FORM 6 - K
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Report of Foreign Private Issuer
Pursuant to Rule 13a - 16 or 15d - 16 of
the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
As of 7/20/2020
Ternium S.A.
(Translation of Registrant's name into English)
Ternium S.A.
26, Boulevard Royal - 4th floor
26, Boulevard Royal - 4th floor
L-2449 Luxembourg
(352) 2668-3152
(Address of principal executive offices)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant files or will file annual reports under cover Form 20-F or 40-F.
Form 20-F a Form 40-F __
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant by furnishing the information contained in this Form is also thereby furnishing the information to the Commission pursuant to Rule 12G3-2(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Yes __ No a
If “Yes” is marked, indicate below the file number assigned to the registrant in connection with Rule 12g3-2(b):
Not applicable
The attached material is being furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Rule 13a-16 and Form 6-K under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
This report contains Ternium S.A.’s 2019 Sustainability Report.
SIGNATURE
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
TERNIUM S.A.
By: /s/ Pablo Brizzio By: /s/ Máximo Vedoya
Name: Pablo Brizzio Name: Máximo Vedoya
Title: Chief Financial Officer Title: Chief Executive Officer
Dated: July 20, 2020
 |
 |
2. Ternium |
Contents | |
4 | About Ternium's Reporting |
7 | The Company |
14 | Chairman's Letter |
19 | A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation |
22 | Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy |
38 | Improving Our Safety Performance |
46 | Minimizing Ternium's Environmental Footprint |
56 | Realizing People's Full Potential |
66 | Strengthening of Ternium's Value Chain |
70 | Helping Our Communities Thrive |
79 | Commitment to Integrity |
89 | GRI and UN Global Compact Information |
Ternium S.A. (the “Company”) is a Luxembourg company and its American Depositary Shares, or ADSs, are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE: TX). We refer to Ternium S.A. and its consolidated subsidiaries as “we,” “our” or “Ternium.” | TX LISTED NYSE | The financial and operational information contained in this report is based on Ternium’s operational data and on the Company’s consolidated financial statements, which were prepared in accordance with IFRS and IFRIC interpretations as issued by the IASB and adopted by the European Union and presented in U.S. dollars ($) and metric tons. |
3. Sustainability Report 2019 |
'
About Ternium's Reporting | |
Ternium's 2019 Sustainability Report
This report intends to be an integral discussion of Ternium's progress towards achieving its objectives in a sustainable way. It has been prepared taking into account the guidelines established by worldsteel, the UN Global Compact and the Global Reporting Initiative.
Ternium's Sources of Corporate Information
 |  |  |  | |||
Annual Report on Form 20-F | Consolidated Management Report | Sustainability Report | Ternium.com | |||
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Guidelines
Ternium's Sustainability Report for the year 2019 follows the GRI standard core option of the reporting levels.
In order to comply with this standard, Ternium has assessed its sustainability report in light of the GRI principles of Stakeholder Inclusiveness, Sustainability Context, Materiality and Completeness. The company
has carried out a Materiality Analysis according to the GRI four-step process. The result of this analysis has been included on page 90, by means of a materiality matrix that ranks relevant economic, environmental and social topics according to their influence on stakeholders' assessments and decisions, and according to their significance to Ternium. The GRI standards that Ternium has selected to fulfill, in accordance with the reporting requirements of those topics, have been
4. Ternium |
included in the GRI Index on pages 92 to 94 of this sustainability report. The historical data related to these standards, as well as other historical data, has been included on pages 95 to 101 of this sustainability report.
UN Global Compact Initiative
In 2019, Ternium joined the UN Global Compact Initiative with a commitment to integrate its principles into the company's strategy, culture and day-to-day operations. Ternium has engaged in collaborative projects to advance the broader development goals of the United Nations, particularly the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The company's contribution to the UN Global Compact SDGs is reported throughout the document and has been indexed on page 102 of this sustainability report.
New Ternium.com
In September 2019, Ternium launched a new corporate website with a new approach to interact with its stakeholders. The company has established different goals for this project:
Firstly, to increase the importance of the website as a go-to resource for current and potential customers, encouraging them to engage with Ternium’s wide range of products and solutions. As a company that operates in various countries, Ternium.com aims to link customers to its local commercial contacts while keeping a seamless brand vision, through new relevant and localized content supported by cutting-edge easy-to-use navigation tools.
Secondly, to improve the navigation experience of the investor relations section with the addition of new trends in design and functionality. The new features facilitate access to corporate messages and reports, and the new resources enhance interactions with the company.
Thirdly, as a leading steel manufacturer, Ternium.com has been conceived as a relevant means of communication to raise awareness on the role that steel plays today and will play in the future, as we build an increasingly sustainable society.
Forward looking Statements
This sustainability report contains “forward-looking statements”, including with respect to certain of our plans and current goals and expectations relating to Ternium’s future financial condition and performance, which are provided to allow potential investors the opportunity to understand management’s beliefs and opinions in respect of the future so that they may use such beliefs and opinions as one factor in evaluating an investment in Ternium’s securities. All forward-looking statements are based on management’s present expectations of future events and are subject to a number of factors and uncertainties that may cause actual results, performance or events to differ materially from those expressed or implied by those statements. By their nature, certain disclosures relating to these expectations are only estimates and could be materially different from what actually occurs in the future. As a result, actual future gains or losses that may affect Ternium’s financial condition and results of operations could differ materially from those that have been estimated. You should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this sustainability report. Except as required by law, we are not under any obligation, and expressly disclaim any obligation, to update or alter any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of changes of circumstances or management’s estimates or opinions, new information, future events or otherwise.
Risk factors
For a detailed description of Ternium’s main risk factors, please see the section "Risk Factors" included in the Company's annual report on form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2019.
These risks include but are not limited to risks relating to the steel industry and mining activities, risks relating to countries in which Ternium operates, risks relating to our business, including uncertainties as to gross domestic product, related market demand, global production capacity, tariffs, cyclicality in the industries that purchase steel products, risks relating to the Company’s structure and regulatory risks, as well as other factors beyond Ternium’s control.
5. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
6. Ternium |
The Company | |
Ternium is Latin America’s leading flat steel producer. We operate manufacturing facilities, service centers and distribution centers in several countries in the region and the southern United States, serving customers from various industries. | ||
$10.2 BILLION ANNUAL NET SALES OF STEEL AND OTHER PRODUCTS. | 12.5 MILLION TONS OF FINISHED AND SEMI-FINISHED STEEL SHIPMENTS. | 20,000 EMPLOYEES OF 27 NATIONALITIES. |
7. Sustainability Report 2019 |
The Company | |
 |
worldsteel Sustainable Champion. In 2019, Ternium was honored with this recognition for the second consecutive year for its contribution to sustainability initiatives and reporting. |
Profile
Ternium is Latin America’s leading flat steel producer with an annual crude steel production capacity of 12.4 million tons. It operates in Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, the southern United States and Central America through regional manufacturing facilities, service centers and its own distribution network. In addition, Ternium participates in the control group of Usiminas, a leading flat steel company in the Brazilian market.
The company's customers range from small businesses to large global companies in the automotive, home appliances, heat, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC), construction, capital goods, container, food and energy industries across the Americas. Ternium’s industrial system has various production technologies that provide a diversified cost structure, based on different types of raw material and energy sources, and a flexible production configuration. The industrial system includes proprietary iron ore mines and processing facilities, steelmaking facilities, finishing facilities, service centers and a broad distribution network to offer slabs, billets, hot-rolled products, cold-rolled products, galvanized and electro-galvanized sheets, pre-painted sheets, tinplate, welded pipes, rebars and wire rods as well as slit and cut-to-length products.
Ternium's innovative culture, industrial expertise and long-term view enable the company to continuously achieve new breakthroughs in industrial excellence, competitiveness and customer service. Ternium is the leading supplier of flat steel products in Mexico and Argentina, has a significant position as supplier of steel products in Colombia and in other Latin American coumtries, and is a competitive player in the international steel market for steel products.
Through its network of commercial offices in several countries in Latin America, the United States and Europe, Ternium maintains an international presence that allows it to reach customers outside its local markets, achieves improved effectiveness in the supply of products and in the procurement of semi-finished steel, and maintains a fluent commercial relationship with its customers by providing continuous services and assistance.
We operate with a broad and long-term perspective, and we work towards improving the quality of life of our employees, their families and the company's local communities.
8. Ternium |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation • Quest for excellence in industrial management and technology • Focus on differentiation through sophisticated products and services • Proactive approach to environment, health and safety • Recruitment, training, and retention of talent • Fostering of steel value chain • Deep ties with our communities • Commitment to integrity | ||||
Environment, Health and Safety
We devote significant resources to environment, and occupational health and safety (EHS), as we believe they are key to our long-term sustainability. We have standardized EHS management systems. Our employees are well trained in EHS and our management is accountable for EHS performance. Ternium's occupational health and safety system is certified under OHSAS 18001, and its environment and energy system is certified under ISO 14001 and ISO 50001. The company regularly invests in state-of-the-art technologies to reduce its environmental footprint and minimize safety risks.
Integrity
We believe integrity is key to Ternium's long term sustainability. The Company’s Board has an Audit Committee solely composed of independent directors and an Internal Audit Department, which reports to the Chairman of the Board and, with respect to internal control over financial reporting, to the Audit Committee and meets organizational independence and objectivity standards. Ternium has a Business Conduct Compliance Officer reporting to the CEO and a compliance department that oversees SOX certifications and related party transactions. The company's employees are trained and accountable for ensuring a transparent behavior. Ternium has established different policies, codes and procedures for this purpose. In addition, it has
confidential channels to report all types of alleged breaches of the Code of Conduct and its principles.
Communities
We believe that having deep ties with Ternium's communities is also fundamental to the company's long- term sustainability. We are having a significant positive impact on Ternium's communities, both from a human perspective as well as in terms of economic development. We work together with local institutions to enhance the communities' education and welfare. We provide scholarships, internships, teachers' training and infrastructure funding. We also organize and fund volunteering programs and health prevention campaigns, and sponsor sports, social and arts events.
Steel Industry Value Chain
We support approximately 1,800 small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), customers and suppliers through our ProPymes program to strengthen the steel value chain in our markets. ProPymes provides training, industrial and business consultancy, institutional assistance, commercial support and financial aid. The program plays an active role at universities, business schools, government agencies and industrial associations. ProPymes has helped create an industrial network that encourages the professionalization and quest for excellence of SMEs.
9. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
10. Ternium |
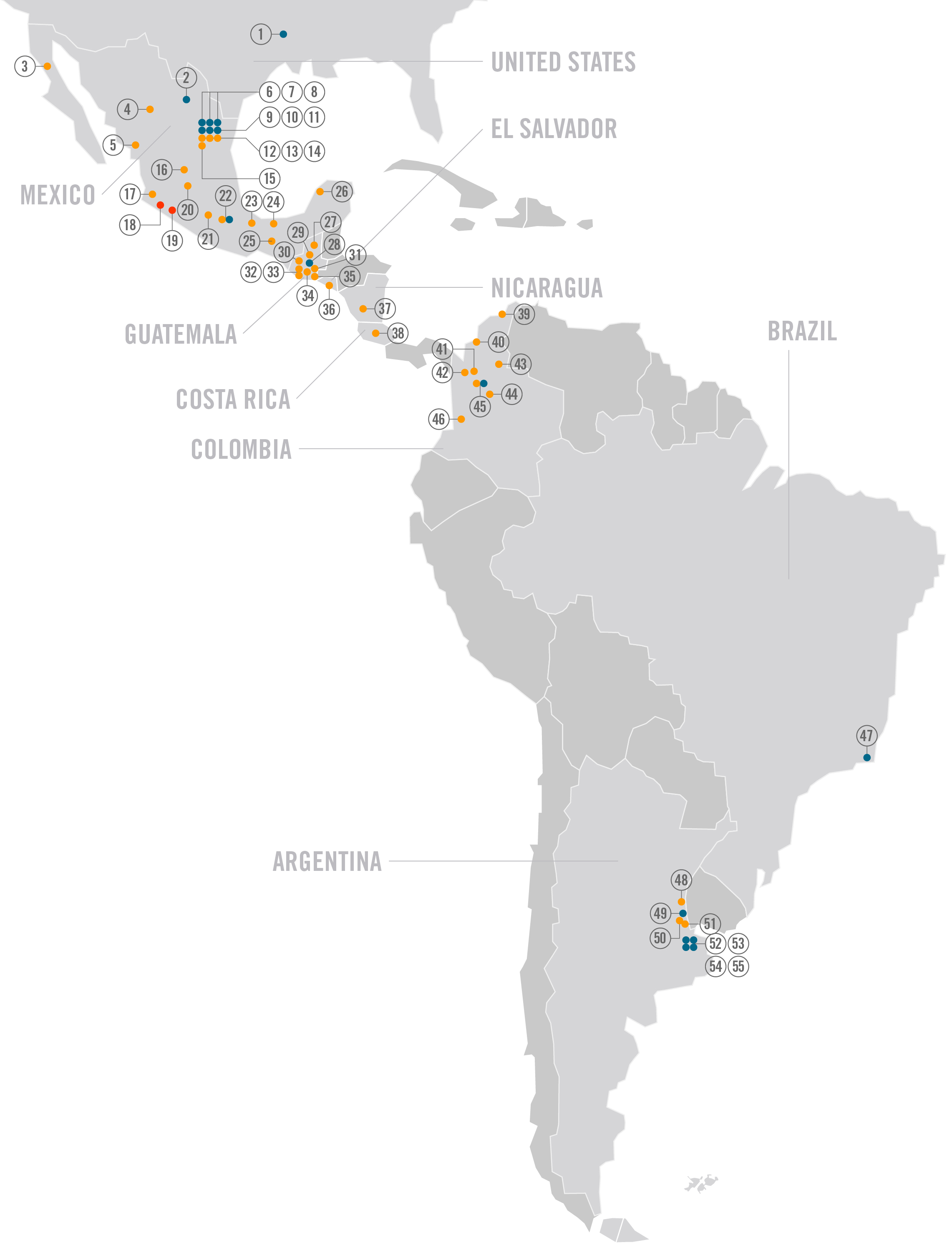
Ternium's manufacturing facilities, service centers and distribution centers are located in Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, the southern United States, Guatemala and other Central American countries. The company's mining operations are located in Mexico. | |||||
01. 02. 03. 04. 05. 06. 07. 08. 09. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. | Shreveport Monclova Baja California Chihuahua Culiacán Guerrero* Pesquería Universidad Churubusco* Apodaca Juventud* Edificios Metálicos Apodaca Industrial Apodaca Comercial Norte San Luis Guadalajara Las Encimas Peña Colorada León México | 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. | Puebla Veracruz Tuxtla Villahermosa Mérida Petén Villa Nueva* Cobán Huehuetenango Teculután Quetzaltenango Occidente Norte Juitapa San Salvador Managua San José Barranquilla Montería Medellín Itagüí | 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. | Bucaramanga Bogotá Manizales Cali Río de Janeiro Rosario San Nicolás Serviacero III Sidercrom Haedo* Canning* Florencio Varela* Ensenada |
(*) Includes service or distribution centers | |||||
FACILITIES • Steel production and processing • Service or distribution centers • Iron ore mining and processing | |||||
11. Sustainability Report 2019 |
The Company | |
 |
Sophisticated steel products and services. The Mexican automotive sector is the largest in Latin America and the seventh largest worldwide. |
TERNIUM'S STEEL MARKETS
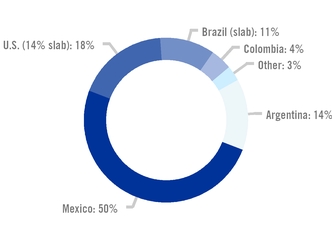
Ternium's customers range from small businesses to large global companies in the construction and industrial sectors. We report steel shipments under three geographical regions: Mexico, the Southern Region and Other Markets.
Mexico
The Mexican steel market is the largest in Latin America. The industrial sector, which in 2019 accounted for 53% of Ternium’s total shipments in the country, is the main driver behind an attractive high-end steel market segment.
Ternium's largest industrial customer in Mexico is the automotive industry. With 3.8 million vehicles produced in 2019, the local industrial hub is the largest in Latin America and ranks seventh in the world behind China, the US, Japan, Germany, India and South Korea.
The Mexican manufacturing industry is a fundamental part of a complex supply chain within the USMCA, and is prepared to supply highly sophisticated products for demanding end-user markets. In addition to the
automotive industry, the Mexican home appliance, HVAC and lighting manufacturers have also reached a high level of sophistication, requiring innovative and high-end steel products.
Southern Region
The Southern Region encompasses the steel markets of
Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay. The Argentine steel market, the third largest in Latin America, accounts for most of Ternium's shipments in this region.
Ternium's industrial customer base in Argentina represented approximately 47% of Ternium’s total shipments in the country in 2019. The Argentine automotive industry, the third largest in Latin America, is part of the value chain within the Mercosur, a customs union encompassing Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay and Paraguay that has eliminated or significantly reduced import duties, tariffs and other trade barriers among member states.
Other relevant industrial sectors in Argentina include the agro machinery, cans and home appliance manufactures, and the oil & gas sector.
12. Ternium |
 |
High-end steel. An attractive market segment. |
Other Markets
Ternium’s finished steel customers in the Other Markets segment are mainly in the construction and energy-related industries in Colombia, the United States and Central America. Following the acquisition of Ternium Brasil in September 2017, Ternium started shipping steel slabs to third party steel companies mainly in the United States and Brazil.
A small share of Ternium’s shipments is destined for steel markets outside the Americas. Sales to Europe, Asia and Africa are carried out mainly through Ternium’s commercial office in Spain.
TERNIUM'S STEEL SHIPMENTS BY COUNTRY 2019 |
ATTRACTIVE HIGH-END STEEL MARKET SEGMENTS |
53% PARTICIPATION OF SHIPMENTS TO INDUSTRIAL CUSTOMERS IN MEXICO. |
47% PARTICIPATION OF SHIPMENTS TO INDUSTRIAL CUSTOMERS IN ARGENTINA. |
67 MILLION TONS OF STEEL CONSUMED IN LATIN AMERICA IN 2019, MAINLY IN MEXICO, BRAZIL, ARGENTINA AND COLOMBIA. |
13. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
14. Ternium |
Chairman’s Letter | |
Over the past months, the global economy has been deeply affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. The measures taken around the world to contain the spread of the virus have resulted in a global crisis, whose speed and severity is unprecedented in recent history. Though, in many parts of the world, businesses are reopening, people are gradually returning to work, and developed country governments have implemented massive economic stimulus programs, the pandemic continues to spread and the recovery from the crisis will take time and hasten change in many fields.
Latin America is particularly affected, as its economies were already under stress and the number of affected persons continues to rise. We took prompt action to adjust the company for the crisis and a high level of ongoing uncertainty.
To protect our people and assure a safe working environment, we introduced new work protocols including mandatory use of face masks, temperature checks, strict social distancing rules and disinfection policies for company transportation, site entry and common working areas as well as applying work-from-home policies and testing every person showing compatible symptoms and their close contacts.
To secure the financial stability of the company, we are making full use of the opportunities we have for industrial integration to optimize production and overhead costs, reducing inventories and working capital and quickly adjusting our operations to the reduction in sales. We are delaying some of our investment projects, pushing out the startups of our new hot rolling mill in Pesqueria, Mexico, and our new rebar mill in Colombia, and thereby reducing our capital expenditure commitments for this year to $600 million from the $850 we had originally planned. We also elected to suspend our annual dividend payment for the 2019 fiscal year.
To support our communities, we established and deployed a $5.5 million fund to strengthen local medical response capabilities, using our global procurement network to provide ventilators, intensive care equipment and protective gear as well as constructing and operating a field hospital with 100 beds for the community of Monterrey in Mexico and providing infrastructure and equipment for intensive care units to other hospitals in Ensenada in Argentina and in Rio de Janeiro in Brazil. Our employees have responded with solidarity and purpose in joining these initiatives.
At a time like this, the support we provide to our smaller customers and suppliers through the ProPymes program is particularly relevant and we are reinforcing the financial help we provide to members of the program with $8.0 million applied among 125 companies, together with assistance in raising financing from local financial institutions. Our training programs have been reinforced with more webinars and online workshops reaching over 1,200 persons. Equally, as the gradual recovery advances, our Webservice digital integration portal, which is used by our commercial customers to place 80% of their orders, will facilitate safe working practices.
As we reflect on our achievements during the past year, this crisis is a reminder of the importance of a long-term management focus that addresses all aspects of the company’s performance and its relations with customers, suppliers, employees and the communities that sustain us. To better report on the actions we carry out on this respect, this year we completely
15. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Chairman's Letter | |
redesigned our Sustainability Report and strengthened it by using the guidelines established by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), including consultations with our stakeholders to determine material topics to cover.
Our operational and financial results in 2019, though down from the outstanding results of the previous year, were solid, with an EBITDA of $1.5 billion on sales of $10.2 billion. Even after investments of $1.1 billion in our expansion program, our free cash flow amounted to $595 million and we ended the year with net debt of $1.5 billion, which has declined further in the year to date.
We continue to consolidate our position as a leading Latin American steel producer with a strong focus on serving the industrial and construction sectors. In Mexico, we started up new galvanizing and painting lines expanding our product range for industrial markets, which account for over 50% of our sales in the country. With the recent enactment of the new USMCA agreement confirming a free trade area across North America, the Mexican automotive and industrial sector is well positioned for a post-pandemic recovery. Although we have delayed the planned start-up of our new hot rolling mill in Pesquería until 2021, this new mill will strengthen our competitiveness through further broadening our range of high-end industrial products and allowing further integration of our industrial system by using high quality steel slabs from our mill in Brazil. In times when regional supply chains are being strengthened, the new line will also reinforce our import substitution strategy.
