
MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company 2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference A Berkshire Hathaway Company

Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains statements that do not directly or exclusively relate to historical facts. These statements are “forward- looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Forward-looking statements can typically be identified by the use of forward- looking words, such as “will,” “may,” “could,” “project,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “expect,” “estimate,” “continue,” “intend,” “potential,” “plan,” “forecast” and similar terms. These statements are based upon MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company’s (“MidAmerican”) and its subsidiaries’ (collectively, the “Company”) current intentions, assumptions, expectations and beliefs and are subject to risks, uncertainties and other important factors. Many of these factors are outside the control of the Company and could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. These factors include, among others: – general economic, political and business conditions, as well as changes in, and compliance with, laws and regulations, including reliability and safety standards, affecting the Company’s operations or related industries; – changes in, and compliance with, environmental laws, regulations, decisions and policies that could, among other items, increase operating and capital costs, reduce facility output, accelerate facility retirements or delay facility construction or acquisition; – the outcome of rate cases and other proceedings conducted by regulatory commissions or other governmental and legal bodies and the Company’s ability to recover costs in rates in a timely manner; – changes in economic, industry, competition or weather conditions, as well as demographic trends, new technologies and various conservation, energy efficiency and distributed generation measures and programs, that could affect customer growth and usage, electricity and natural gas supply or the Company’s ability to obtain long-term contracts with customers and suppliers; – a high degree of variance between actual and forecasted load or generation that could impact the Company’s hedging strategy and the cost of balancing its generation resources with its retail load obligations; – performance and availability of the Company’s facilities, including the impacts of outages and repairs, transmission constraints, weather, including wind, solar and hydroelectric conditions, and operating conditions; – changes in prices, availability and demand for wholesale electricity, coal, natural gas, other fuel sources and fuel transportation that could have a significant impact on generating capacity and energy costs; – the financial condition and creditworthiness of the Company’s significant customers and suppliers; – changes in business strategy or development plans; – availability, terms and deployment of capital, including reductions in demand for investment-grade commercial paper, debt securities and other sources of debt financing and volatility in the London Interbank Offered Rate, the base interest rate for MidAmerican’s and its subsidiaries’ credit facilities;

Forward-Looking Statements – changes in MidAmerican’s and its subsidiaries’ credit ratings; – risks relating to nuclear generation; – the impact of certain contracts used to mitigate or manage volume, price and interest rate risk, including increased collateral requirements, and changes in commodity prices, interest rates and other conditions that affect the fair value of certain contracts; – the impact of inflation on costs and the Company’s ability to recover such costs in regulated rates; – increases in employee healthcare costs, including the implementation of the Affordable Care Act; – the impact of investment performance and changes in interest rates, legislation, healthcare cost trends, mortality and morbidity on pension and other postretirement benefits expense and funding requirements; – changes in the residential real estate brokerage and mortgage industries and regulations that could affect brokerage and mortgage transaction levels; – unanticipated construction delays, changes in costs, receipt of required permits and authorizations, ability to fund capital projects and other factors that could affect future facilities and infrastructure additions; – the availability and price of natural gas in applicable geographic regions and demand for natural gas supply; – the impact of new accounting guidance or changes in current accounting estimates and assumptions on the Company’s consolidated financial results; – the Company’s ability to successfully integrate NV Energy, Inc. (“NVE” or “NV Energy”) and future acquired operations into its business; – the effects of catastrophic and other unforeseen events, which may be caused by factors beyond the Company's control or by a breakdown or failure of the Company's operating assets, including storms, floods, fires, earthquakes, explosions, landslides, mining accidents, litigation, wars, terrorism and embargoes; and – other business or investment considerations that may be disclosed from time to time in MidAmerican’s filings with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) or in other publicly disseminated written documents. Further details of the potential risks and uncertainties affecting the Company are described in MidAmerican’s filings with the SEC. The Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. The foregoing factors should not be construed as exclusive. This presentation includes certain non-GAAP financial measures as defined by the SEC’s Regulation G. Refer to the Appendix in this presentation for a reconciliation of those non-GAAP financial measures to the most directly comparable GAAP measures.

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Patrick J. Goodman Executive Vice President and CFO MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company
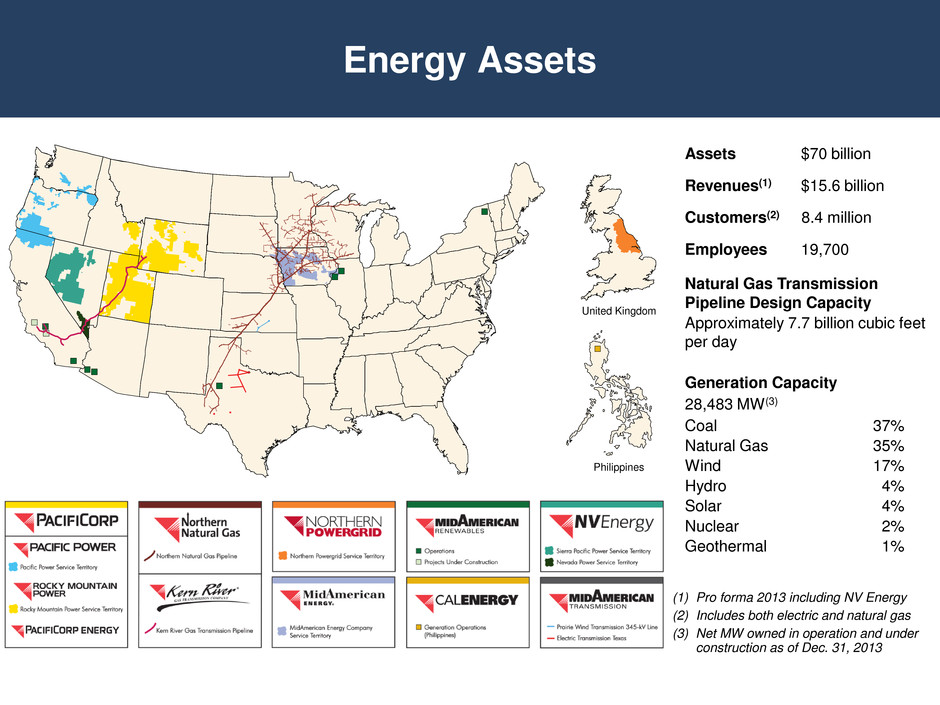
Energy Assets (1) Pro forma 2013 including NV Energy (2) Includes both electric and natural gas (3) Net MW owned in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 Assets $70 billion Revenues(1) $15.6 billion Customers(2) 8.4 million Employees 19,700 Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline Design Capacity Approximately 7.7 billion cubic feet per day Generation Capacity 28,483 MW(3) Coal 37% Natural Gas 35% Wind 17% Hydro 4% Solar 4% Nuclear 2% Geothermal 1% United Kingdom Philippines

• Diversified portfolio of regulated assets – Weather, customer, regulatory, generation, economic and catastrophic risk diversity • Berkshire Hathaway ownership – Access to capital from Berkshire Hathaway allows us to take advantage of market opportunities – Berkshire Hathaway is a long-term holder of assets; its owner for life philosophy promotes stability and helps make MidAmerican the buyer of choice in the eyes of certain sellers and regulators – Tax appetite of Berkshire Hathaway allows us to realize significant tax benefits • No dividend requirement – Cash flow is retained in the business and used to help fund growth and improve credit metrics • Stable operating cash flows – 93% of pro forma EBITDA from investment-grade regulated subsidiaries MidAmerican Competitive Advantage

Diverse Operations with Significant Scale • MidAmerican’s integrated utilities operate in 11 states • Northern Powergrid has 3.9 million end-users, making it the third-largest distribution company in Great Britain • MidAmerican Energy Pipeline Group transported approximately 8% of the total natural gas consumed in the U.S. in 2013 • MidAmerican Solar has 1,271 MW in operation and under construction – a significant amount of solar electric capacity operating in the U.S. • MidAmerican has 4,747 MW of wind generation in operation and under construction – nearly 7% of the U.S. wind market • Comparable companies MidAmerican Net Income Actual 2013: $1.64 billion Pro Forma 2013: $1.87 billion Company Name Dec. 31, 2013 Market Cap (billions) FY 2013 Net Income (billions) Duke Energy $48.7 $2.67 Dominion Resourc s $37.6 $1.70 NextEra Energy Inc. $37.2 $1.91 Southern Company $36.5 $1.64 Exelon Corp. $23.5 $1.72

Unemployment Rates 2.0% 4.0% 6.0% 8.0% 10.0% 12.0% 14.0% 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Nevada U.K. Oregon Utah Wyoming Iowa

Revenue and EBITDA Diversification MidAmerican 2013 Pro Forma Energy Revenue(1): $13.8 Billion MidAmerican 2013 Pro Forma Consolidated EBITDA(2): $5.7 Billion (1) Excludes HomeServices and equity income, which add further diversification (2) Refer to the Appendix for the calculation of EBITDA; percentages exclude Corporate/other Iowa 17.1% Utah 16.4% Oregon 9.0% Wyoming 6.3% Illinois 5.8% Washington 2.6% Idaho 2.6% Other 3.9% FERC 6.9% United Kingdom 7.4% Philippines 0.9% Nevada 21.1% MidAmerican Funding 14.1% PacifiCorp 35.9% Northern Powergrid 12.0% MidAmerican Energy Pipeline Group 11.6% MidAmerican Renewables 3.8% HomeServices 3.1% NV Energy 19.5% • Diversification of revenue sources reduces regulatory concentrations • In 2013, 93% of pro forma EBITDA was from investment-grade regulated subsidiaries

$1.7 $13.2 $14.1 $15.7 $18.7 $0 $5 $10 $15 $20 2001 2010 2011 2012 2013 Billions MidAmerican Financial Summary $6.5 $31.9 $34.2 $37.6 $50.1 $0 $20 $40 $60 2001 2010 2011 2012 2013 Billions $143 $1,238 $1,331 $1,472 $1,636 $0 $500 $1,000 $1,500 $2,000 2001 2010 2011 2012 2013 Millions $847 $2,759 $3,220 $4,327 $4,669 $0 $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 $4,000 $5,000 2001 2010 2011 2012 2013 Millions Net Income Attributable to MidAmerican MidAmerican Shareholders’ Equity Property, Plant and Equipment (Net) Cash Flows From Operations • Continued solid growth and returns

Reportable Segment Information Years Ended Dec. 31 Years Ended Dec. 31 ($ millions) 2013 2012 2011 Operating Income: PacifiCorp 1,275$ 1,034$ 1,099$ MidAmerican Funding 357 369 428 NV Energy (42) - - MidAmerican Energy Pipeline Group 446 465 468 Northern Powergrid Holdings 501 565 615 MidAmerican Renewables 223 93 106 HomeServices 129 62 24 Corporate/other (54) (21) (56) Total operating income 2,835 2,567 2,684 Interest expense (1,222) (1,176) (1,196) Capitalized interest 84 54 40 Allowance for equity funds 78 74 72 Other, net 66 56 (7) Income before income tax expense and equity (loss) income 1,841 1,575 1,593 Income tax expense 130 148 294 Equity (loss) income (35) 68 53 Net income 1,676 1,495 1,352 Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests 40 23 21 Net income attributable to MidAmerican shareholders 1,636$ 1,472$ 1,331$
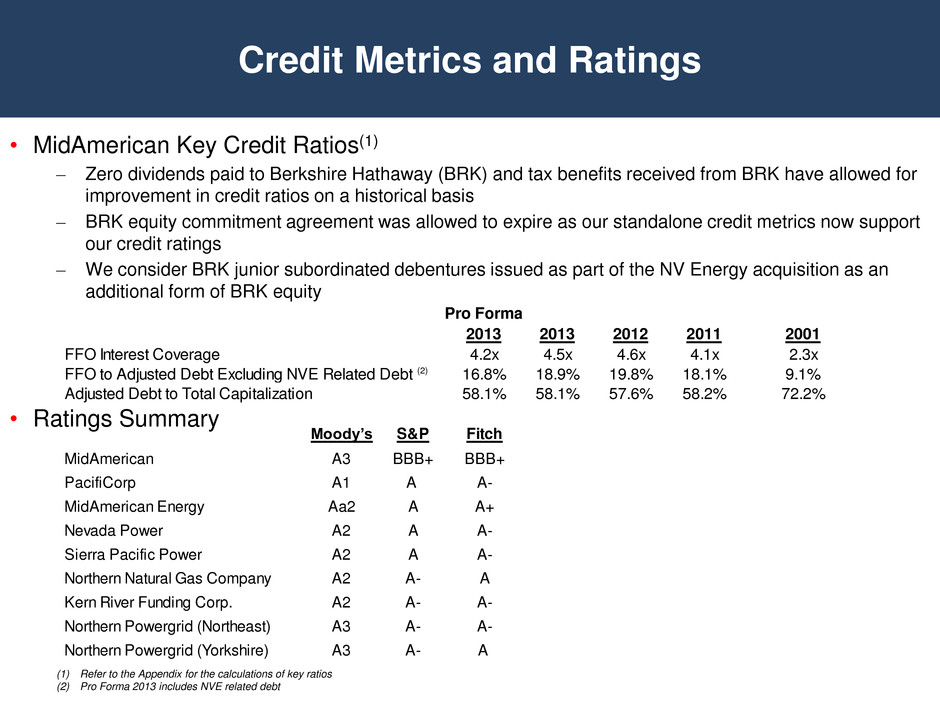
• MidAmerican Key Credit Ratios(1) – Zero dividends paid to Berkshire Hathaway (BRK) and tax benefits received from BRK have allowed for improvement in credit ratios on a historical basis – BRK equity commitment agreement was allowed to expire as our standalone credit metrics now support our credit ratings – We consider BRK junior subordinated debentures issued as part of the NV Energy acquisition as an additional form of BRK equity • Ratings Summary Credit Metrics and Ratings (1) Refer to the Appendix for the calculations of key ratios (2) Pro Forma 2013 includes NVE related debt Moody’s S&P Fitch MidAmerican A3 BBB+ BBB+ PacifiCorp A1 A A- MidAmerican Energy Aa2 A A+ Nevada Power A2 A A- Sierra Pacific Power A2 A A- Northern Natural Gas Company A2 A- A Kern River Funding Corp. A2 A- A- Northern Powergrid (Northeast) A3 A- A- Northern Powergrid (Yorkshire) A3 A- A Pro Forma 2013 2013 2012 2011 2001 FFO Interest Coverage 4.2x 4.5x 4.6x 4.1x 2.3x to Adjusted Debt Excluding NVE Related Debt (2) 16.8% 18.9% 19.8% 18. % 9.1% Adjusted Debt to Total Capitalization 58.1 5 .1 57.6 5 .2 72.2%
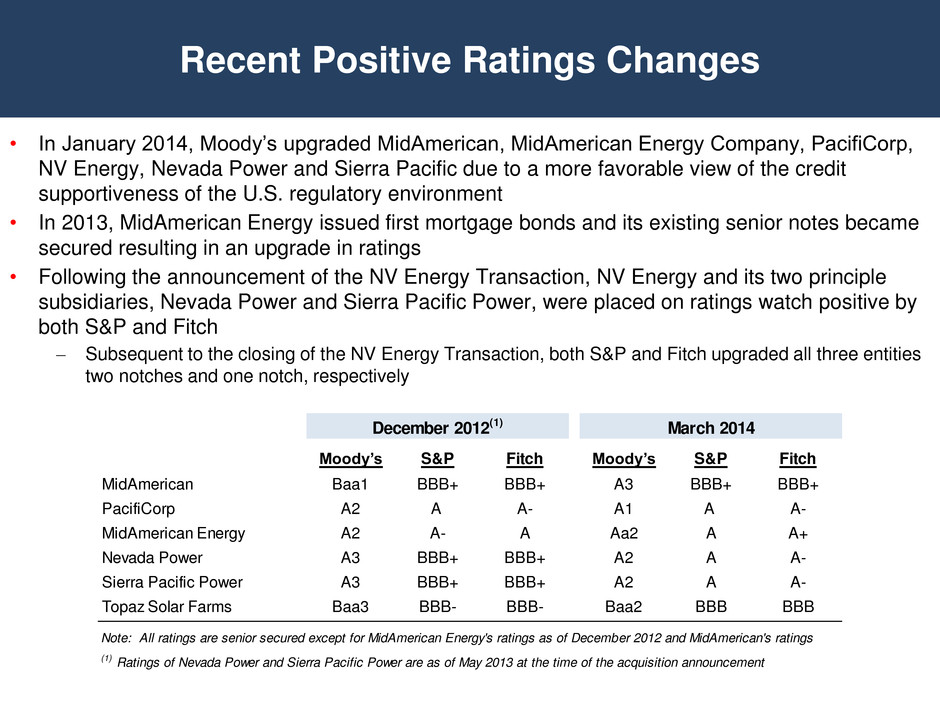
Recent Positive Ratings Changes • In January 2014, Moody’s upgraded MidAmerican, MidAmerican Energy Company, PacifiCorp, NV Energy, Nevada Power and Sierra Pacific due to a more favorable view of the credit supportiveness of the U.S. regulatory environment • In 2013, MidAmerican Energy issued first mortgage bonds and its existing senior notes became secured resulting in an upgrade in ratings • Following the announcement of the NV Energy Transaction, NV Energy and its two principle subsidiaries, Nevada Power and Sierra Pacific Power, were placed on ratings watch positive by both S&P and Fitch – Subsequent to the closing of the NV Energy Transaction, both S&P and Fitch upgraded all three entities two notches and one notch, respectively December 2012(1) March 2014 Moody’s S&P Fitch Moody’s S&P Fitch MidAmerican Baa1 BBB+ BBB+ A3 BBB+ BBB+ PacifiCorp A2 A A- A1 A A- MidAmerican Energy A2 A- A Aa2 A A+ Nevada Power A3 BBB+ BBB+ A2 A A- Sierra Pacific Power A3 BBB+ BBB+ A2 A A- Topaz Solar Farms Baa3 BBB- BBB- Baa2 BBB BBB Note: All ratings are senior secured except for MidAmerican Energy's ratings as of December 2012 and MidAmerican's ratings (1) Ratings of Nevada Power and Sierra Pacific Power are as of May 2013 at the time of the acquisition announcement

