UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |
For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2020
OR
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 1-9494
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
(Address of principal executive offices and zip code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (212 ) 755-8000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | ||
Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None | ||
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of large accelerated filer, accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, and emerging growth company in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | Emerging growth company | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of July 31, 2019, the aggregate market value of the registrant's voting and non-voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $11,273,922,094 using the closing sales price on July 31, 2019 of $93.92.
As of March 16, 2020, the registrant had outstanding 121,191,337 shares of its common stock, $.01 par value per share.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE.
The following documents are incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K: Registrant's Proxy Statement Dated April 20, 2020 (Part III).
TIFFANY & CO.
K-1
Tiffany & Co.
Table of Contents
Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2020
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
The historical trends and results reported in this annual report on Form 10-K should not be considered an indication of future performance. Further, statements contained in this annual report on Form 10-K that are not statements of historical fact, including those that refer to plans, assumptions and expectations for future periods, are "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, each as amended. Forward-looking statements by their nature address matters that are, to different degrees, uncertain, such as statements about the consummation of the proposed Merger (as defined under "Item 1. Business - Entry into Merger Agreement") and the anticipated benefits thereof. Forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements that can be identified by the use of words such as 'expects,' 'projects,' 'anticipates,' 'assumes,' 'forecasts,' 'plans,' 'believes,' 'intends,' 'estimates,' 'pursues,' 'scheduled,' 'continues,' 'outlook,' 'may,' 'will,' 'can,' 'should' and variations of such words and similar expressions. Examples of forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements we make regarding the Company's plans, assumptions, expectations, beliefs and objectives with respect to the proposed Merger; store openings and closings; store productivity; the renovation of the Company's New York Flagship store, including the timing and cost thereof, and the temporary relocation of its retail operations to 6 East 57th Street; product introductions; sales; sales growth; sales trends; store traffic; the Company's strategy and initiatives and the pace of execution thereon; the amount and timing of investment spending; the Company's objectives to compete in the global luxury market and to improve financial performance; retail prices; gross margin; operating margin; expenses; interest expense and financing costs; effective income tax rate; the nature, amount or scope of charges resulting from recent revisions to the U.S. tax code; net earnings and net earnings per share; share count; inventories; capital expenditures; cash flow; liquidity; currency translation; macroeconomic and geopolitical conditions; growth opportunities; litigation outcomes and recovery related thereto; amounts recovered under Company insurance policies; contributions to Company pension plans; and certain ongoing or planned real estate, product, marketing, retail, customer experience, manufacturing, supply chain, information systems development, upgrades and replacement, and other operational initiatives and strategic priorities.
These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future results and are based upon the current views, assumptions and plans of management, and speak only as of the date on which they are made and are subject to a number of factors, risks and uncertainties, many of which are outside of our control. You should not place undue reliance on such statements. Actual results could therefore differ materially from the planned, assumed or expected results expressed in, or implied by, these forward-looking statements. While we cannot predict all of the factors that could form the basis of such differences, key factors, risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to: the recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus, and changes in financial, business, travel and tourism, political, public health and other conditions, circumstances, requirements and practices resulting therefrom; global macroeconomic and geopolitical developments; changes in interest and foreign currency rates; changes in taxation policies and regulations (including changes effected by the recent revisions to the U.S. tax code) or changes in the guidance related to, or interpretation of, such policies and regulations; shifting tourism trends; regional instability; violence (including terrorist activities); political activities or events (including the potential for rapid and unexpected changes in government, economic and political policies, the imposition of additional duties, tariffs, taxes and other charges or other barriers to trade, including as a result of changes in diplomatic and trade relations or agreements with other countries); weather conditions that may affect local and tourist consumer spending; changes in consumer confidence, preferences and shopping patterns, as well as our ability to accurately predict and timely respond to such changes; shifts in the Company's product and geographic sales mix; variations in the cost and availability of diamonds, gemstones and precious metals; adverse publicity regarding the Company and its products, the Company's third-party vendors or the diamond or jewelry industry more generally; any non-compliance by third-party vendors and suppliers with the Company's sourcing and quality standards, codes of conduct, or contractual requirements as well as applicable laws and regulations; changes in our competitive landscape; disruptions impacting the Company's business and operations; failure to successfully implement or make changes to the Company's information systems; changes in the cost and timing estimates associated with the renovation of the Company's New York Flagship store; delays caused by third parties involved in the aforementioned renovation; any casualty, damage or destruction to the Company's New York Flagship store or 6 East 57th Street location; the Company's ability to successfully control costs and execute on, and achieve the expected benefits from, the operational initiatives and strategic priorities referenced above; conditions to the completion of the proposed Merger may not be satisfied or the regulatory approvals required for the proposed Merger may not be obtained, in each case, on the terms expected or on the anticipated schedule which contemplates closing of the acquisition in the middle of 2020; the occurrence of any event, change or other circumstance that could give rise to the termination of the Merger Agreement (as defined under "Item 1. Business – Entry into Merger Agreement") or affect the ability of the parties to recognize the benefits
TIFFANY & CO.
K-2
of the proposed Merger; the effect of the announcement or pendency of the proposed Merger on the Company's business relationships, operating results and business generally; risks that the proposed Merger disrupts the Company's current plans and operations and potential difficulties in the Company's employee retention as a result of the proposed Merger; potential litigation that may be instituted against the Company or its directors or officers related to the proposed Merger or the Merger Agreement and any adverse outcome of any such litigation; the amount of the costs, fees, expenses and other charges related to the proposed Merger, including in the event of any unexpected delays; other risks to consummation of the proposed Merger, including the risk that the proposed Merger will not be consummated within the expected time period, or at all, which may affect the Company's business and the price of the common stock of the Registrant; and any adverse effects on the Company by other general industry, economic, business and/or competitive factors. Consequences of material differences in results as compared with those anticipated in the forward-looking statements could include, among other things, business disruption, operational problems, financial loss, legal liability to third parties and similar risks. Developments relating to these and other factors may also warrant changes to the Company's operating and strategic plans, including with respect to store openings, closings and renovations, capital expenditures, information systems development, inventory management, and continuing execution on, or timing of, the aforementioned initiatives and priorities. Such consequences and changes could also cause actual results to differ materially from the expected results expressed in, or implied by, the forward-looking statements.
Additional information about potential risks and uncertainties that could affect the Company's business and financial results is included under "Item 1A. Risk Factors" and "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2020, the definitive proxy statement on Schedule 14A that the Company filed on January 6, 2020, and in the Company's other filings made with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") from time to time, which are available via the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. Readers of this Annual Report on Form 10-K should consider the risks, uncertainties and factors outlined above and in this Form 10-K in evaluating, and are cautioned not to place undue reliance on, the forward-looking statements contained herein. The Company undertakes no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances, except as required by applicable law or regulation.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-3
PART I
Item 1. Business.
GENERAL HISTORY AND NARRATIVE DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Tiffany & Co. (the "Registrant") is a holding company that operates through Tiffany and Company ("Tiffany") and the Registrant's other subsidiary companies (collectively, the "Company"). Charles Lewis Tiffany founded Tiffany's business in 1837. He incorporated Tiffany in New York in 1868. The Registrant acquired Tiffany in 1984 and completed the initial public offering of the Registrant's Common Stock in 1987. The Registrant, through its subsidiaries, sells jewelry and other items that it manufactures or has made by others to its specifications.
All references to years relate to fiscal years that end on January 31 of the following calendar year.
ENTRY INTO MERGER AGREEMENT
On November 24, 2019, the Registrant entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the "Merger Agreement") by and among the Registrant, LVMH Moët Hennessy – Louis Vuitton SE, a societas Europaea (European company) organized under the laws of France ("Parent"), Breakfast Holdings Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Parent ("Holding"), and Breakfast Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and a direct wholly owned subsidiary of Holding ("Merger Sub"). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into the Registrant (the "Merger"), with the Registrant continuing as the surviving company in the Merger and a wholly owned indirect subsidiary of Parent.
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the Merger Agreement, at the effective time of the Merger (the "Effective Time"), each share of Common Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time (other than shares of Common Stock owned by the Registrant, Parent or any of their respective wholly owned subsidiaries, and shares of Common Stock owned by stockholders of the Registrant who have properly demanded and not withdrawn a demand for appraisal rights under Delaware law) will be converted into the right to receive $135.00 in cash, without interest and less any required tax withholding.
The consummation of the proposed Merger is subject to various conditions, including, among others, customary conditions relating to (a) the adoption of the Merger Agreement by holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of the Registrant's Common Stock entitled to vote on such matter at the meeting of stockholders of the Registrant (the "Special Meeting") held to vote on the adoption of the Merger Agreement and (b) the expiration or earlier termination of the applicable waiting period under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976 (as amended, and all rules and regulations promulgated thereunder, collectively, the "HSR Act"). As previously announced, on February 3, 2020, the waiting period under the HSR Act in connection with the proposed Merger expired, and on February 4, 2020, the Company held the Special Meeting, at which the holders of shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of the close of business on the record date for the Special Meeting considered and voted to approve (i) the adoption of the Merger Agreement and (ii) by non-binding, advisory vote, certain compensation arrangements for the Company's named executive officers in connection with the proposed Merger. The proposed Merger remains subject to satisfaction or waiver of the remaining customary closing conditions, including, among others, (A) certain non-U.S. regulatory approvals, (B) clearance by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States ("CFIUS"), (C) the absence of a law or order in effect that enjoins, prevents or otherwise prohibits the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement issued by a governmental entity; (D) the absence of any legal proceeding seeking to enjoin, prevent or otherwise prohibit the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement instituted by a governmental entity of competent jurisdiction; and (E) the absence of a Material Adverse Effect (as defined in the Merger Agreement). The obligation of each party to consummate the proposed Merger is also conditioned on the accuracy of the other party's representations and warranties (subject to certain materiality exceptions) and the other party's compliance, in all material respects, with its covenants and agreements under the Merger Agreement.
The Merger Agreement provides for certain customary termination rights of the Registrant and Parent, including the right of either party to terminate the Merger Agreement if the Merger is not completed on or before August 24, 2020 (the "Outside Date"), provided that the Outside Date may be extended up to an additional 90 days by either party if all conditions are satisfied other than the receipt of regulatory approvals and CFIUS clearance or absence of legal
TIFFANY & CO.
K-4
restraints. The Merger Agreement also provides that the Registrant will be required to pay Parent a termination fee of $575.0 million in certain circumstances.
For additional information related to the Merger Agreement, please refer to the Company's Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A (the "Definitive Proxy Statement") filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") on January 6, 2020.
MAINTENANCE OF THE TIFFANY & CO. BRAND
The TIFFANY & CO. brand (the "Brand") is the single most important asset of Tiffany and, indirectly, of the Company. The strength of the Brand goes beyond trademark rights (see "TRADEMARKS" below) and is derived from consumer perceptions of the Brand. Management monitors the strength of the Brand through focus groups and survey research.
Management believes that consumers associate the Brand with high-quality gemstone jewelry, particularly diamond jewelry; sophisticated style and romance; excellent customer service; an elegant store and online environment; upscale store locations; "classic" product positioning; and distinctive and high-quality packaging materials (most significantly, the TIFFANY & CO. blue box). Tiffany's business plan includes expenses to maintain the strength of the Brand, such as the following:
• | Maintaining its position within the high-end of the jewelry market requires Tiffany to invest significantly in diamond and gemstone inventory, as well as platinum and gold, which carry a lower overall gross margin; it also causes some consumers to view Tiffany as beyond their price range; |
• | To provide excellent service, stores must be well staffed with knowledgeable professionals; |
• | Elegant stores in the best "high street" and luxury mall locations are more expensive and difficult to secure and maintain, but reinforce the Brand's luxury connotations through association with other luxury brands; |
• | While the "classic" positioning of much of Tiffany's product line supports the Brand and requires sufficient display space in its stores, management's strategic priorities also include the accelerated introduction of new design collections primarily in jewelry, but also in non-jewelry products, which could result in a necessary reallocation of product display space; |
• | Tiffany's packaging supports consumer expectations with respect to the Brand but is expensive; and |
• | A significant amount of marketing across print, digital and social media, as well as public relations events are required to both reinforce the Brand's association with luxury, sophistication, style and romance, as well as to market specific products. |
All of the foregoing require that management make tradeoffs between business initiatives that might generate incremental sales and earnings and Brand maintenance objectives. This is a dynamic process. To the extent that management deems that product, marketing or distribution initiatives will unduly and negatively affect the strength of the Brand, such initiatives have been and will be curtailed or modified appropriately. At the same time, Brand maintenance suppositions are regularly questioned by management to determine if any tradeoff between sales and earnings is truly worth the positive effect on the Brand. At times, management has determined, and may in the future determine, that the strength of the Brand warranted, or that it will permit, more aggressive and profitable product, marketing or distribution initiatives.
REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
The Company has four reportable segments: (i) Americas, (ii) Asia-Pacific, (iii) Japan and (iv) Europe. All non-reportable segments are included within Other. The Company transacts business within certain of its segments through the following channels: (i) retail, (ii) Internet, (iii) catalog, (iv) business-to-business (products drawn from the retail product line and items specially developed for the business market) and (v) wholesale distribution (merchandise sold to independent distributors for resale). The Company's segment information for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 is reported in "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note Q. Segment Information."
TIFFANY & CO.
K-5
Americas
Sales in the Americas represented 43% of worldwide net sales in 2019, while sales in the United States ("U.S.") represented 86% of net sales in the Americas. Sales are transacted through the following channels: retail (in the U.S., Canada and Latin America), Internet and catalog (in the U.S. and Canada), business-to-business (in the U.S.) and wholesale distribution (in Latin America and the Caribbean).
Retail sales in the Americas are transacted in 124 Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores in (number of stores at January 31, 2020 included in parentheses): the U.S. (94), Canada (13), Mexico (10), Brazil (6) and Chile (1). Included within these totals are 14 Company-operated stores located within various department stores in Canada and Mexico. Included in the U.S. retail stores is the New York Flagship store, which represented less than 10% of worldwide net sales in 2019.
Asia-Pacific
Sales in Asia-Pacific represented 28% of worldwide net sales in 2019, while sales in Greater China represented approximately 60% of net sales in Asia-Pacific. Sales are transacted through the following channels: retail, Internet (in Australia and China), business-to-business (in China) and wholesale distribution.
Retail sales in Asia-Pacific are transacted in 91 Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores in (number of stores at January 31, 2020 included in parentheses): China (34), Korea (15), Australia (11), Hong Kong (10), Taiwan (7), Singapore (5), Macau (4), Malaysia (2), Thailand (2) and New Zealand (1). Included within these totals are 35 Company-operated stores located within various department stores.
Japan
Sales in Japan represented 15% of worldwide net sales in 2019. Sales are transacted through the following channels: retail, Internet, business-to-business and wholesale distribution.
Retail sales in Japan are transacted in 58 Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores. Included within this total are 53 stores located within department stores, generating approximately 75% of net sales in Japan. There are four large department store groups in Japan. The Company operates TIFFANY & CO. stores in locations controlled by these groups as follows (number of locations at January 31, 2020 included in parentheses): Isetan Mitsukoshi Ltd. (14), Takashimaya Co., Ltd. (9), J. Front Retailing Co., Ltd. (Daimaru and Matsuzakaya department stores) (8) and Seven & i Holding Co., Ltd. (Sogo and Seibu department stores) (4). The Company also operates 18 stores in other department stores.
Europe
Sales in Europe represented 11% of worldwide net sales in 2019, while sales in the United Kingdom ("U.K.") represented approximately 40% of net sales in Europe. Sales are transacted through the following channels: retail, Internet and wholesale distribution.
Retail sales in Europe are transacted in 48 Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores in (number of stores at January 31, 2020 included in parentheses): the U.K. (12), Italy (9), Germany (7), France (5), Spain (3), Switzerland (3), the Netherlands (2), Russia (2), Austria (1), Belgium (1), the Czech Republic (1), Denmark (1) and Ireland (1). Included within these totals are 11 Company-operated stores located within various department stores. The Company currently operates e-commerce enabled websites within the following countries: U.K., Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands and Spain.
Other
Other consists of all non-reportable segments, including: (i) retail sales transacted in five Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores in the United Arab Emirates ("U.A.E.") and wholesale distribution in the Emerging Markets region; (ii) wholesale sales of diamonds (see "PRODUCT SUPPLY CHAIN – Supply of Diamonds" below); and (iii) licensing agreements.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-6
Licensing Agreements. The Company receives earnings from a licensing agreement with Luxottica Group S.p.A., for the development, production and distribution of TIFFANY & CO. brand eyewear, and from a licensing agreement with Coty Inc., for the development, production and distribution of TIFFANY & CO. brand fragrance products. The earnings received from these licensing agreements represented less than 1% of worldwide net sales in 2019.
Retail Distribution Base
Management regularly evaluates opportunities to optimize its retail store base. This includes evaluating potential markets for new TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as the renovation, relocation, or closure of existing stores. Considerations include the characteristics of the markets to be served, consumer demand and the proximity of other luxury brands and existing TIFFANY & CO. locations. Management recognizes that over-saturation of any market could diminish the distinctive appeal of the Brand, but believes that there are a number of opportunities remaining in new and existing markets that will meet the requirements for a TIFFANY & CO. location in the future.
The following chart details the number of TIFFANY & CO. retail locations operated by the Company since 2015:
Americas | ||||||||||||||
Year: | U.S. | Canada & Latin America | Asia-Pacific | Japan | Europe | Emerging Markets | Total | |||||||
2015 | 95 | 29 | 81 | 56 | 41 | 5 | 307 | |||||||
2016 | 95 | 30 | 85 | 55 | 43 | 5 | 313 | |||||||
2017 | 94 | 30 | 87 | 54 | 46 | 4 | 315 | |||||||
2018 | 93 | 31 | 90 | 55 | 47 | 5 | 321 | |||||||
2019 | 94 | 30 | 91 | 58 | 48 | 5 | 326 | |||||||
E-Commerce, Catalog and Phone Orders
The Company currently operates e-commerce enabled websites in 14 countries, as well as informational websites in several additional countries. To a lesser extent, sales are also generated through catalogs that the Company distributes in certain countries as well as orders placed via telephone in certain markets. Sales transacted on those websites, through catalogs or via telephone accounted for 7% of worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017. Management believes that its websites serve an important marketing role in building brand awareness and attracting customers to the Company's stores. In addition, the Company offers a select assortment of its products through third party websites.
Products
The Company's principal product category is jewelry, which represented 92%, 92% and 91% of worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The Company offers an extensive selection of TIFFANY & CO. brand jewelry at a wide range of prices. Designs are developed by employees, suppliers, independent designers and independent "named" designers (see "MATERIAL DESIGNER LICENSE" below).
The Company also sells watches, home and accessories products and fragrances, which represented, in total, 6%, 7% and 7% of worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. The remainder of worldwide net sales was attributable to wholesale sales of diamonds and earnings from third-party licensing agreements.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-7
Sales by Reportable Segment of TIFFANY & CO. Jewelry by Category
2019 | % of total Americas Sales | % of total Asia-Pacific Sales | % of total Japan Sales | % of total Europe Sales | % of total Reportable Segment Sales | |||||
Jewelry collections a | 55 | % | 63 | % | 38 | % | 60 | % | 55 | % |
Engagement jewelry b | 21 | % | 29 | % | 38 | % | 24 | % | 26 | % |
Designer jewelry c | 14 | % | 6 | % | 17 | % | 12 | % | 12 | % |
2018 | ||||||||||
Jewelry collections a | 53 | % | 61 | % | 37 | % | 60 | % | 54 | % |
Engagement jewelry b | 21 | % | 31 | % | 37 | % | 23 | % | 26 | % |
Designer jewelry c | 14 | % | 7 | % | 18 | % | 12 | % | 12 | % |
2017 | ||||||||||
Jewelry collections a | 53 | % | 59 | % | 30 | % | 60 | % | 52 | % |
Engagement jewelry b | 22 | % | 31 | % | 39 | % | 25 | % | 27 | % |
Designer jewelry c | 14 | % | 8 | % | 22 | % | 12 | % | 13 | % |
a) This category includes jewelry in a wide range of prices within the Company's high jewelry and named jewelry collections such as Tiffany Paper Flowers®, Tiffany Victoria®, Tiffany Soleste®, Tiffany Keys, Tiffany T, Tiffany HardWear and Return to Tiffany®, among others. Jewelry in this category is primarily crafted using precious metals (platinum, gold or sterling silver) and may contain diamonds and/or other gemstones.
b) This category includes engagement rings and wedding bands. Most jewelry in this category contains diamonds and is constructed of platinum and/or gold.
c) | This category includes only jewelry that is attributed to one of the Company's "named" designers: Elsa Peretti (see "MATERIAL DESIGNER LICENSE" below), Paloma Picasso and Jean Schlumberger. Jewelry in this category is primarily crafted using precious metals (platinum, gold or sterling silver) and may contain diamonds and/or other gemstones. |
ADVERTISING, MARKETING, PUBLIC AND MEDIA RELATIONS
The Company's strategy is to invest in marketing and public relations programs designed to build awareness of the Brand, its heritage and its products, as well as to enhance the Brand's relevance and association among consumers with quality and luxury. The Company regularly advertises in newspapers and magazines, as well as through digital and social media. Public and media relations activities are also significant to the Company's business. The Company engages in a program of media activities and marketing events to maintain consumer awareness of the Brand and TIFFANY & CO. products. It also publishes its well-known Blue Book to showcase its high-end jewelry. In 2019, 2018 and 2017, the Company spent $378.8 million, $394.1 million and $314.9 million, representing 8.6%, 8.9% and 7.6% of worldwide net sales in those respective years, on advertising, marketing and public and media relations, which include costs for media, production, catalogs, Internet, visual merchandising (in-store and window displays), marketing events and other related items.
In addition, management believes that the Brand is enhanced by philanthropic efforts, including charitable sponsorships and monetary and merchandise donations. The Company also periodically makes donations to The Tiffany & Co. Foundation, a private foundation established to support nonprofit organizations. The philanthropic efforts of this Foundation are primarily focused on environmental conservation.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-8
TRADEMARKS
The designations TIFFANY ® and TIFFANY & CO.® are the principal trademarks of Tiffany, and also serve as tradenames. Tiffany has obtained and is the proprietor of trademark registrations for TIFFANY and TIFFANY & CO., as well as the TIFFANY BLUE BOX ®, the TIFFANY BLUE BOX design, TIFFANY BLUE ® and the color Tiffany Blue for a variety of product categories and services in the U.S. and in other countries.
Tiffany maintains a program to protect its trademarks and institutes legal action where necessary to prevent others either from registering or using marks which are considered to create a likelihood of confusion with the Company or its products.
Tiffany has been generally successful in such actions and management considers that the Company's worldwide rights in its principal trademarks, TIFFANY and TIFFANY & CO., are strong. However, use of the designation TIFFANY by third parties on related or unrelated goods or services, frequently transient in nature, may not come to the attention of Tiffany or may not rise to a level of concern warranting legal action.
Tiffany actively pursues those who produce or sell counterfeit TIFFANY & CO. goods through civil action and cooperation with criminal law enforcement agencies. However, counterfeit TIFFANY & CO. goods remain available in many markets because it is not possible or cost-effective to eradicate the problem. The cost of enforcement is expected to continue to rise. In recent years, there has been an increase in the availability of counterfeit goods, predominantly silver jewelry, on the Internet and in various markets by street vendors and small retailers. Tiffany pursues infringers through leads generated internally and through a network of investigators, legal counsel, law enforcement and customs authorities worldwide. The Company responds to such infringing activity by taking various actions, including sending cease and desist letters, cooperating with law enforcement in criminal prosecutions, initiating civil proceedings and participating in joint actions and anti-counterfeiting programs with other like-minded third party rights holders.
Despite the general fame of the TIFFANY and TIFFANY & CO. name and mark for the Company's products and services, Tiffany is not the sole person entitled to use the name TIFFANY in every category of use in every country of the world; for example, in some countries, third parties have registered the name TIFFANY in connection with certain product categories (including, in the U.S., the category of bedding and, in certain foreign countries, the categories of food, cosmetics, clothing, paper goods and tobacco products) under circumstances where Tiffany's rights were not sufficiently clear under local law, and/or where management concluded that Tiffany's foreseeable business interests did not warrant the expense of legal action.
MATERIAL DESIGNER LICENSE
Since 1974, Tiffany has been the sole licensee for the intellectual property rights necessary to make and sell jewelry and other products designed by Elsa Peretti and bearing her trademarks. The designs of Ms. Peretti accounted for 7%, 8% and 9% of the Company's worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Tiffany is party to an Amended and Restated Agreement (the "Peretti Agreement") with Ms. Peretti, which largely reflects the long-standing rights and marketing and royalty obligations of the parties. Pursuant to the Peretti Agreement, Ms. Peretti grants Tiffany an exclusive license, in all of the countries in which Peretti-designed jewelry and products are currently sold, to make, have made, advertise and sell these items. Ms. Peretti continues to retain ownership of the copyrights for her designs and her trademarks and remains entitled to exercise approval and consultation rights with respect to important aspects of the promotion, display, manufacture and merchandising of the products made in accordance with her designs. Under and in accordance with the terms set forth in the Peretti Agreement, Tiffany is required to display the licensed products in stores, to devote a portion of its advertising budget to the promotion of the licensed products, to pay royalties to Ms. Peretti for the licensed products sold, to maintain total on-hand and on-order inventory of non-jewelry licensed products (such as tabletop products) at approximately $8.0 million and to take certain actions to protect Ms. Peretti's intellectual property, including to maintain trademark registrations reasonably necessary to sell the licensed products in the markets in which the licensed products are sold by Tiffany.
The Peretti Agreement has a term that expires in 2032 and is binding upon Ms. Peretti, her heirs, estate, trustees and permitted assignees. During the term of the Peretti Agreement, Ms. Peretti may not sell, lease or otherwise dispose of her copyrights and trademarks unless the acquiring party expressly agrees with Tiffany to be bound by the
TIFFANY & CO.
K-9
provisions of the Peretti Agreement. The Peretti Agreement is terminable by Ms. Peretti in the event of a material breach by Tiffany (subject to a cure period) or upon a change of control of Tiffany or the Company. It is terminable by Tiffany only in the event of a material breach by Ms. Peretti or following an attempt by Ms. Peretti to revoke the exclusive license (subject, in each case, to a cure period).
PRODUCT SUPPLY CHAIN
The Company's strategic priorities include maintaining substantial control over its product supply chain through internal jewelry manufacturing and direct diamond sourcing. The Company manufactures jewelry in New York, Rhode Island and Kentucky, polishes and performs certain assembly work on jewelry in the Dominican Republic and crafts silver hollowware in Rhode Island. In total, these internal manufacturing facilities produce approximately 60% of the jewelry sold by the Company. The balance, and almost all non-jewelry items, is purchased from third parties. The Company may increase the percentage of internally-manufactured jewelry in the future, but management does not expect that the Company will ever manufacture all of its needs. Factors considered by management in its decision to use third-party manufacturers include access to or mastery of various product-making skills and technology, support for alternative capacity, product cost and the cost of capital investments. To supply its internal manufacturing facilities, the Company processes, cuts and polishes rough diamonds at its facilities outside the U.S. and sources precious metals, rough diamonds, polished diamonds and other gemstones, as well as certain fabricated components, from third parties.
Supply of Diamonds. The Company regularly purchases parcels of rough diamonds for polishing and further processing. The vast majority of diamonds acquired by the Company originate from Botswana, Canada, Namibia, Russia and South Africa. The Company has diamond processing operations in Belgium, Botswana, Cambodia, Mauritius and Vietnam that prepare and/or cut and polish rough diamonds for its use. The Company conducts operations in Botswana through a subsidiary in which local third parties own minority, non-controlling interests, allowing the Company to access rough diamond allocations reserved for local manufacturers. The Company maintains a relationship and has an arrangement with these local third parties; however, if circumstances warrant, the Company could seek to replace its existing local partners or operate without local partners.
The Company secures supplies of rough diamonds primarily through arrangements with diamond producers and, to a lesser extent, on the secondary market. Most of this supply comes from arrangements in which the Company accesses rough diamonds that are offered for sale (including as a sightholder), although with no contractual purchase obligation for such rough diamonds. A smaller portion of rough diamond purchases is made through agreements in which the Company is required to purchase a minimum volume of rough diamonds (anticipated to be approximately $30.0 million in 2020). All such supply arrangements are generally at the market price prevailing at the time of purchase.
As a result of the manner in which rough diamonds are typically assorted for sale, it is occasionally necessary for the Company to knowingly purchase, as part of a larger assortment, rough diamonds that do not meet the Company's quality standards or assortment needs. The Company seeks to recover its costs related to these diamonds by selling such diamonds to third parties (generally other diamond polishers), which has the effect of modestly reducing the Company's overall gross margins. Any such sales are included in the Other non-reportable segment.
In recent years, an average of approximately 75% (by volume) of the polished diamonds used in the Company's jewelry that are 0.18 carats and larger and individually registered ("individually registered diamonds") has been produced from rough diamonds that the Company has purchased. The balance of the Company's needs for individually registered diamonds is purchased from polishers or polished-diamond dealers generally through purchase orders for fixed quantities. The Company's relationships with polishers and polished-diamond dealers may be terminated at any time by either party, but such a termination would not discharge either party's obligations under unfulfilled purchase orders accepted prior to the termination. It is the Company's intention to continue to supply the substantial majority of its needs for individually registered diamonds, as well as a majority of its needs for melee diamonds of less than 0.18 carats used in the Company's jewelry, by purchasing rough diamonds.
Conflict Diamonds. Media attention has been drawn to the issue of "conflict" diamonds. This term is used to refer to diamonds extracted from war-torn geographic regions and sold by rebel forces to fund insurrection. Allegations have also been made that trading in such diamonds supports terrorist activities. Management believes that it is not possible in most purchasing scenarios to distinguish diamonds produced in conflict regions from diamonds produced in other regions once they have been polished. Therefore, concerned participants in the diamond trade, including the
TIFFANY & CO.
K-10
Company and nongovernment organizations, seek to exclude "conflict" diamonds, which represent a small fraction of the world's supply, from legitimate trade through an international system of certification and legislation known as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme. All rough diamonds the Company buys, crossing an international border, must be accompanied by a Kimberley Process certificate and all trades of rough and polished diamonds must conform to a system of warranties that references the aforesaid scheme. It is not expected that such efforts will substantially affect the supply of diamonds. In addition, concerns over human rights abuses in Zimbabwe, Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo underscore that the aforementioned system has not deterred the production of diamonds in state-sanctioned mines under poor working conditions. The Company has informed its vendors that it does not intend to purchase Zimbabwean, Angolan or Congolese-produced diamonds. Accordingly, the Company has implemented the Diamond Source Warranty Protocol, which requires vendors to provide a warranty, and a qualified independent audit certificate, that loose polished diamonds were not obtained from Zimbabwean, Angolan or Congolese mines. As part of its diamond source initiative, the Company also requires its vendors to affirmatively state the region or country of origin of any polished diamonds sold to the Company that are 0.18 carats and larger and individually registered.
