”) in the EU. In September 2015, the European Commission published its CMU Action Plan, which set out a range of initiatives that the Commission intends to undertake between 2015 and 2019. This plan was updated in September 2016, and the European Commission will conduct a mid-term review of CMU during 2017. Some examples of CMU-related initiatives include a review of the EU regulatory framework for financial services, a review of the macroprudential framework, a new Prospectus Regulation, a new Securitization Regulation, and a project to address national barriers to free movement of capital and cross-border funds distribution.
Investment Services in Europe
The AIFMD has a direct effect on our alternative fund manager clients and our depository business and other products offered across Europe. AIFMD imposes heightened obligations upon depositories, which have both operational and, potentially, capital effects. The European Securities and Markets Authority is expected to publish guidelines on asset segregation under AIFMD in 2017.
Our businesses servicing regulated funds in Europe are also affected by the revised directive governing undertakings for collective investment in transferable securities, known as UCITS V.
BNY Mellon 89
Risk Factors |
Making or continuing an investment in securities issued by us involves certain risks that you should carefully consider. The following discussion sets forth the most significant risk factors that could affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. Some of these risks are interrelated and the occurrence of one may exacerbate the effect of others. However, other factors, other than those discussed below or in other of our reports filed with or furnished to the SEC, also could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations. We cannot assure you that the risk factors described below or elsewhere in our reports address all potential risks that we may face. These risk factors also serve to describe factors which may cause our results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements included herein or in other documents or statements that make reference to this Annual Report. See “Forward-looking Statements.”
Operational Risk
An information security event or technology disruption that results in a loss of information or impacts our ability to provide services to our clients may materially adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We use communications and information systems to conduct our business. Our businesses rely heavily on technology, and are vulnerable to attacks and technology disruptions which are occurring globally with greater frequency. Our information systems are subjected to cyber threats, including hacker attacks, computer viruses or other malicious software, denial of service efforts, limited unavailability of service, phishing attacks and unauthorized access attempts. While we deploy a broad range of sophisticated defenses, it is possible we could suffer a material impact or disruption. The security of our computer systems, software and networks, and those functions that we may outsource, may continue to be subjected to cyber threats that could result in failures or disruptions in our business. In addition, as our business areas evolve due to the introduction of technology, new service offering requirements for our clients and customers, or changes in regulation relative to these service offerings, the business processes that this technology supports could introduce unforeseen risks that could materially impact business operations.
Despite our efforts to ensure the integrity of our systems and information, it is possible that we may not be able to anticipate or to implement effective preventive measures against all cyber threats, or detect all such threats, especially because the techniques used change frequently or are not recognized until after they are launched, and because attacks can originate from a wide variety of sources, including outside third parties such as persons who are involved with organized crime or who may be linked to terrorist organizations or hostile foreign governments. Those parties may also attempt to place individuals within BNY Mellon or fraudulently induce employees, vendors, customers or other users of our systems to disclose sensitive information in order to gain access to our data or that of our customers or clients.
Security events may occur through intentional or unintentional acts by individuals or groups having authorized or unauthorized access to our systems or our clients’ or counterparties’ information, which may include confidential information. These individuals or groups include employees, vendors and customers, as well as hackers. An event that results in the loss of information may require us to reconstruct lost data, reimburse clients for data and credit monitoring services, result in loss of customer business, or damage to our computers or systems and those of our customers and counterparties. These impacts could be costly and time-consuming and materially negatively impact our business operations, financial condition and reputation.
Additionally, security events or disruptions of our information systems, or those of our service providers or industry utilities, could impact our ability to provide services to our clients, which could expose us to liability for damages, result in the loss of business, damage our reputation, subject us to regulatory scrutiny or sanctions or expose us to litigation, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Upgrading our computer systems, software and networks may also subject us to disruptions or security events due to the complexity and interconnectedness of our systems, software and networks. The failure to upgrade or maintain these computer systems, software and networks could also make us vulnerable to attack and unauthorized access and misuse. There can be no assurance that any such failures, interruptions or security events will not occur or, if they do occur, that they will be adequately
90 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
addressed. We may be required to expend significant additional resources to modify, investigate or remediate vulnerabilities or other exposures arising from information systems’ security risks. Information security events related to us or other large financial institutions, service providers or industry utilities could disrupt the overall functioning of the financial system.
As a result of the importance of communications and information systems to our business, we could also be adversely affected if attacks affecting the third-party providers of our technology, communications or other services impair our ability to process transactions and communicate with customers and counterparties. For a discussion of operational risk, see “Risk Management – Operational risk” and “Business Continuity.”
If our technology or that of a third party or vendor fails, or isn’t sufficiently updated, or if we fail to develop and market new technology to meet our clients’ needs, or protect our intellectual property, our business may be materially adversely affected.
Our businesses are highly dependent on our ability to process large volumes of data requiring global capabilities and scale from our technology platforms. If our technology, or that of a third party, fails we could experience, and have in the past experienced, production and system outages or failures. Any such outage or failure could, among other things, adversely affect our ability to effect transactions or service our clients, which could expose us to liability for damages, result in the loss of business, damage our reputation, subject us to regulatory scrutiny or sanctions or expose us to litigation, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
As our businesses evolve, the technology used becomes increasingly complex and relies on the continued effectiveness of the programming code and integrity of the data that is inputted. These rapid technological changes, together with competitive pressures, require us to make significant and ongoing investments in technology to develop competitive new products and services or adopt new technologies. Our financial performance depends in part on our ability to develop and market these new products and services in a timely manner at a competitive price and adopt or develop new technologies that differentiate our products or
provide cost efficiencies. The unsuccessful implementation of technological upgrades and new products and services may adversely impact our ability to service and retain customers. The costs we incur in enhancing our technology could be substantial and may not ultimately improve our competitiveness or profitability. We maintain controls designed to reduce the risk of the unsuccessful implementation of our models, systems or processes, but such risk cannot be completely eliminated.
As a result of financial entities and technology systems across the globe becoming more interdependent and complex, a technology failure that significantly degrades, deletes or compromises the systems or data of one or more financial entities or suppliers could have a material impact on counterparties or other market participants, including us. Any such failure could, among other things, adversely affect our ability to effect transactions, service our clients, manage our exposure to risk or expand our businesses. While we continue to improve and invest in the resiliency of our technology systems, there can be no guarantee that a technology outage will not occur.
Third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities, including exchanges, clearing houses, financial intermediaries or vendors that provide services or security solutions for our operations, could also be sources of technology risk to us, including from breakdowns or failures of their own systems or capacity constraints.
The failure to maintain an adequate technology infrastructure with effective cybersecurity controls relative to the type, size and complexity of operations, markets and products traded, access to trading venues and our market interconnectedness could impact operations and impede our productivity and growth, which could cause our earnings to decline or could impact our ability to comply with regulatory obligations leading to regulatory fines and sanctions. In addition, the failure to ensure adequate review and consideration of critical business changes prior to and during introduction and deployment of key technological systems or failure to adequately align evolving client commitments and expectations with operational capabilities could have a negative impact on our operations.
BNY Mellon 91
Risk Factors (continued) |
We rely on a variety of measures to protect our intellectual property and proprietary information, including copyrights, trademarks, patents and controls on access and distribution. These measures may not prevent misappropriation or infringement of our intellectual property or proprietary information and a resulting loss of competitive advantage.
Furthermore, if a third party were to assert a claim of infringement or misappropriation of its proprietary rights, obtained through patents or otherwise, against us, we could be required to spend significant amounts to defend such claims, develop alternative methods of operations, pay substantial money damages, obtain a license from the third party or possibly stop providing one or more products or services.
If our resolution plan is determined not to be credible or not to facilitate an orderly resolution under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, our business, reputation, results of operation and financial condition could be materially negatively impacted. The application of our Title I preferred resolution strategy or resolution under the Title II orderly liquidation authority could adversely affect our liquidity and financial condition and our security holders.
Large BHCs must develop and submit to the Federal Reserve and the FDIC for review plans for their rapid and orderly resolution in the event of material financial distress or failure. BNY Mellon and The Bank of New York Mellon each file periodic complementary resolution plans. In April 2016, the Federal Reserve and the FDIC jointly determined that our 2015 resolution plan was not credible or would not facilitate an orderly resolution under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. The agencies issued a joint notice of deficiencies and shortcomings and the actions that must be taken to address them, which we responded to in an Oct. 1, 2016 submission. In December 2016, the agencies jointly determined that our Oct. 1, 2016 submission adequately remedied the identified deficiencies. If the agencies determine that our future submissions are not credible or would not facilitate an orderly resolution under the U.S. Bankruptcy Code, and we fail to address the deficiencies in a timely manner, the agencies may jointly impose more stringent capital, leverage or liquidity requirements or restrictions on our growth, activities or operations. If we continue to fail to adequately remedy any deficiencies identified in future submissions, we could be required to divest assets or operations that
the agencies determine necessary to facilitate our orderly resolution.
Following the receipt of feedback from the Federal Reserve and the FDIC in April 2016 on our 2015 resolution plan, we determined that, in the event of our material financial distress or failure, our preferred resolution strategy under Title I of the Dodd-Frank Act is a single point of entry strategy.
As part of the advance planning to effectuate our single point of entry strategy should it ever be necessary, we intend to pre-position capital and liquidity resources currently held at the Parent with an intermediate holding company (an “IHC”), which resources could be used to recapitalize and/or provide liquidity support to certain bank and non-bank material entities in the event of our material financial distress or failure. The IHC would sit at the top-tier subsidiary level beneath the Parent and hold the equity interests in various non-bank entities. We also intend to execute a support agreement with the IHC and certain other BNY Mellon entities, which will provide a contractual basis for the provision of such resources to such bank and non-bank material entities to keep them solvent, liquid, and sufficiently capitalized, as appropriate, in connection with our single point of entry strategy.
If the Parent were to become subject to a bankruptcy proceeding and our single point of entry strategy is successful, creditors of some or all of our material entities would receive full recoveries on their claims, while Parent’s security holders, including unsecured debt holders, could face significant losses, potentially including the loss of their entire investment. It is possible that the application of the single point of entry strategy – in which the Parent would be the only legal entity to enter resolution proceedings – could result in greater losses to holders of our unsecured debt securities than the losses that could result from the application of a different resolution strategy. Further, if the single point of entry strategy is not successful, our liquidity and financial condition would be adversely affected and our security holders may, as a consequence, be in a worse position than if the strategy had not been implemented.
In addition, Title II of the Dodd-Frank Act established an orderly liquidation process in the event of the failure of a large systemically important financial institution, such as BNY Mellon, in order to avoid or mitigate serious adverse effects on the U.S. financial
92 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
system. Specifically, when a U.S. G-SIB, such as BNY Mellon is in default or danger of default, and certain specified conditions are met, the FDIC may be appointed receiver under the orderly liquidation authority instead of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code.
U.S. supervisors have indicated that a single point of entry strategy may be a desirable strategy to resolve a large financial institution such as BNY Mellon under Title II in a manner that would, similar to our preferred strategy under our Title I resolution plan, impose losses on shareholders, unsecured debt holders and other unsecured creditors of the top-tier holding company (in our case, the Parent), while permitting the holding company’s subsidiaries to continue to operate and remain solvent. Under such a strategy, assuming the Parent entered resolution proceedings and its subsidiaries remained solvent, losses at the subsidiary level could be transferred to the Parent and ultimately borne by the Parent’s security holders (including holders of the Parent’s unsecured debt securities), while third-party creditors of the Parent’s subsidiaries would receive full recoveries on their claims. Accordingly, the Parent’s security holders (including unsecured debt securities and other unsecured creditors) could face losses in excess of what otherwise would have been the case.
We are subject to extensive government rulemaking, regulation and supervision. These rules and regulations have, and in the future may, compel us to change how we manage our businesses, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, these rules and regulations have increased our compliance and operational risk and costs.
We operate in a highly regulated environment, and are subject to a comprehensive statutory and regulatory regime, including oversight by governmental agencies both inside and outside the U.S. Since the 2008 financial crisis, domestic and international policy makers and regulators have substantially increased their focus on the financial services industry. New or modified regulations and related regulatory guidance and supervisory oversight are significantly altering the regulatory framework in which we operate and have affected how we analyze certain business opportunities, increased our regulatory capital and liquidity requirements, altered the revenue profile of certain of our core activities and imposed additional costs
on us. In addition, the changes to the regulatory frameworks and environment in which we operate could otherwise materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and have other negative consequences. Uncertainty about the timing and scope of current and future regulations, as well as the cost of complying with any new regulatory regimes, could have a negative effect on our businesses. The regulatory and supervisory focus of U.S. banking agencies is primarily intended to protect the safety and soundness of the banking system and federally insured deposits, and not to protect investors in our securities. Moreover, the regulatory and supervisory standards and expectations in one jurisdiction may not conform with standards or expectations in other jurisdictions. Even within a particular jurisdiction, the standards and expectations of multiple supervisory agencies exercising authority over our affairs may not be fully harmonized. Additionally, banking regulators have wide supervisory discretion in the ongoing examination and enforcement of applicable banking statutes, regulations, and guidelines, and may restrict our ability to engage in certain activities or acquisitions, or may require us to maintain more capital or highly liquid assets.
In common with their U.S. counterparts, European policy makers and regulators have also increased their focus on financial services providers, and our European operations are directly affected and will continue to be affected by changes to the regulatory environment.
The Dodd-Frank Act has had, and will likely continue to have, a significant impact on the regulatory structure of the global financial markets and has imposed, and is expected to continue to impose, significant additional costs on us. While U.S. regulators have finalized many regulations to implement various provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act, additional regulations or modifications to existing regulations, may occur. In addition, there is uncertainty about the timing and scope of any changes to the Dodd-Frank Act and the regulations adopted since the financial crisis, as well as the cost of complying with any new regulatory regimes. In light of this uncertainty, as well as the discretion afforded to federal regulators, the full impact of this legislation on us, our business strategies and financial performance is not known at this time, may not be known for a number of years and could materially adversely impact us. The related findings
BNY Mellon 93
Risk Factors (continued) |
of various regulatory and commission studies, the interpretations issued as part of the rulemaking process and the final regulations that are issued with respect to various elements of the Dodd-Frank Act may cause changes that impact the profitability of our business activities and require that we change certain of our business practices and plans. These changes will continue to expose us to additional regulatory costs and require us to invest significant management attention and resources to make any necessary changes, all of which could impact our profitability.
Several provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act, such as the Volcker Rule, resolution planning requirements, and enhanced prudential standards for financial institutions designated as SIFIs, impose or are expected to impose significant additional operational, compliance and risk management costs both in the near-term, as we develop and integrate appropriate systems and procedures, and on a recurring basis thereafter, as we monitor, support and refine those systems and procedures.
The U.S. capital rules subject us and our U.S. banking subsidiaries to more stringent capital requirements, which could restrict growth, activities or operations, trigger divestiture of assets or operations or limit our ability to return capital to shareholders. We must also separately obtain final approval from the agencies for the use of certain models used to calculate risk-weighted assets under the Advanced Approach. As discussed in additional detail in “Supervision and Regulation,” the U.S. G-SIB capital surcharge began to be phased in on Jan. 1, 2016 and will become fully effective on Jan. 1, 2019. For 2017, the G-SIB surcharge applicable to BNY Mellon is 1.5%, subject to applicable phase-ins. Failure to meet current or future capital requirements could materially adversely affect our financial condition. Additional impacts relating to compliance with these rules could include, but are not limited to, potential dilution of existing shareholders and competitive disadvantage compared to financial institutions not under the same regulatory framework. In addition, the SLR subjects us to a more stringent leverage requirement, which could restrict growth, activities, operations or could result in certain restrictions on capital distributions and discretionary bonus payments.
The LCR requires us to increase our holdings of high quality and potentially lower-yielding liquid assets.
In calculating the LCR, we must also determine which deposits should be considered to be stable deposits for purposes of the Final LCR Rule. Stable deposits must meet a series of requirements and typically receive favorable outflow treatment under the LCR. BNY Mellon uses qualitative and quantitative analysis to identify core stable deposits. It is possible that our LCR could fall below 100% as a consequence of the inherent uncertainties associated with this analysis (including as a result of additional guidance from our regulators). In addition to facing potential regulatory consequences (which could be significant), we may be required to remedy this shortfall by liquidating assets in our investment portfolio or raising additional debt, each of which could materially negatively impact our net interest revenue.
When the final rule regarding the NSFR is ultimately implemented in the U.S., those requirements could also require BNY Mellon to further increase its holdings of high quality, and potentially lower-yielding, liquid assets, and to reevaluate the composition of its liabilities structure to include more longer-dated debt.
Our businesses are also subject to significant regulation in numerous jurisdictions around the world relating to, among other things, the safeguarding, administration and management of client assets and client funds.
Various new, revised and proposed European Union directives and regulations have an impact on our provision of many of our products and services. Implementation of these European Union directives and regulations has affected our operations and risk profile, including the Capital Requirements Directive/Regulation, the Bank Recovery and Resolution Directive, the Deposit Guarantee Scheme Directive, the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II/Regulation, the Alternative Investment Fund Managers Directive, the Directive on Undertakings for Collective Investments in Transferable Securities and the Payment Services Directive.
Changes in regulatory requirements can significantly affect the products and services that we provide to clients (including by way of client-initiated requests for changes to products and services, in addition to changes we initiate). Accordingly, changes to products and services as a result of regulatory change
94 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
may impact our own costs on a one-off or ongoing basis.
The evolving regulatory environment, including changes to existing regulations and the introduction of new regulations, may contribute to decisions we may make to suspend, reduce or withdraw from existing businesses, activities or initiatives, which may result in potential lost revenue or significant restructuring or related costs or exposures.
Failure to comply with laws, regulations or policies applicable to our business could result in sanctions by regulatory or governmental authorities, civil money penalties and reputational damage, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. If violations do occur, they could damage our reputation, increase our legal and compliance costs, and ultimately adversely impact our results of operations. Laws, regulations or policies currently affecting us and our subsidiaries may change at any time. Regulatory and governmental authorities may also change their interpretation of these statutes and regulations. Therefore, our business may also be adversely affected by future changes in laws, regulations, policies or interpretations or regulatory approaches to compliance and enforcement.
See “Supervision and Regulation” for additional information regarding the potential impact of the regulatory environment on our business.
Failure to satisfy regulatory standards, including “well capitalized” and “well managed” status or capital adequacy and liquidity rules more generally, could result in limitations on our activities and adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Under regulatory capital adequacy rules and other regulatory requirements, BNY Mellon and our subsidiary banks must meet thresholds that include quantitative measures of assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items, subject to qualitative judgments by regulators about components, risk weightings and other factors. As discussed in “Supervision and Regulation,” BNY Mellon is registered with the Federal Reserve as a BHC and an FHC. An FHC’s ability to maintain its status as an FHC is dependent upon a number of factors, including its U.S. bank subsidiaries’ qualifying on an ongoing basis as “well capitalized” and “well
managed” under the banking agencies’ prompt corrective action regulations as well as applicable Federal Reserve regulations. Failure by an FHC or one of its U.S. bank subsidiaries to qualify as “well capitalized” and “well managed”, if unremedied over a period of time, would cause it to lose its status as an FHC and could affect the confidence of clients in it, compromising its competitive position. Additionally, an FHC that does not continue to meet all the requirements for FHC status could lose the ability to undertake new activities or make acquisitions that are not generally permissible for BHCs without FHC status or to continue such activities.
Our U.S. bank subsidiaries are also subject to regulatory capital requirements and the failure by one of our bank subsidiaries to maintain its status as “well capitalized” could lead to, among other things, higher FDIC assessments and could have reputational and associated business consequences. For example, as of Dec. 31, 2015, one of our bank subsidiaries, BNY Mellon, N.A., was not “well capitalized” under U.S. regulatory standards, because its Total capital ratio was 9.89%, which was below the 10% “well capitalized” threshold. Shortly after this issue was discovered, the Parent contributed capital that raised BNY Mellon, N.A.’s Total capital ratio above the well capitalized threshold. While there were no material impacts to either BNY Mellon, N.A. or BNY Mellon arising out of this isolated event, we can provide no assurances that a similar event occurring in the future would not have a material impact. Moreover, the occurrence of a more significant decline in regulatory ratios by BNY Mellon or one of our U.S. bank subsidiaries or failure to maintain status as “adequately capitalized” would lead to regulatory sanctions and limitations and could lead the federal banking agencies to take “prompt corrective action.”
If our company or our subsidiary banks failed to meet the minimum capital rules and other regulatory requirements, we may not be able to deploy capital in the operation of our business or distribute capital to stockholders, which may adversely affect our business. If we are not able to meet the additional, more stringent, capital adequacy standards that were recently promulgated, we may not remain “well capitalized.” See “Supervision and Regulation,” “Liquidity and dividends” and “Capital – Capital adequacy.”
BNY Mellon and its domestic subsidiary banks must maintain an LCR at least equal to 100% beginning in
BNY Mellon 95
Risk Factors (continued) |
2017 to satisfy regulatory minimums. Failure to comply with the LCR requirements may result in supervisory or enforcement actions.
Failure to meet current or future capital or liquidity requirements, including those imposed by the U.S. capital rules, the LCR, or by regulators in implementing other portions of the Basel III framework, could materially adversely affect our financial condition. The current regulatory environment is fluid, with requirements frequently being introduced and amended. See “Supervision and Regulation.” Compliance with regulatory capital and liquidity requirements may impact our ability to return capital to shareholders and may impact our operations by requiring us to liquidate assets, increase borrowings, issue additional equity or other securities, or cease or alter certain operations, which may adversely affect our results of operations.
Although we expect to continue to satisfy our regulatory capital and liquidity requirements, there can be no assurances that we will not need to hold significantly more regulatory capital and liquid assets than we currently estimate in order to satisfy applicable standards. An inability to meet regulatory expectations regarding these matters may also negatively impact the assessment of BNY Mellon and its U.S. banking subsidiaries by U.S. banking regulators and our ability to make capital distributions.
Finally, our estimated regulatory capital ratios, liquidity metrics, and related components are based on our current interpretation, expectations and understanding of the applicable rules and are subject to, among other things, ongoing regulatory review, regulatory approval of certain statistical models, additional refinements, modifications or enhancements (whether required or otherwise) to our models, and further implementation guidance. Any modifications resulting from these ongoing reviews or the continued implementation of the U.S. capital rules, the LCR, the resolution planning process, and related amendments could result in changes in our risk-weighted assets, capital components, liquidity inflows and outflows, HQLA, or other elements involved in the calculation of these measures, which could negatively impact these ratios. Further, because operational risk is currently measured based not only upon our historical operational loss experience but also upon ongoing events in the banking industry generally, our level of operational
risk-weighted assets could significantly increase or otherwise remain elevated for the foreseeable future and may potentially be subject to significant volatility, negatively impacting our capital and liquidity ratios. The uncertainty caused by these factors could ultimately impact our ability to meet our goals, supervisory requirements, and regulatory standards.
Regulatory or enforcement actions or litigation could materially adversely affect our results of operations or harm our businesses or reputation.
Like many major financial institutions, we and our affiliates are the subject of inquiries, investigations, lawsuits and proceedings by counterparties, clients, other third parties and regulatory and other governmental agencies in the U.S. and abroad, as well as the Department of Justice and state attorneys general. See “Legal proceedings” in Note 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of material legal and regulatory proceedings in which we are involved. The number of these investigations and proceedings, as well as the amount of penalties and fines sought, has increased substantially in recent years for many firms in the financial services industry, including us. We may become subject to heightened regulatory scrutiny, inquiries or investigations, and potentially client-related inquiries or claims, relating to broad, industry-wide concerns that could lead to increased expenses or reputational damage. Since the 2008 financial crisis, significant settlements by a number of large financial institutions with governmental entities have been publicly announced. The trend of large settlements with governmental entities may adversely affect the outcomes for other financial institutions in similar actions, especially where governmental officials have announced that the large settlements will be used as the basis or a template for other settlements. Separately, policy makers in the European Union continue to focus on conduct rules around the protection of client assets.
In addition, the DOJ has announced a policy of requiring companies to provide investigators with all relevant facts relating to the individuals responsible for the alleged misconduct in order to qualify for any cooperation credit in civil and criminal investigations of corporate wrongdoing, which may result in our incurring increased fines and penalties if the DOJ determines that we have not provided sufficient information about applicable individuals in
96 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
connection with an investigation, as well as increased costs in responding to DOJ investigations. It is possible that other governmental authorities will adopt similar policies.
The complexity of the federal and state regulatory and enforcement regimes in the U.S., coupled with the global scope of our operations and the increased aggressiveness of the regulatory environment worldwide, also means that a single event may give rise to a large number of overlapping investigations and regulatory proceedings, either by multiple federal and state agencies in the U.S. or by multiple regulators and other governmental entities in different jurisdictions. Responding to inquiries, investigations, lawsuits and proceedings, regardless of the ultimate outcome of the matter, is time-consuming and expensive and can divert the attention of our senior management from our business. The outcome of such proceedings may be difficult to predict or estimate until late in the proceedings, which may last a number of years.
Certain of our subsidiaries are subject to periodic examination, special inquiries and potential proceedings by regulatory authorities. If compliance failures or other violations are found during an examination, inquiry or proceeding, a regulatory agency could initiate actions and impose sanctions for violations, including, for example, regulatory agreements, cease and desist orders, civil monetary penalties or termination of a license and could lead to litigation by investors or clients, any of which could cause our earnings to decline.
Our businesses involve the risk that clients or others may sue us, claiming that we or third parties for whom they say we are responsible have failed to perform under a contract or otherwise failed to carry out a duty perceived to be owed to them, including perceived fiduciary or contractual duties. This risk may be heightened during periods when credit, equity or other financial markets are deteriorating in value or are particularly volatile, or when clients or investors are experiencing losses. As a publicly held company, we are also subject to the risk of claims under the federal securities laws. Volatility in our stock price increases this risk.
Actions brought against us may result in lawsuits, enforcement actions, injunctions, settlements, damages, fines or penalties, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or
results of operations or require changes to our business. Claims for significant monetary damages are asserted in many of these legal actions, while claims for disgorgement, penalties and/or other remedial sanctions may be sought in regulatory matters. Although we establish accruals for our litigation and regulatory matters in accordance with applicable accounting guidance when those matters proceed to a stage where they present loss contingencies that are both probable and reasonably estimable, nonetheless there may be a possible material exposure to loss in excess of any amounts accrued, or in excess of any loss contingencies disclosed as reasonably possible. Such loss contingencies may not be probable and reasonably estimable until the proceedings have progressed significantly, which could take several years and occur close to resolution of the matter.
Each of the risks outlined above could result in increased regulatory supervision and affect our ability to attract and retain customers or maintain access to the capital markets.
Our businesses may be negatively affected by adverse events, publicity, government scrutiny or other reputational harm.
We are subject to reputational, legal and regulatory risk in the ordinary course of our business. The 2008 financial crisis and current political and public sentiment have resulted in a significant amount of adverse media coverage of financial institutions. Harm to our reputation can result from numerous sources, including adverse publicity arising from events occurring at BNY Mellon or in the financial markets, our perceived failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements, the purported actions of our employees, alleged financial reporting irregularities involving ourselves or other large and well-known companies and perceived conflicts of interest. Our reputation could also be harmed by the failure of an affiliate, joint venture or a vendor or other third party with which we do business to comply with laws or regulations. Damage to our reputation could affect the confidence of clients, rating agencies, regulators, employees, stockholders and other stakeholders and could in turn have an impact on our business and results of operations.
Additionally, governmental scrutiny from regulators, legislative bodies and law enforcement agencies with respect to financial services companies has increased
BNY Mellon 97
Risk Factors (continued) |
dramatically. Press coverage and other public statements that assert some form of wrongdoing (including, in some cases, press coverage and public statements that do not directly involve BNY Mellon) often result in some type of investigation or in lawsuits. Certain enforcement authorities have recently required admissions of wrongdoing, and in some cases, criminal pleas, as part of the resolution of matters brought by them against financial institutions. Any such resolution of a matter involving BNY Mellon could lead to increased exposure to civil litigation, could adversely affect our reputation and ability to do business in certain products and in certain jurisdictions and could have other negative effects.
A failure to deliver appropriate standards of service and quality by either us or our vendors, or a failure to appropriately describe our products and services can result in customer dissatisfaction, lost revenue, higher operating costs, heightened regulatory scrutiny and litigation. Should any of these or other events or factors that can undermine our reputation occur, there is no assurance that the additional costs and expenses that we may need to incur to address the issues giving rise to the reputational harm would not adversely affect our earnings and results of operations.
Our business may be materially adversely affected by operational risk.
Given the nature of our businesses, which includes our critical role in the clearance of U.S. government securities, we are required to process large numbers of transactions each day on an accurate and timely basis. The transactions we process or execute are operationally complex and can involve numerous parties, jurisdictions, regulations and systems, and as such, are subject to execution and processing errors and failures. Our ability to conduct our business or service our clients could then be negatively impacted, which could adversely affect our results of operations due to potentially higher expenses and lower revenues, could lower our capital ratios, create liability for us or our clients or negatively impact our reputation. Recurring operational issues may raise concerns among regulators regarding our culture, governance and control environment.
Affiliates or third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities, could also be sources of execution and processing errors and
failures. In certain jurisdictions we may be deemed to be statutorily liable for operational errors, fraud or breakdowns by these affiliates or third parties. Additionally, as a result of recent regulations, including the Alternative Investment Fund Managers Directive and the Undertakings for Collective Investment in Transferable Securities V, where, in the European Economic Area we act as depositary, the Company could be exposed to restitution risk for, among other things, errors or fraud perpetrated by a sub-custodian resulting in a loss or delay in return of client’s securities. Where we are not acting as a European Economic Area depositary, but where we provide custody services to an European Economic Area depositary, we may accept similar liabilities to that depositary as a matter of contract.
In addition, our operational loss risk projections are informed by certain external losses, including certain fines and penalties levied against other institutions in the financial services industry, particularly those that relate to businesses in which we operate, and as a result such external losses could impact the amount of capital that we are required to hold. For a discussion of operational risk see “Risk Management – Operational risk” and “Business Continuity.”
A failure or circumvention of our controls and procedures could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition.
Management regularly reviews and updates our internal controls, disclosure controls and procedures, and corporate governance policies and procedures. Any system of controls, however well designed and operated, is based in part on certain assumptions and can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurances that the objectives of the system will be met. Any failure or circumvention of our controls and procedures or failure to comply with regulations related to controls and procedures could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition. If we identify material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting or are otherwise required to restate our financial statements, we could be required to implement expensive and time-consuming remedial measures and could lose investor confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports. In addition, there are risks that individuals, either employees or contractors, may circumvent established control mechanisms in order to, for
98 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
example, exceed exposure, liquidity, trading or investment management limitations, or commit fraud.
Our risk management framework may not be effective in mitigating risk and reducing the potential for losses.
Our risk management framework seeks to mitigate risk and loss to us. We have established comprehensive policies and procedures and an internal control framework designed to provide a sound operational environment for the types of risk to which we are subject, including operational risk, credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk and strategic risk. We have also established frameworks to mitigate risk and loss to us as a result of the actions of affiliates or third parties with which we do business or that facilitate our business activities. However, as with any risk management framework, there are inherent limitations to our current and future risk management strategies, including risks that we have not appropriately anticipated or identified.
In certain instances, we rely on models to measure, monitor and predict risks. However, these models are inherently limited because they involve techniques, including the use of historical data in some circumstances, and judgments that cannot anticipate every economic and financial outcome in the markets in which we operate, nor can they anticipate the specifics and timing of such outcomes. There is no assurance that these models will appropriately capture all relevant risks or accurately predict future events or exposures. The 2008 financial crisis and resulting regulatory reform highlighted both the importance and some of the limitations of managing unanticipated risks, and our regulators remain focused on ensuring that financial institutions build and maintain robust risk management policies. If our regulators perceive the quality of our risk models and framework to be insufficient, it may negatively impact our regulators’ evaluations of our capital plans and stress tests. Accurate and timely enterprise-wide risk information is necessary to enhance management’s decision-making in times of crisis. If our risk management framework proves ineffective or if our enterprise-wide management information is incomplete or inaccurate, we could suffer unexpected losses, which could materially adversely affect our results of operations or financial condition.
In addition, our businesses and the markets in which we operate are continuously evolving. We may fail to
fully understand the implications of changes in our businesses or the financial markets or fail to adequately or timely enhance our risk framework to address those changes. If our risk framework is ineffective, either because it fails to keep pace with changes in the financial markets, regulatory requirements, our businesses, our counterparties, clients or service providers or for other reasons, we could incur losses, suffer reputational damage or find ourselves out of compliance with applicable regulatory or contractual mandates or expectations.
An important aspect of our risk management framework is creating a risk culture in which all employees fully understand that there is risk in every aspect of our business and the importance of managing risk as it relates to their job functions. We continue to enhance our risk management program to support our risk culture, ensuring that it is sustainable and appropriate to our role as a major financial institution. Nonetheless, if we fail to create the appropriate environment that sensitizes all of our employees to managing risk, our business could be adversely impacted. For more information on how we monitor and manage our risk management framework, see “Risk Management – Risk management overview.”
Change or uncertainty in monetary, tax and other governmental policies may impact our businesses, profitability and ability to compete.
The monetary, tax and other policies of various governments, agencies and regulatory authorities both in the U.S. and globally have a significant impact on interest rates, currencies, commodity pricing (including oil) and overall financial market performance, which can impact our business and results of operations. As a result of the 2008 financial crisis, there have been significant changes in these policies, which have imposed additional compliance, legal, review and response costs that have impacted our profitability. Changes in these policies are beyond our control and can be difficult to predict and we cannot determine the ultimate effect that any such changes would have upon our business, financial condition or results of operations. For example, the Federal Reserve regulates the supply of money and credit in the U.S. and its policies influence our cost of funds for lending, investing and capital raising activities and the return we earn on those loans and investments, all of which affect our net interest margin. Low interest rate policies have resulted in
BNY Mellon 99
Risk Factors (continued) |
waivers of money market fund fees in addition to reductions in our spread-based income and net interest revenue. While the recent rate increase in the Federal Funds effective rate to between 0.50% and 0.75% has significantly reduced the amount of such fee waivers, they have not been eliminated.
The actions of the Federal Reserve also could materially affect the value of financial instruments we hold, activity levels, liquidity and volatility in the financial markets, and impact our borrowers, potentially increasing the risk that they may fail to repay their loans.
We are subject to political, economic, legal, operational and other risks that are inherent in operating globally and which may adversely affect our business.
In conducting our business and maintaining and supporting our global operations, which includes vendors and other third parties, we are subject to risks of loss from the outbreak of hostilities and various unfavorable political, economic, legal or other developments, including social or political instability, changes in governmental policies or policies of central banks, sanctions, expropriation, nationalization, confiscation of assets, price, capital and exchange controls, unfavorable tax rates and tax court rulings and changes in laws and regulations. Our business benefits from active global trade. If the recent political developments in the U.S. and Europe result in new barriers to global business, our global growth may be negatively impacted.
Our international clients accounted for 34% of our revenue in 2016. Our non-U.S. businesses are subject to extensive regulation by various non-U.S. regulators, including governments, securities exchanges, central banks and other regulatory bodies, in the jurisdictions in which those businesses operate. In many countries, the laws and regulations applicable to the financial services industry are uncertain and evolving, and may be applied with extra scrutiny to non-domestic companies, and it may be difficult for us to determine the exact requirements of local laws in every market or manage our relationships with multiple regulators in various jurisdictions. Our inability to remain in compliance with local laws in a particular market and manage our relationships with regulators could have an adverse effect not only on our businesses in that market but also on our reputation generally.
The failure to properly mitigate such risks, or the failure of our operating infrastructure to support such international activities could result in operational failures and regulatory fines or sanctions, which could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
In addition, we are subject in our global operations to rules and regulations relating to corrupt and illegal payments and money laundering, economic sanctions and embargo programs administered by the U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control and similar bodies and governmental agencies worldwide, and laws relating to doing business with certain individuals, groups and countries, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, the USA PATRIOT Act, the Iran Threat Reduction and Syria Human Rights Act of 2012 and the UK Bribery Act. While we have invested and continue to invest significant resources in training and in compliance monitoring, the geographical diversity of our operations, employees, clients and customers, as well as the vendors and other third parties that we deal with, presents the risk that we may be found in violation of such rules, regulations or laws and any such violation could subject us to significant penalties or adversely affect our reputation. In addition, such rules could impact our ability to engage in business with certain individuals, entities, groups and countries, which could materially adversely affect certain of our businesses and results of operations.
Our businesses and operations from time to time enter into new regions. Various emerging and frontier market countries have experienced severe economic and financial disruptions, including significant devaluations of their currencies, defaults or threatened defaults on sovereign debt, capital and currency exchange controls, and low or negative growth rates in their economies. Crime, corruption, war or military actions, and a lack of an established legal and regulatory framework are additional challenges. Revenue from international operations and trading in non-U.S. securities and other obligations may be subject to negative fluctuations as a result. The possible effects of any of these conditions may adversely affect our business and results of operations.
100 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
Acts of terrorism, natural disasters, pandemics and global conflicts may have a negative impact on our business and operations.
Acts of terrorism, natural disasters, pandemics, global conflicts or other similar catastrophic events could have a negative impact on our business and operations. While we have business continuity and disaster recovery plans in place, such events could still damage our facilities, disrupt or delay normal business operations (including communications and technology), result in harm or cause travel limitations on our employees, with a similar impact on our clients, suppliers and counterparties. Catastrophic events could also negatively impact the purchase of our products and services if those events result in reduced capital markets activity, lower asset price levels, or disruptions in general economic activity, or in financial market settlement functions, which could negatively impact our business and results of operation. In addition, war, terror attacks, political unrest, global conflicts, efforts to combat terrorism and other potential military activities and outbreaks of hostilities may lead to an increase in delinquencies, bankruptcies or defaults that could result in our experiencing higher levels of non-performing assets, net charge-offs and provisions for credit losses, negatively impacting our business and operations.
Market Risk
Ongoing concerns about the financial stability of certain countries, the failure or instability of any of our significant global counterparties, new barriers to global trade or a breakup of the EU or Eurozone could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
There remain ongoing concerns about the financial stability of certain countries, including the possibility of sovereign debt defaults and bank failures, which could result in the exit of countries from the EU or the Eurozone. This has led to, and could continue to lead to, declines in market liquidity, a contraction of available credit, and diminished economic growth and business confidence in those countries, with potential collateral consequences to other countries as well.
Recent political developments in the U.S. and Europe may result in a partial or full break-up of the EU, Eurozone or the North American Free-Trade
Agreement (“NAFTA”). The exit of countries from the EU or Eurozone or the dissolution of those bodies could lead to redenomination of certain obligations of obligors in exiting countries. Any such exit and redenomination would cause significant uncertainty with respect to outstanding obligations of counterparties and debtors in any exiting country, whether sovereign or otherwise, and could lead to complex and lengthy disputes and litigation. The withdrawal of the U.S. from NAFTA or the imposition of import tariffs could also create market uncertainty and stress. Market uncertainty and stress could also cause, among other things, severe disruption to equity markets, significant increases in bond yields generally, potential failure or default of financial institutions, including those of systemic importance, a significant decrease in global liquidity, a freeze-up of global credit markets and a potential worldwide recession.
The interdependencies among world economies, including the EU, Eurozone and the members of NAFTA, as well as interdependencies of financial institutions, have contributed to concerns regarding the stability of financial markets generally and certain economies and institutions in particular. Financial services institutions are interdependent as a result of trading, clearing, counterparty or other relationships. We routinely execute transactions with global counterparties, including brokers and dealers, commercial banks, investment banks, mutual and hedge funds, and other institutional clients. As a result, defaults or non-performance by, or even rumors or questions about, one or more global financial institutions, or the financial markets generally, have in the past led to market-wide liquidity problems and could lead to losses by us or by other institutions in the future.
We are primarily exposed to disruptions in global markets in a number of principal areas – on our balance sheet, in certain interest-bearing deposits with banks, loans, trading assets and investment securities, as well as fee revenue. Additionally, market disruptions could lead to, among other things, a negative impact on our fee revenue and a “flight to safety,” triggering increased client deposits and altering the size and composition of our balance sheet, which could adversely impact our leverage-based regulatory capital measures. For additional information regarding our exposure to certain countries, please see “International operations – Country risk exposure.”
BNY Mellon 101
Risk Factors (continued) |
Given the scope of our global operations, clients and counterparties, persistent disruptions in the global financial markets, the failure of a significant global financial institution, even if not an immediate counterparty to us, or the attempt of a country to abandon the euro or persistent weakness in a leading global currency could have a material adverse impact on our business or results of operations.
The United Kingdom’s referendum decision to leave the EU has had and may continue to have negative effects on global economic conditions, global financial markets, and our business and results of operations.
In 2016, the UK voted to leave the EU in a nation-wide referendum. This has created an uncertain political and economic environment in the UK, and may create such environments in other EU member states. Political and economic uncertainty has in the past led to, and the outcome of the referendum and the withdrawal of the UK from the EU could lead to, declines in market liquidity and activity levels, volatile market conditions, a contraction of available credit, lower or negative interest rates, weaker economic growth and reduced business confidence.
The referendum outcome means that the long-term nature of the UK’s relationship with the EU is unclear, and there is considerable uncertainty as to when the framework for any such relationship governing both the access of the UK to EU markets and vice versa will be determined and implemented. As a result, we, including our European affiliates, may face additional operational, regulatory and compliance costs. In addition, the regulatory, tax and supervisory regimes applicable to our European operations are expected to change; however, the nature and timing of such changes are uncertain and cannot be predicted. Certain of our European operations are conducted through subsidiaries located in the UK and other EU member states. If our UK subsidiaries are not able to retain their EU financial services “passport,” or an equivalent version of access to enable cross-border services throughout the EU single market without needing to obtain local authorizations then we may incur costs to move operations and, potentially, personnel from our UK operations to our operations in other EU member states. The outcome of the referendum has also created uncertainty with regard to divergent regulatory standards, which may affect the
operational capabilities such as the transfer of data between the UK and EU after the UK leaves the EU.
Following the referendum, volatility in the exchange rate for the British pound has increased. The decrease in the British pound compared to the U.S. dollar since the referendum has had, and may continue to have, a negative effect on our Investment Management business, which typically has more non- U.S. dollar denominated revenues than expenses. Volatility in exchange rates may also have a negative effect on our Investment Services business, which typically has more non-U.S. dollar denominated expenses than revenues.
The effects of the result of the referendum, including those described above, could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Weakness and volatility in financial markets and the economy generally may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
As a financial institution, our businesses, including our Investment Management, Global Markets, Depositary Receipts and Securities Lending businesses, are particularly sensitive to economic and market conditions, including in the capital and credit markets. When these markets are volatile or disruptive, we could experience a decline in our marked-to-market assets, including in our securities portfolio and our equity investments, including seed capital. Our results of operations may be materially affected by conditions in the financial markets and the economy generally, both in the U.S. and elsewhere around the world. A variety of factors impact global economies and financial markets, including interest rates, commodity pricing, such as the continued weakness in oil prices, instability of certain markets, political instability, volatile debt and equity market values, the strong U.S. dollar, high unemployment and governmental budget deficits (including, in the U.S., at the federal, state and municipal level), contagion risk from possible default by other countries on sovereign debt, declining business and consumer confidence and the risk of increased inflation. Any resulting economic pressure on consumers and lack of confidence in the financial markets may adversely affect certain portions of our business, financial condition and results of operations. In particular, we face the following risks
102 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
in connection with these factors, some of which are discussed at greater length in separate risk factors:
• | A continuing low interest rate environment, geopolitical tension, continuing low oil prices, and economic instability in countries around the world can at times increase the demand for low-risk investments, particularly in U.S. Treasuries and the dollar. A “flight to safety” has historically increased BNY Mellon’s balance sheet, which has negatively impacted, and could continue to negatively impact, our leverage-based regulatory capital measures. A sustained “flight to safety” has historically triggered a decline in trading, capital markets and cross-border activity. Declining volumes in these activities would likely decrease our revenue, which would negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition and, if sustained in the long term, our business. |
• | The fees earned by our Investment Management business are higher as assets under management and/or investment performance increase. Those fees are also impacted by the composition of the assets under management, with higher fees for some asset categories as compared to others. Uncertain and volatile capital markets could result in reductions in assets under management because of investors’ decisions to withdraw assets or from simple declines in the value of assets under management as markets decline. Uncertain and volatile financial markets may also result in changes in customer allocations of funds among money market, equity, fixed income or other investment alternatives. Those changes in allocation may be from higher fee investments to lower fee investments. For example, at Dec. 31, 2016, we estimate that a 5% change in global equity markets, spread evenly throughout the year, would impact fee revenue by less than 1% and diluted earnings per common share by $0.02 to $0.04. |
• | Market conditions resulting in lower transaction volumes could have an adverse effect on the revenues and profitability of certain of our businesses such as clearing, settlement, payments and trading. |
• | Uncertain and volatile capital markets, particularly declines, could reduce the value of our investments in securities, including pension and other post-retirement plan assets. |
• | Derivative instruments we hold to hedge and manage exposure to market risks including interest rate risk, equity price risk, foreign currency risk and credit risk associated with our products and businesses might not perform as intended or expected, resulting in higher realized losses and unforeseen stresses on liquidity. Our derivative-based hedging strategies also rely on the performance of counterparties to such derivatives. These counterparties may fail to perform for various reasons resulting in losses on under-collateralized positions. |
• | Our ability to continue to operate certain pooled investment funds at a net asset value of $1.00 per unit and to allow unrestricted cash redemptions by investors in those pooled funds (or by investors in other funds managed by us which are invested in those pooled investment funds) may be adversely affected by depressed mark-to-market prices of the underlying portfolio securities held by such funds, or by material defaults on such securities or by the level of liquidity that could be achieved from the portfolio securities in such funds. We may be faced with claims from investors and exposed to financial loss as a result of our operation of such funds. |
• | Continuing weakness in oil prices may continue to negatively impact capital markets and may impact the ability of certain of our clients, including oil and gas exploration and production companies and sovereign funds in oil-exporting countries, to continue using our services or repay outstanding loans. Increased defaults among oil and gas exploration and production companies may also negatively impact the high-yield market and our high-yield funds. |
• | Market volatility could produce downward pressure on our stock price and credit availability without regard to our underlying financial strength. |
• | The process we use to estimate our projected credit losses and to ascertain the fair value of securities held by us is subject to uncertainty in that it requires use of statistical models and difficult, subjective and complex judgments, including forecasts of economic conditions and how these conditions might impair the ability of our borrowers and others to meet their obligations. In uncertain and volatile capital markets, our ability to estimate our projected |
BNY Mellon 103
Risk Factors (continued) |
credit losses may be impaired, which could adversely affect our overall profitability and results of operations.
We use various models and strategies to assess and control our market risk exposures but those are subject to inherent limitations. Our models, which rely on historical trends and assumptions, may not be sufficiently predictive of future results due to limited historical patterns, extreme or unanticipated market movements and illiquidity, especially during severe market downturns or stress events. The models that we use to assess and control our market risk exposures also reflect assumptions about the degree of correlation among prices of various asset classes or other market indicators. In addition, market conditions in recent years have involved unprecedented dislocations and highlight the limitations inherent in using historical data to manage risk. In times of market stress or other unforeseen circumstances, such as the market conditions experienced in 2008 and 2009, previously uncorrelated indicators may become correlated, or previously correlated indicators may move in different directions. These types of market movements have at times limited the effectiveness of our hedging strategies and have caused us to incur significant losses, and they may do so in the future. For a discussion of our management of market risk, see “Risk Management – Market risk.”
Changes in interest rates could have a material adverse effect on our profitability.
Our net interest revenue and cash flows are sensitive to changes in short-term interest rates and changes in valuations in the debt or equity markets over which we have no control. Our net interest revenue is the difference between the interest income earned on our interest-earning assets, such as the loans we make and the securities we hold in our investment securities portfolio, and the interest expense incurred on our interest-bearing liabilities, such as deposits and borrowed money. Notwithstanding the recent increase in the Fed Funds effective rate to between 0.50% and 0.75%, we remain in a historically low-rate environment.
A continuing low short-term rate environment will likely adversely impact our revenue and results of operations by:
• | continued compression of our net interest spreads, depending on our balance sheet position; |
• | constraining our ability to achieve a net interest margin consistent with historical averages; |
• | sustained weakness of our spread-based revenues, resulting in continued voluntary waiving of particular fees on certain money market mutual funds and related distribution fees by us in order to prevent the yields on such funds from becoming uneconomic; and |
• | adversely impacting the value of fixed-rate mortgage-backed securities we hold if there are increases in mortgage prepayment speeds, which can be caused by refinancing activity. |
Additionally, low short-term rates may result in excess deposits with high potential runoff rates, which in turn would increase our assets and result in further pressure on our LCR measure.
A rise in interest rates could trigger one or more of the following, which could adversely impact our business, results of operations and financial condition, including:
• | less liquidity in bonds and fixed income funds in the case of a sharp rise in interest rates resulting in lower performance, yield and fees; |
• | increased number of delinquencies, bankruptcies or defaults and more nonperforming assets and net charge-offs, as borrowers may have more difficulty making higher interest payments; |
• | difficulty in modeling predicted deposit levels and depositor behavior, which could impact our ability to manage liquidity and capital; |
• | decreases in deposit levels and higher redemptions from our fixed income funds or separate accounts, as clients move funds into investments with higher rates of return; |
• | decreases in stable deposit levels, which may result in further pressure on our LCR measure; |
• | a decline in our risk-based capital ratios; |
• | reduction in accumulated other comprehensive income (“OCI”) in our shareholders’ equity and therefore our tangible common equity due to the impact of rising long term rates on our available for sale securities in our investment portfolio; and |
• | higher funding costs. |
104 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
A more detailed discussion of the interest rate and market risks we face is contained in “Risk Management.”
We may experience write-downs of securities that we own and other losses related to volatile and illiquid market conditions, reducing our earnings and impacting our financial condition.
We maintain an investment securities portfolio of various holdings, types and maturities. At Dec. 31, 2016, these securities were primarily classified as available-for-sale, which are recorded on our balance sheet at fair value with unrealized gains or losses reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax. The securities in our held-to-maturity portfolio, recorded on our balance sheet at amortized cost, were $40.9 billion and comprised approximately 36% of our investment securities portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016. To the extent unhedged, the accounting and regulatory treatment of our investment securities portfolio in an available-for-sale accounting environment may have more volatility than a more traditional held-for-investment loan portfolio, or a securities portfolio comprised exclusively of U.S. Treasury securities.