Selected Credit Metrics Regulated Utilities Regulated Pipelines and Electric Distribution 2013 2012 2011 2013 2012 2011 PacifiCorp Northern Natural Gas FFO Interest Coverage 5.0x 4.8x 4.8x FFO Interest Coverage 7.9x 6.3x 6.5x FFO to Debt 22.1% 21.3% 21.6% FFO to Debt 33.9% 30.8% 32.6% Debt to Total Capitalization 46.9% 47.3% 48.6% Debt to Total Capitalization 39.8% 41.1% 42.7% MidAmerican Energy Kern River FFO Interest Coverage 6.9x 7.7x 8.1x FFO Interest Coverage 7.2x 7.0x 5.9x FFO to Debt 24.9% 29.2% 36.1% FFO to Debt 40.5% 39.5% 31.7% Debt to Total Capitalization 48.0% 47.3% 48.8% Debt to Total Capitalization 39.8% 41.6% 45.2% Nevada Power Northern Powergrid FFO Interest Coverage 3.5x 4.1x 3.7x FFO Interest Coverage 4.2x 4.7x 4.6x FFO to Debt 14.8% 20.2% 18.0% FFO to Debt 17.9% 21.4% 25.4% Debt to Total Capitalization 55.3% 53.3% 54.8% Debt to Total Capitalization 45.2% 47.4% 49.2% Sierra Pacific Power FFO Interest Coverage 4.9x 5.2x 4.3x FFO to Debt 20.2% 23.3% 19.2% Debt to Total Capitalization 54.2% 53.2% 54.7%

Return on Equity (1) 2012 excludes $102 million after-tax impact of charges for USA Power litigation and certain fire and other damage claims (2) Excludes one-time items and merger related expenses Net Income Divided by Average Equity Entity 2013 2012 Allowed ROE PacifiCorp 9.0% 8.4% (1) 9.8% MidAmerican Energy 9.5% 10.4% 11.0% Nevada Power 7.9% (2) 9.0% 10.0% Sierra Pacific Power 8.6% (2) 8.5% 9.8% Northern Natural Gas 11.6% 10.9% 12.0% Kern River 10.5% 11.3% 11.55%

$- $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 $4,000 $5,000 $6,000 $7,000 2010A 2011A 2012A 2013A 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 MidAmerican Capital Expenditures MidAmerican Cash Flows from Operations MidAmerican Renewables Capital Expenditures MidAmerican Renewables Cash Flows from Operations $ millio ns Capital Expenditures and Cash Flows • MidAmerican and its subsidiaries will spend approximately $13.2 billion over the next three years for development and maintenance capital expenditures, which includes new environmental capital expenditures, transmission, and generation project expansions, including solar, wind and natural gas plant additions – MidAmerican Renewables is projected to spend approximately $2.8 billion over the next two years Free Cash Flow

$0 $1,000 $2,000 $3,000 $4,000 $5,000 $6,000 $7,000 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 $ m illio ns PacifiCorp MidAmerican Funding Northern Powergrid Holdings MidAmerican Renewables MidAmerican Energy Pipeline Group and Other NV Energy Projected Capital Expenditures For each year, the left column represents current projections and the right column represents prior year projections. • Excluding NV Energy and 100% ownership of CE Generation, 2014-2022 capital expenditures projections have been increased by $1.1 billion from prior year projections primarily due to the Wind VIII investment at MidAmerican Energy in 2014 and 2015

Renewable Investments • Acquisition of 50% interest in CE Generation and Wailuku from TransAlta – Announced the definitive agreements on Feb. 20, 2014 to add 221 MW of natural gas generation, 163 MW of geothermal generation and 5 MW of hydroelectric generation for a purchase price of $194 million • Continue to look for additional wind and solar opportunities Owned Wind and Solar Generation Capacity (MW) Regulated Unregulated Regulated MidAmerican MidAmerican PacifiCorp Energy Renewables Total 1999-2011 1,031 1,878 - 2,909 2012 - 407 497 904 2013 - 44 324 368 2014-2015 - 1,006 831 1,837 Total 1,031 3,335 1,652 6,018 Investment (billions) $2 $6 $7 $15

Changing Capacity Mix Coal 37% Natural Gas 35% Nuclear 2% Hydro 4% Geothermal, Solar, Wind 22% 2000 MEHC Coal 31% Natural Gas 40% Nuclear 2% Hydro 4% Geothermal, Solar, Wind 23% Coal 51% Natural Gas 27% Nuclear 7% Hydro 2% Geothermal, Solar, Wind 12% Other 1% 2013 MEHC 2016 MEHC
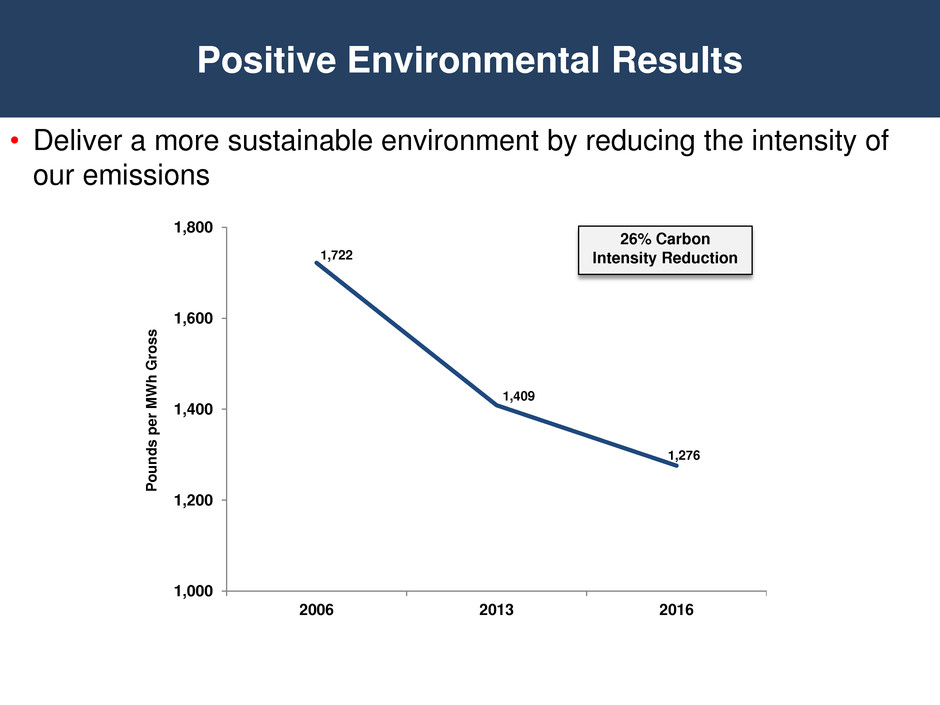
Positive Environmental Results • Deliver a more sustainable environment by reducing the intensity of our emissions 1,000 1,200 1,400 1,600 1,800 2006 2013 2016 1,722 1,276 26% Carbon Intensity Reduction P o u n d s per M W h G ros s 1,409

MidAmerican Transmission • MidAmerican Transmission’s current asset base is comprised of a 50% equity interest in Electric Transmission Texas LLC (“ETT”) and a 25% equity interest in Prairie Wind Transmission – ETT owns and operates electric transmission assets in Texas (ERCOT); as of Dec. 31, 2013, a total of $2.2 billion of transmission assets were in-service and an estimated $800 million is to be placed in-service between 2014 and 2023 – Prairie Wind Transmission is a joint venture in Kansas (SPP); construction began during 2012, and the assets are expected to cost approximately $170 million and be completed on or before December 2014 • California ISO awarded a project to Pacific Gas and Electric Company and MidAmerican Transmission consortium – 59 miles, 230 kV transmission line linking two substations in central California – $157 million estimated total project cost • Canadian affiliate of MidAmerican Transmission, in partnership with an affiliate of TransAlta, has been short-listed to bid on the $1.7 billion Fort McMurray West project – Bids are due in November 2014

HomeServices of America • Purchase of Prudential franchise business has led to establishing the Berkshire Hathaway HomeServices brand 0 2 4 6 8 10 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 -$40 -$20 $0 $20 $40 $60 $80 $100 (millions) (millions) U.S. Home Sales HomeServices of America Net Income National Association of Realtors Existing Home Sales

Financing Plan 2014 • PacifiCorp – In March 2014, issued $425 million of 10-year bonds at 3.60% • MidAmerican Energy – Completed April 2014 debt issuance of $850 million, comprised of three tranches: $150 million at 2.40% due 2019; $300 million at 3.50% due 2024; $400 million at 4.40% due 2044 • Proceeds will be used to redeem prior to maturity, the $350 million principal amount of our 4.65% senior notes maturing in October 2014, and to use the remainder for general corporate purposes • MidAmerican – Plan to increase the size of the parent revolver to support additional development opportunities – Plan to repay $300 million of Berkshire junior subordinated debentures in 2014

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Paul Caudill President NV Energy

NV Energy Overview • Headquartered in Las Vegas, Nevada • 2,500 employees • 1.2 million electricity and 0.2 million natural gas customers • Provides service to approximately 90% of Nevada population, along with tourist population of 40 million annually • 6,078 MW(1) owned generation capacity • Generating capacity by fuel type(1) – Natural gas and other 82% – Coal 18% (1) Net MW owned in operation as of Dec. 31, 2013 NV Energy Electric Service Territory CALIFORNIA ARIZONA UTAH NEVADA NV Energy Gas Service Territory Coal Plants Natural Gas Plants Energy Recovery Plant

Economic Outlook and Load Growth 2013 compared to 2012 • Mine sales up 6.2%, but total industrial sales up only 0.4% due to retrenchment in the tourism industry • Commercial loads declined 0.1% • Residential loads increased 1.6% fueled by the return of customer growth Forecast for 2014 and 2015 • Mine and retail load increase, other non- residential load growth remains subdued • Slow residential growth as energy efficiency gains partially offset the addition of new customers Key Drivers • No income tax and low business tax rates contribute to economic growth • Unemployment, still at elevated levels, is expected to continue to decline • Several large retail developments, as well as mine expansions, will drive growth in 2014 and 2015 • Over last five years, NVE has acquired on average 273 GWh in electricity savings through customer participation in energy efficiency programs, at a cost of less than $0.02 per kWh Annual Growth Rates: 2010 = 4.2% 2011 = 2.5% 2012 = 0.2% 2013 = 0.8% 2014 = 0.7% 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Fcst 2015 Fcst T W h NV Energy Retail Load Weather-Normalized Nevada Power Sierra Pacific Power 2010 = -0.7% 2011 = 0.8% 2012 = 1.6% 2013 = 0.7% 2014 = 0.6% 2015 = 0.6% Annual Growth Rate

• NV Energy is a summer peaking utility driven by the loads in the Las Vegas area 2013 Monthly Retail Customer Demand 0 1,000 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 6,000 7,000 8,000 2013 Monthly Peak Demand, MW Nevada Power Sierra Pacific Power

• Key regulatory objectives – Begin implementing a stakeholder improvement plan, centered on frequent, candid and open communications – Continue to improve relationship with PUCN, the PUCN staff, the consumer advocate and key stakeholders – Capitalize upon successful resolution of merger proceeding – Endeavor to resolve Nevada Power general rate case in a manner that advances corporate goals of providing balanced outcomes and predictable rates Regulatory Strategy

• Emission Reduction and Capacity Replacement plan – An opportunity to establish a new vision for Nevada by retiring coal- fueled generating units early and replacing the units with at least 200 MW of clean, efficient and cost-effective solar generation – Nevada Power must file before May 1, 2014 – Must propose coal retirement plan (300 MW before Dec. 31, 2014, 250 MW before Dec. 31, 2017, and 250 MW before Dec. 31, 2019) – Must propose plan for issuing three 100 MW requests for renewable energy proposals – Present plan for the addition of 550 MW of non-technology specific and 50 MW of renewable replacement capacity, owned by Nevada Power – Stakeholder outreach to begin in April 2014 Major 2014 Filings Senate Bill 123 (Coal Retirements)

• NV Energy filed a request with the PUCN to withdraw the application to merge Nevada Power and Sierra Pacific on March 14, 2014 • This request is in response to several changes that have occurred since the application was filed on May 31, 2013 – First, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (“FERC”) approved an agreement between Nevada Power and Sierra Pacific which allows the two utilities to share energy resources – Second, NV Energy joined the MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company family – Other developments include the passage of Senate Bill 123, and the completion of the One Nevada Transmission Line (“ON Line”) • As part of this request, NV Energy will continue to work with the PUCN, the BCP and other stakeholders throughout the year to determine if consolidation of the utilities is in the best interest of our customers • NV Energy will make a decision by year’s end regarding which course of action will best benefit our customers and seek input on that decision from the PUCN, BCP and key stakeholders before moving forward as appropriate in 2015 Nevada Power/Sierra Pacific Power Merger Filing Update

• Consistent with statutory requirements to file a rate case every three years, Nevada Power plans to file general rate case in May 2014 – In the process of preparing filing and expect any increase to be minor – Requesting recovery of a number of assets (Beltway Operations Center, ON Line, smart meter project and other costs) Major 2014 Filings Nevada Power General Rate Case

• Energy Imbalance Market filing – Announced in November 2013 a plan to join California Independent System Operator Energy Imbalance Market – Required by MidAmerican-NV Energy Transaction settlement to obtain PUCN approval – Plan to file in April 2014 – Currently engaged in outreach and educational efforts with key stakeholders – NV Energy’s “In-service date” is Oct. 1, 2015 Major 2014 Filings Energy Imbalance Market

0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 1996 2001 2004 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Target N VE OS H A I n c iden c e R a te Safety Performance Trajectory

Generating Assets • NV Energy owns 61 generating units with capacity totaling 6,078 MW • Through Feb. 17, 2014, large gas plant equivalent availability factor was 95.86% against a goal of 93.02%, and the coal plant equivalent availability factor was 96.18% against a goal of 89.19% Coal 14% Natural gas and other 58% Purchased 28% NV Energy 2013 Resource Mix (MWh)

Transmission Assets • Statewide transmission network (newly interconnected) • Backbone transmission system – 500 kV (10 @ 403 miles) – 345 kV (16 @ 992 miles) – 230 kV (44 @ 978 miles) – Underlying 138 kV and 120 kV transmission network (189 @ 1,753 miles) • Interconnections – Bonneville Power Administration – California Independent System Operator – Idaho Power Company – Los Angeles Department of Water & Power – PacifiCorp East – Western area lower Colorado • Transmission service – Network service to 6 external entities amounting to 400 MW – Firm point-point service to 6 external entities; over 800 MW
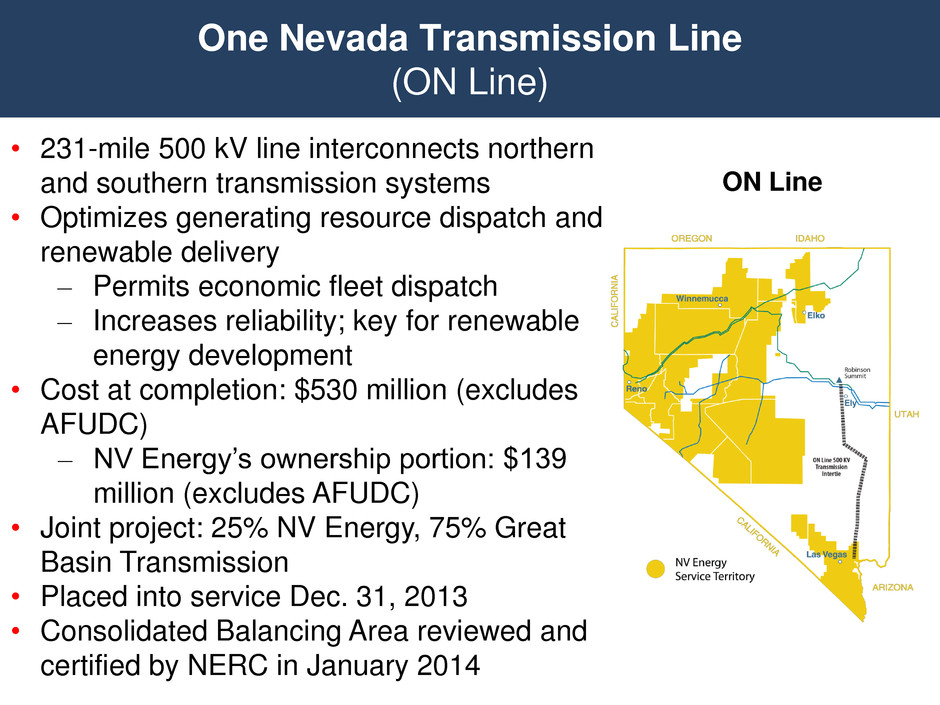
ON Line One Nevada Transmission Line (ON Line) • 231-mile 500 kV line interconnects northern and southern transmission systems • Optimizes generating resource dispatch and renewable delivery – Permits economic fleet dispatch – Increases reliability; key for renewable energy development • Cost at completion: $530 million (excludes AFUDC) – NV Energy’s ownership portion: $139 million (excludes AFUDC) • Joint project: 25% NV Energy, 75% Great Basin Transmission • Placed into service Dec. 31, 2013 • Consolidated Balancing Area reviewed and certified by NERC in January 2014