Worldwide Availability and Price of Diamonds. The availability and price of diamonds are dependent on a number of factors, including global consumer demand, the political situation in diamond-producing countries, the opening of new mines, the continuance of the prevailing supply and marketing arrangements for rough diamonds and levels of industry liquidity. In recent years, there has been substantial volatility in the prices of both rough and polished diamonds. Prices for rough diamonds do not necessarily reflect current demand for polished diamonds.
In addition, the supply and prices of rough and polished diamonds in the principal world markets have been and continue to be influenced by the Diamond Trading Company ("DTC"), an affiliate of the De Beers Group. Although the DTC's historical ability to control worldwide production has diminished due to its lower share of worldwide production and changing policies in diamond-producing countries, the DTC continues to supply a meaningful portion of the world market for rough, gem-quality diamonds and continues to impact diamond supply through its marketing and advertising initiatives. A significant portion of the diamonds that the Company purchased in 2019 had their source with the DTC.
Sustained interruption in the supply of diamonds, an overabundance of supply or a substantial change in the marketing arrangements described above could adversely affect the Company and the retail jewelry industry as a whole. Changes in the marketing and advertising spending of the DTC and its direct purchasers could affect consumer demand for diamonds.
The Company purchases conflict-free rough and polished diamonds, in highly graded color and clarity ranges. Management does not foresee a shortage of diamonds in these quality ranges in the short term but believes that, unless new mines are developed, rising demand will eventually create such a shortage and lead to higher prices.
Synthetic and Treated Diamonds. Synthetic diamonds (diamonds manufactured but not naturally occurring) and treated diamonds (naturally occurring diamonds subject to treatment processes, such as irradiation) are produced in growing quantities. Although significant questions remain as to the ability of producers to generate synthetic and/or treated diamonds economically within a full range of sizes and natural diamond colors, and as to consumer acceptance of these diamonds, such diamonds are becoming a larger factor in the market. Should synthetic and/or treated diamonds be offered in significant quantities, the supply of and prices for natural diamonds may be affected. The Company does not produce and does not intend to purchase or sell such diamonds.
Purchases of Precious Metals and Other Polished Gemstones. Precious metals and other polished gemstones used in making jewelry are purchased from a variety of sources for use in the Company's internal manufacturing operations and/or for use by third-party manufacturers contracted to supply Tiffany merchandise. The silver, gold and platinum sourced directly by the Company principally come from two sources: (i) in-ground, large-scale deposits of metals, primarily in the U.S., that meet the Company's standards for responsible mining and (ii) metals from recycled sources. While the Company may supply precious metals to a manufacturer, it cannot determine, in all circumstances, whether the finished goods provided by such manufacturer were actually produced with Company-supplied precious metals.
The Company generally enters into purchase orders for fixed quantities with precious metals and other polished gemstone vendors. Purchases are generally made at prevailing market prices, which have, with respect to precious metals, experienced substantial volatility in recent years. These relationships may be terminated at any time by
TIFFANY & CO.
K-11
either party; such termination would not discharge either party's obligations under unfulfilled purchase orders accepted prior to the termination. The Company believes that there are numerous alternative sources for other polished gemstones and precious metals and that the loss of any single supplier would not have a material adverse effect on its operations.
Finished Jewelry. Finished jewelry is purchased from approximately 50 manufacturers. However, the Company does not enter into long-term supply arrangements with its finished goods vendors. The Company does enter into merchandise vendor agreements with nearly all of its finished goods vendors. The merchandise vendor agreements establish non-price terms by which the Company may purchase and by which vendors may sell finished goods to the Company. These terms include payment terms, shipping procedures, product quality requirements, merchandise specifications and vendor social responsibility requirements. The Company generally enters into purchase orders for fixed quantities of merchandise with its vendors. These relationships may be terminated at any time by either party; such termination would not discharge either party's obligations under unfulfilled purchase orders accepted prior to termination. The Company actively seeks alternative sources for its best-selling jewelry items to mitigate any potential disruptions in supply. However, due to the craftsmanship involved in a small number of designs, the Company may have difficulty finding readily available alternative suppliers for those jewelry designs in the short term.
Watches. The Company sells TIFFANY & CO. brand watches, which are designed, produced, marketed and distributed through certain of the Company's subsidiaries. The Company has relationships with approximately 30 component and subassembly vendors to manufacture watches. The terms of the Company's contractual relationships with these vendors are substantially similar to those described under "Finished Jewelry" above. Sales of these TIFFANY & CO. brand watches represented approximately 1% of worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017.
COMPETITION
The global jewelry industry is competitively fragmented. The Company encounters significant competition in all product categories. Some competitors specialize in just one area in which the Company is active. Many competitors have established worldwide, national or local reputations for style, quality, expertise and customer service similar to the Company and compete on the basis of that reputation. Certain other jewelers and retailers compete primarily through advertised price promotion. The Company competes on the basis of the Brand's reputation for high-quality products, customer service and distinctive merchandise and does not engage in price promotional advertising.
Competition for engagement jewelry sales is particularly and increasingly intense. The Company's retail prices for diamond jewelry reflect the rarity of the stones it offers and the rigid parameters it exercises with respect to the cut, clarity and other diamond quality factors which increase the beauty of the diamonds, but which also increase the Company's cost. The Company competes in this market by emphasizing quality.
SEASONALITY
As a jeweler and specialty retailer, the Company's business is seasonal in nature, with the fourth quarter typically representing approximately one-third of annual net sales and a higher percentage of annual net earnings. Management expects such seasonality to continue.
EMPLOYEES
As of January 31, 2020, the Company employed an aggregate of approximately 14,100 full-time and part-time persons. Of those employees, approximately 5,500 are employed in the United States.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
The Company files annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, proxy and information statements and amendments to reports filed or furnished pursuant to Sections 13(a), 14 and 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Copies of these reports and statements may be obtained, free of charge, on the Company's website at https://investor.tiffany.com/financial-information.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-12
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
As is the case for any retailer, the Company's success in achieving its objectives and expectations is dependent upon general economic conditions, competitive conditions and consumer attitudes. However, certain factors are specific to the Company and/or the markets in which it operates. The following "risk factors" are specific to the Company; these risk factors affect the likelihood that the Company will achieve the objectives and expectations communicated by management. The risk factors described below are not the only ones faced by the Company and additional risks and uncertainties not presently known or that are currently deemed immaterial also may impair the Company's business operations. Management's strategies are subject to the risks described herein and may be subject to other risks that have not yet been identified.
(i) The announcement and pendency of the proposed Merger may adversely affect the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
Uncertainty about the effect of the proposed Merger on the Company's employees, customers, and other parties may have an adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations regardless of whether the proposed Merger is completed. These risks to the Company's business include, among others, the following, all of which may be exacerbated by a delay in the completion of the proposed Merger: (i) the impairment of the Company's ability to attract, retain, and motivate its employees; (ii) the diversion of significant management time and attention from ongoing business operations towards the completion of the proposed Merger; (iii) difficulties maintaining relationships with customers, suppliers and other business partners; (iv) delays or deferments of certain business decisions by the Company's customers, suppliers and other business partners; (v) the inability to pursue alternative business opportunities or make appropriate changes to the Company's business because the Merger Agreement requires the Company to, subject to certain exceptions, including as required by a Governmental Entity or by applicable Law (in each case as defined in the Merger Agreement), conduct its business in the ordinary course of business and to not engage in certain kinds of transactions prior to the completion of the proposed Merger without the prior written consent of Parent (such consent not to be unreasonably conditioned, withheld or delayed), even if such actions could prove beneficial; (vi) litigation relating to the proposed Merger and the costs related thereto; and (vii) the incurrence of significant costs, expenses and fees for professional services and other transaction costs in connection with the proposed Merger.
(ii) Failure to consummate the proposed Merger within the expected time frame or at all may have a material adverse impact on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
There can be no assurance that the proposed Merger will be consummated. The consummation of the proposed Merger is subject to various conditions, including, among others, customary conditions relating to (i) the receipt of certain non-U.S. regulatory approvals; (ii) clearance by the CFIUS; (iii) the absence of a law or order in effect that enjoins, prevents or otherwise prohibits the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement issued by a governmental entity; (iv) the absence of any legal proceeding seeking to enjoin, prevent or otherwise prohibit the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement instituted by a governmental entity of competent jurisdiction; and (v) the absence of a Material Adverse Effect (as defined in the Merger Agreement). There can be no assurance that these and other conditions to closing will be satisfied in a timely manner or at all.
In connection with the proposed Merger, the Registrant and its directors were named as defendants in four lawsuits brought by purported stockholders challenging the proposed Merger and seeking various forms of injunctive relief and money damages. While the plaintiffs of these lawsuits have voluntarily dismissed their claims, the Registrant may be subject to additional future litigation challenging the proposed Merger. If any future plaintiffs are successful in obtaining an injunction prohibiting the consummation of the proposed Merger, then such injunction may prevent the Merger from becoming effective within the expected time frame or at all, either of which could have a material adverse impact on the Company's business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Merger Agreement also provides that the Merger Agreement may be terminated by the Company or Parent under certain circumstances, and in certain specified circumstances upon termination of the Merger Agreement, the Company will be required to pay Parent a termination fee of $575.0 million. Depending on the circumstances requiring the Company to make this payment, doing so may materially adversely affect its business, financial condition and results of operations.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-13
There can be no assurance that an adequate remedy will be available to the Company in the event of a breach of the Merger Agreement by Parent or its affiliates or that the Company will, wholly or partially, recover for any damages incurred by it in connection with the proposed Merger. A failed transaction may result in negative publicity and a negative impression of the Company among its customers or in the investment community or business community generally. Further, any disruptions to the Company's business resulting from the announcement and pendency of the proposed Merger, including any adverse changes in the Company's relationships with its customers, partners, suppliers and employees, may continue or accelerate in the event of a failed transaction. In addition, if the proposed Merger is not completed, and there are no other parties willing and able to acquire the Company at a price of $135.00 per share or higher, on terms acceptable to the Company, the share price of the Company's Common Stock will likely decline to the extent that the current market price of the Company's Common Stock reflects an assumption that the proposed Merger will be completed. Also, the Company has incurred, and will continue to incur, significant costs, expenses, and fees for professional services and other transaction costs in connection with the proposed Merger, for which it will have received little or no benefit if the proposed Merger is not completed. Many of these fees and costs will be payable by the Company if the proposed Merger is not completed and may relate to activities that the Company would not have undertaken other than to complete the proposed Merger.
(iii) The recent outbreak of the novel coronavirus has had a significant effect on the Company's sales results to date in fiscal 2020, and could have a significant negative impact on the Company's business, revenues, financial condition and results of operations in that year.
An outbreak of a novel strain of coronavirus, COVID-19, was identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019 and was subsequently recognized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization on March 11, 2020. This coronavirus outbreak has severely restricted the level of economic activity around the world. In response to this coronavirus outbreak, the governments of many countries, states, cities and other geographic regions have taken preventative or protective actions, such as imposing restrictions on travel and business operations and advising or requiring individuals to limit or forego their time outside of their homes. Temporary closures of businesses have been ordered and numerous other businesses have temporarily closed voluntarily. Further, individuals' ability to travel has been curtailed through mandated travel restrictions and may be further limited through additional voluntary or mandated closures of travel-related businesses. These actions have expanded significantly in the past several weeks and are expected to continue to expand in scope, type and impact. For example, on March 15, 2020, following an unscheduled meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee, the United States Federal Reserve reduced the target range for the federal funds rate to 0 to 0.25 percent, down from a range of 1 to 1.25 percent, in connection with the coronavirus's impact on the United States' economy.
In recent weeks, this coronavirus outbreak and the related preventative and protective actions have impacted the Company's business globally, including through store closures, reductions in operating hours and/or decreased store traffic. For example, from January 24 through March 19, 2020, management estimates that this coronavirus outbreak contributed to the loss of approximately 30 out of 54 retail trading days (accounting for the effect of individual store closures as well as reductions in store operating hours) across all of the Company's stores in the Chinese Mainland. In addition, as of March 19, 2020, the Company has temporarily closed all of its stores in the United States and Canada, and has temporarily closed nearly all of its stores across Europe and the United Kingdom. The Company has also experienced significantly reduced customer traffic from January 24 through March 19 in its stores that have been open during such period, which management believes has resulted in part from a reduction in tourism as well as restrictions on travel and limitations affecting individuals' ability to spend time in public areas. All of the foregoing developments have had a significant effect on the Company's sales results to date in its fiscal year ending January 31, 2021 ("fiscal 2020") and are expected to continue to have a significant effect on its financial results. These developments and effects are expected to continue and may also significantly affect the Company's business in other geographic areas where this coronavirus has spread and may continue to spread.
The Company's business is particularly sensitive to reductions in discretionary consumer spending. The Company cannot predict the degree to, or the time period over, which its business will be affected by this coronavirus outbreak. For example, this coronavirus outbreak could continue to impede global economic activity, leading to a further decline in discretionary spending by local customers and tourists, and resulting in additional significant effects on the Company's business, revenues, financial condition and results of operations. There are numerous uncertainties associated with this coronavirus outbreak, including the number of individuals who will become infected, whether a vaccine or cure that mitigates the effect of the virus will be synthesized, and, if so, when such vaccine or cure will be ready to be used, the extent of the protective and preventative measures that have been put in place by both governmental entities and other businesses and those that may be put in place in the future,
TIFFANY & CO.
K-14
whether the virus's impact will be seasonal and numerous other uncertainties. The Company intends to continue to execute on its strategic plans and operational initiatives during the coronavirus outbreak. However, the aforementioned uncertainties may result in delays or modifications to these plans and initiatives.
This coronavirus outbreak has also impacted, and may continue to impact, the Company's office locations, manufacturing and servicing facilities and distribution centers, as well as those of its third party vendors, including through the effects of facility closures, reductions in operating hours, staggered shifts and other social distancing efforts, labor shortages, decreased productivity and unavailability of raw materials or components. For example, the Company has experienced reduced capacity in its manufacturing and servicing facilities in New York as a result of state-imposed temporary occupancy restrictions, as well as a government-mandated temporary closure of its diamond processing operation in Mauritius. This coronavirus outbreak may also impact distribution and logistics providers' ability to operate or increase their operating costs. These supply chain effects may negatively affect the Company's ability to meet consumer demand and may increase the Company's costs of production and distribution.
For the reasons set forth above and other reasons that may come to light if this coronavirus outbreak and any associated protective or preventative measures expand, as of the date hereof, the Company cannot reasonably estimate the impact to the Company's business, revenues, financial condition or results of operations; however, such impact could be significantly negative.
(iv) Challenging global economic conditions and related low levels of consumer confidence over a prolonged period of time could adversely affect the Company's sales and earnings.
As a retailer of goods which are discretionary purchases, the Company's sales results are particularly sensitive to changes in economic conditions and consumer confidence. Consumer confidence is affected by general business conditions; domestic and international political uncertainties and/or developments; changes in the market value of equity securities and real estate; inflation; interest rates and the availability of consumer credit; tax rates; and expectations of future economic conditions and employment prospects.
Consumer spending for discretionary goods generally declines during times of falling consumer confidence, which negatively affects the Company's sales and earnings.
Certain competitors may react to such conditions by reducing retail prices and promoting such reductions; such reductions and/or inventory liquidations can have a short-term adverse effect on the Company's sales, especially given the Company's policy of not engaging in price promotional activity.
The Company has invested in and operates a significant number of stores in Greater China and anticipates continuing to do so. Any slowdown in the Chinese economy could have a negative impact on the sales and profitability of stores in Greater China as well as stores in other markets that serve Chinese tourists.
Uncertainty surrounding the current global economic environment makes it more difficult for the Company to forecast operating results. The Company's forecasts employ the use of estimates and assumptions. Actual results could differ from forecasts, and those differences could be material.
(v) Sales may decline or remain flat in the Company's fourth fiscal quarter, which includes the Holiday selling season.
The Company's business is seasonal in nature, with the fourth quarter typically representing approximately one-third of annual net sales and a higher percentage of annual net earnings. Poor sales results during the fourth quarter would have an adverse effect on annual earnings and inventories in the short term.
(vi) The Company conducts operations globally, the risks of which could increase its costs, reduce its profits or disrupt its business.
The Company operates globally and generates a majority of its worldwide net sales outside the United States. It also has both U.S. and foreign manufacturing operations, and relies on certain U.S. and foreign third-party vendors and suppliers. As a result, the Company is subject to the risks of doing business globally, including:
• | the laws, regulations and policies of governments relating to investments, loans and operations, the costs or desirability of complying with local practices and customs and the impact of various anti-corruption and other laws affecting the activities of U.S. companies abroad; |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-15
• | uncertainties from changes in U.S. or foreign taxation policies; |
• | compliance by third party vendors and suppliers with the Company's sourcing and quality standards, codes of conduct, or contractual requirements as well as applicable laws and regulations; |
• | import and export licensing requirements and regulations, as well as unforeseen changes in regulatory requirements; |
• | political or economic instability in foreign countries, including the potential for rapid and unexpected changes in government, economic and political policies, such as the U.K.'s recent exit from the European Union ("E.U."), as discussed below; |
• | political or civil unrest, including protests and other civil disruption, such as the ongoing business disruption in Hong Kong; |
• | acts of terrorism or the threat of international boycotts or U.S. anti-boycott legislation as a result of, for example, changes in government policies of foreign countries in response to actions taken by the U.S. government; |
• | the imposition of additional duties, tariffs, taxes and other charges or other barriers to trade, including as a result of changes in diplomatic and trade relations or agreements with other countries; |
• | challenges inherent in oversight of foreign operations, systems and controls; |
• | potential negative consequences from foreign governments' currency management practices; |
• | uncertainties as to enforcement of certain contract and other rights; and |
• | inventory risk exposures. |
Changes in these regulatory, political, economic, or monetary policies and other factors could require the Company to significantly modify its current business practices and may adversely affect its future financial results. For example, the Company could be adversely impacted by U.S. trade policies, legislation, treaties and tariffs, including trade policies and tariffs affecting China and, the E.U., as well as retaliatory tariffs by such countries. Such tariffs and, if enacted, any further legislation or actions taken by the U.S. government that restrict trade, such as additional tariffs or trade barriers, and other protectionist or retaliatory measures taken by governments in Europe, Asia and elsewhere, could have a negative effect on the Company's ability to sell products in those markets.
Additionally, in June 2016, voters in the U.K. approved an advisory referendum to withdraw from the E.U., commonly referred to as "Brexit." On January 31, 2020, the U.K. officially terminated its membership in the E.U. pursuant to the terms of a withdrawal agreement concluded between the U.K. and E.U. Among other terms, the withdrawal agreement provides for a transition period through December 31, 2020, during which the U.K.'s existing trade relationship with the E.U. will remain in place and the U.K. will continue to follow the E.U.'s rules. Negotiations during the transition period to determine the U.K.'s future relationship with the E.U., including the terms of a future trade deal, are expected to be complex and it is not clear at this time what, if any, agreements will be reached by the current December 31, 2020 transition period deadline. Changes related to Brexit could significantly disrupt the free movement of goods, services, and people between the U.K. and the E.U., and result in potential higher costs of conducting business in Europe. Brexit could also lead to legal uncertainty and potentially divergent national laws and regulations in the U.K. and the E.U. The Company may incur additional costs and expenses as it adapts to these potentially divergent regulatory frameworks, and may face additional complexity with regard to immigration and travel rights for its employees located in the U.K. and the E.U. There may also be similar referendums or votes in other European countries in which the Company does business. The U.K.'s withdrawal from the E.U. and the uncertainty surrounding the terms of this withdrawal, as well as the impact of any similar circumstances that may arise elsewhere in Europe, could increase the Company's costs and adversely impact consumer and investor confidence.
While these factors, and the effect thereof, are difficult to predict, any one or more of them could lower the Company's revenues, increase its costs, reduce its earnings or disrupt its business.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-16
(vii) Revisions to the U.S. tax code, including changes in the guidance related to, or interpretation and application of, such revisions could materially affect the Company's tax obligations, provision for income taxes and effective tax rate.
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. enacted comprehensive tax legislation, commonly referred to as the 2017 U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the "2017 Tax Act"), which significantly affected U.S. tax law by changing how the U.S. imposes income tax on U.S. taxpayers. In particular, these changes impact the U.S. taxation of earnings in the jurisdictions in which the Company operates, the measurement of its deferred tax assets and liabilities and the tax impact in the event the Company were to repatriate the earnings of its non-U.S. subsidiaries to the U.S. The provisions of the 2017 Tax Act may be subject to further interpretation by the U.S. Treasury Department and the Internal Revenue Service, which have broad authority to issue regulations and interpretative guidance that may significantly impact how the Company will apply such provisions. Further regulatory or accounting guidance regarding the 2017 Tax Act could materially affect the Company's future financial results.
(viii) A strengthening of the U.S. dollar against foreign currencies would negatively affect the Company's sales and profitability.
The Company operates retail stores in more than 20 markets outside of the U.S. and, as a result, is exposed to market risk from fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, including, among others, the Japanese Yen, Euro, British Pound and Chinese Yuan. In 2019, sales in countries outside of the U.S. in aggregate represented a substantial portion of the Company's net sales and earnings from operations. A strengthening of the U.S. dollar against foreign currencies would require the Company to raise its retail prices in various locations outside of the U.S. in order to maintain its worldwide relative pricing structure, or reduce its profit margins. Consumers in those markets may not accept significant price increases on the Company's goods; thus, there is a risk that a strengthening of the U.S. dollar would result in reduced sales and profitability. In addition, a weakening of any foreign currency relative to other currencies may negatively affect spending by foreign tourists in the various regions where the Company operates retail stores which would adversely affect its net sales and profitability.
The reported results of operations of the Company's international subsidiaries are exposed to foreign exchange rate fluctuations as the financial results of the applicable subsidiaries are translated from the local currency into U.S. dollars during the process of financial statement consolidation. If the U.S. dollar strengthens against foreign currencies, the translation of these foreign currency-denominated transactions would decrease consolidated net sales and profitability. See "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" for a discussion of such impacts.
(ix) Political activities, regional instability and/or conflict, public health crises or similar events could disrupt tourist travel and local consumer spending.
Regional and global conflicts or crises, such as military actions, terrorist activities and natural disasters, geopolitical or regulatory developments (and any related protests), public health crises and other similar events and conditions in the various regions and cities where the Company operates retail stores may negatively affect spending by both foreign tourists and local consumers. The Company's retail stores, many of which are located in major metropolitan areas globally, may in fact have close proximity to the locations of such events – for example, the Company's operations in Hong Kong have experienced significant business disruptions since the beginning of the protests in that market in 2019. The occurrence of the types of events or conditions described above, or the related effect of security measures implemented to address the possibility of such occurrences, could affect consumer traffic and/or spending in one or more of the Company's locations, which could adversely affect the Company's sales and earnings.
(x) Changes in the Company's product or geographic sales mix could affect the Company's profitability.
The Company sells an extensive selection of jewelry and other merchandise at a wide range of retail price points that yield different gross profit margins. Additionally, the Company's geographic regions achieve different operating profit margins due to a variety of factors including product mix, store size and occupancy costs, labor costs, retail pricing and fixed versus variable expenses. The increasing availability of, and ease of access to, retail price information across markets, primarily through the Internet, may affect consumers' decisions regarding in which geographies to shop. If the Company's sales mix were to shift toward products or geographic regions that are significantly different than the Company's plans, it could have an effect, either positively or negatively, on its expected profitability.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-17
(xi) Metrics the Company may report that are based on customer data it collects are subject to inherent challenges in measurement, and inaccuracies in that data or the resulting metrics could lead to decisions that adversely impact the Company's business.
The Company regularly reviews customer sales and similar data to evaluate retail sales trends, measure its performance and make strategic decisions. The Company reviews its sales data attributed to local customers, which the Company defines as sales to customers who identify themselves as being residents of the same country as the retail store in which the applicable sale was completed, and sales attributed to foreign tourists, which the Company defines as sales to customers who identify themselves as being residents of a different country than the country of the retail store in which the applicable sale was completed, to evaluate growth and other sales trends within the Company's global customer base. These metrics are calculated using internal Company data that reflects residency information self-reported by its customers at the time of sale, or, for customers who do not self-report, that is based on certain pre-established default assumptions. While the Company believes this to be a reasonable method for collecting the applicable data, there are inherent challenges in collecting such data and measuring these aspects of its sales performance across its global customer population. For example, the default assumptions referred to above could result in a significant understatement or overstatement of sales attributed to local customers or foreign tourists. In addition, the collected data has not been validated by an independent third party, and the resulting metrics may differ from similar estimates published by third parties or from similarly titled metrics of other retailers.
Errors or inaccuracies in the Company's data or metrics could result in incomplete or inaccurate internal analyses, which may compromise the validity and reliability of conclusions the Company draws from such analyses and may further result in ineffective decision-making. For instance, such inaccuracies could result in an overstatement of sales to foreign tourists, which could lead the Company to allocate sales and marketing resources in a manner that would not result in optimal retail sales performance. If these metrics or the underlying data are used to inform management's strategies or initiatives, but reflect material errors or inaccuracies, the Company's business may be negatively affected.
(xii) Increases in costs of diamonds, other gemstones and precious metals or reduced supply availability may adversely affect the Company's ability to produce and sell products at desired profit margins.
Most of the Company's jewelry offerings are made with diamonds, other gemstones and/or precious metals. A significant increase in the costs or change in the supply of these commodities could adversely affect the Company's business, which is vulnerable to the risks inherent in the trade for such commodities. A substantial increase or decrease in the cost or supply of precious metals, high-quality rough and polished diamonds (within the quality grades, colors and sizes that customers demand) and/or other gemstones could affect, negatively or positively, customer demand, sales and gross profit margins. Additionally, should synthetic diamonds (diamonds manufactured but not naturally occurring) and/or treated diamonds (naturally occurring diamonds subject to treatment processes, such as irradiation) be offered in significant quantities and gain consumer acceptance, the supply of, demand for and prices for natural diamonds may be affected.
(xiii) The Company may be unable to secure and retain sufficient space for its retail stores in prime locations, and maintaining the Company's brand image and desirability to consumers requires significant investment in store construction, maintenance and periodic renovation.
The Company, positioned as a luxury goods retailer, has established its retail presence in choice store locations. Management regularly evaluates opportunities to optimize its retail store base, including potential markets for new TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as the renovation and relocation of its existing stores. Maintaining the Company's brand image and desirability to consumers requires that stores be constructed and maintained in a manner consistent with that brand image. This requires significant capital investment, including for periodic renovations of existing stores. Renovations of existing stores may also result in temporary disruptions to an individual store's business. If the Company cannot secure and retain store locations on suitable terms in prime and desired luxury shopping locations, or if its investments to construct and/or renovate existing stores do not generate sufficient incremental sales and/or profitability or significantly disrupt sales and/or profitability during renovations, the Company's sales and/or earnings performance could be jeopardized.
For example, in 2018, the Company announced its plans to undertake a complete renovation of the New York Flagship store. The New York Flagship store closed in January 2020, at which time the Company began its complete renovation and temporarily moved its operations to the "Tiffany Flagship Next Door" at 6 East 57th Street. This
TIFFANY & CO.
K-18
renovation is expected to be completed in the fourth quarter of 2021. The full renovation project will require significant capital investment and may result in business and/or consumer traffic disruptions. Significant delays or cost overruns are also possible during the construction period, which could significantly increase the cost of this renovation project and adversely impact the Company's future financial results. There can be no assurance that the results of this renovation project will appeal to the Company's customers or will increase the Company's sales or profitability.
(xiv) The value of the TIFFANY & CO. and TIFFANY trademarks could decline due to third-party use and infringement.
The TIFFANY & CO. and TIFFANY trademarks are assets that are essential to the competitiveness and success of the Company's business, and the Company takes appropriate action to protect them. The Company actively pursues those who produce or sell counterfeit TIFFANY & CO. goods through civil action and cooperation with criminal law enforcement agencies. However, use of the designation TIFFANY by third parties on related goods or services and the Company's failure or inability to protect against such use could adversely affect and dilute the value of the
TIFFANY & CO. brand.
Notwithstanding the general success of the Company's enforcement actions, such actions have not stopped the imitation and counterfeiting of the Company's merchandise or the infringement of the trademark, and counterfeit TIFFANY & CO. goods remain available in most markets. In recent years, there has been an increase in the availability of counterfeit goods, predominantly silver jewelry, on the Internet and in various markets by street vendors and small retailers. The continued sale of counterfeit merchandise or merchandise that infringes the Company's trademarks could have an adverse effect on the TIFFANY & CO. brand by undermining the Company's reputation for quality goods and making such goods appear less desirable to consumers of luxury goods. Damage to the TIFFANY & CO. brand could result in lost sales and earnings.
(xv) The Company's business is dependent upon the distinctive appeal of the TIFFANY & CO. brand.
The TIFFANY & CO. brand's association with quality and luxury is integral to the success of the Company's business. The Company's expansion plans for retail, e-commerce and other direct selling operations and merchandise development, production and management support the appeal of the TIFFANY & CO. brand. Consequently, poor maintenance, promotion and positioning of the TIFFANY & CO. brand, as well as market over-saturation, may adversely affect the business by diminishing the distinctive appeal of the TIFFANY & CO. brand and tarnishing its image. This could result in lower sales and earnings.
In addition, adverse publicity regarding TIFFANY & CO. and its products, as well as adverse publicity in respect of, or resulting from, the Company's third-party vendors or the diamond or jewelry industries more generally, could adversely affect the Company's business. For example, the Company sources from third-party vendors certain products that, from time to time, may not, or may contain raw materials that do not, meet the Company's sourcing and quality standards as well as applicable requirements and regulations. In such instances, although the Company may have recourse against such third-party vendors, the Company may self-report to the relevant regulatory agencies, recall affected products and/or pay potential fines.
Any of the above could harm the TIFFANY & CO. brand and reputation, cause a loss of consumer confidence in the TIFFANY & CO. brand, its products and the industry, and/or negatively affect the Company's results of operations.
The considerable expansion in the use of social media in recent years has compounded the potential scope of any negative publicity.
(xvi) Any material disruption of, or a failure to successfully implement or make changes to, information systems could negatively impact the Company's business.