Our investment securities portfolio represents a greater proportion of our consolidated total assets (approximately 34% at Dec. 31, 2016), and our loans represent a smaller proportion of our consolidated total assets (approximately 19% at Dec. 31, 2016), in comparison to many other major U.S. financial institutions due to our custody and trust bank business model. As such, our capital levels and results of operations and financial condition are materially exposed to the risks associated with our investment portfolio.
If any of our available-for-sale securities experience an other-than-temporary impairment, it would negatively impact our earnings. If our held-to-maturity securities experience a loss in fair value, it would negatively impact the fair value of our securities portfolio, although it would not impact our earnings unless a credit event occurred. Many of these securities experienced significant liquidity, valuation and credit quality deterioration during the 2008 financial crisis and could experience a similar deterioration in another financial crisis. Non-U.S. mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities with exposures to European countries, whose sovereign-debt markets have experienced increased stress since
2011, may continue to experience stress in the future. U.S. state and municipal bonds have also experienced stress in light of fiscal concerns.
Under the U.S. capital rules, after-tax changes in the fair value of available-for-sale investment securities are included in CET1 capital. Since loans held for investment, or securities in a held-to-maturity accounting classification, are not subject to a fair-value accounting framework, changes in the fair value of these instruments (other than incurred credit losses) are not similarly included in the determination of CET1 capital. As a result, we may experience increased variability in our CET1 capital relative to other major financial institutions who maintain a lower proportion of their consolidated total assets in an available-for-sale accounting classification.
Generally, the fair value of available-for-sale securities in the securities portfolio is determined based upon market values available from third-party sources. During periods of market disruption, it may be difficult to value certain of our investment securities if trading becomes less frequent and/or market data becomes less observable. As a result, valuations may include inputs and assumptions that are less observable or require greater estimation and judgment as well as valuation methods which are more complex. These values may not be ultimately realizable in a market transaction, and such values may change very rapidly as market conditions change and valuation assumptions are modified. Decreases in value may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial condition. If any of our securities suffer credit losses, as we experienced with some of our investments in 2009, we may recognize the credit losses as an other-than-temporary impairment which could impact our revenue in the quarter in which we recognize the losses. The decision on whether to record an other-than- temporary impairment or write-down is determined in part by management’s assessment of the financial condition and prospects of a particular issuer, projections of future cash flows and recoverability of the particular security. Management’s conclusions on such assessments are highly judgmental and include assumptions and projections of future cash flows which may ultimately prove to be incorrect as assumptions, facts and circumstances change. On the other hand, securities held in a held-to-maturity accounting environment are limited in the actions we can take absent a significant deterioration in the
BNY Mellon 105
Risk Factors (continued) |
issuer’s creditworthiness. Therefore we may be constrained in our ability to liquidate a held-to-maturity security that is deteriorating in value, which would negatively impact the fair value of our securities portfolio. If our determinations change about our intention or ability to not sell securities that have experienced a reduction in fair value below its amortized cost, we could be required to recognize an other-than-temporary loss in earnings for the entire difference between fair value and amortized cost.
For information regarding our investment securities portfolio, refer to “Consolidated balance sheet review – Investment securities” and for information regarding the sensitivity of and risks associated with the market value of portfolio investments and interest rates, refer to “Critical accounting estimates – Fair value – Securities” and “– Other-than-temporary impairment.”
We are dependent on fee-based business for a substantial majority of our revenue and our fee-based revenues could be adversely affected by slowing in market activity, weak financial markets, underperformance and/or negative trends in savings rates or in investment preferences.
Our principal operational focus is on fee-based business, which is distinct from commercial banking institutions that earn most of their revenues from loans and other traditional interest-generating products and services. In 2016, approximately 79% of our total revenue was fee-based. Our fee-based businesses include investment management and performance fees, custody, corporate trust, depositary receipts, clearing, collateral management and treasury services, which are highly competitive businesses.
Fees for many of our products and services are based on the volume of transactions processed, the market value of assets managed and administered, securities lending volume and spreads, and fees for other services rendered. Corporate actions, cross-border investing, global mergers and acquisitions activity, new debt and equity issuances, and secondary trading volumes all affect the level of our revenues. If the volumes of these activities decrease due to weak financial markets or otherwise, our revenues will also decrease, which would negatively impact our results of operations. Declining margins and fees have negatively impacted certain of our fee-based revenues in recent years.
Poor investment returns in our investment management business, due to either weak market conditions or underperformance (relative to our competitors or to benchmarks) by funds or accounts that we manage or investment products that we design or sell, could result in reduced market values of portfolios that we manage and/or administer and may affect our ability to retain existing assets and to attract new clients or additional assets from existing clients. Market and regulatory trends are driving investable assets toward investment in lower fee asset management products at reduced margins for our clients, which may ultimately negatively impact revenue. Similarly, significant declines in the volume of capital markets activity would reduce the number of transactions we process and the amount of securities we lend and therefore would also have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our business generally benefits when individuals invest their savings in mutual funds and other collective funds, unit investment trusts or exchange- traded funds, or contribute more to defined contribution plans. A decline in the savings rates of individuals or a change in investment preferences that leads to less investment in mutual funds or other collective funds, or a shift to lower fee investment products, could adversely impact our revenues. Specifically, if the recent shift in investor preference to lower fee products continues, our investment management revenues could be negatively impacted. A decline in our investment management revenues could result in a decline in the fair value in our Asset Management reporting unit, which is one of the two reporting units in our Investment Management segment. If the fair value of the Asset Management reporting unit declines below its carrying value, we may be required to take an impairment charge.
Our FX revenue may be adversely affected by decreases in market volatility and the cross-border investment activity of our clients.
Our foreign exchange trading generates revenues which are influenced by market pressures, which continue to be increasingly competitive, the volume of client transactions and the spread realized on these transactions. The level of volume and spreads is affected by market volatility, the level of cross-border assets held in custody for clients, the level and nature of underlying cross-border investments and other transactions undertaken by corporate and institutional clients. Our clients’ cross-border investing activity
106 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
could decrease in reaction to economic and political uncertainties, including changes in laws or regulations governing cross-border transactions, such as currency controls or tariffs. Uncertainties resulting from terrorist attacks and/or military actions may also negatively affect cross-border investments activity, which could negatively impact revenue.
Volumes and/or spreads in some of our products tend to benefit from currency volatility and are likely to decrease during times of lower currency volatility. These revenues also depend on our ability to manage the risk associated with the currency transactions we execute and program pricing.
Furthermore, a shift by custody clients from the standing instruction programs to other trading options combined with competitive market pressures on the foreign exchange business is negatively impacting our FX revenue. Continued growth of electronic FX trading capabilities is resulting in a shift of volume to lower margin channels.
Credit and Liquidity Risk
The failure or perceived weakness of any of our significant counterparties, many of whom are major financial institutions and sovereign entities, and our assumption of credit and counterparty risk, could expose us to loss and adversely affect our business.
We have exposure to many different industries and counterparties, particularly financial institutions as a result of trading, clearing, counterparty or other relationships. We routinely execute transactions with counterparties in the financial industry as well as sovereigns and other governmental or quasi-governmental entities, and other institutional clients. Our direct exposure consists of the extension of credit to clients and the extension of credit on our balance sheet. In addition to traditional credit activities, we also extend and incur intraday credit exposure in order to facilitate our various processing and intermediation activities. Our ability to engage in routine funding or other transactions could be adversely affected by the actions and commercial soundness of other financial institutions or sovereign entities, as defaults or non-performance by (or even rumors or questions about such default or non-performance) one or more financial institutions, or the financial services industry generally, have in the past led to market-wide liquidity problems and could lead to losses or defaults by us or by other institutions
(including our counterparties and/or clients) in the future. The consolidation of financial institutions during the recent financial crisis and the failures of other financial institutions have increased the concentration of our counterparty risk.
As a result of our membership in several industry clearing or settlement exchanges, we may be required to guarantee obligations and liabilities or provide financial support in the event that other members do not honor their obligations or default. These obligations may be limited to members that dealt with the defaulting member or to the amount (or a multiple of the amount) of our contribution to a member’s guarantee fund, or, in a few cases, the obligation may be unlimited.
The degree of client demand for short-term credit also tends to increase during periods of market turbulence, exposing us to further counterparty-related risks. For example, investors in mutual funds for which we act as custodian may engage in significant redemption activity due to adverse market or economic news. We may then extend short-term credit to clients as a result of our relationship with such clients and the nature of various cash and securities settlement processes. This may negatively impact our leverage-based capital ratios, and in times of sustained market volatility, may result in significant leverage-based ratio declines.
For some types of clients, we provide credit to allow them to leverage their portfolios, which may expose us to potential loss if the client experiences credit difficulties. We are also generally not able to net exposures across counterparties that are affiliated entities and may not be able to net exposures to the same legal entity across multiple products. In addition, we may incur a loss in relation to one entity or product even though our exposure to one of the entities’ affiliates is over-collateralized. Moreover, not all of our counterparty exposure is secured and, when our exposure is secured, the realizable market value of the collateral may have declined by the time we exercise our rights against that collateral. This risk may be particularly acute if we are required to sell the collateral into an illiquid or temporarily impaired market. Disputes with counterparties as to the valuation of collateral significantly increase in times of market stress and illiquidity.
We act as lender’s agent in securities lending transactions between our customers, acting as lenders,
BNY Mellon 107
Risk Factors (continued) |
and financial counterparties, including broker-dealers, acting as borrowers, wherein securities are lent by our customers and the loans are secured by a pledge of cash or securities posted by such financial counterparties. Typically, in the case of cash collateral, we invest the cash collateral pursuant to each customer’s investment guidelines and instructions. In certain cases, we agree to indemnify our customers against a default by the borrower under a securities lending transaction and, therefore, may have to buy-in the loaned securities with the cash collateral or the proceeds from the liquidation of the non-cash collateral. In those instances, we, rather than our customers, are exposed to the risks of the defaulting counterparty in the securities lending transaction.
From time to time, we assume concentrated credit risk at the individual obligor, counterparty or group level, potentially exposing us to a single market or political event or a correlated set of events. For example, we may be exposed to defaults by companies located in countries with deteriorating economic conditions, including Brazil and Turkey, or by companies in certain industries, such as utilities and oil and gas companies. Such concentrations may be material. Our material counterparty exposures change daily, and the counterparties or groups of related counterparties to which our risk exposure is material also varies during any reported period; however, our largest exposures tend to be to other financial institutions, clearing organizations, and governmental entities, both inside and outside of the U.S. Concentration of counterparty exposure presents significant risks to us and to our clients because the failure or perceived weakness of our counterparties (or in some cases of our clients’ counterparties) has the potential to expose us to risk of financial loss. Changes in market perception of the financial strength of particular financial institutions or sovereign issuers can occur rapidly, are often based on a variety of factors and are difficult to predict.
Under evolving regulatory restrictions on credit exposure, which include a broadening of the measure of credit exposure, we may be required to limit our exposures to specific obligors or groups, including financial institutions, to levels that we may currently exceed. These credit exposure restrictions under such evolving regulations may adversely affect our businesses and may require that we modify our operating models or the policies and practices we use.
Although our overall business is subject to these interdependencies, several of our businesses are particularly sensitive to them, including our currency and other trading activities, our securities lending and securities finance businesses and our investment management business. If we experience any of the losses described above, it may materially and adversely affect our results of operations.
Any material reduction in our credit ratings or the credit ratings of our principal bank subsidiaries, The Bank of New York Mellon or BNY Mellon, N.A., could increase the cost of funding and borrowing to us and our rated subsidiaries and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition and on the value of the securities we issue.
Our debt and preferred stock and the debt and deposits of our principal bank subsidiaries, The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon, N.A., are currently rated investment grade by the major rating agencies. These rating agencies regularly evaluate us and our rated subsidiaries and their outlook on us and our rated subsidiaries. Their credit ratings are based on a number of factors, including our financial strength, performance, prospects and operations as well as factors not entirely within our control, including conditions affecting the financial services industry generally as well as the U.S. government. In addition, rating agencies employ different models and formulas to assess the financial strength of a rated company, and from time to time rating agencies have, in their discretion, altered these models. Changes to rating agency models, general economic conditions, or other circumstances outside of our control could impact a rating agency’s judgment of the rating or outlook it assigns us or our rated subsidiaries.
In view of the difficulties experienced in recent years by many financial institutions, we believe that the rating agencies have heightened their level of scrutiny, increased the frequency and scope of their credit reviews, have requested additional information, and have adjusted upward the requirements employed in their models for maintenance of rating levels. There can be no assurance that we or our rated subsidiaries will maintain our respective credit ratings or outlook on our securities. For example, in October 2016, S&P stated that in light of the resubmissions by the eight U.S. G-SIBs of their resolution plans, S&P will include the ramifications of structural changes resulting from those resolution plans in its
108 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
evaluations of the U.S. G-SIBs’ credit profiles. If S&P determines that such structural changes increase risks to our debtholders, our ratings could be negatively impacted.
A material reduction in our credit ratings or the credit ratings of our rated subsidiaries could have a material adverse effect on our access to credit markets, the related cost of funding and borrowing, our credit spreads, our liquidity and on certain trading revenues, particularly in those businesses where counterparty creditworthiness is critical. In addition, in connection with certain over-the-counter derivatives contracts and other trading agreements, counterparties may require us or our rated subsidiaries to provide additional collateral or to terminate these contracts and agreements and collateral financing arrangements in the event of a credit ratings downgrade below certain ratings levels. The requirement to provide additional collateral or terminate these contracts and agreements could impair our liquidity by requiring us to find other sources of financing or to make significant cash payments or securities movements. A downgrade by any one rating agency, depending on the agency’s relative ratings of the firm at the time of the downgrade, may have an impact which is comparable to the impact of a downgrade by all rating agencies. If a rating agency downgrade were to occur during broader market instability, our options for responding to events may be more limited and more expensive. An increase in the costs of our funding and borrowing, or an impairment of our liquidity, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. A material reduction in our credit ratings also could decrease the number of investors and counterparties willing or permitted to do business with or lend to us and adversely affect the value of the securities we have issued or may issue in the future.
We cannot predict what actions rating agencies may take, or what actions we may elect or be required to take in response thereto, which may adversely affect us. Our and our subsidiaries’ ratings could be downgraded at any time and without any notice by any of the rating agencies. For further discussion on the impact of a credit rating downgrade, see “Disclosure of contingent features in OTC derivative instruments” in Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected if we do not effectively manage our liquidity.
BNY Mellon’s operating model and overall strategy rely heavily on our access to global capital markets and financial market utilities. Without such access, it would be difficult to process payments and settle and clear transactions on behalf of our clients. Deterioration in our liquidity position, whether actual or perceived, can impact our market access by affecting participants’ willingness to transact with us. Change to our liquidity can be caused by various factors, such as funding mismatches, market constraints disabling asset to cash conversion, inability to issue debt, run-off of core deposits, and contingent liquidity events such as additional collateral posting. Changes in economic conditions or exposure to credit, market, operational, legal, and reputational risks can also affect our liquidity.
Our business is dependent in part on our ability to meet our cash and collateral obligations at a reasonable cost for both expected and unexpected cash flows. We also must manage liquidity risks on an intraday basis, in a manner designed to ensure that we can access required funds during the business day to make payments or settle immediate obligations, often in real time. We receive client deposits through a variety of investment management and investment servicing businesses and we rely on those deposits as a low-cost and stable source of funding. Our ability to continue to receive those deposits, and other short- term funding sources, is subject to variability based on a number of factors, including volume and volatility in the global securities markets, the relative interest rates that we are prepared to pay for those deposits, and the perception of the safety of those deposits or other short-term obligations relative to alternative short-term investments available to our clients. We could lose deposits if we suffer a significant decline in the level of our business activity, our credit ratings are materially downgraded, interest rates rise, or we are subject to significant negative press or significant regulatory action or litigation, among other reasons. If we were to lose a significant amount of deposits we may need to replace such funding with more expensive funding and/or reduce assets, which would reduce our net interest revenue.
In addition, the Parent’s access to the debt capital markets is a significant source of liquidity. Events or
BNY Mellon 109
Risk Factors (continued) |
circumstances often outside of our control, such as market disruptions, government fiscal and monetary policies, or loss of confidence by securities purchasers or counterparties in us or in the funds markets, could limit our access to capital markets, increase our cost of borrowing, adversely affect our liquidity, or impair our ability to execute our business plan. In addition, clearing organizations, regulators, clients and financial institutions with which we interact may exercise the right to require additional collateral based on market perceptions or market conditions, which could further impair our access to and cost of funding. Market perception of sovereign default risks can also lead to inefficient money markets and capital markets, which could further impact BNY Mellon’s funding availability and cost. Conversely, if we experience excess liquidity inflows, it could increase interest expense, limit our financial flexibility, and increase the size of our total assets in a manner that could have a negative impact on our capital ratios.
Recently adopted and proposed regulations have been designed to address certain liquidity risks of large banking organizations, including BNY Mellon. The LCR and the Dodd-Frank Act’s enhanced prudential standards impose liquidity management requirements on us that require us to increase our holdings of highly liquid, but potentially lower-yielding assets. These regulations also impact our ability to hold certain deposits deemed to pose a higher risk of runoff in the event of financial distress.
Under the U.S. capital rules, the size of the capital surcharge that applies to large U.S. banking organizations is based in part on a banking organization’s reliance on short-term wholesale funding, including certain types of deposit funding, which may increase the cost of such funding. Furthermore, certain non-U.S. authorities, including the European Commission, have proposed legislation or regulations requiring large banks to incorporate a separate subsidiary in countries in which they operate, and to maintain independent capital and liquidity at foreign subsidiaries. If adopted, these requirements could hinder our ability to efficiently manage our funding and liquidity in a centralized manner. There can be no assurances that these measures will be successful in limiting BNY Mellon’s liquidity risk.
As a holding company, we also rely on dividends and interest from our subsidiaries for funding. However,
there are various legal limitations on the extent to which our bank and other subsidiaries can finance or otherwise supply funds to us (by dividend or otherwise) and certain of our affiliates. If we are not able to obtain funds from our subsidiaries, we could be required to replace such funds through more expensive means and/or reduce higher-yielding assets. Recently, The Bank of New York Mellon, our primary subsidiary, has not distributed regular quarterly dividends to the Parent in order to increase its Tier 1 capital in advance of the SLR becoming effective, which may impact the Parent’s future liquidity.
If we are unable to raise funds using the methods described above, we would likely need to finance or liquidate unencumbered assets, such as our investment portfolio, central bank deposits and bank placements, to meet funding needs. We may be unable to sell some of our assets, or we may have to sell assets at a discount from market value, either of which could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. Further, our ability to sell assets may be impaired if other market participants are seeking to sell similar assets at the same time, which could occur in a liquidity or other market crisis. Additionally, if we experience cash flow mismatches, deposit run-off or market constraints resulting from our inability to convert assets to cash or access capital markets, our liquidity could be severely impacted. During periods of market uncertainty, our level of client deposits has in recent years tended to increase; however, because these deposits have high potential runoff rates, we have historically deposited these so-called excess deposits with central banks and in other highly liquid and low-yielding instruments.
If we are unable to continue to fund our assets through deposits or access capital markets on favorable terms or if we suffer an increase in our borrowing costs or otherwise fail to manage our liquidity effectively, our liquidity, net interest margin, financial results and condition may be materially adversely affected. In certain cases, this could require us to raise additional capital through the issuance of preferred or common stock, which could dilute the ownership of existing stockholders, or reduce our common stock dividend to preserve capital.
For a further discussion of our liquidity, see “Liquidity and dividends.”
110 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
We could incur losses if our allowance for credit losses, including loan and lending related commitments reserves, is inadequate.
When we loan money, commit to loan money or provide credit or enter into another contract with a counterparty, we incur credit risk, or the risk of loss if our borrowers do not repay their loans or our counterparties fail to perform according to the terms of their agreements. Our revenues and profitability are adversely affected when our borrowers default, in whole or in part, on their loan obligations to us or when there is a significant deterioration in the credit quality of our loan portfolio. We reserve for potential future credit losses by recording a provision for credit losses through a charge to earnings. The allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments represents management’s estimate of probable losses inherent in our credit portfolio. We use a quantitative methodology, and qualitative framework for determining the allowance for loan losses and the allowance for lending-related commitments. Within this qualitative framework, management applies judgment when assessing internal risk factors and environmental factors to compute an additional allowance for each component of the loan portfolio. As is the case with any such judgments, we could fail to identify these factors or accurately estimate their impact. We cannot provide any assurance as to whether charge-offs related to our credit exposure may occur in the future. Current and future market and economic developments may increase default and delinquency rates and negatively impact the quality of our credit portfolio, which may impact our charge-offs. Although our current estimates contemplate current conditions and how we expect them to change in the future, it is reasonably possible that actual conditions could be worse than anticipated in those estimates, which could materially affect our results of operations and financial condition. See “Critical accounting estimates.”
Strategic Risk
New lines of business, new products and services or transformational or strategic project initiatives may subject us to additional risks, and the failure to implement these initiatives could affect our results of operations.
From time to time, we may launch new lines of business, offer new products and services within existing lines of business or undertake
transformational or strategic projects. There are substantial risks and uncertainties associated with these efforts. We invest significant time and resources in developing and marketing new lines of business, products and services and executing on our transformational and strategic initiatives. For example, we have devoted considerable resources to developing new technology solutions for our clients, including the NEXEN Digital Ecosystem. If this product is not successful, it could adversely impact our reputation, business and results of operation.
Regulatory requirements can affect whether initiatives are able to be brought to market in a manner that is timely and attractive to our customers. Initial timetables for the development and introduction of new lines of business or new products or services and price and profitability targets may not be met. Furthermore, our revenues and costs may fluctuate because new businesses or products and services generally require startup costs while revenues may take time to develop, which may adversely impact our results of operations.
From time to time we undertake transformational or strategic project initiatives. Significant effort and resources are necessary to manage and oversee the successful completion of these initiatives. These initiatives often place significant demands on management and a limited number of employees with subject matter expertise and may involve significant costs to implement as well as increase operational risk as employees learn to process transactions under new systems. The failure to properly execute on these transformational or strategic initiatives could adversely impact our business, reputation and results of operations.
Our strategic transactions present risks and uncertainties and could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
From time to time, to achieve our strategic objectives, we have acquired, disposed of, or invested in (including through joint venture relationships) companies and businesses, and may do so in the future. Our ability to pursue or complete strategic transactions is in certain instances subject to regulatory approval and we cannot be certain when or if, or on what terms and conditions, any required regulatory approvals would be granted. Moreover, to the extent we pursue a strategic transaction, there can
BNY Mellon 111
Risk Factors (continued) |
be no guarantee that the transaction will close when anticipated, or at all. If a strategic transaction does not close, or if the strategic transaction fails to maximize shareholder value or required regulatory approval is not obtained, it could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Each acquisition poses integration challenges, including successfully retaining and assimilating clients and key employees, capitalizing on certain revenue synergies and integrating the acquired company’s culture, control functions, systems and technology. In some cases, acquisitions involve entry into new businesses or new geographic or other markets, and these situations also present risks and uncertainties in instances where we may be inexperienced in these new areas. We may be required to spend a significant amount of time and resources to integrate these acquisitions. The anticipated integration benefits may take longer to achieve than projected and the time and cost needed to consolidate control functions, platforms and systems may significantly exceed our estimates. If we fail to successfully integrate strategic acquisitions, including doing so in a timely and cost-effective manner, we may not realize the expected benefits, which could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, we may incur expenses, costs, losses, penalties, taxes and other liabilities related to the conduct of the acquired businesses prior to the date of our ownership (including in connection with the defense and/or settlement of legal and regulatory claims, investigations and proceedings) which may not be recoverable through indemnification or otherwise. If the purchase price we pay in an acquisition exceeds the fair value of assets acquired less the liabilities we assume, then we may need to recognize goodwill on our consolidated balance sheet. Goodwill is an intangible asset that is not eligible for inclusion in regulatory capital under applicable requirements. Further, if the value of the acquisition declines, we may be required to record an impairment charge.
Each disposition also poses challenges, including separating the disposed businesses, products and systems in a way that is cost-effective and is not disruptive to us or our customers. In addition, the inherent uncertainty involved in the process of evaluating, negotiating or executing a potential sale of one of our companies or businesses may cause the
loss of key clients, employees, and business partners which could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Joint ventures and non-controlling investments contain potentially increased financial, legal, reputational, operational, regulatory and/or compliance risks. Notwithstanding our controls and risk management framework, which are designed to manage these risks, we may be dependent on joint venture partners, controlling shareholders or management who may have business interests, strategies or goals that are inconsistent with ours. Business decisions or other actions or omissions of the joint venture partner, controlling shareholders or management may adversely affect the value of our investment, impacting our results of operations, result in litigation or regulatory action against us and otherwise damage our reputation and brand.
We are subject to competition in all aspects of our business, which could negatively affect our ability to maintain or increase our profitability.
Many businesses in which we operate are intensely competitive around the world. Competitors include other banks, trading firms, broker dealers, investment banks, asset managers, insurance companies, financial technology firms and a variety of other financial services and advisory companies whose products and services span the markets in which we operate. We compete on the basis of a number of factors, including transaction execution, capital or access to capital, products and services, innovation, reputation, lending limits, rates and price. Larger and more geographically diverse companies, and financial technology firms that are not subject to the same level of regulation, may be able to offer financial products and services at more competitive prices than we are able to offer. Pricing pressures, as a result of the willingness of competitors to offer comparable or improved products or services at a lower price, may result in a reduction in the price we can charge for our products and services, which could, and in some cases has, negatively affected our ability to maintain or increase our profitability. Low economic growth may result in clients exiting markets, which could lead to a loss of business by us.
In addition, technological advances have made it possible for other types of non-depository institutions, such as financial technology firms, outsourcing companies and data processing
112 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
companies, to offer a variety of products and services competitive with certain areas of our business.
Markets, and the manner in which our clients interact and transact within markets, can evolve quickly, particularly if new or disruptive technologies are introduced. Our failure to either anticipate, or participate in, the transformational change within a given market could result in potential negative financial impact. Competitors may develop technological advances that could negatively impact our transaction execution or the pricing of our clearing, settlement, payments and trading activities. Increased competition in any of these areas may require us to make additional capital investments in our businesses in order to remain competitive. For example, a number of financial institutions are researching ways to adapt robotics and distributed ledger technology to bank services. If we are not able to adapt these technologies as successfully as our peers, we may become less competitive.
Furthermore, recently implemented and proposed regulations may impact our ability to conduct certain of our businesses in a cost-effective manner or at all. The more restrictive laws and regulations applicable to the largest U.S. financial services institutions, including the U.S. capital rules, can put us at a competitive disadvantage relative to both our non-U.S. competitors and certain U.S. competitors. See “Supervision and Regulation.” A decline in our competitive position could adversely affect our ability to maintain or increase our profitability.
Our business may be adversely affected if we are unable to attract and retain employees.
Our success depends, in large part, on our ability to attract new employees, retain and motivate our existing employees, and continue to compensate our employees competitively amid heightened regulatory restrictions. Competition for the most skilled employees in most activities in which we engage can be intense, and we may not be able to recruit and retain key personnel.
We rely on certain employees with subject matter expertise to assist in the implementation of important initiatives. As technology and risk management increase in focus in the financial industry, competition for technologists and risk personnel has intensified in recent years, which could constrain our
ability to execute on certain of our strategic initiatives.
Our ability to attract and retain key executives and other employees may be hindered as a result of final regulations applicable to incentive compensation and other aspects of our compensation programs. These regulations, which are expected to include mandatory deferrals, clawback requirements and other limits on incentive compensation, may not apply to some of our competitors and to other institutions with which we compete for talent.
The loss of employees’ skills, knowledge of the market, industry experience, and the cost of finding replacements may hurt our business. If we are unable to continue to attract and retain highly qualified employees, our performance, including our competitive position, could be adversely affected.
Other Risks
Tax law changes or challenges to our tax positions with respect to historical transactions may adversely affect our net income, effective tax rate and our overall results of operations and financial condition.
In the course of our business, we receive inquiries and challenges from both U.S. and non-U.S. tax authorities on the amount of taxes we owe. If we are not successful in defending these inquiries and challenges, we may be required to adjust the timing or amount of taxable income or deductions or the allocation of income among tax jurisdictions, all of which can require a greater provision for taxes or otherwise negatively affect earnings. Probabilities and outcomes are reviewed as events unfold, and adjustments to the reserves are made when necessary, but the reserves may prove inadequate because we cannot necessarily accurately predict the outcome of any challenge, settlement or litigation or the extent to which it will negatively affect us or our business. In addition, new tax laws or the expiration of or changes in existing tax laws, or the interpretation of those laws worldwide, could have a material impact on our business or net income. Our actions taken in response to, or reliance upon, such changes in the tax laws may impact our tax position in a manner that may result in lower earnings. See Note 10 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further information.
BNY Mellon 113
Risk Factors (continued) |
Changes in accounting standards governing the preparation of our financial statements and future events could have a material impact on our reported financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and other financial data.
From time to time, the FASB, the SEC and bank regulators change the financial accounting and reporting standards governing the preparation of our financial statements or the interpretation of those standards. See “Recent Accounting Developments.” These changes are difficult to predict and can materially impact how we record and report our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and other financial data. In some cases, we may be required to apply a new or revised standard retroactively or to apply an existing standard differently, also retroactively, in each case potentially resulting in the restatement of our prior period financial statements and our related disclosures.
Additionally, our accounting policies and methods are fundamental to how we record and report our financial condition and results of operations. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates based upon assumptions about future economic and market conditions which affect reported amounts and related disclosures in our financial statements. Amounts subject to estimates are items such as the allowance for loan losses and lending-related commitments, the fair value of financial instruments and derivatives, other-than-temporary impairment, goodwill and other intangibles and pension accounting. Among other effects, such changes in estimates could result in future impairments of investment securities, goodwill and intangible assets and establishment of allowances for loan losses and lending-related commitments as well as changes in pension and post-retirement expense. If subsequent events occur that are materially different than the assumptions and estimates we used, our reported financial condition, results of operation and cash flows may be materially negatively impacted. See “Recent Accounting Developments” for a discussion of recent developments to our accounting standards.
The Parent is a non-operating holding company, and as a result, is dependent on dividends from its subsidiaries, including its principal subsidiary banks, to meet its obligations, including its obligations with respect to its securities, and to
provide funds for payment of dividends to its stockholders and stock repurchases.
The Parent is a non-operating holding company, whose principal assets and sources of income are its principal U.S. bank subsidiaries - The Bank of New York Mellon and BNY Mellon, N.A. - and its other subsidiaries. The Parent is a legal entity separate and distinct from its banks and other subsidiaries and, therefore, it relies in part on dividends, interest, distributions, and other payments from these bank and other subsidiaries to meet its obligations, including its obligations with respect to its securities, and to provide funds for payment of common and preferred dividends to its stockholders, to the extent declared by the Board of Directors. Recently, The Bank of New York Mellon, our primary subsidiary, has not distributed regular quarterly dividends to the Parent to build capital in advance of the implementation of the SLR as a binding measure.
There are various legal limitations on the extent to which our bank and other subsidiaries can finance or otherwise supply funds to the Parent (by dividend or otherwise) and certain of our affiliates. Many of our subsidiaries, including our bank subsidiaries, are subject to laws and regulations that restrict dividend payments or authorize regulatory bodies to block or reduce the flow of funds from those subsidiaries to the Parent or other subsidiaries. These restrictions can reduce the amount of funds available to meet the Parent’s obligations. In addition, our bank subsidiaries would not be permitted to distribute a dividend if doing so would constitute an unsafe and unsound practice or if the payment would reduce their capital to an inadequate level. Our bank subsidiaries are also subject to restrictions on their ability to lend to or transact with affiliates, minimum regulatory capital and liquidity requirements, and restrictions on their ability to use funds deposited with them in bank or brokerage accounts to fund their businesses.
We evaluate and manage liquidity on a legal entity basis. Legal entity liquidity is an important consideration as there are legal and other limitations on our ability to utilize liquidity from one legal entity to satisfy the liquidity requirements of another, including the Parent.
Although we maintain cash positions for liquidity at the holding company level, if our bank subsidiaries or other subsidiaries were unable to supply the Parent with cash over time, the Parent could become unable
114 BNY Mellon
Risk Factors (continued) |
to meet its obligations (including its obligations with respect to its securities), declare or pay dividends in respect of its capital stock, or perform stock repurchases. See “Supervision and Regulation” and “Liquidity and dividends” and Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Because the Parent is a holding company, its rights and the rights of its creditors, including the holders of its securities, to a share of the assets of any subsidiary upon the liquidation or recapitalization of the subsidiary will be subject to the prior claims of the subsidiary’s creditors (including, in the case of our banking subsidiaries, their depositors) except to the extent that the Parent may itself be a creditor with recognized claims against the subsidiary. The rights of holders of securities issued by the Parent to benefit from those distributions will also be junior to those prior claims. Consequently, securities issued by the Parent will be effectively subordinated to all existing and future liabilities of our subsidiaries.
Our ability to return capital to shareholders is subject to the discretion of our board of directors and may be limited by U.S. banking laws and regulations, including those governing capital and the approval of our capital plan, applicable provisions of Delaware law or our failure to pay full and timely dividends on our preferred stock.
Holders of our common and preferred stock are only entitled to receive such dividends or other distributions of capital as our Board of Directors may declare out of funds legally available for such payments. Although we have historically declared cash dividends on our common and preferred stock, we are not required to do so. In addition to the Board of Directors’ approval, our ability to take certain actions, including our ability to make certain acquisitions, declare dividends or repurchase our common stock, is dependent on, among other things, Federal Reserve non-objection under the annual regulatory review of the results of the CCAR process and the supervisory stress tests required under the Dodd-Frank Act. These evaluations, in turn, are dependent on, among other things, our successful demonstration that we can maintain capital levels above regulatory minimums in the event of a stressed market environment, as well as the Federal Reserve’s assessment of the robustness of our capital adequacy qualitative process and the assumptions and analysis underlying the capital plan. There can be no assurance that the Federal Reserve will not object to
our future capital plans or that we will perform adequately on our supervisory stress tests. If the Federal Reserve objects to our proposed capital actions or we underperform on our stress tests, we may be required to revise our stress-testing or capital management approaches, resubmit our capital plan or postpone, cancel or alter our planned capital actions, and we would not be permitted to make any capital distributions other than those to which the Federal Reserve has indicated in writing its non-objection. In addition, if there have been or will be changes in our risk profile (including a material change in business strategy or risk exposure), financial condition or corporate structure, we may be required to resubmit our capital plan to the Federal Reserve.
Our ability to accurately predict or explain the outcome of the CCAR process is influenced by evolving supervisory criteria. The Federal Reserve’s annual assessment of our capital adequacy and planning process involves not only a quantitative assessment through the Federal Reserve’s proprietary stress test models but also a qualitative assessment. The qualitative assessment involves a number of factors and is expected to continue to evolve on an ongoing basis as a result of the Federal Reserve’s horizontal review of capital plan submissions. Similarly, the Federal Reserve may, as part of its stated goal to continually evolve its annual stress testing requirements, adjust several parameters of the annual stress testing process, including the severity of the stress test scenario and the addition of components deemed important by the Federal Reserve (e.g., a counterparty failure). Further, because it is not clear how the Federal Reserve’s proprietary stress test models and qualitative assessment may differ from the modeling techniques and capital planning practices employed by us, it is foreseeable that our stress test results (using our own models, estimation methodologies and processes) may not be consistent with those disclosed by the Federal Reserve. In addition, the Federal Reserve may consider, at some point in the future, that some or all of the G-SIB surcharge or other buffers be integrated into its post-stress test minimum capital requirements.
The Federal Reserve’s instructions for the 2017 CCAR provided that, for large BHCs like BNY Mellon, common stock dividend payout ratios exceeding 30% of after-tax net income available to common shareholders under certain baseline scenarios will receive particularly close scrutiny. A
BNY Mellon 115
Risk Factors (continued) |
failure to increase dividends along with our competitors, or any reduction of, or elimination of, our common stock dividend would likely adversely affect the market price of our common stock, impact our return on equity, and market perceptions of BNY Mellon.
Our ability to declare or pay dividends on, or purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire, shares of our common stock or any of our shares that rank junior to preferred stock as to the payment of dividends and/or the distribution of any assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of BNY Mellon will be prohibited, subject to certain exceptions, in the event that we do not declare and pay in full dividends for the then-current dividend period of our Series A preferred stock or the last preceding dividend period of our Series C, Series D, Series E or Series F preferred stock.
In addition, regulatory capital rules that are or will be applicable to us including the U.S. capital rules, the SLR, TLAC, or the U.S. G-SIB Rule may limit or otherwise restrict how we utilize our capital, including common stock dividends and stock repurchases, and may require us to increase or alter the mix of our outstanding regulatory capital instruments. Any requirement to increase our regulatory capital ratios or alter the composition of our capital could require us to liquidate assets or otherwise change our business and/or investment plans, which may negatively affect our financial results. Further, any requirement to maintain higher levels of capital may constrain our ability to return capital to shareholders either in the form of common stock dividends or stock repurchases.
116 BNY Mellon
Recent Accounting Developments |
Recent accounting developments
ASU 2017-04, Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment
In January 2017, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”), Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment. This ASU simplifies the annual goodwill impairment test by eliminating GAAP’s Step 2 procedure that would otherwise be required if the first step of the annual test indicates that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value. Under this ASU, the amount of goodwill impairment would be determined by the excess of the carrying value of a reporting unit over its fair value, rather than the Step 2 calculation that would estimate the implied goodwill using the fair values of all assets, including previously unrecorded intangibles, and liabilities at the date of the test. To date, the Company has not been required to prepare a Step 2 computation for any of its reporting units. The Company will early adopt this standard in 2017.
ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows – Restricted Cash
In November 2016, FASB issued an ASU, Statement of Cash Flows – Restricted Cash. This ASU provides guidance on the presentation of restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents in the statement of cash flows and is effective for the first quarter of 2018. Earlier application is permitted. BNY Mellon is assessing the impacts of the new standard, but would not expect this ASU to materially affect the results of operations or financial condition.
ASU 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows – Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments
In August 2016, the FASB issued an ASU, Statement of Cash Flows – Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments. This ASU provides guidance on eight specific cash flow presentation issues and is effective for the first quarter of 2018. Earlier application is permitted, however all of the amendments must be adopted in the same period. BNY Mellon is assessing the impacts of the new standard, but would not expect this ASU to materially affect the results of operations or financial condition.
ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses
In June 2016, the FASB issued an ASU, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses. This ASU introduces a new current expected credit losses model, which will apply to financial assets subject to credit losses and measured at amortized cost, including held-to-maturity securities and certain off-balance sheet credit exposures. The guidance will also change current practice for the impairment model for available-for-sale debt securities. The available-for-sale debt securities model will require the use of an allowance to record estimated credit losses and subsequent recoveries. This ASU is effective for the first quarter of 2020. Earlier application is permitted beginning with the first quarter of 2019. BNY Mellon has begun its implementation efforts and is currently identifying key interpretive issues, and will assess existing credit loss forecasting models and processes against the new guidance to determine what modifications may be required. The extent of the impact to our financial statements upon adoption depends on several factors including the remaining expected life of financial instruments at the time of adoption, the establishment of an allowance for expected credit loss on held to maturity securities, and the macroeconomic conditions and forecasts that exist at that date.
ASU 2016-09, Compensation – Stock Compensation
In March 2016, the FASB issued an ASU, Compensation – Stock Compensation. This standard simplifies several aspects of the accounting for share-based payment transactions, including income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities and classification on the statement of cash flows. This ASU is effective for the first quarter of 2017. The adoption of the ASU will result in increased volatility to the Company’s income tax expense but is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s balance sheet or equity. The income tax volatility is dependent on the Company’s stock price at dates restricted stock units vest, which occur on award vesting dates primarily in the first quarter of each year, and when employees choose to exercise stock options.
BNY Mellon 117
Recent Accounting Developments (continued) |
ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, which provides guidance on the recognition of revenue related to the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. The ASU will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. GAAP when it becomes effective. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-08, Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net), which clarifies the guidance in determining revenue recognition as principal versus agent. In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-10, Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing, which provides guidance in accounting for immaterial performance obligations and shipping and handling. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-12, Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients, which provides clarification on assessing the collectability criterion, presentation of sales taxes, measurement date for non-cash consideration and completed contracts at transition, and provides a practical expedient for contract modifications. In December 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-20, Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers which provides amended guidance on narrow aspects of ASU 2014-09. The new standards are effective for the first quarter of 2018, with early adoption permitted no earlier than the first quarter of 2017. The standards permit the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method upon transition.
The Company has substantially completed its evaluation of the potential impact of this guidance on our accounting policies, and based on that evaluation, we expect the timing of most of our revenue recognition to remain the same and the impacts to not be material. To date, the impacts we have identified primarily relate to deferring and amortizing certain sales commission costs related to obtaining customer contracts and the timing of recognizing the contra revenue related to certain payments made to customers. The Company is considering using the retrospective method of adoption, but has not yet finalized its decision as we are still evaluating the related costs and benefits, including disclosure requirements in the year of adoption if the retrospective method is not used.
ASU 2016-07, Investments – Equity Method and Joint Ventures
In March 2016, the FASB issued an ASU, Investments – Equity Method and Joint Ventures, which eliminates the requirement to retrospectively apply the equity method when an increase in ownership interest in the investee prompts a change from the cost method to the equity method. This ASU is effective for first quarter of 2017. The Company will apply this ASU prospectively.
ASU 2016-02, Leases
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases. The primary objective of this ASU is to increase transparency and comparability by recognizing lease assets and liabilities on the balance sheet and expand related disclosures. ASU 2016-02 requires a “right-of-use” asset and a payment obligation liability on the balance sheet for most leases and subleases. Additionally, depending on the lease classification under the standard, it may result in different expense recognition patterns and classification than under existing accounting principles. For leases classified as finance leases, it will result in higher expense recognition in the earlier periods and lower expense in the later periods of the lease.
The standard is effective for the first quarter of 2019, with early adoption permitted. The standard requires that a modified retrospective transition approach be used by lessees and lessors to recognize and measure leases at the beginning of the earliest period presented. This modified retrospective approach includes a number of optional practical expedients that entities may elect to apply. We are currently evaluating the potential impact of the leasing standard on our consolidated financial statements and evaluating the practical expedients that may be elected. Upon adoption, the implementation of the leasing standard is expected to result in an immaterial increase in both assets and liabilities.
ASU 2016-01, Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. The ASU requires investments in equity securities that do not result in consolidation and are not accounted for under the
118 BNY Mellon
Recent Accounting Developments (continued) |
equity method to be measured at fair value with changes in the fair value recognized through net income, unless one of two available exceptions apply. The first exception, a scope exception, allows Federal Reserve Bank Stock, Federal Home Loan Bank stock and other exchange memberships held by broker dealers to remain accounted for at cost, less impairment. The second exception, a practicability exception, will be available for equity investments that do not have readily determinable fair values and do not qualify for the practical expedient to estimate fair value under ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement. To the extent the practicability exception applies, such investments will be accounted for at cost adjusted for impairment, if any, plus or minus changes from observable price changes.
The amendments also require an entity to present separately in other comprehensive income the portion of the total change in the fair value of a liability resulting from the entity’s “own credit risk” when the entity has elected to measure the liability at fair value. The amendments also eliminate the requirement to disclose the methods and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair values of financial instruments measured at amortized cost that are on the balance sheet.
This ASU is effective for the first quarter of 2018. If certain requirements are met, early adoption of the “own credit risk” provision is permitted; early adoption of the other provisions is not permitted. The FASB requires a modified retrospective method of adoption. BNY Mellon does not expect the adoption of this ASU to have a material impact.
BNY Mellon 119
Business Continuity |
We are prepared for events, such as information security incidents, technology disruptions, acts of terrorism, natural disasters, pandemics or global conflicts, that could damage our physical facilities, cause delay or disruptions to operational functions, including telecommunications networks, or impair our employees, clients, vendors and counterparties. Key elements of our business continuity strategies are extensive planning and testing, and diversity of business operations, data centers and telecommunications infrastructure.
We have established multiple geographically diverse locations for our funds transfer and broker-dealer services operational units, which provide redundant functionality to facilitate uninterrupted operations.
Our securities clearing, commercial paper, mutual fund accounting and custody, securities lending, master trust, Unit Investment Trust, corporate trust, item processing, wealth management and treasury units have common functionality in multiple sites designed to facilitate continuance of operations or rapid recovery. In addition, we have recovery positions for approximately 12,900 employees on a global basis of which over 6,400 are proprietary.
We continue to enhance geographic diversity for business operations by moving additional personnel to growth centers outside of existing major urban centers. We replicate 100% of our critical production computer data to multiple recovery data centers.
We have an active telecommunications diversity program. All major buildings are provisioned with connectivity from diverse telecommunication carriers. Additionally, we design our critical connectivity to take advantage of separate carrier entrances built into our facilities. This maximizes resiliency by allowing for end to end separation of primary and alternative communications.
In 2003, the Federal Reserve, OCC and SEC jointly published the Interagency Paper, “Sound Practices to Strengthen the Resilience of the U.S. Financial System” (“Sound Practices Paper”). The purpose of the document was to define the guidelines for the
financial services industry and other interested parties regarding “best practices” related to business continuity planning. Under these guidelines, we are a key clearing and settlement organization required to meet a higher standard for business continuity.
We believe we meet substantially all of the requirements of the Sound Practices Paper. As a core clearing and settlement organization, we believe that we are at the forefront of the industry in improving business continuity practices.
We are committed to seeing that requirements for business continuity are met not just within our own facilities, but also within those of our service providers whose operation is critical to our safety and soundness. To that end, we have a Third Party Governance Program in place to review new and existing service providers to see that they meet our standards for business continuity, as well as for information security, financial stability, personnel practices, etc.
We developed comprehensive plans, including increased remote working by staff for one or more periods lasting several weeks, to prepare for events that would cause significantly reduced staffing levels.
Although we are committed to observing best practices as well as meeting regulatory requirements, geopolitical uncertainties and other external factors will continue to create risk that cannot always be identified and anticipated.
Due to the nature of our business and our robust business recovery systems and processes, we are not materially impacted by climate change, nor do we expect material impacts in the near term. We have, and will continue to, implement processes and capital projects to deal with the risks of the changing climate. The Company has invested in the development of products and services that support the markets related to climate change.
120 BNY Mellon
Supplemental Information (unaudited) |
Supplemental information - Explanation of GAAP and Non-GAAP financial measures
BNY Mellon has included in this Annual Report certain Non-GAAP financial measures based on fully phased-in CET1 and other risk-based capital ratios, the fully phased-in SLR and tangible common shareholders’ equity. BNY Mellon believes that the CET1 and other risk-based capital ratios on a fully phased-in basis, the SLR on a fully phased-in basis and the ratio of tangible common shareholders’ equity to tangible assets of operations are measures of capital strength that provide additional useful information to investors, supplementing the capital ratios which are, or were, required by regulatory authorities. The tangible common shareholders’ equity ratio, which excludes goodwill and intangible assets, net of deferred tax liabilities, includes changes in investment securities valuations which are reflected in total shareholders’ equity. In addition, this ratio is expressed as a percentage of the actual book value of assets, as opposed to a percentage of a risk-based reduced value established in accordance with regulatory requirements, although BNY Mellon in its reconciliation has excluded certain assets which are given a zero percent risk-weighting for regulatory purposes and the assets of consolidated investment management funds to which BNY Mellon has limited economic exposure. Further, BNY Mellon believes that the return on tangible common equity measure, which excludes goodwill and intangible assets, net of deferred tax liabilities, is a useful additional measure for investors because it presents a measure of those assets that can generate income. BNY Mellon has provided a measure of tangible book value per common share, which it believes provides additional useful information as to the level of tangible assets in relation to shares of common stock outstanding.
BNY Mellon has presented revenue measures, which exclude the effect of noncontrolling interests related to consolidated investment management funds, gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building; and expense measures, which exclude amortization of intangible assets, M&I, litigation and restructuring charges, the
(recovery) impairment related to Sentinel and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. Earnings per share, return on equity, operating leverage and operating margin measures, which exclude some or all of these items, are also presented. Return on equity measures also exclude the tax benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim and the net charge related to the disallowance of certain foreign tax credits. Operating margin measures may also exclude the provision for credit losses and the net negative impact of money market fee waivers, net of distribution and servicing expense. BNY Mellon believes that these measures are useful to investors because they permit a focus on period-to-period comparisons, which relate to the ability of BNY Mellon to enhance revenues and limit expenses in circumstances where such matters are within BNY Mellon’s control. M&I expenses primarily relate to acquisitions and generally continue for approximately three years after the transaction. Litigation charges represent accruals for loss contingencies that are both probable and reasonably estimable, but exclude standard business-related legal fees. Restructuring charges relate to our streamlining actions, Operational Excellence Initiatives and migrating positions to Global Delivery Centers. Excluding these charges mentioned above permits investors to view expenses on a basis consistent with how management views the business.
The presentation of income (loss) from consolidated investment management funds, net of net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests related to the consolidation of certain investment management funds permits investors to view revenue on a basis consistent with how management views the business. BNY Mellon believes that these presentations, as a supplement to GAAP information, give investors a clearer picture of the results of its primary businesses.
Each of these measures as described above is used by management to monitor financial performance, both on a company-wide and on a business-level basis.
BNY Mellon 121
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
The following table presents the reconciliation of net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and diluted earnings per common share.
Reconciliation of net income and diluted EPS – GAAP to Non-GAAP | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | Growth in diluted EPS | |||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per common share amounts) | Net income | Diluted EPS | Net income | Diluted EPS | Net income | Diluted EPS | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2016 vs. 2014 (a) | |||||||||||||||||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – GAAP | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3.15 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2.71 | $ | 2,494 | $ | 2.15 | 16 | % | 21 | % | |||||||||
Add: M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | 1,130 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax impact of M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | (16 | ) | (29 | ) | (270 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Impact of M&I, litigation and restructuring charges – after-tax | 33 | 0.03 | 56 | 0.05 | 860 | 0.74 | |||||||||||||||||||
Add: (Recovery) impairment charge related to Sentinel | (13 | ) | 170 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Tax impact of net recovery (impairment charge) related to Sentinel | 5 | (64 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Recovery) impairment charge related to Sentinel – after-tax | (8 | ) | (0.01 | ) | 106 | 0.09 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Add: Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax impact of charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | (23 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives – after-tax | — | — | — | — | 81 | 0.07 | |||||||||||||||||||
Less: Gain on the sale of our investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 490 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax impact of gain on the sale of our investment in Wing Hang | — | — | (175 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our investment in Wing Hang – after-tax | — | — | — | — | 315 | 0.27 | |||||||||||||||||||
Less: Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 346 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax impact of gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | (142 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building – after-tax | — | — | — | — | 204 | 0.18 | |||||||||||||||||||
Less: Benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim | — | — | 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim – after-tax | — | — | — | — | 150 | 0.13 | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-GAAP adjustments – after-tax | 25 | 0.02 | 162 | 0.14 | 272 | 0.23 | |||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – Non-GAAP | $ | 3,450 | $ | 3.17 | $ | 3,215 | $ | 2.85 | $ | 2,766 | $ | 2.39 | (b) | 11 | % | 15 | % | ||||||||
(a) | Annualized. |
(b) | Does not foot due to rounding. |
The following table presents the reconciliation of total revenue.