At the center of the growing community in Pesquería, Mexico, lies the Roberto Rocca Technical School. Last year, the first cohort of students graduated following three years of study focused on technical education, including industrial apprenticeships. During the annual worldsteel assembly held in Monterrey in October 2019, Ternium received the Steelie Award for “Excellence in Education and Training” based on the achievements of the school and its pupils. Aside from our response to the pandemic, education at all levels remains the focus of our community programs, not only in terms of money spent but also in terms of the design and organization of programs that can contribute to improving the level of education, particularly technical education, and open educational opportunities at all levels in the communities where we operate.
Last year marked the 50th anniversary of the origins of the company in the inauguration of a cold rolling mill at Ensenada in Argentina. The construction and start-up of this greenfield plant, carried out by a highly motivated team of young professionals, has shaped the culture and management ethos of the company to this day. Providing a stimulating working environment and effective opportunities for employee training, education and development is a constant focus in our management efforts and critical to maintaining high levels of employee motivation. In August 2019, we inaugurated an in-house corporate university with responsibility for organizing knowledge and training across the company and developing a curriculum with participation from outside universities that provide employees the tools for their own education and development. In 2019, Ternium’s employees had an average of 62 hours of training and 662 employees participated in management development programs. In our most recent pulse survey on employee satisfaction, with an 87% participation rate, 83% of the respondents expressed their satisfaction with Ternium as a place to work.
16. Ternium |
Safety and minimizing the environmental impact of our operations are paramount in our management focus and routines. In total, we invested $120 million during 2019 in projects aimed at improving our environmental, energy and safety performance by modernizing our facilities. Major investments include those aimed at reducing particulate emissions at our steel shops, significantly improving air quality and working conditions, and reducing water consumption rates in our facilities in Mexico which are located in a region of high water stress. We also advanced with the certification of our energy intensive operations under the new ISO 50001 standard. Now most of our steelmaking, hot rolling and finishing facilities in Brazil, Argentina and Mexico are either certified or under certification.
During the year, we revised our health and safety strategy, developing specific practices to prevent situations where our employees or contractors are exposed to severe injury, and establishing safety committees to strengthen the consultation and participation of workers and their representatives on health and safety issues.
We are active participants in worldsteel’s climate action initiatives, joining the recent Step Up Program to reduce carbon emissions through benchmarking, and have committed ourselves to the UN Global Compact and to advance its Sustainable Development Goals. In the past five years, we have implemented a number of energy savings initiatives which have yielded an annual reduction of 298,000 tons of carbon emissions. We are also working with industrial gases companies serving the soft drink bottling industry to recycle carbon emissions captured in our production system which should yield further annual savings of 60,000 tons. The challenge of reducing emissions to meet the Paris Agreement commitments is, however, of a different order of magnitude and will require a coordinated response from our industry alongside governments, customers and suppliers. Our ambition is to be at the forefront of our industry’s response to this challenge.
As we prepare for the future, we are confident that the company is well positioned to continue a path of sustainable growth as a leading supplier of steel products to the industrial sector in the Americas. Our ongoing investment program, the transformation of our industrial system using Industry 4.0 technologies, and the long-term focus developed since the origins of the company 50 years ago will enhance our competitive position and the sustainability of our operations over the coming years.
During these difficult times, I would like to give special thanks to our employees, who are showing exemplary solidarity and resilience. I would also like to thanks our customers, suppliers and investors for their ongoing support.
July 20, 2020
 |
Paolo Rocca
Chairman
17. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
18. Ternium |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation |
Ternium's value proposition aims to achieve profitable operations on a sustainable basis, through a management approach that comprehends the interests of shareholders, employees, customers and suppliers, as well as of the community. | |||
$10.3 BILLION ECONOMIC VALUE GENERATED IN 2019 | |||
$827 MILLION EMPLOYEES | $1.1 BILLION CAPEX | $357 MILLION TAXES | |
$7.7 BILLION SUPPLIERS | $352 MILLION CAPITAL PROVIDERS | ||
$10 MILLION RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT | $7 MILLION COMMUNITY INVESTMENTS | ||
19. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
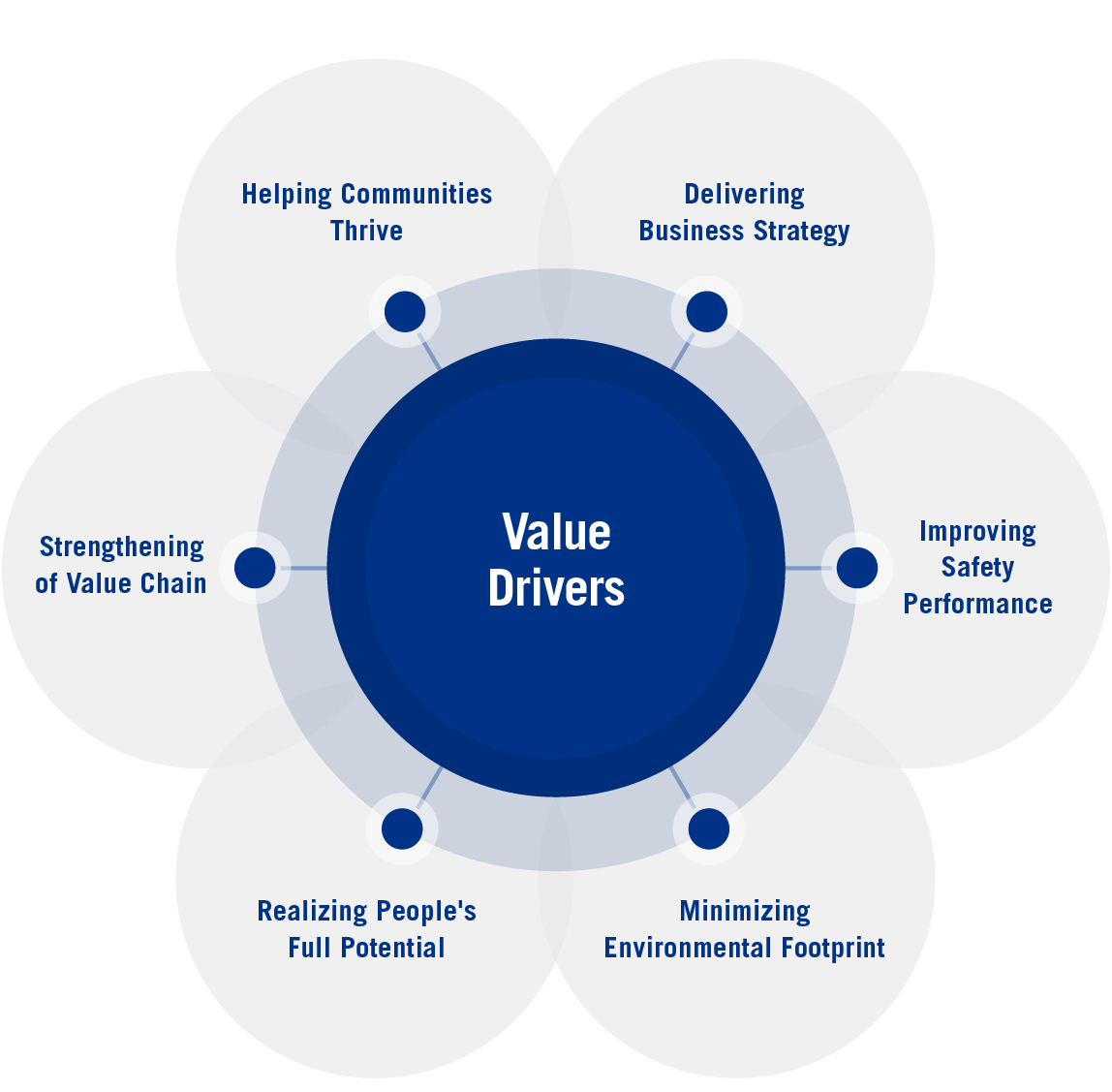
Value Drivers
 |
20. Ternium |
Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy • Focus on higher margin value-added products. • Pursue strategic growth opportunities. • Implement Ternium's best practices. • Maximize the benefits arising from Ternium's distribution network. • Enhance Ternium's position as a competitive steel producer. SEE PAGE 22 | |
Improving Our Safety Performance • Prevent all work-related injuries and illnesses, and achieve zero accidents • Promote healthy and safe operations in the steel industry value chain. SEE PAGE 38 | |
Minimizing Ternium's Environmental Footprint • Use natural resources responsibly. • Pursue excellence in environmental performance. • Protect biodiversity. SEE PAGE 46 | |
Realizing People's Full Potential • Attract and retain talented employees. • Promote a culture of excellence throughout the company. SEE PAGE 56 | |
Strengthening Ternium's Value Chain • Promote a collaborative network to foster performance excellence. • Help small and medium-sized customers and suppliers grow. SEE PAGE 66 | |
Helping Our Communities Thrive • Foster education. • Support initiatives that strengthen our communities. SEE PAGE 70 | |
21. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy | |
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
   | |
4.4 MILLION TON ANNUAL CAPACITY OF NEW HOT-ROLLING MILL IN MEXICO, WITH EXPECTED START UP IN 2021. | |
Elements of strategy | Actions | |
Focus on high-margin value-added products | New laboratory, project launch for new research center | |
Research and development of products and processes | ||
Pursue strategic growth opportunities | New galvanizing and painting lines (start-up in 2019) | |
Progress in the construction of the new hot-rolling mill | ||
Progress in the construction of the new steel bar & coil mill | ||
Implement Ternium's best practices | Integration and optimization on newly-acquired Rio de Janeiro unit | |
Maximize the benefits arising from Ternium's distribution network | Full range of products and services | |
On-line purchasing platform (Webservice) | ||
Just-in-time and short notice supply agreements | ||
Enhance Ternium's position as a competitive steel producer | Continuous improvement program | |
Industry 4.0 initiatives | ||
22. Ternium |
 |
Implementation of best practices. Ternium’s managerial, commercial and production experience generates benefits and savings in acquired new businesses. |
Ternium's Business Strategy
Ternium's main strategic objective is to enhance stakeholder value by further consolidating the company’s position as a leading steel producer in Latin America and a strong player in the Americas, while strengthening its competitiveness. The main elements of this strategy are:
FOCUS ON HIGHER MARGIN VALUE-ADDED PRODUCTS
We intend to continue to shift Ternium’s sales mix toward higher margin value-added products, such as cold-rolled sheets and coated and tailor-made products, and services, such as just-in-time delivery and inventory management. For example, during 2019 Ternium inaugurated a new hot-dip galvanizing line and a new painting line, and made progress on the construction of a new state-of-the-art hot-rolling mill at its facility in Pesquería, Mexico.
PURSUE STRATEGIC GROWTH OPPORTUNITIES
We have a history of strategically growing our businesses through acquisitions and joint ventures. In addition to pursuing organic growth, we intend to continue to identify and actively pursue growth-enhancing strategic opportunities to consolidate Ternium’s presence in its main markets and expand it to the rest of the Americas, increase its integration,
Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy • New state-of-the-art hot-dipped galvanizing and painting lines in Mexico. • New cutting-edge hot-rolling mill in Mexico (2021). • Integration of the Rio de Janeiro high-end steel mill. • Strengthened product research and development capabilities. • Digital transformation agenda. • Continuous improvement plan. • Solid financial performance. |
23. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
TOTAL CRUDE1 AND HOT-ROLLED2 STEEL PRODUCTION CAPACITY MILLION TONS PER YEAR. |
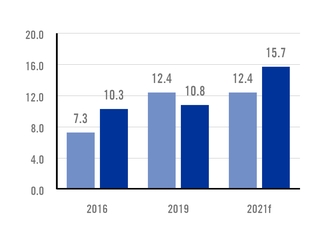
n 1 Crude steel: flat steel slabs and long steel billets n 2 Hot-rolled steel: flat steel coils and long steel rods |
expand its offerings of value-added products, and enhance its production and distribution capabilities.
IMPLEMENT TERNIUM’S BEST PRACTICES
We believe that the implementation of Ternium’s managerial, commercial and production best practices in acquired and new facilities and businesses should generate benefits and savings.
MAXIMIZE THE BENEFITS ARISING FROM TERNIUM’S BROAD DISTRIBUTION NETWORK
We intend to maximize the benefits from Ternium’s broad distribution, sales and marketing network to reach customers in major steel markets with a comprehensive range of value-added products and services and to continue to expand its customer base and improve the value of its product mix.
ENHANCE TERNIUM’S POSITION AS A COMPETITIVE STEEL PRODUCER
We are focused on improving utilization levels of our plants, increasing efficiency and further reducing production costs from levels that we already consider to be among the most competitive in the steel industry through, among other measures, capital investments and further integration of our facilities. In addition, we aim at obtaining better purchase conditions and prices
68% SLAB CAPACITY INCREASE ON 2017 ACQUISITION. 47% HOT-ROLLED COILS CAPACITY EXPANSION IN 2021. | |
by combining the demand of products and services by both Ternium and our affiliate Tenaris. We pursue this goal through Exiros, a purchase and sale agency which we own 50/50 with Tenaris. Exiros has offices in various countries and is in charge of the procurement of a majority of our raw materials and other products and services.
A Significant Expansion of Ternium’s Industrial Capabilities
In September 2017, the company acquired a state-of-the-art slab facility in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with an annual production capacity of 5 million tons of high-end steel slabs, a deep-water harbor and a 490 MW combined cycle power plant.
With the addition of this mill, total crude steel production capacity of Ternium's industrial system increased 5.0 million tons to 12.4 million tons.
The Rio de Janeiro unit has provided Ternium with new business opportunities, particularly in Mexico. Following its acquisition, the company started the construction of new hot-rolling, hot-dipped galvanizing and painting lines in its Pesquería Industrial Center, Mexico, and strengthened its product research and
24. Ternium |
 |
Steel production and processing. A relentless quest for excellence in operating performance. |
development capabilities. In addition, Ternium started the construction of a greenfield reinforcing bars facility in Palmar de Varela, Colombia.
The results of this transformation process started in 2018 with the inauguration of a new laboratory in Pesquería, which increased Ternium's product research capabilities for high-end industrial requirements. During 2019, the company started-up its new hot-dip galvanizing and painting lines in Pesquería, adding 350,000 and 120,000 tons of annual production capacity to Ternium's industrial system, respectively. These new facilities incorporated the most advanced painting technology to the Mexican steel industry, providing high-end value-added products for the HVAC and automotive industries.
Ternium's new hot-rolling mill in Mexico will have an annual production capacity of 4.4 million tons, with an option to increase capacity in the future by an additional 300,000 tons. With the addition of this new mill, Ternium's industrial system will increase total flat steel hot-rolling production capacity by 47% to 13.8 million tons. In addition, expected synergies between Ternium's new hot-rolling mill and its cold-rolling mill in Pesquería will result in an annual production capacity increase of
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM TO MAXIMIZE EFFICIENCY |
44 PRODUCTION LINES ACHIEVED NEW RECORD OUTPUT IN 2019. |
68 TEAMS WORKING TO MAXIMIZE EFFICIENCY, MINIMIZE COSTS AND IMPROVE ENVIRONMENTAL, SAFETY AND QUALITY PERFORMANCE. |
300,000-tons of cold-rolled coils. Ternium's state-of-the-art hot-rolling mill in Pesquería will represent a significant technological leap forward in the country's steel production capacity. The company’s product range will encompass a broader dimensional offering with the most advanced steel grades. In addition, customer service will be enhanced and the value chain lead-times reduced.
This, combined with the company's service center and distribution capabilities in the country, will enable Ternium to expand its footprint in Mexico with cutting-edge new products and substitute high-value-added steel imports targeting the demanding and innovative automotive industry, as well as the home appliance, machinery, energy and construction sectors. The new hot-rolling mill will source high-end slabs from our facility in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and from third parties.
Ternium's new reinforcing bar facility will enable the expansion of its market share in Colombia's construction sector by substituting imports. In addition, the company's new facility will enable the upstream integration of its operations by replacing current purchases of reinforcing bars from third parties.
25. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
2019 Award in "Innovation". Granted by the Nuevo Leon Automotive Industry Cluster in Mexico for the design of a new heavy-duty trailer model. Ternium and one of its customers developed the new model, which enables a more efficient transportation of extra-heavy steel coils. | ||||
RESCHEDULED INVESTMENT PLAN FOLLOWING COVID-19 OUTBREAK
In order to mitigate the impact of expected lower sales resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic induced recession, Ternium has recently reduced its planned capital expenditures for the year 2020 by an estimated $250 million, to $600 million. Consequently, the inauguration of Ternium's new hot-rolling mill in the Pesquería Industrial Center has been postponed from 2020 to 2021, and the commissioning of the new reinforced bar facility in Palmar de Varela has been postponed from March 2020 until the second half of 2020. The final reduction in Ternium's capital expenditures in 2020 will depend on the pace of recovery of economic activity and steel market demand.
Strengthened Product Research and Development Capabilities
Steel is a highly versatile metal, offering a wide space for product innovation. For example, over 70% of the structural steel parts used to build a car today involve solutions that did not exist 20 years ago.
The properties of the steel products required by Ternium's customers are usually the result of a combination of their metal composition and the way metal gets processed into finished steel products. Ternium’s business strategy
is based on offering a complete range of value-added,
high-end products, with an emphasis on creating and manufacturing increasingly sophisticated steel products for new applications and industries.
A COLLABORATIVE APPROACH TO PRODUCT RESEARCH AND DEVELOMENT
At Ternium, we carry out applied research efforts in different ways. We develop steel products through in-house programs, joint projects with leading industrial customers, joint efforts with recognized universities or research centers, and through our participation in international consortia.
Ternium has identified synergies in collaborating with its customers in the early stages of their projects. Anticipating our customers' upcoming steel product requirements through our participation in joint development projects is key not only to build customer relationships but also to plan and develop new processes, which may sometimes require the addition of new equipment and technology.
Ternium’s research programs are open to a broad-based international network of industry consortia. Over 50 universities and research laboratories from both the public and private sectors collaborate with Ternium. The goal is to find and develop the best solutions to
26. Ternium |
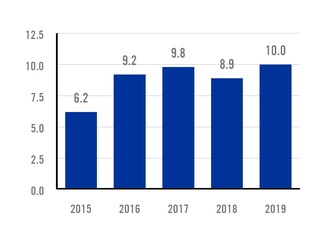
AUTOMOBILE INDUSTRY CERTIFICATIONS NUMBER OF CERTIFICATIONS APPROVED |
support an agenda aimed at achieving better and more sustainable steel. Research spans the entire production cycle, from primary steel making and metallurgy, to rolling and galvanizing.
Ternium is a member of WorldAutoSteel, an organization comprising some of the world’s major steel producers. Under the auspices of worldsteel, the group regularly updates the automotive industry on upcoming new steel capabilities available to meet their design and manufacturing requirements.
The company is engaged in over 120 ongoing product development projects in partnership with industrial customers, and over 50 ongoing research projects including in-house developments and others involving university researchers and students from some of the world’s most prestigious institutions. We have been increasingly engaging universities in our research efforts in order to expand and further diversify Ternium’s research network and capabilities. This initiative fosters the development of fundamental knowledge and know-how at participating universities while enabling the optimization of Ternium’s in-house research resources. In 2019, approximately thirty undergraduate and postgraduate students pursuing degrees in engineering, materials science and metallurgy took part in the program.
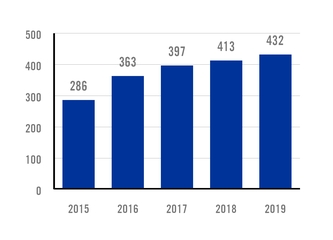
INVESTMENT IN PRODUCT RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT $ MILLION |
INVESTING IN NEW EQUIPMENT AND TECHNOLOGIES FOR HIGH-END STEEL
The inauguration of the Ternium Industrial Center in Pesquería, Mexico, in 2013, gave way to an intensive product development period. We broadened our product range offering to include sophisticated high-end steel products required by the manufacturing industry, particularly automotive manufacturers. These developments were made possible with the addition of new production technologies to our industrial system at the Pesquería unit, such as cold-rolled steel and galvanized products that provide corrosion resistance to external vehicle parts.
Furthermore, the installation in 2015 of state-of-the-art cooling technology in the hot strip mill of our Churubusco unit in Mexico, has allowed developing and processing new advanced high-strength steel grades, including dual phase, ferrite-bainite, martensitic and complex phase grades. Based on these new capabilities, we have further widened our high-end product portfolio for customers in the automotive, metalmechanic, home appliance, oil & gas and electric motors industries.
Advancing Ternium's Digital Transformation
Since Ternium's origins in 1969 with the inauguration of
the Ensenada manufacturing unit in Argentina, the
27. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
"Steel to Make", a media campaign in Argentina aimed at consolidating a seamless brand recognition to support Ternium's regional leadership. The campaign highlighted the use of steel in everyday life and its importance for our future. | ||||
company has acquired various steelmaking and steel
processing facilities in Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, the United States and Central America, that resulted in a myriad of legacy industrial information technology (IT) systems. Ternium's business model required a unified industrial system able to offer an ample range of products and services to its customer base. The implementation of this unified model implied a significant effort of digital transformation. For example, after the acquisition of Hylsamex in 2005 and Grupo Imsa in 2007, there were 28 different information technology systems that had to be consolidated into a single one.