• In February 2014, a stormwater pipe break beneath an ash basin at a retired Duke Energy coal fired generating plant caused a release of coal ash into the Dan River – Up to 39,000 tons of ash was released into the Dan River – Cleanup is ongoing and local residents are concerned about impacts to drinking water and the environment – The pond was ranked as a significant hazard by the EPA • When operational, the Duke Energy Dan River facility handled ash from its coal combustion process in a ‘wet’ form and stored it in on-site ash basins Ash Ponds

• To contrast, NV Energy’s Reid Gardner and North Valmy facilities manage their waste streams in a different process – NV Energy has no active, or former ash ponds. Once generated, ash is removed from the boilers in dry form and either sold for beneficial use or disposed in permitted, on-site landfills for final disposal – Reid Gardner and North Valmy are zero discharge facilities and do not place any waste streams into the nearby Muddy and Humboldt Rivers Ash Ponds

• Nevada has a renewable portfolio standard determined as a percent of retail energy sales: Period Requirement 2011-2012 15% 2013-2014 18% 2015-2019 20% 2020-2024 22% 2025 and after 25% • NV Energy – South met 20.3% in 2013 • NV Energy – North met 34.7% in 2013 • Over 1,000 megawatts of renewable generation – Mainly geothermal (approximately 75%) – Almost exclusively through power purchase agreements Renewable Portfolio Standard

• As of Dec. 31, 2013, there were 3,317 Distributed Generation (DG) Systems totaling 61,746 kW connected to the NV Energy grid – This represents 27.2% of the statewide metering cap • NV Energy and MidAmerican’s other utilities are focusing on the following key areas: – Rates and rate designs for retail sales of utility services to DG customers that reflect the costs of serving such customers & provide appropriate incentives for DG production that will benefit the grid – Appropriate prices to pay for DG production if the utility is required to purchase that production – Opportunities for the regulated utilities to own, lease or otherwise be involved in providing DG services requested by customers Impacts of Distributed Generation

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Pat Reiten President and CEO Pacific Power

PacifiCorp Overview • Headquartered in Portland, Oregon • 6,000 employees • 1.8 million electricity customers • 136,000 square miles of service territory • 11,240 MW(1) owned generation capacity • Generating capacity by fuel type(1) – Coal 55% – Natural gas 25% – Hydro(2) 10% – Wind, geothermal and other(2) 10% (1) Net MW owned in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 (2) All or some of the renewable energy attributes associated with generation from these generating facilities may be: (a) used in future years to comply with renewable portfolio standards or other regulatory requirements or (b) sold to third parties in the form of renewable energy credits or other environmental commodities (a) Access to other entities’ transmission lines through wheeling arrangements
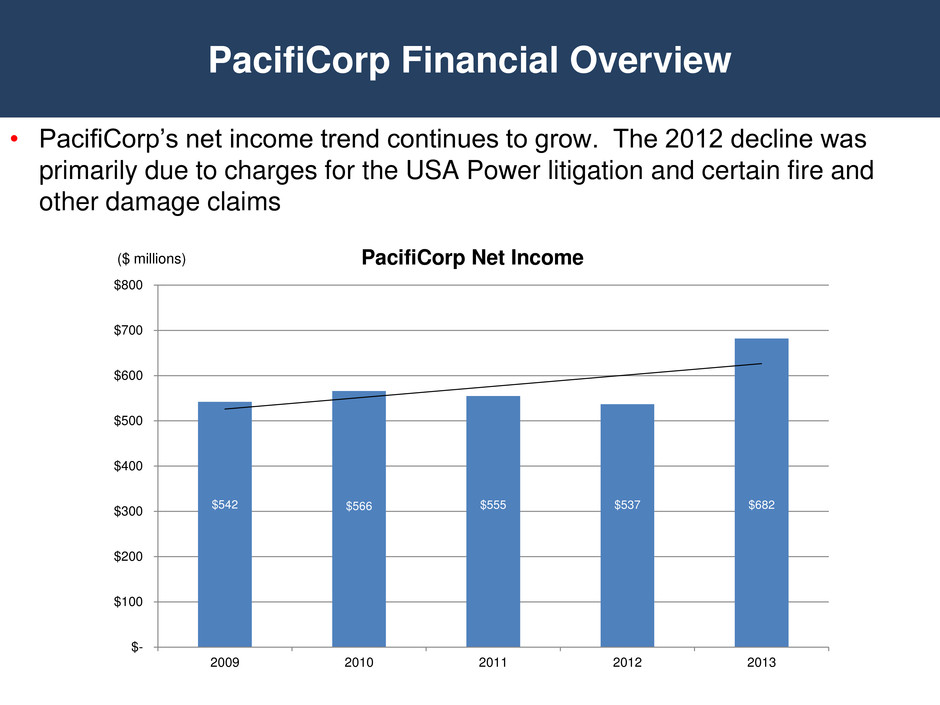
PacifiCorp Financial Overview • PacifiCorp’s net income trend continues to grow. The 2012 decline was primarily due to charges for the USA Power litigation and certain fire and other damage claims $542 $566 $555 $537 $682 $- $100 $200 $300 $400 $500 $600 $700 $800 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 PacifiCorp Net Income ($ millions)

PacifiCorp Financial Overview • PacifiCorp’s continued progress with intensive cost management efforts to minimize customer rate increases while maintaining strong system reliability, safety, customer service and plant equivalent availability levels have resulted in: – Reduced capital expenditures – Generally flat operations and maintenance expenditures $1,607 $1,506 $1,346 $1,065 $1,096 $0 $200 $400 $600 $800 $1,000 $1,200 $1,400 $1,600 $1,800 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 - Forecast PacifiCorp Capital Expenditures ($ millions) $1,081 $1,103 $1,242 $1,114 $0 $200 $400 $600 $800 $1,000 $1,200 $1,400 2010 2011 2012 2013 PacifiCorp O&M Expense ($ millions) (1) Includes $165 million of charges related to USA Power litigation and certain fire and other damage claims (1)

Diversification – Retail Revenue PacifiCorp ($4.5 billion) PacifiCorp ($4.5 billion) Rocky Mountain Power ($2.9 billion) Pacific Power ($1.6 billion) Residential 38% Commercial 31% Industrial 27% Irrigation 3% Other 1% Oregon 27% Washington 7% California 2% Utah 43% Idaho 6% Wyoming 15% Residential 32% Commercial 29% Industrial 35% Irrigation 3% Other 1% Residential 49% Commercial 36% Industrial 12% Irrigation 3% Other 0%

• 733,000 electric customers, plus PacifiCorp transmission and customer services functions • Weather-normalized retail load in 2013 was flat compared to 2012 at 17.6 TWh • 2013 general rate case outcomes – Oregon: $24 million (2%) effective January 2014 – Washington: $17 million (6%) effective December 2013 • Network reliability has continued to improve over the last seven years • Excellent customer satisfaction results in all customer classes Pacific Power Overview Pacific Power Service Territory CALIFORNIA ARIZONA UTAH NEVADA MONTANA IDAHO OREGON WASHINGTON COLORADO WYOMING

Oregon • Transition adjustment mechanism rates became effective for a rate increase of $2 million (less than 1%), effective January 2013. • Pacific Power filed a general rate case in March 2013 that included: – Revised depreciation rates – Separate tariff rider for the Lake Side 2 natural gas-fueled generating plant, once it is in service • The commission approved Pacific Power’s request for a separate tariff rider to recover the revenue requirement associated with the Mona-to-Oquirrh transmission project, effective June 2013. The separate tariff increases rates $10 million (1%) overall Regulatory Accomplishments

Oregon (continued) • A multi-party stipulation was filed with the commission in July 2013 resolving all issues in the case. Key provisions of the settlement include: – Overall base price increase of $24 million (2%) effective January 2014 – Revised depreciation rates, resolving all issues in the separate depreciation study proceeding – Same rate of return approved in the 2012 Oregon general rate case, with a small update to the cost of long-term debt – Rate case stay-out provision for 2014 – Separate tariff rider for Lake Side 2 once the plant is placed in service in mid-2014 • The commission issued a final order in the 2014 transition adjustment mechanism proceeding in October 2013. • The final net power cost update reflected a rate decrease of $3 million, effective January 2014 • The commission approved the multi-party stipulation; rates became effective January 2014 Regulatory Accomplishments

California • Annual attrition adjustment associated with the post-test year adjustment mechanism became effective January 2013, for a rate increase of $1 million (1%) • Rate increase of $0.3 million (0.3%) became effective March 2013 for the Clover substation (transmission) and Swift fish collector investments • Rate increase of $1 million (1%) became effective for the Mona-to-Oquirrh transmission project July 2013 • Commission approved petition authorizing Pacific Power to make a post-test year adjustment mechanism attrition filing for rates effective January 2015, in exchange for not filing a general rate case with a 2015 test year. Pacific Power’s petition was supported by all parties • Filed the 2014 energy cost adjustment clause application, requesting an overall rate increase of $0.2 million (0.2%) with a proposed January 2014 effective date • Commission approved Pacific Power’s 2013 energy cost adjustment clause application, increase rates $0.4 million (0.4%), effective September 2013 Regulatory Accomplishments
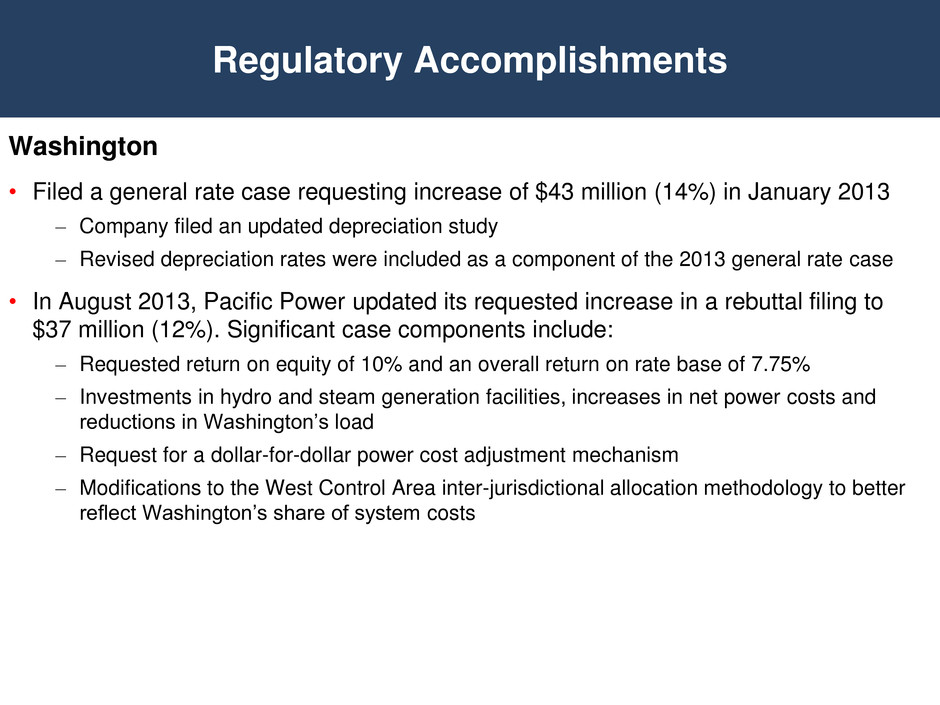
Washington • Filed a general rate case requesting increase of $43 million (14%) in January 2013 – Company filed an updated depreciation study – Revised depreciation rates were included as a component of the 2013 general rate case • In August 2013, Pacific Power updated its requested increase in a rebuttal filing to $37 million (12%). Significant case components include: – Requested return on equity of 10% and an overall return on rate base of 7.75% – Investments in hydro and steam generation facilities, increases in net power costs and reductions in Washington’s load – Request for a dollar-for-dollar power cost adjustment mechanism – Modifications to the West Control Area inter-jurisdictional allocation methodology to better reflect Washington’s share of system costs Regulatory Accomplishments

Washington (continued) • Commission issued final order approving a rate increase of $17 million (6%) overall, effective December 2013 – Key elements of the commission’s decision include: Authorized return on equity of 9.5%, an equity component in the capital structure of 49.1%, an overall return on rate base of 7.36% Rejection of Pacific Power’s proposal for a power cost adjustment mechanism Rejection of Pacific Power’s proposed modifications to the West Control Area inter-jurisdictional allocation methodology Rejection of inclusion of California and Oregon qualified facilities in the development of net power costs • Commission approved the new depreciation rates, effective January 2014 Regulatory Accomplishments

2013 Washington General Rate Case Appeal • Filed a petition in January 2014 appealing for judicial review, challenging the Washington Utilities and Transportation Commission’s final order in Pacific Power’s 2013 general rate case, regarding adoption of a hypothetical capital structure and rejection of the inclusion of Washington’s share of the costs associated with power purchase agreements with renewable energy qualified facilities in California and Oregon in net power costs – The Public Counsel Division of the Washington Attorney General's Office and Boise White Paper, LLC intervened in the appeal – Pacific Power filed an application for direct review by the Division II Court of Appeals Regulatory Accomplishments

2013 • After five years of weather-normalized load decline, 2013 loads were flat at 17.6 TWh • Residential loads down; commercial and industrial loads up slightly Forecast for 2014 and 2015 • Projected increases in 2014 and 2015 to 17.8 TWh and 17.9 TWh, respectively • Commercial sales increase due to projected load growth in existing data centers • Slow residential growth as energy efficiency gains offset the addition of new customers • Industrial load growth due to continued economic recovery Economic Outlook and Load Growth 17.0 17.2 17.4 17.6 17.8 18.0 18.2 18.4 18.6 18.8 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Fcst 2015 Fcst T W h Pacific Power Retail Load Weather-Normalized Annual Growth Rates: 2009 = (3.7%) 2010 = (0.7%) 2011 = (0.7%) 2012 = (0.4%) 2013 = 0.0% 2014 = 1.2% 2015 = 0.7%

• O&M expenses have generally remained flat over the past several years while accomplishing more output O&M Expense Results $260 $275 $268 $264 $0.0 $50.0 $100.0 $150.0 $200.0 $250.0 $300.0 2010 2011 2012 2013 ($ millions)