Reconciliation of revenue – GAAP to Non-GAAP | Growth | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per common share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2016 vs. 2014 (a) | ||||||||
Fee and other revenue – GAAP | $ | 12,073 | $ | 12,082 | $ | 12,649 | |||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds – GAAP | 26 | 86 | 163 | ||||||||||
Net interest revenue – GAAP | 3,138 | 3,026 | 2,880 | ||||||||||
Total revenue – GAAP | 15,237 | 15,194 | 15,692 | — | % | (1 | )% | ||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 10 | 68 | 84 | ||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our equity investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 490 | ||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 346 | ||||||||||
Total revenue, as adjusted – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 15,227 | $ | 15,126 | $ | 14,772 | 1 | % | 2 | % | |||
(a) | Annualized. |
122 BNY Mellon
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
The following table presents the total payout ratio.
Total payout ratio | 2016 | ||
(dollars in millions) | |||
Capital deployed: | |||
Common stock dividends | $ | 778 | |
Common stock repurchased | 2,398 | ||
Total capital deployed | $ | 3,176 | |
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – GAAP | $ | 3,425 | |
Add: M&I, Litigation and restructuring charges – after-tax | 33 | ||
Recovery related to Sentinel – after-tax | (8 | ) | |
Adjusted net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – Non-GAAP | $ | 3,450 | |
Payout ratio – GAAP | 93 | % | |
Adjusted payout ratio – Non-GAAP | 92 | % | |
The following table presents the reconciliation of the pre-tax operating margin ratio.
Reconciliation of income before income taxes – pre-tax operating margin | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes – GAAP | $ | 4,725 | $ | 4,235 | $ | 3,563 | $ | 3,777 | $ | 3,357 | |||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 10 | 68 | 84 | 80 | 76 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our equity investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 490 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 346 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Add: Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | 298 | 342 | 384 | ||||||||||||||
M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | 1,130 | 70 | 559 | ||||||||||||||
(Recovery) impairment charge related to Sentinel | (13 | ) | 170 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 104 | 12 | 16 | ||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes, as adjusted – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 4,988 | $ | 4,683 | $ | 4,175 | $ | 4,121 | $ | 4,240 | |||||||||
Fee and other revenue – GAAP | $ | 12,073 | $ | 12,082 | $ | 12,649 | $ | 11,856 | $ | 11,448 | |||||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds – GAAP | 26 | 86 | 163 | 183 | 189 | ||||||||||||||
Net interest revenue – GAAP | 3,138 | 3,026 | 2,880 | 3,009 | 2,973 | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue – GAAP | 15,237 | 15,194 | 15,692 | 15,048 | 14,610 | ||||||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 10 | 68 | 84 | 80 | 76 | ||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our equity investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 490 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 346 | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue, as adjusted – Non-GAAP (a) | $ | 15,227 | $ | 15,126 | $ | 14,772 | $ | 14,968 | $ | 14,534 | |||||||||
Pre-tax operating margin – GAAP (b) | 31 | % | (c) | 28 | % | (c) | 23 | % | 25 | % | 23 | % | |||||||
Adjusted pre-tax operating margin – Non-GAAP (a)(b) | 33 | % | (c) | 31 | % | (c) | 28 | % | 28 | % | 29 | % | |||||||
(a) | Non-GAAP information for all periods presented excludes the net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds, amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges. Non-GAAP information for 2016 and 2015 also excludes the (recovery) impairment charge related to the Sentinel loan. Non-GAAP information for 2014 also excludes the gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. Non-GAAP information for 2013 and 2012 also excludes the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. |
(b) | Income before taxes divided by total revenue. |
(c) | Our GAAP earnings include tax-advantaged investments such as low income housing, renewable energy, bank-owned life insurance and tax-exempt securities. The benefits of these investments are primarily reflected in tax expense. If reported on a tax-equivalent basis, these investments would increase revenue and income before taxes by $317 million for 2016 and $242 million for 2015 and would increase our pre-tax operating margin by approximately 1.4% for 2016 and 1.1% for 2015. |
BNY Mellon 123
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
The following table presents the reconciliation of operating leverage.
Operating leverage | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 vs. | |||||
(dollars in millions) | 2015 | |||||||
Total revenue – GAAP | $ | 15,237 | $ | 15,194 | 0.28% | |||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 10 | 68 | ||||||
Total revenue, as adjusted – Non-GAAP | $ | 15,227 | $ | 15,126 | 0.67% | |||
Total noninterest expense – GAAP | $ | 10,523 | $ | 10,799 | (2.56)% | |||
Less: Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | ||||||
M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | ||||||
Total noninterest expense, as adjusted – Non-GAAP | $ | 10,237 | $ | 10,453 | (2.07)% | |||
Operating leverage – GAAP (a) | 284 | bps | ||||||
Adjusted operating leverage – Non-GAAP (a)(b) | 274 | bps | ||||||
(a) | Operating leverage is the rate of increase (decrease) in total revenue less the rate of increase (decrease) in total noninterest expense. |
(b) | Non-GAAP operating leverage for all periods presented excludes the net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds, amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges. |
The following table presents the reconciliation of the equity to assets ratio and book value per common share.
Equity to assets and book value per common share | Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions, unless otherwise noted) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity at period end – GAAP | $ | 38,811 | $ | 38,037 | $ | 37,441 | $ | 37,497 | $ | 36,414 | |||||
Less: Preferred stock | 3,542 | 2,552 | 1,562 | 1,562 | 1,068 | ||||||||||
BNY Mellon common shareholders’ equity at period end – GAAP | 35,269 | 35,485 | 35,879 | 35,935 | 35,346 | ||||||||||
Less: Goodwill | 17,316 | 17,618 | 17,869 | 18,073 | 18,075 | ||||||||||
Intangible assets | 3,598 | 3,842 | 4,127 | 4,452 | 4,809 | ||||||||||
Add: Deferred tax liability – tax deductible goodwill (a) | 1,497 | 1,401 | 1,340 | 1,302 | 1,130 | ||||||||||
Deferred tax liability – intangible assets (a) | 1,105 | 1,148 | 1,216 | 1,222 | 1,310 | ||||||||||
BNY Mellon tangible common shareholders’ equity at period end – Non-GAAP | $ | 16,957 | $ | 16,574 | $ | 16,439 | $ | 15,934 | $ | 14,902 | |||||
Total assets at period end – GAAP | $ | 333,469 | $ | 393,780 | $ | 385,303 | $ | 374,516 | $ | 359,226 | |||||
Less: Assets of consolidated investment management funds | 1,231 | 1,401 | 9,282 | 11,272 | 11,481 | ||||||||||
Subtotal assets of operations – Non-GAAP | 332,238 | 392,379 | 376,021 | 363,244 | 347,745 | ||||||||||
Less: Goodwill | 17,316 | 17,618 | 17,869 | 18,073 | 18,075 | ||||||||||
Intangible assets | 3,598 | 3,842 | 4,127 | 4,452 | 4,809 | ||||||||||
Cash on deposit with the Federal Reserve and other central banks (b) | 58,146 | 116,211 | 99,901 | 105,384 | 90,040 | ||||||||||
Tangible total assets of operations at period end – Non-GAAP | $ | 253,178 | $ | 254,708 | $ | 254,124 | $ | 235,335 | $ | 234,821 | |||||
BNY Mellon shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP | 11.6 | % | 9.7 | % | 9.7 | % | 10.0 | % | 10.1 | % | |||||
BNY Mellon common shareholders’ equity to total assets ratio – GAAP | 10.6 | % | 9.0 | % | 9.3 | % | 9.6 | % | 9.8 | % | |||||
BNY Mellon tangible common shareholders’ equity to tangible assets of operations ratio – Non-GAAP | 6.7 | % | 6.5 | % | 6.5 | % | 6.8 | % | 6.3 | % | |||||
Year-end common shares outstanding (in thousands) | 1,047,488 | 1,085,343 | 1,118,228 | 1,142,250 | 1,163,490 | ||||||||||
Book value per common share – GAAP | $ | 33.67 | $ | 32.69 | $ | 32.09 | $ | 31.46 | $ | 30.38 | |||||
Tangible book value per common share – Non-GAAP | $ | 16.19 | $ | 15.27 | $ | 14.70 | $ | 13.95 | $ | 12.81 | |||||
(a) | Deferred tax liabilities are based on fully phased-in Basel III rules. |
(b) | Assigned a zero percentage risk-weighting by the regulators. |
124 BNY Mellon
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
The following table presents the reconciliation of the returns on common equity and tangible common equity.
Return on common equity and tangible common equity | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2015 - 2016 (a) | |||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | |||||||||||||||||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation – GAAP | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2,494 | $ | 2,040 | $ | 2,419 | |||||||
Add: Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | 298 | 342 | 384 | ||||||||||||
Less: Tax impact of amortization of intangible assets | 81 | 89 | 104 | 122 | 137 | ||||||||||||
Adjusted net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation excluding amortization of intangible assets – Non-GAAP | 3,581 | 3,225 | 2,688 | 2,260 | 2,666 | ||||||||||||
Add: M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | 1,130 | 70 | 559 | ||||||||||||
(Recovery) impairment charge related to Sentinel | (13 | ) | 170 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Tax impact of gain on the sale of our equity investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 175 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Tax impact of the gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 142 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 104 | 12 | 16 | ||||||||||||
Net charge related to the disallowance of certain foreign tax credits | — | — | — | 593 | — | ||||||||||||
Less: Tax impact of M&I, litigation and restructuring charges | 16 | 29 | 270 | 25 | 220 | ||||||||||||
Tax impact of (recovery) impairment charge related to Sentinel | (5 | ) | 64 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our equity investment in Wing Hang | — | — | 490 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Gain on the sale of our One Wall Street building | — | — | 346 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Tax impact of charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 23 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||
Benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim | — | — | 150 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Adjusted net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation, as adjusted – Non-GAAP (b) | $ | 3,606 | $ | 3,387 | $ | 2,960 | $ | 2,907 | $ | 3,017 | |||||||
Average common shareholders’ equity | $ | 35,504 | $ | 35,564 | $ | 36,618 | $ | 34,832 | $ | 34,333 | |||||||
Less: Average goodwill | 17,497 | 17,731 | 18,063 | 17,988 | 17,967 | ||||||||||||
Average intangible assets | 3,737 | 3,992 | 4,305 | 4,619 | 4,982 | ||||||||||||
Add: Deferred tax liability – tax deductible goodwill (c) | 1,497 | 1,401 | 1,340 | 1,302 | 1,130 | ||||||||||||
Deferred tax liability – intangible assets (c) | 1,105 | 1,148 | 1,216 | 1,222 | 1,310 | ||||||||||||
Average tangible common shareholders’ equity – Non-GAAP | $ | 16,872 | $ | 16,390 | $ | 16,806 | $ | 14,749 | $ | 13,824 | |||||||
Return on common equity – GAAP | 9.6 | % | 8.6 | % | 6.8 | % | 5.9 | % | 7.0 | % | 9.1 | % | |||||
Adjusted return on common equity – Non-GAAP (b) | 10.2 | % | 9.5 | % | 8.1 | % | 8.3 | % | 8.8 | % | 9.8 | % | |||||
Return on tangible common equity – Non-GAAP | 21.2 | % | 19.7 | % | 16.0 | % | 15.3 | % | 19.3 | % | 20.4 | % | |||||
Adjusted return on tangible common equity – Non-GAAP (b) | 21.4 | % | 20.7 | % | 17.6 | % | 19.7 | % | 21.8 | % | 21.0 | % | |||||
(a) | Annualized. |
(b) | Non-GAAP information for all periods presented excludes the amortization of intangible assets and M&I, litigation and restructuring charges. Non-GAAP information for 2016 and 2015 also excludes the (recovery) impairment charge related to the Sentinel loan. Non-GAAP information for 2014 also excludes the gains on the sales of our equity investment in Wing Hang and our One Wall Street building, the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives, and benefit primarily related to a tax carryback claim. Non-GAAP information for 2013 also excludes the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives, and the net charge related to the disallowance of certain foreign tax credits. Non-GAAP information for 2012 also excludes the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives. |
(c) | Deferred tax liabilities are based on fully phased-in Basel III rules. |
BNY Mellon 125
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
The following table presents income from consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests.
Income from consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds | $ | 26 | $ | 86 | $ | 163 | $ | 183 | $ | 189 | |||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 10 | 68 | 84 | 80 | 76 | ||||||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests | $ | 16 | $ | 18 | $ | 79 | $ | 103 | $ | 113 | |||||
The following table presents the revenue line items in the Investment Management business impacted by the consolidated investment management funds.
Income from consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests - Investment Management business | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Investment management fees | $ | 11 | $ | 15 | $ | 66 | $ | 80 | $ | 81 | |||||
Other (Investment income) | 5 | 3 | 13 | 23 | 32 | ||||||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds, net of noncontrolling interests | $ | 16 | $ | 18 | $ | 79 | $ | 103 | $ | 113 | |||||
The following table presents the reconciliation of the pre-tax operating margin for the Investment Management business.
Pre-tax operating margin - Investment Management business | |||||||||
(dollars in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Income before income taxes – GAAP | $ | 967 | $ | 1,048 | $ | 892 | |||
Add: Amortization of intangible assets | 82 | 97 | 118 | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | 6 | (1 | ) | — | |||||
Charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives | — | — | 104 | ||||||
Adjusted income before income taxes excluding amortization of intangible assets, provision for credit losses and the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives – Non-GAAP | $ | 1,055 | $ | 1,144 | $ | 1,114 | |||
Total revenue – GAAP | $ | 3,751 | $ | 3,906 | $ | 3,931 | |||
Less: Distribution and servicing expense | 404 | 378 | 423 | ||||||
Adjusted total revenue net of distribution and servicing expense – Non-GAAP | $ | 3,347 | $ | 3,528 | $ | 3,508 | |||
Pre-tax operating margin – GAAP (a) | 26 | % | 27 | % | 23 | % | |||
Adjusted pre-tax operating margin, excluding amortization of intangible assets, provision for credit losses, the charge related to investment management funds, net of incentives and distribution and servicing expense – Non-GAAP (a) | 32 | % | 32 | % | 32 | % | |||
(a) | Income before taxes divided by total revenue. |
126 BNY Mellon
Supplemental Information (unaudited) (continued) |
Rate/volume analysis
Rate/volume analysis (a) | 2016 over (under) 2015 | 2015 over (under) 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
Due to change in | Due to change in | ||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions, presented on an FTE basis) | Average balance | Average rate | Net change | Average balance | Average rate | Net change | |||||||||||||
Interest revenue | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks (primarily foreign banks) | $ | (34 | ) | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | (85 | ) | $ | (49 | ) | $ | (134 | ) | |||
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | (5 | ) | 33 | 28 | (8 | ) | (29 | ) | (37 | ) | |||||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 16 | 70 | 86 | 54 | 7 | 61 | |||||||||||||
Margin loans | (19 | ) | 77 | 58 | 25 | — | 25 | ||||||||||||
Non-margin loans: | |||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices: | |||||||||||||||||||
Consumer | 41 | 1 | 42 | 21 | (3 | ) | 18 | ||||||||||||
Commercial | 40 | 31 | 71 | 49 | (31 | ) | 18 | ||||||||||||
Foreign offices | (10 | ) | 43 | 33 | 7 | (13 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||
Total non-margin loans | 71 | 75 | 146 | 77 | (47 | ) | 30 | ||||||||||||
Securities: | |||||||||||||||||||
U.S. government obligations | (13 | ) | 13 | — | 79 | (11 | ) | 68 | |||||||||||
U.S. government agency obligations | 23 | (4 | ) | 19 | 171 | 15 | 186 | ||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions - tax exempt | (28 | ) | 10 | (18 | ) | (36 | ) | 10 | (26 | ) | |||||||||
Other securities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices | (44 | ) | (48 | ) | (92 | ) | (7 | ) | 74 | 67 | |||||||||
Foreign offices | (18 | ) | 48 | 30 | 25 | (132 | ) | (107 | ) | ||||||||||
Total other securities | (62 | ) | — | (62 | ) | 18 | (58 | ) | (40 | ) | |||||||||
Trading securities (primarily domestic) | (12 | ) | (3 | ) | (15 | ) | (55 | ) | 10 | (45 | ) | ||||||||
Total securities | (92 | ) | 16 | (76 | ) | 177 | (34 | ) | 143 | ||||||||||
Total interest revenue | $ | (63 | ) | $ | 305 | $ | 242 | $ | 240 | $ | (152 | ) | $ | 88 | |||||
Interest expense | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits: | |||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices: | |||||||||||||||||||
Money market rate accounts | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 1 | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | |||
Savings | — | — | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||
Demand deposits | — | 1 | 1 | — | 2 | 2 | |||||||||||||
Time deposits | — | 12 | 12 | 1 | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | |||||||||||
Total domestic offices | — | 11 | 11 | 3 | (2 | ) | 1 | ||||||||||||
Foreign offices: | |||||||||||||||||||
Banks | (2 | ) | 4 | 2 | 19 | (40 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||||||||
Other | — | (34 | ) | (34 | ) | (2 | ) | (24 | ) | (26 | ) | ||||||||
Total foreign offices | (2 | ) | (30 | ) | (32 | ) | 17 | (64 | ) | (47 | ) | ||||||||
Total interest-bearing deposits | (2 | ) | (19 | ) | (21 | ) | 20 | (66 | ) | (46 | ) | ||||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | — | 42 | 42 | 2 | 5 | 7 | |||||||||||||
Trading liabilities | 1 | (4 | ) | (3 | ) | (21 | ) | 5 | (16 | ) | |||||||||
Other borrowed funds: | |||||||||||||||||||
Domestic offices | (2 | ) | 2 | — | — | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||
Foreign offices | 1 | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||
Total other borrowed funds | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | 4 | 3 | ||||||||||
Commercial paper | — | 3 | 3 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | 4 | 1 | 5 | 1 | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||||||
Long-term debt | 32 | 80 | 112 | 3 | (3 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
Total interest expense | $ | 34 | $ | 103 | $ | 137 | $ | 4 | $ | (58 | ) | $ | (54 | ) | |||||
Changes in net interest revenue | $ | (97 | ) | $ | 202 | $ | 105 | $ | 236 | $ | (94 | ) | $ | 142 | |||||
(a) | Changes which are solely due to balance changes or rate changes are allocated to such categories on the basis of the respective percentage changes in average balances and average rates. Changes in interest revenue or interest expense arising from the combination of rate and volume variances are allocated proportionately to rate and volume based on their relative absolute magnitudes. |
BNY Mellon 127
Selected Quarterly Data (unaudited) |
Selected Quarterly Data | Quarter ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions, except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Dec. 31 | Sept. 30 | June 30 | March 31 | Dec. 31 | Sept. 30 | June 30 | March 31 | ||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated income statement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total fee and other revenue | $ | 2,954 | $ | 3,150 | $ | 2,999 | $ | 2,970 | $ | 2,950 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 3,067 | $ | 3,012 | |||||||||
Income (loss) from consolidated investment management funds | 5 | 17 | 10 | (6 | ) | 16 | (22 | ) | 40 | 52 | |||||||||||||||
Net interest revenue | 831 | 774 | 767 | 766 | 760 | 759 | 779 | 728 | |||||||||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,790 | 3,941 | 3,776 | 3,730 | 3,726 | 3,790 | 3,886 | 3,792 | |||||||||||||||||
Provision for credit losses | 7 | (19 | ) | (9 | ) | 10 | 163 | 1 | (6 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||||||
Noninterest expense | 2,631 | 2,643 | 2,620 | 2,629 | 2,692 | 2,680 | 2,727 | 2,700 | |||||||||||||||||
Income before taxes | 1,152 | 1,317 | 1,165 | 1,091 | 871 | 1,109 | 1,165 | 1,090 | |||||||||||||||||
Provision for income taxes | 280 | 324 | 290 | 283 | 175 | 282 | 276 | 280 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income | 872 | 993 | 875 | 808 | 696 | 827 | 889 | 810 | |||||||||||||||||
Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (2 | ) | (6 | ) | (2 | ) | 9 | (3 | ) | 6 | (36 | ) | (31 | ) | |||||||||||
Net income applicable to shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | 870 | 987 | 873 | 817 | 693 | 833 | 853 | 779 | |||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock dividends | (48 | ) | (13 | ) | (48 | ) | (13 | ) | (56 | ) | (13 | ) | (23 | ) | (13 | ) | |||||||||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 822 | $ | 974 | $ | 825 | $ | 804 | $ | 637 | $ | 820 | $ | 830 | $ | 766 | |||||||||
Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.77 | $ | 0.90 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.74 | $ | 0.67 | |||||||||
Diluted earnings per common share | 0.77 | 0.90 | 0.75 | 0.73 | 0.57 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.67 | |||||||||||||||||
Average balances | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | $ | 77,119 | $ | 88,168 | $ | 112,182 | $ | 104,001 | $ | 104,181 | $ | 104,724 | $ | 102,081 | $ | 103,231 | |||||||||
Securities | 117,660 | 118,405 | 118,002 | 118,538 | 119,532 | 121,188 | 128,641 | 123,476 | |||||||||||||||||
Trading assets | 2,288 | 2,176 | 2,152 | 3,320 | 2,786 | 2,737 | 3,253 | 3,046 | |||||||||||||||||
Loans | 63,647 | 61,578 | 60,284 | 61,196 | 61,964 | 61,657 | 61,076 | 57,935 | |||||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets | 287,947 | 296,703 | 318,433 | 310,678 | 312,610 | 315,672 | 318,596 | 308,104 | |||||||||||||||||
Assets of operations | 343,138 | 350,190 | 372,974 | 363,245 | 366,875 | 371,328 | 375,999 | 366,083 | |||||||||||||||||
Total assets | 344,142 | 351,230 | 374,220 | 364,554 | 368,590 | 373,453 | 378,279 | 368,411 | |||||||||||||||||
Deposits | 227,948 | 236,728 | 249,155 | 244,961 | 246,212 | 254,799 | 255,606 | 249,112 | |||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt | 24,986 | 23,930 | 22,838 | 21,556 | 21,418 | 21,070 | 20,625 | 20,199 | |||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock | 3,542 | 3,284 | 2,552 | 2,552 | 2,552 | 2,552 | 2,313 | 1,562 | |||||||||||||||||
Total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common shareholders’ equity | 35,171 | 35,767 | 35,827 | 35,252 | 35,664 | 35,588 | 35,516 | 35,486 | |||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin (FTE) | 1.17 | % | 1.06 | % | 0.98 | % | 1.01 | % | 0.99 | % | 0.98 | % | 1.00 | % | 0.97 | % | |||||||||
Annualized return on common equity (a) | 9.3 | % | 10.8 | % | 9.3 | % | 9.2 | % | 7.1 | % | 9.1 | % | 9.4 | % | 8.8 | % | |||||||||
Pre-tax operating margin | 30 | % | 33 | % | 31 | % | 29 | % | 23 | % | 29 | % | 30 | % | 29 | % | |||||||||
Common stock data (a) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Market price per share range: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
High | $ | 49.54 | $ | 42.02 | $ | 42.61 | $ | 40.29 | $ | 44.73 | $ | 45.45 | $ | 44.10 | $ | 41.44 | |||||||||
Low | 38.68 | 36.50 | 35.44 | 32.20 | 37.48 | 36.46 | 39.87 | 35.63 | |||||||||||||||||
Average | 45.10 | 39.94 | 39.78 | 36.26 | 42.02 | 41.56 | 42.61 | 38.95 | |||||||||||||||||
Period end close | 47.38 | 39.88 | 38.85 | 36.83 | 41.22 | 39.15 | 41.97 | 40.24 | |||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends per common share | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 | |||||||||||||||||
Market capitalization (b) | 49,630 | 42,167 | 41,479 | 39,669 | 44,738 | 42,789 | 46,441 | 45,130 | |||||||||||||||||
(a) | At Dec. 31, 2016, there were 28,015 shareholders registered with our stock transfer agent, compared with 29,136 at Dec. 31, 2015 and 30,525 at Dec. 31, 2014. In addition, there were 44,542 of BNY Mellon’s current and former employees at Dec. 31, 2016 who participate in BNY Mellon’s 401(k) Retirement Savings Plan. All shares of BNY Mellon’s common stock held by the Plan for its participants are registered in the name of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation, as trustee. |
(b) | At period end. |
128 BNY Mellon
Forward-looking Statements |
Some statements in this document are forward-looking. These include all statements about the usefulness of Non-GAAP measures, the future results of BNY Mellon, our businesses, financial, liquidity and capital condition, results of operations, goals, strategies, outlook, objectives, expectations (including those regarding our performance results, regulatory, market, economic or accounting developments, legal proceedings and other contingencies), effective tax rate, estimates (including those regarding capital ratios), intentions (including those regarding our resolution strategy), targets, opportunities and initiatives.
In this report, any other report, any press release or any written or oral statement that BNY Mellon or its executives may make, words, such as “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “anticipate,” “likely,” “target,” “expect,” “intend,” “continue,” “seek,” “believe,” “plan,” “goal,” “could,” “should,” “would,” “may,” “will,” “strategy,” “synergies,” “opportunities,” “trends” and words of similar meaning, may signify forward-looking statements.
Actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied as a result of a number of factors, including those discussed in “Risk Factors,” such as: an information security event or technology disruption that results in a loss of information or impacts our ability to provide services to our clients and any material adverse effect on our business and results of operations; failure of our technology or that of a third party or vendor, or if we neglect to update our technology, develop and market new technology to meet clients’ needs or protect our intellectual property and any material adverse effect on our business; a determination that our resolution plan is not credible and any material negative impact on our business, reputation, results of operation and financial condition and the application of our Title I preferred resolution strategy or resolution under the Title II orderly liquidation authority and any adverse effects on our liquidity, financial condition and security holders; extensive government rulemaking regulation, and supervision, which have, and in the future may, compel us to change how we manage our businesses, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations and have increased our compliance and operational risks and costs; failure to satisfy regulatory standards, including “well capitalized” and “well managed” status or capital adequacy and liquidity rules, and any resulting limitations on our activities, or adverse
effects on our business and financial condition; regulatory or enforcement actions or litigation and any material adverse effect on our results of operations or harm to our businesses or reputation; adverse events, publicity, government scrutiny or other reputational harm and any negative effect on our businesses; operational risk and any material adverse effect on our business; failure or circumvention of our controls and procedures and any material adverse effect on our business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition; failure of our risk management framework to be effective in mitigating risk and reducing the potential for losses; change or uncertainty in monetary, tax and other governmental policies and the impact on our businesses, profitability and ability to compete; political, economic, legal, operational and other risks inherent in operating globally and any adverse effect on our business; acts of terrorism, natural disasters, pandemics and global conflicts and any negative impact on our business and operations; ongoing concerns about the financial stability of certain countries, the failure or instability of any of our significant global counterparties, new barriers to global trade or a breakup of the EU or Eurozone and any material adverse effect on our business and results of operations; the United Kingdom’s referendum decision to leave the EU and any negative effects on global economic conditions, global financial markets, and our business and results of operations; weakness and volatility in financial markets and the economy generally and any material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition; changes in interest rates and any material adverse effect on our profitability; write-downs of securities that we own and other losses related to volatile and illiquid market conditions and any reduction in our earnings or impact on our financial condition; our dependence on fee-based business for a substantial majority of our revenue and the adverse effects of a slowing in market activity, weak financial markets, underperformance and/or negative trends in savings rates or in investment preferences; any adverse effect on our foreign exchange revenues from decreased market volatility or cross-border investment activity of our clients; the failure or perceived weakness of any of our significant counterparties, and our assumption of credit and counterparty risk, which could expose us to loss and adversely affect our business; any material reduction in our credit ratings or the credit ratings of our principal bank subsidiaries, which could increase the cost of funding and borrowing to us and our rated
BNY Mellon 129
Forward-looking Statements (continued) |
subsidiaries and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition and on the value of the securities we issue; any adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations of not effectively managing our liquidity; the potential to incur losses if our allowance for credit losses is inadequate; the risks relating to new lines of business, new products and services or transformational or strategic project initiatives and the failure to implement these initiatives, which could affect our results of operations; the risks and uncertainties relating to our strategic transactions and any adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition; competition in all aspects of our business and any negative effect on our ability to maintain or increase our profitability; failure to attract and retain employees and any adverse effect on our business; tax law changes or challenges to our tax positions and any adverse effect on our net income, effective tax rate and overall results of operations and financial condition; changes in accounting standards and any material impact on our reported financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and other financial data; risks associated
with being a non-operating holding company, including our dependence on dividends from our subsidiaries to meet obligations, to provide funds for payment of dividends and for stock repurchases; and the impact of provisions of U.S. banking laws and regulations, including those governing capital and the approval of our capital plan, applicable provisions of Delaware law or failure to pay full and timely dividends on our preferred stock, on our ability to return capital to shareholders.
Investors should consider all risks in our 2016 Annual Report and any subsequent reports filed with the SEC by BNY Mellon pursuant to the Exchange Act. All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date on which such statements are made, and BNY Mellon undertakes no obligation to update any statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which such forward-looking statement is made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. The contents of BNY Mellon’s website or any other websites referenced herein are not part of this report.
130 BNY Mellon
Acronyms |
ABS | Asset-backed security |
APAC | Asia-Pacific region |
ASC | Accounting Standards Codification |
ASU | Accounting Standards Update |
AUC/A | Assets under custody and/or administration |
AUM | Assets under management |
BHCs | Bank holding companies |
bps | basis points |
CCAR | Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review |
CD | Certificates of deposit |
CET1 | Common Equity Tier 1 capital |
CFTC | Commodity Futures Trading Commission |
CLO | Collateralized loan obligation |
CVA | Credit valuation adjustment |
DVA | Debit valuation adjustment |
EMEA | Europe, the Middle East and Africa |
ERISA | Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 |
ESOP | Employee Stock Ownership Plan |
EVE | Economic Value of Equity |
FASB | Financial Accounting Standards Board |
FCA | Financial Conduct Authority |
FDIC | Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation |
FHC | Financial holding company |
FINRA | Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. |
FTE | Fully taxable equivalent |
GAAP | Generally accepted accounting principles |
G-SIBs | Global systemically important banks |
HQLA | High-quality liquid assets |
LIBOR | London Interbank Offered Rate |
LCR | Liquidity coverage ratio |
LTD | External long-term debt |
M&I | Merger and integration |
MBS | Mortgage-backed security |
MMF | Money market funds |
N/A | Not applicable or Not available |
NAV | Net asset value |
N/M | Not meaningful |
NSFR | Net stable funding ratio |
NYSE | New York Stock Exchange |
OCC | Office of the Comptroller of the Currency |
OCI | Other comprehensive income |
OTC | Over-the-counter |
OTTI | Other-than-temporary impairment |
PSU | Performance units |
REIT | Real estate investment trust |
RMBS | Residential mortgage-backed security |
RSU | Restricted stock units |
RWA | Risk-weighted assets |
S&P | Standard & Poor’s |
SBIC | Small Business Investment Company |
SBLC | Standby letters of credit |
SEC | Securities and Exchange Commission |
SIFIs | Systemically important financial institutions |
SLR | Supplementary Leverage Ratio |
TCE | Tangible common equity |
TDR | Troubled debt restructuring |
TLAC | Total loss-absorbing capacity |
VaR | Value-at-risk |
VIE | Variable interest entity |
VME | Voting model entity |
BNY Mellon 131
Glossary |
Accumulated benefit obligation - The actuarial present value of benefits (vested and non-vested) attributed to employee services rendered.
Alt-A securities - A mortgage risk categorization that falls between prime and subprime. Borrowers behind these mortgages will typically have clean credit histories but the mortgage itself will generally have issues that increase its risk profile.
Alternative investments - Usually refers to investments in hedge funds, leveraged loans, subordinated and distressed debt, real estate and foreign currency overlay. Examples of alternative investment strategies are: long-short equity, event-driven, statistical arbitrage, fixed income arbitrage, convertible arbitrage, short bias, global macro and equity market neutral.
Asset-backed security (“ABS”) - A financial security backed by a loan, lease or receivables against assets other than real estate and mortgage-backed securities.
Assets under custody and/or administration (“AUC/A”) - Assets that we hold directly or indirectly on behalf of clients under a safekeeping or custody arrangement or for which we provide administrative services for clients. The following types of assets under administration are not and historically have not been included in AUC/A: performance and risk analytics, transfer agency and asset aggregation services. To the extent that we provide more than one AUC/A service for a client’s assets, the value of the asset is only counted once in the total amount of AUC/A.
Assets under management (“AUM”) - Includes assets beneficially owned by our clients or customers which we hold in various capacities that are either actively or passively managed, as well as the value of hedges supporting customer liabilities. These assets and liabilities are not on our balance sheet.
CAMELS - An international bank-rating system where bank supervisory authorities rate institutions according to six factors. The six factors are Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management quality, Earnings, Liquidity and Sensitivity to Market Risk.
Collateral management - A comprehensive program designed to simplify collateralization and expedite securities transfers for buyers and sellers.
Collateralized loan obligation (“CLO”) - A debt security backed by a pool of commercial loans.
Collective trust fund - An investment fund formed from the pooling of investments by investors.
Common Equity Tier 1 capital (“CET1”) - The sum of surplus (net of treasury stock), retained earnings, accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), and common equity Tier 1 minority interest subject to certain limitations, minus certain regulatory adjustments and deductions.
Counterparty risk (default risk) - The risk that a counterparty will not pay as obligated on a contract, trade or transaction.
Credit derivatives - Contractual agreements that provide insurance against a credit event of one or more referenced credits. Such events include bankruptcy, insolvency and failure to meet payment obligations when due.
Credit risk - The risk of loss due to borrower or counterparty default.
Credit valuation adjustment (“CVA”) - The market value of counterparty credit risk on OTC derivative transactions.
Currency swaps - An agreement to exchange stipulated amounts of one currency for another currency.
Debit valuation adjustment (“DVA”) - The market value of our credit risk on OTC derivative transactions.
Depositary Receipts - A negotiable security that generally represents a non-U.S. company’s publicly traded equity.
Derivative - A contract or agreement whose value is derived from changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, prices of securities or commodities, credit worthiness for credit default swaps or financial or commodity indices.
Earnings allocated to participating securities - Amount of undistributed earnings, after payment of taxes, preferred stock dividends and the required adjustment for common stock dividends declared, that is allocated to securities that are eligible to receive a portion of the Company’s earnings.
132 BNY Mellon
Glossary (continued) |
Economic capital - The amount of capital required to absorb potential losses and reflects the probability of remaining solvent over a one-year time horizon.
Economic value of equity (“EVE”) - An aggregation of discounted future cash flows of assets and liabilities over a long-term horizon.
Eurozone - Formed by European Union Member States whose currency is the euro (€) and in which a single monetary policy is conducted under the responsibility of the Governing Council of the European Central Bank. The Eurozone currently includes Germany, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Austria, Finland, Italy, Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Greece, Estonia, Cyprus, Malta, Slovenia, Slovakia, Latvia and Lithuania.
Fiduciary risk - The risk arising from our role as trustee, executor, investment agent or guardian in accordance with governing documents, prudent person principles and applicable laws, rules and regulations.
Foreign currency options - Similar to interest rate options except they are based on foreign exchange rates. Also, see interest rate options in this glossary.
Foreign currency swaps - An agreement to exchange stipulated amounts of one currency for another currency at one or more future dates.
Foreign exchange contracts - Contracts that provide for the future receipt or delivery of foreign currency at previously agreed-upon terms.
Forward rate agreements - Contracts to exchange payments on a specified future date, based on a market change in interest rates from trade date to contract settlement date.
Fully taxable equivalent (“FTE”) - Basis for comparison of yields on assets having ordinary taxability with assets for which special tax exemptions apply. The FTE adjustment reflects an increase in the interest yield or return on a tax-exempt asset to a level that would be comparable had the asset been fully taxable.
Generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) - Accounting rules and conventions defining acceptable practices in preparing financial statements in the U.S. The FASB is the primary source of accounting rules.
Grantor Trust - A legal, passive entity through which pass-through securities are sold to investors.
Hedge fund - A fund which is allowed to use diverse strategies that are unavailable to mutual funds, including selling short, leverage, program trading, swaps, arbitrage and derivatives.
High-quality liquid assets (“HQLA”) - Unencumbered assets of the types identified in the U.S. LCR rule, which the U.S. banking agencies describe as able to be convertible into cash with little or no expected loss of value during a period of liquidity stress.
Impairment - When an asset’s market value is less than its carrying value.
Interest rate options - Contracts to modify interest rate risk in exchange for the payment of a premium when the contract is initiated. As a writer of interest rate options, we receive a premium in exchange for bearing the risk of unfavorable changes in interest rates. Conversely, as a purchaser of an option, we pay a premium for the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a financial instrument or currency at predetermined terms in the future.
Interest rate sensitivity - The exposure of net interest income to interest rate movements.
Interest rate swaps - Contracts in which a series of interest rate flows in a single currency are exchanged over a prescribed period. Interest rate swaps are the most common type of derivative contract that we use in our asset/liability management activities.
Investment grade - Represents Moody’s long-term rating of Baa3 or better; and/or a Standard & Poor’s, Fitch or DBRS long-term rating of BBB- or better; or if unrated, an equivalent rating using our internal risk ratings. Instruments that fall below these levels are considered to be non-investment grade.
Joint venture - A company or entity owned and operated by a group of companies for a specific business purpose, no one of which has a majority interest.
Leverage ratio - Tier 1 capital divided by quarterly average total assets, as defined by the regulators.
BNY Mellon 133
Glossary (continued) |
Liquidity coverage ratio (“LCR”) - A Basel III framework requirement for banks and BHCs to measure liquidity. It is designed to ensure that certain banking organizations, including BNY Mellon, maintain a minimum amount of unencumbered HQLA sufficient to withstand the net cash outflow under a hypothetical standardized acute liquidity stress scenario for a 30-day time horizon.
Litigation risk - Arises when in the ordinary course of business, we are named as defendants or made parties to legal actions.
Master netting agreement - An agreement between two counterparties that have multiple contracts with each other that provides for the net settlement of all contracts through a single payment in the event of default or termination of any one contract.
Mortgage-backed security (“MBS”) - An asset-backed security whose cash flows are backed by the principal and interest payments of a set of mortgage loans.
Net interest margin - The result of dividing net interest revenue by average interest-earning assets.
Notice of proposed rulemaking - A public notice issued by law when one of the independent agencies of the U.S. government wishes to add, remove or change a rule or regulation as part of the rulemaking process.
Operating leverage - The rate of increase (decrease) in total revenue less the rate of increase (decrease) in total noninterest expense.
Other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”) - An impairment charge taken on a security whose fair value has fallen below the carrying value on the balance sheet and its value is not expected to recover through the holding period of the security.
Performance fees - Fees received by an investment advisor based upon the fund’s performance for the period relative to various predetermined benchmarks.
Pre-tax operating margin - Income before taxes for a period divided by total revenue for that period.
Prime securities - A classification of securities collateralized by loans to borrowers who have a high-value and/or a good credit history.
Private equity/venture capital - Investment in start-up companies or those in the early processes of developing products and services with perceived, long-term growth potential.
Projected benefit obligation - The actuarial present value of all benefits accrued on employee service rendered prior to the calculation date, including allowance for future salary increases if the pension benefit is based on future compensation levels.
Rating agency - An independent agency that assesses the credit quality and likelihood of default of an issue or issuer and assigns a rating to that issue or issuer.
Real estate investment trust (“REIT”) - An investor-owned corporation, trust or association that sells shares to investors and invests in income-producing property.
Repurchase agreement (“Repo”) - An instrument used to raise short term funds whereby securities are sold with an agreement for the seller to buy back the securities at a later date.
Reputational risk - Arises when events or actions that negatively impact our reputation lead to a loss of existing clients and could make it more challenging to acquire new business.
Residential mortgage-backed security (“RMBS”) - An asset-backed security whose cash flows are backed by principal and interest payments of a set of residential mortgage loans.
Restructuring charges - Typically result from the consolidation and/or relocation of operations.
Return on assets - Net income applicable to common shareholders divided by average assets.
Return on common equity - Net income applicable to common shareholders divided by average common shareholders’ equity.
Return on tangible common equity - Net income applicable to common shareholders, excluding amortization of intangible assets, divided by average tangible common shareholders’ equity.
Securities lending transaction - A fully collateralized transaction in which the owner of a security agrees to lend the security through an agent (such as The Bank of New York Mellon) to a
134 BNY Mellon
Glossary (continued) |
borrower, usually a broker/dealer or bank, on an open, overnight or term basis, under the terms of a prearranged contract, which generally matures in less than 90 days.
Sub-custodian - A local provider (e.g., a bank) contracted to provide specific custodial-related services in a selected country or geographic area.
Subprime securities - A classification of securities collateralized by loans to borrowers who have a tarnished or limited credit history.
Supplementary Leverage Ratio (“SLR”) - An Advanced Approach banking organization’s Basel III SLR is the simple arithmetic mean of the ratio of its Tier 1 capital to total leverage exposure (which is broadly defined to capture both on- and off-balance sheet exposures).
Tangible common shareholders’ equity - Common equity less goodwill and intangible assets adjusted for deferred tax liabilities associated with non-tax deductible intangible assets and tax deductible goodwill.
Unfunded commitments - Legally binding agreements to provide a defined level of financing until a specified future date.
Value-at-risk (“VaR”) - A measure of the dollar amount of potential loss at a specified confidence level from adverse market movements in an ordinary market environment.
Variable interest entity (“VIE”) - An entity that: (1) lacks enough equity investment at risk to permit the entity to finance its activities without additional financial support from other parties; (2) has equity owners that lack the right to make significant decisions affecting the entity’s operations; and/or (3) has equity owners that do not have an obligation to absorb or the right to receive the entity’s losses or return.
BNY Mellon 135
Report of Management on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting |
Management of BNY Mellon is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for BNY Mellon, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act.
BNY Mellon’s management, including its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, has assessed the effectiveness of BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013). Based upon such assessment, management believes that, as of December 31, 2016, BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based upon those criteria.
KPMG LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited BNY Mellon’s 2016 financial statements included in this Annual Report under “Financial Statements and Notes,” has issued a report with respect to the effectiveness of BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting. This report appears on page 137.