With that target in mind, by 2009 we were able to bring Ternium on-line in real time with a single, unified information technology system, spanning all of its facilities. Once this process was completed, the company extended its digital tools to its customers and suppliers, enabling the integration of its processes with theirs.
This integration was implemented through the development of a digital marketplace called "WebService". Nowadays, approximately 80% of Ternium’s commercial orders are placed through this tool, enabling an efficient business to business interaction.
CERTIFICATION OF TERNIUM'S INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SYSTEMS
In May 2017, after a two-year preparation process, Ternium certified its information technology system under the ISO 20000 standard. This standard describes the best practices in the management of an organization's IT processes and services.
This certification process has helped the company to optimize costs, resources and processes, enhance customer satisfaction, strengthen the performance assessment of its IT system, increase compliance with multiple regulations, and increase overall business competitiveness.
SMART FACTORY
Ternium is making progress in the construction of a SMART factory, the acronym for Social, Mobile, Analytics, Robotics and (internet of) Things. This concept, supported by the company’s unified information technology platform, ensures a constant stream of knowledge and information (data and events) that will lead its facilities to a more productive and efficient evolutionary stage.
Users achieve a more efficient performance by interacting from any location (offices, facilities or elsewhere) through different kinds of devices.
28. Ternium |
 |
2,100 cameras to oversee a safe operating environment. The assessment of worker distance from suspended loads is one of the functionalities comprising an early alarm system. |
Employees working in Ternium's industrial, commercial and maintenance areas are equipped with mobile devices that enable them to perform all their tasks from any location with a remarkable increase in productivity.
Analytics and data correlation detect patterns for various applications to increase safety and efficiency, and to reduce costs. Through video-feed analysis (machine learning), new applications include real-time detection and reporting of unsafe situations or behavior within the facilities to prevent accidents and, using drone technology, the identification of potential damages in either tall structures or confined spaces, whether internal or external, as well as the assessment of bulk material stockpiles. Drones substitute human inspection at height and minimize the risks inherent to this type of tasks. In 2019, the system autonomously issued 440 maintenance tickets, removing human inspection at 55 roofs.
We installed 2,100 cameras for tracking operations in our Mexican, Argentine and Brazilian facilities, enabling the implementation of an early alarm system.
Through video analytics, 500 of those cameras are able to assess distances from suspended loads, moving vehicles and entrapment
 |
Implementation of mobile monitoring capabilities. Efficient, real-time analysis of equipment parameters during maintenance inspections. |
areas, verify the observance of marked pathways and social distancing, and monitor the use of safety helmets, vests and face masks. Deviations from protocols are automatically reported to the relevant manager with the ultimate purpose of preventing accidents based on early detection.
In addition, radio frequency identification (RFID) technology enables the automated handling of steel products in the yards, speeding up logistics and increasing safety. Ternium’s RFID project is intended to identify and track each coil from the moment it reaches the yards until shipment, facilitating inspections procedures, improving inspectors' safety and reducing operations lead times. The tracking system has already been implemented in 27 stockpile yards in Mexico and Argentina.
In the maintenance area, analytics and data correlation technology has proved its potential with the prediction of failures two to three weeks in advance. During 2019, we applied this technology to the continuous casters at the company's Mexican and Argentine facilities.
We plan to apply this technology in the company's most critical production lines to shield strategic equipment and significantly reduce non-operational interruptions and,
29. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
 |
Inspection at height. During 2019, the system autonomously issued 440 maintenance tickets, removing human inspection at 55 roofs. |
therefore, the impact on the production process. In order to support Ternium's analytics needs across all business functions, we have implemented a single technological platform, known as Data Lake, that meets all our big data and analytics requirements.
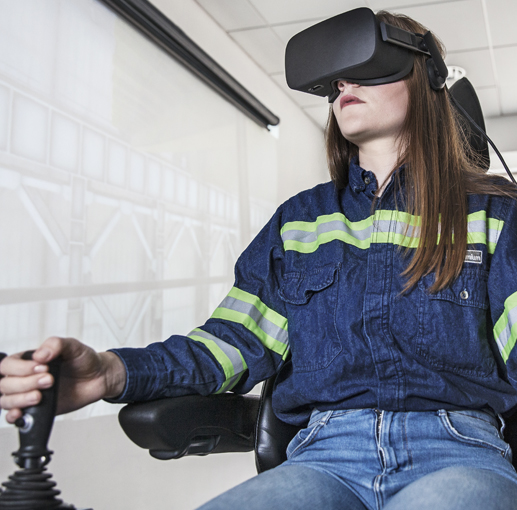
Other projects aimed at improving safety and productivity are the use of virtual reality software for training purposes, the use of augmented reality for experts providing remote assistance to operators, 3D printing and the use of 3D scanning for several applications. We have also developed virtual reality software to train employees on risk perception. This software simulates risky situations in 3D, depicting potential sequences that could end up in fatal accidents.
In addition, we have successfully finished the proof-of-concept stage for replacing on-site crane training exercises with virtual reality training facilities, simulating the cabins of the three types of cranes used by Ternium: magnetic crane, hook crane and dump. We have also developed a virtual reality software to train our personnel on specific operating procedures performed in the secondary metallurgy area of our steel shop in Argentina. In Mexico, we are developing
projects to train employees in water leakage protocols and in productivity enhancement using digital twin technology. This technology generates a digital replica of physical assets, processes, people, sites, systems and devices that can be used for various purposes.
Ternium has seven administrative robots in operation, running automated processes and tasks in the areas of accounts payable, accounts receivable, sales back office and industrial engineering administration. We are advancing projects to gain productivity in accounts payable tasks in Mexico and Argentina, where more than 50% of all suppliers' invoices are expected to be loaded in our systems using robots.
CONCERTED RESEARCH EFFORTS IN THE QUEST FOR INNOVATIVE IT SOLUTIONS
Through cooperation agreements with two universities, Ternium has engaged 110 students in twenty Industry 4.0 projects. The objective of this new initiative is to develop innovative IT solutions aimed at improving the company's operations in the areas of health & safety, maintenance, automation, management, commercial, quality and raw materials.
30. Ternium |
Virtual reality training. During 2019, the company incorporated new VR training modules for the operation of cranes as well as steel making equipment. |
 |
31. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Ternium has recently reinforced its financial profile, which has been traditionally robust, through a quick deployment of economic and financial measures to better face the recession induced by the COVID-19 outbreak. |
2019 Economic and Financial Performance
GOOD RESULTS IN A CHALLENGING YEAR
During 2019, shipments in the Mexican market were 6.3 million tons, representing 50% of Ternium’s total steel shipments. Apparent flat steel use decreased in the year reflecting a softer commercial market in 2019 and a strong level of shipments in the first half of 2018 in anticipation of rising steel prices.
Shipments in the Southern Region reached 1.9 million tons in 2019, or 15% of Ternium’s consolidated shipments in the steel segment. Most of Ternium’s shipments in the region are destined for the Argentine market. Apparent steel use decreased significantly in Argentina in 2019, as the country's macroeconomic situation deteriorated.
Shipments in the Other Markets region reached 4.3 million tons in 2019, or 34% of Ternium’s consolidated shipments in the steel segment. Our major shipment destinations in the Other Markets region were the United States, Brazil, Colombia and Central America.
Net sales in 2019 were $10.2 billion, including net sales of steel products for $9.9 billion on steel shipments of 12.5 million tons, net sales of other products for $296.1 million and net sales of iron ore products for $364 million on iron ore shipments of 3.6 million tons.
Most of the iron ore production was consumed in our own steel operations. Steel revenue per ton was $790
in 2019. Steel prices declined in North America during the year, following a strong pricing environment in 2018.
EBITDA reached $1.5 billion in 2019 with EBITDA margin of 15%, remaining at an industry-leading level of profitability.
Net income attributable to Ternium's equity owners was $564.3 million, or $2.87 per ADS. Free cash flow was $595.4 million, with a high level of capital expenditures being partially offset by a $572.7 million reduction in working capital.
SOUND FINANCIAL POSITION
In 2019, the company’s capital expenditures were $1.1 billion, $532.0 million higher than in 2018, as Ternium's investment program progressed as planned.
The main investments during the year included those made for new hot-rolling, hot-dipped galvanizing and painting production capacity in the company’s Pesquería industrial center, a new steel bar and coil mill in Colombia, the improvement of environmental and safety conditions at certain facilities, the expansion of connectivity, integration and automation of our operations, and those made in the iron ore mining operations.
Ternium's net debt position reached $1.5 billion at the end of December 2019, with a net debt to last twelve months EBITDA ratio of 1.0.
32. Ternium |
Economic and Financial Performance | |
2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
STEEL SALES VOLUME (THOUSAND TONS) | ||||||||||||||
Mexico | 6,305.0 | 6,544.8 | 6,622.8 | 6,405.2 | 5,933.4 | |||||||||
Southern Region | 1,938.3 | 2,301.1 | 2,456.0 | 2,220.8 | 2,552.2 | |||||||||
Other Markets | 4,268.0 | 4,105.2 | 2,517.7 | 1,138.1 | 1,114.6 | |||||||||
Total | 12,511.3 | 12,951.1 | 11,596.5 | 9,764.1 | 9,600.2 | |||||||||
IRON ORE SALES VOLUME (THOUSAND TONS) | 3,575.9 | 3,616.3 | 3,551.1 | 3,309.6 | 3,635.6 | |||||||||
FINANCIAL INDICATORS ($ MILLION) | ||||||||||||||
Net sales | 10,192.8 | 11,453.4 | 9,700.3 | 7,224.0 | 7,877.4 | |||||||||
Operating income | 864.6 | 2,108.4 | 1,456.8 | 1,141.7 | 639.3 | |||||||||
EBITDA(1) | 1,525.7 | 2,697.7 | 1,931.1 | 1,548.6 | 1,073.1 | |||||||||
EBITDA MARGIN (% OF NET SALES) | ||||||||||||||
EBITDA PER TON ($)(2) | ||||||||||||||
Equity in earnings (losses) of non-consolidated companies | 61.0 | 102.8 | 68.1 | 14.6 | (272.8 | ) | ||||||||
Profit before income tax expense | 826.6 | 2,031.6 | 1,359.8 | 1,118.5 | 267.1 | |||||||||
Profit for the year attributable to: | ||||||||||||||
Owners of the Parent | 564.3 | 1,506.6 | 886.2 | 595.6 | 8.1 | |||||||||
Non-controlling interest | 65.8 | 155.5 | 136.7 | 111.3 | 51.7 | |||||||||
Profit for the year | 630.0 | 1,662.1 | 1,022.9 | 706.9 | 59.8 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures | 1,052.3 | 520.3 | 409.4 | 435.5 | 466.6 | |||||||||
Free cash flow(3) | 595.4 | 1,219.0 | (25.5 | ) | 664.1 | 856.8 | ||||||||
BALANCE SHEET ($ MILLION) | ||||||||||||||
Total assets | 12,935.5 | 12,547.9 | 12,122.6 | 8,322.9 | 8,062.6 | |||||||||
Financial debt | 2,188.7 | 2,037.0 | 3,221.9 | 1,218.6 | 1,521.0 | |||||||||
Net financial debt(4) | 1,453.4 | 1,734.9 | 2,748.3 | 884.3 | 1,132.3 | |||||||||
Total liabilities | 5,220.6 | 5,063.3 | 6,269.8 | 3,156.3 | 3,259.6 | |||||||||
Capital and reserves attributable to the owners of the parent | 6,611.7 | 6,393.3 | 5,010.4 | 4,391.3 | 4,033.1 | |||||||||
Non-controlling interest | 1,103.2 | 1,091.3 | 842.3 | 775.3 | 769.8 | |||||||||
STOCK DATA ($ PER SHARE/ADS(5)) | ||||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | 0.29 | 0.77 | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.00 | |||||||||
Basic earnings per ADS | 2.87 | 7.67 | 4.51 | 3.03 | 0.04 | |||||||||
Dividend per ADS paid in the year | 1.20 | 1.10 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.90 | |||||||||
Weighted average number of shares outstanding(6) (million shares) | 1,963.1 | 1,963.1 | 1,963.1 | 1,963.1 | 1,963.1 | |||||||||
(1) EBITDA is operating income adjusted to exclude depreciation and amortization.
(2) Consolidated EBITDA divided by steel shipments
(3) Free cash flow equals net cash provided by operating activities less capital expenditures.
(4) Net financial debt equals total financial debt less cash and cash equivalents plus other investments.
(5) Each ADS represents 10 shares.
(6) Ternium S.A. has an authorized share capital of a single class of 3.5 billion shares having a nominal value of $1.00 per share. As of December 31, 2019, there were 2,004,743,442 shares issued. All issued shares are fully paid. In addition, as of December 31, 2019 Ternium S.A. held 41,666,666 shares as treasury shares, representing 3% of the subscribed capital.
33. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Why to Invest in Mexico |
Why to invest in Mexico |
The Mexican steel market is the largest in Latin America. Steel consumption growth in Mexico over the last decades has been mainly driven by a dynamic manufacturing industry. The result has been an attractive steel market with a significant demand for high-end steel products. |
TERNIUM HAS A LEADING POSITION IN THE MEXICAN MARKET | |
8 PRODUCTION FACILITIES INTEGRATED AND/OR DOWNSTREAM | 7 SERVICE CENTERS DELIVERING CUSTOMIZED PRODUCTS JUST-IN-TIME OR ON SHORT NOTICE |
12 DISTRIBUTION CENTERS TOGETHER WITH A BROAD NETWORK OF REGIONAL DISTRIBUTORS | |
The Largest Steel Market in Latin America
SOLID GROWTH FOR A LONG PERIOD
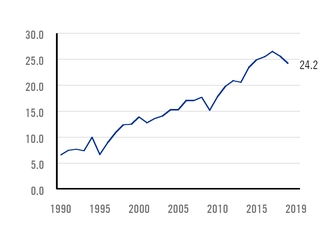
Compound annual growth rate of Mexican steel consumption during the last 30 years reached 4.6%, leading to an average of 192 kilograms of steel consumed per person by 2019.
The rate of steel consumption achieved by the Mexican economy was approximately two times higher than that of other Latin American nations with a developed industrial sector. With 24.2 million tons of steel consumed in 2019, Mexico is the largest steel consumer in the region.
TERNIUM'S LARGEST STEEL MARKET
Ternium's net sales in Mexico accounted for 54% of the company’s total net sales of steel products in 2019. The majority of Ternium's flat steel products are sold to industrial customers, which usually require more sophisticated services and high-value-added steel products, with the balance being sold to construction companies and distributors.
Mexican Competitive Advantages
Mexico's privileged conditions to home a competitive and innovative manufacturing sector have been behind its success story.
LOGISTICS
The country's geographic location provides a competitive logistics base to reach every major market.
TRADE AGREEMENTS
The Mexican industrial sector has access to the US and Canadian markets through the US, Mexico and Canada Agreement (USMCA), and to other major economic regions and trade blocks through other trade agreements in place, including a free trade agreement with the European Union (FTA EU-MX) and Japan (a.k.a. Agreement Between Japan and the United Mexican States for the Strengthening of the Economic Partnership).
34. Ternium |
Why to Invest in Mexico |
 |
Ternium's Pesquería unit. Inaugurated in 2013, the new industrial center has incorporated cold-rolling, galvanizing and painting facilities, and will incorporate a new hot-rolling mill in 2021. |
In addition, Mexico has trade agreements in place with Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, Brunei, Colombia, Chile, Costa Rica, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Malaysia, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Norway, Peru, Singapore, Switzerland, Uruguay and Vietnam.
Growth Opportunities
We compete in the Mexican steel market with other domestic steel producers, and with US and other foreign steel producers. Local steel producers, including Ternium, represent a little over half of total apparent flat steel use in Mexico, with the balance of the country's flat steel consumption being supplied from abroad.
According to Canacero, the Mexican chamber of the iron and steel industry, imports of finished flat steel products into Mexico accounted for approximately 8.2 million tons in 2019.
Ternium believes that it is very well positioned to compete with foreign producers and substitute imports in Mexico. The company believes it has built
APPARENT STEEL USE - MEXICO MILLION TONS |
35. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Why to Invest in Mexico |
 | |
" | |
The new state-of-the-art hot-rolling mill at Pesquería Industrial Center will enable us to consolidate our leadership in the Mexican flat steel market”. Máximo Vedoya CEO | |
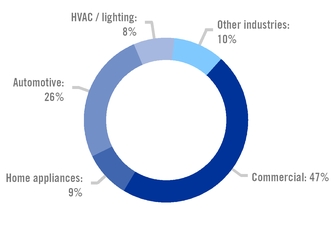
TERNIUM'S STEEL SHIPMENTS IN MEXICO BY INDUSTRY 2019 |
a solid differentiation strategy leaning on its unique industrial presence in the country, as well as on its cost competitiveness.
TERNIUM'S COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES AS A LOCAL STEEL PRODUCER
Ternium's industrial presence together with its own network of distribution centers and commercial offices enable the company to provide logistics and stock management services. In addition, Ternium offers its customers an integrated connectivity platform that has 75 functions covering the entire customer relationship process. For more information on Ternium's Webservice Platform, see page 22 "Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy".
Ternium's ProPymes program has been focusing its efforts on the development of small and medium-sized customers and suppliers in Mexico. The prosperity of small and medium-sized companies, and the development of a collaborative industrial network have strengthened the country's steel industry value chain.
The consequent improved competitiveness has led to a virtuous cycle of increased exports as well as imports substituted by locally manufactured new products. For more information on the ProPymes program, see page 66 "Strengthening Ternium's Value Chain".
In addition, Ternium has further enhanced its differentiation strategy by investing in state-of-the-art technologies. This strategy included the inauguration of its Pesquería Industrial Center in 2013, with new cold-rolling and galvanizing mills, an expansion of this industrial center in 2019, with the inauguration of new galvanizing and painting lines, and a further expansion expected by 2021, with a new state-of-the-art hot-rolling mill.
Together with the technological upgrade of its facilities, Ternium has increased its product research and development capabilities in the country in order to broaden its range of product offerings, particularly in the high-end steel segment, with the aim of fulfilling all industry requirements.
36. Ternium |
Why to Invest in Mexico |
Furthermore, Ternium's product research and development area has provided technical assistance to its customers, maximizing the performance of the company's steel products and the manufacturing processes downstream in the Mexican steel industry value chain.
APPARENT FLAT STEEL USE IN MEXICO BY SEGMENT 2019 |
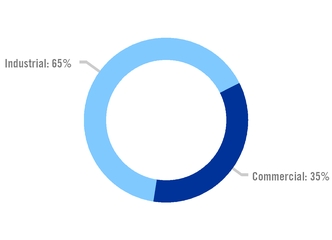
APPARENT FLAT STEEL USE IN MEXICO BY ORIGIN 2019 |
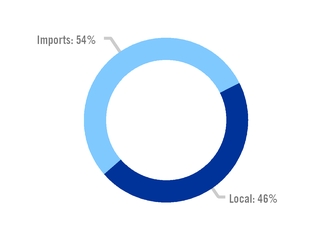
Source: Canacero |
The US, Mexico and Canada
free trade agreement, or USMCA, came into effect on July 1, 2020. The new agreement, which resulted from the renegotiation of NAFTA between the three member states, encourages the production of cars and trucks within the trade block.
 |
Strengthened research capabilities in Mexico through the inauguration of a new laboratory and the construction of a new research center, launched during 2019. |
37. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Improving Our Safety Performance | |
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
   | |
DEC 2019 NEW CORPORATE STRATEGY ON OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT TO ADVANCE OUR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AGENDA. | |
Goals | Measures | |
Prevent all work-related injuries and illnesses, and achieve zero accidents | Occupational health and safety policy | |
-Identify and eliminate operational hazards | Occupational health and safety management system | |
-Operate in compliance with established protocols | Safety-focused capital expenditure plan | |
-Raise people's awareness of non-compliance risks | Integral program for critical steel production processes and iron ore tailings dams | |
-Identify and rectify unsafe acts or situations | Periodical management tours at the facilities, training activities, workshops and conferences to raise awareness | |
Extensive communication to engage and commit Ternium's and contractor's employees | ||
Promote healthy and safe operations in the steel industry value chain | Code of conduct for suppliers | |
-Evaluate suppliers' occupational health and safety policies and performance | Safe supplier program | |
-Raise people's awareness of non-compliance risks | Safety training of third-party employees | |
Participation of suppliers in deviations reporting | ||
38. Ternium |
 |
Fast implementation of COVID-19 mitigation measures. New protocols for on-site working and work-from-home policy whenever possible. |
Ternium ranks occupational health and safety (OH&S) performance as its top priority, with the conviction that all injuries and work-related illnesses can and must be prevented. Each of the company's and third-party employees' OH&S is our top concern.
COVID-19 Outbreak
Ternium is focused on safeguarding the OH&S of its employees, customers and suppliers based on best practices that comply with and, in some cases, exceed local governmental directives. Beyond implementing work-from-home policies wherever possible, the company has looked to protect the safety of those employees working on-site by adopting stringent social distancing, temperature check and disinfection policies at all transportation, site admission, working post and cafeteria locations, among other initiatives. In addition, Ternium has developed a protocol to track suspect or positive contagion cases and the successful reintegration of returning workers.