Operational Capital Management Approach • 2014 Ten-Year Capital plan continues efficiency and cost reductions initiatives began in 2012 • 2014 Capital plan increased 4% from the 2013 plan while delivering greater volumes in several areas: – Improved economic conditions resulted in 32% increase in planned new service connections – Asset replacement volumes increased based upon inspection and test program results – Compliance-driven work volumes increased based upon emergent compliance requirements and reviews of ongoing efforts New Service Load Growth Other Mandated / Regulatory Replacement Technology Subtransmission and Distribution Capital Investment Allocation
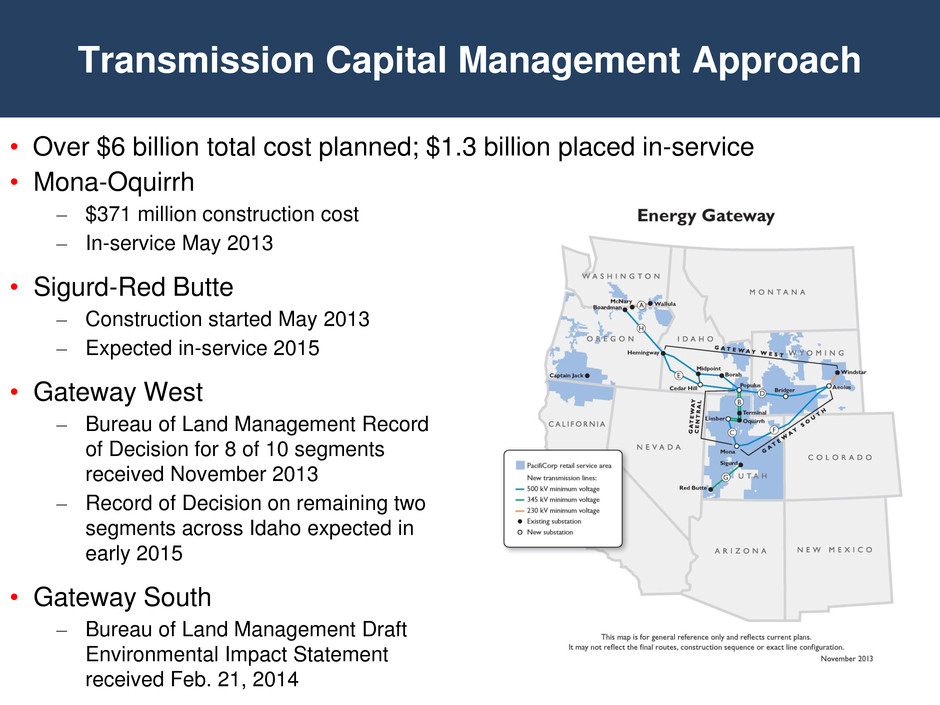
• Over $6 billion total cost planned, • Mona-Oquirrh – $371 million construction cost – In-service May 2013 • Sigurd-Red Butte – Construction started May 2013 – Expected in-service 2015 • Gateway West – Bureau of Land Management Record of Decision for 8 of 10 segments received November 2013 – Record of Decision on remaining two segments across Idaho expected in early 2015 • Gateway South – Bureau of Land Management Draft Environmental Impact Statement received Feb. 21, 2014 Transmission Capital Management Approach ed; $1.3 billion placed in-service

• Automatically optimizes load and generation every five minutes – More efficiently dispatches resources – Modest cost to establish – $21 million to $129 million expected joint annual benefits – Actual benefits depend upon transmission availability • Simulation and testing begin July 8, 2014 • Go-live Oct. 1, 2014 • FERC process – ISO filed tariff revisions Feb. 28, 2014 – PacifiCorp filed tariff revisions March 25, 2014 Both seeking FERC orders by June 20, 2014 Energy Imbalance Market
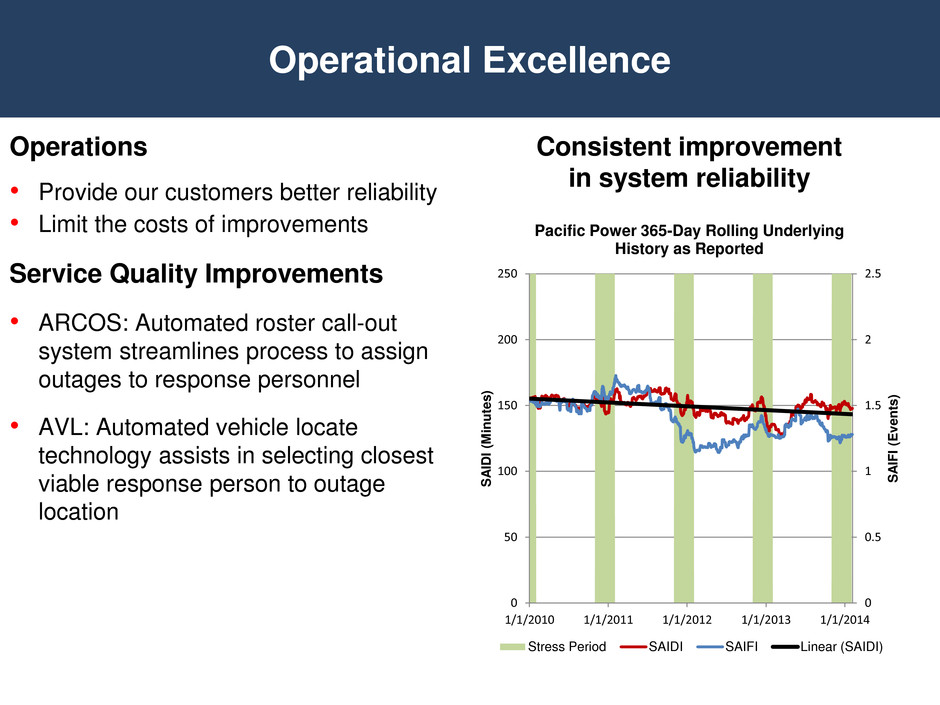
Operations • Provide our customers better reliability • Limit the costs of improvements Service Quality Improvements • ARCOS: Automated roster call-out system streamlines process to assign outages to response personnel • AVL: Automated vehicle locate technology assists in selecting closest viable response person to outage location Operational Excellence Consistent improvement in system reliability 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 0 50 100 150 200 250 1/1/2010 1/1/2011 1/1/2012 1/1/2013 1/1/2014 S A IFI ( E v en ts ) S A IDI ( M in u te s ) Pacific Power 365-Day Rolling Underlying History as Reported Stress Period SAIDI SAIFI Linear (SAIDI)

Employee Commitment 2.27 2.90 2.02 2.31 2.24 2.58 1.33 1.08 2.17 2.01 1.73 1.73 1.57 1.49 1.25 0.77 0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Pacific Power MidAmerican Safety Culture and Work Environment Pacific Power Incidents 2013 vs 2012 29% improvement 2013 vs 2011 63% improvement 2013: 17 incidents 2012: 24 incidents 2011: 46 incidents OSHA Recordable Rate

• MSI Commercial Customer Satisfaction – Achieved top decile ranking – No. 4 nationally among 85 utilities – Improvement from No. 18 in 2012 • MSI Residential Customer Satisfaction – Achieved top quartile ranking – No. 13 nationally among 90 utilities • TQS Customer Satisfaction – Achieved top decile ranking – No. 3 nationally among 101 operating utilities – Significantly contributed to MidAmerican’s No. 1 ranking among 52 holding companies – “Very satisfied” ratings from 95.7% of customers (Pacific Power’s third highest score ever) Pacific Power 2013 Customer Satisfaction Ranking

Key Customer Satisfaction Initiative Measurement MidAmerican Pacific Power Rocky Mountain Power MidAmerican Energy Year % Very Satisfied National Ranking % Very Satisfied National Ranking % Very Satisfied National Ranking % Very Satisfied National Ranking 2007 89.9% 1st 88.4% 2nd 88.2% 4th 93.1% 1st 2008 90.7% 1st 90.7% 2nd 90.1% 3rd 91.3% 1st 2009 91.9% 1st 95.2% 1st 92.7% 2nd 88.6% 8th 2010 93.0% 1st 97.5% 1st 91.8% 7th 91.5% 9th 2011 91.2% 2nd 90.9% 7th 88.3% 13th 94.5% 3rd 2012 92.3% 3rd 85.4% 15th 94.9% 3rd 94.0% 4th 2013 95.3% 1st 95.7% 3rd 95.0% 5th 95.4% 4th

• Paperless Billing Customer Participation – 29% vs. 15% industry average • 2013 Edison Electric Institute Study – Best-in-class performance in: bill accuracy, meter reading accuracy and total customer service expense per customer • 2013 Green Power Leadership Award – “Best Marketing Campaign” for Blue Sky enrollment program • 246 GWh Annual Average Electricity Savings – Through customer participation in energy-efficiency programs at a cost of less than $.03 per KWh over the last five years Customer Service • 2014 MidAmerican – Leading cross-platform initiative to share best practices and improve customer satisfaction • Small, Growing Net Metering Activity Wind 3 Solar 2,765 Mixed 19 California (kW) Wind 91 Solar 26,660 Mixed 374 Other 1,502 Oregon (kW) Wind 23 Solar 1,066 Washington (kW)

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Rich Walje President and CEO Rocky Mountain Power
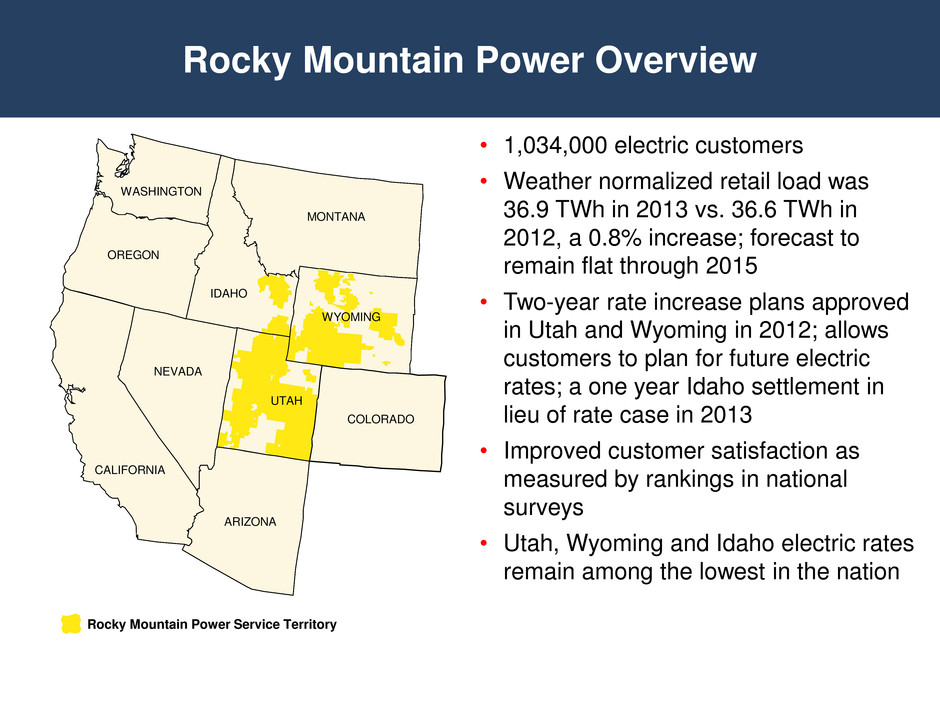
Rocky Mountain Power Overview • 1,034,000 electric customers • Weather normalized retail load was 36.9 TWh in 2013 vs. 36.6 TWh in 2012, a 0.8% increase; forecast to remain flat through 2015 • Two-year rate increase plans approved in Utah and Wyoming in 2012; allows customers to plan for future electric rates; a one year Idaho settlement in lieu of rate case in 2013 • Improved customer satisfaction as measured by rankings in national surveys • Utah, Wyoming and Idaho electric rates remain among the lowest in the nation Rocky Mountain Power Service Territory CALIFORNIA ARIZONA UTAH NEVADA MONTANA IDAHO OREGON WASHINGTON COLORADO WYOMING

Utah • $54 million (3%) step two increase from the Utah 2012 general rate increase became effective September 2013 • Recovery of $8 million of deferred net power costs approved through the energy balancing account; collection occurs over two years effective March 2013 • Recovery of an additional $15 million deferred net power costs approved through the energy balancing account; collected over two years effective November 2013 • Commission approved a $3 million credit returned to customers over one year through the renewable energy credit balancing account effective June 2013 2013 Regulatory Accomplishments

Wyoming • The $18 million (3%) step two increase from the Wyoming 2012 general rate increase became effective October 2013 • 2013 energy cost adjustment mechanism filing resulted in a recovery of $17 million over three years effective May 2013 • 2013 renewable energy credit and SO2 adjustment mechanism resulted in a $15 million increase effective May 2013 Idaho • A settlement in lieu of a general rate case in 2013 resulted in a rate increase of $2 million (1%) in January 2014 and a Lake Side 2 power plant cost tracker that will be included in the energy cost adjustment mechanism starting in January 2015 • Recovery of $16 million deferred power costs through the energy cost adjustment mechanism effective April 2013 2013 Regulatory Accomplishments

• Energy cost recovery and renewable energy credit balancing account mechanisms in place in each state • Customers pay the costs and receive the benefits associated with fluctuating power costs and sales of renewable energy credits; balanced outcome between the company and customers • In Utah and Wyoming, 70% of the difference between base net power costs established in a general rate case and actual power costs are deferred and recovered • In Idaho, 90% of the difference between base net power costs established in a general rate case and actual power costs are deferred and recovered • In all states, 100% of the difference between base REC sales and actual sales are deferred and recovered/refunded • Annual filings are required to seek recovery/refund of deferred energy costs and REC sales – Idaho filing made in January 2014, requesting $13 million in deferred net power costs – Utah filing made in March 2014 requesting $28 million in deferred power costs and $17 million in deferred REC sales – Wyoming filing made in March 2014 requesting $17 million in deferred power costs and $4 million in deferred REC sales Cost Adjustment Mechanisms

• A Utah general rate case requesting $76 million (4%) was filed January 2014; if approved new rates effective September 2014 • Proposed changes to the Utah back-up service tariff were filed December 2013; the proposed changes, which are being addressed coincident with the rate case, make the tariff more cost compensatory and mandatory for all customers with onsite generation facilities over one megawatt • A Wyoming general rate case requesting $36 million (5%) was filed March 2014; if approved new rates will become effective January 2015 • A rate case in Idaho can be filed after May 2015, with new rates effective January 2016, or later • The company continues to review and evaluate strategies for resolution of pending or new cases, including the use of multi-year rate plans and alternative cost recovery mechanisms Rate Case Activities

Economic Outlook and Load Growth 2013 compared to 2012 • Industrial sales up 2.9% in all states • Commercial loads flat • Residential loads declined 2.0% primarily because of energy efficiency Forecast for 2014 and 2015 • Sales increase due to projected load growth in existing data centers • Slow residential growth as energy efficiency gains offset the addition of new customers Key Drivers • Low electricity prices contribute to economic growth • Low state unemployment levels in Utah, Idaho and Wyoming • Utah ranked third in Forbes list of Best States for Business in 2013; second fastest growing state in the U.S. • Over the last five years, RMP has achieved on average 280 GWh in electricity savings through customer participation in energy efficiency programs, at a cost of less than $.03 per kWh Annual Growth Rates: 2010 = 4.2% 2011 = 2.5% 2012 = 0.2% 2013 = 0.8% 2014 = 0.7% 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Fcst 2015 Fcst T W h Rocky Mountain Power Retail Load Weather Normalized Annual Growth Rates: 2010 = 4.2% 2011 = 2.5% 2012 = 0.2% 2013 = 0.8% 2014 = 0.7% 2015 = 0.3%

Capital Management Approach • The 2014 capital plan continues 2012 efficiency improvements • Funding to connect new customers is held level as increasing customer connections are offset by improvements in equipment utilization and cost reduction initiatives • Funding to comply to local, state or federal mandates and regulations is lower based on new approaches to address reliability standards and peak load forecasts • Delivered greater volumes in several areas: – 31% increase in planned new service connections driven by continued improvement in economic conditions – 8% decrease in unit cost in commercial new connects – 9% increase in distribution pole and cable replacement volumes to maintain asset health and system reliability New Service Load Growth Replacement Mandated / Regulatory Other Subtransmission and Distribution Capital Investment Allocation (2014 – 2023)
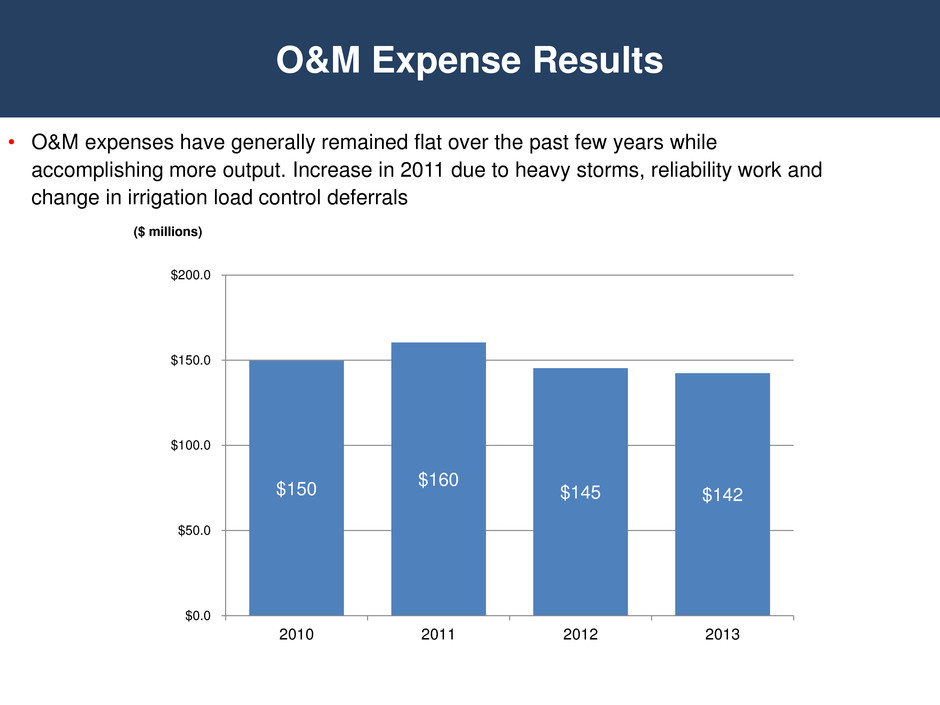
O&M Expense Results • O&M expenses have generally remained flat over the past few years while accomplishing more output. Increase in 2011 due to heavy storms, reliability work and change in irrigation load control deferrals $150 $160 $145 $142 $0.0 $50.0 $100.0 $150.0 $200.0 2010 2011 2012 2013 ($ millions)