136 BNY Mellon
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation:
We have audited The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation’s (“BNY Mellon”) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). BNY Mellon’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Report of Management on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, BNY Mellon maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheet of BNY Mellon as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, and our report dated February 28, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
New York, New York
February 28, 2017
BNY Mellon 137
Item 1. Financial Statements |
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Income Statement
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Fee and other revenue | |||||||||
Investment services fees: | |||||||||
Asset servicing | $ | 4,244 | $ | 4,187 | $ | 4,075 | |||
Clearing services | 1,404 | 1,375 | 1,335 | ||||||
Issuer services | 1,026 | 978 | 968 | ||||||
Treasury services | 547 | 555 | 564 | ||||||
Total investment services fees | 7,221 | 7,095 | 6,942 | ||||||
Investment management and performance fees | 3,350 | 3,438 | 3,492 | ||||||
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue | 701 | 768 | 570 | ||||||
Financing-related fees | 219 | 220 | 169 | ||||||
Distribution and servicing | 166 | 162 | 173 | ||||||
Investment and other income | 341 | 316 | 1,212 | ||||||
Total fee revenue | 11,998 | 11,999 | 12,558 | ||||||
Net securities gains — including other-than-temporary impairment | 79 | 82 | 92 | ||||||
Noncredit-related portion of other-than-temporary impairment (recognized in other comprehensive income) | 4 | (1 | ) | 1 | |||||
Net securities gains | 75 | 83 | 91 | ||||||
Total fee and other revenue | 12,073 | 12,082 | 12,649 | ||||||
Operations of consolidated investment management funds | |||||||||
Investment income | 35 | 115 | 503 | ||||||
Interest of investment management fund note holders | 9 | 29 | 340 | ||||||
Income from consolidated investment management funds | 26 | 86 | 163 | ||||||
Net interest revenue | |||||||||
Interest revenue | 3,575 | 3,326 | 3,234 | ||||||
Interest expense | 437 | 300 | 354 | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 3,138 | 3,026 | 2,880 | ||||||
Total revenue | 15,237 | 15,194 | 15,692 | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | (11 | ) | 160 | (48 | ) | ||||
Noninterest expense | |||||||||
Staff | 5,733 | 5,837 | 5,845 | ||||||
Professional, legal and other purchased services | 1,185 | 1,230 | 1,339 | ||||||
Software | 647 | 627 | 620 | ||||||
Net occupancy | 590 | 600 | 610 | ||||||
Distribution and servicing | 405 | 381 | 428 | ||||||
Furniture and equipment | 247 | 280 | 322 | ||||||
Sub-custodian | 245 | 270 | 286 | ||||||
Business development | 245 | 267 | 268 | ||||||
Other | 940 | 961 | 1,031 | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | 298 | ||||||
Merger and integration, litigation and restructuring charges | 49 | 85 | 1,130 | ||||||
Total noninterest expense | 10,523 | 10,799 | 12,177 | ||||||
Income | |||||||||
Income before income taxes | 4,725 | 4,235 | 3,563 | ||||||
Provision for income taxes | 1,177 | 1,013 | 912 | ||||||
Net income | 3,548 | 3,222 | 2,651 | ||||||
Net (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests (includes $(10), $(68) and $(84) related to consolidated investment management funds, respectively) | (1 | ) | (64 | ) | (84 | ) | |||
Net income applicable to shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | 3,547 | 3,158 | 2,567 | ||||||
Preferred stock dividends | (122 | ) | (105 | ) | (73 | ) | |||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2,494 | |||
138 BNY Mellon
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Income Statement (continued)
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation used for the earnings per share calculation | |||||||||
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2,494 | |||
Less: Earnings allocated to participating securities | 52 | 43 | 43 | ||||||
Net income applicable to the common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation after required adjustment for the calculation of basic and diluted earnings per common share | $ | 3,373 | $ | 3,010 | $ | 2,451 | |||
Average common shares and equivalents outstanding of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | ||||||
Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||
(in thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||
Basic | 1,066,286 | 1,104,719 | 1,129,897 | |||
Common stock equivalents | 15,672 | 17,290 | 20,037 | |||
Less: Participating securities | (9,945 | ) | (9,498 | ) | (12,454 | ) |
Diluted | 1,072,013 | 1,112,511 | 1,137,480 | |||
Anti-dilutive securities (a) | 31,695 | 28,736 | 43,735 | |||
Earnings per share applicable to the common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (b) | |||||||||
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in dollars) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Basic | $ | 3.16 | $ | 2.73 | $ | 2.17 | |||
Diluted | $ | 3.15 | $ | 2.71 | $ | 2.15 | |||
(a) | Represents stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units and participating securities outstanding but not included in the computation of diluted average common shares because their effect would be anti-dilutive. |
(b) | Basic and diluted earnings per share under the two-class method are determined on the net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation reported on the income statement less earnings allocated to participating securities. |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
BNY Mellon 139
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Comprehensive Income Statement
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Net income | $ | 3,548 | $ | 3,222 | $ | 2,651 | |||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | |||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | (850 | ) | (599 | ) | (806 | ) | |||
Unrealized (loss) gain on assets available-for-sale: | |||||||||
Unrealized (loss) gain arising during the period | (242 | ) | (363 | ) | 413 | ||||
Reclassification adjustment | (49 | ) | (52 | ) | (58 | ) | |||
Total unrealized (loss) gain on assets available-for-sale | (291 | ) | (415 | ) | 355 | ||||
Defined benefit plans: | |||||||||
Prior service cost arising during the period | — | — | 2 | ||||||
Net (loss) arising during the period | (108 | ) | (65 | ) | (479 | ) | |||
Foreign exchange adjustment | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||
Amortization of prior service credit, net loss and initial obligation included in net periodic benefit cost | 57 | 69 | 77 | ||||||
Total defined benefit plans | (51 | ) | 4 | (401 | ) | ||||
Net unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedges | (4 | ) | 8 | (15 | ) | ||||
Total other comprehensive (loss), net of tax (a) | (1,196 | ) | (1,002 | ) | (867 | ) | |||
Total comprehensive income | 2,352 | 2,220 | 1,784 | ||||||
Net (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (1 | ) | (64 | ) | (84 | ) | |||
Other comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | 31 | 36 | 125 | ||||||
Comprehensive income applicable to the shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 2,382 | $ | 2,192 | $ | 1,825 | |||
(a) | Other comprehensive (loss) attributable to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders was $(1,165) million for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016, $(966) million for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 and $(742) million for the year ended Dec. 31, 2014. |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
140 BNY Mellon
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Balance Sheet
Dec. 31, | ||||||
(dollars in millions, except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Assets | ||||||
Cash and due from: | ||||||
Banks | $ | 4,822 | $ | 6,537 | ||
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 58,041 | 113,203 | ||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | 15,086 | 15,146 | ||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 25,801 | 24,373 | ||||
Securities: | ||||||
Held-to-maturity (fair value of $40,669 and $43,204) | 40,905 | 43,312 | ||||
Available-for-sale | 73,822 | 75,867 | ||||
Total securities | 114,727 | 119,179 | ||||
Trading assets | 5,733 | 7,368 | ||||
Loans (includes $- and $422, at fair value) | 64,458 | 63,703 | ||||
Allowance for loan losses | (169 | ) | (157 | ) | ||
Net loans | 64,289 | 63,546 | ||||
Premises and equipment | 1,303 | 1,379 | ||||
Accrued interest receivable | 568 | 562 | ||||
Goodwill | 17,316 | 17,618 | ||||
Intangible assets | 3,598 | 3,842 | ||||
Other assets (includes $1,339 and $1,087, at fair value) | 20,954 | 19,626 | ||||
Subtotal assets of operations | 332,238 | 392,379 | ||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds, at fair value: | ||||||
Trading assets | 979 | 1,228 | ||||
Other assets | 252 | 173 | ||||
Subtotal assets of consolidated investment management funds, at fair value | 1,231 | 1,401 | ||||
Total assets | $ | 333,469 | $ | 393,780 | ||
Liabilities | ||||||
Deposits: | ||||||
Noninterest-bearing (principally U.S. offices) | $ | 78,342 | $ | 96,277 | ||
Interest-bearing deposits in U.S. offices | 52,049 | 51,704 | ||||
Interest-bearing deposits in Non-U.S. offices | 91,099 | 131,629 | ||||
Total deposits | 221,490 | 279,610 | ||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | 9,989 | 15,002 | ||||
Trading liabilities | 4,389 | 4,501 | ||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | 20,987 | 21,900 | ||||
Other borrowed funds | 754 | 523 | ||||
Accrued taxes and other expenses | 5,867 | 5,986 | ||||
Other liabilities (including allowance for lending-related commitments of $112 and $118, also includes $597 and $392, at fair value) | 5,635 | 5,490 | ||||
Long-term debt (includes $363 and $359, at fair value) | 24,463 | 21,547 | ||||
Subtotal liabilities of operations | 293,574 | 354,559 | ||||
Liabilities of consolidated investment management funds, at fair value: | ||||||
Trading liabilities | 282 | 229 | ||||
Other liabilities | 33 | 17 | ||||
Subtotal liabilities of consolidated investment management funds, at fair value | 315 | 246 | ||||
Total liabilities | 293,889 | 354,805 | ||||
Temporary equity | ||||||
Redeemable noncontrolling interests | 151 | 200 | ||||
Permanent equity | ||||||
Preferred stock – par value $0.01 per share; authorized 100,000,000 shares; issued 35,826 and 25,826 shares | 3,542 | 2,552 | ||||
Common stock – par value $0.01 per share; authorized 3,500,000,000 shares; issued 1,333,706,427 and 1,312,941,113 shares | 13 | 13 | ||||
Additional paid-in capital | 25,962 | 25,262 | ||||
Retained earnings | 22,621 | 19,974 | ||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax | (3,765 | ) | (2,600 | ) | ||
Less: Treasury stock of 286,218,126 and 227,598,128 common shares, at cost | (9,562 | ) | (7,164 | ) | ||
Total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders’ equity | 38,811 | 38,037 | ||||
Nonredeemable noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 618 | 738 | ||||
Total permanent equity | 39,429 | 38,775 | ||||
Total liabilities, temporary equity and permanent equity | $ | 333,469 | $ | 393,780 | ||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
BNY Mellon 141
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Operating activities | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,548 | $ | 3,222 | $ | 2,651 | |||
Net (income) attributable to noncontrolling interests | (1 | ) | (64 | ) | (84 | ) | |||
Net income applicable to shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | 3,547 | 3,158 | 2,567 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||
Provision for credit losses | (11 | ) | 160 | (48 | ) | ||||
Pension plan contributions | (108 | ) | (70 | ) | (72 | ) | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 1,502 | 1,457 | 1,292 | ||||||
Deferred tax (benefit) expense | (126 | ) | 47 | (853 | ) | ||||
Net securities (gains) | (75 | ) | (83 | ) | (91 | ) | |||
Change in trading assets and liabilities | 1,522 | (414 | ) | 2,636 | |||||
Originations of loans held-for-sale | (350 | ) | (1,106 | ) | — | ||||
Proceeds from the sales of loans originated for sale | 831 | 725 | — | ||||||
Change in accruals and other, net | (486 | ) | 253 | (947 | ) | ||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 6,246 | 4,127 | 4,484 | ||||||
Investing activities | |||||||||
Change in interest-bearing deposits with banks | (327 | ) | 4,225 | 16,010 | |||||
Change in interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 53,347 | (16,521 | ) | 7,677 | |||||
Purchases of securities held-to-maturity | (6,673 | ) | (16,060 | ) | (3,498 | ) | |||
Paydowns of securities held-to-maturity | 4,907 | 3,698 | 1,885 | ||||||
Maturities of securities held-to-maturity | 3,738 | 1,222 | 102 | ||||||
Purchases of securities available-for-sale | (27,470 | ) | (33,785 | ) | (69,101 | ) | |||
Sales of securities available-for-sale | 7,580 | 19,016 | 31,254 | ||||||
Paydowns of securities available-for-sale | 8,826 | 8,776 | 7,253 | ||||||
Maturities of securities available-for-sale | 11,347 | 14,689 | 11,012 | ||||||
Net change in loans | (1,483 | ) | (4,615 | ) | (7,904 | ) | |||
Sales of loans and other real estate | 173 | 362 | 312 | ||||||
Change in federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | (1,407 | ) | (4,071 | ) | (11,141 | ) | |||
Net change in seed capital investments | (114 | ) | 287 | (253 | ) | ||||
Purchases of premises and equipment/capitalized software | (825 | ) | (601 | ) | (791 | ) | |||
Proceeds from the sale of premises and equipment | 65 | — | 585 | ||||||
Acquisitions, net of cash | (38 | ) | (9 | ) | (28 | ) | |||
Dispositions, net of cash | 1 | 17 | 64 | ||||||
Other, net | (444 | ) | 3,583 | 4,887 | |||||
Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | 51,203 | (19,787 | ) | (11,675 | ) | ||||
Financing activities | |||||||||
Change in deposits | (54,738 | ) | 11,890 | 2,247 | |||||
Change in federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | (5,013 | ) | 3,533 | 1,821 | |||||
Change in payables to customers and broker-dealers | (911 | ) | 719 | 5,474 | |||||
Change in other borrowed funds | 225 | (394 | ) | 135 | |||||
Change in commercial paper | — | — | (96 | ) | |||||
Net proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt | 6,229 | 4,986 | 4,686 | ||||||
Repayments of long-term debt | (2,953 | ) | (3,659 | ) | (4,376 | ) | |||
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options | 438 | 326 | 370 | ||||||
Issuance of common stock | 27 | 26 | 26 | ||||||
Issuance of preferred stock | 990 | 990 | — | ||||||
Treasury stock acquired | (2,398 | ) | (2,355 | ) | (1,669 | ) | |||
Common cash dividends paid | (778 | ) | (760 | ) | (760 | ) | |||
Preferred cash dividends paid | (122 | ) | (105 | ) | (73 | ) | |||
Other, net | (46 | ) | (12 | ) | 44 | ||||
Net cash (used for) provided by financing activities | (59,050 | ) | 15,185 | 7,829 | |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (114 | ) | 42 | (128 | ) | ||||
Change in cash and due from banks | |||||||||
Change in cash and due from banks | (1,715 | ) | (433 | ) | 510 | ||||
Cash and due from banks at beginning of period | 6,537 | 6,970 | 6,460 | ||||||
Cash and due from banks at end of period | $ | 4,822 | $ | 6,537 | $ | 6,970 | |||
Supplemental disclosures | |||||||||
Interest paid | $ | 406 | $ | 295 | $ | 344 | |||
Income taxes paid | 1,010 | 1,015 | 1,363 | ||||||
Income taxes refunded | 307 | 901 | 144 | ||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
142 BNY Mellon
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders | Non- redeemable noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | Total permanent equity | Redeemable non- controlling interests/ temporary equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Preferred stock | Common stock | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax | Treasury stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 2,552 | $ | 13 | $ | 25,262 | $ | 19,974 | $ | (2,600 | ) | $ | (7,164 | ) | $ | 738 | $ | 38,775 | (a) | $ | 200 | |||||||
Shares issued to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 55 | |||||||||||||||||||
Redemption of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (102 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Other net changes in noncontrolling interests | — | — | (24 | ) | — | — | — | (130 | ) | (154 | ) | 38 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | — | — | — | 3,547 | — | — | 10 | 3,557 | (9 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive (loss) | — | — | — | — | (1,165 | ) | — | — | (1,165 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Dividends: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock at $0.72 per share | — | — | — | (778 | ) | — | — | — | (778 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock | — | — | — | (122 | ) | — | — | — | (122 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | — | — | — | — | — | (2,398 | ) | — | (2,398 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Employee benefit plans | — | — | 27 | — | — | — | — | 27 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Direct stock purchase and dividend reinvestment plan | — | — | 21 | — | — | — | — | 21 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock issued | 990 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 990 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock awards and options exercised | — | — | 676 | — | — | — | — | 676 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2016 | $ | 3,542 | $ | 13 | $ | 25,962 | $ | 22,621 | $ | (3,765 | ) | $ | (9,562 | ) | $ | 618 | $ | 39,429 | (a) | $ | 151 | |||||||
(a) | Includes total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common shareholders’ equity of $35,485 million at Dec. 31, 2015 and $35,269 million at Dec. 31, 2016. |
BNY Mellon 143
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity (continued)
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders | Non- redeemable noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | Total permanent equity | Redeemable non- controlling interests/ temporary equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Preferred stock | Common stock | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | Treasury stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 13 | $ | 24,626 | $ | 17,683 | $ | (1,634 | ) | $ | (4,809 | ) | $ | 1,033 | $ | 38,474 | (a) | $ | 229 | |||||||
Adjustment for the cumulative effect of applying ASU 2015-02 for the consolidation of a legal entity | — | — | — | — | — | — | 602 | 602 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Adjustment for the cumulative effect of applying ASU 2015-02 for the deconsolidation of a legal entity | — | — | — | — | — | — | (866 | ) | (866 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Adjusted balance at Jan. 1, 2015 | 1,562 | 13 | 24,626 | 17,683 | (1,634 | ) | (4,809 | ) | 769 | 38,210 | 229 | |||||||||||||||||
Shares issued to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 48 | |||||||||||||||||||
Redemption of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (92 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Other net changes in noncontrolling interests | — | — | (26 | ) | — | — | — | (73 | ) | (99 | ) | 29 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 3,158 | — | — | 68 | 3,226 | (4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive (loss) | — | — | — | — | (966 | ) | — | (26 | ) | (992 | ) | (10 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Dividends: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock at $0.68 per share | — | — | — | (762 | ) | — | — | — | (762 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock | — | — | — | (105 | ) | — | — | — | (105 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | — | — | — | — | — | (2,355 | ) | — | (2,355 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Employee benefit plans | — | — | 25 | — | — | — | — | 25 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Direct stock purchase and dividend reinvestment plan | — | — | 21 | — | — | — | — | 21 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock issued | 990 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 990 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock awards and options exercised | — | — | 616 | — | — | — | — | 616 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 2,552 | $ | 13 | $ | 25,262 | $ | 19,974 | $ | (2,600 | ) | $ | (7,164 | ) | $ | 738 | $ | 38,775 | (a) | $ | 200 | |||||||
(a) | Includes total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common shareholders’ equity of $35,879 million at Dec. 31, 2014 and $35,485 million at Dec. 31, 2015. |
144 BNY Mellon
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (and its subsidiaries) |
Consolidated Statement of Changes in Equity (continued)
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders | Non- redeemable noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | Total permanent equity | Redeemable non- controlling interests/ temporary equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | Preferred stock | Common stock | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | Treasury stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2013 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 13 | $ | 24,002 | $ | 15,952 | $ | (892 | ) | $ | (3,140 | ) | $ | 783 | $ | 38,280 | (a) | $ | 230 | |||||||
Shares issued to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 63 | |||||||||||||||||||
Redemption of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | — | — | (31 | ) | — | — | — | — | (31 | ) | (103 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Other net changes in noncontrolling interests | — | — | 10 | — | — | — | 277 | 287 | 53 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 2,567 | — | — | 84 | 2,651 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive (loss) | — | — | — | — | (742 | ) | — | (111 | ) | (853 | ) | (14 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Dividends: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock at $0.66 per share | — | — | — | (763 | ) | — | — | — | (763 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock | — | — | — | (73 | ) | — | — | — | (73 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | — | — | — | — | — | (1,669 | ) | — | (1,669 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued under: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Employee benefit plans | — | — | 24 | — | — | — | — | 24 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Direct stock purchase and dividend reinvestment plan | — | — | 21 | — | — | — | — | 21 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock awards and options exercised | — | — | 600 | — | — | — | — | 600 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 13 | $ | 24,626 | $ | 17,683 | $ | (1,634 | ) | $ | (4,809 | ) | $ | 1,033 | $ | 38,474 | (a) | $ | 229 | |||||||
(a) | Includes total The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common shareholders’ equity of $35,935 million at Dec. 31, 2013 and $35,879 million at Dec. 31, 2014. |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
BNY Mellon 145
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
Note 1 - Summary of significant accounting and reporting policies
Nature of operations
BNY Mellon is a global leader in providing a broad range of financial products and services in domestic and international markets. Through our two principal businesses, Investment Management and Investment Services, we serve the following major classes of customers - institutions, corporations and high net worth individuals. For institutions and corporations, we provide the following services:
• | investment management; |
• | trust and custody; |
• | foreign exchange; |
• | fund administration; |
• | global collateral services; |
• | securities lending; |
• | depositary receipts; |
• | corporate trust; |
• | global payment/cash management; |
• | banking services; and |
• | clearing services. |
For individuals, we provide mutual funds, separate accounts, wealth management and private banking services. BNY Mellon’s investment management businesses provide investment products in many asset classes and investment styles on a global basis.
Basis of presentation
The accounting and financial reporting policies of BNY Mellon, a global financial services company, conform to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and prevailing industry practices.
In the opinion of management, all adjustments necessary for a fair presentation of financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the periods presented have been made. These financial statements should be read in conjunction with BNY Mellon’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016. Certain immaterial reclassifications have been made to prior periods to place them on a basis comparable with current period presentation.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates based upon assumptions about future economic and market conditions which affect reported amounts and related disclosures in our financial statements. Although our current estimates contemplate current conditions and how we expect them to change in the future, it is reasonably possible that actual conditions could be worse than anticipated in those estimates, which could materially affect our results of operations and financial condition. Amounts subject to estimates are items such as the allowance for loan losses and lending-related commitments, the fair value of financial instruments and derivatives, other-than-temporary impairment, goodwill and other intangibles and pension accounting. Among other effects, such changes in estimates could result in future impairments of investment securities, goodwill and intangible assets and establishment of allowances for loan losses and lending-related commitments as well as changes in pension and post-retirement expense.
Change in accounting methodology
Effective Oct. 1, 2016, we changed the accounting method for the amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts on mortgage-backed securities from the prepayment method (also referred to as the retrospective method) to the contractual method, which are both acceptable methods under FASB ASC 310, Receivables. The calculation performed under the prepayment method was based on estimating principal prepayment assumptions, principally driven by interest rates, and estimating the remaining lives of securities. This method resulted in retrospective adjustments each period to reflect changes in those estimates as if the updated estimated lives had been applied since the acquisition of the securities. Under the contractual method, no assumption is made concerning prepayments. As principal prepayments occur, a portion of the unamortized premium or discount is recorded in interest revenue such that the effective yield of a security remains constant throughout the life of the security.
We have determined that the contractual method is the preferable method of accounting as it is more aligned with our approach to asset/liability management, it reduces reliance on complex
146 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
estimates and judgments, and it is consistent with the method predominantly used by our peers. The impact of this change was not considered material to prior periods and, as a result, the cumulative effect of the change of approximately $15 million was reflected as a positive adjustment to net interest revenue in the fourth quarter of 2016. We estimate that net interest revenue for 2016 would have been higher had we continued to use the prepayment method, but have not specifically quantified the impact subsequent to the effective date as the estimated amortization is also immaterial.
Parent financial statements
The Parent financial statements in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of the Parent; those of a wholly-owned financing subsidiary that functions as a financing entity for BNY Mellon and its subsidiaries; and MIPA, LLC, a single-member limited liability company, created to hold and administer corporate-owned life insurance. Financial data for the Parent, the financing subsidiary and the single-member limited liability company are combined for financial reporting purposes because of the limited function of these entities and the unconditional guarantee by BNY Mellon of their obligations.
Acquired businesses
The income statement and balance sheet include results of acquired businesses accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting pursuant to ASC 805, Business Combinations and equity investments from the dates of acquisition. Contingent purchase consideration was measured at its fair value and recorded on the purchase date. Any subsequent changes in the fair value of a contingent consideration liability is recorded through the income statement.
Equity method investments, including renewable energy investments
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of BNY Mellon and its subsidiaries. Equity investments of less than a majority but at least 20% ownership are accounted for by the equity method and classified as other assets. Earnings on these investments are reflected in fee and other revenue as investment services fees, investment management and performance fees or investment and other income, as appropriate, in the period earned.
A loss in value of an equity investment that is determined to be other-than-temporary, is recognized by reducing the carrying value of the equity investment down to its fair value.
Renewable energy investment projects through limited liability companies are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. The hypothetical liquidation at book value (“HLBV”) methodology is used to determine the loss that is recognized in each quarter. HLBV estimates the liquidation value at the beginning and end of each quarter, with the difference recognized as the amount of loss under the equity method.
The pre-tax losses are reported in investment and other income section of the income statement. The corresponding tax benefits and credits are recorded as a reduction to provision for income taxes on the income statement. The pre-tax losses, tax benefits and credits are included in our projected annual effective tax rate.
See Note 6 for the amount of our renewable energy investments. Below are our most significant equity method investments, other than the investments in renewable energy.
Equity method investments at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||
(dollars in millions) | Percentage ownership | Book value | |||||
CIBC Mellon | 50.0 | % | $ | 509 | |||
Siguler Guff | 20.0 | % | $ | 256 | |||
ConvergEx | 33.9 | % | $ | 76 | (a) | ||
(a) | In addition to the common ownership interest noted, BNY Mellon also holds an interest in ConvergEx nonvoting Series B preferred units. The book value at Dec. 31, 2016 is reflective of our combined common and preferred interests in ConvergEx. |
Variable interest and voting model entities
We evaluate an entity for possible consolidation in accordance with ASC 810, Consolidation and ASU 2015-02, Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis, which we adopted effective Jan. 1, 2015. We first determine whether or not we have variable interests in the entity, which are investments or other interests that absorb portions of an entity’s expected losses or receive portions of the entity’s expected returns. Our variable interests may include decision-maker or service provider fees, direct and indirect investments and investments made by related parties, including
BNY Mellon 147
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
related parties under common control. If it is determined that we do not have a variable interest in the entity, no further analysis is required and the entity is not consolidated.
If we hold a variable interest in the entity, further analysis is performed to determine if the entity is a VIE or a voting model entity (“VME”).
We consider the underlying facts and circumstances of individual entities when assessing whether or not an entity is a VIE. An entity is determined to be a VIE if the equity investors:
• | do not have sufficient equity at risk for the entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support; or |
• | lack one or more of the following characteristics of a controlling financial interest: |
• | the power, through voting rights or similar rights, to direct the activities of an entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance; |
• | the obligation to absorb the expected losses of the entity; and |
• | the right to receive the expected residual returns of the entity. |
We consolidate a VIE if it is determined that we have a controlling financial interest in the entity. We have a controlling financial interest in a VIE when we have both 1) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance and 2) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits of the VIE that could potentially be significant to that VIE.
For entities that do not meet the definition of a VIE, the entity is considered a VME. We consolidate these entities if we can exert control over the financial and operating policies of an investee, which can occur if we have a 50% or more voting interest in the entity.
Trading securities, available-for-sale securities, and held-to-maturity securities
Securities are accounted for under ASC 320, Investments - Debt and Equity Securities. Securities are classified as trading, available-for-sale or held-to-maturity investment securities when they are purchased. Securities are classified as trading
securities when our intention is to resell the securities. Securities are classified as available-for-sale securities when we intend to hold the securities for an indefinite period of time or when the securities may be used for tactical asset/liability purposes and may be sold from time to time to effectively manage interest rate exposure, prepayment risk and liquidity needs. Securities are classified as held-to-maturity securities when we intend to hold them until maturity.
Trading securities are measured at fair value and included in trading assets on the balance sheet. Trading revenue includes both realized and unrealized gains and losses. The liability incurred on short-sale transactions, representing the obligation to deliver securities, is included in trading liabilities at fair value.
Available-for-sale securities are measured at fair value. The difference between fair value and amortized cost representing unrealized gains or losses on assets classified as available-for-sale, are recorded net of tax as an addition to or deduction from OCI, unless a security is deemed to have OTTI. Gains and losses on sales of available-for-sale securities are reported in the income statement. The cost of debt and equity securities sold is determined on a specific identification and average cost method, respectively. Held-to-maturity securities are measured at amortized cost.
Income on investment securities purchased is adjusted for amortization of premium and accretion of discount on a level yield basis.
We routinely conduct periodic reviews to identify and evaluate each investment security to determine whether OTTI has occurred. We examine various factors when determining whether an impairment, representing the fair value of a security being below its amortized cost, is other than temporary. The following are examples of factors that we consider:
• | The length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than the amortized cost basis; |
• | Whether management has an intent to sell the security; |
• | Whether the decline in fair value is attributable to specific adverse conditions affecting a particular investment; |
148 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
• | Whether the decline in fair value is attributable to specific conditions, such as conditions in an industry or in a geographic area; |
• | Whether a debt security has been downgraded by a rating agency; |
• | Whether a debt security exhibits cash flow deterioration; and |
• | For each non-agency RMBS, we compare the remaining credit enhancement that protects the individual security from losses against the projected losses of principal and/or interest expected to come from the underlying mortgage collateral, to determine whether such credit losses might directly impact the relevant security. |
When we do not intend to sell the security and it is more likely than not that we will not be required to sell the security prior to recovery of its cost basis, the credit component of an OTTI of a debt security is recognized in earnings and the non-credit component is recognized in OCI.
The determination of whether a credit loss exists is based on the best estimate of the present value of cash flows to be collected from the debt security. Generally, cash flows are discounted at the effective interest rate implicit in the debt security at the time of acquisition. For debt securities that are beneficial interests in securitized financial assets and are not high credit quality, ASC 325, Investments - Other, provides that cash flows be discounted at the current yield used to accrete the beneficial interest.
If we intend to sell the security or it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the security prior to recovery of its cost basis, the non-credit component of OTTI is recognized in earnings and subsequently accreted to interest income on an effective yield basis over the life of the security.
For held-to-maturity debt securities, the amount of OTTI recorded in OCI for the non-credit portion of a previous OTTI is amortized prospectively, as an increase to the carrying amount of the security, over the remaining life of the security on the basis of the timing of future estimated cash flows of the securities.
The accounting policies for the determination of the fair value of financial instruments and OTTI have been identified as “critical accounting estimates” as they require us to make numerous assumptions based
on available market data. See Note 3 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for these disclosures.
Loans and leases
Loans are reported net of any unearned income and deferred fees and costs. Certain loan origination and upfront commitment fees, as well as certain direct loan origination and commitment costs, are deferred and amortized as a yield adjustment over the lives of the related loans. Loans held for sale are carried at the lower of cost or fair value.
Unearned revenue on direct financing leases is accreted over the lives of the leases in decreasing amounts to provide a constant rate of return on the net investment in the leases. Revenue on leveraged leases is recognized on a basis to achieve a constant yield on the outstanding investment in the lease, net of the related deferred tax liability, in the years in which the net investment is positive. Gains and losses on residual values of leased equipment sold are included in investment and other income. Considering the nature of these leases and the number of significant assumptions, there is risk associated with the income recognition on these leases should any of the assumptions change materially in future periods.
A modified loan is considered a TDR if the debtor is experiencing financial difficulties and the creditor grants a concession to the debtor that would not otherwise be considered. A TDR may include a transfer of real estate or other assets from the debtor to the creditor, or a modification of the term of the loan. TDRs are accounted for as impaired loans (see the Nonperforming assets policy).
Nonperforming assets
Commercial loans are placed on nonaccrual status when principal or interest is past due 90 days or more, or when there is reasonable doubt that interest or principal will be collected.
When a first lien residential mortgage loan reaches 90 days delinquent, it is subject to an impairment test and may be placed on nonaccrual status. At 180 days delinquent, the loan is subject to further impairment testing. The loan will remain on accrual status if the realizable value of the collateral exceeds the unpaid principal balance plus accrued interest. If the loan is
BNY Mellon 149
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
impaired, a charge-off is taken and the loan is placed on nonaccrual status. At 270 days delinquent, all first lien mortgages are placed on nonaccrual status. Second lien mortgages are automatically placed on nonaccrual status when they reach 90 days delinquent.
When a loan is placed on nonaccrual status, previously accrued and uncollected interest is reversed against current period interest revenue. Interest receipts on nonaccrual and impaired loans are recognized as interest revenue or are applied to principal when we believe the ultimate collectability of principal is in doubt. Nonaccrual loans generally are restored to an accrual basis when principal and interest become current and remain current for a specified period.
A loan is considered to be impaired when it is probable that we will be unable to collect all principal and interest amounts due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement. An impairment allowance on loans $1 million or greater is required to be measured based upon the loan’s market price, the present value of expected future cash flows, discounted at the loan’s initial effective interest rate, or at fair value of the collateral if the loan is collateral dependent. If the loan valuation is less than the recorded value of the loan, an impairment allowance is established by a provision for credit loss. Impairment allowances are not needed when the recorded investment in an impaired loan is less than the loan valuation.
Allowance for loan losses and allowance for lending-related commitments
The allowance for loan losses, shown as a valuation allowance to loans, and the allowance for lending-related commitments recorded in other liabilities are referred to as BNY Mellon’s allowance for credit losses. The accounting policy for the determination of the adequacy of the allowances has been identified as a “critical accounting estimate” as it requires us to make numerous complex and subjective estimates and assumptions relating to amounts which are inherently uncertain.
The allowance for loan losses is maintained to absorb losses inherent in the loan portfolio as of the balance sheet date based on our judgment. The allowance determination methodology is designed to provide procedural discipline in assessing the appropriateness
of the allowance. Credit losses are charged against the allowance. Recoveries are added to the allowance.
The methodology for determining the allowance for lending-related commitments considers the same factors as the allowance for loan losses, as well as an estimate of the probability of drawdown. We utilize a quantitative methodology and qualitative framework for determining the allowance for loan losses and the allowance for lending-related commitments. Within this qualitative framework, management applies judgment when assessing internal risk factors and environmental factors to compute an additional allowance for each component of the loan portfolio.
The three elements of the allowance for loan losses and the allowance for lending-related commitments include the qualitative allowance framework. The three elements are:
• | an allowance for impaired credits of $1 million or greater; |
• | an allowance for higher risk-rated credits and pass-rated credits; and |
• | an allowance for residential mortgage loans. |
Our lending is primarily to institutional customers. As a result, our loans are generally larger than $1 million. Therefore, the first element, impaired credits, is based on individual analysis of all impaired loans of $1 million and greater. The allowance is measured by the difference between the recorded value of impaired loans and their impaired value. Impaired value is either the present value of the expected future cash flows from the borrower, the market value of the loan, or the fair value of the collateral, if the loan is collateral dependent.
The second element, higher risk-rated credits and pass-rated credits, is based on our incurred loss model. Individual credit analyses are performed on such loans before being assigned a credit rating. All borrowers are collectively evaluated based on their credit rating. The loss inherent in each loan incorporates the borrower’s credit rating, facility rating and maturity. The loss given default, derived from the facility rating, incorporates a recovery expectation and an estimate of the use of the facility at default (usage given default). The borrower’s probability of default is derived from the associated credit rating. Borrower ratings are reviewed at least annually and are periodically mapped to third-party
150 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
databases, including rating agency and default and recovery databases, to ensure ongoing consistency and validity. Higher risk-rated credits are reviewed quarterly.
The third element, the allowance for residential mortgage loans, is determined by segregating six mortgage pools into delinquency periods ranging from current through foreclosure. Each of these delinquency periods is assigned a probability of default. A specific loss given default is assigned for each mortgage pool. BNY Mellon assigns all residential mortgage pools, except home equity lines of credit, a probability of default and loss given default based on default and loss data derived from internal historical data related to our residential mortgage portfolio. The resulting incurred loss factor (the probability of default multiplied by the loss given default) is applied against the loan balance to determine the allowance held for each pool. For home equity lines of credit, probability of default and loss given default are based on external data from third-party databases due to the small size of the portfolio and insufficient internal data.
The qualitative framework is used to determine an additional allowance for each portfolio based on the factors below:
Internal risk factors:
• | Nonperforming loans to total non-margin loans; |
• | Criticized assets to total loans and lending-related commitments; |
• | Borrower concentration; and |
• | Significant concentrations in high risk industries and countries. |
Environmental risk factors:
• | U.S. non-investment grade default rate; |
• | Unemployment rate; and |
• | Change in real gross domestic product. |
The objective of the qualitative framework is to capture incurred losses that may not have been fully captured in the quantitative reserve, which is based primarily on historical data. Management determines the qualitative allowance each period based on judgment informed by consideration of internal and external risk factors and other considerations that may be deemed relevant during the period. Once determined in the aggregate, our qualitative allowance is then allocated to each of our loan classes
based on the respective classes’ quantitative allowance balances with the allocations adjusted, when necessary, for class specific risk factors.
For each risk factor, we calculate the minimum and maximum values, and percentiles in-between, to evaluate the distribution of our historical experience. The distribution of historical experience is compared to the risk factor’s current quarter observed experience to assess the current risk inherent in the portfolio and overall direction/trend of a risk factor relative to our historical experience.
Based on this analysis, we assign a risk level - no impact, low, moderate, high and elevated - to each risk factor for the current quarter. Management assesses the impact of each risk factor to determine an aggregate risk level. We do not quantify the impact of any particular risk factor. Management’s assessment of the risk factors, as well as the trend in the quantitative allowance, supports management’s judgment for the overall required qualitative allowance. A smaller qualitative allowance may be required when our quantitative allowance has reflected incurred losses associated with the aggregate risk level. A greater qualitative allowance may be required if our quantitative allowance does not yet reflect the incurred losses associated with the aggregate risk level.
The allocation of the allowance for credit losses is inherently judgmental, and the entire allowance for credit losses is available to absorb credit losses regardless of the nature of the loss.
Premises and equipment
Premises and equipment are carried at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the owned asset and, for leasehold improvements, over the lesser of the remaining term of the leased facility or the estimated economic life of the improvement. For owned and capitalized assets, estimated useful lives range from 2 to 40 years. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred, while major improvements are capitalized and amortized to operating expense over their identified useful lives.
BNY Mellon 151
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Software
BNY Mellon capitalizes costs relating to acquired software and internal-use software development projects that provide new or significantly improved functionality. We capitalize projects that are expected to result in longer-term operational benefits, such as replacement systems or new applications that result in significantly increased operational efficiencies or functionality. All other costs incurred in connection with an internal-use software project are expensed as incurred. Capitalized software is recorded in other assets.
Identified intangible assets and goodwill
Identified intangible assets with estimable lives are amortized in a pattern consistent with the assets’ identifiable cash flows or using a straight-line method over their remaining estimated benefit periods if the pattern of cash flows is not estimable. Intangible assets with estimable lives are reviewed for possible impairment when events or changed circumstances may affect the underlying basis of the asset. Goodwill and intangibles with indefinite lives are not amortized, but are assessed annually for impairment, or more often if events and circumstances indicate it is more likely than not they may be impaired. The accounting policy for valuing and impairment testing of identified intangible assets and goodwill has been identified as a “critical accounting estimate” as it requires us to make numerous complex and subjective estimates. See Note 5 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional disclosures related to goodwill and intangible assets.
Investments in qualified affordable housing projects
Investments in qualified affordable housing projects through a limited liability entity are accounted for utilizing the proportional amortization method. Under the proportional amortization method, the initial cost of the investment is amortized to the provision for income taxes in proportion to the tax credits and other tax benefits received. The net investment performance, including tax credits and other benefits received, is recognized in the income statement as a component of income tax expense. Additionally, the value of the commitments to fund qualified affordable housing projects is included in other assets on the balance sheet and a liability is recorded for the unfunded portion.
Seed capital
Seed capital investments are generally classified as other assets and carried at fair value. Unrealized gains and losses on seed capital investments are recorded in investment and other income. Certain risk retention investments in our CLOs are classified as available-for-sale securities. Any unrealized gains and losses are recorded net of tax, as an addition to or deduction from, other comprehensive income, unless the investment is deemed to have OTTI.
Noncontrolling interests
Noncontrolling interests included in permanent equity are adjusted for the income or (loss) attributable to the noncontrolling interest holders and any distributions to those shareholders. Redeemable noncontrolling interests are reported as temporary equity. BNY Mellon recognizes changes in the redemption value of the redeemable noncontrolling interests as they occur and adjusts the carrying value to be equal to the redemption value.
Fee revenue
We record investment services fees, investment management fees, foreign exchange and other trading revenue, financing-related fees, distribution and servicing, and other revenue when the services are provided and earned based on contractual terms, when amounts are determined and collectability is reasonably assured.
Additionally, we recognize revenue from non-refundable, upfront implementation fees under outsourcing contracts using a straight-line method, commencing in the period the ongoing services are performed through the expected term of the contractual relationship. Incremental direct set-up costs of implementation, up to the related implementation fee or minimum fee revenue amount, are deferred and amortized over the same period that the related implementation fees are recognized. If a client terminates an outsourcing contract prematurely, the unamortized deferred incremental direct set-up costs and the unamortized deferred up-front implementation fees related to that contract are recognized in the period the contract is terminated.
Performance fees are recognized in the period in which the performance fees are earned and become determinable. Performance fees are generally
152 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
calculated as a percentage of the applicable portfolio’s performance in excess of a benchmark index or a peer group’s performance. When a portfolio underperforms its benchmark or fails to generate positive performance, subsequent years’ performance must generally exceed this shortfall prior to fees being earned. Amounts billable, which are subject to a clawback if future performance thresholds in current or future years are not met, are not recognized since the fees are potentially uncollectible. These fees are recognized when it is determined that they will be collected. When a multi-year performance contract provides that fees earned are billed ratably over the performance period, only the portion of the fees earned that are non-refundable are recognized.
Net interest revenue
Revenue on interest-earning assets and expense on interest-bearing liabilities are recognized based on the effective yield of the related financial instrument. The amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts are included in interest revenue and are adjusted for prepayments when they occur. Negative interest incurred on assets or charged on liabilities is presented as contra interest income and contra expense, respectively.
Foreign currency translation
Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated to U.S. dollars at the rate of exchange on the balance sheet date. Transaction gains and losses are included in the income statement. Translation gains and losses on investments in foreign entities with functional currencies that are not the U.S. dollar are recorded as foreign currency translation adjustments in OCI. Revenue and expense transactions are translated at the applicable daily rate or the weighted average monthly exchange rate when applying the daily rate is not practical.
Pension
The measurement date for BNY Mellon’s pension plans is Dec. 31. Plan assets are determined based on fair value generally representing observable market prices. The projected benefit obligation is determined based on the present value of projected benefit distributions at an assumed discount rate. The discount rate utilized is based on the yield curves of high-quality corporate bonds available in the
marketplace. The net periodic pension expense or credit includes service costs (if applicable), interest costs based on an assumed discount rate, an expected return on plan assets based on an actuarially derived market-related value, amortization of prior service cost and amortization of prior years’ actuarial gains and losses.
Actuarial gains and losses include gains or losses related to changes in the amount of the projected benefit obligation or plan assets resulting from demographic or investment experience different than assumed, changes in the discount rate or other assumptions. To the extent an actuarial gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the projected benefit obligation or the market-related value of plan assets, the excess is generally recognized over the future service periods of active employees. Effective June 30, 2015, benefit accruals under the U.S. pension plans were frozen. Future unrecognized actuarial gains and losses for the U.S. plans that exceed a threshold amount are amortized over the average future life expectancy of plan participants with a maximum of 15 years.
Our expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is based on anticipated returns for each applicable asset class. Anticipated returns are weighted for the expected allocation for each asset class and are based on forecasts for prospective returns in the equity and fixed income markets, which should track the long-term historical returns for these markets. We also consider the growth outlook for U.S. and global economies, as well as current and prospective interest rates.
The market-related value utilized to determine the expected return on plan assets is based on the fair value of plan assets adjusted for the difference between expected returns and actual performance of plan assets. The difference between actual experience and expected returns on plan assets is included as an adjustment in the market-related value over a five-year period.
BNY Mellon’s accounting policy regarding pensions has been identified as a “critical accounting estimate” as it requires management to make numerous complex and subjective assumptions relating to amounts which are inherently uncertain. See Note 16 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional disclosures related to pensions.
BNY Mellon 153
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Severance
BNY Mellon provides separation benefits for U.S.-based employees through The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation Supplemental Unemployment Benefit Plan. These benefits are provided to eligible employees separated from their jobs for business reasons not related to individual performance. Basic separation benefits are generally based on the employee’s years of continuous benefited service. Severance for employees based outside of the U.S. is determined in accordance with local agreements and legal requirements. Severance expense is recorded when management commits to an action that will result in separation and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated.
Income taxes
We record current tax liabilities or assets through charges or credits to the current tax provision for the estimated taxes payable or refundable for the current year. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recorded for future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. A deferred tax valuation allowance is established if it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. A tax position that fails to meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold will result in either reduction of current or deferred tax assets, and/or recording of current or deferred tax liabilities. Interest and penalties related to income taxes are recorded as income tax expense.
Derivative financial instruments
Derivative contracts, such as futures contracts, forwards, interest rate swaps, foreign currency swaps and options and similar products used in trading activities are recorded at fair value. Gains and losses are included in foreign exchange and other trading revenue. Unrealized gains are recognized as trading assets and unrealized losses are recognized as trading liabilities, after taking into consideration master netting agreements.
We enter into various derivative financial instruments for non-trading purposes primarily as part of our
asset/liability management process. These derivatives are designated as either fair value or cash flow hedges of certain assets and liabilities when we enter into the derivative contracts. Gains and losses associated with fair value hedges are recorded in income as well as any change in the value of the related hedged item associated with the designated risks being hedged. Gains and losses on cash flow hedges are recorded in OCI, until reclassified into earnings in the same period the hedged item impacts earnings. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses related to a hedged net investment in a foreign operation, net of their tax effect, are recorded with cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments within OCI.
We formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk-management objectives and strategy for undertaking various hedging transactions.
We formally assess, both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis, whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly effective and whether those derivatives are expected to remain highly effective in future periods. At inception, the potential causes of ineffectiveness related to each of our hedges is assessed to determine if we can expect the hedge to be highly effective over the life of the transaction and to determine the method for evaluating effectiveness on an ongoing basis.
Recognizing that changes in the value of derivatives used for hedging or the value of hedged items could result in significant ineffectiveness, we have processes in place that are designed to identify and evaluate such changes when they occur. Quarterly, we perform a quantitative effectiveness assessment and record any ineffectiveness in current earnings.
We discontinue hedge accounting prospectively when we determine that a derivative is no longer an effective hedge or the derivative expires, is sold, or management discontinues the derivative’s hedge designation. Subsequent gains and losses on these derivatives are included in foreign exchange and other trading revenue. For discontinued fair value hedges, the accumulated gain or loss on the hedged item is amortized on a yield basis over the remaining life of the hedged item. Accumulated gains and losses, net of tax effect, from discontinued cash flow hedges are reclassified from OCI and recognized in
154 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
current earnings in foreign exchange and other trading revenue as the hedged item impacts earnings.
The accounting policy for the determination of the fair value of derivative financial instruments has been identified as a “critical accounting estimate” as it requires us to make numerous assumptions based on the available market data. See Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional disclosures related to derivative financial instruments.
Statement of cash flows
We have defined cash as cash and due from banks. Cash flows from hedging activities are classified in the same category as the items hedged.
Stock-based compensation
Compensation expense relating to share-based payments is recognized in the income statement, on a straight-line basis, over the applicable vesting period.
Certain of our stock compensation grants vest when the employee retires. New grants with this feature are expensed by the first date the employee is eligible to retire.
Note 2 - Acquisitions and dispositions
We sometimes structure our acquisitions with both an initial payment and later contingent payments tied to post-closing revenue or income growth. Contingent payments totaled $4 million in 2016.
At Dec. 31, 2016, we are potentially obligated to pay additional consideration which, using reasonable assumptions, could range from $0 million to $18 million over the next three years, but could be higher as certain of the arrangements do not contain a contractual maximum. The acquisitions and disposition described below did not have a material impact on BNY Mellon’s results of operations.
Acquisition in 2016
On April 1, 2016, BNY Mellon acquired the assets of Atherton Lane Advisers, LLC, a U.S.-based investment manager with approximately $2.45 billion in AUM and servicer for approximately 700 high net
worth clients, for cash of $38 million, plus contingent payments measured at $22 million. Goodwill related to this acquisition totaled $29 million and is included in the Investment Management business. The customer relationship intangible assets related to this acquisition is included in the Investment Management business, with an estimated life of 14 years, and totaled $30 million at acquisition.
Acquisition in 2015
On Jan. 2, 2015, BNY Mellon acquired Cutwater Asset Management, a U.S.-based, fixed income and solutions specialist with approximately $23 billion in AUM.
Disposition in 2015
On July 31, 2015, BNY Mellon sold Meriten Investment Management GmbH, a German-based investment management boutique, for $40 million. As a result of this sale, we recorded an after-tax loss of $12 million. Goodwill of $22 million and customer relationship intangible assets of $9 million were removed from the balance sheet as a result of this sale.
Acquisitions in 2014
On May 1, 2014, BNY Mellon acquired the remaining 65% interest of HedgeMark International, LLC for $26 million. Since 2011, BNY Mellon held a 35% ownership stake in HedgeMark. Goodwill related to this acquisition totaled $47 million and is included in the Investment Services business. The customer relationship intangible asset related to this acquisition is included in our Investment Services business and totaled $1 million at acquisition.
Dispositions in 2014
On April 23, 2014, BNY Mellon sold the subsidiary that conducted corporate trust business in Mexico that was part of our Investment Services business, for $65 million. As a result of this sale, we recorded an after-tax gain of $4 million. In addition, goodwill of $8 million and customer relationship intangible assets of $1 million were removed from the balance sheet as a result of this sale.
BNY Mellon 155
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Note 3 - Securities
The following tables present the amortized cost, the gross unrealized gains and losses and the fair value of securities at Dec. 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Securities at Dec. 31, 2016 | Gross unrealized | |||||||||||
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Gains | Losses | ||||||||||
Available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 14,373 | $ | 115 | $ | 181 | $ | 14,307 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 366 | 2 | 9 | 359 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 3,392 | 38 | 52 | 3,378 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 22,929 | 148 | 341 | 22,736 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 620 | 31 | 13 | 638 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 517 | 4 | 8 | 513 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 931 | 8 | 11 | 928 | ||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 6,505 | 28 | 84 | 6,449 | ||||||||
CLOs | 2,593 | 6 | 1 | 2,598 | ||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | 1,729 | 4 | 6 | 1,727 | ||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 2,126 | 24 | 9 | 2,141 | ||||||||
Corporate bonds | 1,391 | 22 | 17 | 1,396 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 12,248 | 261 | 20 | 12,489 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 1,952 | 19 | 10 | 1,961 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 2 | 1 | — | 3 | ||||||||
Money market funds | 842 | — | — | 842 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (a) | 1,080 | 286 | 9 | 1,357 | ||||||||
Total securities available-for-sale (b) | $ | 73,596 | $ | 997 | $ | 771 | $ | 73,822 | ||||
Held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 11,117 | $ | 22 | $ | 41 | $ | 11,098 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 1,589 | — | 6 | 1,583 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 19 | — | 1 | 18 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 25,221 | 57 | 299 | 24,979 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 78 | 4 | 2 | 80 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 142 | — | 4 | 138 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 7 | — | — | 7 | ||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 721 | 1 | 10 | 712 | ||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 74 | 1 | — | 75 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 1,911 | 42 | — | 1,953 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 26 | — | — | 26 | ||||||||
Total securities held-to-maturity | $ | 40,905 | $ | 127 | $ | 363 | $ | 40,669 | ||||
Total securities | $ | 114,501 | $ | 1,124 | $ | 1,134 | $ | 114,491 | ||||
(a) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(b) | Includes gross unrealized gains of $62 million and gross unrealized losses of $190 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income related to investment securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized gains and losses are primarily related to Agency RMBS and will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. |
Securities at Dec. 31, 2015 | Gross unrealized | |||||||||||
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Gains | Losses | ||||||||||
Available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 12,693 | $ | 175 | $ | 36 | $ | 12,832 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 386 | 2 | 1 | 387 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 3,968 | 91 | 13 | 4,046 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 23,549 | 239 | 287 | 23,501 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 782 | 31 | 20 | 793 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 1,072 | 10 | 21 | 1,061 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 1,400 | 8 | 16 | 1,392 | ||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 4,031 | 24 | 35 | 4,020 | ||||||||
CLOs | 2,363 | 1 | 13 | 2,351 | ||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | 2,909 | 1 | 17 | 2,893 | ||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 2,125 | 46 | 3 | 2,168 | ||||||||
Corporate bonds | 1,740 | 26 | 14 | 1,752 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 13,036 | 211 | 30 | 13,217 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 2,732 | 46 | 3 | 2,775 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 3 | 1 | — | 4 | ||||||||
Money market funds | 886 | — | — | 886 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (a) | 1,435 | 362 | 8 | 1,789 | ||||||||
Total securities available-for-sale (b) | $ | 75,110 | $ | 1,274 | $ | 517 | $ | 75,867 | ||||
Held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 11,326 | $ | 25 | $ | 51 | $ | 11,300 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 1,431 | — | 6 | 1,425 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 20 | — | 1 | 19 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 26,036 | 134 | 205 | 25,965 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 118 | 5 | 2 | 121 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 224 | 1 | 10 | 215 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 9 | — | — | 9 | ||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 503 | — | 9 | 494 | ||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 76 | — | — | 76 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 3,538 | 22 | 11 | 3,549 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 31 | — | — | 31 | ||||||||
Total securities held-to-maturity | $ | 43,312 | $ | 187 | $ | 295 | $ | 43,204 | ||||
Total securities | $ | 118,422 | $ | 1,461 | $ | 812 | $ | 119,071 | ||||
(a) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(b) | Includes gross unrealized gains of $84 million and gross unrealized losses of $248 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income related to investment securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized gains and losses are primarily related to Agency RMBS and will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. |
156 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Securities at Dec. 31, 2014 | Gross unrealized | |||||||||||
Amortized cost | Fair value | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Gains | Losses | ||||||||||
Available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 19,592 | $ | 420 | $ | 15 | $ | 19,997 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 342 | 3 | 2 | 343 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 5,176 | 95 | 24 | 5,247 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 32,568 | 357 | 325 | 32,600 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 942 | 37 | 26 | 953 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 1,551 | 25 | 25 | 1,551 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 1,927 | 39 | 7 | 1,959 | ||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 3,105 | 36 | 9 | 3,132 | ||||||||
CLOs | 2,128 | 9 | 7 | 2,130 | ||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | 3,241 | 5 | 6 | 3,240 | ||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 2,788 | 80 | — | 2,868 | ||||||||
Corporate bonds | 1,747 | 45 | 7 | 1,785 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 17,062 | 224 | 2 | 17,284 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 2,162 | 7 | — | 2,169 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 94 | 1 | — | 95 | ||||||||
Money market funds | 763 | — | — | 763 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (a) | 1,747 | 471 | 4 | 2,214 | ||||||||
Total securities available-for-sale (b) | $ | 96,935 | $ | 1,854 | $ | 459 | $ | 98,330 | ||||
Held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 5,047 | $ | 32 | $ | 16 | $ | 5,063 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 344 | — | 3 | 341 | ||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 24 | 1 | 1 | 24 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 14,006 | 200 | 44 | 14,162 | ||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 153 | 9 | 2 | 160 | ||||||||
Other RMBS | 315 | 2 | 8 | 309 | ||||||||
Commercial MBS | 13 | — | — | 13 | ||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 1,031 | 24 | — | 1,055 | ||||||||
Total securities held-to-maturity | $ | 20,933 | $ | 268 | $ | 74 | $ | 21,127 | ||||
Total securities | $ | 117,868 | $ | 2,122 | $ | 533 | $ | 119,457 | ||||
(a) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(b) | Includes gross unrealized gains of $60 million and gross unrealized losses of $282 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income related to investment securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized gains and losses are primarily related to Agency RMBS and will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. |
The following table presents the gross securities gains, losses and impairments.
Net securities gains (losses) | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Realized gross gains | $ | 86 | $ | 90 | $ | 114 | |||
Realized gross losses | (4 | ) | (2 | ) | (4 | ) | |||
Recognized gross impairments | (7 | ) | (5 | ) | (19 | ) | |||
Total net securities gains | $ | 75 | $ | 83 | $ | 91 | |||
In 2015, Agency MBS, sovereign debt and U.S. Treasury securities with an aggregate amortized cost of $11.6 billion and fair value of $11.6 billion were transferred from available-for-sale securities to held-to-maturity securities. Additionally, in 2013, Agency RMBS securities with an amortized cost of $7.3 billion and fair value of $7.0 billion were transferred from available-for-sale securities to held-to-maturity securities. These actions, in addition to realizing gains on the sales of securities, are expected to mute the impact to our accumulated other comprehensive income in the event of a rise in interest rates.
Temporarily impaired securities
At Dec. 31, 2016, the unrealized losses on the investment securities portfolio were primarily attributable to an increase in interest rates from date of purchase, and for certain securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity, an increase in interest rates through the date they were transferred. Specifically, $190 million of the unrealized losses at Dec. 31, 2016 and $248 million at Dec. 31, 2015 reflected in the available-for-sale sections of the tables below relate to certain securities (primarily Agency RMBS) that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized losses will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. The transfer created a new cost basis for the securities. As a result, if these securities have experienced unrealized losses since the date of transfer, the corresponding fair value and unrealized losses would be reflected in the held-to-maturity sections of the following tables. We do not intend to sell these securities and it is not more likely than not that we will have to sell these securities.
BNY Mellon 157
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The following tables show the aggregate related fair value of investments with a continuous unrealized loss position for less than 12 months and those that have been in a continuous unrealized loss position for 12 months or more at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively.