New Occupational Health and Safety Corporate Strategy
According to Ternium's OH&S policy, the assessment of risks and management of our people's OH&S must be integrated into all our business processes. Management is responsible and accountable for
achieving excellence in OH&S performance as part of a comprehensive set of goals. In December 2019, Ternium launched a new corporate strategy on OH&S. We are committed to taking every possible step to protect the safety and health of our employees and the people of the communities in which we operate. This vision has acted as a framework to adjust our strategies and to adopt new ones, including the alignment of our safety culture to our vision, the prevention of severe accidents or fatalities, the achievement of excellence in process safety management, the engagement of employees through effective communication and the engagement of customers' and suppliers' managers and employees to embrace our vision and goals. In 2019, Ternium invested $50 million under its safety-focused capital expenditures plan.
Occupational Health and Safety Management System
Ternium has an OH&S management system to oversee its production units, which abides by the company's OH&S policy, and local and national laws and regulations. The company periodically audits its processes and procedures, which helps us find new opportunities to improve our safety management systems and ensure their compliance with our policy. Ternium’s steelmaking and steel processing facilities in Mexico, Argentina, Colombia and
39. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Improving Health and Safety Performance • Proactive approach to occupational health and safety management • Standardized OH&S management system • Extensive employee training • Management accountable for OH&S performance • Certified OH&S management system • Capital expenditures program to reduce H&S risks | ||||
Guatemala have their OH&S management system certified under international standards by third party certification bodies. The company’s facilities in Mexico have completed the migration process of their OH&S management system to ISO 45001:2018, and have
obtained the certification in this new standard. Ternium’s Rio de Janeiro unit in Brazil and its mining facilities in Mexico are undergoing a migration and certification process, which is expected to be completed within the next two years.
Aligning Our Safety Culture to Our Vision
Ternium’s continuous quest for a virtuous safety culture leans on its top management’s effective leadership. The company’s senior management has identified measurable, repeatable, proactive and leading safety attitudes to deploy along the organization, as part of a strategy to align people’s safety culture with the company’s vision.
SAFETY FIRST PROGRAM
The Safety First program fosters a pro-active approach to safety issues to prevent incidents and accidents. One of the program's main tool is the Safety Hour initiative, in which middle and senior managers tour operating areas for an hour, three times a week, to identify safe behaviors to be consolidated or unsafe acts or situations to be
addressed through an open dialogue with employees. This exchange helps identify potential risks and enables a fluid and constructive feedback to implement effective preventive measures. In 2019, the company held a total of 147,100 Safety Hour sessions, with the regular participation of 1,600 employees and contractors, that helped to detect, record and correct 177,500 deviations. In addition, these sessions helped to recognize 106,800 full-compliance cases. Furthermore, management performed safety verification audits (SVAs) at the facilities to evaluate compliance with policies, procedures and practices in relation to relevant OH&S topics. In 2019, a new record 200,000 SVAs were performed.
TEN LIFE-SAVING RULES
Ternium has established Ten Life-Saving Rules, which lists the actions that all employees must follow in order to protect their lives and that of their colleagues. The rules are the result of a process that included worldsteel's guidance, and the contribution of focus groups and studies performed to detect the main causes of risks in our operations. The rules are backed by practices and routines to follow and reflect the scope of safety regulations in the countries where Ternium operates. The rules have been extensively communicated throughout Ternium’s operations to foster employees',
40. Ternium |
 |
Safety hour (hora segura) at the Villa Nueva unit, Guatemala. An articulated on-site exchange to implement effective preventive measures. |
customers' and suppliers' awareness, and have been audited to ensure their observance. In 2019, we held 42,800 compliance audits.
TERNIUM’S ANNUAL SAFETY DAY
Since 2014, every July 22nd we have been holding Ternium's Annual Safety Day, an occasion to prompt a renewed commitment to improving safety and increasing risk awareness, in the belief that every accident can and must be prevented. During this event, we hold safety management meetings and discussions to review our performance in the past year and agree on concrete actions to improve safety in every facility.
TRAINING PROGRAMS
Management is committed to training Ternium's employees, customers and suppliers on the appropriate application of the company’s OH&S management systems in performing their tasks, and to raising awareness of risks. In 2019, Ternium delivered 487,600 safety training hours to 15,700 employees, customers and suppliers.
TASK REJECTION TOOL
This tool aims at strengthening people’s determination not to start or, if started, to suspend a task under certain conditions. The Task Rejection tool helps people prevent
injuries risks stemming from the lack of effective control over identified safety risks.
Prevention of Severe Injuries or Fatalities
A steel industry-wide analysis found out that, over time, the downward trend in fatal accidents has been slower than the trend for non-fatal accidents, mainly due to causality differences. Accordingly, the company has increased its efforts to identify severe injury or fatality precursors. In order to do so, we identify non-controlled repetitive precursors through interviews with employees, based on critical control and verification methodologies.
Process Safety Management
Iron ore processing, and steel production and processing include potentially hazardous processes. Ternium has identified critical processes in some of its facilities, and developed specific tools to manage them. In addition, during 2019 Ternium launched a new program focused on the identification of risk factors in critical processes and the development of specific strategies aimed at eliminating the exposure to severe personal injury.
Engaging Through Effective Communication
Over the years, Ternium has increased the visibility of safety issues through its communications platforms.
41. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
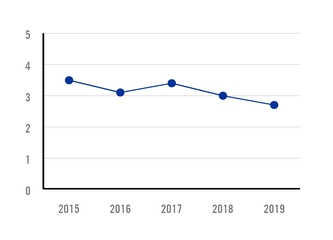
INJURY FREQUENCY RATE (IFR) TOTAL QUANTITY OF INJURIES PER MILLION HOURS WORKED |
Our agenda includes videos, articles and the coverage of selected events. To engage the company’s employees and raise awareness on safety issues, we have developed a new communications system aimed at sharing key messages with employees operating at every location, including posts at the company’s communications platforms and other distribution channels. We have also implemented the Five-Minutes Safety Talks, an open-dialogue instance for blue-collar supervisors and their teams to analyze OH&S issues selected every week by senior management.
Engaging Customers' and Suppliers' Managers and Employees
We aim at having all contractors' employees embrace our vision and goals. With this purpose, we have launched several initiatives including working meetings with contractor’s top managers and the participation of their employees in Ternium's OH&S workshops. We have recently launched an OH&S improvement plan for contractors. This plan has been developed based on contractors' best practices, which were identified through a benchmark of contractors' operations at the company's facilities in different locations and countries.
Accidents and incidents
In 2019, Ternium recorded an injury frequency rate (IFR) of 2.7 injuries per million of hours worked, compared to
LOST TIME INJURY FREQUENCY RATE (LTIFR) 1 QUANTITY OF DAY-LOSS INJURIES PER MILLION HOURS WORKED |
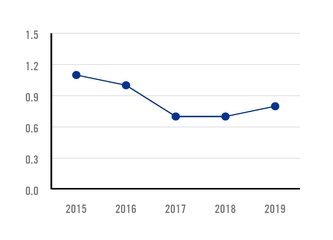
an IFR of 3.0 in 2018. The lost time injury frequency rate (LTIFR) was 0.8 day-loss injuries per million hours worked in 2019, compared to an LTIFR of 0.7 in 2018. The year-over-year increase in LTIFR in 2019 reflected mainly the effect of construction works carried out for the new facilities in Pesquería, Mexico, and Palmar de Varela, Colombia.
Analysis of Accidents and Incidents
Ternium's management follows specific protocols when a workplace accident or incident occurs, regardless of the damage or injury, or lack of, cause by an event. The research and analysis of an event is conducted by multidisciplinary teams that include the participation of the manager with direct responsibilities in the area involved.
An event is analyzed through a causal factor tree methodology that has been homologated at Ternium. Management uses all available resources that could contribute to the understanding of an event, including the evidence collected by nearby cameras. Once causes are fully understood, the company implements a new preventive action plan structured in hierarchy of controls. This methodology was incorporated in the company’s occupational health and safety management system in 2019.
42. Ternium |
 |
Las Encinas, Mexico. Ternium has a proactive approach to safe mining operations. |
Health and Well-being
Ternium’s comprehensive occupational health program embodies the company’s commitment to providing a healthy workplace, with equipment and technology that ensures the well-being of its workforce. The health management system includes periodic workplace monitoring and risk analysis to evaluate and control a range of activity-related factors with the potential to affect employees’ health, including chemical, biological, physical, ergonomic and psychological risks. Our corporate procedures and guidelines in relation to the level of indoor air quality, noise and vibrations pursue stricter threshold levels than those defined by the more rigorous international standards. Some of our facilities, like the Ternium Industrial Center in Pesquería, built in 2013, adopted the best-available technologies from the design phase. In other facilities, particularly those we acquired, we are consistently adopting the best-available technologies as part of our drive to continuously improve our sites' air quality.
Tailings Dams Reinforcement
Ternium has equity interests in two iron ore mining companies in Mexico: a 100% interest in Las Encinas and a 50% interest in Consorcio Peña Colorada. The company operates extractive, processing and logistical operations,
STRICTER STABILITY STUDIES FOR TAILINGS DAMS |
$19 MILLION INVESTED IN 2019 BY TERNIUM AND PEÑA COLORADA. |
4 TAILINGS DAMS SUBJECT TO ONGOING REINFORCEMENT PLANS, FOLLOWING NEW STUDIES CARRIED OUT WITH THIRD PARTY CONSULTANTS. |
including tailings dams. Over time, Ternium has conducted stability studies of its tailings dams, with the help of consultant companies, using increasingly strict standards for seismic areas and, as a result, has been carrying out several investment projects to reinforce certain dams.
In late 2019 and early 2020, Ternium and Consorcio Peña Colorada concluded new stability studies in certain of their tailings dams that are closed or stand-by, in order to proceed to final closure with stricter and more conservative standards for seismic areas. As a result of those studies, performed by recognized consultant companies, and in order to meet those new stability standards and mitigate risks, Ternium and Consorcio Peña Colorada are planning to reinforce certain stand-by and closed tailings dam sections in Alzada and Guasimas, respectively.
In addition, a new paste plant was started-up in July 2019 near Consorcio Peña Colorada's Arrayanal dam, to increase the efficiency and speed of water recovery from the dam tailings. With this initiative, Ternium expects to increase the solid content of tailings from 45% to 68%, increasing the stability of the dam and freeing space for additional tailings.
43. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
On the Right Path. Ternium has established safety committees to formalize the consultation and participation of workers and their representatives on occupational health and safety issues. |
 |
44. Ternium |
Occupational Health And Safety Policy | |
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – | Ternium, an integrated steel company, along with its subsidiaries is committed to the occupational safety and health of its personnel, clients, contractors, and suppliers. The company’s occupational safety and health policy is the baseline for sustainable development across all its operations. Policy adherence, dissemination, and compliance apply and are to be promoted throughout Ternium and its subsidiaries. Looking out for the occupational safety and health of every person who works for the company or is inside its facilities is an essential value. To that end, we promote our commitment through the following principles: All work-related injuries and illnesses can and should be prevented. Compliance with all applicable legal and other regulations to which Ternium voluntarily agrees. Continuous improvement of all processes related to staff's health and safety. Occupational safety and health must be integrated into all company processes. No emergency situation, production process or results justify putting people’s occupational safety or health at risk. Commitment from and training of the entire staff is essential. Working safely is an employment condition. Every person is responsible for looking after his/her own safety and the safety of others. In each company, everyone is responsible for occupational health and safety: The company provides the means and resources for activities to be carried out safely so as to preserve everyone's physical integrity and occupational health. Managers are in charge of the occupational health and safety of everyone who works for them or is in their area. All other workers must comply with regulations and instructions, and work with their managers to detect, control, and resolve any dangerous situations. Contractor companies and their staff must comply with the Safety Regulations in force at the facilities where they provide services. People who enter the facility must comply with the applicable Safety Regulations. Health and Safety staff must take preventive measures through support, advising and auditing. At Ternium and its subsidiaries, these principles are shared throughout the entire value chain and in all the communities where it operates in order to promote people's healthcare and safety. |
March 2018 | |
 | |
Máximo Vedoya CEO Ternium | |
45. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Minimizing Ternium's Environmental Footprint | |
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
    | |
 | |
$70 MILLION INVESTED IN 2019 TO REDUCE TERNIUM'S ENVIRONMENTAL FOOTPRINT. | |
Goals | Measures | |
Use natural resources responsibly | Environment and Energy Policy | |
-Minimize consumption of raw materials and other inputs | Steel scrap recycling (self-generated and from third-parties) | |
-Minimize waste generation | Intake of recycled and treated water (replacing subsurface) | |
Investment in energy and material efficiency projects | ||
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) | ||
Participation at worldsteel's and Alacero's environmental committees and worldsteel's Climate Action | ||
Pursue excellence in environmental performance | Environment and energy management system | |
-Preserve water and air quality | Investments to control particulate emissions and discharges | |
-Maximize energy efficiency of Ternium's infrastructure | Sustainable building solutions at new facilities | |
Environmental performance certification | ||
Protect biodiversity | Field works at greenfield projects to preserve biodiversity | |
Support to Sepetiba Bay and Iberá Wetlands initiatives | ||
46. Ternium |
Minimizing Ternium's Environmental Footprint • Standardized management system certified under ISO 14001 and 50001 • Continuous progress in environmental management performance • Management performance accountability • Investment in best available technologies | ||||
The protection of the environment is a fundamental value for Ternium. The company seeks to reach the highest standards of environmental and energy performance in order to minimize the environmental footprint of its operations. To achieve this, we are continuously working on the improvement of Ternium's production system. The company's Environmental and Energy Policy states Ternium's views regarding the preservation of the environment.
The monitoring of the company's environmental performance leans on an environmental and energy management system encompassing all its production units. Ternium periodically audits and certifies its systems and procedures. This process helps us identify improvement opportunities, update the company's environmental management processes and make sure Ternium complies with legal regulations.
Ternium’s steel and mining operations are subject to a broad range of environmental laws and regulations relating to the protection of the environment, such as land use; air emissions; wastewater treatment and discharge; the use, handling and disposal of hazardous or toxic materials and the handling and disposal of solid wastes. Ternium’s corporate environmental and energy policy commits each of its business units to comply with all
applicable environmental laws and regulations, and aims to achieve the highest standards of environmental performance as a basis to enhance sustainable development. Compliance with environmental laws and regulations and monitoring of regulatory changes are addressed primarily at national level. Ternium has not been subject to any material penalty for environmental violations in 2019.
Ternium's environmental and energy management system at its steel production facilities is certified under ISO 14001, ISO's environmental management standard. This standard was created by the International Organization for Standardization, a network of national standardization institutes that work together with governments, the industry and consumer representatives with the purpose of supporting the implementation of an environment management plan in public and private organizations.
In addition, Ternium is certifying the system at its energy intensive operations under ISO 50001, ISO's energy management standard. The system has already been certified at the Rio de Janeiro unit, at the steel shop of the San Nicolás unit and at the Pesquería unit (downstream facility), and is undergoing the certification process at the steel shop of the Guerrero unit and the hot-rolling mill of
47. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Ternium's steel shops in Puebla and Nuevo León, Mexico, capture carbon dioxide from its production process to deliver it mostly to the beverage industry, for use in soft drinks production. The company has recently launched a new project to increase its carbon dioxide capturing capacity, which is expected to be completed in 2021. This project will enable a yearly increase in carbon dioxide emission savings of up to 60,000 tons, to a total of 270,000 tons. |
the San Nicolás unit. Ternium's environmental and energy management system will help the company maximize its efforts to reducing carbon emissions. The targets of the company in this regard are in line with those of the countries in which Ternium has operations and are expected to contribute to the achievement of the goals of the Paris Agreement adopted at the UN climate change conference.
A Material at the Heart of a Low-Carbon Economy
Ternium subscribes to worldsteel's position as for the role of steel in our present and future. Abundant iron ore resources, endless recyclability and unparalelled performance make steel the material of choice in a low-carbon circular economy. We rely on steel for our housing, transport, food and water supply, energy production, tools and healthcare. Almost everything around us is either made of steel or manufactured by equipment made of steel. Steel is a highly versatile metal, offering a wide space for the development of new workable and light products. Innovation is driving to increasingly sophisticated ferrous castings, enabling a new generation of stronger and lighter structures, with lower carbon footprint, that are essential inputs for the automotive, engineering, energy and transport industries. Iron ore is currently the main raw material for steel production, a material that ranks among
the most common in the world. Steel scrap has been growing as an alternative raw material for steel production. In addition to keeping the attributes and performance of steel upon recycling, steel scrap has magnetic properties that enable feasible separation technologies. The use of steel scrap reduces carbon emissions from the steel life cycle. In combination with a long history of significant efforts to increase recycling rates, this has resulted in steel leading the recycling statistics, for example in cars and cans. Furthermore, its biodegradable nature positions steel as a solution to our society's waste disposal challenge.
Steel recycling is limited by the availability of scrap, due to the relatively long life of steel-based products and infrastructure. Developing economies have relatively young infrastructure stocks and have, therefore, limited amounts of obsolete steel scrap to use in steelmaking. However, as these economies’ climb the development curve, and infrastructure enters the replacement phase, availability of obsolete scrap increases, supporting a shift from steelmaking technologies based on iron ore to steelmaking technologies relying more heavily on steel scrap. In time, this shift will have a significant impact on trends in iron ore and steel scrap consumption globally.
48. Ternium |
EMISSION INTENSITY CARBON DIOXIDE TONS EMITTED PER TON OF STEEL PRODUCED. YEAR-END. |
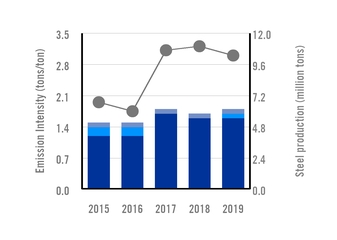
n Scope 1: direct n Scope 2: energy upstream | n Scope 3: raw materials upstream • Steel production | ||
Energy and Climate Action
The steel industry is energy intensive. There are two main technologies for producing steel: the blast furnace / basic oxygen furnace (BF/BOF) route, which consumes mainly iron ore and uses metallurgical coal as its main energy source; and the electric arc furnace (EAF) route, which consumes mainly steel scrap and/or direct reduced iron and uses electricity as its main energy input. Direct reduced iron is produced out of iron ore and uses natural gas as a reduction agent. The steel industry has a strong commitment towards the reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, through the development of innovative steel products for a successful low carbon society and the improvement of steel production processes. According to worldsteel, in the last 50 years the steel industry reduced its energy consumption per ton of crude steel produced by 60%. Yet, steel production accounts for approximately 8% of all human-made GHG emissions.
As a member of worldsteel, Ternium is signatory of worldsteel's sustainability policy and joins its efforts, through the company's participation in several programs, to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. As a participating member, Ternium submits to worldsteel its performance indicators to contribute to its statistics and databases, which enable steelmaking companies to benchmark
ENERGY INTENSITY GIGAJOULES CONSUMED PER TON OF STEEL PRODUCED. YEAR-END. |
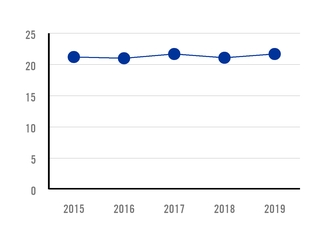
performance, share best practices and ultimately set improvement plans for their industrial processes. In 2008, worldsteel launched its Climate Action Recognition Program. Since its launch, Ternium has been recognized by worldsteel for its compliance with the program's requirements for carbon dioxide emission reporting.
In 2019, Ternium joined worldsteel’s Step Up Program. This initiative supports the steel industry's efforts to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by means of better operational models and benchmarking of operating technologies. Based on the Step Up Program findings, Ternium seeks to identify opportunities to improve the efficiency of its operations, mainly related to raw materials usage, energy input, materials yields and maintenance models.
Ternium's carbon dioxide emissions totaled 18.5 million tons in 2019, 3% lower than in 2018. Steel production totaled 10.3 million tons, decreasing 6% year-over-year. Average carbon dioxide emissions per ton of crude steel produced, including scopes 1, 2 and 3, was 1.8 tons in 2019, 2% higher than in 2018 mainly due to a net lower operating rate. Ternium's average energy consumption per ton of crude steel produced was 22 gigajoules in 2019, 3% higher year-over-year for the same reason. Ternium's
49. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
 |
Adopting the best-available technologies. In the last five years, Ternium has made investments of approximately $137 million to improve the capture and treatment of air emissions. |
carbon footprint includes only carbon dioxide emissions, as the incidence of other greenhouse gases is negligible.
The assessment of the company's energy consumption is based on worldsteel's sectoral approach methodology in accordance with ISO 14404.
In 2014, Ternium launched an energy efficiency program, an initiative aimed at reducing GHG emissions by identifying opportunities to implement energy savings at its production facilities. Since 2014, we have completed 366 projects under this program that, in the aggregate, have reduced Ternium's yearly carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 298,000 tons, comparable to the yearly emissions from 117,000 cars.
During 2019, Ternium's Rio de Janeiro unit started purchasing biomethane from a nearby waste landfill. The company expects to gradually increase the use of biomethane to replace natural gas, for up to 30% of its historical consumption level, with the consequent avoidance of carbon dioxide emissions in the landfill.
Air Quality
Some of Ternium's facilities, like the company's Industrial Center in Pesquería, adopted the best-available
technologies from the design phase. In other facilities, particularly those acquired, Ternium is enhancing its air quality monitoring systems and is consistently adopting the best-available technologies as part of its drive to continuously improve its environmental performance.
Ternium has made investments of approximately $137 million in its facilities in the last five years to improve the capture and treatment of air emissions. In 2019, the company concluded the construction of a new bag filter for the fume and dust capturing system at its steel shop in the Puebla unit in Mexico, and made progress in the improvement of the fume and dust capturing system at its steel shop in the San Nicolás unit in Argentina.