Operational Excellence Operations • All operations, maintenance and capital programs planned with individual units of work output • For each activity an efficiency target is established to reduce unit costs • Projects and programs scope challenged to ensure least cost solution • $187 million operations and maintenance expense savings over 10 years beginning 2012 • $251 million capital savings, primarily distribution and local transmission, over 10 years beginning 2012 Service Quality Improvements • Long term plan to achieve first quartile reliability using optimal improvement tactics • Tools address outage restoration metrics to improve timeliness of restoration, in concert with previous practices that focused on eliminating repeat outage events • Projects will reduce reoccurrence of outages, reduce the number of customers affected by any given outage and minimize the average duration of the outages that occur 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 0 50 100 150 200 250 1/1/2010 1/1/2011 1/1/2012 1/1/2013 1/1/2014 S A IF I (E v e n ts ) S A ID I (M inut e s ) Rocky Mountain Power 365-Day Rolling Underlying History as Reported Stress Period SAIDI SAIFI Linear (SAIDI) Can this picture be made larger and/or more legible Distribution Line Faults - Overhead & Underground $531 $1,054 $698 $1,774 $400 $700 $1,000 $1,300 $1,600 $1,900 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Dist OH Fault Repair Dist UG Fault Repair Dist OH Fault YTD Dist UG Fault YTD Fault Initiative Implementation Un it Co st 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr 2013 Jan 2012

Operational Excellence Irrigation Demand Response Program • 202 MW of peak demand response from Idaho and Utah irrigation load in 2013 • Performance-based third-party aggregator contract for 2013 – New program design resulted in a $5 million reduction in costs from 2012 (47% improvement) – Third-party assumed performance risk Air Conditioner Demand Response Program • 109 MW of peak demand response from Utah in 2013 • Transitioning to a 2-way system for 2014 – Replace 107,000 devices within 7 months – Installing new wireless mesh communication system Safety • Safety has greatly improved over the last eight years • Continues as a top priority in 2014 4.28 3.65 2.55 1.21 1.16 1.11 1.83 1.63 0.66 0 1 2 3 4 5 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 OSHA Recordable Rate
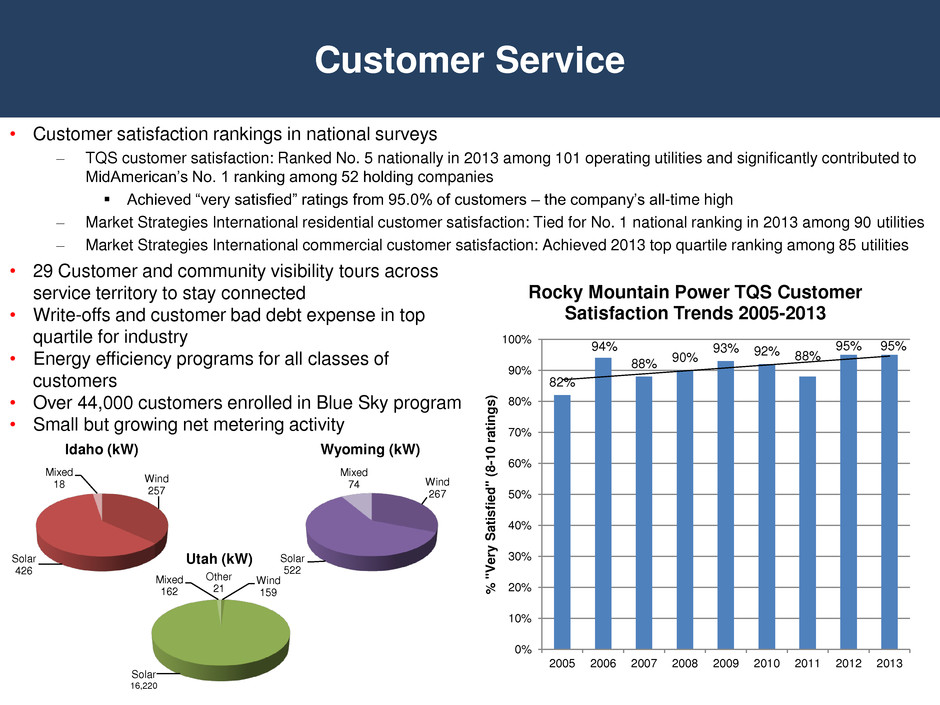
• Customer satisfaction rankings in national surveys – TQS customer satisfaction: Ranked No. 5 nationally in 2013 among 101 operating utilities and significantly contributed to MidAmerican’s No. 1 ranking among 52 holding companies Achieved “very satisfied” ratings from 95.0% of customers – the company’s all-time high – Market Strategies International residential customer satisfaction: Tied for No. 1 national ranking in 2013 among 90 utilities – Market Strategies International commercial customer satisfaction: Achieved 2013 top quartile ranking among 85 utilities Customer Service • 29 Customer and community visibility tours across service territory to stay connected • Write-offs and customer bad debt expense in top quartile for industry • Energy efficiency programs for all classes of customers • Over 44,000 customers enrolled in Blue Sky program • Small but growing net metering activity 82% 94% 88% 90% 93% 92% 88% 95% 95% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 % " V e ry S atis fied " (8 -1 0 r ati n g s ) Rocky Mountain Power TQS Customer Satisfaction Trends 2005-2013 Wind 257 Solar 426 Mixed 18 Idaho (kW) Wind 159 Solar 16,220 Mixed 162 Other 21 Utah (kW) Wind 267 Solar 522 Mixed 74 Wyoming (kW)

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Micheal Dunn President and CEO PacifiCorp Energy

Diversified Resource Portfolio 11,240 MW(1) generation capacity • 6,150 MW coal • 2,866 MW natural gas • 1,145 MW hydroelectric • 1,031 MW wind • 34 MW geothermal • 14 MW other (1) Net MW owned in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 (a) Access to other entities’ transmission lines through wheeling arrangements

Generating Capacity by Fuel Type March 31, 2006 Dec. 31, 2013 8,470 MW (1) 11,240 MW (1) Coal 72% Natural Gas 13% Hydroelectric 14% Wind, Geothermal and Other 1% (1) Net MW owned in operation and under construction Coal 55% Natural Gas 25% Hydroelectric 10% Wind, Geothermal and Other 10%

• 645-MW combined-cycle combustion turbine generating facility • The project is forecast to achieve commercial operation by mid-2014 • First fire and synchronization of the combustion turbines occurred Jan. 31, 2014 and Feb. 1, 2014 • Steam blows completed Feb. 10, 2014 • First synchronization of steam turbine – March 21, 2014 • Plant emission and performance tuning – April 2014 • Performance and emissions testing – May 2014 Lake Side 2 Construction Status

Lake Side 2 Progress – One Year February 2014 February 2013

Capital Requirements Note: Excluding AFUDC 2014-2016 Capital Plan ($ millions) Current 2014-2016 Previous 2014-2016 New generation and conversion $ 66 $ 75 Environmental compliance 422 418 Hydro projects 64 51 Maintenance capital 687 717 $1,239 $1,261 5% 34% 5% 56%

Environmental Rules Impacts • Regional Haze Rules • Mercury and Air Toxics Standard • Clean Water Act 316(b) Cooling Water Intake Rule Making • Coal Combustion Residuals Rule Making • Steam Electric Power Generating Effluent Guidelines • Greenhouse Gas 111(d)

• By April 2015, 5,759 MW(1) operated or wholly owned – 96% will be controlled by scrubbers – 65% will be controlled by baghouses – 100% will meet mercury emissions requirements – Carbon Units 1 and 2 (172 MW) retired • Future Projects – Installation of selective catalytic reduction at the Jim Bridger plant – Naughton Unit 3 (330 MW) converted to gas in 2015(2) Coal-Fueled Environmental Position (1)Excludes minority-owned Craig, Colstrip and Hayden plants (2)Natural gas conversion of Naughton Unit 3 may ultimately be deferred to 2018 pending EPA approval

• PacifiCorp Energy Ash Ponds – Seven active ash ponds – Four ash ponds are located at a facility on the North Platte River – Three are not located near significant water bodies – Two ponds are rated as “significant” hazard potential, three as “low” hazard potential, and two unrated (no hazard potential) Ash Ponds

• Implemented in 2009 • Initial assessments of all ash ponds were completed by geotechnical experts • Routine monitoring of ash ponds includes: – Daily checks by plant personnel – Bi-annual inspections by plant personnel with a focus on areas of concern as identified by geotechnical assessments – Five year comprehensive assessments by third-party geotechnical experts – Additional investigations and monitoring by geotechnical experts as necessary PacifiCorp Energy Ash Pond Monitoring Program

PacifiCorp Capital Cost of Compliance Project Regional Haze Rules HAPs MACT CCR Management Effluent Limitations Clean Water Act Scrubbers, Baghouses, Low-NOx Burners and Selective Catalytic Reduction $1.3 billion Coal Fleet Mercury Controls $21 million Coal Fleet Coal Combustion Residue Management (including asset retirement obligation) $358 million Effluent Limitation Guidelines $24 million Clean Water Act § 316(b) Compliance $5 million 2014-2016 $388 million 2014-2016 $21 million 2013-2015: $99 million 2014-2016 $17 million Note: Including AFUDC and escalation Total 2014-2023 PacifiCorp Environmental Capital: $1.7 billion (2014-2016 $525 million) 2014-2016 $0.25 million

PacifiCorp CO2 Emission Intensity Note: PacifiCorp’s share of generation 1,000 1,100 1,200 1,300 1,400 1,500 1,600 1,700 1,800 1,900 2,000 0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000 70,000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 L b s C O 2 /M W h M W h G ene rate d ( 0 0 0's ) Coal Hydro Geothermal and Other Natural Gas Wind CO2 lb/MWh

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference William Fehrman President and CEO MidAmerican Energy Company

• Headquartered in Des Moines, Iowa • 3,500 employees • 1.4 million electric and natural gas customers in four Midwestern states • 11,000 square miles of service territory • 8,444 MW(1) of owned generation capacity • Generating capacity by fuel type(1) 12/31/13 – Coal 40% – Natural Gas and Other 15% – Wind(2) 40% – Nuclear and Hydroelectric 5% (1) Net MW owned in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 (2) All or some of the renewable energy attributes associated with generation from these generating facilities may be: (a) used in future years to comply with renewable portfolio standards or other regulatory requirements or (b) sold to third parties in the form of renewable energy credits or other environmental commodities SOUTH DAKOTA NEBRASKA KANSAS MISSOURI ILLINOIS WISCONSIN MINNESOTA IOWA MidAmerican Energy Service Territory Major Generating Facilities Wind Projects Wind Projects Under Construction MidAmerican Energy Company Overview

• Economic and Load Data – Service territory has experienced moderate economic growth – 2013 retail electric sales growth due to continued industrial growth – Forecast loads for 2014 and 2015 reflect strong growth rates, particularly for industrial class due to announced data center expansions within the MidAmerican Energy service territory Business Update 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 Fcst 2015 Fcst T W h MidAmerican Energy Retail Load Weather-Normalized Annual Growth Rates: 2010 = 4.2% 2011 = 1.2% 2012 = 0.6% 2013 = 1.7% 2014 = 6.7% 2015 = 3.4%

• MidAmerican Energy had not increased Iowa electric base rates since 1995 • Iowa Utilities Board (“IUB”) approved an adjustment clause to recover increased costs of $39 million (3% increase) in 2012 and an additional $37 million (3% increase from 2012) in 2013, resulting in a total annualized increase of $76 million • Base rate increase request filed May 17, 2013 • Interim increase of $45 million (annualized) plus 2012 rider rolled into base rates, effective Aug. 17, 2013 • IUB order dated March 17, 2014 • Stepped increase in annualized base rates totaling $135 million - $45 million through 2014; $45 million at Jan. 1, 2015 and Jan. 1, 2016 Iowa Electric Rate Activity

• Energy adjustment clause – Recovery of change in retail fuel costs – Wholesale margins retained by MidAmerican Energy – Recovery of pre-tax change in production tax credits as they expire • Transmission rider – Recovery of Midcontinent Independent System Operator-billed costs • Ten-year equalization of rates among three current pricing zones • Revenue sharing mechanism – 80% sharing with customers on returns exceeding 11%, 100% sharing with customers on returns exceeding 14% • Customer share of revenue sharing retained by MidAmerican Energy and used to reduce rate base Iowa Electric Rate Activity
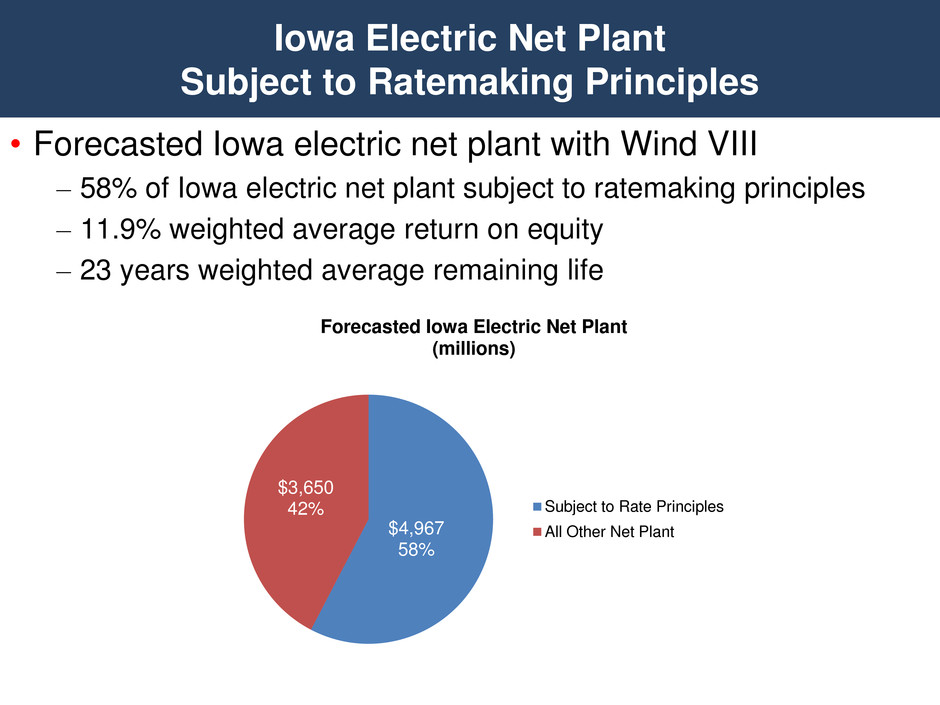
• Forecasted Iowa electric net plant with Wind VIII – 58% of Iowa electric net plant subject to ratemaking principles – 11.9% weighted average return on equity – 23 years weighted average remaining life Iowa Electric Net Plant Subject to Ratemaking Principles Annual Growth Rates: 2010 = 4.2% 2011 = 1.2% 2012 = 0.6% 2013 = 1.7% 2014 = 6.7% 2015 = 3.4% $4,967 58% $3,650 42% Forecasted Iowa Electric Net Plant (millions) Subject to Rate Principles All Other Net Plant

• MidAmerican Energy received approval from the Iowa Utilities Board to add 1,050 MW of new wind generation in Iowa through 2015 – Approval allows ROE of 11.625% for the life of the assets – $1.9 billion cost cap established – Construction of 44 MW was completed in 2013 – Construction of the remaining 1,006 MW to be completed in 2014-2015 – Turbine purchases and balance of plant under fixed-price contracts – Largest single economic development project in Iowa history Wind VIII Expansion

• Projects delivered at a cost that provides significant value to customers due to: – Fixed rate credits to the energy adjustment clause of $3.3 million, $6.6 million and $10.0 million in 2015, 2016 and 2017, respectively – Production tax credits for 10 years from the in-service date for all projects – Low-cost generation in the future • MidAmerican Energy continues to evaluate additional wind generation opportunities in Iowa Wind VIII Expansion

MidAmerican Energy Wind Resources (1) Net MW owned in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 (2) Amount is based on the cost cap approved by the IUB MW Total Cost ($ millions) 2004 161 $164 2005 200 225 2006 99 177 2007 202 389 2008 623 1,291 2011 593 960 2012 407 660 2013-2015 1,050 1,900(2) Total 3,335 $5,766 Owned Wind Generation Capacity (1)