The Company is increasingly dependent on its information systems to operate its business, including in designing, manufacturing, marketing and distributing its products, as well as processing transactions, managing inventory and accounting for and reporting its results. Given the complexity of the Company's global business, it is critical that the Company maintain the uninterrupted operation of its information systems. Despite the Company's preventative efforts, its information systems may be vulnerable to damage, disruption or shutdown due to power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, systems failures, security breaches or natural
TIFFANY & CO.
K-19
disasters. Damage, disruption or shutdown of the Company's information systems may require a significant investment to repair or replace them, and the Company could suffer interruptions in its operations in the interim.
In addition, in the ordinary course of business, the Company regularly evaluates and makes changes and upgrades to its information systems. The Company is in the process of executing its multi-year effort to evaluate and, where appropriate, to upgrade and/or replace certain of its information systems, including systems for global customer relationship management, order management and inventory management. These system changes and upgrades can require significant capital investments and dedication of resources. While the Company follows a disciplined methodology when evaluating and making such changes, there can be no assurances that the Company will successfully implement such changes, that such changes will be implemented without delays, that such changes will occur without disruptions to its operations or that the new or upgraded systems will achieve the desired business objectives.
Any damage, disruption or shutdown of the Company's information systems, or the failure to successfully implement new or upgraded systems, such as those referenced above, could have a direct material adverse effect on the Company's results of operations, could undermine the Company's ability to execute on its strategic and operational initiatives, and could also affect the Company's reputation, its ability to compete effectively, its relationship with customers and the TIFFANY & CO. brand, which could result in reduced sales and profitability.
(xvii) New and existing data privacy laws and/or a significant data security breach of the Company's information systems could increase the Company's operational costs, subject the Company to claims and otherwise adversely affect its business.
The protection of customer, employee and Company information is important to the Company, and its customers and employees expect that their personal data will be adequately protected. In addition, the regulatory environment surrounding information security and data privacy is becoming increasingly demanding, with evolving requirements in respect of personal data use and processing, including significant penalties for non-compliance, in the various jurisdictions in which the Company does business. For example, the E.U. General Data Protection Regulation that came into force in 2018, as well as the California Consumer Privacy Act that came into force on January 1, 2020, have caused, and will continue to cause, the Company to incur additional compliance costs related thereto. Although the Company has developed and implemented systems, policies, procedures and internal controls that are designed to protect personal data and Company information, prevent data loss and other security breaches, and otherwise identify, assess and analyze cybersecurity risks, such measures cannot provide absolute security. For example, the Company faces a complex and evolving threat landscape in which cybercriminals, nation-states and "hacktivists" employ a complex array of techniques designed to access personal data and other information, including the use of stolen access credentials, malware, ransomware, phishing, structured query language ("SQL") injection attacks and distributed denial-of-service attacks, which may penetrate the Company's systems despite its extensive and evolving protective information security measures. Further, the Company relies on its software and hardware providers to issue timely patches for known vulnerabilities; however, the failure of software and hardware companies to release or to timely release effective patching and the Company's reliance on patches or inability to patch software and hardware vulnerabilities, could expose it to increased risk of attack, data loss and data breach. The Company has experienced, and expects to continue to experience, attempts from cybercriminals and other third parties to gain unauthorized access to its information technology and other information systems. Although these attempts have not had a material impact on the Company to date, in the future the Company could experience attacks that could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition or results of operations.
Additionally, the Company's implementation of new information technology or information systems and/or increased use and reliance on web-based hosted (i.e., cloud computing) applications and systems for the storage, processing and transmission of information, including customer and employee personal data, could expose the Company, its employees and its customers to a risk of loss or misuse of such information. The Company's efforts to protect personal data and Company information may also be adversely impacted by data security or privacy breaches that occur at its third-party vendors. While the Company's contractual arrangements with such third-party vendors provide for the protection of personal data and Company information, the Company cannot control these vendors or their systems and cannot guarantee that a data security or privacy breach of their systems will not occur in the future.
A significant violation of applicable privacy laws or the occurrence of a cybersecurity incident resulting in breach of personal data or Company information could result in the temporary suspension of some or all of the Company's operating and/or information systems, damage the Company's reputation, its relationships with customers, vendors
TIFFANY & CO.
K-20
and service providers and the TIFFANY & CO. brand and could result in lost data, lost sales, sizable fines, increased insurance premiums, substantial breach-notification and other remediation costs and lawsuits as well as adversely affect results of operations. The Company may also incur additional costs in the future related to the implementation of additional security measures to protect against new or enhanced data security and privacy threats, to comply with state, federal and international laws that may be enacted to address personal data processing risks and data security threats or to investigate or address potential or actual data security or privacy breaches.
(xviii) The loss or a prolonged disruption in the operation of the Company's centralized distribution centers could adversely affect its business and operations.
The Company maintains two separate distribution centers in close proximity to one another in New Jersey. Both are dedicated to warehousing merchandise; one handles worldwide store replenishment and the other processes direct-to-customer orders. Although the Company believes that it has appropriate contingency plans, unforeseen disruptions impacting one or both locations for a prolonged period of time may result in delays in the delivery of merchandise to stores or in fulfilling customer orders.
(xix) The loss or a prolonged disruption in the operation of the Company's internal manufacturing facilities could adversely affect its business and operations.
The Company's internal manufacturing facilities produce approximately 60% of the jewelry sold by the Company. Any prolonged disruption to their operations would require the Company to seek alternate sources of production and could have a negative effect on inventory availability and sales until such sources are established.
(xx) If the Company is unable to effectively anticipate and respond to changes in consumer preferences and shopping patterns, or introduce new products or programs that appeal to new or existing customers, the Company's sales and profitability could be adversely affected.
The Company's continued success depends on its ability to anticipate and respond in a timely and cost-effective manner to changes in consumer preferences for jewelry and other luxury goods, attitudes towards the global jewelry industry as a whole, as well as the manner and locations in which consumers purchase such goods. The Company recognizes that consumer tastes cannot be predicted with certainty and are subject to change, which is compounded by the expanding use of digital and social media by consumers and the speed by which information and opinions are shared. The Company's product development strategy is to introduce new design collections, primarily jewelry, and/or expand certain existing collections annually. If the Company is unable to anticipate and respond in a timely and cost-effective manner to changes in consumer preferences and shopping patterns, including the development of an engaging omnichannel experience for its customers, the Company's sales and profitability could be adversely affected.
In addition, approximately 75% of the Company's stores are located within luxury department stores and shopping malls and benefit from the ability of those locations to generate consumer traffic. A substantial decline in department store and/or mall traffic may negatively impact the Company's ability to maintain or increase its sales in existing stores, as well as its ability to open new stores.
(xxi) Environmental and climate changes could affect the Company's business.
The Company operates retail stores in more than 20 markets and has both domestic and foreign manufacturing operations that are susceptible to the risks associated with climate change. Such risks include those related to the physical impacts of climate change, such as more frequent and severe weather events and/or long term shifts in climate patterns, and risks related to the transition to a lower-carbon economy, such as reputational, market and/or regulatory risks. Climate change and climate events could result in social, cultural and economic disruptions in these areas, including supply chain disruptions, the disruption of local infrastructure and transportation systems that could limit the ability of the Company's employees and/or its customers to access the Company's stores or manufacturing locations, damage to such stores or locations or reductions in material availability and quality. These events could also compound adverse economic conditions and impact consumer confidence and discretionary spending. Despite the fact that the Company is pursuing numerous initiatives to reduce its environmental footprint, including efforts related to energy efficiency, renewable energy use and carbon offsets, there remains the risk that insufficient global cooperation could lead to increased negative impacts from climate change. While the Company has an ongoing
TIFFANY & CO.
K-21
program for reviewing its vulnerability to the impacts of severe weather events and other risks associated with climate change, these events could nonetheless negatively affect the Company's business and operations.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None
Item 2. Properties.
The Company leases its various store premises (other than the New York Flagship store, which is owned by the Company) under arrangements that generally range from 3 to 10 years. The following table provides information on the number of locations and square footage of Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores as of January 31, 2020:
Total Stores | Total Gross Retail Square Footage | Gross Retail Square Footage Range | Average Gross Retail Square Footage | |||||
Americas*: | ||||||||
New York Flagship | 1 | 45,500 | 45,500 | 45,500 | ||||
Other stores | 123 | 690,000 | 1,100-17,600 | 5,600 | ||||
Asia-Pacific | 91 | 282,400 | 700-13,400 | 3,100 | ||||
Japan: | ||||||||
Tokyo Ginza | 1 | 13,300 | 13,300 | 13,300 | ||||
Other stores | 57 | 149,000 | 700-7,500 | 2,600 | ||||
Europe: | ||||||||
London Old Bond Street | 1 | 22,400 | 22,400 | 22,400 | ||||
Other stores | 47 | 165,700 | 400-18,200 | 3,500 | ||||
Emerging Markets | 5 | 9,200 | 400-3,600 | 1,800 | ||||
Total | 326 | 1,377,500 | 400-45,500 | 4,200 | ||||
* The total gross retail square footage for the New York Flagship is through its closure for renovation in January 2020, and Other stores does not include the total gross retail square footage for the Tiffany Flagship Next Door.
Excluded from the store count and square footage amounts above are pop-up stores (stores with lease terms of 24 months or less).
NEW YORK FLAGSHIP STORE
The Company owns the building, but not the air rights above the building, housing its New York Flagship store at 727 Fifth Avenue, which was designed to be a retail store for Tiffany and is well located for this function. In 2018, the Company announced its plans to undertake a complete renovation of the New York Flagship store. The New York Flagship store closed in January 2020, at which time the Company began its complete renovation and temporarily moved its operations to the "Tiffany Flagship Next Door" at 6 East 57th Street. This renovation is expected to be completed in the fourth quarter of 2021. Sales in this store represented less than 10% of worldwide net sales in 2019, 2018 and 2017.
RETAIL SERVICE CENTER
The Company's Retail Service Center ("RSC"), located in Parsippany, New Jersey, comprises approximately 370,000 square feet. Approximately half of the building is devoted to office and information technology operations and half to warehousing, shipping, receiving, merchandise processing and other distribution functions. The RSC receives merchandise and replenishes retail stores. The Company has a 20-year lease for this facility, which expires in 2025, and has two 10-year renewal options.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-22
CUSTOMER FULFILLMENT CENTER
The Company owns the Customer Fulfillment Center ("CFC") in Whippany, New Jersey and leases the land on which the facility resides. The CFC is approximately 266,000 square feet and is primarily used for warehousing merchandise and processing direct-to-customer orders. The land lease expires in 2032 and the Company has the right to renew the lease for an additional 20-year term.
MANUFACTURING AND DESIGN FACILITIES
The Company owns and operates jewelry manufacturing facilities in Cumberland, Rhode Island and Lexington, Kentucky, leases a jewelry manufacturing facility in Pelham, New York, leases a facility in the Dominican Republic which performs certain functions such as jewelry polishing and assembly and leases a facility containing its Jewelry Design and Innovation Workshop in New York, New York. Lease expiration dates range from 2023 to 2029. The owned and leased facilities total approximately 244,000 square feet.
The Company leases a facility in Belgium and owns facilities in Botswana, Cambodia, Mauritius and Vietnam (although the land in Botswana, Cambodia and Vietnam is leased) that prepare, cut and/or polish rough diamonds for use by Tiffany. These facilities total approximately 277,000 square feet and the lease expiration dates range from 2020 to 2062.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
Litigation Matters. The Company is from time to time involved in routine litigation incidental to the conduct of its business, including proceedings to protect its trademark rights, litigation with parties claiming infringement of patents and other intellectual property rights by the Company, litigation instituted by persons alleged to have been injured upon premises under the Company's control and litigation with present and former employees and customers. Although litigation with present and former employees is routine and incidental to the conduct of the Company's business, as well as for any business employing significant numbers of employees, such litigation can result in large monetary awards when a civil jury is allowed to determine compensatory and/or punitive damages for actions such as those claiming discrimination on the basis of age, gender, race, religion, disability or other legally-protected characteristic or for termination of employment that is wrongful or in violation of implied contracts. However, the Company believes that all such litigation currently pending to which it is a party or to which its properties are subject will be resolved without any material adverse effect on the Company's financial position, earnings or cash flows.
Merger-related Litigation. As previously disclosed, on December 30, 2019 and January 3, 2020, purported stockholders of the Registrant filed complaints against the Registrant and the members of the Board of Directors of the Registrant in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware, captioned Stein v. Tiffany & Co., et al., Case No. 1:19-cv-11926 (S.D.N.Y.), and Thompson v. Tiffany & Co., et al., Case No. 1:20-cv-00009 (D. Del.), respectively. The complaints alleged that a preliminary version of the proxy statement that the Registrant filed with the SEC on December 18, 2019 was materially incomplete, false or misleading in certain respects. On January 8, 2020, two additional complaints were filed against the Registrant and the members of the Board of Directors of the Registrant in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York by purported stockholders of the Registrant, captioned Federman v. Tiffany & Co., et al., Case No. 1:20-cv-00159 (S.D.N.Y.), and Daka v. Tiffany & Co., et al., Case No. 1:20-cv-00170 (S.D.N.Y.), respectively. The complaints alleged that the Definitive Proxy Statement was materially incomplete, false or misleading in certain respects. Each of the four aforementioned Stein, Thompson, Federman and Daka actions purported to seek injunctive relief and money damages. The plaintiffs in all of the Stein, Thompson, Federman and Daka actions have since voluntarily dismissed their actions.
Gain Contingency. On February 14, 2013, Tiffany and Company and Tiffany (NJ) LLC (collectively, the "Tiffany plaintiffs") initiated a lawsuit against Costco Wholesale Corp. ("Costco") for trademark infringement, false designation of origin and unfair competition, trademark dilution and trademark counterfeiting (the "Costco Litigation"). The Tiffany plaintiffs sought injunctive relief, monetary recovery and statutory damages on account of Costco's use of "Tiffany" on signs in the jewelry cases at Costco stores used to describe certain diamond engagement rings that were not manufactured by Tiffany. Costco filed a counterclaim arguing that the TIFFANY trademark was a generic term for multi-pronged ring settings and seeking to have the trademark invalidated, modified or partially canceled in that respect. On September 8, 2015, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York (the "Court") granted
TIFFANY & CO.
K-23
the Tiffany plaintiffs' motion for summary judgment of liability in its entirety, dismissing Costco's genericism counterclaim and finding that Costco was liable for trademark infringement, trademark counterfeiting and unfair competition under New York law in its use of "Tiffany" on the above-referenced signs. On September 29, 2016, a civil jury rendered its verdict, finding that Costco's profits on the sale of the infringing rings should be awarded at $5.5 million, and further finding that an award of punitive damages was warranted. On October 5, 2016, the jury awarded $8.25 million in punitive damages. The aggregate award of $13.75 million was not final, as it was subject to post-verdict motion practice and ultimately to adjustment by the Court. On August 14, 2017, the Court issued its ruling, finding that the Tiffany plaintiffs are entitled to recover (i) $11.1 million in respect of Costco's profits on the sale of the infringing rings (which amount is three times the amount of such profits, as determined by the Court), (ii) prejudgment interest on such amount (calculated at the applicable statutory rate) from February 15, 2013 through August 14, 2017, (iii) an additional $8.25 million in punitive damages, and (iv) Tiffany's reasonable attorneys' fees, and, on August 24, 2017, the Court entered judgment in the amount of $21.0 million in favor of the Tiffany plaintiffs (reflecting items (i) through (iii) above). On February 7, 2019, the Court awarded the Tiffany plaintiffs $5.9 million in respect of the aforementioned attorneys' fees and costs, bringing the total judgment to $26.9 million. The Court has denied a motion made by Costco for a new trial; however, Costco has also filed an appeal from the judgment before the Second Circuit Court of Appeals. A three-judge panel presided over an appellate hearing on January 23, 2020, and that panel's decision is pending. As the Tiffany plaintiffs may not enforce the Court's judgment during the appeals process, the Company has not recorded any amount in its consolidated financial statements related to this gain contingency as of January 31, 2020. The Company expects that this matter will not ultimately be resolved until, at the earliest, a future date during the Company's fiscal year ending January 31, 2021.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not Applicable.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-24
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
In calculating the aggregate market value of the voting stock held by non-affiliates of the Company shown on the cover page of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, 761,162 shares of Common Stock beneficially owned by the executive officers and directors of the Company (exclusive of shares which may be acquired on exercise of stock options) were excluded, on the assumption that certain of those persons could be considered "affiliates" under the provisions of Rule 405 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
The Company's Common Stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol "TIF". On March 16, 2020, the high and low selling prices quoted on such exchange were $126.42 and $115.09. On March 16, 2020, there were 13,106 holders of record of the Company's Common Stock.
The following graph compares changes in the cumulative total shareholder return on the Company's Common Stock for the previous five fiscal years to returns for the same five-year period on (i) the Standard & Poor's 500 Stock Index and (ii) the Standard & Poor's 500 Consumer Discretionary Index. Cumulative shareholder return is defined as changes in the closing price of the stock and such indices, plus the reinvestment of any dividends paid. The graph assumes an investment of $100 on January 31, 2015 in the Company's Common Stock and in each of the two indices, as well as the reinvestment of any subsequent dividends. The increase in the cumulative shareholder return on the Company's Common Stock for the year ended January 31, 2020 primarily reflects the acquisition price of $135.00 per share of Common Stock related to the proposed Merger. See "Item 1. Business - Entry into Merger Agreement" for additional information regarding the proposed Merger.
Total returns are based on market capitalization; indices are weighted at the beginning of each period for which a return is indicated. The stock performance shown in the graph is not intended to forecast or to be indicative of future performance.
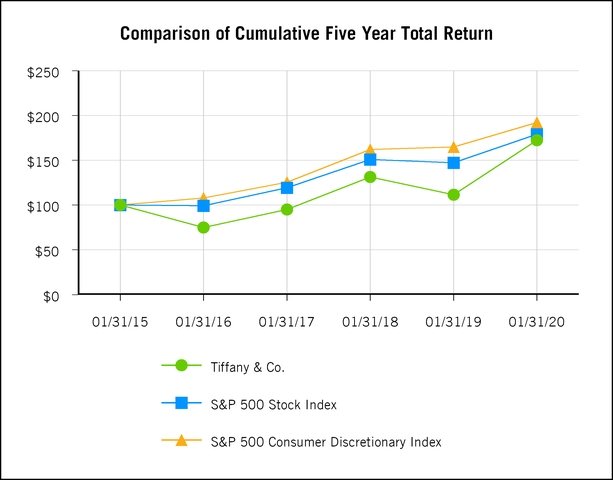
TIFFANY & CO.
K-25
1/31/15 | 1/31/16 | 1/31/17 | 1/31/18 | 1/31/19 | 1/31/20 | |||||||
Tiffany & Co. | $ 100.00 | $ 75.10 | $ 94.93 | $ 131.35 | $ 111.54 | $ 172.32 | ||||||
S&P 500 Stock Index | 100.00 | 99.33 | 119.24 | 150.73 | 147.24 | 179.17 | ||||||
S&P 500 Consumer Discretionary Index | 100.00 | 107.77 | 125.53 | 161.93 | 164.71 | 192.26 | ||||||
Dividends
It is the Company's policy to pay a quarterly dividend on its Common Stock, subject to declaration by its Board of Directors. In 2018, a dividend of $0.50 per share of Common Stock was paid on April 10, 2018. On May 24, 2018, the Company announced a 10% increase in its regular quarterly dividend rate to a new rate of $0.55 per share of Common Stock, which was paid on July 10, 2018, October 10, 2018 and January 10, 2019.
A dividend of $0.55 per share of Common Stock was paid on April 10, 2019. On June 4, 2019, the Company announced a 5% increase in its regular quarterly dividend rate to a new rate of $0.58 per share of Common Stock, which was paid on July 10, 2019, October 10, 2019 and January 10, 2020.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
In May 2018, the Registrant's Board of Directors approved a new share repurchase program (the "2018 Program"). The 2018 Program, which became effective June 1, 2018 and expires on January 31, 2022, authorizes the Company to repurchase up to $1.0 billion of its Common Stock through open market transactions, including through Rule 10b5-1 plans and one or more accelerated share repurchase ("ASR") or other structured repurchase transactions, and/or privately negotiated transactions. As of January 31, 2020, $471.6 million remained available under the 2018 Program; however, pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, and subject to certain limited exceptions, the Company may not repurchase its Common Stock other than in connection with the forfeiture provisions of Company equity awards or the cashless exercise or tax withholding provisions of such Company equity awards, in each case, granted under the Company's stock-based compensation plans. Accordingly, the Company did not repurchase any shares of its Common Stock during the fourth quarter of 2019 pursuant to the 2018 Program, and does not expect to repurchase any shares of its Common Stock in connection with the 2018 Program prior to the Merger or earlier termination of the Merger Agreement.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-26
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The following table sets forth selected financial data, certain of which have been derived from the Company's consolidated financial statements for fiscal years 2015-2019, which ended on January 31 of the following calendar year:
(in millions, except per share amounts, percentages, ratios, stores and employees) | 2019 b, c | 2018 c | 2017 d | 2016 e | 2015 f | ||||||||||
EARNINGS DATA | |||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 4,424.0 | $ | 4,442.1 | $ | 4,169.8 | $ | 4,001.8 | $ | 4,104.9 | |||||
Gross profit | 2,761.9 | 2,811.0 | 2,610.7 | 2,499.0 | 2,505.2 | ||||||||||
Selling, general & administrative expenses | 2,029.3 | 2,020.7 | 1,801.3 | 1,752.6 | 1,706.1 | ||||||||||
Earnings from operations | 732.6 | 790.3 | 809.4 | 746.4 | 799.1 | ||||||||||
Net earnings | 541.1 | 586.4 | 370.1 | 446.1 | 463.9 | ||||||||||
Net earnings per diluted share | 4.45 | 4.75 | 2.96 | 3.55 | 3.59 | ||||||||||
Weighted-average number of diluted common shares | 121.6 | 123.5 | 125.1 | 125.5 | 129.1 | ||||||||||
BALANCE SHEET AND CASH FLOW DATA | |||||||||||||||
Total assets a | $ | 6,660.1 | $ | 5,333.0 | $ | 5,468.1 | $ | 5,097.6 | $ | 5,121.6 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 874.7 | 792.6 | 970.7 | 928.0 | 843.6 | ||||||||||
Inventories, net | 2,463.9 | 2,428.0 | 2,253.5 | 2,157.6 | 2,225.0 | ||||||||||
Short-term borrowings and long-term debt (including current portion) | 1,032.0 | 996.8 | 1,003.5 | 1,107.1 | 1,095.8 | ||||||||||
Stockholders' equity | 3,335.4 | 3,130.9 | 3,248.2 | 3,028.4 | 2,929.5 | ||||||||||
Working capital a | 2,905.1 | 3,041.4 | 3,258.5 | 2,940.8 | 2,778.5 | ||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities | 670.9 | 531.8 | 932.2 | 705.7 | 817.4 | ||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 320.6 | 282.1 | 239.3 | 222.8 | 252.7 | ||||||||||
Stockholders' equity per share | 27.53 | 25.77 | 26.10 | 24.33 | 23.10 | ||||||||||
Cash dividends paid per share | 2.29 | 2.15 | 1.95 | 1.75 | 1.58 | ||||||||||
RATIO ANALYSIS AND OTHER DATA | |||||||||||||||
As a percentage of net sales: | |||||||||||||||
Gross profit | 62.4 | % | 63.3 | % | 62.6 | % | 62.4 | % | 61.0 | % | |||||
Selling, general & administrative expenses | 45.9 | % | 45.5 | % | 43.2 | % | 43.8 | % | 41.6 | % | |||||
Earnings from operations | 16.6 | % | 17.8 | % | 19.4 | % | 18.7 | % | 19.5 | % | |||||
Net earnings | 12.2 | % | 13.2 | % | 8.9 | % | 11.1 | % | 11.3 | % | |||||
Capital expenditures | 7.2 | % | 6.4 | % | 5.7 | % | 5.6 | % | 6.2 | % | |||||
Return on average assets a | 9.0 | % | 10.9 | % | 7.0 | % | 8.7 | % | 9.0 | % | |||||
Return on average stockholders' equity | 16.7 | % | 18.4 | % | 11.8 | % | 15.0 | % | 16.1 | % | |||||
Total debt-to-equity ratio | 30.9 | % | 31.8 | % | 30.9 | % | 36.6 | % | 37.4 | % | |||||
Dividends as a percentage of net earnings | 51.1 | % | 45.0 | % | 65.5 | % | 49.0 | % | 43.8 | % | |||||
Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores | 326 | 321 | 315 | 313 | 307 | ||||||||||
Number of employees | 14,100 | 14,200 | 13,100 | 11,900 | 12,200 | ||||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-27
NOTES TO SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
a. | In connection with the adoption of ASC 842 – Leases on February 1, 2019, the Company established a lease liability and corresponding right-of-use asset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. The following amounts are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet for operating leases as of January 31, 2020: (i) Operating lease right-of-use asset of $1.1 billion; (ii) Current portion of operating lease liabilities of $202.8 million and (iii) Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities of $1.0 billion. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies and Note K. Leases" for additional information. |
b. | Financial information and ratios for 2019 include $21.2 million of pre-tax expense ($17.1 million after tax expense, or $0.14 per diluted share) related to the proposed Merger. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note B. Entry into Merger Agreement" for additional information. |
c. | Financial information and ratios for 2019 and 2018 reflect a lower effective income tax rate, primarily resulting from the 2017 U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note P. Income Taxes" for additional information. |
d. | Financial information and ratios for 2017 include $146.2 million, or $1.17 per diluted share, of net tax expense related to the enactment of the 2017 U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note P. Income Taxes" for additional information. |
e. | Financial information and ratios for 2016 include the following amounts, totaling $38.0 million of pre-tax expense ($24.0 million after tax expense, or $0.19 per diluted share): |
• | $25.4 million of pre-tax expense ($16.0 million after tax expense, or $0.13 per diluted share) associated with an asset impairment charge related to software costs capitalized in connection with the development of a finished goods inventory management and merchandising information system; and |
• | $12.6 million of pre-tax expense ($8.0 million after tax expense, or $0.06 per diluted share) associated with impairment charges related to financing arrangements with diamond mining and exploration companies. |
f. | Financial information and ratios for 2015 include the following amounts, totaling $46.7 million of pre-tax expense ($29.9 million after tax expense, or $0.24 per diluted share): |
• | $37.9 million of pre-tax expense ($24.3 million after tax expense, or $0.19 per diluted share) associated with impairment charges related to a financing arrangement with Koidu Limited, a diamond mining and exploration company; and |
• | $8.8 million of pre-tax expense ($5.6 million after tax expense, or $0.05 per diluted share) associated with severance related to staffing reductions and subleasing of certain office space for which only a portion of the Company's future rent obligations would be recovered. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-28
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements and related notes. All references to years relate to fiscal years which ended on January 31 of the following calendar year.
ENTRY INTO MERGER AGREEMENT
On November 24, 2019, Tiffany & Co. (the "Registrant") entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the "Merger Agreement") by and among the Registrant, LVMH Moët Hennessy - Louis Vuitton SE, a societas Europaea (European company) organized under the laws of France ("Parent"), Breakfast Holdings Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Parent ("Holding"), and Breakfast Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and a direct wholly owned subsidiary of Holding ("Merger Sub"). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into the Registrant (the "Merger"), with the Registrant continuing as the surviving company in the Merger and a wholly owned indirect subsidiary of Parent.
For additional information related to the Merger Agreement, please refer to the Registrant's Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") on January 6, 2020 and "Item 1. Business – Entry into Merger Agreement."
KEY STRATEGIC PRIORITIES
The Company's key strategic priorities are to:
• | Amplify an evolved brand message. |
The Brand is the single most important asset of Tiffany and, indirectly, of the Company. Management intends to increasingly invest in and evolve marketing and public relations programs through a variety of media designed to build awareness of the Brand, its heritage and its products, as well as to enhance the Brand's association with quality and luxury by consumers.
• | Renew the Company's product offerings and enhance in-store presentations. |
The Company's product development strategy is to accelerate the introduction of new design collections, primarily in jewelry, but also in non-jewelry products, and/or expand certain existing collections annually, all of which are intended to appeal to existing and new customers.
To ensure a superior shopping experience, the Company is focused on enhancing the design of its stores, as well as the creative visual presentation of its merchandise, to provide an engaging luxury experience in both its new and existing stores.
• | Deliver an exciting omnichannel customer experience. |
Management intends to continue to expand and optimize its global store base by evaluating potential markets for new TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as through the renovation, relocation, or closing of existing stores. Management will also continue to pursue opportunities to grow sales through its e-commerce websites and utilize the websites to drive store traffic. In addition, the Company employs highly qualified sales and customer service professionals and is focused on developing effective omnichannel relationships with its customers.
• | Strengthen the Company's competitive position and lead in key markets. |
The global jewelry industry is competitively fragmented. While the Company enjoys a strong reputation and large customer base, it encounters significant competition in all product categories and geographies. By focusing on enhanced marketing communications, product development and optimization of its store base and digital capabilities, the Company's objective is to be an industry leader in key markets.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-29
• | Cultivate a more efficient operating model. |
The Company is focused on improving its business operations through new systems, more effective processes and cost restraint, to drive margin growth. This includes realizing greater efficiencies in its product supply chain and other operations, and enhancing its global procurement capabilities. The Company has developed a substantial product supply infrastructure for the procurement and processing of diamonds and the manufacturing of jewelry. This infrastructure is intended to ensure adequate product supply and favorable product costs while adhering to the Company's quality and ethical standards.
• | Inspire an aligned and agile organization to win. |
The Company's success depends upon its people and their effective execution of the Company's strategic priorities. The Company's management strives to motivate and develop employees with the core competencies and adaptability needed to achieve its objectives.
By pursuing these key strategic priorities, management is committed to the following long-term financial objectives:
• | To achieve sustainable sales growth. |
Management's objective is to generate mid-single-digit percentage worldwide sales increases, primarily through comparable sales growth, as well as through modest store square footage growth.
• | To increase retail productivity and profitability. |
Management is focused on increasing the frequency of store and website visits and the percentage of store and website visitors who make a purchase, as well as optimizing utilization of store square footage, and growing sales, average price per unit sold and sales per square foot.
• | To achieve improved operating margins, through both improved gross margins and efficient expense management. |
Management's long-term objective is to improve gross margins, including through controlling product input costs, realizing greater efficiencies in its product supply chain and adjusting retail prices when appropriate. Additionally, management is focused on efficient selling, general and administrative expense management, thereby generating sales leverage on fixed costs. These efforts are collectively intended to generate a higher rate of operating earnings growth relative to sales growth, and management targets an improvement in operating margin of 50 basis points per year over the long term.