In addition, Ternium concluded works in the electrostatic precipitator of the sinter facilities at its Rio de Janeiro unit in Brazil. To mitigate dust emissions in all its operations, Ternium implemented specific solutions, such as retaining walls and live fences at bulk storage yards, washing systems for truck tires and road pavement.
In 2019, Ternium launched a project to capture and
contain emissions at the iron ore handling equipment and direct reduction facilities in its Guerrero unit in Mexico. In addition, the company launched a project to control sulfur
50. Ternium |
WATER INTAKE - MEXICAN STEEL FACILITIES MILLION CUBIC METERS. |
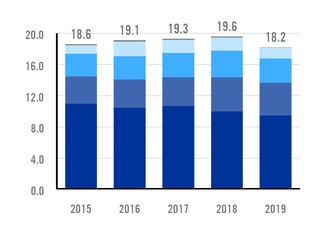
n Subsurface n Recycled | n Third party treated n Municipal | n Sewage |
Water Management
In steel manufacturing, in which water plays a major role, most water is recycled and returned to the source. Ternium is fully aware of its responsibility for managing water resources. Its water management strategy is designed on a case-by-case basis in accordance with the specific situation at each of its operating sites.
The company continuously incorporates best available technologies to improve water management and water discharge monitoring systems. For example, Ternium has recently revamped a water treatment facility in the steel shop of the San Nicolás unit, to improve the quality of recirculated and discharged water. Ternium has invested a total of $72 million in the last five years to improve its water management.
WATER INTAKE AND USE
Many of the company's facilities are located in areas of low water-stress risk. However, Ternium's Mexican facilities are placed in water stressed regions.
INVESTING TO IMPROVE WATER PERFORMANCE INDICATORS |
48% OF WATER INTAKE IN MEXICO COMES FROM EITHER TREATED, RECYCLED OR SEWAGE SOURCES. |
1.6 MILLION CUBIC METERS DECREASE IN SUBSURFACE WATER INTAKE IN 2019 COMPARED TO 2015. |
Consequently, Ternium has developed specific strategies to minimize water usage, reflected in a water consumption rate of 4.3 cubic meters per ton of crude steel produced in its steel shops in Mexico.
In this country, Ternium has consistently reduced the consumption of subsurface water by increasing the usage of treated or sewage water. As a result, the company's consumption of subsurface water decreased from 11.0 million cubic meters in 2015 to 9.4 million cubic meters in 2019, or 52% of total water consumption.
Total water consumption in 2019 also included a 23% share of third party treated water, a 17% share of external sewage water and an 8% share of recycled water.
WASTEWATER DISCHARGE
Ternium permanently monitors wastewater discharges, in compliance with local environmental regulations. The company designs capital expenditure projects to incorporate best available technologies and monitoring systems to reduce and improve the quality of water discharges. During 2019, the company concluded the construction of a new runoff water pumping station for the coal and coke yards, the coking batteries sector, the
51. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
CO-PRODUCTS KILOGRAMS PER TON OF STEEL PRODUCED. |
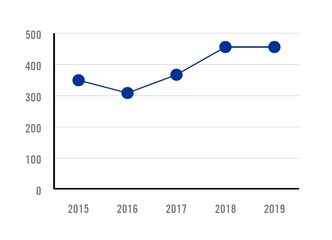
co-products facilities and nearby areas at its San Nicolás unit in Argentina. In addition, it built new infrastructure to prevent discharges to the Paraná river in the event of extreme weather conditions.
This investment followed other investments in previous years like the gas scrubbing circuit-close at a blast furnace and a new runoff water capturing system at the sinter yard.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Ternium supports worldsteel's efforts and customer requirements to assess the environmental impact of steel products. The aim of this program is to document and improve the overall environmental profile of the company's offerings.
A steel LCA involves a thorough inventory of the energy and materials that are required across the industry value chain, according to ISO 14040 and 14044, to determine the global warming potential of steel products, among other indicators. In 2019, Ternium incorporated 63% of its crude steel production to its LCA inventory reporting, reaching a total LCA inventory reporting of 92% in the year.
OPTIMIZING MATERIAL EFFICIENCY AT THE GUERRERO UNIT, MEXICO |
86,000 TONS OF MIX ROCK® SOLD TO THE CEMENT INDUSTRY IN 2019. |
79% OF DUST AT THE GUERRERO STEEL SHOP TURNED INTO VALUABLE CO-PRODUCTS. |
In addition, the company has developed environmental product declarations (EPDs) of eight products, as required for certain market segments. More information on Ternium's EPDs are available at our website.
Environmental Certifications
LEED
We design Ternium's new facilities considering the best available sustainable building solutions. In Pesquería, Mexico, Ternium's technical school and the industrial buildings of Ternium's production facilities were certified under the Leadership in Energy and Environment Design Certification standards of the U.S. Green Building Council. In 2019, Ternium received the Green Building Leadership award, in recognition for reaching environmental performance excellence in Mexico.
CLEAN INDUSTRY
In Mexico, most of Ternium's steel and in-use mining facilities have Clean Industry certificates issued by the local environmental authorities. The standard of this program was created by the Mexican government and ema, a technical rating and standardization institute.
52. Ternium |
 |
Iberá Wetlands, Santiago del Estero, Argentina. Ternium sponsors the projects of the Rewilding Argentina Foundation in the wetlands, part of the National Geographic Society's Last Wild Places initiative. |
Material Efficiency
In Ternium we continuously develop strategies to maximize the use of co-products and reduce the production of waste. We believe that the recovery and proper use of co-products is central to the application of circular economy concepts in the steel industry's value chain.
The use of co-products reduces the consumption of raw materials and energy, with a positive effect on carbon dioxide emissions and waste generation. All the steel scrap generated in Ternium's facilities is recycled. In addition, the company purchases steel scrap generated by other steel processors in its value-chain and steel scrap gathered by recyclers. In 2019, Ternium recycled 2.8 million tons of steel scrap to produce new steel with all its properties, representing 27% of its total crude steel production.
The granulated slag generated in the blast furnaces is sold to the cement industry. The re-use of granulated slag as a substitute for clinker enabled carbon dioxide emission savings in the cement production process of 1.3 million tons in 2019. The slag generated in the steel shop is also used to consolidate roads. In addition, Ternium has sinter and briquetting facilities that enable it to recycle different materials captured by
its air and water cleaning equipment, including iron ore fines, coal, lime and dolomite. Furthermore, the dust generated by the electric-arc furnaces at Ternium's Guerrero and Puebla units, Mexico, is transformed into Mix Rock®, an innovative co-product developed and registered by Ternium. Mix Rock® enabled the re-use of dust and slag as a substitute for iron ore in the clinker production process at the cement industry. In 2019, Ternium sold 86,000 tons of Mix Rock®.
The processing of metallurgical coal for the steelmaking production process yields significant volumes of co-product gases. These gases stem from the distillation process in the coking batteries. Ternium cleans coking battery gases and obtains chemical products like tar, benzol and hydrated lime that are sold to third parties. In addition, once the gases obtained from the coking batteries, blast furnaces and, in the case of the Rio de Janeiro unit, the steel shop, are cleaned, they are used to produce steam for the generation of electricity.
All these processes have enabled Ternium to achieve a material efficiency rate of 99.6% in 2019, with 4.8 million tons of co-products generated and 60,300 tons of waste disposed of. Co-products mainly include blast furnace and
53. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
 |
Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Ternium has recently launched, together with local institutions, a project aimed at enhancing the conservation techniques for the boto cinza, a bay dolphin. |
steel shop slag, iron oxide and chemical substances.
Biodiversity Care
SEPETIBA BAY
Ternium's Rio de Janeiro unit is located near a coastline area rich in mangroves in the Sepetiba bay in Brazil, where it has its port. The company protects the fauna and flora of 600 hectares of mangroves. In addition, Ternium has recently launched, together with the Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro and the Instituto Boto Cinza, a project to study a dolphin that inhabits the bay, the boto cinza. Under this project, the specimens will be tagged in order to study their habits and enhance conservation techniques.
IBERÁ WETLANDS
Ternium sponsors the projects of the Rewilding Argentina Foundation at the Iberá wetlands, a protected area located at the northeast of Argentina. These projects have recently been incorporated to National Geographic Society's Last Wild Places initiative. They seek to reintroduce in this area species that are considered extinct or endangered, such as the giant otter
and the yaguareté, a kind of jaguar. Ternium contributed with steel products to build a new shoreline pen for a couple of giant otters brought from European zoos and for the yaguareté breeding center. This center now holds the offspring of the first breeding couple of yaguaretés.
TERNIUM'S PRESERVATION WORKS
Ternium performs field works aimed at preserving local biodiversity before starting the construction of new facilities and carries out a continuous control and surveillance program in areas intended for conservation in steel and mining operations. The company defines various areas of ecological connectivity between its terrain and the natural ecosystems, and develops rescue programs to release wildlife in those areas and install wildlife connectivity gates for reptiles, amphibians and small mammals.
54. Ternium |
Environment and Energy Policy | |
– – – – – – – – – – – – | Ternium is an integrated steel company committed on preserving the environment. Its goal is to achieve the highest standards in environmental and energy performance as a basis for sustainable development throughout its operations in regards to company employees, the community and future generations. The company has committed to develop a high-quality performance, integrated and eco-efficient production system based on continuous improvement. Caring for the environment is a fundamental value, and its principles are the following: Compliance with the applicable legislation, as well as any voluntary agreements in relation to environmental protection and energy use, consumption and efficiency. All levels in each area, throughout the company, are responsible for the results of environmental protection. The commitment of all our personnel is essential, as is the training provided. Environmental protection and energy efficiency are responsibilities of Ternium’s staff as well as of its subsidiaries, suppliers and contractor personnel. Environmental and energy dimensions are an integral part of the company's management processes. Continuous improvement in environmental and energy performance is actively promoted throughout the company, in addition to all the efforts necessary to achieve the objectives and established goals. Pollution must be prevented at the source, controlling the most significant environmental aspects of our operations and minimizing their impacts and risks. Promoting the acquisition of energy efficient products, technologies, services and implementing projects that enhance our energy performance. Use energy and natural resources efficiently. Encourage the use of best technologies and practices, as well as renewable energies, when feasible. In each company, everyone is responsible for environmental and energy management: The company supplies the means and resources to enable compliance with this policy, thereby supporting the sustainability of all operations, depending on the operations context. All persons entering company facilities, such as own personnel, suppliers, contractors and customers, must comply with this policy. The company seeks to share these principles throughout its value chain and across the communities where it operates, to promote the protection of the environment, encourage the efficient use and consumption of energy resources and foster an open dialogue with stakeholders. This Policy applies to Ternium and its subsidiaries. It will be actively disseminated with a view to ensuring compliance throughout the organization. |
June 2018 | |
 | |
Máximo Vedoya CEO Ternium | |
55. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Realizing Our People's Full Potential | |
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
    | |
20,000 EMPLOYEES LOCATED MAINLY IN THE AMERICAS. | |
Goals | Measures | |
Attract and retain talented employees | Code of Conduct | |
-Be an equal opportunity and equal treatment organization | Diversity Policy and diversity acknowledgment activities | |
-Enable career development in an appealing work environment | Health care and other benefits for employees and families | |
Personal development plan | ||
Mandatory internal job application system (hiring process) | ||
Work climate improvement initiatives | ||
Promote a culture of excellence throughout the company | Ternium University (launched in 2019) | |
-Enhance employees' skills and cultivate the company's values | Training programs | |
-Develop a world-class management team | Performance evaluation system | |
56. Ternium |
 |
New Diversity Policy. With 27 nationalities represented among Ternium's staff, the company aims at consolidating a culture of inclusion. |
Over the last decade, Ternium has become a leading flat steel producer in Latin America by virtue of its main asset: a team of committed, innovative, industrious, diverse and highly qualified individuals. As of December 31, 2019, Ternium's team was composed of 20,061 employees, the majority of whom are distributed throughout our facilities and offices in the Americas. As Ternium has embarked on a new phase of growth, we rely on the talent and determination of our people to successfully shape our company in this stage.
Ternium has a human resources policy guiding our efforts in managing talent and attracting and retaining motivated employees. Ternium is an equal opportunity employer that embraces diversity in its different forms, including age, gender, nationality, race, ethnicity and creed. We believe that the coexistence of diverse perspectives helps our teams achieve rational solutions to challenges and more effectively and creatively accomplish their goals.
Over the years, Ternium has grown increasingly diverse and we will continue to welcome and adopt new and different viewpoints. Mexicans, Argentines, Brazilians
83% OVERALL SATISFACTION ON WORKING AT TERNIUM, ACCORDING TO A PULSE SURVEY OF SALARIED EMPLOYEES. 451 NEW INITIATIVES IN 2019 TO ENHANCE EMPLOYEES' WORKING EXPERIENCE. |
57. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
HEADCOUNT # OF EMPLOYEES |
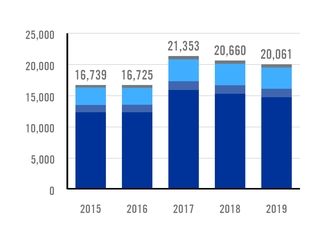
n Hourly employees n Hourly employee supervisors | n Salaried employees n Management |
and Colombians account for the largest share of the company's team members, yet a total of 27 nationalities are represented among Ternium's staff. Following the introduction of its Diversity Policy in 2018, the company launched a training program and the Lean In Circles initiative in 2019, to consolidate its culture of inclusion.
Tenium's Code of Conduct forbids unlawful discrimination in employment relations and grants all persons the right to apply for a position in the company or to be considered for a new position based on the skills required. In 2019, 63% of the company's management positions throughout the organization, encompassing senior managers, were held by nationals of the relevant country.
Labor Benefits and Work Climate
The countries in which Ternium has operations have in place labor regulations providing for basic labor benefits, such as life and disability insurance, health assistance, parental leaves and pension systems. In addition to legal labor benefits, Ternium has in place several other programs. The Flexible Working program offers employees access to on-demand office space located closer to their homes, aimed at reducing commuting time.
HEADCOUNT BY NATIONALITY DECEMBER 2019 |
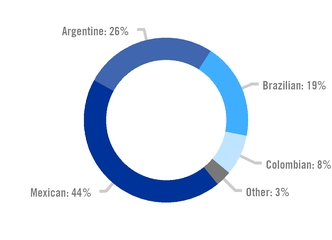
The Flexible Schedule program offers employees the option to accommodate their working schedules every Monday and Friday, year-round. In addition, the company has programs focused on clinical examination, disease prevention campaigns, sports and addictions control, scholarship and leisure programs for employees’ children, and loan programs for home improvement and special situations.
Since 2006, we periodically commission international consultancy agencies to conduct confidential surveys among Ternium's employees. We develop corporate and regional action plans based on the results of these surveys and tackle areas of opportunity to improve overall labor climate. In addition, we conduct pulse surveys in order to evaluate the effectiveness of the new initiatives implemented to enhance the working experience.
In 2019, we defined 451 new initiatives to improve the working experience at the company. Our latest poll, carried out in 2019 in pulse format, included 3,555 salaried employees across our operations and had a participation rate of 87%. The poll showed overall satisfaction by 83% of participants.
58. Ternium |
 |
Training is a key component of Ternium's strategy in its pursuit for performance excellence. |
Development and Training
Our constant pursuit of excellence in Ternium's operations requires a continuous search for improvement and innovation from our teams. We believe training is a key tool to achieve this goal. Over the last five years, each salaried employee has received an average of 47 hours per year of training and each hourly employee has received an average of 107 hours per year of training.
TERNIUM UNIVERSITY
In August 2019, the company inaugurated its corporate university. With the mission of learning, sharing and growing, Ternium University provides its employees with career development activities and programs. In addition, this project is expected to support the company's business transformation through its culture, to develop and shape the company's leadership, and to foster excellence in technical and functional skills and in the development of professional networks.
The project, launched in 2018, involved a team of 50 professionals from the Human Resources, Corporate Communication and Information Technology areas of the company. Ternium University is expected to be fully operational during 2021.
 |
Ternium's corporate university provides its employees with career development activities and programs. |
Ternium's programs for professionals spans a person’s entire career, from the initial level as a young professional to management levels. During 2019, 662 employees participated in different management academy programs.
Among these initiatives, the Leaders’ Development Program provides dedicated training for the company’s current and future leaders. The course is designed to enhance middle management leadership skills, as they advance their careers.
Approximately half of the company’s middle-level managers have taken part in the program. The leadership course is a joint effort with the EGADE Business School of Monterrey, Mexico, and the Torcuato Di Tella University of Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Our program for hourly employee supervisors includes a 40-hour course discussing the components of the supervisory role with a focus on hard and soft skills. This course has received the Excellence in Practice Award from the Association for Talent Development. A total of approximately 1,300 supervisors have completed the course since its launch in 2015.
59. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
HEADCOUNT BY GENDER %, DECEMBER 2019 |
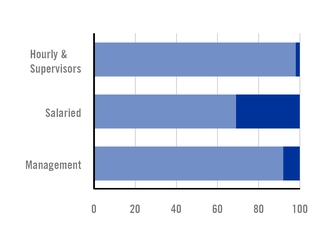
n Female n Male |
In addition, Ternium has a program designed for employees near retirement, and offers outplacement support to certain managers on a case-by-case basis.
Encouraging Innovative Initiatives
We strive to run safe operations, creating value for our customers, increasing productivity, enhancing the value chain's competitiveness, achieving a highly efficient and sustainable industrial system and establishing a long-term presence in our thriving communities. These tasks require our commitment to a continuous quest for excellence and improvement, and a culture of innovation throughout our organization. We believe that a fresh approach to old and new challenges and staying up-to-date with the fast-paced changes in technology are key elements required to achieve step changes in our activities, including health and safety management, environmental stewardship, energy efficiency, product and process development, training design and community improvement.
We encourage our employees to team up to develop new ideas and foster a culture of inclusion and diversity as a way to facilitate innovative results. During 2019, Ternium launched, under the company’s Diversity+ program, the Lean In Together initiative. The first stage of the program
HEADCOUNT BY AGE %, DECEMBER 2019 |
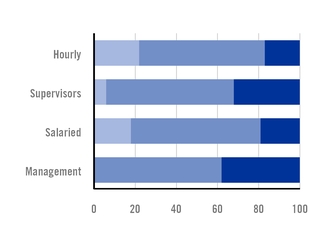
n More than 50 years n Between 30 and 50 years | n Less than 30 years |
Training for diversity. In 2019, 679 leaders of diverse nationalities, genders, cultures and generations were trained on the value of diversity in the workplace. |
60. Ternium |
EMPLOYEES TRAINING AVERAGE HOURS OF TRAINING PER YEAR AND EMPLOYEE. |
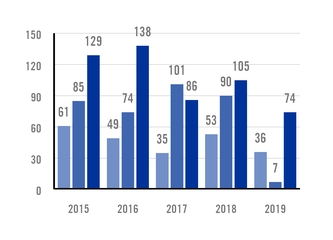
n Hourly Employees n Hourly employee supervisors n Salaried employees and management |
included ten pilot networks and 140 participants, with nine collaborative networks encompassing employees from the same countries and with different profiles, and one collaborative network encompassing managers from different countries. Participants raised their awareness on identity, unconscious biases, global perspective, cross-cultural leadership and inclusive spaces, and learned on the strategic management of differences.
Performance Management
The individual performance of each of Ternium's salaried employees is assessed annually through a formal performance assessment process. The results of the evaluation process drives different aspects of an employee's corporate life, such as compensation and career development, training requirements and performance improvement opportunities.
Ternium relies on a human resources IT system to manage its performance assessment processes. The system includes a set of measurable objectives for each employee under a 360-degree approach to the process. This is a key component of the performance assessment process as it ensures that everyone’s goals are in line
PERFORMANCE AND CAREER DEVELOPMENT REVIEW % OF WHITE COLLAR EMPLOYEES |
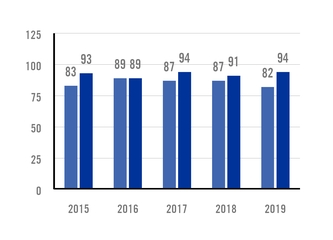
n Upward feedback n (Internal) client-customer opinion |
with the company’s objectives and guarantees transparency and fairness in the assessment of each employee’s work throughout the year.
The evaluation of the accomplishment of objectives is addressed through a combination of different views: the actual employee, internal customers, assessment committees and feedback meetings, as well as mid-year reviews. The system offers employees additional options to provide and receive assessments, including the possibility of submitting client-supplier opinions related to specific objectives.
In addition, the system includes an upward feedback tool for management positions accessible to the manager’s supervisor. Although this tool is not mandatory, 94% of our managers received feedback in 2019's performance assessments, an indication of the credibility achieved by Ternium´s procedures. A performance assessment process based on a measurable set of objectives is an important aspect of our Human Resources Policy. It aims at improving our employees’ working experience throughout their careers and their relationship with their supervisors.
61. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Ternium's 50th Anniversary |
Ternium's 50th Anniversary |
Back in 1969, the company inaugurated its Ensenada unit in Argentina, its first facility. The execution of this greenfield project and its start-up process, carried out by a trained and motivated team of young professionals, shaped Ternium's management profile. |
THE COMPANY'S FIRST FACILITY | |
11 MONTHS TOOK THE CONSTRUCTION OF THE ENSENADA UNIT'S GREENFIELD FACILITY | 2,000 PEOPLE WORKING ON THE FACILITIES' CONSTRUCTION SITE |
3 MONTHS TO GET THE MILL UP AND RUNNING | |
A 50 Year Legacy
The startup of a greenfield project constitutes a memorable milestone for any company. Even more so if it is the first one.