• Of MidAmerican Energy’s nearly 4,100 MW of operated coal-fueled generation: – 100% of generation has nitrogen oxides controls Low-NOx burners and/or over-fire air on all units One selective catalytic reduction system on Walter Scott, Jr. Energy Center Unit 4 Two selective non-catalytic reduction systems on Neal Energy Center Units 3 and 4 – 55% of generation has scrubbers and baghouses for sulfur dioxide control – 20% of generation has activated carbon injection for mercury control Environmental Position

• By 2016, nearly 700 MW of operated coal-fueled generation will be limited to natural gas or retired, resulting in 100% of coal-fueled generation controlled with scrubbers, baghouses and mercury controls, and 63% with post-combustion NOx controls • Neal Unit 4 scrubber and baghouse project recently completed • Neal Unit 3 and Ottumwa Generating Station scrubber and baghouse projects to be completed by the end of 2014 • Walter Scott Unit 3, Louisa, Neal Unit 3 and Neal Unit 4 activated carbon injection systems for mercury control to be completed by April 2015 Environmental Position

• Anticipated future projects – Ash pond closures – Bottom ash dry handling – Cooling water intake structure retrofits for fish handling Environmental Position

• MidAmerican Energy ash ponds – Seven active ash ponds and one inactive ash pond. The inactive pond does not contain water – Five ash ponds are located at facilities on the Missouri River; three ash ponds are located at facilities on the Mississippi River – All underground infrastructure that traverse ponds pose little risk of failure due to locations in dry areas of a pond, lack of direct connection to surface water, or use in maintaining pond levels prior to discharge – All ponds were ranked “low hazard” by EPA Ash Ponds

• Implemented in 2011 • Includes information on maintenance history of each pond and specifies appropriate operating and maintenance criteria to manage risk • Requires facilities to complete pond inspections, including: – Quarterly visual inspections to review physical conditions and check for signs of erosion, animal activity, seepage, etc. – Annual structural integrity inspections – Periodic third-party engineering inspections MidAmerican Energy Ash Pond Monitoring Program
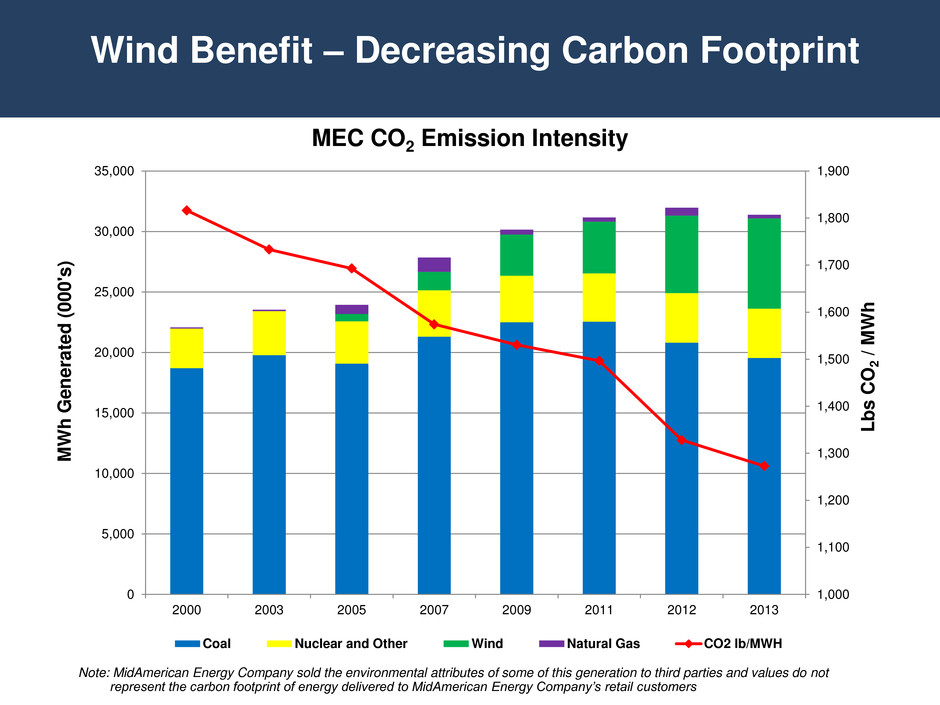
Wind Benefit – Decreasing Carbon Footprint Note: MidAmerican Energy Company sold the environmental attributes of some of this generation to third parties and values do not represent the carbon footprint of energy delivered to MidAmerican Energy Company’s retail customers 1,000 1,100 1,200 1,300 1,400 1,500 1,600 1,700 1,800 1,900 0 5,000 10,000 15,000 20,000 25,000 30,000 35,000 2000 2003 2005 2007 2009 2011 2012 2013 L b s C O 2 / M W h M W h Ge n e rate d (000's ) MEC CO2 Emission Intensity Coal Nuclear and Other Wind Natural Gas CO2 lb/MWH

MidAmerican Energy Company Capital Cost of Compliance Total 2014-2023 MidAmerican Energy Environmental Capital: $467 million (2014-2016: $139 million) Project CAIR/CSAPR Permitting MATS 316(b) CCR Management Neal Units 3 and 4 and Ottumwa: Scrubber and Baghouse $90 million (2014-2016: $90 million) Ottumwa: Selective Catalytic Reduction $127 million (2014-2016: $0 million) Neal Units 3 and 4: Selective Noncatalytic Reduction $10 million (2014-2016: $10 million) Louisa: Low NOx Burner $21 million (2014-2016: $0 million) Coal Fleet Mercury Controls $15 million (2014-2016 $15 million) Coal Fleet Cooling Water Intake Structure Retrofit $10 million (2014-2016 $0 million) Coal Fleet Ash Pond Closures $148 million (2014-2016: $20 million) Coal Fleet Bottom Ash Dry Handling $46 million (2014-2016: $4 million) Subtotal: $217 million (2014-2016: $90 million) $31 million (2014-2016: $10 million) $15 million (2014-2016: $15 million) $10 million (2014-2016: $0 million) $194 million (2014-2016: $24 million) Note: Including AFUDC

• MidAmerican Energy plans to construct portions of four 345-kV multi-value projects within the MISO footprint, totaling approximately 245 miles; approved by the MISO board in Dec. 2011 • Expenditures predominantly in 2014-2017, totaling approximately $528 million, excluding equity AFUDC • MVP are eligible for incentive rate treatment in MISO tariff, including construction work in progress in rate base and recovery of prudent costs incurred if projects are abandoned Transmission Development

• MVP revenue requirements broadly recovered from all MISO load; approximately 95% recovered from other MISO participants • MVP expected to provide multiple benefits, including improved reliability, reduced congestion, and support for additional generation development • All transmission investments utilize forward-looking rate treatment in MISO tariff, mitigating rate lag Transmission Development

• MidAmerican is committed to being an industry leader in enhancing physical security at its critical asset sites using current and emerging technologies • Since 2007, MidAmerican has been investing in its critical assets to improve physical security • MidAmerican has ranked its asset sites into different security categories; as a result additional assets have been identified as critical • MidAmerican has executive leadership with U.S. security clearance and maintains close coordination with federal and state intelligence organizations Industry Discussion – Physical Asset Security

• All enhancements will provide greater protections against coordinated attacks • MidAmerican will continue to meet with state regulators and stakeholders to communicate improvements, risk mitigation and any related costs • Overall, take immediate and prudent actions while continuing to assess and transition to future security mitigation technology and processes Industry Discussion – Physical Asset Security

• Transmission Integrity Management/Distribution Integrity Management – Identify threats and reduce pipeline risks – Develop preventative and mitigative measures – Measure performance and evaluate effectiveness Mitigating Risk – Gas Pipeline Integrity Programs 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Miles of Cast Iron Main at End of Year • Typical Integrity Management Outcomes – Pipeline system replacements, i.e., Cast Iron Retirement, to be completed by end of 2014 – Expanded Public Awareness Programs i.e., general public education, public official training, excavators, etc.

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Mark Hewett President and CEO, MidAmerican Energy Pipeline Group President and CEO, Northern Natural Gas Company

• 840 employees • 14,700-mile interstate natural gas transmission pipeline system • Market Area design capacity of 5.5 Bcf/day plus 2.0 Bcf/day Field Area delivery capacity to the Market Area • Five natural gas storage facilities, with a total firm capacity of more than 73 Bcf and more than 2.0 Bcf of peak day delivery capability • Access to five major traditional supply regions and direct access to two non- traditional (tight sands and shale) supply regions • Annual average deliveries of 953 Bcf over the prior three years Overview

• Continued to demonstrate financial strength even during flat price spreads • Successfully renegotiated 1.2 Bcf/day of Market Area contracts at higher rates • Increased Field Area revenue by 6% compared to 2012 and 18% compared to 2011 – Approximately 45% of 2013 Field Area revenue from long-term contracts • Successfully restructured condensate sales contract through March 2015 • Executed long-term contract with CF Industries with $74 million facility addition to serve their fertilizer plant expansion • Increased the integrity and reliability of the pipeline while managing operating costs and staffing • Earned slightly above our allowed rate of return 2013 Business Update

• Challenges and opportunities in early 2014 – Market Area Deliveries – impact from Polar vortex Average market area delivery record of over 4 Bcf/day for the first two months of the year Averaged 675,000 Dth/day more than 2013 and 945,000 Dth/day more than 2012 in January and February Peak day on Jan. 6, 2014, of 5.14 Bcf – 7% higher than previous peak of 4.82 Bcf January and February 2014 was 27% colder than normal, compared to 4% colder than normal for 2013 and 14% warmer than normal for 2012 – Increased supply of Field Area gas into the Market Area for 1st quarter 2014 compared to 2013 Revenue is $28.6 million higher and volumes 560,000 Dth/day higher – TransCanada pipeline rupture – no receipts from Viking Worked with customers to deliver unscheduled natural gas of up to 300,000 Dth/day Coordinated with Minnesota and Wisconsin customers to divert deliveries and scheduled volumes Met all firm deliveries through diligent efforts of our teams – Signed long-term contracts with two shippers to expand capacity in Permian region 2014 Business Update

• Reticulated system – economically unfeasible to replicate • Optionality with Field Area – tremendous advantage for customers and Northern Natural Gas to capture opportunities • Long-term contracts with stable markets • Northern Natural Gas’ prices are competitive with other pipelines (minimizes level of discounting needed in competitive markets) • Focus on customer satisfaction – In February 2014, Mastio & Company announced that in the results of their annual survey that Northern Natural Gas ranked No. 1 out of 16 mega-pipelines and No. 2 out of 42 interstate pipelines in customer satisfaction – At the same time, one of Northern Natural Gas’ main competitors had posted a force majeure and operational flow orders placing it at risk of not delivering on their firm entitlement This competitor is also rated 38 out of 42 interstate pipelines – Another competitor of Northern Natural Gas is rated 29 out of 42 interstate pipelines Competitive Advantages

• 90% of revenue is from demand charges • 64% of 2013 transportation and storage demand revenue was from highly-rated utilities • In 2013, completed approximately 1.2 Bcf/day in contract renewals with a 3% increase in rates, which provides additional $3 million in annual revenue • 86% of 2013 storage revenue resulted from long-term contracts, with an average remaining contract life of approximately eight years Northern Natural Gas currently contracts 100% of its firm storage service annually • Long-term contracts with creditworthy counterparties – top 10 customer groups have a weighted average credit rating of A3/BBB+ Revenue Stability and Long-term Contracts Transportation - Market 79% Transportation - Field 11% Storage 10% 2014-2015 15% 2016-2017 33% 2018-2019 39% 2020-2021 2% 2022+ 11% Average remaining contract life of approximately 5 years 2013 Transportation and Storage Revenue $566 Million Market Area Transportation Contract Maturities (1) (1) Based on maximum daily quantities of market area entitlement in decatherms as of Feb. 28, 2014

• CF Industries – Port Neal Expansion – Nitrogen fertilizer plant expansion in Northwest Iowa – Contract effective date of December 2014 – Total capital expenditures of approximately $74 million – Signed an 11-year contract with entitlement of 88,000 Dth/day – Fixed rate contract with annual demand revenue of $24 million – Agreement was competitive with their other option, Northern Border Pipeline • Permian Expansion – Signed long-term contracts with two different shippers for incremental entitlement of 158,000 Dth/day Contracts expire in 2019 – In-service date of November 2014 Some volumes are being served currently with existing capacity – Total capital expenditures of approximately $13 million – Annual average revenue of $8 million between 2014 and 2019 – Source is from shale oil and other midstream parties Expansion Projects
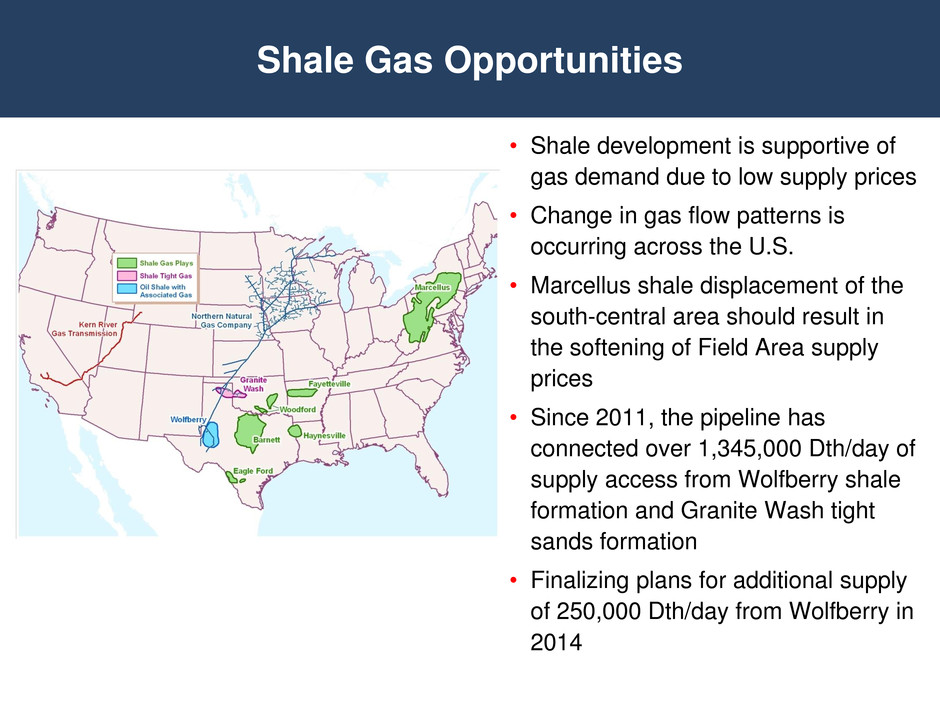
• Shale development is supportive of gas demand due to low supply prices • Change in gas flow patterns is occurring across the U.S. • Marcellus shale displacement of the south-central area should result in the softening of Field Area supply prices • Since 2011, the pipeline has connected over 1,345,000 Dth/day of supply access from Wolfberry shale formation and Granite Wash tight sands formation • Finalizing plans for additional supply of 250,000 Dth/day from Wolfberry in 2014 Shale Gas Opportunities

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Gary Hoogeveen President Kern River Gas Transmission Company

Overview • Headquartered in Salt Lake City, Utah • 150 employees • 1,700-mile interstate natural gas transmission pipeline system • Delivers natural gas from Rocky Mountain basin to markets in Utah, Nevada and California • Design capacity: 2.2 million Dth per day of natural gas • Over 95% of capacity contracted under long-term contracts CALIFORNIA UTAH WYOMING ARIZONA NEVADA

• Continue to sell available firm capacity long-term at rates above near-term market value – Limited amount of un-contracted firm capacity 102,000 Dth/day, < 5% of total firm capacity – Value of capacity is projected to increase nearly 60% over the next three years $0.23/Dth in 2015 to $0.37/Dth in 2017 • Provide a competitive delivered cost to Southern California and Southern Nevada • Earned slightly above our allowed rate of return in 2013 • Growth of natural gas-fueled electric generation in the Southwest U.S. and Mexico increases demand for U.S. pipeline capacity and provides incremental opportunity for Kern River • Scheduled throughput averaged 112% of design capacity Business Update

Competitive Advantage • Kern River is the lowest delivered cost interstate pipeline option to Southern California • Directly connected to end-use markets in Nevada and California – Avoid rate stack • State of the art transmission system • Limited incremental cost to comply with stricter pipeline safety standards • Exceptional customer service – In the 18th Edition Mastio & Company pipeline industry survey, Kern River ranked No. 1 out of 42 interstate pipelines in customer satisfaction – Kern River has been No.1 in four of the last six years and No. 2 in the other two years