• | To improve inventory and other asset productivity and cash flow. |
Management's long-term objective is to maintain inventory growth at a rate less than sales growth, with greater focus on efficiencies in product sourcing and manufacturing as well as optimizing store inventory levels, all of which is intended to contribute to improvements in cash flow and return on assets.
• | To maintain a capital structure that provides financial strength and the ability to invest in strategic initiatives. |
2019 SUMMARY
• | Worldwide net sales were approximately unchanged compared to the prior year. Comparable sales decreased 1% from the prior year. On a constant-exchange-rate basis (see "Non-GAAP Measures" below), worldwide net sales increased 1% and comparable sales were approximately unchanged. |
• | The Company added a net of five TIFFANY & CO. stores (opening four in Japan, two in the Americas, two in Asia-Pacific and one in Europe, while closing two stores in the Americas, one store in Asia-Pacific and one store in Japan) and relocated or renovated 18 existing stores. Gross retail square footage increased 3%, net. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-30
• | Earnings from operations as a percentage of net sales ("operating margin") decreased 120 basis points, which included the impact of costs recorded in 2019 related to the proposed Merger, as described below under "Non-GAAP Measures." Excluding these costs, operating margin decreased 80 basis points due to a decrease in gross margin. |
• | The Company's effective income tax rate increased to 21.6% in 2019 from 21.1% in 2018. |
• | Net earnings decreased to $541.1 million, or $4.45 per diluted share, in 2019 from $586.4 million, or $4.75 per diluted share, in 2018. Net earnings in 2019 included the impact of costs related to the proposed Merger, as described below under "Non-GAAP Measures." Excluding these costs, net earnings decreased to $558.2 million, or $4.59 per diluted share. |
• | Inventories, net did not change significantly from 2018. |
• | Cash flow from operating activities was $670.9 million in 2019, compared with $531.8 million in 2018. Free cash flow (see "Non-GAAP Measures") was $350.3 million in 2019, compared with $249.7 million in 2018. |
• | The Company returned capital to shareholders by paying regular quarterly dividends (which were increased 5% effective July 2019 to $0.58 per share, or an annualized rate of $2.32 per share) and by repurchasing 1.8 million shares of its Common Stock for $163.4 million. |
NOVEL CORONAVIRUS
As discussed under "Item 1A. Risk Factors," an outbreak of a novel strain of the coronavirus, COVID-19, was recently identified in China and has subsequently been recognized as a pandemic by the World Health Organization. This coronavirus outbreak has severely restricted the level of economic activity around the world. In response to this coronavirus outbreak the governments of many countries, states, cities and other geographic regions have taken preventative or protective actions, such as imposing restrictions on travel and business operations and advising or requiring individuals to limit or forego their time outside of their homes. Management expects that these actions could have a negative impact on local and tourist spending around the world. Temporary closures of businesses have been ordered and numerous other businesses have temporarily closed voluntarily. Further, individuals' ability to travel has been curtailed through mandated travel restrictions and may be further limited through additional voluntary or mandated closures of travel-related businesses. These actions have expanded significantly in the past several weeks and are expected to continue to expand. Given the uncertainty regarding the spread of this coronavirus, the related financial impact cannot be reasonably estimated at this time, although the aforementioned actions and related impacts are expected to continue and may also significantly affect the Company's business in other geographic areas in which the coronavirus has spread and may continue to spread. The Company intends to continue to execute on its strategic plans and operational initiatives during the coronavirus outbreak. However, the uncertainties associated with the protective and preventative measures being put in place or recommended by both governmental entities and other businesses, among other uncertainties, may result in delays or modifications to these plans and initiatives.
As a result, this coronavirus outbreak has had a significant effect on the Company's sales results to date in fiscal 2020 and is expected to continue to have a significant effect on its financial results during the current fiscal year. For example, from January 24 through March 19, 2020, management estimates that this coronavirus outbreak contributed to the loss of approximately 30 out of 54 retail trading days (accounting for the effect of individual store closures as well as reductions in store operating hours) across all of the Company's stores in the Chinese Mainland. In addition, as of March 19, 2020, the Company has temporarily closed all of its stores in the United States and Canada, and has temporarily closed nearly all of its stores across Europe and the United Kingdom. The Company has also experienced significantly reduced customer traffic from January 24 through March 19 in its stores that have been open during such period, which management believes has resulted in part from a reduction in tourism as well as restrictions on travel and limitations affecting individuals' ability to spend time in public areas, with attendant sales declines to date in fiscal 2020 in those stores.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-31
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
See "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Results of Operations" in the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2019 for a comparative discussion of the Company's operating results and financial condition for its fiscal years ended January 31, 2019 and 2018.
Non-GAAP Measures
The Company reports information in accordance with U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles ("GAAP"). Internally, management also monitors and measures its performance using certain sales and earnings measures that include or exclude amounts, or are subject to adjustments that have the effect of including or excluding amounts, from the most directly comparable GAAP measure ("non-GAAP financial measures"). The Company presents such non-GAAP financial measures in reporting its financial results to provide investors with useful supplemental information that will allow them to evaluate the Company's operating results using the same measures that management uses to monitor and measure its performance. The Company's management does not, nor does it suggest that investors should, consider non-GAAP financial measures in isolation from, or as a substitute for, financial information prepared in accordance with GAAP. These non-GAAP financial measures presented here may not be comparable to similarly-titled measures used by other companies.
Net Sales. The Company's reported net sales reflect either a translation-related benefit from strengthening foreign currencies or a detriment from a strengthening U.S. dollar. Internally, management monitors and measures its sales performance on a non-GAAP basis that eliminates the positive or negative effects that result from translating sales made outside the U.S. into U.S. dollars ("constant-exchange-rate basis"). Sales on a constant-exchange-rate basis are calculated by taking the current year's sales in local currencies and translating them into U.S. dollars using the prior year's foreign currency exchange rates. Management believes this constant-exchange-rate basis provides a useful supplemental basis for the assessment of sales performance and of comparability between reporting periods. The following table reconciles the sales percentage increases (decreases) from the GAAP to the non-GAAP basis versus the previous year.
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
GAAP Reported | Translation Effect | Constant- Exchange- Rate Basis | GAAP Reported | Translation Effect | Constant- Exchange- Rate Basis | ||||||||||||
Net Sales: | |||||||||||||||||
Worldwide | — | % | (1 | )% | 1 | % | 7 | % | 1 | % | 6 | % | |||||
Americas | (2 | ) | — | (2 | ) | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||
Asia-Pacific | 2 | (3 | ) | 5 | 13 | — | 13 | ||||||||||
Japan | 1 | 1 | — | 8 | 2 | 6 | |||||||||||
Europe | (1 | ) | (3 | ) | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||
Other | (2 | ) | — | (2 | ) | (20 | ) | — | (20 | ) | |||||||
Comparable Sales: | |||||||||||||||||
Worldwide | (1 | )% | (1 | )% | — | % | 4 | % | — | % | 4 | % | |||||
Americas | (2 | ) | — | (2 | ) | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||
Asia-Pacific | (1 | ) | (4 | ) | 3 | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||
Japan | — | 1 | (1 | ) | 7 | 2 | 5 | ||||||||||
Europe | (1 | ) | (3 | ) | 2 | (2 | ) | 1 | (3 | ) | |||||||
Other | (9 | ) | — | (9 | ) | (15 | ) | — | (15 | ) | |||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-32
2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
GAAP Reported | Translation Effect | Constant- Exchange- Rate Basis | GAAP Reported | Translation Effect | Constant- Exchange- Rate Basis | ||||||||||||
Jewelry sales by product category: | |||||||||||||||||
Jewelry collections | 2 | % | (1 | )% | 3 | % | 11 | % | — | % | 11 | % | |||||
Engagement jewelry | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | — | 4 | — | 4 | |||||||||
Designer jewelry | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | ||||||
Statements of Earnings. Internally, management monitors and measures its earnings performance excluding certain items listed below. Management believes excluding such items provides a useful supplemental basis for the assessment of the Company's results relative to the corresponding period in the prior year. The following tables reconcile certain GAAP amounts to non-GAAP amounts:
(in millions, except per share amounts) | GAAP | Charges related to the proposed Merger a | Non-GAAP | ||||||||
Year Ended January 31, 2020 | |||||||||||
Gross Profit | $ | 2,761.9 | $ | 1.0 | $ | 2,762.9 | |||||
As a % of sales | 62.4 | % | 0.1 | % | 62.5 | % | |||||
Selling, general & administrative expenses | 2,029.3 | (20.2 | ) | 2,009.1 | |||||||
As a % of sales | 45.9 | % | (0.5 | )% | 45.4 | % | |||||
Earnings from operations | 732.6 | $ | 21.2 | 753.8 | |||||||
As a % of sales | 16.6 | % | 0.4 | % | 17.0 | % | |||||
Provision for income taxes | 149.2 | $ | 4.1 | 153.3 | |||||||
Effective income tax rate | 21.6 | % | (0.1 | ) | 21.5 | % | |||||
Net earnings | 541.1 | 17.1 | 558.2 | ||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | 4.45 | 0.14 | 4.59 | ||||||||
a | Costs recorded in 2019 related to the proposed Merger. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note B. Entry into Merger Agreement" for additional information. |
Free Cash Flow. Internally, management monitors its cash flow on a non-GAAP basis. Free cash flow is calculated by deducting capital expenditures from net cash provided by operating activities. The ability to generate free cash flow demonstrates how much cash the Company has available for discretionary and non-discretionary purposes after deduction of capital expenditures. The Company's operations require regular capital expenditures for the opening, renovation and expansion of stores and distribution and manufacturing facilities as well as ongoing investments in information technology. Management believes this provides a useful supplemental basis for assessing the Company's operating cash flows. The following table reconciles GAAP net cash provided by operating activities to non-GAAP free cash flow:
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities a | $ | 670.9 | $ | 531.8 | $ | 932.2 | |||
Less: Capital expenditures a | (320.6 | ) | (282.1 | ) | (239.3 | ) | |||
Free cash flow | $ | 350.3 | $ | 249.7 | $ | 692.9 | |||
a | See "Liquidity and Capital Resources" below for further information on the Company's cash flows. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-33
Comparable Sales
Comparable sales include sales transacted in Company-operated stores open for more than 12 months. Sales from e-commerce sites are included in comparable sales for those sites that have been operating for more than 12 months. Sales for relocated stores are included in comparable sales if the relocation occurs within the same geographical market. In all markets, the results of a store in which the square footage has been expanded or reduced remain in the comparable sales base.
Net Sales
The Company generates sales through its retail, Internet, wholesale, business-to-business and catalog channels (see "Item 1. Business - Reportable Segments").
Net sales by segment were as follows:
(in millions) | 2019 | % of Total Net Sales | 2018 | % of Total Net Sales | 2017 | % of Total Net Sales | 2019 vs 2018 % Change in Net Sales | 2018 vs 2017 % Change in Net Sales | ||||||||||||||||
Americas | $ | 1,924.0 | 43 | % | $ | 1,960.3 | 44 | % | $ | 1,870.9 | 45 | % | (2 | )% | 5 | % | ||||||||
Asia-Pacific | 1,258.2 | 28 | 1,239.0 | 28 | 1,095.0 | 26 | 2 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||
Japan | 649.8 | 15 | 643.0 | 15 | 596.3 | 14 | 1 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
Europe | 498.3 | 11 | 504.4 | 11 | 489.0 | 12 | (1 | ) | 3 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 93.7 | 2 | 95.4 | 2 | 118.6 | 3 | (2 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||||||||||||
$ | 4,424.0 | $ | 4,442.1 | $ | 4,169.8 | — | % | 7 | % | |||||||||||||||
Net Sales — 2019 compared with 2018. In 2019, worldwide net sales were approximately unchanged compared to 2018. On a constant-exchange-rate basis, worldwide sales increased 1%.
In 2019, jewelry sales represented 92% of worldwide net sales. Jewelry sales by product category were as follows:
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||
Jewelry collections | $ | 2,420.2 | $ | 2,374.3 | $ | 45.9 | 2 | % | ||||||
Engagement jewelry | 1,139.5 | 1,157.4 | (17.9 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||
Designer jewelry | 514.1 | 544.5 | (30.4 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||
The increase in net sales in the Jewelry collections category was driven primarily by the Tiffany T collection and High jewelry, partially offset by softness in other collections, while net sales in the Engagement jewelry and Designer jewelry categories reflected decreases across the categories.
Changes in net sales by reportable segment were as follows:
(in millions) | Comparable Sales | Non-comparable Sales | Wholesale/ Other | Total | |||||||||||
Americas | $ | (39.4 | ) | $ | 3.4 | $ | (0.3 | ) | $ | (36.3 | ) | ||||
Asia-Pacific | (5.7 | ) | 0.6 | 24.3 | 19.2 | ||||||||||
Japan | 2.4 | 4.7 | (0.3 | ) | 6.8 | ||||||||||
Europe | (6.9 | ) | 2.3 | (1.5 | ) | (6.1 | ) | ||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-34
In 2019, jewelry sales represented 89%, 98%, 93% and 96% of total net sales in the Americas, Asia-Pacific, Japan and Europe, respectively. Changes in jewelry sales relative to the prior year were as follows:
Average Price per Unit Sold | ||||||||
As Reported | Impact of Currency Translation | Number of Units Sold | ||||||
Change in Jewelry Sales | ||||||||
Americas | 10 | % | — | % | (12 | )% | ||
Asia-Pacific | 8 | (3 | ) | (7 | ) | |||
Japan | 3 | 1 | (4 | ) | ||||
Europe | 10 | (3 | ) | (10 | ) | |||
Management believes the changes in average price per jewelry unit sold and the number of jewelry units sold include the effect of the Company's strategy of increasing average price per unit sold by growing sales of High jewelry and other gold and diamond jewelry within the Jewelry collections category at a faster rate than sales within the Engagement jewelry category and silver jewelry within the Jewelry collections category.
Americas. In 2019, total net sales decreased $36.3 million, or 2%, which included comparable sales decreasing $39.4 million, or 2%. Sales decreased across most of the region, which management attributed to lower spending by foreign tourists. On a constant-exchange-rate basis, total net sales and comparable sales decreased 2%.
Management attributed the increase in the average price per jewelry unit sold to a shift in sales mix to gold jewelry and High jewelry within the Jewelry collections category. The decrease in the number of jewelry units sold reflected decreases in all product categories.
Asia-Pacific. In 2019, total net sales increased $19.2 million, or 2%, which included comparable sales decreasing $5.7 million, or 1%. Total sales growth reflected increased wholesale sales and business sales. Additionally, total sales growth reflected double-digit sales growth in the Chinese Mainland, which was partially offset by a decrease in net sales in Hong Kong of 30%, which management attributed to significant disruptions that began earlier in 2019. Sales performance was mixed in other markets in the region. Management attributed these sales results to higher spending by local customers, partially offset by lower spending by foreign tourists. On a constant-exchange-rate basis, total net sales increased 5% and comparable sales increased 3%.
Management attributed the increase in the average price per jewelry unit sold to a shift in sales mix to High jewelry and gold jewelry within the Jewelry collections category. The decrease in the number of jewelry units sold reflected decreases in all product categories.
Japan. In 2019, total net sales increased $6.8 million, or 1%, and comparable sales were largely unchanged from the prior year. On a constant-exchange-rate basis, total net sales were largely unchanged and comparable sales decreased 1%.
Management attributed the increase in the average price per jewelry unit sold to a shift in sales mix to gold jewelry within the Jewelry collections category and to Engagement jewelry. The decrease in the number of jewelry units sold primarily reflected a decrease in the Jewelry collections and Designer jewelry categories, partly offset by an increase in the Engagement jewelry category.
Europe. In 2019, total net sales decreased $6.1 million, or 1%, which included comparable sales decreasing $6.9 million, or 1%. Management attributed the decrease in total net sales to the effect of foreign currency translation. On a constant-exchange-rate basis, total net sales and comparable sales increased 2%. Management attributed these sales results to modest changes in spending by local customers and foreign tourists.
Management attributed the increase in the average price per jewelry unit sold to a shift in sales mix to gold jewelry within the Jewelry collections category. The decrease in the number of jewelry units sold reflected decreases in the Jewelry collections and Designer jewelry categories.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-35
Other. In 2019, total net sales decreased $1.7 million, or 2%, primarily due to a decrease in wholesale sales of diamonds and lower comparable sales.
Store Data. In 2019, the Company increased gross retail square footage by 3%, net, through store openings, closings and relocations. The Company opened 9 stores and closed four: opening four in Japan, two in Asia-Pacific (in China), two in the Americas (in the U.S.), and one in Europe (in the U.K.), while closing two stores in the Americas (one each in the U.S. and Latin America), one store in Asia-Pacific (in China) and one store in Japan. In addition, the Company relocated or renovated 18 existing stores.
Sales per gross square foot generated by all company-operated stores were approximately $2,700 in 2019 and $2,800 in 2018.
Excluded from the store counts and sales per gross square foot amounts above are pop-up stores (stores with lease terms of 24 months or less).
Gross Margin
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
As reported: | |||||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 2,761.9 | $ | 2,811.0 | $ | 2,610.7 | |||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales | 62.4 | % | 63.3 | % | 62.6 | % | |||||
On a Non-GAAP basis*: | |||||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 2,762.9 | |||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales | 62.5 | % | |||||||||
*See "Non-GAAP Measures" above for additional information.
Gross margin (gross profit as a percentage of net sales) decreased 90 basis points in 2019, partly reflecting a shift in sales mix toward higher price point jewelry, as well as sales deleverage on operating expenses. Additionally, the prior year period included the impact of an $8.5 million charge recorded in the third quarter of 2018 related to the bankruptcy filing of a metal refiner to which the Company entrusted precious scrap metal.
Management periodically reviews and adjusts its retail prices when appropriate to address product input cost increases, specific market conditions and changes in foreign currencies/U.S. dollar relationships. Its long-term strategy is to continue that approach, although significant increases in product input costs or weakening foreign currencies can affect gross margin negatively over the short-term until management makes necessary price adjustments. Among the market conditions that management considers are consumer demand for the product category involved, which may be influenced by consumer confidence and competitive pricing conditions. Management uses derivative instruments to mitigate certain foreign exchange and precious metal price exposures (see "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data – Note I. Hedging Instruments"). Management adjusted retail prices in both 2019 and 2018 across most geographic regions and product categories, some of which were intended to mitigate the impact of foreign currency fluctuations.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-36
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
As reported: | |||||||||||
SG&A expenses | $ | 2,029.3 | $ | 2,020.7 | $ | 1,801.3 | |||||
SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales ("SG&A expense ratio") | 45.9 | % | 45.5 | % | 43.2 | % | |||||
On a Non-GAAP basis*: | |||||||||||
SG&A expenses | $ | 2,009.1 | |||||||||
SG&A expense ratio | 45.4 | % | |||||||||
*See "Non-GAAP Measures" above for additional information.
SG&A expenses did not change significantly in 2019, which included certain costs related to the proposed Merger (see "Non-GAAP Measures" for further details). In addition to those costs, SG&A expenses in 2019 reflected decreased labor and incentive compensation costs, decreased marketing costs and decreased professional services costs, largely offset by increased store occupancy and depreciation expenses.
Excluding the 2019 items noted in "Non-GAAP Measures", SG&A expenses in 2019 decreased $11.6 million, or 1%, compared to 2018.
There was no significant effect on SG&A expense changes from foreign currency translation. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales increased 40 basis points compared to 2018. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales decreased 10 basis points when excluding the aforementioned costs related to the proposed Merger (see "Non-GAAP Measures").
The Company's SG&A expenses are largely fixed or controllable in nature (including, but not limited to, marketing costs, employees' salaries and benefits, fixed store rent and depreciation expenses), with the total of such costs representing approximately 80 - 85% of total SG&A expenses, and the remainder comprised of variable items (including, but not limited to, variable store rent, sales commissions and fees paid to credit card companies).
Earnings from Operations
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
As reported: | |||||||||||
Earnings from operations | $ | 732.6 | $ | 790.3 | $ | 809.4 | |||||
Operating margin | 16.6 | % | 17.8 | % | 19.4 | % | |||||
On a Non-GAAP basis*: | |||||||||||
Earnings from operations | $ | 753.8 | |||||||||
Operating margin | 17.0 | % | |||||||||
*See "Non-GAAP Measures" above for additional information.
Earnings from operations decreased $57.7 million, or 7%, in 2019 and operating margin decreased 120 basis points, which included the impact of costs related to the proposed Merger (see "Non-GAAP Measures"), as well as a decrease in gross margin. Excluding these costs, operating margin decreased 80 basis points.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-37
Results by segment were as follows:
(in millions) | 2019 | % of Net Sales | 2018 | % of Net Sales | 2017 | % of Net Sales | ||||||||||||||
Earnings from operations*: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Americas | $ | 382.2 | 19.9 | % | $ | 386.7 | 19.7 | % | $ | 399.0 | 21.3 | % | ||||||||
Asia-Pacific | 254.3 | 20.2 | 311.5 | 25.1 | 287.7 | 26.3 | ||||||||||||||
Japan | 229.7 | 35.4 | 237.2 | 36.9 | 209.3 | 35.1 | ||||||||||||||
Europe | 83.1 | 16.7 | 86.2 | 17.1 | 90.4 | 18.5 | ||||||||||||||
Other | 11.3 | 12.1 | (6.4 | ) | (6.7 | ) | 3.6 | 3.0 | ||||||||||||
960.6 | 1,015.2 | 990.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
Unallocated corporate expenses | (206.8 | ) | (4.7 | )% | (224.9 | ) | (5.1 | )% | (180.6 | ) | (4.3 | )% | ||||||||
Earnings from operations before other operating expenses | 753.8 | 17.0 | % | 790.3 | 17.8 | % | 809.4 | 19.4 | % | |||||||||||
Other operating expenses | (21.2 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Earnings from operations | $ | 732.6 | 16.6 | % | $ | 790.3 | 17.8 | % | $ | 809.4 | 19.4 | % | ||||||||
* | Percentages represent earnings from operations as a percentage of each segment's net sales. |
On a segment basis, the ratio of earnings from operations to each segment's net sales in 2019 compared with 2018 was as follows:
• | Americas – the ratio increased 20 basis points due to a decrease in the SG&A expense ratio, primarily resulting from decreased labor and incentive compensation costs and decreased marketing spending, largely offset by a decrease in gross margin; |
• | Asia-Pacific – the ratio decreased 490 basis points due to sales deleverage on operating expenses largely attributed to business disruptions in Hong Kong, with store-related expenses in Asia Pacific growing at a higher rate than net sales, and a decrease in gross margin; |
• | Japan – the ratio decreased 150 basis points primarily due to sales deleverage on operating expenses; and |
• | Europe – the ratio decreased 40 basis points due to a decrease in gross margin, largely offset by a decrease in the SG&A expense ratio attributable to a decrease in marketing spending. |
Unallocated corporate expenses include costs related to administrative support functions which the Company does not allocate to its segments. Such unallocated costs include those for centralized information technology, finance, legal and human resources departments. Unallocated corporate expenses decreased by $18.1 million, or 8%, in 2019, due to decreased labor and incentive compensation costs. Additionally, the prior year period included the impact of an $8.5 million charge recorded in the third quarter of 2018 related to the bankruptcy filing of a metal refiner to which the Company entrusted precious scrap metal.
The 2019 amount included in other operating expenses in the table above reflects $21.2 million for costs incurred related to the proposed Merger (see "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note B. Entry into Merger Agreement").
Interest Expense and Financing Costs
Interest expense and financing costs decreased $1.2 million, or 3%, in 2019.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-38
Other Expense, Net
Other expense, net includes the non-service cost components of net periodic benefit cost, interest income and gains/losses on investment activities and foreign currency transactions. Other expense, net decreased $3.3 million, or 46%, in 2019.
Provision for Income Taxes
The effective income tax rate was 21.6% in 2019 compared with 21.1% in 2018.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
The Company's liquidity needs have been, and are expected to remain, primarily a function of its ongoing, seasonal and expansion-related working capital requirements and capital expenditure needs. Over the long term, the Company manages its cash and capital structure to maintain a strong financial position that provides flexibility to pursue strategic priorities. Management regularly assesses its working capital needs, capital expenditure requirements, debt service, dividend payouts and future investments. Management believes that cash on hand, internally generated cash flows and the funds available under its revolving credit facilities are sufficient to support the Company's liquidity and capital requirements for the foreseeable future.
At January 31, 2020, the Company's cash and cash equivalents totaled $874.7 million, of which approximately 30% was held in locations outside the U.S. where the Company has determined to maintain its assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed earnings to support its continued expansion and investments in such foreign locations. To the extent the Company were to repatriate such funds, it may incur withholding taxes, state income taxes and the tax expense or benefit associated with foreign currency gains or losses. The Company believes it has sufficient sources of cash in the U.S. to fund its U.S. operations without the need to repatriate those funds held outside the U.S. See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note P. Income Taxes" for additional information. In addition, the Company had Short-term investments of $22.7 million at January 31, 2020.
The following table summarizes cash flows from operating, investing and financing activities:
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in): | |||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 670.9 | $ | 531.8 | $ | 932.2 | |||||
Investing activities | (279.3 | ) | (29.9 | ) | (481.1 | ) | |||||
Financing activities | (307.9 | ) | (674.3 | ) | (421.1 | ) | |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (1.6 | ) | (5.7 | ) | 12.7 | ||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 82.1 | $ | (178.1 | ) | $ | 42.7 | ||||
Operating Activities
The Company had net cash inflows from operating activities of $670.9 million in 2019 and $531.8 million in 2018. The increase in 2019 compared to 2018 primarily reflected decreases in inventory purchases, partly offset by a decrease in earnings.
Working Capital. Working capital (current assets less current liabilities) decreased to $2.9 billion at January 31, 2020 from $3.0 billion at January 31, 2019. The decrease in 2019 compared with 2018 included an increase in current liabilities (which reflects the adoption of ASC 842 – Leases in the current period, which established the Current portion of operating lease liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet).
Accounts receivable, net at January 31, 2020 decreased 2% from January 31, 2019. Currency translation had no significant effect on the change compared to the prior year.
Inventories, net at January 31, 2020 did not change significantly from January 31, 2019. Currency translation had no significant effect on the change compared to the prior year.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-39
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities at January 31, 2020 were 5% higher than at January 31, 2019, which primarily reflected an increase in accounts payable for store-related expenditures and professional services.
Investing Activities
The Company had net cash outflows from investing activities of $279.3 million in 2019 and $29.9 million in 2018. The increase in net cash outflows in 2019 compared to 2018 was driven by net cash flows resulting from purchases and sales of marketable securities and short-term investments and an increase in capital expenditures in 2019.
Marketable Securities and Short-Term Investments. The Company invests a portion of its cash in marketable securities and short-term investments. The Company had $37.0 million of net sales of marketable securities and short-term investments during 2019, compared with $240.0 million in 2018.
Capital Expenditures. Capital expenditures are typically related to the opening, renovation and/or relocation of stores (which represented approximately 55% and 60% of capital expenditures in 2019 and 2018, respectively), as well as distribution and manufacturing facilities and ongoing investments in information technology. Capital expenditures were $320.6 million in 2019 and $282.1 million in 2018, representing 7% and 6% of worldwide net sales in 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The Company's New York Flagship store closed in January 2020, at which time the Company began its complete renovation and temporarily moved its operations to the "Tiffany Flagship Next Door" at 6 East 57th Street. The renovation of the New York Flagship store is expected to lower diluted earnings per share by approximately $0.10 - $0.12 in fiscal years 2020 and 2021, due to the incremental costs associated with the adjacent space, and is expected to be completed in the fourth quarter of 2021.
Financing Activities
The Company had net cash outflows from financing activities of $307.9 million in 2019 and $674.3 million in 2018.
Borrowings. The Company had net proceeds from (repayments of) borrowings as follows:
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
Short-term borrowings: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from (repayments of) credit facility borrowings, net | $ | 1.5 | $ | (18.4 | ) | $ | (67.8 | ) | |||
Proceeds from other credit facility borrowings | 133.1 | 49.3 | 39.2 | ||||||||
Repayments of other credit facility borrowings | (96.1 | ) | (32.0 | ) | (96.1 | ) | |||||
Net proceeds from (repayments of) total borrowings | $ | 38.5 | $ | (1.1 | ) | $ | (124.7 | ) | |||
Credit Facilities. On October 25, 2018, the Registrant, along with certain of its subsidiaries designated as borrowers thereunder, entered into a five-year multi-bank, multi-currency committed unsecured revolving credit facility, including a letter of credit subfacility, consisting of basic commitments in an amount up to $750.0 million (which commitments may be increased, subject to certain conditions and limitations, at the request of the Registrant) (the "Credit Facility"). The Credit Facility replaced the Registrant's previously existing $375.0 million four-year unsecured revolving credit facility and $375.0 million five-year unsecured revolving credit facility, which were each terminated and repaid in connection with the Registrant's entry into the Credit Facility.
The Credit Facility matures in 2023, provided that such maturity may be extended for one or two additional one-year periods at any time with the consent of the applicable lenders, as further described in the agreement governing such facility.
Commercial Paper. In August 2017, the Registrant and one of its wholly owned subsidiaries established a commercial paper program (the "Commercial Paper Program") for the issuance of commercial paper in the form of short-term promissory notes in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $750.0 million. Borrowings under the Commercial Paper Program may be used for general corporate purposes. The aggregate amount of borrowings that the Company is currently authorized to have outstanding under the Commercial Paper Program and the Registrant's
TIFFANY & CO.
K-40
Credit Facility is $750.0 million. The Registrant guarantees the obligations of its wholly owned subsidiary under the Commercial Paper Program. Maturities of commercial paper notes may vary, but cannot exceed 397 days from the date of issuance. Notes issued under the Commercial Paper Program rank equally with the Registrant's present and future unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness.
Other Credit Facilities. Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement. In June 2019, the Registrant's indirect, wholly owned subsidiary, Tiffany & Co. (Shanghai) Commercial Company Limited ("Tiffany-Shanghai"), entered into a three-year multi-bank revolving credit agreement (the "Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement"). The Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement has an aggregate borrowing limit of RMB 408.0 million ($59.0 million at January 31, 2020), which may be increased to the RMB equivalent of $100.0 million, subject to certain conditions and limitations, at the request of Tiffany-Shanghai. The Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement, which matures in July 2022, was made available to refinance amounts outstanding under Tiffany-Shanghai's previously existing RMB 990.0 million three-year multi-bank revolving credit agreement (the "2016 Agreement"), which expired pursuant to its terms on July 11, 2019, as well as for Tiffany-Shanghai's ongoing general working capital requirements. The participating lenders make loans, upon Tiffany-Shanghai's request, for periods of up to 12 months at the applicable interest rates equal to 95% of the applicable rate as announced by the People's Bank of China (provided, that if such announced rate is below zero, the applicable interest rate shall be deemed to be zero). In June 2019, in connection with the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement, the Registrant entered into a Guaranty Agreement by and between the Registrant and the facility agent under the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement (the "Guaranty"). At January 31, 2020, there was $33.0 million available to be borrowed under the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement and $26.0 million was outstanding.