This is the history of Propulsora Siderúrgica's facility in Argentina, today the Ensenada unit, which back in 1969 gave shape to the vision and values of Agostino Rocca, founder of the Techint Group, and the group of young engineers who decided to embrace a unique industrial challenge.
Now, as it celebrates its 50th anniversary, its industrial legacy has expanded around the globe, reflecting the values and commitment of its founders and the group of talented engineers who, at a very young age, embraced the dream of creating an industrial colossus in what had been an isolated estuary.
The Challenge
The facilities included a cold-rolling mill and a port with an annual production capacity of 350,000 tons. From its inception, Propulsora's plant was envisioned to become a milestone in the development of the entire Techint Group. The development of the project, its construction and inauguration took 33 months.
For the company it was not only a complex technological challenge but a great responsibility, as Propulsora was expected to meet Argentina’s rapidly growing demand for steel. But building the mill was not the only challenge faced by the company at the time. More importantly, it had to bring together a team of talented professionals with the skills, passion and commitment to get it up and running.
The Team
“If you want new things to happen, you need to hire young people”, said Agostino Rocca at the time. The company chose to hire young people with little experience but with optimal development potential, people with a mental and professional structure prone to change, flexible, with a strong sense of integration between personal and business objectives.
62. Ternium |
Ternium's 50th Anniversary |
The company wanted to develop a creative environment where the weight of all individuals was given by their specific tasks and responsibilities and not by external symbols of authority.
Having placed such a huge capital in the hands of people with great enthusiasm and potential but with
really few developed competencies was definitively not a minor risk, but it meant a turning point in the
professional profile of the Techint Group.
Training
Even while works at the mill site continued, a group of close to 120 people traveled to Italy in early 1969 to be trained at an Italsider facility in Novi Ligure.
The experience abroad, in a foreign country, gave birth to Propulsora’s team spirit, in circumstances that led people to build stronger ties with their partners.
Construction of the Facility
The construction of the facilities was completed within just eleven months by Techint S.A.C.I., which was responsible for civil works, electrical and mechanical assembly, with more than 2,000 people working on the site.
This was a true EPC (Engineering, Procurement and Construction) project, which required an integrated and efficient interaction between the different functions.
Considering the speed at which decisions had to be made, observing tight schedules and rigid cost controls, the organizational autonomy was only possible thanks to the total harmony between all different participants.
Start-Up
As the “Novi Ligure team” came back to Ensenada in September 1969, they were surprised to see that the mill was already there. However, there was no time to contemplate the new industrial beauty.
 |
Ternium's first facility. 50 years later the company is positioned as Latin America's leading flat steel producer. |
 |
An eleven-month project built in what used to be an empty marshland. |
63. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Ternium's 50th Anniversary |
 |
Start-up. By the end of 1969, the Ensenada mill was up and running. |
 |
The Ensenada unit. It took 33 months from project design to the facilities' start-up. |
64. Ternium |
Ternium's 50th Anniversary |
The team had now to get it up and running in a record time of three months. And so they did.
On November 7, 1969, the annealing plant began operating and the opening of the port took place the following day. On November 13th, just 26 months after the main orders were issued, the first steel sheets cut at the plant began to leave the packing lines.
On December 23, the first coil in the scaling line was processed and the first cold-rolled coil by Propulsora was expected to leave the tandem the following day, which technically - and symbolically - took place on Christmas eve.
A few days later, in his year-end wishes to company employees, Roberto Rocca expressed:
“We have reached the end of this year (1969) with the satisfaction of having carried out the most important work of all that we have planned and promoted to date: Propulsora."
"We focus on it all our capacity, our passion and professional and entrepreneurial pride to fulfill our commitment to give the country a modern industrial plant that contributes to its economic development.”
“Everything has been possible for a unity of efforts, in which many qualities were combined: vision of the future, affection for the country, personal drive and eagerness for progress. Therein lays our success. In that imponderable predisposition you all have to get things done.”
 | |
" | |
We have reached the end of this year (1969) with the satisfaction of having carried out the most important work of all that we have planned and promoted to date: Propulsora.” Roberto Rocca President of the Techint Group between 1978 and 2001 | |
65. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Strengthening Ternium's Value Chain | |||
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
    | |
1,800 SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES PARTICIPATE IN THIS ENDEVOUR TO STRENGTHEN THEIR BUSINESSES AND TERNIUM'S VALUE CHAIN. | |
Goals | Measures | |
Promote a collaborative network to foster excellence performance | Engagement of universities and business schools | |
Engagement of industrial chambers | ||
Engagement of special-purpose governmental agencies | ||
ProPymes conferences | ||
Help small and medium-sized customers and suppliers grow | Training programs for managers, employees and workers | |
-Enhance competitiveness and foster capital expenditures | Assistance in the development of industrial projects and management tools | |
-Identify and pursue business opportunities | Endorsement of industrial projects before commercial banks, working capital financing | |
Assistance in the implementation of institutional projects | ||
Assistance in the development of commercial relationships | ||
66. Ternium |
Small and medium-sized enterprises in the steel industry value chain in Argentina are encouraged to expand their businesses abroad with the support of Propymes Exporta. This initiative offers industrial, commercial and financial support to help companies achieve their business goals, leveraging on their export potential. | ||||
Ternium offers support to small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) through a program that provides a variety of services, including training, industrial assistance, institutional assistance, commercial support and financial aid. With the participation of approximately 1,800 companies, our ProPymes program fosters the development of the industrial value chain in Mexico and Argentina. ProPymes has helped create an industrial network that encourages the professionalization and quest for excellence of SMEs, which, based on knowledge sharing, reciprocal learning and exchange of experiences, aims at the implementation along the whole value chain of the best practices utilized in the industry.
Why Should Ternium Help Other Companies?
Ternium believes that its role as a large industrial company in Latin America is to strengthen its value chain. The ProPymes program was first launched in Argentina in 2002, during a deep economic crisis that severely affected many companies in the steel industry value chain. It has been named after the acronym PYME, which in Spanish stands for SME. In Mexico, the program was introduced four years later.
ProPymes institutionalizes the cooperation between Ternium and the company’s small and medium-sized customers and suppliers. Ternium works with SMEs to
help them reach their potential, enhancing their professional, management and financial capabilities, and helping them participate competitively in both domestic and foreign markets. A strengthened value chain fosters, in turn, the development of industrial infrastructure at Ternium's main markets, with increased steel demand and enhanced competitiveness.
ProPymes Assistance Services
TRAINING
ProPymes designs and implements an annual training agenda. The course contents are continuously updated to offer our customers and suppliers the best available tools and management practices for their salaried and hourly employees, as well as for managers. Every year the program incorporates additional subjects to the curriculum to meet SMEs' increasingly sophisticated range of needs, as they advance their learning curves.
Training activities are performed in-house or at universities or business schools. During 2019, ProPymes has sponsored training courses for 5,300 attendants, who spent an aggregate 87,400 hours in class.
INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT
ProPymes' industrial assistance services focus on a broad array of issues from the use of automation technology, the
67. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
PROPYMES' SPONSORED INDUSTRIAL PROJECTS # OF PROJECTS |
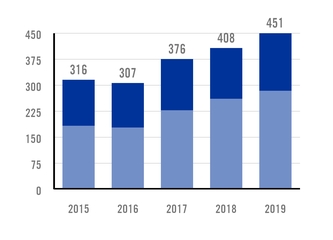
n Mexico n Argentina |
optimization of production facilities and quality certifications, to the development of environment, health and safety protocols and human resources management. During 2019, ProPymes assisted 451 SMEs with their industrial projects.
INSTITUTIONAL INITIATIVES
ProPymes institutional assistance helps SMEs develop strategies aimed at ensuring a level playing field in the local market, given the potential threat of increased unfairly traded imports.
Assistance initiatives include those for the setting of industry chambers, the development of technical standards for industrial products and those aimed
at improving SMEs competitiveness. In addition,
we help SMEs set their own corporate social programs through the implementation of a support program for technical educational institutes.
COMMERCIAL SUPPORT
ProPymes assists suppliers in the development of new products for Ternium and/or any of its affiliated companies. In addition, it assists SMEs in the development process required to become a supplier of large companies to gain new customers for automotive,
PROPYMES SPONSORED TECHNICAL SCHOOLS # OF SCHOOLS |
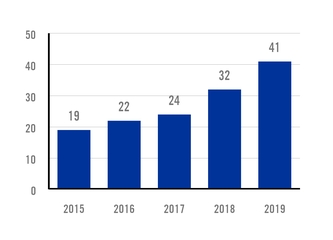
oil & gas and other industrial sectors.
ProPymes also offers SMEs the possibility to leveraging on the Techint Group's global network of commercial offices in order to enhance their market reach.
FINANCIAL ASSISTANCE
The financial assistance services aim at fostering investments to enhance productivity and increase SMEs' installed capacity. The scope of ProPymes assistance includes the development of the project, its budget and the application for commercial bank financing or government-sponsored low-cost financing instruments. Since its creation, the program has helped obtain financing or financed projects of Ternium's customers for an amount of $123 million.
Advancing the SMEs Agenda
SMEs making up Ternium’s value chain are key players
for the social integration of their communities, as they generate a substantial share of total industrial jobs
in Latin America. The ProPymes program plays an important role in advancing the SME policy agenda
in Mexico and Argentina.
Ternium organizes major events under the auspices of
68. Ternium |
Community technical schools are sponsored by small and medium-sized enterprises in the steel industry value chain in Argentina. This initiative, coordinated by ProPymes and inspired by Ternium's Technical Gene community program, aims at improving the infrastructure of technical educational institutes, and teachers and students training activities. | ||||
the ProPymes initiative, bringing SMEs' representatives together with government officials, economists and journalists to discuss the sector’s economic context and outlook. In Mexico, the ProPymes biannual event showcases awards for SMEs excelling in areas such as industrial safety, logistics services, delivery, raw material handling and other services. The occasion also includes a Supplier of the Year award. In Argentina, the event features several panels designed to allow SME executives share their experiences and lessons learned.
ECOSISTEMA PYME
Since 2017, the Argentine government sponsors the Ecosistema Pyme program, or SME Ecosystem,
which considers the ProPymes program a model to be replicated by other large companies in the support
of their sector's value chain.
In Argentina, the stories of SMEs that are part of Ternium’s ProPymes program appeared in video-narrations published in the web platform of one of the country’s largest media groups and have been widely circulated on social media. Different companies owners were featured sharing how their enterprises started and grew, the difficulties they had to overcome, and the potential they envision for the future.
 |
18th ProPymes' seminar in Argentina. |
69. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Helping Our Communities Thrive | |
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
    | |
   | |
$60 MILLION INVESTED IN THE LAST FIVE YEARS TO FOSTER EDUCATION AND LIFE QUALITY. | |
Goals | Measures | |
Foster education | Construction and operation of a technical school (ETRR in Pesquería) and sponsorship of other technical schools | |
-Achieve excellence in technical education | Maintenance and refurbishing of community schools | |
-Support schools and outstanding students | Implementation of a special education program for children | |
Financial support to high-school, undergraduate and graduate students | ||
Support initiatives that strengthen our communities | Funding of health care infrastructure and equipment | |
-Fund health care infrastructure and humanitarian initiatives | Construction and operation of a field hospital (COVID-19) | |
-Promote cultural activities | Building and donation of houses and a school (earthquake) | |
-Foster sport activities | Sponsorship of diverse cultural exhibitions and events | |
Arrangement of city races and other sport activities | ||
70. Ternium |
 |
Roberto Rocca Technical School in Pesquería, Mexico. In 2019, the first cohort of students graduated from the school after three years of study. |
Our community programs reflect over seven decades of the Techint Group's worldwide industrial tradition. The principle guiding our work is that an industrial project like ours can only be sustainable if community and industry grow together. In recent years, we have concentrated our community action on four main areas: education, culture, volunteer work and health. Our strategic programs were designed to be implemented at local level, taking into account the particular circumstances of each community where we operate.
We believe that education is the key to prosperous community growth and have developed educational programs covering the entire school cycle, from elementary to higher level, helping all children to fulfill their potential and become active contributors to society. In 2019, 70% of our $6,6 million community relations budget was invested in education.
As a multi-cultural and multi-lingual company, we enrich and broaden people’s cultural horizons in the communities where we work, fostering diversity and inclusion by promoting cultural activities.
We encourage our employees to volunteer for community activities aimed at helping those in need,
with a special focus on refurbishing schools, as a way of cultivating pride and integration in our communities.
With the aim of improving people's life quality and fostering welfare, we support health care initiatives mainly by funding improvements in the health care infrastructure of Ternium's communities. More recently, Ternium launched a special $5.5 million funding program to strengthen health care infrastructure to face the COVID-19 outbreak at its communities in Mexico, Argentina, Brazil and Colombia.
Developing High Standards of Technical Education
The Roberto Rocca Technical Schools program (ETRR, for its acronym in Spanish), which operates purpose-built schools, was launched to educate high school students from our communities using innovative teaching methods and the latest technology in both classroom and laboratory. The schools, named after one of the company’s founders, is dedicated to promoting technical education and enterprise, offering students different levels of scholarships, depending on their needs.
The first school, inaugurated in 2013 in the city of Campana, Argentina by our sister company Tenaris,
71. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
COMMUNITY PROGRAMS $ MILLION |
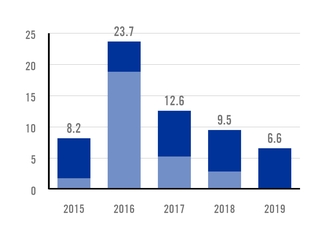
n Ongoing programs n Construction of Roberto Rocca Technical School in Pesquería, Mexico |
has a capacity of 420 students. In 2016, Ternium opened a second technical school, which now has 372 students in the town of Pesquería, Nuevo León, Mexico.
In 2019, both schools saw their first classes graduate after three years of study in Mexico and seven years in Argentina. Many of these students are the first in their families to finish high school and go on to university. Like their peers in European countries, ETRR Pesquería students receive 1,600 hours of teaching per year, as well as more than 600 hours of industrial internships.
In order to help students develop Industry 4.0 skills, we have adapted the Maker project-based-learning teaching methodology to encourage them to think in different ways, fostering innovation and teamwork, as well as other personal abilities including critical thinking and communication skills. In 2019, we trained 15 teachers to use this methodology; students produced 97 projects they subsequently exhibited, putting some into practice to benefit their local communities. ETRR students participated in the World Educational Robot Contest (WER) with one team participating at the international finals in Shangai, China.
SUPPORT IN NUMBERS |
$29 MILLION INVESTED IN OUR FLAGSHIP EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM, THE ROBERTO ROCCA TECHNICAL SCHOOL IN PESQUERÍA, MEXICO |
1,200 SCHOLARSHIPS FOR HIGH SCHOOL AND UNDERGRADUATE STUDENTS UNDER SEVERAL PROGRAMS |
We believe that academic excellence is fostered by gifted teachers who are truly committed to both students and the community. In 2015, the ETRR pioneered in Argentina a comprehensive teacher performance assessment system, involving student surveys, on-the-ground class observation, and school committee evaluation. The ability to benchmark and guide improvement is the cornerstone of our teacher development plan, which rewards performance, attendance, the use of technology and training.
During 2019, 23 teachers were evaluated and 3,777 training hours were provided in Mexico as part of their continuous development.
In October 2019, during the annual worldsteel assembly in Monterrey, Mexico, Ternium received
the Steelie Award for “Excellence in Education and Training” on account of the work done in the Pesquería ETRR. As creativity and self-expression
are essential to our students’ all-round development, we organized the second Literary Contest for the Roberto Rocca Technical School's network as part
of our literary activity program. The winning pieces were presented at the International Book Fair in Monterrey, Mexico.
72. Ternium |
TECHNICAL GENE PROGRAM # OF PARTICIPANTS |
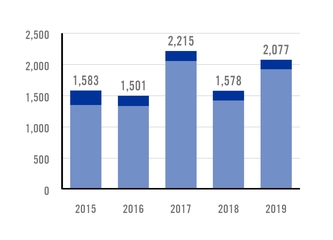
n Teachers n Students |
Strengthening Technical Education Community-Wide
The Technical Gene program provides support for infrastructure and equipment, as well as teacher training, school management and on-the-job training internships for high-school students, sharing teaching and learning practices, and concepts developed in the Roberto Rocca Technical Schools program.
It provides opportunities for high-school students in our local communities to develop industry 4.0 skills by offering them specific tools to guide their learning.
In addition to providing infrastructure and equipment, the focus of the program is to train students and bring schools closer to industry, an approach that also includes on-the-job internships. Furthermore, a project was launched in San Nicolás and Ramallo to improve maths teaching skills. 21 teachers at five technical high-schools participated in the project, causing a direct impact on 571 students.
The third edition of Technical Gene Makers was held in San Nicolás and 105 students participated and brainstormed innovative projects to add value to the local community.
AFTER SCHOOL PROGRAM PARTICIPATION # OF STUDENTS |
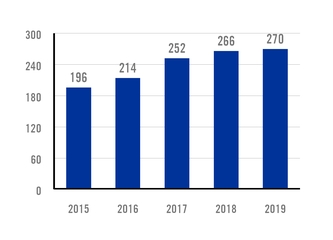
Quality Education for the Communities
Ternium has different programs aimed at improving skills and education in developing communities near its facilities. We organize workshop academies in Pihuamo, Aquila and Alzada in Mexico. In addition, through the AfterSchool program, we provide support to primary schools in San Nicolás de los Garza, Mexico, and in Ramallo, Argentina. The AfterSchool Program was designed for communities with considerable school dropout rates. Last year, in the two countries hosting the program, 270 children aged between six and twelve enrolled in these activities.
Focused on STEM subjects (Science, Technology, Engineering, Math), the program offers primary school children extra hours of quality education four days a week to encourage them to commit to learning and further their personal development in the longer term. During 2019, we strengthened the AfterSchool model with new maths content and related project-based learning methodologies. After just one year, the results showed students had improved their maths skills from those of a low level at a low-performing school to the
73. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
equivalent of a medium level at a mid-performing school, amounting to the progress of an entire year.
Participants not only improved their maths abilities but also developed other life skills and a sense of purpose after attending the program for several years: 84% of students improved their perseverance, 83% improved critical thinking, and more than 75% are keen to pursue STEM careers.
Encouraging Excellence Among High-School Students
Launched in 1976 in Argentina, the Merit Awards program was initially designed to benefit the children of Ternium's employees but has long since been extended to the wider community. It focuses on stimulating academic performance and commitment among high-school students living in our communities.
In 2019, we awarded 759 scholarships to outstanding students in six countries, including Brazil for the first time. In addition, we launched a pilot project in Brazil, for eligible students, for the on-line application to 60 high-school scholarships.
Roberto Rocca Education Program
The Roberto Rocca Education Program awards fellowships and scholarships to promote engineering and applied sciences studies at undergraduate and graduate level in countries where we have a major presence. In 2019, the program funded 15 fellowships for students pursuing for their PhDs at universities outside their country, and 305 scholarships for undergraduate students at universities in their home countries. In addition, the program was implemented for the first time in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
We also reinforced our relationships with universities based in the UK, The Netherlands and Germany, with two PhD fellows currently carrying out their industrial practices at our R&D centers and five visits from other PhD fellows. In addition, we held three webinars and are pursuing quarterly follow-up activities with each university.
Culture and Tradition to Foster Diversity and Integration
For Ternium and its sister companies in the Techint Group, art and culture are a source of innovation as well as a means of celebrating diversity and exploring
 |
Improving schools. 300 employees, teachers, graduates and relatives volunteered to enhance the Roberto Coelho municipal school in Santa Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. |
74. Ternium |
MERIT AWARDS # OF SCHOLARSHIPS |
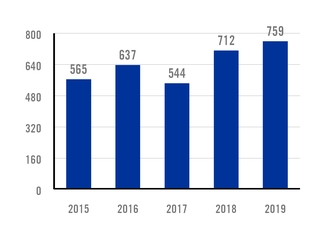
humanity. The cornerstone of our cultural activities is based on our association with the PROA Foundation, which in addition to its activities in the community in Buenos Aires, provides us with invaluable expertise and experience to guide us in the selection and development of content in our arts programs.
In 2019, Ternium earmarked 21% of its community budget for cultural activities in 3 countries. In 2019, together with the PROA Foundation, we organized 5 film festivals in Mexico and Argentina, attracting a total of 11.604 participants to 35 screenings. Also, under the guidance of the PROA Foundation, we collect and preserve photographic data recording the history of the locations and communities where we operate.
Volunteering: Making a Difference
We are committed to making a difference and strengthening a sense of pride in belonging to the communities where we operate. Ternium employees and their families regularly volunteer to improve local school infrastructure, joining students, their relatives, school teachers and neighbors in this effort. In 2019, a total of 1,878 volunteers in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Guatemala and Mexico joined efforts to transform schools, putting in 16,611 hours of volunteer
ROBERTO ROCCA EDUCATION PROGRAM # OF SCHOLARSHIPS |
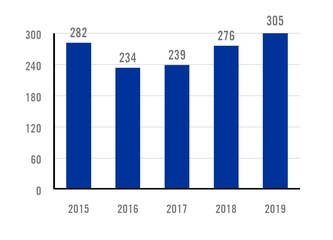
time. The activities involved Ternium employees working together with members of the local community to refurbish school buildings, lead classroom readings and share vocational talks to
students in schools in vulnerable areas, not only an opportunity to improve infrastructure but also to strengthen personal relationships.