Temporarily impaired securities at Dec. 31, 2016 | Less than 12 months | 12 months or more | Total | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | ||||||||||||||
Available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 8,489 | $ | 181 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 8,489 | $ | 181 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | 257 | 9 | — | — | 257 | 9 | ||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 1,058 | 33 | 131 | 19 | 1,189 | 52 | ||||||||||||||
Agency RMBS | 14,766 | 141 | 1,673 | 200 | 16,439 | 341 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 21 | — | 332 | 13 | 353 | 13 | ||||||||||||||
Other RMBS | 26 | — | 136 | 8 | 162 | 8 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial MBS | 302 | 7 | 163 | 4 | 465 | 11 | ||||||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 3,570 | 78 | 589 | 6 | 4,159 | 84 | ||||||||||||||
CLOs | 443 | 1 | 404 | — | 847 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | 276 | 1 | 357 | 5 | 633 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 594 | 16 | 7 | 1 | 601 | 17 | ||||||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 1,521 | 20 | 63 | — | 1,584 | 20 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (a) | 25 | — | 47 | 9 | 72 | 9 | ||||||||||||||
Other debt securities | 742 | 10 | 50 | — | 792 | 10 | ||||||||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 712 | 9 | — | — | 712 | 9 | ||||||||||||||
Total securities available-for-sale (b) | $ | 32,802 | $ | 506 | $ | 3,952 | $ | 265 | $ | 36,754 | $ | 771 | ||||||||
Held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 6,112 | $ | 41 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,112 | $ | 41 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | 1,533 | 6 | — | — | 1,533 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | — | — | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
Agency RMBS | 19,498 | 297 | 102 | 2 | 19,600 | 299 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 4 | — | 48 | 2 | 52 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 621 | 10 | — | — | 621 | 10 | ||||||||||||||
Other RMBS | 15 | — | 123 | 4 | 138 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Total securities held-to-maturity | $ | 27,783 | $ | 354 | $ | 277 | $ | 9 | $ | 28,060 | $ | 363 | ||||||||
Total temporarily impaired securities | $ | 60,585 | $ | 860 | $ | 4,229 | $ | 274 | $ | 64,814 | $ | 1,134 | ||||||||
(a) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(b) | Gross unrealized losses for 12 months or more of $190 million were recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income and related to investment securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized losses are primarily related to Agency RMBS and will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. There were no gross unrealized losses for less than 12 months. |
158 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Temporarily impaired securities at Dec. 31, 2015 | Less than 12 months | 12 months or more | Total | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | Fair value | Unrealized losses | ||||||||||||||
Available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 6,343 | $ | 36 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,343 | $ | 36 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | 148 | 1 | 10 | — | 158 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 143 | 2 | 117 | 11 | 260 | 13 | ||||||||||||||
Agency RMBS | 8,500 | 44 | 1,316 | 243 | 9,816 | 287 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 72 | — | 417 | 20 | 489 | 20 | ||||||||||||||
Other RMBS | 2 | — | 298 | 21 | 300 | 21 | ||||||||||||||
Commercial MBS | 567 | 9 | 224 | 7 | 791 | 16 | ||||||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 2,551 | 31 | 172 | 4 | 2,723 | 35 | ||||||||||||||
CLOs | 1,599 | 10 | 455 | 3 | 2,054 | 13 | ||||||||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | 2,001 | 10 | 546 | 7 | 2,547 | 17 | ||||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 338 | 10 | 128 | 4 | 466 | 14 | ||||||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 2,063 | 30 | 43 | — | 2,106 | 30 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (a) | 45 | 1 | 52 | 7 | 97 | 8 | ||||||||||||||
Other debt securities | 505 | 3 | — | — | 505 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 515 | 3 | — | — | 515 | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Total securities available-for-sale (b) | $ | 25,392 | $ | 190 | $ | 3,778 | $ | 327 | $ | 29,170 | $ | 517 | ||||||||
Held-to-maturity: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 9,121 | $ | 51 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9,121 | $ | 51 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | 1,122 | 6 | — | — | 1,122 | 6 | ||||||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | 4 | 1 | — | — | 4 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
Agency RMBS | 16,491 | 171 | 1,917 | 34 | 18,408 | 205 | ||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 40 | — | 29 | 2 | 69 | 2 | ||||||||||||||
Other RMBS | 9 | — | 166 | 10 | 175 | 10 | ||||||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | 494 | 9 | — | — | 494 | 9 | ||||||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 2,161 | 11 | — | — | 2,161 | 11 | ||||||||||||||
Total securities held-to-maturity | $ | 29,442 | $ | 249 | $ | 2,112 | $ | 46 | $ | 31,554 | $ | 295 | ||||||||
Total temporarily impaired securities | $ | 54,834 | $ | 439 | $ | 5,890 | $ | 373 | $ | 60,724 | $ | 812 | ||||||||
(a) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(b) | Includes gross unrealized losses for less than 12 months of $8 million and gross unrealized losses for 12 months or more of $240 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income related to investment securities that were transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. The unrealized losses are primarily related to Agency RMBS and will be amortized into net interest revenue over the contractual lives of the securities. |
The following table shows the maturity distribution by carrying amount and yield (on a tax equivalent basis) of our investment securities portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016.
Maturity distribution and yield on investment securities at Dec. 31, 2016 | U.S. Treasury | U.S. government agencies | State and political subdivisions | Other bonds, notes and debentures | Mortgage/ asset-backed and equity securities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Amount | Yield (a) | Amount | Yield (a) | Amount | Yield (a) | Amount | Yield (a) | Amount | Yield (a) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Securities available-for-sale: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One year or less | $ | 2,195 | 0.85 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 274 | 2.71 | % | $ | 3,745 | 0.97 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 6,214 | |||||||||||
Over 1 through 5 years | 5,472 | 1.49 | 113 | 1.30 | 1,738 | 2.92 | 11,688 | 1.02 | — | — | 19,011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Over 5 through 10 years | 3,292 | 1.71 | 246 | 2.34 | 1,147 | 3.51 | 2,378 | 1.13 | — | — | 7,063 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Over 10 years | 3,348 | 3.11 | — | — | 219 | 1.90 | 176 | 1.67 | — | — | 3,743 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 32,621 | 2.59 | 32,621 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Asset-backed securities | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4,325 | 1.95 | 4,325 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity securities (b) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 845 | — | 845 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 14,307 | 1.82 | % | $ | 359 | 2.01 | % | $ | 3,378 | 3.04 | % | $ | 17,987 | 1.03 | % | $ | 37,791 | 2.46 | % | $ | 73,822 | |||||||||||
Securities held-to-maturity: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
One year or less | $ | 1,327 | 0.86 | % | $ | 350 | 0.83 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 511 | 0.57 | % | $ | — | — | % | $ | 2,188 | |||||||||||
Over 1 through 5 years | 7,890 | 1.23 | 1,189 | 1.19 | 1 | 7.03 | 847 | 0.61 | — | — | 9,927 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Over 5 through 10 years | 1,900 | 1.91 | 50 | 2.02 | 3 | 6.76 | 653 | 0.71 | — | — | 2,606 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Over 10 years | — | — | — | — | 15 | 5.34 | — | — | — | — | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 26,169 | 2.73 | 26,169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 11,117 | 1.30 | % | $ | 1,589 | 1.13 | % | $ | 19 | 5.69 | % | $ | 2,011 | 0.63 | % | $ | 26,169 | 2.73 | % | $ | 40,905 | |||||||||||
(a) | Yields are based upon the amortized cost of securities. |
(b) | Includes money market funds. |
BNY Mellon 159
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Other-than-temporary impairment
We routinely conduct periodic reviews of all securities to determine whether OTTI has occurred. Such reviews may incorporate the use of economic models. Various inputs to the economic models are used to determine if an unrealized loss on securities is other-than-temporary. For example, the most significant inputs related to non-agency RMBS are:
• | Default rate - the number of mortgage loans expected to go into default over the life of the transaction, which is driven by the roll rate of loans in each performance bucket that will ultimately migrate to default; and |
• | Severity - the loss expected to be realized when a loan defaults. |
To determine if an unrealized loss is other-than-temporary, we project total estimated defaults of the underlying assets (mortgages) and multiply that calculated amount by an estimate of realizable value upon sale of these assets in the marketplace (severity) in order to determine the projected collateral loss. In determining estimated default rate and severity assumptions, we review the performance of the underlying securities, industry studies, market forecasts, as well as our view of the economic outlook affecting collateral. We also evaluate the current credit enhancement underlying the bond to determine the impact on cash flows. If we determine that a given security will be subject to a write-down or loss, we record the expected credit loss as a charge to earnings.
The table below shows the projected weighted-average default rates and loss severities for the 2007, 2006 and late 2005 non-agency RMBS and the securities previously held in the Grantor Trust that we established in connection with the restructuring of our investment securities portfolio in 2009, at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Projected weighted-average default rates and loss severities | |||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||
Default rate | Severity | Default rate | Severity | ||||||
Alt-A | 30 | % | 54 | % | 33 | % | 57 | % | |
Subprime | 49 | % | 70 | % | 52 | % | 72 | % | |
Prime | 18 | % | 39 | % | 18 | % | 40 | % | |
The following table presents pre-tax net securities gains by type.
Net securities gains | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Agency RMBS | $ | 22 | $ | 10 | $ | 13 | |||
Foreign covered bonds | 10 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
Non-agency RMBS | 8 | 7 | 17 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 4 | 45 | 25 | ||||||
Other | 31 | 19 | 33 | ||||||
Total net securities gains | $ | 75 | $ | 83 | $ | 91 | |||
The following tables reflect investment securities credit losses recorded in earnings. The beginning balance represents the credit loss component for which OTTI occurred on debt securities in prior periods. The additions represent the first time a debt security was credit impaired or when subsequent credit impairments have occurred. The deductions represent credit losses on securities that have been sold, are required to be sold, or for which it is our intention to sell.
Debt securities credit loss roll forward | ||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Beginning balance as of Jan. 1 | $ | 91 | $ | 93 | ||
Add: Initial OTTI credit losses | — | — | ||||
Subsequent OTTI credit losses | 7 | 5 | ||||
Less: Realized losses for securities sold | 10 | 7 | ||||
Ending balance as of Dec. 31 | $ | 88 | $ | 91 | ||
Pledged assets
At Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon had pledged assets of $102 billion, including $84 billion pledged as collateral for potential borrowings at the Federal Reserve Discount Window. The components of the assets pledged at Dec. 31, 2016 included $87 billion of securities, $8 billion of loans, $4 billion of interest-bearing deposits with banks and $3 billion of trading assets.
If there has been no borrowing at the Federal Reserve Discount Window, the Federal Reserve generally allows banks to freely move assets in and out of their pledged assets account to sell or repledge the assets for other purposes. BNY Mellon regularly moves assets in and out of its pledged assets account at the Federal Reserve.
160 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
At Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon had pledged assets of $101 billion, including $84 billion pledged as collateral for potential borrowing at the Federal Reserve Discount Window. The components of the assets pledged at Dec. 31, 2015 included $88 billion of securities, $8 billion of loans, $3 billion of trading assets and $2 billion of interest-bearing deposits with banks.
At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, pledged assets included $6 billion and $7 billion, respectively, for which the recipients were permitted to sell or repledge the assets delivered.
We also obtain securities as collateral including receipts under resale agreements, securities borrowed, derivative contracts and custody agreements on terms which permit us to sell or repledge the securities to others. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, the market value of the securities received that can be sold or repledged was $50 billion and $52 billion, respectively. We routinely sell or repledge these securities through delivery to third parties. As of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, the market value of securities collateral sold or repledged was $20 billion and $17 billion, respectively.
Restricted cash and securities
Cash and securities may also be segregated under federal and other regulations or requirements. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, cash segregated under federal and other regulations or requirements was $3 billion and $4 billion, respectively. Restricted cash is included in interest-bearing deposits with banks on the consolidated balance sheet. Securities segregated for these purposes were $2 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $1 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. Restricted securities were sourced from securities purchased under resale agreements at Dec. 31, 2016 and are included in federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements on the consolidated balance sheet. Restricted securities are included in trading assets on the consolidated balance sheet at Dec. 31, 2015.
Note 4 - Loans and asset quality
Loans
The table below provides the details of our loan portfolio and industry concentrations of credit risk at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Loans | Dec. 31, | |||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Domestic: | ||||||
Financial institutions | $ | 6,342 | $ | 6,640 | ||
Commercial | 2,286 | 2,115 | ||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 15,555 | 13,247 | ||||
Commercial real estate | 4,639 | 3,899 | ||||
Lease financings | 989 | 1,007 | ||||
Other residential mortgages | 854 | 1,055 | ||||
Overdrafts | 1,055 | 911 | ||||
Other | 1,202 | 1,137 | ||||
Margin loans | 17,503 | 19,340 | ||||
Total domestic | 50,425 | 49,351 | ||||
Foreign: | ||||||
Financial institutions | 8,347 | 9,259 | ||||
Commercial | 331 | 227 | ||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 99 | 100 | ||||
Commercial real estate | 15 | 46 | ||||
Lease financings | 736 | 850 | ||||
Other (primarily overdrafts) | 4,418 | 3,637 | ||||
Margin loans | 87 | 233 | ||||
Total foreign | 14,033 | 14,352 | ||||
Total loans (a) | $ | 64,458 | $ | 63,703 | ||
(a) | Net of unearned income of $527 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $674 million at Dec. 31, 2015 primarily on domestic and foreign lease financings. |
Our loan portfolio consists of three portfolio segments: commercial, lease financings and mortgages. We manage our portfolio at the class level which consists of six classes of financing receivables: commercial, commercial real estate, financial institutions, lease financings, wealth management loans and mortgages and other residential mortgages.
The following tables are presented for each class of financing receivable, and provide additional information about our credit risks and the adequacy of our allowance for credit losses.
BNY Mellon 161
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Allowance for credit losses
Transactions in the allowance for credit losses are summarized as follows:
Allowance for credit losses activity for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016 | Wealth management loans and mortgages | Other residential mortgages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Commercial | Commercial real estate | Financial institutions | Lease financings | All Other | Foreign | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 82 | $ | 59 | $ | 31 | $ | 15 | $ | 19 | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | 35 | $ | 275 | ||||||||||
Charge-offs | — | — | — | — | — | (2 | ) | — | — | (2 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Recoveries | — | — | 13 | — | — | 5 | — | 1 | 19 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net recoveries | — | — | 13 | — | — | 3 | — | 1 | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||
Provision | — | 14 | (18 | ) | (2 | ) | 4 | (9 | ) | — | — | (11 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Ending balance | $ | 82 | $ | 73 | $ | 26 | $ | 13 | $ | 23 | $ | 28 | $ | — | $ | 36 | $ | 281 | ||||||||||
Allowance for: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan losses | $ | 25 | $ | 52 | $ | 8 | $ | 13 | $ | 19 | $ | 28 | $ | — | $ | 24 | $ | 169 | ||||||||||
Lending-related commitments | 57 | 21 | 18 | — | 4 | — | — | 12 | 112 | |||||||||||||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4 | $ | 5 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | — | — | — | 2 | 3 | — | — | — | 5 | |||||||||||||||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | 2,286 | $ | 4,639 | $ | 6,342 | $ | 985 | $ | 15,550 | $ | 854 | $ | 19,760 | (a) | $ | 14,033 | $ | 64,449 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | 25 | 52 | 8 | 11 | 16 | 28 | — | 24 | 164 | |||||||||||||||||||
(a) | Includes $1,055 million of domestic overdrafts, $17,503 million of margin loans and $1,202 million of other loans at Dec. 31, 2016. |
Allowance for credit losses activity for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 | Wealth management loans and mortgages | Other residential mortgages | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Commercial | Commercial real estate | Financial institutions | Lease financings | All Other | Foreign | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 60 | $ | 50 | $ | 31 | $ | 32 | $ | 22 | $ | 41 | $ | — | $ | 44 | $ | 280 | ||||||||||
Charge-offs | — | — | (170 | ) | — | — | (2 | ) | — | — | (172 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Recoveries | — | — | 1 | — | — | 6 | — | — | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net (charge-offs) recoveries | — | — | (169 | ) | — | — | 4 | — | — | (165 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Provision | 22 | 9 | 169 | (17 | ) | (3 | ) | (11 | ) | — | (9 | ) | 160 | |||||||||||||||
Ending balance | $ | 82 | $ | 59 | $ | 31 | $ | 15 | $ | 19 | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | 35 | $ | 275 | ||||||||||
Allowance for: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan losses | $ | 24 | $ | 37 | $ | 9 | $ | 15 | $ | 15 | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | 23 | $ | 157 | ||||||||||
Lending-related commitments | 58 | 22 | 22 | — | 4 | — | — | 12 | 118 | |||||||||||||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | — | $ | 1 | $ | 171 | $ | — | $ | 8 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 180 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | 2,115 | $ | 3,496 | $ | 6,469 | $ | 1,007 | $ | 13,239 | $ | 1,035 | $ | 21,388 | (a) | $ | 14,352 | $ | 63,101 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | 24 | 36 | 9 | 15 | 14 | 34 | — | 23 | 155 | |||||||||||||||||||
(a) | Includes $911 million of domestic overdrafts, $19,340 million of margin loans and $1,137 million of other loans at Dec. 31, 2015. |
162 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Allowance for credit losses activity for the year ended Dec. 31, 2014 | Wealth management loans and mortgages | Other residential mortgages | All Other | Foreign | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Commercial | Commercial real estate | Financial institutions | Lease financings | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 83 | $ | 41 | $ | 49 | $ | 37 | $ | 24 | $ | 54 | $ | — | $ | 56 | $ | 344 | ||||||||||
Charge-offs | (12 | ) | (2 | ) | — | — | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | — | (3 | ) | (20 | ) | |||||||||||||
Recoveries | 1 | — | 1 | — | — | 2 | — | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net (charge-offs) recoveries | (11 | ) | (2 | ) | 1 | — | (1 | ) | — | — | (3 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Provision | (12 | ) | 11 | (19 | ) | (5 | ) | (1 | ) | (13 | ) | — | (9 | ) | (48 | ) | ||||||||||||
Ending balance | $ | 60 | $ | 50 | $ | 31 | $ | 32 | $ | 22 | $ | 41 | $ | — | $ | 44 | $ | 280 | ||||||||||
Allowance for: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan losses | $ | 17 | $ | 32 | $ | 17 | $ | 32 | $ | 17 | $ | 41 | $ | — | $ | 35 | $ | 191 | ||||||||||
Lending-related commitments | 43 | 18 | 14 | — | 5 | — | — | 9 | 89 | |||||||||||||||||||
Individually evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 8 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 8 | ||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | — | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
Collectively evaluated for impairment: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loan balance | $ | 1,390 | $ | 2,503 | $ | 5,603 | $ | 1,282 | $ | 11,087 | $ | 1,222 | $ | 22,495 | (a) | $ | 13,521 | $ | 59,103 | |||||||||
Allowance for loan losses | 17 | 32 | 17 | 32 | 16 | 41 | — | 35 | 190 | |||||||||||||||||||
(a) | Includes $1,348 million of domestic overdrafts, $20,034 million of margin loans and $1,113 million of other loans at Dec. 31, 2014. |
Nonperforming assets
The table below presents the distribution of our nonperforming assets.
Nonperforming assets (in millions) | Dec. 31, | |||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||
Nonperforming loans: | ||||||
Other residential mortgages | $ | 91 | $ | 102 | ||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 8 | 11 | ||||
Lease financings | 4 | — | ||||
Commercial real estate | — | 2 | ||||
Financial institutions | — | 171 | ||||
Total nonperforming loans | 103 | 286 | ||||
Other assets owned | 4 | 6 | ||||
Total nonperforming assets | $ | 107 | $ | 292 | ||
At Dec. 31, 2016, undrawn commitments to borrowers whose loans were classified as nonaccrual or reduced rate were not material. Nonperforming
loans decreased primarily reflecting the settlement agreement in the bankruptcy proceedings of Sentinel.
Lost interest
The table below presents the amount of lost interest income.
Lost interest | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Amount by which interest income recognized on nonperforming loans exceeded reversals | |||||||||
Total | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1 | |||
Foreign | — | — | — | ||||||
Amount by which interest income would have increased if nonperforming loans at year-end had been performing for the entire year | |||||||||
Total | $ | 6 | $ | 6 | $ | 7 | |||
Foreign | — | — | — | ||||||
BNY Mellon 163
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Impaired loans
The tables below provide information about our impaired loans. We use the discounted cash flow method as the primary method for valuing impaired loans.
Impaired loans | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Average recorded investment | Interest income recognized | Average recorded investment | Interest income recognized | Average recorded investment | Interest income recognized | ||||||||||||||
Impaired loans with an allowance: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11 | $ | — | ||||||||
Commercial real estate | 1 | — | 1 | — | 2 | — | ||||||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 5 | — | 6 | — | 8 | — | ||||||||||||||
Lease financings | 3 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Foreign | — | — | — | — | 3 | — | ||||||||||||||
Total impaired loans with an allowance | 9 | — | 7 | — | 24 | — | ||||||||||||||
Impaired loans without an allowance: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | — | ||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | 102 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 2 | — | 2 | — | 2 | — | ||||||||||||||
Total impaired loans without an allowance (a) | 105 | — | 2 | — | 3 | — | ||||||||||||||
Total impaired loans | $ | 114 | $ | — | $ | 9 | $ | — | $ | 27 | $ | — | ||||||||
(a) | When the discounted cash flows, collateral value or market price equals or exceeds the carrying value of the loan, then the loan does not require an allowance under the accounting standard related to impaired loans. |
Impaired loans | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Recorded investment | Unpaid principal balance | Related allowance (a) | Recorded investment | Unpaid principal balance | Related allowance (a) | |||||||||||||
Impaired loans with an allowance: | |||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | — | $ | 1 | $ | 3 | $ | 1 | |||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 1 | |||||||||||||
Lease financings | 4 | 4 | 2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Total impaired loans with an allowance | 7 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 10 | 2 | |||||||||||||
Impaired loans without an allowance: | |||||||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | — | — | N/A | 171 | 312 | N/A | |||||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 2 | 2 | N/A | 2 | 2 | N/A | |||||||||||||
Total impaired loans without an allowance (b) | 2 | 2 | N/A | 173 | 314 | N/A | |||||||||||||
Total impaired loans (c) | $ | 9 | $ | 12 | $ | 5 | $ | 180 | $ | 324 | $ | 2 | |||||||
(a) | The allowance for impaired loans is included in the allowance for loan losses. |
(b) | When the discounted cash flows, collateral value or market price equals or exceeds the carrying value of the loan, then the loan does not require an allowance under the accounting standard related to impaired loans. |
(c) | Excludes an aggregate of less than $1 million and $2 million of impaired loans in amounts individually less than $1 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively. The allowance for loan loss associated with these loans totaled less than $1 million at both Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively. |
Past due loans
The table below sets forth information about our past due loans.
Past due loans and still accruing interest | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Days past due | Total past due | Days past due | Total past due | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 30-59 | 60-89 | >90 | 30-59 | 60-89 | >90 | |||||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate | $ | 78 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 78 | $ | 57 | $ | 11 | $ | — | $ | 68 | |||||||||
Other residential mortgages | 20 | 6 | 7 | 33 | 22 | 5 | 4 | 31 | |||||||||||||||||
Financial institutions | 1 | 27 | — | 28 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 21 | 2 | — | 23 | 69 | 2 | 1 | 72 | |||||||||||||||||
Total past due loans | $ | 120 | $ | 35 | $ | 7 | $ | 162 | $ | 148 | $ | 18 | $ | 5 | $ | 171 | |||||||||
164 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Troubled debt restructurings (“TDRs”)
A modified loan is considered a TDR if the debtor is experiencing financial difficulties and the creditor grants a concession to the debtor that would not otherwise be considered. A TDR may include a
transfer of real estate or other assets from the debtor to the creditor, or a modification of the term of the loan. Not all modified loans are considered TDRs.
The following table presents TDRs that occurred in 2016 and 2015.
TDRs | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding recorded investment | Outstanding recorded investment | ||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions) | Number of contracts | Pre-modification | Post-modification | Number of contracts | Pre-modification | Post-modification | |||||||||||||||
Other residential mortgages | 70 | $ | 14 | $ | 16 | 68 | $ | 13 | $ | 16 | |||||||||||
Wealth management loans and mortgages | 2 | — | — | 4 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total TDRs | 72 | $ | 14 | $ | 16 | 72 | $ | 13 | $ | 16 | |||||||||||
Other residential mortgages
The modifications of the other residential mortgage loans in 2016 and 2015 consisted of reducing the stated interest rates and, in certain cases, a forbearance of default and extending the maturity dates. The modified loans are primarily collateral dependent for which the value is based on the fair value of the collateral.
TDRs that subsequently defaulted
There were 34 residential mortgage loans and one wealth management loan that had been restructured in
a TDR during the previous 12 months and have subsequently defaulted in 2016. The total recorded investment of these loans was $8 million.
Credit quality indicators
Our credit strategy is to focus on investment grade clients that are active users of our non-credit services. Each customer is assigned an internal credit rating which is mapped to an external rating agency grade equivalent, if possible, based upon a number of dimensions which are continually evaluated and may change over time.
The following tables set forth information about credit quality indicators.
Commercial loan portfolio
Commercial loan portfolio – Credit risk profile by creditworthiness category | Commercial | Commercial real estate | Financial institutions | |||||||||||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Investment grade | $ | 2,397 | $ | 2,026 | $ | 3,823 | $ | 2,678 | $ | 11,459 | $ | 13,965 | ||||||||
Non-investment grade | 220 | 316 | 831 | 1,267 | 3,230 | 1,934 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 2,617 | $ | 2,342 | $ | 4,654 | $ | 3,945 | $ | 14,689 | $ | 15,899 | ||||||||
The commercial loan portfolio is divided into investment grade and non-investment grade categories based on rating criteria largely consistent with those of the public rating agencies. Each customer in the portfolio is assigned an internal credit rating. These internal credit ratings are generally
consistent with the ratings categories of the public rating agencies. Customers with ratings consistent with BBB- (S&P)/Baa3 (Moody’s) or better are considered to be investment grade. Those clients with ratings lower than this threshold are considered to be non-investment grade.
BNY Mellon 165
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Wealth management loans and mortgages
Wealth management loans and mortgages – Credit risk profile by internally assigned grade | ||||||
(in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||
Wealth management loans: | ||||||
Investment grade | $ | 7,127 | $ | 6,529 | ||
Non-investment grade | 260 | 171 | ||||
Wealth management mortgages | 8,267 | 6,647 | ||||
Total | $ | 15,654 | $ | 13,347 | ||
Wealth management non-mortgage loans are not typically rated by external rating agencies. A majority of the wealth management loans are secured by the customers’ investment management accounts or custody accounts. Eligible assets pledged for these loans are typically investment grade fixed-income securities, equities and/or mutual funds. Internal ratings for this portion of the wealth management portfolio, therefore, would equate to investment grade external ratings. Wealth management loans are provided to select customers based on the pledge of other types of assets, including business assets, fixed assets or a modest amount of commercial real estate. For the loans collateralized by other assets, the credit quality of the obligor is carefully analyzed, but we do not consider this portfolio of loans to be investment grade.
Credit quality indicators for wealth management mortgages are not correlated to external ratings. Wealth management mortgages are typically loans to high net worth individuals, which are secured primarily by residential property. These loans are primarily interest-only, adjustable rate mortgages with a weighted-average loan-to-value ratio of 61% at origination. In the wealth management portfolio, less than 1% of the mortgages were past due at Dec. 31, 2016.
At Dec. 31, 2016, the wealth management mortgage portfolio consisted of the following geographic concentrations: California - 24%; New York - 19%; Massachusetts - 12%; Florida - 7%; and other - 38%.
Other residential mortgages
The other residential mortgage portfolio primarily consists of 1-4 family residential mortgage loans and totaled $854 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $1,055
million at Dec. 31, 2015. These loans are not typically correlated to external ratings. Included in this portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016 are $221 million of mortgage loans purchased in 2005, 2006 and the first quarter of 2007 that are predominantly prime mortgage loans, with a small portion of Alt-A loans. As of Dec. 31, 2016, the purchased loans in this portfolio had a weighted-average loan-to-value ratio of 76% at origination and 14% of the serviced loan balance was at least 60 days delinquent. The properties securing the prime and Alt-A mortgage loans were located (in order of concentration) in California, Florida, Virginia, the tri-state area (New York, New Jersey and Connecticut) and Maryland.
Overdrafts
Overdrafts primarily relate to custody and securities clearance clients and totaled $5,461 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $4,483 million at Dec. 31, 2015. Overdrafts occur on a daily basis in the custody and securities clearance business and are generally repaid within two business days.
Other loans
Other loans primarily include loans to consumers that are fully collateralized with equities, mutual funds and fixed income securities.
Margin loans
We had $17,590 million of secured margin loans on our balance sheet at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $19,573 million at Dec. 31, 2015. Margin loans are collateralized with marketable securities and borrowers are required to maintain a daily collateral margin in excess of 100% of the value of the loan. We have rarely suffered a loss on these types of loans and do not allocate any of our allowance for credit losses to margin loans.
Reverse repurchase agreements
Reverse repurchase agreements are transactions fully collateralized with high-quality liquid securities. These transactions carry minimal credit risk and therefore are not allocated an allowance for credit losses.
166 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Note 5 - Goodwill and intangible assets
Goodwill
The tables below provide a breakdown of goodwill by business.
Goodwill by business (in millions) | Investment Management | (a) | Investment Services | (b) | Other | (a)(b) | Consolidated | ||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 9,328 | $ | 8,471 | $ | 70 | $ | 17,869 | |||||||
Acquisition (dispositions) | 10 | — | (22 | ) | (12 | ) | |||||||||
Foreign currency translation | (128 | ) | (105 | ) | (3 | ) | (236 | ) | |||||||
Other (c) | (3 | ) | — | — | (3 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 9,207 | $ | 8,366 | $ | 45 | $ | 17,618 | |||||||
Acquisitions (dispositions) | 29 | (2 | ) | — | 27 | ||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | (238 | ) | (91 | ) | — | (329 | ) | ||||||||
Other (c) | 2 | (4 | ) | 2 | — | ||||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2016 | $ | 9,000 | $ | 8,269 | $ | 47 | $ | 17,316 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the reclassification of goodwill associated with Meriten from Investment Management to the Other segment in 2015. |
(b) | Includes the reclassification of goodwill associated with credit-related activities from the Other segment to Investment Services in 2016. |
(c) | Other changes in goodwill include purchase price adjustments and certain other reclassifications. |
Total goodwill decreased in 2016 compared with 2015 primarily reflecting the impact of foreign exchange translation on non-U.S. dollar denominated goodwill.
Intangible assets
The tables below provide a breakdown of intangible assets by business.
Intangible assets – net carrying amount by business (in millions) | Investment Management | (a) | Investment Services | Other | (a) | Consolidated | |||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 1,911 | $ | 1,355 | $ | 861 | $ | 4,127 | |||||||
Acquisitions (dispositions) | 9 | — | (9 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Amortization | (97 | ) | (162 | ) | (2 | ) | (261 | ) | |||||||
Foreign currency translation | (16 | ) | (7 | ) | (1 | ) | (24 | ) | |||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 1,807 | $ | 1,186 | $ | 849 | $ | 3,842 | |||||||
Acquisitions (dispositions) | 30 | 2 | — | 32 | |||||||||||
Amortization (b) | (82 | ) | (155 | ) | — | (237 | ) | ||||||||
Foreign currency translation | (38 | ) | (1 | ) | — | (39 | ) | ||||||||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2016 | $ | 1,717 | $ | 1,032 | $ | 849 | $ | 3,598 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the reclassification of intangible assets associated with Meriten from Investment Management to the Other segment in 2015. |
(b) | Includes $6 million of impairment charges related to the write-down of intangible assets in the Investment Management business, to their respective fair values. |
Intangible assets decreased in 2016 compared with 2015 primarily reflecting amortization. Amortization of intangible assets was $237 million in 2016, $261 million in 2015 and $298 million in 2014. In 2016,
we recorded $6 million of impairment charges related to the write-down of intangible assets in the Investment Management business, to their respective fair values.
BNY Mellon 167
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The table below provides a breakdown of intangible assets by type.
Intangible assets | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Gross carrying amount | Accumulated amortization | Net carrying amount | Remaining weighted- average amortization period | Gross carrying amount | Accumulated amortization | Net carrying amount | |||||||||||||
Subject to amortization: (a) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Customer relationships—Investment Management | $ | 1,439 | $ | (1,136 | ) | $ | 303 | 12 years | $ | 1,593 | $ | (1,235 | ) | $ | 358 | |||||
Customer contracts—Investment Services | 2,249 | (1,590 | ) | 659 | 10 years | 2,260 | (1,450 | ) | 810 | |||||||||||
Other | 37 | (33 | ) | 4 | 2 years | 40 | (31 | ) | 9 | |||||||||||
Total subject to amortization | 3,725 | (2,759 | ) | 966 | 10 years | 3,893 | (2,716 | ) | 1,177 | |||||||||||
Not subject to amortization: (b) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Trade name | 1,348 | N/A | 1,348 | N/A | 1,358 | N/A | 1,358 | |||||||||||||
Customer relationships | 1,284 | N/A | 1,284 | N/A | 1,307 | N/A | 1,307 | |||||||||||||
Total not subject to amortization | 2,632 | N/A | 2,632 | N/A | 2,665 | N/A | 2,665 | |||||||||||||
Total intangible assets | $ | 6,357 | $ | (2,759 | ) | $ | 3,598 | N/A | $ | 6,558 | $ | (2,716 | ) | $ | 3,842 | |||||
(a) | Excludes fully amortized intangible assets. |
(b) | Intangible assets not subject to amortization have an indefinite life. |
Estimated annual amortization expense for current intangibles for the next five years is as follows:
For the year ended Dec. 31, | Estimated amortization expense (in millions) | |||
2017 | $ | 208 | ||
2018 | 178 | |||
2019 | 108 | |||
2020 | 98 | |||
2021 | 75 | |||
Impairment testing
BNY Mellon’s three business segments include eight reporting units for which goodwill impairment testing is performed on an annual basis. The Investment Management segment consists of two reporting units. The Investment Services segment consists of five reporting units. One reporting unit is included in the Other segment.
The goodwill impairment test is performed in two steps. The first step compares the estimated fair value of the reporting unit with the carrying amount, including goodwill. If the estimated fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, goodwill of the reporting unit is considered not impaired. However, if the carrying amount of the reporting unit were to exceed its estimated fair value, a second step would be performed that would compare the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. An impairment
loss would be recorded to the extent that the carrying amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair value.
BNY Mellon conducted an annual goodwill impairment test on all eight reporting units in the second quarter of 2016. The estimated fair value of the eight reporting units exceeded the carrying value and no goodwill impairment was recognized.
Intangible assets not subject to amortization are tested for impairment annually or more often if events or circumstances indicate they may be impaired.
Note 6 - Other assets
Other assets | Dec. 31, | |||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Corporate/bank-owned life insurance | $ | 4,789 | $ | 4,704 | ||
Accounts receivable | 4,060 | 3,535 | ||||
Fails to deliver | 1,732 | 1,494 | ||||
Software | 1,451 | 1,355 | ||||
Renewable energy investments | 1,282 | 640 | ||||
Income taxes receivable | 1,172 | 1,554 | ||||
Equity in a joint venture and other investments | 1,063 | 1,039 | ||||
Tax advantaged low income housing investments | 914 | 918 | ||||
Prepaid pension assets | 836 | 727 | ||||
Fair value of hedging derivatives | 784 | 716 | ||||
Federal Reserve Bank stock | 466 | 453 | ||||
Prepaid expenses | 438 | 464 | ||||
Seed capital | 395 | 245 | ||||
Due from customers on acceptances | 340 | 258 | ||||
Private equity | 43 | 34 | ||||
Other | 1,189 | 1,490 | ||||
Total other assets | $ | 20,954 | $ | 19,626 | ||
168 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Certain seed capital and private equity investments valued using net asset value per share
In our Investment Management business, we manage investment assets, including equities, fixed income, money market and alternative investment funds for institutions and other investors. As part of that activity, we make seed capital investments in certain funds. BNY Mellon also holds private equity investments, specifically in SBICs, which are
compliant with the Volcker Rule. Seed capital and private equity investments are included in other assets.
The fair value of certain of these investments has been estimated using the NAV per share of BNY Mellon’s ownership interest in the funds. The table below presents information about BNY Mellon’s investments in seed capital and private equity investments that have been valued using NAV.
Seed capital and private equity investments valued using NAV | |||||||||||||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Fair value | Unfunded commitments | Redemption frequency | Redemption notice period | Fair value | Unfunded commitments | Redemption frequency | Redemption notice period | |||||||||||
Seed capital and other funds (a) | $ | 171 | $ | 1 | Daily-quarterly | 1-180 days | $ | 83 | $ | 1 | Daily-quarterly | 1-180 days | |||||||
Private equity investments (SBICs) (b) | 43 | 46 | N/A | N/A | 34 | 58 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 214 | $ | 47 | $ | 117 | $ | 59 | |||||||||||
(a) | Other funds include various leveraged loans, structured credit funds and hedge funds. Redemption notice periods vary by fund. |
(b) | Private equity investments primarily include Volcker Rule-compliant investments in SBICs that invest in various sectors of the economy. Private equity investments do not have redemption rights. Distributions from such investments will be received as the underlying investments in the private equity investments are liquidated. |
Qualified affordable housing project investments
We invest in affordable housing projects primarily to satisfy the Company’s requirements under the Community Reinvestment Act. Our total investment in qualified affordable housing projects totaled $914 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $918 million at Dec. 31, 2015. Commitments to fund future investments in qualified affordable housing projects totaled $369 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $393 million at Dec. 31, 2015. A summary of the commitments to fund future investments is as follows: 2017—$152 million; 2018—$119 million; 2019—$81 million; 2020—$2 million; 2021—$1 million and 2022 and thereafter—$14 million.
Tax credits and other tax benefits recognized were $155 million in 2016, $130 million in 2015 and $128 million in 2014.
Amortization expense included in the provision for income taxes was $115 million in the 2016, $99 million in 2015 and $96 million in 2014.
Note 7 - Deposits
Total time deposits in denominations of $100,000 or greater was $38.9 billion at Dec. 31, 2016, and $72.2 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. At Dec. 31, 2016, the scheduled maturities of all time deposits are as follows: 2017 – $39.8 billion; 2018 – $3 million; 2019 – $- million; 2020 – $- million; 2021 – $- million; and 2022 and thereafter – $- million.
BNY Mellon 169
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Note 8 - Net interest revenue
The following table provides the components of net interest revenue presented on the consolidated income statement.
Net interest revenue | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Interest revenue | |||||||||
Non-margin loans | $ | 873 | $ | 727 | $ | 697 | |||
Margin loans | 265 | 207 | 182 | ||||||
Securities: | |||||||||
Taxable | 1,772 | 1,813 | 1,603 | ||||||
Exempt from federal income taxes | 70 | 82 | 100 | ||||||
Total securities | 1,842 | 1,895 | 1,703 | ||||||
Deposits with banks | 104 | 104 | 238 | ||||||
Deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | 198 | 170 | 207 | ||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 233 | 147 | 86 | ||||||
Trading assets | 60 | 76 | 121 | ||||||
Total interest revenue | 3,575 | 3,326 | 3,234 | ||||||
Interest expense | |||||||||
Deposits in domestic offices | 41 | 30 | 29 | ||||||
Deposits in foreign offices | (25 | ) | 7 | 54 | |||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | 36 | (6 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||
Trading liabilities | 6 | 9 | 25 | ||||||
Other borrowed funds | 8 | 9 | 6 | ||||||
Commercial paper | 5 | 2 | 2 | ||||||
Customer payables | 12 | 7 | 9 | ||||||
Long-term debt | 354 | 242 | 242 | ||||||
Total interest expense | 437 | 300 | 354 | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 3,138 | 3,026 | 2,880 | ||||||
Provision for credit losses | (11 | ) | 160 | (48 | ) | ||||
Net interest revenue after provision for credit losses | $ | 3,149 | $ | 2,866 | $ | 2,928 | |||
Note 9 - Noninterest expense
The following table provides a breakdown of noninterest expense presented on the consolidated income statement.
Noninterest expense | ||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
Staff | $ | 5,733 | $ | 5,837 | $ | 5,845 | ||||
Professional, legal and other purchased services | 1,185 | 1,230 | 1,339 | |||||||
Software | 647 | 627 | 620 | |||||||
Net occupancy | 590 | 600 | 610 | |||||||
Distribution and servicing | 405 | 381 | 428 | |||||||
Furniture and equipment | 247 | 280 | 322 | |||||||
Sub-custodian | 245 | 270 | 286 | |||||||
Business development | 245 | 267 | 268 | |||||||
Bank assessment charges | 219 | 157 | 146 | |||||||
Clearing | 155 | 150 | 129 | |||||||
Communications | 87 | 103 | 119 | |||||||
Other | 479 | 551 | 637 | |||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 237 | 261 | 298 | |||||||
Litigation | 45 | 87 | 953 | |||||||
Merger and integration and restructuring charges (recoveries) | 4 | (2 | ) | 177 | (a) | |||||
Total noninterest expense | $ | 10,523 | $ | 10,799 | $ | 12,177 | ||||
(a) | Primarily includes restructuring charges related to the Streamlining actions program initiated in 2014 and severance. Streamlining actions included rationalizing our staff and simplifying and automating global processes. |
Note 10 - Income taxes
The components of the income tax provision are as follows:
Provision (benefit) for income taxes | Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Current taxes: | |||||||||
Federal | $ | 823 | $ | 551 | $ | 1,273 | |||
Foreign | 327 | 306 | 337 | ||||||
State and local | 153 | 109 | 155 | ||||||
Total current tax expense | 1,303 | 966 | 1,765 | ||||||
Deferred tax expense (benefit): | |||||||||
Federal | (75 | ) | 114 | (672 | ) | ||||
Foreign | (14 | ) | (1 | ) | (98 | ) | |||
State and local | (37 | ) | (66 | ) | (83 | ) | |||
Total deferred tax expense (benefits) | (126 | ) | 47 | (853 | ) | ||||
Provision for income taxes | $ | 1,177 | $ | 1,013 | $ | 912 | |||
170 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The components of income before taxes are as follows:
Income before taxes | Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Domestic | $ | 3,147 | $ | 2,698 | $ | 2,456 | |||
Foreign | 1,578 | 1,537 | 1,107 | ||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 4,725 | $ | 4,235 | $ | 3,563 | |||
The components of our net deferred tax liability are as follows:
Net deferred tax liability | Dec. 31, | |||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 2,694 | $ | 2,631 | ||
Lease financings | 391 | 569 | ||||
Pension obligation | 184 | 155 | ||||
Renewable energy investment | 179 | 68 | ||||
Equity investments | 104 | 113 | ||||
Employee benefits | (471 | ) | (470 | ) | ||
Reserves not deducted for tax | (136 | ) | (274 | ) | ||
Credit losses on loans | (100 | ) | (102 | ) | ||
Securities valuation | (55 | ) | 156 | |||
Other assets | (101 | ) | (109 | ) | ||
Other liabilities | 162 | 42 | ||||
Net deferred tax liability | $ | 2,851 | $ | 2,779 | ||
As of Dec. 31, 2016, we have an available German net operating loss carryforward of $130 million with an indefinite life. Also, we have a U.S. foreign tax credit carryforward of approximately $37 million that will begin to expire in 2025. We believe it is more likely than not that we will fully realize our deferred tax assets.
As of Dec. 31, 2016, we had approximately $6.0 billion of earnings attributable to foreign subsidiaries that have been permanently reinvested abroad and for which no incremental U.S. income tax provision has been recorded. If these earnings were to be repatriated, the estimated U.S. tax liability as of Dec. 31, 2016 would be up to $1.2 billion. Management has no intention of repatriating these earnings to the U.S. in the foreseeable future.
The statutory federal income tax rate is reconciled to our effective income tax rate below:
Effective tax rate | Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
Federal rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % |
State and local income taxes, net of federal income tax benefit | 1.6 | 0.6 | 1.3 | |||
Foreign operations | (5.6 | ) | (6.6 | ) | (3.0 | ) |
Tax credits | (2.2 | ) | (1.4 | ) | (0.8 | ) |
Tax-exempt income | (1.8 | ) | (2.5 | ) | (3.3 | ) |
Leverage lease adjustment | (0.9 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (1.1 | ) |
Carryback claim | — | — | (4.7 | ) | ||
Nondeductible litigation expense | — | — | 2.1 | |||
Other – net | (1.2 | ) | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||
Effective tax rate | 24.9 | % | 23.9 | % | 25.6 | % |
Unrecognized tax positions | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Beginning balance at Jan. 1, – gross | $ | 649 | $ | 669 | $ | 866 | |||
Prior period tax positions: | |||||||||
Increases | 8 | 13 | 58 | ||||||
Decreases | (40 | ) | (21 | ) | (257 | ) | |||
Current period tax positions | 16 | 14 | 19 | ||||||
Settlements | (477 | ) | (26 | ) | (17 | ) | |||
Statute expiration | (10 | ) | — | — | |||||
Ending balance at Dec. 31, – gross | $ | 146 | $ | 649 | $ | 669 | |||
Our total tax reserves as of Dec. 31, 2016 were $146 million compared with $649 million at Dec. 31, 2015. If these tax reserves were unnecessary, $146 million would affect the effective tax rate in future periods. We recognize accrued interest and penalties, if applicable, related to income taxes in income tax expense. Included in the balance sheet at Dec. 31, 2016 is accrued interest, where applicable, of $18 million. The additional tax expense related to interest for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016 was $2 million, compared with $2 million for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015.
It is reasonably possible the total reserve for uncertain tax positions could decrease within the next 12 months by approximately $13 million as a result of adjustments related to tax years that are still subject to examination.
Our federal income tax returns are closed to examination through 2013. Our New York State tax returns are closed to examination through 2012. Our New York City income tax returns are closed to examination through 2010. Our UK income tax returns are closed to examination through 2012.
BNY Mellon 171
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Note 11 - Long-term debt
Long-term debt | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||
(in millions) | Rate | Maturity | Amount | Rate | Amount | ||||||
Senior debt: | |||||||||||
Fixed rate | 1.30 - 5.94% | 2017 - 2026 | $ | 20,005 | 0.70 - 5.94% | $ | 17,724 | ||||
Floating rate | 0.80 - 2.05% | 2018 - 2038 | 2,828 | 0.41 - 1.48% | 2,378 | ||||||
Subordinated debt (a) | 3.00 - 7.50% | 2017 - 2028 | 1,383 | 5.45 - 7.50% | 1,150 | ||||||
Junior subordinated debentures (b) | 1.87% | 2036 | 247 | 6.37 | % | 295 | |||||
Total | $ | 24,463 | $ | 21,547 | |||||||
(a) | Fixed rate. |
(b) | Floating rate at Dec. 31, 2016 and fixed rate at Dec. 31, 2015. |
Total long-term debt that matures during the next five years for BNY Mellon is as follows: 2017 – $750 million, 2018 – $3.6 billion, 2019 – $4.2 billion, 2020 – $4.0 billion and 2021 – $4.3 billion.
Trust-preferred securities
Mellon Capital III, a Delaware statutory trust owned by BNY Mellon, issued trust preferred securities in 2006. At Dec. 31, 2016, the sole assets of Mellon Capital III are junior subordinated debentures of BNY Mellon with maturities and interest rates that match the trust preferred securities. BNY Mellon's obligations provide a full and unconditional guarantee of payment of distributions and other amounts due on the trust preferred securities. The guarantee does not guarantee payment of distributions or other amounts due when Mellon Capital III does not have funds available to make such payments.
In January 2017, we announced that all outstanding trust preferred securities issued by Mellon Capital III will be redeemed on March 20, 2017. The redemption price for the trust-preferred securities will be equal to the par value plus interest accrued up to and excluding the redemption date.
Mellon Capital IV, a Delaware statutory trust owned by BNY Mellon, issued trust preferred securities in June 2007. The sole assets of Mellon Cap IV originally were junior subordinated debentures and a stock purchase contract for preferred stock. Through a remarketing in May 2012, the junior subordinated debentures issued by BNY Mellon and held by Mellon Capital IV were sold to third party investors and then exchanged for BNY Mellon's senior notes, which were sold in a public offering. The proceeds of the sale of the senior notes were used to fund the purchase by Mellon Capital IV of $500 million of BNY Mellon’s Series A preferred stock, which was issued on June 20, 2012. At Dec. 31, 2016, the Series A preferred stock was the sole asset of Mellon Capital IV. See Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional disclosures related to preferred stock, including the Series A preferred stock.
The following tables set forth a summary of the trust preferred securities issued by the Trusts as of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015:
Trust preferred securities at Dec. 31, 2016 (dollar amounts in millions) | Trust-preferred securities issued by the trust | Interest rate | Assets of the trust | (a) | Due date | Call date | Call price | |||||||||
MEL Capital III (b)(c) | $ | 247 | 1.87 | % | $ | 247 | 2036 | 2016 | Par | |||||||
MEL Capital IV | — | — | % | 500 | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total | $ | 247 | $ | 747 | ||||||||||||
(a) | Represents junior subordinated deferrable interest debentures of BNY Mellon in the case of MEL Capital III and BNY Mellon’s Series A preferred stock in the case of MEL Capital IV. |
(b) | Amount was translated from British pound sterling into U.S. dollars on a basis of U.S. $1.23 to £1, the rate of exchange on Dec. 31, 2016. |
(c) | Interest rate changed from fixed rate of 6.37% to floating rate of £ LIBOR plus 134 bps at the first call date. |
172 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Trust preferred securities at Dec. 31, 2015 (dollar amounts in millions) | Trust-preferred securities issued by the trust | Interest rate | Assets of the trust | (a) | Due date | Call date | Call price | |||||||||
MEL Capital III (b) | $ | 296 | 6.37 | % | $ | 295 | 2036 | 2016 | Par | |||||||
MEL Capital IV | — | — | % | 500 | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total | $ | 296 | $ | 795 | ||||||||||||
(a) | Represents junior subordinated deferrable interest debentures of BNY Mellon in the case of MEL Capital III and BNY Mellon’s Series A preferred stock in the case of MEL Capital IV. |
(b) | Amount was translated from British pound sterling into U.S. dollars on a basis of U.S. $1.48 to £1, the rate of exchange on Dec. 31, 2015. |
Note 12 - Securitizations and variable interest entities
BNY Mellon has variable interests in VIEs, which include investments in retail, institutional and alternative investment funds, including CLO structures in which we provide asset management services, some of which are consolidated. The investment funds are offered to our retail and institutional clients to provide them with access to investment vehicles with specific investment objectives and strategies that address the client’s investment needs.
BNY Mellon earns management fees from these funds as well as performance fees in certain funds and may also provide start-up capital for its new funds. The funds are primarily financed by our customers’ investments in the funds’ equity or debt.