The weighted-average interest rate for borrowings outstanding under all of the Company's credit facilities was 4.7% at January 31, 2020 and 3.7% at January 31, 2019.
The ratio of total debt (short-term borrowings and long-term debt) to stockholders' equity was 31% at January 31, 2020 and 32% at January 31, 2019.
At January 31, 2020, the Company was in compliance with all debt covenants.
Once consummated, the proposed Merger may result in certain of the Company's outstanding indebtedness becoming due, and the Company will need to comply with certain covenants of the agreements governing its outstanding indebtedness relating to the proposed Merger. Under the terms of the Merger Agreement, if reasonably requested by Parent, the Company must use its commercially reasonable efforts to, among other things, take actions required to facilitate repayment of the Company's outstanding indebtedness.
For additional information regarding all of the Company's credit facilities, senior note issuances and other outstanding indebtedness, including the impact of the proposed Merger on the covenants in respect thereof, see "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note H. Debt."
Share Repurchases. In May 2018, the Registrant's Board of Directors approved a new share repurchase program (the "2018 Program"). The 2018 Program, which became effective June 1, 2018 and expires on January 31, 2022, authorizes the Company to repurchase up to $1.0 billion of its Common Stock through open market transactions, including through Rule 10b5-1 plans and one or more accelerated share repurchase ("ASR") or other structured repurchase transactions, and/or privately negotiated transactions. As of January 31, 2020, $471.6 million remained available under the 2018 Program; however, pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, and subject to certain limited exceptions, the Company may not repurchase its Common Stock other than in connection with the forfeiture provisions of Company equity awards or the cashless exercise or tax withholding provisions of such Company equity awards, in each case, granted under the Company's stock-based compensation plans. Accordingly, the Company does not expect to repurchase any shares of its Common Stock in connection with the 2018 Program prior to the consummation of the proposed Merger or earlier termination of the Merger Agreement.
During 2018, the Company entered into ASR agreements with two third-party financial institutions to repurchase an aggregate of $250.0 million of its Common Stock. The ASR agreements were entered into under the 2018 Program. Pursuant to the ASR agreements, the Company made an aggregate payment of $250.0 million from available cash on hand in exchange for an initial delivery of 1,529,286 shares of its Common Stock. Final settlement of the ASR agreements was completed in July 2018, pursuant to which the Company received an additional 353,112 shares of its Common Stock. In total, 1,882,398 shares of the Company's Common Stock were repurchased under these ASR agreements at an average cost per share of $132.81 over the term of the agreements.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-41
The Company's share repurchase activity was as follows:
(in millions, except per share amounts) | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||
Cost of repurchases | $ | 163.4 | $ | 421.4 | $ | 99.2 | |||||
Shares repurchased and retired | 1.8 | 3.5 | 1.0 | ||||||||
Average cost per share | $ | 91.15 | $ | 121.28 | $ | 94.86 | |||||
Proceeds from exercised stock options. The Company's proceeds from exercised stock options were $108.4 million and $23.1 million in 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Dividends. The cash dividend on the Company's Common Stock was increased once in each of 2019 and 2018. The Company's Board of Directors declared quarterly dividends which totaled $2.29 and $2.15 per common share in 2019 and 2018, respectively, with cash dividends paid of $276.3 million and $263.8 million in those respective years. The dividend payout ratio (dividends as a percentage of net earnings) was 51% and 45% in 2019 and 2018, respectively. Dividends as a percentage of adjusted net earnings (see "Non-GAAP Measures") were 49% in 2019.
Contractual Cash Obligations and Commercial Commitments
The following is a summary of the Company's contractual cash obligations at January 31, 2020:
(in millions) | Total | 2020 | 2021-2022 | 2023-2024 | Thereafter | ||||||||||
Recorded contractual obligations: | |||||||||||||||
Operating leases a | $ | 1,403.6 | $ | 245.1 | $ | 466.3 | $ | 323.7 | $ | 368.5 | |||||
Short-term borrowings | 147.9 | 147.9 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Long-term debt b | 891.9 | — | 50.0 | 250.0 | 591.9 | ||||||||||
Unrecorded contractual obligations: | |||||||||||||||
Inventory purchase obligations c | 229.8 | 229.8 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Interest on debt d | 557.4 | 35.9 | 70.7 | 67.4 | 383.4 | ||||||||||
Other contractual obligations e | 152.1 | 97.3 | 44.9 | 6.2 | 3.7 | ||||||||||
$ | 3,382.7 | $ | 756.0 | $ | 631.9 | $ | 647.3 | $ | 1,347.5 | ||||||
a) | Includes the minimum rental commitments under non-cancelable operating leases primarily for retail stores, offices, warehouses and distribution facilities (includes imputed interest of $192.4 million, which is not reflected within operating lease liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as of January 31, 2020). See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note K. Leases" for a discussion of the Company's operating leases. |
b) | Amounts exclude any unamortized discount or premium. |
c) | The Company will, from time to time, enter into arrangements to purchase rough diamonds that contain minimum purchase obligations. Inventory purchase obligations associated with these agreements have been estimated at approximately $30.0 million for 2020 and are included in this table. Purchases beyond 2020 that are contingent upon mine production have been excluded as they cannot be reasonably estimated. |
d) | Excludes interest payments on amounts outstanding under available lines of credit, as the outstanding amounts fluctuate based on the Company's working capital needs. |
e) | Consists primarily of technology licensing and service contracts, fixed royalty commitments, construction-in-progress and packaging supplies. |
The summary above does not include the following items:
• | Cash contributions to the Company's pension plan and cash payments for other postretirement obligations. The Company funds its U.S. pension plan's trust in accordance with regulatory limits to provide for current service and for the unfunded benefit obligation over a reasonable period and for current service benefit |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-42
accruals. To the extent that these requirements are fully covered by assets in the Qualified Plan (as defined under "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data – Note O. Employee Benefit Plans"), the Company may elect not to make any contribution in a particular year. No cash contribution was required in 2019 and none is required in 2020 to meet the minimum funding requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. However, the Company periodically evaluates whether to make discretionary cash contributions to the Qualified Plan and made voluntary cash contributions of $30.0 million in 2019 and $11.8 million in 2018. The Company does not currently expect to make any contributions to the Qualified Plan in 2020.
• | Unrecognized tax benefits of $19.7 million and accrued interest and penalties of $2.9 million at January 31, 2020. The final outcome of tax uncertainties is dependent upon various matters including tax examinations, interpretation of the applicable tax laws or expiration of statutes of limitations. The Company believes that its tax positions comply with applicable tax law and that it has adequately provided for these matters. However, the examinations may result in proposed assessments where the ultimate resolution may result in the Company owing additional taxes. |
The following is a summary of the Company's outstanding borrowings and available capacity under its credit facilities at January 31, 2020:
(in millions) | Total Capacity | Borrowings Outstanding | Letters of Credit Issued | Available Capacity | ||||||||
Five-year revolving credit facility a, b | $ | 750.0 | $ | 13.8 | $ | 3.6 | $ | 732.6 | ||||
Other credit facilities c | 247.9 | 134.1 | — | 113.8 | ||||||||
$ | 997.9 | $ | 147.9 | $ | 3.6 | $ | 846.4 | |||||
a) | Matures in 2023. |
b) | The aggregate amount of borrowings that the Company is currently authorized to have outstanding under the Commercial Paper Program and the Credit Facility is $750.0 million. As of January 31, 2020, there were no borrowings outstanding under the Commercial Paper Program. |
c) | Maturities through 2022. |
In addition, the Company has other available letters of credit and financial guarantees of $73.7 million, of which $48.5 million was outstanding at January 31, 2020. Of those available letters of credit and financial guarantees, $46.5 million expires within one year.
Seasonality
As a jeweler and specialty retailer, the Company's business is seasonal in nature, with the fourth quarter typically representing approximately one-third of annual net sales and a higher percentage of annual net earnings. Management expects such seasonality to continue.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company's consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. These principles require management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect amounts reported and disclosed in the financial statements and related notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates and the differences could be material. Periodically, the Company reviews all significant estimates and assumptions affecting the financial statements and records any necessary adjustments.
The development and selection of critical accounting estimates and the related disclosures below have been reviewed with the Audit Committee of the Company's Board of Directors. The following critical accounting policies that rely on assumptions and estimates were used in the preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Inventory. The Company writes down its inventory for discontinued and slow-moving products. This write-down is equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and its net realizable value, and is based on assumptions about future demand and market conditions. Net realizable value is the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of
TIFFANY & CO.
K-43
business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal and transportation. The Company has not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to establish its reserve for discontinued and slow-moving products during the past three years. At January 31, 2020, a 10% change in the reserve for discontinued and slow-moving products would have resulted in a change of $8.1 million in inventory and cost of sales.
Property, plant and equipment and intangible assets and key money. The Company reviews its property, plant and equipment and intangible assets and key money for impairment when management determines that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable due to events or changes in circumstances. Recoverability of these assets is evaluated by comparing the carrying value of the asset with estimated future undiscounted cash flows. If the comparisons indicate that the value of the asset is not recoverable, an impairment loss is calculated as the difference between the carrying value and the fair value of the asset and the loss is recognized during that period. The Company did not record any significant impairment charges in 2019 or 2018.
Goodwill. The Company performs its annual impairment evaluation of goodwill during the fourth quarter of its fiscal year, or when circumstances otherwise indicate an evaluation should be performed. A qualitative assessment is first performed for each reporting unit to determine whether it is more-likely-than-not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value. If it is concluded that this is the case, a quantitative evaluation is performed and an impairment charge is recognized for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit's fair value during that period. The 2019 and 2018 evaluations resulted in no impairment charges.
Income taxes. The Company is subject to income taxes in U.S. federal and state, as well as foreign, jurisdictions. The calculation of the Company's tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax laws and regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions across the Company's global operations. Significant judgments, interpretations and estimates are required in determining consolidated income tax expense. The Company's income tax expense, deferred tax assets and liabilities and reserves for uncertain tax positions reflect management's best assessment of estimated current and future taxes to be paid.
Foreign and domestic tax authorities periodically audit the Company's income tax returns. These audits often examine and test the factual and legal basis for positions the Company has taken in its tax filings with respect to its tax liabilities, including the timing and amount of income and deductions and the allocation of income among various tax jurisdictions ("tax filing positions"). Management believes that its tax filing positions are reasonable and legally supportable. However, in specific cases, various tax authorities may take a contrary position. In evaluating the exposures associated with the Company's various tax filing positions, management records reserves using a more likely-than-not recognition threshold for tax benefits related to the income tax positions taken or expected to be taken. Earnings could be affected to the extent the Company prevails in matters for which reserves have been established or is required to pay amounts in excess of established reserves. At January 31, 2020, total unrecognized tax benefits were $19.7 million. As of January 31, 2020, unrecognized tax benefits are not expected to change materially in the next 12 months. Future developments may result in a change in this assessment.
In evaluating the Company's likelihood to recover its deferred tax assets within the jurisdiction from which they arise, management considers all available evidence. The Company records valuation allowances when management determines it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized in the future.
Following the enactment of the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the "2017 Tax Act") on December 22, 2017, the SEC issued SAB 118 to address the application of U.S. GAAP in situations when a registrant did not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the 2017 Tax Act. Specifically, SAB 118 provided a measurement period for companies to evaluate the impacts of the 2017 Tax Act on their financial statements. This measurement period began in the reporting period that included the enactment date and ended when an entity obtained, prepared and analyzed the information that was needed in order to complete the accounting requirements, but could not exceed one year. The Company adopted the provisions of SAB 118 with respect to the impact of the 2017 Tax Act on its 2017 consolidated financial statements.
Consistent with SAB 118, the Company calculated and recorded reasonable estimates in its 2017 consolidated financial statements for the impact of the one-time transition tax via a mandatory deemed repatriation of post-1986 undistributed foreign earnings and profits (the "Transition Tax") and the remeasurement of its deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. The Company also adopted the provisions of SAB 118 as it related to the assertion of the indefinite reinvestment of foreign earnings and profits. The charges recorded during the fourth quarter of 2017
TIFFANY & CO.
K-44
associated with the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of the Company's deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, as a result of applying the 2017 Tax Act, represented provisional amounts for which the Company's analysis was incomplete but reasonable estimates could be determined. Further, the impact of the 2017 Tax Act on the Company's assertion to indefinitely reinvest foreign earnings and profits was incomplete, as the Company continued to analyze the relevant provisions of the 2017 Tax Act and related accounting guidance.
During 2018, as permitted by SAB 118, the Company completed its analyses under the 2017 Tax Act, including those related to: (i) the provisional estimate recorded during 2017 for the Transition Tax; (ii) the provisional estimate recorded during 2017 to remeasure the Company's deferred tax assets and liabilities; and (iii) the Company's assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed foreign earnings and profits.
As a result of completing these analyses, during 2018, the Company: (i) recorded tax benefits totaling $12.6 million to adjust the provisional estimate recorded in 2017 to remeasure the Company's deferred tax assets and liabilities; (ii) recorded tax benefits totaling $3.3 million to adjust the provisional estimate recorded in 2017 for the Transition Tax; and (iii) determined to maintain its assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed foreign earnings and profits.
For additional information, see "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note P. Income Taxes."
Employee benefit plans. The Company maintains several pension and retirement plans and provides certain postretirement healthcare and life insurance benefits for retired employees. The Company makes certain assumptions that affect the underlying estimates related to pension and other postretirement costs. Significant changes in interest rates, the market value of securities and projected healthcare costs would require the Company to revise key assumptions and could result in a higher or lower charge to earnings.
The Company used a discount rate of 4.25% to determine 2019 expense for its U.S. Qualified Plan, 4.50% for its postretirement plans and 4.25% for its Excess Plan/SRIP (as defined under "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data – Note O. Employee Benefit Plans"). Holding all other assumptions constant, a 0.5% increase in the discount rates would have decreased 2019 pension and postretirement expenses by $6.3 million and $0.8 million, respectively. A decrease of 0.5% in the discount rates would have increased the 2019 pension and postretirement expenses by $7.1 million and $0.4 million, respectively. The discount rate is subject to change each year, consistent with changes in the yield on applicable high-quality, long-term corporate bonds. Management selects a discount rate at which pension and postretirement benefits could be effectively settled based on (i) an analysis of expected benefit payments attributable to current employment service and (ii) appropriate yields related to such cash flows.
The Company used an expected long-term rate of return on pension plan assets of 7.00% to determine its 2019 pension expense. Holding all other assumptions constant, a 0.5% change in the long-term rate of return would have changed the 2019 pension expense by $2.5 million. The expected long-term rate of return on pension plan assets is selected by taking into account the average rate of return expected on the funds invested or to be invested to provide for the benefits included in the projected benefit obligation. More specifically, consideration is given to the expected rates of return (including reinvestment asset return rates) based upon the plan's current asset mix, investment strategy and the historical performance of plan assets.
For postretirement benefit measurement purposes, a 6.50% annual rate of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care was assumed for 2020. The rate was assumed to decrease gradually to 4.75% by 2023 and remain at that level thereafter. A one-percentage-point change in the assumed health-care cost trend rate would not have a significant effect on the Company's accumulated postretirement benefit obligation for the year ended January 31, 2020 or aggregate service and interest cost components of the 2019 postretirement expense.
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data - Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
The Company does not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-45
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
The Company is exposed to market risk from fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, precious metal prices and interest rates, which could affect its consolidated financial position, earnings and cash flows. The Company manages its exposure to market risk through its regular operating and financing activities and, when deemed appropriate, through the use of derivative financial instruments. The Company uses derivative financial instruments as risk management tools and not for trading or speculative purposes.
Foreign Currency Risk
The Company uses foreign exchange forward contracts to offset a portion of the foreign currency exchange risks associated with foreign currency-denominated liabilities, intercompany transactions and forecasted purchases of merchandise between entities with differing functional currencies. The maximum term of the Company's outstanding foreign exchange forward contracts as of January 31, 2020 is 12 months. At January 31, 2020 and 2019, the aggregate fair value of the Company's outstanding foreign exchange forwards was a net asset of $1.4 million and a net liability of $2.1 million, respectively.
The Company entered into cross-currency swaps to hedge the foreign currency exchange risk associated with Japanese yen-denominated and Euro-denominated intercompany loans. These cross-currency swaps are designated and accounted for as cash flow hedges. As of January 31, 2020, the notional amounts of cross-currency swaps accounted for as cash flow hedges and the respective maturity dates were as follows:
Cross-Currency Swap | Notional Amount | ||||||
Effective Date | Maturity Date | (in millions) | (in millions) | ||||
July 2016 | October 2024 | ¥ | 10,620.0 | $ | 100.0 | ||
March 2017 | April 2027 | ¥ | 11,000.0 | 96.1 | |||
May 2017 | April 2027 | ¥ | 5,634.5 | 50.0 | |||
August 2019 | August 2026 | € | 21.1 | 23.6 | |||
At January 31, 2020 and 2019, the aggregate fair value of the Company's outstanding cross-currency swaps was a net asset of $1.0 million and a net liability of $19.9 million, respectively.
At January 31, 2020, for all of the contracts and swaps noted above, a 10% decrease in the hedged foreign currency exchange rates from the prevailing market rates would have resulted in a liability with a fair value of approximately $91.3 million.
Precious Metal Price Risk
The Company periodically hedges a portion of its forecasted purchases of precious metals for use in its internal manufacturing operations in order to manage the effect of volatility in precious metal prices. The Company may use a combination of call and put option contracts in net-zero-cost collar arrangements ("precious metal collars") or forward contracts. If the price of the precious metal at the time of the expiration of the precious metal collar is within the call and put price, the precious metal collar would expire at no cost to the Company. The maximum term of the Company's outstanding precious metal forward contracts and collars as of January 31, 2020 is 18 months. At January 31, 2020 and 2019, the aggregate fair value of the Company's outstanding precious metal derivative instruments was a net asset of $12.8 million and $2.5 million, respectively. At January 31, 2020, a 10% decrease in precious metal prices from the prevailing market rates would have resulted in a liability with a fair value of approximately $4.1 million.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-46
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors of Tiffany & Co.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Tiffany & Co. and its subsidiaries (the "Company") as of January 31, 2020 and 2019, and the related consolidated statements of earnings, of comprehensive earnings, of stockholders' equity and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2020, including the related notes and financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) (collectively referred to as the "consolidated financial statements"). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of January 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2020 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Note C to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for leases as of February 1, 2019.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company's consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-47
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Income Taxes
As described in Notes C and P to the consolidated financial statements, the Company recorded a provision for income taxes of $149 million for the year ended January 31, 2020. As disclosed by management, the calculation of the Company's tax liabilities involves uncertainties in the application of complex tax laws and regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions across the Company's global operations. Significant judgments, interpretations and estimates are required by management in determining consolidated income tax expense. The Company's income tax expense, deferred tax assets and liabilities and reserves for uncertain tax positions reflect management's best assessment of estimated current and future taxes to be paid.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to accounting for income taxes is a critical audit matter are there was significant judgment by management when evaluating complex tax laws and regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions. This in turn led to a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in evaluating the Company's accounting for complex tax laws and regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions, including deferred tax assets and liabilities and management's assessment of the estimated current and future taxes to be paid. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in evaluating the audit evidence obtained.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-48
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to accounting for income taxes, including evaluation of permanent and temporary differences within jurisdictions, the rate reconciliation and the provision to tax return reconciliation. Professionals with specialized skill and knowledge were used to assist in (i) evaluating the provision for income taxes, including the reasonableness of management's judgments and estimates in the application of tax laws and regulations in certain jurisdictions; (ii) testing the current and deferred income tax provision, including evaluation of permanent and temporary differences within certain jurisdictions and management's assessment of the technical merits of the differences; (iii) performing procedures over the Company's rate reconciliation; and (iv) testing the reconciliation of the provision to the tax returns.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
New York, New York
March 20, 2020
We have served as the Company's auditor since 1984.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-49
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
January 31, | |||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | 2020 | 2019 | |||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | $ | |||||
Short-term investments | |||||||
Accounts receivable, net | |||||||
Inventories, net | |||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | |||||||
Total current assets | |||||||
Operating lease right-of-use assets | — | ||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | |||||||
Deferred income taxes | |||||||
Other assets, net | |||||||
$ | $ | ||||||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Short-term borrowings | $ | $ | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | |||||||
Current portion of operating lease liabilities | — | ||||||
Income taxes payable | |||||||
Merchandise credits and deferred revenue | |||||||
Total current liabilities | |||||||
Long-term debt | |||||||
Pension/postretirement benefit obligations | |||||||
Deferred gains on sale-leasebacks | |||||||
Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | — | ||||||
Other long-term liabilities | |||||||
Commitments and contingencies | |||||||
Stockholders' equity: | |||||||
Preferred Stock, $0.01 par value; authorized 2.0 shares, none issued and outstanding | |||||||
Common Stock, $0.01 par value; authorized 240.0 shares, issued and outstanding 121.2 and 121.5 | |||||||
Additional paid-in capital | |||||||
Retained earnings | |||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||
Total Tiffany & Co. stockholders' equity | |||||||
Non-controlling interests | |||||||
Total stockholders' equity | |||||||
$ | $ | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-50
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Net sales | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Cost of sales | |||||||||
Gross profit | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | |||||||||
Earnings from operations | |||||||||
Interest expense and financing costs | |||||||||
Other expense, net | |||||||||
Earnings from operations before income taxes | |||||||||
Provision for income taxes | |||||||||
Net earnings | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Net earnings per share: | |||||||||
Basic | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Diluted | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Weighted-average number of common shares: | |||||||||
Basic | |||||||||
Diluted | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-51
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE EARNINGS
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Net earnings | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Other comprehensive (loss) earnings, net of tax | |||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities | ( | ) | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on hedging instruments | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Unrealized (loss) gain on benefit plans | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Total other comprehensive (loss) earnings, net of tax | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Comprehensive earnings | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-52
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
Total Stockholders' Equity | Retained Earnings | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Non- Controlling Interests | |||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 31, 2017 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and vesting of restricted stock units ("RSUs") | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares withheld related to net share settlement of share-based compensation | ( | ) | — | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
Cash dividends on Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Accrued dividends on share-based awards | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive earnings, net of tax | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-controlling interests | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 31, 2018 | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and vesting of RSUs | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares withheld related to net share settlement of share-based compensation | ( | ) | — | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
Cash dividends on Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Accrued dividends on share-based awards | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Cumulative effect adjustment from adoption of new accounting standards | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-controlling interests | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 31, 2019 | ( | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and vesting of RSUs | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares withheld related to net share settlement of share-based compensation | ( | ) | — | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase and retirement of Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | |||||||||||||||
Cash dividends on Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Accrued dividends on share-based awards | ( | ) | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Cumulative effect adjustment from adoption of new accounting standards | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | ( | ) | — | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-controlling interests | ( | ) | — | — | — | — | — | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 31, 2020 | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-53
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Net earnings | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | |||||||||||
Amortization of gain on sale-leasebacks | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Provision for inventories | |||||||||||
Deferred income taxes | ( | ) | |||||||||
Provision for pension/postretirement benefits | |||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | |||||||||||
Loan impairment charges | |||||||||||
Asset impairment charges | |||||||||||
(Gains) losses on sales of marketable securities | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Changes in assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | ( | ) | |||||||||
Inventories | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Other assets, net | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | |||||||||||
Income taxes payable | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Merchandise credits and deferred revenue | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Other long-term liabilities | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | |||||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Purchases of marketable securities and short-term investments | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sales of marketable securities and short-term investments | |||||||||||
Capital expenditures | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Other, net | |||||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from (repayment of) credit facility borrowings, net | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Proceeds from other credit facility borrowings | |||||||||||
Repayment of other credit facility borrowings | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Repurchase of Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Proceeds from exercised stock options | |||||||||||
Payments related to tax withholding for share-based payment arrangements | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Cash dividends on Common Stock | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Distribution to non-controlling interest | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Financing fees | ( | ) | |||||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | ( | ) | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements. | |||||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-54
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
A. | NATURE OF BUSINESS |
Tiffany & Co. (the "Registrant") is a holding company that operates through Tiffany and Company ("Tiffany") and the Registrant's other subsidiary companies (collectively, the "Company"). The Registrant, through its subsidiaries, designs and manufactures products and operates TIFFANY & CO. retail stores worldwide, and also sells its products through Internet, catalog, business-to-business and wholesale distribution. The Company's principal merchandise offering is jewelry (representing 92 % of worldwide net sales in 2019); it also sells watches, home and accessories products and fragrances.
The Company's reportable segments are as follows:
• | Americas includes sales in Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores in the United States, Canada and Latin America, as well as sales of TIFFANY & CO. products in certain markets through Internet, catalog, business-to-business and wholesale operations; |
• | Asia-Pacific includes sales in Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as sales of TIFFANY & CO. products in certain markets through Internet, business-to-business and wholesale operations; |
• | Japan includes sales in Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as sales of TIFFANY & CO. products through Internet, business-to-business and wholesale operations; |
• | Europe includes sales in Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores, as well as sales of TIFFANY & CO. products in certain markets through Internet and wholesale operations; and |
• | Other consists of all non-reportable segments. Other includes the Emerging Markets region, which includes sales in Company-operated TIFFANY & CO. stores and wholesale operations in the Middle East. In addition, Other includes wholesale sales of diamonds as well as earnings from third-party licensing agreements. |
B. | ENTRY INTO MERGER AGREEMENT |
On November 24, 2019, the Registrant entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the "Merger Agreement") by and among the Registrant, LVMH Moët Hennessy - Louis Vuitton SE, a societas Europaea (European company) organized under the laws of France ("Parent"), Breakfast Holdings Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of Parent ("Holding"), and Breakfast Acquisition Corp., a Delaware corporation and a direct wholly owned subsidiary of Holding ("Merger Sub"). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub will be merged with and into the Registrant (the "Merger"), with the Registrant continuing as the surviving company in the Merger and a wholly owned indirect subsidiary of Parent.
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the Merger Agreement, at the effective time of the Merger (the "Effective Time"), each share of Common Stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time (other than shares of Common Stock owned by the Registrant, Parent or any of their respective wholly owned subsidiaries, and shares of Common Stock owned by stockholders of the Registrant who have properly demanded and not withdrawn a demand for appraisal rights under Delaware law) will be converted into the right to receive $135.00 in cash, without interest and less any required tax withholding.
The consummation of the proposed Merger is subject to various conditions, including, among others, customary conditions relating to (a) the adoption of the Merger Agreement by holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of the Registrant's Common Stock entitled to vote on such matter at the meeting of stockholders of the Registrant (the "Special Meeting") held to vote on the adoption of the Merger Agreement and (b) the expiration or earlier termination of the applicable waiting period under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976 (as amended, and all rules and regulations promulgated thereunder, collectively, the "HSR Act"). As previously announced, on February 3, 2020, the waiting period under the HSR Act in connection with the proposed Merger expired, and on February 4, 2020, the Company held the Special Meeting, at which the holders of shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of the close of business on the record date for the Special Meeting considered and voted to approve
TIFFANY & CO.
K-55
(i) the adoption of the Merger Agreement and (ii) by non-binding, advisory vote, certain compensation arrangements for the Company's named executive officers in connection with the proposed Merger. The proposed Merger remains subject to satisfaction or waiver of the remaining customary closing conditions, including, among others, (A) certain non-U.S. regulatory approvals, (B) clearance by the Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States ("CFIUS"), (C) the absence of a law or order in effect that enjoins, prevents or otherwise prohibits the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement issued by a governmental entity; (D) the absence of any legal proceeding seeking to enjoin, prevent or otherwise prohibit the consummation of the proposed Merger or any other transactions contemplated under the Merger Agreement instituted by a governmental entity of competent jurisdiction; and (E) the absence of a Material Adverse Effect (as defined in the Merger Agreement). The obligation of each party to consummate the proposed Merger is also conditioned on the accuracy of the other party's representations and warranties (subject to certain materiality exceptions) and the other party's compliance, in all material respects, with its covenants and agreements under the Merger Agreement.
The Merger Agreement provides for certain customary termination rights of the Registrant and Parent, including the right of either party to terminate the Merger Agreement if the Merger is not completed on or before August 24, 2020 (the "Outside Date"), provided that the Outside Date may be extended up to an additional 90 days by either party if all conditions are satisfied other than the receipt of regulatory approvals and CFIUS clearance or absence of legal restraints. The Merger Agreement also provides that the Registrant will be required to pay Parent a termination fee of $575.0 million in certain circumstances.
During the three months ended January 31, 2020, the Company incurred expenses of $21.2 million related to the proposed Merger for professional fees and incentive compensation costs.
C. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Fiscal Year
The Company's fiscal year ends on January 31 of the following calendar year. All references to years relate to fiscal years rather than calendar years.
Basis of Reporting
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Tiffany & Co. and its subsidiaries in which a controlling interest is maintained. Controlling interest is determined by majority ownership interest and the absence of substantive third-party participating rights or, in the case of variable interest entities (VIEs), if the Company has the power to significantly direct the activities of a VIE, as well as the obligation to absorb significant losses of or the right to receive significant benefits from the VIE. Intercompany accounts, transactions and profits have been eliminated in consolidation. The equity method of accounting is used for investments in which the Company has significant influence, but not a controlling interest.
Use of Estimates
These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP"); these principles require management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect amounts reported and disclosed in the consolidated financial statements and related notes to the consolidated financial statements. Actual results could differ from these estimates and the differences could be material. Periodically, the Company reviews all significant estimates and assumptions affecting the consolidated financial statements relative to current conditions and records the effect of any necessary adjustments.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are stated at cost plus accrued interest, which approximates fair value. Cash equivalents include highly liquid investments with an original maturity of three months or less and consist of time deposits and/or money market fund investments with a number of U.S. and non-U.S. financial institutions with high credit ratings. The Company's policy restricts the amount invested with any one financial institution.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-56
Short-Term Investments
The Company's short-term investments consist of time deposits and are carried at fair value. At the time of purchase, management determines the appropriate classification of these investments and reevaluates such designation as of each balance sheet date.
Receivables and Financing Arrangements
Receivables. The Company's Accounts receivable, net primarily consists of amounts due from Credit Receivables (defined below), department store operators that host TIFFANY & CO. boutiques in their stores, third-party credit card issuers and wholesale customers. The Company maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses associated with outstanding accounts receivable. The allowance is determined based on a combination of factors including, but not limited to, the length of time that the receivables are past due, management's knowledge of the customer, economic and market conditions and historical write-off experiences.