Revenue Stability and Long Term Contracts Long Term Contract Maturities(1) 2013 Revenue Distribution $359 Million (1) Based on total system design capacity of 2.2 million Dth per day • 95% of revenue is from demand charges • The majority of contracts remain in place through maturity of the project debt in 2016 and 2018 • Weighted average shipper rating of BBB+/Baa1 • Shippers that do not meet credit standards are required to post collateral • Weighted average contract term of nearly six years Demand 95% MOR 3% Other 2% Uncontracted 4% 2014 1% 2016 30% 2017 5% 2018 35% 2019-2020 5% 2025-2028 7% 2031-2033 13%

Strong Demand for Services Daily Average Scheduled Volume 2013 Deliveries by State (1) Based on the 2013 California Gas Report (2) Based on Kern River’s average scheduled volumes to Nevada and Southwest Gas Transmission Company’s system capacity served by El Paso Natural Gas Company, LLC or Transwestern Pipeline Company, LLC. • Delivered approximately 27%(1) of California’s demand for natural gas • Delivered more than 80%(2) of southern Nevada’s natural gas • During 2013, scheduled throughput averaged 112% of design capacity 0 500,000 1,000,000 1,500,000 2,000,000 2,500,000 3,000,000 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Scheduled Design California 70% Nevada 24% Utah 6%

Long-Term Business Outlook Non-coincident Peak Day Deliveries (Dth/d)(1) Utah LDC (Questar Gas) 463,937 Direct-connect end-users 25,562 489,499 Nevada LDC (Southwest Gas) 504,203 Direct-connect end-users 518,654 1,022,857 California LDC (Southern California Gas) - Direct-connect end-users 191,602 191,602 Total 1,703,958 (79% of Kern River capacity) • Questar Gas has multiple interconnects with Questar Pipeline but relies on Kern River to provide peak-day deliveries • Kern River is the sole transporter of natural gas to Southern Nevada, with the exception of 141,000 Dth/d of capacity on Southwest Gas’ southern system • Southern California gas utilities have other pipeline or storage options on a peak day; however, direct-connect end-users rely on Kern River Markets are Dependent on Kern River (1) Based on actual peak day deliveries over the past three years and an analysis of the LDCs’ pipeline supply options

Lowest-Cost Option to Southern California Source: Platts’ M2M Modeled Natural Gas Forward Curves – 10 Year, Feb. 14, 2014; Interstate Pipeline FERC Gas Tariffs; and Kern River Period Two rates. Transportation rates include February 2014 fuel. (1) Period One contracts expire Sept. 30, 2016, then Period Two rates apply (2) Period One contracts expire April 30, 2018, then Period Two rates apply Rockies $3.9800 Rockies $3.9800 Rockies $3.9800 Rockies $3.9800 Rockies $3.9800 San Juan $4.0500 San Juan $4.0500 Permian $4.0500 Aeco $3.5800 $0.1846 $0.2224 $0.2238 $0.3759 $0.4514 $0.4514 $0.2640 $0.4100 $1.1469 $0.3148 $0.1427 $0.2663 $0.2663 $0.2663 $4.2294 $4.3055 $4.3069 $4.5519 $4.6332 $4.6332 $4.5666 $4.9756 $5.4946 $0.0000 $1.0000 $2.0000 $3.0000 $4.0000 $5.0000 $6.0000 Kern River Period 2 Vintage 2016 (1) Kern River Period 2 Expansion 2018 (2) Kern River Period 2 Expansion 2013 Transwestern El Paso El Paso TCPL/GTN/ PG&E NWP/GTN/ PG&E Ruby/PG&E $/D th Natural Gas Price Fuel and Commodity Transportation Demand Rate

Pipeline Diversity Minneapolis: 72oF Los Angeles: 93oF • Northern Natural Gas and Kern River serve diverse markets – Diverse weather impacts – Varying economic drivers – Provides balance of demand Hot Southwest Minneapolis: -10oF Los Angeles: 72oF Cold Midwest

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Phil Jones President and CEO Northern Powergrid Holdings Company
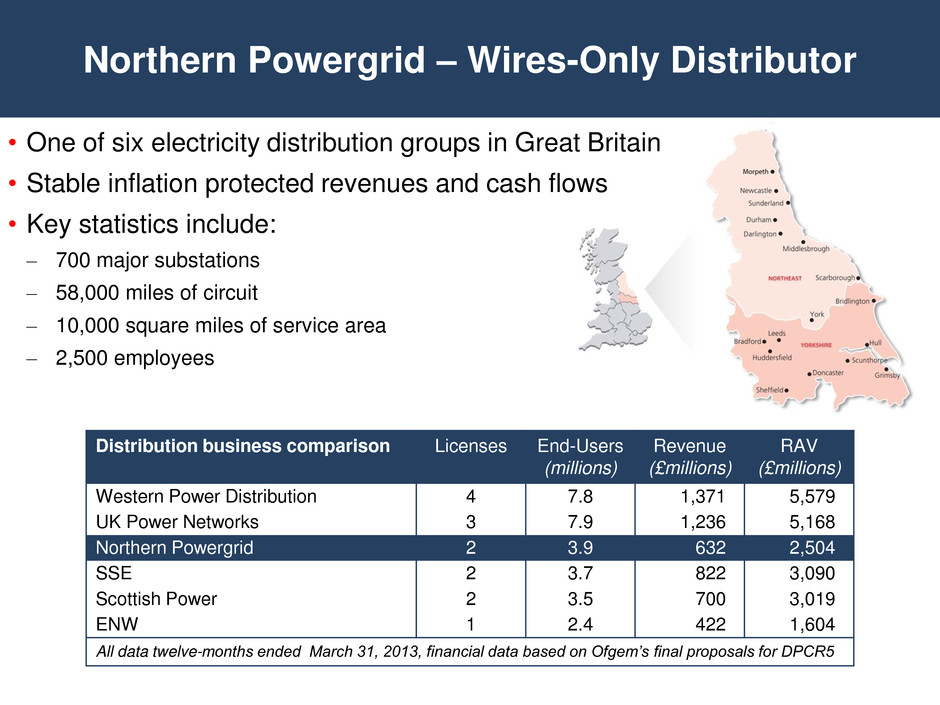
Northern Powergrid – Wires-Only Distributor Distribution business comparison Licenses End-Users (millions) Revenue (£millions) RAV (£millions) Western Power Distribution 4 7.8 1,371 5,579 UK Power Networks 3 7.9 1,236 5,168 Northern Powergrid 2 3.9 632 2,504 SSE 2 3.7 822 3,090 Scottish Power 2 3.5 700 3,019 ENW 1 2.4 422 1,604 All data twelve-months ended March 31, 2013, financial data based on Ofgem’s final proposals for DPCR5 • One of six electricity distribution groups in Great Britain • Stable inflation protected revenues and cash flows • Key statistics include: – 700 major substations – 58,000 miles of circuit – 10,000 square miles of service area – 2,500 employees

Strong Investment Metrics • Return on book equity exceeds expectations • 35% growth in regulated asset value in DPCR5, primarily financed by operating cash flows • Inflation protection applies to revenue and regulated asset value (RAV) - averaging 3.3% p.a. since April 2007 • OpCo operating income remains strong, reflecting revenue growth, with a decrease due to pension expense • Strong credit ratings compare well with the rest of the sector Years Ended Dec. 31, (£ millions) - US GAAP 2013 2012 2011 Revenues 657 653 633 Operating income 323 357 384 Capex 431 286 193 RAV 2,660 2,504 2,334 Interest cover 3.9x 4.3x 4.3x Debt to RAV gearing 56% 55% 56% Ofgem’s DPCR5 final proposals for the 2010-15 period included growth for revenue and RAV – 7% underlying (real) revenue growth – 4% underlying (real) growth in RAV – RAV growth supplemented by 3.3% p.a. inflation from April 2007

• Safety performance is amongst the leaders in a high-performing industry • Delivery of the DPCR5 capex program is the main driver of value in the business; we are on target to hit our outputs for DPCR5, achieving an all-time high capex delivery in 2013 • Staying on target with over 85% of outputs delivered four years into the five- year price control period • Publicly forecast 14% outperformance of total cost allowances, no categories overspent • Customer service is mid-pack but trending positively • Implemented many new web-based services; the first U.K. group to offer online self-service transactions • Consistently exceeded our reliability and availability targets • Successfully delivering the largest smart grid project in the U.K., involving more than 13,000 end-users Strong Operational Performance

Outlook for the RIIO-ED1 Price Control Period 2014-2023 • Public policy reflects growing political pressure on energy affordability – UK government announced £50 per customer energy charge reduction in December 2013 – Parliamentary and regulatory scrutiny of energy companies is building – Competition Markets Authority is reviewing energy supply market – Carbon taxes and environmental schemes are under pressure for review • Utility regulators are reflecting lower risk free rates into allowed returns on equity – Ofgem initially set a base return on equity in a narrow range of 6.7% to 7.0% real, progressively lowering its reference point to 6.3% by November 2013 – The U.K. Competition Commission held a review of the settlement for Northern Ireland Electricity and set a much lower cost of equity than has previously been the norm Consequently, Ofgem has revised down the mid-point of its range by 30bps to 6.0% – The Competition Commission used actual cost as a basis for a cost of debt – Ofgem’s cost of debt is based on the average of an index, currently below 3.0% real • Ofgem will review plans for five of the six companies during Q2-Q3, 2014 – Western Power Distribution’s plan is already approved – Northern Powergrid’s plan was rated as very strong by Ofgem and a number of key stakeholders and requires little change

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Richard Weech President MidAmerican Renewables – International

MidAmerican Solar MidAmerican Geothermal Geothermal Plants Natural Gas Plants MidAmerican Wind MidAmerican Hydro CalEnergy Philippines MidAmerican Renewables

Renewables Portfolio (1) Net owned capacity is after acquiring the 50% interest currently not owned by MidAmerican, announced on Feb. 20, 2014 (2) 82% of the company’s interests in the Imperial Valley projects’ contract capacity are sold to SCE (3) Net MW in operation and under construction as of Dec. 31, 2013 Location Installed PPA Expiration Power Purchaser Facility Net or Contract Capacity (MW) Net Owned Capacity (MW) SOLAR: Topaz California 2013-2015 2040 PG&E 550 550 Agua Caliente Arizona 2012-2013 2039 PG&E 290 142 Solar Star I and II California 2013-2015 2035 SCE 579 579 1,419 1,271 WIND: Pinyon Pines I and II California 2012 2035 SCE 300 300 Bishop Hill II Illinois 2012 2032 Ameren 81 81 381 381 GEOTHERMAL: Imperial Valley Projects (1) California 1982-2000 2016-2039 (2) 327 327 HYDROELECTRIC: Casecnan Project Philippines 2001 2021 NIA 150 128 Wailuku (1) Hawaii 1993 2023 HELCO 10 10 160 138 NATURAL GAS: Saranac (1) New York 1994 2015 TEMUS 240 180 Power Resources (1) Texas 1988 2015 EDF 212 212 Yuma (1) Arizona 1994 2024 SDG&E 50 50 Cordova Illinois 2001 2019 EGC 551 551 1,053 993 Total Generating Capacity (3) 3,340 3,110

• At 550 MWAC delivered, Topaz will be one of the world’s largest solar photovoltaic power plants upon final completion in early 2015 – Project is being completed in 22 development and construction phases, with total projected costs of $2.4 billion – 25-year power purchase agreement with Pacific Gas and Electric Company (A3/BBB/A-) – Fixed-price engineer, procure, construct and 25-year firm price operations and maintenance agreements executed with First Solar (ability to change O&M provider at our option every five years) • Construction and commissioning are on schedule to meet the following installed capacity at year-end – 2013: 241 MW – Capacity turned over with 300 MW actual capacity online – 2014: 533 MW – 2015: 586 MW Topaz Solar Farms Overview

• Through February 2014, project is 75% complete, with more than 6.3 million of the 8.4 million First Solar Series 3 thin-film panels installed • As of February 2014, the plant is delivering 362 MW of electricity to the transmission grid and First Solar has formally turned over 291 MW of the plant to MidAmerican for operation • Independent engineer has confirmed that the project is two months ahead of schedule and on budget, and there are no reasons the substantial completion date (May 18, 2015) and guaranteed commercial operation date (Feb. 18, 2016) cannot be achieved • In 2013, plant generated 428,600 MWh of energy versus a budget of 321,000 MWh – Majority of the favorable variance was the result of early completion of block capacity and resulting energy put to the grid • Effective availability totaled 99.54% Topaz Project Status
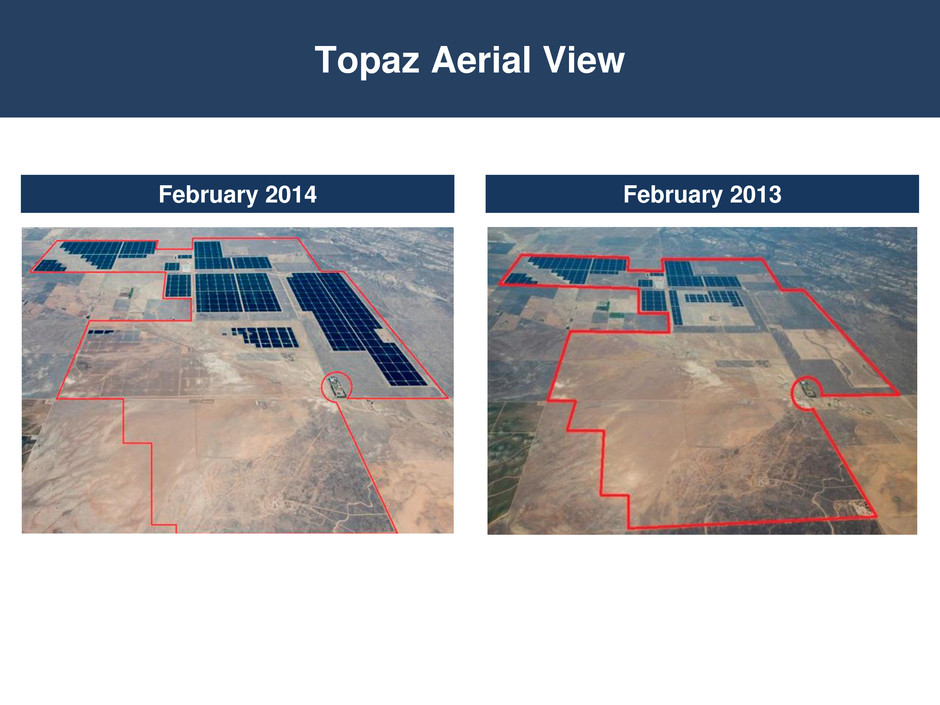
Topaz Aerial View February 2014 February 2013

• 290 MWAC facility located on 2,340 acres in Yuma County, Arizona • MidAmerican Solar is a 49% owner of the project • 25-year power purchase agreement with Pacific Gas and Electric Company (A3/BBB/A-) • Fixed-price engineer, procure, construct and 25-year firm price operations and maintenance agreements executed with First Solar (ability to change O&M provider at our option every five years) – Total project cost of $1.7 billion • Supported by U.S. Department of Energy loan guarantee agreement • Construction and commissioning of plant’s total 315 MW by First Solar was completed in December 2013 – Maximum delivery at the point of interconnection under the PPA limited to 290 MW • Project completed well ahead of the guaranteed substantial completion date of March 31, 2014 • In 2013, plant generated 687,100 MWh of energy versus a budget of 623,000 MWh – Majority of the favorable variance was the result of early completion of block capacity and resulting energy put to the grid • Effective availability totaled 99.48% Agua Caliente Overview

Agua Caliente Aerial View January 2014 February 2013

• At 579 MWAC delivered, the combined Solar Star projects will be one of the world’s largest solar photovoltaic power plants upon final completion in late 2015 – Projects are being completed in 13 development and construction phases, with total projected costs of $2.75 billion – Two 20-year power purchase agreements with Southern California Edison Company (A2/BBB+/A) – Fixed-price engineer, procure, construct and 20-year firm price operations and maintenance agreements executed with SunPower (ability to change O&M provider at our option every five years) • Construction and commissioning are on schedule to meet the following installed capacity at year-end – 2013: 57 MW – Actual installed capacity – 2014: 354 MW – 2015: 579 MW Solar Star Overview

• Through February 2014, project is 44% complete, with more than 0.7 million of the 1.7 million SunPower 435 watt panels installed • As of February 2014, the plant is delivering 175 MW of electricity to the transmission grid and SunPower has formally turned over 57 MW of the plant to MidAmerican for operation • Independent engineer has confirmed that the project remains on schedule and on budget, and there are no reasons the substantial completion date of Oct. 31, 2015, cannot be achieved Solar Star Project Status

Solar Star Aerial View – March 2014

• 81 MW wind farm located in Henry County, approximately 20 miles southeast of Rock Island, Illinois • 50 General Electric 1.62 MW wind turbines • 20-year power purchase agreement with Ameren Illinois Company (Baa1/BBB+/BBB) • $120 million project financing closed on Aug. 21, 2012 • Commercial operation date – Dec. 7, 2012 • Turbines are performing well • Currently meeting or exceeding operational and budgetary targets Bishop Hill II Wind