Additionally, BNY Mellon invests in qualified affordable housing and renewable energy projects, which are designed to generate a return primarily through the realization of tax credits by the Company. The projects, which are structured as limited partnerships and LLCs, are also VIEs, but are not consolidated.
The VIEs discussed above are included in the scope of ASU 2015-02, which was adopted effective Jan. 1, 2015, and are reviewed for consolidation based on the guidance in ASC 810, Consolidation.
We reconsider and reassess whether or not we are the primary beneficiary of a VIE when governing
documents or contractual arrangements are changed which would reallocate the obligation to absorb expected losses or receive expected residual returns between BNY Mellon and the other investors, when BNY Mellon disposes of its variable interests in the fund or when additional variable interests are issued to other investors and when we acquire additional variable interests in the VIE.
The following tables present the incremental assets and liabilities included in BNY Mellon’s consolidated financial statements, after applying intercompany eliminations, as of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015. The net assets of any consolidated VIE are solely available to settle the liabilities of the VIE and to settle any investors’ ownership liquidation requests, including any seed capital invested in the VIE by BNY Mellon.
Investments consolidated at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||
(in millions) | Investment Management funds | Securitizations | Total consolidated investments | |||||||
Available-for-sale securities | $ | — | $ | 400 | $ | 400 | ||||
Trading assets | 979 | — | 979 | |||||||
Other assets | 252 | — | 252 | |||||||
Total assets | $ | 1,231 | (a) | $ | 400 | $ | 1,631 | |||
Trading liabilities | $ | 282 | $ | — | $ | 282 | ||||
Other liabilities | 33 | 363 | 396 | |||||||
Total liabilities | $ | 315 | (a) | $ | 363 | $ | 678 | |||
Nonredeemable noncontrolling interests | $ | 618 | (a) | $ | — | $ | 618 | |||
(a) | Includes VMEs with assets of $114 million, liabilities of $3 million and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests of $25 million. |
BNY Mellon 173
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Investments consolidated at Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
(in millions) | Investment Management funds | Securitizations | Total consolidated investments | |||||||
Available-for-sale securities | $ | — | $ | 400 | $ | 400 | ||||
Trading assets | 1,228 | — | 1,228 | |||||||
Other assets | 173 | — | 173 | |||||||
Total assets | $ | 1,401 | (a) | $ | 400 | $ | 1,801 | |||
Trading liabilities | $ | 229 | $ | — | $ | 229 | ||||
Other liabilities | 17 | 359 | 376 | |||||||
Total liabilities | $ | 246 | (a) | $ | 359 | $ | 605 | |||
Nonredeemable noncontrolling interests | $ | 738 | (a) | $ | — | $ | 738 | |||
(a) | Includes VMEs with assets of $190 million, liabilities of $1 million and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests of $5 million. |
BNY Mellon has not provided financial or other support that was not otherwise contractually required to be provided to our VIEs. Additionally, creditors of any consolidated VIEs do not have any recourse to the general credit of BNY Mellon.
Non-consolidated VIEs
As of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, the following assets and liabilities related to the VIEs where BNY Mellon is not the primary beneficiary are included in our consolidated financial statements.
Non-consolidated VIEs at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||||
(in millions) | Assets | Liabilities | Maximum loss exposure | ||||||
Other | $ | 2,442 | $ | 369 | $ | 2,811 | |||
Non-consolidated VIEs at Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||
(in millions) | Assets | Liabilities | Maximum loss exposure | ||||||
Other (a) | $ | 1,754 | $ | 393 | $ | 2,147 | |||
(a) | The presentation of non-consolidated VIEs was adjusted to place them on a basis comparable with the current period. |
The maximum loss exposure indicated in the above tables relates solely to BNY Mellon’s investments in, and unfunded commitments to, the VIEs.
Note 13 - Shareholders’ equity
Common stock
BNY Mellon has 3.5 billion authorized shares of common stock with a par value of $0.01 per share. At Dec. 31, 2016, 1,047,488,301 shares of common stock were outstanding.
Common stock repurchase program
On March 11, 2015, in connection with the Federal Reserve’s non-objection to our 2015 capital plan, the board of directors authorized a stock purchase program providing for the repurchase of an aggregate of $3.1 billion of common stock beginning in the second quarter of 2015 and continuing through the second quarter of 2016. On June 29, 2016, in connection with the Federal Reserve’s non-objection to our 2016 capital plan, BNY Mellon announced a new stock purchase program providing for the repurchase of an aggregate of $2.14 billion of common stock and the repurchase of up to an additional $560 million of common stock contingent upon the issuance of $750 million of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock. In August 2016, BNY Mellon issued $1 billion of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock, $750 million of which satisfied the contingency for the repurchase of up to $560 million additional common stock in 2016. This new repurchase plan totaling $2.7 billion replaces all previously authorized share repurchase plans. The 2016 capital plan began in the third quarter of 2016 and continues through the second quarter of 2017.
Share repurchases may be executed through repurchase plans designed to comply with Rule 10b5-1 and through derivative, accelerated share repurchase and other structured transactions. In 2016, we repurchased 58.6 million common shares at an average price of $40.91 per common share for a total of $2.4 billion. At Dec. 31, 2016, the maximum dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the June 29, 2016 program, including employee benefit plan repurchases, totaled $1.4 billion.
174 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Preferred stock
BNY Mellon has 100 million authorized shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.01. The following table summarizes BNY Mellon’s preferred stock issued and outstanding at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Preferred stock summary | Liquidation preference per share (in dollars) | Total shares issued and outstanding | |||||||||||||||
Carrying value (a) | |||||||||||||||||
(dollars in millions, unless otherwise noted) | Per annum dividend rate | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
Series A | Noncumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock | Greater of (i) three-month LIBOR plus 0.565% for the related distribution period; or (ii) 4.000% | $ | 100,000 | 5,001 | 5,001 | $ | 500 | $ | 500 | |||||||
Series C | Noncumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock | 5.2 | % | $ | 100,000 | 5,825 | 5,825 | 568 | 568 | ||||||||
Series D | Noncumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock | 4.50% commencing Dec. 20, 2013 to but excluding June 20, 2023, then a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR plus 2.46% | $ | 100,000 | 5,000 | 5,000 | 494 | 494 | |||||||||
Series E | Noncumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock | 4.95% commencing Dec. 20, 2015 to and including June 20, 2020, then a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR plus 3.42% | $ | 100,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 990 | 990 | |||||||||
Series F | Noncumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock | 4.625% commencing March 20, 2017 to and including Sept. 20, 2026, then a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR plus 3.131% | $ | 100,000 | 10,000 | — | 990 | — | |||||||||
Total | 35,826 | 25,826 | $ | 3,542 | $ | 2,552 | |||||||||||
(a) | The carrying value of the Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F preferred stock is recorded net of issuance costs. |
Holders of both the Series A and Series C preferred stock are entitled to receive dividends on each dividend payment date (March 20, June 20, September 20 and December 20 of each year), if declared by BNY Mellon’s Board of Directors. Holders of the Series D preferred stock are entitled to receive dividends, if declared by BNY Mellon’s Board of Directors, on each June 20 and December 20, to but excluding June 20, 2023; and on each March 20, June 20, September 20 and December 20, from and including June 20, 2023. Holders of the Series E preferred stock are entitled to receive dividends, if declared by BNY Mellon’s Board of Directors, on each June 20 and December 20, to and including June 20, 2020; and on each March 20, June 20, September 20 and December 20, from and including September 20, 2020. Holders of the Series F preferred stock are entitled to receive dividends, if declared by BNY Mellon’s Board of Directors, on each March 20 and September 20, commencing March 20, 2017, to and including Sept. 20, 2026; and on each March 20, June 20, September 20 and December 20, commencing Dec. 20, 2026. BNY Mellon’s ability to declare or pay dividends on, or purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire, shares of our common stock or any of our shares that rank junior to the preferred stock as to the payment of dividends
and/or the distribution of any assets on any liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of BNY Mellon will be prohibited, subject to certain restrictions, in the event that we do not declare and pay in full preferred dividends for the then current dividend period of the Series A preferred stock or the last preceding dividend period of the Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F preferred stock.
All of the outstanding shares of the Series A preferred stock are owned by Mellon Capital IV, which will pass through any dividend on the Series A preferred stock to the holders of its Normal Preferred Capital Securities. All of the outstanding shares of the Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F preferred stock are held by the depositary of the depositary shares, which will pass through the applicable portion of any dividend on the Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F preferred stock to the holders of record of their respective depositary shares.
On Dec. 20, 2016, The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation paid the following dividends for the noncumulative perpetual preferred stock for the dividend period ending in December 2016 to holders of record as of the close of business on Dec. 5, 2016:
BNY Mellon 175
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
• | $1,011.11 per share on the Series A Preferred Stock (equivalent to $10.1111 per Normal Preferred Capital Security of Mellon Capital IV, each representing a 1/100th interest in a share of the Series A Preferred Stock); |
• | $1,300.00 per share on the Series C Preferred Stock (equivalent to $0.3250 per depositary share, each representing a 1/4,000th interest in a share of the Series C Preferred Stock); |
• | $2,250.00 per share on the Series D Preferred Stock (equivalent to $22.5000 per depositary share, each representing a 1/100th interest in a share of the Series D Preferred Stock); and |
• | $2,475.00 per share on the Series E Preferred Stock (equivalent to $24.7500 per depositary share, each representing a 1/100th interest in a share of the Series E Preferred Stock). |
The preferred stock is not subject to the operation of a sinking fund and is not convertible into, or exchangeable for, shares of our common stock or any other class or series of our other securities. We may redeem the Series A preferred stock, in whole or in part, at our option. We may also, at our option, redeem the shares of the Series C preferred stock, in whole or in part, on or after the dividend payment date in September 2017, the Series D preferred stock, in whole or in part, on or after the dividend payment date in June 2023, the Series E preferred stock, in whole or in part, on or after the dividend payment date in June 2020, and the Series F preferred stock, in whole or in part, on or after the dividend payment date in September 2026. The Series C, Series D, Series E or Series F preferred stock can be redeemed, in whole but not in part, at any time within 90 days following a regulatory capital treatment event (as defined in each of the Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F’s Certificates of Designation). Redemption of the preferred stock is subject to the prior approval of the Federal Reserve.
Terms of the Series A, Series C, Series D, Series E and Series F preferred stock are more fully described in each of their Certificate of Designations, each of which is filed as an Exhibit to BNY Mellon’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016.
Temporary equity
Temporary equity was $151 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $200 million at Dec. 31, 2015. Temporary equity represents amounts recorded for redeemable noncontrolling interests resulting from equity-classified share-based payment arrangements that are currently redeemable or are expected to become redeemable. The current redemption value of such awards is classified as temporary equity and is adjusted to its redemption value at each balance sheet date.
Capital adequacy
Regulators establish certain levels of capital for bank holding companies and banks, including BNY Mellon and our bank subsidiaries, in accordance with established quantitative measurements. For the Parent to maintain its status as a financial holding company, our bank subsidiaries and BNY Mellon must, among other things, qualify as “well capitalized.”
As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries were “well capitalized.” As of Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon and our U.S. bank subsidiaries, with the exception of BNY Mellon, N.A., were “well capitalized.” As of Dec. 31, 2015, BNY Mellon, N.A. was not “well capitalized” because its Total capital ratio was 9.89%, which was below the 10% “well capitalized” threshold. With the filing of its March 31, 2016 Call Report, BNY Mellon, N.A.’s Total capital ratio was 10.94%, which is above the 10% “well capitalized” threshold.
176 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Our consolidated and largest bank subsidiary, The Bank of New York Mellon, regulatory capital ratios are shown below.
Consolidated and largest bank subsidiary regulatory capital ratios (a) | Dec. 31, | |||
2016 | 2015 | |||
Consolidated regulatory capital ratios: | ||||
CET1 | 10.6 | % | 10.8 | % |
Tier 1 capital ratio | 12.6 | 12.3 | % | |
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 13.0 | 12.5 | ||
Leverage capital ratio | 6.6 | 6.0 | ||
The Bank of New York Mellon regulatory capital ratios: | ||||
CET1 | 13.6 | % | 11.8 | % |
Tier 1 capital ratio | 13.9 | 12.3 | ||
Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratio | 14.2 | 12.5 | ||
Leverage capital ratio | 7.2 | 5.9 | ||
(a) | For the CET1, Tier 1 and Total capital ratios, our effective capital ratios under U.S. capital rules are the lower of the ratios as calculated under the Standardized and Advanced Approaches. The leverage capital ratio is based on Tier 1 capital, as phased-in and quarterly average total assets. For BNY Mellon to qualify as “well capitalized,” its Tier 1 and Total (Tier 1 plus Tier 2) capital ratios must be at least 6% and 10%, respectively. For The Bank of New York Mellon, our largest bank subsidiary, to qualify as “well capitalized,” its CET1, Tier 1, Total and leverage capital ratios must be at least 6.5%, 8%, 10% and 5%, respectively. |
Failure to satisfy regulatory standards, including “well capitalized” status or capital adequacy rules more generally, could result in limitations on our activities and adversely affect our financial condition.
If a bank holding company such as BNY Mellon or bank such as The Bank of New York Mellon or BNY Mellon, N.A. fails to qualify as “adequately capitalized,” regulatory sanctions and limitations are imposed.
The following table presents the components of our transitional CET1, Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital, the risk-weighted assets determined under the Standardized and Advanced Approaches and the average assets used for leverage capital purposes.
Components of transitional capital (a) (in millions) | Dec. 31, | |||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||
CET1: | ||||||
Common shareholders’ equity | $ | 35,794 | $ | 36,067 | ||
Goodwill and intangible assets | (17,314 | ) | (17,295 | ) | ||
Net pension fund assets | (55 | ) | (46 | ) | ||
Equity method investments | (313 | ) | (296 | ) | ||
Deferred tax assets | (19 | ) | (8 | ) | ||
Other | — | (5 | ) | |||
Total CET1 | 18,093 | 18,417 | ||||
Other Tier 1 capital: | ||||||
Preferred stock | 3,542 | 2,552 | ||||
Trust preferred securities | — | 74 | ||||
Disallowed deferred tax assets | (13 | ) | (12 | ) | ||
Net pension fund assets | (36 | ) | (70 | ) | ||
Other | (121 | ) | (25 | ) | ||
Total Tier 1 capital | $ | 21,465 | $ | 20,936 | ||
Tier 2 capital: | ||||||
Trust preferred securities | $ | 148 | $ | 222 | ||
Subordinated debt | 550 | 149 | ||||
Allowance for credit losses | 281 | 275 | ||||
Other | (12 | ) | (12 | ) | ||
Total Tier 2 capital - Standardized Approach | 967 | 634 | ||||
Excess of expected credit losses | 50 | 37 | ||||
Less: Allowance for credit losses | 281 | 275 | ||||
Total Tier 2 capital - Advanced Approach | $ | 736 | $ | 396 | ||
Total capital: | ||||||
Standardized Approach | $ | 22,432 | $ | 21,570 | ||
Advanced Approach | $ | 22,201 | $ | 21,332 | ||
Risk-weighted assets: | ||||||
Standardized Approach | $ | 147,671 | $ | 159,893 | ||
Advanced Approach: | ||||||
Credit Risk | $ | 97,659 | $ | 106,974 | ||
Market Risk | 2,836 | 2,148 | ||||
Operational Risk | 70,000 | 61,262 | ||||
Total Advanced Approach | $ | 170,495 | $ | 170,384 | ||
Average assets for leverage capital purposes | $ | 326,809 | $ | 351,435 | ||
(a) | Reflects transitional adjustments to CET1, Tier 1 capital and Tier 2 capital required in 2016 and 2015 under the U.S. capital rules. |
BNY Mellon 177
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The following table presents the amount of capital by which BNY Mellon and our largest bank subsidiary, The Bank of New York Mellon, exceeded the capital thresholds determined under the transitional rules.
Capital above thresholds at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||
(in millions) | Consolidated | The Bank of New York Mellon | (b) | |||||
CET1 | $ | 8,716 | (a) | $ | 9,644 | |||
Tier 1 capital | 9,530 | (a) | $ | 8,091 | ||||
Total capital | 5,152 | (b) | 5,747 | |||||
Leverage capital | 8,393 | (a) | 5,824 | |||||
(a) | Based on minimum required standards, with applicable buffers. |
(b) | Based on well capitalized standards. |
Note 14 - Other comprehensive income (loss)
Components of other comprehensive income (loss) | Year ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Pre-tax amount | Tax (expense) benefit | After-tax amount | Pre-tax amount | Tax (expense) benefit | After-tax amount | Pre-tax amount | Tax (expense) benefit | After-tax amount | ||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments arising during the period (a) | $ | (518 | ) | $ | (332 | ) | $ | (850 | ) | $ | (518 | ) | $ | (81 | ) | $ | (599 | ) | $ | (715 | ) | $ | (91 | ) | $ | (806 | ) | ||
Total foreign currency translation | (518 | ) | (332 | ) | (850 | ) | (518 | ) | (81 | ) | (599 | ) | (715 | ) | (91 | ) | (806 | ) | |||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on assets available-for-sale: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) arising during period | (388 | ) | 146 | (242 | ) | (535 | ) | 172 | (363 | ) | 582 | (169 | ) | 413 | |||||||||||||||
Reclassification adjustment (b) | (75 | ) | 26 | (49 | ) | (83 | ) | 31 | (52 | ) | (91 | ) | 33 | (58 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net unrealized gain (loss) on assets available-for-sale | (463 | ) | 172 | (291 | ) | (618 | ) | 203 | (415 | ) | 491 | (136 | ) | 355 | |||||||||||||||
Defined benefit plans: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Prior service cost arising during the period | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3 | (1 | ) | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net gain (loss) arising during the period | (151 | ) | 43 | (108 | ) | (105 | ) | 40 | (65 | ) | (766 | ) | 287 | (479 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange adjustment | (1 | ) | 1 | — | — | — | — | (2 | ) | 1 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service credit, net loss and initial obligation included in net periodic benefit cost (b) | 88 | (31 | ) | 57 | 104 | (35 | ) | 69 | 127 | (50 | ) | 77 | |||||||||||||||||
Total defined benefit plans | (64 | ) | 13 | (51 | ) | (1 | ) | 5 | 4 | (638 | ) | 237 | (401 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedges: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized hedge gain (loss) arising during period | (52 | ) | 18 | (34 | ) | — | — | — | 23 | (13 | ) | 10 | |||||||||||||||||
Reclassification adjustment (b) | 45 | (15 | ) | 30 | 11 | (3 | ) | 8 | (41 | ) | 16 | (25 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Net unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedges | (7 | ) | 3 | (4 | ) | 11 | (3 | ) | 8 | (18 | ) | 3 | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Total other comprehensive income (loss) | $ | (1,052 | ) | $ | (144 | ) | $ | (1,196 | ) | $ | (1,126 | ) | $ | 124 | $ | (1,002 | ) | $ | (880 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | (867 | ) | ||||
(a) | Includes the impact of hedges of net investments in foreign subsidiaries. See Note 21 for additional information. |
(b) | The reclassification adjustment related to the unrealized gain (loss) on assets available-for-sale is recorded as net securities gains on the Consolidated Income Statement. The amortization of prior service credit, net loss and initial obligation included in net periodic benefit cost is recorded as staff expense on the Consolidated Income Statement. See Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for the location of the reclassification adjustment related to cash flow hedges on the Consolidated Income Statement. |
178 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Changes in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) attributable to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation shareholders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
ASC 820 Adjustments | Unrealized gain (loss) on assets available-for-sale | Unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedges | Total accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | |||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Foreign currency translation | Pensions | Other post-retirement benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||
2013 ending balance | $ | (388 | ) | $ | (840 | ) | $ | (60 | ) | $ | 387 | $ | 9 | $ | (892 | ) | ||||||||
Change in 2014 | (681 | ) | (396 | ) | (5 | ) | 355 | (15 | ) | (742 | ) | |||||||||||||
2014 ending balance | $ | (1,069 | ) | $ | (1,236 | ) | $ | (65 | ) | $ | 742 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (1,634 | ) | |||||||
Change in 2015 | (563 | ) | (14 | ) | 18 | (415 | ) | 8 | (966 | ) | ||||||||||||||
2015 ending balance | $ | (1,632 | ) | $ | (1,250 | ) | $ | (47 | ) | $ | 327 | $ | 2 | $ | (2,600 | ) | ||||||||
Change in 2016 | (819 | ) | (56 | ) | 5 | (291 | ) | (4 | ) | (1,165 | ) | |||||||||||||
2016 ending balance | $ | (2,451 | ) | $ | (1,306 | ) | $ | (42 | ) | $ | 36 | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (3,765 | ) | |||||||
Note 15 - Stock-based compensation
Our Long-Term Incentive Plans provide for the issuance of stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units (“RSUs”) and other stock-based awards to employees and directors of BNY Mellon. At Dec. 31, 2016, under the Long-Term Incentive Plan approved in April 2014, we may issue 34,283,413 new stock-based awards. Of this amount, 19,569,848 shares (subject to potential increase as provided in the Long-Term Incentive Plan) may be issued as restricted stock or RSUs. Stock-based compensation expense related to retirement eligibility vesting totaled $106 million in 2016, $97 million in 2015 and $88 million in 2014.
Stock options
Our Long-Term Incentive Plans provide for the issuance of stock options at fair market value at the date of grant to officers and employees of BNY Mellon. Generally, each option granted is exercisable between one and 10 years from the date of grant. No stock options were granted in 2016, 2015 and 2014.
The compensation cost that has been charged against income was $2 million for 2016, $10 million for 2015 and $28 million for 2014 (including $1 million recorded in restructuring expense). The total income tax benefit recognized in the income statement was $1 million for 2016, $4 million for 2015 and $11 million for 2014.
A summary of the status of our options as of Dec. 31, 2016, and changes during the year, is presented below:
Stock option activity | Shares subject to option | Weighted-average exercise price | Weighted-average remaining contractual term (in years) | |||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2015 | 35,735,264 | $ | 33.57 | 3.4 | ||
Granted | — | — | ||||
Exercised | (12,746,946 | ) | 34.17 | |||
Canceled/Expired | (1,746,750 | ) | 41.38 | |||
Balance at Dec. 31, 2016 | 21,241,568 | $ | 32.57 | 2.8 | ||
Vested and expected to vest at Dec. 31, 2016 | 21,241,568 | 32.57 | 2.8 | |||
Exercisable at Dec. 31, 2016 | 21,241,568 | 32.57 | 2.8 | |||
Stock options outstanding at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
Options outstanding | Options exercisable (a) | |||||||||||||
Range of exercise prices | Outstanding | Weighted-average remaining contractual life (in years) | Weighted-average exercise price | Exercisable | Weighted-average exercise price | |||||||||
$ 18 to 31 | 13,318,863 | 3.9 | $ | 25.91 | 13,318,863 | $ | 25.91 | |||||||
$ 31 to 41 | 1,587,665 | 0.3 | 40.29 | 1,587,665 | 40.29 | |||||||||
$ 41 to 51 | 6,335,040 | 1.0 | 44.63 | 6,335,040 | 44.63 | |||||||||
$ 18 to 51 | 21,241,568 | 2.8 | $ | 32.57 | 21,241,568 | $ | 32.57 | |||||||
(a) | At Dec. 31, 2015 and 2014, 33,703,283 and 42,137,574 options were exercisable at an average price per common share of $34.27 and $34.38, respectively. |
BNY Mellon 179
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Aggregate intrinsic value of options | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Outstanding at Dec. 31, | $ | 315 | $ | 306 | $ | 409 | |||
Exercisable at Dec. 31, | $ | 315 | $ | 267 | $ | 307 | |||
The total intrinsic value of options exercised was $122 million in 2016, $130 million in 2015 and $118 million in 2014.
Cash received from option exercises totaled $438 million in 2016, $326 million in 2015 and $370 million in 2014. The actual tax benefit realized for the tax deductions from options exercised totaled $3 million in 2016, $21 million in 2015 and $17 million in 2014.
Restricted stock and RSUs
Restricted stock and RSUs are granted under our long-term incentive plans at no cost to the recipient. These awards are subject to forfeiture until certain restrictions have lapsed, including continued employment, for a specified period. The recipient of a share of restricted stock is entitled to voting rights and generally is entitled to dividends on the common stock. An RSU entitles the recipient to receive a share of common stock after the applicable restrictions lapse. The recipient generally is entitled to receive cash payments equivalent to any dividends paid on the underlying common stock during the period the RSU is outstanding but does not receive voting rights.
The fair value of restricted stock and RSUs is equal to the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The expense is recognized over the vesting period, which is zero to four years. The total compensation expense recognized for restricted stock and RSUs was $256 million in 2016, $235 million in 2015 and $243 million in 2014 (including $13 million recorded in restructuring expense). The total income tax benefit recognized in the income statement was $91 million for 2016, $83 million for 2015 and $94 million for 2014.
BNY Mellon’s Executive Committee members were granted a target award of 548,391 performance units (“PSUs”) in 2016 and 630,100 in 2015 that cliff vest in three years based on operating earnings per share with the potential of a risk modifier based on appropriate growth in risk-weighted assets. These awards are marked-to-market as the earnout
percentages are determined at the discretion of the Human Resources Compensation Committee based on a payout table.
BNY Mellon’s Executive Committee members were granted a target award of 719,947 PSUs in 2014 and 942,428 in 2013 that are earned annually based on an earnout percentage calculated using a metric of net income divided by RWA. The awards earned in each of the three performance periods vest at the end of the third performance period. Certain of the awards are granted to Material Risk Takers, as defined under the European Banking Authority, and are required to be marked to market due to discretionary claw-back language contained in their grants.
The following table summarizes our nonvested PSU, restricted stock and RSU activity for 2016.
Nonvested PSU, restricted stock and RSU activity | Number of shares | Weighted- average fair value | |||
Nonvested PSUs, restricted stock and RSUs at Dec. 31, 2015 | 16,983,971 | $ | 34.07 | ||
Granted | 8,331,206 | 35.10 | |||
Vested | (6,808,038 | ) | 32.10 | ||
Forfeited | (511,624 | ) | 34.63 | ||
Nonvested PSUs, restricted stock and RSUs at Dec. 31, 2016 | 17,995,515 | $ | 35.98 | ||
As of Dec. 31, 2016, $194 million of total unrecognized compensation costs related to nonvested PSUs, restricted stock and RSUs is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.6 years.
The total fair value of restricted stock and RSUs that vested was $236 million in 2016, $429 million in 2015 and $229 million in 2014.
Subsidiary Long-Term Incentive Plans
BNY Mellon also has several subsidiary Long-Term Incentive Plans which have issued restricted subsidiary shares to certain employees. These share awards are subject to forfeiture until certain restrictions have lapsed, including continued employment for a specified period of time. The shares are non-voting and non-dividend paying. Once the restrictions lapse, which generally occurs in three to five years, the shares can only be sold, at the option of the employee, to BNY Mellon at a price based generally on the fair value of the subsidiary at
180 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
the time of repurchase. In certain instances BNY Mellon has an election to call the shares.
Note 16 - Employee benefit plans
BNY Mellon has defined benefit and/or defined contribution retirement plans covering substantially all full-time and eligible part-time employees and
other post-retirement plans providing healthcare benefits for certain retired employees. Effective June 30, 2015, the benefit accruals under the U.S. qualified and nonqualified defined benefit plans were frozen. This change resulted in no additional benefits being earned by participants in those plans based on service or pay after June 30, 2015.
Pension and post-retirement healthcare plans
The following tables report the combined data for our domestic and foreign defined benefit pension and post-retirement healthcare plans.
Pension Benefits | Healthcare Benefits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic | Foreign | Domestic | Foreign | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Discount rate | 4.35 | % | 4.48 | % | 2.53 | % | 3.45 | % | 4.35 | % | 4.48 | % | 2.60 | % | 3.60 | % | |||||||||||
Rate of compensation increase | N/A | N/A | 3.60 | 3.51 | 3.00 | 3.00 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||||
Change in benefit obligation (a) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of period | $ | (4,177 | ) | $ | (4,460 | ) | $ | (1,147 | ) | $ | (1,177 | ) | $ | (184 | ) | $ | (210 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (8 | ) | |||
Service cost | — | (30 | ) | (29 | ) | (32 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest cost | (182 | ) | (170 | ) | (36 | ) | (38 | ) | (8 | ) | (8 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||
Employee contributions | — | — | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Amendments | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Actuarial (loss) gain | (106 | ) | 178 | (221 | ) | (1 | ) | 9 | 17 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
Divestitures | — | — | — | 12 | — | — | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
Curtailments | — | 94 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Special termination benefits | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Benefits paid | 191 | 211 | 23 | 17 | 15 | 18 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange adjustment | N/A | N/A | 163 | 73 | N/A | N/A | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of period | (4,274 | ) | (4,177 | ) | (1,248 | ) | (1,147 | ) | (169 | ) | (184 | ) | (2 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||||||
Change in fair value of plan assets | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value at beginning of period | 4,689 | 4,942 | 1,014 | 997 | 92 | 93 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | 387 | (61 | ) | 162 | 40 | 5 | (1 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Employer contributions | 21 | 19 | 87 | 51 | 15 | 18 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Employee contributions | — | — | 1 | 1 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions | — | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Benefit payments | (191 | ) | (211 | ) | (23 | ) | (17 | ) | (15 | ) | (18 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||
Foreign exchange adjustment | N/A | N/A | (151 | ) | (59 | ) | N/A | N/A | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Fair value at end of period | 4,906 | 4,689 | 1,090 | 1,014 | 97 | 92 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Funded status at end of period | $ | 632 | $ | 512 | $ | (158 | ) | $ | (133 | ) | $ | (72 | ) | $ | (92 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | |||||
Amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss consist of: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss (gain) | $ | 1,656 | $ | 1,678 | $ | 461 | $ | 368 | $ | 96 | $ | 111 | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | |||||||||
Prior service cost (credit) | — | — | — | 1 | (59 | ) | (69 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Total (before tax effects) | $ | 1,656 | $ | 1,678 | $ | 461 | $ | 369 | $ | 37 | $ | 42 | $ | (2 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | |||||||||
(a) | The benefit obligation for pension benefits is the projected benefit obligation and for healthcare benefits, it is the accumulated benefit obligation. |
BNY Mellon 181
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Net periodic benefit cost (credit) | Pension Benefits | Healthcare Benefits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic | Foreign | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | (a) | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Weighted-average assumptions as of Jan. 1: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Market-related value of plan assets | $ | 4,830 | $ | 4,696 | $ | 4,430 | $ | 994 | $ | 959 | $ | 898 | $ | 97 | $ | 92 | $ | 86 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||||
Discount rate | 4.48 | % | 4.13 | % | 4.99 | % | 3.45 | % | 3.33 | % | 4.29 | % | 4.48 | % | 4.13 | % | 4.99 | % | 3.60 | % | 3.10 | % | 4.21 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Expected rate of return on plan assets | 7.00 | 7.25 | 7.25 | 5.35 | 5.25 | 6.26 | 7.00 | 7.25 | 7.25 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rate of compensation increase | N/A | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.51 | 3.29 | 3.71 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Components of net periodic benefit cost (credit): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | — | $ | 30 | $ | 58 | $ | 29 | $ | 32 | $ | 33 | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Interest cost | 182 | 170 | 180 | 36 | 38 | 43 | 8 | 8 | 11 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on assets | (330 | ) | (333 | ) | (315 | ) | (51 | ) | (51 | ) | (58 | ) | (7 | ) | (6 | ) | (6 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Prior service (credit) cost | — | (1 | ) | (15 | ) | 1 | — | 1 | (10 | ) | (10 | ) | (10 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net actuarial loss | 69 | 111 | 125 | 17 | 23 | 15 | 8 | 10 | 11 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Settlement loss | 2 | 1 | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Curtailment (gain) | — | (30 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Special termination benefit charge | — | — | 1 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost (credit) | $ | (77 | ) | $ | (52 | ) | $ | 34 | $ | 33 | $ | 42 | $ | 34 | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | 7 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
(a) | As a result of the amendment to the U.S. pension plans, liabilities were re-measured as of Jan. 29, 2015 at a discount rate of 3.73% and the market-related value of plan assets was $4,713 million at Jan. 29, 2015. |
Changes in other comprehensive (income) loss in 2016 | Pension Benefits | Healthcare Benefits | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Domestic | Foreign | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||||
Net loss (gain) arising during period | $ | 49 | $ | 110 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | |||
Recognition of prior years’ net (loss) | (71 | ) | (18 | ) | (8 | ) | — | ||||||
Recognition of prior years’ service (cost) credit | — | (1 | ) | 10 | — | ||||||||
Foreign exchange adjustment | N/A | 1 | N/A | — | |||||||||
Total recognized in other comprehensive (income) loss (before tax effects) | $ | (22 | ) | $ | 92 | $ | (5 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | ||
Amounts expected to be recognized in net periodic benefit cost (income) in 2017 (before tax effects) | Pension Benefits | Healthcare Benefits | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Domestic | Foreign | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||||
Loss recognition | $ | 68 | $ | 34 | $ | 6 | $ | — | |||||
Prior service (credit) recognition | — | — | (10 | ) | — | ||||||||
Domestic | Foreign | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Pension benefits: | |||||||||||||
Prepaid benefit cost | $ | 836 | $ | 724 | $ | — | $ | 3 | |||||
Accrued benefit cost | (204 | ) | (212 | ) | (158 | ) | (136 | ) | |||||
Total pension benefits | $ | 632 | $ | 512 | $ | (158 | ) | $ | (133 | ) | |||
Healthcare benefits: | |||||||||||||
Accrued benefit cost | $ | (72 | ) | $ | (92 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | |
Total healthcare benefits | $ | (72 | ) | $ | (92 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | |
The accumulated benefit obligation for all defined benefit plans was $5.4 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $5.2 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
Plans with obligations in excess of plan assets | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | 224 | $ | 233 | $ | 149 | $ | 132 | |||||
Accumulated benefit obligation | 224 | 233 | 142 | 115 | |||||||||
Fair value of plan assets | 20 | 20 | 76 | 79 | |||||||||
Assumed healthcare cost trend - Domestic post-retirement healthcare benefits
The assumed healthcare cost trend rate used in determining benefit expense for 2017 is 6.25% decreasing to 4.75% in 2022. This projection is based on various economic models that forecast a decreasing growth rate of healthcare expenses over time. The underlying assumption is that healthcare
182 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
expense growth cannot outpace gross national product (“GNP”) growth indefinitely, and over time a lower equilibrium growth rate will be achieved. Further, the growth rate assumed in 2022 bears a reasonable relationship to the discount rate.
An increase in the healthcare cost trend rate of one percentage point for each year would increase the accumulated post-retirement benefit obligation by $10 million, or 6%, and the sum of the service and interest costs by $1 million, or 6%. Conversely, a decrease in this rate of one percentage point for each year would decrease the benefit obligation by $9 million, or 5%, and the sum of the service and interest costs by less than $1 million, or 5%.
Assumed healthcare cost trend - Foreign post-retirement healthcare benefits
An increase in the healthcare cost trend rate of one percentage point for each year would increase the accumulated post-retirement benefit obligation by less than $1 million and the sum of the service and interest costs by less than $1 million. Conversely, a decrease in this rate of one percentage point for each year would decrease the benefit obligation by less than $1 million and the sum of the service and interest costs by less than $1 million.
The following benefit payments for BNY Mellon’s pension and healthcare plans, which reflect expected future service as appropriate, are expected to be paid:
Expected benefit payments | ||||||||
(in millions) | Domestic | Foreign | ||||||
Pension benefits: | ||||||||
Year | 2017 | $ | 258 | $ | 12 | |||
2018 | 268 | 15 | ||||||
2019 | 251 | 16 | ||||||
2020 | 253 | 15 | ||||||
2021 | 258 | 19 | ||||||
2022-2026 | 1,289 | 110 | ||||||
Total pension benefits | $ | 2,577 | $ | 187 | ||||
Healthcare benefits: | ||||||||
Year | 2017 | $ | 13 | $ | — | |||
2018 | 13 | — | ||||||
2019 | 13 | — | ||||||
2020 | 13 | — | ||||||
2021 | 13 | — | ||||||
2022-2026 | 56 | 1 | ||||||
Total healthcare benefits | $ | 121 | $ | 1 | ||||
Plan contributions
BNY Mellon expects to make cash contributions to fund its defined benefit pension plans in 2017 of $22 million for the domestic plans and $64 million for the foreign plans.
BNY Mellon expects to make cash contributions to fund its post-retirement healthcare plans in 2017 of $13 million for the domestic plans and less than $1 million for the foreign plans.
Investment strategy and asset allocation
BNY Mellon is responsible for the administration of various employee pension and healthcare post-retirement benefits plans, both domestically and internationally. The domestic plans are administered by BNY Mellon’s Benefits Administration Committee, a named fiduciary. Subject to the following, at all relevant times, BNY Mellon’s Benefits Investment Committee, another named fiduciary to the domestic plans, is responsible for the investment of plan assets. The Benefits Investment Committee’s responsibilities include the investment of all domestic defined benefit plan assets, as well as the determination of investment options offered to participants in all domestic defined contribution plans. The Benefits Investment Committee conducts periodic reviews of investment performance, asset allocation and investment manager suitability. In addition, the Benefits Investment Committee has oversight of the Regional Governance Committees for the foreign defined benefit plans.
Our investment objective for U.S. and foreign plans is to maximize total return while maintaining a broadly diversified portfolio for the primary purpose of satisfying obligations for future benefit payments.
Equities are the main holding of the plans. Alternative investments (including private equities) and fixed income securities provide diversification and, in certain cases, lower the volatility of returns. In general, equity securities and alternative investments within any domestic plan’s portfolio can be maintained in the range of 30% to 70% of total plan assets, fixed-income securities can range from 20% to 50% of plan assets and cash equivalents can be held in amounts ranging from 0% to 5% of plan assets. Actual asset allocation within the approved ranges varies from time to time based on economic
BNY Mellon 183
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
conditions (both current and forecast) and the advice of professional advisors.
Our pension assets were invested as follows at Dec. 31, 2016 and 2015:
Asset allocations | Domestic | Foreign | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Equities | 58 | % | 63 | % | 52 | % | 57 | % | |
Fixed income | 36 | 31 | 29 | 34 | |||||
Private equities | 1 | 1 | — | — | |||||
Alternative investment | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||
Real estate | — | — | 4 | 5 | |||||
Cash | 2 | 2 | 12 | 1 | |||||
Total pension benefits | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |
We held no The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation stock in our pension plans at Dec. 31, 2016 and 2015. Assets of the U.S. post-retirement healthcare plan are invested in an insurance contract.
Fair value measurement of plan assets
In accordance with ASC 715, Compensation - Retirement Benefits, BNY Mellon has established a three-level hierarchy for fair value measurements of its pension plan assets based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset as of the measurement date. The valuation hierarchy is consistent with guidance in ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, which is detailed in Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for assets measured at fair value, as well as the general classification of such assets pursuant to the valuation hierarchy.
Cash and currency
This category consists primarily of foreign currency balances and is included in Level 1 of the valuation hierarchy. Foreign currency is translated monthly based on current exchange rates.
Common and preferred stock and exchange-traded funds
These investments include equities and exchange-traded funds and are valued at the closing price reported in the active market in which the individual securities are traded, if available. Where there are no readily available market quotations, we determine fair
value primarily based on pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency.
Collective trust funds
Collective trust funds include commingled and U.S. equity funds that have no readily available market quotations. The fair value of the funds are based on the securities in the portfolio, which typically are the amount that the fund might reasonably expect to receive for the securities upon a sale. These funds are valued using observable inputs on either a daily or monthly basis. Collective trust funds are included as Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy.
Fixed income investments
Fixed income investments include U.S. Treasury securities, U.S. government agencies, sovereign government obligations, U.S. corporate bonds and foreign corporate debt funds. U.S. Treasury securities are valued at the closing price reported in the active market in which the individual security is traded and included as Level 1 of the valuation hierarchy. U.S. government agencies, sovereign government obligations, U.S. corporate bonds and foreign corporate debt funds are valued based on quoted prices for comparable securities with similar yields and credit ratings. When quoted prices are not available for identical or similar bonds, the bonds are valued using discounted cash flows that maximize observable inputs, such as current yields of similar instruments, but includes adjustments for certain risks that may not be observable, such as credit and liquidity risks. U.S. government agencies, sovereign government obligations, U.S. corporate bonds and foreign corporate debt funds are primarily included as Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy.
Other assets measured at NAV
Other assets measured at NAV include funds of funds and venture capital and partnership interests, property funds and other funds. There are no readily available market quotations for these funds. The fair value of the funds of funds is based on NAVs of the funds in the portfolio, which reflects the value of the underlying securities. The fair value of the underlying securities is typically the amount that the fund might reasonably expect to receive upon selling those hard to value or illiquid securities within the portfolios. These funds are either valued on a daily or monthly basis. The fair value of the venture capital
184 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
and partnership interests is based on the pension plan’s ownership percentage of the fair value of the underlying funds as provided by the fund managers. These funds are typically valued on a quarterly basis. The pension plan’s venture capital and partnership interests are valued at NAV as a practical expedient for fair value.
The following tables present the fair value of each major category of plan assets as of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, by captions and by ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, valuation hierarchy. There were no transfers between Level 1 and Level 2.
Plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis— domestic plans at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total fair value | ||||||||
Common and preferred stock: | ||||||||||||
U.S. equity | $ | 1,493 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,493 | ||||
Non-U.S. equity | 137 | — | — | 137 | ||||||||
Collective trust funds: | ||||||||||||
Commingled | — | 367 | — | 367 | ||||||||
U.S. equity | — | 1,115 | — | 1,115 | ||||||||
Fixed income: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 523 | — | — | 523 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | — | 66 | — | 66 | ||||||||
Sovereign government obligations | — | 7 | — | 7 | ||||||||
U.S. corporate bonds | — | 823 | — | 823 | ||||||||
Other | — | 48 | — | 48 | ||||||||
Mutual funds | 135 | — | — | 135 | ||||||||
Exchange-traded funds | 6 | — | — | 6 | ||||||||
Other assets measured at NAV: | ||||||||||||
Funds of funds | 138 | |||||||||||
Venture capital and partnership interests | 48 | |||||||||||
Total domestic plan assets, at fair value | $ | 2,294 | $ | 2,426 | $ | — | $ | 4,906 | ||||
Plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis— foreign plans at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total fair value | ||||||||
Equity funds | $ | 371 | $ | 207 | $ | — | $ | 578 | ||||
Sovereign/government obligation funds | — | 95 | — | 95 | ||||||||
Corporate debt funds | — | 208 | 17 | 225 | ||||||||
Cash and currency | 120 | — | — | 120 | ||||||||
Other assets measured at NAV | 72 | |||||||||||
Total foreign plan assets, at fair value | $ | 491 | $ | 510 | $ | 17 | $ | 1,090 | ||||
Plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis— domestic plans at Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total fair value | ||||||||
Common and preferred stock: | ||||||||||||
U.S. equity | $ | 1,473 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,473 | ||||
Non-U.S. equity | 132 | — | — | 132 | ||||||||
Collective trust funds: | ||||||||||||
Commingled | — | 318 | — | 318 | ||||||||
U.S. equity | — | 1,181 | — | 1,181 | ||||||||
Fixed income: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 450 | — | — | 450 | ||||||||
U.S. government agencies | — | 20 | — | 20 | ||||||||
Sovereign government obligations | — | 77 | — | 77 | ||||||||
U.S. corporate bonds | — | 726 | — | 726 | ||||||||
Other | — | 39 | — | 39 | ||||||||
Exchange-traded funds | 60 | — | — | 60 | ||||||||
Other assets measured at NAV: | ||||||||||||
Funds of funds | 153 | |||||||||||
Venture capital and partnership interests | 60 | |||||||||||
Total domestic plan assets, at fair value | $ | 2,115 | $ | 2,361 | $ | — | $ | 4,689 | ||||
Plan assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis— foreign plans at Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total fair value | ||||||||
Equity funds | $ | 375 | $ | 163 | $ | — | $ | 538 | ||||
Sovereign/government obligation funds | 52 | 84 | — | 136 | ||||||||
Corporate debt funds | — | 158 | 19 | 177 | ||||||||
Cash and currency | 5 | — | — | 5 | ||||||||
Other assets measured at NAV | 80 | |||||||||||
Total foreign plan assets, at fair value | $ | 432 | $ | 405 | $ | 19 | $ | 936 | ||||
Changes in Level 3 fair value measurements
The tables below include rollforwards of the plan assets for the years ended Dec. 31, 2016 and 2015 (including the change in fair value), for financial instruments classified in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy.
Fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs—foreign plans—for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016 | |||
(in millions) | Corporate debt funds | ||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 19 | |
Total gains or (losses) included in earnings | (2 | ) | |
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2016 | $ | 17 | |
Change in unrealized gains or (losses) for the period included in earnings for assets held at the end of the reporting period | $ | (2 | ) |
BNY Mellon 185
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Fair value measurements using significant unobservable inputs—foreign plans—for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 | |||
(in millions) | Corporate debt funds | ||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 20 | |
Total gains or (losses) included in earnings | (1 | ) | |
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | 19 | |
Change in unrealized gains or (losses) for the period included in earnings for assets held at the end of the reporting period | $ | (1 | ) |
Funds of funds and venture capital and partnership interests valued using NAV per share
BNY Mellon had pension and post-retirement plan assets invested in funds of funds, venture capital and partnership interests, property funds and other contracts valued using NAV. The fund of funds investments are redeemable at NAV under agreements with the fund of funds managers.
Assets valued using NAV at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Fair value | Unfunded commitments | Redemption frequency | Redemption notice period | ||||
Funds of funds (a) | $ | 158 | $ | — | Monthly | 30-45 days | ||
Venture capital and partnership interests (b) | 48 | 8 | N/A | N/A | ||||
Property funds (c) | 40 | — | Daily-Quarterly | 0-90 days | ||||
Other contracts (d) | 12 | — | N/A | N/A | ||||
Total | $ | 258 | $ | 8 | ||||
Assets valued using NAV at Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Fair value | Unfunded commitments | Redemption frequency | Redemption notice period | ||||
Funds of funds (a) | $ | 177 | $ | — | Monthly | 30-45 days | ||
Venture capital and partnership interests (b) | 60 | 8 | N/A | N/A | ||||
Property funds (c) | 49 | — | Daily-Quarterly | 0-90 days | ||||
Other contracts (d) | 7 | — | N/A | N/A | ||||
Total | $ | 293 | $ | 8 | ||||
(a) | Funds of funds include multi-strategy hedge funds that utilize investment strategies that invest over both long-term investment and short-term investment horizons. |
(b) | Venture capital and partnership interests do not have redemption rights. Distributions from such funds will be received as the underlying investments are liquidated. |
(c) | Property funds include funds invested in regional real estate vehicles that hold direct interest in real estate properties. |
(d) | Other contracts include assets invested in pooled accounts at insurance companies that are privately valued by the asset manager. |
Defined contribution plans
BNY Mellon sponsors defined contribution plans in the U.S. and in certain non-U.S. locations, all of which are administered in accordance with local laws. The most significant defined contribution plan is The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan sponsored by the Company in the U.S and covers substantially all U.S. employees.
Under The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan, the Company matched 100% of the first 4% of an employee’s eligible base pay plus 50% of the next 2% of eligible pay contributed by the participant for a maximum matching contribution of 5% for 2016, 2015 and 2014, subject to statutory limits.
The U.S. qualified and nonqualified defined benefit plans were closed to new participants effective Dec. 31, 2010, at which time an annual non-elective contribution equal to 2% of eligible base pay was added to The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan. For 2014, employees who were hired on or after Jan. 1, 2010 and were not eligible to earn benefits in The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation Pension Plan received the annual non-elective contribution.
Effective June 30, 2015, the benefit accruals under the U.S. qualified and nonqualified defined benefit plans were frozen. Employees, who were hired before Jan. 1, 2010 and were eligible to earn benefits in the pension plan prior to freezing the benefit accrual, received the non-elective contribution starting July 1, 2015. All Company contributions are invested according to participants’ individual elections.
At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation 401(k) Savings Plan owned 14.2 million and 15.6 million shares of our common stock, respectively. The fair value of total assets was $5.7 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $5.2 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. We recorded expense of $224 million in 2016, $209 million in 2015 and $198 million in 2014 primarily for contributions to our defined contribution plans.
We also have an ESOP covering certain domestic full-time employees hired on or before July 1, 2008. The ESOP works in conjunction with the defined benefit pension plan. Employees are entitled to the
186 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
higher of their benefit under the ESOP or such defined benefit pension plan at retirement. Benefits payable under the defined benefit pension plan are offset by the equivalent value of benefits earned under the ESOP.
At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, the ESOP owned 5.7 million and 6.0 million shares of our common stock, respectively. The fair value of total ESOP assets was $273 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $251 million at Dec. 31, 2015. The ESOP was amended effective June 30, 2015 to discontinue the ability of the Company to make contributions to the ESOP. There were no contributions to the ESOP in 2015, prior to amending the plan, or 2014.
The Benefits Investment Committee appointed Fiduciary Counselors, Inc. to serve as the independent fiduciary to (i) make all fiduciary decisions related to the continued prudence of offering the common stock of BNY Mellon or its affiliates as an investment option under the plans, other than plan sponsor decisions, and (ii) select and monitor any actively or passively managed investments (including mutual funds) of BNY Mellon or its affiliates to be offered to participants as investment options under the plans, excluding self-directed accounts.
Note 17 - Company financial information (Parent Corporation)
Our bank subsidiaries are subject to dividend limitations under the Federal Reserve Act, as well as national and state banking laws. Under these statutes, prior regulatory consent is required for dividends in any year that would exceed the bank’s net profits for such year combined with retained net profits for the prior two years. Additionally, such bank subsidiaries may not declare dividends in excess of net profits on hand, as defined, after deducting the amount by which the principal amount of all loans, on which interest is past due for a period of six months or more, exceeds the allowance for credit losses.
The payment of dividends also is limited by minimum capital requirements imposed on banks. As of Dec. 31, 2016, BNY Mellon’s bank subsidiaries exceeded these minimum requirements.
Subsequent to Dec. 31, 2016, our U.S. bank subsidiaries could declare dividends to the Parent of approximately $5.4 billion, without the need for a
regulatory waiver. Currently, The Bank of New York Mellon, our primary subsidiary, is no longer paying regular dividends to the Parent in order to increase its Tier 1 capital in advance of the SLR becoming effective. In addition, at Dec. 31, 2016, non-bank subsidiaries of the Parent had liquid assets of approximately $1.3 billion.