At January 31, 2020, accounts receivable allowances totaled $33.0 million compared to $31.5 million at January 31, 2019.
Inventories
Inventories are valued at the lower of cost or net realizable value using the average cost method, except for certain diamond and gemstone jewelry, which uses the specific identification method.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the following estimated useful lives:
Buildings | 39 years |
Machinery and equipment | 5-15 years |
Office equipment | 3-8 years |
Software | 5-10 years |
Furniture and fixtures | 3-10 years |
Leasehold improvements and building improvements are amortized over the shorter of their estimated useful lives (primarily ranging from 8-10 years) or the related lease terms or building life, respectively. Maintenance and repair costs are charged to earnings while expenditures for major renewals and improvements are capitalized. Upon the disposition of property, plant and equipment, the accumulated depreciation is deducted from the original cost and any gain or loss is reflected in current earnings.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-57
Information Systems Development Costs
Eligible costs incurred during the development stage of information systems projects are capitalized and amortized over the estimated useful life of the related project. Eligible costs include those related to the purchase, development, and installation of the related software. Costs incurred prior to the development stage, as well as costs for maintenance, data conversion, training, and other general and administrative costs, are expensed as incurred. Costs that are capitalized are included in Property, plant and equipment, net in Construction-in-progress while in the development stage and in Software once placed into service.
Intangible Assets and Key Money
Intangible assets, consisting of product rights and trademarks, are recorded at cost and are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives, which range from 15 to 20 years. Intangible assets are reviewed for impairment in accordance with the Company's policy for impairment of long-lived assets (see "Impairment of Long-Lived Assets" below).
Key money is the amount of funds paid to a landlord or tenant to acquire the rights of tenancy under a commercial property lease for a certain property. Key money represents the "right to lease" with an automatic right of renewal. This right can be subsequently sold by the Company or can be recovered should the landlord refuse to allow the automatic right of renewal to be exercised. Key money is amortized over the estimated useful life, 39 years.
The following table summarizes intangible assets and key money, included in Other assets, net:
January 31, 2020 | January 31, 2019 | |||||||||||
(in millions) | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | ||||||||
Product rights | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | ( | ) | ||||
Key money | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||
Trademarks | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||
$ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | ( | ) | |||||
Amortization of intangible assets and key money was $3.3 million for year ended January 31, 2020 and $3.4 million for the years ended January 31, 2019 and 2018. Amortization expense is estimated to be $3.2 million in each of the next five years.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-58
Goodwill
(in millions) | Americas | Asia-Pacific | Japan | Europe | Other | Total | ||||||||||||
January 31, 2018 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
Translation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||||
January 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
Translation | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||||
January 31, 2020 | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||
The Company recorded no impairment charges related to goodwill in 2019, 2018 or 2017.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Leases
The Company leases certain office, distribution, retail and manufacturing facilities, land and equipment. Retail store leases may require the payment of minimum rentals and contingent rent based on a percentage of sales exceeding a stipulated amount. The lease agreements, which expire at various dates through 2062, are subject, in many cases, to renewal options and provide for the payment of taxes, insurance and maintenance. Certain leases contain escalation clauses resulting from the pass through of increases in operating costs, property taxes and the effect on costs from changes in consumer price indices.
The Company determines its lease payments based on predetermined rent escalations (including escalations based on consumer price indices), rent-free periods and other incentives. The Company recognizes rent expense on a straight-line basis over the related terms of such leases, beginning from when the Company takes possession of the leased facility. Variable rents, including contingent rent based on a percentage of sales and adjustments to consumer price indices, are recorded in the period such amounts and adjustments are determined. Lease terms include renewal options when exercise of such options is reasonably certain and within the control of the Company. There is generally no readily determinable discount rate implicit in the Company's leases. Accordingly, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate for a term that corresponds to the applicable lease term in order to measure its lease liabilities.
The amounts of the Company's right-of-use asset and current and non-current lease liabilities are presented separately on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as of January 31, 2020. Substantially all of the Company's leases are operating leases as of January 31, 2020. The Company records lease expense within Cost of sales for leases of manufacturing facilities and within Selling, general and administrative expenses for all other leases.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-59
Hedging Instruments
The Company uses derivative financial instruments to mitigate a portion of its foreign currency, precious metal price and interest rate exposures. Derivative instruments are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at their fair values, as either assets or liabilities, with an offset to current or other comprehensive earnings, depending on whether a derivative is designated as part of an effective hedge transaction and, if it is, the type of hedge transaction.
Marketable Securities
The Company's marketable securities primarily consist of investments in mutual funds and are recorded within Other assets, net, at fair value with realized and unrealized gains and losses recorded in earnings. Marketable securities are held for an indefinite period of time, but may be sold in the future as changes in market conditions or economic factors occur. The fair value of marketable securities is determined based on prevailing market prices.
Merchandise Credits and Deferred Revenue
Merchandise credits and deferred revenue primarily represent outstanding gift cards sold to customers and outstanding credits issued to customers for returned merchandise. All such outstanding items may be tendered for future merchandise purchases. A gift card liability is established when the gift card is sold. A merchandise credit liability is established when a merchandise credit is issued to a customer for a returned item and the original sale is reversed. These liabilities are relieved when revenue is recognized for transactions in which a merchandise credit or gift card is used as a form of payment.
If merchandise credits or gift cards are not redeemed over an extended period of time (for example, approximately three to five years in the U.S.), the value associated with the merchandise credits or gift cards may be subject to remittance to the applicable jurisdiction in accordance with unclaimed property laws. The Company determines the amount of breakage income to be recognized on gift cards and merchandise credits using historical experience to estimate amounts that will ultimately not be redeemed. The Company recognizes such breakage income in proportion to redemption rates of the overall population of gift cards and merchandise credits.
In 2019, the Company recognized net sales of approximately $33.0 million related to the Merchandise credits and deferred revenue balance that existed at January 31, 2019.
Revenue Recognition
The following table disaggregates the Company's net sales by major source:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
Net sales*: | |||||||||||
Jewelry collections | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Engagement jewelry | |||||||||||
Designer jewelry | |||||||||||
All other | |||||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
*Certain reclassifications within the jewelry categories have been made to the prior year amounts to conform to the current year category presentation.
The Company's performance obligations consist primarily of transferring control of merchandise to customers. Sales are recognized upon transfer of control, which occurs when merchandise is taken in an "over-the-counter" transaction or upon receipt by a customer in a shipped transaction, such as through the Internet and catalog channels. Sales are reported net of returns, sales tax and other similar taxes. The Company excludes from the measurement of the transaction price all taxes assessed by a governmental authority and collected by the entity from a customer.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-60
Shipping and handling fees billed to customers are recognized in net sales when control of the underlying merchandise is transferred to the customer. The related shipping and handling charges incurred by the Company represent fulfillment activities and are included in Cost of sales.
The Company maintains a reserve for potential product returns and records (as a reduction to sales and cost of sales) its provision for estimated product returns, which is determined based on historical experience.
As a practical expedient, the Company does not adjust the promised amount of consideration for the effects of a significant financing component when management expects, at contract inception, that the period between the transfer of a product to a customer and when the customer pays for that product is one year or less.
Additionally, outside of the U.S., the Company operates certain TIFFANY & CO. stores within various department stores. Sales transacted at these store locations are recognized upon transfer of control, which occurs when merchandise is taken in an "over-the-counter" transaction. The Company and these department store operators have distinct responsibilities and risks in the operation of such TIFFANY & CO. stores. The Company (i) owns and manages the merchandise; (ii) establishes retail prices; (iii) has merchandising, marketing and display responsibilities; and (iv) in almost all locations provides retail staff and bears the risk of inventory loss. The department store operators (i) provide and maintain store facilities; (ii) in almost all locations assume retail credit and certain other risks; and (iii) act for the Company in the sale of merchandise. In return for their services and use of their facilities, the department store operators retain a portion of net retail sales made in TIFFANY & CO. stores which is recorded as rent expense within Selling, general and administrative expenses.
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales includes costs to internally manufacture merchandise (primarily metals, gemstones, labor and overhead), costs related to the purchase of merchandise from third-parties, inbound freight, purchasing and receiving, inspection, warehousing, internal transfers and other costs associated with distribution and merchandising. Cost of sales also includes royalty fees paid to outside designers and customer shipping and handling charges.
Selling, General and Administrative ("SG&A") Expenses
Advertising, Marketing, Public and Media Relations Costs
Pre-Opening Costs
Costs associated with the opening of new retail stores are expensed in the period incurred.
Stock-Based Compensation
New, modified and unvested share-based payment transactions with employees, such as stock options and restricted stock units, are measured at fair value and recognized as compensation expense over the requisite service period. Compensation expense recognized reflects an estimate of the number of awards expected to vest and incorporates an estimate of award forfeitures based on actual experience. Compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period required to obtain full vesting.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-61
Merchandise Design Activities
Merchandise design activities consist of conceptual formulation and design of possible products and creation of pre-production prototypes and molds. Costs associated with these activities are expensed as incurred.
Foreign Currency
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized by applying statutory tax rates in effect in the years in which the differences between the financial reporting and tax filing bases of existing assets and liabilities are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company records net deferred tax assets to the extent management believes these assets will more likely than not be realized. In making such determination, the Company considers all available evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial results. In the event management were to determine that the Company would be able to realize its deferred income tax assets in the future in excess of their net recorded amounts, the Company would make an adjustment to the valuation allowance, which would reduce the provision for income taxes.
In evaluating the exposures associated with the Company's various tax filing positions, management records reserves using a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold for income tax positions taken or expected to be taken.
The Registrant, its U.S. subsidiaries and the foreign branches of its U.S. subsidiaries file a consolidated Federal income tax return.
Earnings Per Share ("EPS")
Basic EPS is computed as net earnings divided by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted EPS includes the dilutive effect of the assumed exercise of stock options and unvested restricted stock units.
The following table summarizes the reconciliation of the numerators and denominators for the basic and diluted EPS computations:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Net earnings for basic and diluted EPS | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Weighted-average shares for basic EPS | |||||||||
Incremental shares based upon the assumed exercise of stock options and unvested restricted stock units | |||||||||
Weighted-average shares for diluted EPS | |||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-62
For the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, there were 1.3 million, 0.7 million and 0.6 million stock options and restricted stock units excluded from the computations of earnings per diluted share due to their antidilutive effect, respectively.
New Accounting Standards
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13 – Financial Instruments – Credit Losses: Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. ASU 2016-13 amends the impairment model to utilize an expected loss methodology in place of the currently used incurred loss methodology, which will result in more timely recognition of losses. The new standard applies to financial assets measured at amortized cost basis, including receivables that result from revenue transactions and held-to-maturity debt securities. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019, and early adoption was permitted for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company's allowances for doubtful accounts have historically not been significant and management does not expect the adoption of this ASU will have a significant impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-15 – Intangibles – Goodwill and Other – Internal-Use Software: Customer's Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That Is a Service Contract. ASU 2018-15 aligns the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs in such cloud computing arrangements with the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019 and early adoption was permitted. Entities can choose to adopt the new guidance prospectively or retrospectively. The Company does not expect that the adoption of ASU 2018-15 will have a significant impact on its consolidated financial statements. However, the impact of adopting this ASU will ultimately depend on the composition of the Company's cloud computing software arrangements under development at that time.
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-12 – Income Taxes (ASC 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes. This guidance simplifies the approach for intraperiod tax allocations, the methodology for calculating income taxes in an interim period, and the recognition of deferred tax liabilities for outside basis differences. This guidance also clarifies and simplifies other areas of ASC 740. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2020. Early adoption is permitted. Management is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU on the consolidated financial statements.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02 – Leases (ASC 842), which was amended in January 2018 and requires an entity that leases assets to recognize on the balance sheet the assets and liabilities for the rights and obligations created by those leases. Leases are classified as either financing or operating with the applicable classification determining the pattern of expense recognition in the statement of earnings.
The Company adopted this ASU on February 1, 2019 by applying its provisions prospectively and recognizing a cumulative-effect adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings as of February 1, 2019. The Company also elected the package of practical expedients permitted under the transition guidance, which provided that an entity need not reassess: (i) whether any expired or existing contracts are or contain leases, (ii) the lease classification for any expired or existing leases, and (iii) initial direct costs for any existing leases. The Company also elected to not reassess lease terms using hindsight and to combine lease and non-lease components for new leases subsequent to February 1, 2019. Additionally, the Company used its incremental borrowing rate for a term that corresponded to lease terms remaining as of February 1, 2019 to measure its lease liabilities as of that date.
The adoption of ASU 2016-02 resulted in the following impacts to the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet as of February 1, 2019:
• | The establishment of a lease liability of approximately $ |
• | The reclassification of existing balances in respect of unamortized lease incentives and lease straight-line liabilities from Other long-term liabilities to Operating lease right-of-use assets; and |
• | The reclassification of $ |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-63
In August 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-12 – Derivatives and Hedging: Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities, which expanded and refined hedge accounting for both financial and non-financial risk components, aligned the recognition and presentation of the effects of hedging instruments and hedged items in the financial statements, and included certain targeted improvements to ease the application of previous guidance related to the assessment of hedge effectiveness. This ASU was effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The amendments in this ASU were required to be applied on a modified retrospective basis, while presentation and disclosure requirements set forth under this ASU are required prospectively after the date of adoption. Management adopted this ASU on February 1, 2019. The adoption of this ASU did not have any impact on the consolidated financial statements. The disclosures required by this ASU are included in "Note I. Hedging Instruments."
In February 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-02 – Income Statement – Reporting Comprehensive Income: Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, which allowed for the reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income ("AOCI") to retained earnings for the tax effects on deferred tax items included within AOCI (referred to in the ASU as "stranded tax effects") resulting from the reduction of the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate to 21% from 35% that was effected by the 2017 U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. ASU 2018-02 was effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. Management adopted this ASU on February 1, 2019. The adoption of ASU 2018-02 resulted in a reclassification of $26.2 million from AOCI to retained earnings, and had no impact on the Company's results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
D. SUPPLEMENTAL CASH FLOW INFORMATION
Cash paid during the year for:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Interest, net of interest capitalization | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Income taxes | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Supplemental noncash investing and financing activities:
January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Accrued capital expenditures | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
E. | INVENTORIES |
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Finished goods | $ | $ | ||||
Raw materials | ||||||
Work-in-process | ||||||
Inventories, net | $ | $ | ||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-64
F. | PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT |
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Land | $ | $ | ||||
Buildings | ||||||
Leasehold and building improvements | ||||||
Office equipment | ||||||
Software | ||||||
Furniture and fixtures | ||||||
Machinery and equipment | ||||||
Construction-in-progress | ||||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
$ | $ | |||||
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $253.8 million, $223.6 million and $200.8 million, respectively.
G. | ACCOUNTS PAYABLE AND ACCRUED LIABILITIES |
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Accounts payable - trade | $ | $ | ||||
Accrued compensation and commissions | ||||||
Other | ||||||
$ | $ | |||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-65
H. | DEBT |
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Short-term borrowings: | ||||||
Credit Facilities | $ | $ | ||||
Other credit facilities | ||||||
$ | $ | |||||
Long-term debt: | ||||||
Unsecured Senior Notes: | ||||||
2012 4.40% Series B Notes, due July 2042 a | $ | $ | ||||
2014 3.80% Senior Notes, due October 2024 b, c | ||||||
2014 4.90% Senior Notes, due October 2044 b, c | ||||||
2016 0.78% Senior Notes, due August 2026 b, d | ||||||
Less: unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
$ | $ | |||||
a | The agreements governing these Senior Notes require repayments of $ |
b | These agreements require lump sum repayments upon maturity. |
c | These Senior Notes were issued at a discount, which will be amortized until the debt maturity. |
d | These Senior Notes were issued at par, ¥ |
Credit Facilities
On October 25, 2018, the Registrant, along with certain of its subsidiaries designated as borrowers thereunder, entered into a five-year multi-bank, multi-currency committed unsecured revolving credit facility, including a letter of credit subfacility, consisting of basic commitments in an amount up to $750.0 million (which commitments may be increased, subject to certain conditions and limitations, at the request of the Registrant) ("Credit Facility"). The Credit Facility replaced the Registrant's previously existing $375.0 million four-year unsecured revolving credit facility and $375.0 million five-year unsecured revolving credit facility, which were each terminated and repaid in connection with the Registrant's entry into the Credit Facility.
Borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest at a rate per annum equal to, at the option of the Registrant, (1) LIBOR (or other applicable or successor reference rate) for the relevant currency plus an applicable margin based upon the more favorable to the Registrant of (i) a leverage financial metric of the Registrant and (ii) the Registrant's debt rating for long-term unsecured senior, non-credit enhanced debt, or (2) an alternate base rate equal to the highest of (i) the federal funds effective rate plus 0.50 %, (ii) MUFG Bank, Ltd.'s prime rate and (iii) one-month LIBOR plus 1.00 %, plus an applicable margin based upon the more favorable to the Registrant of (x) a leverage financial metric of the Registrant and (y) the Registrant's debt rating for long-term unsecured senior, non-credit enhanced debt.
The Credit Facility also requires payment to the lenders of a facility fee on the amount of the lenders' commitments under the credit facility from time to time at rates based upon the more favorable to the Registrant of (1) a leverage financial metric of the Registrant and (2) the Registrant's debt rating for long-term unsecured senior, non-credit enhanced debt. Voluntary prepayments of the loans and voluntary reductions of the unutilized portion of the commitments under the Credit Facility are permissible without penalty, subject to certain conditions pertaining to minimum notice and minimum reduction amounts.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-66
The Credit Facility is available for working capital and other corporate purposes.
The Credit Facility matures in 2023, provided that such maturity may be extended for one or two additional one-year periods at any time with the consent of the applicable lenders, as further described in the agreement governing such facility.
At January 31, 2020, there were $13.8 million of borrowings outstanding, $3.6 million of letters of credit issued and $732.6 million available for borrowing under the Credit Facility. At January 31, 2019, there were $13.5 million of borrowings outstanding, $6.1 million of letters of credit issued and $730.4 million available for borrowing under the previously existing revolving credit facilities. The weighted-average interest rate for borrowings outstanding was 0.90 % at January 31, 2020 and 1.05 % at January 31, 2019.
Commercial Paper
In August 2017, the Registrant and one of its wholly owned subsidiaries established a commercial paper program (the "Commercial Paper Program") for the issuance of commercial paper in the form of short-term promissory notes in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $750.0 million. Borrowings under the Commercial Paper Program may be used for general corporate purposes. The aggregate amount of borrowings that the Company is currently authorized to have outstanding under the Commercial Paper Program and the Registrant's Credit Facility is $750.0 million. The Registrant guarantees the obligations of its wholly owned subsidiary under the Commercial Paper Program. Maturities of commercial paper notes may vary, but cannot exceed 397 days from the date of issuance. Notes issued under the Commercial Paper Program rank equally with the Registrant's present and future unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness. As of January 31, 2020 and 2019, there were no borrowings outstanding under the Commercial Paper Program.
Other Credit Facilities
Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement. In June 2019, the Registrant's indirect, wholly owned subsidiary, Tiffany & Co. (Shanghai) Commercial Company Limited ("Tiffany-Shanghai"), entered into a three-year multi-bank revolving credit agreement (the "Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement"). The Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement has an aggregate borrowing limit of RMB 408.0 million ($59.0 million at January 31, 2020), which may be increased to the RMB equivalent of $100.0 million, subject to certain conditions and limitations, at the request of Tiffany-Shanghai. The Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement, which matures in July 2022, was made available to refinance amounts outstanding under Tiffany-Shanghai's previously existing RMB 990.0 million three-year multi-bank revolving credit agreement (the "2016 Agreement"), which expired pursuant to its terms on July 11, 2019, as well as for Tiffany-Shanghai's ongoing general working capital requirements. The participating lenders will make loans, upon Tiffany-Shanghai's request, for periods of up to 12 months at the applicable interest rates equal to 95 % of the applicable rate as announced by the People's Bank of China (provided, that if such announced rate is below zero, the applicable interest rate shall be deemed to be zero). In connection with the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement, in June 2019, the Registrant entered into a Guaranty Agreement by and between the Registrant and the facility agent under the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement (the "Guaranty"). At January 31, 2020, there was $33.0 million available to be borrowed under the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement and $26.1 million was outstanding at a weighted-average interest rate of 4.13 %.
Other. The Company has various other revolving credit facilities, primarily in Japan and China. At January 31, 2020, the facilities totaled $188.8 million and $108.0 million was outstanding at a weighted-average interest rate of 5.36 %. At January 31, 2019, the facilities totaled $135.6 million and $73.1 million was outstanding at a weighted-average interest rate of 3.93 %.
Debt Covenants
The agreement governing the Credit Facility includes a specific financial covenant, as well as other covenants that limit the ability of the Company to incur certain subsidiary indebtedness, incur liens and engage in mergers, consolidations and sales of all or substantially all of its and its subsidiaries' assets, in addition to other requirements. The agreement governing the Credit Facility also includes certain "Events of Default" (as defined in the agreement governing the Credit Facility) customary to such borrowings, including a "Change of Control" (as defined in the agreement governing the Credit Facility) of the Registrant, such as the proposed Merger.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-67
The Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement includes certain covenants that limit Tiffany-Shanghai's ability to incur liens and incur certain indebtedness, and the Guaranty requires maintenance by the Registrant of a specific leverage ratio. The Tiffany Shanghai Credit Agreement also includes certain other requirements and "Events of Default" (as defined in the Tiffany-Shanghai Credit Agreement) customary to such borrowings, including the Registrant's shares ceasing to be listed on New York Stock Exchange for 14 consecutive trading days, such as following the proposed Merger.
The indenture governing the 2014 3.80 % Senior Notes and 2014 4.90 % Senior Notes, as amended and supplemented in respect of each such series of Notes (the "Indenture"), contains covenants that, among other things, limit the ability of the Registrant and its subsidiaries under certain circumstances to create liens and impose conditions on the Registrant's ability to engage in mergers, consolidations and sales of all or substantially all of its or its subsidiaries' assets. The Indenture also contains certain "Events of Default" (as defined in the Indenture) customary for indentures of this type. The Indenture does not contain any specific financial covenants.
The agreements governing the 2012 4.40 % Series B Senior Notes and the Yen Notes require maintenance of a specific financial covenant and limit certain changes to indebtedness of the Registrant and its subsidiaries and the general nature of the business, in addition to other requirements customary to such borrowings.
Once consummated, the proposed Merger may result in certain of the Company's outstanding indebtedness becoming due, and the Company will need to comply with certain covenants of the agreements governing its outstanding indebtedness relating to the proposed Merger. Under the terms of the Merger Agreement, if reasonably requested by Parent, the Company must use its commercially reasonable efforts to, among other things, take actions required to facilitate repayment of the Company's outstanding indebtedness.
Long-Term Debt Maturities
Aggregate maturities of long-term debt as of January 31, 2020 are as follows:
Years Ending January 31, | Amount a (in millions) | ||
2021 | $ | ||
2022 | |||
2023 | |||
2024 | |||
2025 | |||
Thereafter | |||
$ | |||
a | Amounts exclude any unamortized discount or premium. |
Letters of Credit
TIFFANY & CO.
K-68
I. HEDGING INSTRUMENTS
Background Information
The Company uses derivative financial instruments, including interest rate swaps, cross-currency swaps, forward contracts and net-zero-cost collar arrangements (combination of call and put option contracts) to mitigate a portion of its exposures to changes in interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates and precious metal prices.
Derivative Instruments Designated as Hedging Instruments. If a derivative instrument meets certain hedge accounting criteria, it is recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at its fair value, as either an asset or a liability, with an offset to current or other comprehensive earnings, depending on whether the hedge is designated as one of the following on the date it is entered into:
• | Fair Value Hedge – A hedge of the exposure to changes in the fair value of a recognized asset or liability or an unrecognized firm commitment. For fair value hedge transactions, the changes in the fair value of the derivative and changes in the fair value of the item being hedged are recorded in current earnings. |
• | Cash Flow Hedge – A hedge of the exposure to variability in the cash flows of a recognized asset, liability or a forecasted transaction. For cash flow hedge transactions, the changes in fair value of derivatives is reported as other comprehensive income ("OCI") and is recognized in current earnings in the period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects current earnings. |
The Company formally documents the nature of and relationships between the hedging instruments and hedged items for a derivative to qualify as a hedge at inception and throughout the hedged period. The Company also documents its risk management objectives, strategies for undertaking the various hedge transactions and method of assessing hedge effectiveness. Additionally, for hedges of forecasted transactions, the significant characteristics and expected terms of a forecasted transaction must be identified, and it must be probable that each forecasted transaction will occur. If it were deemed probable that the forecasted transaction would not occur, the gain or loss on the derivative financial instrument would be recognized in current earnings. Derivative financial instruments qualifying for hedge accounting must maintain a specified level of effectiveness between the hedge instrument and the item being hedged, both at inception and throughout the hedged period.
Derivative Instruments Not Designated as Hedging Instruments. Derivative instruments which do not meet the criteria to be designated as a hedge are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at their fair values, as either assets or liabilities, with an offset to current earnings. The gains or losses on undesignated foreign exchange forward contracts substantially offset foreign exchange losses or gains on the underlying liabilities or transactions being hedged.
The Company does not use derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes.
Types of Derivative Instruments
Interest Rate Swaps – In 2012, the Company entered into forward-starting interest rate swaps to hedge the impact of interest rate volatility on future interest payments associated with the anticipated incurrence of $250.0 million of debt which was incurred in July 2012. The Company accounted for the forward-starting interest rate swaps as cash flow hedges. The Company settled the interest rate swaps in 2012 and recorded a loss within accumulated other comprehensive loss. As of January 31, 2020, $16.1 million remains recorded as a loss in accumulated other comprehensive loss, which is being amortized over the term of the 2042 Notes to which the interest rate swaps related.
In 2014, the Company entered into forward-starting interest rate swaps to hedge the impact of interest rate volatility on future interest payments associated with the anticipated incurrence of long-term debt which was incurred in September 2014. The Company accounted for the forward-starting interest rate swaps as cash flow hedges. The Company settled the interest rate swaps in 2014 and recorded a loss within accumulated other comprehensive loss. As of January 31, 2020, $3.3 million remains recorded as a loss in accumulated other comprehensive loss, which is being amortized over the terms of the respective 2024 Notes or 2044 Notes to which the interest rate swaps related.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-69
Cross-currency Swaps – In 2016, 2017 and 2019, the Company entered into cross-currency swaps to hedge the foreign currency exchange risk associated with Japanese yen-denominated and Euro-denominated intercompany loans. These cross-currency swaps are designated and accounted for as cash flow hedges. As of January 31, 2020, the notional amounts of cross-currency swaps accounted for as cash flow hedges and the respective maturity dates were as follows:
Cross-Currency Swap | Notional Amount | ||||||
Effective Date | Maturity Date | (in millions) | (in millions) | ||||
July 2016 | October 2024 | ¥ | $ | ||||
March 2017 | April 2027 | ¥ | $ | ||||
May 2017 | April 2027 | ¥ | $ | ||||
August 2019 | August 2026 | € | $ | ||||
Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts – The Company uses foreign exchange forward contracts to offset a portion of the foreign currency exchange risks associated with foreign currency-denominated liabilities, intercompany transactions and forecasted purchases of merchandise between entities with differing functional currencies. The Company assesses hedge effectiveness based on the total changes in the foreign exchange forward contracts' cash flows. These foreign exchange forward contracts are designated and accounted for as either cash flow hedges or economic hedges that are not designated as hedging instruments.
As of January 31, 2020, the notional amounts of foreign exchange forward contracts were as follows:
(in millions) | Notional Amount | USD Equivalent | ||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | ||||||
Japanese yen | ¥ | $ | ||||
British pound | £ | |||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | ||||||
U.S. dollar | $ | $ | ||||
Euro | € | |||||
Australian dollar | AU$ | |||||
Czech koruna | CZK | |||||
Japanese yen | ¥ | |||||
New Zealand dollar | NZ$ | |||||
Singapore dollar | S$ | |||||
Chinese renminbi | CNY | |||||
Canadian dollar | CAD | |||||
Danish kroner | DKK | |||||
Korean won | KRW | |||||
The maximum term of the Company's outstanding foreign exchange forward contracts as of January 31, 2020 is 12 months.
Precious Metal Collars and Forward Contracts – The Company periodically hedges a portion of its forecasted purchases of precious metals for use in its internal manufacturing operations in order to manage the effect of volatility in precious metal prices. The Company may use either a combination of call and put option contracts in net-zero-cost collar arrangements ("precious metal collars") or forward contracts. For precious metal collars, if the price of the precious metal at the time of the expiration of the precious metal collar is within the call and put price, the precious metal collar expires at no cost to the Company. The Company accounts for its precious metal collars and forward contracts as cash flow hedges. The Company assesses hedge effectiveness based on the total changes in the precious metal collars and forward contracts' cash flows. As of January 31, 2020, the maximum term over which
TIFFANY & CO.
K-70
the Company is hedging its exposure to the variability of future cash flows for all forecasted precious metals transactions is 18 months. As of January 31, 2020, there were precious metal derivative instruments outstanding for approximately 29,000 ounces of platinum, 557,000 ounces of silver and 84,000 ounces of gold.
Information on the location and amounts of derivative gains and losses in the consolidated financial statements is as follows:
Year Ended January 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Cost of sales | Interest expense and financing costs | Other expense, net | Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | ||||||||
Reported amounts of financial statement line items in which effects of cash flow hedges are recorded | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | ||||||
Derivatives in Cash Flow Hedging Relationships: | ||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain recognized in OCI | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Precious metal collars | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain recognized in OCI | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Cross-currency swaps | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain recognized in OCI | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||||||||
Forward-starting interest rate swaps | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-71
Year Ended January 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Cost of sales | Interest expense and financing costs | Other expense, net | Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | ||||||||
Reported amounts of financial statement line items in which effects of cash flow hedges are recorded | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | ||||||
Derivatives in Cash Flow Hedging Relationships: | ||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain recognized in OCI | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Precious metal collars | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax loss recognized in OCI | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Pre-tax loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Cross-currency swaps | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain recognized in OCI | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax gain reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
Forward-starting interest rate swaps | ||||||||||||
Pre-tax loss reclassified from accumulated OCI into earnings | ( | ) | ||||||||||
The pre-tax gains or losses on derivatives not designated as hedging instruments were not significant for the years ended January 31, 2020 and 2019 and were included in Other expense, net. The Company expects approximately $6.7 million of net pre-tax derivative gains included in accumulated other comprehensive loss at January 31, 2020 will be reclassified into earnings within the next 12 months. The actual amount reclassified will vary due to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates and precious metal prices.