During 2019, 191 houses and a high-school were delivered in the municipalities of Reforma de Pineda and Santiago Laollaga in Oaxaca, Mexico. In 2017, the area was hit by a 7.1-scale earthquake. This endeavor was funded by Ternium and sister companies in the Techint Group, as well as by their employees.
For almost three decades, Toni Ruttiman, who continues to be a source of inspiration for us at Ternium, has worked to unite communities. He has helped to bring together the lives of more than two million people in Latin America and South East Asia, by building suspension bridges with collaboration from those who then benefit from them. So far, he has built 835 bridges in 13 countries, with support from Ternium, which has donated 839 tons of material to his singular but far-sighted mission.
75. Sustainability Report 2019 |
A Comprehensive Approach to Value Creation | |
Making the difference. Ternium, its sister companies in the Techint Group and employees funded the construction of 191 houses and the rebuilding of a high-school in Oaxaca, Mexico, an area hit by a 7.1-scale earthquake in 2017. | ||||
Sports and a Healthy Lifestyle
As part of our drive to promote a healthy lifestyle, we organize the 10K Ternium annual local race in several locations, together with local institutions. In 2019, approximately 4,000 runners participated in the 15th edition of the 10K Ternium in San Nicolás, Argentina; 5,000 runners participated in the 11th edition of the race in Monterrey, Mexico; 1,500 runners participated in the 8th edition of the race in Colima, Mexico; 1,200 runners participated in the 2nd edition of the race in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; and 1,200 runners participated in the 2nd edition of the race in Villa Nueva, Guatemala.
In addition, we organize sport leagues involving schools in neighboring communities. Regarding health care initiatives, the company supports and funds a basic health care unit in Aquila, Mexico, and funds improvements in health care infrastructure in different countries. In addition, we organize health fairs, clinical examinations, and disease and addiction prevention campaigns.
SPECIAL FUNDING PROGRAM FOR COVID-19 OUTBREAK
In response to the COVID-19 outbreak at the end of
2019, we designed a consistent reinforcement plan together with the directors of key hospitals in each of Ternium's communities. The plan considered the age
of the local population and the availability of health care infrastructure, such as intensive care units (ICUs) and protective gear, among other medical equipment. In Monterrey, Mexico, Ternium has built in record time and is operating a field hospital, taking advantage of the operations of Clínica Nova, the company's local health care unit. The field hospital has 100 beds and 10 ICUs for people without health insurance.
In Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, the company has supplied 25 ICUs and ventilators to two local hospitals, and has partnered with Senai, a national network of technical schools, to repair out-of-use ventilators from local hospitals. In Ensenada, Argentina, Ternium supplied 100 beds to a field hospital. The company also supplied ICU equipment and protection gear for doctors. All-in-all, more than 90 ventilators, 1,700 medical equipment and 170,000 safety kits for health professionals were donated to 14 hospitals and health care facilities in four countries.
In addition, Ternium manufactured face masks at its
76. Ternium |
 |
Field hospital in Monterrey, Mexico. In the context of the COVID-19 outbreak, Ternium is very actively helping its communities face these difficult times. |
facilities and in the ETRR for doctors and first responders. Furthermore, the company offered support to local entrepreneurs for manufacturing ventilators, and to hospitals for adapting their facilities.
To foster the sharing of knowledge on treating COVID-19, we created a network of medical professionals alongside our sister company Tenaris. Seventy doctors from local communities in Mexico, Argentina and Brazil participated in a virtual meeting with their colleagues at Humanitas, an Italian network of hospitals controlled by the Techint Group. Through this platform, Humanitas' know-how on dealing with the COVID-19 outbreak in Italy is available at a public virtual campus.
Alongside the Fundación Hermanos Agustín y Enrique Rocca (Agustín y Enrique Rocca Brothers Foundation), and Tenaris, Ternium contributed 20,000 boxes of food for vulnerable families through the #SeamosUno project in Argentina. In addition, Ternium provided food support for 446 families of children participating at its education programs in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and for 44 families of students at the ETRR in Pesquería, Mexico.
FIELD HOSPITAL IN MONTERREY, MEXICO, TO FACE THE COVID-19 OUTBREAK |
100 BEDS IN A NEW FACILITY BUILT AND OPERATED BY TERNIUM TO STRENGTHEN THE COMMUNITY'S HEALTH CARE SYSTEM |
10 FULLY-EQUIPED ADDITIONAL UNITS FOR INTENSIVE CARE |
77. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
78. Ternium |
Commitment to Integrity | |
Integrity is key to Ternium's long-term sustainability. With ethical behavior and the observance of law as a core company value, we continuously work on building a corporate culture of transparency. | ||
64 ON-SITE TRAINING SESSIONS ON TERNIUM'S POLICY ON BUSINESS CONDUCT IN 2019. | 878 ON-SITE PARTICIPANTS FROM MEXICO, ARGENTINA, BRAZIL, COLOMBIA AND GUATEMALA. | 325 THIRD-PARTY EMPLOYEES COMPLETED MANDATORY TRAINING ON E-LEARNING. |
79. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Commitment to Integrity | |
Commitment to Integrity through Strong Corporate Governance • Audit committee (three independent directors) • Internal Audit Department reporting to the Chairman and the Audit Committee • Business Conduct Compliance Officer reporting to the CEO • Compliance department that oversees SOX certifications, related party transactions and conflict minerals • Employee training and accountability to ensure transparent behavior • Confidential channels to report non-compliant behavior | ||||
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS | |
 | |
Ternium S.A. is organized as a public limited liability company (société anonyme) under the laws of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The Company holds controlling stakes in steel companies operating in Latin America and the Southern United States. San Faustin S.A., the holding company of the Techint Group, an international group of companies, has a 62% indirect controlling interest in Ternium.
San Faustin also has controlling interests in Tenaris, a global supplier of steel pipes and related services mainly for the energy industry, which holds an additional 11% interest in Ternium; Tecpetrol, an oil and gas company; Techint, an engineering and
construction company; Tenova, a supplier of equipment and technology for iron mining and steel; and Humanitas, a network of hospitals in Italy.
The Company has an authorized share capital of a single class of 3.5 billion shares having a nominal value of $1.00 per share entitling one vote each. As of December 31, 2019, there were 2,004,743,442 shares issued and outstanding, of which 41,666,666 were held in treasury.
The Company’s ADSs are listed in the New York Stock Exchange. Each ADS represents ten shares. Holders of ADSs only have those rights that are expressly granted to them in the deposit agreement dated January 31, 2006, among the Company, The Bank of New York Mellon (formerly The Bank of New York), as depositary, and all owners and beneficial owners from time to time of ADRs of the Company. ADS holders may not attend or directly exercise voting rights in shareholders’ meetings, but may instruct the depositary how to exercise the voting rights for the shares which underlie their ADSs. Holders of ADSs maintaining non-certificated positions must follow instructions given by their broker or custodian bank.
80. Ternium |
Select Codes | Policies | Procedures | ||
Code of Conduct ––– Code of Conduct for Suppliers ––– Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers | Business Conduct ––– Transparency ––– Anti-Fraud ––– Securities Trading ––– Diversity and Work Environment Free of Harassment ––– Human Rights | Disclosure Procedure (relevant information) ––– Transactions Between Related Parties ––– Conflict Mineral Disclosure | ||
Our articles of association provide that our annual ordinary general shareholders’ meetings shall take place in Luxembourg, or in a foreign country whenever circumstances of force majeure take place, within six months from the end of the previous financial year. There are no limitations currently imposed by Luxembourg law on the rights of non-resident shareholders to hold or vote the Company’s shares.
The Company’s Board of Directors is currently comprised of nine directors (eight male and one female). Four directors are independent under the articles of association and SEC regulations applicable to foreign private issuers. The Board of Directors has an Audit Committee consisting of three independent members. The charter of the Audit Committee sets forth, among other things, the Audit Committee’s purpose and responsibilities, which include the responsibility to review material transactions with related parties to determine whether their terms are consistent with market conditions or are otherwise fair to the Company and/or its subsidiaries. In addition, the Audit Committee reports to the Board of Directors on the adequacy of the systems of internal control over financial reporting.
Ternium has adopted a Code of Conduct incorporating guidelines and standards of integrity and transparency that apply to all directors, officers and employees. The Code of Conduct is periodically reviewed to bring it up to date with the latest trends and incorporate new provisions, if applicable.
In addition, the company has adopted a Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers, a Transparency Policy governing relationships with third parties, a Policy on Business Conduct, a Code of Conduct for Suppliers, an Anti-fraud Policy, a Policy on Securities Trading, a Human Rights Policy and a Policy on Diversity and Work Environment Free of Harassment.
All members of Ternium's Board of Directors, all of its senior managers and 99.7% of its white collar employees (salaried employees and managers, excluding hourly employee supervisors) have acknowledged and committed to abide by its Code of Conduct and Policy on Business Conduct.
Ternium has an Internal Audit area that reports to the Chairman of the Board of Directors and, with respect to internal control over financial reporting, to the Audit
81. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Commitment to Integrity | |
Committee. The Internal Audit area evaluates and reassures the effectiveness of internal control processes, risk management and governance.
Risk Management
Ternium has an established process of risk identification and management. At the helm is the company's Critical Risk Committee (CRC), which assists the CEO on the subject. While management is responsible for identifying and managing risks, the CRC facilitates the identification and assessment of critical risks, the development of mitigating actions and the monitoring of action plans. Critical risks are escalated through the usual reporting lines and decision-making is the responsibility of managers.
The CRC focuses on risks considered critical to the company’s assets, operations or reputation. Ternium has categorized risks according to the potential area impacted, the likelihood of their occurrence and the severity of an eventual impact. The main identified risks include major accidents impacting our operations, cybercrime and environmental accidents. Recently, the
CRC has focused its attention on the main actions and
mitigation plans to tackle the consequences of the COVID-19 outbreak to ensure business continuity.
Business Conduct Compliance Program
Ternium has developed a Business Conduct Compliance Program with the objective to prevent and mitigate bribery and corruption risks. The Compliance Program involves white collar employees and is aimed at promoting the implementation of best practices in business conduct internally and also regarding the relations with customers, suppliers, state-controlled entities and other third parties.
Ternium has appointed a Business Conduct Compliance Officer reporting to the CEO of the Company, who has responsibility for identifying and mitigating corruption risks and fostering a culture of ethical and transparent conduct, and for designing, implementing and supervising the Compliance Program aligned with the requirement of applicable national and international laws against corruption and bribery, such as the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA).
 |
Code of Conduct for Suppliers. Ensuring that governance standards are in place, including ethics, health, safety, human rights and environmental stewardship commitments. |
82. Ternium |
All members of Ternium's Board of Directors, all of its senior managers and 99.7% of its white collar employees have acknowledged and committed to abide by its Code of Conduct and Policy on Business Conduct as of December 31, 2019. | |||
The Business Conduct Compliance team has local presence in the main locations where the company has businesses. The Business Conduct Compliance Program is focused on preventive measures like risk assessment, normative design, communication, advisory, training, certification, monitoring and auditing, including third parties. The function also includes disciplinary actions, remediation and benchmarking. Activities are implemented based on a periodic risk assessment that enables us to identify key factors to be stressed on, particularly at training and risk prevention sessions, based on the employees' likely exposure to conflicting situations. Consequently, only white collar employees participate in the program, while hourly employees and their supervisors are excluded.
Ternium’s Code of Conduct and Policy on Business Conduct clearly define that any corrupt payment is strictly prohibited and will not be tolerated; they also include specific guidelines regarding due diligence when hiring third-parties that act on behalf of Ternium. Charitable and political contributions, as well as hospitality expenses to third parties (meals, gifts and business trips) are regulated by internal procedures. Facilitating payments are forbidden. Communication is essential to build an ethical culture.
Ternium maintains regular communications with its directors, senior managers and employees in order to raise their awareness and keep them alert on possible corruption risks, and to remind them of the applicable principles and regulations. This program includes top-down messages, management meetings, newsletters, articles and announcements on the company's intranet.
The company encourages active participation of all areas, emphasizing the importance of asking for guidance in case of red flags or ambiguous situations.
Ternium has defined specific procedures for hiring professional services providers that act on behalf of or otherwise represent the company before governmental entities, including those retained to assist in obtaining permits or licenses, customs brokers, advisers and law firms. These procedures include a due diligence process, internal authorizations and contract provisions to ensure third-party’s commitment to Ternium’s anti-bribery policies.
Monitoring procedures and audits are carried out regularly to validate the effective implementation of the Compliance Program and the investigation of any conduct contrary to the Policy on Business Conduct or its principles.
83. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Commitment to Integrity | |
 |
Training Program for Third-Party Employees. Ternium's anti bribery training program also reaches third parties that represent or act on behalf of the company. |
Training on Anti-Bribery Policies and Procedures
Ternium has implemented an extensive training program on anti-bribery policies and procedures for its white collar employees. This program enables the company's senior management to engage the
organization behind Ternium's ethical commitment, with a clear set of guidelines and by sharing their values. All white collar employees participate in an on-line mandatory training program and, according to their level of exposure, in an on-site training program as well. 98.2% of Ternium's white collar employees have completed the mandatory training course on the company's Policy on Business Conduct in e-learning format. In 2019, Ternium delivered 64 on-site training sessions to 878 employees in Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, Colombia and Guatemala.
Our anti-bribery training program also reaches third parties that represent or act on behalf of Ternium. 325 third-party employees have completed Ternium's mandatory training program on corruption prevention, which has been implemented in e-learning format.
Code of Conduct for Suppliers
Ternium purchases most of its supplies through Exiros, a specialized procurement company whose ownership we share with Tenaris. Ternium’s suppliers undergo, through Exiros, a rigorous process of selection to ensure governance standards are in place, in line with applicable laws and regulations and our Code of Conduct for Suppliers, which includes, among other items, ethical behavior, compliance with the law, and health, safety, human rights and environmental stewardship commitments.
Compliance Line
Ternium established and encourages the use of a web-based confidential Compliance Line. The company’s compliance line serves as a channel for confidential communication and is available to all employees, suppliers, customers and other stakeholders who wish to report all types of alleged breaches of the Code of Conduct and its principles. Ternium's Compliance Line is available in Spanish, Portuguese and English.
84. Ternium |
 |
A Transparency Policy governs the relationships with third parties. |
Both the identity of the individual who reports an issue as well as the issue itself are treated in a strictly confidential manner, to the extent permitted by relevant legislation. Anonymous reporting is also possible. Internal Audit, which is independent from all operational areas, analyzes all reports received and is supervised by the Audit Committee for issues related to financial reporting.
Ternium implements the necessary actions to avoid retaliation against those who use the Compliance Line in good faith. In 2019, 46% of analyzed complaints ended up in disciplinary actions, including dismissals and termination of commercial relationships. The reports have also helped to improve the company’s internal control environment. Although complaints can be anonymous, in 52% of cases the complainants have identified themselves.
COMPLIANCE LINE |
46% OF ANALYZED COMPLAINTS ENDED UP IN DISCIPLINARY ACTIONS. |
24/7 ON-LINE ACCESS IN SPANISH, PORTUGUESE AND ENGLISH. |
Shareholders' Compliance Line
In addition, Ternium has a web-based confidential channel for investors to communicate their concerns directly to the company's Audit Committee, which is composed of independent directors. All communications received through the Shareholders' Compliance Line are reviewed by our Internal Audit Director. The status of all concerns received through the Shareholders' Compliance Line is reported to the company's Audit Committee.
85. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Board of Directors and Senior Management | |
Board of Directors | Senior Management | |||
Chairman | Paolo Rocca | Chief Executive Officer | Máximo Vedoya | |
Vice-Chairman | Daniel Novegil | Chief Financial Officer | Pablo Brizzio | |
Ubaldo Aguirre (*) | Ternium Mexico | César Alejandro | ||
Roberto Bonatti | President | Jiménez | ||
Carlos Condorelli | ||||
Vincent Decalf (*) | Ternium Argentina | Martín Berardi | ||
Gioia Ghezzi (*) | President | |||
Adrián Lajous (*) | ||||
Gianfelice Rocca | Ternium Brasil | Marcelo Chara | ||
President | ||||
Secretary | Arturo Sporleder | |||
International Business Unit | Héctor Obeso | |||
President | Zunzunegui | |||
Audit Committee | Planning and Global | Oscar Montero | ||
Business Development | ||||
Chairman | Vincent Decalf (*) | General Director | ||
Ubaldo Aguirre (*) | ||||
Adrián Lajous (*) | Engineering, Industrial | Pablo Hernán Bassi | ||
Coordination and EHS | ||||
(*) Independent Directors | Director | |||
Quality Director | Rubén Herrera | |||
Chief Information Officer | Roberto Demidchuk | |||
Human Resources | Rodrigo Piña | |||
Director | ||||
86. Ternium |
Investor Information | |
Investor Relations and Compliance Director | IR Inquiries | |
Sebastián Martí | TERNIUM Investor Relations | |
Phone: +54 11 4018 8389 | ||
U.S. toll free: 866 890 0443 | ||
Luxembourg Office | ADS Depositary Bank | |
26, Boulevard Royal - 4th floor | Bank of New York Mellon | |
L2449 - Luxembourg | BNY Mellon Shareowner Services | |
Luxembourg | P.O. Box 505000 | |
Phone: +352 2668 3152 | Louisville, KY 40233-5000 | |
Fax: +352 2659 8349 | ||
Stock Information | ||
New York Stock Exchange (TX) | ||
CUSIP Number: 880890108 | ||
Internet | ||
www.ternium.com | ||
87. Sustainability Report 2019 |
 |
88. Ternium |
GRI and UN Global Compact Information |
89. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
Ternium's Sustainability Report for the year 2019
follows the core option of the reporting levels of the Global Reporting Initiative standard.
Materiality Analysis for Ternium's Sustainability Report
Ternium's sustainability report’s content was redefined according to the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) principles of Stakeholder Inclusiveness, Sustainability Context, Materiality and Completeness. A Materiality Analysis was carried out according to the GRI four-step process that an organization may go through in order to define the document’s specific content.
Key economic, social and environmental topics were identified through a combination of industry research and benchmarking, international standards and priority subjects (Identification), and then prioritized through a stakeholder consultation process that compiled a total of 1256 responses from employees, suppliers, customers, community organizations, business associations, investors, press, and academic institutions (Prioritization). To conclude the selection of material topics, the results were examined considering the company’s long-term strategy and the programs implemented, resulting in a Materiality Matrix that combines both perspectives (Validation).
MATERIALITY MATRIX
The Materiality Matrix in the following page presents the economic, environmental and social topics that were defined as a priority to include in our 2019 Sustainability Report. They are informed according to GRI Standard core option of the reporting levels throughout the document and, in order to facilitate access, indexed in the following sections.