The bank subsidiaries declared dividends of $160 million in 2016, $182 million in 2015 and $809 million in 2014. The Federal Reserve and the OCC have issued additional guidelines that require bank holding companies and national banks to continually evaluate the level of cash dividends in relation to their respective operating income, capital needs, asset quality and overall financial condition.
The Federal Reserve policy with respect to the payment of cash dividends by bank holding companies provides that, as a matter of prudent banking, a bank holding company should not maintain a rate of cash dividends unless its net income available to common shareholders has been sufficient to fully fund the dividends, and the prospective rate of earnings retention appears to be consistent with the holding company’s capital needs, asset quality and overall financial condition. The Federal Reserve can also prohibit a dividend if payment would constitute an unsafe or unsound banking practice. Any increase in BNY Mellon’s ongoing quarterly dividends would require approval from the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve’s instructions for the 2017 CCAR provided that, for large bank holding companies like us, dividend payout ratios exceeding 30% of after-tax net income would receive particularly close scrutiny.
BNY Mellon and other affected BHCs may pay dividends, repurchase stock, and make other capital distributions only in accordance with a capital plan that has been reviewed by the Federal Reserve and as to which the Federal Reserve has not objected. The Federal Reserve may object to a capital plan if the plan does not show that the covered BHC will meet, for each quarter throughout the nine-quarter planning horizon covered by the capital plan, all minimum regulatory capital ratios under applicable capital rules as in effect for that quarter on a pro forma basis under the base case and stressed scenarios (including a severely adverse scenario provided by the Federal Reserve). The capital plan rules also stipulate that a covered BHC may not make a capital distribution unless after giving effect to the distribution it will
BNY Mellon 187
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
meet all minimum regulatory capital ratios. As part of this process, BNY Mellon also provides the Federal Reserve with estimates of the composition and levels of regulatory capital, risk-weighted assets and other measures under Basel III under an identified scenario. In June 2016, BNY Mellon received confirmation that the Federal Reserve did not object to its 2016 capital plan. The board of directors subsequently approved the repurchase of up to $2.14 billion worth of common stock over a four-quarter period beginning in the third quarter of 2016 and continuing through the second quarter of 2017. The board of directors also approved the additional repurchase of up to $560 million of common stock contingent on a prior issuance of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock, which was satisfied in August 2016 upon BNY Mellon’s issuance of $1 billion of noncumulative perpetual preferred stock. This new share repurchase plan totaling $2.7 billion replaces all previously authorized share repurchase plans.
The Federal Reserve Act limits, and requires collateral for, extensions of credit by our insured subsidiary banks to BNY Mellon and certain of its non-bank affiliates. Also, there are restrictions on the amounts of investments by such banks in stock and other securities of BNY Mellon and such affiliates, and restrictions on the acceptance of their securities as collateral for loans by such banks. Extensions of credit by the banks to each of our affiliates are limited to 10% of such bank’s regulatory capital, and in the aggregate for BNY Mellon and all such affiliates to 20%, and collateral must be between 100% and 130% of the amount of the credit, depending on the type of collateral.
Our insured subsidiary banks are required to maintain reserve balances with Federal Reserve Banks under the Federal Reserve Act and Regulation D. Required
balances averaged $6.0 billion and $6.5 billion for the years 2016 and 2015, respectively.
In the event of impairment of the capital stock of one of the Parent’s national banks or The Bank of New York Mellon, the Parent, as the banks’ stockholder, could be required to pay such deficiency.
The Parent guarantees the debt issued by Mellon Funding Corporation, a wholly-owned financing subsidiary of the Company. The Parent also guarantees committed and uncommitted lines of credit of Pershing LLC and Pershing Limited subsidiaries. The Parent guarantees described above are full and unconditional and contain the standard provisions relating to parent guarantees of subsidiary debt. Additionally, the Parent guarantees or indemnifies obligations of its consolidated subsidiaries as needed. Generally, there are no stated notional amounts included in these indemnifications and the contingencies triggering the obligation for indemnification are not expected to occur. As a result, we are unable to develop an estimate of the maximum payout under these indemnifications. However, we believe the possibility is remote that we will have to make any material payment under these guarantees and indemnifications.
The condensed financial statements of the Parent include the accounts of the Parent; those of a wholly-owned financing subsidiary that functions as a financing entity for BNY Mellon and its subsidiaries; and MIPA, LLC, a single-member limited liability company, created to hold and administer corporate-owned life insurance. Financial data for the Parent, the financing subsidiary and the single-member limited liability company are combined for financial reporting purposes because of the limited function of these entities and the unconditional guarantee by BNY Mellon of their obligations.
188 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The Parent’s condensed financial statements are as follows:
Condensed Income Statement—The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (Parent Corporation)
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Dividends from bank subsidiaries | $ | 125 | $ | 145 | $ | 775 | |||
Dividends from nonbank subsidiaries | 798 | 207 | 44 | ||||||
Interest revenue from bank subsidiaries | 70 | 68 | 67 | ||||||
Interest revenue from nonbank subsidiaries | 121 | 91 | 98 | ||||||
Gain on securities held for sale | — | 3 | 1 | ||||||
Other revenue | 39 | 25 | 24 | ||||||
Total revenue | 1,153 | 539 | 1,009 | ||||||
Interest (including, $88, $69, $62, to subsidiaries, respectively) | 427 | 288 | 257 | ||||||
Other expense | 262 | 64 | 71 | ||||||
Total expense | 689 | 352 | 328 | ||||||
Income before income taxes and equity in undistributed net income of subsidiaries | 464 | 187 | 681 | ||||||
(Benefit) for income taxes | (333 | ) | (98 | ) | (155 | ) | |||
Equity in undistributed net income: | |||||||||
Bank subsidiaries | 2,474 | 2,004 | 910 | ||||||
Nonbank subsidiaries | 276 | 869 | 821 | ||||||
Net income | 3,547 | 3,158 | 2,567 | ||||||
Preferred stock dividends | (122 | ) | (105 | ) | (73 | ) | |||
Net income applicable to common shareholders of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 3,425 | $ | 3,053 | $ | 2,494 | |||
Condensed Balance Sheet—The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (Parent Corporation)
Dec. 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | ||||
Assets: | ||||||
Cash and due from banks | $ | 9,117 | $ | 9,383 | ||
Securities | 1,693 | 26 | ||||
Loans, net of allowance | 7 | 20 | ||||
Investment in and advances to subsidiaries and associated companies: | ||||||
Banks | 32,771 | 30,156 | ||||
Other | 26,630 | 27,405 | ||||
Subtotal | 59,401 | 57,561 | ||||
Corporate-owned life insurance | 744 | 728 | ||||
Other assets | 885 | 1,509 | ||||
Total assets | $ | 71,847 | $ | 69,227 | ||
Liabilities: | ||||||
Deferred compensation | $ | 464 | $ | 473 | ||
Affiliate borrowings | 7,107 | 8,243 | ||||
Other liabilities | 1,445 | 1,623 | ||||
Long-term debt | 24,020 | 20,851 | ||||
Total liabilities | 33,036 | 31,190 | ||||
Shareholders’ equity | 38,811 | 38,037 | ||||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 71,847 | $ | 69,227 | ||
Condensed Statement of Cash Flows—The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation (Parent Corporation)
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Operating activities: | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,547 | $ | 3,158 | $ | 2,567 | |||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | |||||||||
Equity in undistributed net (income) of subsidiaries | (2,750 | ) | (2,873 | ) | (1,731 | ) | |||
Change in accrued interest receivable | 2 | (4 | ) | 23 | |||||
Change in accrued interest payable | 4 | 15 | 18 | ||||||
Change in taxes payable (a) | 452 | 132 | 91 | ||||||
Other, net | (31 | ) | 66 | 2 | |||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,224 | 494 | 970 | ||||||
Investing activities: | |||||||||
Purchases of securities | (1,739 | ) | — | — | |||||
Proceeds from sales of securities | — | 3 | 7 | ||||||
Change in loans | 13 | 56 | (57 | ) | |||||
Acquisitions of, investments in, and advances to subsidiaries | (317 | ) | (358 | ) | (1,603 | ) | |||
Other, net | — | 14 | 107 | ||||||
Net cash (used in) investing activities | (2,043 | ) | (285 | ) | (1,546 | ) | |||
Financing activities: | |||||||||
Net change in commercial paper | — | — | (96 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 6,229 | 4,986 | 4,686 | ||||||
Repayments of long-term debt | (2,700 | ) | (3,650 | ) | (4,071 | ) | |||
Change in advances from subsidiaries | (1,136 | ) | 2,123 | 2,704 | |||||
Issuance of common stock | 465 | 352 | 396 | ||||||
Treasury stock acquired | (2,398 | ) | (2,355 | ) | (1,669 | ) | |||
Issuance of preferred stock | 990 | 990 | — | ||||||
Cash dividends paid | (900 | ) | (865 | ) | (833 | ) | |||
Tax benefit realized on share based payment awards | 3 | 76 | 17 | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 553 | 1,657 | 1,134 | ||||||
Change in cash and due from banks | (266 | ) | 1,866 | 558 | |||||
Cash and due from banks at beginning of year | 9,383 | 7,517 | 6,959 | ||||||
Cash and due from banks at end of year | $ | 9,117 | $ | 9,383 | $ | 7,517 | |||
Supplemental disclosures | |||||||||
Interest paid | $ | 409 | $ | 302 | $ | 275 | |||
Income taxes paid | 1 | 158 | 946 | ||||||
Income taxes refunded | 12 | 103 | 54 | ||||||
(a) | Includes payments received from subsidiaries for taxes of $189 million in 2016, $24 million in 2015 and $452 million in 2014. |
Note 18 - Fair value measurement
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset, or paid to transfer a liability, in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level hierarchy for fair value measurements is utilized based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. BNY Mellon’s own creditworthiness is considered when valuing liabilities.
BNY Mellon 189
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Fair value focuses on exit price in an orderly transaction (that is, not a forced liquidation or distressed sale) between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions. If there has been a significant decrease in the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability, a change in valuation technique or the use of multiple valuation techniques may be appropriate. In such instances, determining the price at which willing market participants would transact at the measurement date under current market conditions depends on the facts and circumstances and requires the use of significant judgment. The objective is to determine from weighted indicators of fair value a reasonable point within the range that is most representative of fair value under current market conditions.
Determination of fair value
We have established processes for determining fair values. Fair value is based upon quoted market prices in active markets, where available. For financial instruments where quotes from recent exchange transactions are not available, we determine fair value based on discounted cash flow analysis, comparison to similar instruments, and the use of financial models. Discounted cash flow analysis is dependent upon estimated future cash flows and the level of interest rates. Model-based pricing uses inputs of observable prices, where available, for interest rates, foreign exchange rates, option volatilities and other factors. Models are benchmarked and validated by an independent internal risk management function. Our valuation process takes into consideration factors such as counterparty credit quality, liquidity, concentration concerns, and observability of model parameters. Valuation adjustments may be made to ensure that financial instruments are recorded at fair value.
Most derivative contracts are valued using internally developed models which are calibrated to observable market data and employ standard market pricing theory for their valuations. An initial “risk-neutral” valuation is performed on each position assuming time-discounting based on an AA credit curve. Then, to arrive at a fair value that incorporates counter-party credit risk, a credit adjustment is made to these results by discounting each trade’s expected exposures to the counterparty using the counterparty’s credit spreads, as implied by the credit default swap market. We also adjust expected liabilities to the counterparty using BNY Mellon’s own credit spreads, as implied by the
credit default swap market. Accordingly, the valuation of our derivative position is sensitive to the current changes in our own credit spreads as well as those of our counterparties.
In certain cases, recent prices may not be observable for instruments that trade in inactive or less active markets. Upon evaluating the uncertainty in valuing financial instruments subject to liquidity issues, we make an adjustment to their value. The determination of the liquidity adjustment includes the availability of external quotes, the time since the latest available quote and the price volatility of the instrument.
Certain parameters in some financial models are not directly observable and, therefore, are based on management’s estimates and judgments. These financial instruments are normally traded less actively. We apply valuation adjustments to mitigate the possibility of error and revision in the model based estimate value. Examples include products where parameters such as correlation and recovery rates are unobservable.
The methods described above for instruments that trade in inactive or less active markets may produce a current fair value calculation that may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. We believe our methods of determining fair value are appropriate and consistent with other market participants. However, the use of different methodologies or different assumptions to value certain financial instruments could result in a different estimate of fair value.
Valuation hierarchy
A three-level valuation hierarchy is used for disclosure of fair value measurements based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. The three levels are described below.
Level 1: Inputs to the valuation methodology are quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. Level 1 assets and liabilities include certain debt and equity securities, derivative financial instruments actively traded on exchanges and U.S. Treasury securities that are actively traded in highly liquid over-the-counter markets.
190 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Level 2: Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices, for example, quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, and inputs that are observable or can be corroborated, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. Level 2 assets and liabilities include debt instruments that are traded less frequently than exchange-traded securities and derivative instruments whose model inputs are observable in the market or can be corroborated by market-observable data. Examples in this category are agency and non-agency mortgage-backed securities, corporate debt securities and over-the-counter derivative contracts.
Level 3: Inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
A financial instrument’s categorization within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Valuation methodology
Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for instruments measured at fair value, as well as the general classification of such instruments pursuant to the valuation hierarchy.
Securities
Where quoted prices are available in an active market, we classify the securities within Level 1 of the valuation hierarchy. Securities include both long and short positions. Level 1 securities include highly liquid government bonds, money market funds, foreign covered bonds and exchange-traded equities.
If quoted market prices are not available, we estimate fair values using pricing models, quoted prices of securities with similar characteristics or discounted cash flows. Examples of such instruments, which would generally be classified within Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy, include agency and non-agency mortgage-backed securities, state and political subdivisions, commercial mortgage-backed securities, sovereign debt, corporate bonds and foreign covered bonds.
For securities where quotes from recent transactions are not available for identical securities, we determine fair value primarily based on pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency that employ financial models or obtain comparison to similar instruments to arrive at “consensus” prices.
Specifically, the pricing sources obtain recent transactions for similar types of securities (e.g., vintage, position in the securitization structure) and ascertain variables such as discount rate and speed of prepayment for the types of transaction and apply such variables to similar types of bonds. We view these as observable transactions in the current marketplace and classify such securities as Level 2. Pricing sources discontinue pricing any specific security whenever they determine there is insufficient observable data to provide a good faith opinion on price.
In addition, we have significant investments in more actively traded agency RMBS and other types of securities such as sovereign debt. The pricing sources derive the prices for these securities largely from quotes they obtain from three major inter-dealer brokers.
In certain cases where there is limited activity or less transparency around inputs to the valuation, we classify those securities in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy. Securities classified within Level 3 may include securities of state and political subdivisions and distressed debt securities.
At Dec. 31, 2016, more than 99% of our securities were valued by pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency. We have no instruments included in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy.
Derivatives
We classify exchange-traded derivatives valued using quoted prices in Level 1 of the valuation hierarchy. Examples include exchange-traded equity and foreign exchange options. Since few other classes of derivative contracts are listed on an exchange, most of our derivative positions are valued using internally developed models that use as their basis readily observable market parameters, and we classify them in Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy. Such derivatives include swaps and options, foreign exchange spot and forward contracts and credit default swaps.
BNY Mellon 191
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Derivatives valued using models with significant unobservable market parameters in markets that lack two-way flow are classified in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy. Examples may include long-dated swaps and options, where parameters may be unobservable for longer maturities; and certain highly structured products, where correlation risk is unobservable. As of Dec. 31, 2016 we have no Level 3 derivatives. Additional disclosures of derivative instruments are provided in Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Loans and unfunded lending-related commitments
Where quoted market prices are not available, we generally base the fair value of loans and unfunded lending-related commitments on observable market prices of similar instruments, including bonds, credit derivatives and loans with similar characteristics. If observable market prices are not available, we base the fair value on estimated cash flows adjusted for credit risk which are discounted using an interest rate appropriate for the maturity of the applicable loans or the unfunded lending-related commitments.
Unrealized gains and losses, if any, on unfunded lending-related commitments carried at fair value are classified in other assets and other liabilities, respectively. Loans and unfunded lending-related commitments carried at fair value are generally classified within Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy.
Seed capital
In our Investment Management business, we manage investment assets, including equities, fixed income, money market and alternative investment funds for institutions and other investors. As part of that activity, we make seed capital investments in certain funds. Seed capital is generally included in other assets. When applicable, we value seed capital based on the published NAV of the fund.
For other types of investments in funds, we consider all of the rights and obligations inherent in our ownership interest, including the reported NAV as well as other factors that affect the fair value of our interest in the fund.
Certain interests in securitizations
For certain interests in securitizations that are classified in securities available-for-sale, trading assets and long-term debt, we use discounted cash flow models, which generally include assumptions of projected finance charges related to the securitized assets, estimated net credit losses, prepayment assumptions and estimates of payments to third-party investors. When available, we compare our fair value estimates and assumptions to market activity and to the actual results of the securitized portfolio.
Other assets measured at NAV
BNY Mellon holds private equity investments, specifically SBICs, which are compliant with the Volcker Rule. There is no readily available market quotations for these investment partnerships. The fair value of the SBICs are based on our ownership percentage of the fair value of the underlying investments as provided by the partnership managers. These investments are typically valued on a quarterly basis. Our SBIC private equity investments are valued at NAV as a practical expedient for fair value.
The following tables present the financial instruments carried at fair value at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, by caption on the consolidated balance sheet and by the three-level valuation hierarchy. We have included credit ratings information in certain of the tables because the information indicates the degree of credit risk to which we are exposed, and significant changes in ratings classifications could result in increased risk for us. There were no material transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 during 2016.
192 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis at Dec. 31, 2016 | Total carrying value | ||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Netting (a) | |||||||||||
Available-for-sale securities: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 14,307 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 14,307 | |||||
U.S. government agencies | — | 359 | — | — | 359 | ||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 66 | 12,423 | — | — | 12,489 | ||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | — | 3,378 | — | — | 3,378 | ||||||||||
Agency RMBS | — | 22,736 | — | — | 22,736 | ||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | — | 638 | — | — | 638 | ||||||||||
Other RMBS | — | 513 | — | — | 513 | ||||||||||
Commercial MBS | — | 928 | — | — | 928 | ||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | — | 6,449 | — | — | 6,449 | ||||||||||
CLOs | — | 2,598 | — | — | 2,598 | ||||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | — | 1,727 | — | — | 1,727 | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 3 | — | — | — | 3 | ||||||||||
Money market funds (b) | 842 | — | — | — | 842 | ||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 1,396 | — | — | 1,396 | ||||||||||
Other debt securities | — | 1,961 | — | — | 1,961 | ||||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 1,876 | 265 | — | — | 2,141 | ||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (c) | — | 1,357 | — | — | 1,357 | ||||||||||
Total available-for-sale securities | 17,094 | 56,728 | — | — | 73,822 | ||||||||||
Trading assets: | |||||||||||||||
Debt and equity instruments (b) | 240 | 2,013 | — | — | 2,253 | ||||||||||
Derivative assets not designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | 4 | 7,583 | — | (6,047 | ) | 1,540 | |||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 6,104 | — | (4,172 | ) | 1,932 | |||||||||
Equity and other contracts | — | 46 | — | (38 | ) | 8 | |||||||||
Total derivative assets not designated as hedging | 4 | 13,733 | — | (10,257 | ) | 3,480 | |||||||||
Total trading assets | 244 | 15,746 | — | (10,257 | ) | 5,733 | |||||||||
Other assets: | |||||||||||||||
Derivative assets designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | — | 415 | — | — | 415 | ||||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 369 | — | — | 369 | ||||||||||
Total derivative assets designated as hedging | — | 784 | — | — | 784 | ||||||||||
Other assets (d) | 268 | 73 | — | — | 341 | ||||||||||
Other assets measured at net asset value (d) | 214 | ||||||||||||||
Total other assets | 268 | 857 | — | — | 1,339 | ||||||||||
Subtotal assets of operations at fair value | 17,606 | 73,331 | — | (10,257 | ) | 80,894 | |||||||||
Percentage of assets prior to netting | 19 | % | 81 | % | — | % | |||||||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds: | |||||||||||||||
Trading assets | 296 | 683 | — | — | 979 | ||||||||||
Other assets | 168 | 84 | — | — | 252 | ||||||||||
Total assets of consolidated investment management funds | 464 | 767 | — | — | 1,231 | ||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 18,070 | $ | 74,098 | $ | — | $ | (10,257 | ) | $ | 82,125 | ||||
Percentage of assets prior to netting | 20 | % | 80 | % | — | % | |||||||||
BNY Mellon 193
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis at Dec. 31, 2016 | Total carrying value | ||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Netting (a) | |||||||||||
Trading liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Debt and equity instruments | $ | 349 | $ | 236 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 585 | |||||
Derivative liabilities not designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | 4 | 7,629 | — | (6,634 | ) | 999 | |||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 6,103 | — | (3,363 | ) | 2,740 | |||||||||
Equity and other contracts | — | 115 | — | (50 | ) | 65 | |||||||||
Total derivative liabilities not designated as hedging | 4 | 13,847 | — | (10,047 | ) | 3,804 | |||||||||
Total trading liabilities | 353 | 14,083 | — | (10,047 | ) | 4,389 | |||||||||
Long-term debt (b) | — | 363 | — | — | 363 | ||||||||||
Other liabilities - derivative liabilities designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | — | 545 | — | — | 545 | ||||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 52 | — | — | 52 | ||||||||||
Total other liabilities - derivative liabilities designated as hedging | — | 597 | — | — | 597 | ||||||||||
Subtotal liabilities of operations at fair value | 353 | 15,043 | — | (10,047 | ) | 5,349 | |||||||||
Percentage of liabilities prior to netting | 2 | % | 98 | % | — | % | |||||||||
Liabilities of consolidated investment management funds: | |||||||||||||||
Trading liabilities | — | 282 | — | — | 282 | ||||||||||
Other liabilities | 3 | 30 | — | — | 33 | ||||||||||
Total liabilities of consolidated investment management funds | 3 | 312 | — | — | 315 | ||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | 356 | $ | 15,355 | $ | — | $ | (10,047 | ) | $ | 5,664 | ||||
Percentage of liabilities prior to netting | 2 | % | 98 | % | — | % | |||||||||
(a) | ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, permits the netting of derivative receivables and derivative payables under legally enforceable master netting agreements and permits the netting of cash collateral. Netting is applicable to derivatives not designated as hedging instruments included in trading assets or trading liabilities, and derivatives designated as hedging instruments included in other assets or other liabilities. Netting is allocated to the derivative products based on the net fair value of each product. |
(b) | Includes certain interests in securitizations. |
(c) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(d) | Includes private equity investments and seed capital. |
194 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis at Dec. 31, 2015 | Total carrying value | ||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Netting (a) | |||||||||||
Available-for-sale securities: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 12,832 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 12,832 | |||||
U.S. government agencies | — | 387 | — | — | 387 | ||||||||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | 35 | 13,182 | — | — | 13,217 | ||||||||||
State and political subdivisions | — | 4,046 | — | — | 4,046 | ||||||||||
Agency RMBS | — | 23,501 | — | — | 23,501 | ||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS | — | 793 | — | — | 793 | ||||||||||
Other RMBS | — | 1,061 | — | — | 1,061 | ||||||||||
Commercial MBS | — | 1,392 | — | — | 1,392 | ||||||||||
Agency commercial MBS | — | 4,020 | — | — | 4,020 | ||||||||||
CLOs | — | 2,351 | — | — | 2,351 | ||||||||||
Other asset-backed securities | — | 2,893 | — | — | 2,893 | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 4 | — | — | — | 4 | ||||||||||
Money market funds (b) | 886 | — | — | — | 886 | ||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 1,752 | — | — | 1,752 | ||||||||||
Other debt securities | — | 2,775 | — | — | 2,775 | ||||||||||
Foreign covered bonds | 1,966 | 202 | — | — | 2,168 | ||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS (c) | — | 1,789 | — | — | 1,789 | ||||||||||
Total available-for-sale securities | 15,723 | 60,144 | — | — | 75,867 | ||||||||||
Trading assets: | |||||||||||||||
Debt and equity instruments (b) | 1,232 | 2,167 | — | — | 3,399 | ||||||||||
Derivative assets not designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | 10 | 10,034 | — | (8,071 | ) | 1,973 | |||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 4,905 | — | (2,981 | ) | 1,924 | |||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 15 | 120 | — | (63 | ) | 72 | |||||||||
Total derivative assets not designated as hedging | 25 | 15,059 | — | (11,115 | ) | 3,969 | |||||||||
Total trading assets | 1,257 | 17,226 | — | (11,115 | ) | 7,368 | |||||||||
Loans | — | 422 | — | — | 422 | ||||||||||
Other assets: | |||||||||||||||
Derivative assets designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | — | 497 | — | — | 497 | ||||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 219 | — | — | 219 | ||||||||||
Total derivative assets designated as hedging | — | 716 | — | — | 716 | ||||||||||
Other assets (d) | 192 | 62 | — | — | 254 | ||||||||||
Other assets measured at net asset value (d) | 117 | ||||||||||||||
Total other assets | 192 | 778 | — | — | 1,087 | ||||||||||
Subtotal assets of operations at fair value | 17,172 | 78,570 | — | (11,115 | ) | 84,744 | |||||||||
Percentage of assets prior to netting | 18 | % | 82 | % | — | % | |||||||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds: | |||||||||||||||
Trading assets | 455 | 773 | — | — | 1,228 | ||||||||||
Other assets | 157 | 16 | — | — | 173 | ||||||||||
Total assets of consolidated investment management funds | 612 | 789 | — | — | 1,401 | ||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 17,784 | $ | 79,359 | $ | — | $ | (11,115 | ) | $ | 86,145 | ||||
Percentage of assets prior to netting | 18 | % | 82 | % | — | % | |||||||||
BNY Mellon 195
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis at Dec. 31, 2015 | Total carrying value | ||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Netting (a) | |||||||||||
Trading liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Debt and equity instruments | $ | 422 | $ | 152 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 574 | |||||
Derivative liabilities not designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | 5 | 9,957 | — | (8,235 | ) | 1,727 | |||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 4,682 | — | (2,567 | ) | 2,115 | |||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 5 | 147 | — | (67 | ) | 85 | |||||||||
Total derivative liabilities not designated as hedging | 10 | 14,786 | — | (10,869 | ) | 3,927 | |||||||||
Total trading liabilities | 432 | 14,938 | — | (10,869 | ) | 4,501 | |||||||||
Long-term debt (b) | — | 359 | — | — | 359 | ||||||||||
Other liabilities - derivative liabilities designated as hedging: | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate | — | 372 | — | — | 372 | ||||||||||
Foreign exchange | — | 20 | — | — | 20 | ||||||||||
Total other liabilities - derivative liabilities designated as hedging | — | 392 | — | — | 392 | ||||||||||
Subtotal liabilities of operations at fair value | 432 | 15,689 | — | (10,869 | ) | 5,252 | |||||||||
Percentage of liabilities prior to netting | 3 | % | 97 | % | — | % | |||||||||
Liabilities of consolidated investment management funds: | |||||||||||||||
Trading liabilities | — | 229 | — | — | 229 | ||||||||||
Other liabilities | 1 | 16 | — | — | 17 | ||||||||||
Total liabilities of consolidated investment management funds | 1 | 245 | — | — | 246 | ||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | 433 | $ | 15,934 | $ | — | $ | (10,869 | ) | $ | 5,498 | ||||
Percentage of liabilities prior to netting | 3 | % | 97 | % | — | % | |||||||||
(a) | ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging, permits the netting of derivative receivables and derivative payables under legally enforceable master netting agreements and permits the netting of cash collateral. Netting is applicable to derivatives not designated as hedging instruments included in trading assets or trading liabilities, and derivatives designated as hedging instruments included in other assets or other liabilities. Netting is allocated to the derivative products based on the net fair value of each product. |
(b) | Includes certain interests in securitizations. |
(c) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
(d) | Includes private equity investments and seed capital. |
196 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Details of certain items measured at fair value on a recurring basis | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total carrying value (a) | Ratings | Total carrying value (a) | Ratings | ||||||||||||||||||||||
AAA/ AA- | A+/ A- | BBB+/ BBB- | BB+ and lower | AAA/ AA- | A+/ A- | BBB+/ BBB- | BB+ and lower | ||||||||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-agency RMBS, originated in: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2007 | $ | 58 | — | % | — | % | — | % | 100 | % | $ | 66 | — | % | — | % | — | % | 100 | % | |||||
2006 | 98 | — | — | — | 100 | 115 | — | — | — | 100 | |||||||||||||||
2005 | 180 | 23 | 5 | 9 | 63 | 234 | 19 | 9 | 13 | 59 | |||||||||||||||
2004 and earlier | 302 | 5 | 3 | 24 | 68 | 378 | 4 | 4 | 26 | 66 | |||||||||||||||
Total non-agency RMBS | $ | 638 | 9 | % | 3 | % | 14 | % | 74 | % | $ | 793 | 8 | % | 4 | % | 16 | % | 72 | % | |||||
Commercial MBS - Domestic, originated in: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2009-2016 | $ | 674 | 84 | % | 16 | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 626 | 83 | % | 17 | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
2008 | 14 | 100 | — | — | — | 16 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
2007 | 190 | 71 | 29 | — | — | 304 | 62 | 22 | 16 | — | |||||||||||||||
2006 | 3 | 7 | 93 | — | — | 384 | 76 | 24 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total commercial MBS - Domestic | $ | 881 | 81 | % | 19 | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 1,330 | 76 | % | 20 | % | 4 | % | — | % | |||||
Foreign covered bonds: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Canada | $ | 1,320 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 1,014 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
United Kingdom | 280 | 100 | — | — | — | 363 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Netherlands | 160 | 100 | — | — | — | 214 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Other | 381 | 100 | — | — | — | 577 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total foreign covered bonds | $ | 2,141 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 2,168 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
European floating rate notes - available-for-sale: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
United Kingdom | $ | 379 | 90 | % | 10 | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 780 | 85 | % | 15 | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
Netherlands | 125 | 100 | — | — | — | 222 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Ireland | 58 | — | — | 100 | — | 121 | — | 45 | 55 | — | |||||||||||||||
Total European floating rate notes - available-for-sale | $ | 562 | 83 | % | 7 | % | 10 | % | — | % | $ | 1,123 | 79 | % | 15 | % | 6 | % | — | % | |||||
Sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
United Kingdom | $ | 3,209 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | $ | 2,941 | 100 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||||
France | 1,998 | 100 | — | — | — | 2,008 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Spain | 1,749 | — | — | 100 | — | 1,955 | — | — | 100 | — | |||||||||||||||
Germany | 1,347 | 100 | — | — | — | 1,683 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Italy | 1,130 | — | — | 100 | — | 1,398 | — | — | 100 | — | |||||||||||||||
Netherlands | 1,061 | 100 | — | — | — | 1,055 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Belgium | 1,005 | 100 | — | — | — | 1,108 | 100 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Ireland | 736 | — | 100 | — | — | 772 | — | — | 100 | — | |||||||||||||||
Other (b) | 254 | 71 | — | — | 29 | 297 | 68 | — | 32 | — | |||||||||||||||
Total sovereign debt/sovereign guaranteed | $ | 12,489 | 70 | % | 6 | % | 23 | % | 1 | % | $ | 13,217 | 68 | % | — | % | 32 | % | — | % | |||||
Non-agency RMBS (c), originated in: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
2007 | $ | 387 | — | % | — | % | — | % | 100 | % | $ | 502 | — | % | — | % | — | % | 100 | % | |||||
2006 | 391 | — | — | — | 100 | 530 | — | 1 | — | 99 | |||||||||||||||
2005 | 437 | — | 2 | 1 | 97 | 580 | — | 2 | 1 | 97 | |||||||||||||||
2004 and earlier | 142 | 2 | 2 | 17 | 79 | 177 | — | 3 | 9 | 88 | |||||||||||||||
Total non-agency RMBS (c) | $ | 1,357 | — | % | 1 | % | 2 | % | 97 | % | $ | 1,789 | — | % | 1 | % | 1 | % | 98 | % | |||||
(a) | At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, foreign covered bonds and sovereign debt were included in Level 1 and Level 2 in the valuation hierarchy. All other assets in the table are Level 2 assets in the valuation hierarchy. |
(b) | Includes $73 million of noninvestment grade sovereign debt at Dec. 31, 2016 and $95 million of investment grade sovereign debt at Dec. 31, 2015 related to Brazil. |
(c) | Previously included in the Grantor Trust. The Grantor Trust was dissolved in 2011. |
Changes in Level 3 fair value measurements
Our classification of a financial instrument in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy is based on the significance of the unobservable factors to the overall fair value measurement. However, these instruments generally include other observable components that are actively quoted or validated to third-party sources; accordingly, the gains and losses in the table below include changes in fair value due to observable parameters as well as the unobservable parameters in our valuation methodologies. We also frequently
manage the risks of Level 3 financial instruments using securities and derivatives positions that are Level 1 or 2 instruments which are not included in the table; accordingly, the gains or losses below do not reflect the effect of our risk management activities related to the Level 3 instruments.
The Company has a Level 3 Pricing Committee which evaluates the valuation techniques used in determining the fair value of Level 3 assets and liabilities.
BNY Mellon 197
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The tables below include a roll forward of the balance sheet amounts for the years ended Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015 (including the change in fair value), for financial instruments classified in Level 3 of the valuation hierarchy.
Fair value measurements for assets using significant unobservable inputs for the year ended Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||
(in millions) | Loans | |||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | — | ||
Transfers into Level 3 | 19 | |||
Total gains or (losses) for the period included in earnings | 2 | (a) | ||
Purchases, issuances and sales: | ||||
Purchases | 113 | |||
Issuances | 1 | |||
Sales | (135 | ) | ||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2016 | $ | — | ||
Change in unrealized gains or (losses) for the period included in earnings for assets held at the end of the reporting period | $ | — | ||
(a) | Reported in investment and other income. |
Fair value measurements for assets using significant unobservable inputs for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
Available-for-sale securities | Trading assets | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | State and political subdivisions | Derivative assets | (a) | Other assets | Total assets | |||||||||||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 11 | $ | 9 | $ | 35 | $ | 55 | ||||||||
Transfers out of Level 3 | — | (3 | ) | — | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
Total gains or (losses) for the period | ||||||||||||||||
Included in earnings (or changes in net assets) | — | (b) | (1 | ) | (c) | 10 | (d) | 9 | ||||||||
Purchases, sales and settlements: | ||||||||||||||||
Purchases | — | — | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||
Sales | — | — | (48 | ) | (48 | ) | ||||||||||
Settlements | (11 | ) | (5 | ) | — | (16 | ) | |||||||||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Change in unrealized gains or (losses) for the period included in earnings for assets held at the end of the reporting period | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
(a) | Derivative assets are reported on a gross basis. |
(b) | Realized gains (losses) are reported in securities gains (losses). Unrealized gains (losses) are reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) except for the credit portion of OTTI losses which are recorded in securities gains (losses). |
(c) | Reported in foreign exchange and other trading revenue. |
(d) | Reported in investment and other income. |
Fair value measurements for liabilities using significant unobservable inputs for the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||
Trading liabilities | |||||
(in millions) | Derivative liabilities | (a) | |||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2014 | $ | 9 | |||
Transfers out of Level 3 | (3 | ) | |||
Total (gains) or losses for the period included in earnings | (1 | ) | (b) | ||
Settlements | (5 | ) | |||
Fair value at Dec. 31, 2015 | $ | — | |||
Change in unrealized (gains) or losses for the period included in earnings for liabilities held at the end of the reporting period | $ | — | |||
(a) | Derivative liabilities are reported on a gross basis. |
(b) | Reported in foreign exchange and other trading revenue. |
198 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis
Under certain circumstances, we make adjustments to fair value our assets, liabilities and unfunded lending-related commitments although they are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis. An example would be the recording of an impairment of an asset.
The following tables present the financial instruments carried on the consolidated balance sheet by caption and by level in the fair value hierarchy as of Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, for which a nonrecurring change in fair value has been recorded during the years ended Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis at Dec. 31, 2016 | Total carrying value | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
Loans (a) | $ | — | $ | 84 | $ | 7 | $ | 91 | ||||
Other assets (b) | — | 4 | — | 4 | ||||||||
Total assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis | $ | — | $ | 88 | $ | 7 | $ | 95 | ||||
Assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis at Dec. 31, 2015 | Total carrying value | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
Loans (a) | $ | — | $ | 97 | $ | 174 | $ | 271 | ||||
Other assets (b) | — | 6 | — | 6 | ||||||||
Total assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis | $ | — | $ | 103 | $ | 174 | $ | 277 | ||||
(a) | During the years ended Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, the fair value of these loans decreased $2 million and $2 million, respectively, based on the fair value of the underlying collateral based on guidance in ASC 310, Receivables, with an offset to the allowance for credit losses. |
(b) | Includes other assets received in satisfaction of debt. |
Estimated fair value of financial instruments
The carrying amounts of our financial instruments (i.e., monetary assets and liabilities) are determined under different accounting methods - see Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The following disclosure discusses these instruments on a uniform fair value basis. However, active markets do not exist for a significant portion of these instruments. For financial instruments where quoted prices from identical assets and liabilities in active markets do not exist, we determine fair value based on discounted cash flow analysis and comparison to similar instruments. Discounted cash flow analysis is dependent upon estimated future cash flows and the level of interest rates. Other judgments would result in different fair values. The fair value information supplements the basic financial statements and other traditional financial data presented throughout this report.
A summary of the practices used for determining fair value and the respective level in the valuation hierarchy for financial assets and liabilities not recorded at fair value follows.
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks and interest-bearing deposits with banks
The estimated fair value of interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks is equal to the book value as these interest-bearing deposits are generally considered cash equivalents. These instruments are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy. The estimated fair value of interest-bearing deposits with banks is generally determined using discounted cash flows and duration of the instrument to maturity. The primary inputs used to value these transactions are interest rates based on current LIBOR market rates and time to maturity. Interest-bearing deposits with banks are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements
The estimated fair value of federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements is based on inputs such as interest rates and tenors. Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
BNY Mellon 199
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Securities held-to-maturity
Where quoted prices are available in an active market for identical assets and liabilities, we classify the securities as Level 1 within the valuation hierarchy. Level 1 securities include U.S. Treasury securities and foreign covered bonds.
If quoted market prices are not available for identical assets, we estimate fair value using pricing models, quoted prices of securities with similar characteristics or discounted cash flows. Examples of such instruments, which would generally be classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy, include certain agency and non-agency mortgage-backed securities, commercial mortgage-backed securities and state and political subdivision securities. For securities where quotes from active markets are not available for identical securities, we determine fair value primarily based on pricing sources with reasonable levels of price transparency that employ financial models or obtain comparison to similar instruments to arrive at “consensus” prices.
Specifically, the pricing sources obtain active market prices for similar types of securities (e.g., vintage, position in the securitization structure) and ascertain variables such as discount rate and speed of prepayment for the types of transaction and apply such variables to similar types of bonds. We view these as observable transactions in the current marketplace and classify such securities as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Loans
For residential mortgage loans, fair value is estimated using discounted cash flow analysis, adjusting where appropriate for prepayment estimates, using interest rates currently being offered for loans with similar terms and maturities to borrowers. The estimated fair value of margin loans and overdrafts is equal to the book value due to the short-term nature of these assets. The estimated fair value of other types of loans, including our term loan program, is determined using discounted cash flows. Inputs include current LIBOR market rates adjusted for credit spreads. These loans are generally classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Other financial assets
Other financial assets include cash, the Federal Reserve Bank stock and accrued interest receivable. Cash is classified as Level 1 within the valuation hierarchy. The Federal Reserve Bank stock is not redeemable or transferable. The estimated fair value of the Federal Reserve Bank stock is based on the issue price and is classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy. Accrued interest receivable is generally short-term. As a result, book value is considered to equal fair value. Accrued interest receivable is included as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Noninterest-bearing and interest-bearing deposits
Interest-bearing deposits consist of money market rate and demand deposits, savings deposits and time deposits. Except for time deposits, book value is considered to equal fair value for these deposits due to their short duration to maturity or payable on demand feature. The fair value of interest-bearing time deposits is determined using discounted cash flow analysis. Inputs primarily consist of current LIBOR market rates and time to maturity. For all noninterest-bearing deposits, book value is considered to equal fair value as a result of the short duration of the deposit. Interest-bearing and noninterest-bearing deposits are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements
The estimated fair value of federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements is based on inputs such as interest rates and tenors. Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Payables to customers and broker-dealers
The estimated fair value of payables to customers and broker-dealers is equal to the book value, due to the demand feature of the payables to customers and broker-dealers, and are classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
200 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Borrowings
Borrowings primarily consist of overdrafts of subcustodian account balances in our Investment Services businesses and accrued interest payable. The estimated fair value of overdrafts of subcustodian account balances in our Investment Services businesses is considered to equal book value as a result of the short duration of the overdrafts and is included as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy. Overdrafts are typically repaid within two days. Accrued interest payable is generally short-term. As a result, book value is considered to equal fair value. Accrued interest payable is included as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
Long-term debt
The estimated fair value of long-term debt is based on current rates for instruments of the same remaining maturity or quoted market prices for the same or similar issues. Long-term debt is classified as Level 2 within the valuation hierarchy.
The following tables present the estimated fair value and the carrying amount of financial instruments not carried at fair value on the consolidated balance sheet at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, by caption on the consolidated balance sheet and by the valuation hierarchy.
Summary of financial instruments | Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total estimated fair value | Carrying amount | ||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | $ | — | $ | 58,041 | $ | — | $ | 58,041 | $ | 58,041 | |||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | — | 15,091 | — | 15,091 | 15,086 | ||||||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | — | 25,801 | — | 25,801 | 25,801 | ||||||||||
Securities held-to-maturity | 11,173 | 29,496 | — | 40,669 | 40,905 | ||||||||||
Loans (a) | — | 62,829 | — | 62,829 | 62,564 | ||||||||||
Other financial assets | 4,822 | 1,112 | — | 5,934 | 5,934 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 15,995 | $ | 192,370 | $ | — | $ | 208,365 | $ | 208,331 | |||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Noninterest-bearing deposits | $ | — | $ | 78,342 | $ | — | $ | 78,342 | $ | 78,342 | |||||
Interest-bearing deposits | — | 141,418 | — | 141,418 | 143,148 | ||||||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | — | 9,989 | — | 9,989 | 9,989 | ||||||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | — | 20,987 | — | 20,987 | 20,987 | ||||||||||
Borrowings | — | 960 | — | 960 | 960 | ||||||||||
Long-term debt | — | 24,184 | — | 24,184 | 24,100 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | — | $ | 275,880 | $ | — | $ | 275,880 | $ | 277,526 | |||||
(a) | Does not include the leasing portfolio. |
BNY Mellon 201
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Summary of financial instruments | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total estimated fair value | Carrying amount | ||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits with the Federal Reserve and other central banks | $ | — | $ | 113,203 | $ | — | $ | 113,203 | $ | 113,203 | |||||
Interest-bearing deposits with banks | — | 15,150 | — | 15,150 | 15,146 | ||||||||||
Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | — | 24,373 | — | 24,373 | 24,373 | ||||||||||
Securities held-to-maturity | 11,376 | 31,828 | — | 43,204 | 43,312 | ||||||||||
Loans (a) | — | 61,421 | — | 61,421 | 61,267 | ||||||||||
Other financial assets | 6,537 | 1,096 | — | 7,633 | 7,633 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 17,913 | $ | 247,071 | $ | — | $ | 264,984 | $ | 264,934 | |||||
Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||
Noninterest-bearing deposits | $ | — | $ | 96,277 | $ | — | $ | 96,277 | $ | 96,277 | |||||
Interest-bearing deposits | — | 182,410 | — | 182,410 | 183,333 | ||||||||||
Federal funds purchased and securities sold under repurchase agreements | — | 15,002 | — | 15,002 | 15,002 | ||||||||||
Payables to customers and broker-dealers | — | 21,900 | — | 21,900 | 21,900 | ||||||||||
Borrowings | — | 698 | — | 698 | 698 | ||||||||||
Long-term debt | — | 21,494 | — | 21,494 | 21,188 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | — | $ | 337,781 | $ | — | $ | 337,781 | $ | 338,398 | |||||
(a) | Does not include the leasing portfolio. |
The table below summarizes the carrying amount of the hedged financial instruments, the notional amount of the hedge and the unrealized gain (loss) (estimated fair value) of the derivatives.
Hedged financial instruments | Carrying amount | Notional amount of hedge | ||||||||||
Unrealized | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Gain | (Loss) | ||||||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
Securities available-for-sale | $ | 9,184 | $ | 9,233 | $ | 83 | $ | (342 | ) | |||
Long-term debt | 20,511 | 20,450 | 330 | (203 | ) | |||||||
Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
Securities available-for-sale | $ | 7,978 | $ | 7,918 | $ | 16 | $ | (359 | ) | |||
Long-term debt | 18,231 | 17,850 | 479 | (14 | ) | |||||||
Note 19 - Fair value option
We elected fair value as an alternative measurement for selected financial assets and financial liabilities.
The following table presents the assets and liabilities, by type, of consolidated investment management funds recorded at fair value.
Assets and liabilities of consolidated investment management funds, at fair value | ||||||
Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||
(in millions) | ||||||
Assets of consolidated investment management funds: | ||||||
Trading assets | $ | 979 | $ | 1,228 | ||
Other assets | 252 | 173 | ||||
Total assets of consolidated investment management funds | $ | 1,231 | $ | 1,401 | ||
Liabilities of consolidated investment management funds: | ||||||
Trading liabilities | $ | 282 | $ | 229 | ||
Other liabilities | 33 | 17 | ||||
Total liabilities of consolidated investment management funds | $ | 315 | $ | 246 | ||
BNY Mellon values the assets and liabilities of its consolidated asset management funds using quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets or observable inputs such as quoted prices
202 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
for similar assets or liabilities. Quoted prices for either identical or similar assets or liabilities in inactive markets may also be used. Accordingly, fair value best reflects the interests BNY Mellon holds in the economic performance of the consolidated asset management funds. Changes in the value of the assets and liabilities are recorded in the income statement as investment income of consolidated investment management funds and in the interest of investment management fund note holders, respectively.
We elected the fair value option on $419 million of loans at Dec. 31, 2015 with a fair value of $422 million. The loans were valued using observable market inputs to discount expected loan cash flows and are included in Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy. There were no loans for which the fair value option was elected at Dec. 31, 2016.
We have elected the fair value option on $240 million of long-term debt. The fair value of this long-term debt was $363 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $359 million at Dec. 31, 2015. The long-term debt is valued using observable market inputs and is included in Level 2 of the valuation hierarchy.
The following table presents the changes in fair value of the loans and long-term debt and the location of the changes in the consolidated income statement.
Impact of changes in fair value in the income statement (a) | |||||||||
Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Loans: | |||||||||
Investment and other income | $ | 12 | $ | 3 | $ | — | |||
Long-term debt: | |||||||||
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue (losses) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (12 | ) | $ | (26 | ) |
(a) | The changes in fair value of the loans and long-term debt are approximately offset by economic hedges included in foreign exchange and other trading revenue. |
Note 20 - Commitments and contingent liabilities
In the normal course of business, various commitments and contingent liabilities are outstanding that are not reflected in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Our significant trading and off-balance sheet risks are securities, foreign currency and interest rate risk
management products, commercial lending commitments, letters of credit and securities lending indemnifications. We assume these risks to reduce interest rate and foreign currency risks, to provide customers with the ability to meet credit and liquidity needs and to hedge foreign currency and interest rate risks. These items involve, to varying degrees, credit, foreign currency and interest rate risk not recognized in the balance sheet. Our off-balance sheet risks are managed and monitored in manners similar to those used for on-balance sheet risks. Significant industry concentrations related to credit exposure at Dec. 31, 2016 are disclosed in the financial institutions portfolio exposure table and the commercial portfolio exposure table below.
Financial institutions portfolio exposure (in billions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||
Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | |||||||
Securities industry | $ | 3.8 | $ | 19.2 | $ | 23.0 | |||
Banks | 7.9 | 2.0 | 9.9 | ||||||
Asset managers | 1.5 | 6.2 | 7.7 | ||||||
Insurance | 0.1 | 3.8 | 3.9 | ||||||
Government | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | ||||||
Other | 1.3 | 1.6 | 2.9 | ||||||
Total | $ | 14.7 | $ | 33.7 | $ | 48.4 | |||
Commercial portfolio exposure (in billions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||
Loans | Unfunded commitments | Total exposure | |||||||
Manufacturing | $ | 1.1 | $ | 6.7 | $ | 7.8 | |||
Energy and utilities | 0.6 | 4.7 | 5.3 | ||||||
Services and other | 0.6 | 4.3 | 4.9 | ||||||
Media and telecom | 0.3 | 1.8 | 2.1 | ||||||
Total | $ | 2.6 | $ | 17.5 | $ | 20.1 | |||
Major concentrations in securities lending are primarily to broker-dealers and are generally collateralized with cash. Securities lending transactions are discussed below.
The following table presents a summary of our off-balance sheet credit risks, net of participations.
Off-balance sheet credit risks | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||
(in millions) | ||||||
Lending commitments | $ | 51,270 | $ | 54,505 | ||
Standby letters of credit (a) | 4,185 | 4,915 | ||||
Commercial letters of credit | 339 | 303 | ||||
Securities lending indemnifications (b) | 317,690 | 294,108 | ||||
(a) | Net of participations totaling $662 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $809 million at Dec. 31, 2015. |
(b) | Excludes the indemnification for securities for which BNY Mellon acts as an agent on behalf of CIBC Mellon clients, which totaled $61 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $54 billion at Dec. 31, 2015. |
BNY Mellon 203
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Also included in lending commitments are facilities that provide liquidity for variable rate tax-exempt securities wrapped by monoline insurers. The credit approval for these facilities is based on an assessment of the underlying tax-exempt issuer and considers factors other than the financial strength of the monoline insurer.
The total potential loss on undrawn lending commitments, standby and commercial letters of credit, and securities lending indemnifications is equal to the total notional amount if drawn upon, which does not consider the value of any collateral.
Since many of the commitments are expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total amount does not necessarily represent future cash requirements. A summary of lending commitment maturities is as follows: $28.9 billion in less than one year, $22.1 billion in one to five years and $277 million over five years.
Standby letters of credit (“SBLC”) principally support corporate obligations and were collateralized with cash and securities of $293 million and $299 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, respectively. At Dec. 31, 2016, $2.7 billion of the SBLCs will expire within one year and $1.5 billion in one to five years.