For information regarding the location and amount of the derivative instruments in the Consolidated Balance Sheet, see "Note J. Fair Value of Financial Instruments."
Concentration of Credit Risk
A number of major international financial institutions are counterparties to the Company's derivative financial instruments. The Company enters into derivative financial instrument agreements only with counterparties meeting certain credit standards (an investment grade credit rating at the time of the agreement) and limits the amount of agreements or contracts it enters into with any one party. The Company may be exposed to credit losses in the event of nonperformance by individual counterparties or the entire group of counterparties.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-72
J. | FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. U.S. GAAP establishes a fair value hierarchy which requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. U.S. GAAP prescribes three levels of inputs that may be used to measure fair value:
Level 1 – Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities, which are considered to be most reliable.
Level 2 – Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data.
Level 3 – Unobservable inputs reflecting the reporting entity's own assumptions, which require the most judgment.
The Company's derivative instruments are considered Level 2 instruments for the purpose of determining fair value. The Company's foreign exchange forward contracts, as well as its put option contracts and cross-currency swaps, are primarily valued using the appropriate foreign exchange spot rates. The Company's precious metal forward contracts and collars are primarily valued using the relevant precious metal spot rate. For further information on the Company's hedging instruments and program, see "Note I. Hedging Instruments."
Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value at January 31, 2020 are classified in the table below in one of the three categories described above:
Estimated Fair Value | Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
Financial assets | |||||||||||||||
Time deposits a | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Marketable securities b | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Cross-currency swaps c | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Total financial assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Estimated Fair Value | Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
Financial liabilities | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts d | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts d | |||||||||||||||
Cross-currency swaps d | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts d | |||||||||||||||
Total financial liabilities | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-73
Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value at January 31, 2019 are classified in the table below in one of the three categories described above:
Estimated Fair Value | Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
Financial assets | |||||||||||||||
Time deposits a | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Marketable securities b | $ | ||||||||||||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts c | |||||||||||||||
Total financial assets | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Estimated Fair Value | Total Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
Financial liabilities | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Precious metal forward contracts d | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts d | |||||||||||||||
Cross-currency swaps d | |||||||||||||||
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign exchange forward contracts d | |||||||||||||||
Total financial liabilities | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||
a | Included within Short-term investments. |
b | Included within Other assets, net. |
c | Included within Prepaid expenses and other current assets or Other assets, net based on the maturity of the contract. |
d | Included within Accounts payable and accrued liabilities or Other long-term liabilities based on the maturity of the contract. |
The fair values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities approximate their carrying values due to the short-term maturities of these assets and liabilities and as such are measured using Level 1 inputs. The fair value of debt with variable interest rates approximates carrying value and is measured using Level 2 inputs. The fair value of debt with fixed interest rates was determined using the quoted market prices of debt instruments with similar terms and maturities, which are considered Level 2 inputs. The total carrying value of short-term borrowings and long-term debt was approximately $1.0 billion at January 31, 2020 and 2019 and the corresponding fair value was approximately $1.2 billion at January 31, 2020 and $1.0 billion at January 31, 2019.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-74
K. | LEASES |
Amounts recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings were as follows:
(in millions) | Year Ended January 31, 2020 | ||
Fixed operating lease expense | $ | ||
Variable operating lease expense | |||
Sublease income | ( | ) | |
Net lease expense | $ | ||
The weighted average remaining lease term was seven years and the weighted average discount rate was 3.8 % for all of the Company's operating leases as of January 31, 2020.
The following table provides supplemental cash flow information related to the Company's operating leases:
(in millions) | Year Ended January 31, 2020 | ||
Cash outflows from operating activities attributable to operating leases | $ | ||
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for operating leases liabilities | |||
The following table reconciles the undiscounted cash flows expected to be paid in each of the next five fiscal years and thereafter to the operating lease liability recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheet for operating leases existing as of January 31, 2020.
Years ending January 31, | Minimum Lease Payments as of January 31, 2020 (in millions) | ||
2021 | $ | ||
2022 | |||
2023 | |||
2024 | |||
2025 | |||
Thereafter | |||
Total minimum lease payments | |||
Less: amount of total minimum lease payments representing interest | ( | ) | |
Present value of future total minimum lease payments | |||
Less: current portion of operating lease liabilities | ( | ) | |
Long-term portion of operating lease liabilities | $ | ||
As of January 31, 2020, there were nine executed agreements in respect of store relocations, new stores, office space and other facilities without commencement dates, which had total commitments of $88.7 million.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-75
As previously disclosed in "Note J. Commitments and Contingencies" to the consolidated financial statements included in the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 31, 2019, under previous lease accounting, future minimum lease payments for operating leases having an initial or remaining non-cancelable lease term in excess of one year were as follows:
Years ending January 31, | Minimum Lease Payments as of January 31, 2019 (in millions) | ||
2020 | $ | ||
2021 | |||
2022 | |||
2023 | |||
2024 | |||
Thereafter | |||
Total minimum lease payments | $ | ||
The Company entered into sale-leaseback arrangements for its Retail Service Center, a distribution and administrative office facility in New Jersey, in 2005 and for the TIFFANY & CO. stores in Tokyo's Ginza shopping district and on London's Old Bond Street in 2007. These sale-leaseback arrangements resulted in total deferred gains of $144.5 million, which were amortized in SG&A expenses over periods ranging from 15 to 20 years. As of January 31, 2019, $31.1 million of these deferred gains remained on the Company's Consolidated Balance Sheet and were reclassified to opening retained earnings in the first quarter of 2019 in accordance with ASU 2016-02 (see "Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies – New Accounting Standards" for additional information).
Rent expense for the Company's operating leases consisted of the following:
Years Ended January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||
Minimum rent for retail locations | $ | $ | ||||
Contingent rent based on sales | ||||||
Office, distribution and manufacturing facilities and equipment | ||||||
Gains on sale-leaseback arrangements | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
Sublease income | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
$ | $ | |||||
L. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Diamond Sourcing Activities
The Company has agreements with various diamond producers to purchase a minimum volume of rough diamonds at prevailing fair market prices. Under those agreements, management anticipates that it will purchase approximately $30.0 million of rough diamonds in 2020. The Company also regularly purchases rough and polished diamonds from other suppliers, although it has no contractual obligations to do so. Purchases beyond 2020 under the aforementioned agreements cannot be reasonably estimated.
Contractual Cash Obligations and Contingent Funding Commitments
At January 31, 2020, the Company's contractual cash obligations and contingent funding commitments were for inventory purchases of $229.8 million (which includes the $30.0 million obligation discussed in Diamond Sourcing Activities above), as well as for other contractual obligations of $152.1 million (primarily for construction-in-
TIFFANY & CO.
K-76
progress, technology licensing and service contracts, advertising and media agreements and fixed royalty commitments).
Litigation
Litigation Matters. The Company is from time to time involved in routine litigation incidental to the conduct of its business, including proceedings to protect its trademark rights, litigation with parties claiming infringement of patents and other intellectual property rights by the Company, litigation instituted by persons alleged to have been injured upon premises under the Company's control and litigation with present and former employees and customers. Although litigation with present and former employees is routine and incidental to the conduct of the Company's business, as well as for any business employing significant numbers of employees, such litigation can result in large monetary awards when a civil jury is allowed to determine compensatory and/or punitive damages for actions such as those claiming discrimination on the basis of age, gender, race, religion, disability or other legally-protected characteristic or for termination of employment that is wrongful or in violation of implied contracts. However, the Company believes that all such litigation currently pending to which it is a party or to which its properties are subject will be resolved without any material adverse effect on the Company's financial position, earnings or cash flows.
Gain Contingency. On February 14, 2013, Tiffany and Company and Tiffany (NJ) LLC (collectively, the "Tiffany plaintiffs") initiated a lawsuit against Costco Wholesale Corp. ("Costco") for trademark infringement, false designation of origin and unfair competition, trademark dilution and trademark counterfeiting (the "Costco Litigation"). The Tiffany plaintiffs sought injunctive relief, monetary recovery and statutory damages on account of Costco's use of "Tiffany" on signs in the jewelry cases at Costco stores used to describe certain diamond engagement rings that were not manufactured by Tiffany. Costco filed a counterclaim arguing that the TIFFANY trademark was a generic term for multi-pronged ring settings and seeking to have the trademark invalidated, modified or partially canceled in that respect. On September 8, 2015, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York (the "Court") granted the Tiffany plaintiffs' motion for summary judgment of liability in its entirety, dismissing Costco's genericism counterclaim and finding that Costco was liable for trademark infringement, trademark counterfeiting and unfair competition under New York law in its use of "Tiffany" on the above-referenced signs. On September 29, 2016, a civil jury rendered its verdict, finding that Costco's profits on the sale of the infringing rings should be awarded at $5.5 million, and further finding that an award of punitive damages was warranted. On October 5, 2016, the jury awarded $8.25 million in punitive damages. The aggregate award of $13.75 million was not final, as it was subject to post-verdict motion practice and ultimately to adjustment by the Court. On August 14, 2017, the Court issued its ruling, finding that the Tiffany plaintiffs are entitled to recover (i) $11.1 million in respect of Costco's profits on the sale of the infringing rings (which amount is three times the amount of such profits, as determined by the Court); (ii) prejudgment interest on such amount (calculated at the applicable statutory rate) from February 15, 2013 through August 14, 2017; (iii) an additional $8.25 million in punitive damages; and (iv) Tiffany's reasonable attorneys' fees, and, on August 24, 2017, the Court entered judgment in the amount of $21.0 million in favor of the Tiffany plaintiffs (reflecting items (i) through (iii) above). On February 7, 2019, the Court awarded the Tiffany plaintiffs $5.9 million in respect of the aforementioned attorneys' fees and costs, bringing the total judgment to $26.9 million. The Court has denied a motion made by Costco for a new trial; however, Costco has also filed an appeal from the judgment before the Second Circuit Court of Appeals. A three-judge panel presided over an appellate hearing on January 23, 2020, and that panel's decision is pending. As the Tiffany plaintiffs may not enforce the Court's judgment during the appeals process, the Company has not recorded any amount in its consolidated financial statements related to this gain contingency as of January 31, 2020. The Company expects that this matter will not ultimately be resolved until, at the earliest, a future date during the Company's fiscal year ending January 31, 2021.
Environmental Matter
In 2005, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA") designated a 17-mile stretch of the Passaic River (the "River") part of the Diamond Alkali "Superfund" site. This designation resulted from the detection of hazardous substances emanating from the site, which was previously home to the Diamond Shamrock Corporation, a manufacturer of pesticides and herbicides. Under the Superfund law, the EPA will negotiate with potentially responsible parties to agree on remediation approaches and may also enter into settlement agreements pursuant to an allocation process.
The Company, which operated a silverware manufacturing facility near a tributary of the River from approximately 1897 to 1985, is one of more than 300 parties (the "Potentially Responsible Parties") designated in litigation as potentially responsible parties with respect to the River. The EPA issued general notice letters to 125 of these
TIFFANY & CO.
K-77
parties. The Company, along with approximately 70 other Potentially Responsible Parties (collectively, the "Cooperating Parties Group" or "CPG") voluntarily entered into an Administrative Settlement Agreement and Order on Consent ("AOC") with the EPA in May 2007 to perform a Remedial Investigation/Feasibility Study (the "RI/FS") of the lower 17 miles of the River. In June 2012, most of the CPG voluntarily entered into a second AOC related to focused remediation actions at Mile 10.9 of the River. The actions under the Mile 10.9 AOC are complete (except for continued monitoring), the Remedial Investigation ("RI") portion of the RI/FS was submitted to the EPA on February 19, 2015, and the Feasibility Study ("FS") portion of the RI/FS was submitted to the EPA on April 30, 2015. The Company nonetheless remained in the CPG until October 24, 2017. The Company has accrued for its financial obligations under both AOCs, which have not been material to its financial position or results of operations in previous financial periods or on a cumulative basis.
The FS presented and evaluated three options for remediating the lower 17 miles of the River, including the approach recommended by the EPA in its Focused Feasibility Study discussed below, as well as a fourth option of taking no action, and recommended an approach for a targeted remediation of the entire 17-mile stretch of the River. The estimated cost of the approach recommended by the CPG in the FS is approximately $483.0 million. The RI and FS are being reviewed by the EPA and other governmental agencies and stakeholders. Ultimately, the Company expects that the EPA will identify and negotiate with any or all of the potentially responsible parties regarding any remediation action that may be necessary, and issue a Record of Decision with a proposed approach to remediating the entire lower 17-mile stretch of the River.
Separately, on April 11, 2014, the EPA issued a proposed plan for remediating the lower eight miles of the River, which is supported by a Focused Feasibility Study (the "FFS"). The FFS evaluated three remediation options, as well as a fourth option of taking no action. Following a public review and comment period and the EPA's review of comments received, the EPA issued a Record of Decision on March 4, 2016 that set forth a remediation plan for the lower eight miles of the River (the "RoD Remediation"). The RoD Remediation is estimated by the EPA to cost $1.38 billion. The Record of Decision did not identify any party or parties as being responsible for the design of the remediation or for the remediation itself. The EPA did note that it estimates the design of the necessary remediation activities will take three to four years, with the remediation to follow, which is estimated to take an additional six years to complete.
On March 31, 2016, the EPA issued a letter to approximately 100 companies (including the Company) (collectively, the "notified companies") notifying them of potential liability for the RoD Remediation and of the EPA's planned approach to addressing the cost of the RoD Remediation, which included the possibility of a de-minimis cash-out settlement (the "settlement option") for certain parties. In April of 2016, the Company notified the EPA of its interest in pursuing the settlement option, and accordingly recorded an immaterial liability representing its best estimate of its minimum liability for the RoD Remediation, which was based on the amount of a potential de-minimis settlement. On March 30, 2017, the EPA issued offers related to the settlement option to 20 parties; while the Company was not one of the parties receiving such an offer, the EPA indicated at that time that the settlement option might be made available to additional parties beyond those notified on March 30, 2017. On October 24, 2019, the EPA informed certain of the notified parties (including the Company) that the early settlement option would not be made available to them at that time.
In the absence of a viable settlement option with the EPA, the Company is unable to determine its participation in the overall RoD Remediation, if any, relative to the other potentially responsible parties, or the allocation of the estimated cost thereof among the potentially responsible parties, until such time as the EPA reaches an agreement with any potentially responsible party or parties to fund the RoD Remediation (or pursues legal or administrative action to require any potentially responsible party or parties to perform, or pay for, the RoD Remediation). With respect to the RI/FS (which is distinct from the RoD Remediation), until a Record of Decision is issued with respect to the RI/FS, neither the ultimate remedial approach for the remaining upper nine miles of the relevant 17-mile stretch of the River and its cost, nor the Company's participation, if any, relative to the other potentially responsible parties in this approach and cost, can be determined.
In October 2016, the EPA announced that it entered into a legal agreement with Occidental Chemical Corporation ("OCC"), pursuant to which OCC agreed to spend $165.0 million to perform the engineering and design work required in advance of the clean-up contemplated by the RoD Remediation. OCC has waived any rights to collect contribution from the Company (the "Waiver") for certain costs, including those associated with such engineering and design work, incurred by OCC through July 14, 2016. However, on June 29, 2018, OCC filed a lawsuit in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey against Tiffany and Company and 119 other companies (the "defendant
TIFFANY & CO.
K-78
companies") seeking to have the defendant companies reimburse OCC for certain response costs incurred by OCC in connection with its and its predecessors' remediation work relating to the River, other than those costs subject to the Waiver. OCC is also seeking a declaratory judgment to hold the defendant companies liable for their alleged shares of future response costs, including costs related to the RoD Remediation. The suit does not quantify damages sought, and the Company is unable to determine at this time whether, or to what extent, the OCC lawsuit will impact the cost allocation described in the immediately preceding paragraph or will otherwise result in any liabilities for the Company.
Given the uncertainties described above, the Company's liability, if any, beyond that already recorded for its obligation under the 2007 AOC and the Mile 10.9 AOC, cannot be determined at this time. However, the Company does not expect that its ultimate liability related to the relevant 17-mile stretch of the River will be material to its financial position, in light of the number of companies that have previously been identified as Potentially Responsible Parties (i.e., the more than 300 parties that were initially designated in litigation as potentially responsible parties), which includes, but goes well beyond those approximately 70 CPG member companies that participated in the 2007 AOC and the Mile 10.9 AOC, and the Company's relative participation in the costs related to the 2007 AOC and Mile 10.9 AOC. It is nonetheless possible that any resulting liability when the uncertainties discussed above are resolved could be material to the Company's results of operations or cash flows in the period in which such uncertainties are resolved.
Other
In the normal course of business, the Company entrusts precious scrap metals generated through its internal manufacturing operations to metal refiners. In November 2018, one such refiner filed for relief under chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. As a result, the Company recognized a charge of $8.5 million during the three months ended October 31, 2018, which represented the carrying value of such precious scrap metals entrusted to the refiner, net of expected insurance recoveries.
During 2018, the Company received an offer of AUD $48.0 million as compensation for the previous acquisition of the premises containing one of its leased retail stores and an administrative office in Sydney, Australia under compulsory acquisition laws in Australia. The Company did not accept the offer of compensation and has filed an appeal of the compensation amount with the Land and Environment Court in Australia. In accordance with local law, the Company received an advance payment of 90 % ($31.1 million, based on foreign currency exchange rates on the date of receipt) of the offered compensation during the fourth quarter of 2018. The appeal process is inherently uncertain and the Land and Environment Court will make an independent assessment of the amount of compensation in this matter, which may require the Company to repay all or a portion of the advance payment. Therefore, the Company cannot currently determine an amount, or any minimum amount, it ultimately expects to realize in connection with this matter. Accordingly, the Company did not recognize any gain in the accompanying Consolidated Statement of Earnings for the year ended January 31, 2020 or 2019. Instead, the Company recognized the advance payment within Cash and cash equivalents and as a liability within Accounts payable and accrued liabilities as of January 31, 2019. The Company classified $19.2 million of the advance payment within operating cash flows and $11.9 million within investing cash flows on the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the year ended January 31, 2019, with such classification determined by the nature of the underlying components of the cash receipt.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-79
M. STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
January 31, | |||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax: | |||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | |
Deferred hedging gain (loss) | ( | ) | |||||
Net unrealized loss on benefit plans | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||
$ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | ||
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||
Income tax (expense) benefit | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Unrealized gain on marketable securities | |||||||||
Reclassification for gain included in net earnings | ( | ) | |||||||
Income tax benefit | |||||||||
Unrealized loss on marketable securities, net of tax | ( | ) | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on hedging instruments | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Reclassification adjustment for (gain) loss included in net earnings a | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Income tax (expense) benefit | ( | ) | |||||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on hedging instruments, net of tax | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Net actuarial (loss) gain | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Amortization of net loss included in net earnings b | |||||||||
Amortization of prior service credit included in net earnings b | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||
Income tax benefit (expense) | ( | ) | |||||||
Net unrealized (loss) gain on benefit plans, net of tax | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Total other comprehensive (loss) earnings, net of tax | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ||
a | These (gains) losses are reclassified into Interest expense and financing costs and Cost of sales (see "Note I. Hedging Instruments" for additional details). |
b | These losses (gains) are included in the computation of net periodic benefit cost (see "Note O. Employee Benefit Plans" for additional details) and are reclassified into Other expense, net. |
Stock Repurchase Program
In May 2018, the Registrant's Board of Directors approved a new share repurchase program (the "2018 Program"). The 2018 Program, which became effective June 1, 2018 and expires on January 31, 2022, authorizes the Company to repurchase up to $1.0 billion of its Common Stock through open market transactions, including through Rule 10b5-1 plans and one or more accelerated share repurchase ("ASR") or other structured repurchase transactions, and/or privately negotiated transactions. The 2018 Program replaced the Company's previous share repurchase program approved in January 2016, under which the Company was authorized to repurchase up to
TIFFANY & CO.
K-80
$500.0 million of its Common Stock. As of January 31, 2020, $471.6 million remained available under the 2018 Program; however, pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, and subject to certain limited exceptions, the Company may not repurchase its Common Stock other than in connection with the forfeiture provisions of Company equity awards or the cashless exercise or tax withholding provisions of such Company equity awards, in each case, granted under the Company's stock-based compensation plans.
During 2018, the Company entered into ASR agreements with two third-party financial institutions to repurchase an aggregate of $250.0 million of its Common Stock. The ASR agreements were entered into under the 2018 Program. Pursuant to the ASR agreements, the Company made an aggregate payment of $250.0 million from available cash on hand in exchange for an initial delivery of 1,529,286 shares of its Common Stock. Final settlement of the ASR agreements was completed in July 2018, pursuant to which the Company received an additional 353,112 shares of its Common Stock. In total, 1,882,398 shares of the Company's Common Stock were repurchased under these ASR agreements at an average cost per share of $132.81 over the term of the agreements.
The Company's share repurchase activity was as follows:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Cost of repurchases | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Shares repurchased and retired | |||||||||
Average cost per share | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Cash Dividends
The Company's Board of Directors declared quarterly dividends which, on an annual basis, totaled $2.29 , $2.15 and $1.95 per share of Common Stock in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
On February 20, 2020 , the Company's Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.58 per share of Common Stock. This dividend will be paid on April 10, 2020 to stockholders of record on March 20, 2020 .
Cumulative Effect Adjustment From Adoption of New Accounting Standards
The amounts presented within this line item on the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity represent the effects of the Company's adoption, on a modified retrospective basis, of ASU 2016-02 - Leases and ASU 2018-02 - Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income: Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (each as discussed in "Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies") for the year ended January 31, 2020, and ASU 2014-09 - Revenue from Contracts with Customers and ASU 2016-01 - Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities for the year ended January 31, 2019.
N. STOCK COMPENSATION PLANS
The Company has two stock compensation plans under which awards may be made: the Employee Incentive Plan and the Directors Equity Compensation Plan, both of which were approved by the Company's stockholders. No award may be made under the Employee Incentive Plan after May 22, 2024 or under the Directors Equity Compensation Plan after May 25, 2027.
Under the Employee Incentive Plan, the maximum number of common shares authorized for issuance is 8.7 million. Awards may be made to employees of the Company in the form of stock options, stock appreciation rights, shares of stock (or rights to receive shares of stock) and cash. Awards made in the form of non-qualified stock options, tax-qualified incentive stock options or stock appreciation rights have a maximum term of 10 years from the grant date and may not be granted for an exercise price below fair market value.
The Company has granted time-vesting restricted stock units ("RSUs"), performance-based restricted stock units ("PSUs") and stock options under the Employee Incentive Plan. Stock options and RSUs typically vest in increments of 25 % per year over four years. PSUs vest at the end of a three-year period. PSU grant terms provide that vesting is
TIFFANY & CO.
K-81
contingent on the Company's performance against objectives established by the Compensation Committee of the Company's Board of Directors. The PSUs and RSUs require no payment from the employee. PSU and RSU payouts are in shares of Company stock at vesting (aside from fractional dividend equivalents, which are settled in cash). Compensation expense is recognized using the fair market value of the award at the date of grant and recorded ratably over the vesting period. However, PSU compensation expense may be adjusted over the vesting period based on interim estimates of performance against the established objectives. Award holders are not entitled to receive dividends or dividend equivalents on PSUs or RSUs granted prior to January 2017 or on unvested stock options. PSUs and RSUs granted in or after January 2017 accrue dividend equivalents that may only be paid or delivered upon vesting of the underlying stock units.
Under the Directors Equity Compensation Plan, the maximum number of shares of Common Stock authorized for issuance is 1.0 million (subject to adjustment); awards may be made to non-employee directors of the Company in the form of stock options or shares of stock but may not exceed $750,000 of total compensation (including without limitation, non-equity compensation and the grant-date fair value of options or stock awards, or any combination of options and stock awards) that may be awarded to any one participant in any single fiscal year of the Company in connection with his or her service as a member of the Board of Directors; provided, however, that this limitation shall not apply to a non-executive chairperson of the Board of Directors. Awards made in the form of stock options may have a maximum term of 10 years from the grant date and may not be granted for an exercise price below fair market value. Director options vest immediately. Director RSUs vest at the end of a one-year period.
The Company uses newly issued shares to satisfy stock option exercises and the vesting of PSUs and RSUs.
The fair value of each option award is estimated on the grant date using a Black-Scholes option valuation model and compensation expense is recognized ratably over the vesting period. The valuation model uses the assumptions noted in the following table. Expected volatilities are based on historical volatility of the Company's stock. The Company uses historical data to estimate the expected term of the option that represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free interest rate for periods within the expected term of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the grant date.
Years Ended January 31, | ||||||
2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||
Dividend yield | % | % | % | |||
Expected volatility | % | % | % | |||
Risk-free interest rate | % | % | % | |||
Expected term in years | ||||||
A summary of the Company's stock option activity is presented below:
Number of Shares (in millions) | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term in Years | Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in millions) | ||||||
Outstanding at January 31, 2019 | $ | $ | |||||||
Granted | |||||||||
Exercised | ( | ) | |||||||
Forfeited/canceled | |||||||||
Outstanding at January 31, 2020 | $ | $ | |||||||
Exercisable at January 31, 2020 | $ | $ | |||||||
The weighted-average grant-date fair value of options granted for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $16.57 , $16.97 and $18.33 , respectively. The total intrinsic value (market value on date of exercise less
TIFFANY & CO.
K-82
grant price) of options exercised during the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $52.8 million, $16.3 million and $31.2 million, respectively.
A summary of the Company's RSU activity is presented below:
Number of Shares (in millions) | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | ||||
Non-vested at January 31, 2019 | $ | ||||
Granted | |||||
Vested | ( | ) | |||
Forfeited | ( | ) | |||
Non-vested at January 31, 2020 | $ | ||||
A summary of the Company's PSU activity is presented below:
Number of Shares (in millions) | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | ||||
Non-vested at January 31, 2019 | $ | ||||
Granted | |||||
Vested | ( | ) | |||
Forfeited/canceled | |||||
Non-vested at January 31, 2020 | $ | ||||
The weighted-average grant-date fair value of RSUs granted for the years ended January 31, 2019 and 2018 was $103.40 and $91.96 , respectively. The weighted-average grant-date fair value of PSUs granted for the years ended January 31, 2019 and 2018 was $85.26 and $108.99 , respectively. The total fair value of RSUs vested during the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $28.1 million, $24.3 million and $22.2 million, respectively. The total fair value of PSUs vested during the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 was $9.8 million, $2.7 million and $3.4 million, respectively.
As of January 31, 2020, there was $94.7 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested share-based compensation arrangements granted under the Employee Incentive Plan and Directors Equity Compensation Plan. The expense is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 3.0 years.
Total compensation cost for stock-based compensation awards recognized in income and the related income tax benefit was $33.2 million and $6.5 million for the year ended January 31, 2020, $34.1 million and $6.8 million for the year ended January 31, 2019 and $28.0 million and $8.5 million for the year ended January 31, 2018. Total stock-based compensation cost capitalized in inventory was not significant.
O. | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS |
Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits
The Company maintains the following pension plans: a noncontributory defined benefit pension plan qualified in accordance with the Internal Revenue Service Code ("Qualified Plan") covering substantially all U.S. employees hired before January 1, 2006, a non-qualified unfunded retirement income plan ("Excess Plan") covering certain U.S. employees hired before January 1, 2006 and affected by Internal Revenue Service Code compensation limits, a non-qualified unfunded Supplemental Retirement Income Plan ("SRIP") covering certain executive officers of the Company hired before January 1, 2006 and noncontributory defined benefit pension plans in certain of its international locations ("Other Plans").
TIFFANY & CO.
K-83
Qualified Plan benefits are based on (i) average compensation in the highest paid five years of the last 10 years of employment ("average final compensation") and (ii) the number of years of service. The normal retirement age under the Qualified Plan is age 65; however, participants who retire with at least 10 years of service may elect to receive reduced retirement benefits starting at age 55. The Company funds the Qualified Plan's trust in accordance with regulatory limits to provide for current service and for the unfunded benefit obligation over a reasonable period and for current service benefit accruals. To the extent that these requirements are fully covered by assets in the Qualified Plan, the Company may elect not to make any contribution in a particular year. No cash contribution was required in 2018 and none is required in 2019 to meet the minimum funding requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act. However, the Company periodically evaluates whether to make discretionary cash contributions to the Qualified Plan and made voluntary cash contributions of $30.0 million in 2019, $11.8 million in 2018 and $15.0 million in 2017. The Company does not currently expect to make any contributions to the Qualified Plan in 2020.
The Qualified Plan, Excess Plan and SRIP exclude all employees hired on or after January 1, 2006. Instead, employees hired on or after January 1, 2006 are eligible to receive a defined contribution retirement benefit under the Employee Profit Sharing and Retirement Savings ("EPSRS") Plan (see "Employee Profit Sharing and Retirement Savings Plan" below). Employees hired before January 1, 2006 continue to be eligible for and accrue benefits under the Qualified Plan.
The Excess Plan uses the same retirement benefit formula set forth in the Qualified Plan, but includes earnings that are excluded under the Qualified Plan due to Internal Revenue Service Code qualified pension plan limitations. Benefits payable under the Qualified Plan offset benefits payable under the Excess Plan. Employees vested under the Qualified Plan are vested under the Excess Plan; however, benefits under the Excess Plan are subject to forfeiture if employment is terminated for cause and, for those who leave the Company prior to age 65, if they fail to execute and adhere to noncompetition and confidentiality covenants. Under the Excess Plan, participants who retire with at least 10 years of service may elect to receive reduced retirement benefits starting at age 55.
The SRIP supplements the Qualified Plan, Excess Plan and Social Security by providing additional payments upon a participant's retirement. SRIP benefits are determined by a percentage of average final compensation; this percentage increases as specified service plateaus are achieved. Benefits payable under the Qualified Plan, Excess Plan and Social Security offset benefits payable under the SRIP. Under the SRIP, benefits vest when a participant both (i) attains age 55 while employed by the Company and (ii) has provided at least 10 years of service. In certain limited circumstances, early vesting can occur due to a change in control. Benefits under the SRIP are forfeited if benefits under the Excess Plan are forfeited.
Benefits for the Other Plans are typically based on monthly eligible compensation and the number of years of service. Benefits are typically payable in a lump sum upon retirement, termination, resignation or death if the participant has completed the requisite service period.
The Company accounts for pension expense using the projected unit credit actuarial method for financial reporting purposes. The actuarial present value of the benefit obligation is calculated based on the expected date of separation or retirement of the Company's eligible employees.