SIGNIFICANT PARTICIPATION IN TERNIUM'S MATERIALITY SURVEY |
1,300 STAKEHOLDERS SHARED THEIR PRIORITY PERCEPTIONS ABOUT TERNIUM'S BUSINESS. |
22 TOPICS RANKED WITHIN THREE CATEGORIES: ECONOMIC, SOCIAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL. |
90. Ternium |
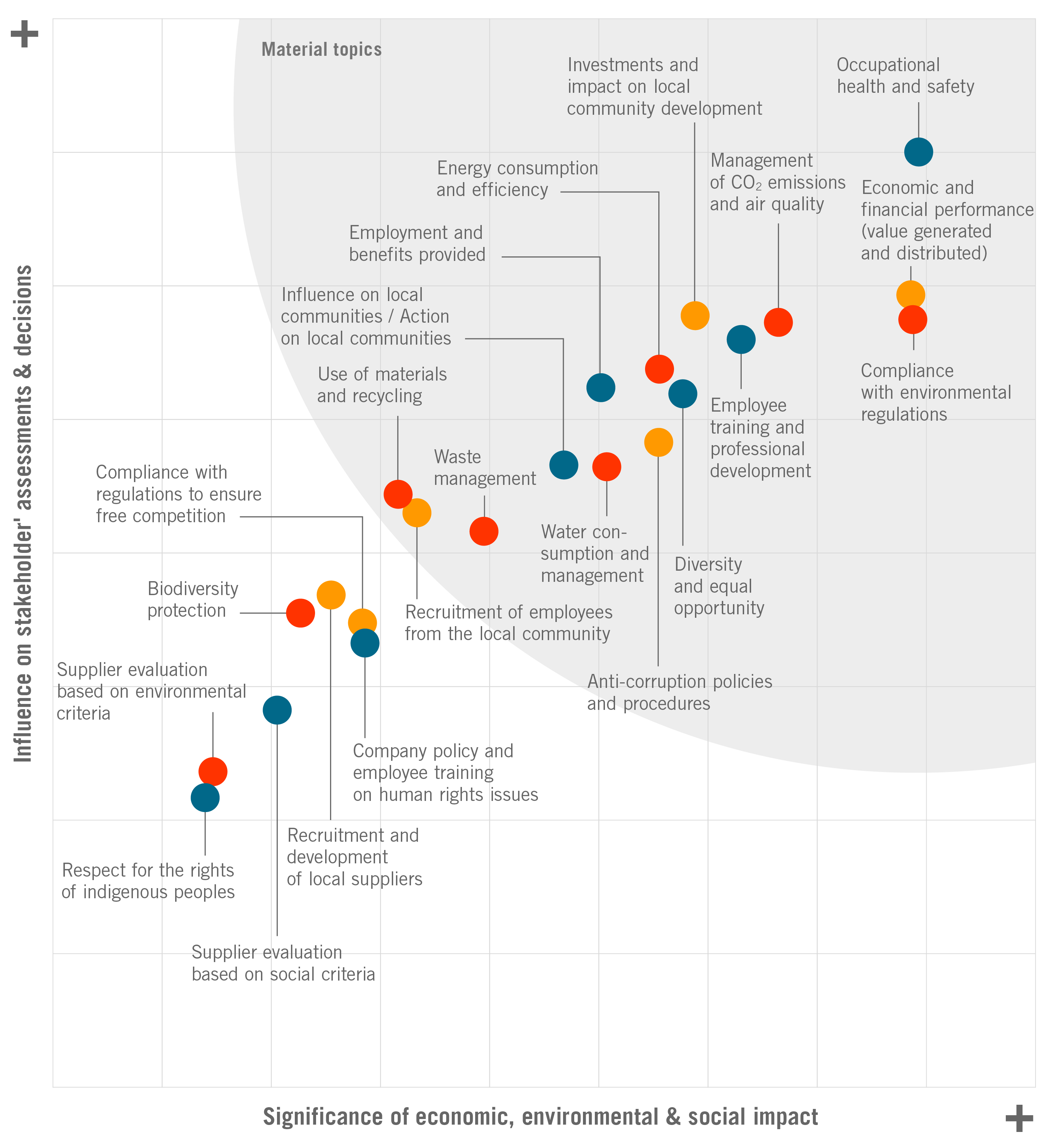 |
–––––––––––––––– • Economic topics • Environmental topics • Social topics |
91. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
GRI Index | ||||||
Topic | GRI Standard | GRI Topic | Page | |||
General Disclosures | ||||||
Organization Profile | GRI 102-1 | Name of the organization | 3 | |||
GRI 102-2 | Activities, brands, products, and services We do not sell products that are banned in certain markets or that were the subject of stakeholder questions or public debate. | 7-13 | ||||
GRI 102-3 | Location of headquarters Principal executive offices | 87 | ||||
GRI 102-4 | Location of operations | 10-11 | ||||
GRI 102-5 | Ownership and legal form | 79-85 | ||||
GRI 102-6 | Markets served | 7-13 | ||||
GRI 102-7 | Scale of the organization | 7-13 | ||||
GRI 102-8 | Information on employees and other workers | 56-61 | ||||
GRI 102-9 | Supply chain | 10-11 22-33 See 20-F 2019 | ||||
GRI 102-10 | Significant changes to the organization and its supply chain | 10-11 22-33 See 20-F 2019 | ||||
GRI 102-11 | Precautionary Principle or approach | 4-5 | ||||
GRI 102-12 | External initiatives | 4-5 | ||||
GRI 102-13 | Memberships of associations | 22-33 | ||||
Strategy | GRI 102-14 | Statement from the most senior decision-maker | 15-17 34-37 | |||
Ethics and integrity | GRI 102-16 | Values, principles, standards and norms of behavior | 79-85 | |||
Governance | GRI 102-18 | Governance structure | 79-85 98-100 | |||
Stakeholder engagement | GRI 102-40 | List of stakeholder groups | 90 | |||
GRI 102-41 | Collective bargaining agreements | 97 | ||||
GRI 102-42 | Identifying and selecting stakeholders | 19-21 90 | ||||
GRI 102-43 | Approach to stakeholder engagement | 90-91 | ||||
GRI 102-44 | Key topics and concerns raised | 90-91 | ||||
Reporting Practices | GRI 102-45 | Entities included in the consolidated financial statements | See 20-F 2019 | |||
GRI 102-46 | Defining report content and topic Boundaries | 4-5 | ||||
GRI 102-47 | List of material topics | 90-91 92-94 | ||||
92. Ternium |
GRI Index (cont.) | ||||||
Topic | GRI Standard | GRI Topic | Page | |||
GRI 102-48 | Restatements of information | See 20-F 2019 | ||||
GRI 102-49 | Changes in reporting | 4-5 | ||||
GRI 102-50 | Reporting period | 4-5 | ||||
GRI 102-51 | Date of most recent report: 2019-03-19 | |||||
GRI 102-52 | Reporting cycle: Annual | |||||
GRI 102-53 | Contact point for questions regarding the report | 87 | ||||
GRI 102-54 | Claims of reporting in accordance with the GRI Standards | 90-91 | ||||
GRI 102-55 | GRI content index | 92-94 | ||||
GRI 102-56 | External assurance At the time of the report, external assurance is not mandatory | |||||
Material Topic | ||||||
Economic Performance | GRI 201-1 | Direct economic value generated and distributed* | 19-21 | |||
GRI 202-2 | Proportion of senior management hired from the local community | 56-61 | ||||
GRI 203-1 | Infrastructure investments and services supported | 22-33 46-55 | ||||
Ethics and integrity | GRI 205-2 | Communication and training about anticorruption policies and procedures | 79-85 | |||
Environmental topics | GRI 301-2 | Recycled input materials used | 46-55 95-96 | |||
GRI 302-3 | Energy intensity | 46-55 95-96 | ||||
GRI 303-1 | Interactions with water as a shared resource | 46-55 | ||||
GRI 303-2 | Management of water discharge-related impacts | 46-55 | ||||
GRI 303-3 | Water recycled and reused | 46-55 95-96 | ||||
GRI 305-4 | GHG emissions intensity | 46-55 | ||||
GRI 306-2 | Waste by type and disposal method | 46-55 95-96 | ||||
GRI 307-1 | Non-compliance with environmental laws and regulations | 46-55 | ||||
Social topics | GRI 401-2 | Benefits provided to fulltime employees that are not provided to temporary or part-time employees | 56-61 | |||
GRI 403-1 | Occupational health and safety management system | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-2 | Hazard identification, risk assessment, and incident investigation | 38-45 | ||||
93. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
GRI Index (cont.) | ||||||
Topic | GRI Standard | GRI Topic | Page | |||
GRI 403-3 | Occupational health services | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-4 | Worker participation, consultation, and communication on occupational health and safety | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-5 | Worker training on occupational health and safety | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-6 | Promotion of worker health | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-7 | Prevention and mitigation of occupational health and safety impacts directly linked by business relationships | 38-45 | ||||
GRI 403-8 | Workers covered by an occupational health and safety management system | 100 | ||||
GRI 404-1 | Average hours of training per year per employee | 100 | ||||
GRI 404-2 | Programs for upgrading employee skills and transition assistance programs. | 56-61 | ||||
GRI 404-3 | Percentage of employees receiving regular performance and career development reviews | 100-101 | ||||
GRI 405-1 | Diversity of governance bodies and employees | 97-100 | ||||
GRI 413-1 | Operations with local community engagement, impact assessments, and development programs | 70-77 | ||||
*“Direct Economic Value Generated” equals net sales plus interest income, proceeds from the sale of property, plant & equipment, other operating income, equity in earnings of associated companies and inflation adjustment results, less other financial losses. “Employees” equals labor costs. “Taxes” equals current income tax expense plus cost of sales and SG&A taxes, less the effect of changes in tax law. “Suppliers” equals cost of sales plus SG&A, less labor costs, depreciation of property, plant and equipment, amortization of intangible assets, allowance for obsolescence, cost of sales and SG&A taxes, R&D expenditures and community investments ($6.6 million). “Capital Providers” equals dividends paid in cash to company's shareholders and non-controlling interest, plus interest expense. | ||||||
94. Ternium |
Historical Data
In this section, Ternium compiled the historical data and additional information related to the selected environmental and social topics for its 2019 Sustainability Report, according to the materiality
matrix. Historical data related to the selected economic topics has been compiled in the table on page 33. Also, the company compiled in this section additional data that it deemed relevant to disclose.
Environmental Topics | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
Environmental and Energy Management Systems | |||||||||||
% of Employees and Contractors Working in Registered Production Facilities | % | 74.5% | 97.4% | 97.9% | |||||||
% of steel produced under ISO 14001 certificated facilities | % | 58% | 100% | 100% | |||||||
% of steel produced under ISO 50001 certificated facilities | % | 42% | 42% | 63% | |||||||
Mining operations certified with ISO 14001 | % operations | 50% | 50% | 100% | |||||||
Investment in Environment and Energy | $ million | 70.8 | 73.1 | 69.5 | |||||||
Energy and Emissions | |||||||||||
Energy intensity | [GJ/ton crude steel] | 21.8 | 21.1 | 21.7 | |||||||
Emission intensity | [t CO2/ton crude steel] | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.8 | |||||||
Direct Emission - scope 1 | [t CO2/ton crude steel] | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.6 | |||||||
Energy upstream emissions - scope 2 | [t CO2/ton crude steel] | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | |||||||
Other upstream emissions - scope 3 | [t CO2/ton crude steel] | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||
Water and Effluents* | |||||||||||
Subsurface water intake | thousand cubic meters | 10,742 | 10,040 | 9,439 | |||||||
Provision from third parties treated water | thousand cubic meters | 3,683 | 4,357 | 4,229 | |||||||
Provision from municipality | thousand cubic meters | 59 | 62 | 41 | |||||||
Provision from municipal sewage | thousand cubic meters | 3,142 | 3,422 | 3,093 | |||||||
95. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
Environmental Topics (cont.) | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
Internal recycled water | thousand cubic meters | 1,740 | 1,682 | 1,390 | |||||||
Water withdrawal intensity for Mexican steel shops | [m3/ ton crude steel] | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.3 | |||||||
Fresh water | millions m3 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 8.8 | |||||||
Other water | millions m3 | 10.7 | 10.0 | 9.4 | |||||||
*The information regarding water and effluents is only reported for the production facilities in Mexico placed in areas of water-scarce | |||||||||||
Materials and waste | |||||||||||
Material Efficiency | % | 99.7% | 99.6% | 99.6% | |||||||
Steel scrap recycled | million tons | 2.5 | 2.9 | 2.8 | |||||||
Co Products* | million tons | 2.8 | 5.0 | 4.8 | |||||||
Recycled input materials used (steel scrap/new steel)* | % | 33% | 27% | 27% | |||||||
Blast Furnace slag to cement industry* | million tons | 1.2 | 1.9 | 1.7 | |||||||
MixRock® to cement industry | thousands tons | 89.8 | 94.4 | 86.0 | |||||||
Annual weight of tailings waste (mining) | million tons | 4.1 | 4.6 | 4.5 | |||||||
Accumulated total weight of tailings waste (mining) | million tons | 61.2 | 75.4 | 79.9 | |||||||
Hazardous and Non hazardous Waste sent to Landfill | thousands tons | 34.5 | 68.3 | 60.3 | |||||||
Hazardous and Non hazardous Waste sent to co-processing | thousands tons | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |||||||
*Blast furnace from Rio de Janeiro unit was incorporated in September 2017 | |||||||||||
Waste by type and disposal method The disclosure between hazardous and non hazardous wastes, was not available for all Ternium operations. It will be included in the 2020 Sustainability Report. | |||||||||||
96. Ternium |
Social Topics | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
Headcount | |||||||||||
Management | # of People | 466 | 478 | 494 | |||||||
Salaried | # of People | 3,508 | 3,478 | 3,402 | |||||||
Hourly | # of People | 15,977 | 15,377 | 14,808 | |||||||
Supervisors | # of People | 1,402 | 1,327 | 1,357 | |||||||
Total | # of People | 21,353 | 20,660 | 20,061 | |||||||
Employees covered by collective bargaining agreements* | % | 70% | 70% | 68% | |||||||
*Percentage of total employees covered by collective bargaining agreements for the year 2017 does not consider headcount from Brazil's facility | |||||||||||
Diversity of governance bodies and employees | |||||||||||
Management by gender, age and nationality | |||||||||||
Male | % | 92% | 92% | 92% | |||||||
Female | % | 8% | 8% | 8% | |||||||
30-50 years old | % | 60% | 61% | 62% | |||||||
over 50 years old | % | 40% | 39% | 38% | |||||||
Argentine | % | 30% | 29% | 29% | |||||||
Mexican | % | 45% | 48% | 49% | |||||||
Brazilian | % | 16% | 14% | 14% | |||||||
Colombian | % | 4% | 4% | 3% | |||||||
Other Nationality | % | 5% | 5% | 5% | |||||||
Salaried by gender, age and nationality | |||||||||||
Male | % | 69% | 69% | 69% | |||||||
Female | % | 31% | 31% | 31% | |||||||
under 30 years old | % | 19% | 19% | 18% | |||||||
97. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
Social Topics (cont.) | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
30-50 years old | % | 63% | 62% | 63% | |||||||
over 50 years old | % | 18% | 19% | 19% | |||||||
Argentine | % | 19% | 20% | 18% | |||||||
Mexican | % | 45% | 47% | 49% | |||||||
Brazilian | % | 21% | 20% | 19% | |||||||
Colombian | % | 9% | 8% | 7% | |||||||
Other Nationality | % | 6% | 6% | 6% | |||||||
Hourly by gender, age and nationality | |||||||||||
Male | % | 98% | 98% | 98% | |||||||
Female | % | 2% | 2% | 2% | |||||||
under 30 years old | % | 25% | 24% | 22% | |||||||
30-50 years old | % | 58% | 60% | 61% | |||||||
over 50 years old | % | 16% | 17% | 17% | |||||||
Argentine | % | 29% | 28% | 27% | |||||||
Mexican | % | 43% | 44% | 43% | |||||||
Brazilian | % | 20% | 19% | 19% | |||||||
Colombian | % | 7% | 7% | 8% | |||||||
Other Nationality | % | 2% | 2% | 2% | |||||||
Supervisors by gender, age and nationality | |||||||||||
Male | % | 98% | 98% | 98% | |||||||
Female | % | 2% | 2% | 2% | |||||||
under 30 years old | % | 6% | 7% | 6% | |||||||
30-50 years old | % | 62% | 60% | 62% | |||||||
98. Ternium |
Social Topics (cont.) | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
over 50 years old | % | 32% | 33% | 32% | |||||||
Argentine | % | 28% | 29% | 26% | |||||||
Mexican | % | 50% | 53% | 54% | |||||||
Brazilian | % | 15% | 9% | 11% | |||||||
Colombian | % | 5% | 6% | 6% | |||||||
Other Nationality | % | 3% | 3% | 3% | |||||||
As of the date of this report, the Board of Directors has 9 members, one of them is a woman. Regarding distribution by age, all of them are over 50 years old. The distribution by nationality is the following: 4 of them are Italian citizens, 3 of them are Argentine citizens, 1 is a French and Luxembourg citizen and 1 is a Mexican citizen. The Senior Management is composed by 11 members, all of them are male. The distribution by age is the following: 3 of them are in the range of 30-50 years old and 8 of them are over 50 years old. The composition by nationality is the following: 9 of them are Argentine citizens and 2 of them are Mexican citizens. | |||||||||||
Proportion of top management hired from the local community | |||||||||||
Country | |||||||||||
Mexico | % | 44% | 42% | 41% | |||||||
Brazil | % | 40% | 64% | 62% | |||||||
Argentina | % | 100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||
Colombia | % | 50% | 50% | 50% | |||||||
Average hours of training per year per employee | |||||||||||
Management | Hs/per year | 37 | 53 | 36 | |||||||
Salaried | Hs/per year | 35 | 53 | 36 | |||||||
Hourly | Hs/per year | 86 | 105 | 74 | |||||||
Supervisors | Hs/per year | 101 | 90 | 7 | |||||||
Total | Hs/per year | 78 | 94 | 62 | |||||||
Male | Hs/per year | 81 | 97 | 64 | |||||||
Female | Hs/per year | 37 | 51 | 40 | |||||||
Performance and career development reviews | |||||||||||
Management & Salaried (M&S) | % | 97% | 93% | 97% | |||||||
Hourly | % | 42% | 47% | 54% | |||||||
99. Sustainability Report 2019 |
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | |
Social Topics (cont.) | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
Supervisors | % | 97% | 97% | 98% | |||||||
Upwardfeedback (M&S) | % | 94% | 91% | 94% | |||||||
Client-Customer opinion (M&S) | % | 87% | 87% | 82% | |||||||
Health and Safety | |||||||||||
Lost time injuries frequency rate | day-loss injuries/per million hours worked | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.8 | |||||||
Injuries frequency rate | quantity/million hours worked | 3.4 | 3.0 | 2.7 | |||||||
Safety training hours | # hours per year | 586,240 | 564,341 | 487,649 | |||||||
Safety training hours participation | # of employees and contractors | 12,116 | 18,609 | 15,666 | |||||||
Safety hours program walks | # of sessions | 128,463 | 116,347 | 147,093 | |||||||
Safety hours program participation | # of employees and contractors | 842 | 1,016 | 1,632 | |||||||
Ten Life-Saving Rules compliance audits | # per year | 17,409 | 29,907 | 42,788 | |||||||
Health and Safety audits | # per year | 132,246 | 171,410 | 199,772 | |||||||
Positive approaches* | # per year | 43,193 | 57,024 | 106,704 | |||||||
H&S System Coverage | % of employees and contractors | 100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||
H&S System Coverage (internally audited) | % of employees and contractors | 100% | 100% | 100% | |||||||
H&S System Coverage (externally certified) | % of employees and contractors | 66% | 67% | 67% | |||||||
Investment in Health and Safety | $ million | 35 | 49 | 50 | |||||||
*Positive approach is used with employees to identify safe behaviors to be reinforced Promotion of worker health Most of Ternium's employees and their families have access to private health care systems managed by their respective unions, affiliate companies or companies controlled by Ternium. The health care systems are funded through employees' and Ternium's mandatory contributions together with, in certain cases, Ternium's voluntary contributions. In addition, the company funds and manages health care programs for the broader communities, such as health fairs, clinical examinations, and disease and addiction prevention campaigns, aimed at increasing the community’s awareness and gaining of a basic understanding of how to prevent and take care of various health issues. The company supports and funds a basic health care unit in Aquila, Mexico, and funds improvements in health care infrastructure in different countries. For more information see "Helping our communities thrive - Support to the Public Health Care System" elsewhere in this annual report. | |||||||||||
100. Ternium |
Social Topics (cont.) | |||||||||||
2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |||||||||
Community | |||||||||||
Internship Hours | hours/Per year | 27,600 | 34,600 | 63,800 | |||||||
Community Investments | $ million | 12.6 | 9.5 | 6.6 | |||||||
Education Investments | $ million | 10.0 | 6.2 | 4.6 | |||||||
Community Budget for cultural activities | % | 11 | % | 28 | % | 21% | |||||
Technical Gene program - Teachers | # of Participants | 156 | 152 | 148 | |||||||
Technical Gene program - Students | # of Participants | 2,059 | 1,426 | 1,929 | |||||||
After school program participation | # of Students | 252 | 266 | 270 | |||||||
Merit Awards Program | # of Scholarships | 546 | 712 | 759 | |||||||
Roberto Rocca Education Program (undergraduate) | # of Scholarships | 239 | 276 | 305 | |||||||
Roberto Rocca Education Program (PhDs) | # of Scholarships | 18 | 12 | 15 | |||||||
Volunteering Program | # of volunteers | 1,257 | 1,644 | 1,878 | |||||||
Volunteering Program | hours / per year | 9,709 | 9,996 | 16,611 | |||||||
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Program (ProPymes) | |||||||||||
Small and medium-sized enterprises participation | # SMEs | 1,500 | 1,600 | 1,800 | |||||||
Sponsored training courses | # attendants | 4,264 | 4,700 | 5,300 | |||||||
Sponsored training courses | hours in class /per year | 86,047 | 92,000 | 87,400 | |||||||
Propymes sponsored technical schools | # of Schools | 24 | 32 | 41 | |||||||
Propymes sponsored industrial projects | # of Projects | 376 | 408 | 451 | |||||||
Finance assistance | $ million | 6.4 | 6.6 | 6.0 | |||||||
Integrity | |||||||||||
Training sessions on Ternium's policy on business conduct (on-site) | # sessions | 83 | 79 | 64 | |||||||
Training sessions on Ternium's policy on business conduct (on-site) | # participants | 916 | 1,603 | 878 | |||||||
Acknowledgment and commitment to abide Ternium's Code of Conduct and Policy on Business Conduct | % white-collar employees | 99.4 | % | 99.7 | % | 99.7 | % | ||||
Training course on the company's Policy on Business Conduct (e-learning) | % white-collar employees | 98.7 | % | 97.0 | % | 98.2 | % | ||||
Compliance Line's substantiation rate | % | 31 | % | 40 | % | 46 | % | ||||
101. Sustainability Report 2019 |
UN Sustainable Development Goals Index |
Ternium's Contribution to UN Sustainable Development Goals | ||||||||||||||||||
SD Goal | Topics | Pages | ||||||||||||||||
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | ||||||||||||
 | • | • | 38, 70 | Topics 1 Delivering Ternium's Business Strategy ––– 2 Improving Our Safety Performance ––– 3 Minimizing Ternium's Environmental Footprint ––– 4 Realizing People's Full Potential ––– 5 Strengthening Ternium's Value Chain ––– 6 Helping Our Communities Thrive ––– 7 Commitment to Integrity | ||||||||||||||
 | • | • | • | 56, 66, 70 | ||||||||||||||
 | • | 56 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | 46 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | • | • | • | 22, 38, 56, 7O | |||||||||||||
 | • | • | • | 22, 66, 70 | ||||||||||||||
 | • | • | • | 56, 66, 70 | ||||||||||||||
 | • | 70 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | 46 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | 46 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | 46 | ||||||||||||||||
 | • | 46 |  | |||||||||||||||
 | • | • | 38, 79 | |||||||||||||||
 | • | • | • | 22, 66, 70 | ||||||||||||||
102. Ternium |
www.ternium.com |