We must recognize, at the inception of an SBLC and foreign and other guarantees, a liability for the fair value of the obligation undertaken in issuing the guarantee. The fair value of the liability, which was recorded with a corresponding asset in other assets, was estimated as the present value of contractual customer fees. The estimated liability for losses related to these commitments and SBLCs, if any, is included in the allowance for lending-related commitments. The allowance for lending-related commitments was $112 million at Dec. 31, 2016 and $118 million at Dec. 31, 2015.
Payment/performance risk of SBLCs is monitored using both historical performance and internal ratings criteria. BNY Mellon’s historical experience is that SBLCs typically expire without being funded. SBLCs below investment grade are monitored closely for payment/performance risk. The table below shows SBLCs by investment grade:
Standby letters of credit | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||
Investment grade | 89 | % | 86 | % |
Non-investment grade | 11 | % | 14 | % |
A commercial letter of credit is normally a short-term instrument used to finance a commercial contract for the shipment of goods from a seller to a buyer. Although the commercial letter of credit is contingent upon the satisfaction of specified conditions, it represents a credit exposure if the buyer defaults on the underlying transaction. As a result, the total contractual amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. Commercial letters of credit totaled $339 million at Dec. 31, 2016 compared with $303 million at Dec. 31, 2015.
A securities lending transaction is a fully collateralized transaction in which the owner of a security agrees to lend the security (typically through an agent, in our case, The Bank of New York Mellon), to a borrower, usually a broker-dealer or bank, on an open, overnight or term basis, under the terms of a prearranged contract, which normally matures in less than 90 days.
We typically lend securities with indemnification against borrower default. We generally require the borrower to provide collateral with a minimum value of 102% of the fair value of the securities borrowed, which is monitored on a daily basis, thus reducing credit risk. Market risk can also arise in securities lending transactions. These risks are controlled through policies limiting the level of risk that can be undertaken. Securities lending transactions are generally entered into only with highly rated counterparties. Securities lending indemnifications were secured by collateral of $331 billion at Dec. 31, 2016 and $306 billion at Dec. 31, 2015.
CIBC Mellon, a joint venture between BNY Mellon and the Canadian Imperial Bank of Commerce (“CIBC”), engages in securities lending activities. CIBC Mellon, BNY Mellon, and CIBC jointly and severally indemnify securities lenders against specific types of borrower default. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, $61 billion and $54 billion, respectively, of borrowings at CIBC Mellon for which BNY Mellon acts as agent on behalf of CIBC Mellon clients, were secured by collateral of $64 billion and $56 billion, respectively. If, upon a default, a borrower’s collateral was not sufficient to cover its related
204 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
obligations, certain losses related to the indemnification could be covered by the indemnitors.
We expect many of these guarantees to expire without the need to advance any cash. The revenue associated with guarantees frequently depends on the credit rating of the obligor and the structure of the transaction, including collateral, if any.
Operating leases
Net rent expense for premises and equipment was $301 million in 2016, $329 million in 2015 and $328 million in 2014.
At Dec. 31, 2016, we were obligated under various noncancelable lease agreements, some of which provide for additional rents based upon real estate taxes, insurance and maintenance and for various renewal options. A summary of the future minimum rental commitments under noncancelable operating leases, net of related sublease revenue, is as follows: 2017—$334 million; 2018—$265 million; 2019—$241 million; 2020—$221 million; 2021—$198 million and 2022 and thereafter—$870 million.
Exposure for certain administrative errors
In connection with certain offshore tax-exempt funds that we manage, we may be liable to the funds for certain administrative errors. The errors relate to the resident status of such funds, potentially exposing the Company to a tax liability related to the funds’ earnings. The Company is in discussions with tax authorities regarding the funds. With the charge recorded in 2014 for this matter, we believe we are appropriately accrued and the additional reasonably possible exposure is not significant.
Indemnification arrangements
We have provided standard representations for underwriting agreements, acquisition and divestiture agreements, sales of loans and commitments, and other similar types of arrangements and customary indemnification for claims and legal proceedings related to providing financial services that are not otherwise included above. Insurance has been purchased to mitigate certain of these risks. Generally, there are no stated or notional amounts included in these indemnifications and the contingencies triggering the obligation for indemnification are not expected to occur.
Furthermore, often counterparties to these transactions provide us with comparable indemnifications. We are unable to develop an estimate of the maximum payout under these indemnifications for several reasons. In addition to the lack of a stated or notional amount in a majority of such indemnifications, we are unable to predict the nature of events that would trigger indemnification or the level of indemnification for a certain event. We believe, however, that the possibility that we will have to make any material payments for these indemnifications is remote. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we have not recorded any material liabilities under these arrangements.
Clearing and settlement exchanges
We are a noncontrolling equity investor in, and/or member of, several industry clearing or settlement exchanges through which foreign exchange, securities, derivatives or other transactions settle. Certain of these industry clearing and settlement exchanges require their members to guarantee their obligations and liabilities and/or to provide liquidity support in the event other members do not honor their obligations. We believe the likelihood that a clearing or settlement exchange (of which we are a member) would become insolvent is remote. Additionally, certain settlement exchanges have implemented loss allocation policies that enable the exchange to allocate settlement losses to the members of the exchange. It is not possible to quantify such mark-to-market loss until the loss occurs. In addition, any ancillary costs that occur as a result of any mark-to-market loss cannot be quantified. At Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015, we have not recorded any material liabilities under these arrangements.
Legal proceedings
In the ordinary course of business, BNY Mellon and its subsidiaries are routinely named as defendants in or made parties to pending and potential legal actions. We also are subject to governmental and regulatory examinations, information-gathering requests, investigations and proceedings (both formal and informal). Claims for significant monetary damages are often asserted in many of these legal actions, while claims for disgorgement, restitution, penalties and/or other remedial actions or sanctions may be sought in regulatory matters. It is inherently difficult to predict the eventual outcomes of such matters given their complexity and the particular facts and
BNY Mellon 205
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
circumstances at issue in each of these matters. However, on the basis of our current knowledge and understanding, we do not believe that judgments, settlements or orders, if any, arising from these matters (either individually or in the aggregate, after giving effect to applicable reserves and insurance coverage) will have a material adverse effect on the consolidated financial position or liquidity of BNY Mellon, although they could have a material effect on net income in a given period.
In view of the inherent unpredictability of outcomes in litigation and governmental and regulatory matters, particularly where (i) the damages sought are substantial or indeterminate, (ii) the proceedings are in the early stages, or (iii) the matters involve novel legal theories or a large number of parties, as a matter of course there is considerable uncertainty surrounding the timing or ultimate resolution of litigation and governmental and regulatory matters, including a possible eventual loss, fine, penalty or business impact, if any, associated with each such matter. In accordance with applicable accounting guidance, BNY Mellon establishes accruals for litigation and governmental and regulatory matters when those matters proceed to a stage where they present loss contingencies that are both probable and reasonably estimable. In such cases, there may be a possible exposure to loss in excess of any amounts accrued. BNY Mellon will continue to monitor such matters for developments that could affect the amount of the accrual, and will adjust the accrual amount as appropriate. If the loss contingency in question is not both probable and reasonably estimable, BNY Mellon does not establish an accrual and the matter will continue to be monitored for any developments that would make the loss contingency both probable and reasonably estimable. BNY Mellon believes that its accruals for legal proceedings are appropriate and, in the aggregate, are not material to the consolidated financial position of BNY Mellon, although future accruals could have a material effect on net income in a given period.
For certain of those matters described here for which a loss contingency may, in the future, be reasonably possible (whether in excess of a related accrued liability or where there is no accrued liability), BNY Mellon is currently unable to estimate a range of reasonably possible loss. For those matters described here where BNY Mellon is able to estimate a reasonably possible loss, the aggregate range of such reasonably possible loss is up to $930 million in
excess of the accrued liability (if any) related to those matters.
The following describes certain judicial, regulatory and arbitration proceedings involving BNY Mellon:
Standing Instruction Matters
Beginning in 2009, government authorities conducted inquiries and BNY Mellon was named as a defendant in lawsuits by various government and private entities relating to whether BNY Mellon’s pricing of standing instruction foreign exchange transactions with custody clients was improper. BNY Mellon announced various settlements in 2015, which are all now final, and has effectively resolved virtually all of the standing instruction FX-related matters.
Mortgage-Securitization Trusts Proceedings
The Bank of New York Mellon has been named as a defendant in a number of legal actions brought by MBS investors alleging that the trustee has expansive duties under the governing agreements, including the duty to investigate and pursue breach of representation and warranty claims against other parties to the MBS transactions. These actions include a lawsuit brought in New York State court on June 18, 2014, and later re-filed in federal court, by a group of institutional investors who purport to sue on behalf of 249 MBS trusts.
Matters Related to R. Allen Stanford
In late December 2005, Pershing LLC became a clearing firm for Stanford Group Co. (“SGC”), a registered broker-dealer that was part of a group of entities ultimately controlled by R. Allen Stanford. Stanford International Bank (“SIB”), also controlled by Stanford, issued certificates of deposit (“CDs”). Some investors allegedly wired funds from their SGC accounts to purchase CDs. In 2009, the SEC charged Stanford with operating a Ponzi scheme in connection with the sale of CDs, and SGC was placed into receivership. Alleged purchasers of CDs have filed 15 lawsuits against Pershing that are pending in Texas, including two putative class actions. The purchasers allege that Pershing, as SGC’s clearing firm, assisted Stanford in a fraudulent scheme and assert contractual, statutory and common law claims. In addition, one FINRA arbitration matter brought by alleged purchasers remains pending.
Brazilian Postalis Litigation
BNY Mellon Servicos Financeiros DTVM S.A. (“DTVM”), a subsidiary that provides a number of
206 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
asset services in Brazil, acts as administrator for certain investment funds in which the exclusive investor is a public pension fund for postal workers called Postalis-Instituto de Seguridade Social dos Correios e Telégrafos (“Postalis”). On Aug. 22, 2014, Postalis sued DTVM in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil for losses related to a Postalis investment fund for which DTVM serves as fund administrator. Postalis alleges that DTVM failed to properly perform alleged duties, including duties to conduct due diligence of and exert control over the fund manager, Atlântica Administração de Recursos (“Atlântica”), and Atlântica’s investments. On March 12, 2015, Postalis filed a lawsuit in Rio de Janeiro against DTVM and BNY Mellon Administração de Ativos Ltda. (“Ativos”) alleging failure to properly perform alleged duties relating to another fund of which DTVM is administrator and Ativos is investment manager. On Dec. 14, 2015, Associaceão Dos Profissionais Dos Correiros, a Brazilian postal workers association, filed a lawsuit in São Paulo against DTVM and other defendants alleging that DTVM improperly contributed to investment losses in the Postalis portfolio. On Dec. 17, 2015, Postalis filed three additional lawsuits in Rio de Janeiro against DTVM and Ativos alleging failure to properly perform alleged duties and liabilities for losses with respect to investments in several other funds. On Feb. 4, 2016, Postalis filed another lawsuit in Brasilia against DTVM, Ativos and BNY Mellon Alocação de Patrimônio Ltda., an investment management subsidiary, alleging failure to properly perform duties and liability for losses with respect to investments in various other funds of which the defendants were administrator and/or manager.
Depositary Receipt Matters
Between late December 2015 and February 2016, four putative class action lawsuits were filed against BNY Mellon asserting claims relating to BNY Mellon’s foreign exchange pricing when converting dividends and other distributions from non-U.S. companies in its role as depositary bank to Depositary Receipt issuers. The claims are for breach of contract and violations of ERISA. The lawsuits have been consolidated into two suits which are pending in federal court in the Southern District of New York.
Brazilian Silverado Litigation
DTVM acts as administrator for the Fundo de Investimento em Direitos Creditórios Multisetorial Silverado Maximum (“Silverado Maximum Fund”), which invests in commercial credit receivables. On
June 2, 2016, the Silverado Maximum Fund sued DTVM in its capacity as administrator, along with Deutsche Bank S.A. - Banco Alemão in its capacity as custodian and Silverado Gestão e Investimentos Ltda. in its capacity as investment manager. The Fund alleges that each of the defendants failed to fulfill its respective duty, and caused losses to the Fund for which the defendants are jointly and severally liable.
Note 21 - Derivative instruments
We use derivatives to manage exposure to market risk including interest rate risk, equity price risk and foreign currency risk, as well as credit risk. Our trading activities are focused on acting as a market-maker for our customers and facilitating customer trades in compliance with the Volcker Rule.
The notional amounts for derivative financial instruments express the dollar volume of the transactions; however, credit risk is much smaller. We perform credit reviews and enter into netting agreements and collateral arrangements to minimize the credit risk of derivative financial instruments. We enter into offsetting positions to reduce exposure to foreign currency, interest rate and equity price risk.
Use of derivative financial instruments involves reliance on counterparties. Failure of a counterparty to honor its obligation under a derivative contract is a risk we assume whenever we engage in a derivative contract. There were no counterparty default losses recorded in 2016. Recoveries of less than $1 million were recorded in 2015.
Hedging derivatives
We utilize interest rate swap agreements to manage our exposure to interest rate fluctuations. For hedges of available-for-sale investment securities, deposits and long-term debt, the hedge documentation specifies the terms of the hedged items and the interest rate swaps and indicates that the derivative is hedging a fixed rate item and is a fair value hedge, that the hedge exposure is to the changes in the fair value of the hedged item due to changes in benchmark interest rates, and that the strategy is to eliminate fair value variability by converting fixed rate interest payments to LIBOR.
The available-for-sale investment securities hedged consist of U.S. Treasury bonds, agency commercial
BNY Mellon 207
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
mortgage-backed securities, sovereign debt and covered bonds that had original maturities of 30 years or less at initial purchase. The swaps on all of these investment securities are not callable. All of these securities are hedged with “pay fixed rate, receive variable rate” swaps of similar maturity, repricing and fixed rate coupon. At Dec. 31, 2016, $9.3 billion face amount of securities were hedged with interest rate swaps that had notional values of $9.2 billion.
The fixed rate long-term debt instruments hedged generally have original maturities of five to 30 years. We issue both callable and non-callable debt. The non-callable debt is hedged with “receive fixed rate, pay variable rate” swaps with similar maturity, repricing and fixed rate coupon. Callable debt is hedged with callable swaps where the call dates of the swaps exactly match the call dates of the debt. At Dec. 31, 2016, $20.5 billion par value of debt was hedged with interest rate swaps that had notional values of $20.5 billion.
In addition, we enter into foreign exchange hedges. We use forward foreign exchange contracts with maturities of nine months or less to hedge our Indian rupee, British pound, Hong Kong dollar, euro, Singapore dollar and Canadian dollar foreign exchange exposure with respect to foreign currency forecasted revenue and expense transactions in entities that have the U.S. dollar as their functional currency. As of Dec. 31, 2016, the hedged forecasted foreign currency transactions and designated forward foreign exchange contract hedges were $313 million (notional), with a pre-tax gain of $7 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income. This gain will be reclassified to income or expense over the next nine months.
Forward foreign exchange contracts are also used to hedge the value of our net investments in foreign subsidiaries. These forward foreign exchange contracts have maturities of less than two years. The derivatives employed are designated as hedges of changes in value of our foreign investments due to exchange rates. Changes in the value of the forward foreign exchange contracts offset the changes in value
of the foreign investments due to changes in foreign exchange rates. The change in fair market value of these forward foreign exchange contracts is deferred and reported within foreign currency translation adjustments in shareholders’ equity, net of tax. At Dec. 31, 2016, forward foreign exchange contracts with notional amounts totaling $6.9 billion were designated as hedges.
We use forward foreign exchange contracts with remaining maturities of two months or less as hedges against our foreign exchange exposure with respect to certain short-term borrowings in currencies other than the functional currency of the issuing entity. These hedges are designated as cash flow hedges and are effected such that their maturities and notional values match those of the corresponding transactions. As of December 31, 2016, the hedged balance sheet items and designated foreign exchange contract hedges were $533 million (notional), with a pre-tax gain of $5.9 million recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income. This gain will be reclassified to net interest revenue over the next two months.
In addition to forward foreign exchange contracts, we also designate non-derivative financial instruments as hedges of our net investments in foreign subsidiaries. Those non-derivative financial instruments designated as hedges of our net investments in foreign subsidiaries were all long-term liabilities of BNY Mellon in various currencies, and, at Dec. 31, 2016, had a combined U.S. dollar equivalent value of $408 million.
Ineffectiveness related to derivatives and hedging relationships was recorded in income as follows:
Ineffectiveness | Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Fair value hedges of securities | $ | (0.5 | ) | $ | 4.1 | $ | (20.6 | ) | |
Fair value hedges of long-term debt | (3.1 | ) | (6.3 | ) | (14.6 | ) | |||
Cash flow hedges | — | — | 0.1 | ||||||
Other (a) | — | — | (0.1 | ) | |||||
Total | $ | (3.6 | ) | $ | (2.2 | ) | $ | (35.2 | ) |
(a) | Includes ineffectiveness recorded on foreign exchange hedges. |
208 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The following table summarizes the notional amount and credit exposure of our total derivative portfolio at Dec. 31, 2016 and Dec. 31, 2015.
Impact of derivative instruments on the balance sheet | Notional value | Asset derivatives fair value | Liability derivatives fair value | |||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | Dec. 31, 2016 | Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: (a) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 29,683 | $ | 25,768 | $ | 415 | $ | 497 | $ | 545 | $ | 372 | ||||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 7,796 | 6,839 | 369 | 219 | 52 | 20 | ||||||||||||||
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments | $ | 784 | $ | 716 | $ | 597 | $ | 392 | ||||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: (b) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 325,412 | $ | 519,428 | $ | 7,587 | $ | 10,044 | $ | 7,633 | $ | 9,962 | ||||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 530,729 | 576,253 | 6,104 | 4,905 | 6,103 | 4,682 | ||||||||||||||
Equity contracts | 1,167 | 1,923 | 46 | 127 | 112 | 151 | ||||||||||||||
Credit contracts | 160 | 319 | — | 8 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | $ | 13,737 | $ | 15,084 | $ | 13,851 | $ | 14,796 | ||||||||||||
Total derivatives fair value (c) | $ | 14,521 | $ | 15,800 | $ | 14,448 | $ | 15,188 | ||||||||||||
Effect of master netting agreements (d) | (10,257 | ) | (11,115 | ) | (10,047 | ) | (10,869 | ) | ||||||||||||
Fair value after effect of master netting agreements | $ | 4,264 | $ | 4,685 | $ | 4,401 | $ | 4,319 | ||||||||||||
(a) | The fair value of asset derivatives and liability derivatives designated as hedging instruments is recorded as other assets and other liabilities, respectively, on the balance sheet. |
(b) | The fair value of asset derivatives and liability derivatives not designated as hedging instruments is recorded as trading assets and trading liabilities, respectively, on the balance sheet. |
(c) | Fair values are on a gross basis, before consideration of master netting agreements, as required by ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. |
(d) | Effect of master netting agreements includes cash collateral received and paid of $1,119 million and $909 million, respectively, at Dec. 31, 2016, and $792 million and $546 million, respectively, at Dec. 31, 2015. |
Impact of derivative instruments on the income statement (in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives in fair value hedging relationships | Location of gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivatives | Gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivatives Year ended Dec. 31, | Location of gain or(loss) recognized in income on hedged item | Gain or (loss) recognized in hedged item Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | Net interest revenue | $ | (274 | ) | $ | (85 | ) | $ | (921 | ) | Net interest revenue | $ | 270 | $ | 83 | $ | 886 | ||||||||||
Derivatives in cash flow hedging relationships | Gain or (loss) recognized in accumulated OCI on derivatives (effective portion) Year ended Dec. 31, | Location of gain or (loss) reclassified from accumulated OCI into income (effective portion) | Gain or (loss) reclassified from accumulated OCI into income (effective portion) Year ended Dec. 31, | Location of gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivatives (ineffective portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing) | Gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivatives (ineffectiveness portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing) Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
FX contracts | $ | (18 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | Net interest revenue | $ | (18 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (2 | ) | Net interest revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
FX contracts | — | — | (6 | ) | Other revenue | — | — | (3 | ) | Other revenue | — | — | 0.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
FX contracts | (16 | ) | 9 | 36 | Trading revenue | (16 | ) | 9 | 36 | Trading revenue | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
FX contracts | (18 | ) | (8 | ) | (6 | ) | Salary expense | (11 | ) | (19 | ) | 10 | Salary expense | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | (52 | ) | $ | — | $ | 22 | $ | (45 | ) | $ | (11 | ) | $ | 41 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.1 | ||||||||||||
Derivatives in net investment hedging relationships | Gain or (loss) recognized in accumulated OCI on derivatives (effective portion) Year ended Dec. 31, | Location of gain or (loss) reclassified from accumulated OCI into income (effective portion) | Gain or (loss) reclassified from accumulated OCI into income (effective portion) Year ended Dec. 31, | Location of gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivative (ineffective portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing) | Gain or (loss) recognized in income on derivatives (ineffectiveness portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing) Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
FX contracts | $ | 652 | $ | 474 | $ | (367 | ) | Net interest revenue | $ | — | $ | 1 | $ | (1 | ) | Other revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (0.1 | ) | ||||||||||
BNY Mellon 209
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Trading activities (including trading derivatives)
We manage trading risk through a system of position limits, a VaR methodology based on Monte Carlo simulations and other market sensitivity measures. Risk is monitored and reported to senior management by a separate unit on a daily basis. Based on certain assumptions, the VaR methodology is designed to capture the potential overnight pre-tax dollar loss from adverse changes in fair values of all trading positions. The calculation assumes a one-day holding period for most instruments, utilizes a 99% confidence level and incorporates the non-linear characteristics of options. The VaR model is one of several statistical models used to develop economic capital results, which is allocated to lines of business for computing risk-adjusted performance.
As the VaR methodology does not evaluate risk attributable to extraordinary financial, economic or other occurrences, the risk assessment process includes a number of stress scenarios based upon the risk factors in the portfolio and management’s assessment of market conditions. Additional stress scenarios based upon historical market events are also performed. Stress tests, by their design, incorporate the impact of reduced liquidity and the breakdown of observed correlations. The results of these stress tests are reviewed weekly with senior management.
Revenue from foreign exchange and other trading included the following:
Foreign exchange and other trading revenue | Year ended Dec. 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
Foreign exchange | $ | 687 | $ | 743 | $ | 578 | ||||
Other trading revenue (loss) | 14 | 25 | (8 | ) | ||||||
Total foreign exchange and other trading revenue | $ | 701 | $ | 768 | $ | 570 | ||||
Foreign exchange includes income from purchasing and selling foreign currencies and currency forwards, futures and options. Other trading revenue reflects results from futures and forward contracts, interest rate swaps, structured foreign currency swaps, options, equity derivatives and fixed income and equity securities.
Counterparty credit risk and collateral
We assess credit risk of our counterparties through regular examination of their financial statements,
confidential communication with the management of those counterparties and regular monitoring of publicly available credit rating information. This and other information is used to develop proprietary credit rating metrics used to assess credit quality.
Collateral requirements are determined after a comprehensive review of the credit quality of each counterparty. Collateral is generally held or pledged in the form of cash or highly liquid government securities. Collateral requirements are monitored and adjusted daily.
Additional disclosures concerning derivative financial instruments are provided in Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Disclosure of contingent features in OTC derivative instruments
Certain OTC derivative contracts and/or collateral agreements of The Bank of New York Mellon, our largest banking subsidiary and the subsidiary through which BNY Mellon enters into the substantial majority of its OTC derivative contracts and/or collateral agreements, contain provisions that may require us to take certain actions if The Bank of New York Mellon’s public debt rating fell to a certain level. Early termination provisions, or “close-out” agreements, in those contracts could trigger immediate payment of outstanding contracts that are in net liability positions. Certain collateral agreements would require The Bank of New York Mellon to immediately post additional collateral to cover some or all of The Bank of New York Mellon’s liabilities to a counterparty.
The following table shows the fair value of contracts falling under early termination provisions that were in net liability positions as of Dec. 31, 2016 for three key ratings triggers:
If The Bank of New York Mellon’s rating was changed to (Moody’s/S&P) | Potential close-out exposures (fair value) (a) | |||
A3/A- | $ | 121 | million | |
Baa2/BBB | $ | 805 | million | |
Ba1/BB+ | $ | 2,066 | million | |
(a) | The amounts represent potential total close-out values if The Bank of New York Mellon’s rating were to immediately drop to the indicated levels. |
210 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The aggregated fair value of contracts impacting potential trade close-out amounts and collateral obligations can fluctuate from quarter to quarter due to changes in market conditions, changes in the composition of counterparty trades, new business or changes to the agreement definitions establishing close-out or collateral obligations.
Additionally, if The Bank of New York Mellon’s debt rating had fallen below investment grade on Dec. 31, 2016, existing collateral arrangements would have required us to have posted an additional $209 million of collateral.
The following tables present derivative instruments and financial instruments that are either subject to an enforceable netting agreement or offset by collateral arrangements. There were no derivative instruments or financial instruments subject to a legally enforceable netting agreement for which we are not currently netting.
Offsetting of derivative assets and financial assets at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Gross assets recognized | Gross amounts offset in the balance sheet | Net assets recognized on the balance sheet | Gross amounts not offset in the balance sheet | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | (a) | Financial instruments | Cash collateral received | Net amount | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives subject to netting arrangements: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 7,205 | $ | 6,047 | $ | 1,158 | $ | 321 | $ | — | $ | 837 | |||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 5,265 | 4,172 | 1,093 | 202 | — | 891 | |||||||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 44 | 38 | 6 | — | — | 6 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives subject to netting arrangements | 12,514 | 10,257 | 2,257 | 523 | — | 1,734 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives not subject to netting arrangements | 2,007 | — | 2,007 | — | — | 2,007 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives | 14,521 | 10,257 | 4,264 | 523 | — | 3,741 | |||||||||||||
Reverse repurchase agreements | 17,588 | 481 | (b) | 17,107 | 17,104 | — | 3 | ||||||||||||
Securities borrowing | 8,694 | — | 8,694 | 8,425 | — | 269 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 40,803 | $ | 10,738 | $ | 30,065 | $ | 26,052 | $ | — | $ | 4,013 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the effect of netting agreements and net cash collateral received. The offset related to the OTC derivatives was allocated to the various types of derivatives based on the net positions. |
(b) | Offsetting of reverse repurchase agreements relates to our involvement in the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation, where we settle government securities transactions on a net basis for payment and delivery through the Fedwire system. |
BNY Mellon 211
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Offsetting of derivative assets and financial assets at Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Gross assets recognized | Gross amounts offset in the balance sheet | Net assets recognized on the balance sheet | Gross amounts not offset in the balance sheet | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | (a) | Financial instruments | Cash collateral received | Net amount | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives subject to netting arrangements: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 9,554 | $ | 8,071 | $ | 1,483 | $ | 432 | $ | — | $ | 1,051 | |||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 3,981 | 2,981 | 1,000 | 63 | — | 937 | |||||||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 123 | 63 | 60 | — | — | 60 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives subject to netting arrangements | 13,658 | 11,115 | 2,543 | 495 | — | 2,048 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives not subject to netting arrangements | 2,142 | — | 2,142 | — | — | 2,142 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives | 15,800 | 11,115 | 4,685 | 495 | — | 4,190 | |||||||||||||
Reverse repurchase agreements | 17,088 | 357 | (b) | 16,731 | 16,726 | — | 5 | ||||||||||||
Securities borrowing | 7,630 | — | 7,630 | 7,373 | — | 257 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 40,518 | $ | 11,472 | $ | 29,046 | $ | 24,594 | $ | — | $ | 4,452 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the effect of netting agreements and net cash collateral received. The offset related to the OTC derivatives was allocated to the various types of derivatives based on the net positions. |
(b) | Offsetting of reverse repurchase agreements relates to our involvement in the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation, where we settle government securities transactions on a net basis for payment and delivery through the Fedwire system. |
Offsetting of derivative liabilities and financial liabilities at Dec. 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Gross liabilities recognized | Gross amounts offset in the balance sheet | Net liabilities recognized on the balance sheet | Gross amounts not offset in the balance sheet | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | (a) | Financial instruments | Cash collateral pledged | Net amount | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives subject to netting arrangements: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 8,116 | $ | 6,634 | $ | 1,482 | $ | 1,266 | $ | — | $ | 216 | |||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 4,957 | 3,363 | 1,594 | 355 | — | 1,239 | |||||||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 104 | 50 | 54 | 54 | — | — | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives subject to netting arrangements | 13,177 | 10,047 | 3,130 | 1,675 | — | 1,455 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives not subject to netting arrangements | 1,271 | — | 1,271 | — | — | 1,271 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives | 14,448 | 10,047 | 4,401 | 1,675 | — | 2,726 | |||||||||||||
Repurchase agreements | 8,703 | 481 | (b) | 8,222 | 8,222 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Securities lending | 1,615 | — | 1,615 | 1,522 | — | 93 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 24,766 | $ | 10,528 | $ | 14,238 | $ | 11,419 | $ | — | $ | 2,819 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the effect of netting agreements and net cash collateral paid. The offset related to the OTC derivatives was allocated to the various types of derivatives based on the net positions. |
(b) | Offsetting of repurchase agreements relates to our involvement in the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation, where we settle government securities transactions on a net basis for payment and delivery through the Fedwire system. |
212 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Offsetting of derivative liabilities and financial liabilities at Dec. 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Gross liabilities recognized | Gross amounts offset in the balance sheet | Net liabilities recognized on the balance sheet | Gross amounts not offset in the balance sheet | ||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | (a) | Financial instruments | Cash collateral pledged | Net amount | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives subject to netting arrangements: | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate contracts | $ | 10,188 | $ | 8,235 | $ | 1,953 | $ | 1,795 | $ | — | $ | 158 | |||||||
Foreign exchange contracts | 3,409 | 2,567 | 842 | 274 | — | 568 | |||||||||||||
Equity and other contracts | 145 | 67 | 78 | 71 | — | 7 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives subject to netting arrangements | 13,742 | 10,869 | 2,873 | 2,140 | — | 733 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives not subject to netting arrangements | 1,446 | — | 1,446 | — | — | 1,446 | |||||||||||||
Total derivatives | 15,188 | 10,869 | 4,319 | 2,140 | — | 2,179 | |||||||||||||
Repurchase agreements | 7,737 | 357 | (b) | 7,380 | 7,380 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Securities lending | 1,801 | — | 1,801 | 1,727 | — | 74 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 24,726 | $ | 11,226 | $ | 13,500 | $ | 11,247 | $ | — | $ | 2,253 | |||||||
(a) | Includes the effect of netting agreements and net cash collateral paid. The offset related to the OTC derivatives was allocated to the various types of derivatives based on the net positions. |
(b) | Offsetting of repurchase agreements relates to our involvement in the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation, where we settle government securities transactions on a net basis for payment and delivery through the Fedwire system. |
Secured borrowings
The following tables present the contract value of repurchase agreements and securities lending transactions accounted for as secured borrowings by the type of collateral provided to counterparties.
Repurchase agreements and securities lending transactions accounted for as secured borrowings at Dec. 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
Remaining contractual maturity of the agreements | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Overnight and continuous | Up to 30 days | 30 days or more | Total | ||||||||
Repurchase agreements: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 2,488 | $ | 4 | $ | — | $ | 2,492 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 396 | 10 | — | 406 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 3,294 | 386 | — | 3,680 | ||||||||
Corporate bonds | 304 | — | 694 | 998 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 146 | — | 563 | 709 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 375 | — | 43 | 418 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 7,003 | $ | 400 | $ | 1,300 | $ | 8,703 | ||||
Securities lending: | ||||||||||||
U.S. government agencies | $ | 39 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 39 | ||||
Other debt securities | 477 | — | — | 477 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 1,099 | — | — | 1,099 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 1,615 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,615 | ||||
Total borrowings | $ | 8,618 | $ | 400 | $ | 1,300 | $ | 10,318 | ||||
BNY Mellon 213
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Repurchase agreements and securities lending transactions accounted for as secured borrowings at Dec. 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
Remaining contractual maturity of the agreements | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Overnight and continuous | Up to 30 days | 30 days or more | Total | ||||||||
Repurchase agreements: | ||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | $ | 2,226 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,226 | ||||
U.S. government agencies | 319 | 42 | 5 | 366 | ||||||||
Agency RMBS | 3,158 | — | — | 3,158 | ||||||||
Corporate bonds | 372 | — | 665 | 1,037 | ||||||||
Other debt securities | 106 | — | 149 | 255 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 664 | — | 31 | 695 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 6,845 | $ | 42 | $ | 850 | $ | 7,737 | ||||
Securities lending: | ||||||||||||
U.S. government agencies | $ | 35 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 35 | ||||
Other debt securities | 254 | — | — | 254 | ||||||||
Equity securities | 1,512 | — | — | 1,512 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 1,801 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,801 | ||||
Total borrowings | $ | 8,646 | $ | 42 | $ | 850 | $ | 9,538 | ||||
BNY Mellon’s repurchase agreements and securities lending transactions primarily encounter risk associated with liquidity. We are required to pledge collateral based on predetermined terms within the agreements. If we were to experience a decline in the fair value of the collateral pledged for these transactions, additional collateral could be required to be provided to the counterparty; therefore, decreasing the amount of assets available for other liquidity needs that may arise. BNY Mellon also offers tri-party collateral agency services in the tri-party repo market where we are exposed to credit risk. In order to mitigate this risk, we require dealers to fully secure intraday credit.
Note 22 - Lines of business
We have an internal information system that produces performance data along product and service lines for our two principal businesses and the Other segment.
Business accounting principles
Our business data has been determined on an internal management basis of accounting, rather than the generally accepted accounting principles used for consolidated financial reporting. These measurement principles are designed so that reported results of the businesses will track their economic performance.
Business results are subject to reclassification when organizational changes are made or when improvements are made in the measurement principles. In 2016, BNY Mellon reclassified the results of our credit-related activities to the Investment Services segment from the Other segment. This reclassification reflects our strategy to provide credit services to our Investment Services clients and did not impact the consolidated results. Also, concurrent with this reclassification, the provision for credit losses associated with the respective credit portfolios is now reflected in each business segment. All prior periods have been restated.
Beginning in 2016, we revised the net interest revenue for our business to reflect adjustments to our transfer pricing methodology to better reflect the value of certain deposits. Also in 2016, we refined the expense allocation process for indirect expenses to simplify the expenses recorded in the Other segment to include only expenses not directly attributable to the Investment Management and Investment Services operations. These changes did not impact the consolidated results.
The accounting policies of the businesses are the same as those described in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
214 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
The primary types of revenue for our two principal businesses and the Other segment are presented below:
Business | Primary types of revenue |
Investment Management | • Investment management and performance fees from: Mutual funds Institutional clients Private clients High net worth individuals and families, endowments and foundations and related entities • Distribution and servicing fees • Other revenue from seed capital investments |
Investment Services | • Asset servicing fees, including institutional trust and custody fees, accounting, broker-dealer services, securities lending and collateral and liquidity services • Issuer services fees, including Corporate Trust and Depositary Receipts • Clearing services fees • Treasury services fees, including global payment services, trade finance and cash management • Foreign exchange revenue • Financing-related fees and net interest revenue from credit-related activities |
Other segment | • Net interest-revenue and lease-related gains (losses) from leasing operations • Gain (loss) on securities and net interest revenue from corporate treasury activity • Other trading revenue from derivatives and other trading activity • Results of business exits |
The results of our businesses are presented and analyzed on an internal management reporting basis:
• | Revenue amounts reflect fee and other revenue generated by each business. Fee and other revenue transferred between businesses under revenue transfer agreements is included within other revenue in each business. |
• | Revenues and expenses associated with specific client bases are included in those businesses. For example, foreign exchange activity associated with clients using custody products is included in Investment Services. |
• | Net interest revenue is allocated to businesses based on the yields on the assets and liabilities generated by each business. We employ a funds transfer pricing system that matches funds with the specific assets and liabilities of each business based on their interest sensitivity and maturity characteristics. |
• | The provision for credit losses associated with the respective credit portfolios is reflected in each business segment. |
• | Incentive expense related to restricted stock is allocated to the businesses. |
• | Support and other indirect expenses are allocated to businesses based on internally developed methodologies. |
• | Recurring FDIC expense is allocated to the businesses based on average deposits generated within each business. |
• | Litigation expense is generally recorded in the business in which the charge occurs. |
• | Management of the investment securities portfolio is a shared service contained in the Other segment. As a result, gains and losses associated with the valuation of the securities portfolio are included in the Other segment. |
• | Client deposits serve as the primary funding source for our investment securities portfolio. We typically allocate all interest revenue to the businesses generating the deposits. Accordingly, accretion related to the portion of the investment securities portfolio restructured in 2009 has been included in the results of the businesses. |
• | M&I expense is a corporate level item and is recorded in the Other segment. |
• | Restructuring charges relate to corporate-level initiatives and were therefore recorded in the Other segment. |
• | Balance sheet assets and liabilities and their related income or expense are specifically assigned to each business. Businesses with a net liability position have been allocated assets. |
• | Goodwill and intangible assets are reflected within individual businesses. |
BNY Mellon 215
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Total revenue includes approximately $2.2 billion in 2016, $2.3 billion in 2015 and $2.3 billion in 2014 of international operations domiciled in the UK which
comprised 14%, 15% and 15% of total revenue, respectively.
The following consolidating schedules show the contribution of our businesses to our overall profitability.
For the year ended Dec. 31, 2016 | Investment Management | Investment Services | Other | Consolidated | ||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
Fee and other revenue | $ | 3,424 | (a) | $ | 8,299 | $ | 366 | $ | 12,089 | (a) | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 327 | 2,797 | 14 | 3,138 | ||||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,751 | (a) | 11,096 | 380 | 15,227 | (a) | ||||||||||
Provision for credit losses | 6 | 8 | (25 | ) | (11 | ) | ||||||||||
Noninterest expense | 2,778 | 7,342 | 394 | 10,514 | (b) | |||||||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 967 | (a) | $ | 3,746 | $ | 11 | $ | 4,724 | (a)(b) | ||||||
Pre-tax operating margin (c) | 26 | % | 34 | % | N/M | 31 | % | |||||||||
Average assets | $ | 30,169 | $ | 273,808 | $ | 54,500 | $ | 358,477 | ||||||||
(a) | Both fee and other revenue and total revenue include the net income from consolidated investment management funds of $16 million, representing $26 million of income and noncontrolling interests of $10 million. Income before taxes is net of noncontrolling interests of $10 million. |
(b) | Noninterest expense includes a loss attributable to noncontrolling interest of $9 million related to other consolidated subsidiaries. |
(c) | Income before taxes divided by total revenue. |
For the year ended Dec. 31, 2015 | Investment Management | Investment Services | Other | Consolidated | ||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
Fee and other revenue | $ | 3,587 | (a) | $ | 8,177 | $ | 336 | $ | 12,100 | (a) | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 319 | 2,622 | 85 | 3,026 | ||||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,906 | (a) | 10,799 | 421 | 15,126 | (a) | ||||||||||
Provision for credit losses | (1 | ) | 28 | 133 | 160 | |||||||||||
Noninterest expense | 2,859 | 7,502 | 434 | 10,795 | (b) | |||||||||||
Income (loss) before taxes | $ | 1,048 | (a) | $ | 3,269 | $ | (146 | ) | $ | 4,171 | (a)(b) | |||||
Pre-tax operating margin (c) | 27 | % | 30 | % | N/M | 28 | % | |||||||||
Average assets | $ | 30,928 | $ | 286,617 | $ | 54,642 | $ | 372,187 | ||||||||
(a) | Both fee and other revenue and total revenue include the net income from consolidated investment management funds of $18 million, representing $86 million of income and noncontrolling interests of $68 million. Income before taxes is net of noncontrolling interests of $68 million. |
(b) | Noninterest expense includes a loss attributable to noncontrolling interest of $4 million related to other consolidated subsidiaries. |
(c) | Income before taxes divided by total revenue. |
For the year ended Dec. 31, 2014 | Investment Management | Investment Services | Other | Consolidated | ||||||||||||
(dollar amounts in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
Fee and other revenue | $ | 3,657 | (a) | $ | 7,882 | $ | 1,189 | $ | 12,728 | (a) | ||||||
Net interest revenue | 274 | 2,468 | 138 | 2,880 | ||||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,931 | (a) | 10,350 | 1,327 | 15,608 | (a) | ||||||||||
Provision for credit losses | — | (21 | ) | (27 | ) | (48 | ) | |||||||||
Noninterest expense | 3,039 | 8,241 | 897 | 12,177 | ||||||||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 892 | (a) | $ | 2,130 | $ | 457 | $ | 3,479 | (a) | ||||||
Pre-tax operating margin (b) | 23 | % | 21 | % | N/M | 22 | % | |||||||||
Average assets | $ | 37,655 | $ | 271,477 | $ | 63,434 | $ | 372,566 | ||||||||
(a) | Both fee and other revenue and total revenue include net income from consolidated investment management funds of $79 million, representing $163 million of income and noncontrolling interests of $84 million. Income before taxes is net of noncontrolling interests of $84 million. |
(b) | Income before taxes divided by total revenue. |
216 BNY Mellon
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued) |
Note 23 - International operations
International activity includes Investment Management and Investment Services fee revenue generating businesses, foreign exchange trading activity, loans and other revenue producing assets and transactions in which the customer is domiciled outside of the United States and/or the international activity is resident at an international entity. Due to the nature of our international and domestic activities, it is not possible to precisely distinguish our international operations between internationally and domestically domiciled customers.
As a result, it is necessary to make certain subjective assumptions such as:
• | Income from international operations is determined after internal allocations for interest revenue, taxes, expenses and provision for credit losses. |
• | Expense charges to international operations include those directly incurred in connection with such activities, as well as an allocable share of general support and overhead charges. |
Total assets, total revenue, income before income taxes and net income of our international operations are shown in the table below.
International operations | International | Total International | Total Domestic | |||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | EMEA | APAC | Other | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets at period end (a) | $ | 73,303 | (b) | $ | 18,074 | $ | 1,350 | $ | 92,727 | $ | 240,742 | $ | 333,469 | |||||||||
Total revenue | 3,744 | (b) | 922 | 549 | 5,215 | 10,022 | 15,237 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 1,263 | 485 | 286 | 2,034 | 2,691 | 4,725 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | 1,013 | 389 | 229 | 1,631 | 1,917 | 3,548 | ||||||||||||||||
2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets at period end (a) | $ | 76,679 | (b) | $ | 17,829 | $ | 1,176 | $ | 95,684 | $ | 298,096 | $ | 393,780 | |||||||||
Total revenue | 3,932 | (b) | 904 | 577 | 5,413 | 9,781 | 15,194 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 1,436 | 451 | 269 | 2,156 | 2,079 | 4,235 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | 1,163 | 365 | 218 | 1,746 | 1,476 | 3,222 | ||||||||||||||||
2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets at period end (a) | $ | 86,189 | (b) | $ | 16,812 | $ | 1,516 | $ | 104,517 | $ | 280,786 | $ | 385,303 | |||||||||
Total revenue | 3,931 | (b) | 1,383 | 645 | 5,959 | 9,733 | 15,692 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 985 | 913 | 365 | 2,263 | 1,300 | 3,563 | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | 775 | 719 | 287 | 1,781 | 870 | 2,651 | ||||||||||||||||
(a) | Total assets include long-lived assets, which are not considered by management to be significant in relation to total assets. Long-lived assets are primarily located in the United States. |
(b) | Includes revenue of approximately $2.2 billion, $2.3 billion and $2.3 billion and assets of approximately $29.6 billion, $33.2 billion and $46.2 billion in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, of international operations domiciled in the UK, which is 14%, 15% and 15% of total revenue and 9%, 8% and 12% of total assets, respectively. |
Note 24 - Supplemental information to the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
Noncash investing and financing transactions that, appropriately, are not reflected in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows are listed below.
Noncash investing and financing transactions | Year ended Dec. 31, | ||||||||
(in millions) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Transfers from loans to other assets for other real estate owned (“OREO”) | $ | 4 | $ | 7 | $ | 4 | |||
Change in assets of consolidated VIEs | 170 | 7,881 | 1,990 | ||||||
Change in liabilities of consolidated VIEs | 69 | 7,423 | 2,462 | ||||||
Change in nonredeemable noncontrolling interests of consolidated investment management funds | 120 | 295 | 250 | ||||||
Securities purchased not settled | 75 | — | 55 | ||||||
Securities sales not settled | — | 11 | 750 | ||||||
Available-for-sale securities transferred to held-to-maturity | — | 11,602 | — | ||||||
Held-to-maturity securities transferred to available-for-sale | 10 | — | — | ||||||
Premises and equipment/capitalized software funded by capital lease obligations | 13 | 49 | 31 | ||||||
BNY Mellon 217
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation and subsidiaries (“BNY Mellon”) as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of BNY Mellon’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of BNY Mellon as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated February 28, 2017 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of BNY Mellon’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
New York, New York
February 28, 2017
218 BNY Mellon
Directors, Executive Committee and Other Executive Officers |
Effective February 28, 2017
Directors | ||||
Linda Z. Cook | Edmund F. (Ted) Kelly | Michael Cole-Fontayn | ||
Managing Director and Member of the | Retired Chairman | Chairman, | ||
Executive Committee of EIG Global Energy | Liberty Mutual Group | Europe, Middle East and Africa | ||
Partners, an investment firm, and Chief | Multi-line insurance company | |||
Executive Officer of Harbour Energy, Ltd., | J. David Cruikshank | |||
an energy investment vehicle | John A. Luke, Jr. | Chairman, | ||
Non-Executive Chairman | Asia Pacific | |||
Nicholas M. Donofrio | WestRock Company | |||
Retired Executive Vice President, | Global paper and packaging company | Thomas P. (Todd) Gibbons * | ||
Innovation and Technology | Chief Financial Officer | |||
IBM Corporation | Jennifer B. Morgan | |||
Developer, manufacturer and provider of | President of SAP North America | Mitchell E. Harris * | ||
advanced information technologies and services | Global software company | Chief Executive Officer, | ||
Investment Management | ||||
Joseph J. Echevarria | Mark A. Nordenberg | |||
Retired Chief Executive Officer | Chancellor Emeritus, | Monique R. Herena * | ||
Deloitte LLP | Chair of the Institute of Politics and | Chief Human Resources Officer | ||
Global provider of audit, consulting, financial | Distinguished Service Professor of Law | |||
advisory, risk management, tax and related | University of Pittsburgh | Kurtis R. Kurimsky * | ||
services | Major public research university | Corporate Controller | ||
Edward P. Garden | Catherine A. Rein | Suresh Kumar | ||
Chief Investment Officer and a founding partner, | Retired Senior Executive Vice President and | Chief Information Officer | ||
Trian Fund Management, L.P. | Chief Administrative Officer | |||
Alternative investment management firm | MetLife, Inc. | J. Kevin McCarthy * | ||
Insurance and financial services company | General Counsel | |||
Jeffrey A. Goldstein | ||||
Senior Advisor, Hellman & Friedman LLC | Elizabeth E. Robinson | Michelle M. Neal * | ||
Private equity firm | Former Global Treasurer, Partner and Managing | President, | ||
Director of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. | BNY Mellon Markets Group | |||
Gerald L. Hassell | Global financial services company | |||
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | Brian T. Shea * | |||
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | Samuel C. Scott III | Chief Executive Officer, | ||
Retired Chairman, President and | Investment Services | |||
John M. Hinshaw | Chief Executive Officer | |||
Former Executive Vice President and | Ingredion Incorporated (formerly Corn Products | Douglas H. Shulman | ||
Chief Customer Officer at | International, Inc.) | Head of Client Service Delivery | ||
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Company | Global ingredient solutions provider | |||
Global provider of IT, technology and enterprise | James S. Wiener * | |||
products and solutions | Executive Committee and Other Executive | Chief Risk Officer | ||
Officers | ||||
Gerald L. Hassell * | ||||
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
* | Designated as an Executive Officer. |
BNY Mellon 219
Performance Graph |
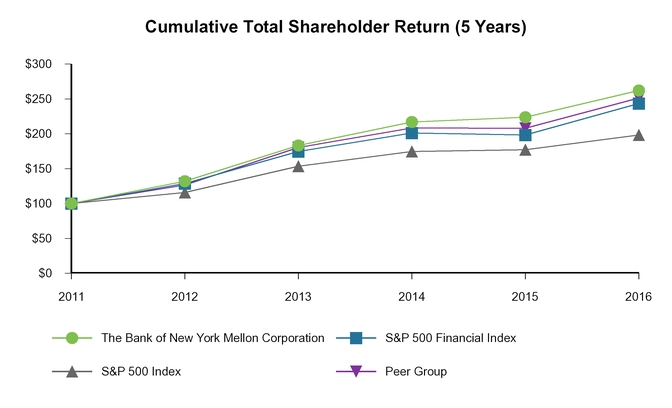
Cumulative shareholder returns (a) | Dec. 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(in dollars) | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation | $ | 100.0 | $ | 132.1 | $ | 183.2 | $ | 216.7 | $ | 223.9 | $ | 262.0 | |||||||||||
S&P 500 Financial Index | 100.0 | 128.8 | 174.7 | 201.3 | 198.2 | 243.4 | |||||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Index | 100.0 | 116.0 | 153.6 | 174.6 | 177.0 | 198.2 | |||||||||||||||||
Peer Group | 100.0 | 126.5 | 180.5 | 208.3 | 208.0 | 251.4 | |||||||||||||||||
(a) | Returns are weighted by market capitalization at the beginning of the measurement period. |
This graph shows The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation’s cumulative total shareholder returns over the five-year period from Dec. 31, 2011 to Dec. 31, 2016. Our peer group is composed of financial services companies which provide investment management and investment servicing. We also utilize the S&P 500 Financial Index as a benchmark against our performance. The graph shows the cumulative total returns for the same five-year period of the S&P 500 Financial Index, the S&P 500 Index as well as our peer group listed below. The comparison assumes a $100 investment on Dec. 31, 2011 in The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation common stock, in the S&P 500 Financial Index, in the S&P 500 Index and in the peer group detailed below and assumes that all dividends were reinvested.
Peer Group | ||
BlackRock, Inc. The Charles Schwab Corporation Franklin Resources, Inc. JPMorgan Chase & Co. | Morgan Stanley Northern Trust Corporation The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. Prudential Financial, Inc. | State Street Corporation U.S. Bancorp Wells Fargo & Company |
220 BNY Mellon