• 300 MW wind farm located in the Tehachapi/Mojave region of Kern County, California, approximately 75 miles north of Los Angeles • 100 Vestas 3.0 MW wind turbines • 23-year power purchase agreement with Southern California Edison Company (A2/BBB+/A) • Assumed existing project financing • Commercial operation date – Jan. 1, 2013 • Turbines are performing well • Currently meeting or exceeding operational and budgetary targets Pinyon Pines Wind I and II

Questions

2014 Fixed-Income Investor Conference Gregory E. Abel Chairman, President and CEO MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company

Vision To be the best energy company in serving our customers, while delivering sustainable energy solutions MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company Core Principles

Questions

Appendix

MidAmerican Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) As a result of changes in accounting guidance, certain amounts have been reclassified to conform to the other periods presented (2) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Adjusted Interest divided by Adjusted Interest (3) Debt includes short-term debt, MidAmerican senior debt, MidAmerican subordinated debt and subsidiary debt (including current maturities) (4) FFO to Adjusted Debt Excluding NVE Related Debt equals FFO divided by Adjusted Debt Excluding NVE Related Debt (5) Adjusted Debt to Total Capitalization equals Adjusted Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 2001(1) Net cash flows from operating activities 4,669$ 4,327$ 3,220$ 847$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities, net of effects from acquisitions (449) (40) 382 (196) FFO 4,220$ 4,287$ 3,602$ 651$ Adjusted Interest Interest expense 1,222$ 1,176$ 1,196$ 587$ Interest expense on subordinated debt (3) - (26) (88) Adjusted Interest 1,219$ 1,176$ 1,170$ 499$ FFO Interest Coverage(2) 4.5x 4.6x 4.1x 2.3x Adjusted Debt Debt(3) 32,244$ 21,622$ 19,937$ 8,050$ Subordinated debt (2,594) - (22) (888) Adjusted Debt 29,650$ 21,622$ 19,915$ 7,162$ NVE Acquisition Financing Debt (2,000) NVE Subsidiary Debt (5,296) Adjusted Debt Excluding NVE Related Debt 22,354$ FFO to Adjusted Debt Excluding NVE Related Debt(4) 18.9% 19.8% 18.1% 9.1% Capitalization Total MidAmerican shareholders’ equity 18,711$ 15,742$ 14,092$ 1,708$ Adjusted debt 29,650 21,622 19,915 7,162 Subordinated debt 2,594 - 22 888 Noncontrolling interests 105 168 173 165 Capitalization 51,060$ 37,532$ 34,202$ 9,923$ Adjusted Debt to Total Capitalization(5) 58.1% 57.6% 58.2% 72.2%
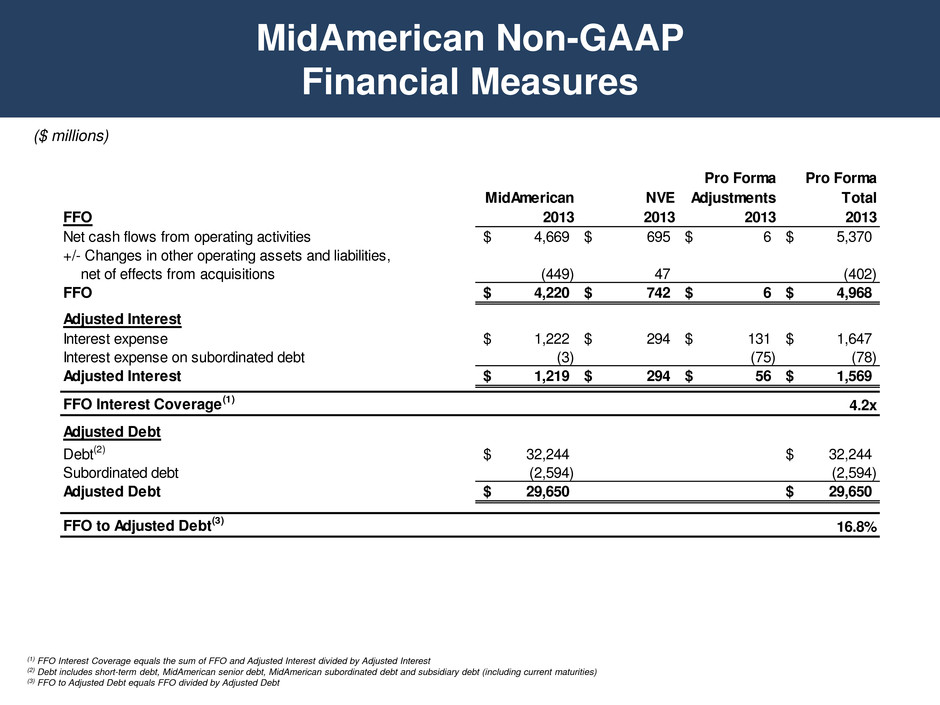
MidAmerican Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Adjusted Interest divided by Adjusted Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt, MidAmerican senior debt, MidAmerican subordinated debt and subsidiary debt (including current maturities) (3) FFO to Adjusted Debt equals FFO divided by Adjusted Debt ($ millions) Pro Forma Pro Forma MidAmerican NVE Adjustments Total FFO 2013 2013 2013 2013 Net cash flows from operating activities 4,669$ 695$ 6$ 5,370$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities, net of effects from acquisitions (449) 47 (402) FFO 4,220$ 742$ 6$ 4,968$ Adjusted Interest Interest expense 1,222$ 294$ 131$ 1,647$ Interest expense on subordinated debt (3) (75) (78) Adjusted Interest 1,219$ 294$ 56$ 1,569$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 4.2x Adjusted Debt Debt(2) 32,244$ 32,244$ Subordinated debt (2,594) (2,594) Adjusted Debt 29,650$ 29,650$ FFO to Adjusted Debt(3) 16.8%

MidAmerican Non-GAAP Financial Measures ($ millions) MidAmerican and NV Energy Pro Forma EBITDA for the year ended Dec. 31, 2013 MidAmerican NV Energy EBITDA As Reported Pro Forma Adjustment Historical Pro Forma Adjustment Pro Forma Combined Net income 1,676$ 43$ 162$ 26$ 1,907$ Interest expense 1,222 - 294 131 1,647 Capitalized interest (84) - - (8) (92) Income tax expense 130 15 107 (8) 244 Depreciation and amortization 1,560 - 400 - 1,960 EBITDA 4,504$ 58$ 963$ 141$ 5,666$

PacifiCorp Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 1,553$ 1,627$ 1,636$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities (34) (169) (144) FFO 1,519$ 1,458$ 1,492$ Interest expense 379$ 380$ 392$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 5.0x 4.8x 4.8x Debt (2) 6,877$ 6,861$ 6,901$ FFO to Debt(3) 22.1% 21.3% 21.6% Capitalization PacifiCorp shareholders’ equity 7,787$ 7,644$ 7,312$ Debt 6,877 6,861 6,901 Capitalization 14,664$ 14,505$ 14,213$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 46.9% 47.3% 48.6%

MidAmerican Energy Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 735$ 1,276$ 770$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities 151 (323) 354 FFO 886$ 953$ 1,124$ Interest expense 151$ 143$ 158$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 6.9x 7.7x 8.1x Debt (2) 3,552$ 3,259$ 3,115$ FFO to Debt(3) 24.9% 29.2% 36.1% Capitalization MidAmerican Energy shareholder's equity 3,845$ 3,635$ 3,271$ Debt 3,552 3,259 3,115 Noncontrolling interests - - 1 Capitalization 7,397$ 6,894$ 6,387$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 48.0% 47.3% 48.8%
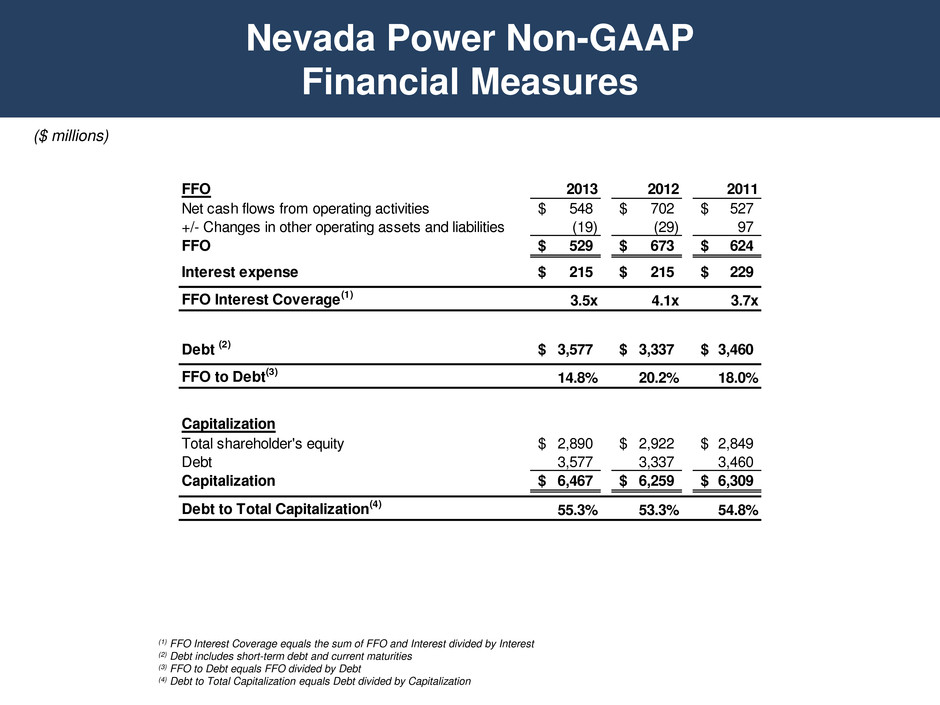
Nevada Power Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 548$ 702$ 527$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities (19) (29) 97 FFO 529$ 673$ 624$ Interest expense 215$ 215$ 229$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 3.5x 4.1x 3.7x Debt (2) 3,577$ 3,337$ 3,460$ FFO to Debt(3) 14.8% 20.2% 18.0% Capitalization Total shareholder's equity 2,890$ 2,922$ 2,849$ Debt 3,577 3,337 3,460 Capitalization 6,467$ 6,259$ 6,309$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 55.3% 53.3% 54.8%

Sierra Pacific Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 226$ 197$ 176$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities 16 78 50 FFO 242$ 275$ 226$ Interest expense 62$ 65$ 69$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 4.9x 5.2x 4.3x Debt (2) 1,200$ 1,179$ 1,179$ FFO to Debt(3) 20.2% 23.3% 19.2% Capitalization Total shareholder's equity 1,016$ 1,039$ 975$ Debt 1,200 1,179 1,179 Capitalization 2,216$ 2,218$ 2,154$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 54.2% 53.2% 54.7%

Northern Natural Gas Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 264$ 304$ 286$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities 41 (27) 24 FFO 305$ 277$ 310$ Interest expense 44$ 52$ 56$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 7.9x 6.3x 6.5x Debt (2) 899$ 899$ 950$ FFO to Debt(3) 33.9% 30.8% 32.6% Capitalization Northern Natural Gas shareholder’s equity 1,360$ 1,290$ 1,274$ Debt 899 899 950 Capitalization 2,259$ 2,189$ 2,224$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 39.8% 41.1% 42.7%

Kern River Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 220$ 249$ 227$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities 2 (1) - FFO 222$ 248$ 227$ Interest expense 36$ 41$ 46$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 7.2x 7.0x 5.9x Debt (2) 548$ 628$ 716$ FFO to Debt(3) 40.5% 39.5% 31.7% Capitalization Partners’ capital 829$ 880$ 868$ Debt 548 628 716 Capitalization 1,377$ 1,508$ 1,584$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 39.8% 41.6% 45.2%

Northern Powergrid Non-GAAP Financial Measures (1) FFO Interest Coverage equals the sum of FFO and Interest divided by Interest (2) Debt includes short-term debt and current maturities (3) FFO to Debt equals FFO divided by Debt (4) Debt to Total Capitalization equals Debt divided by Capitalization ($ millions) FFO 2013 2012 2011 Net cash flows from operating activities 501$ 413$ 362$ +/- Changes in other operating assets and liabilities (44) 103 183 FFO 457$ 516$ 545$ Interest expense 141$ 139$ 151$ FFO Interest Coverage(1) 4.2x 4.7x 4.6x Debt (2) 2,546$ 2,408$ 2,146$ FFO to Debt(3) 17.9% 21.4% 25.4% Capitalization Northern Powergrid shareholders’ equity 3,027$ 2,611$ 2,161$ Debt 2,546 2,408 2,146 Noncontrolling interests 56 56 56 Capitalization 5,629$ 5,075$ 4,363$ Debt to Total Capitalization(4) 45.2% 47.4% 49.2%
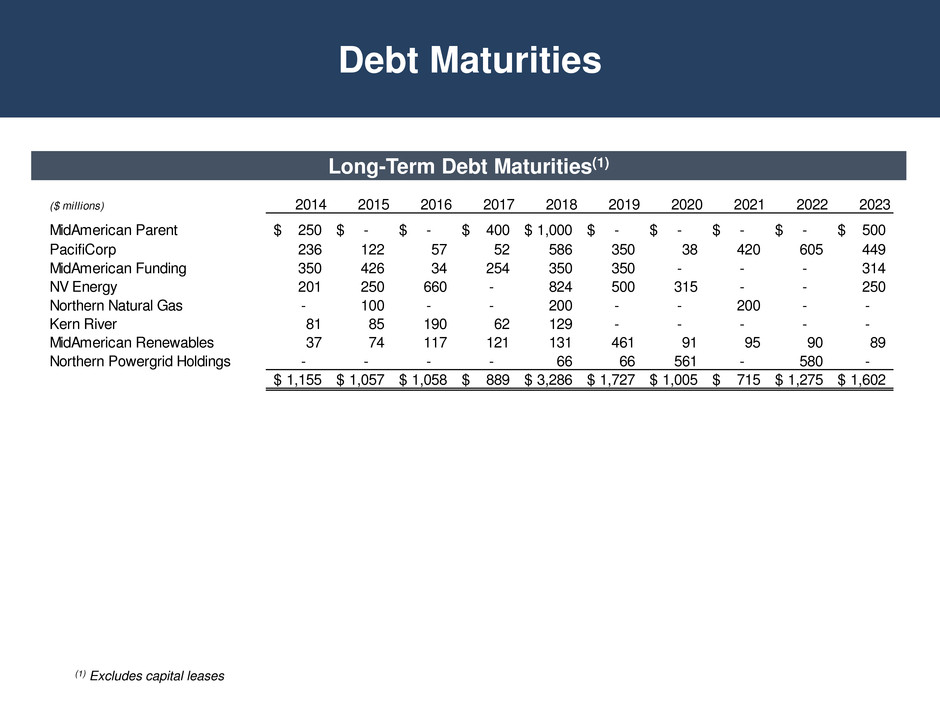
Debt Maturities Long-Term Debt Maturities(1) (1) Excludes capital leases ($ millions) 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 MidAmerican Parent 250$ -$ -$ 400$ 1,000$ -$ -$ -$ -$ 500$ PacifiCorp 236 122 57 52 586 350 38 420 605 449 MidAmerican Funding 350 426 34 254 350 350 - - - 314 NV Energy 201 250 660 - 824 500 315 - - 250 Northern Natural Gas - 100 - - 200 - - 200 - - Kern River 81 85 190 62 129 - - - - - MidAmerican Renewables 37 74 117 121 131 461 91 95 90 89 Northern Powergrid Holdings - - - - 66 66 561 - 580 - 1,155$ 1,057$ 1,058$ 889$ 3,286$ 1,727$ 1,005$ 715$ 1,275$ 1,602$

MidAmerican Debt Summary Consolidated MidAmerican Energy Holdings Company Long-Term Securities Summary as of Dec. 31, 2013 Wt. Avg. Wt. Avg. $ (millions) Coupon Life (Years) (1) MidAmerican Parent 6,616 5.45% 17.3 MidAmerican Funding 3,838 4.56% 12.1 PacifiCorp 6,933 5.02% 15.4 NV Energy 5,296 5.68% 11.1 Northern Natural Gas Company 900 4.90% 14.6 Kern River Gas Transmission Company 548 5.53% 2.6 Northern Powergrid Holdings(2) 2,487 6.26% 12.7 MidAmerican Renewables 2,800 5.45% 12.0 Total MidAmerican Long-Term Debt 29,418 5.32% 13.9 MidAmerican Parent Junior Subordinated Debentures 2,594 3.00% 30.0 Northern Electric Preferred Stock - Perpetual 56 8.06% 30.0 PacifiCorp Preferred Stock - Perpetual 2 6.75% 30.0 Total MidAmerican Preferred Stock and Jr. Sub. Debentures 2,652 3.11% 30.0 Total MidAmerican Long-Term Securities 32,070 5.13% 15.2 (1) Weighted average life assumes perpetual preferred stock has an average life of 30 years (2) USD to GBP exchange rate at $1.6535/pound