The Company provides certain health-care and life insurance benefits ("Other Postretirement Benefits") for certain retired employees and accrues the cost of providing these benefits throughout the employees' active service period until they attain full eligibility for those benefits. Substantially all of the Company's U.S. full-time employees hired on or before March 31, 2012 may become eligible for these benefits if they reach normal or early retirement age while working for the Company. The cost of providing postretirement health-care benefits is shared by the retiree and the Company, with retiree contributions evaluated annually and adjusted in order to maintain the Company/retiree cost-sharing target ratio. The life insurance benefits are noncontributory. The Company's employee and retiree health-care benefits are administered by an insurance company, and premiums on life insurance are based on prior years' claims experience.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-84
Obligations and Funded Status
The following tables provide a reconciliation of benefit obligations, plan assets and funded status of the pension and other postretirement benefit plans as of the measurement date:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||||||
Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
Change in benefit obligation: | |||||||||||||
Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||
Service cost | |||||||||||||
Interest cost | |||||||||||||
Participants' contributions | |||||||||||||
MMA retiree drug subsidy | |||||||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||
Benefits paid | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Projected benefit obligation at end of year | |||||||||||||
Change in plan assets: | |||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | |||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | ( | ) | |||||||||||
Employer contributions | |||||||||||||
Participants' contributions | |||||||||||||
MMA retiree drug subsidy | |||||||||||||
Benefits paid | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | |||||||||||||
Funded status at end of year | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | |
Actuarial losses in 2019 reflect decreases in the discount rates for all plans.
The following tables provide additional information regarding the Company's pension plans' projected benefit obligations and assets (included in pension benefits in the table above) and accumulated benefit obligation:
January 31, 2020 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Qualified | Excess/SRIP | Other | Total | ||||||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Fair value of plan assets | ||||||||||||
Funded status | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) |
Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-85
January 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | Qualified | Excess/SRIP | Other | Total | ||||||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Fair value of plan assets | ||||||||||||
Funded status | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) | $ | ( | ) |
Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
At January 31, 2020, the Company had a current liability of $9.0 million and a non-current liability of $374.5 million for pension and other postretirement benefits. At January 31, 2019, the Company had a current liability of $9.0 million and a non-current liability of $312.4 million for pension and other postretirement benefits.
Pre-tax amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive loss consisted of:
January 31, | |||||||||||||
Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||
Net actuarial loss (gain) | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | |||||||
Prior service cost (credit) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||
Total before tax | $ | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | |||||||
Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost and
Other Amounts Recognized in Other Comprehensive Earnings
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | ||||||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||
Interest cost | |||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost (credit) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
Amortization of net loss (gain) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost | |||||||||||||||||||
Net actuarial loss (gain) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||
Recognized actuarial (loss) gain | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||
Recognized prior service (cost) credit | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||
Total recognized in other comprehensive earnings | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||||||||||||
Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost and other comprehensive earnings | $ | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | $ | ( | ) | $ | |||||||||
The non-service cost components of the net periodic benefit cost are included within Other expense, net on the Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-86
Assumptions
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations:
January 31, | ||||
2020 | 2019 | |||
Discount rate: | ||||
Qualified Plan | % | % | ||
Excess Plan/SRIP | % | % | ||
Other Plans | % | % | ||
Other Postretirement Benefits | % | % | ||
Rate of increase in compensation: | ||||
Qualified Plan | % | % | ||
Excess Plan | % | % | ||
SRIP | % | % | ||
Other Plans | % | % | ||
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit cost:
Years Ended January 31, | ||||||
2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||
Discount rate: | ||||||
Qualified Plan | % | % | % | |||
Excess Plan/SRIP | % | % | % | |||
Other Plans | % | % | % | |||
Other Postretirement Benefits | % | % | % | |||
Expected return on plan assets | % | % | % | |||
Rate of increase in compensation: | ||||||
Qualified Plan | % | % | % | |||
Excess Plan | % | % | % | |||
SRIP | % | % | % | |||
Other Plans | % | % | % | |||
The expected long-term rate of return on Qualified Plan assets is selected by taking into account the average rate of return expected on the funds invested or to be invested to provide for benefits included in the projected benefit obligation. More specifically, consideration is given to the expected rates of return (including reinvestment asset return rates) based upon the plan's current asset mix, investment strategy and the historical performance of plan assets.
For postretirement benefit measurement purposes, a 6.50 % annual rate of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care was assumed for 2020. This rate was assumed to decrease gradually to 4.75 % by 2023 and remain at that level thereafter.
Plan Assets
The Company's investment objectives related to the Qualified Plan's assets are the preservation of principal and balancing the management of interest rate risk associated with the duration of the plan's liabilities with the achievement of a reasonable rate of return over time. The Qualified Plan's assets are allocated based on an
TIFFANY & CO.
K-87
expectation that equity securities will outperform debt securities over the long term, but that as the plan's funded status (assets relative to liabilities) increases, the amount of assets allocated to fixed income securities which match the interest rate risk profile of the plan's liabilities will increase. The Company's target asset allocation based on its funded status as of January 31, 2020 is as follows: approximately 50 % in equity securities; approximately 35 % in fixed income securities; and approximately 15 % in other securities. The Company attempts to mitigate investment risk by rebalancing the asset allocation periodically.
The fair value of the Qualified Plan's assets at January 31, 2020 and 2019 by asset category is as follows:
Fair Value at | Fair Value Measurements Using Inputs Considered as* | |||||||||||
(in millions) | January 31, 2020 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||
Equity securities: | ||||||||||||
U.S. equity securities | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Mutual funds | ||||||||||||
Fixed income securities: | ||||||||||||
Government bonds | ||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | ||||||||||||
Other types of investments: | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | ||||||||||||
Mutual funds | ||||||||||||
Net assets in fair value hierarchy | ||||||||||||
Investments at NAV practical expedient a | ||||||||||||
Plan assets at fair value | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Fair Value at | Fair Value Measurements Using Inputs Considered as* | |||||||||||
(in millions) | January 31, 2019 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||
Equity securities: | ||||||||||||
U.S. equity securities | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Mutual fund | ||||||||||||
Fixed income securities: | ||||||||||||
Government bonds | ||||||||||||
Corporate bonds | ||||||||||||
Other types of investments: | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | ||||||||||||
Mutual funds | ||||||||||||
Net assets in fair value hierarchy | ||||||||||||
Investments at NAV practical expedient a | ||||||||||||
Plan assets at fair value | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
* | See "Note J. Fair Value of Financial Instruments" for a description of the levels of inputs. |
a | In accordance with ASC 820-10, certain investments that are measured at fair value using the net asset value ("NAV") per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. The fair value amounts presented in this table are intended to permit reconciliation of the fair value hierarchy to the Qualified Plan's fair value of plan assets at the end of each respective year. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-88
Valuation Techniques
Investments within the fair value hierarchy. Securities traded on the national securities exchange (certain government bonds) are valued at the last reported sales price or closing price on the last business day of the fiscal year. Investments traded in the over-the-counter market and listed securities for which no sales were reported (certain government bonds, corporate bonds and mortgage obligations) are valued at the last reported bid price. Certain fixed income investments are held in separately managed accounts and those investments are valued using the underlying securities in the accounts.
Investments in mutual funds are stated at fair value as determined by quoted market prices based on the NAV of shares held by the Qualified Plan at year-end. Investments in U.S. equity securities are valued at the closing price reported on the active market on which the individual securities are traded.
Investments measured at NAV. This category consists of common/collective trusts and limited partnerships.
Common/collective trusts include investments in U.S. and international large, middle and small capitalization equities. Investments in common/collective trusts are stated at estimated fair value, which represents the NAV of shares held by the Qualified Plan as reported by the investment advisor. The NAV is based on the value of the underlying assets owned by the common/collective trust, minus its liabilities and then divided by the number of shares outstanding. The NAV is used as a practical expedient to estimate fair value.
The Qualified Plan maintains investments in limited partnerships that are valued at estimated fair value based on financial information received from the investment advisor and/or general partner. The NAV is based on the value of the underlying assets owned by the fund, minus its liabilities and then divided by the number of shares outstanding. The NAV is used as a practical expedient to estimate fair value.
Benefit Payments
The Company estimates the following future benefit payments:
Years Ending January 31, | Pension Benefits (in millions) | Other Postretirement Benefits (in millions) | ||||
2021 | $ | $ | ||||
2022 | ||||||
2023 | ||||||
2024 | ||||||
2025 | ||||||
2026-2030 | ||||||
Employee Profit Sharing and Retirement Savings ("EPSRS") Plan
The Company maintains an EPSRS Plan that covers substantially all U.S.-based employees. Under the profit-sharing feature of the EPSRS Plan, the Company made contributions, in the form of newly issued Company Common Stock through 2014, to the employees' accounts based on the achievement of certain targeted earnings objectives established by, or as otherwise determined by, the Company's Board of Directors. Beginning in 2015, these contributions were made in cash. The EPSRS Plan provides a retirement savings feature, a profit sharing feature and a defined contribution retirement benefit ("DCRB"). The DCRB is provided to eligible employees hired on or after January 1, 2006. Contributions related to the retirement savings feature and profit sharing feature for a particular plan year are made the following year.
Under the retirement savings feature of the EPSRS Plan, employees who meet certain eligibility requirements may participate by contributing up to 50 % of their annual compensation, not to exceed Internal Revenue Service limits, and the Company may provide a matching cash contribution of 50 % of each participant's contributions, with a maximum matching contribution of 3 % of each participant's total compensation. The Company recorded expense of $9.2 million, $8.6 million and $8.2 million in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, related to the retirement savings feature of the EPSRS Plan.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-89
Under the profit-sharing feature of the EPSRS Plan, contributions are made in cash and are allocated within the respective participant's account based on investment elections made under the EPSRS Plan. If the participant has made no election, the contribution will be invested in the appropriate default target fund as determined by each participant's date of birth. Under the retirement savings portion of the EPSRS Plan, employees may invest their contributions and the related matching contribution to their accounts in a similar manner. Under both the profit-sharing and retirement savings features, employees may elect to invest a portion of the contributions to their accounts in Company stock. At January 31, 2020, investments in Company stock represented 19 % of total EPSRS Plan assets. The Company recorded expense of $4.9 million and $3.9 million in 2018 and 2017, respectively, related to the profit sharing feature of the EPSRS Plan and did not record any such expense in 2019.
Under the DCRB, the Company makes contributions each year to each employee's account at a rate based upon age and years of service. These contributions are deposited into individual accounts in each employee's name to be invested in a manner similar to the profit-sharing and retirement savings portions of the EPSRS Plan (except that DCRB contributions may not be invested in Company stock). The Company recorded expense of $7.2 million, $4.7 million and $5.2 million in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, related to the DCRB.
Deferred Compensation Plan
The Company has a non-qualified deferred compensation plan for directors, executives and certain management employees, whereby eligible participants may defer a portion of their compensation for payment at specified future dates, upon retirement, death or termination of employment. This plan also provides for an excess defined contribution retirement benefit ("Excess DC benefit") for certain eligible executives and management employees, hired on or after January 1, 2006. The Excess DC benefit is credited to the eligible employee's account, based on the compensation paid to the employee in excess of the IRS limits for contributions under the DCRB Plan. Under the plan, the deferred compensation is adjusted to reflect performance, whether positive or negative, of selected investment options chosen by each participant during the deferral period. The amounts accrued under the plans were $27.6 million and $22.6 million at January 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and are reflected in Other long-term liabilities. The Company does not promise or guarantee any rate of return on amounts deferred.
P. INCOME TAXES
U.S. Federal Income Tax Reform
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the "2017 Tax Act") was enacted in the U.S. This enactment resulted in a number of significant changes to U.S. federal income tax law for U.S. taxpayers. Changes in tax law are accounted for in the period of enactment. As such, the Company's 2017 consolidated financial statements reflected the estimated immediate tax effect of the 2017 Tax Act. The 2017 Tax Act contains a number of key provisions, including, among other items:
• | The reduction of the statutory U.S. federal corporate income tax rate from 35.0% to 21.0% effective January 1, 2018; |
• | A one-time transition tax via a mandatory deemed repatriation of post-1986 undistributed foreign earnings and profits (the "Transition Tax"); |
• | A deduction for Foreign Derived Intangible Income ("FDII") for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017; |
• | A tax on global intangible low-taxed income ("GILTI") for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017; |
• | A limitation on net interest expense deductions to 30% of adjusted taxable income for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017; |
• | Broader limitations on the deductibility of compensation of certain highly compensated employees; |
• | The ability to elect to accelerate tax depreciation on certain qualified assets; |
• | A territorial tax system providing a 100% dividends received deduction on certain qualified dividends from foreign subsidiaries for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017; |
• | The Base Erosion and Anti-Abuse Tax ("BEAT") for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017; and |
• | Changes in the application of the U.S. foreign tax credit regulations for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-90
Additionally, on December 22, 2017, the SEC issued SAB 118 to address the application of U.S. GAAP in situations when a registrant did not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the 2017 Tax Act. Specifically, SAB 118 provided a measurement period for companies to evaluate the impacts of the 2017 Tax Act on their financial statements. This measurement period began in the reporting period that included the enactment date and ended when an entity obtained, prepared and analyzed the information that was needed in order to complete the accounting requirements, but could not exceed one year. The Company adopted the provisions of SAB 118 with respect to the impact of the 2017 Tax Act on its 2017 consolidated financial statements.
During the year ended January 31, 2018, the Company recorded an estimated net tax expense of $146.2 million as a result of the effects of the 2017 Tax Act. The tax effects recorded included:
• | Estimated tax expense of $ |
• | Estimated tax expense of $ |
• | A tax benefit of $ |
Consistent with SAB 118, the Company calculated and recorded reasonable estimates for the impact of the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of its deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, as set forth above. The Company also adopted the provisions of SAB 118 as it related to the assertion of the indefinite reinvestment of foreign earnings and profits. The charges associated with the Transition Tax and the remeasurement of the Company's deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities, as a result of applying the 2017 Tax Act, represented provisional amounts for which the Company's analysis was incomplete but reasonable estimates could be determined and were recorded during the fourth quarter of 2017. Further, the impact of the 2017 Tax Act on the Company's assertion to indefinitely reinvest foreign earnings was incomplete as the Company was analyzing the relevant provisions of the 2017 Tax Act and related accounting guidance.
During the year ended January 31, 2019, as permitted by SAB 118, the Company completed its analyses under the 2017 Tax Act, including those related to: (i) the provisional estimate recorded during the year ended January 31, 2018 for the Transition Tax; (ii) the provisional estimate recorded during the year ended January 31, 2018 to remeasure the Company's deferred tax assets and liabilities; and (iii) the Company's assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed foreign earnings and profits.
As a result of completing these analyses, during the year ended January 31, 2019, the Company: (i) recorded tax benefits totaling $12.6 million to adjust the provisional estimate recorded in the year ended January 31, 2018 to remeasure the Company's deferred tax assets and liabilities; (ii) recorded tax benefits totaling $3.3 million to adjust the provisional estimate recorded in the year ended January 31, 2018 for the Transition Tax; and (iii) determined to maintain its assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed foreign earnings and profits.
The Company continues to maintain its assertion to indefinitely reinvest undistributed foreign earnings and profits, which amounted to approximately $1.0 billion as of January 31,2020.
Upon distribution of those foreign earnings and profits in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to U.S. state and local taxes, taxes on foreign currency gains and withholding taxes payable in various jurisdictions, which may be partially offset by foreign tax credits. Determination of the amount of the unrecognized deferred tax liability is not practicable because of the complexities associated with its hypothetical calculation.
The Company expects to continue to account for the tax on GILTI as a period cost and therefore has not adjusted any of the deferred tax assets and liabilities of its foreign subsidiaries in connection with the 2017 Tax Act.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-91
Income Taxes
Earnings from operations before income taxes consisted of the following:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
United States | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Foreign | |||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||
Components of the provision for income taxes were as follows:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Current: | |||||||||
Federal | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
State | |||||||||
Foreign | |||||||||
Deferred: | |||||||||
Federal | ( | ) | |||||||
State | ( | ) | |||||||
Foreign | ( | ) | |||||||
( | ) | ||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||
Reconciliations of the provision for income taxes at the statutory Federal income tax rate to the Company's effective income tax rate were as follows:
Years Ended January 31, | ||||||
2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||
Statutory Federal income tax rate | % | % | % | |||
State income taxes, net of Federal benefit | ||||||
Foreign losses with no tax benefit | ||||||
Effect of Foreign Operations | ( | ) | ||||
Net change in uncertain tax positions | ( | ) | ||||
Domestic manufacturing deduction | ( | ) | ||||
Foreign Derived Intangible Income deduction | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
Impact of the 2017 Tax Act | ||||||
Other | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
% | % | % | ||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-92
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) consisted of the following:
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | $ | $ | — | |||
Pension/postretirement benefits | ||||||
Accrued expenses | ||||||
Share-based compensation | ||||||
Depreciation and amortization | ||||||
Foreign and state net operating losses | ||||||
Sale-leasebacks | ||||||
Inventory | ||||||
Unearned income | ||||||
Other | ||||||
Valuation allowance | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||
Operating lease right-of-use assets | ( | ) | — | |||
Foreign tax credit and other tax liabilities | ( | ) | ( | ) | ||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | $ | ||||
The Company has recorded a valuation allowance against certain deferred tax assets related to foreign net operating loss carryforwards where management has determined it is more likely than not that deferred tax assets will not be realized in the future. The overall valuation allowance relates to tax loss carryforwards and temporary differences for which no benefit is expected to be realized. Tax loss carryforwards of $21.8 million exist in certain foreign jurisdictions. Whereas some of these tax loss carryforwards do not have an expiration date, others expire at various times from 2020 through 2036.
The following table reconciles the unrecognized tax benefits:
Years ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of year | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Gross increases – tax positions in prior period | |||||||||
Gross decreases – tax positions in prior period | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||||
Gross increases – tax positions in current period | |||||||||
Settlements | ( | ) | |||||||
Lapse of statute of limitations | ( | ) | |||||||
Unrecognized tax benefits at end of year | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
The amount of tax benefits included in the balance of unrecognized tax benefits at January 31, 2020 that, if recognized, would affect the effective income tax rate was $18.5 million.
The Company recognizes expense for interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits within the provision for income taxes. The Company recognized a benefit of $1.3 million in 2019, a benefit of $6.2 million in 2018 and
TIFFANY & CO.
K-93
expense of $2.0 million in 2017 for interest and penalties. Accrued interest and penalties, which amounted to $2.9 million and $4.2 million at January 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively, is included within Accounts payable and accrued liabilities and Other long-term liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The Company conducts business globally and, as a result, is subject to taxation in the U.S. and various state and foreign jurisdictions. As a matter of course, tax authorities regularly audit the Company. The Company's tax filings are currently being examined by a number of tax authorities, both in the U.S. and in foreign jurisdictions. Ongoing audits where subsidiaries have a material presence include New York City (tax years 2011–2015) and New York State (tax years 2012–2018). Tax years from 2010–present are open to examination in the U.S. Federal jurisdiction and 2006–present are open in various state, local and foreign jurisdictions. As part of these audits, the Company engages in discussions with taxing authorities regarding tax positions. As of January 31, 2020, unrecognized tax benefits are not expected to change materially in the next 12 months. Future developments may result in a change in this assessment.
Q. SEGMENT INFORMATION
Net sales by geographic area are presented by attributing revenues from external customers on the basis of the country in which the merchandise is sold. In deciding how to allocate resources and assess performance, the Company's Chief Operating Decision Maker regularly evaluates the performance of its reportable segments on the basis of net sales and earnings from operations, after the elimination of inter-segment sales and transfers. The accounting policies of the reportable segments are the same as those described in "Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Certain information relating to the Company's segments is set forth below:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||
Net sales: | |||||||||||
Americas | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Asia-Pacific | |||||||||||
Japan | |||||||||||
Europe | |||||||||||
Total reportable segments | |||||||||||
Other | |||||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
Earnings from operations*: | |||||||||||
Americas | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Asia-Pacific | |||||||||||
Japan | |||||||||||
Europe | |||||||||||
Total reportable segments | |||||||||||
Other | ( | ) | |||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
* | Represents earnings from operations before (i) unallocated corporate expenses, (ii) Interest expense and financing costs and Other expense, net, and (iii) other operating expenses. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-94
The Company's Chief Operating Decision Maker does not evaluate the performance of the Company's assets on a segment basis for internal management reporting and, therefore, such information is not presented. The following table sets forth a reconciliation of the segments' earnings from operations to the Company's consolidated earnings from operations before income taxes:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Earnings from operations for segments | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Unallocated corporate expenses | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||
Interest expense and financing costs and Other expense, net | ( | ) | ( | ) | ( | ) | |||
Other operating expenses | ( | ) | |||||||
Earnings from operations before income taxes | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Unallocated corporate expenses include certain costs related to administrative support functions which the Company does not allocate to its segments. Such unallocated costs include those for centralized information technology, finance, legal and human resources departments.
Other operating expenses in the year ended January 31, 2020 represent charges related to the proposed Merger. See "Note B. Entry into Merger Agreement" for additional details.
Sales to unaffiliated customers by geographic area were as follows:
Years Ended January 31, | |||||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||
Net sales: | |||||||||
United States | $ | $ | $ | ||||||
Japan | |||||||||
Other countries | |||||||||
$ | $ | $ | |||||||
Net sales information for classes of similar products is presented in "Note C. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Long-lived assets by geographic area were as follows:
January 31, | ||||||
(in millions) | 2020 | 2019 | ||||
Long-lived assets: | ||||||
United States | $ | $ | ||||
Japan | ||||||
Other countries | ||||||
$ | $ | |||||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-95
R. QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
2019 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | April 30 | July 31 | October 31 | January 31 a | ||||||||
Net sales | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Gross profit | ||||||||||||
Earnings from operations | ||||||||||||
Net earnings | ||||||||||||
Net earnings per share: | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Diluted | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
2018 Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | April 30 | July 31 | October 31 | January 31 | ||||||||
Net sales | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Gross profit | ||||||||||||
Earnings from operations | ||||||||||||
Net earnings | ||||||||||||
Net earnings per share: | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
Diluted | $ | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||
a | Net earnings included $ |
Basic and diluted earnings per share are computed independently for each quarter presented. Accordingly, the sum of the quarterly earnings per share may not agree with the calculated full year earnings per share.
S. SUBSEQUENT EVENT
TIFFANY & CO.
K-96
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Based on their evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended), the Registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, the Registrant's disclosure controls and procedures are effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Registrant in the reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms and (ii) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
In the ordinary course of business, the Registrant reviews its system of internal control over financial reporting and makes changes to its systems and processes to improve controls and increase efficiency, while ensuring that the Registrant maintains an effective internal control environment. Changes may include activities such as implementing new, more efficient systems and automating manual processes.
The Registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer have determined that there have been no changes in the Registrant's internal control over financial reporting during the most recently completed fiscal quarter covered by this report identified in connection with the evaluation described above that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Registrant's internal control over financial reporting.
The Registrant's management, including its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, necessarily applied their judgment in assessing the costs and benefits of such controls and procedures. By their nature, such controls and procedures cannot provide absolute certainty, but can provide reasonable assurance regarding management's control objectives. Our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer have concluded that the Registrant's disclosure controls and procedures are (i) designed to provide such reasonable assurance and (ii) effective at that reasonable assurance level.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-97
Report of Management
Management's Responsibility for Financial Information. The Company's consolidated financial statements were prepared by management, who are responsible for their integrity and objectivity. The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and, as such, include amounts based on management's best estimates and judgments.
Management is further responsible for maintaining a system of internal accounting control designed to provide reasonable assurance that the Company's assets are adequately safeguarded, and that the accounting records reflect transactions executed in accordance with management's authorization. The system of internal control is continually reviewed and is augmented by written policies and procedures, the careful selection and training of qualified personnel and a program of internal audit.
The consolidated financial statements have been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm. Their report is shown on page K-47. The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors, which is composed solely of independent directors, reviewed and discussed with the Company's management and the independent registered public accounting firm, as appropriate, specific accounting, financial reporting and internal control matters. Both the independent registered public accounting firm and the internal auditors have full and free access to the Audit Committee. Each year the Audit Committee selects the firm that is to perform audit services for the Company.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting using the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations ("COSO") of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued in 2013. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Based on this evaluation, management concluded that internal control over financial reporting was effective as of January 31, 2020 based on criteria in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the COSO. The effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2020 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is shown on page K-47.
/s/ Alessandro Bogliolo
Chief Executive Officer
/s/ Mark J. Erceg
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
Item 9B. Other Information.
None
TIFFANY & CO.
K-98
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Incorporated by reference from the sections titled "Executive Officers of the Company," "Item 1. Election of the Board," and "Board of Directors and Corporate Governance" in Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020.
CODE OF ETHICS AND OTHER CORPORATE GOVERNANCE DISCLOSURES
Registrant has adopted a Code of Business and Ethical Conduct for its Directors, Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and all other officers of the Registrant. A copy of this Code is posted on the corporate governance section of the Registrant's website, https://investor.tiffany.com/index.php/corporate-governance; go to "Code of Conduct."
See Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020, for additional information within the section titled "Business Conduct Policy and Code of Ethics."
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Incorporated by reference from the sections titled "Board of Directors and Corporate Governance" and "Compensation of the CEO and Other Executive Officers" in Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
Incorporated by reference from the sections titled "Ownership of the Company" and "Compensation of the CEO and Other Executive Officers" in Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Incorporated by reference from the sections titled "Board of Directors and Corporate Governance" and "Transactions with Related Persons" in Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
Incorporated by reference from the section titled "Relationship with Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm" in Registrant's Proxy Statement dated April 20, 2020.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-99
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) List of Documents Filed As Part of This Report:
1. Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of January 31, 2020 and 2019.
Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Earnings for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
2. Financial Statement Schedules
The following financial statement schedule should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements:
Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves for the years ended January 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
All other schedules have been omitted since they are not applicable, not required, or because the information required is included in the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto.
3. Exhibits
The information called for by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Exhibit Index in this report.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
Not Applicable.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-100
EXHIBIT INDEX
Exhibit Table (numbered in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K)
Exhibit No. Description | |
4.9 | Upon the request of the Securities and Exchange Commission, Registrant will furnish a copy of all instruments defining the rights of holders of all other long-term debt of Registrant. |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-101
Exhibit No. Description | |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-102
Exhibit No. Description | |
101 | The following financial information from Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2020, filed with the SEC, formatted in Inline Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets; (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Earnings; (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Earnings; (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity; (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows; (vi) the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements; and (vii) Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves. |
104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). |
Executive Compensation Plans and Arrangements
Exhibit No. Description | |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-103
Exhibit No. Description | |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-104
Exhibit No. Description | |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-105
Exhibit No. Description | |
TIFFANY & CO.
K-106
TIFFANY & CO.
K-107
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Date: March 20, 2020 | TIFFANY & CO. | |
(Registrant) | ||
By: /s/ Alessandro Bogliolo | ||
Alessandro Bogliolo | ||
Chief Executive Officer | ||
TIFFANY & CO.
K-108
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
By: | /s/ Alessandro Bogliolo | By: | /s/ Mark J. Erceg | |
Alessandro Bogliolo | Mark J. Erceg | |||
Chief Executive Officer | Executive Vice President, | |||
(Principal Executive Officer) (Director) | Chief Financial Officer | |||
(Principal Financial Officer) | ||||
By: | /s/ Michael Rinaldo | By: | /s/ Rose Marie Bravo | |
Michael Rinaldo | Rose Marie Bravo | |||
Vice President, Controller | Director | |||
(Principal Accounting Officer) | ||||
By: | /s/ Hafize Gaye Erkan | By: | /s/ Roger N. Farah | |
Hafize Gaye Erkan | Roger N. Farah | |||
Director | Director | |||
By: | /s/ Jane Hertzmark Hudis | By: | /s/ Abby F. Kohnstamm | |
Jane Hertzmark Hudis | Abby F. Kohnstamm | |||
Director | Director | |||
By: | /s/ James E. Lillie | By: | /s/ William A. Shutzer | |
James E. Lillie | William A. Shutzer | |||
Director | Director | |||
By: | /s/ Robert S. Singer | By: | /s/ Annie Young - Scrivner | |
Robert S. Singer | Annie Young - Scrivner | |||
Director | Director | |||
March 20, 2020
TIFFANY & CO.
K-109
Tiffany & Co. and Subsidiaries
Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves
(in millions)
Column A | Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | ||||||||||||
Additions | ||||||||||||||||
Description | Balance at beginning of period | Charged to costs and expenses | Charged to other accounts | Deductions | Balance at end of period | |||||||||||
Year Ended January 31, 2020: | ||||||||||||||||
Reserves deducted from assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable allowances: | ||||||||||||||||
Doubtful accounts | $ | $ | $ | $ | a | $ | ||||||||||
Sales returns | b | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory liquidation and obsolescence | c | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory shrinkage | d | |||||||||||||||
Deferred tax valuation allowance | e | |||||||||||||||
a) Uncollectible accounts written off.
b) Adjustment related to sales returns previously provided for.
c) Liquidation of inventory previously written down to net realizable value.
d) Physical inventory losses.
e) Reversal of deferred tax valuation allowance and recognition of deferred tax asset.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-110
Tiffany & Co. and Subsidiaries
Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves
(in millions)
Column A | Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | ||||||||||||
Additions | ||||||||||||||||
Description | Balance at beginning of period | Charged to costs and expenses | Charged to other accounts | Deductions | Balance at end of period | |||||||||||
Year Ended January 31, 2019: | ||||||||||||||||
Reserves deducted from assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable allowances: | ||||||||||||||||
Doubtful accounts | $ | $ | $ | $ | a | $ | ||||||||||
Sales returns | b | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory liquidation and obsolescence | c | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory shrinkage | d | |||||||||||||||
Deferred tax valuation allowance | e | |||||||||||||||
a) Uncollectible accounts written off.
b) Adjustment related to sales returns previously provided for.
c) Liquidation of inventory previously written down to net realizable value.
d) Physical inventory losses.
e) Reversal of deferred tax valuation allowance and utilization of deferred tax loss carryforward.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-111
Tiffany & Co. and Subsidiaries
Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves
(in millions)
Column A | Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | ||||||||||||
Additions | ||||||||||||||||
Description | Balance at beginning of period | Charged to costs and expenses | Charged to other accounts | Deductions | Balance at end of period | |||||||||||
Year Ended January 31, 2018: | ||||||||||||||||
Reserves deducted from assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable allowances: | ||||||||||||||||
Doubtful accounts | $ | $ | $ | $ | a | $ | ||||||||||
Sales returns | b | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory liquidation and obsolescence | c | |||||||||||||||
Allowance for inventory shrinkage | d | |||||||||||||||
Deferred tax valuation allowance | e | |||||||||||||||
a) Uncollectible accounts written off.
b) Adjustment related to sales returns previously provided for.
c) Liquidation of inventory previously written down to net realizable value.
d) Physical inventory losses.
TIFFANY & CO.
K-112